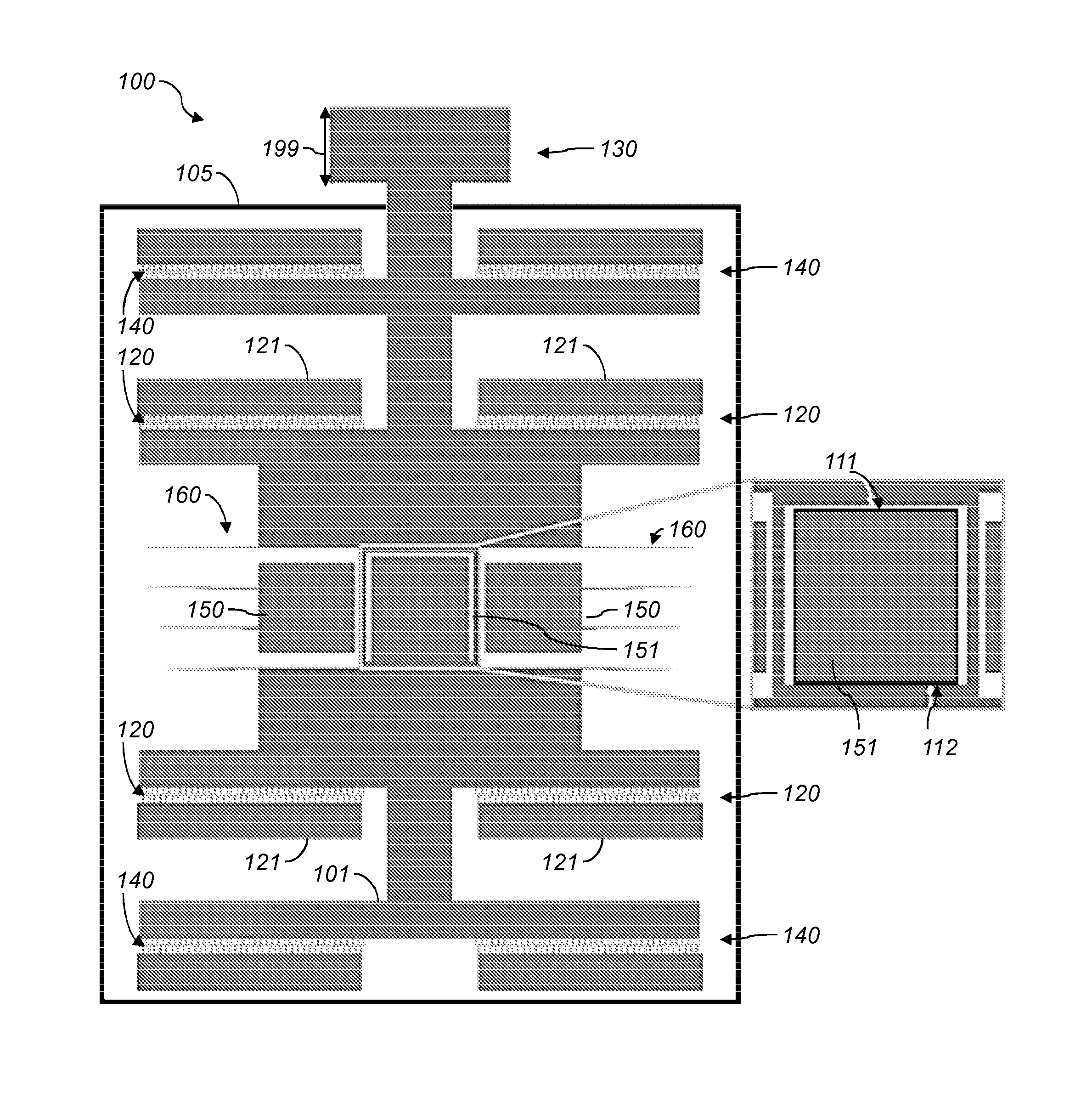
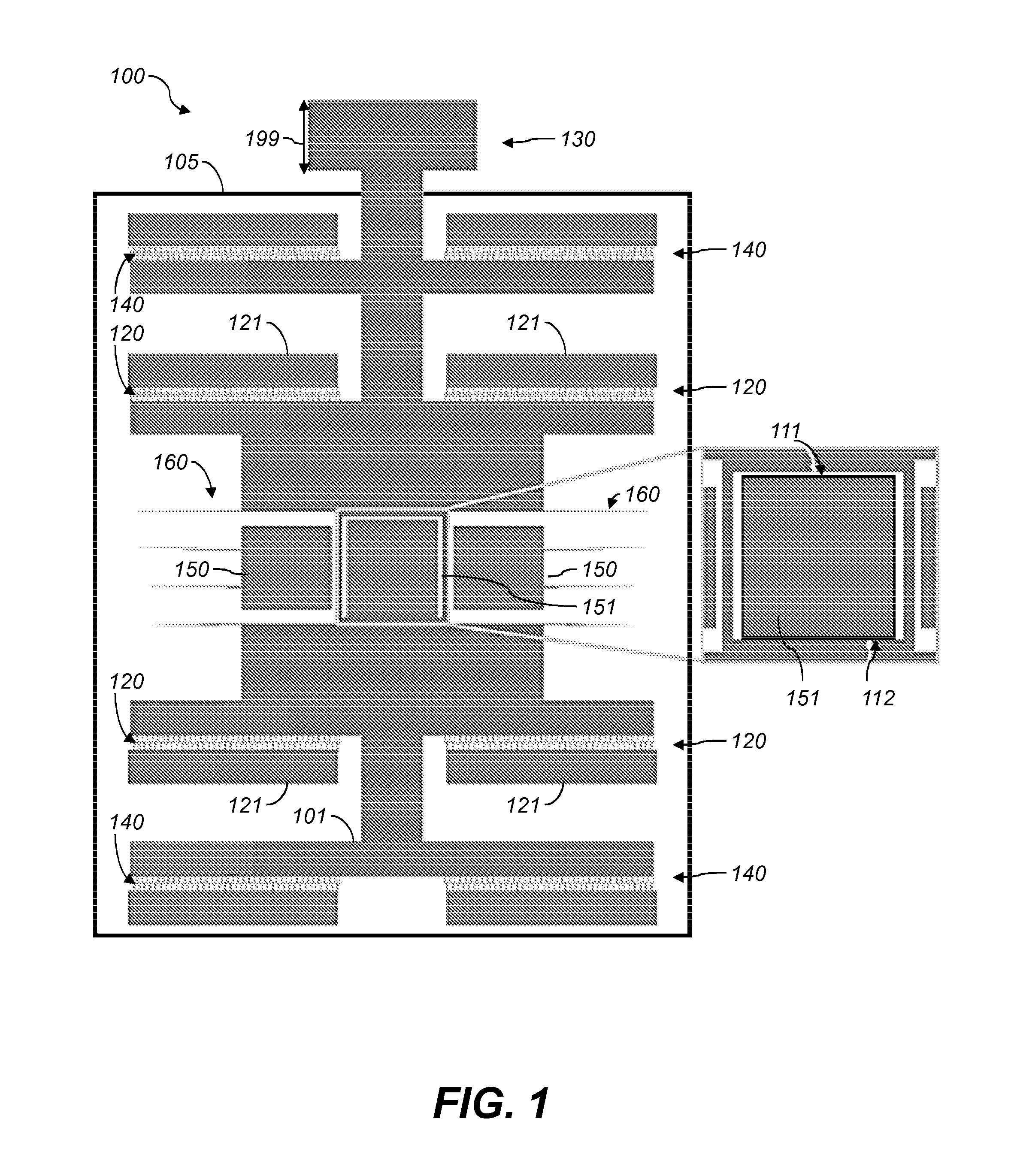
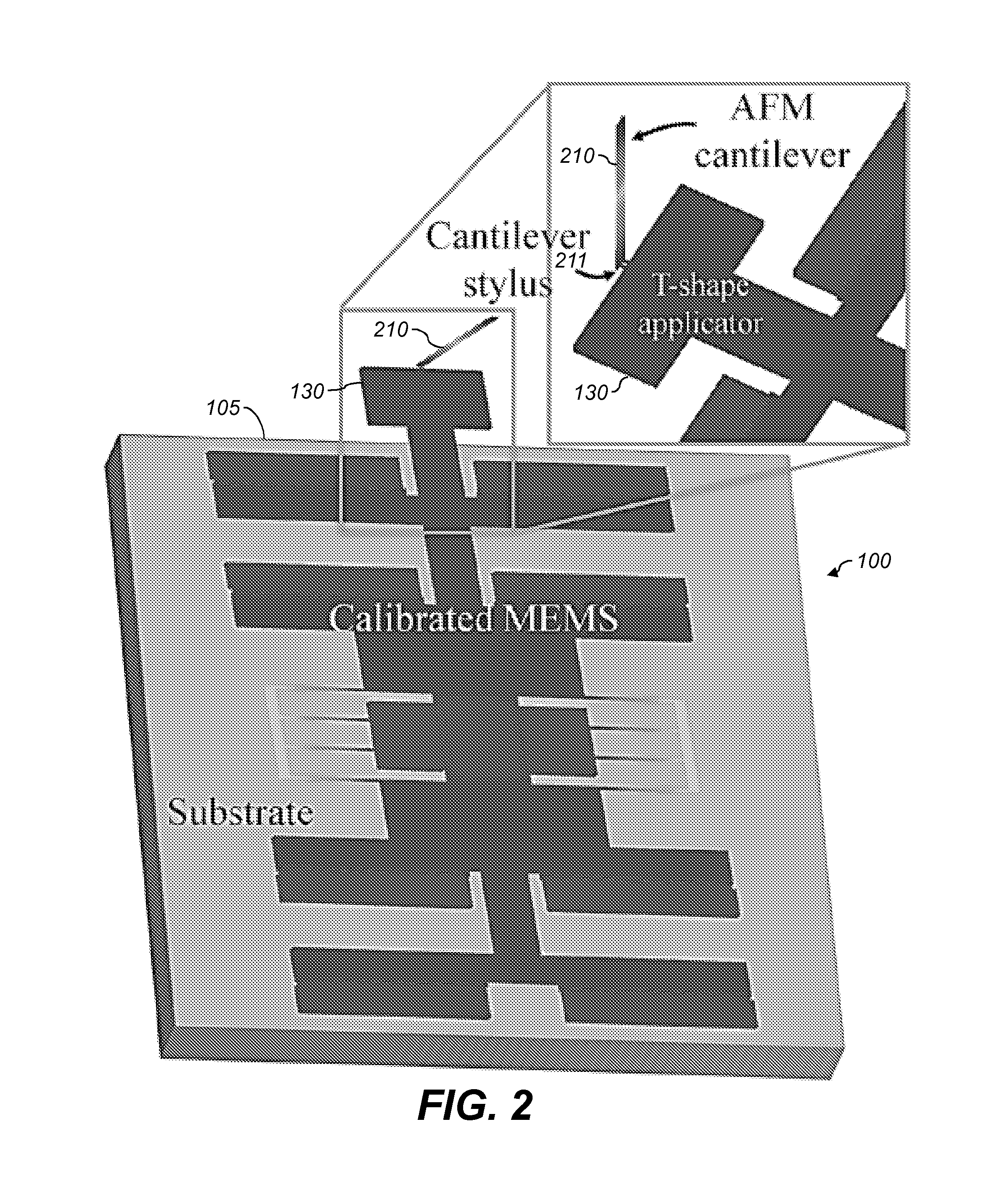
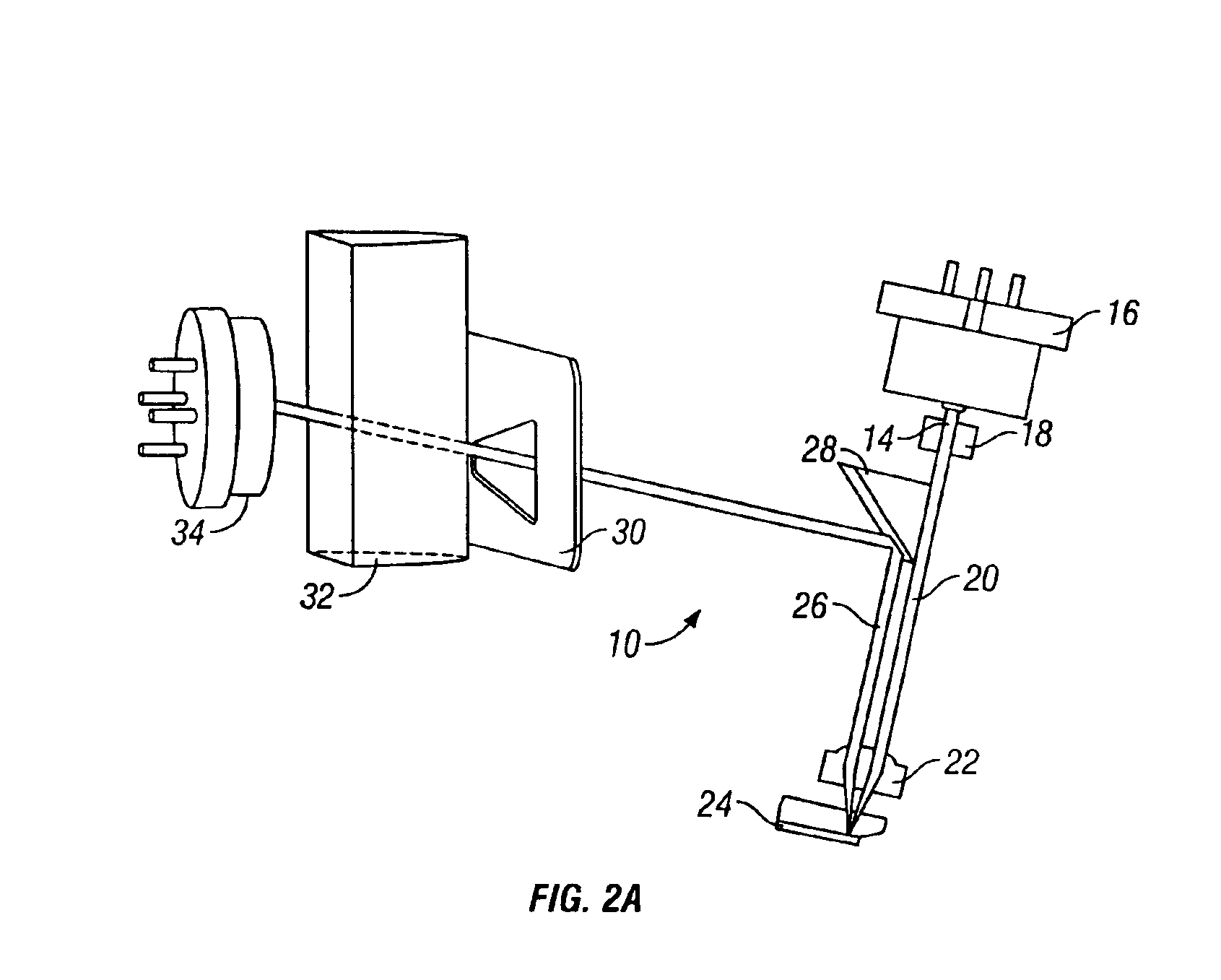
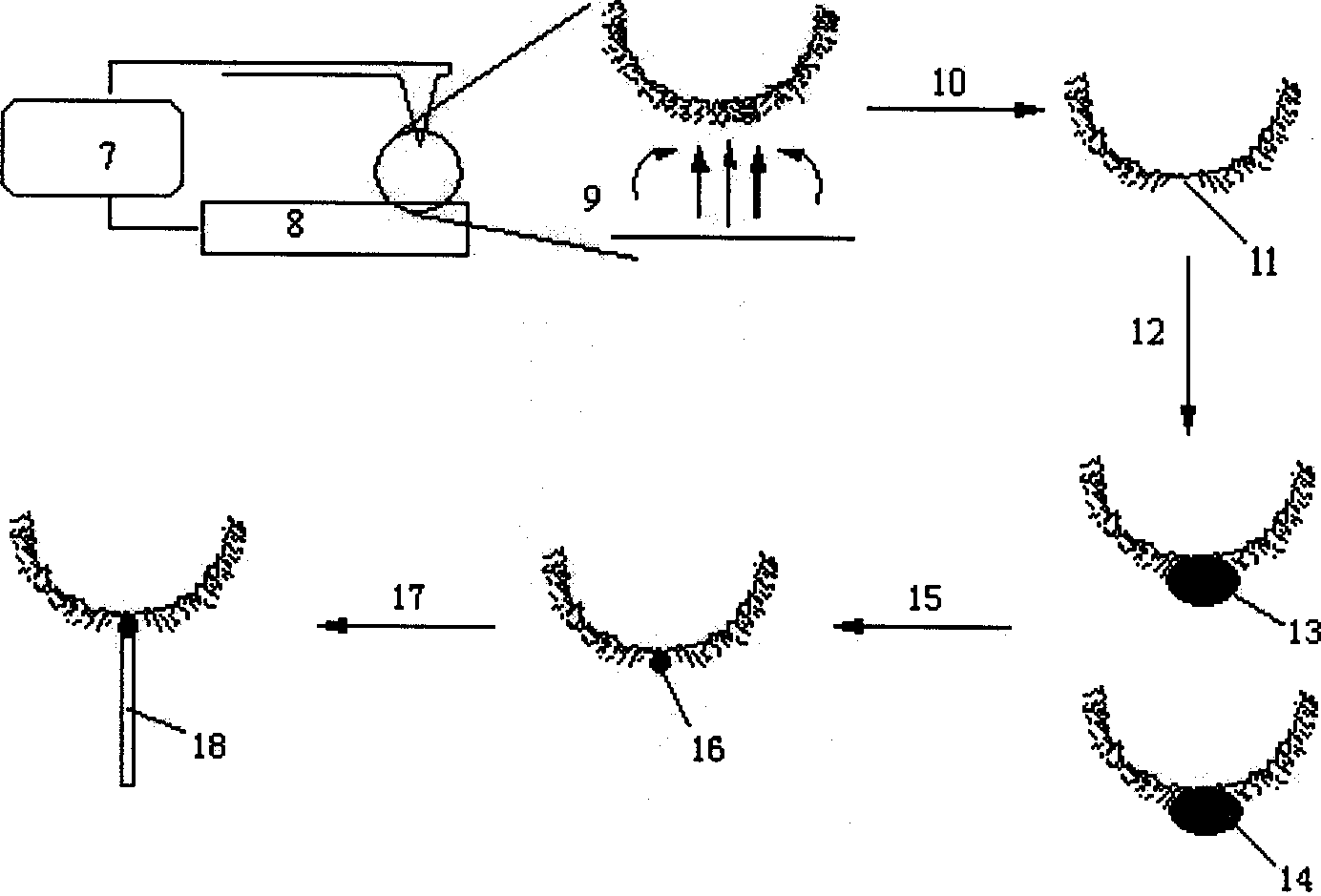
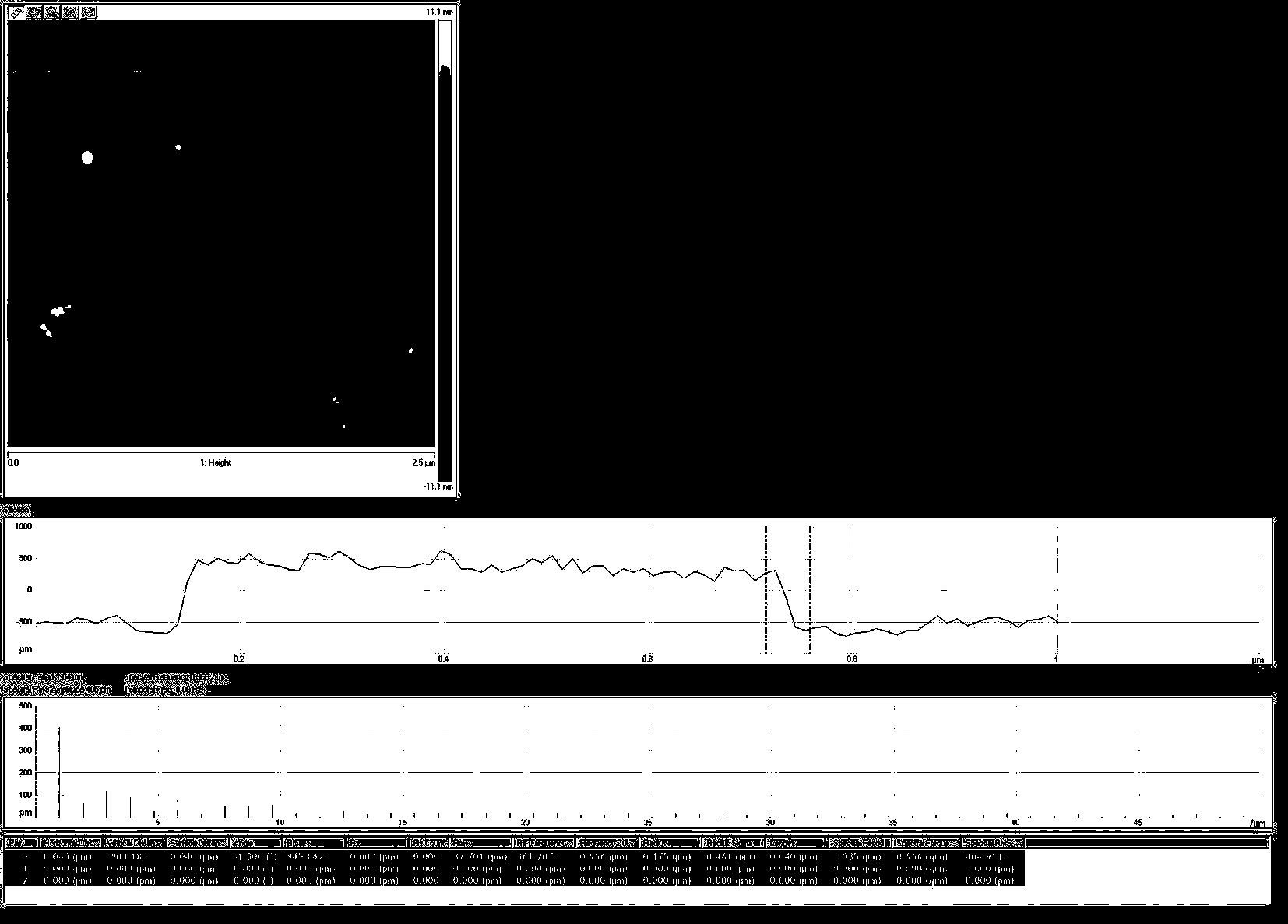
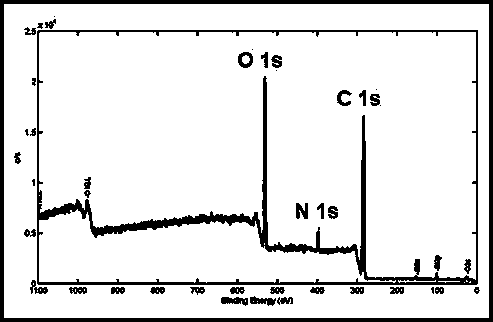
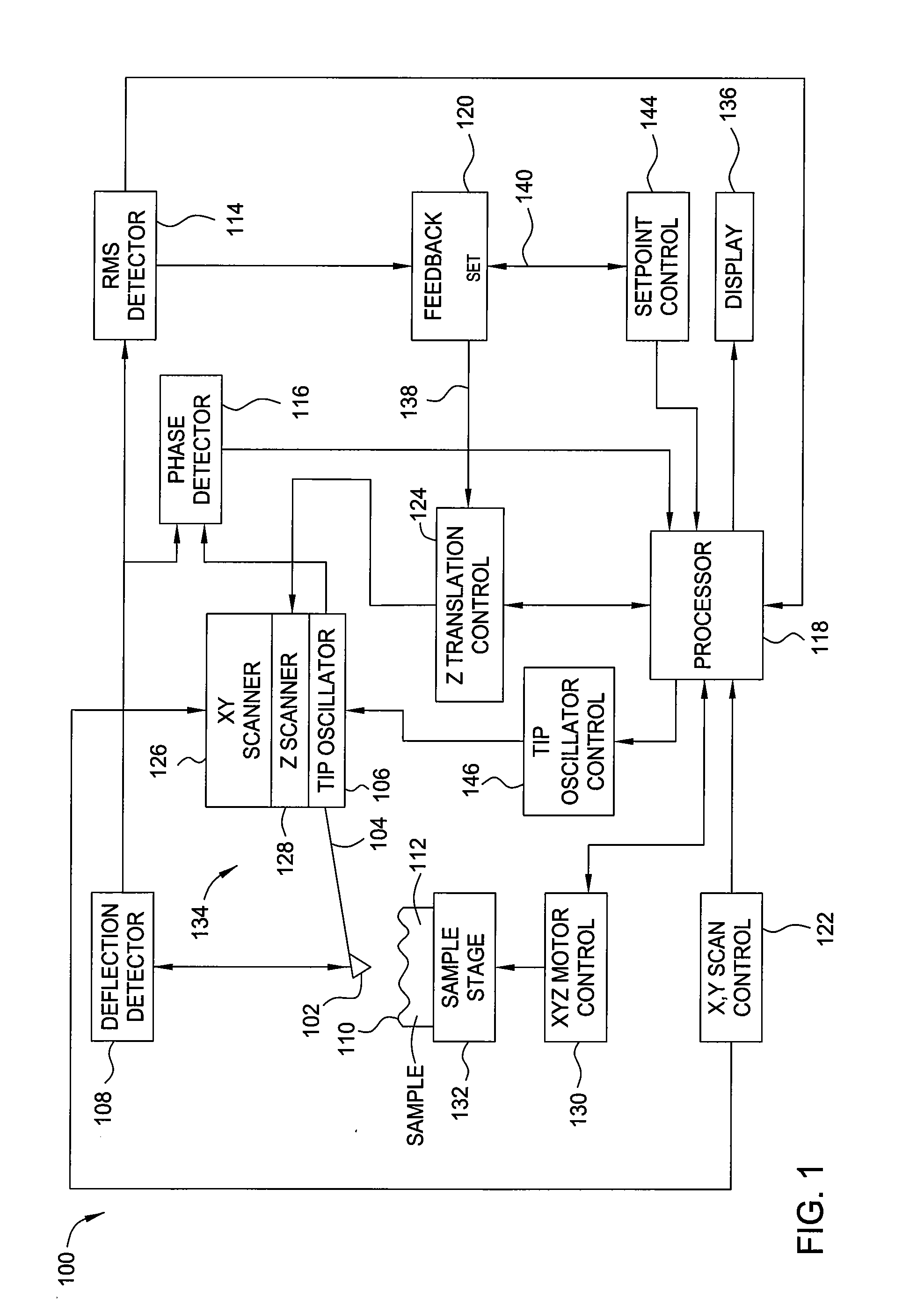
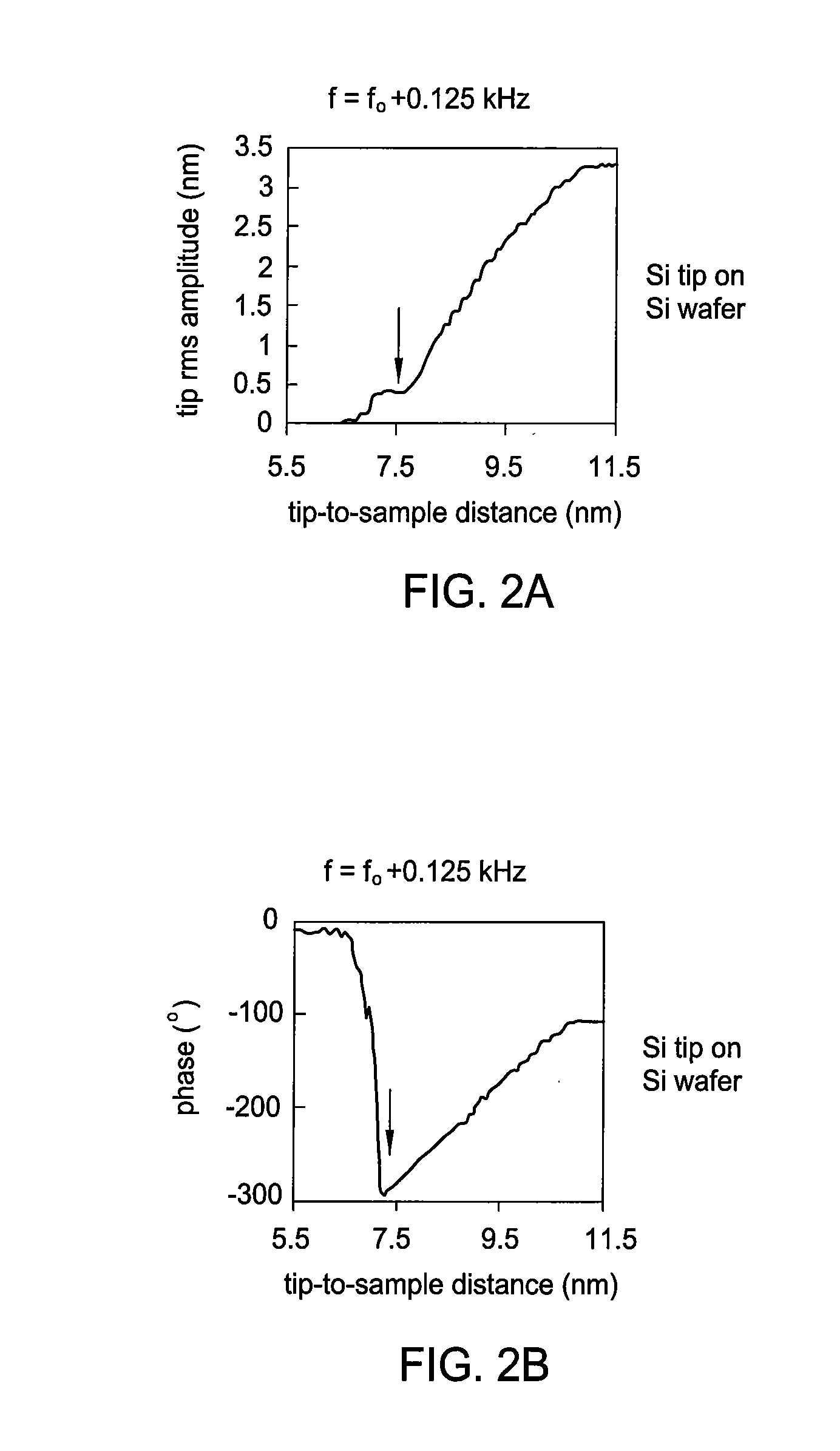
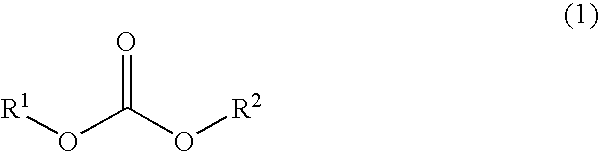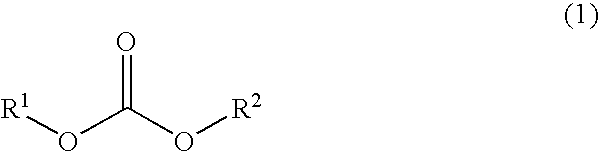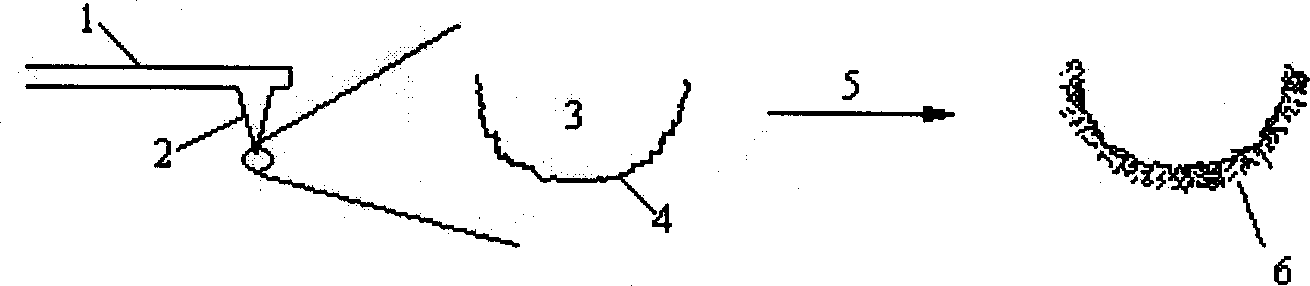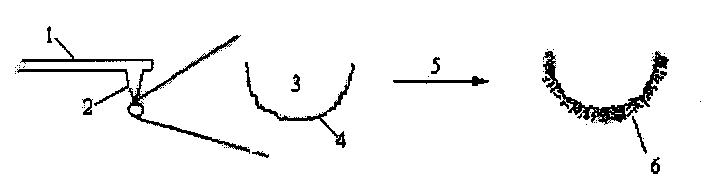Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
401 results about "Afm atomic force microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atomic Force Microscopy. The atomic force microscope (AFM) was developed to overcome a basic drawback with STM – it can only image conducting or semiconducting surfaces. The AFM has the advantage of imaging almost any type of surface, including polymers, ceramics, composites, glass, and biological samples.
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20090087689A1Improve high-speed running stabilityMaintain good propertiesMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageAtomic force microscopyMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic recording medium comprises a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a nonmagnetic support. In the magnetic recording medium, a number of protrusions equal to or greater than 10 nm in height on the magnetic layer surface, as measured by an atomic force microscope, ranges from 50 to 500 / 1,600 μm2, the binder comprises a polyurethane resin with a weight average molecular weight ranging from 100,000 to 200,000, and the magnetic layer further comprises a carbonic ester having a molecular weight ranging from 360 to 460.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
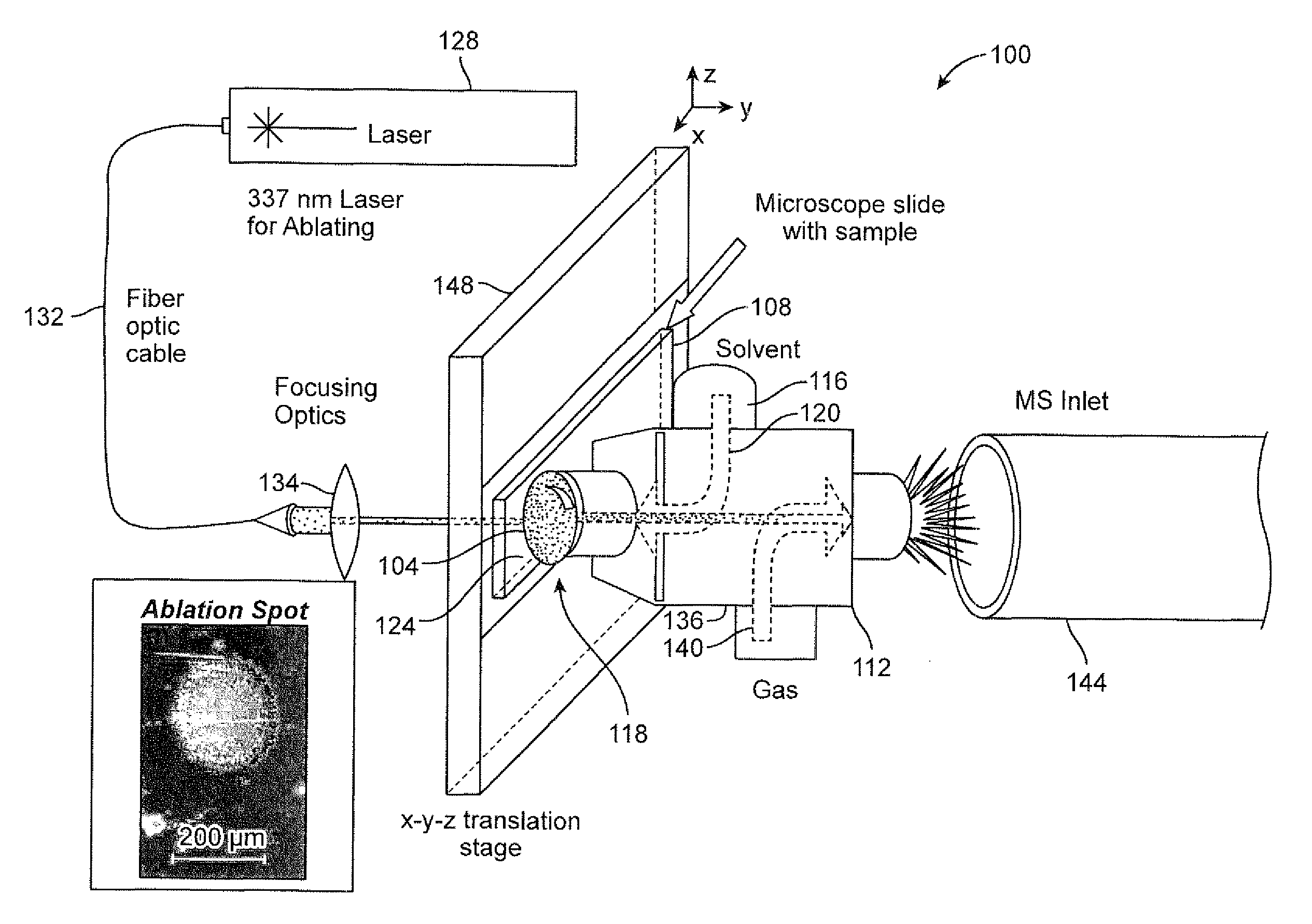
Systems and methods for laser assisted sample transfer to solution for chemical analysis
ActiveUS20120079894A1Stop the flowParticle separator tubesWithdrawing sample devicesAtomic force microscopyAnalyte
Systems and methods are described for laser ablation of an analyte from a specimen and capturing of the analyte in a dispensed solvent to form a testing solution. A solvent dispensing and extraction system can form a liquid microjunction with the specimen. The solvent dispensing and extraction system can include a surface sampling probe. The laser beam can be directed through the surface sampling probe. The surface sampling probe can also serve as an atomic force microscopy probe. The surface sampling probe can form a seal with the specimen. The testing solution including the analyte can then be analyzed using an analytical instrument or undergo further processing.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
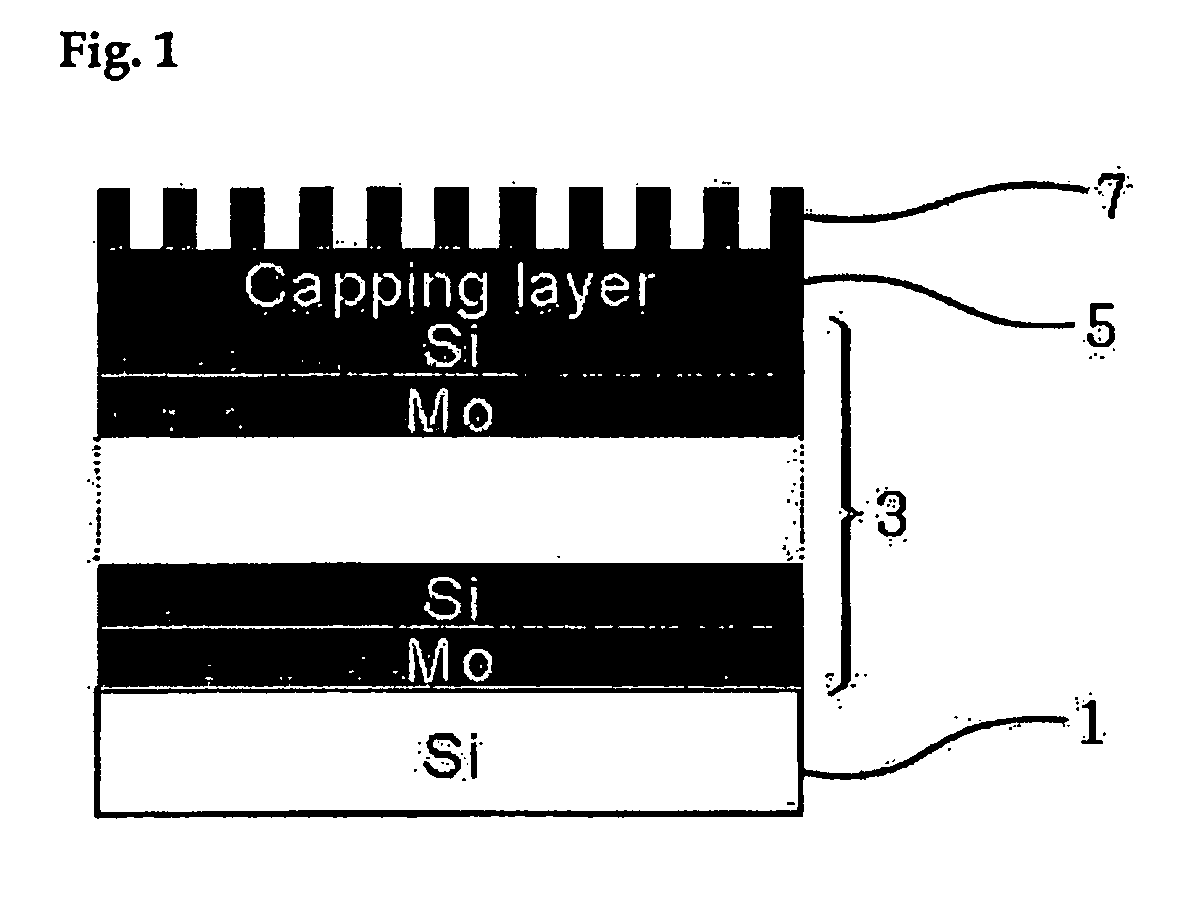
Diffraction grating, organic el element using the same, and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveUS20120132897A1Low wavelength dependenceReduce directivityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesWavenumberAfm atomic force microscopy
A diffraction grating having a transparent supporting substrate; and a cured resin layer which is stacked on the transparent supporting substrate and which has concavities and convexities formed on a surface thereof, wherein when a Fourier-transformed image is obtained by performing two-dimensional fast Fourier transform processing on a concavity and convexity analysis image obtained by analyzing a shape of the concavities and convexities formed on the surface of the cured resin layer by use of an atomic force microscope, the Fourier-transformed image shows a circular or annular pattern substantially centered at an origin at which an absolute value of wavenumber is 0 μm−1, and the circular or annular pattern is present within a region where an absolute value of wavenumber is within a range of 10 μm−1 or less.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP +1
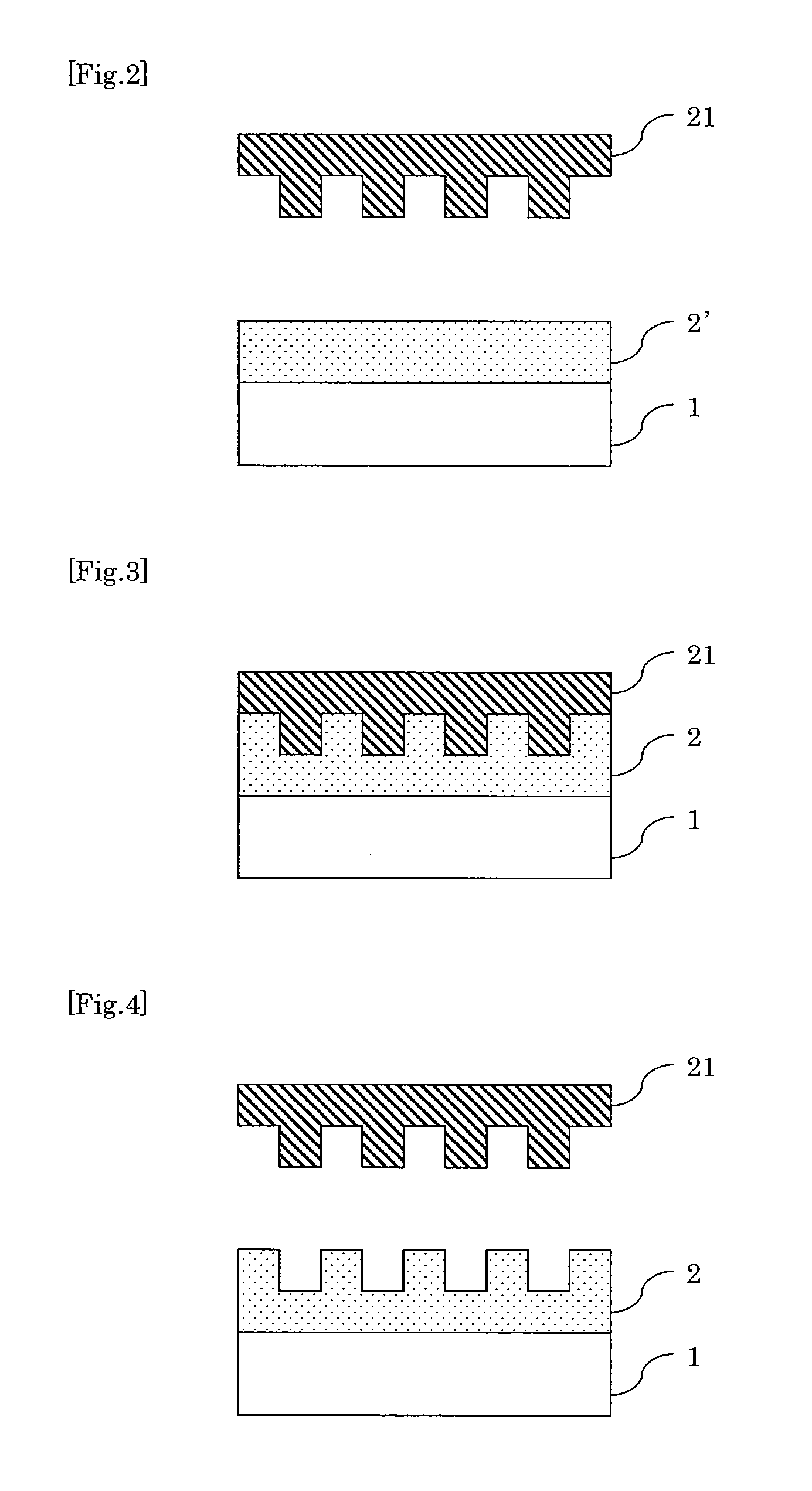
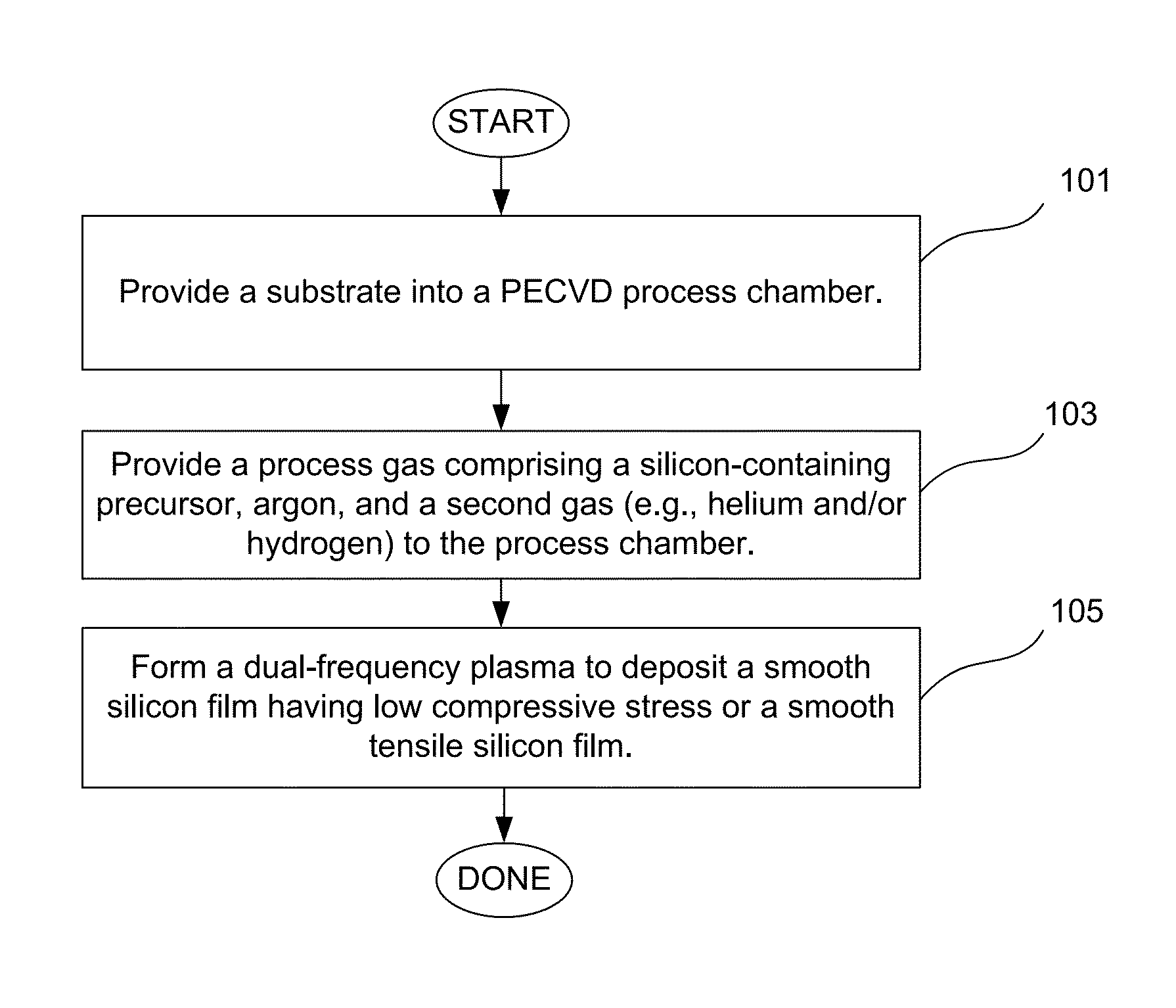
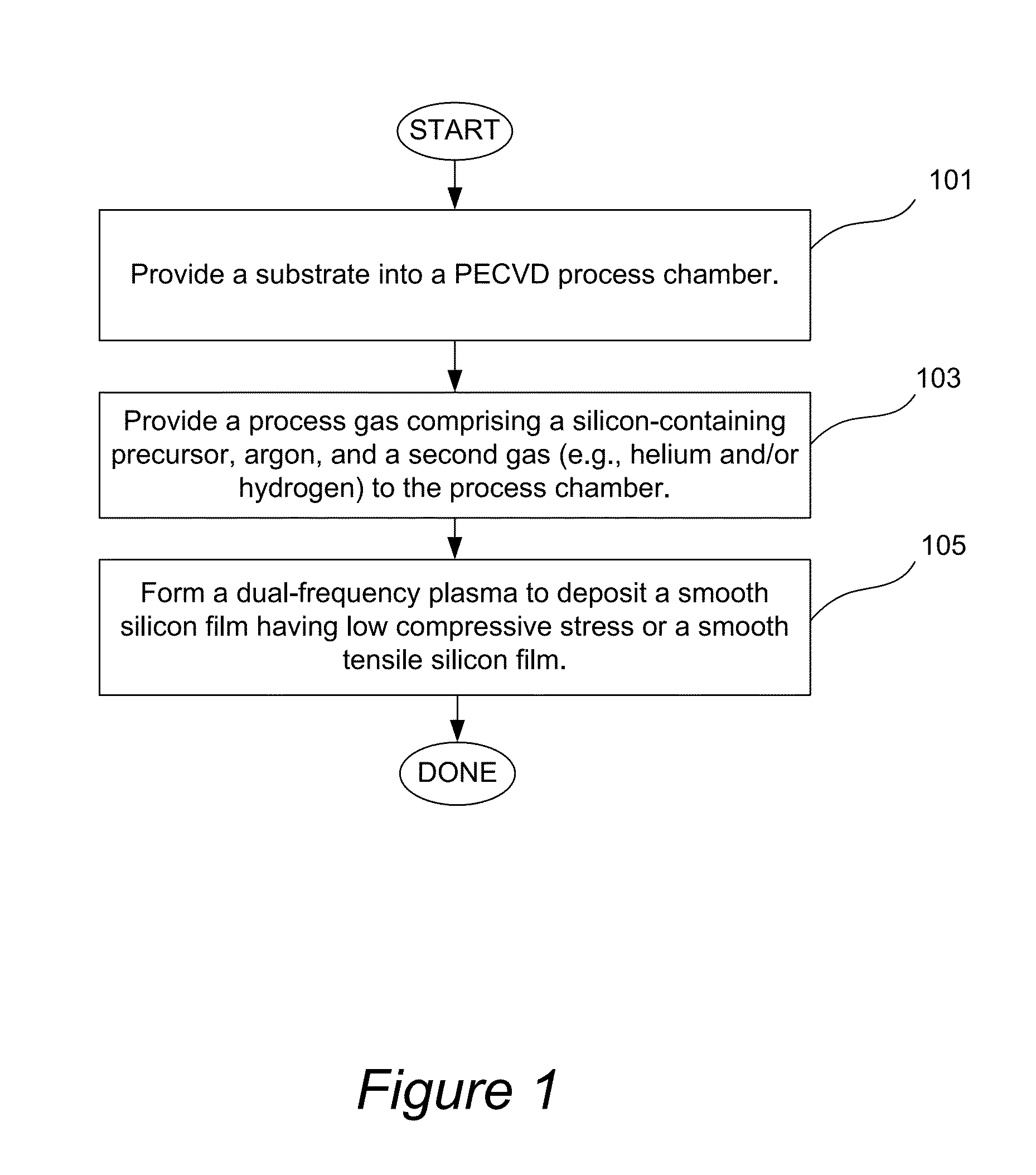
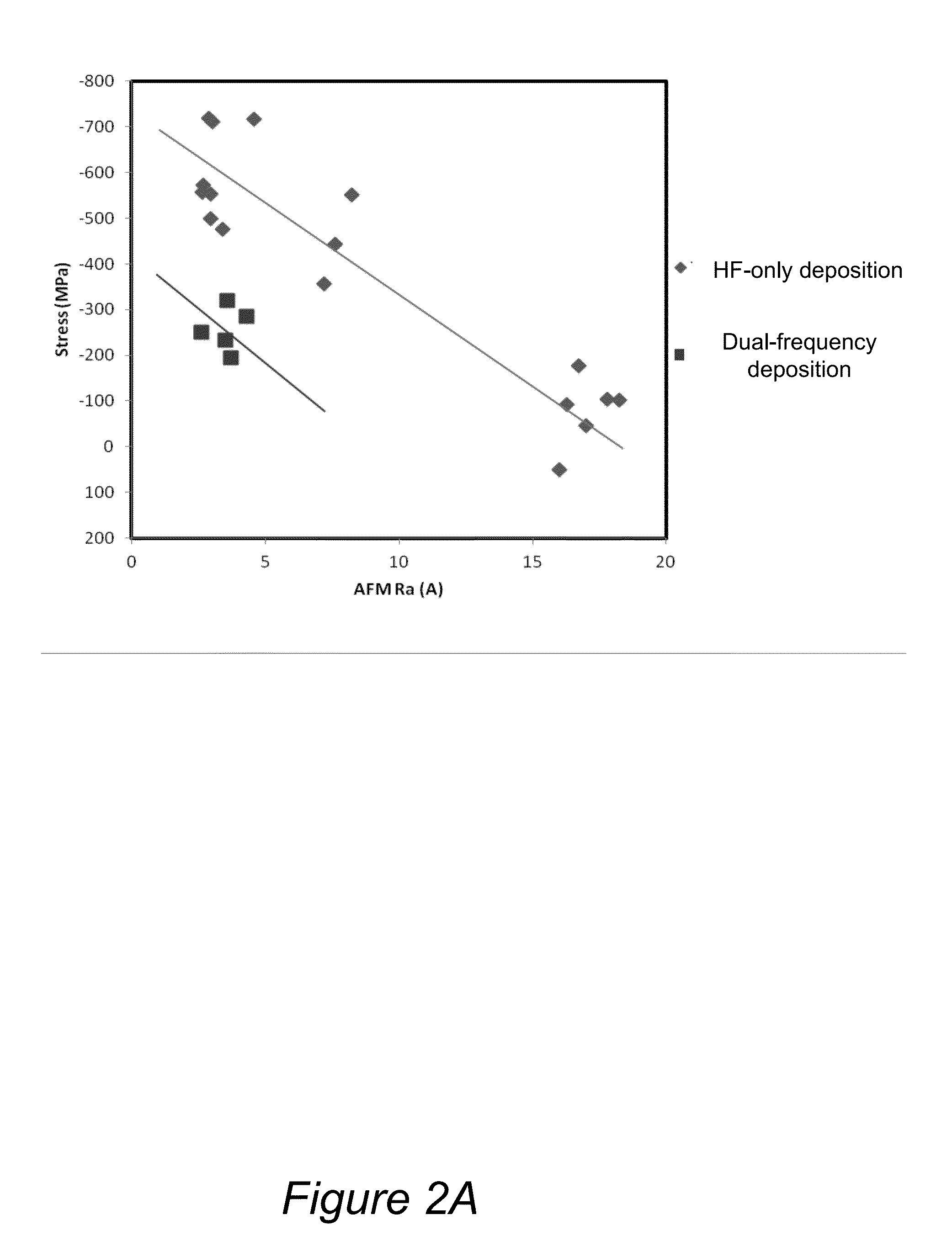
Pecvd deposition of smooth silicon films
ActiveUS20130316518A1Reduce compressive stressReduce roughnessLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic force microscopySilanes
Smooth silicon films having low compressive stress and smooth tensile silicon films are deposited by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) using a process gas comprising a silicon-containing precursor (e.g., silane), argon, and a second gas, such as helium, hydrogen, or a combination of helium and hydrogen. Doped smooth silicon films and smooth silicon germanium films can be obtained by adding a source of dopant or a germanium-containing precursor to the process gas. In some embodiments dual frequency plasma comprising high frequency (HF) and low frequency (LF) components is used during deposition, resulting in improved film roughness. The films are characterized by roughness (Ra) of less than about 7 Å, such as less than about 5 Å as measured by atomic force microscopy (AFM), and a compressive stress of less than about 500 MPa in absolute value. In some embodiments smooth tensile silicon films are obtained.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Microelectromechanical system and methods of use
InactiveUS20150177272A1Travel can be limitedThermometers using physical/chemical changesAcceleration measurementAccelerometerGyroscope
Methods of measuring displacement of a movable mass in a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) include driving the mass against two displacement-stopping surfaces and measuring corresponding differential capacitances of sensing capacitors such as combs. A MEMS device having displacement-stopping surfaces is described. Such a MEMS device can be used in a method of measuring properties of an atomic force microscope (AFM) having a cantilever and a deflection sensor, or in a temperature sensor having a displacement-sensing unit for sensing a movable mass permitted to vibrate along a displacement axis. A motion-measuring device can include pairs of accelerometers and gyroscopes driven 90° out of phase.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Aromatic Polyamide Porous Film, Process for Producing the Same and Secondary Battery
InactiveUS20080113177A1Increase stiffnessIncrease capacitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesPolymer scienceAfm atomic force microscopy
The problem addressed by this invention is to provide an aromatic polyamide porous film excellent in the capability of being thinned and capable of easily exhibiting stable porosity properties even if it is used for a long period of time at high temperature. This invention can be achieved by an aromatic polyamide porous film that contains an aromatic polyamide as a main component and is such that when an atomic force microscope is used to measure a range of S μm2 at least on one surface, the sectional area S(10) μm2 obtained at a depth of 10 nm from the surface and the sectional area S(20) μm2 obtained at a depth of 20 nm from the surface satisfy the following formulae simultaneously.0.01≦S(10) / S≦0.35≦S(20) / S(10)≦20
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Surface and site-specific polymerization by direct-write lithography
Polymeric microstructures and nanostructures can be prepared with use of a tip to pattern a surface. A tip can be used to pattern a structure which can initiate polymerization. The structure can be then exposed to monomer to induce polymerization at the structure. Alternatively, a tip can be used to pattern a surface with a monomer in which the surface is treated with polymerization catalyst so that polymerization occurs at the patterning site. Ring-opening metathesis polymerization can be carried out with use of the tip to control the polymerization. The tip can be a sharp tip as used in for example an atomic force microscope tip. Norbornene types of monomers can be used. Biological macromolecules can be also prepared.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Graphene-clad atomic force microscope probe and manufacturing method and application thereof
InactiveCN104360107AExtended service lifeReduce lossScanning probe microscopyAfm atomic force microscopyMegasonic cleaning
The invention belongs to the field of atomic force microscopes and relates to a graphene-clad atomic force microscope probe and a manufacturing method and application thereof. The graphene-clad atomic force microscope probe comprises a probe base, a cantilever arm and a tip; the cantilever arm and the tip are provided with a metal layer; the tip is further provided with a graphene layer. The manufacturing method includes the steps of 1, preparing graphene solution, to be specific, adding 5-10mg of graphene to 1mL of water, and performing ultrasonic dispersion for 10min with an ultrasonic cleaner to obtain 5-10mg / mL graphene solution; and 2, preparing the graphene-clad atomic force microscope probe, to be specific, dipping the tip of the atomic force microscope probe with the metal layer on the cantilever arm and the tip, into the graphene solution of the step 1, and performing mechanical stirring for 30-60s before extracting the probe to allow natural airing.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
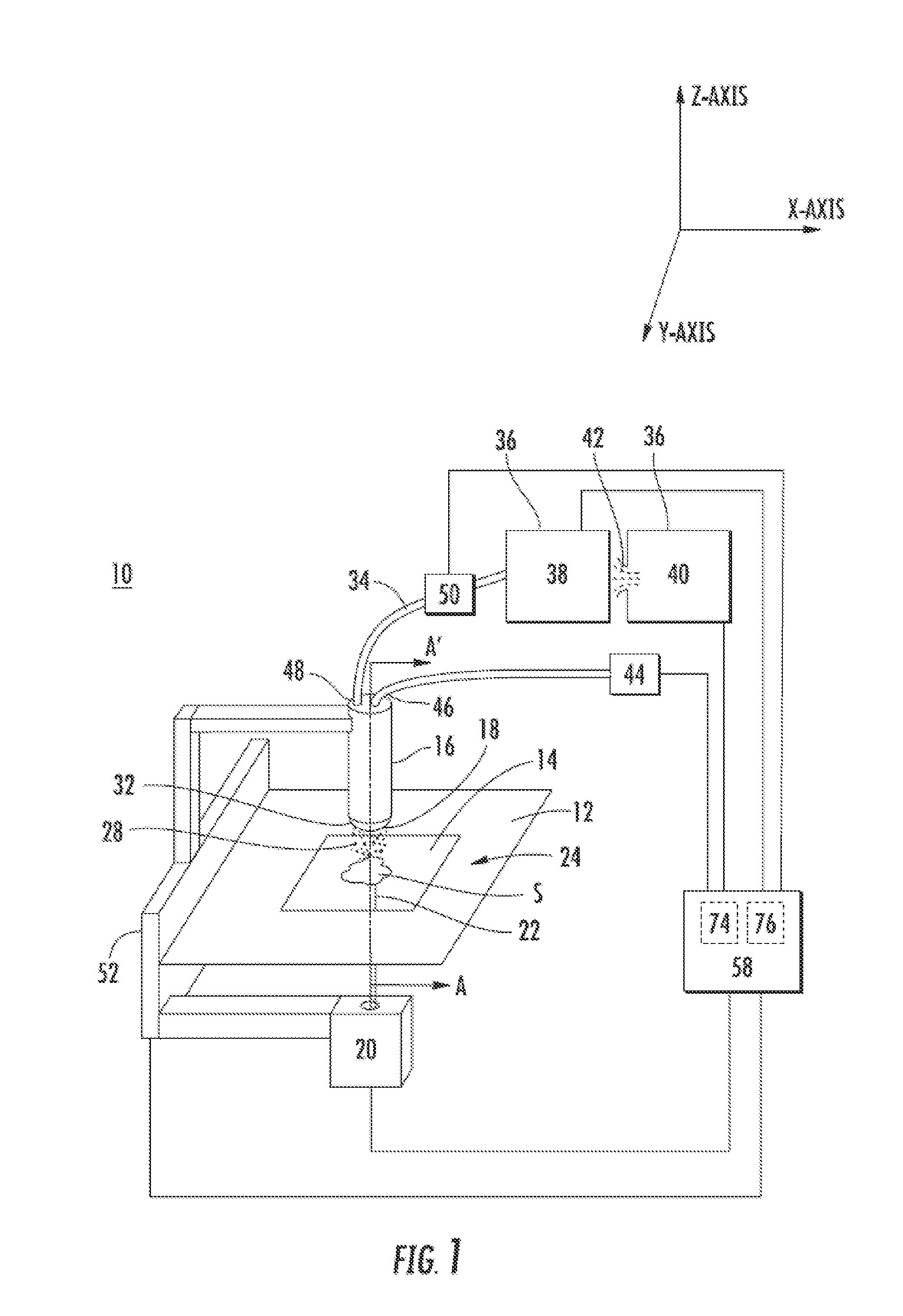
Measurement head for atomic force microscopy and other applications
InactiveUS6871527B2Small and rigid packageIncrease stiffnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAtomic force microscopyLight beam
An improvement for atomic force microscopes, more generally for light beam detecting systems, but also in part applicable to scanning probe microscopes, providing significant novel features and advantages. Particular features include using different objective lens regions for incident and reflected light, a flexure that allows three dimensional motion of the optics block, forming the housing and optics block of a composite material or ceramic, arranging the components so that the beam never hits a flat surface at normal incidence, and providing a resonant frequency of cantilever vibration greater than 850 HZ between the cantilever and sample and the cantilever and focusing lens.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing probe tip of nano tube
InactiveCN1434461AEasy to controlGuaranteed efficient growthSurface/boundary effectInstrumental componentsPtru catalystHydrophile
The invention is a method for manufacturing nano tube probe tip; the pin applies to various mode of atom microscope. At first, the method decorates hydrophobe single layer film on the surface of various silicon probe pin, then it uses electrical field to eliminate the film or oxides the film into hydrophile film, it calculates the size of the activated area through the action that the pin acts onthe standard sample surface, then it fixed catalyst particles in the hydrophile area on the surface of the pin, finally, puts the pin which carries catalyst nano particles in the nano reactor and forms into nano tube.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
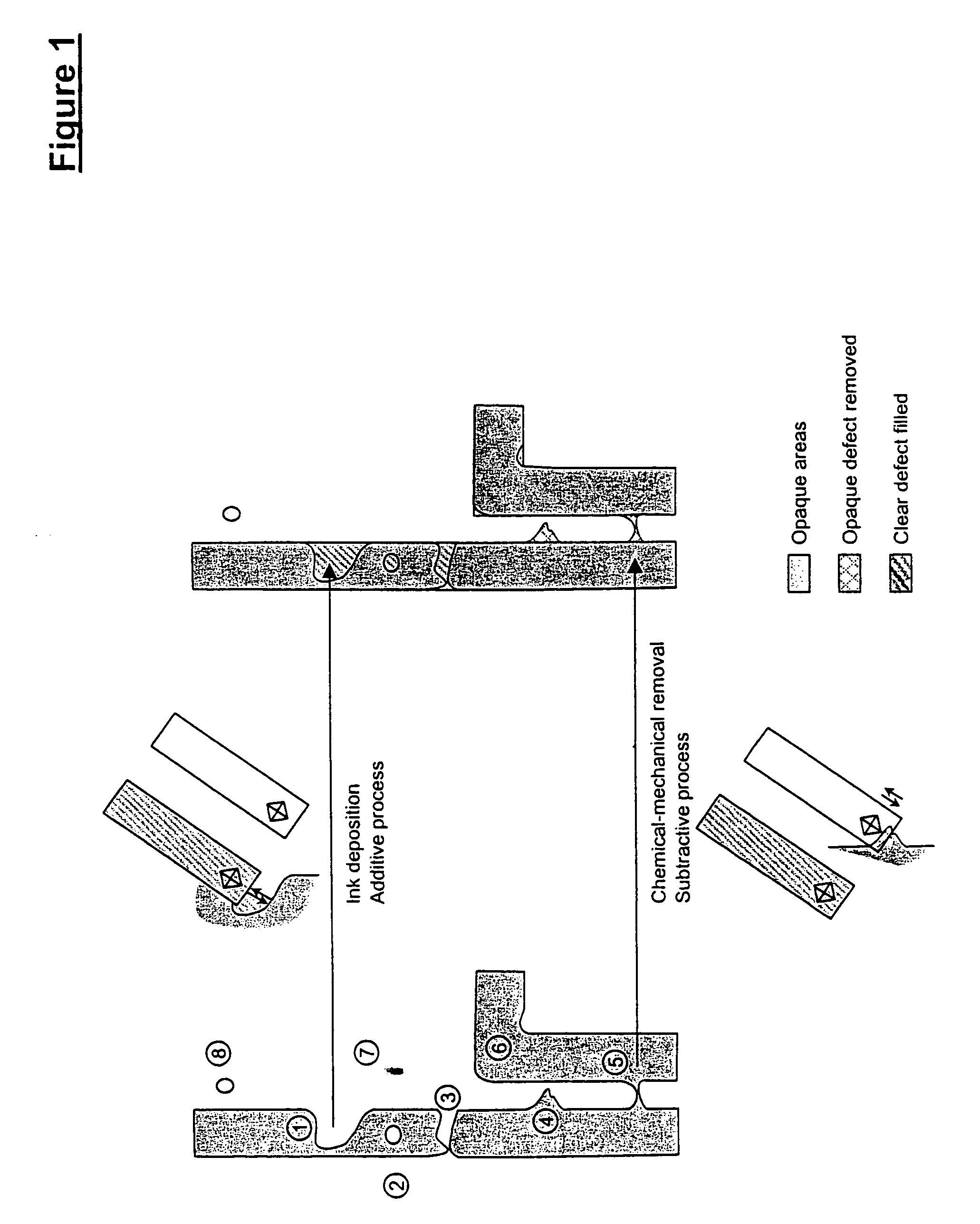
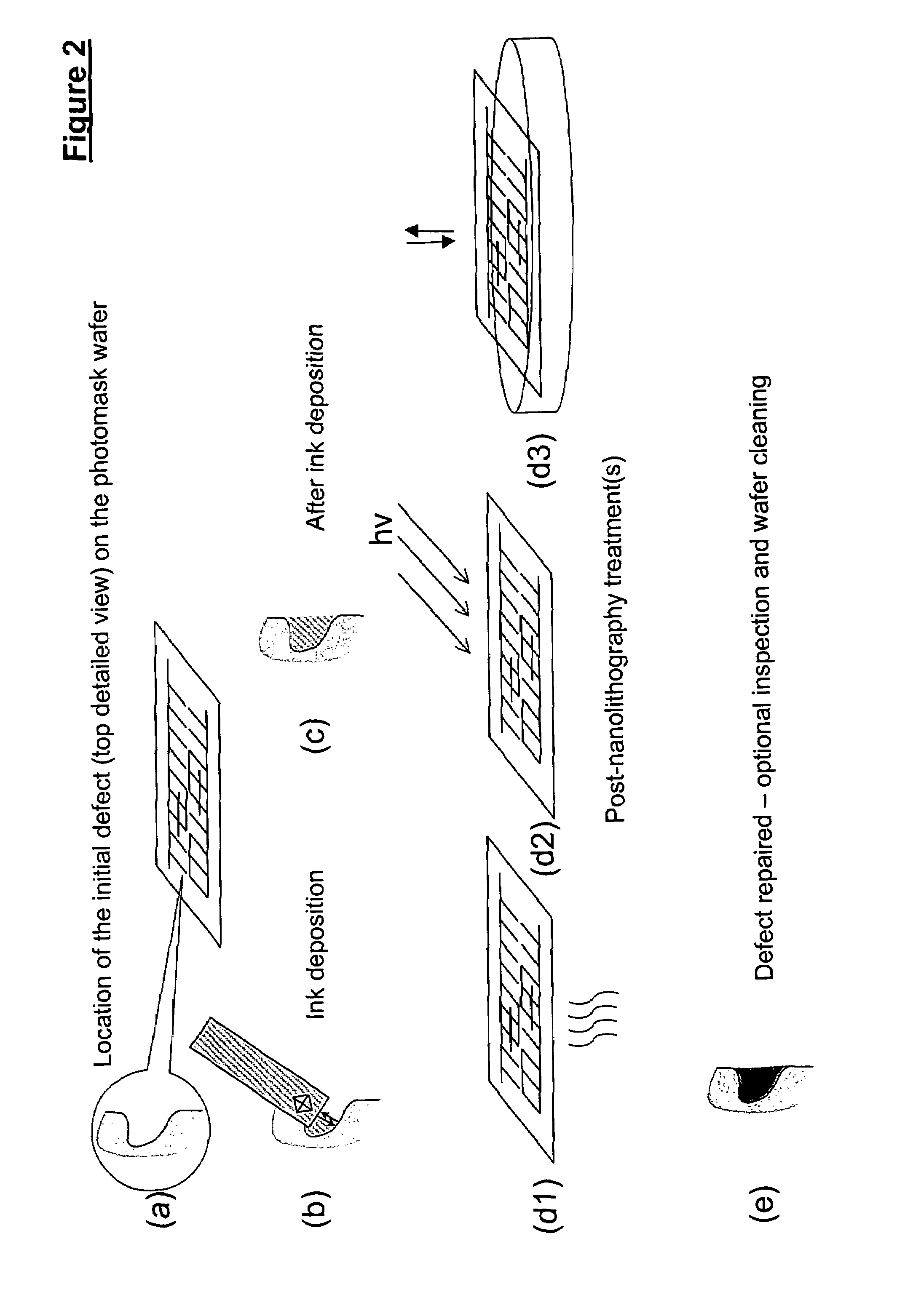
Methods for additive repair of phase shift masks by selectively depositing nanometer-scale engineered structures on defective phase shifters
InactiveUS7691541B2Improve performanceShorten the timeMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanolithographyOptical transparency
Photomask repair and fabrication with use of direct-write nanolithography, including use of scanning probe microscopic tips (e.g., atomic force microscope tips, etc.) for deposition of ink materials including sol-gel inks. Additive methods can be combined with subtractive methods. Holes can be filled with nanostructures. Heights of the nanostructures filling the holes can be controlled without losing control of the lateral dimensions of the nanostructures. Phase shifters on phase shifting masks (PSMs) are additively repaired with selectively deposited sol-gel material that is converted to solid oxide, which has optical transparency and index of refraction adapted for the phase shifters repaired.
Owner:NANOINK INC
Light extraction transparent substrate for organic el element, and organic el element using the same
InactiveUS20140042426A1Light extraction efficiencyChromaticity is decreasedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFast Fourier transformAfm atomic force microscopy
A light extraction transparent substrate for an organic EL element includes a transparent supporting substrate; a diffraction grating having a first concavity and convexity layer having first concavities and convexities formed on a surface thereof, which is located on a surface of the transparent supporting substrate, and a microlens having a second concavity and convexity layer having second concavities and convexities formed on a surface thereof, which is located on a surface of the transparent supporting substrate. When a Fourier-transformed image is obtained by performing two-dimensional fast Fourier transform processing on a concavity and convexity analysis image obtained by analyzing the shape of each of the first and second concavities and convexities by use of an atomic force microscope, the Fourier-transformed image shows a circular or annular pattern substantially centered at an origin at which an absolute value of wavenumber is 0 μm−1.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Low-temperature environmentally-friendly preparation method of nitrogen edge doped graphene
The invention relates to a low-temperature environmentally-friendly preparation method of nitrogen edge doped graphene, and belongs to the field of novel carbon nano-materials. The preparation method is characterized in that graphite powder and a nitrogen-containing polymer solid are mixed and subjected to continuous ball milling at a certain ball milling speed under the normal temperature and normal pressure so as to obtain a nitrogen edge doped graphene nanosheet, wherein no liquid agents are added during preparation. By analyzing through a scanning electron microscope and an atomic force microscope, the product is a lamellar structure which is uniform in dispersion and less than 1 nanometer in thickness. The analysis result of an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shows that the prepared product contains nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and other elements, and therefore, that the nitrogen edge doped graphene nanosheet is successfully prepared can be verified.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
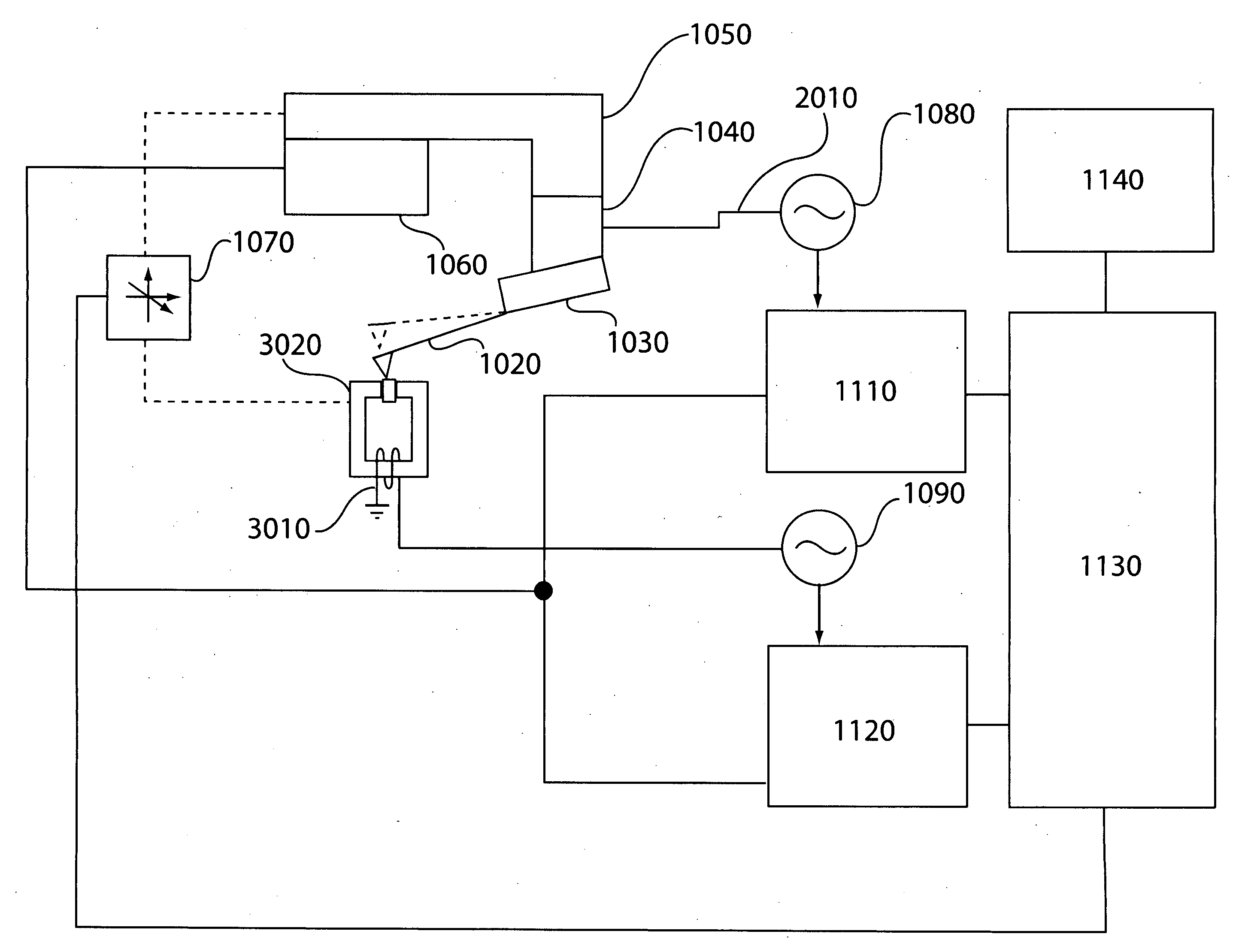
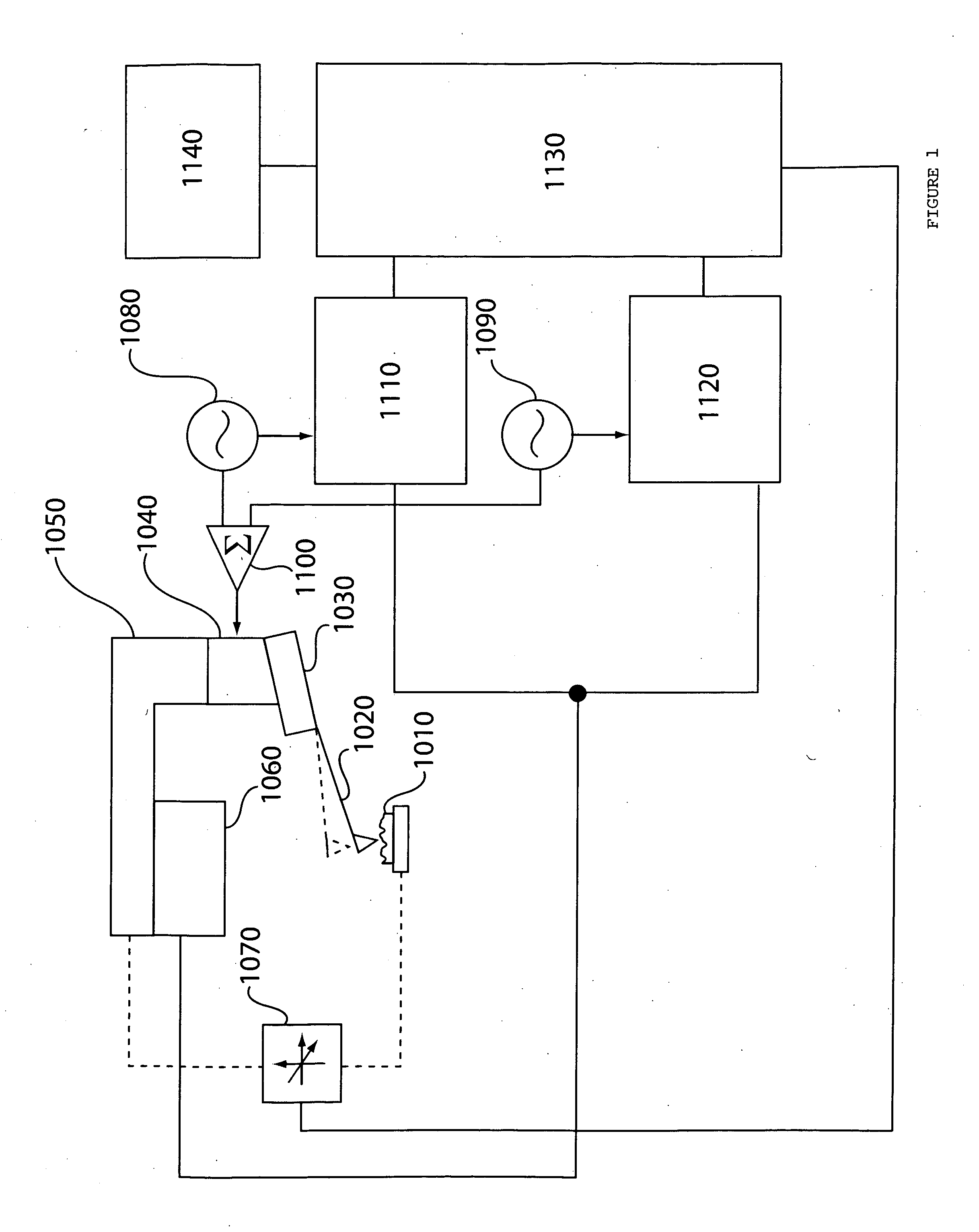
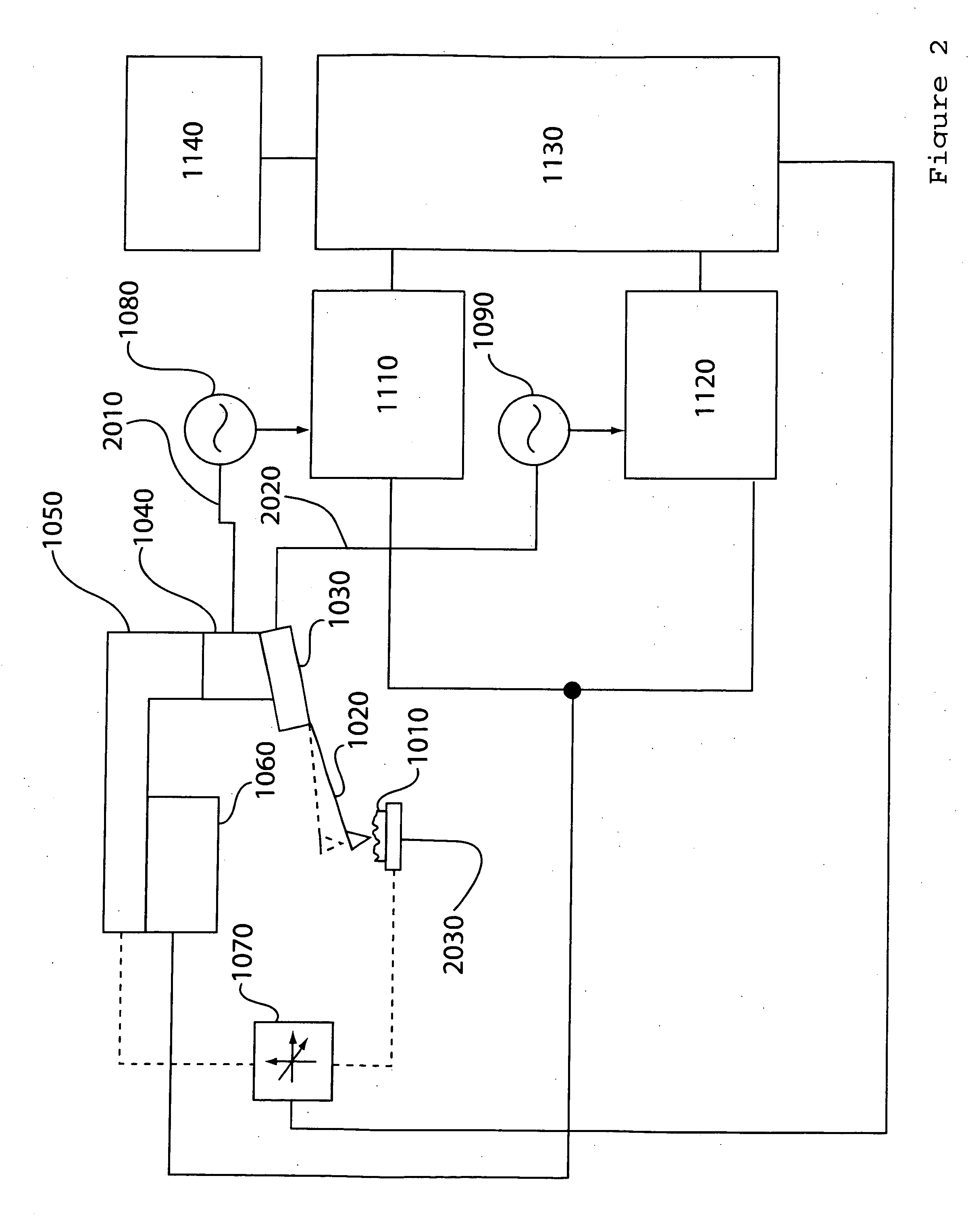
Atomic force microscope technique for minimal tip damage
InactiveUS20070277599A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSurface/boundary effectEngineeringMicroscope
Methods and apparatus for automatically determining a feedback setpoint for use in operating an atomic force microscope (AFM) are provided. The setpoint may be determined by modulating a feedback setpoint while monitoring for a change in a detector signal. In an effort to avoid tip damage and remain in non-contact, attractive mode during use, a setpoint just above a setpoint corresponding to a detected change in a parameter of the detector signal, such as an abrupt change in phase, may be used to operate the AFM.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Multiple frequency atomic force microscopy
ActiveUS20070245815A1Good effectReduce harmNanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsAtomic force microscopyHarmonic
An apparatus and technique for extracting information carried in higher eigenmodes or harmonics of an oscillating cantilever or other oscillating sensors in atomic force microscopy and related MEMs work is described.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR ASYLUM RES INC +1
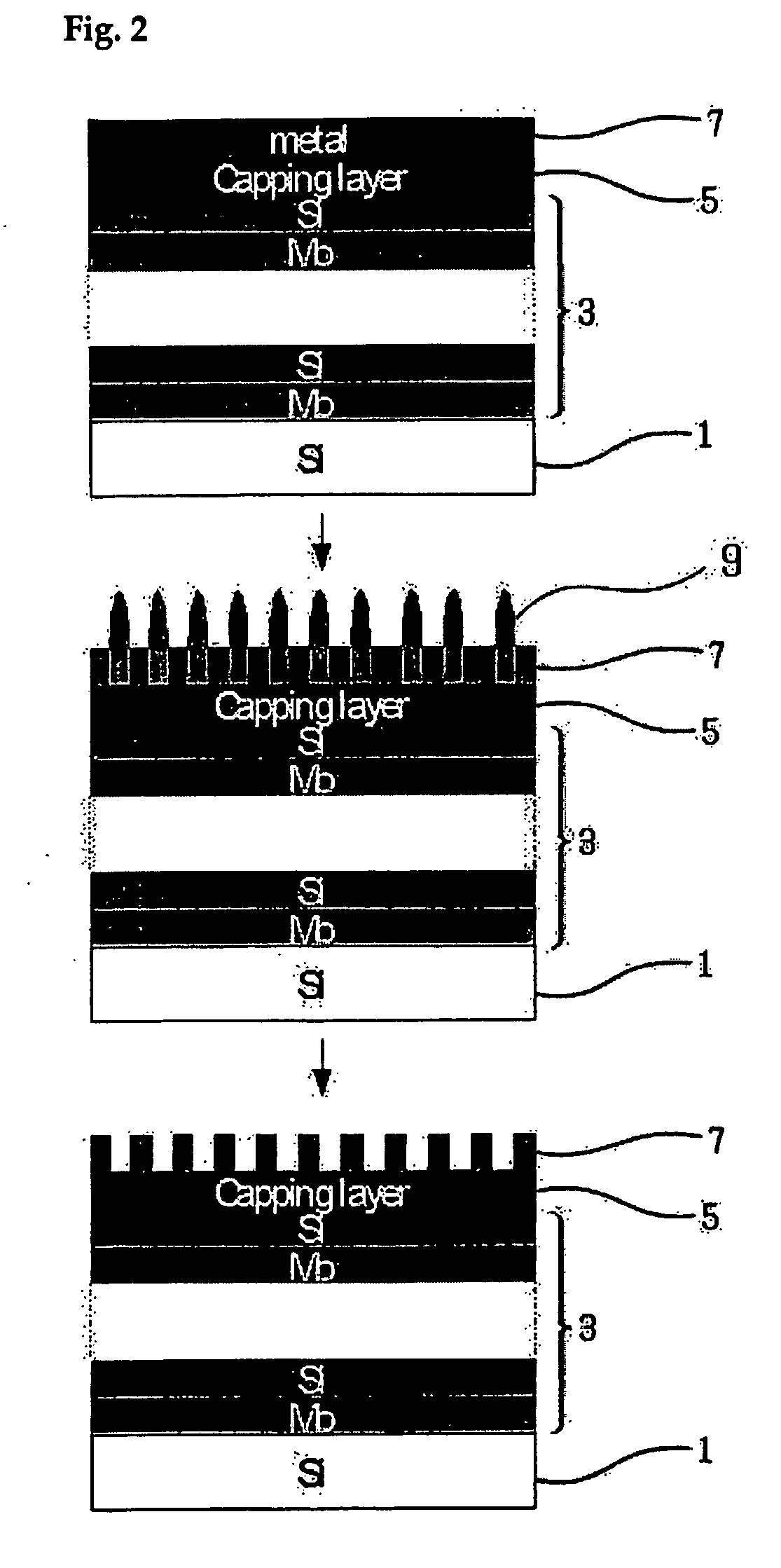
Fabrication method of extreme ultraviolet radiation mask mirror using atomic force microscope lithography
InactiveUS20070054196A1Reduce pollutionReduce surface roughnessMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsExtreme ultravioletRadiation exposure
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a reflective multi-layered thin film mirror for an extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV) exposure process that is one of the next generation exposure process masks using an atomic force microscope (AFM). This reflective multi-layered thin film mirror for extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV) exposure process allows metal oxide structures with fixed height and width to be obtained using anodic oxidization phenomenon between the cantilever tip of a atomic force microscope and an absorber material during the patterning of an absorber layer on a multi-layered thin film of a substrate, followed by forming the ultra-fine line width absorber patterns via etching of the metal oxide structure. Use of the manufacturing process of this invention is advantageous in manufacturing of extreme ultraviolet radiation exposure mask mirrors with high resolution and in manufacturing of reflective multi-layered thin film mirrors with minute absorber pattern sizes (less than 20 nm line width) compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
Manufacturing method of a piezoelectric micro-cantilever beam probe
InactiveCN101580223AResolve interferenceKeep sharpDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingField emission deviceElectricity
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a piezoelectric micro-cantilever beam probe, belonging to the technical field of micro-mechanical sensors and actuators. The invention is characterized in that a partial piezoelectric layer is adopted to realize integration of the manufacturing technique of a nano silicon needle point and the manufacturing technique of a piezoelectric film. In the manufacturing process, the nano silicon needle point adopts anisotropic wet corrosion method with a mask; the piezoelectric film is manufactured by adopting a sol-gel method. The invention has the beneficial effects of having both functions of sensing and executing by adopting the piezoelectric film as a sensitive part, being capable of finishing the whole technological process by adopting a dry etching and wet etching technique, having lower requirements on the technological equipment, being capable of being produced in batches and reducing the cost of products. The piezoelectric micro-cantilever beam probe manufactured by the method can be used for atomic force microscopes, nano-imprint storage devices and field emission devices.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Measuring method for dislocation density of heteroepitaxially grown gallium nitride
InactiveCN103487453AConvenient and quick analysis testAccurately Calculate DensityPreparing sample for investigationScanning probe microscopyPotassium hydroxideAfm atomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a method for observing the dislocation type of a heteroepitaxial growth material of gallium nitride (GaN) and measuring the dislocation density. The method is characterized by directly observing the dislocation type of the surface of a gallium nitride epitaxial film by using etching of molten potassium hydroxide and a potassium hydroxide and magnesia eutectic mixture in combination with a scanning electron microscope and an atomic force microscope, analyzing and researching the characteristics and the distribution of dislocations of different types and calculating the dislocation density. The method is convenient and fast and is suitable for analytical testing of nitrides which grow through different processes. The characteristics of dislocations of different types in different nitride samples can be researched to obtain the distribution of various dislocations on the surface, and the densities and the total dislocation density of the dislocations of various types can be accurately calculated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Probe unit of microscope with atomic force and manufacturing method
InactiveCN1661355AGood orientationUniform diameterSurface/boundary effectScanning probe microscopyCarbon nanotubeCantilever
The present invention relates to an atomic force microscope probe device and its making method. It includes a probe seat, a cantilever which is fixed on the probe seat and has at least a tail end on which a probe point can be set and a carbon nano tube which is set on the tail end of said cantilever and used as probe point, in which the top portion of said probe cantilever tail end is formed into a plane with hole, and said carbon nano tube can be grown out from said hole which is basically perpendicular to said plane.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Single-cell/single-molecule imaging light/electricity comprehensive tester based on multifunctional probe
ActiveCN103197102AHigh spatio-temporal resolutionReal-time detection and analysis of biochemical mechanismsScanning probe microscopyDiseaseInsulation layer
The invention discloses a single-cell / single-molecule imaging light / electricity comprehensive tester based on a multifunctional probe. The tester comprises the multifunctional nano-probe, a sample pool, an atomic force microscope system, a light source unit, an electricity testing unit, a cell sample locating system and a photon testing unit. The light source unit, the electricity testing unit, the cell sample locating system and the photon testing unit are respectively connected with a data collection and analyzing unit. The multifunctional nano-probe comprises an optical fiber layer, a nano electrode layer and an insulation layer. The nano electrode layer and the insulation layer are wrapped on the outer wall of the optical fiber layer in sequence. The synchronization comprehensive tester comprises a manufacturing method of the nano-probe which can carry out atomic force scanning imaging on single-cells / single-molecules and carry out light / electricity testing at the same time, a manufacturing method of the sample pool and relevant optics, electricity and mechanics testing and analyzing instruments. Temporal-spatial resolution and the range of target objects which can be tested are greatly improved, the tester can be widely used in biology and medicine and be used for fundamental research and disease testing under the level of sub-cells and molecules, and the tester has great development significance on tumor early diagnosis, medicine development and agricultural science.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Diffraction grating, organic EL element using the same, and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveUS8541778B2Low wavelength dependenceReduce directivityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesFast Fourier transformAfm atomic force microscopy
A diffraction grating having a transparent supporting substrate; and a cured resin layer which is stacked on the transparent supporting substrate and which has concavities and convexities formed on a surface thereof, wherein when a Fourier-transformed image is obtained by performing two-dimensional fast Fourier transform processing on a concavity and convexity analysis image obtained by analyzing a shape of the concavities and convexities formed on the surface of the cured resin layer by use of an atomic force microscope, the Fourier-transformed image shows a circular or annular pattern substantially centered at an origin at which an absolute value of wavenumber is 0 μm−1, and the circular or annular pattern is present within a region where an absolute value of wavenumber is within a range of 10 μm−1 or less.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP +1
Atomic force microscope as an analyzing tool for biochip
InactiveUS20100261615A9Easy to adaptImprove the forceLibrary screeningNanotechnologyAfm atomic force microscopyAnalysis tools
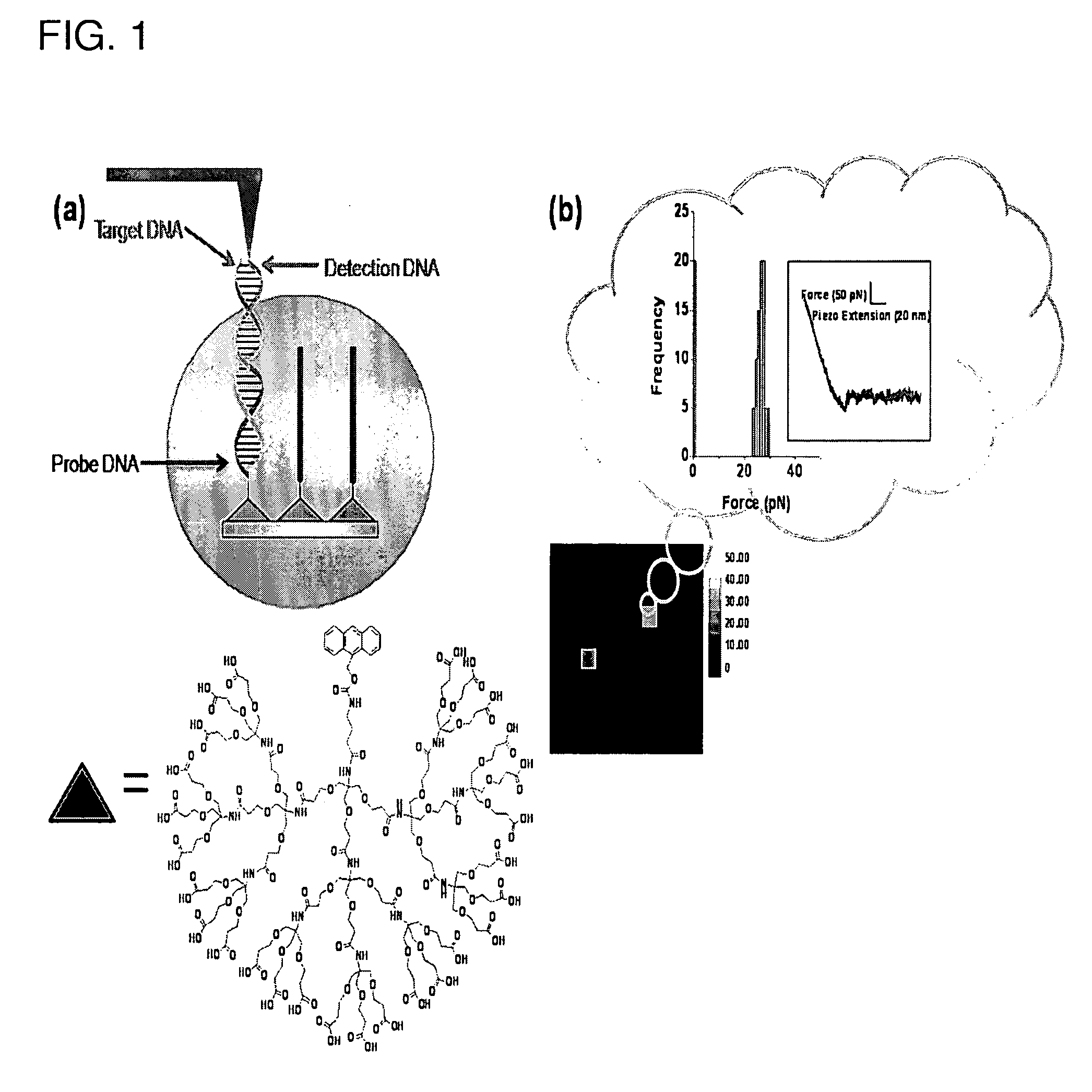
The present application discloses a method for detecting a presence of target ligand in a fluid medium which includes the steps of: (i) contacting the fluid medium with a solid substrate that includes an array of dendrons on its surface, wherein each of the dendron includes a central atom, a probe that is attached to the central atom optionally through a linker, and a base portion attached to the central atom and having a plurality of termini that are attached to the surface of the solid support; and (ii) determining the presence of a probe-target ligand complex by measuring binding force between the bound ligand and detection molecule tethered to the tip of an atomic force microscope (“AFM”), which detection molecule has affinity for the ligand, wherein measurement of an increase in force between the probe-target ligand complex and the detection molecule by AFM indicates the presence of the probe-target ligand complex.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
High resolution, high speed multi-frequency dynamic study of visco-elastic properites
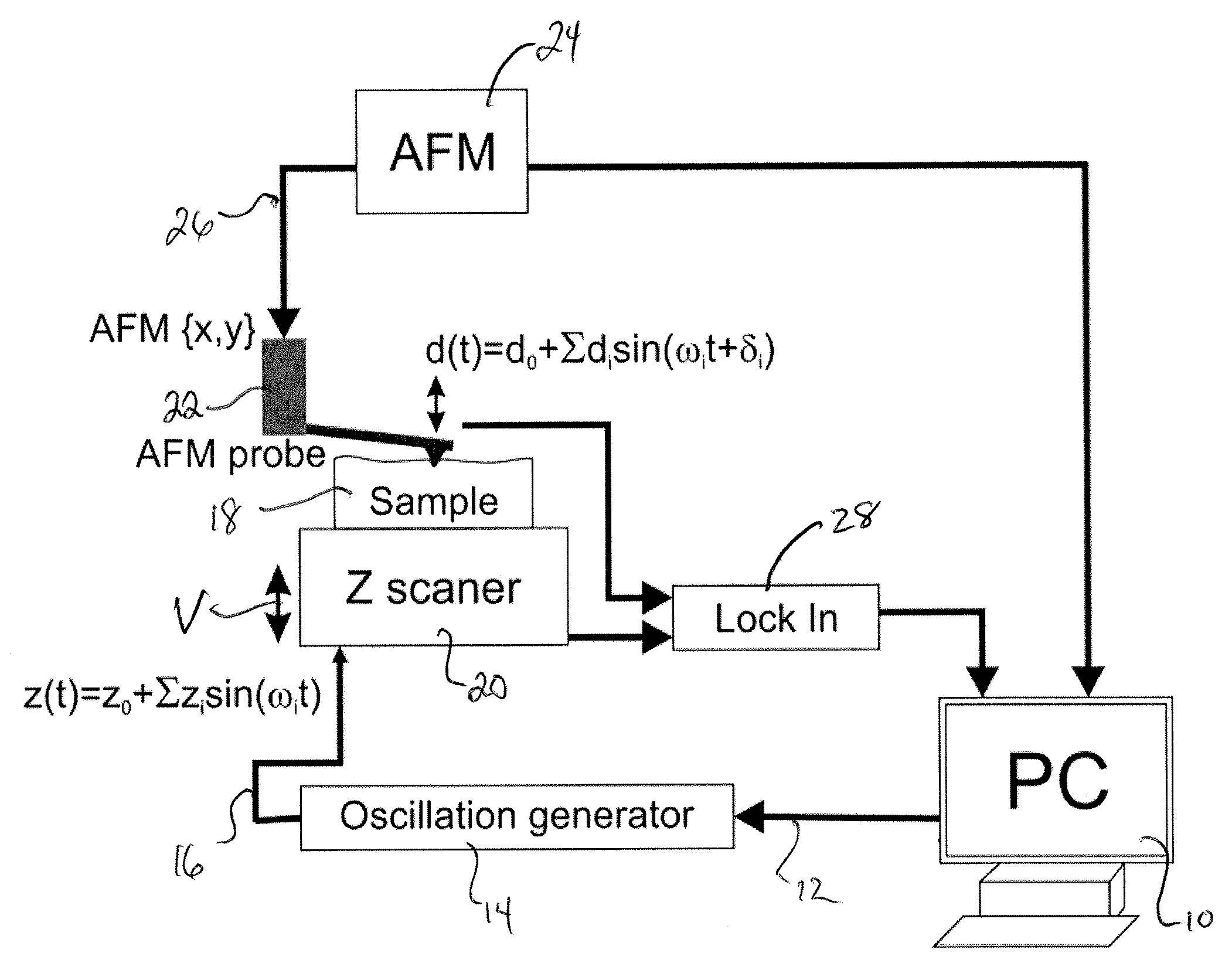
The present invention provides an apparatus and method including hardware and software, which allows collecting and analyzing of data to obtain information about mechanical properties of soft materials. This allows surface mapping of viscoelastic properties in a high-resolution and fast manner. It also allows finding the degree of nonlinearity of the material response of the sample during the measurements. The apparatus can be used as a stand-alone device, or an add-on to either the existing atomic force microscope or nanoindenter device.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
Atomic force microscope tip holder for imaging in liquid
InactiveUS20050241392A1Eliminate negative effectsIncrease drive frequencyFluid pressure measurementNanotechnologyElectricityTrapping
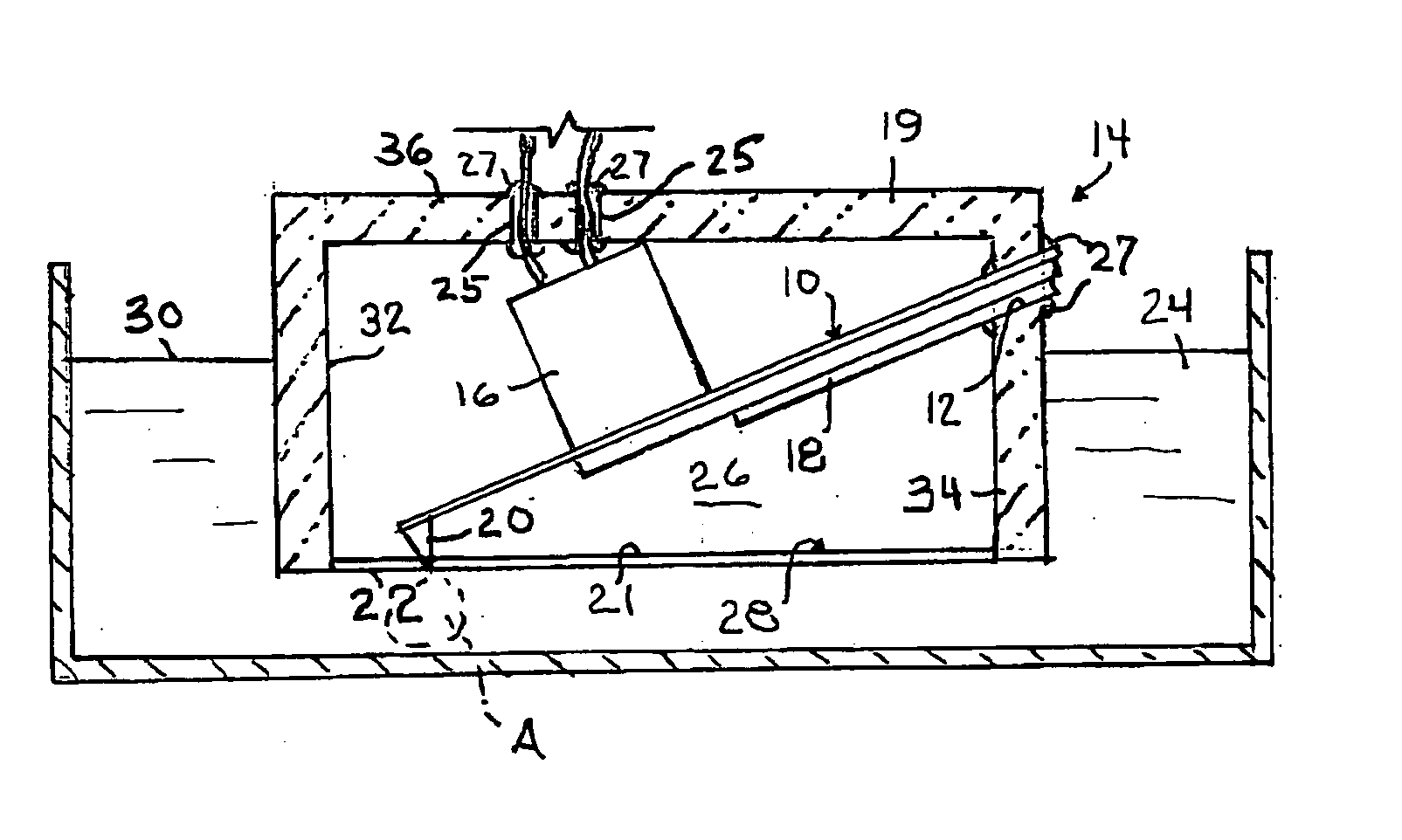
An atomic force microscope (ARM) tip holder includes a vessel open at the bottom with gas-tight walls and top. A piezoelectrically activated cantilever vibratory tip holder is secured at one end within the vessel and extends to a tip-holding end at a location proximate a liquid level established when the vessel is placed open end downward in a liquid trapping air or gas. Only a small portion of the tip extends into the liquid to contact the specimen for examination by e.g. “tapping mode” AFM. Presence of the cantilever and part of the tip in gas virtually eliminates the loss of performance encountered with liquid submersion.
Owner:LYUBCHENKO YURI L
Preparation method and use method of polishing solution for silicon carbide
InactiveCN102127371AEnhanced chemical processingFacilitate chemical reactionsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolishing compositions with abrasivesSurface roughnessMagnification
The invention provides polishing solution used on the surface of the high quality polished silicon carbide wafer, a preparation method of the polishing solution and a use method of the polishing solution. The polishing solution is prepared from deionized water, silica polishing solution, auxiliary oxidant and pH regulator. The polishing solution prepared by the method is odorless, has state and no precipitate and can be dispersed evenly and properly recycled; when the polishing solution is used to process the wafer, the removal rate is high; the processed silicon carbide wafer is brighter; the wafer has no unnoticeable scratches and is smooth and uniform when observed by a microscope with 50 fold magnification; and the surface roughness can reach nanometer level stably through the detection of an atomic force microscope. The cycle count of the polishing solution can be adjusted by changing the amounts of the added auxiliary oxidant and pH regulator or the ratio of the auxiliary oxidant and the pH regulator.
Owner:苏州天科合达蓝光半导体有限公司 +2
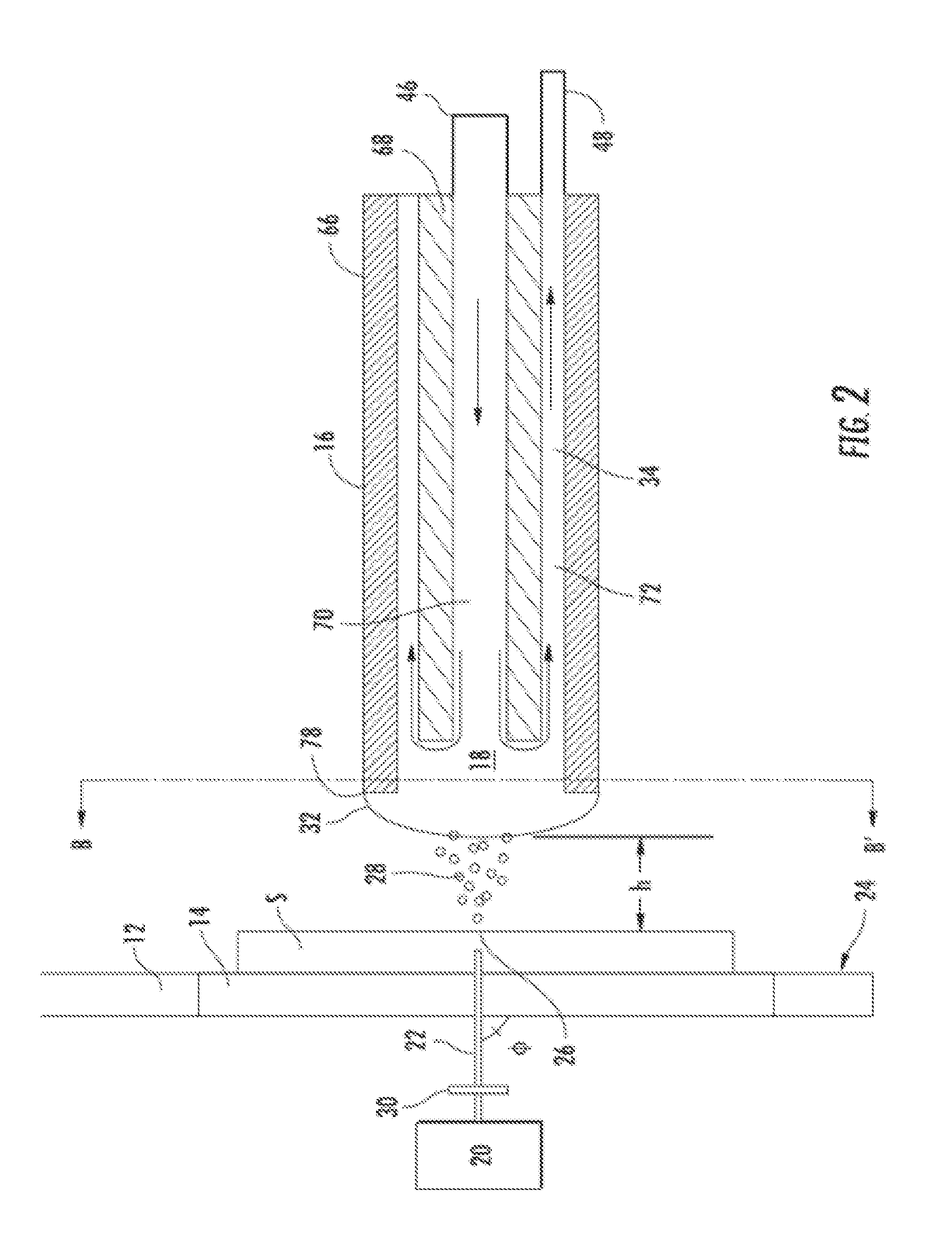
Two-dimensional micro-motion platform for atomic force microscope and micro-mechanical parameter test method
ActiveCN101339816ASurface/boundary effectInstrumental componentsAfm atomic force microscopyMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a 2D micro-positioning platform for an atomic force microscope and a measuring method of mechanical parameters. The 2D micro-positioning platform is characterized in that the center of the 2D micro-positioning platform is provided with a hole for equipping a PZT scanning tube, wherein an X position and a Y position perpendicular to each other are provided with two adjusting knobs respectively, the two adjusting knobs are connected with two drive rods which are connected with the PZT scanning tube, and the 2D micro-positioning platform is fixed on a base. The moving range of the 2D micro-positioning platform of the invention is 3*3 square mm in the horizontal direction; and the maximum scanning shift of the PZT scanning tube is 20Mum. By utilizing an AFM microscope with the improved 2D micro-positioning platform, the mechanical parameters of a fixed point on a microstructure can be tested, the mechanical-displacement function test of micro point-to-point and the continuous elastic coefficient test in a micro area can be carried out, and all the tests produce good consistency results.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic signal reproduction system and magnetic signal reproduction method
ActiveUS20090168265A1Good electromagnetic characteristicMaintenance characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storagePhysicsMicrometer
The present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a magnetic layer comprising a hexagonal ferrite powder and a binder on one surface of a nonmagnetic support and a backcoat layer on the other surface of the nonmagnetic support. A power spectrum density at a pitch of 10 micrometers ranges from 800 to 10,000 nm3 on the magnetic layer surface, a power spectrum density at a pitch of 10 micrometers ranges from 20,000 to 80,000 nm3 on the backcoat layer surface, the magnetic layer has a center surface average surface roughness Ra, as measured by an atomic force microscope, ranging from 0.5 to 2.5 nm, and the hexagonal ferrite powder has an average plate diameter ranging from 10 to 40 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Fluorescence axial localization with nanometer accuracy and precision
InactiveUS9103784B1Precise alignmentEasy alignmentPhotometryMicroscopesFluorescenceUltimate tensile strength
We describe a new technique, standing wave axial nanometry (SWAN), to image the axial location of a single nanoscale fluorescent object with sub-nanometer accuracy and 3.7 nm precision. A standing wave, generated by positing an atomic force microscope tip over a focused laser beam, is used to excite fluorescence; axial position is determined from the phase of the mission intensity.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
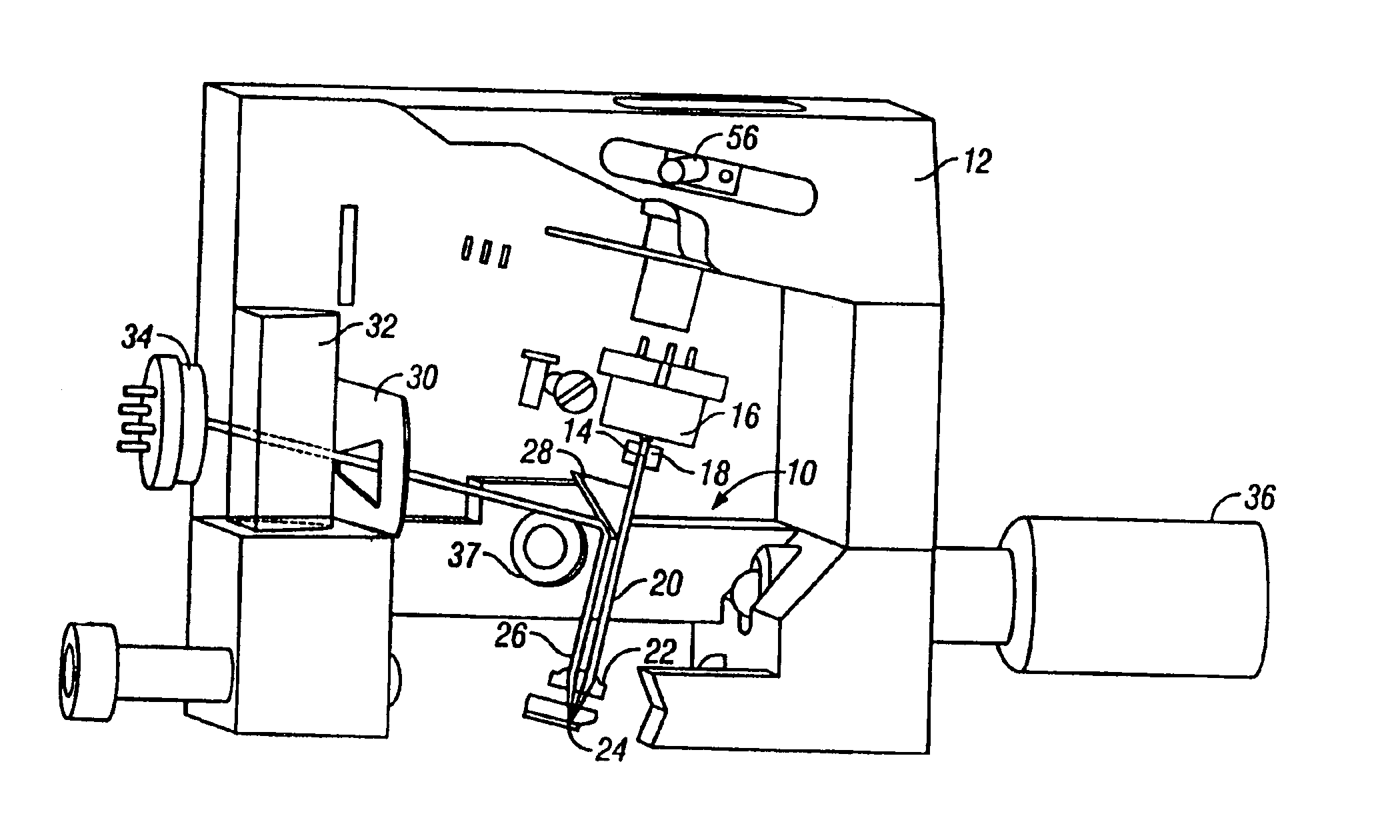
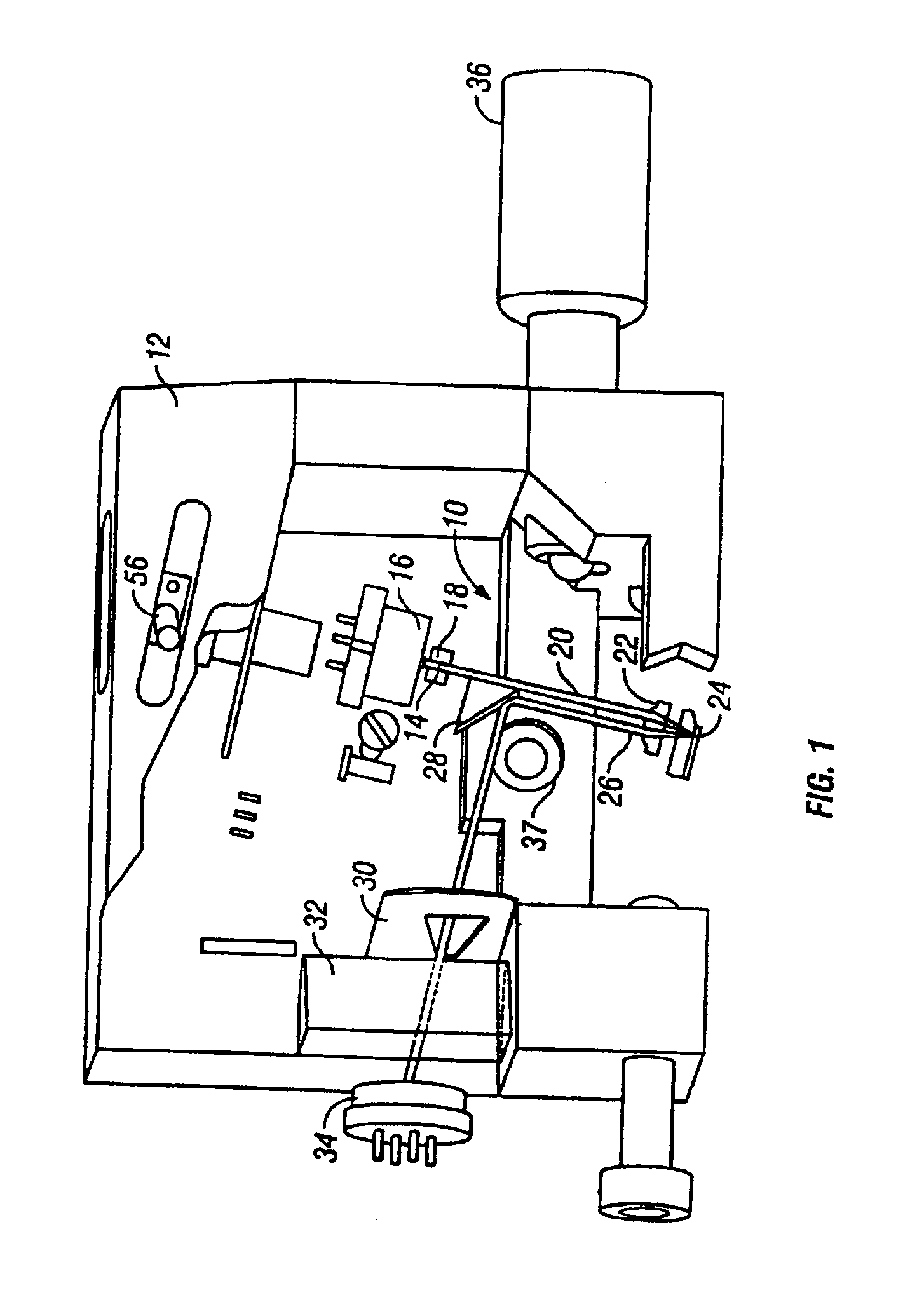
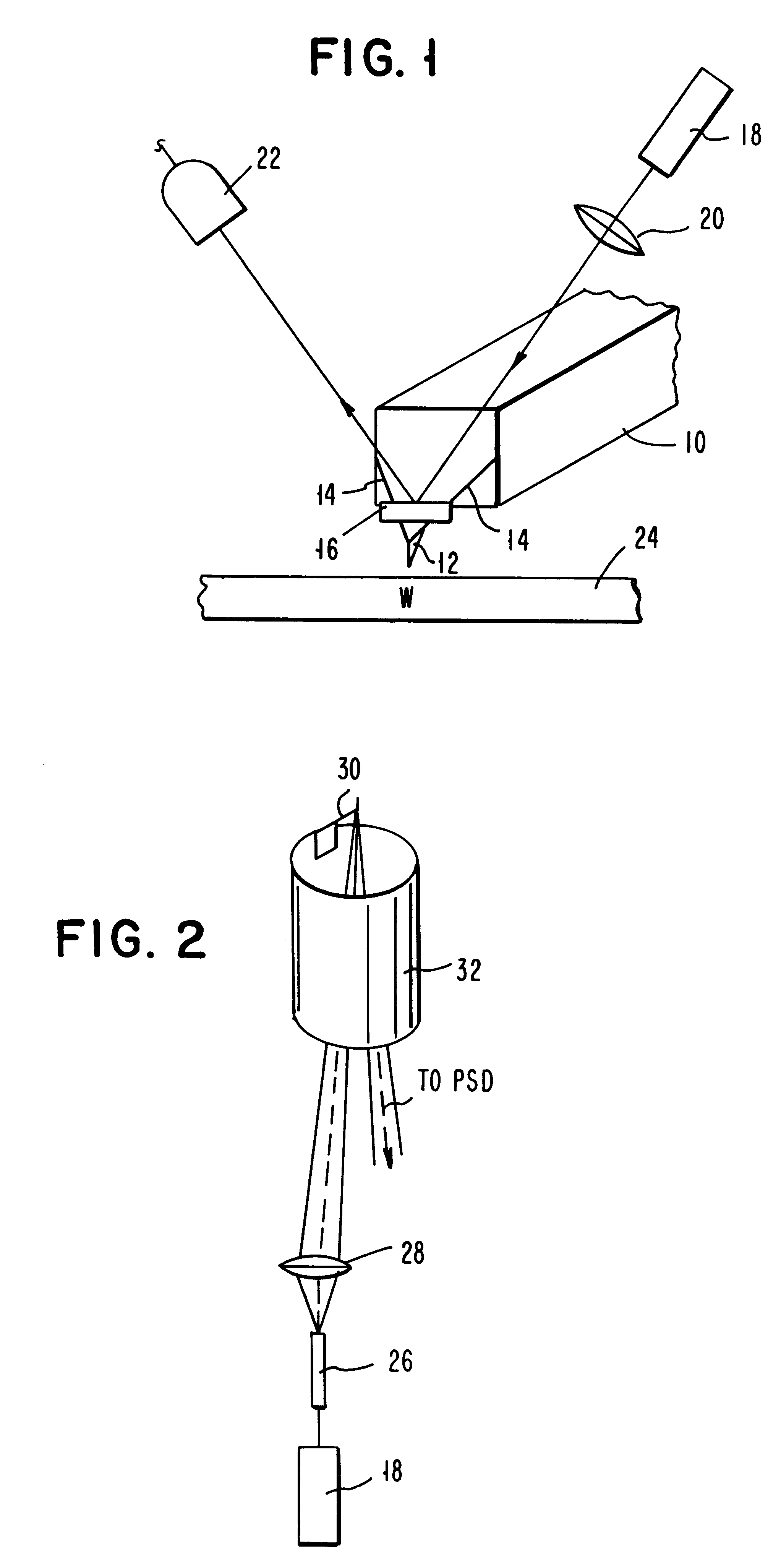
Atomic force microscopy
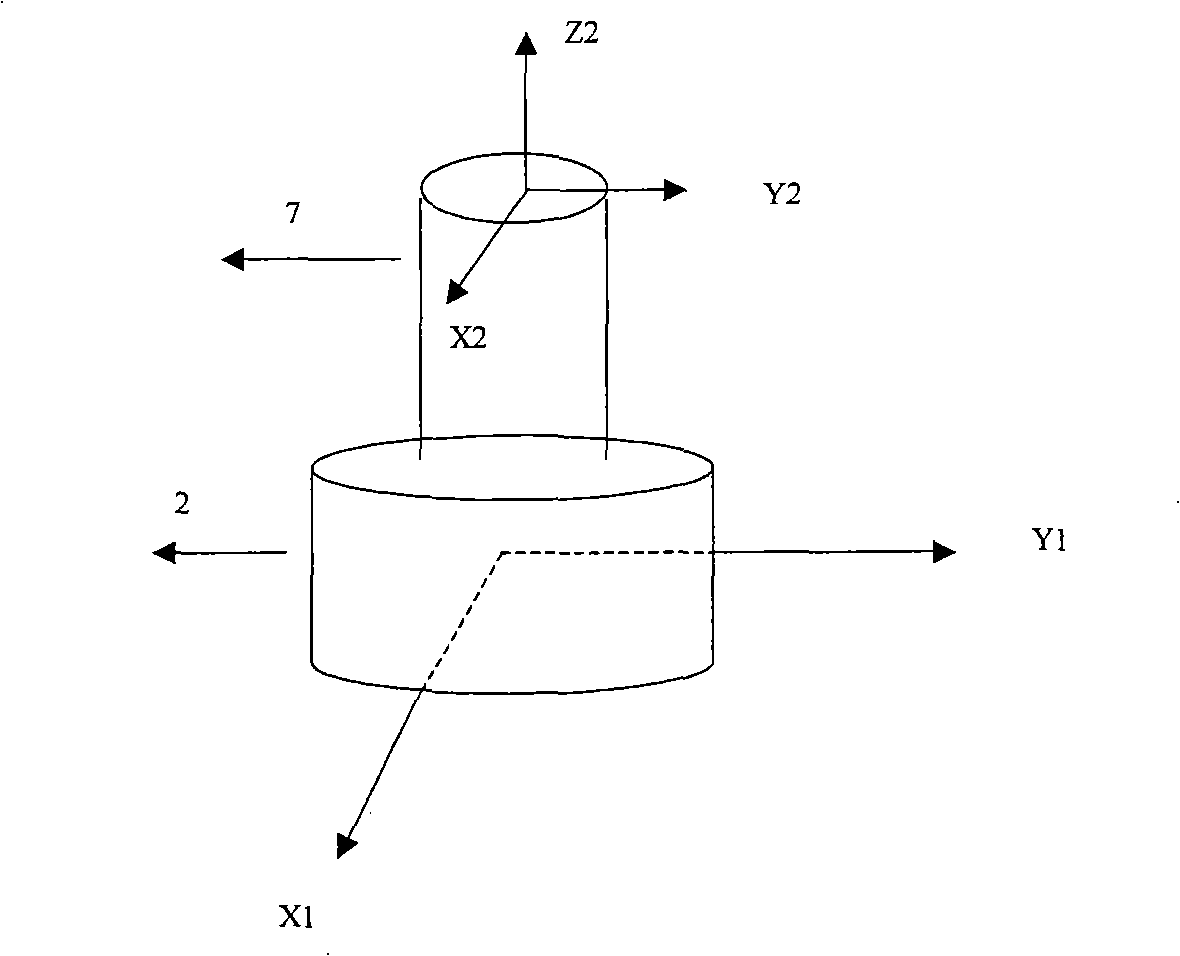
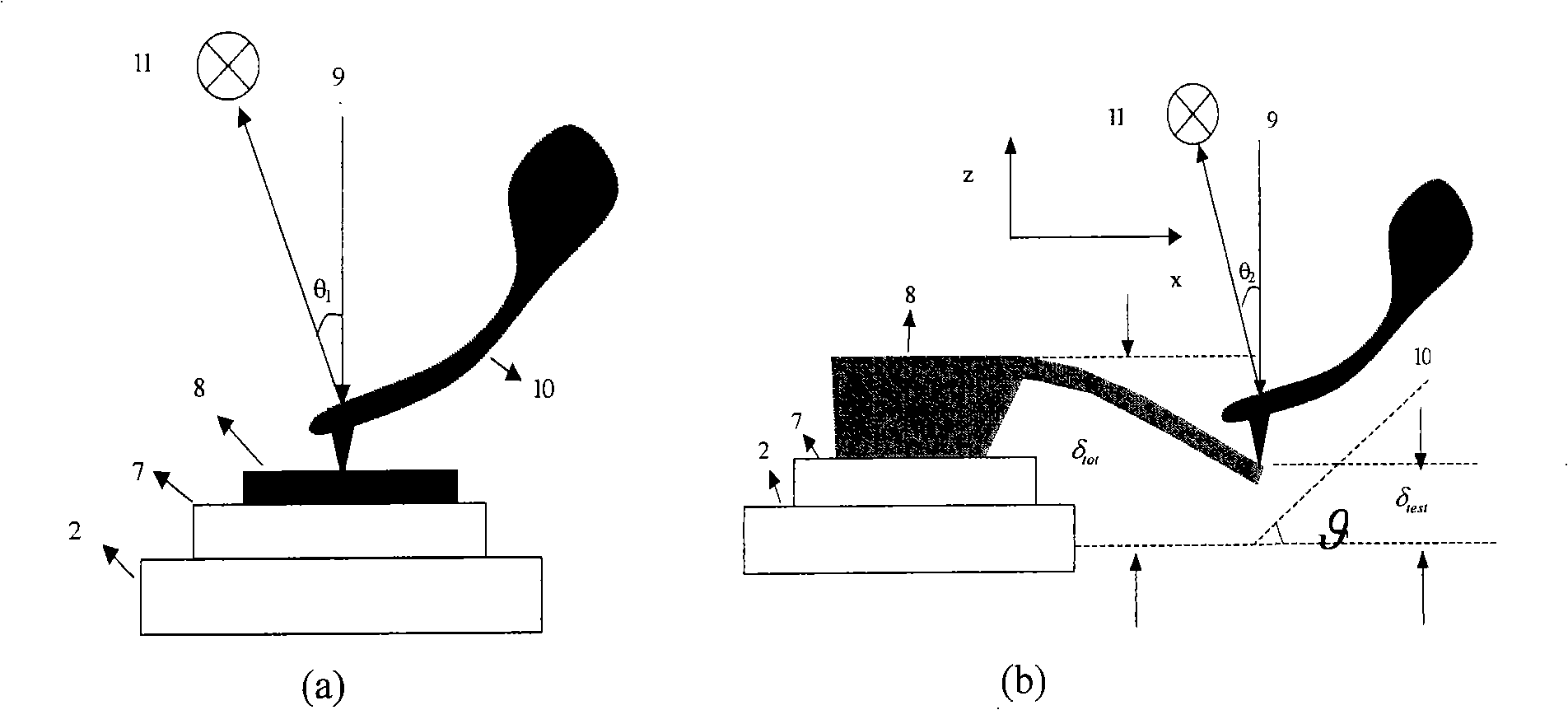
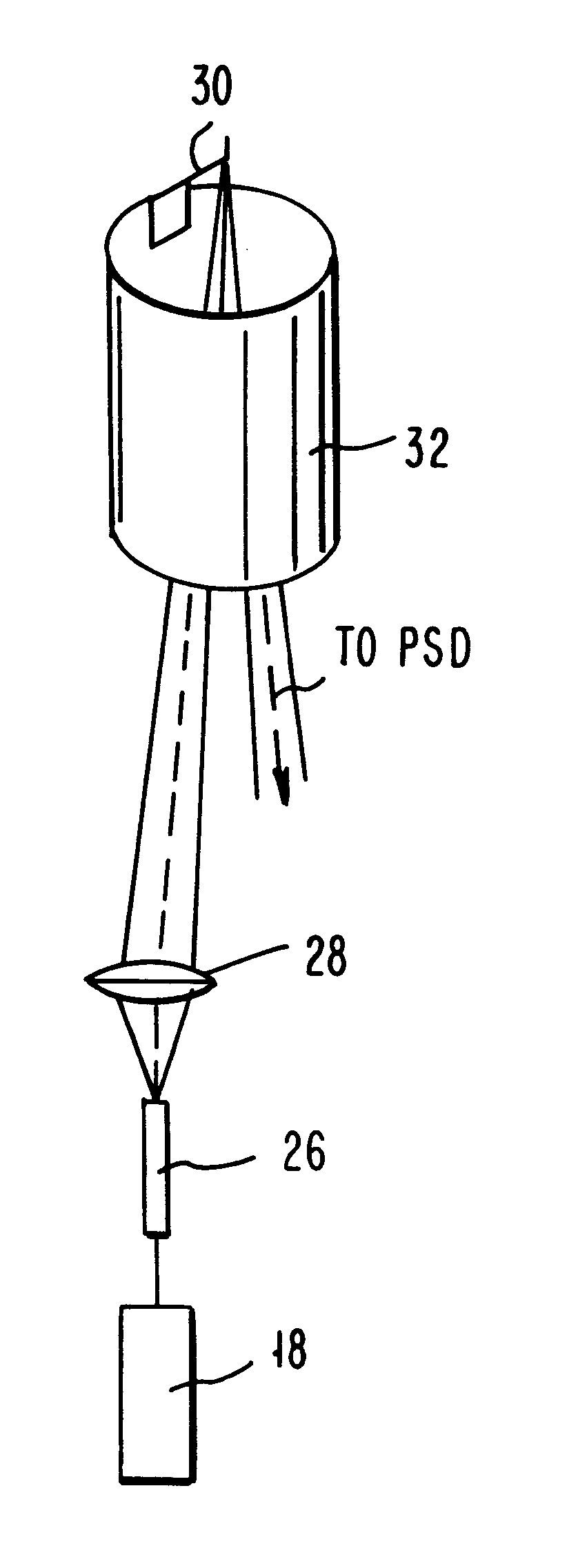
InactiveUSRE37299E1Convenient ArrangementMore compact designNanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic force microscopyImage resolution
An atomic force microscope includes a tip mounted on a micromachined cantilever. As the tip scans a surface to be investigated, interatomic forces between the tip and the surface induce displacement of the tip. A laser beam is transmitted to and reflected from the cantilever for measuring the cantilever orientation. In a preferred embodiment the laser beam has an elliptical shape. The reflected laser beam is detected with a position-sensitive detector, preferably a bicell. The output of the bicell is provided to a computer for processing of the data for providing a topographical image of the surface with atomic resolution.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor structure and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveCN102290379ANo impuritiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPolymeric surfaceAfm atomic force microscopy
A semiconductor device having a polymer layer and a method of fabricating the same is provided. A two-step plasma treatment for a surface of the polymer layer includes a first plasma process to roughen the surface of the polymer layer and loosen contaminants, and a second plasma process to make the polymer layer smoother or make the polymer layer less rough. An etch process may be used between the first plasma process and the second plasma process to remove the contaminants loosened by the first plasma process. In an embodiment, the polymer layer exhibits a surface roughness between about 1% and about 8% as measured by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) with the index of surface area difference percentage (SADP) and / or has surface contaminants of less than about 1% of Ti, less than about 1% of F, less than about 1.5% Sn, and less than about 0.4% of Pb.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com