Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Low wavelength dependence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
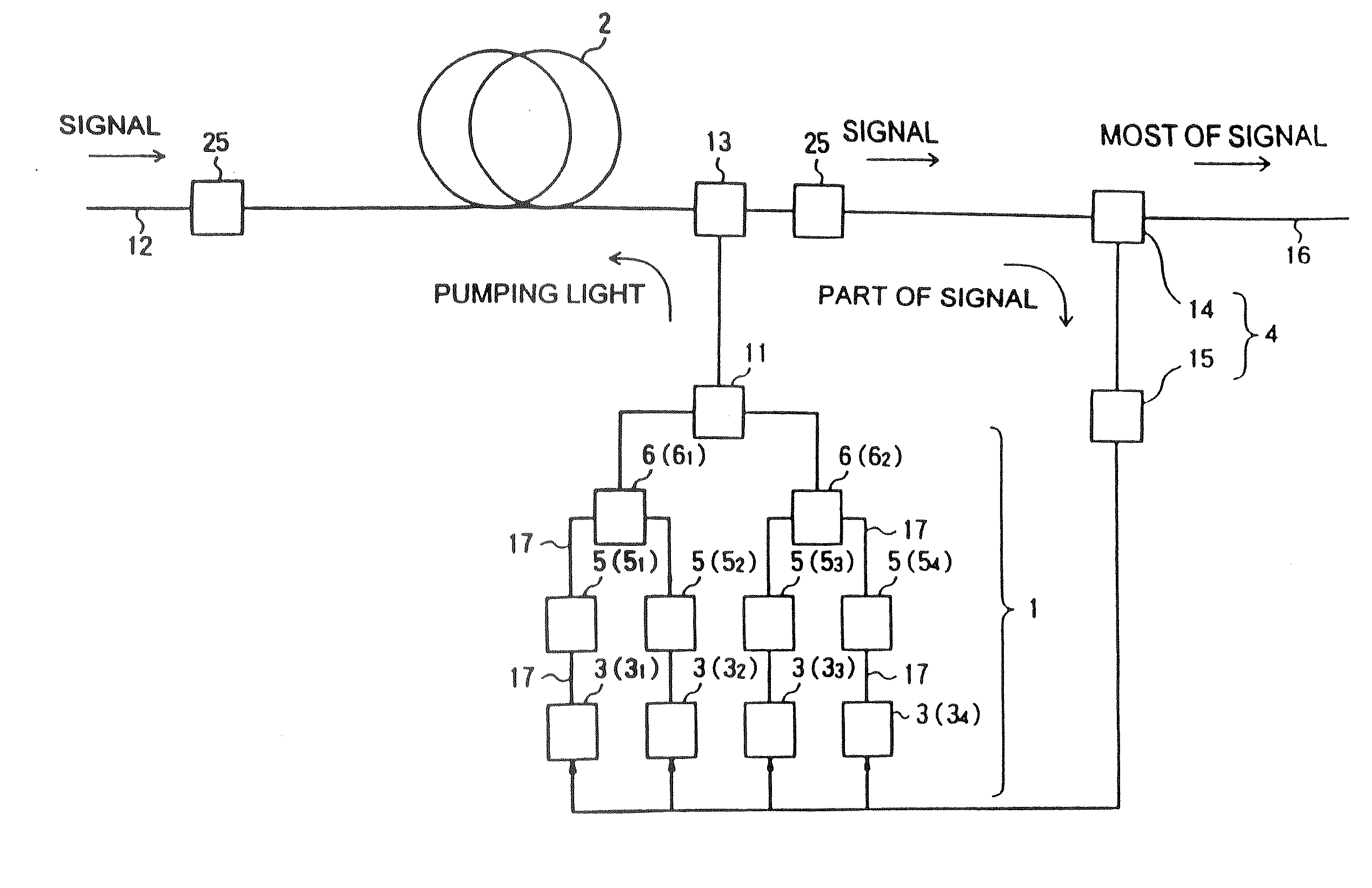
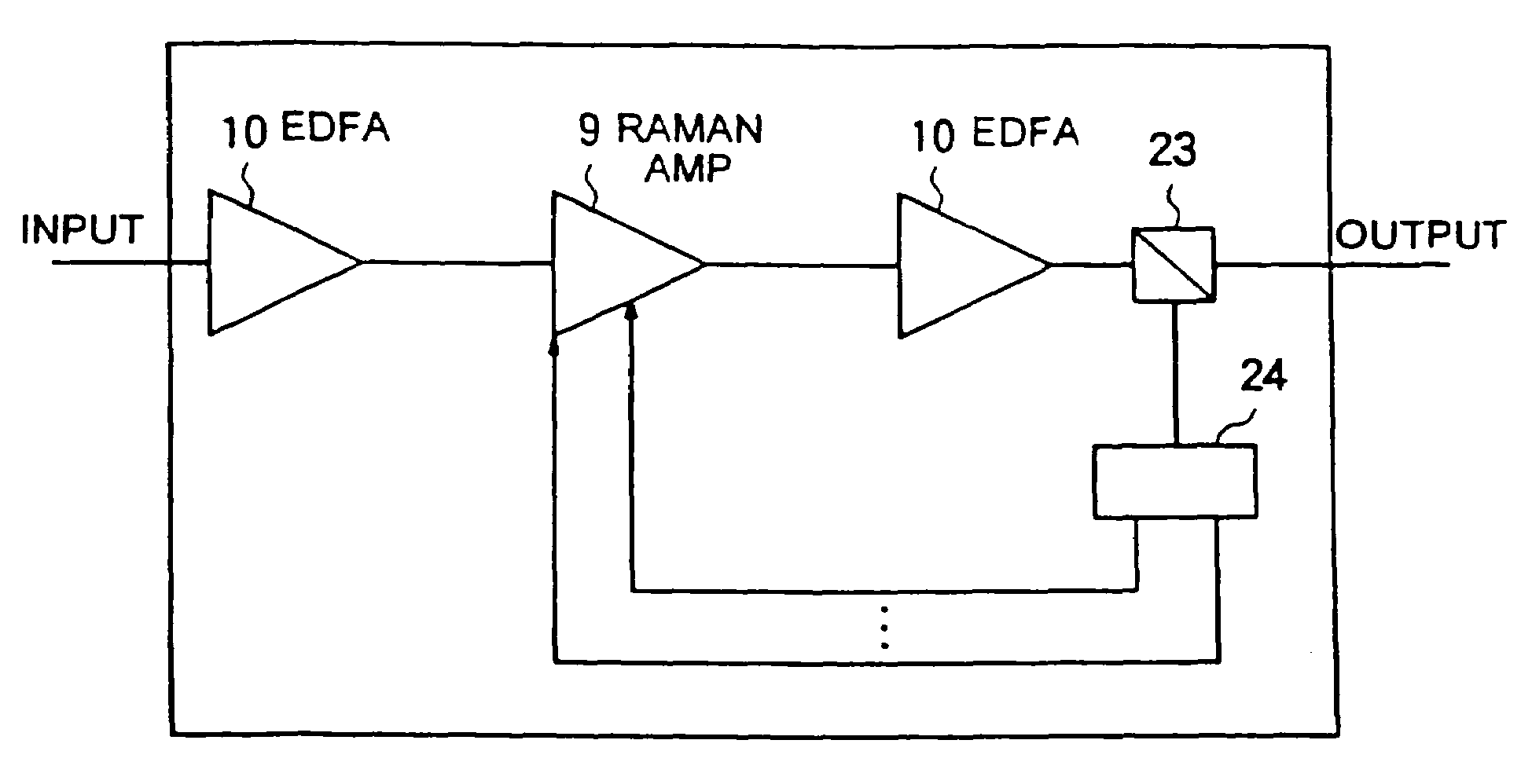
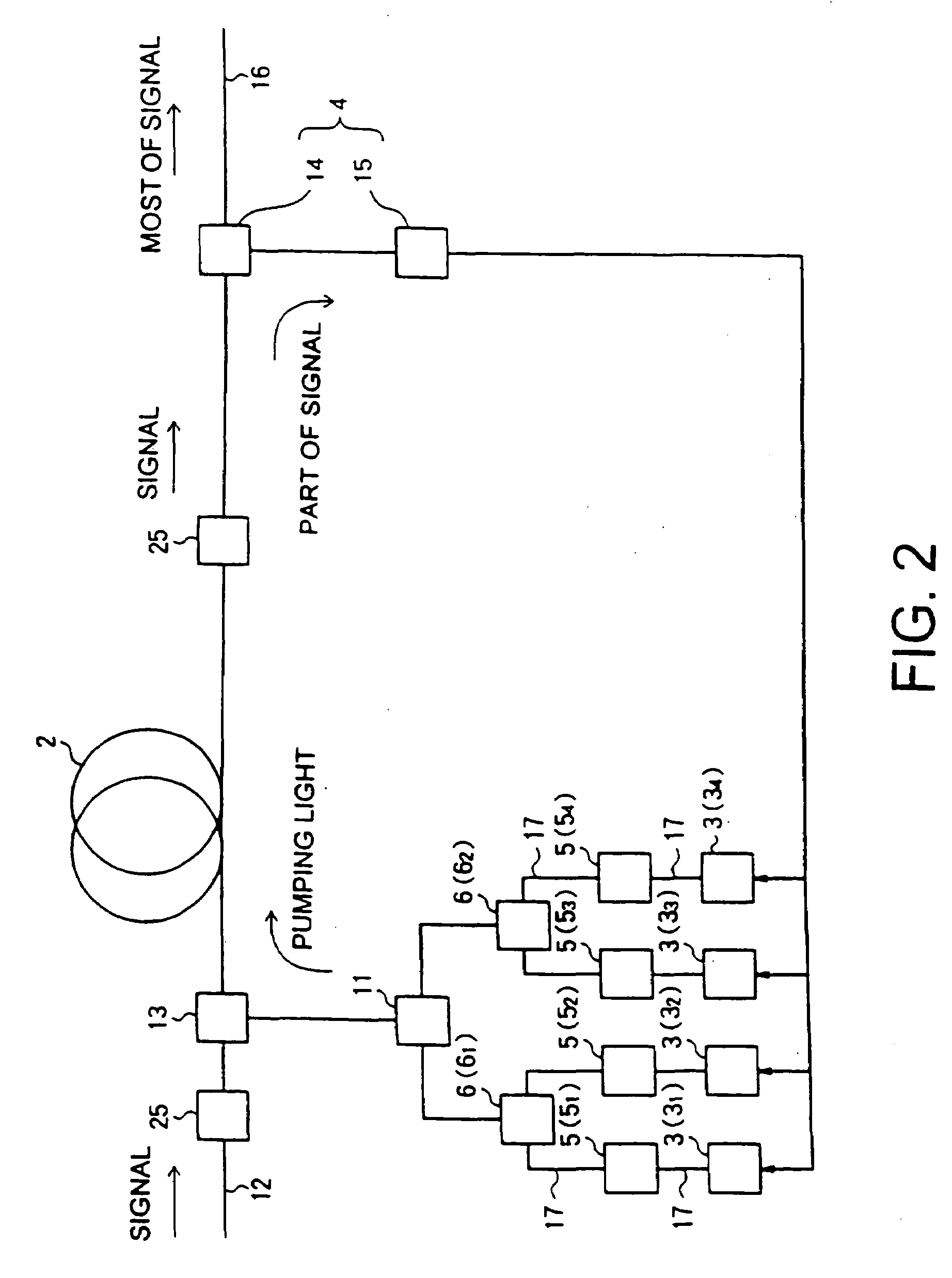
Raman amplifier, optical repeater, and raman amplification method
InactiveUS20070247701A1Soften propertyWide bandLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsLong wavelengthLight source
A Raman amplifier according to the present invention comprises a plurality of pumping means using semiconductor lasers of Fabry-Perot, DFB, or DBR type or MOPAs, and pumping lights outputted from the pumping means have different central wavelengths, and interval between the adjacent central wavelength is greater than 6 nm and smaller than 35 nm. An optical repeater according to the present invention comprises the above-mentioned Raman amplifier and adapted to compensate loss in an optical fiber transmission line by the Raman amplifier. In a Raman amplification method according to the present invention, the shorter the central wavelength of the pumping light the higher light power of said pumping light. In the Raman amplifier according to the present invention, when a certain pumping wavelength is defined as a first channel, and second to n-th channels are defined to be arranged with an interval of about 1 THz toward a longer wavelength side, the pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the first to n-th channels are multiplexed, and an pumping light having a wavelength spaced apart from the n-th channel by 2 THz or more toward the longer wavelength side is combined with the multiplexed light, thereby forming the pumping light source. The pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the channels other than (n-1)-th and (n-2)-th channels may be multiplexed, thereby forming the pumping light source. The pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the channels other than (n-2)-th and (n-3)-th channels may be multiplexed, thereby forming the pumping light source.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Diffraction grating, organic el element using the same, and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveUS20120132897A1Low wavelength dependenceReduce directivityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesWavenumberAfm atomic force microscopy
A diffraction grating having a transparent supporting substrate; and a cured resin layer which is stacked on the transparent supporting substrate and which has concavities and convexities formed on a surface thereof, wherein when a Fourier-transformed image is obtained by performing two-dimensional fast Fourier transform processing on a concavity and convexity analysis image obtained by analyzing a shape of the concavities and convexities formed on the surface of the cured resin layer by use of an atomic force microscope, the Fourier-transformed image shows a circular or annular pattern substantially centered at an origin at which an absolute value of wavenumber is 0 μm−1, and the circular or annular pattern is present within a region where an absolute value of wavenumber is within a range of 10 μm−1 or less.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP +1
Transparent laminate, method for producing the same, and plasma display panel
InactiveUS6855369B2Little dependenceImprove visibilityMirrorsOptical filtersTransmittanceRefractive index
In a transparent laminate, n thin-film units (n=3 or 4) are laminated unit by unit successively on a surface of a substrate, and a high-refractive-index transparent thin film is deposited on a surface of the laminate of the n thin-film units, each of the n thin-film units consisting of a high-refractive-index thin film and a silver transparent conductive thin film. When the silver transparent conductive thin films are deposited by a vacuum dry process, the temperature T(K) of the transparent substrate at the time of film deposition is set to be in a range 340≦T≦410, whereby the transparent laminate having a standard deviation of visible light transmittance which is not larger than 5% in a wave range of from 450 to 650 nm can be produced.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Polarizer and display device including polarizer
ActiveUS20090009865A1Good optical performanceHigh mechanical strengthPolarising elementsSpecial surfacesTransmittanceDisplay device
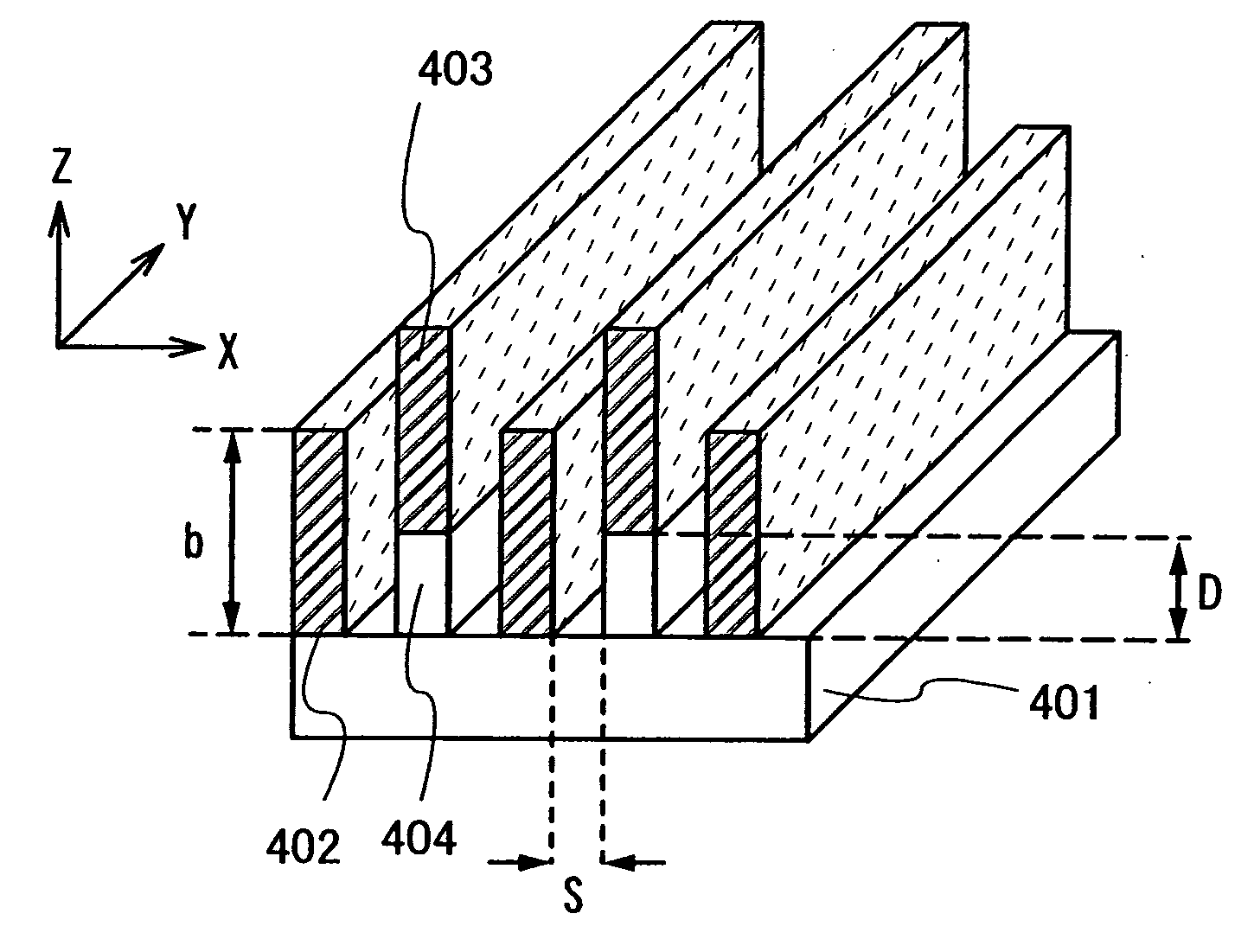
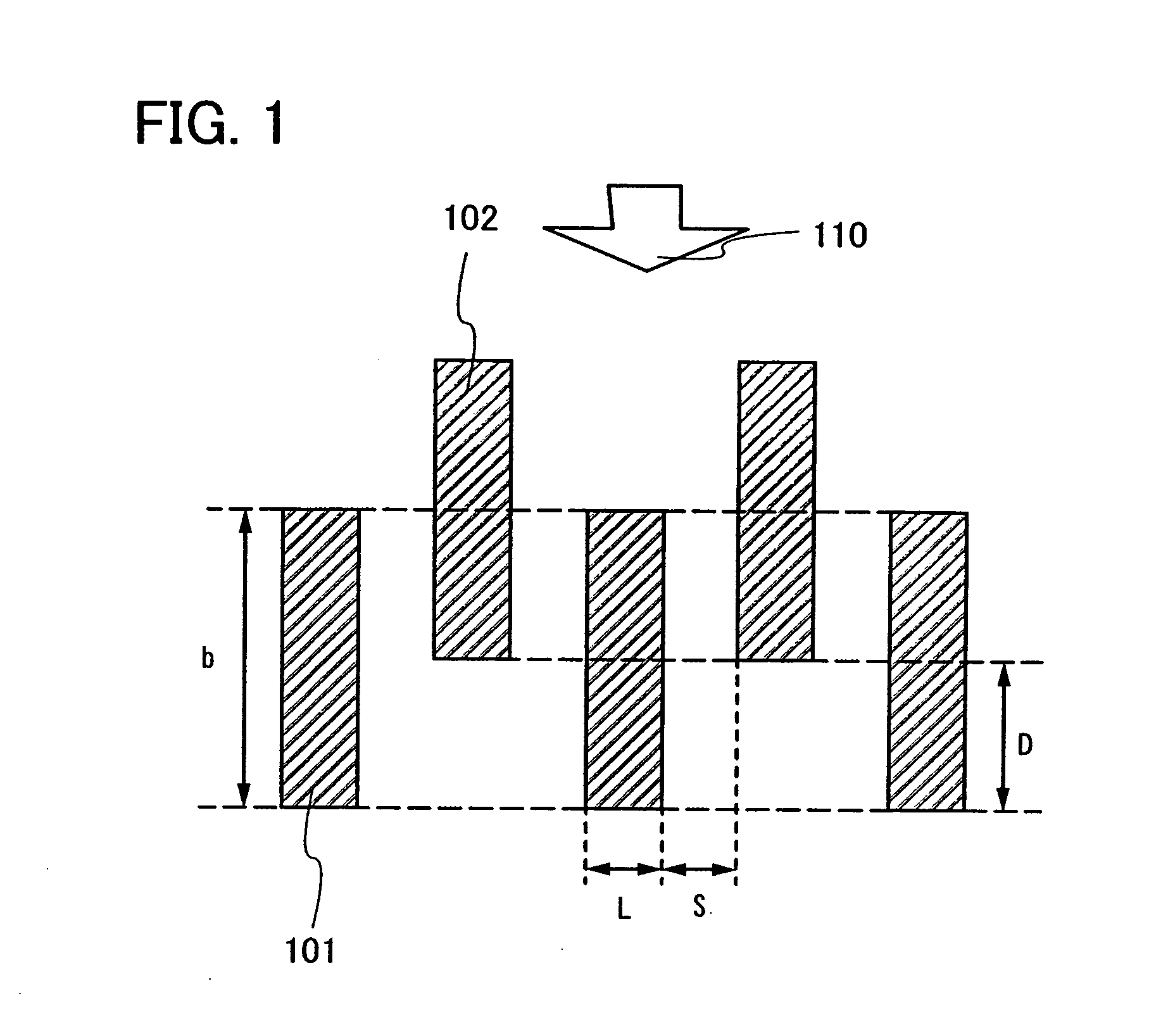
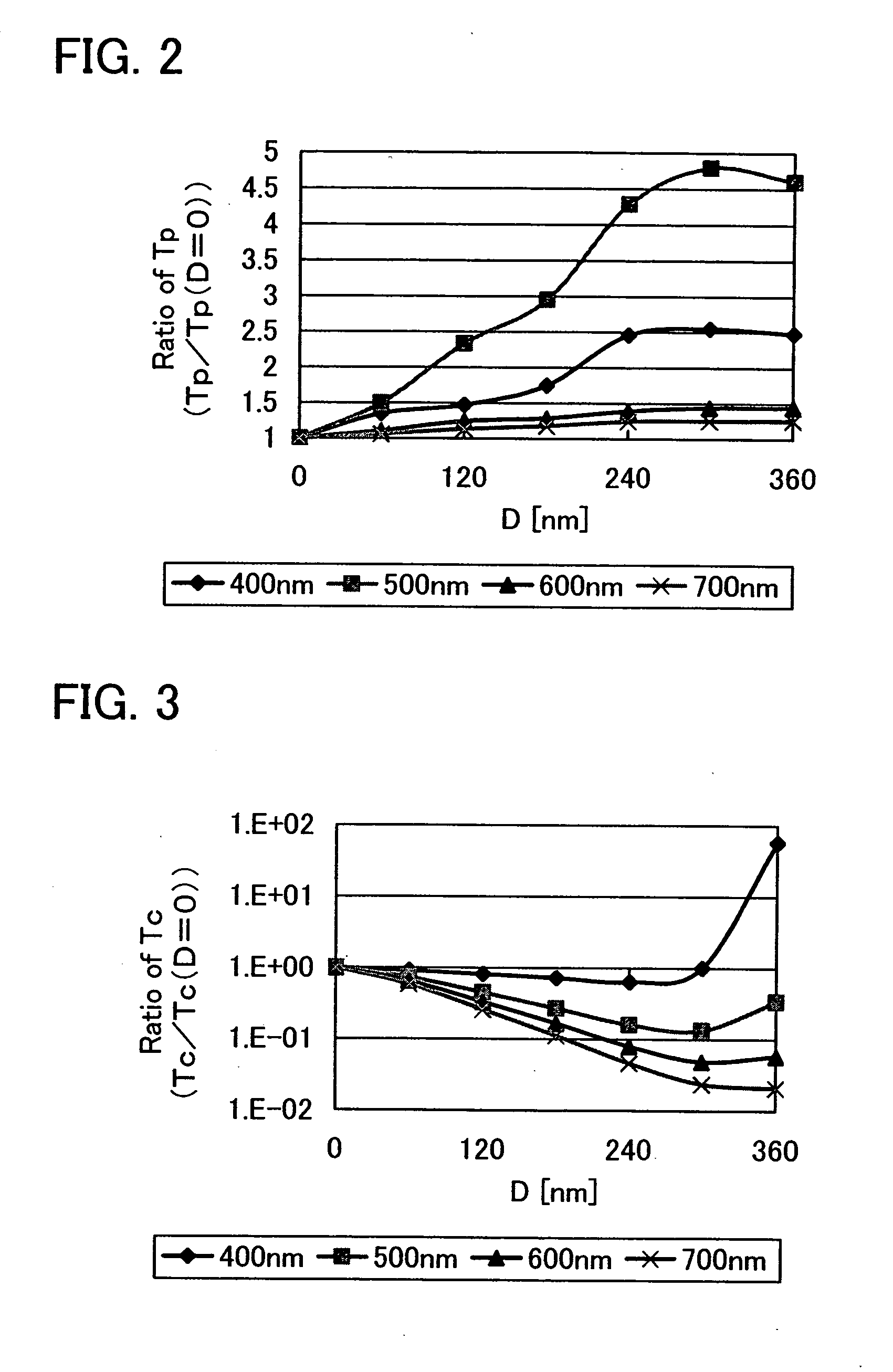
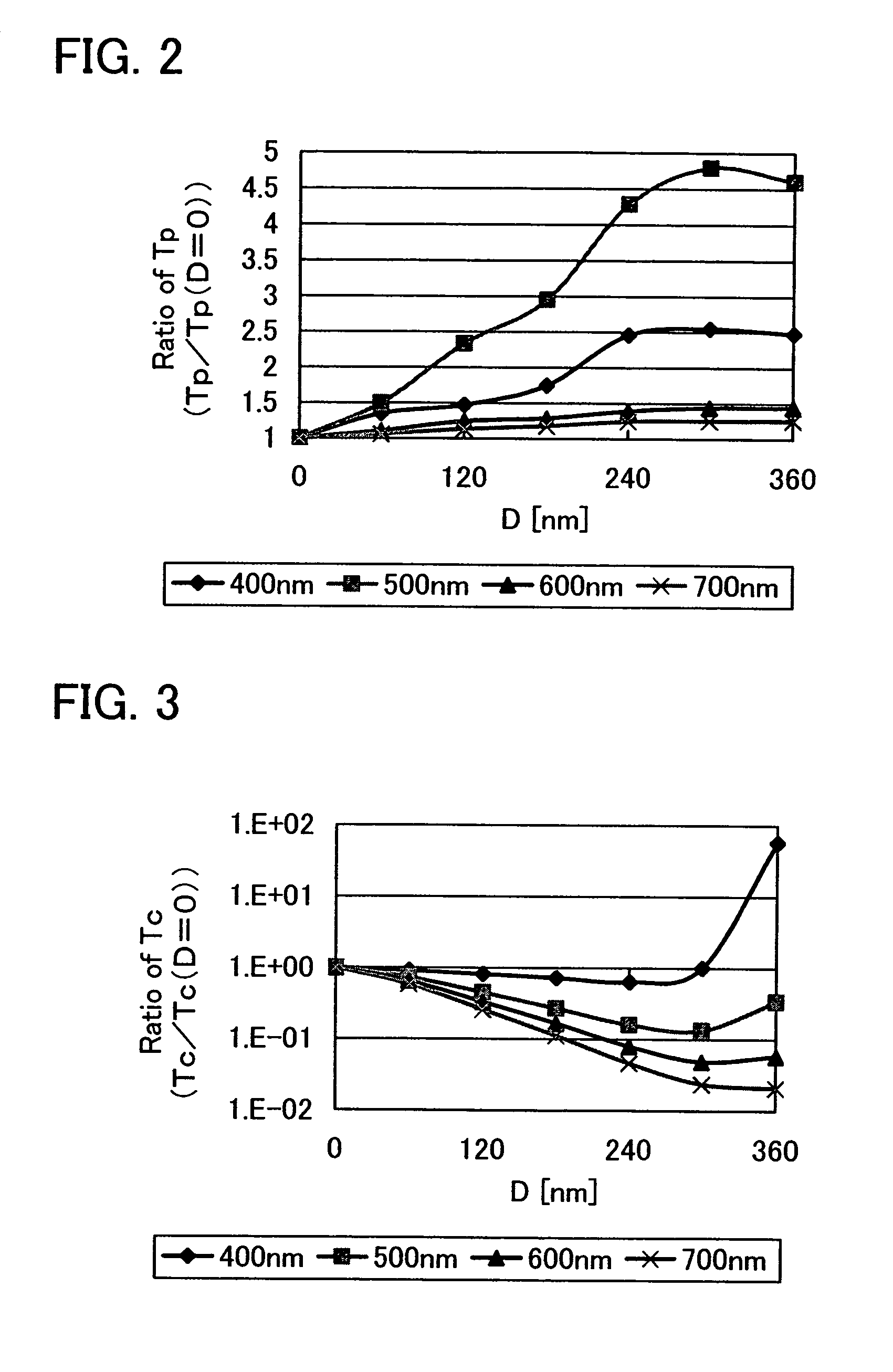
A polarizer in which parallel transmittance TP is increased and crossed transmittance TC is provided. Instead of arranging a plurality of all metal wires on one plane, a plurality of metal wires is separately formed on at least two different parallel planes, and adjacent meal wires among the plurality of metal wires are staggered in the polarizer. The heights of a first group of metal wires formed on a first plane and a second group of metal wires formed on a second plane, from a surface of the light-transmitting substrate are different. Further, a metal wire of the second group is provided to be more distant from the light-transmitting substrate than the first group of metal wires by distance D, and the distance D is smaller than the thickness of the first group of metal wires.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Wire-grid polarizer and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20130044373A1Improve reflectivityLow angle dependencyPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsWire gridTransmittance
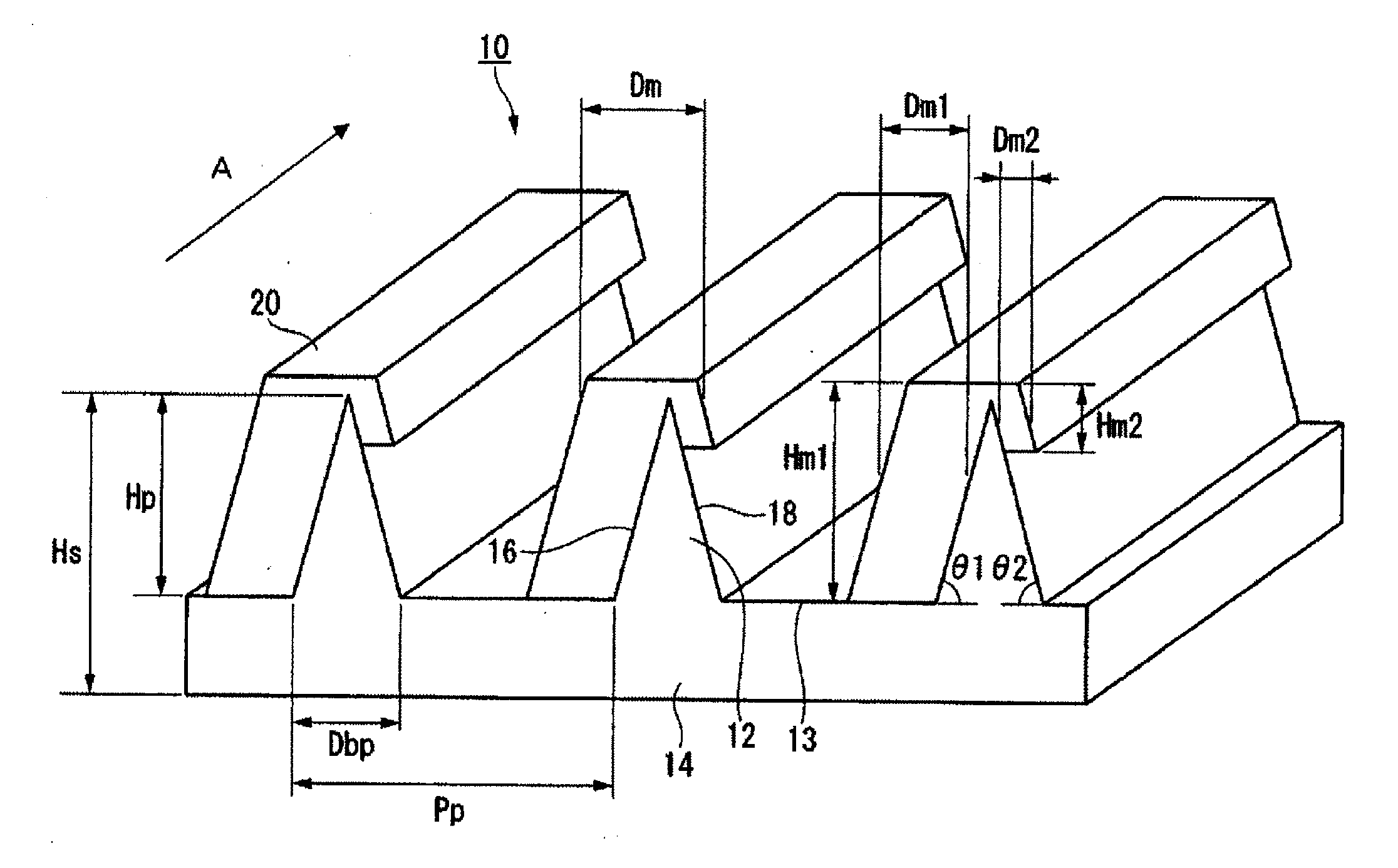
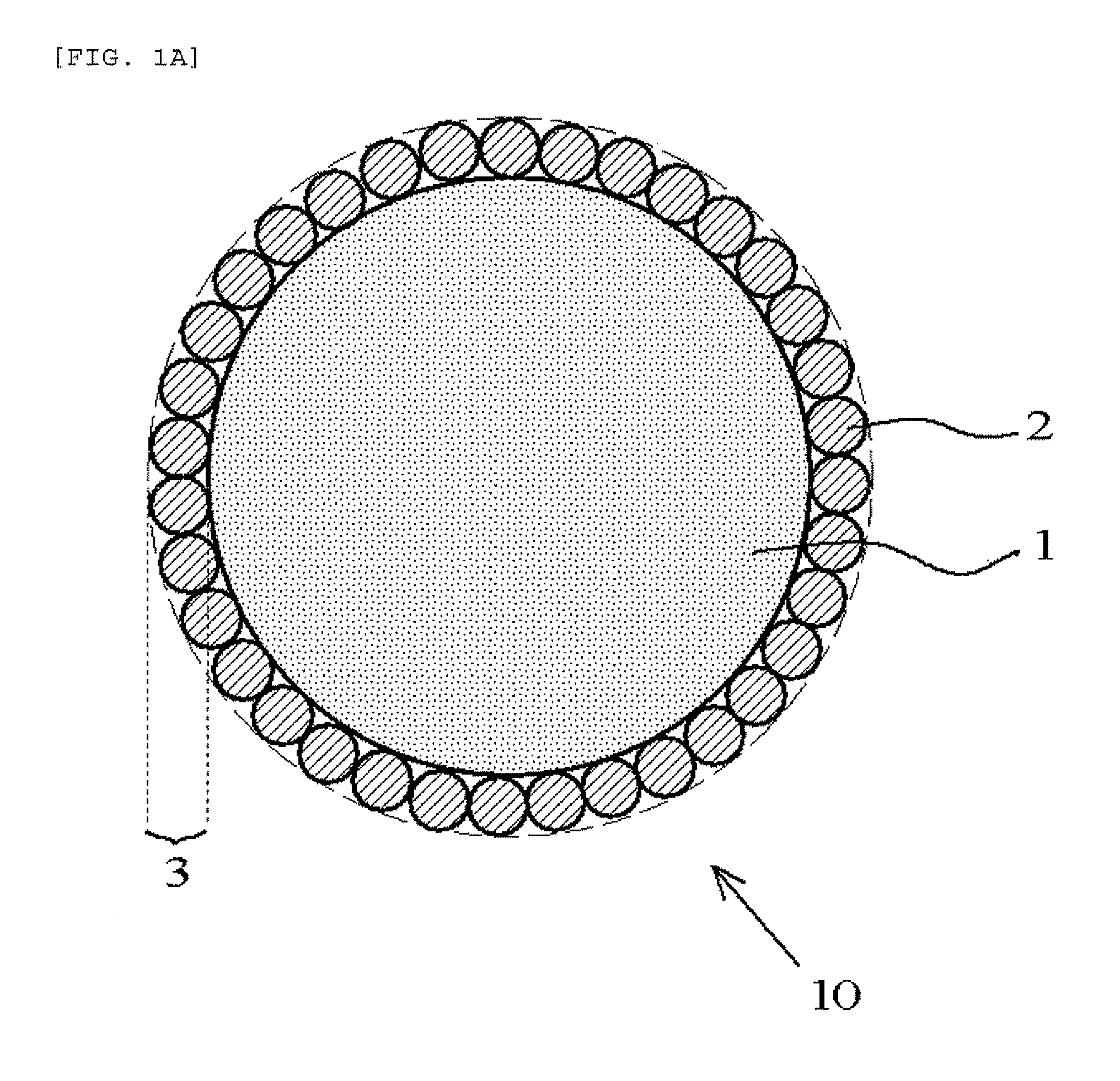
Disclosed are a wire grid polarizer, which exhibits high polarization, p-polarized light transmittance, and s-polarized light reflectance in the visible light region, and the optical characteristics of which have low angular dependence and wavelength dependence, and a manufacturing method for the same. A wire grid polarizer (10) comprises a light transmissive substrate (14), on the surface of which a multiplicity of convex strips (12), the width of which gradually narrows from the base to the apex, is formed parallel to one another with intervening flat spots (13) formed between the convex strips (12), and at a specified pitch (Pp), and a metallic layer (20), which covers the entire surface of a first side face (16) of the convex strip (12) and a portion of the flat spot (13) adjacent thereto, and either does not cover a second side face (18) of the convex strip (12) or covers a portion of a second side face (18); and a manufacturing method forms a metallic layer (20) by vapor depositioning a metal or metal compound from a direction that is substantially orthogonal to the length direction of the convex strips (12) and forms a 25-40 DEG angle relative to the height direction of the convex strips (12) on the side of the first side face (16), under conditions in which the deposition amount is 40-60 nm.
Owner:AGC INC
Optical waveguide device and optical waveguide module
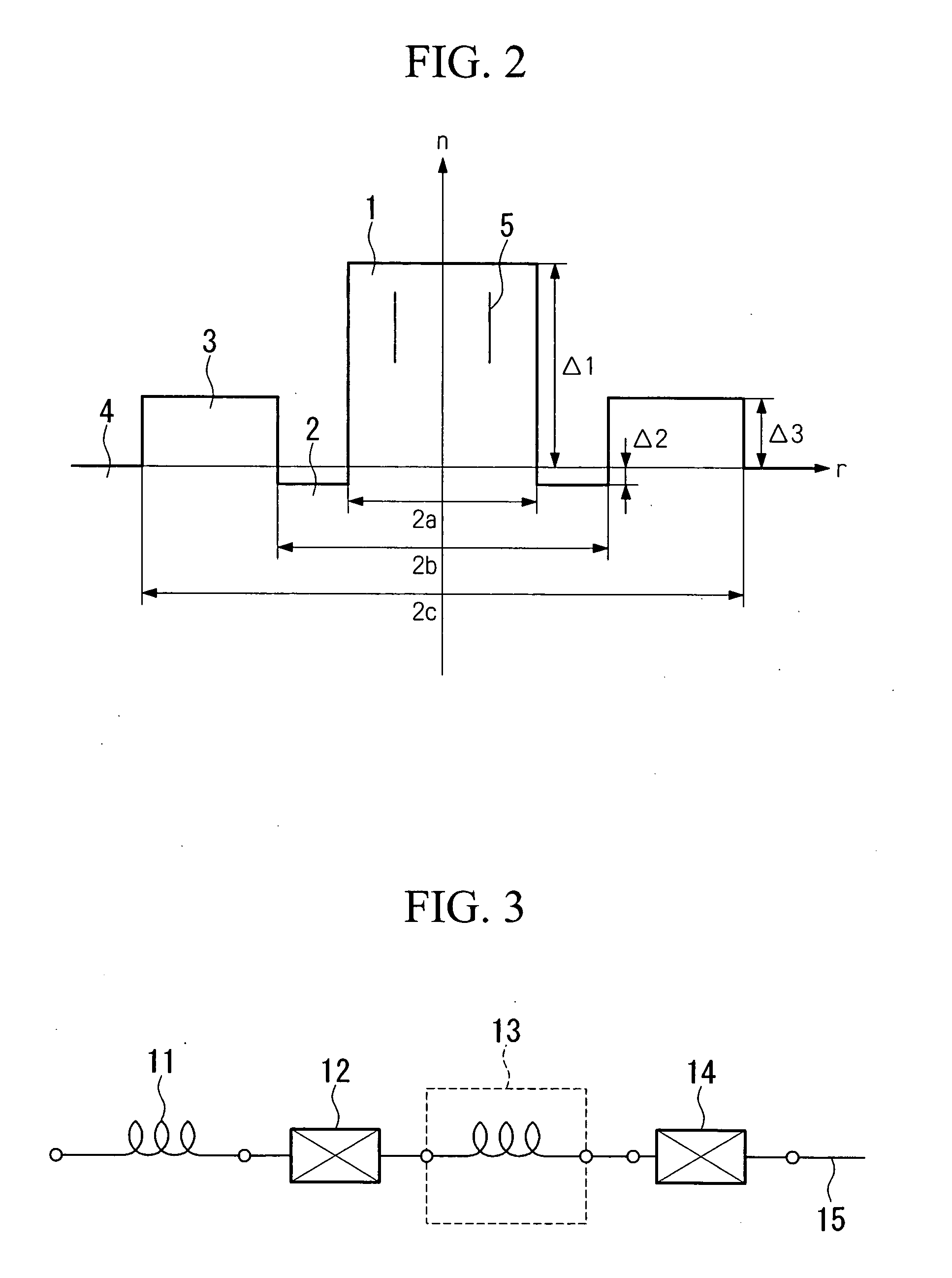
InactiveUS7212709B2Reduce lossLow wavelength dependenceCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideMultiplexingLength wave
An object of the present invention is to provide an optical waveguide device and an optical waveguide module having the function to multiplex / demultiplex or couple / decouple optical signals and particularly to provide an optical waveguide device and an optical waveguide module for realizing low optical loss, reducing wavelength dependence and ensuring easier shape management in the manufacturing and inspection processes. The optical waveguide device and optical waveguide module are provided with a substrate, one or more first waveguides, a plurality of second waveguides, and a slab waveguide for connecting the first waveguides and the second waveguides. At a region where the second waveguides are connected to the slab waveguide, a plurality of waveguide paths are provided for respectively connecting the second waveguides. Width of the waveguide paths is constant. The width of the separation gap between waveguide paths progressively increases as it becomes further away from the slab waveguide.
Owner:NEC CORP
Higher order mode dispersion compensating fiber and mode converter for higher order fiber
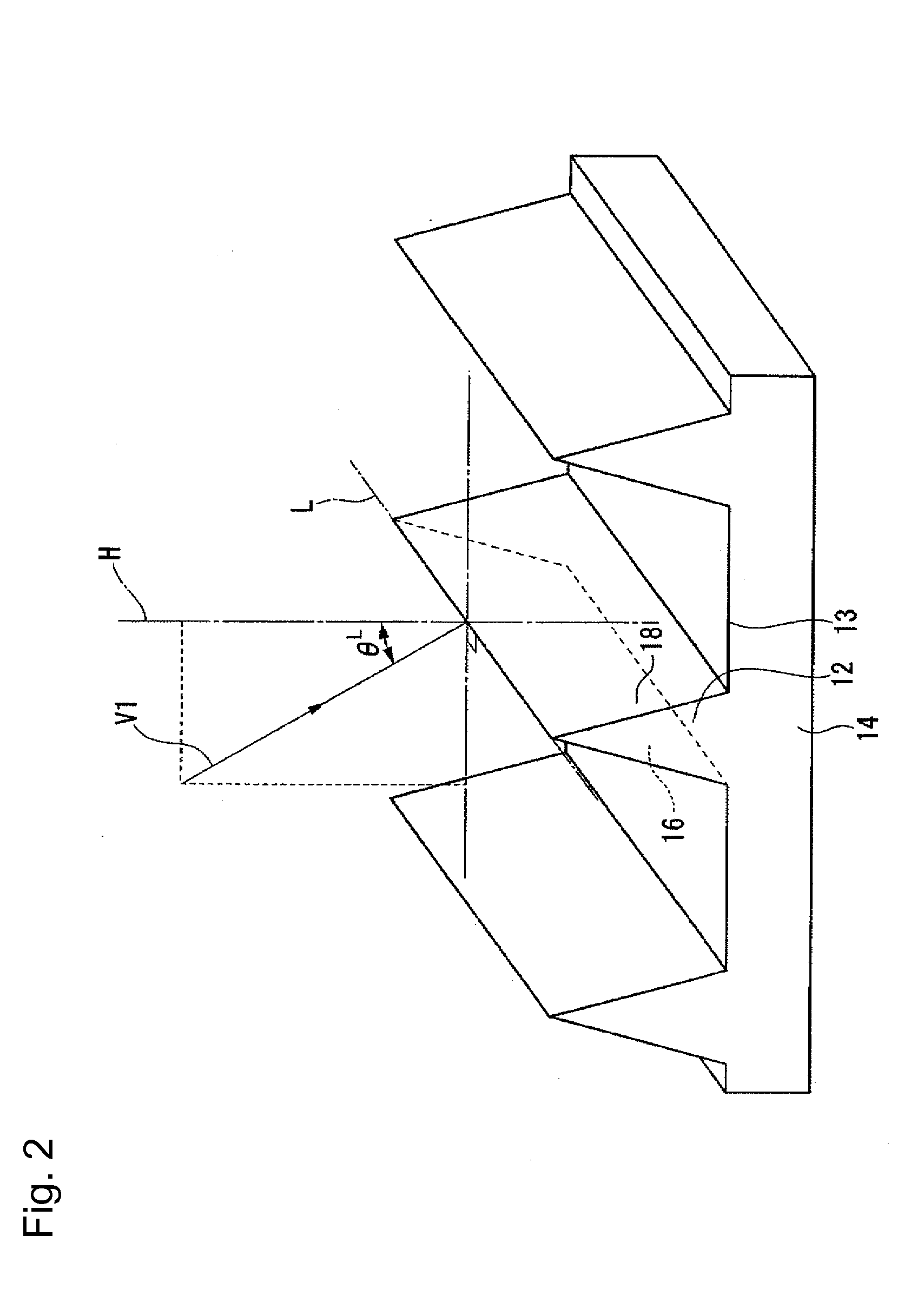
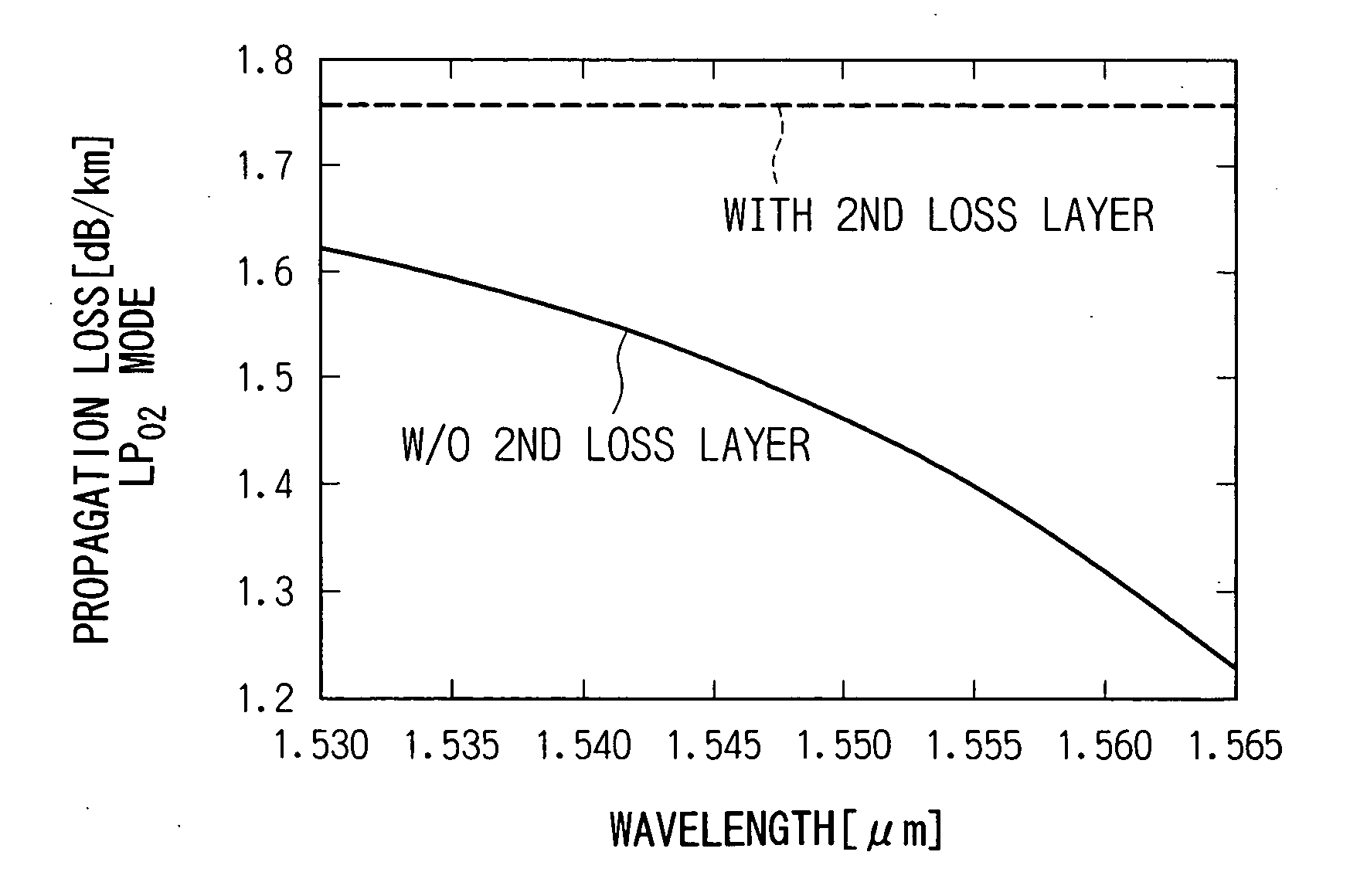
InactiveUS20050013572A1Low wavelength dependenceOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesEngineeringDispersion compensation
A higher order mode dispersion compensating fiber includes an optical fiber and a first loss layer which is provided within the fiber and which attenuates a lower order mode propagating through the optical fiber while not attenuating a higher order mode which is higher than the lower order mode. A dispersion compensating fiber mode converter for a higher order fiber includes a single mode fiber; a higher order mode dispersion compensating fiber; and a fused and extended portion which has been formed by fusing and extending the single mode fiber and the higher order mode fiber. The fused and extended portion converts between the LP01 mode of the single mode fiber and the LP02 mode of the higher order mode dispersion compensating fiber.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Broadband fiber optic tap
ActiveUS7116870B2Wide wavelength rangeWavelength insensitiveCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideTotal internal reflectionBroadband
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
Electrochromic element and method of forming same
InactiveUS8614848B2Low wavelength dependenceReduce reflected lightWave amplification devicesNon-linear opticsTransmittanceRefractive index
An electrochromic element includes a pair of transparent electrodes, and an electrolyte layer and an electrochromic layer disposed between the pair of transparent electrodes. Transmittance of light is changed by a voltage applied to the pair of transparent electrodes. The electrochromic layer includes a first electrochromic layer and a second electrochromic layer stacked upon each other. Both of the first and second electrochromic layers are made of titanium oxide. The first electrochromic layer is in contact with one of the pair of transparent electrodes. The second electrochromic layer is in contact with an electrolyte-layer side of the first electrochromic layer. A refractive index n0 of the transparent electrode in contact with the first electrochromic layer, a refractive index n1 of the first electrochromic layer, and a refractive index n2 of the second electrochromic layer satisfy the relationship n0<n1<n2.
Owner:CANON KK
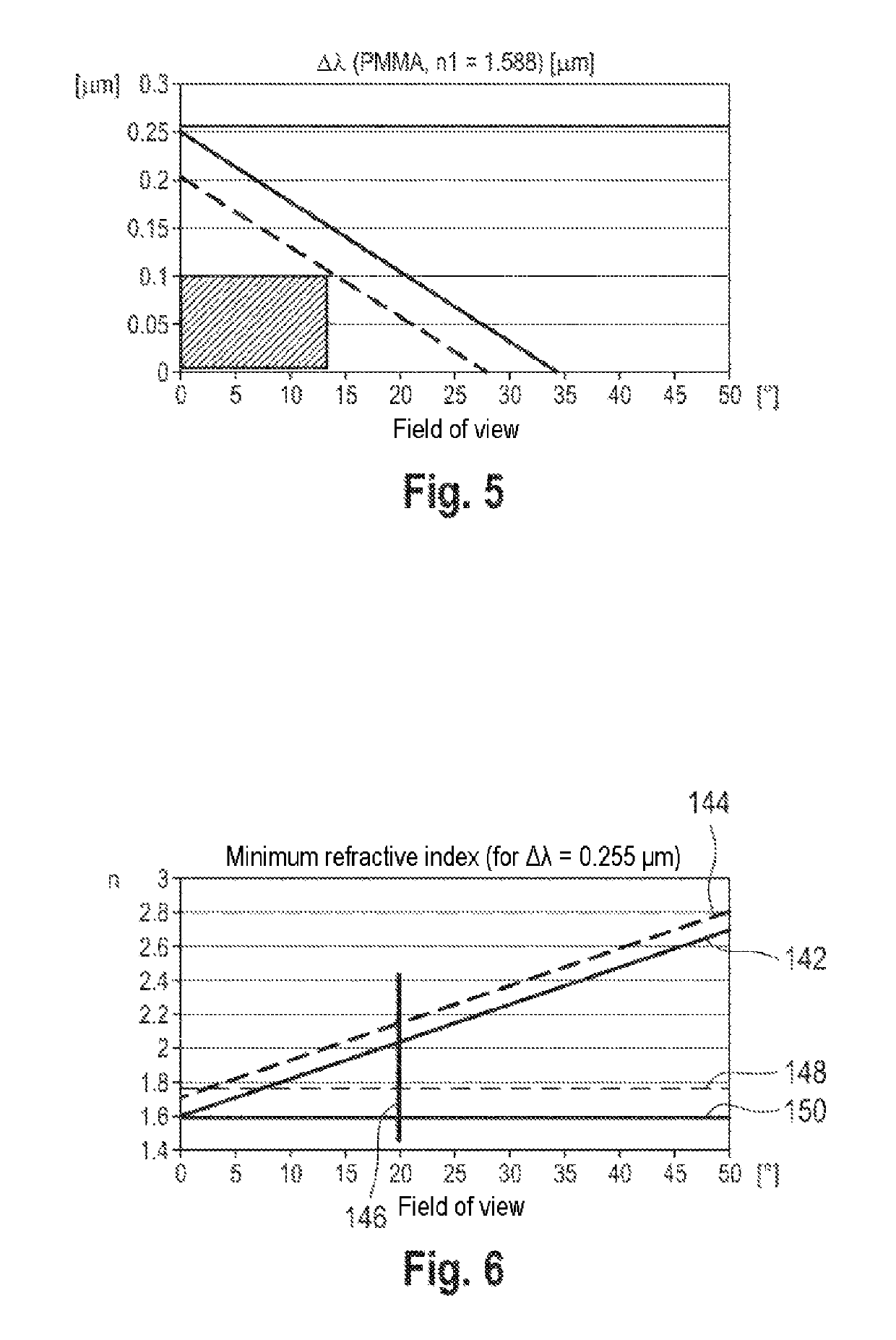
Optical system and method for transmitting a source image
ActiveUS10394032B2Low wavelength dependenceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesTotal internal reflectionCoupling
An optical system for transmitting a source image is provided. Light having a field angle spectrum emanates from the source image. The optical system includes an optical waveguide arrangement, in which light can propagate by total internal reflection. The optical system also includes a diffractive optical input coupling arrangement for coupling the light emanating from the source image into the optical waveguide arrangement. The optical system further includes a diffractive optical output coupling arrangement for coupling the light that has propagated in the optical waveguide arrangement out from the optical waveguide arrangement. The disclosure also provides related methods.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
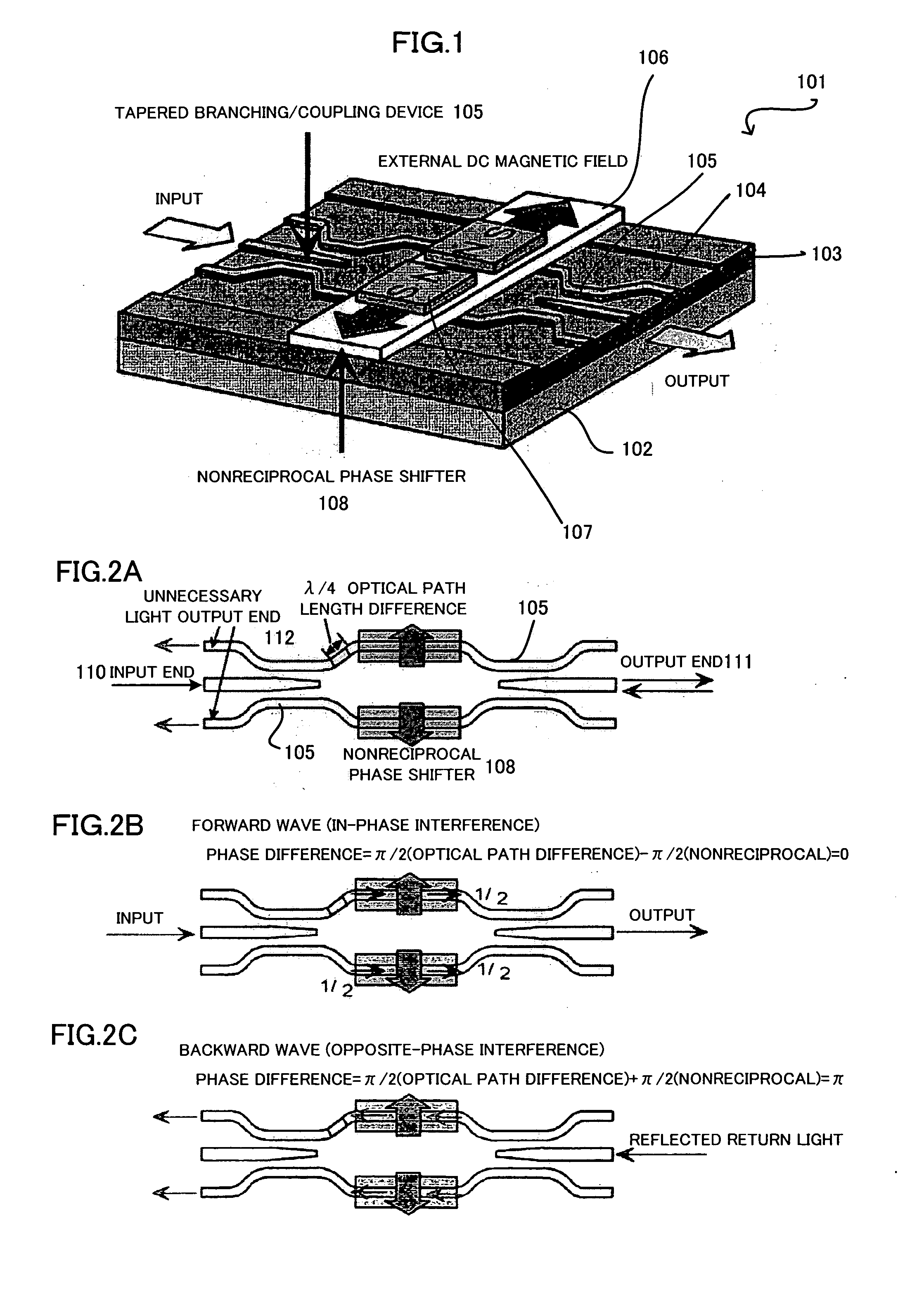
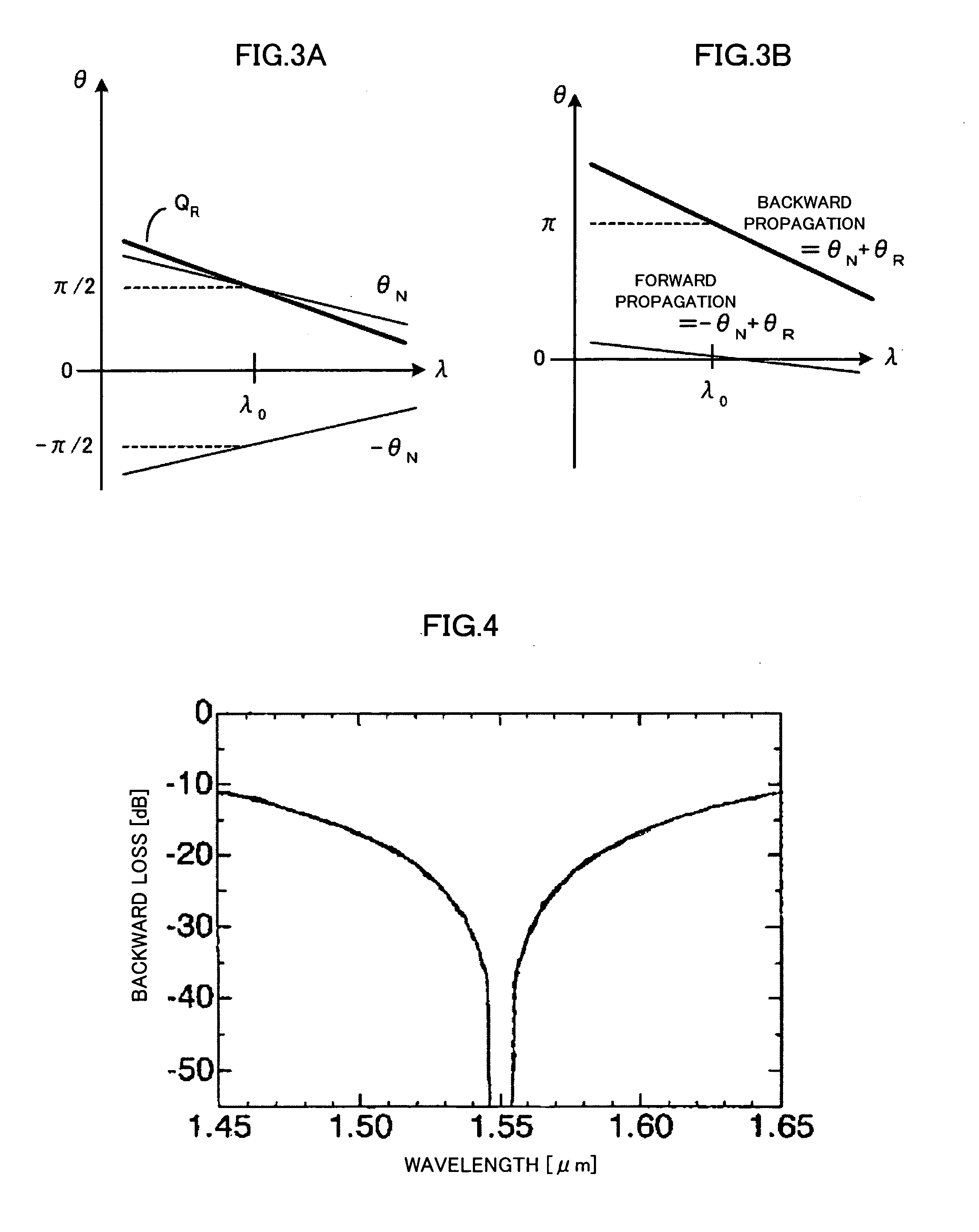
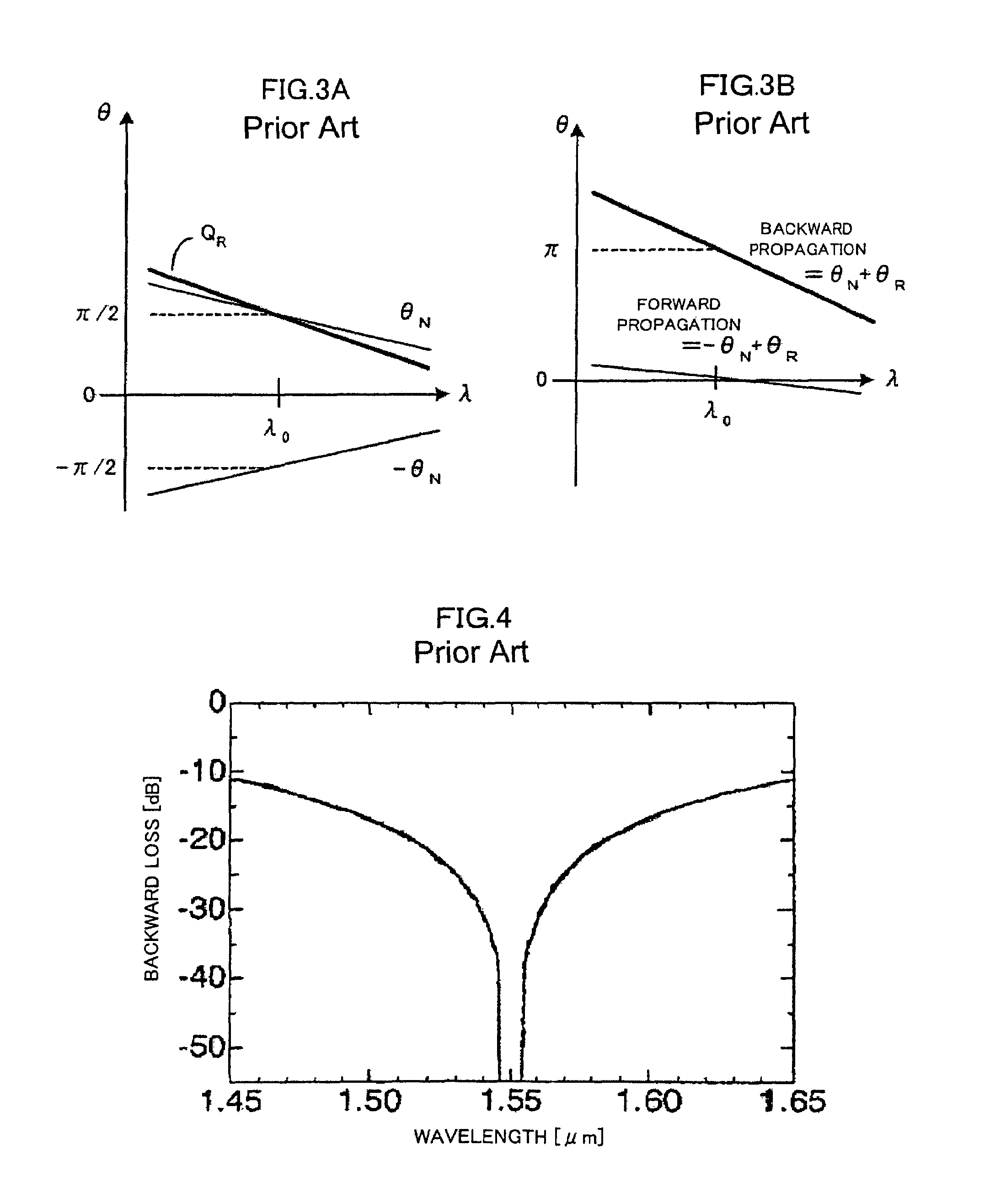
Waveguide-Type Broadband Optical Isolator
InactiveUS20090003757A1Broadened usable operating wavelength rangeWavelength-dependence of backward propagating waves reducedOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsBroadbandLight wave
A waveguide-type broadband optical isolator according to the present invention, comprising: a reciprocal phase shifter which makes a phase difference 3π / 2 between a first light wave propagating through a first waveguide and a second light wave propagating through a second waveguide, with a fundamental operating wavelength λ, and a nonreciprocal phase shifter which provides a phase difference π / 2 for forward propagating waves and a phase difference −π / 2 for backward propagating waves.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Diffraction grating, organic EL element using the same, and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveUS8541778B2Low wavelength dependenceReduce directivityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesFast Fourier transformAfm atomic force microscopy
A diffraction grating having a transparent supporting substrate; and a cured resin layer which is stacked on the transparent supporting substrate and which has concavities and convexities formed on a surface thereof, wherein when a Fourier-transformed image is obtained by performing two-dimensional fast Fourier transform processing on a concavity and convexity analysis image obtained by analyzing a shape of the concavities and convexities formed on the surface of the cured resin layer by use of an atomic force microscope, the Fourier-transformed image shows a circular or annular pattern substantially centered at an origin at which an absolute value of wavenumber is 0 μm−1, and the circular or annular pattern is present within a region where an absolute value of wavenumber is within a range of 10 μm−1 or less.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP +1
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7167221B2Reduce reflectivityReduce optical reflectionNon-linear opticsVisibilityLiquid-crystal display
A color filter (30) includes a black matrix (33), and the black matrix has a first antireflection layer (331) and a second antireflection layer (332) on the first antireflection layer. Each antireflection layer includes a first antireflection film (3311, 3321) having a first refraction index, and a second antireflection film (3312, 3322) having a second refraction index which is different to the first refraction index. Because of so-called destructive interference of outside source light beams reflected from various interfaces defined by the first and second antireflection films, net reflection of the light beams by the black matrix back to an outside of the color filter is minimal. For similar reasons, net reflection of internal source light beams by the black matrix back to an inside of the color filter is minimal. As a result, visibility of a liquid crystal display device (300) employing the color filter is improved.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Polarizer and display device including polarizer
ActiveUS8493658B2Reduce irregularitiesReduce light transmittancePolarising elementsCoatingsTransmittanceDisplay device
A polarizer in which parallel transmittance TP is increased and crossed transmittance TC is provided. Instead of arranging a plurality of all metal wires on one plane, a plurality of metal wires is separately formed on at least two different parallel planes, and adjacent meal wires among the plurality of metal wires are staggered in the polarizer. The heights of a first group of metal wires formed on a first plane and a second group of metal wires formed on a second plane, from a surface of the light-transmitting substrate are different. Further, a metal wire of the second group is provided to be more distant from the light-transmitting substrate than the first group of metal wires by distance D, and the distance D is smaller than the thickness of the first group of metal wires.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light-reflective anisotropic conductive adhesive and light-emitting device
ActiveUS20140001419A1Low wavelength dependenceImprove efficiencyNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesConductive materialAnisotropic conductive adhesiveLight emitting device
A light-reflective anisotropic conductive adhesive used for anisotropic conductive connection of a light-emitting element to a wiring substrate includes a thermosetting resin composition, conductive particles, and light-reflective insulating particles. The light-reflective insulating particles are formed by subjecting titanium oxide particles to a surface treatment with one kind selected from the group consisting of Al2O3, SiO, SiO2, ZnO, ZnO2, and ZrO2. The amount of the titanium oxide contained in the light-reflective insulating particles is 85 to 93%. The particle diameter of the light-reflective insulating particles is 0.2 to 0.3 μm, and the particle diameter of the conductive particles is 2 to 10 μm.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Broadband fiber optic tap
ActiveUS20060045426A1Wide wavelength rangeReduce the amount of lightCoupling light guidesTotal internal reflectionBroadband
A broadband optical fiber tap for transferring optical energy out of an optical fiber having an optical fiber with a primary and secondary microbends for the purpose of coupling optical energy into the higher-order modes of the fiber, and a reflecting surface formed in the cladding of the fiber and positioned at an angle so as to reflect, by total internal reflection, higher-order mode energy away from the optical fiber. In the preferred embodiment, the two microbends are spaced apart by a distance approximately equal to one-half of the intermodal beat length for LP01 and LP11 modes of a single-mode fiber.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
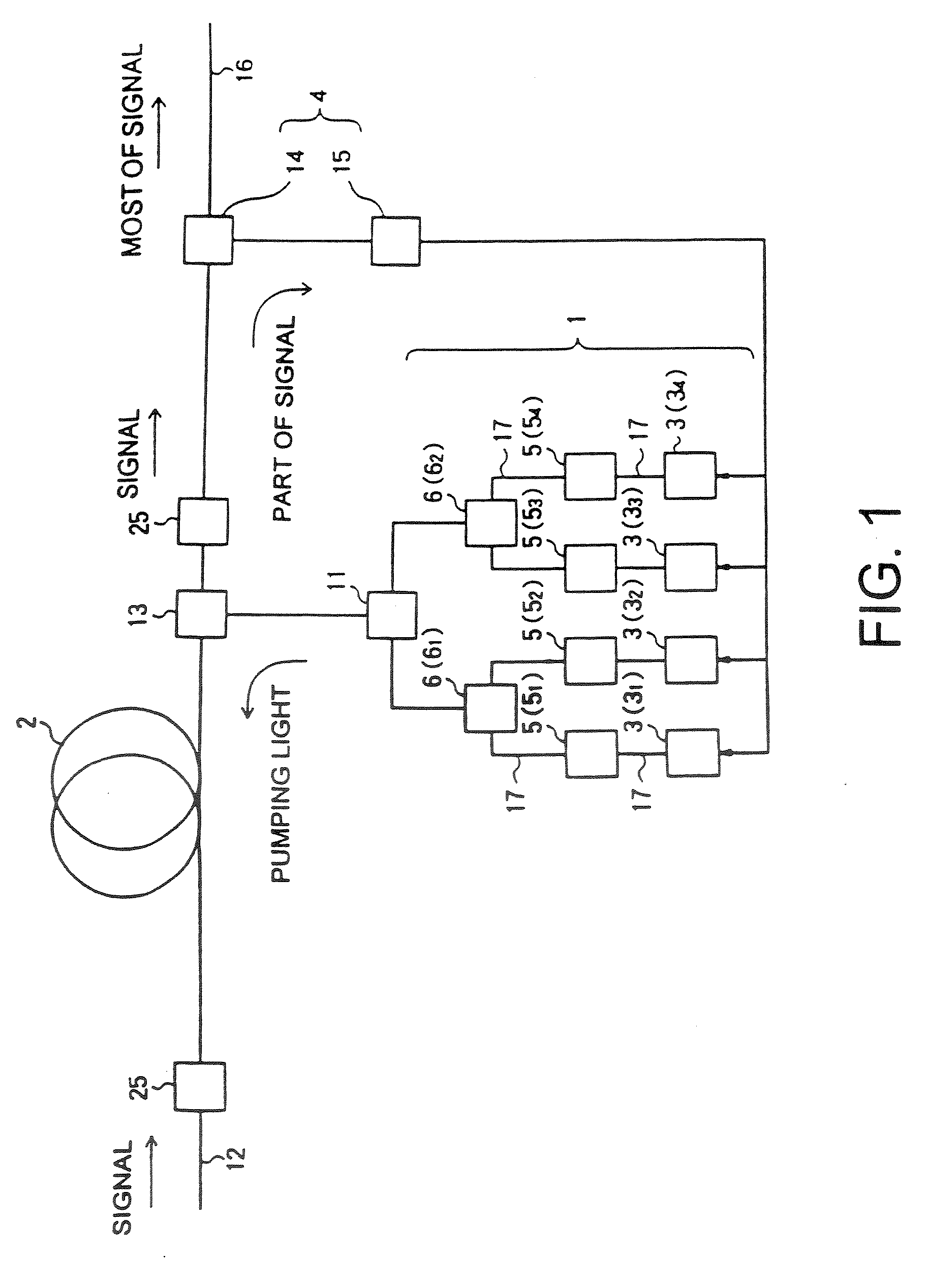
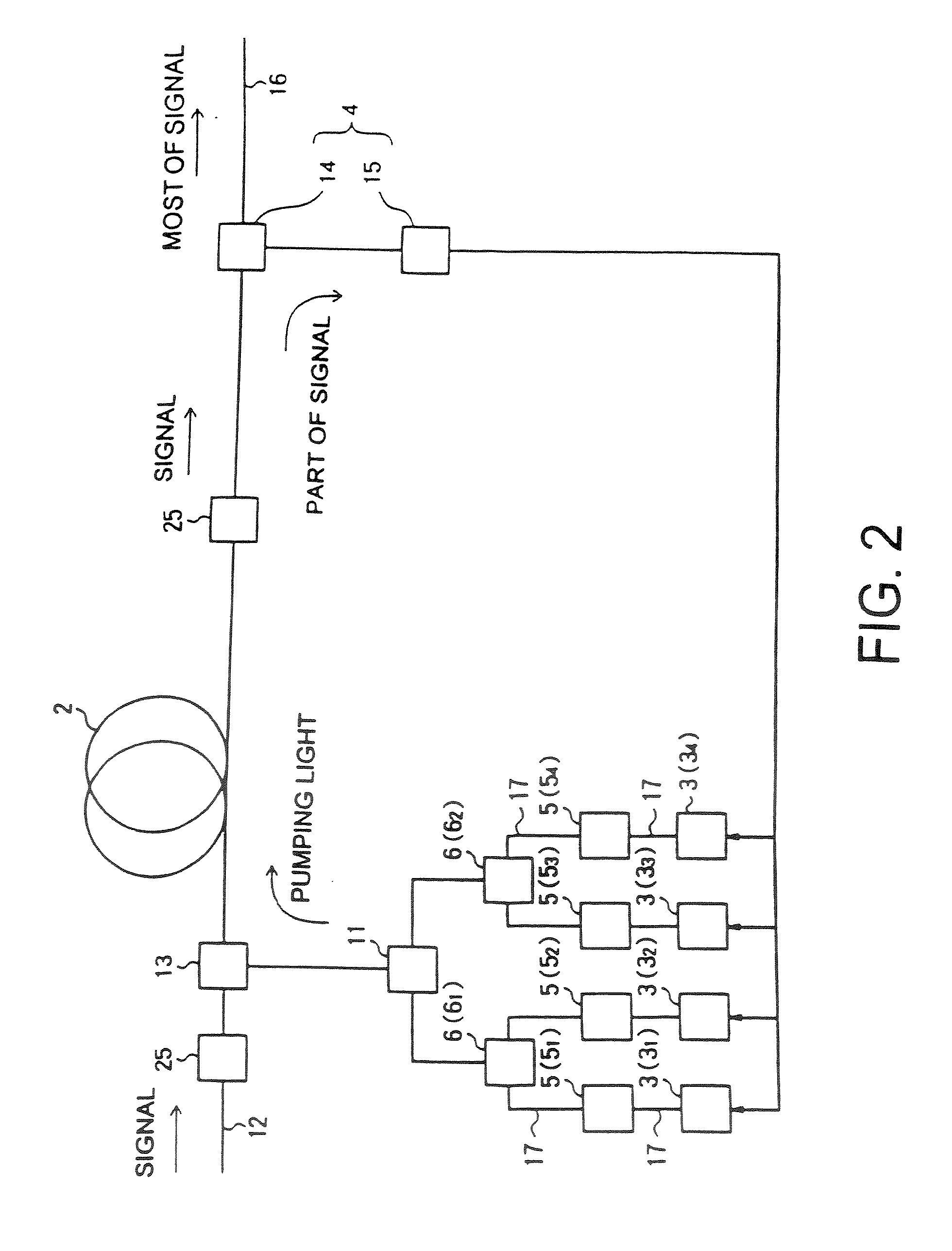
Raman amplifier, optical repeater, and raman amplification method
InactiveUS7548368B2Low wavelength dependenceImprove pumping capacityLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsMultiplexingRaman amplifiers
A Raman amplifier according to the present invention comprises a plurality of pumping means using semiconductor lasers of Fabry-Perot, DFB, or DBR type or MOPAs, and pumping lights outputted from the pumping means have different central wavelengths, and interval between the adjacent central wavelength is greater than 6 nm and smaller than 35 nm. An optical repeater according to the present invention comprises the above-mentioned Raman amplifier and adapted to compensate loss in an optical fiber transmission line by the Raman amplifier. In a Raman amplification method according to the present invention, the shorter the central wavelength of the pumping light the higher light power of said pumping light. In the Raman amplifier according to the present invention, when a certain pumping wavelength is defined as a first channel, and second to n-th channels are defined to be arranged with an interval of about 1 THz toward a longer wavelength side, the pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the first to n-th channels are multiplexed, and an pumping light having a wavelength spaced apart from the n-th channel by 2 THz or more toward the longer wavelength side is combined with the multiplexed light, thereby forming the pumping light source. The pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the channels other than (n-1)-th and (n-2)-th channels may be multiplexed, thereby forming the pumping light source. The pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the channels other than (n-2)-th and (n-3)-th channels may be multiplexed, thereby forming the pumping light source.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Common-path integrated low coherence interferometry system and method therefor
ActiveUS20190003820A1Improve performanceLow wavelength dependenceUsing optical meansSignaling systemLength wave
A low coherence interferometry imaging system comprising a common-path interferometer that is at least partially integrated as part of a planar lightwave circuit is disclosed. Imaging systems in accordance with the present invention are implemented in integrated optics without the inclusion of highly wavelength-sensitive components. As a result, they exhibit less wavelength dependence than PLC-based interferometers of the prior art. Further, the common-path interferometer arrangement of the present invention avoids polarization and wavelength dispersion effects that plague prior-art PLC-based interferometers. Still further, an integrated common-path interferometer is smaller and less complex than other integrated interferometers, which makes it possible to integrate multiple interferometers on a single chip, thereby enabling multi-signal systems, such as plane-wave parallel OCT systems.
Owner:ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT BIJ DE UNIV VAN
Wire-grid polarizer and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20110286094A1Improve reflectivityLow angle dependencyPolarising elementsSpecial surfacesWire gridOptical property
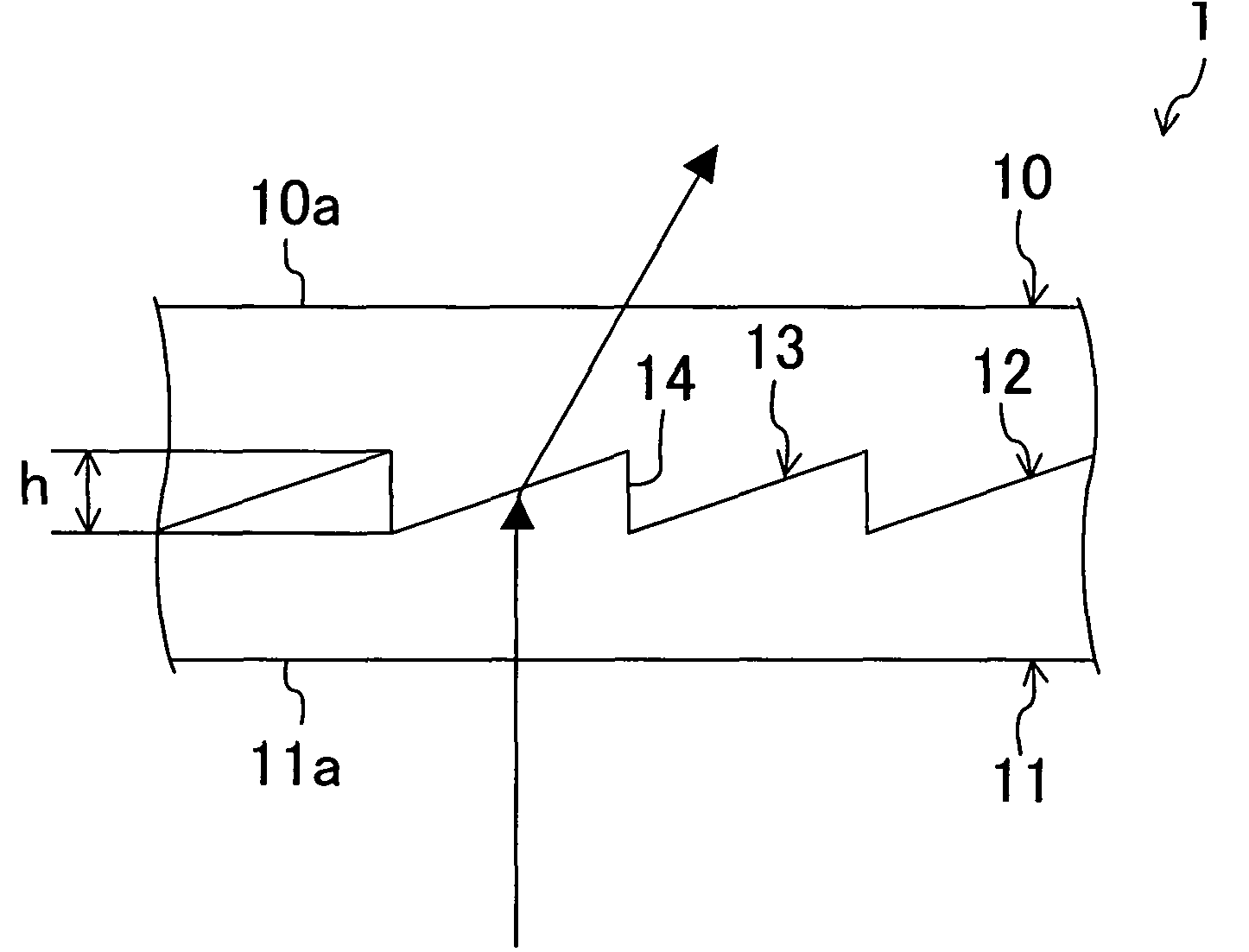
Provided are a wire-grid polarizer, which has not only a high degree of polarization, a high p-polarized light transmittance and a high s-polarized light reflectance but also a low angle dependency and a low wavelength dependency in terms of optical properties in a visible light region, and a process for producing the same.A wire-grid polarizer 10 comprising a light-transmitting substrate 14 having a plurality of ridges 12 formed in parallel to one another at certain pitches Pp through respective flat portions 13 disposed between adjacent ridges 12, each of the ridges having a width gradually reduced from a base portion to a top portion thereof, and a metal layer 20 composed of metal or a metal compound, the metal layer covering the entirety of a first lateral face 16 of each ridge 12 and a part of the flat portion 13 adjacent to the first lateral face 16 such that a second lateral face 18 of each ridge 12 is covered with no metal layer or is partially covered with the metal layer; and a process for forming the metal layer 20 by vapor-depositing metal or a metal compound on the first lateral face from a direction that is substantially orthogonal to a longitudinal direction of the ridges 12 and forms an angle of from 25 to 40 degrees toward the first lateral face 16 with respect to a height direction of the ridge 12 under conditions where the metal layer is disposed at a deposition amount of from 40 to 60 nm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Light-reflective anisotropic conductive adhesive and light-emitting device
ActiveUS8852462B2Avoid heavy dependenceImprove efficiencyNon-insulated conductorsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesInorganic particleAnisotropic conductive adhesive
A light-reflective anisotropic conductive adhesive used for anisotropic conductive connection of a light-emitting element to a wiring board includes a thermosetting resin composition containing a silicone resin and a curing agent, conductive particles and light-reflective insulating particles. The light-reflective insulating particle is at least one kind of inorganic particles selected from the group consisting of titanium oxide, boron nitride, zinc oxide, silicon oxide, and aluminum oxide. The silicone resin is a glycidyloxyalkyl-alicyclic alkyl-modified organopolysiloxane.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
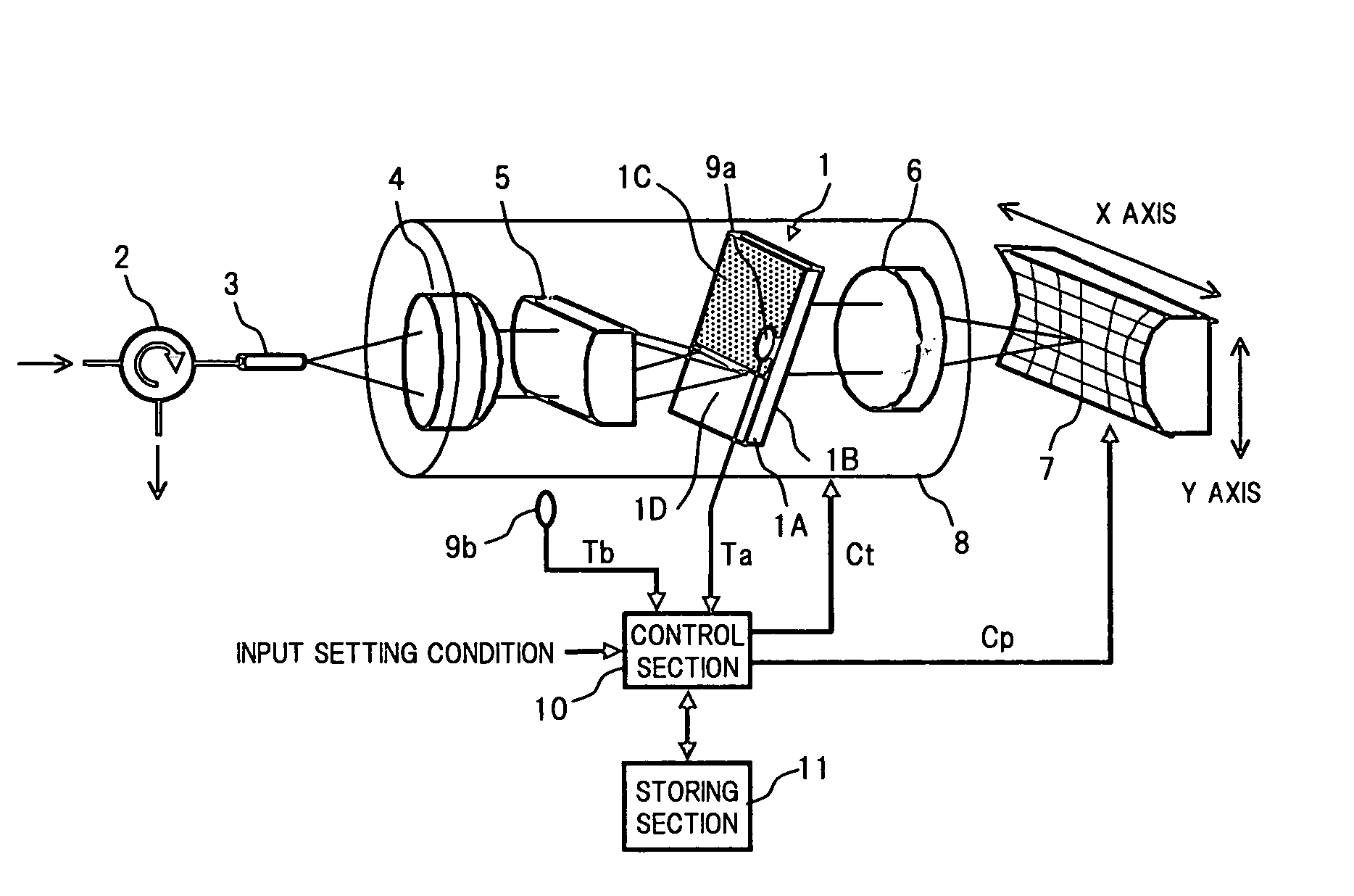
Control method of wavelength dispersion compensator, and wavelength dispersion compensator
InactiveUS20050047786A1Increase valueLow wavelength dependenceLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFree formLength wave
It is an object of the present invention to provide a control technique for reducing wavelength dependence of wavelength dispersion values and also for suppressing a change in wavelength transmission characteristic with a temperature variation or the like, in a VIPA-type wavelength dispersion compensator. In order to achieve the object, the present VIPA-type wavelength dispersion compensator comprises: a VIPA plate capable of emitting incident lights in different directions according to wavelengths; a free-form surface mirror reflecting, at a previously set position, the lights of respective wavelengths emitted from the VIPA plate to return the reflected lights to the VIPA plate; a case provided with a heater which variably changes the temperature of the VIPA plate, a temperature sensor measuring the temperature of the VIPA plate and the ambient temperature; and a control section that reads out data which is measured or the like before starting the operation to be stored in a storing section, according to the measurement result of the temperature sensor, and optimizes the position of the free-form surface mirror and the temperature of the VIPA plate based on the read data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Control method of wavelength dispersion compensator, and wavelength dispersion compensator
InactiveUS7418206B2Low wavelength dependenceAvoid changeLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFree formLength wave
It is an object of the present invention to provide a control technique for reducing wavelength dependence of wavelength dispersion values and also for suppressing a change in wavelength transmission characteristic with a temperature variation or the like, in a VIPA-type wavelength dispersion compensator. In order to achieve the object, the present VIPA-type wavelength dispersion compensator comprises: a VIPA plate capable of emitting incident lights in different directions according to wavelengths; a free-form surface mirror reflecting, at a previously set position, the lights of respective wavelengths emitted from the VIPA plate to return the reflected lights to the VIPA plate; a case provided with a heater which variably changes the temperature of the VIPA plate, a temperature sensor measuring the temperature of the VIPA plate and the ambient temperature; and a control section that reads out data which is measured or the like before starting the operation to be stored in a storing section, according to the measurement result of the temperature sensor, and optimizes the position of the free-form surface mirror and the temperature of the VIPA plate based on the read data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Waveguide-type broadband optical isolator
InactiveUS7664346B2Broadened usable operating wavelength rangeWavelength-dependence of backward propagating waves reducedOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsOptical isolatorPhase difference
A waveguide-type broadband optical isolator according to the present invention, comprising: a reciprocal phase shifter which makes a phase difference 3π / 2 between a first light wave propagating through a first waveguide and a second light wave propagating through a second waveguide, with a fundamental operating wavelength λ, and a nonreciprocal phase shifter which provides a phase difference π / 2 for forward propagating waves and a phase difference −π / 2 for backward propagating waves.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Polymerizable liquid crystal composition, optical anisotropic material, optical element and optical head device
InactiveUS7534370B2Improve efficiencyLow wavelength dependenceLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryPhenyl groupMesogen
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Spatially relaying radiation components
ActiveUS20140036352A1Reduce non-linearityAvoid nonlinear effectsMirrorsOptical filtersLight beamLength wave
A method of spatially relaying a first radiation component (1) having a first wavelength and a second radiation component (2) having a second wavelength different from the first radiation component (1), using an optical relaying device (10) which comprises a transparent plate (11) having anti-reflection coatings (12, 13) on both side surfaces thereof, comprises transmitting the first radiation component (1) across the optical relaying device (10) with predetermined incident (a) and emergent angles (β), resp., wherein said anti-reflection coatings (12, 13) being effective for the first radiation component (1) at the incident and emergent angles (α, β), resp., and reflecting the second radiation component (2) at the optical relaying device (10) with a predetermined reflection angle (a) being equal to at least one of said incident and emergent angles (α, β), wherein the first and second radiation components (1, 2) are split from each other toward different directions or combined into a common beam path. Furthermore, an optical relaying device (10) and a resonator device, in particular enhancement cavity device (100) and a laser resonator, are described.
Owner:PRONIN OLEG
Process for producing gray tone mask
InactiveUS20100294651A1Low wavelength dependenceReduce exposureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSpectral transmittanceLength wave
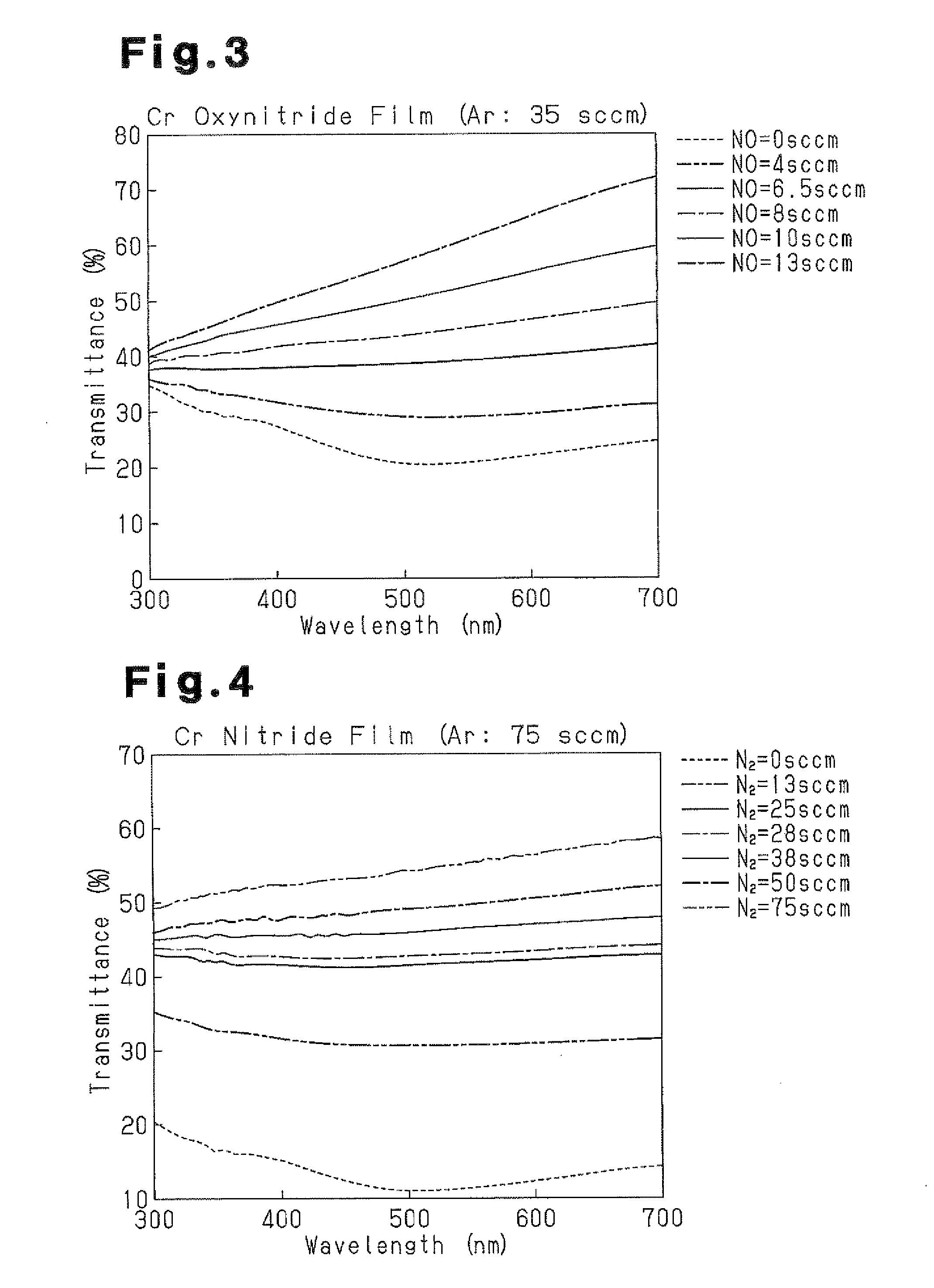
A method for manufacturing a gray-tone mask that decreases the wavelength dependency with respect to an exposure wavelength under stable and simple film formation conditions. A reactive sputtering method that sputters a pure Cr target in an atmosphere of Ar and NO is used to form a Cr nitride film having a single-layer structure. Based on a plurality of different spectral transmittance curves obtained under a plurality of film formation conditions having different NO concentrations, a target concentration (intermediate value) for NO is obtained that sets the transmittance uniformity of the semi-transparent film to 1.0% or less in the range of 365 nm to 436 nm or 4.0% or less in the range of 300 nm to 500 nm. Then, a semi-transparent film is formed by using the NO target concentration.
Owner:ULVAC COATING
Diffractive optical element, objective optical system including the same, and optical pickup including the same
ActiveUS7801008B2Low wavelength dependenceHigh design freedomRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupDiffraction order
A diffractive optical element includes a first optical part and a second optical part bonded to each other with a bonded surface therebetween configured as a diffraction surface. In this diffractive optical element, the diffraction order of diffracted light with the largest quantity of light out of diffracted light for one of a plurality of kinds of laser beams obtained on the diffraction surface is different from the diffraction order for at least another laser beam.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Variable optical attenuator (VOA)
InactiveUS8620131B2High extinctionLow wavelength dependenceStatic indicating devicesCoupling light guidesPower flowLight beam
A variable optical attenuator includes a collimating unit that collimates an incident light beam, a polarization splitting member that separates the collimated light beam into a first polarized light beam having a first polarization and a second polarized light beam having a second polarization, a birefringence control unit through which the first and second polarized light beams pass, the birefringence control unit including a liquid crystal cell having a birefringence is controlled by a voltage or current, wherein the birefringence of the liquid crystal cell is substantially zero when no voltage or current is applied thereto, and a reflection member that reflects the first and second polarized light beams output from the birefringence control unit. The variable optical attenuator has high stability, high precision, and low volume.
Owner:INLC TECH
Faraday rotation device and optical device using same
InactiveUS20050141075A1Improved in wavelength and temperature characteristicReduced in wavelength dependence and temperature-dependent lossNon-linear opticsFiberMagnetization
Optical devices including a Faraday rotation devices improved in wavelength and temperature characteristics and an optical attenuator reduced in wavelength dependence and temperature-dependent loss. The Faraday rotation device has permanent magnets magnetized in an axial direction of through-holes, and Faraday elements having a same Faraday rotation direction with respect to a same magnetization direction. The permanent magnets are directed in the same magnetization direction along an optical path, where part of the Faraday elements are accommodated in the through-hole of the permanent magnet, and the remaining Faraday elements are arranged between the magnets, whereby the Faraday elements are to be applied by magnetic fields in opposite directions. For a device variable in Faraday rotation angle, an electromagnet is provided. An input fiber collimator and polarizer are provided on an input side of with the Faraday elements while an analyzer and output fiber collimator are on an output side.
Owner:KOHOKU KOGYO CO LTD
Optical hybrid lens and method for producing an optical hybrid lens
ActiveUS20180188553A1Reduce building heightReduce overall chromatic aberrationDiffraction gratingsGratingRefractive lens
An optical hybrid lens comprises a substrate having a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface. A sub-wavelength grating lens is disposed on the first surface and comprises a plurality of posts. The plurality of posts is arranged on the first surface and the posts extend from the first surface. A refractive lens is arranged on the sub-wavelength grating lens at least partly enclosing the plurality of posts. Alternatively, the refractive lens is arranged on the second surface.
Owner:AMS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com