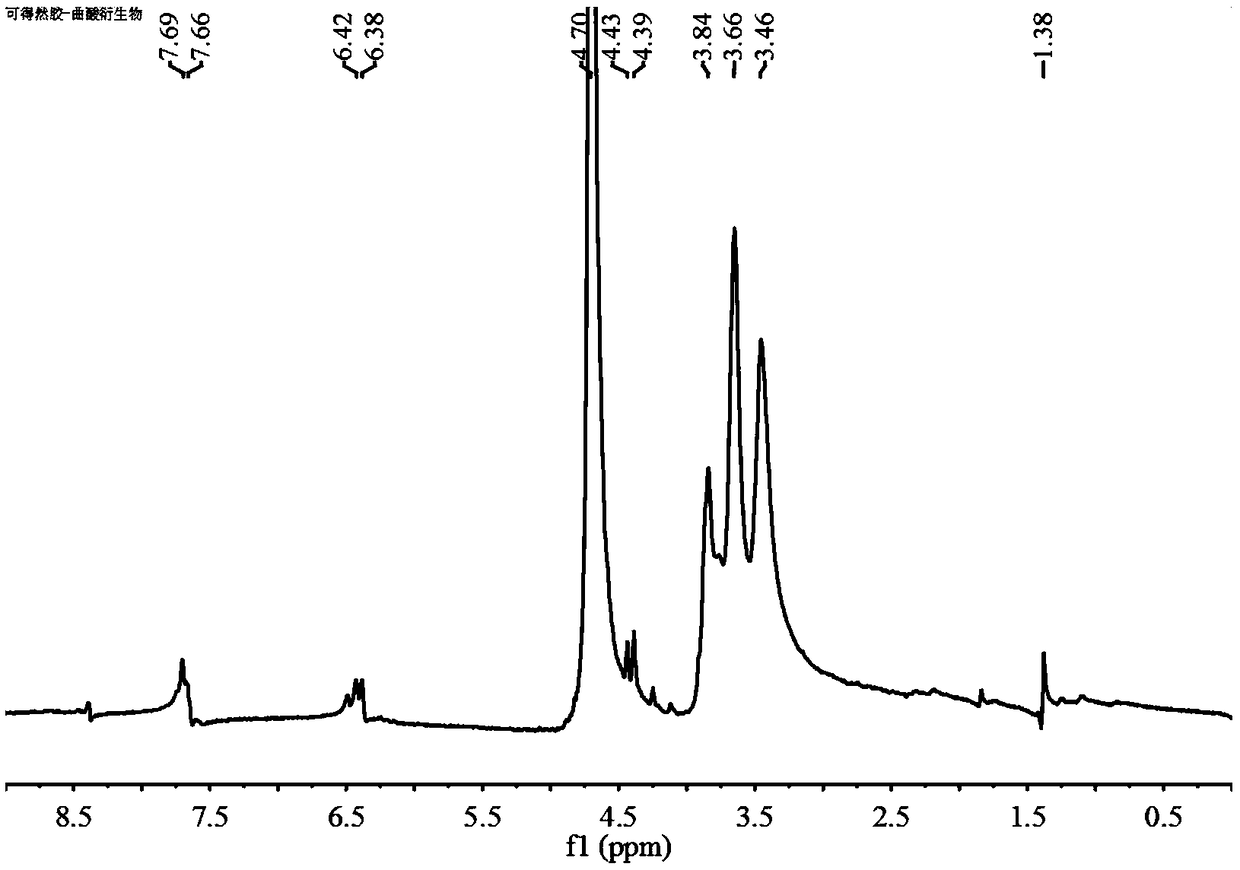
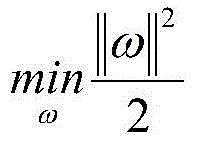Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Biological age" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biological age, also called physiological age, is a measure of how well or poorly your body is functioning relative to your actual calendar age.
Method of age management
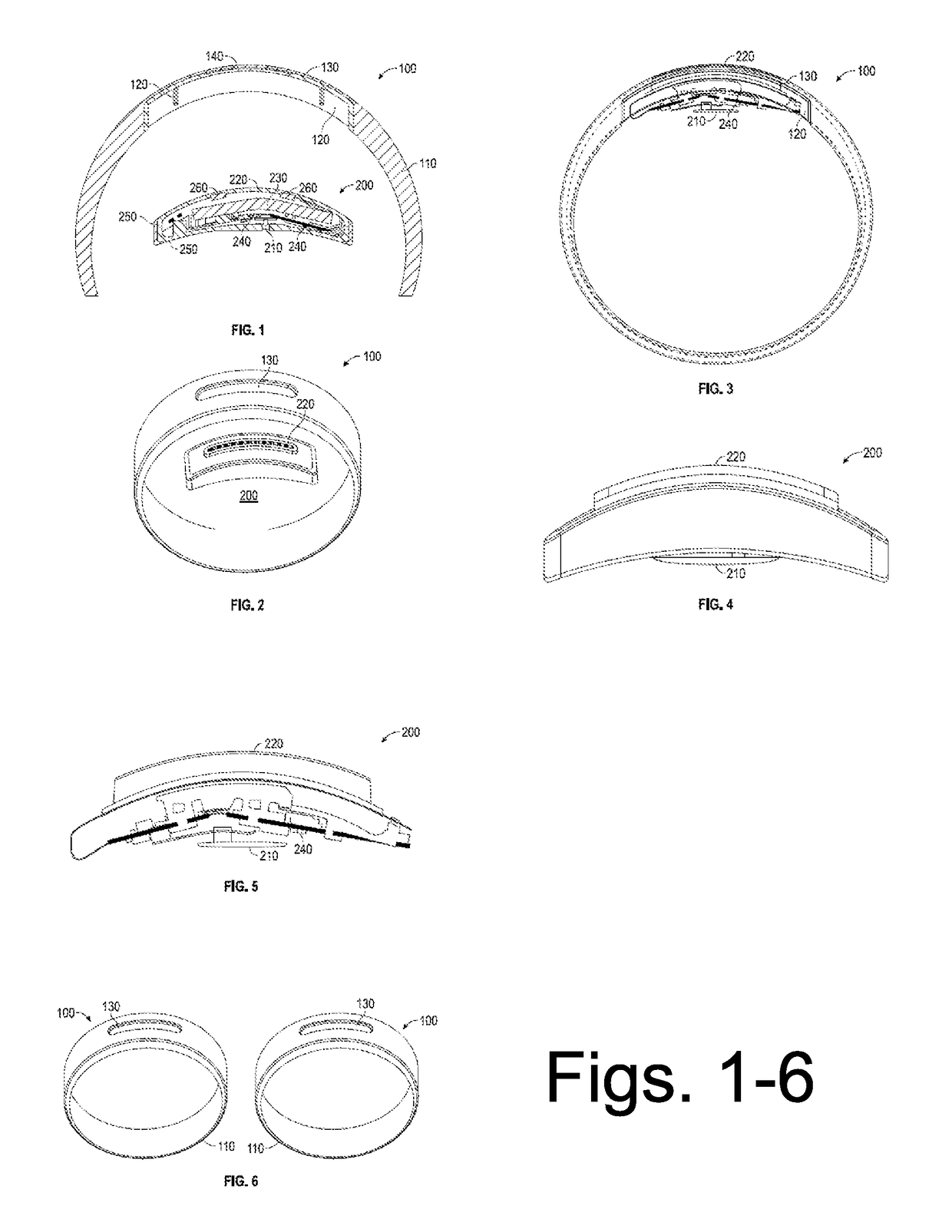
InactiveUS20130317315A1Medical devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringApproaches of managementMedicine
A method of age management, by consulting with a patient, performing comprehensive testing on the patient, determining the physiological, functional, and biological age of the patient, and recommending and performing treatments based on the physiological, functional, and biological age of the patient. The performing comprehensive testing is further defined as performing a test of standard plus functional medicine testing, complete hormonal panel, infectious disease panel, tumor markers panel, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ONE LIFE HEALTH
Biomarkers of aging for detection and treatment of disorders
InactiveUS20130040844A1Modulate activityVirusesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNeural cell
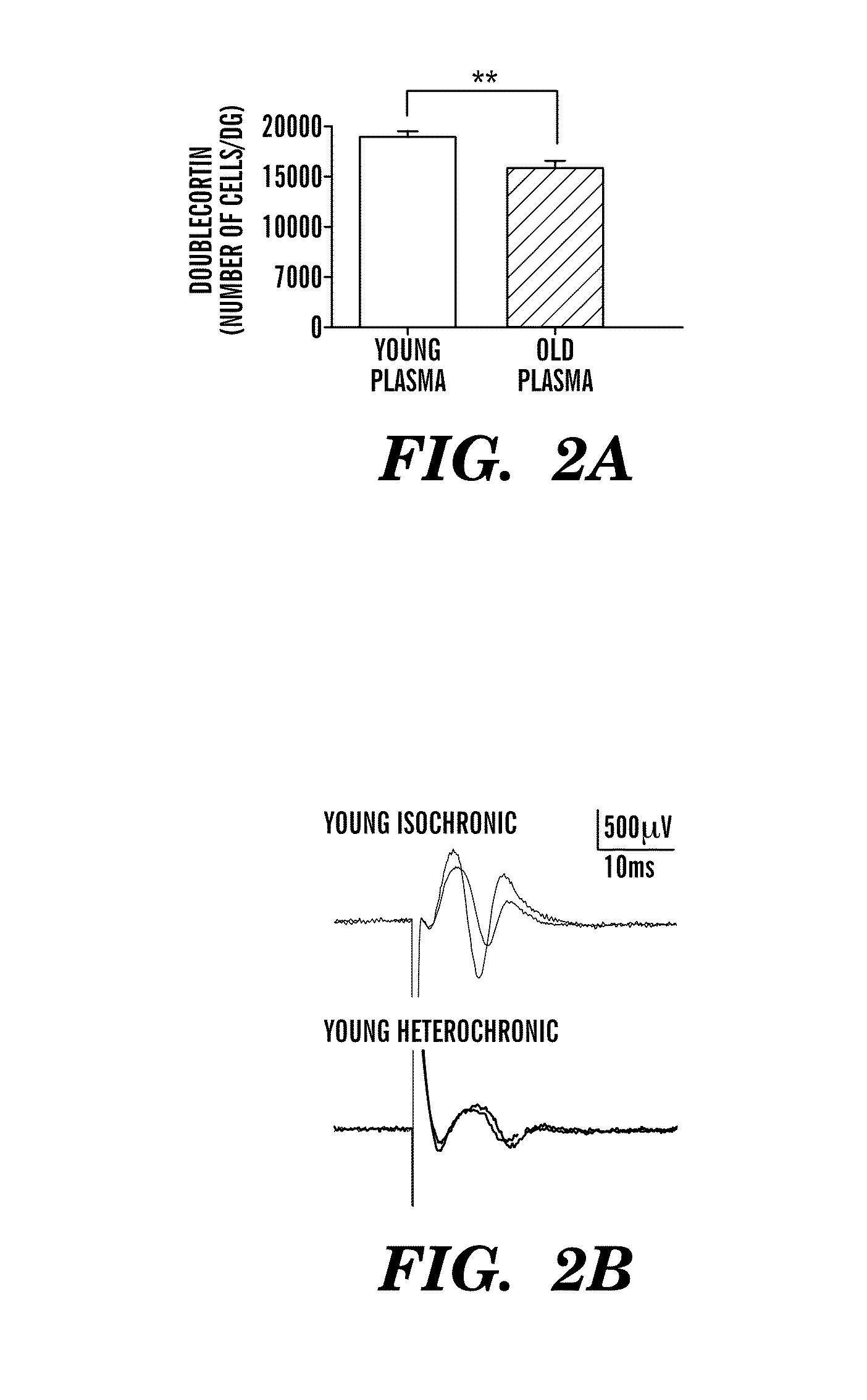
Provided are methods of diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of aging using biomarkers that have been discovered to be linked to biological aging process. Methods for increasing neural cell regeneration and cognitive function are also provided. The methods are, at least in part, based on a discovery that altered expression patterns of certain biological markers are associated with biological aging processes. These markers comprise at least Eotaxin / CCL11, 2-microglobulin, MCP-1 and Hap-toglobulin, increased expression of which has been shown to be associated with increase in biological aging process.
Owner:DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS VA +1
Biomarkers of aging for detection and treatment of disorders
InactiveUS20140255424A1Modulate activityVirusesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNeural cell
Provided are methods of diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of aging using biomarkers that have been discovered to be linked to biological aging process. Methods for increasing neural cell regeneration and cognitive function are also provided. The methods are, at least in part, based on a discovery that altered expression patterns of certain biological markers are associated with biological aging processes. These markers comprise at least Eotaxin / CCL11, β2-microglobulin, MCP-1 and Haptoglobulin, increased expression of which has been shown to be associated with increase in biological aging process.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Polyurethane sealing glue
ActiveCN101613587AImprove wear resistanceIncrease elasticityOther chemical processesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyolPlasticizer
The invention belongs to the technical field of building materials, and particularly relates to polyurethane sealing glue. The polyurethane sealing glue is characterized in that the polyurethane sealing glue consists of component A and component B, and the ratio of the component A to the component B in portion by weight is 1:1-10, wherein the component A is polyurethane prepolymer; and the component B comprises the following compositions in portion by weight: 16 to 30 portions of polyether polyol, 2 to 15 portions of plasticizer, 40 to 70 portions of filler, 0.1 to 2 portions of catalyst, and 0.1 to 2 portions of thixotropic agent. The polyurethane sealing glue has the advantages of good abrasion resistance, low-temperature flexibility, wide performance adjustable range, large mechanical strength, good adhesive property, good elasticity, good rebound resilience, good weather resisting property, good oil resistivity and biological ageing resistance, is suitable for dynamic joint, and does not contain volatile solvent and other small molecular substances; the service life of the polyurethane sealing glue can reach 15 to 20 years; and the solid content of the polyurethane sealing glue is 100 percent.
Owner:NANTONG YANYI COATING TECH
Method for analyzing the biological age of a subject
The present invention is a method for analyzing the biological age of a subject. The method analyzes the biological age as it relates to a number of factors indicating levels of health, energy production and metabolism. The method may also be used to calculate a subject's biological age and treat the factors associated with biological age.
Owner:SHALLENBERGER FRANK
Alzheimer's disease signature markers and methods of use
InactiveUS20140304845A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker (petroleum)Biology
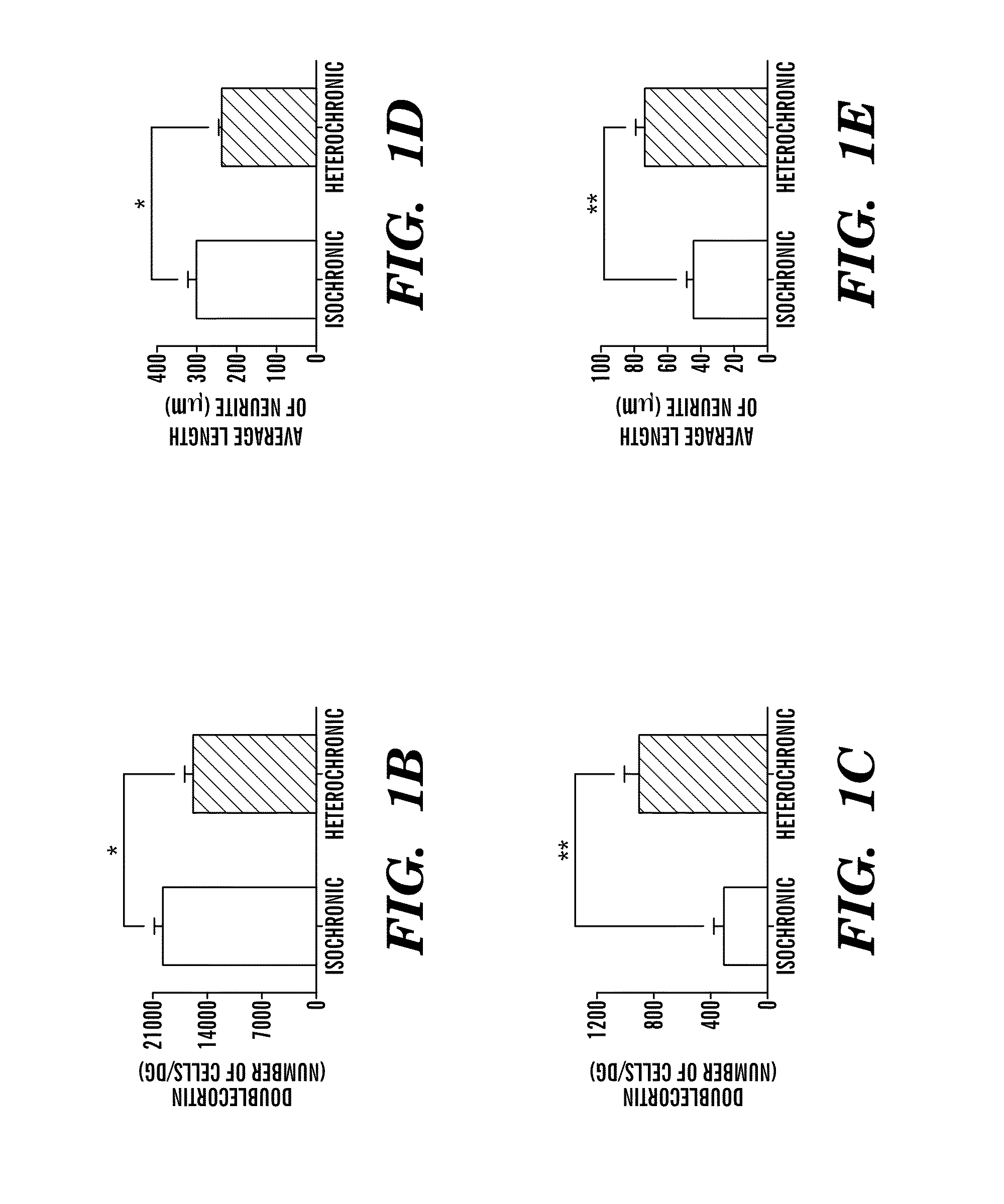
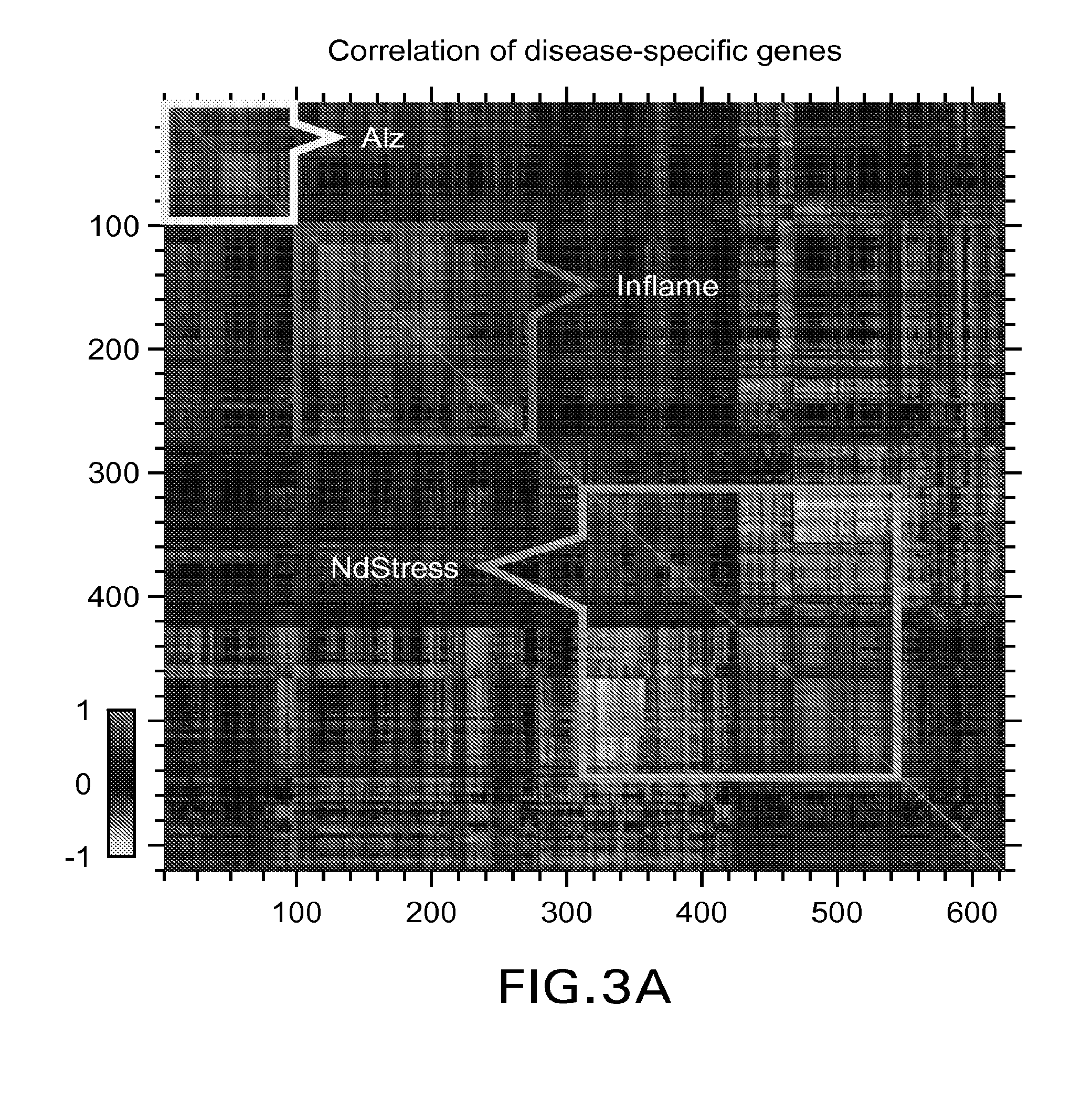
Methods, biomarkers, and expression signatures are disclosed for assessing the disease progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In one embodiment, BioAge (biological age), NdStress (neurodegenerative stress), Alz (Alzheimer), and Inflame (inflammation) are used as biomarkers of AD progression. In another aspect, the invention comprises a gene signature for evaluating disease progression. In still another embodiment, methods for evaluating disease progression are provided. In yet another embodiment, the invention can be used to identify animal models for use in the development and evaluation of therapeutics for the treatment of AD.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Methods and kits for determining biological age and longevity based on gene expression profiles
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method for analyzing the biological age of a subject
The present invention is a method for analyzing the biological age of a subject. The method analyzes the biological age as it relates to a number of factors indicating levels of health, energy production and metabolism. The method may also be used to calculate a subject's biological age and treat the factors associated with biological age.
Owner:SHALLENBERGER FRANK
Identification of genetic markers of biological age and metabolism
A method of measuring the biological age of a multicellular organism is disclosed. In one embodiment this method comprises the steps of obtaining a sample of nucleic acid isolated from the organism's organ, tissue or cell and determining the expression pattern of a panel of sequences within the nucleic acid that have been predetermined by either increase or decrease in response to biological aging of the organ, tissue or cell. A method of obtaining biomarkers of aging is also disclosed. This method comprises the step of comparing a gene expression profile of a young multicellular organism subject's organ, tissue or cells; a gene expression profile from a chronologically aged subject's organ, tissue or cell; and a gene expression profile from a chronologically aged but biologically younger subject's organ, tissue or cell and identifying gene expression alterations that are observed when comparing the young subjects and the chronologically aged subjects and are not observed or reduced in magnitude when comparing the young subjects and the chronologically aged but biologically younger subjects.
Owner:WEINDRUCH RICHARD H +2
Method for obtaining biological age of individual child based on oral microbial community
ActiveCN106202989ASimplify the collection processSimple processing capacitySpecial data processing applicationsRegression analysisCrowds
The invention provides a method for obtaining biological age of an individual child based on an oral microbial community. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a sample containing oral microorganisms of the individual child; extracting DNAs of the oral microorganisms; and transforming DNA information into microbial community information, performing regressive analysis on the oral microbial community information and age by utilizing a random forest algorithm, building a regressive model, and obtaining the age of the individual child in Chinese population. According to the scheme provided by the method, the biological age of the individual child in the Chinese population can be accurately obtained; oral saliva or dental plaque samples can be non-invasively, simply and quickly obtained; and the age of the individual child is detected for a long term, so that a physiological health state of a host can be quickly judged, a clue can be provided for health monitoring, and early diagnosis speed of diseases can be increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
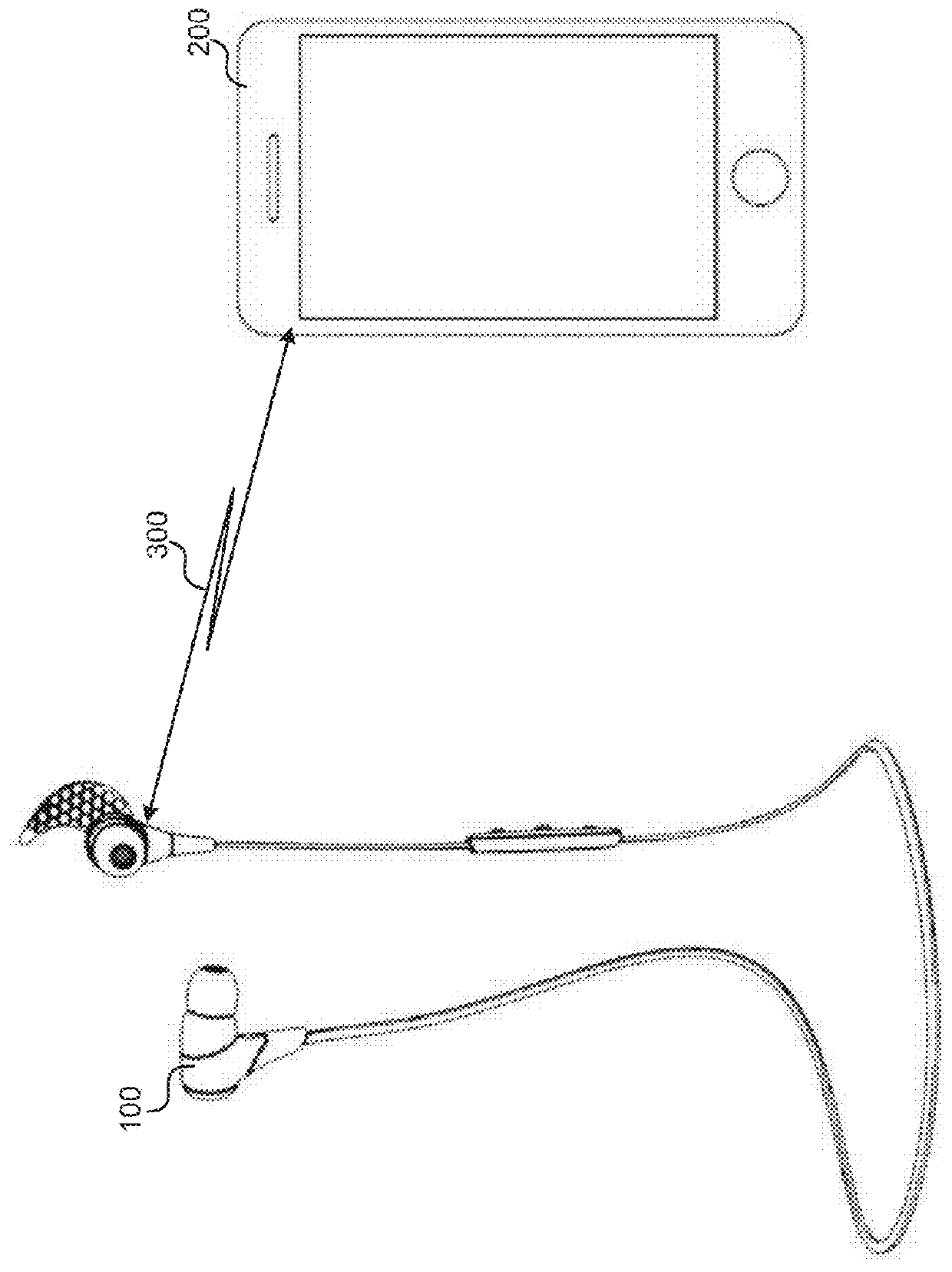
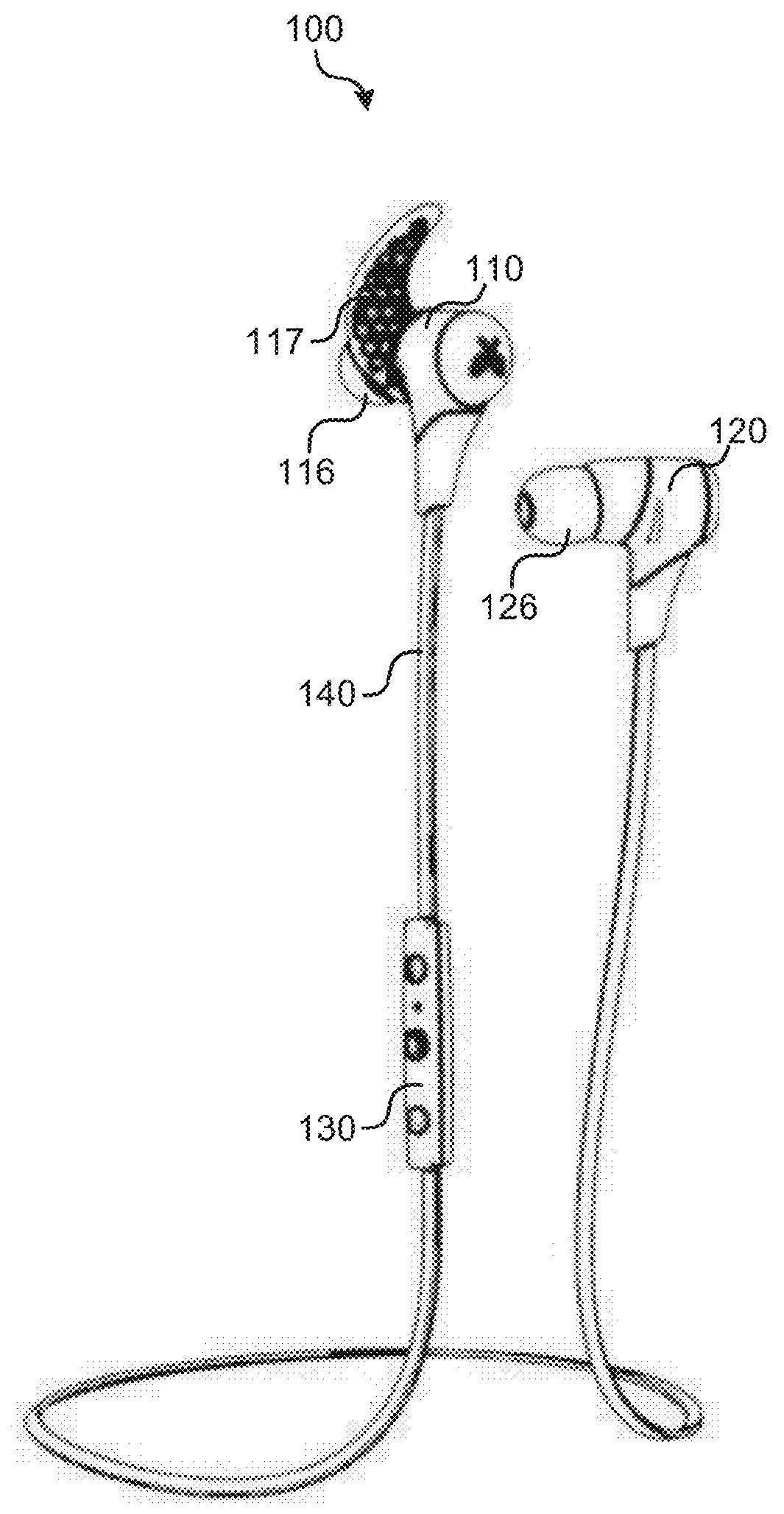
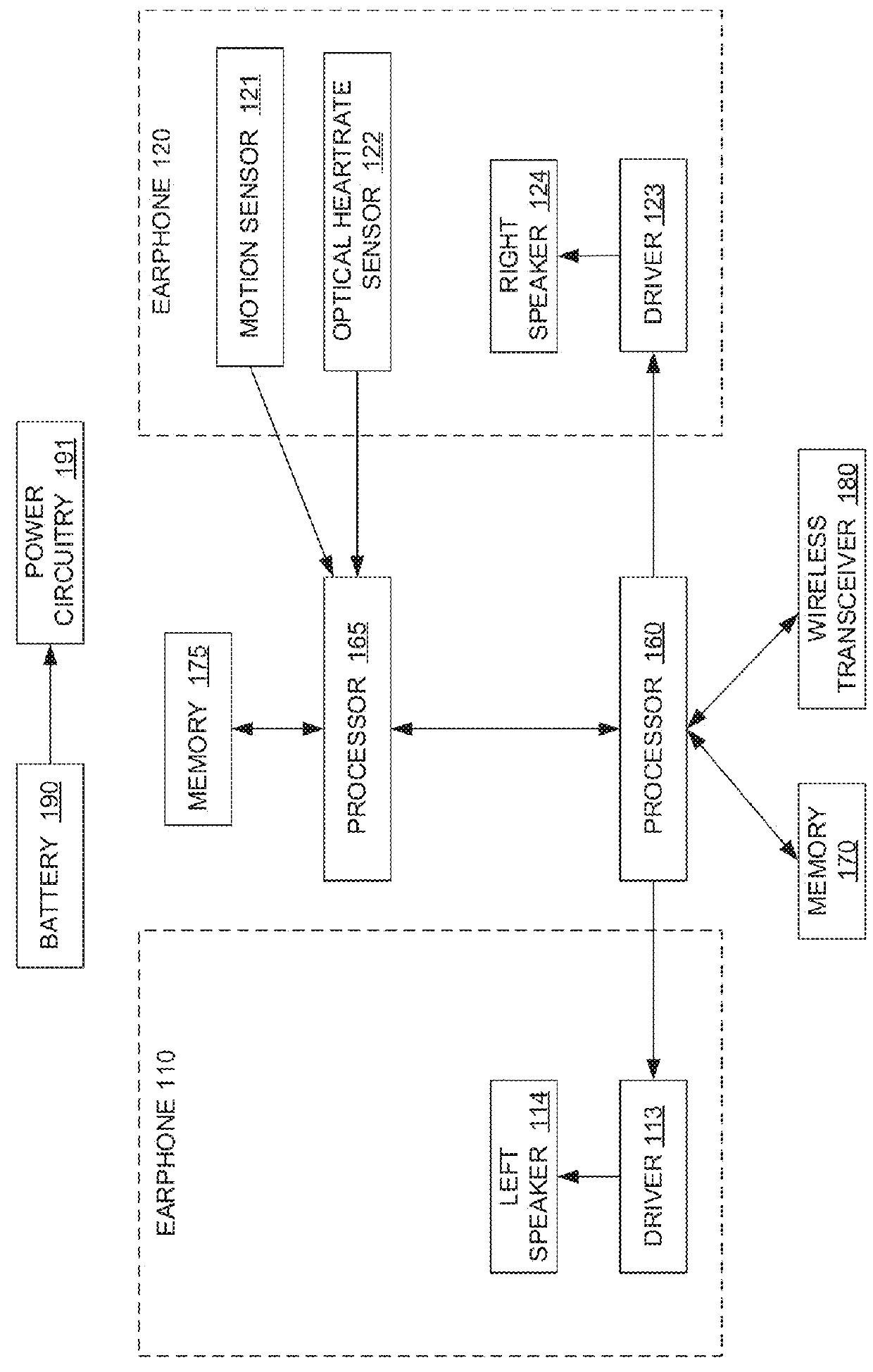
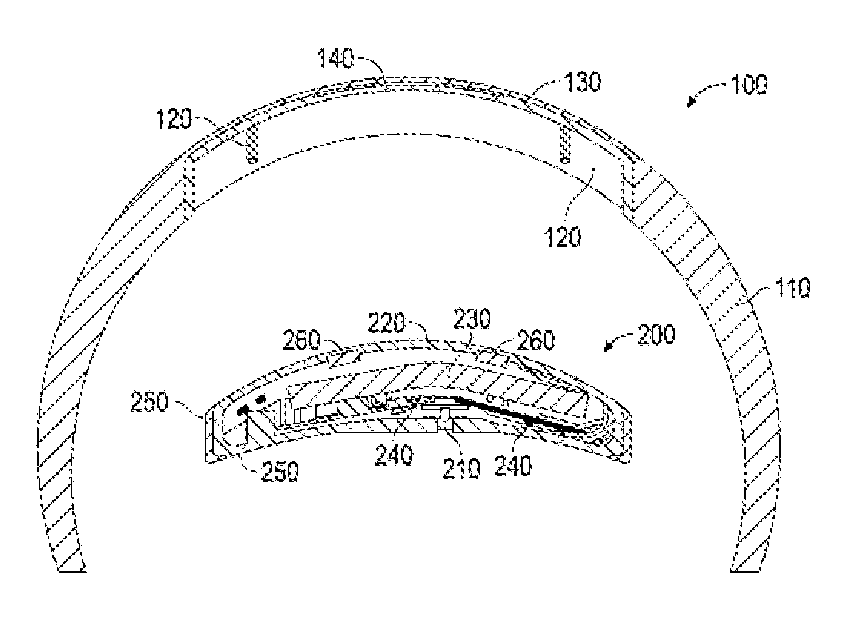
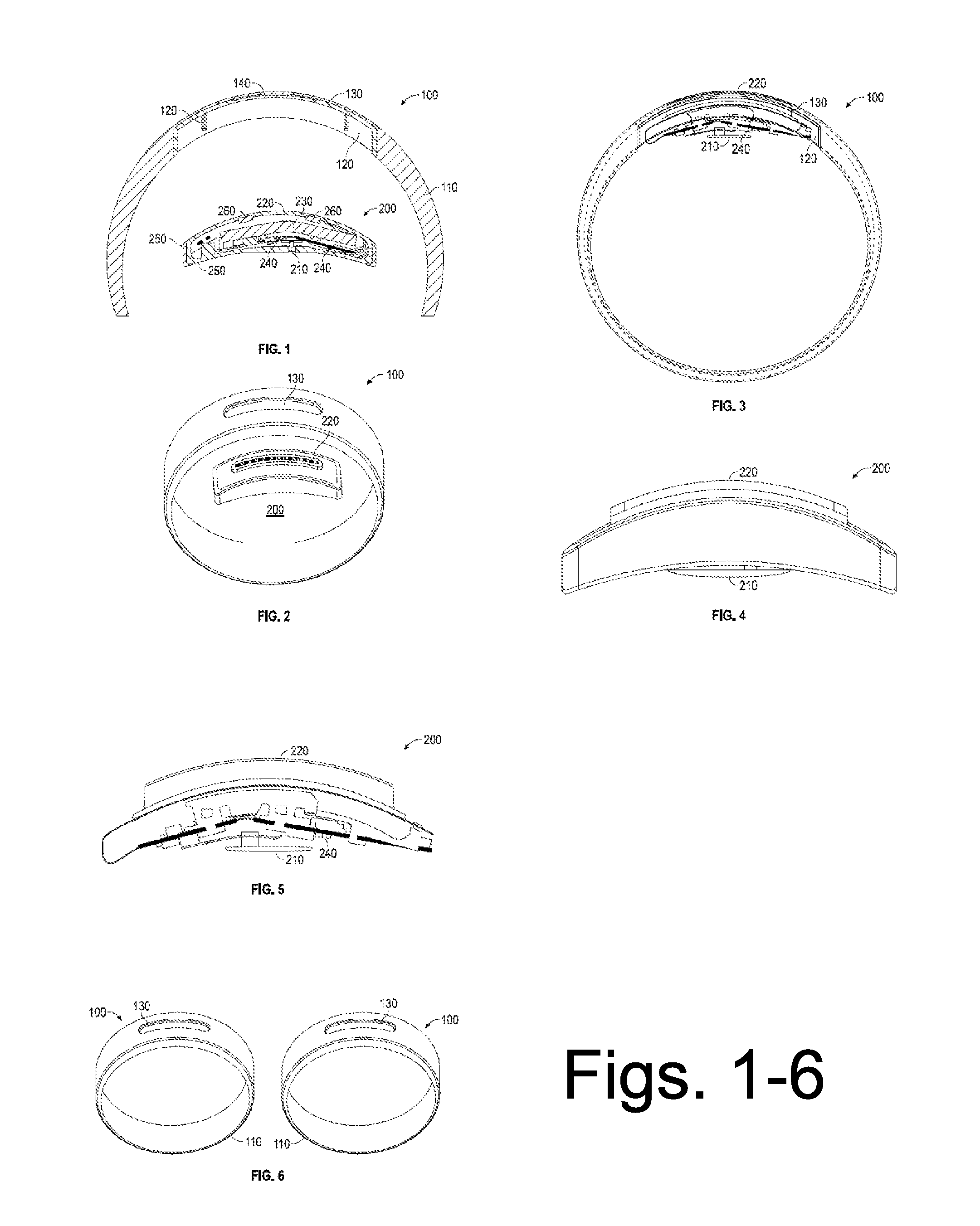
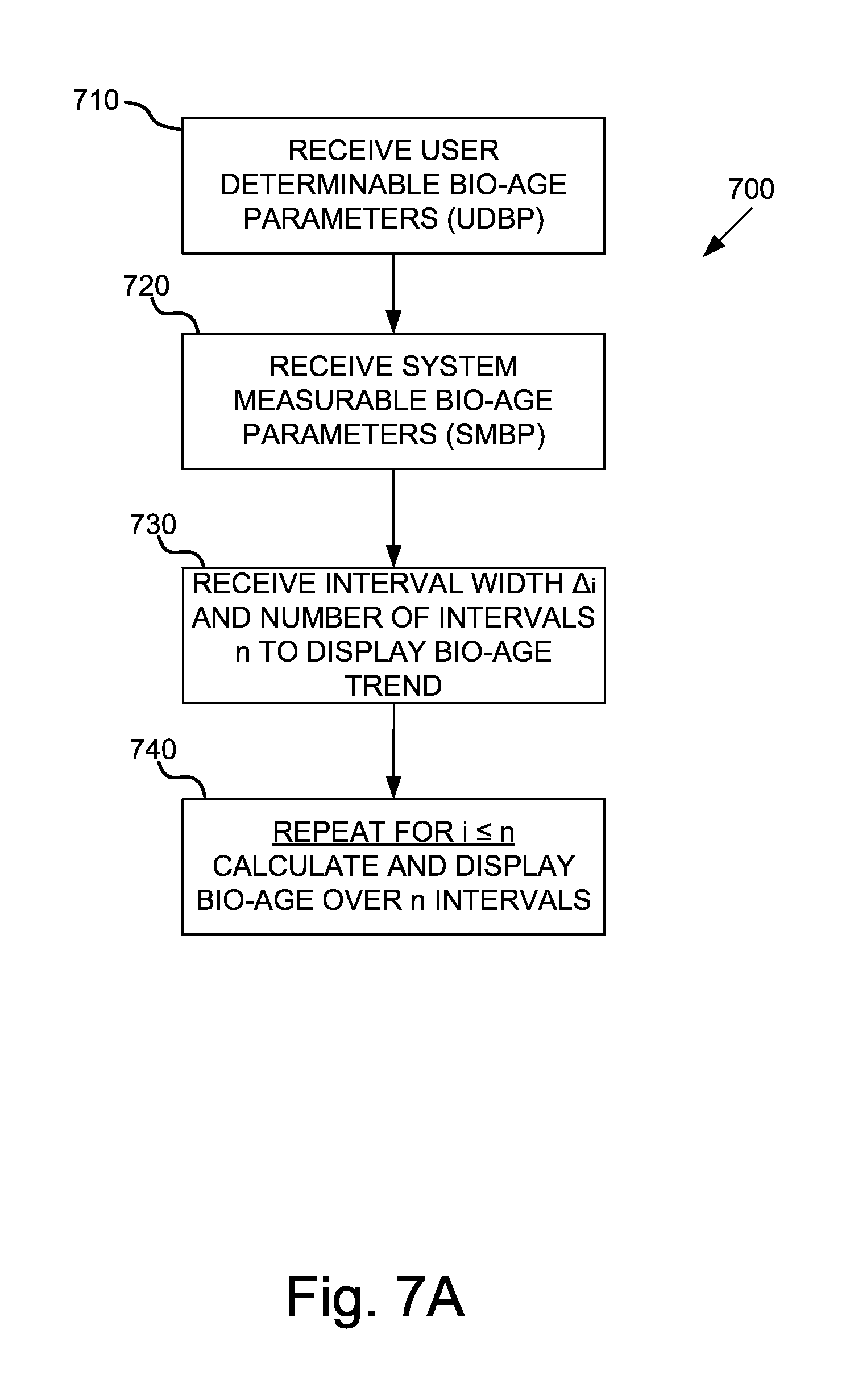
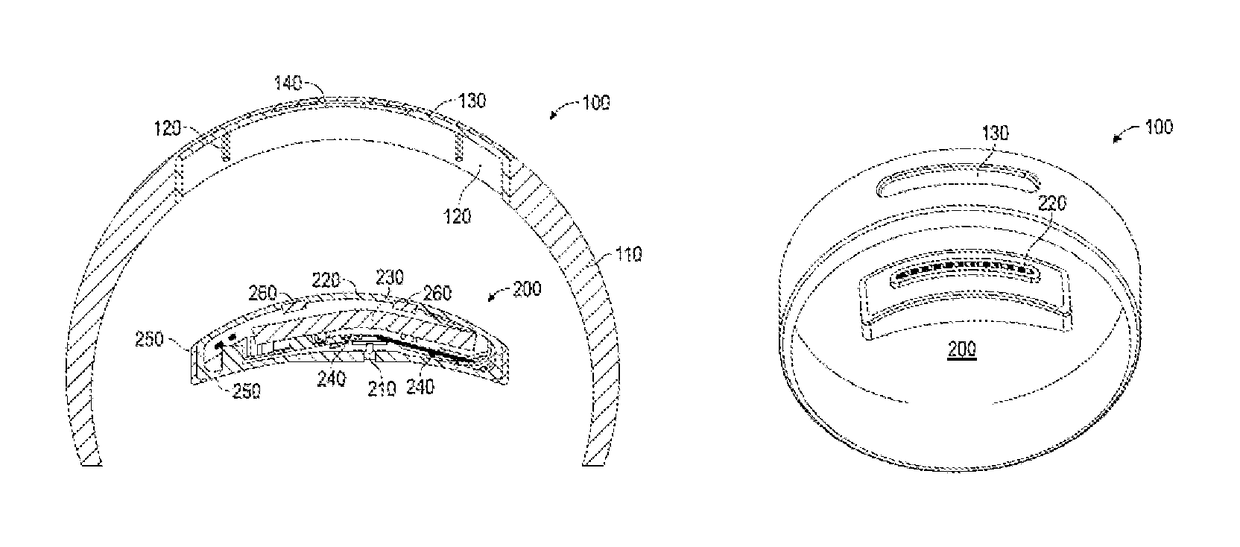
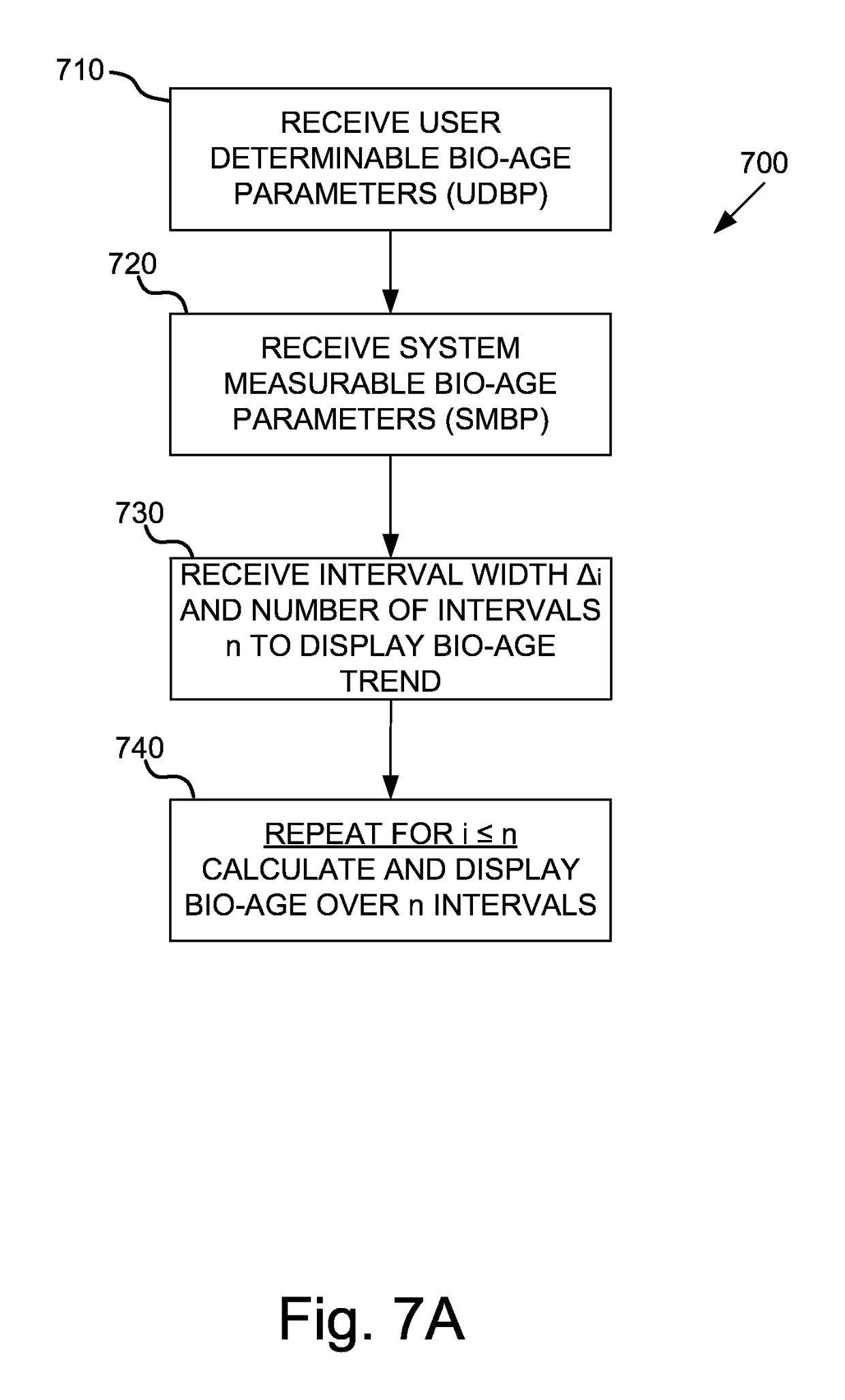
System and method for tracking biological age over time based upon heart rate variability using earphones with biometric sensors
InactiveUS20160029974A1Physical therapies and activitiesEvaluation of blood vesselsElectricityRR interval
Systems and methods are provided for using earphones with biometric sensors to track a user's biological age over time. In one embodiment, the system includes earphones, including: speakers; a processor; and a heartrate sensor electrically coupled to the processor. In this embodiment, the system also includes a memory coupled to a processor and having instructions stored that, when executed by the processor: receive one or more user determinable biological age parameters including an actual age of the user; determine one or more system measurable biological age parameters based on signals generated by the heartrate sensor; calculate a biological age factor as a function of the user determinable biological age parameters and the system measurable biological age parameters; calculate the user's biological age as a function of the biological age factor and the user's actual age; and display on a display the user's biological age.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Production technology of special water dropper for preventing root system from being invaded by subsurface drop irrigation
ActiveCN101899179AImprove heat resistanceImprove aging resistanceWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsHeat resistanceEngineering
The invention relates to a production technology of a special water dropper for preventing a root system from being invaded by subsurface drop irrigation, comprising the following steps: (1) evenly mixing high pressure polyethylene, N-di-propyl-4-trifluoromet, antioxidant aging agent and biological aging inhibitor to obtain a mixture; (2) successfully heating, plasticizing, extruding, shaping, cooling, granulating and drying the mixture, and preparing into root-removal anti-aging master batch; and (3) after the root-removal anti-aging master batch obtained in step (2) is evenly mixed with injection-class low pressure polyethylene and master batch, heating, plasticizing, closing mould, injecting, pressurizing, cooling and shaping to obtain the finished product. The method of the invention can ensure that a functional auxiliary material with small content is evenly and integrally mixed, and plasticizing dispersing evenness in the injection process of the finished product is obviously improved; and meanwhile, the method can effectively improve the heat resistance, the aging resistance and the corrosion resistance of the finished product.
Owner:GANSU DAYU WATER SAVING
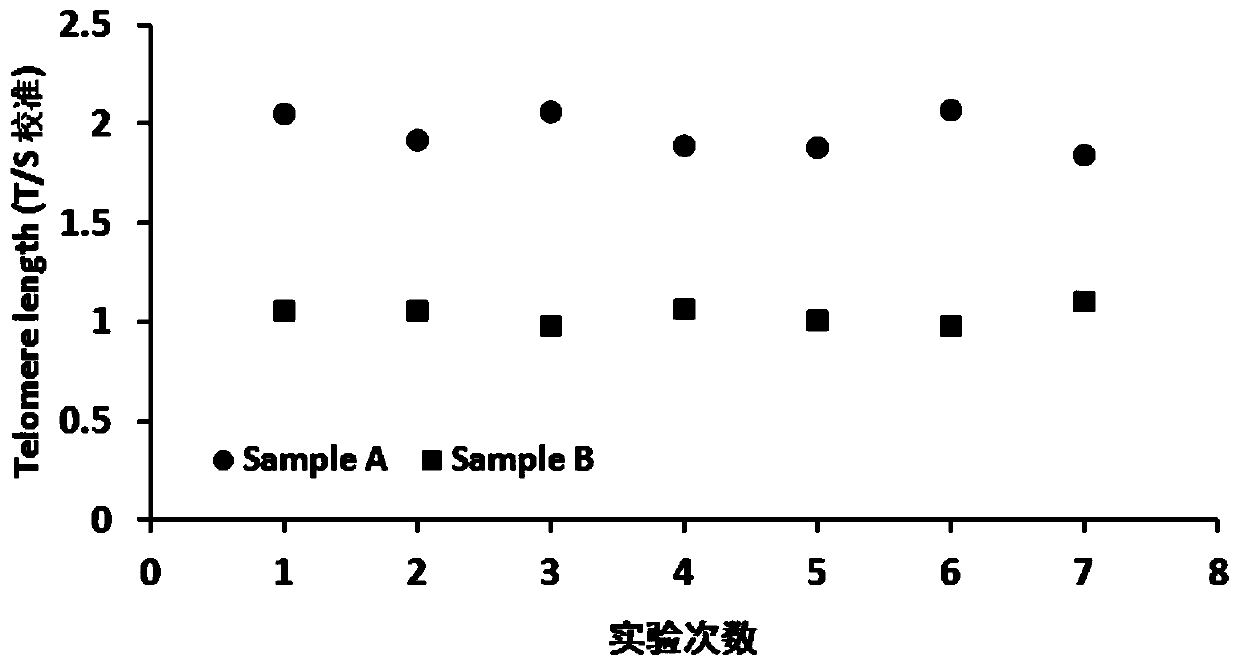
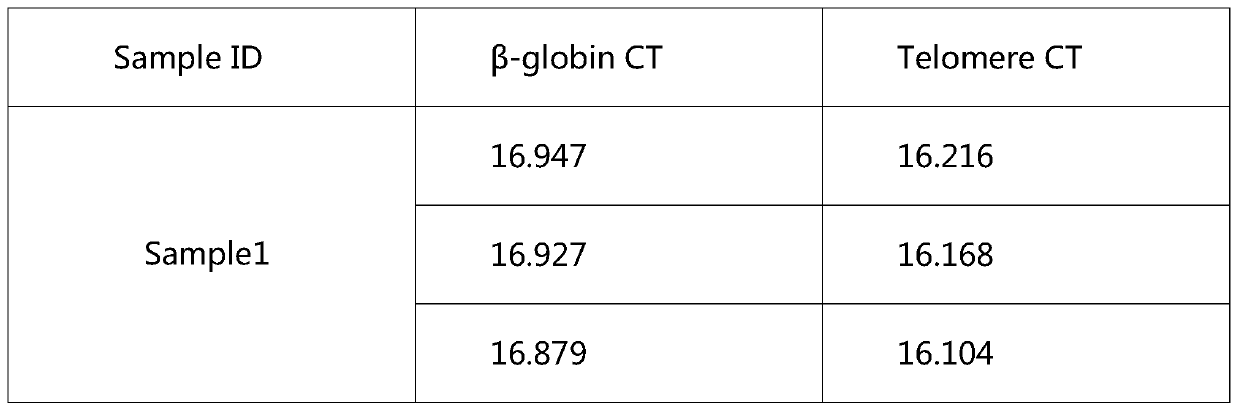
Telomere length detection kit and method and biological age evaluation method thereof
PendingCN110408684AAccurate detectionAccurate dynamic evaluation analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesModel system
The invention discloses a kit for telomere length detection. The kit includes a telomere gene primer sequence and a reference gene primer sequence. The invention also discloses a biological age evaluation method, which comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a Chinese population telomere length detection calibration T / S database; (2) fitting algorithm according to the above telomere lengthcalibration T / S value-age model distribution diagram, and establishing a telomere length-biological age algorithm model system. With the application of the kit and by using the calibration T / S ratioas the telomere length evaluation standard, accurate detection and dynamic evaluation analysis of telomere length can be realized. With the application of the kit, scientific evaluation of biologicalage can be realized through a biological age database and a calculation model system. With the application of the kit for telomere length detection, the effect is stable, raw materials are cheap and easily-available, and experiment operation is simple and feasible.
Owner:陕西九州医学检验有限公司
Method for preparing developing polyurethane
InactiveCN101392048ALong lasting developing effectExcellent developabilitySurgeryCatheterPolymer scienceBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method of developing polyurethane, which pertains to the technical field of high polymer material. The preparation method comprises the steps that: firstly, polymers, diatomic alcohol and diisocyanate are mixed; the mixture of the diatomic alcohol and the diisocyanate is stirred and reacts under the protection of nitrogen gas to obtain a prepolymer; after the temperature thereof is raised, the prepolymer is added with a chain extender and stirred for reaction; and the polymers are cured. As the chain extender contains developing atoms and developing groups are connected with the polyurethane by the effect of chemical bonds, the developing polyurethane prepared by the preparation method has long lasting development effect, good stability, biocompatibility and anticoagulant performance, arouses no inflammation in human bodies, is biological aging resistant and animalcule resistant, has good physical properties, can be sterilized by usual methods, is easy to be processed and takes advantages over non-developing polyurethane when being applied to heart valves, conduits and vascular stents. The preparation method is flexible, effective, simple and easy to be realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Measurement and quantification of 17 ketosteroid-sulfates as a biomarker of biological age
InactiveUS6326209B1Simple methodShort processOrganic chemistryDisease diagnosisKetosteroidImproved method
The present invention provides an improved method for using the measurement of total urinary 17 KS-S, referred to herein as the urinary Anabolic / Catabolic Index (ACI), as part of a biomarker for biological age.
Owner:UNIGEN PHARM INC
Method for analyzing the biological age of a subject
InactiveUS20050228237A1Increased energy productionIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryMedicineOrganism
The present invention is a method for analyzing biological age of a subject. The method analyzes the biological age as it relates to a number of factors indicating levels of health, energy production and metabolism. The method may also be used to calculate a subject's biological age and treat the factors associated with biological age.
Owner:SHALLENBERGER FRANK
Biological aging-accelerating additive for white wine
InactiveCN102424795ASolve the production problems of ripeningEasy to operateAlcoholic beverage preparationMicroorganism based processesTotal nitrogenAqueous solution
The invention relates to the field of food and discloses a biological aging-accelerating additive applied to white wine, prepared from the following components: greater than or equal to 0.2-3.9% of total nitrogen in dry basis, greater than or equal to 70% of polysaccharide in sum of glucan and mannose, greater than or equal to 43% of mannan oligosaccharides, less than or equal to 6.7% of water, less than or equal to 10.0% of ash and 2% of a water solution with the pH of 2.9-7.0. The invention also provides a preparation method of the biological aging-accelerating additive.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Biological age step-by-step predication method based on support vector machine
InactiveCN104966106AImprove operational efficiencyReduce dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineUnknown age
The invention discloses a biological age step-by-step predication method based on a support vector machine, and relates to the biological age step-by-step predication method based on the support vector machine. The invention aims to solve the problems that a conventional biological age predication method is low in predication efficiency, low in accuracy, high in cost, and complex. According to the technical scheme, the biological age step-by-step predication method comprises: step I, preparing a biological age data set; step II, distinguishing a biological sample with known ages from a biological sample with unknown ages; step III, carrying out inter-group classifying; step IV, generating a corresponding support vector machine model; step V, establishing an optimal support vector machine model; step VI, establishing an optical characteristic sub set; step VII, obtaining the group type of an age group corresponding to the biological sample with known ages in the test set; step VIII, carrying out inter-group classifying; step IX, generating an inter-group classified support vector machine model; and step X, obtaining the exact age of a test set sample in certain age group. The biological age step-by-step predication method is applied to the biological age predication field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Deep transcriptomic markers of human biological aging and methods of determining a biological aging clock
A method of creating a biological aging clock for a subject can include: (a) receiving a transcriptome signature derived from a tissue or organ of the subject; (b) creating input vectors based on the transcriptome signature; (c) inputting the input vectors into a machine learning platform; (d) generating a predicted biological aging clock of the tissue or organ based on the input vectors by the machine learning platform, wherein the biological aging clock is specific to the tissue or organ; and (e) preparing a report that includes the biological aging clock that identifies a predicted biological age of the tissue or organ.
Owner:INSILICO MEDICINE IP LTD
Methods of screening for compounds that inhibit expression of biomarker sequences differentially expressed with age in mice
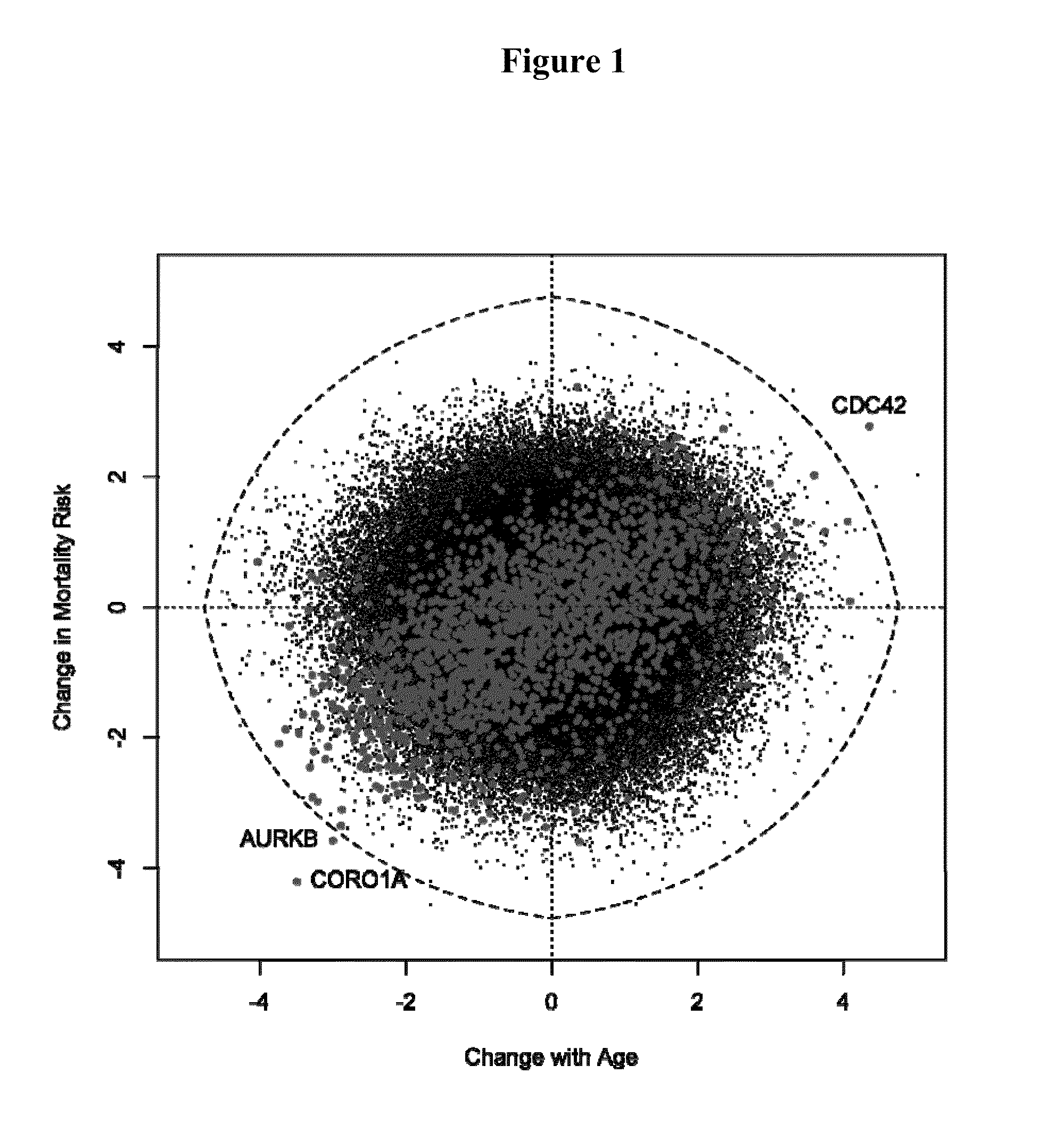
InactiveUS7041449B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyMulticellular organism
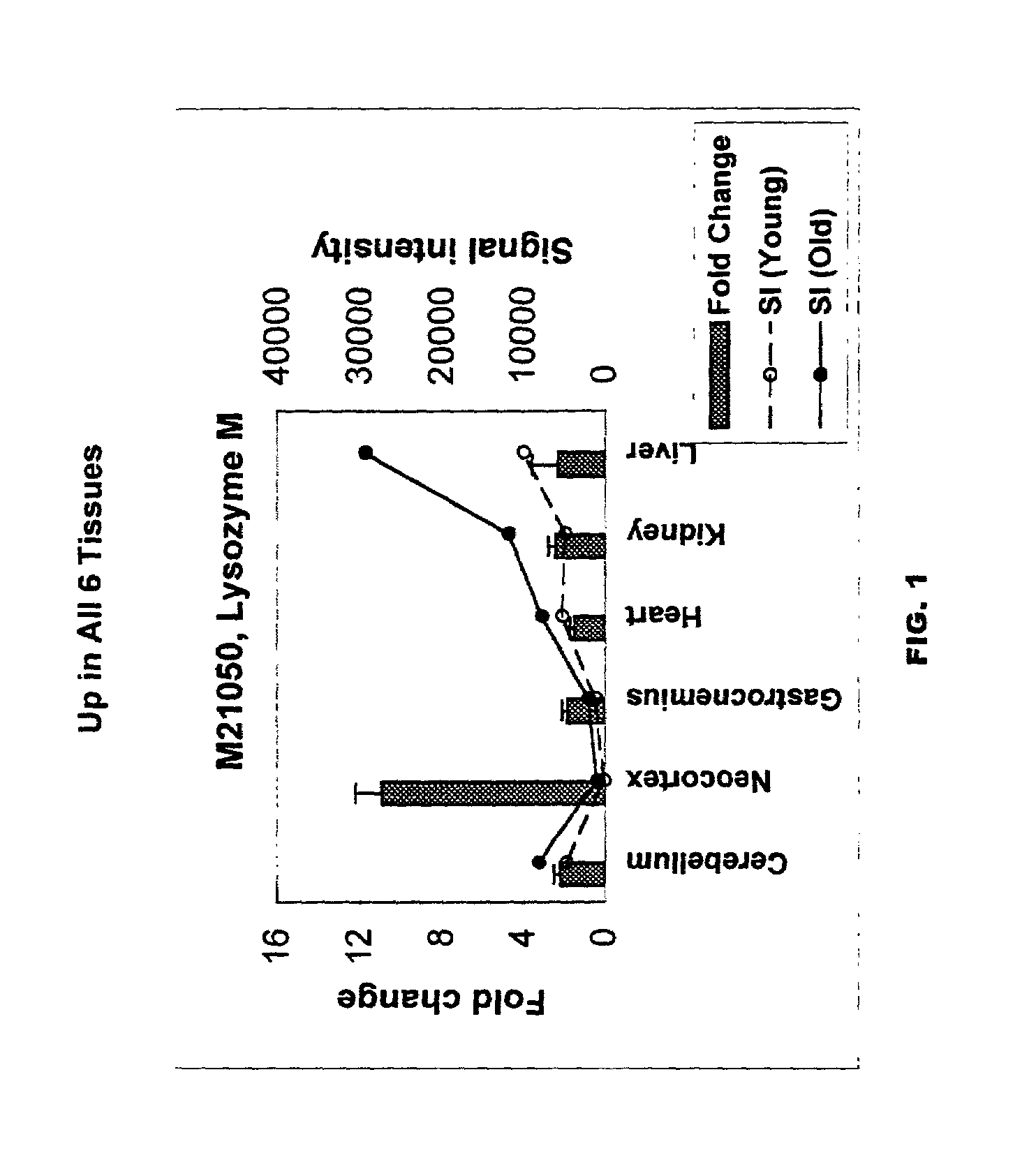
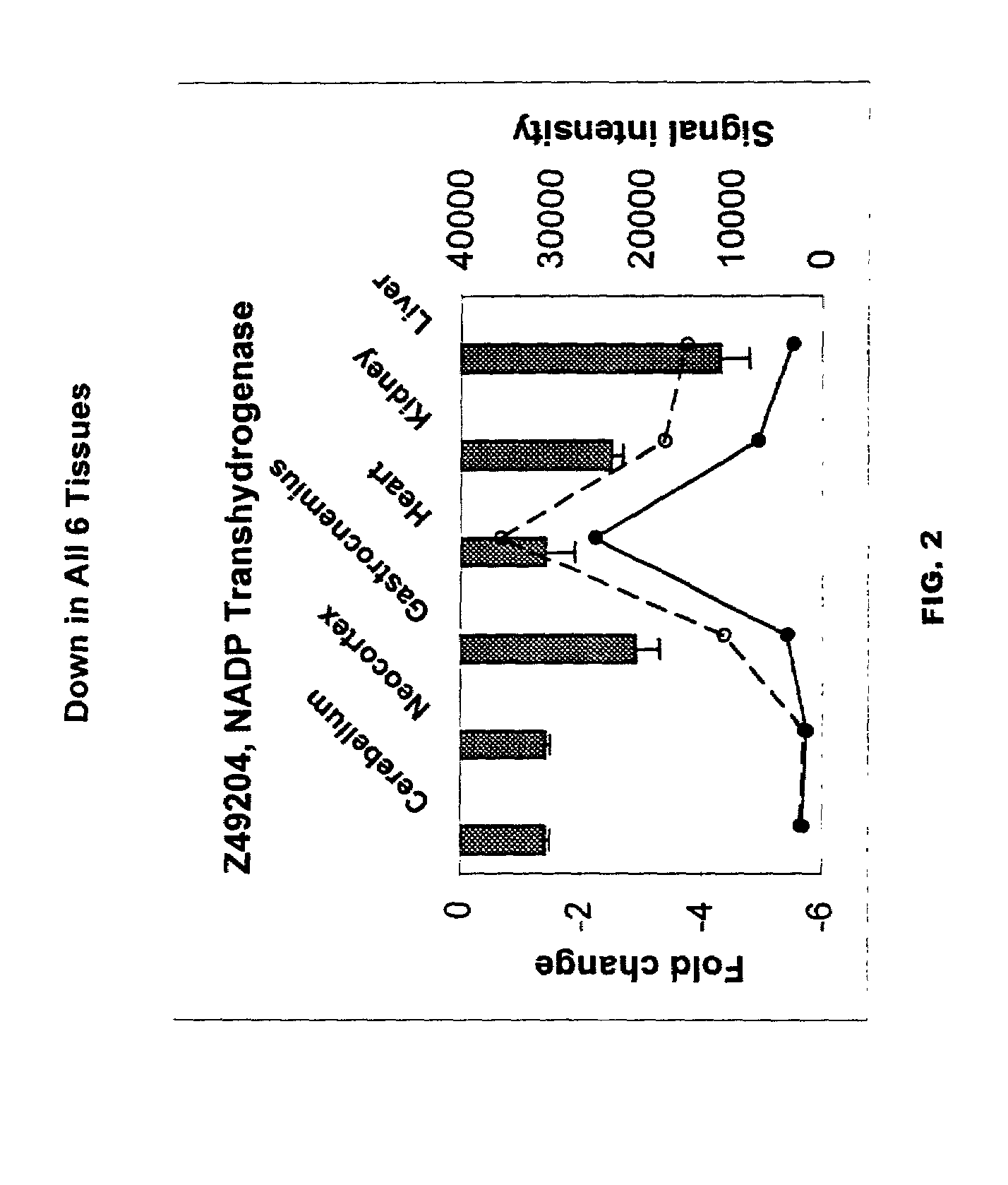
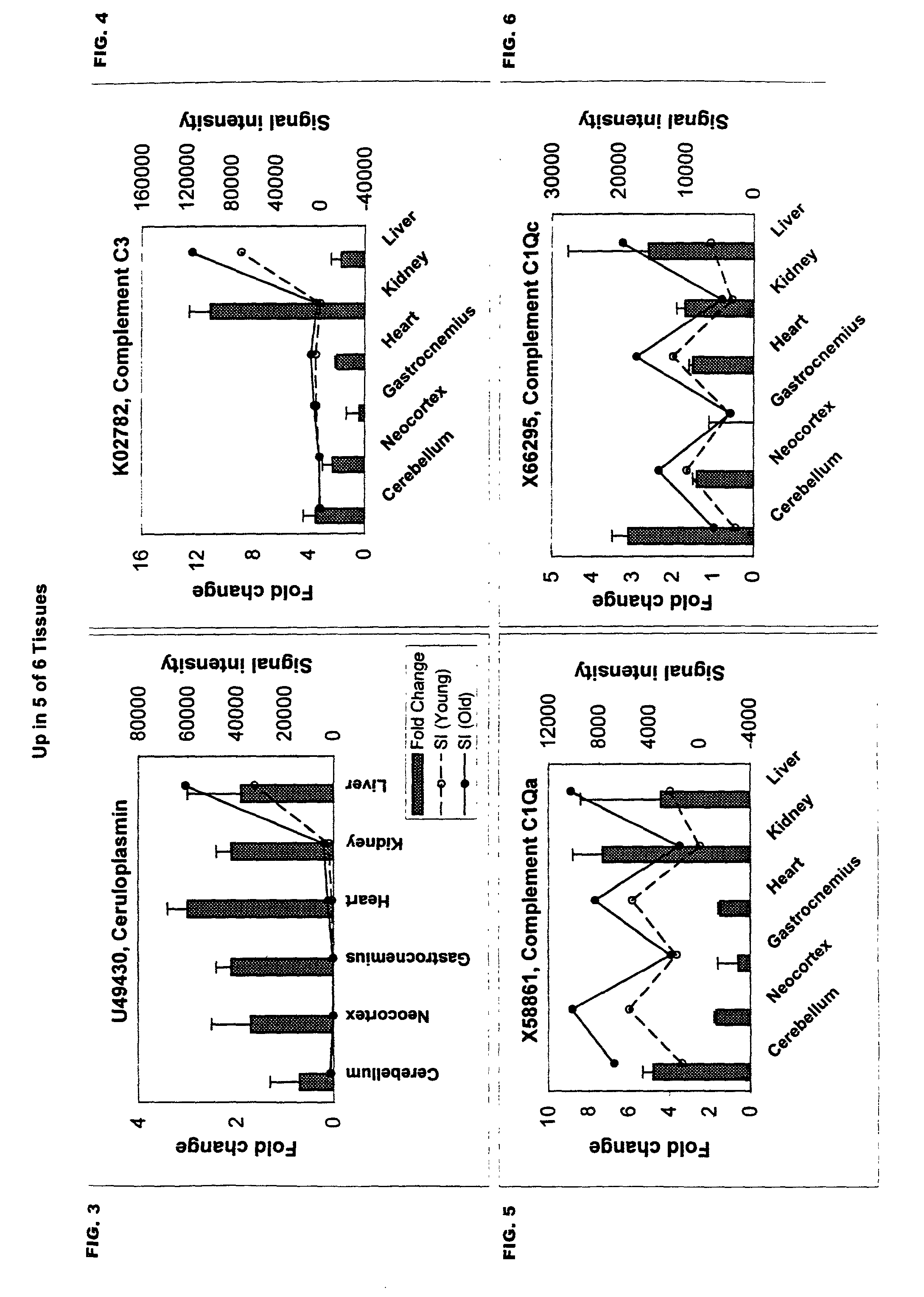
A method of measuring the biological age of a multicellular organism is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: (a) obtaining a sample of nucleic acid isolated from the organism's organ, tissue or cell, wherein the nucleic acid is RNA or a cDNA copy of RNA and (b) determining the gene expression pattern of at least one of the genes selected from the group consisting of M21050, Z49204, U49430, K02782, X58861, X66295, M22531, X67809, U19118, M64086, M63695, U39066, X92590, X56518, AA182189, X16493, U20344, X16834, X82648, D00754, D16313, L38971 and X15789.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
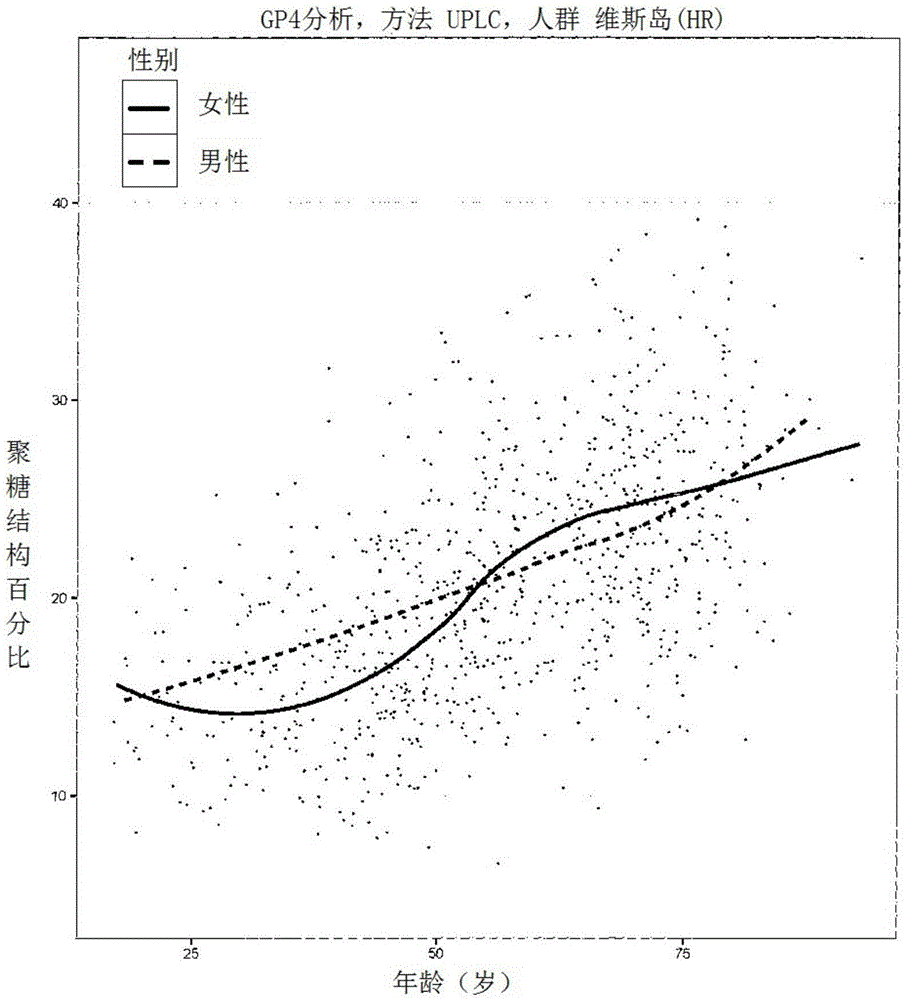
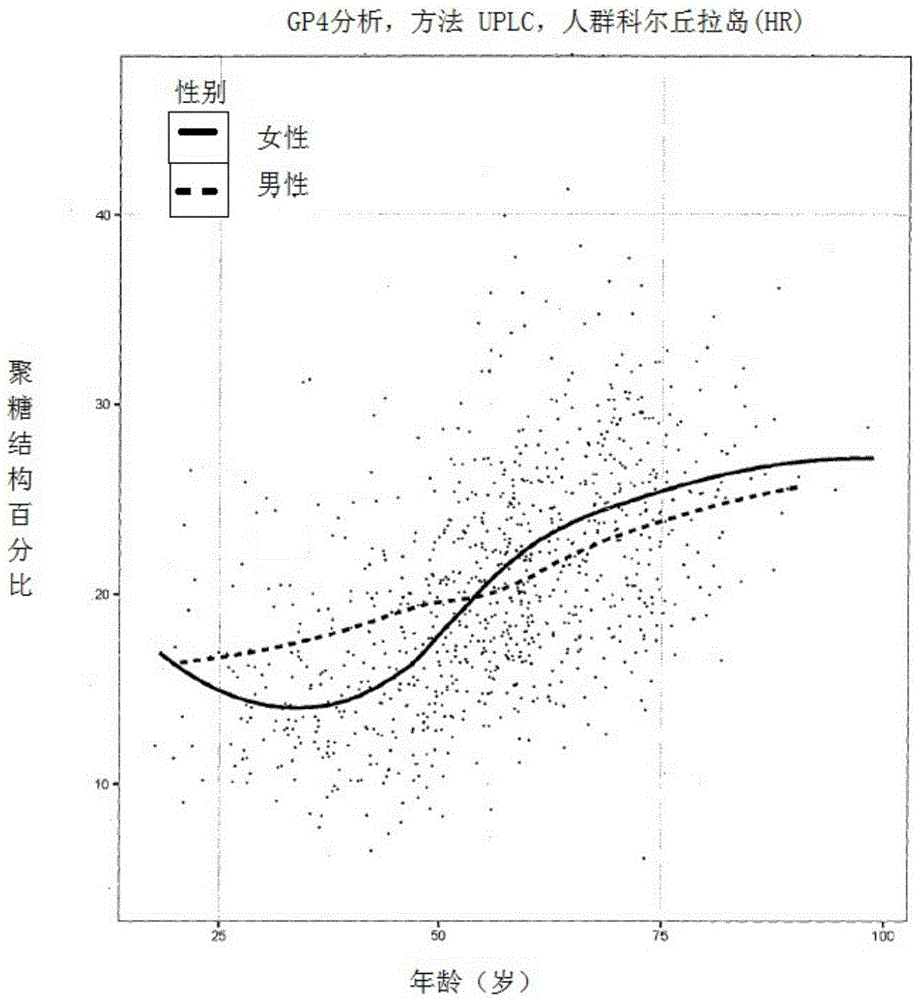
Method for the analysis of N-glycans attached to immunoglobulin G from human blood plasma and its use
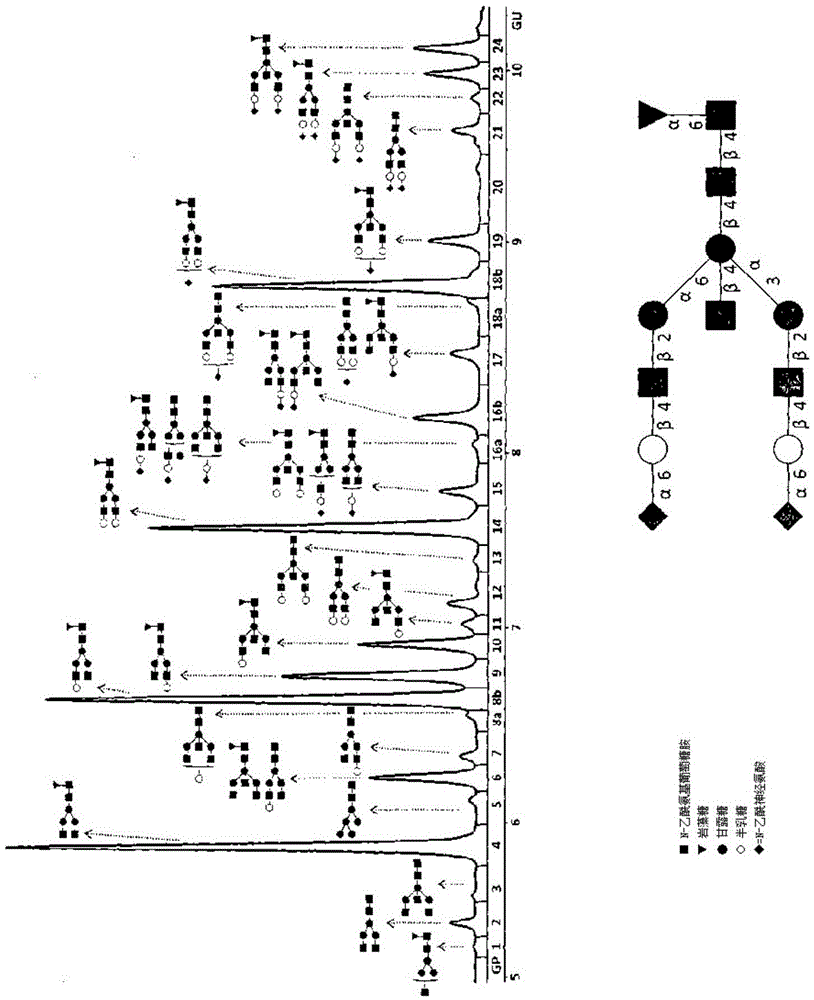
The invention discloses a method for the analysis of N-glycans attached to immunoglobulin G (IgG) or IgG N-glycopeptides from human blood plasma in which relative abundance of two or more glycans is determined, out of total six, and for these glycans it is determined that they strongly correlate with age. The glycans have the following structures: F(6)A2 (GP4): R1, R2, R3, R4=H F(6)A2B (GP6): R1=GlcNAc; R2, R3, R4 H F(6)A2[6]G1 (GP8): R1, R3, R4=H; R2= Gal F(6)A2G2 (GP14): R1=H; R2, R3=Gal; R4=H F(6)A2BG2 (GP15): R1=GlcNAc; R2, R3=Gal; R4=H F(6)A2G2S1 (GP18): R1=H; R2, R3=Gal; R4=NeuAc GlcNAc=N-acetylglucosamine Fuc=fucose Man=mannose NeuAc=N-acetylneuraminic acid Gal=galactose From the results of the analysis, Glycan Age Index (GAI) is calculated, and it is useful for: prediction of biological age of a tested individual; monitoring efficacy of methods that slow down the ageing process; monitoring progression of diseases that are developed as a result of the ageing process advancement, like: inflammatory diseases (including atherosclerosis), autoimmune diseases, tumours, diabetes, arthritis, osteoporosis, and Alzheimer disease; and evaluation of overall condition / health of a body.
Owner:ZHONGKE YAMEI MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
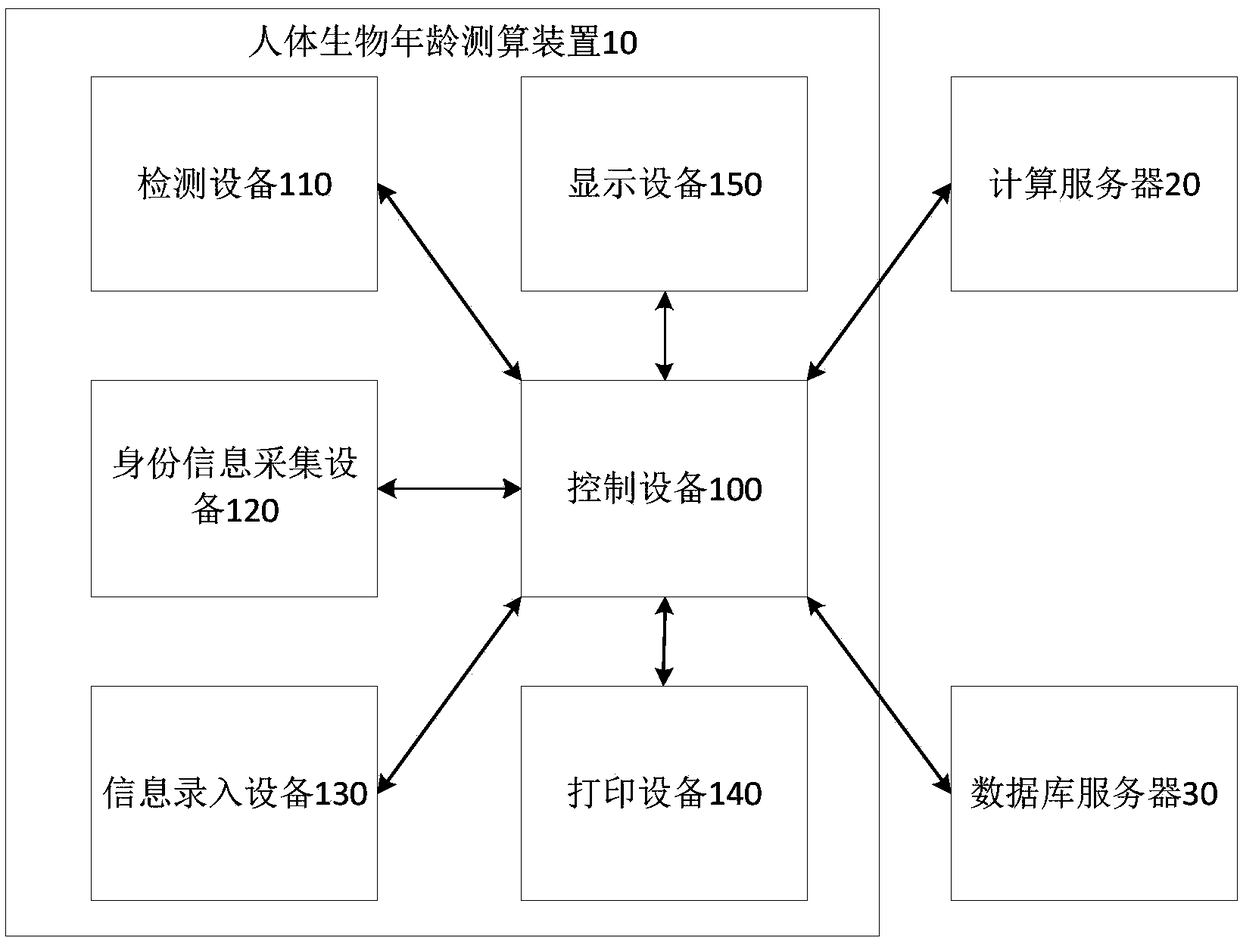
Human biological age measuring-calculating device and system
ActiveCN108847284AObvious and understandable technical solutionObvious and understandable beneficial effectMedical communicationHealth-index calculationDatabase serverComputer science
The invention provides a human biological age measuring-calculating device and system, and relates to the technical field of biological age measurement and calculation. The device comprises a controller, and a detector, an identity information collector and an information logging unit connected with the controller, and the controller is also connected with a calculation server and a database server. The detector detects the first reference biological age of a user, the identity information collector collects identity information of the user, and the information logging unit logs in private information of the user. The controller obtains the historical biological age of the user from the database server, and carry out calculation on the basis of the first reference biological age, the historical biological age and the private information to obtain the biological age of the user. A calculation model used to calculate the biological age can be updated via the calculation server. The biological age calculated by the device can reflect the aging condition of the user comprehensively and accurately.
Owner:莱博科技控股集团股份有限公司
Method for synthesizing organic fluorine modified polysiloxane linen finishing agent
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing organic fluorine modified polysiloxane linen finishing agent, belonging to the technical field of linen finishing agent. Polymethyl hydrogen polysiloxane, methyl methacrylate and fluorinated olefin are used as raw materials which have wide sources and moderate price and ensure sufficient addition reaction, easy reaction product separation and purification and high yield of organic fluorine modified polysiloxane linen finishing agent. Being the organic fluorine modified product with a stable structure, the finishing agent has good biological aging resistance, dose not repel the animal body, has no harmful effect on the environment, is green and environmental friendly and ensures that the linen fabric has durable finishing effect, resists water, oil and foul. The method adopts the hydrosilylation reaction and the simple reaction route and ensures high conversion rate.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
System and method for tracking biological age over time based upon heart rate variability
ActiveUS20150120202A1Diagnostic signal processingHealth-index calculationRR intervalFetal Heart Rate Variability
A system and method for tracking biological age over time based upon heart rate variability includes an activity monitoring device configured to measure and transmit one or more biological age parameters, including heart rate variability, to a biological age calculation and display module configured to calculate a biological age factor as a function of the biological age parameters, calculate biological age as a function of the biological age factor and the user's actual age, and display the biological age.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Preparation method of polyester fiber compounding type silicon dioxide aerogel cold insulation felt
The invention discloses a preparation method of polyester fiber compounding type silicon dioxide aerogel cold insulation felt. The method comprises the following steps of (1) preparing a silicon dioxide aerogel solution, wherein the silicon dioxide aerogel solution is prepared from the following raw materials of a silicon source precursor, a solvent, a hydrolysis catalyst and a modifying agent; (2) compounding and shaping polyester fiber felt aerogel; (3) maturing the compounded and shaped polyester fiber felt aerogel; (4) aging the matured polyester fiber felt aerogel; (5) performing secondary maturing on the aged polyester fiber felt aerogel; (6) performing surface modification on the polyester fiber felt aerogel subjected to secondary maturing; (7) drying and detecting the polyester fiber felt aerogel subjected to surface modification. The prepared polyester fiber compounding type silicon dioxide aerogel cold insulation felt disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the heat isolation / cold insulation performance is excellent; the adjustable range is wide; the applicability is high; the biological aging resistance is realized; the anti-condensation and hydrophobic performance are good; the construction is convenient. The preparation method avoids a solvent replacement step; the operation is simple and easy; the process is controllable; the production continuity is realized.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE WUJIANG MACHINERY & ELECTRICITYEQUIP
System and method for tracking biological age over time based upon heart rate variability
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
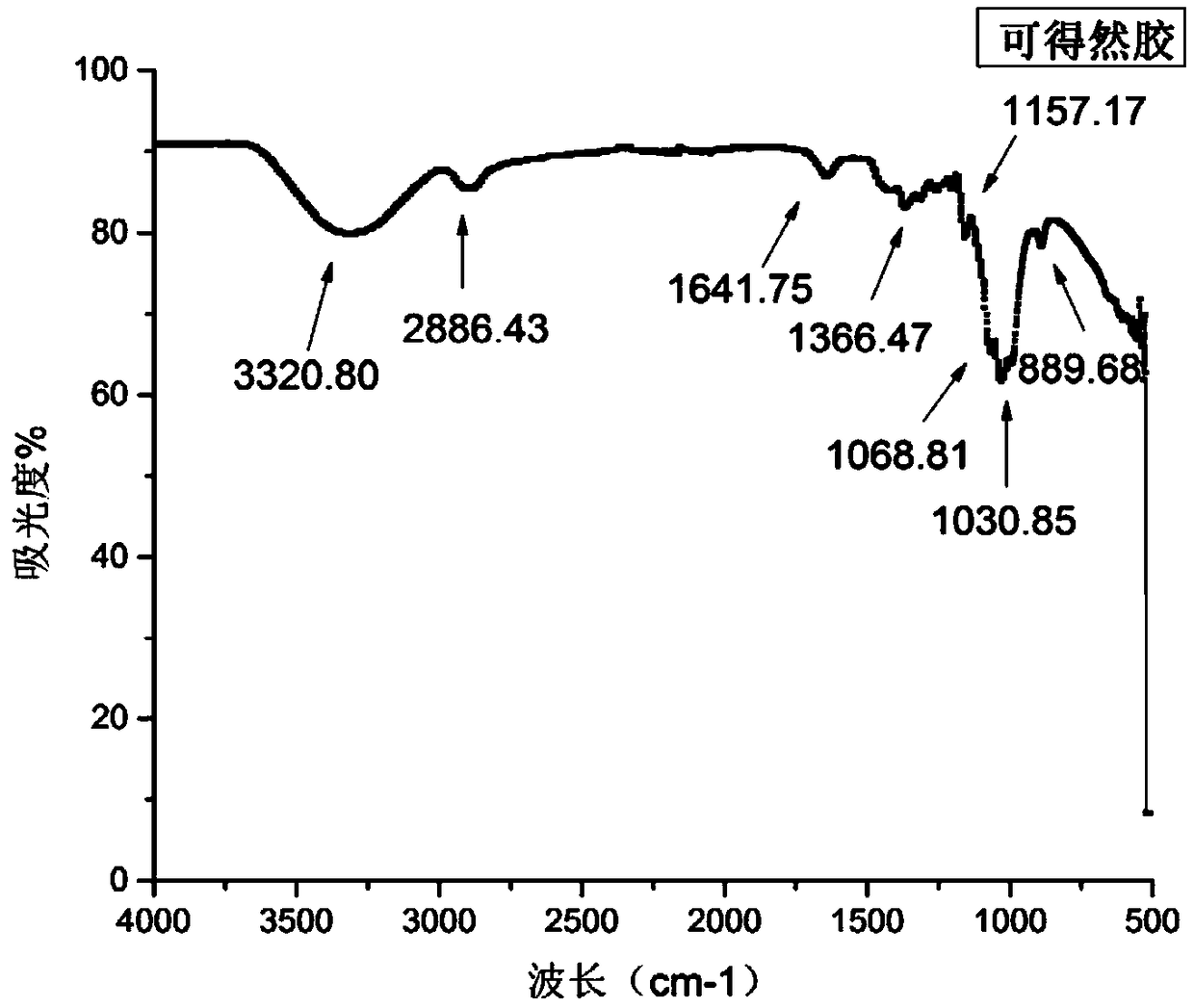
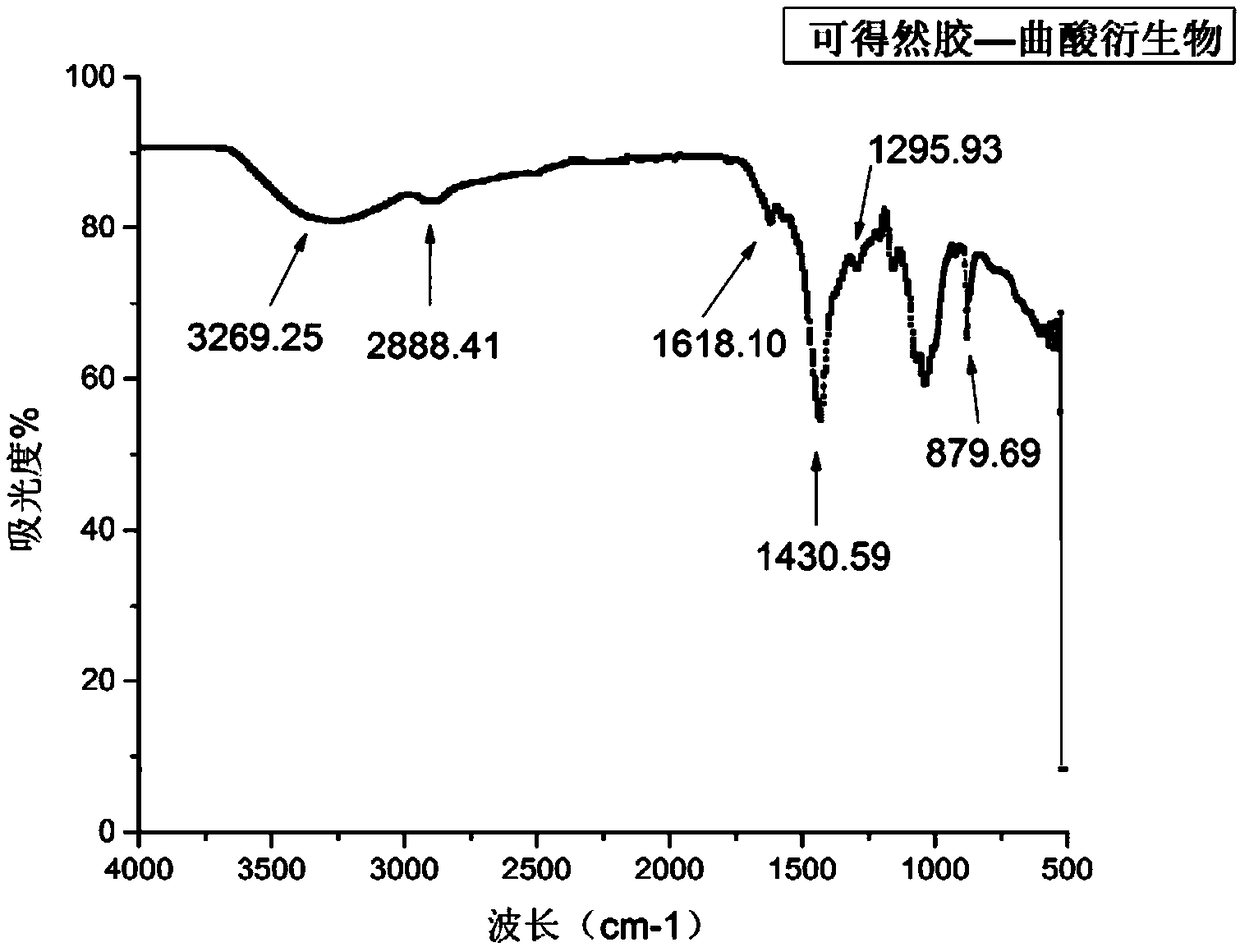
Method for preparing curdlan gum-kojic acid derivatives
The invention discloses a method for preparing curdlan gum-kojic acid derivatives, and belongs to the field of antioxidants. The method has the advantages that kojic acid is led onto curdlan gum to prepare the curdlan gum-kojic acid derivatives, accordingly, the curdlan gum is soluble in water and also can have the antibacterial properties and the oxidation resistance of the kojic acid, biologicalaging can be delayed, biological aging symptoms can be improved, and effects of moisturizing skin and enhancing skin barrier can be realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
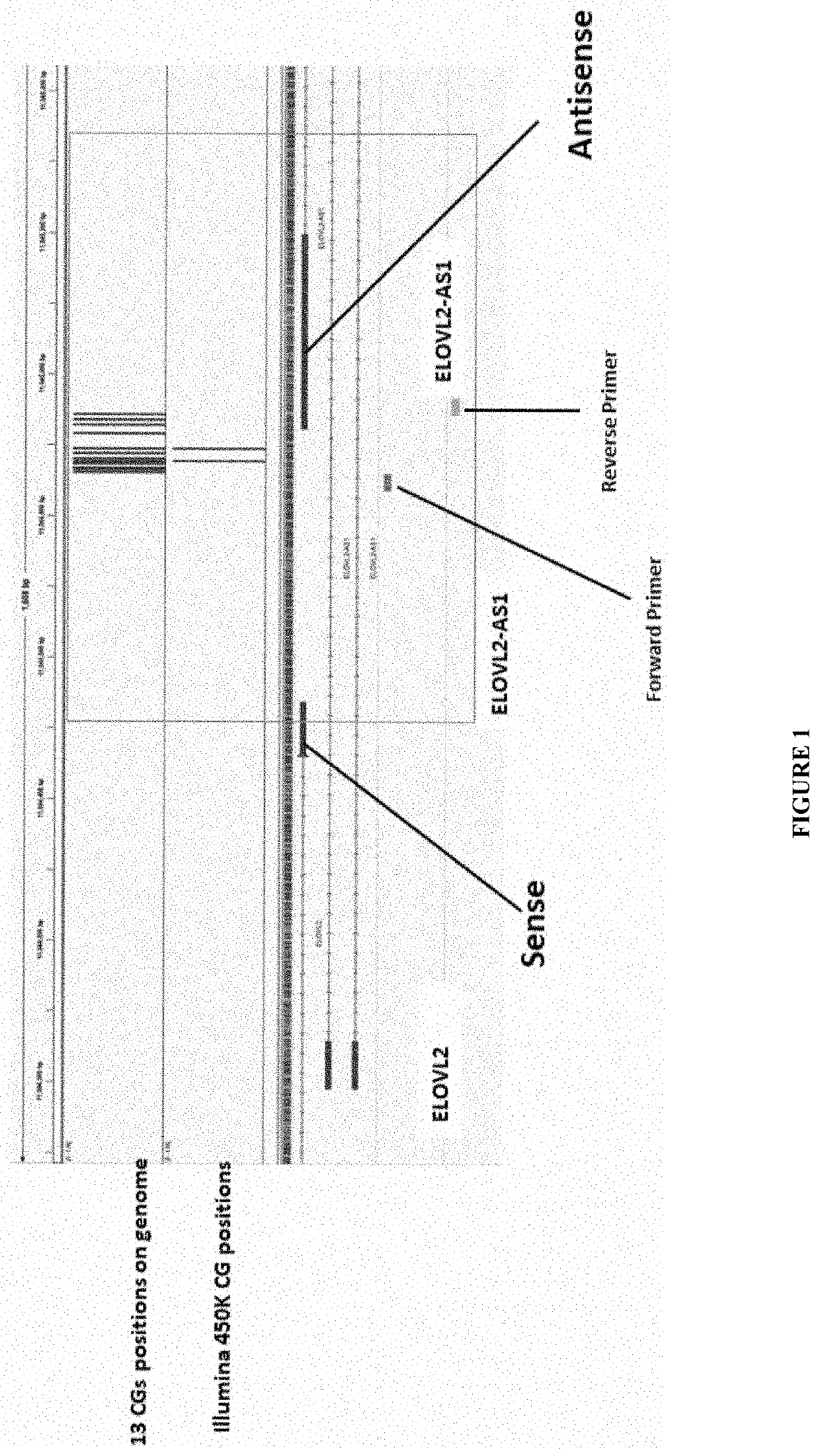
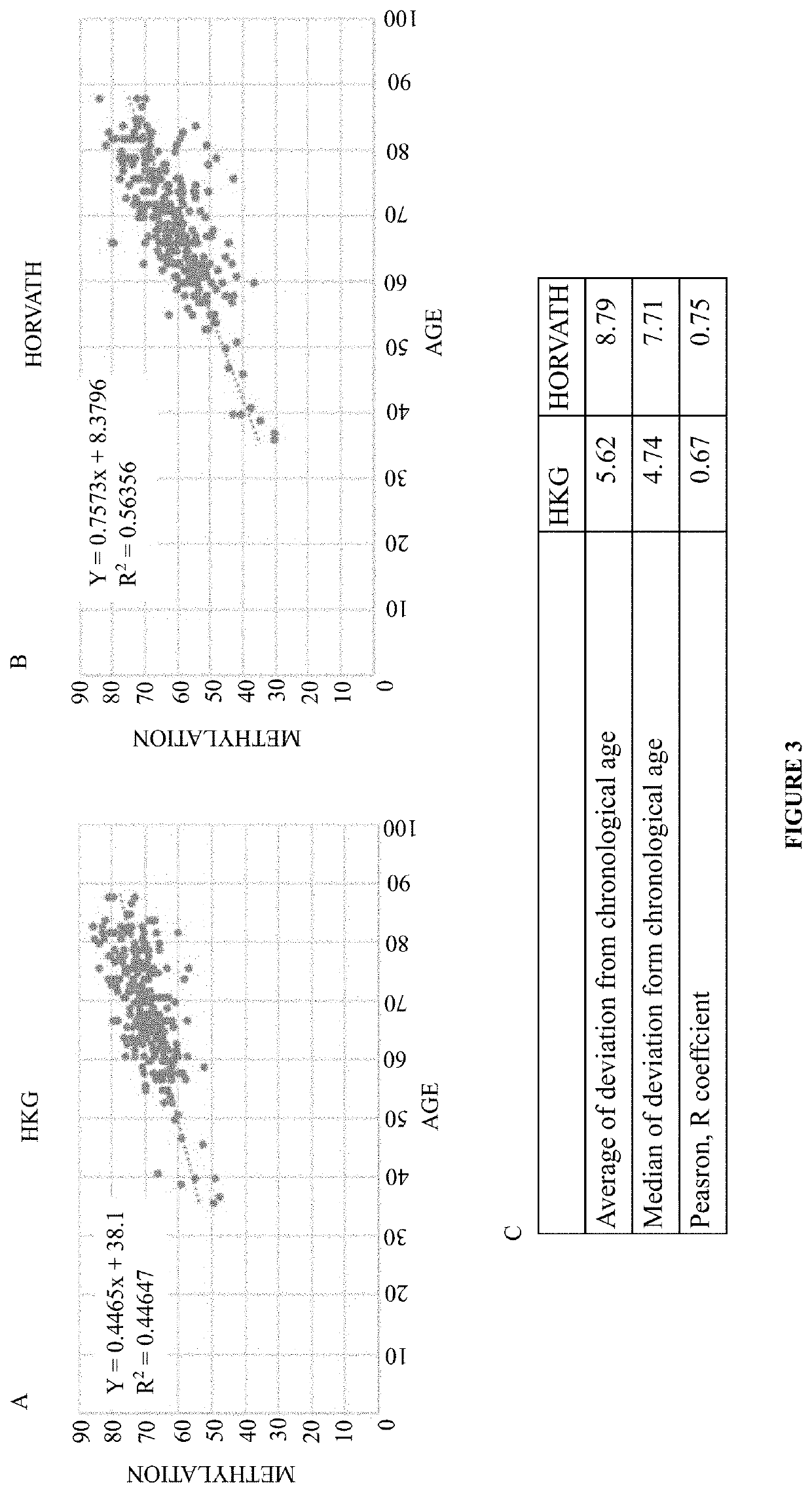
Epiaging ; novel ecosystem for managing healthy aging
PendingUS20220228217A1Accurate predictionAccurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDNA methylationLifestyle habits
The present invention relates to method for calculating biological age of a subject and across multiple subjects by performing polygenic DNA methylation on biomarkers which comprise measuring the methylation status of 13 CG sites positioned in a putative antisense region to ElovL2 gene, ElovL2 AS1 region. Further, the present invention provides a computer-implemented method for providing recommendations for lifestyle changes in form of a self-learning “ecosystem” for lifestyle management of biological aging using a novel measurement of the DNA methylation clock as a continuous dynamic outcome. The present invention also relates to combination of DNA methylation biomarkers for calculating biological age, a kit for determining the biological age. Further, the present invention discloses the use of the disclosed methods for calculating biological age in a method of assessing the effect of the effect of a biological intervention and in a method of screening for an anti-ageing agent.
Owner:HKG EPITHERAPEUTICS LTD
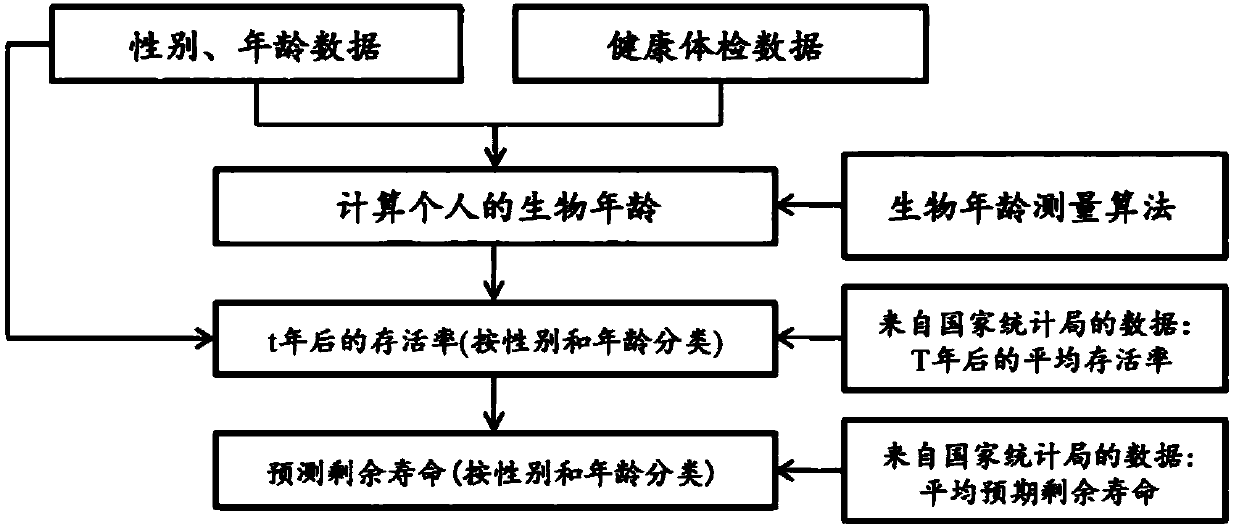
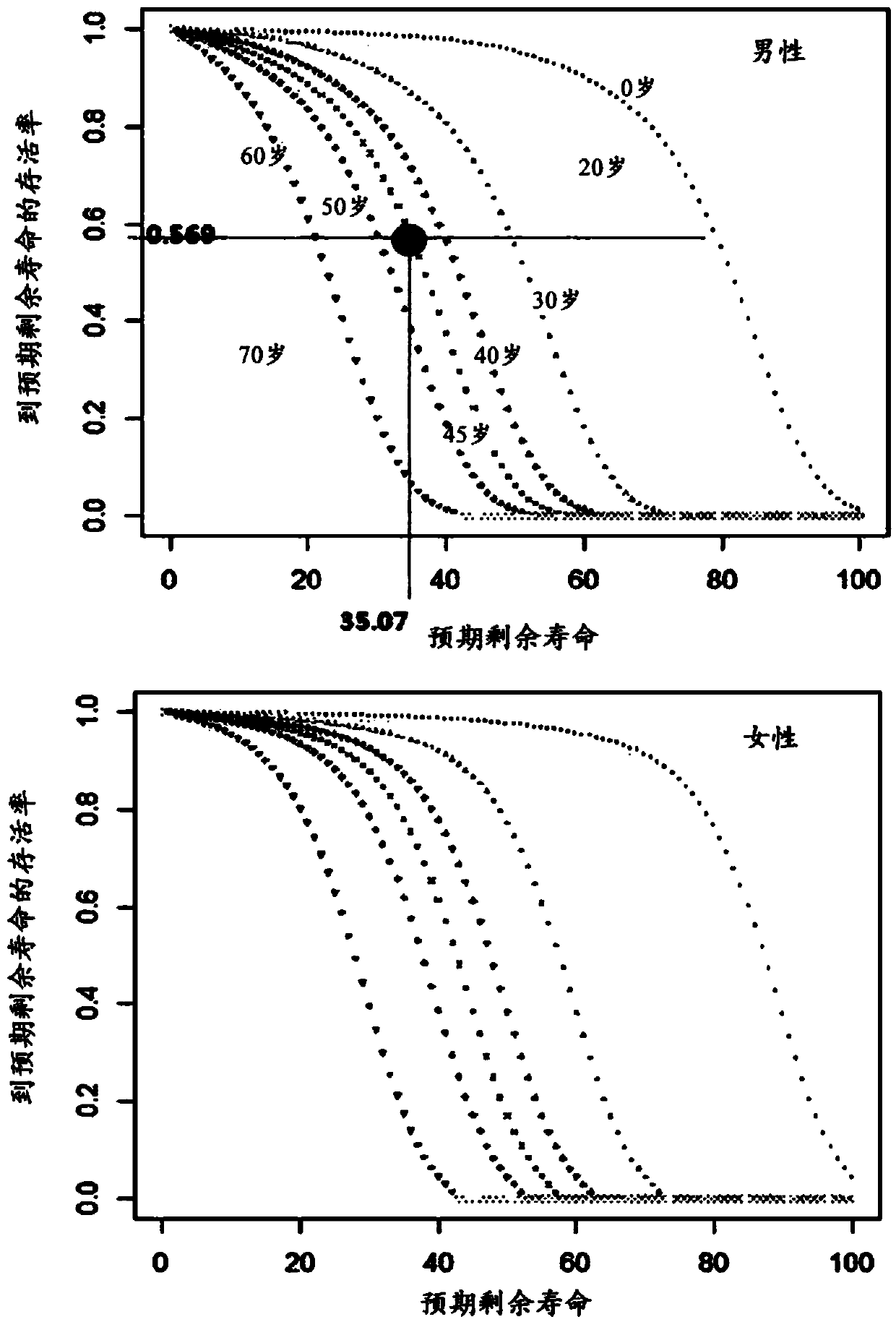
Method for predicting residual life using biological age
The invention relates to a method for measuring a remaining life of a person by using a biological age and a survival probability and, more specifically, to a method for measuring a survival probability by using a biological age measured through a biological age measurement algorithm to which a health medical examination result is reflected and a method for measuring a remaining life by using thebiological age and the survival probability measured by the method. According to the invention, a remaining life can be predicted more accurately than a remaining life method which does not consider an existing biological age.
Owner:BIOAGE
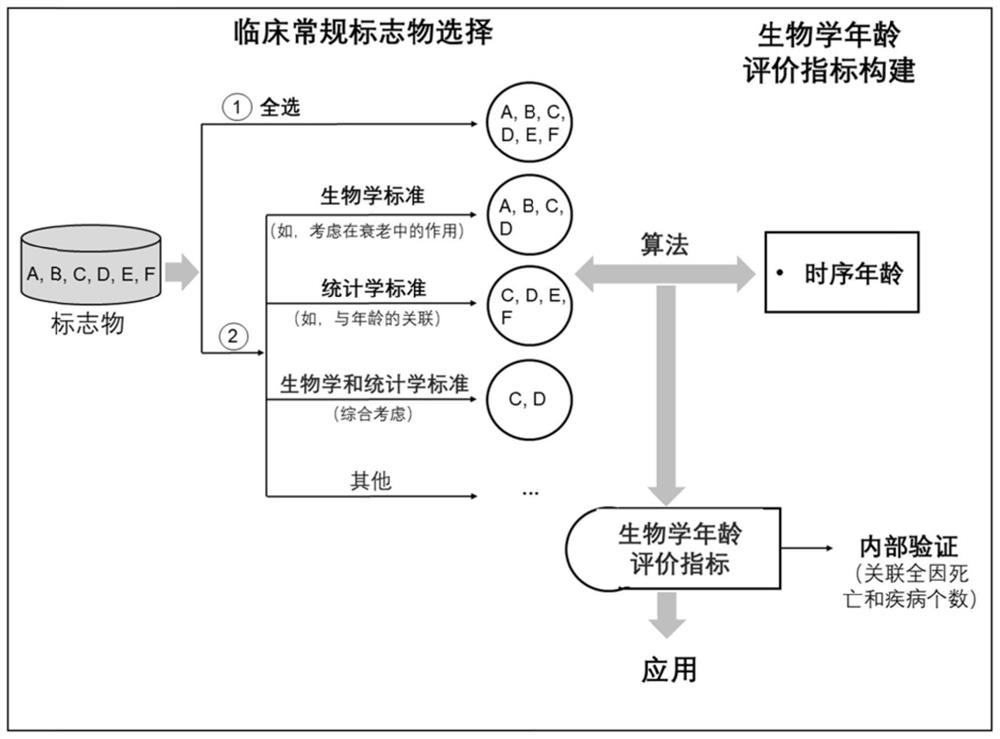
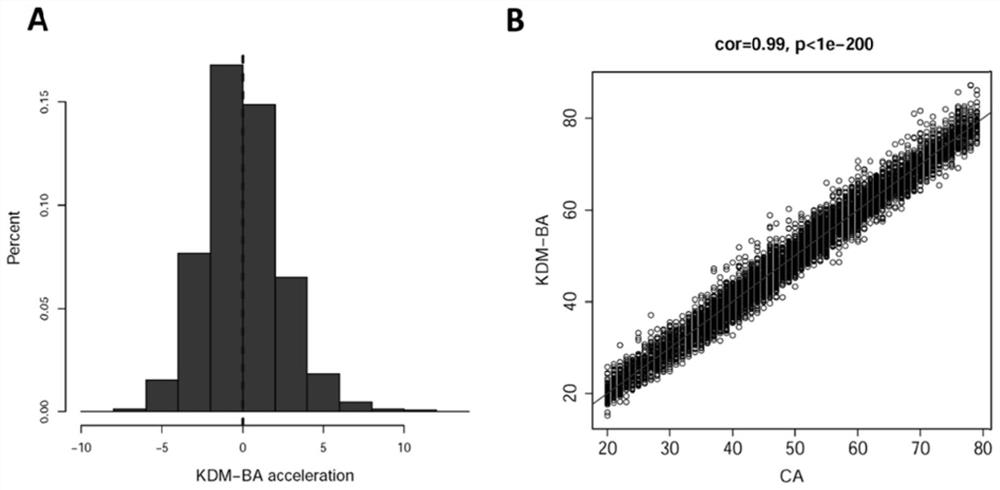
Method for constructing evaluation model for biological age of Chinese population based on clinical markers, and evaluation method
PendingCN111816307AImprove predictive performancePracticalHealth-index calculationDiseaseClinical marker
The invention discloses a method for constructing an evaluation model for the biological age of a Chinese population based on clinical markers. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selectingclinical routine markers representing different pathophysiological systems or functions; (2) constructing a biological age evaluation model by utilizing the selected markers based on a KDM algorithm;(3) evaluating the obtained biological age evaluation model, and if the effect of the model is poor, returning to the steps (1) and (2) and carrying out the next round of model construction operation,or if the effect meets requirements, outputting the constructed biological age evaluation model. The method can be applied to early identification and prevention of aging of people in China and intervention effect evaluation of senile diseases, and has practicability and huge application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com