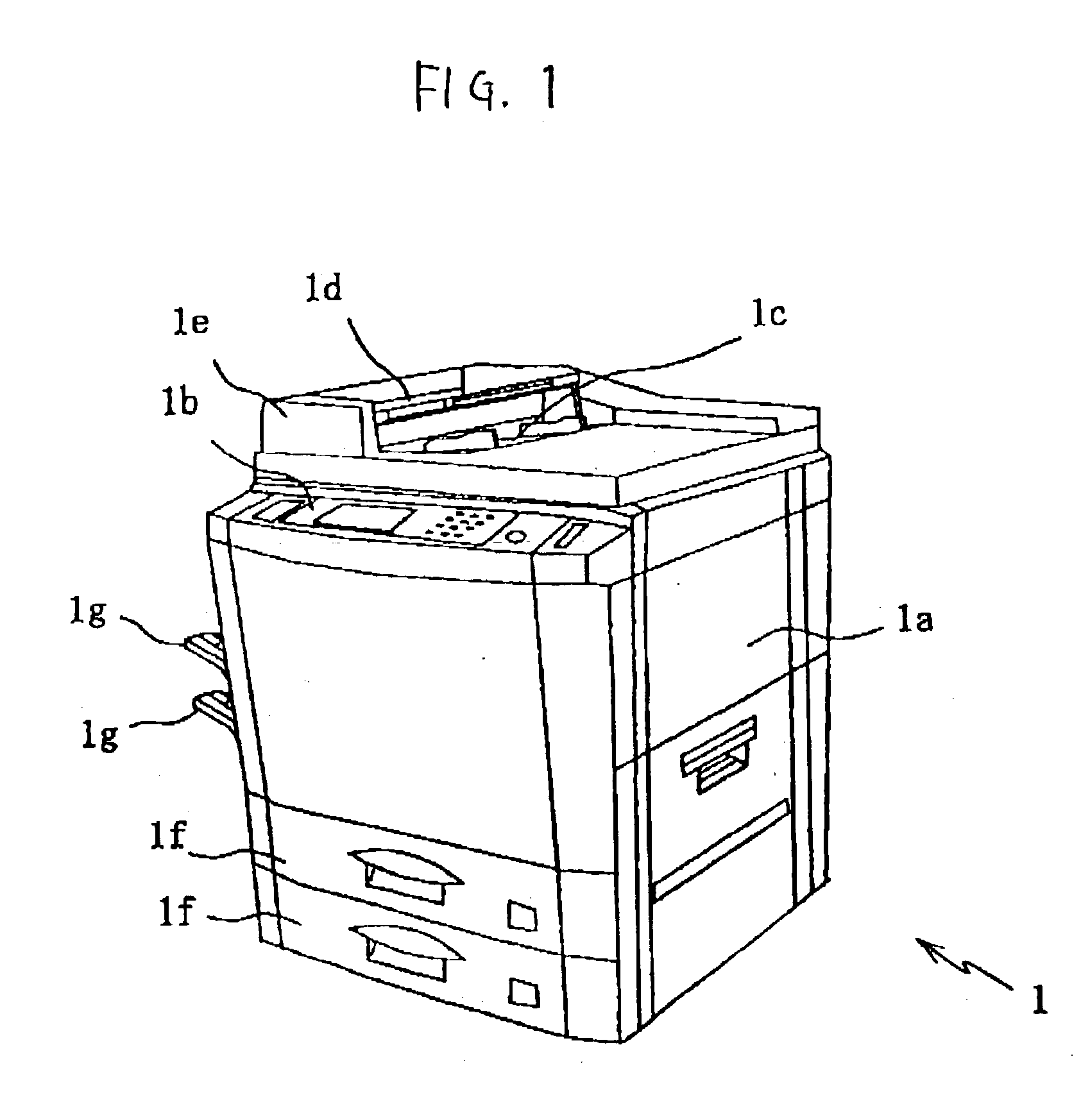
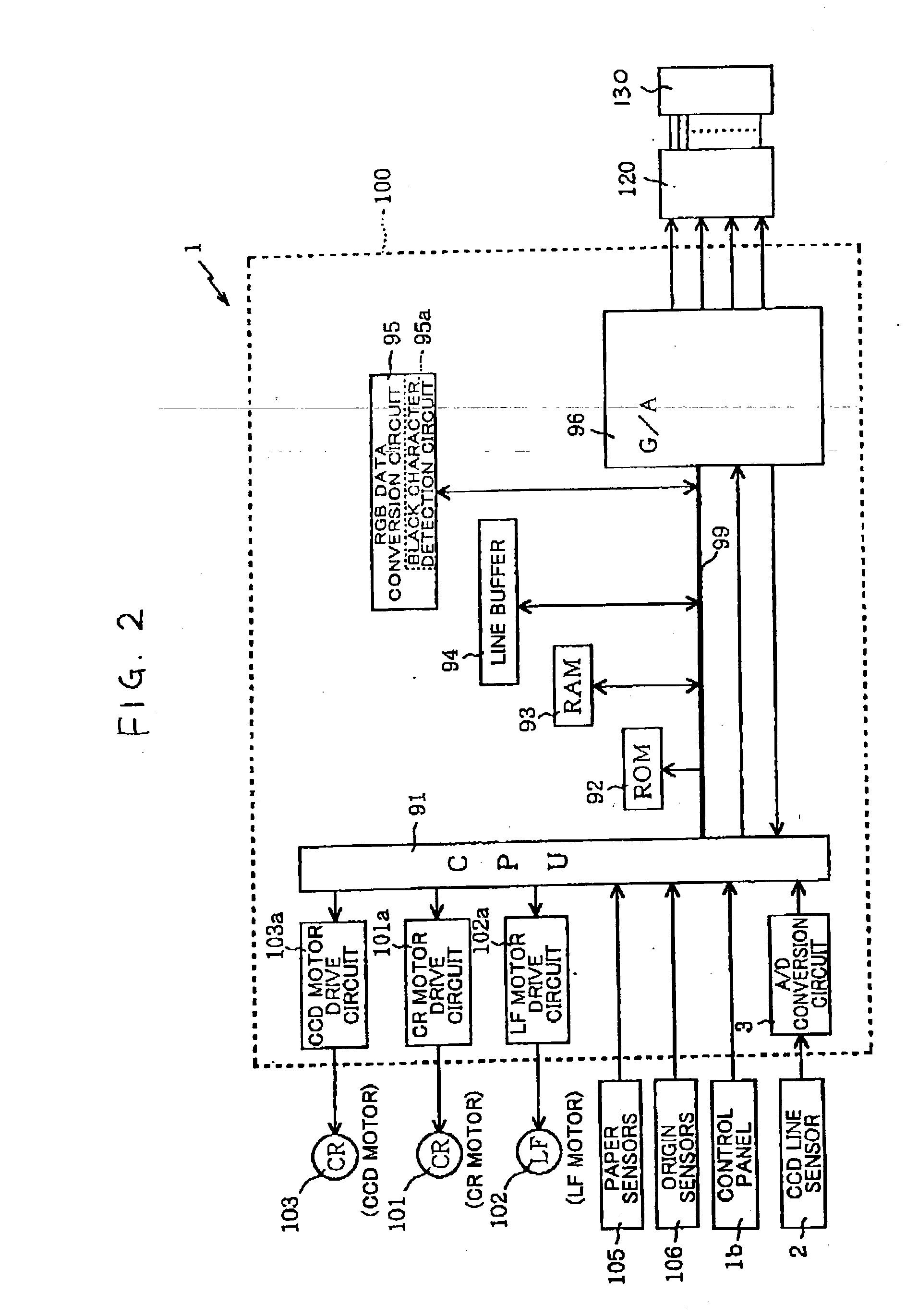
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
989 results about "Fine line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
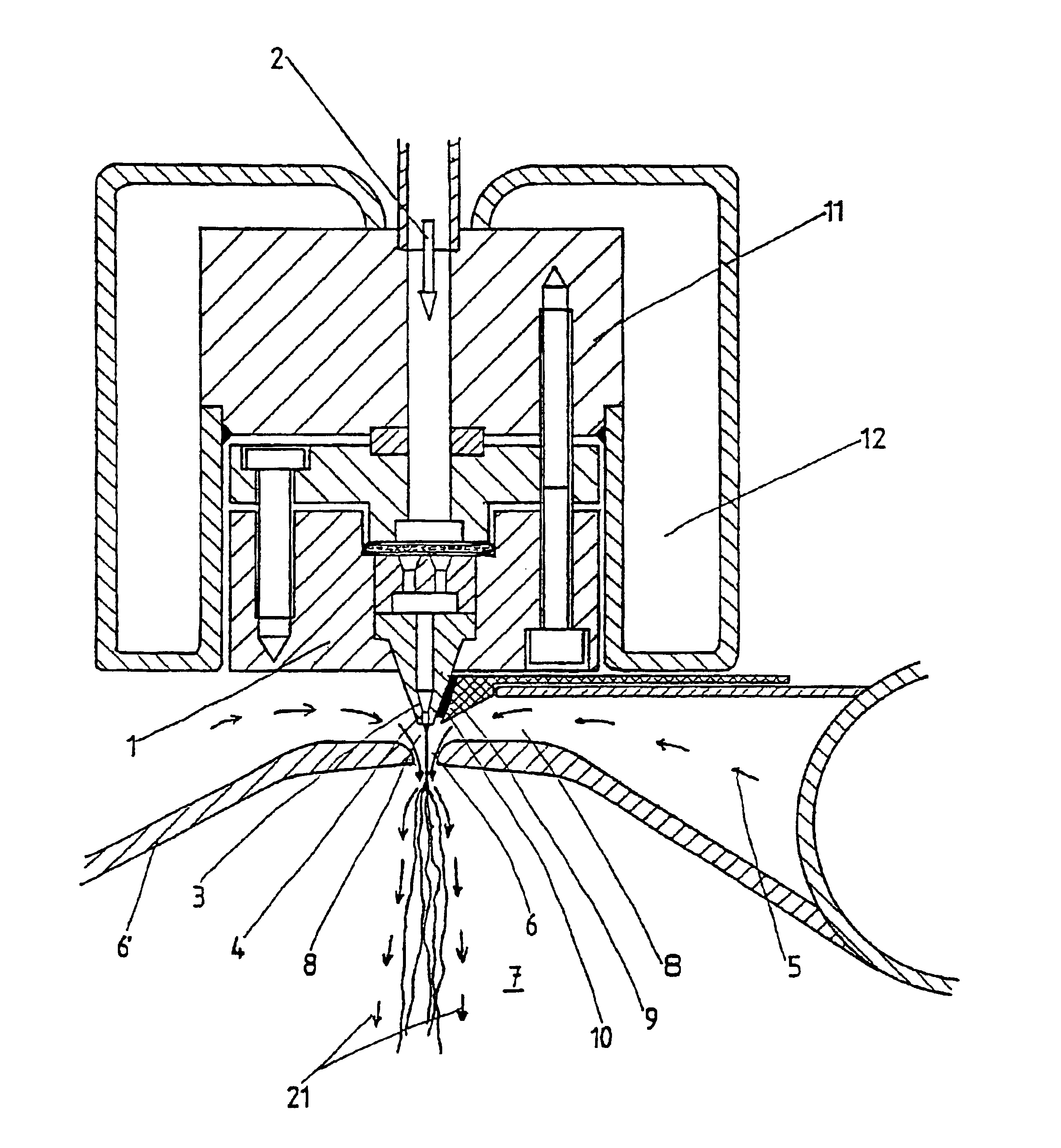
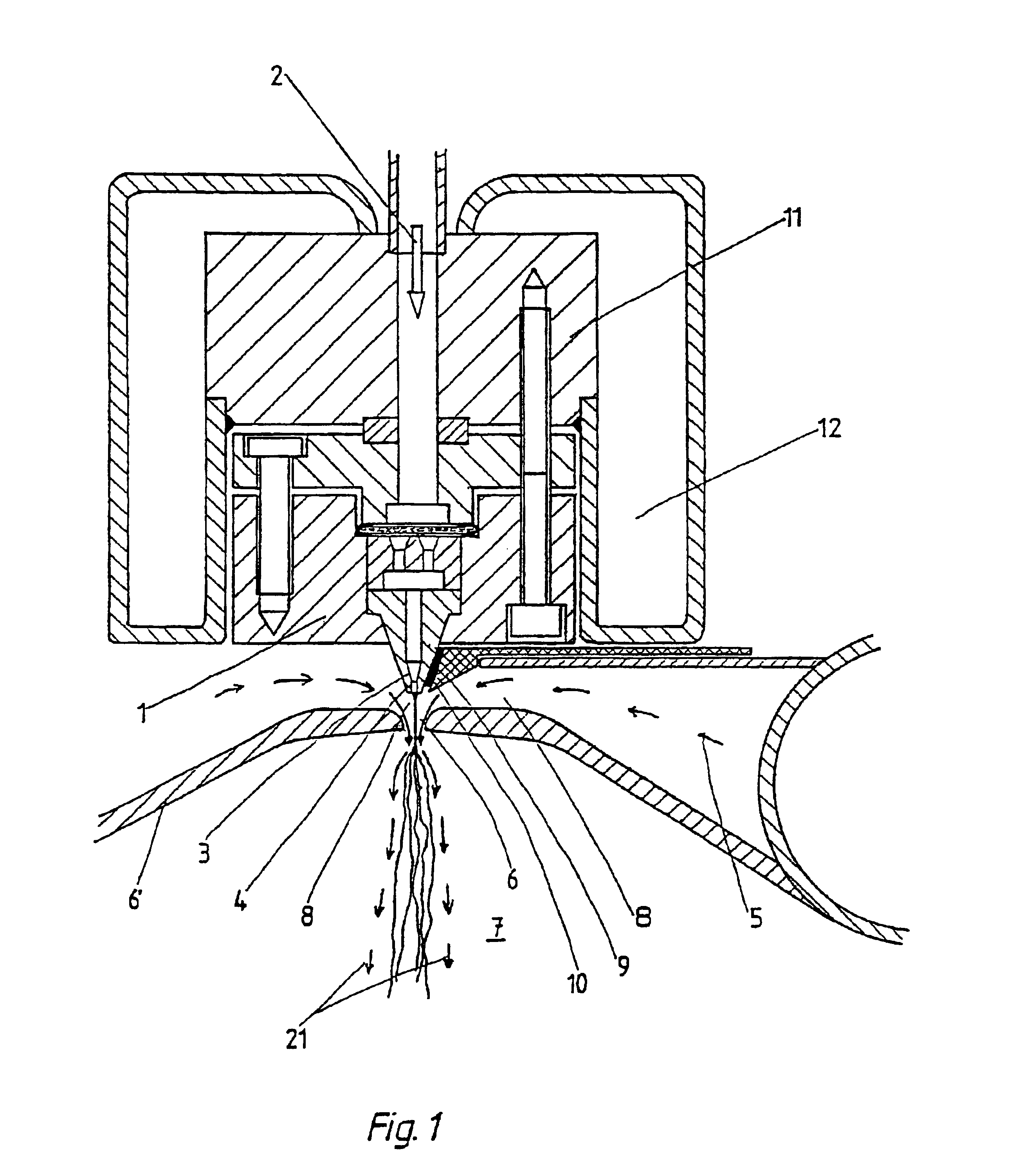
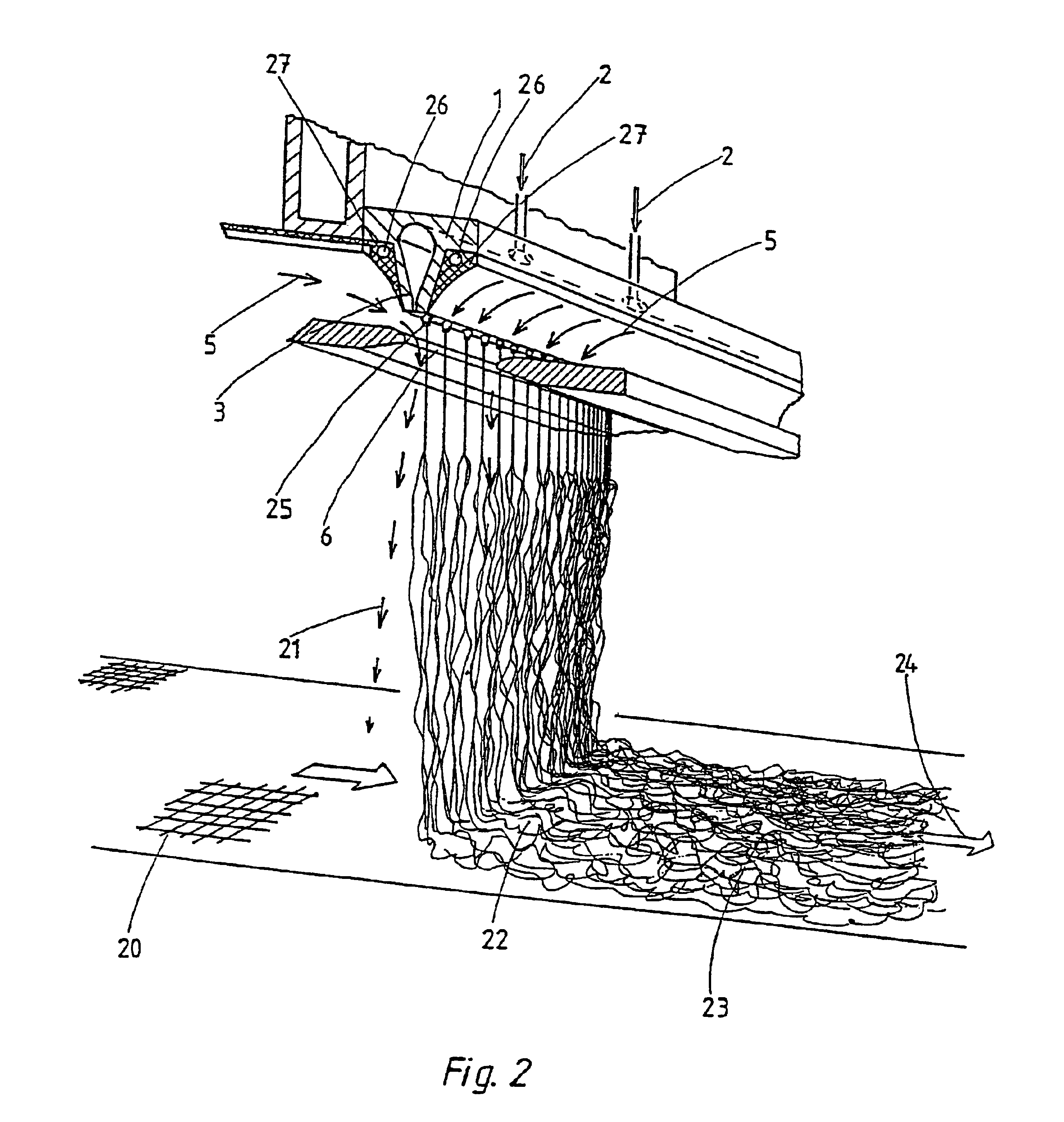
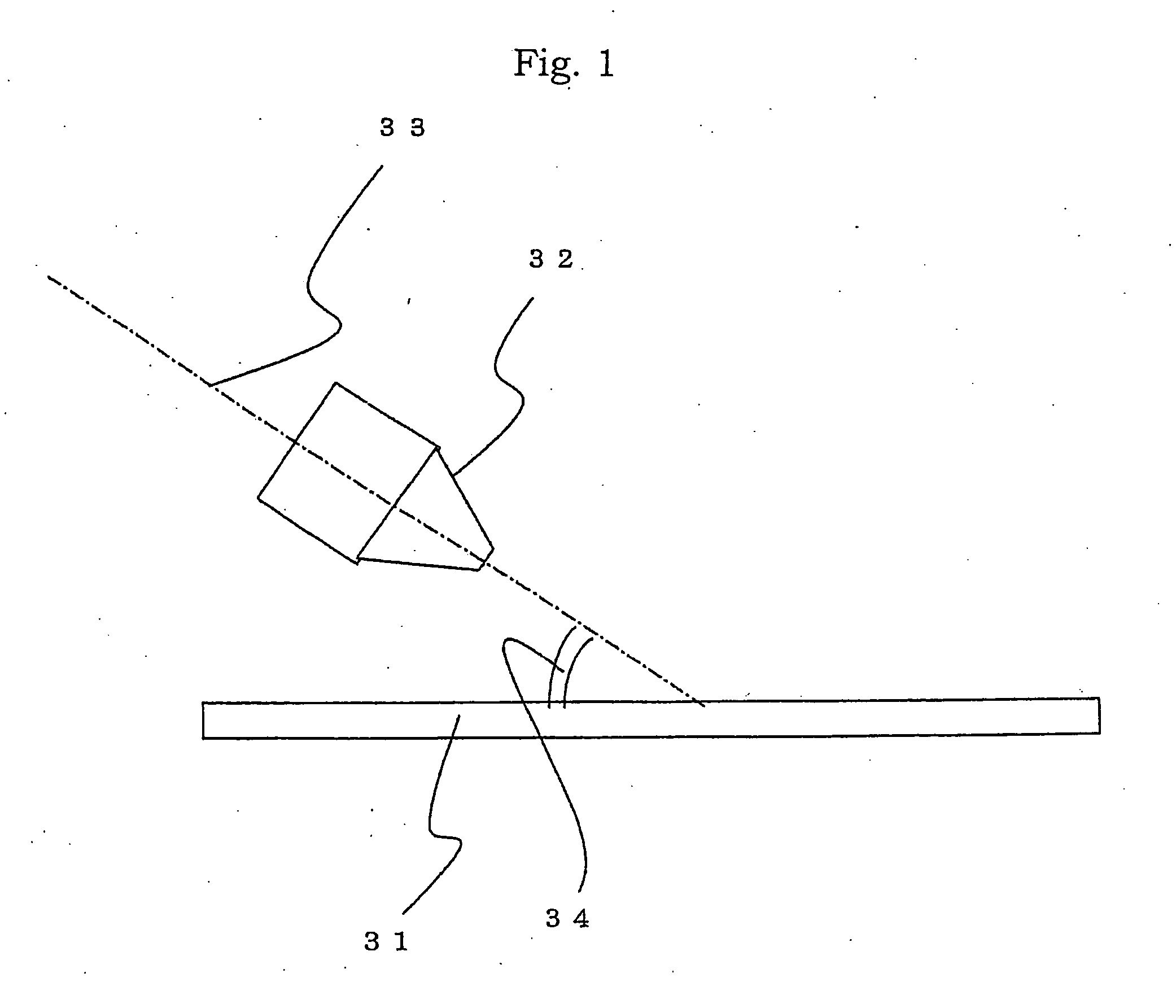
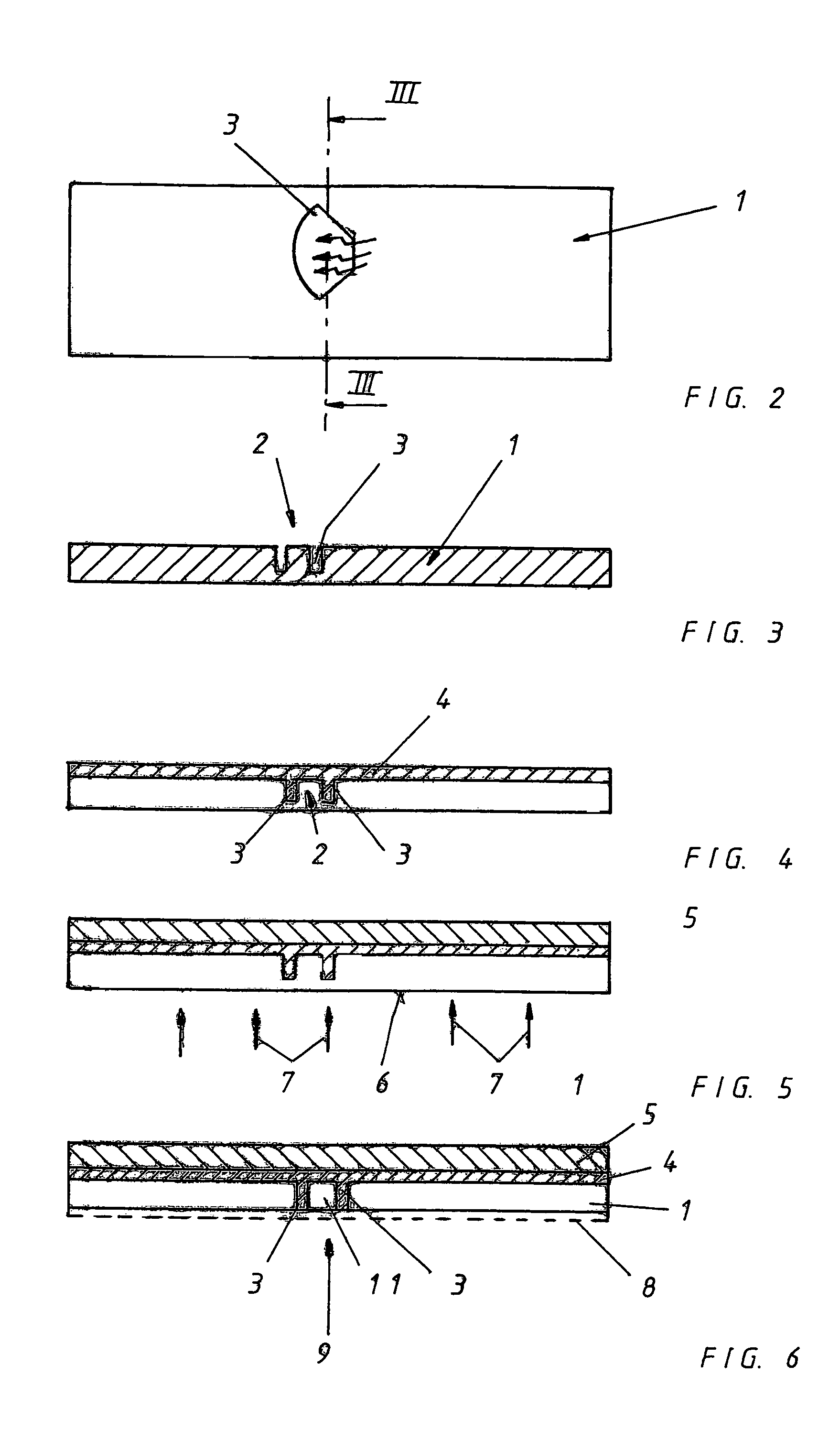
Method and device for the production of an essentially continous fine thread
InactiveUS6800226B1Simple and economical mannerReduced strengthSpinnerette packsMelt spinning methodsFine lineYarn
The invention relates to a method and a device for the production of essentially continuous fine threads made of meltable polymers. The polymer melt is spun from at least one spin hole (5) and the spun thread is attenuated using gas flows which are accelerated to achieve high speeds by means of a Laval nozzle (6). As a result of the specific geometry of the melt hole (4) and the position thereof in respect to the Laval nozzle (6), the temperature of the polymer melt, the throughout per spin hole and the pressures determining the velocity of the gas flow upstream and downstream from the Laval nozzle (6) are controlled in such a way that the thread reaches an internal hydrostatic pressure before solidifying, whereby said thread bursts into a plurality of fine threads.
Owner:GERKING LUDER
Skin care compositions including hexapeptide complexes and methods of their manufacture
InactiveUS20060198800A1Reduce fine lineReduce wrinklesOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFine lineWrinkle skin
Skin care compositions disclosed herein include, at a minimum, safe and effective amounts of at least one wrinkle reduction agent, which is a hexapeptide, and a natural exfoliating complex. The skin care compositions provide natural skin exfoliation, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and improve skin elasticity and firmness.
Owner:GUTHY-RENKER
Compositions and delivery methods for the treatment of wrinkles, fine lines and hyperhidrosis
The present invention describes compositions and methods for treating, preventing and improving the appearance of skin, particularly, treating, preventing, ameliorating, reducing and / or eliminating fine lines and / or wrinkles of skin, wherein the compositions include limonoid constituents which inhibit acetylcholine release at neuromuscular junctions of skeletal muscle so as to relax the muscles involved with wrinkling, folding and creasing of skin, e.g., facial movement and expression. The limonoids preferably include the plant alkaloids toosendanin and azadirachtin. The compositions, which also are used to treat hyperhidrosis, are preferably applied to the skin, or are delivered by directed means to a site in need thereof.
Owner:AVON PROD INC
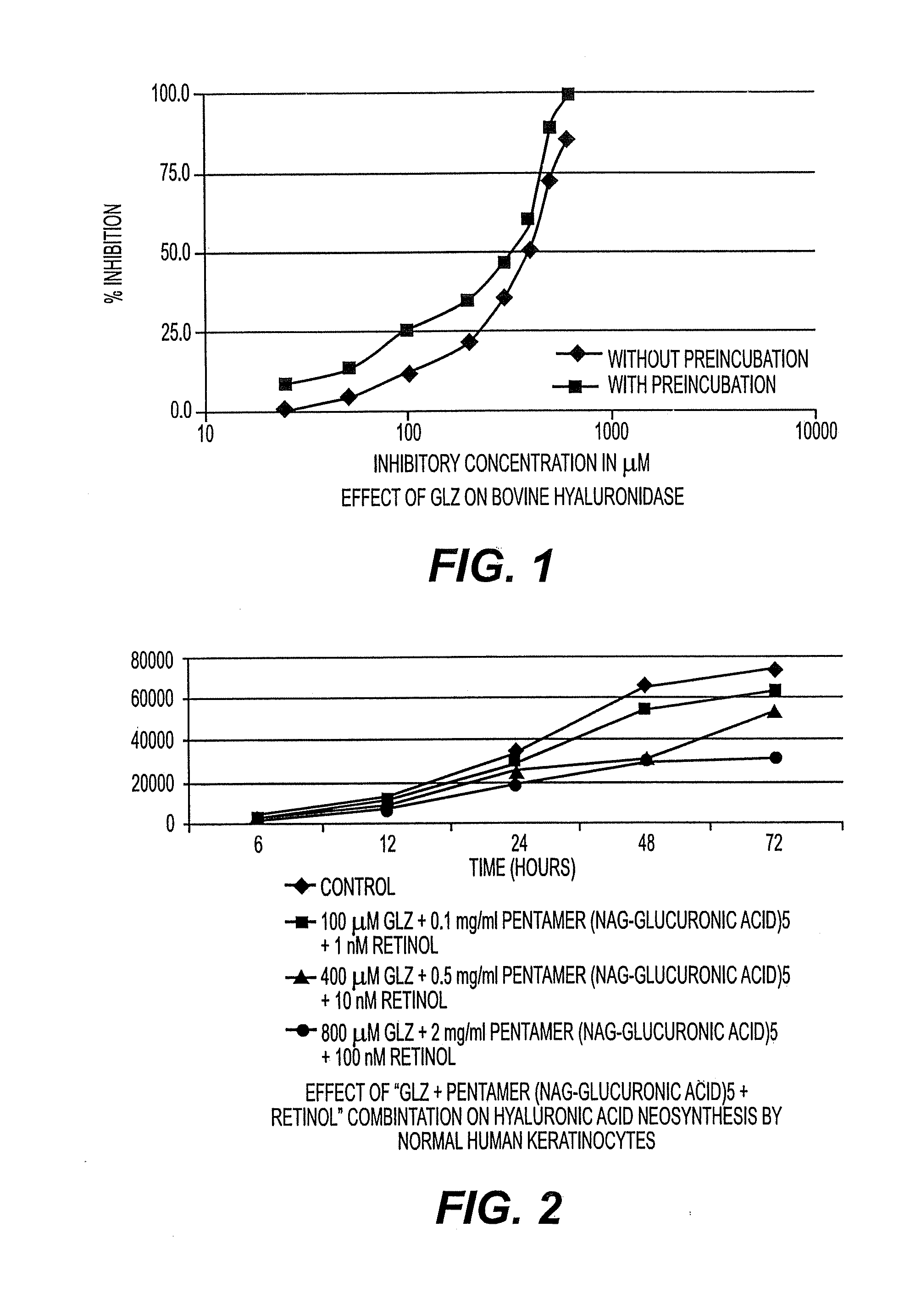
Phamaceutical/cosmetic compositions comprising hyaluronic acid and treatment of dermatological conditions therewith
InactiveUS20090018102A1Improve bioavailabilityReduce in quantityCosmetic preparationsBiocideFine lineWrinkle skin
Pharmaceutical / cosmetic compositions containing a dermatologically effective amount of hyaluronic acid, at least one retinoid and / or salt and / or derivative thereof, at least one oligosaccharide and at least one inhibitor of hyaluronic acid degradation, formulated into a physiologically acceptable medium therefor, are useful for the treatment of wrinkles, fine lines, fibroblast depletions and scars.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC
Flexible Nanogenerators
ActiveUS20090066195A1Overcome disadvantagesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFine lineFiber
A small scale electrical generator includes an elongated substrate and a first piezoelectric fine wire. The first piezoelectric fine wire is disposed along a surface of the substrate. The first piezoelectric fine wire has a first end and a spaced-apart second end. A first conductive contact secures the first end of the fine wire to a first portion of the substrate and a second conductive contact secures the second end of the fine wire to a second portion of the substrate. A fabric made of interwoven strands that includes fibers from which piezoelectric nanowires extend radially therefrom and conductive nanostructures extend therefrom is configured to generate electricity.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Use of allantoin as a pro-collagen synthesis agent in cosmetic compositions
InactiveUS20080108681A1Improving appearance and texture and firmnessIncrease synthesisCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsFine lineWrinkle skin
Compositions comprising allantoin and an acceptable carrier and methods of using such compositions to increase pro-collagen synthesis in skin are disclosed. Compositions of the present invention may be used to decrease the signs of skin aging such as wrinkles and fine lines. Compositions of the present invention may be topically administered, orally administered or parenterally, such as administration by injection. When topically administered, additive ingredients such as penetration enhancers, fragrances, and moisturizers and cosmetic adjuvants may be included in compositions of the present invention.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Method and apparatus for skin treatment
Disclosed is a system and method for treatment of skin disorders. More particularly, the disclosed invention is directed toward the use of multiple light sources for treating skin with or without the use of a topical compositions or photomodulation enhancing agents. Dual light emitting diodes may, for example, be used at relatively low power (less than about 10 J / cm2) to photomodulate skin or living tissue to reduce wrinkles, fine lines, acne, acne bacteria, and other skin disorders.
Owner:GENTLEWAVES
Electrode formation method, electrode and solar battery
InactiveUS20050221613A1High aspect ratioSolution has disadvantageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationFine lineLine width
A method for forming an electrode according to the present invention includes a step of discharging a paste containing an electrode material from a discharge port of a nozzle, and drawing a fine-line pattern on a surface of a semiconductor substrate, and a step of drying and baking the drawn fine-line pattern, and forming a fine-line electrode. Herein, in the drawing step, the nozzle is arranged so that a central axis of the nozzle is inclined at a predetermined inclination angle with respect to the surface of the semiconductor substrate, and so that the discharge port is proximate to the surface of the semiconductor substrate at a predetermined distance, the nozzle and the semiconductor substrate are moved relatively to each other in a drawing direction of the fine-line pattern, and relative movement speeds of the nozzle and the semiconductor substrate are adjusted, thereby drawing the fine-line pattern so that a line width of the fine-line pattern is smaller than an inner diameter of the discharge port of the nozzle.
Owner:SHARP KK
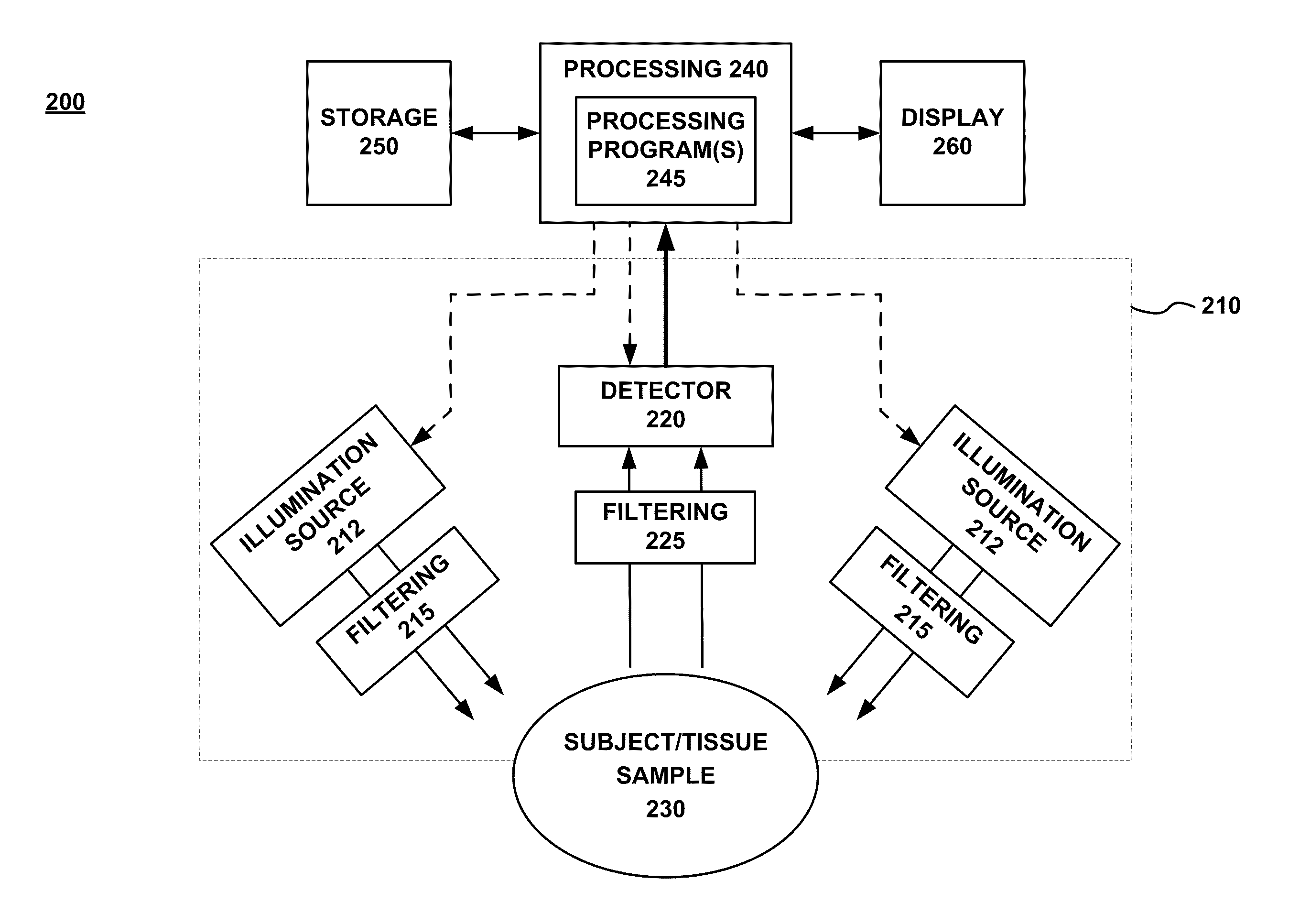
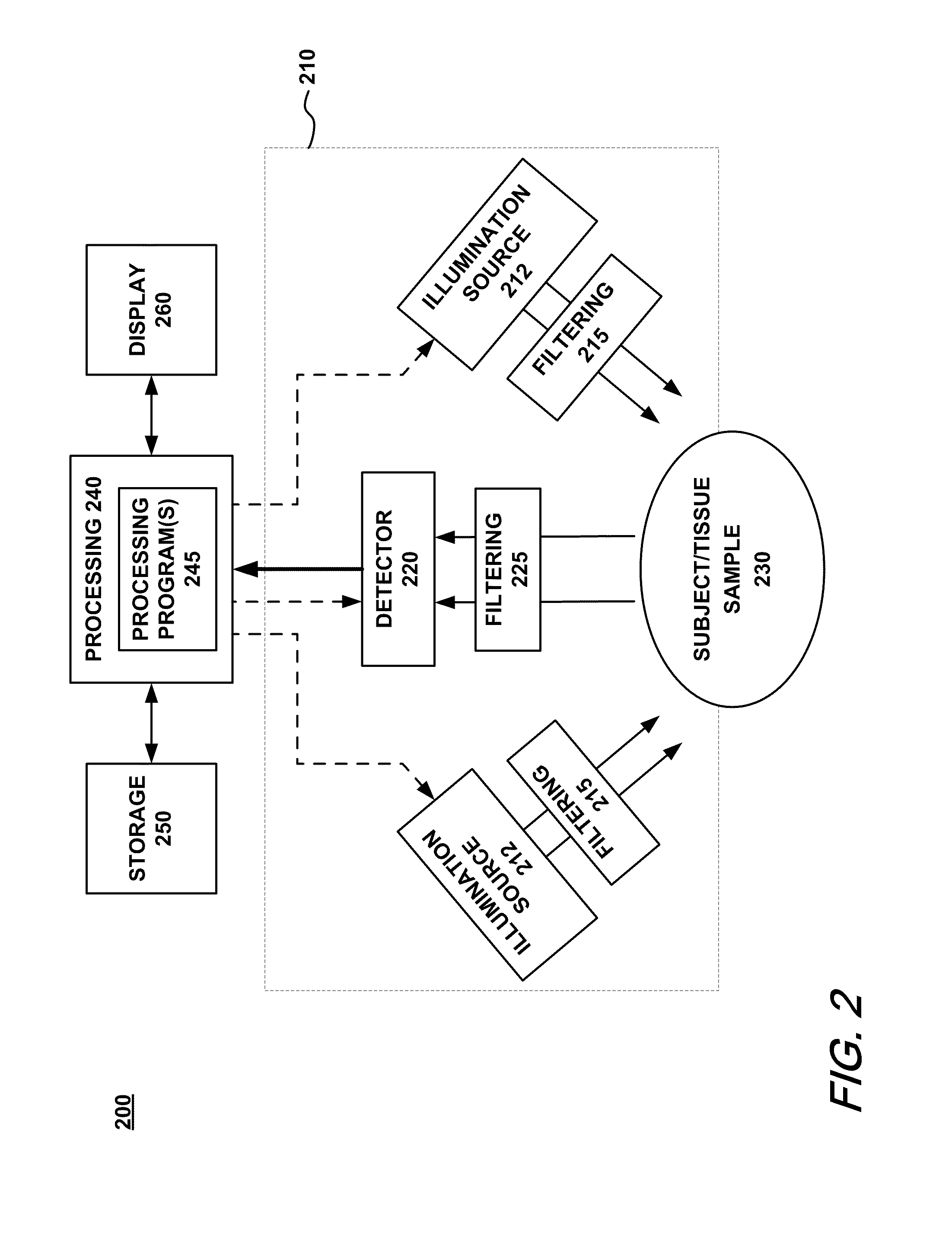
Reflectance imaging and analysis for evaluating tissue pigmentation
Methods and apparatus are described that provide the ability to estimate the diffuse reflection component of an image of tissue such as skin captured without cross-polarization. It is thereby possible to estimate skin pigmentation information from an image of skin captured conventionally, such as, for example, a total reflection image, obtained in a conventional manner by shining white light on the skin and capturing the reflected light. The image may also be a partially diffuse reflection image, such as a low quality cross-polarized image. The diffuse reflection component of a captured image can then be further processed to obtain Red and Brown pigmentation images, useful for indicating the distribution of hemoglobin and melanin, the primary chromophores of skin. Additionally, a standard captured image of skin can be analyzed to obtain an estimate of the surface reflection component of the reflected light. The surface reflection component can then be used to generate a surface reflection image, useful for showing the distribution of light on the skin and to highlight superficial features such as wrinkles, fine lines, folds, pores, texture, and visible spots.
Owner:CANFIELD SCI
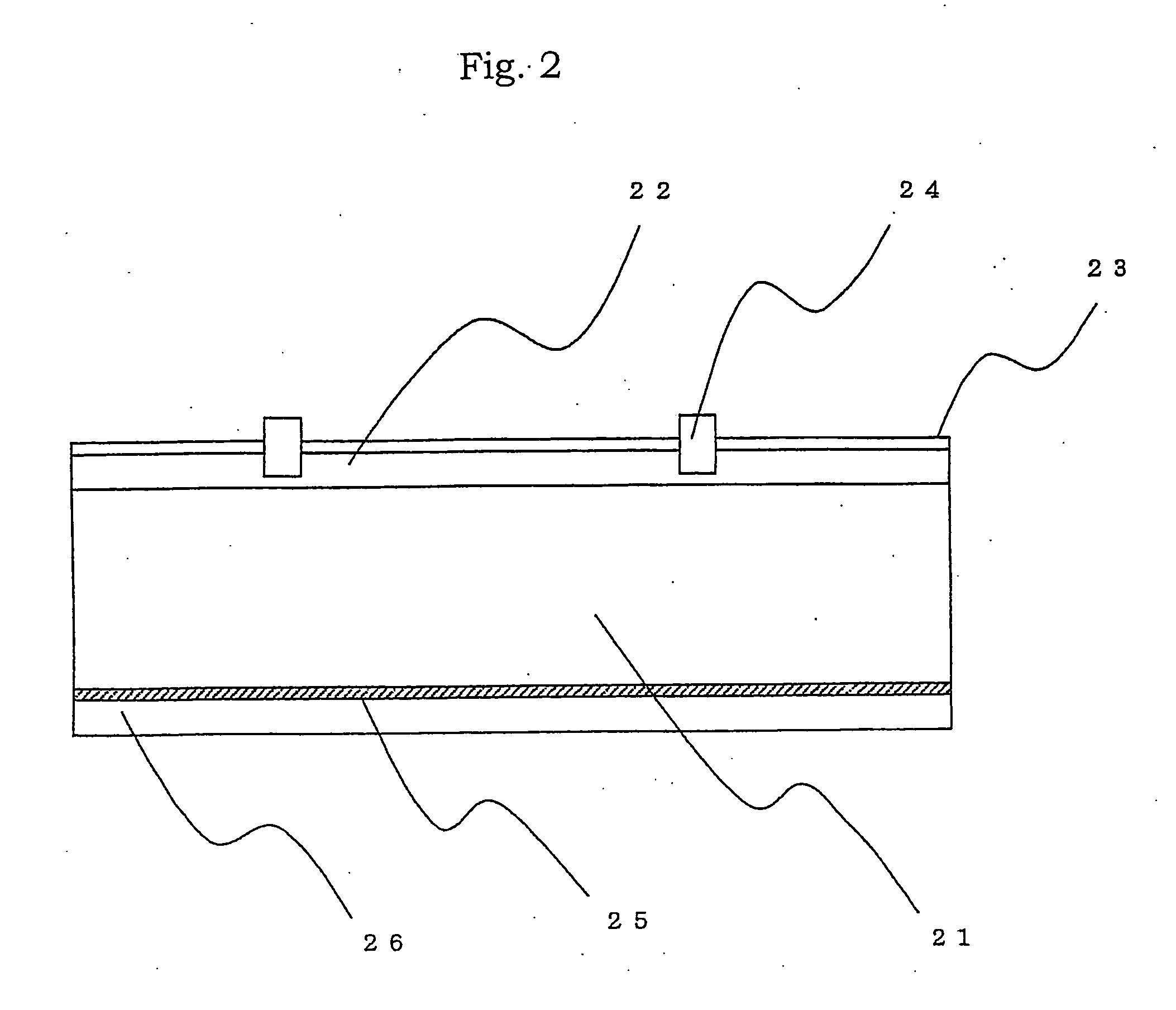
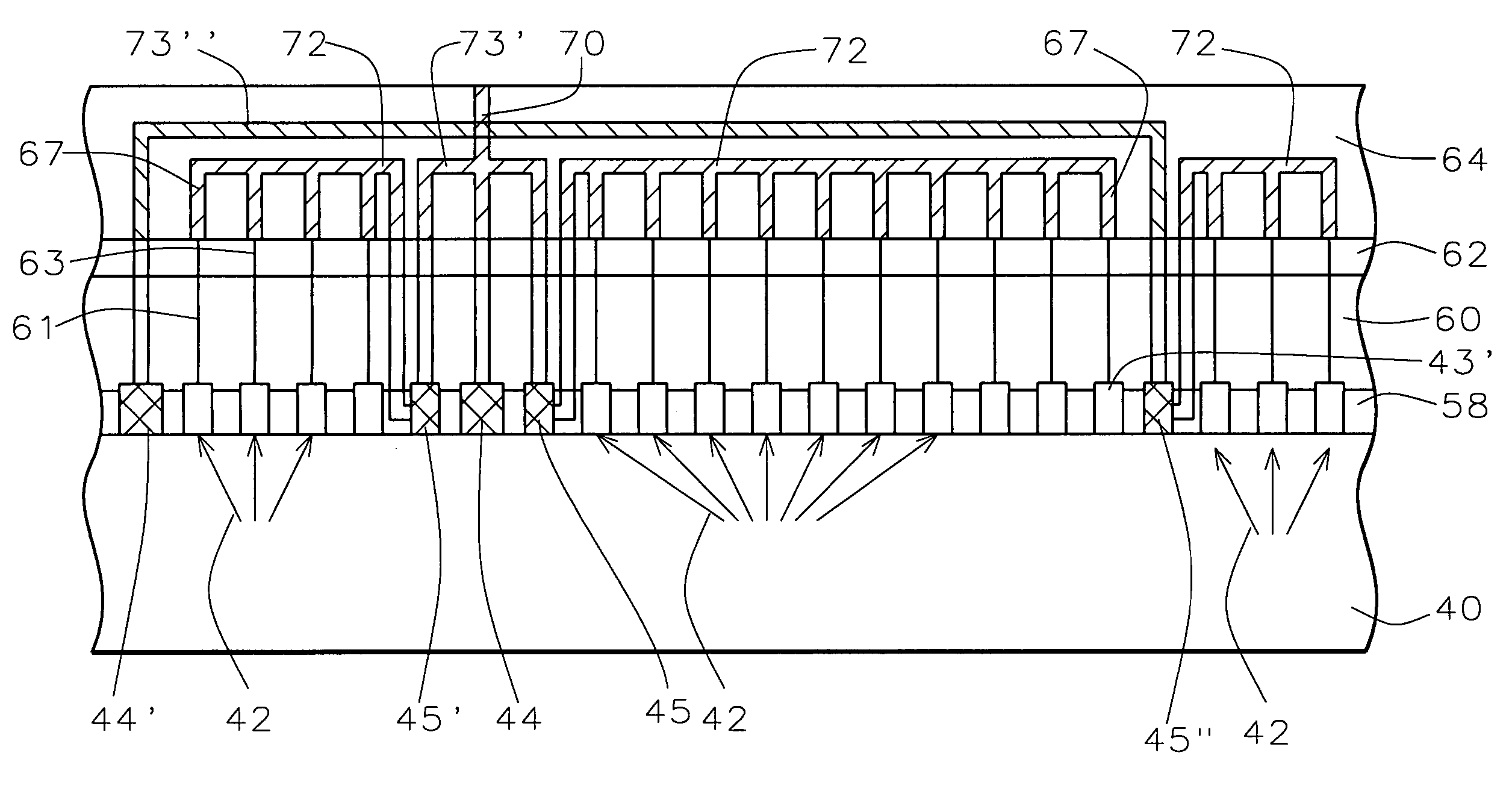
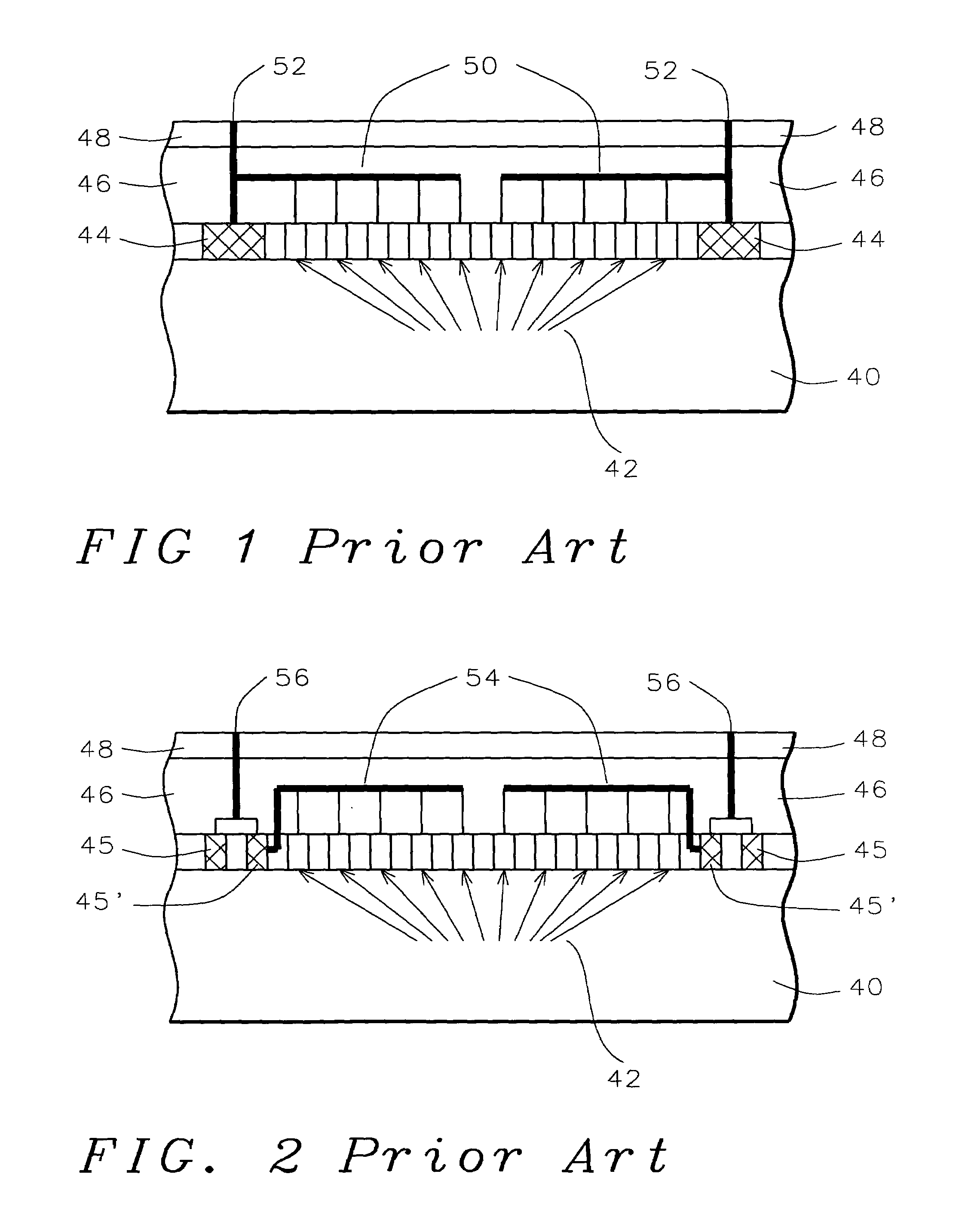
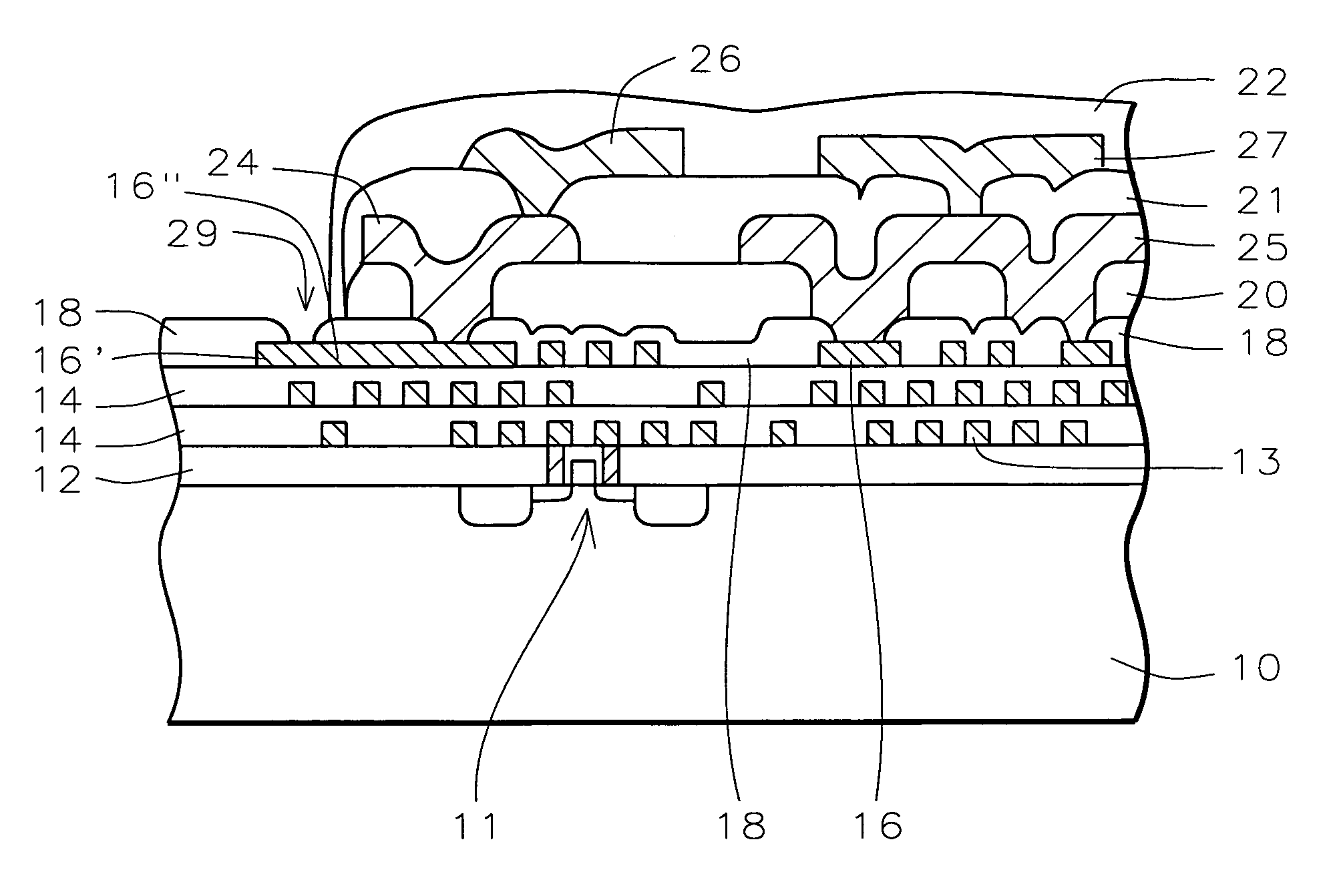
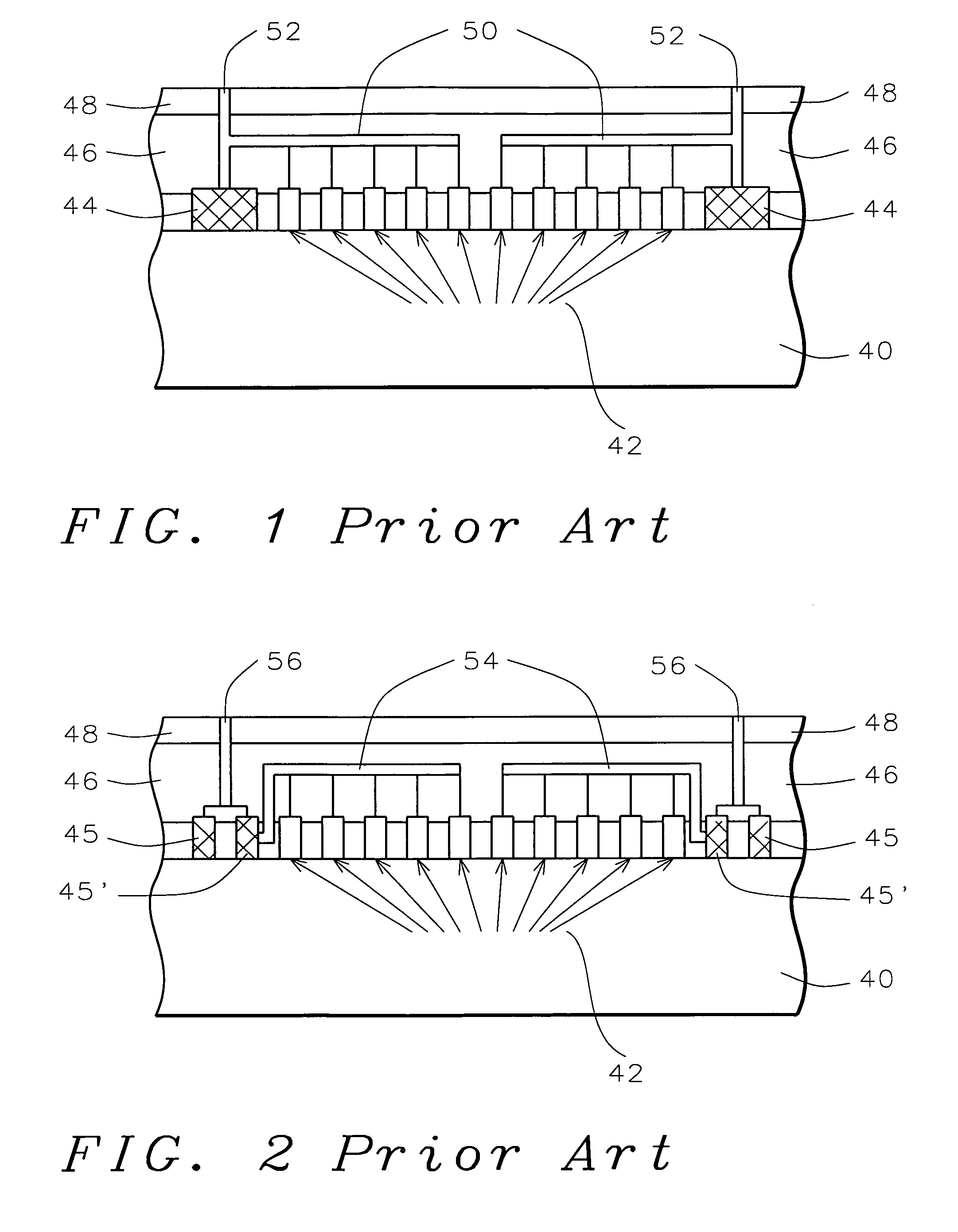
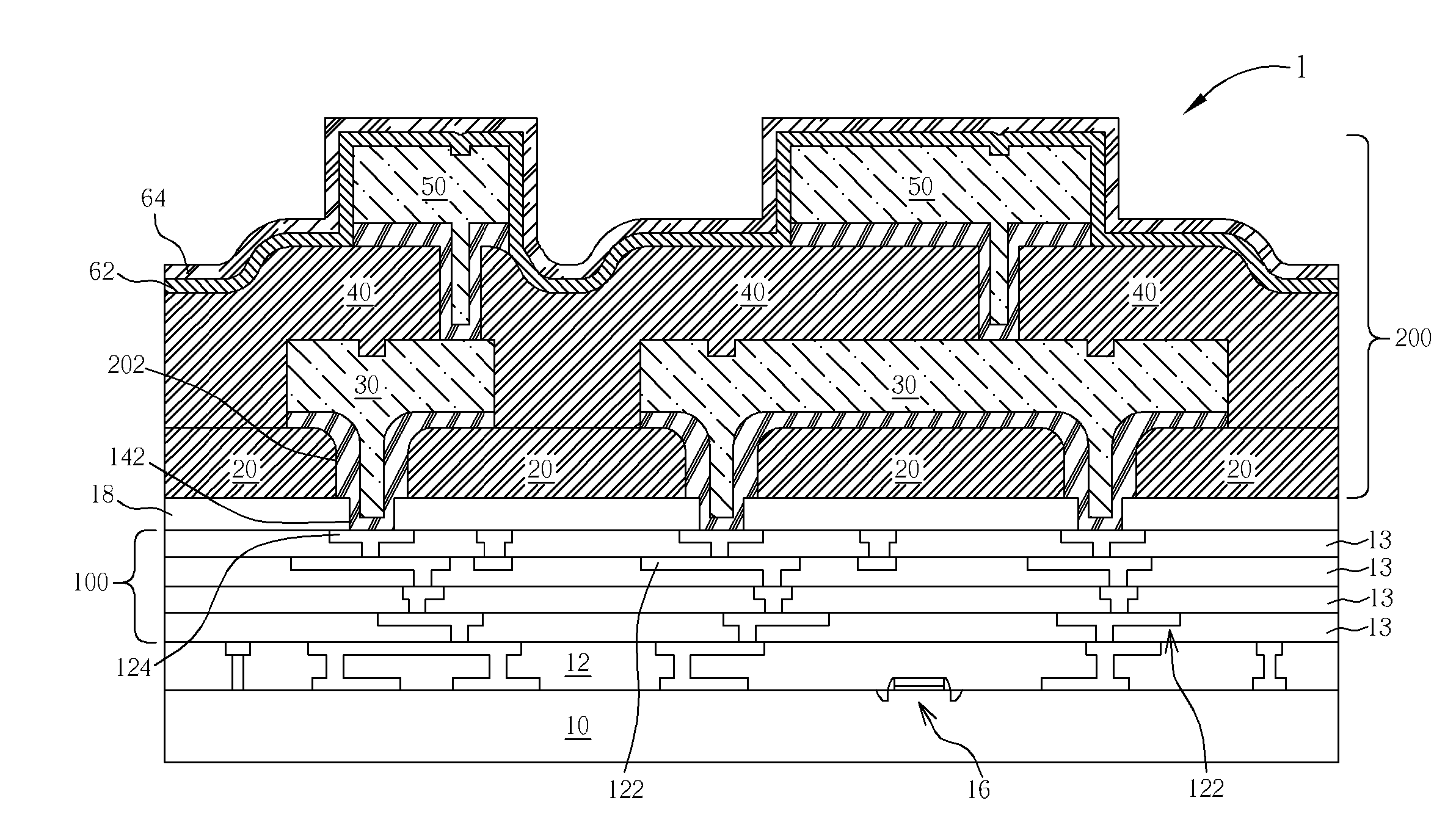
Post passivation interconnection schemes on top of the IC chips
InactiveUS20050104177A1Increase resistanceIncrease capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricFine line
A new method is provided for the creation of interconnect lines. Fine line interconnects are provided in a first layer of dielectric overlying semiconductor circuits that have been created in or on the surface of a substrate. A layer of passivation is deposited over the layer of dielectric and a thick second layer of dielectric is created over the surface of the layer of passivation. Thick and wide post-passivation interconnect lines are created in the thick second layer of dielectric. The first layer of dielectric may also be eliminated, creating the wide thick passivation interconnect network on the surface of the layer of passivation that has been deposited over the surface of a substrate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
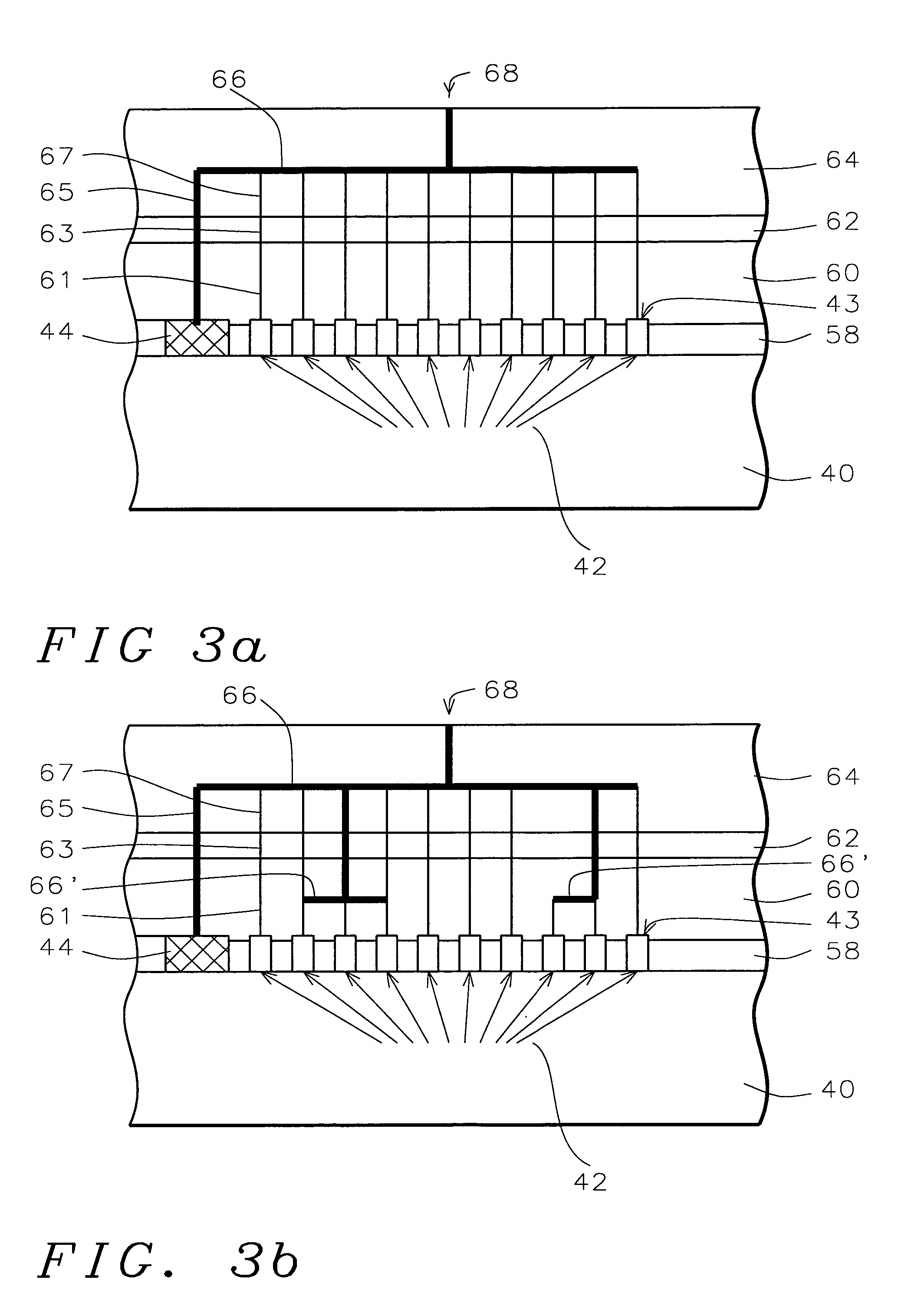
Post passivation interconnection schemes on top of the IC chips
InactiveUS7230340B2High resistivityRemove restrictionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFine lineDielectric
A new method is provided for the creation of interconnect lines. Fine line interconnects are provided in a first layer of dielectric overlying semiconductor circuits that have been created in or on the surface of a substrate. A layer of passivation is deposited over the layer of dielectric, a thick second layer of dielectric is created over the surface of the layer of passivation. Thick and wide interconnect lines are created in the thick second layer of dielectric. The first layer of dielectric may also be eliminated, creating the wide thick interconnect network on the surface of the layer of passivation that has been deposited over the surface of a substrate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for producing buttons, ornamental and instrument panels with fine symbols, and a button produced with the method
ActiveUS7134205B2Exemption stepsEasy to viewButtonsLamination ancillary operationsFine lineEngraving
A button, knob or control key with an etchable support plate which is engraved on the backside with a fine symbol by laser, erosion or mechanical engraving, which only cuts into the material of the support plate, but not through the support plate. The backside of the support plate is optionally coated. A foil is applied on the laminated layer and affixed thereto. The front side of the support plate is treated with a material-removing substance. The material removal with the material-removing substance is performed until the engraving extending into the support plate is at least partially or completely exposed on the front side. Application of a protective layer to the front side of the support plate from which the material was removed. A function symbol is provided on the button such that it can be backlit. It is engraved in a fine line width providing a sharp optical definition erosion, mechanical engraving.
Owner:FAURECIA ANGELL DEMMEL
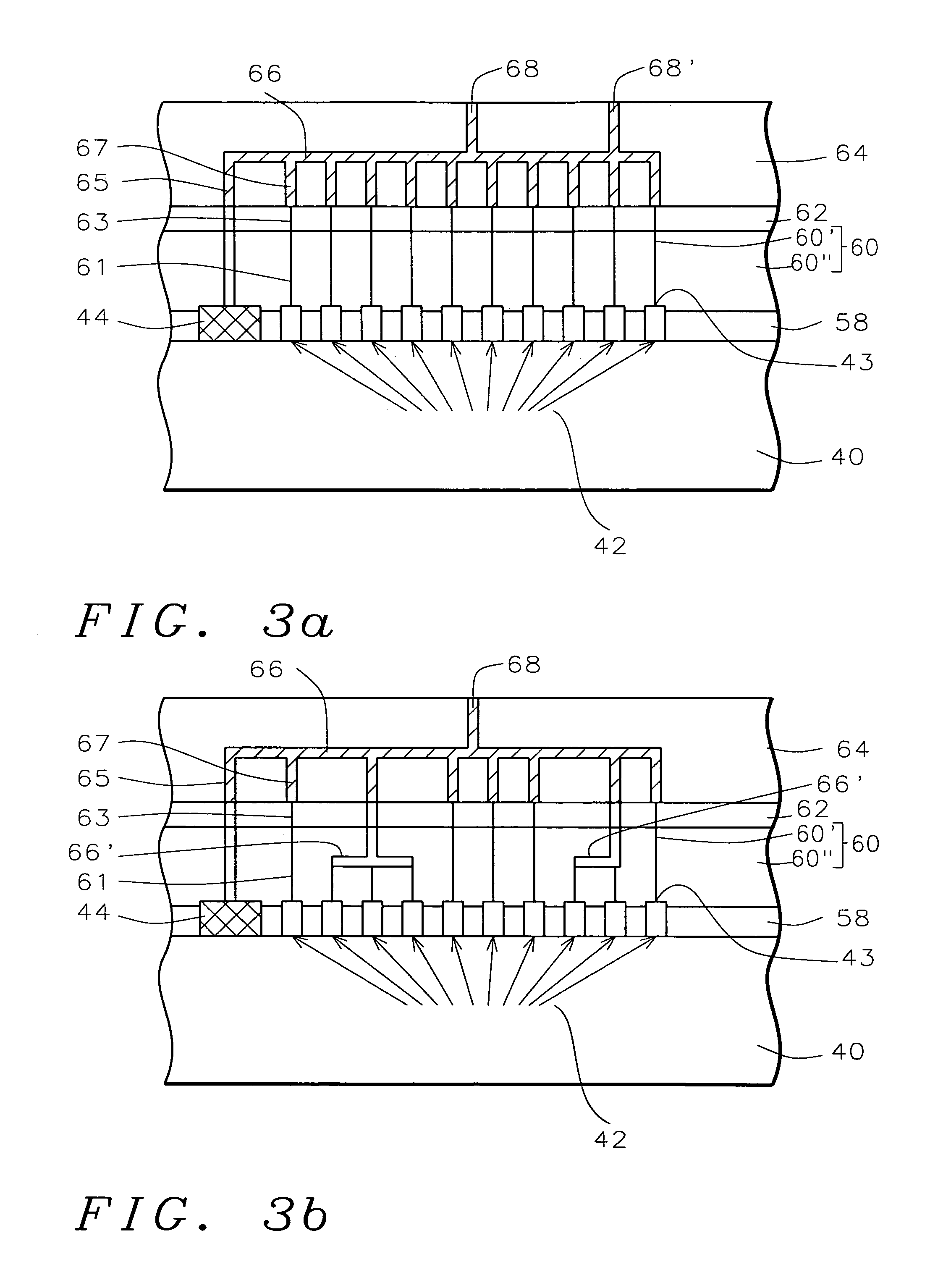
Post passivation interconnection schemes on top of the IC chips
InactiveUS7372161B2Increase resistanceIncrease capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricFine line
A new method is provided for the creation of interconnect lines. Fine line interconnects are provided in a first layer of dielectric overlying semiconductor circuits that have been created in or on the surface of a substrate. A layer of passivation is deposited over the layer of dielectric and a thick second layer of dielectric is created over the surface of the layer of passivation. Thick and wide post-passivation interconnect lines are created in the thick second layer of dielectric. The first layer of dielectric may also be eliminated, creating the wide thick passivation interconnect network on the surface of the layer of passivation that has been deposited over the surface of a substrate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Emulsion containing organosilicon-based portions of hollow spheres
The present invention relates to a composition in the form of an emulsion containing portions of hollow spheres of organosilicon-based material, the portions of hollow spheres having a mean diameter ranging from 0.05 to 10 μm. The invention also relates to physiologically acceptable emulsion compositions comprising hollow spheres, and to a process for fading out skin surface defects, in particular to reduce the sheen of the skin and / or to fade out pores, shadows under the eyes, marks, wrinkles and / or fine lines, comprising the topical application to the skin of the above-mentioned compositions.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Adjustable pitch impeller
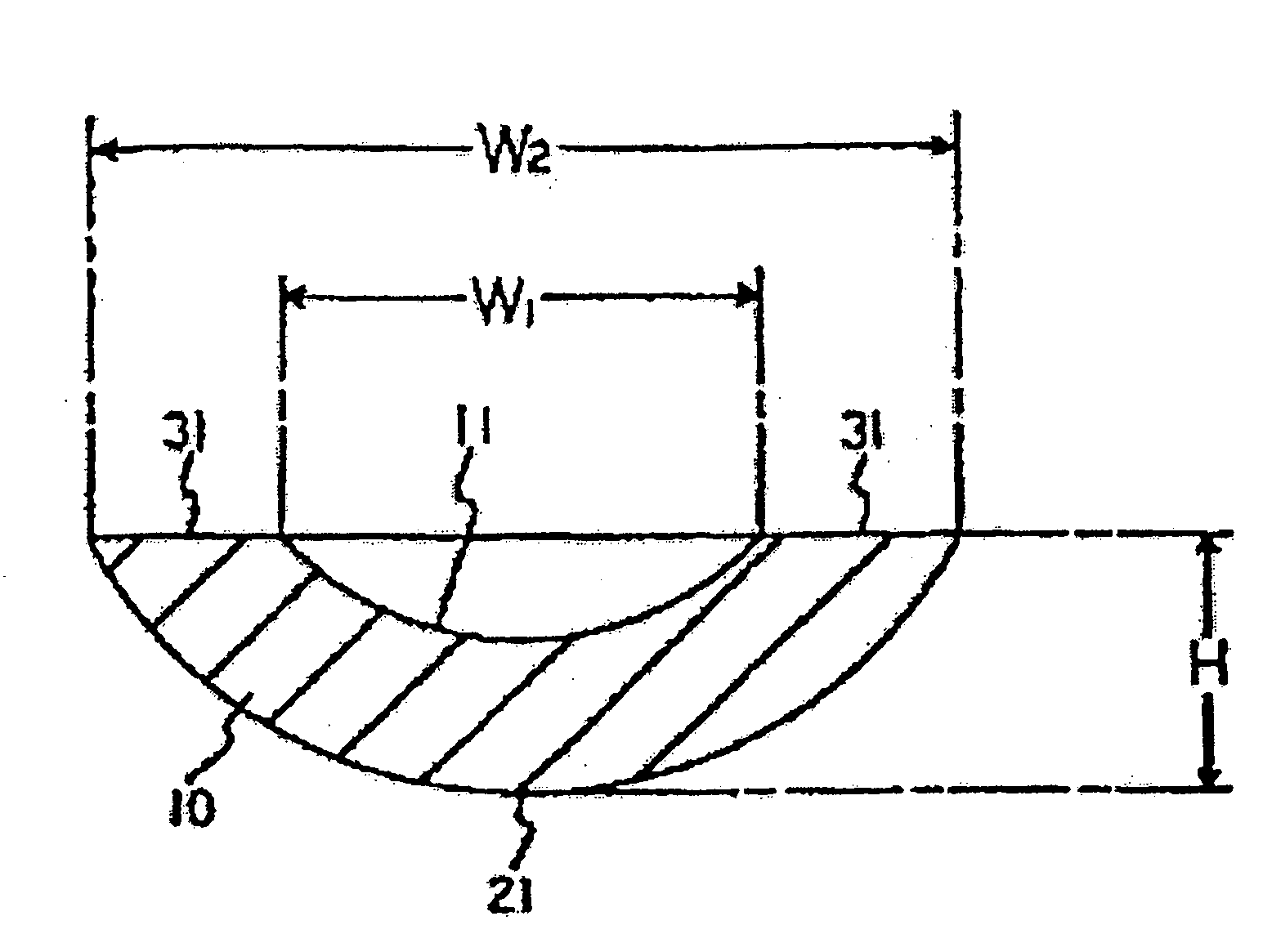
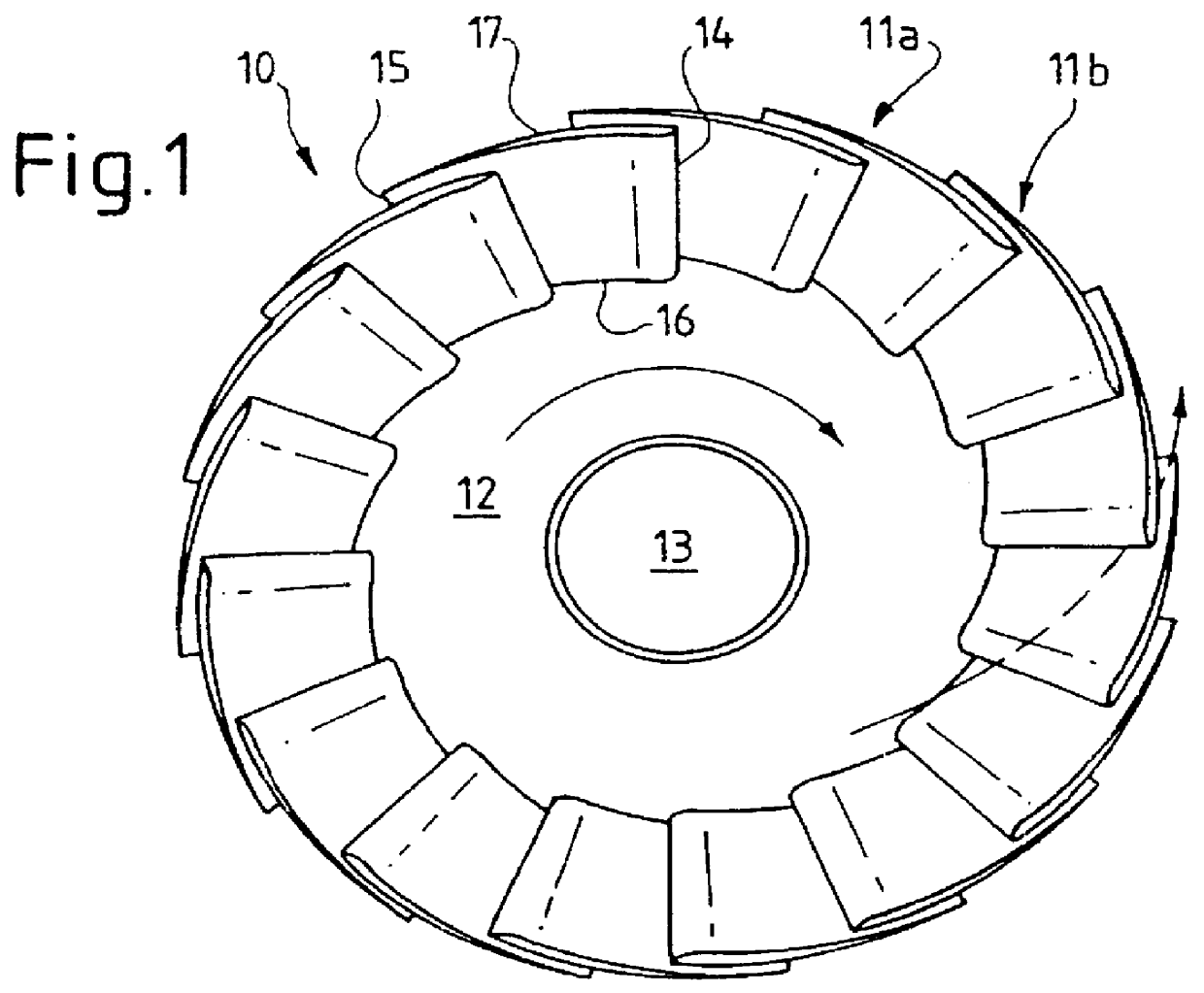
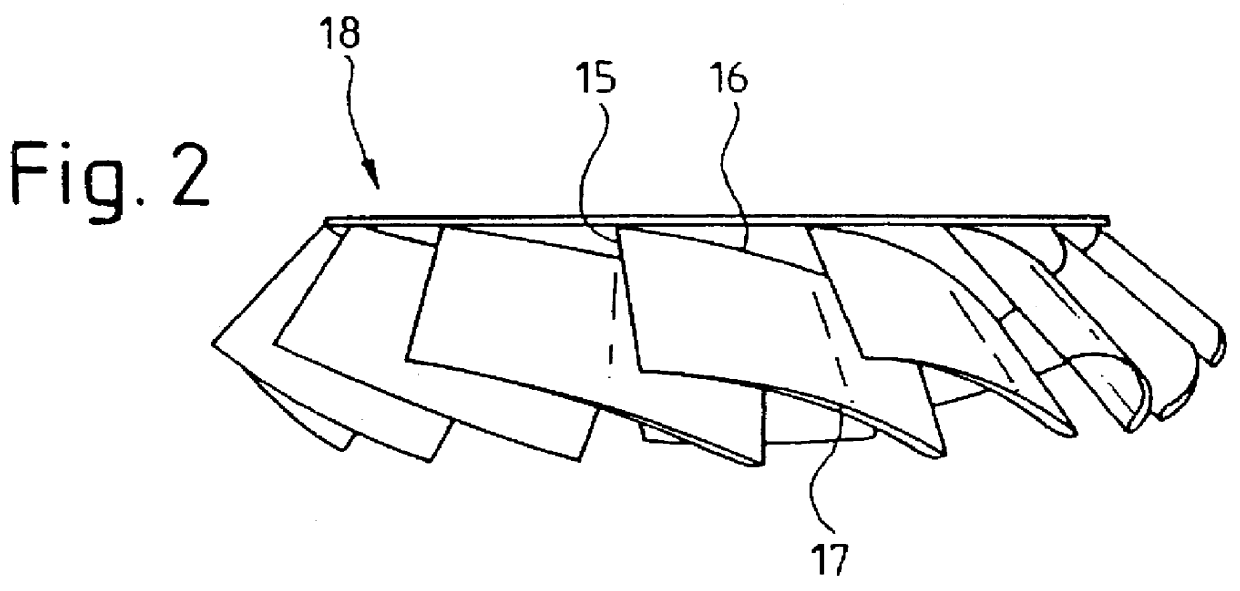
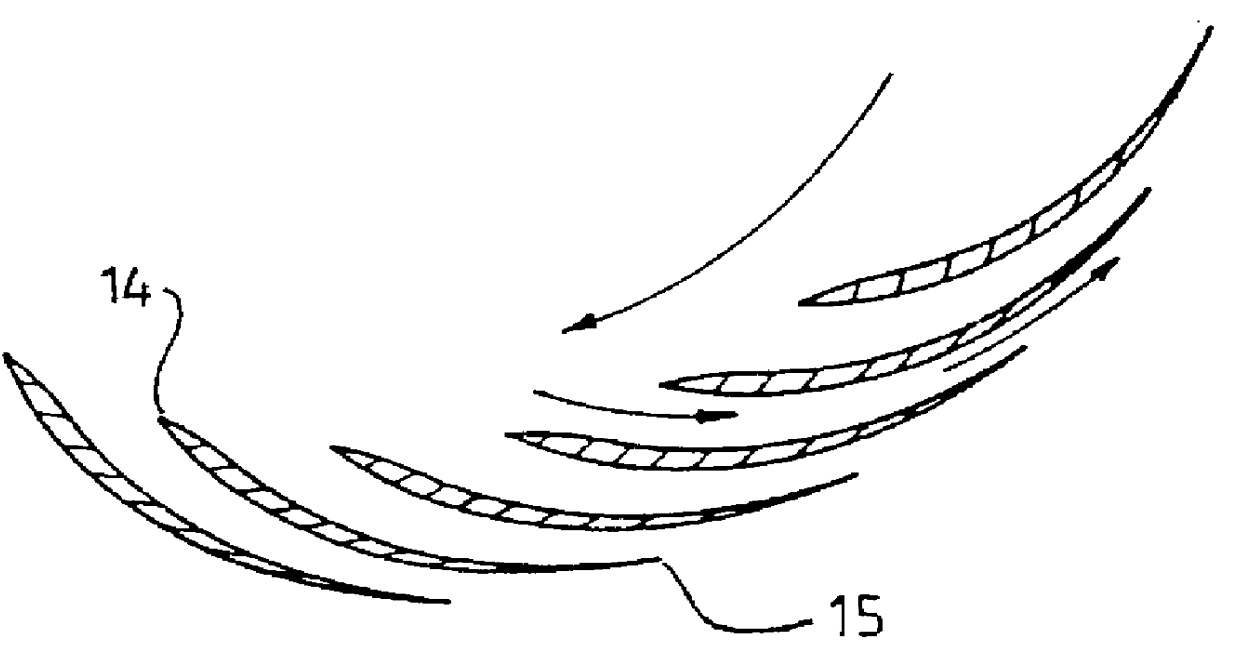
An impeller has a plurality of rotating passageways which can be defined between adjacent blades, the blades having a curved root portion and able to pivot across a part spherical hub to maintain a fine line contact. The passageways have a convergence to improve the efficiency of the impeller. The hub can be split into two relatively rotating portions, with the blades attached to each portion to provide an efficient means to vary the pitch of the blades.
Owner:NEW FLUID TECH
Combination therapies for treating photodamaged skin
Combination therapies for reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles on aged skin or non-precancerous, normal photodamaged section of skin, in a patient not being treated for viral infection or skin cancer comprising (i) topical application of an imidazoquinoline amine derivative in a dermatologically-acceptable carrier in further combination with one or more cosmetic treatments selected from the group consisting of: (i) Light Emitting Diode (L.E.D.) Light Therapy; (ii) Intense Pulsed Light (I.P.L.) Therapy; (iii) laser skin resurfacing; (iv) mechanical exfoliation; (v) superficial, medium depth or deep chemical peels; (vi) radiofrequency treatment; (vii) ultrasound treatment; (viii) intradermal and intraepidermal injections with hyaluronic acid and derivatives thereof; and (ix) cryosurgery.
Owner:BAUMANN LESLIE
Two-stage laser system for aligners
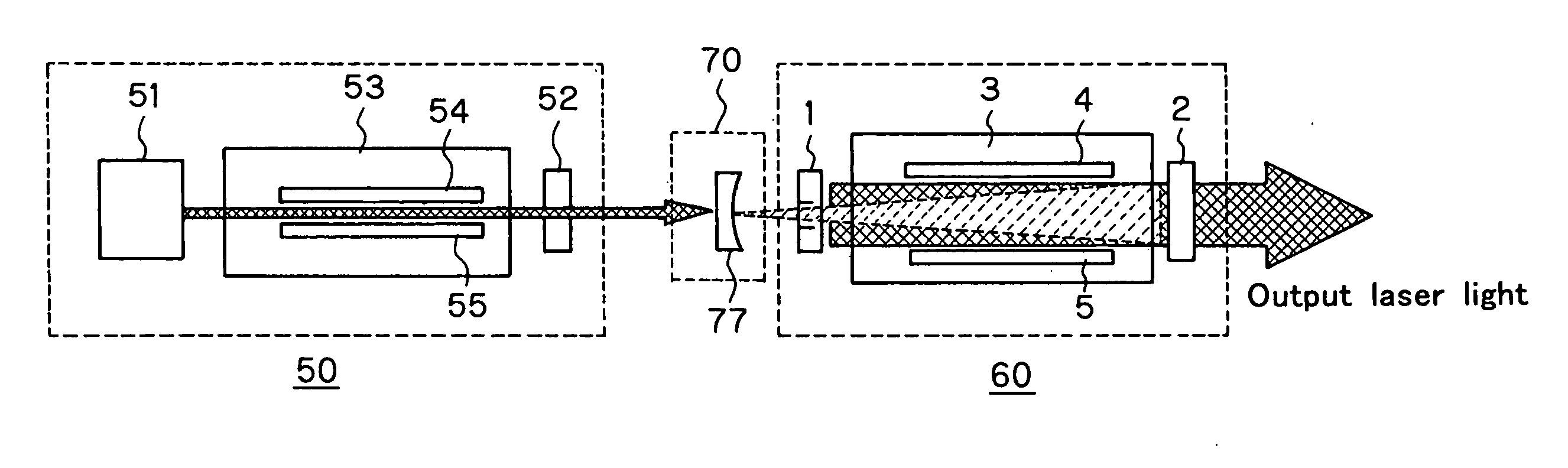
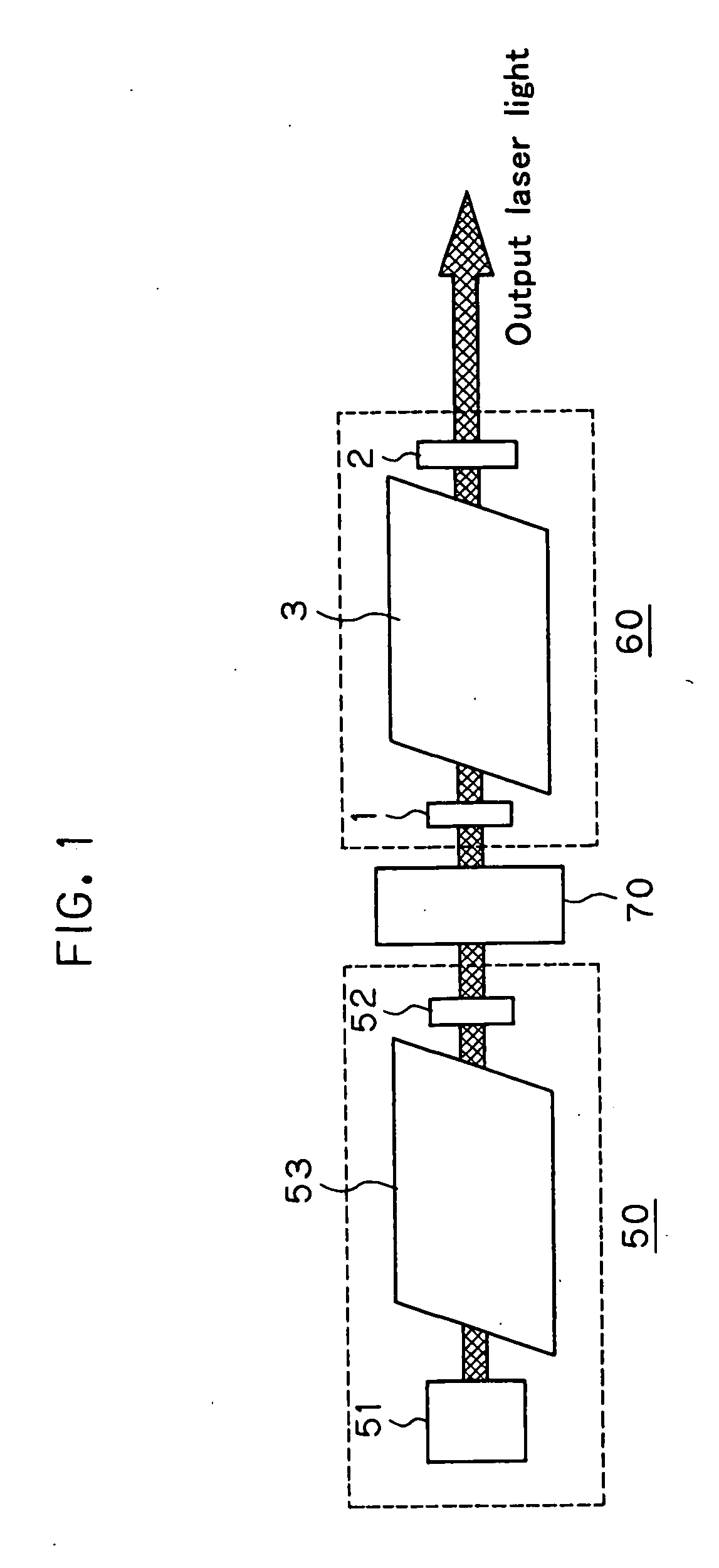
ActiveUS20070091968A1Reduce spacingImprove stabilityLaser arrangementsActive medium materialFine lineLaser light
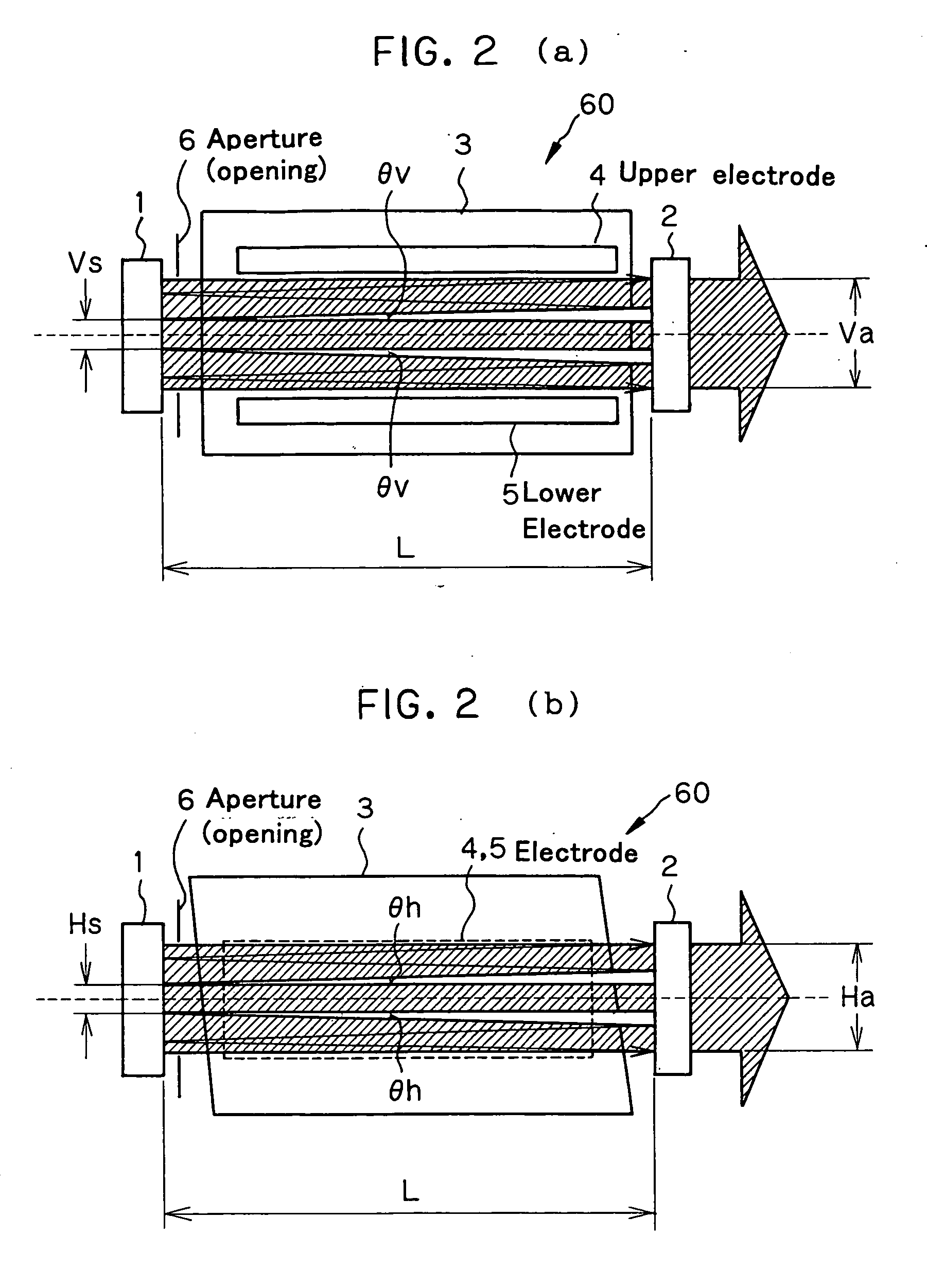
The invention relates to a two-stage laser system well fit for semiconductor aligners, which is reduced in terms of spatial coherence while taking advantage of the high stability, high output efficiency and fine line width of the MOPO mode. The two-stage laser system for aligners comprises an oscillation-stage laser (50) and an amplification-stage laser (60). Oscillation laser light having divergence is used as the oscillation-stage laser (50), and the amplification-stage laser (60) comprises a Fabry-Perot etalon resonator made up of an input side mirror (1) and an output side mirror (2). The resonator is configured as a stable resonator.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Solar cell and solar cell module
ActiveUS20120031457A1Increase manufacturing costAvoiding characteristicPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationFine lineSolar cell
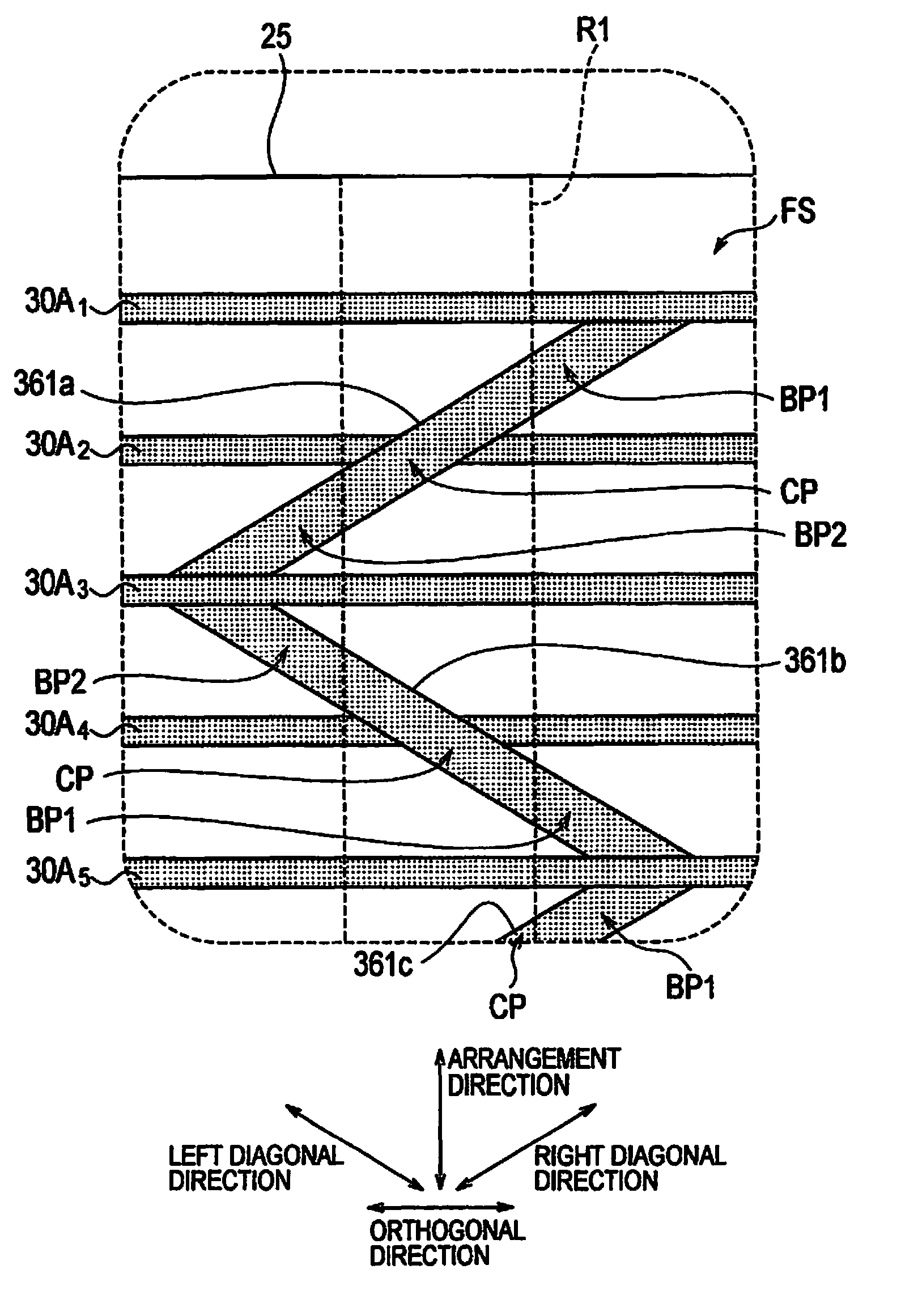
A solar cell (10) provided with connecting wires (351) which are connected to light receiving surface side fine-line electrodes (30A). The connecting wires (351) have expanding portions (BP1, BP2) which expand from the connection region (R1) where wiring member is to be connected. The expanding portions (BP1, BP2) expand in an orthogonal direction orthogonal to the longitudinal direction of the wiring material in a state where the wiring member is connected to the connecting wires (351).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
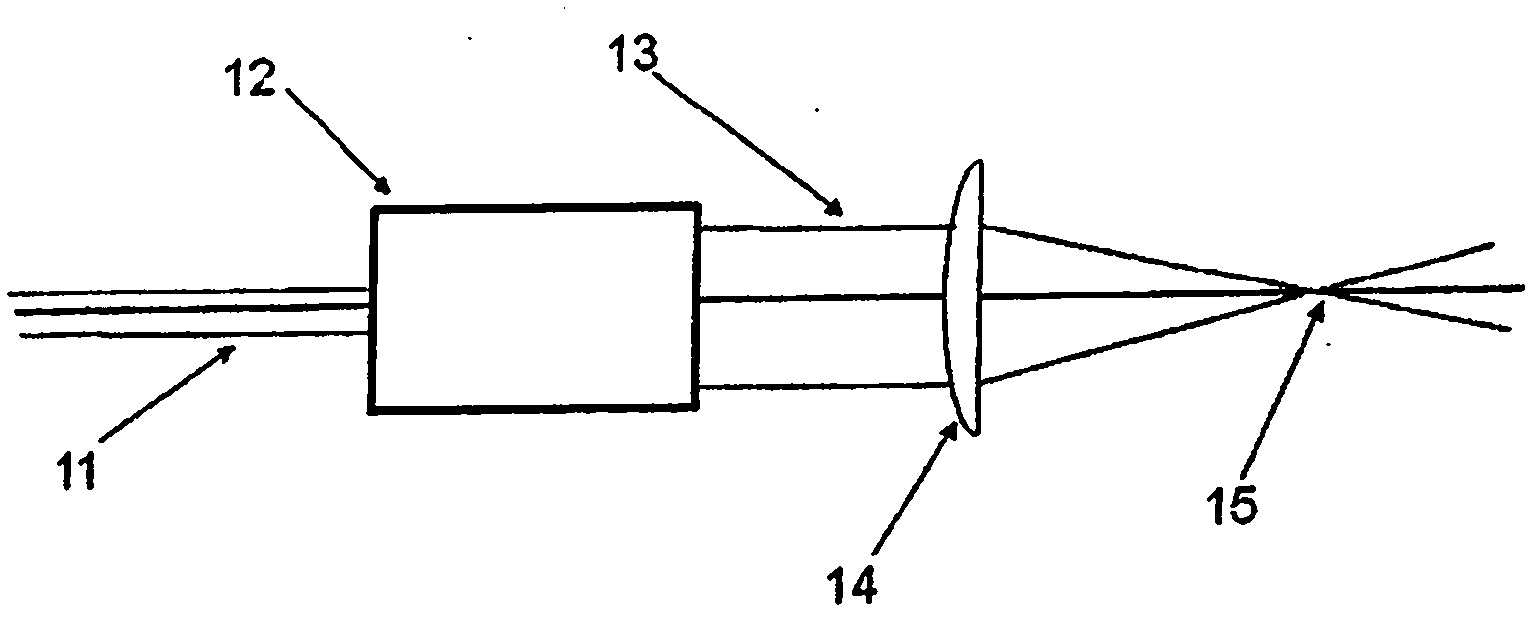
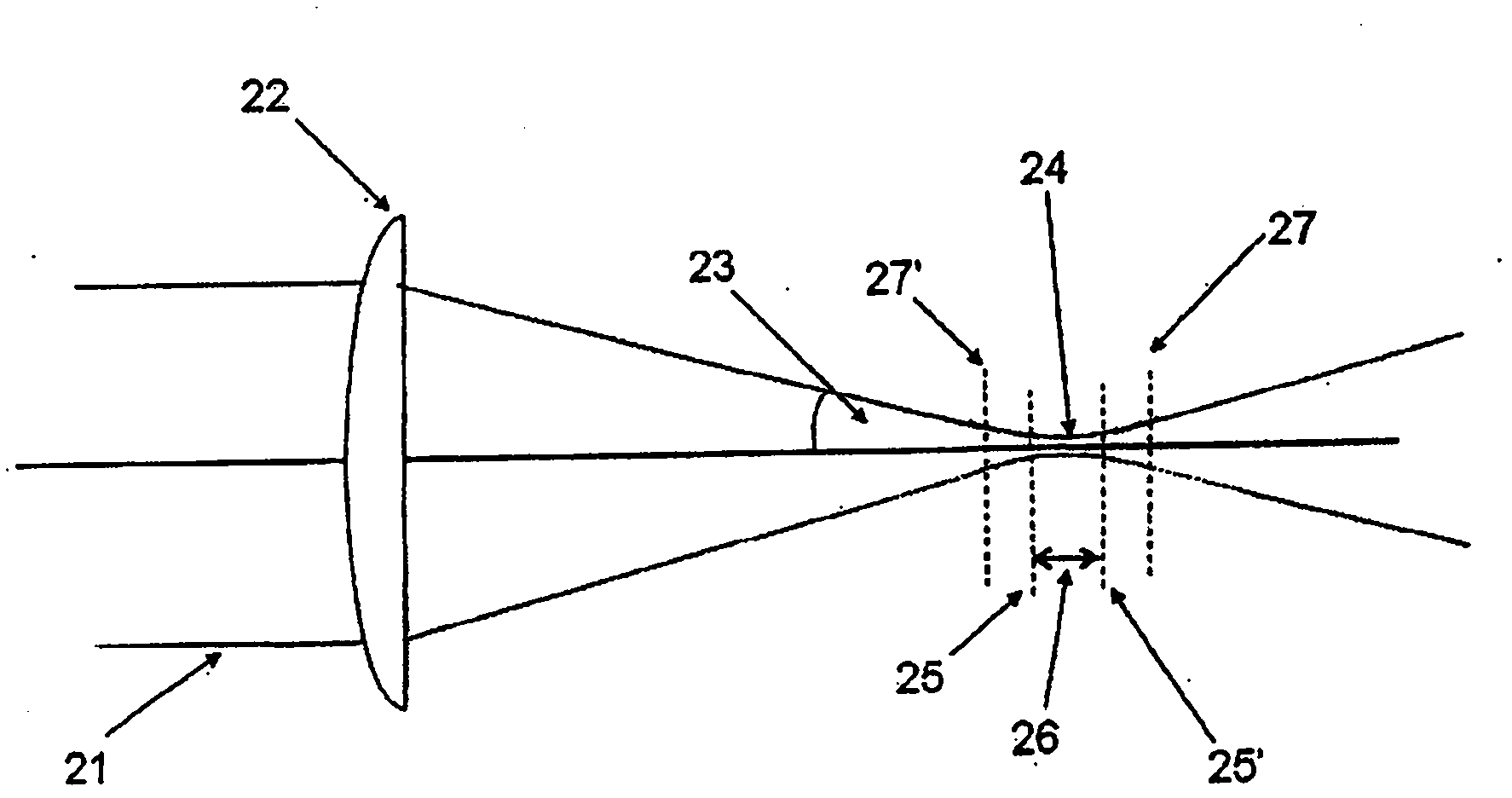
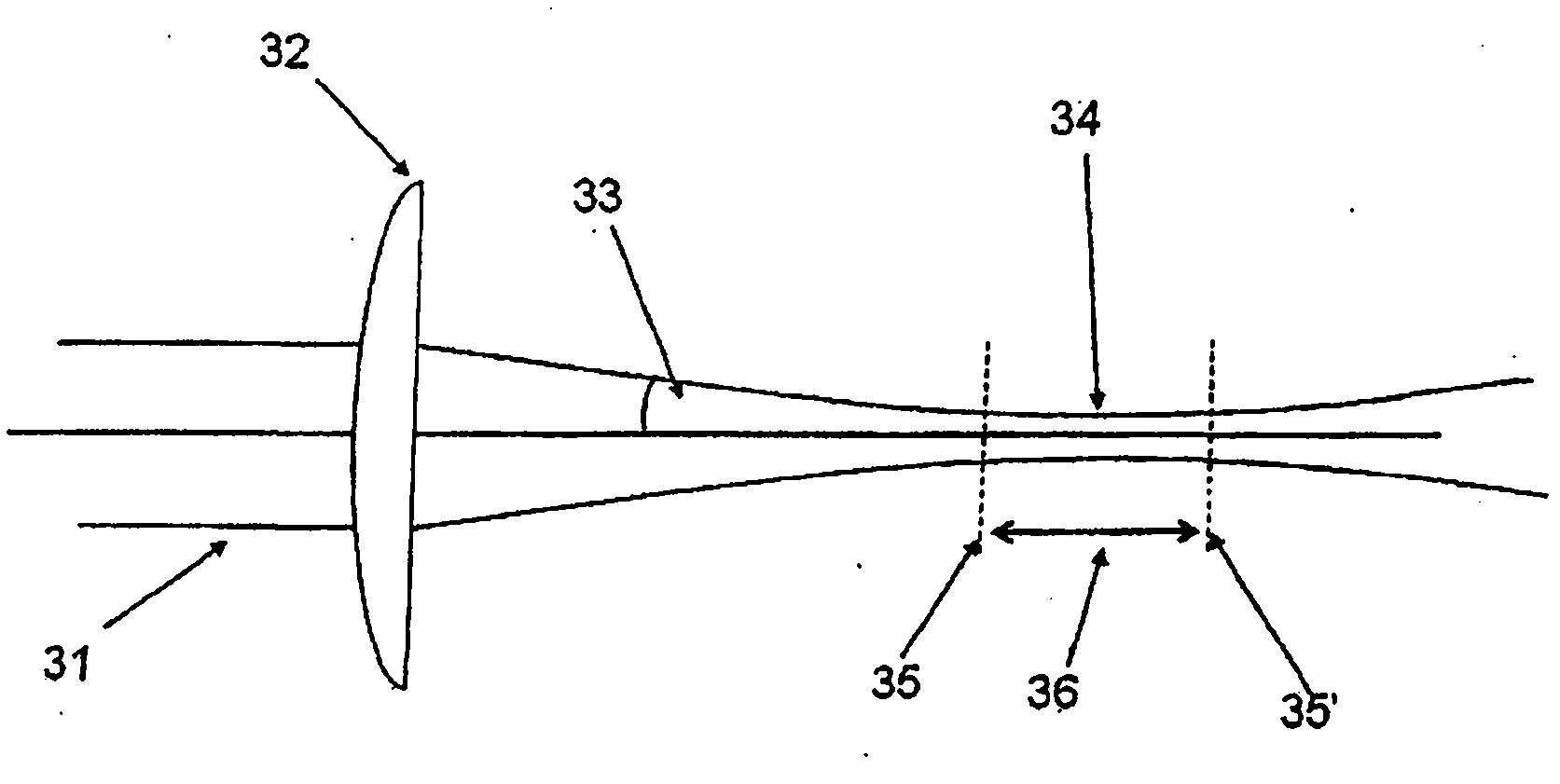
Method and apparatus for controlling the size of a laser beam focal spot
A method and apparatus is described that allows the width of fine line structures ablated or cured by a focussed laser beam on the surface of flat substrates to be dynamically changed while the beam is in motion over the substrate surface while simultaneously maintaining the beam focal point accurately on the surface. A three-component variable optical telescope is used to independently control the beam diameter and collimation by movement of first and second optical components relative to the third optical component. The method allows different focal spot diameters and different ablated or cured line widths to be rapidly selected and ensures that the beam shape in the focal spot remains constant and the depth of focus is always maximized.
Owner:盈天实业(深圳)有限公司
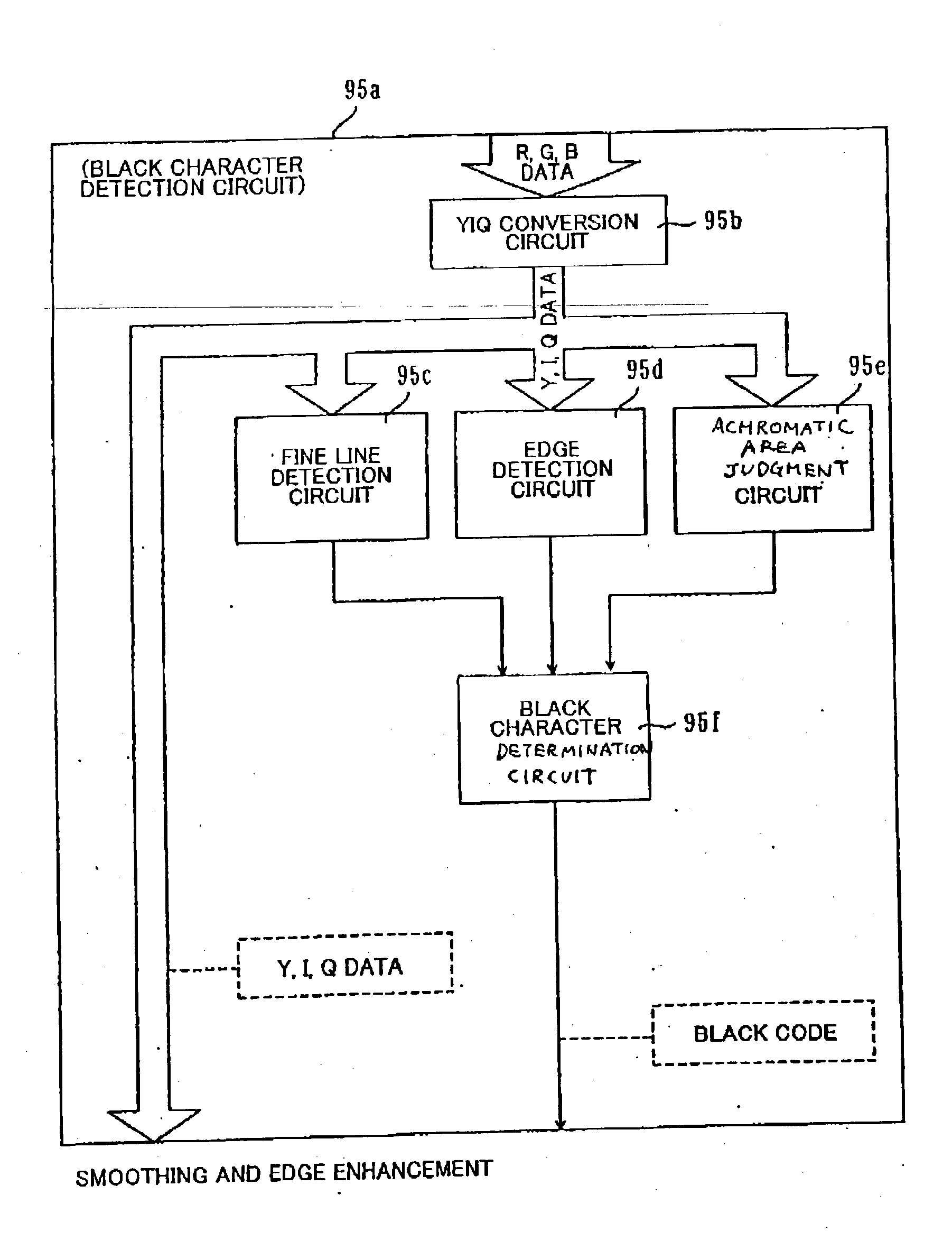
Image processing device and image processing method
In a black character detection processing, RGB data read from a line buffer is converted into YIQ data. For a subject pixel, a subject area centered on the subject pixel is set, and a judgment pixel that has the lowest brightness in the subject area is set. Then, a judgment area is set as being centered on the judgment pixel. If the absolute values of the averages of chroma components I and Q in the judgment area are both less than the corresponding thresholds T1 and T2, the subject pixel is determined as being an achromatic pixel. Black codes are added to fine-line pixels and edge pixels if the fine-line pixels and edge pixels are determined as being achromatic. Thus, the fine-line pixels and edge pixels can be specified as to be printed in black monochromatic ink. Therefore, black character or similar fine-line or edge part images can be outputted with high quality.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Printable medium for etching oxidic, transparent and conductive layers
InactiveUS20100068890A1Maintain good propertiesImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationFine lineSolar cell
The present invention relates to novel printable etching media having improved properties for use in the process for the production of solar cells. These are corresponding particle-containing compositions by means of which extremely fine lines and structures can be etched very selectively without damaging or attacking adjacent areas.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Compositions and methods of their use for improving the condition and appearance of skin
InactiveUS20060134059A1Increase gene expressionReduction in signCosmetic preparationsBiocideFine lineWrinkle skin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating, preventing and improving the condition and aesthetic appearance of skin, particularly, treating, preventing, ameliorating, reducing and / or eliminating fine lines and / or wrinkles of skin, where the compositions include natural plant constituents which increase expression levels genes associated with the dermatological signs of aging. The compositions of the invention are topically applied to the skin, or are delivered by directed means to a site in need thereof, once daily in an amount effective in improving the condition and aesthetic appearance of skin.
Owner:AVON PROD INC
Topical skin care formulation
Disclosed is a multi-beneficial topical skin care composition, and methods for its use, that can hydrate skin, increase the firmness of skin, reduce the appearance of fine lines or wrinkles on skin, and reduce the appearance of age spots on skin. The composition can include a combination of skin active ingredients comprising euterpe oleracea fruit extract, punica granatum sterols, caprooyl tetrapeptide-3, tocopherol or tocopherol acetate, and niacinamide, a combination of skin moisturizing agents comprising glycerin and butyrospermum parkii, a photo stable combination of sunscreen agents providing the composition with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least about 15, and a dermatologically acceptable vehicle which imparts a non-greasy feel when applied to skin.
Owner:MARY KAY INC
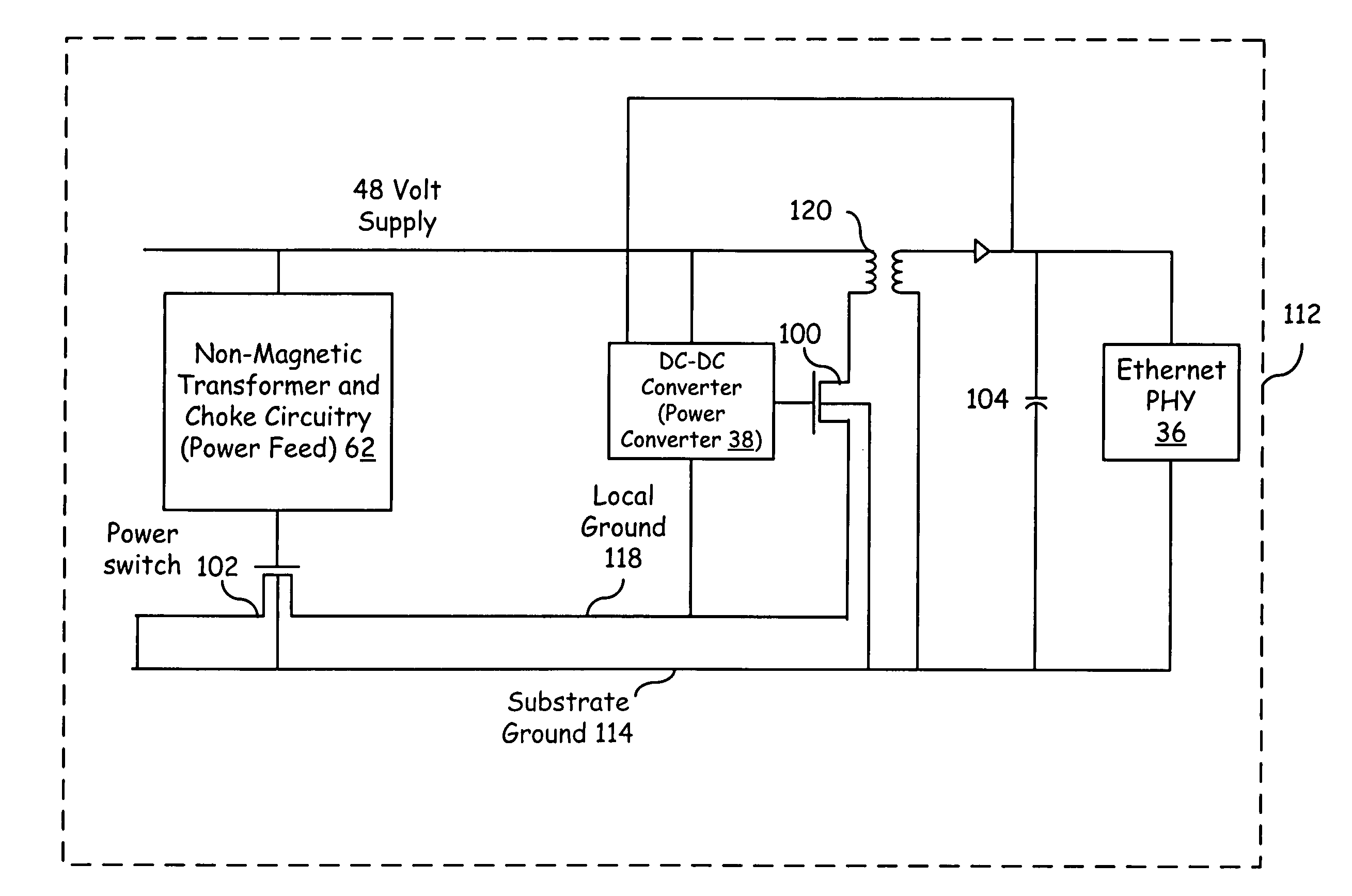
Integrated DC/DC converter substrate connections
Embodiments of the present invention provide an integrated circuit (IC) having an integrated DC-DC power converter therein. This IC is operable to support the distribution of combined power and data signals in a network environment such as an Ethernet network according to protocols such as the power over Ethernet (PoE) protocol. The IC includes a DC-DC power converter, a power feed circuit, and a network physical layer (PHY) module, wherein the PHY module may contain fine line structures susceptible to damage when exposed to excessive voltages. To prevent or reduce the likelihood of damage to the PHY module from voltages supplied to the DC-DC power converter, a common substrate ground is shared between the IC components.
Owner:KINETIC TECH INT HLDG LP
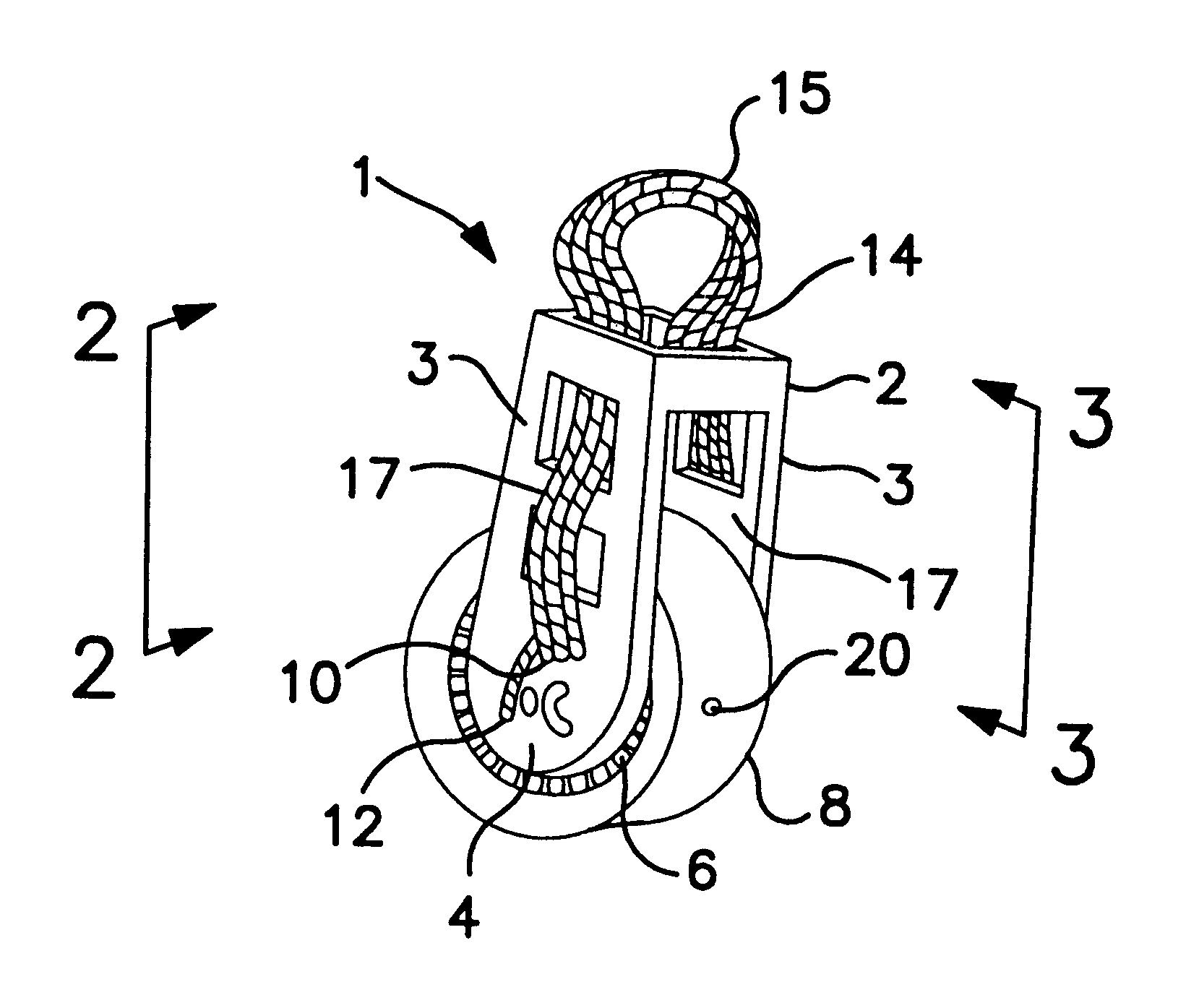
Bearing block tether using fine lines
InactiveUS6305669B1Reduce weightEasily and removably attached to a boat deck or the likePortable liftingWind acting propulsive elementsSet screwFine line
A bearing block has a head, a central hub, bearing means facilitating rotation of the sheave about the central hub. The block further has locking means for removably locking a length of high strength, fibrous material, such as cord, to the block for tethering the block to a boat deck or the like. The locking means may be a part of the block head, cheeks, or may be located at the block central hub. Preferred locking means are a plurality of passages for the cord ends to pass through, with set screws in two of the passages for removably holding the cord ends therein. A center portion of the cord length thus forms a loop for tethering the block.
Owner:HARKEN INC
Display apparatus
InactiveCN102830490AIncrease contrastReduce power consumptionOptical elementsFine lineConductive materials
The invention provides a display apparatus whch includes: a spectacle type frame mounted on a head portion of an observer; and an image display apparatus installed in the frame. The image display apparatus includes an image forming device, and an optical device allowing light output from the image forming device to be incident thereon, to be guided therein, and to be output therefrom. A dimmer which adjusts the amount of external light incident from the outside is disposed in an area of the optical device where the light is output. The dimmer includes a first transparent substrate and a second transparent substrate facing the first substrate, first and second electrodes which are mounted on the first and second substrates, respectively, and an electrolyte sealed between the first and second substrates and containing metal ions. The first electrode includes a conductive material of a fine line shape. The second electrode includes a transparent electrode layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
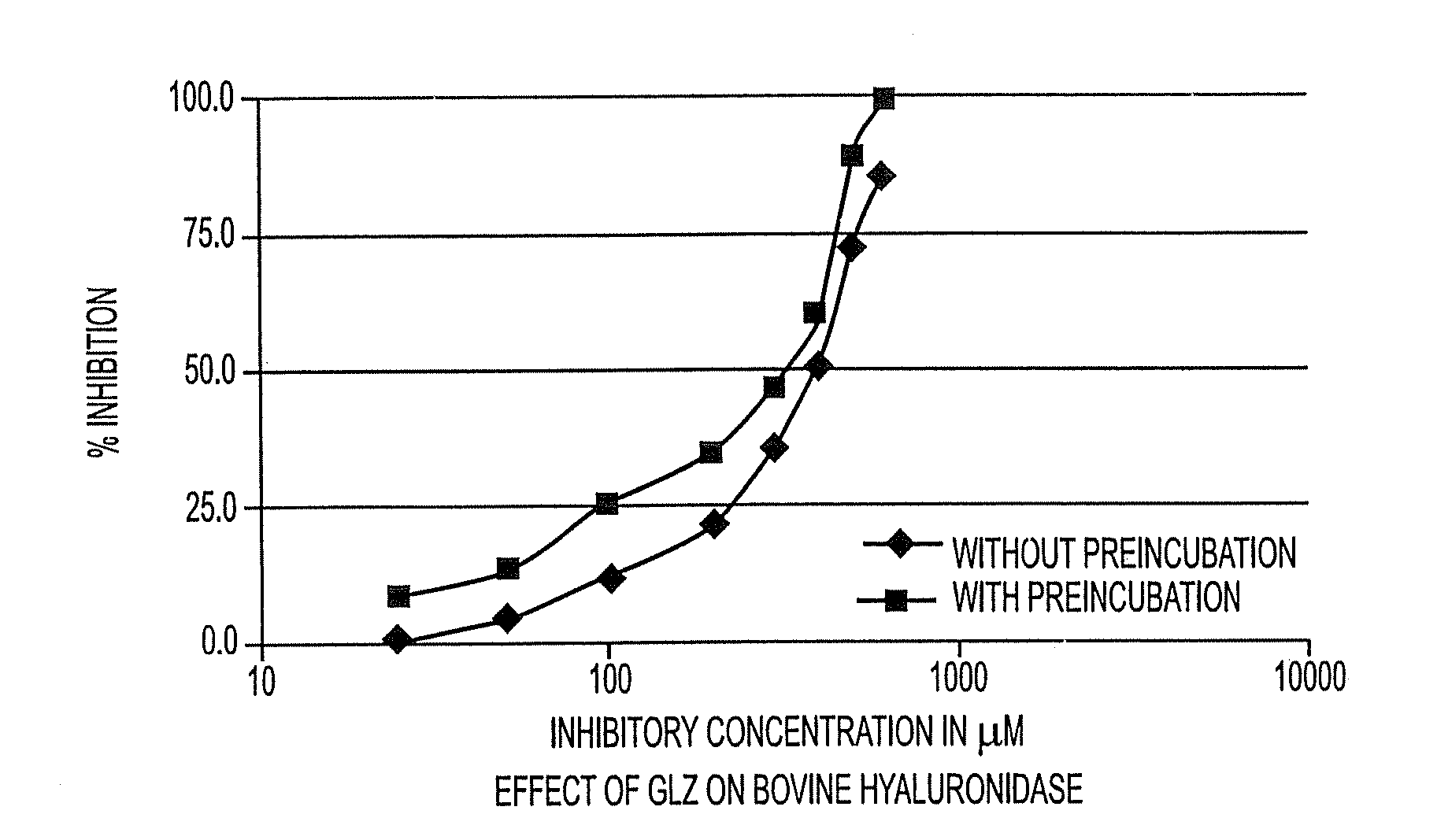
Novel topical skin care and nutraceutical applications of Glabridin or extracts containing a defined amount (4-90%) of Glabridin
InactiveUS20040121031A1Avoid damagePrevent photoagingCosmetic preparationsBiocideFine lineTyrosinase
This application is a continuation-in-part of pending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10 / 065,995 by the authors, filed on Dec. 9, 2002, for a Commercial Process for Isolation and Purification of Glabridin with High Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity and its Cosmetic Compositions and Methods Of Use. The current invention discloses the use of Glabridin containing Licorice extract (4-90% Glabridin) as metalloprotease and hyaluronidase inhibiting component in cosmetic topical or oral formulations. These extracts and particularly Glabridin, are useful in anti-wrinkle and anti-aging products, providing elasticity, firmness, tone and texture to the skin, ameliorating fine lines and crows feet in under eye preparations, and prevent skin and hair damage due to UV rays, inflammation and itch, diaper rashes in baby products, as massage or toning oils or emulsion for babies.
Owner:SAMI LABS LTD
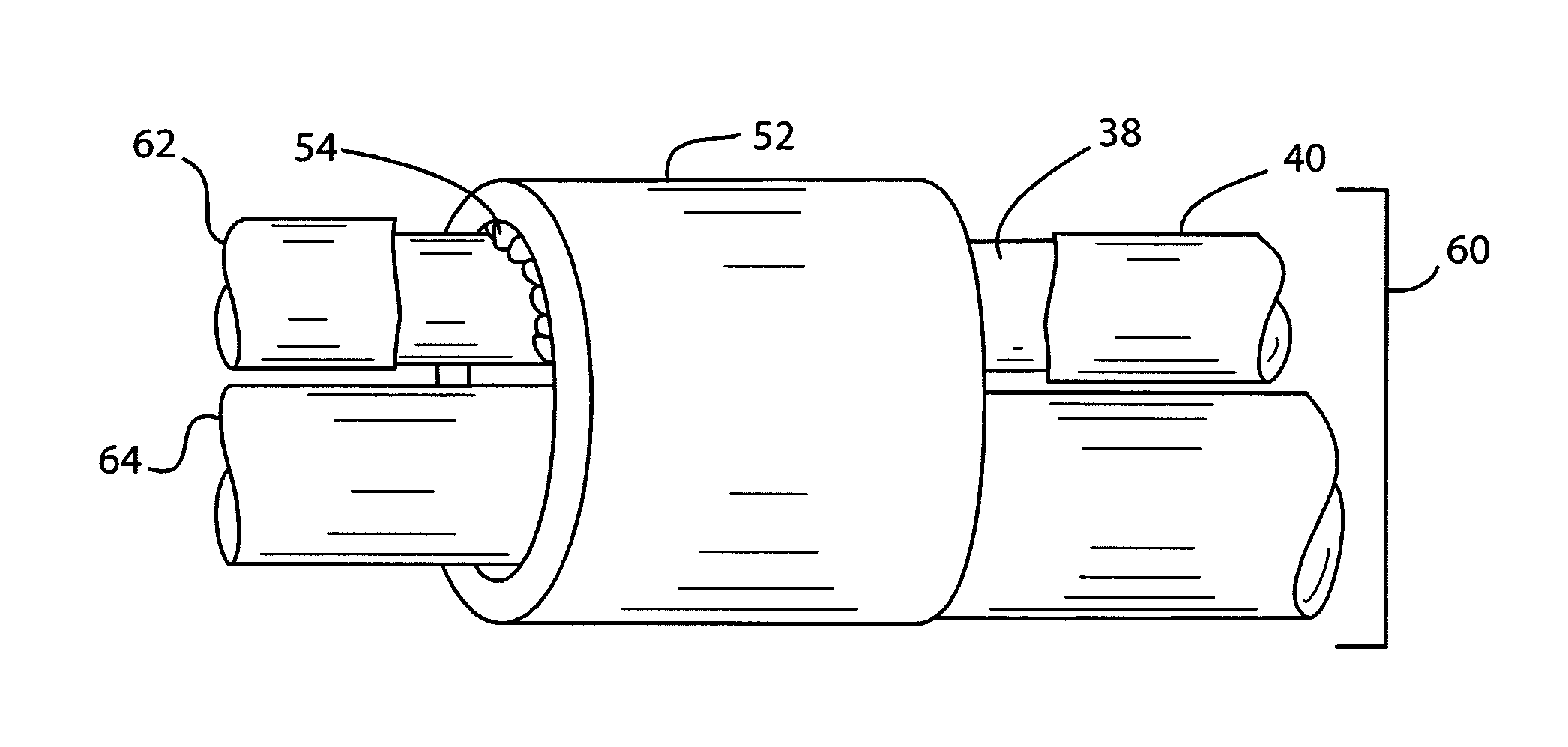
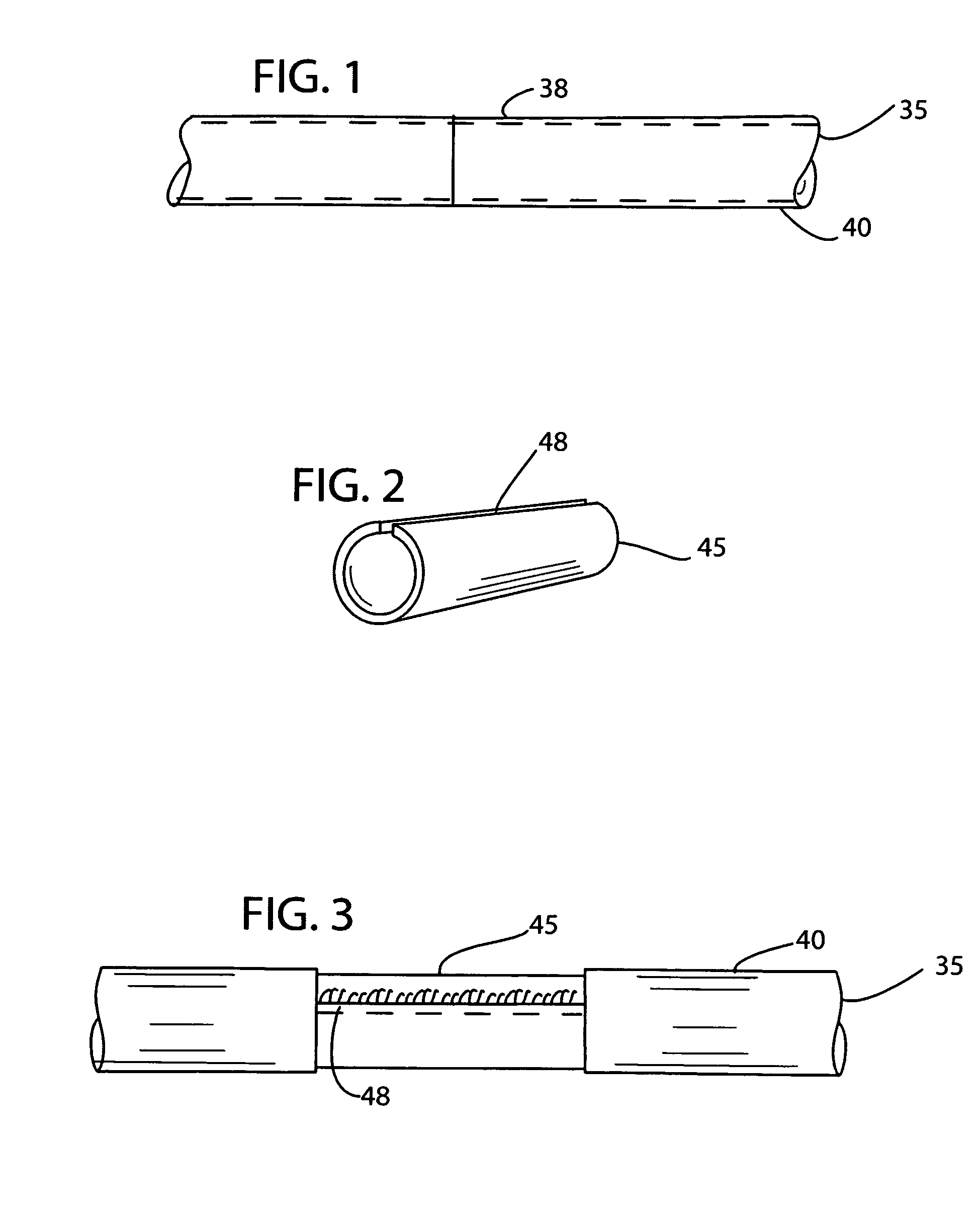
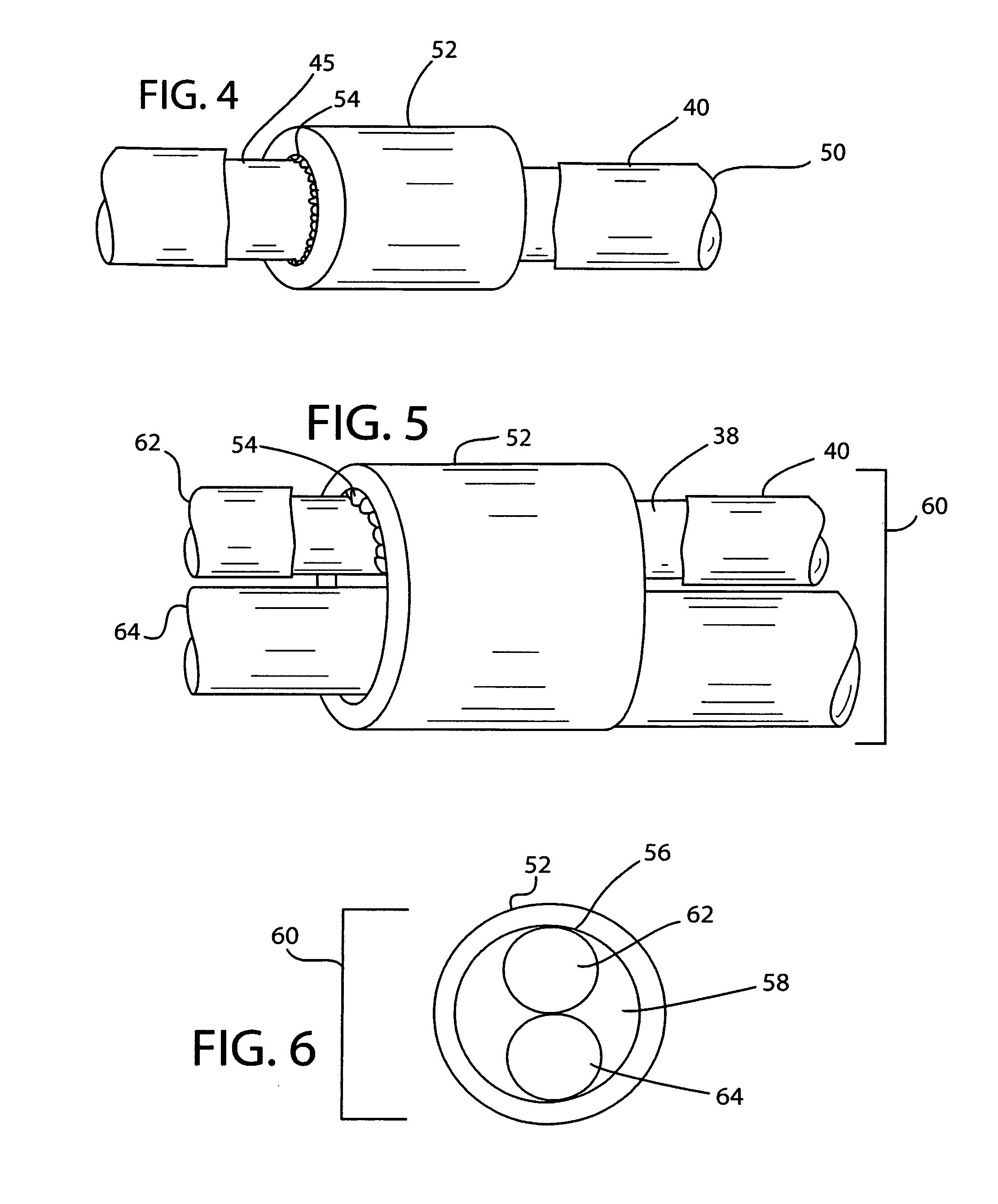
Electrode and connector attachments for a cylindrical glass fiber wire lead
InactiveUS20110220408A1Improve conductivityLow electrical resistanceSpinal electrodesLine/current collector detailsFine lineElectrical conductor
A cardiac pacemaker or other CRT device has one or more fine wire leads to the heart. Formed of a glass, silica, sapphire or crystalline quartz fiber with a metal coating, a unipolar lead can have an outer diameter as small as about 300 microns or even smaller. The metal buffer coating may be deposited directly on the glass / silica fiber, or upon an intermediate layer between the glass / silica fiber and metal, consisting of carbon and / or polymer. The resulting metallized glass / silica fibers are extremely durable, can be bent through small radii and will not fatigue even from millions of iterations of flexing. Bipolar fine wire leads can include several insulated metallized glass / silica fibers residing side by side, or can be coaxial with two or more insulated metal conductive paths. An outer protective sheath of a flexible polymer material can be included. The fine wire lead incorporates a thin metal conductor, which poses unique challenges for attachment to standardized connectors, as well as stimulation electrodes. The present invention describes means and materials for creating robust and durable electrically conductive connections between the fine wire lead body and a proximal standardized connector and distal ring and tip electrodes.
Owner:CARDIA ACCESS
High performance integrated circuit device and method of making the same
InactiveUS20060267198A1Increase resistanceIncrease parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFine lineInterconnection
A new interconnection scheme is described, comprising both coarse and fine line interconnection schemes in an IC chip. The coarse metal interconnection, typically formed by selective electroplating technology, is located on top of the fine line interconnection scheme. It is especially useful for long distance lines, clock, power and ground buses, and other applications such as high Q inductors and bypass lines. The fine line interconnections are suited for local interconnections. The combined structure of coarse and fine line interconnections forms a new interconnection scheme that not only enhances IC speed, but also lowers power consumption.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Use of fibers in a care composition or a make-up composition to make the skin matte
InactiveUS20020028222A1Avoid injurySatisfied with the resultCosmetic preparationsBiocideFine lineSkin complexion
The present application relates to the use of fibers in a skincare composition or a make-up composition for the skin, to make the complexion matte, smooth and / or uniform, and / or to fade out skin relief defects. The fibers are in particular polyamide fibers having a length of from 1 mum to 10 mm and a shape factor of from 5 to 150. The composition used gives the skin a covering index of greater than 0.1 and preferably greater than 0.13. The invention also relates to a cosmetic treatment process for fading the complexion matte, smooth and / or uniform, and / or for fading out microreliefs, wrinkles, fine lines and pores in the skin, comprising the application to the skin of fibers in a cosmetic composition.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com