Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
727 results about "Stethoscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
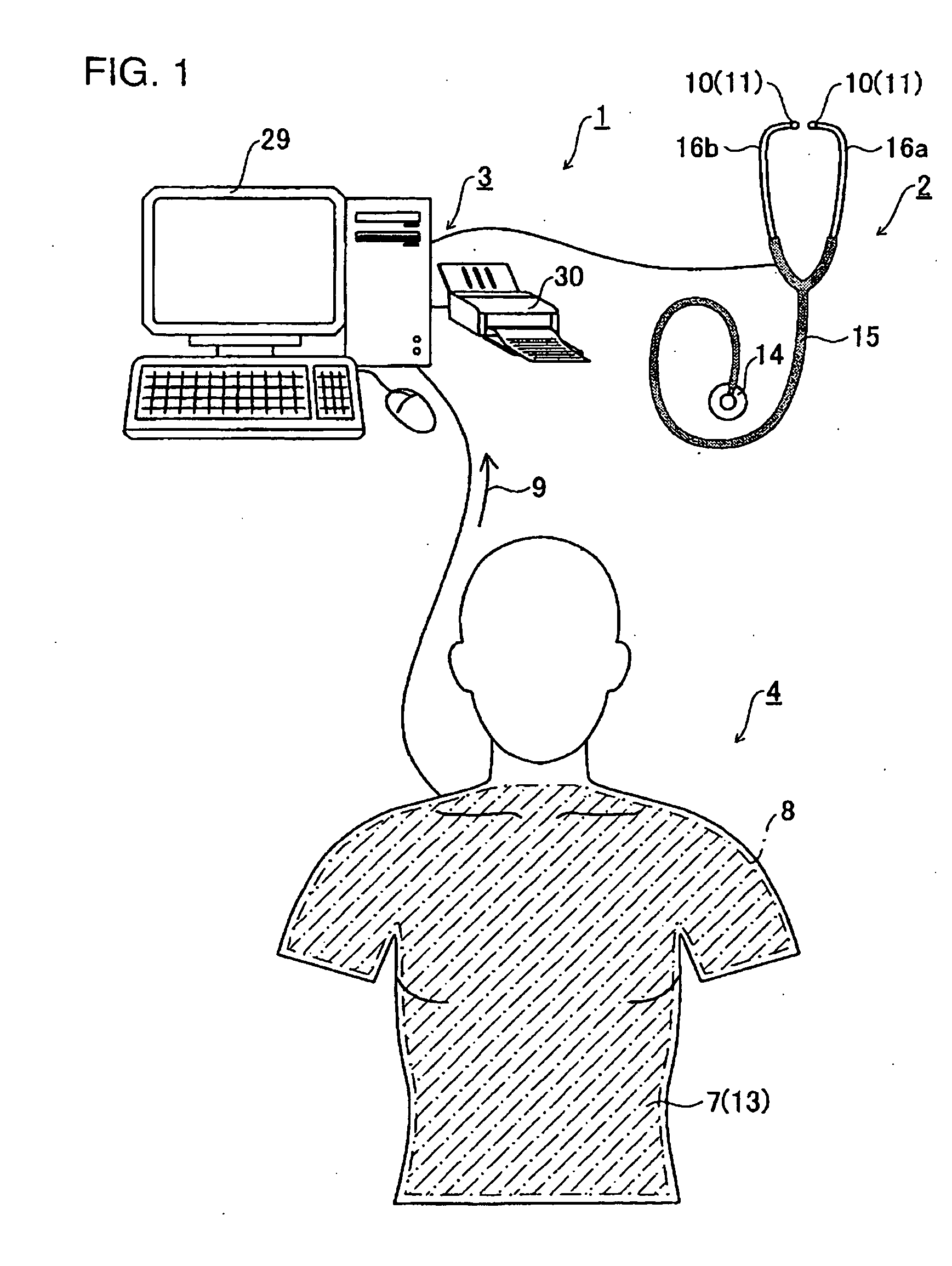
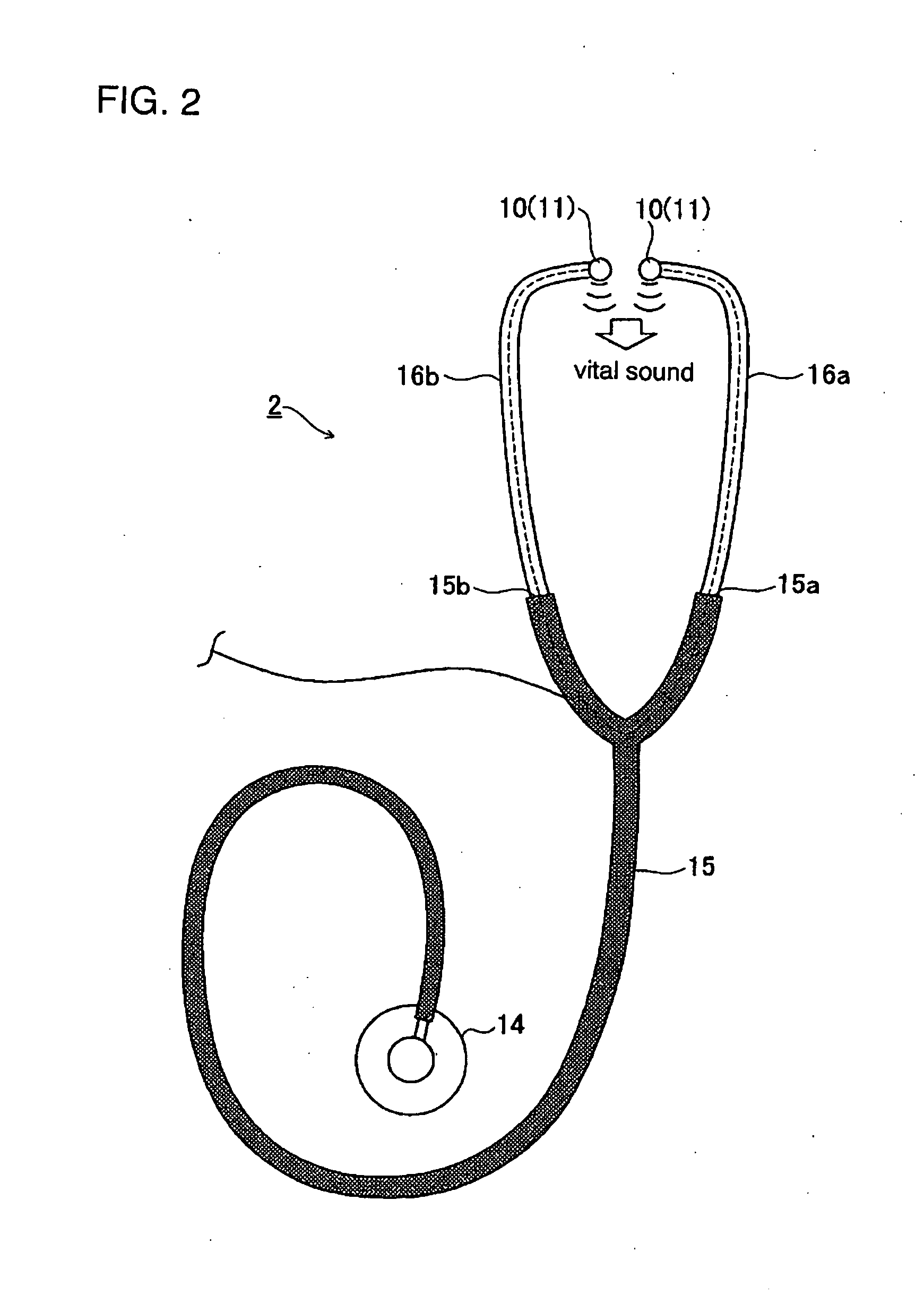
The stethoscope is an acoustic medical device for auscultation, or listening to the internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. A stethoscope can be used to listen to the sounds made by the heart, lungs or intestines, as well as blood flow in arteries and veins. In combination with a manual sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used when measuring blood pressure.
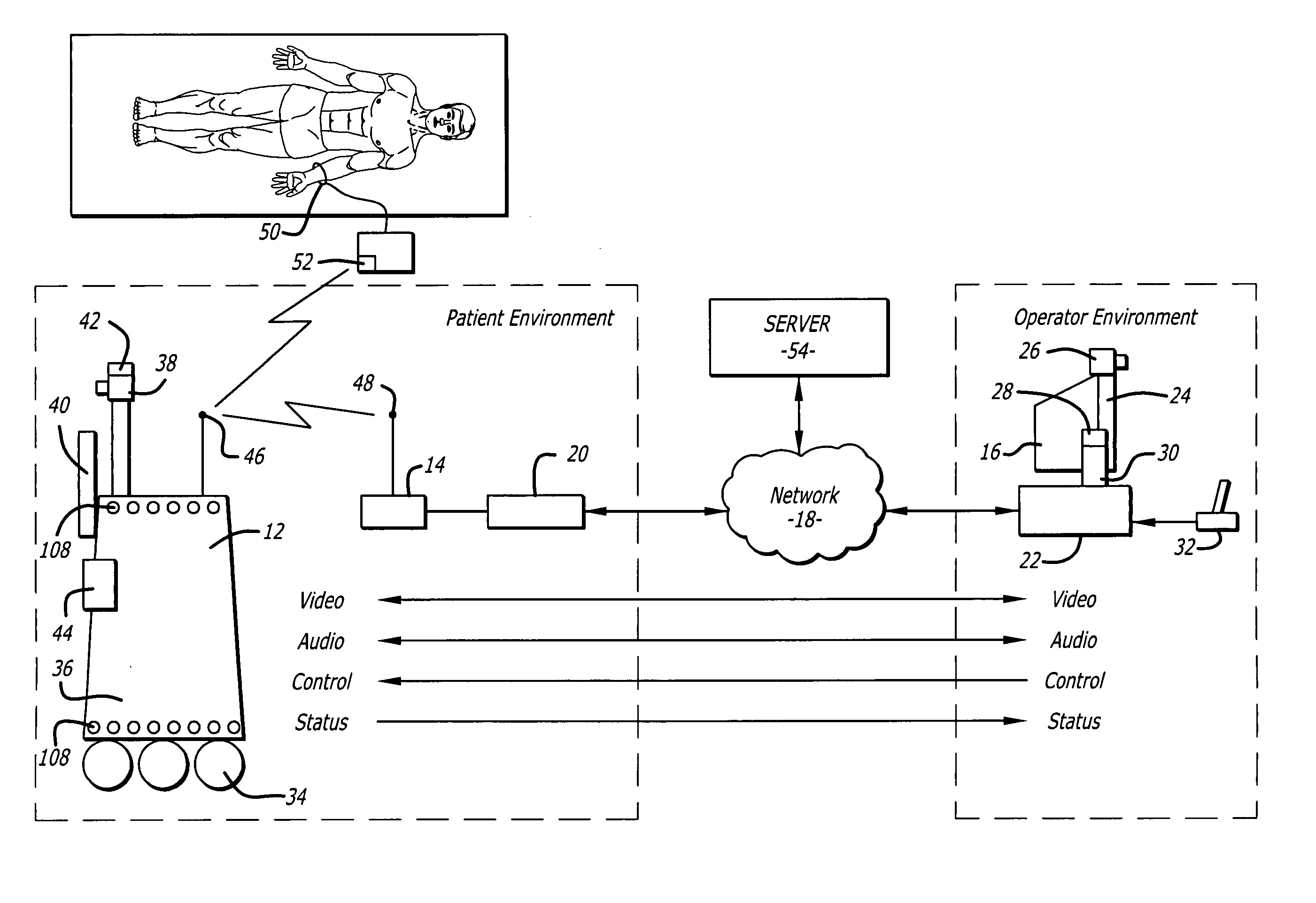
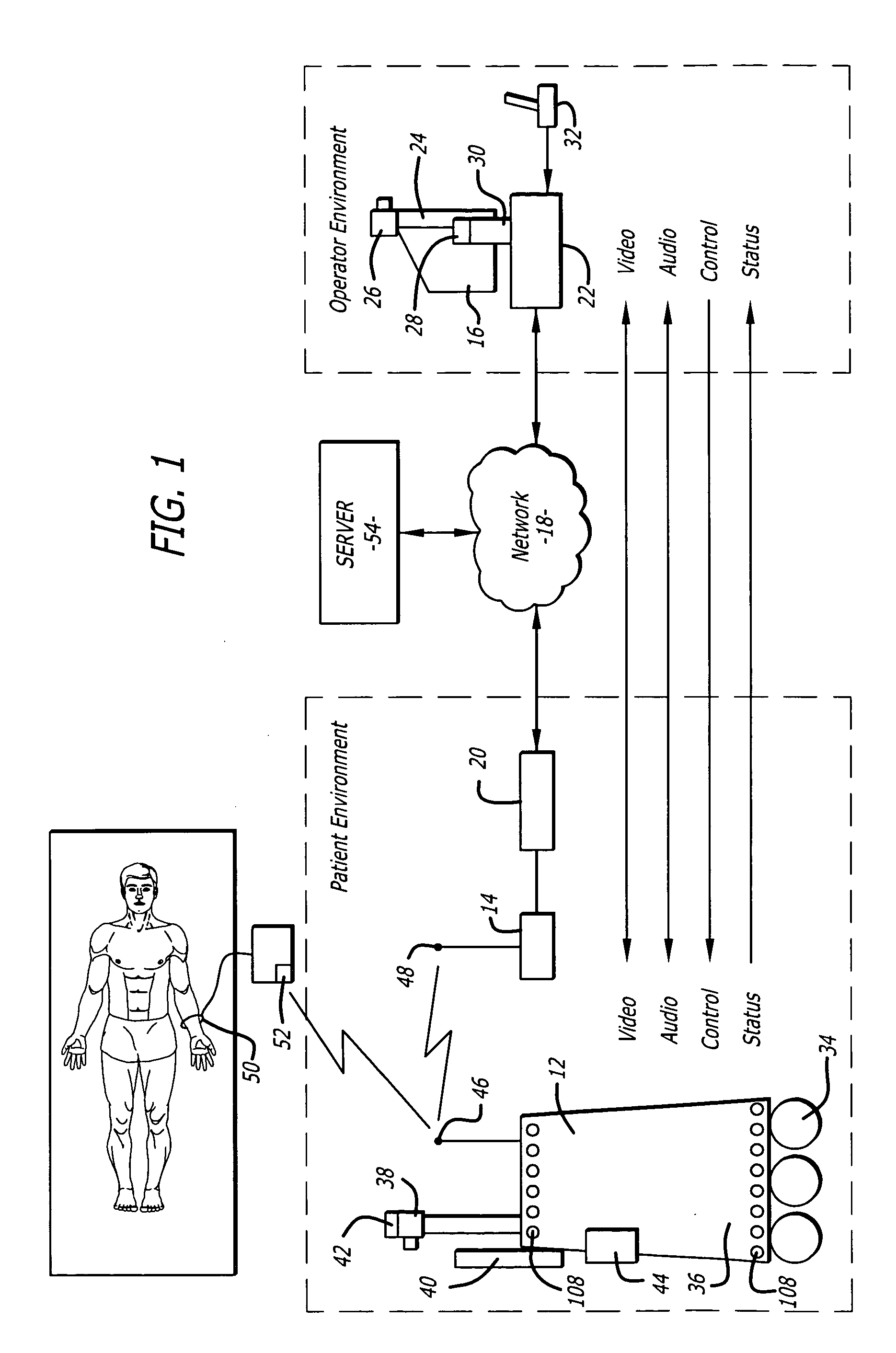
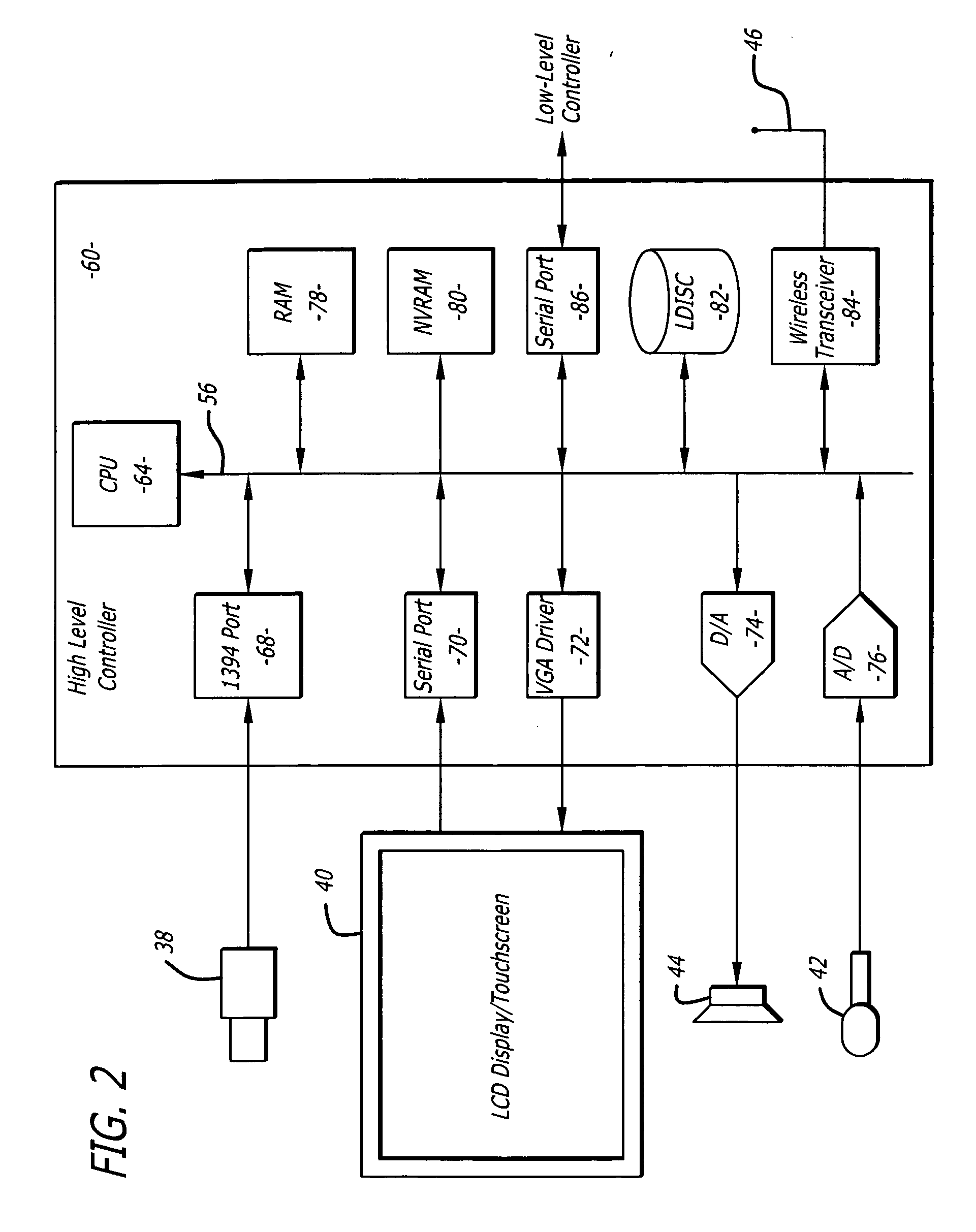
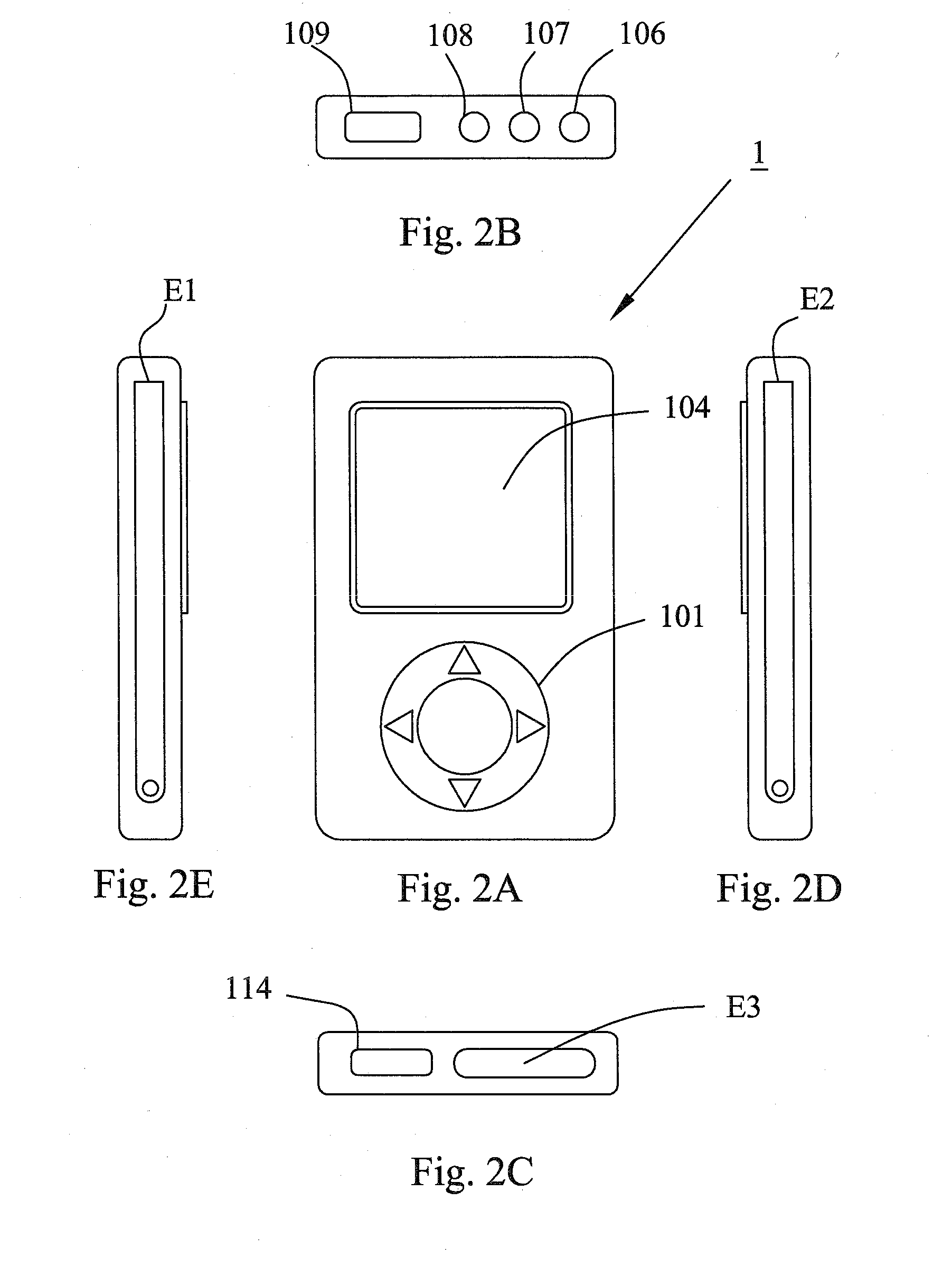
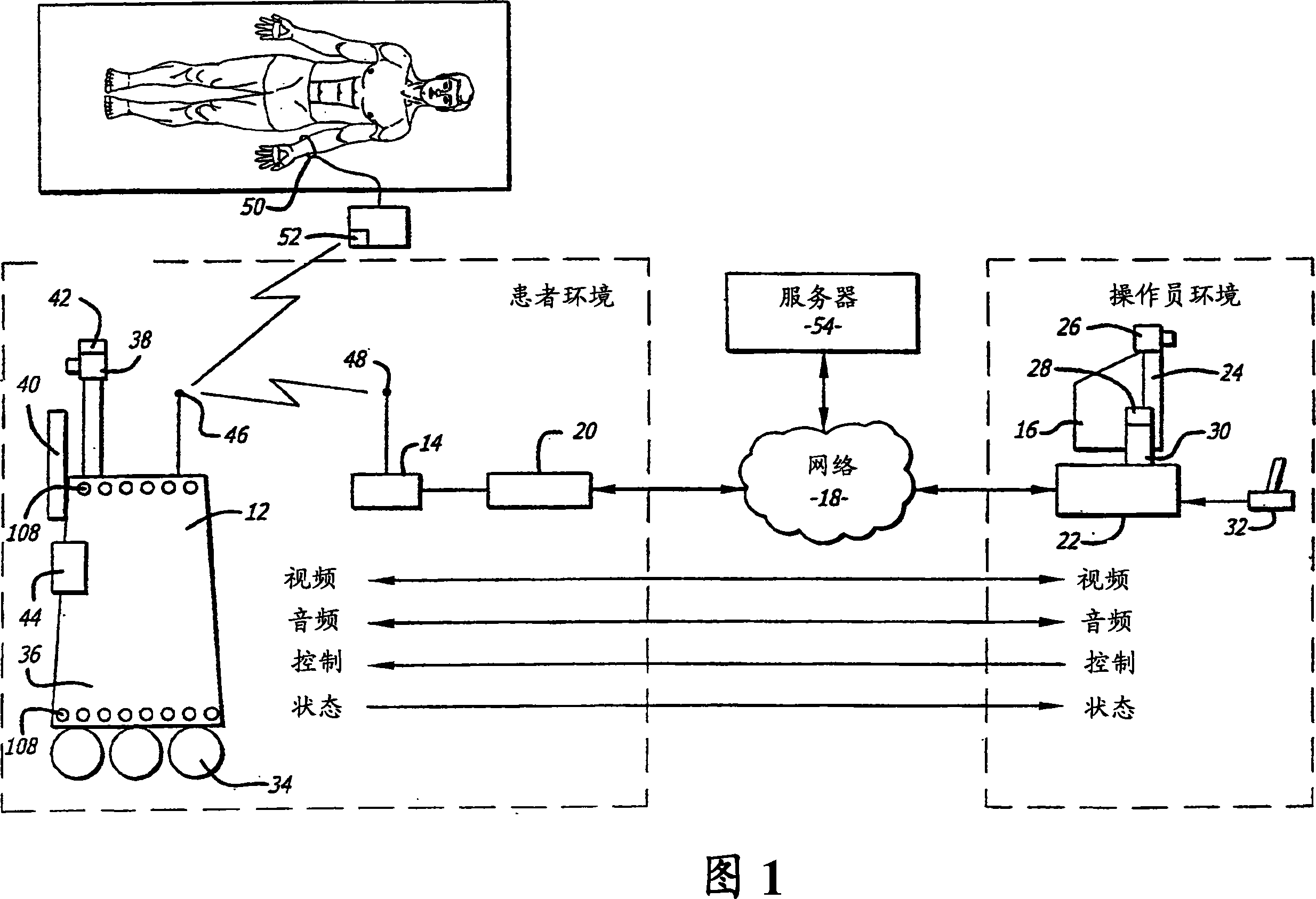
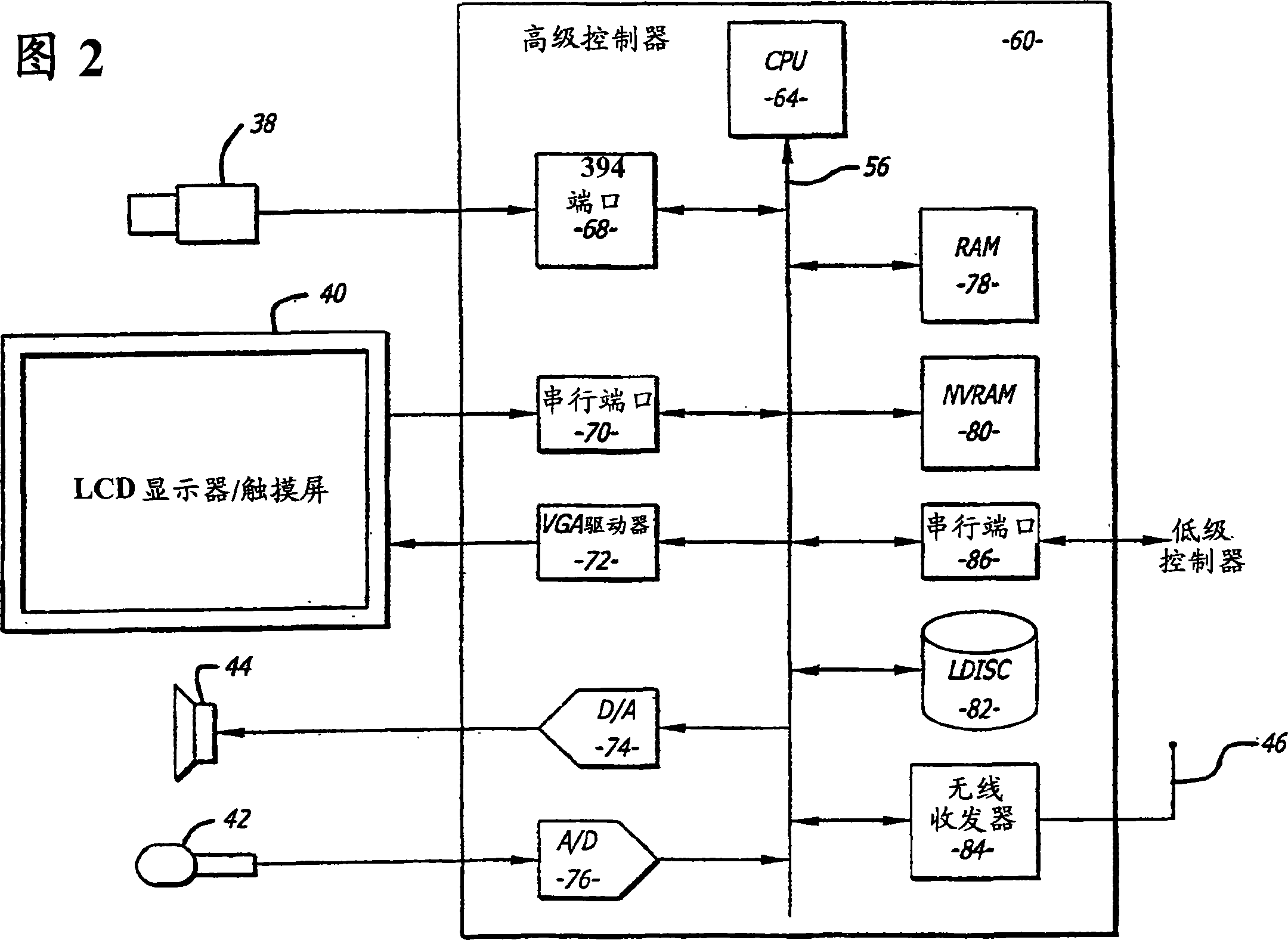
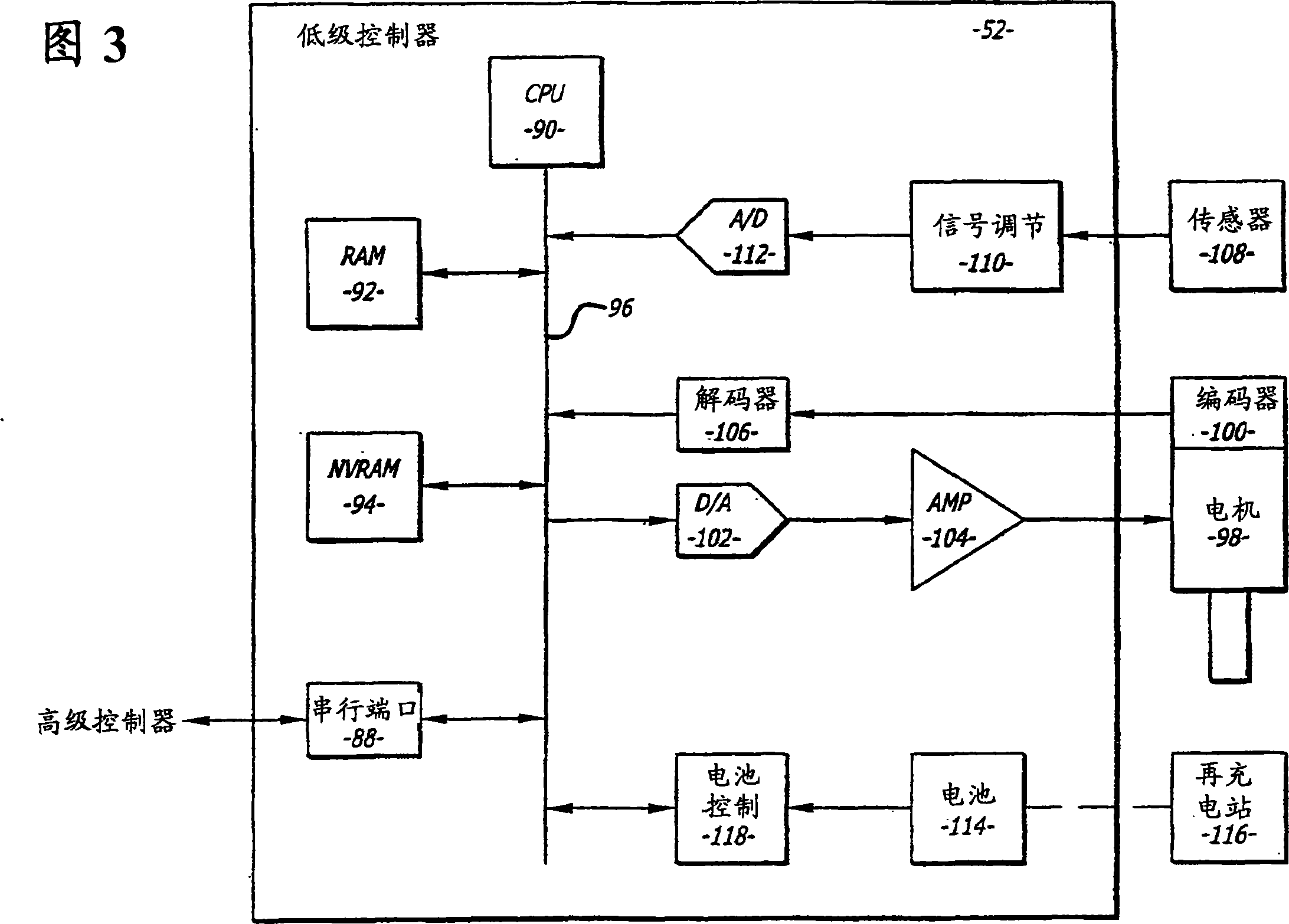
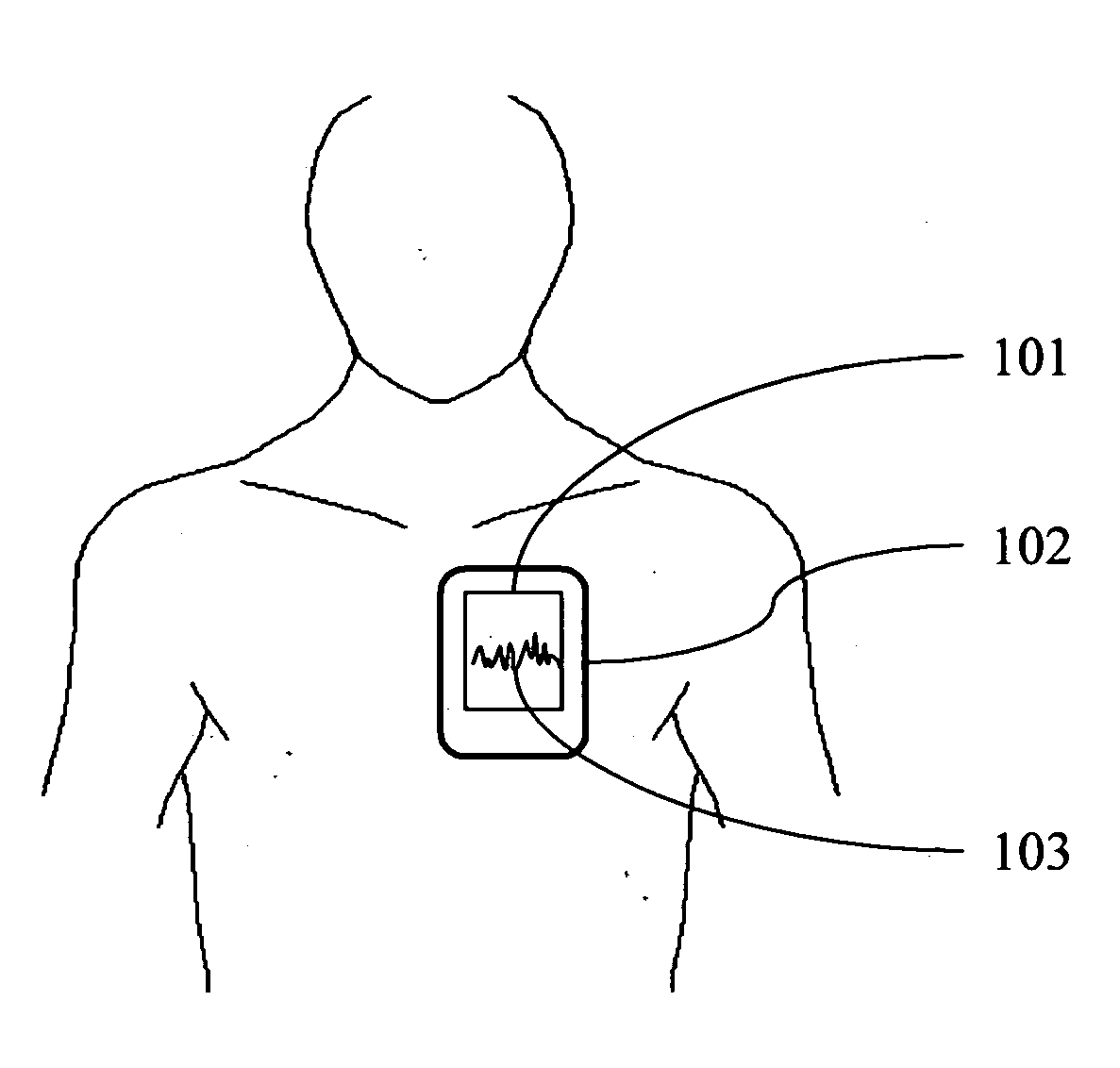
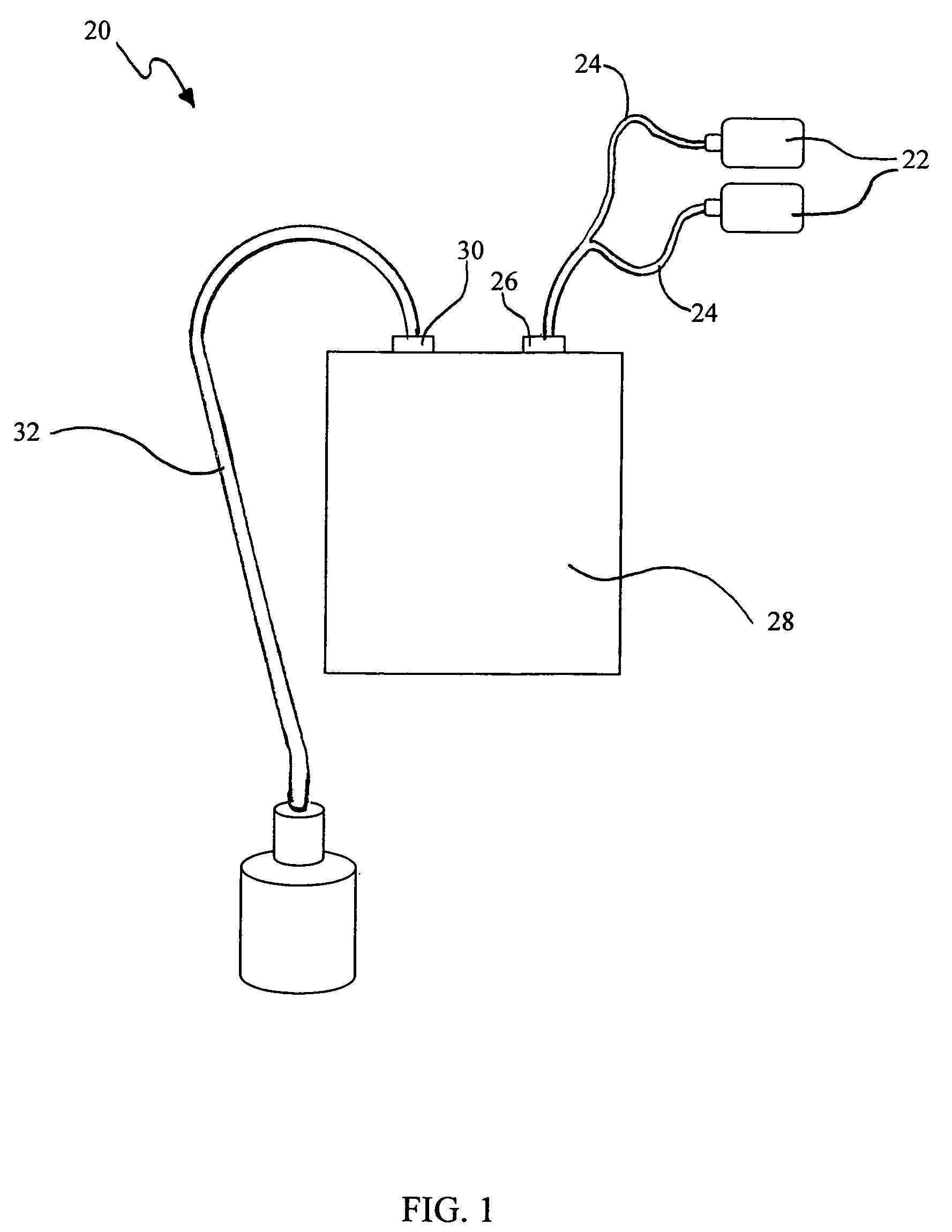
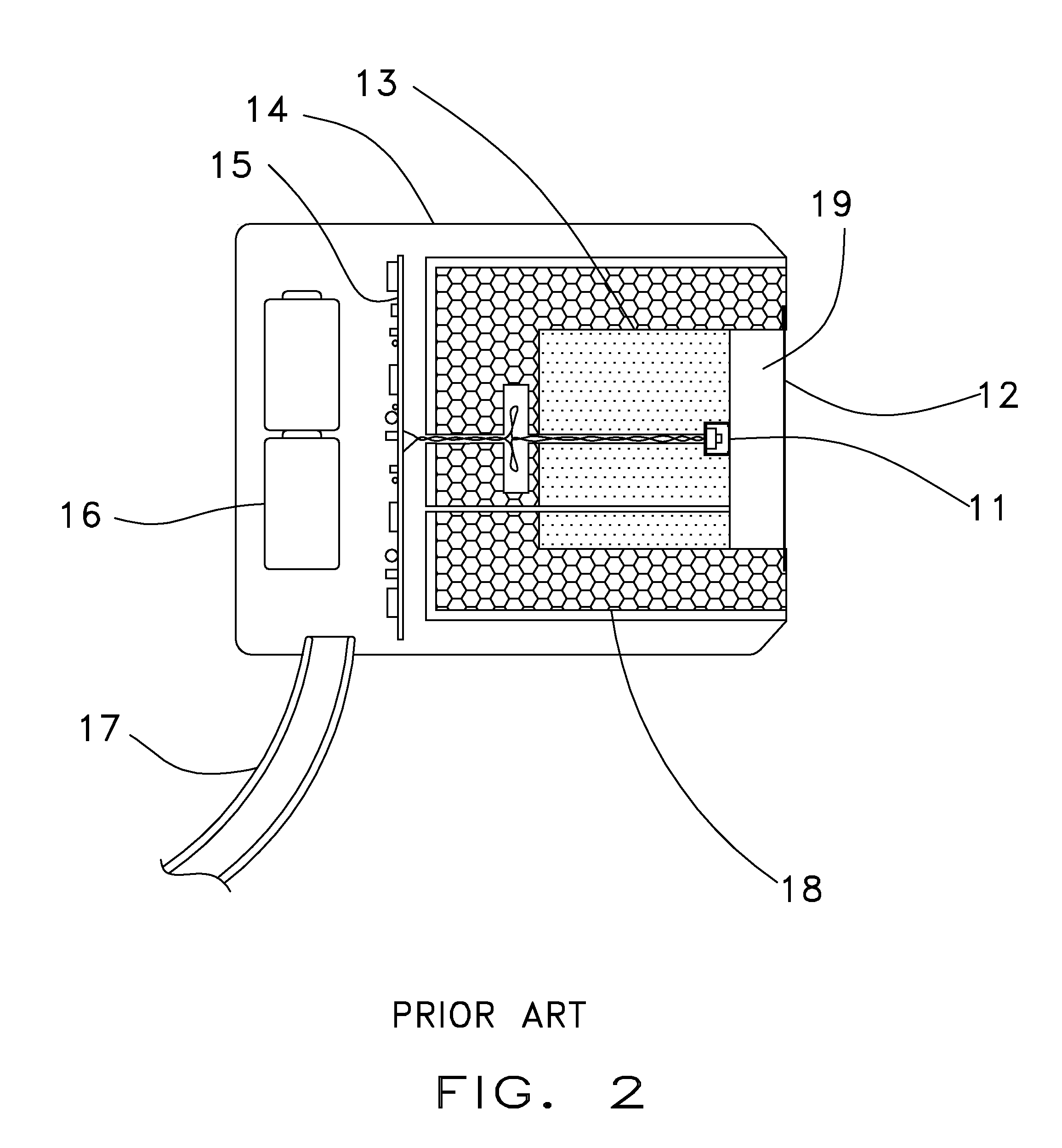
Tele-presence system that allows for remote monitoring/observation and review of a patient and their medical records
A system that includes a mobile platform and a remote station. The remote station may be a personal computer coupled to the remote platform through a broadband network. A user can control movement of the mobile platform through the remote station. A medical monitoring device such as a stethoscope or EKG monitor can be coupled to the mobile platform and used to take patient data. The data can be transmitted to the remote station by the mobile platform. The medical monitoring device(s) may be wirelessly coupled to the mobile platform. The system may include a server that can provide an electronic medical record to the remote station. The remote station may have a monitor that displays the electronic medical record and an image captured by a camera of the mobile platform. The system allows a doctor at the remote station to more fully examine a patient while viewing past medical records.
Owner:JONATA SUB TWO INC +1
High sensitivity noise immune stethoscope
ActiveUS20070165872A1Efficient couplingHigh elastic modulusTransducer detailsStethoscopeEngineeringActive systems
A physiological sensing stethoscope suitable for use in high-noise environments is disclosed. The stethoscope is designed to be substantially matched to the mechanical impedance of monitored physiological activity and substantially mismatched to the mechanical impedance of air-coupled acoustic activity. One embodiment of the stethoscope utilizes a passive acoustic system. Another embodiment utilizes an active Doppler system. The passive and active systems can be combined in one stethoscope enabling switching from a passive mode to an active mode suitable for use in very high-noise environments. The stethoscope is suitable for use in environments having an ambient background noise of 100 dBA and higher. The passive includes a head having a housing, a flexural disc mounted with the housing, and an electromechanical stack positioned between the housing and the flexural disc in contact with the skin of a patient. The active system detects Doppler shifts using a high-frequency transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ACTIVE SIGNAL TECH
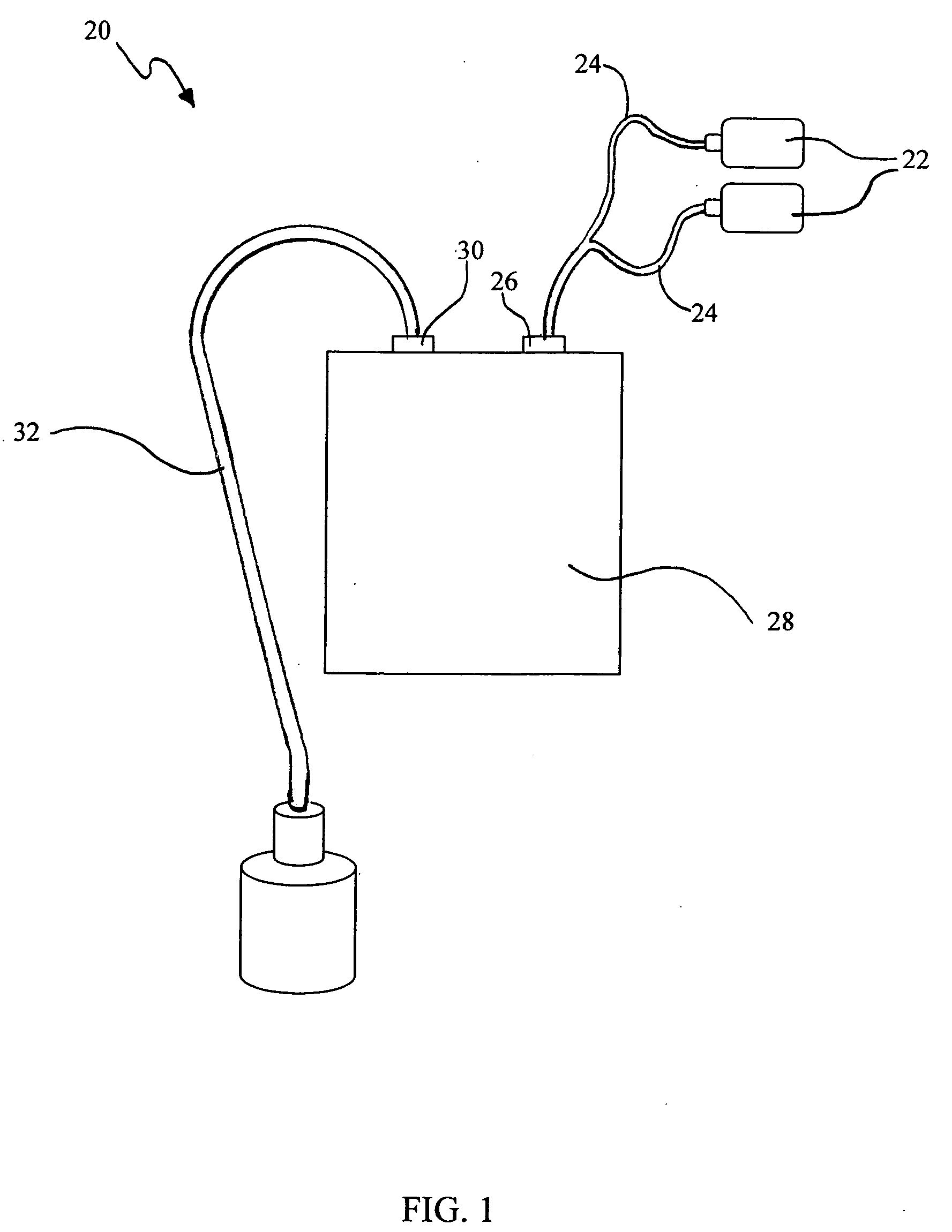
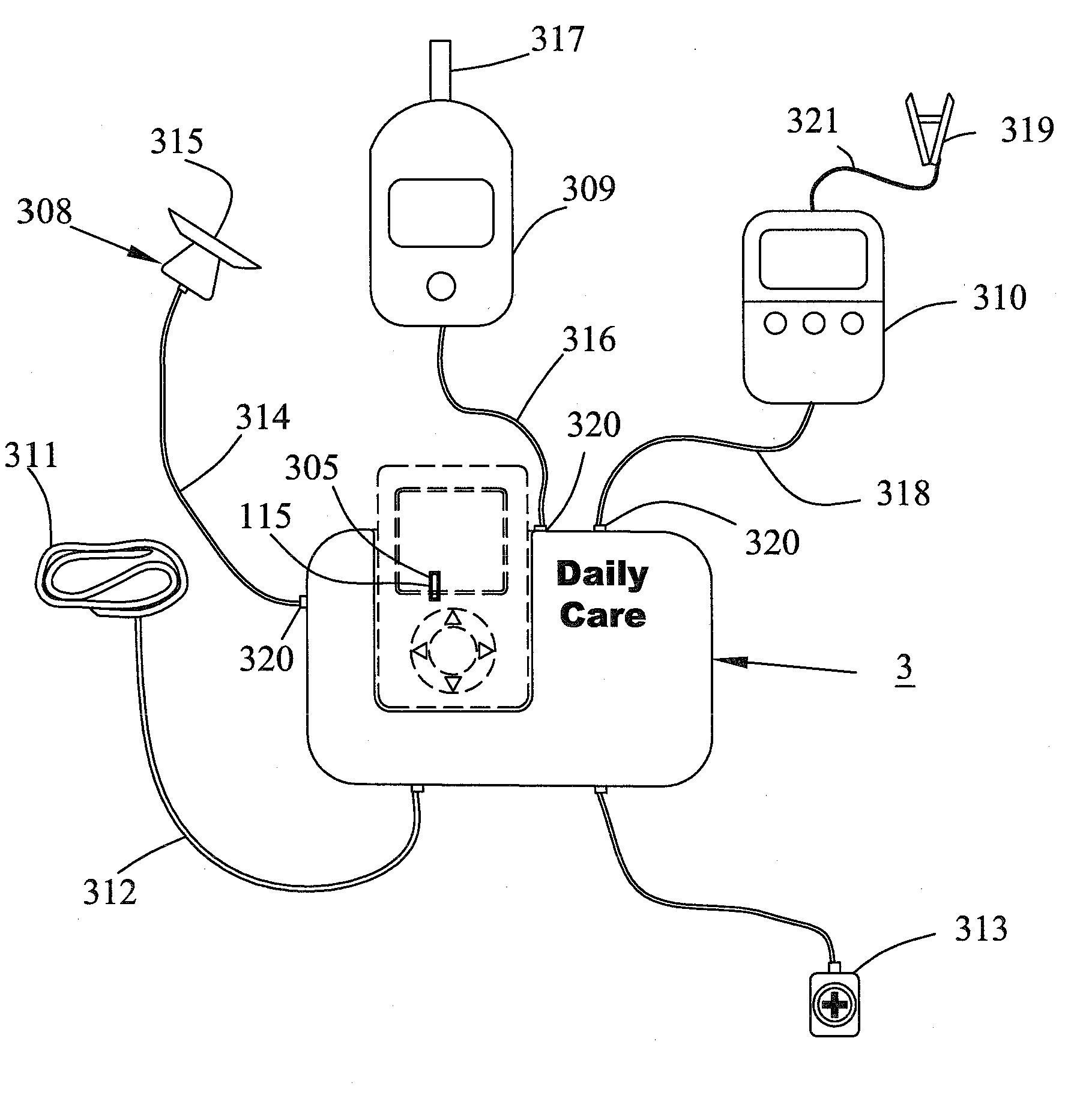
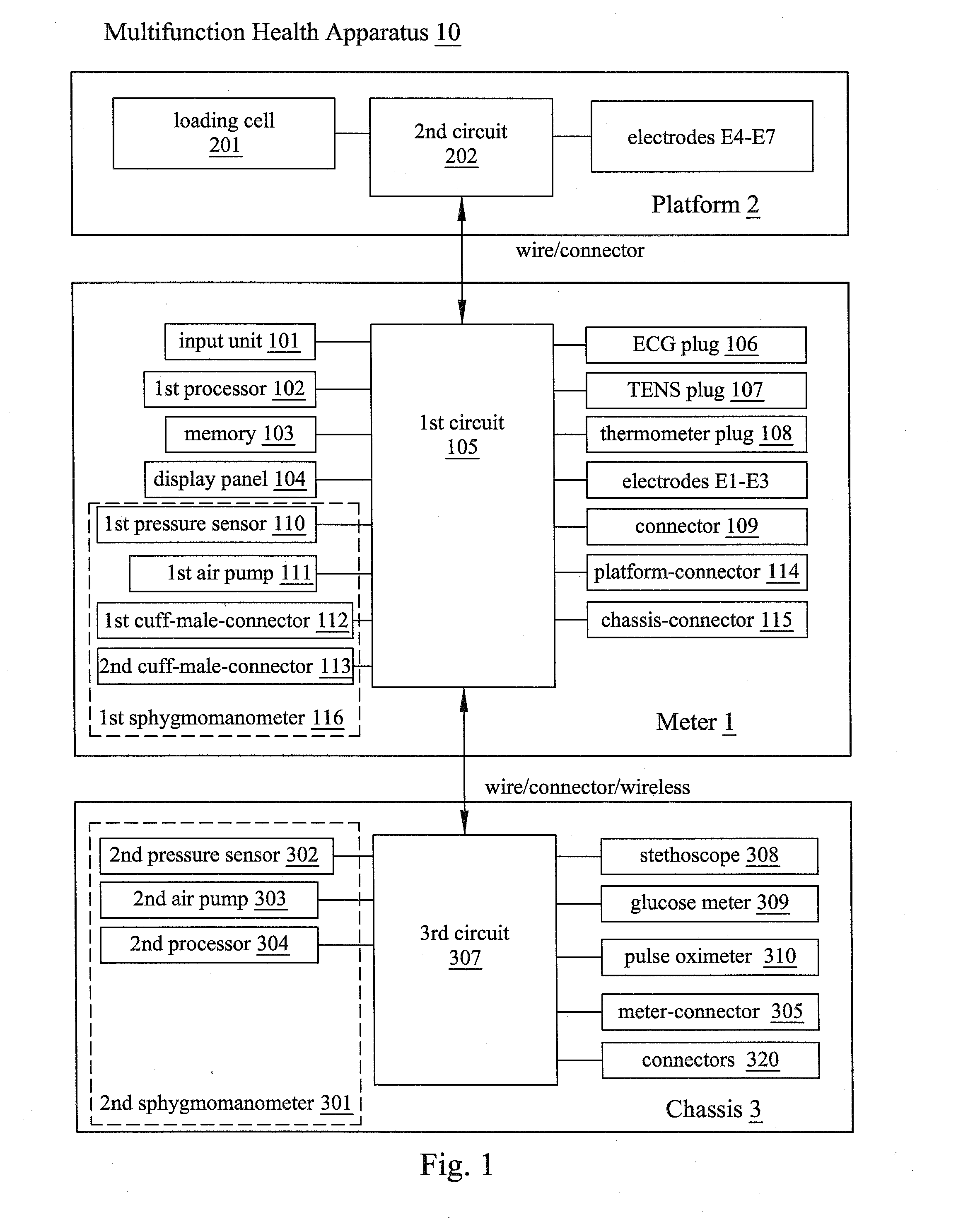
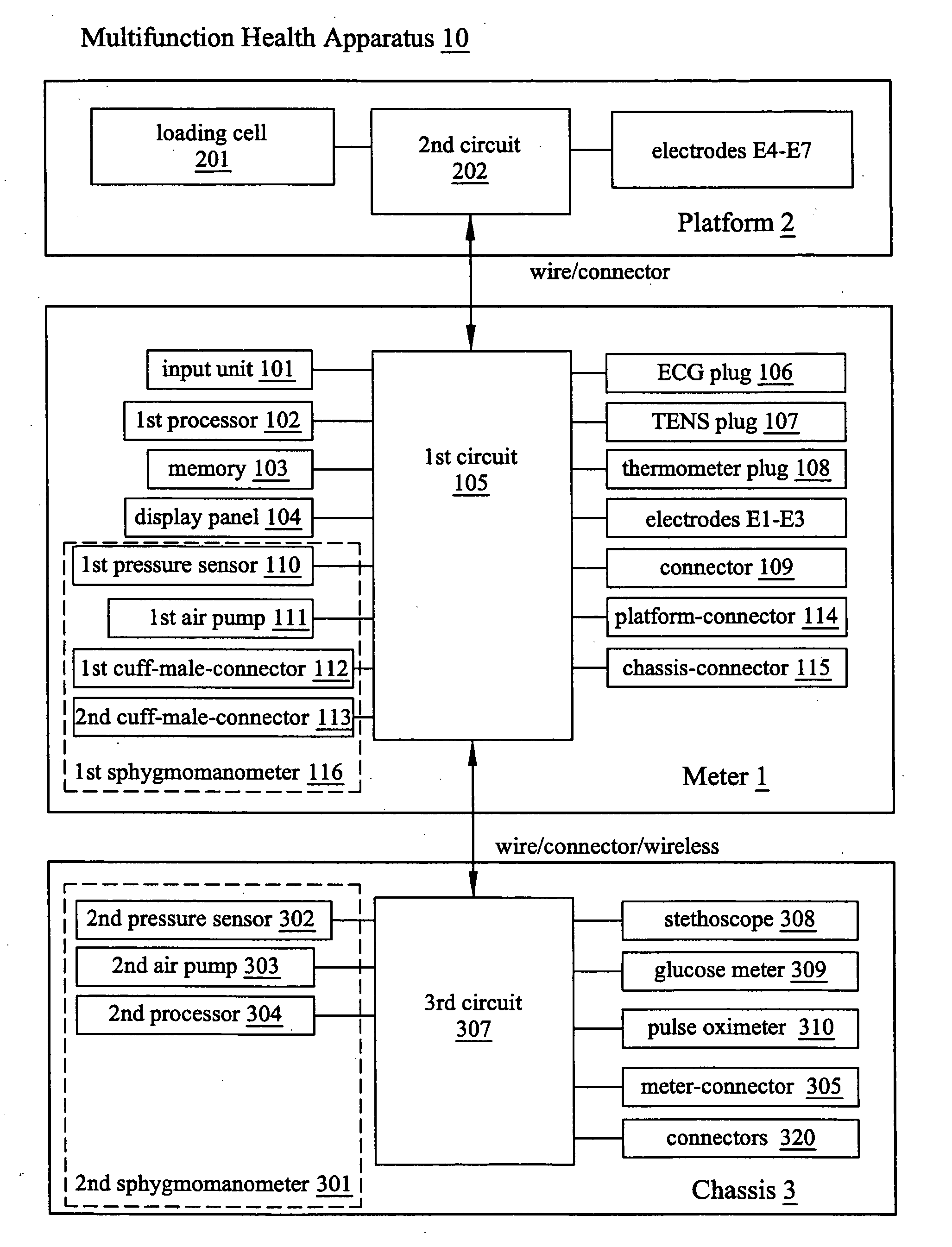
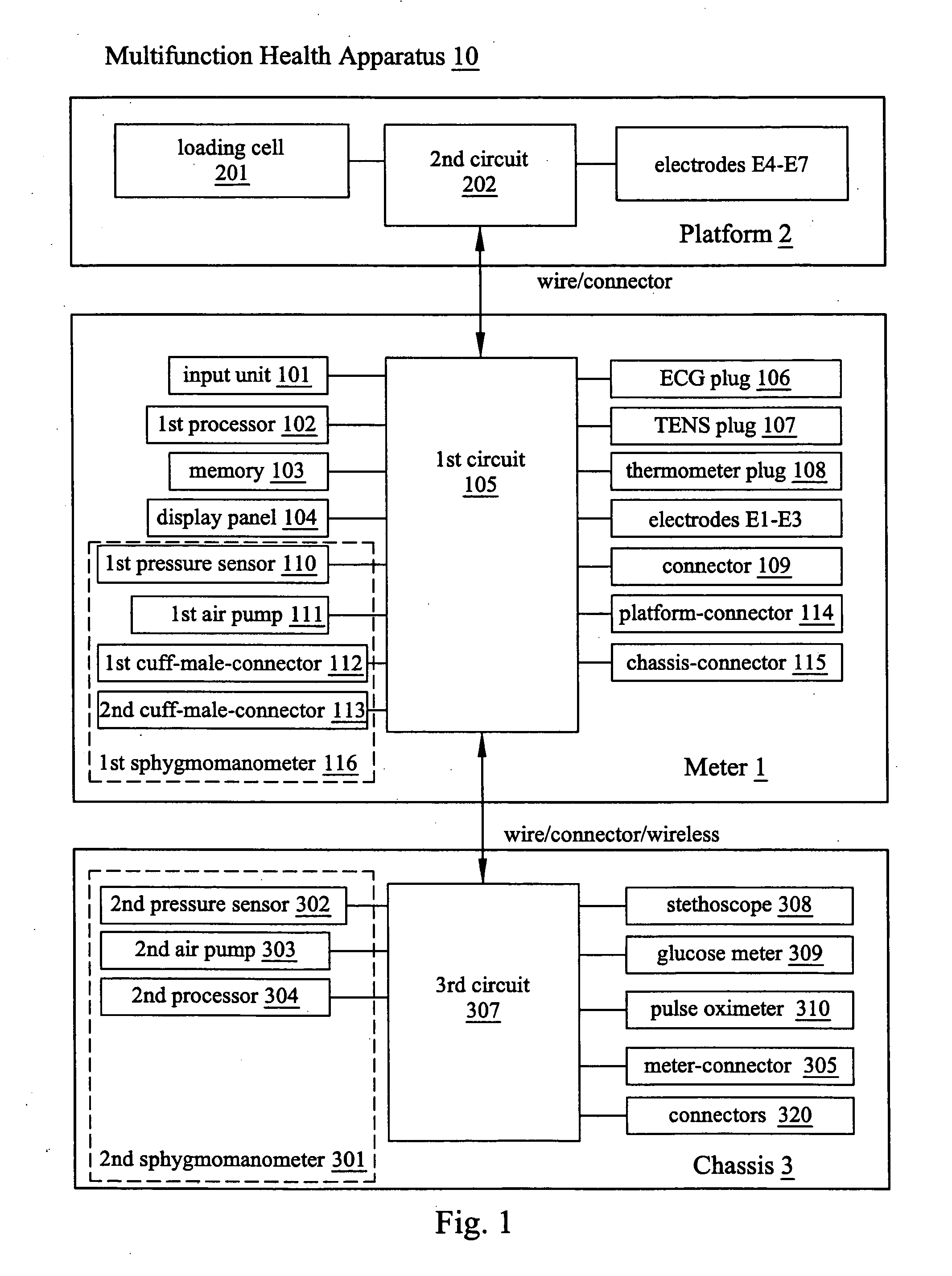
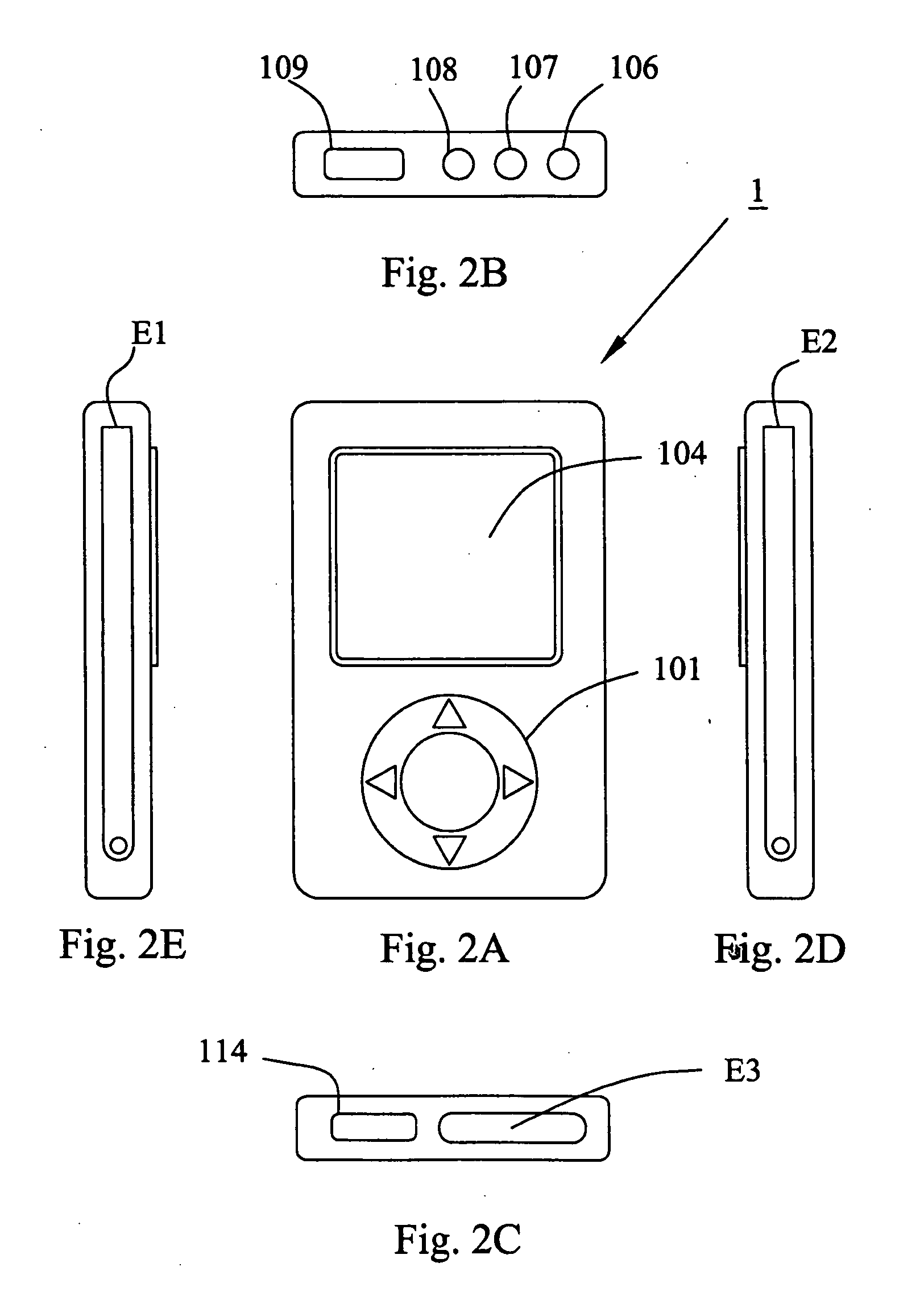
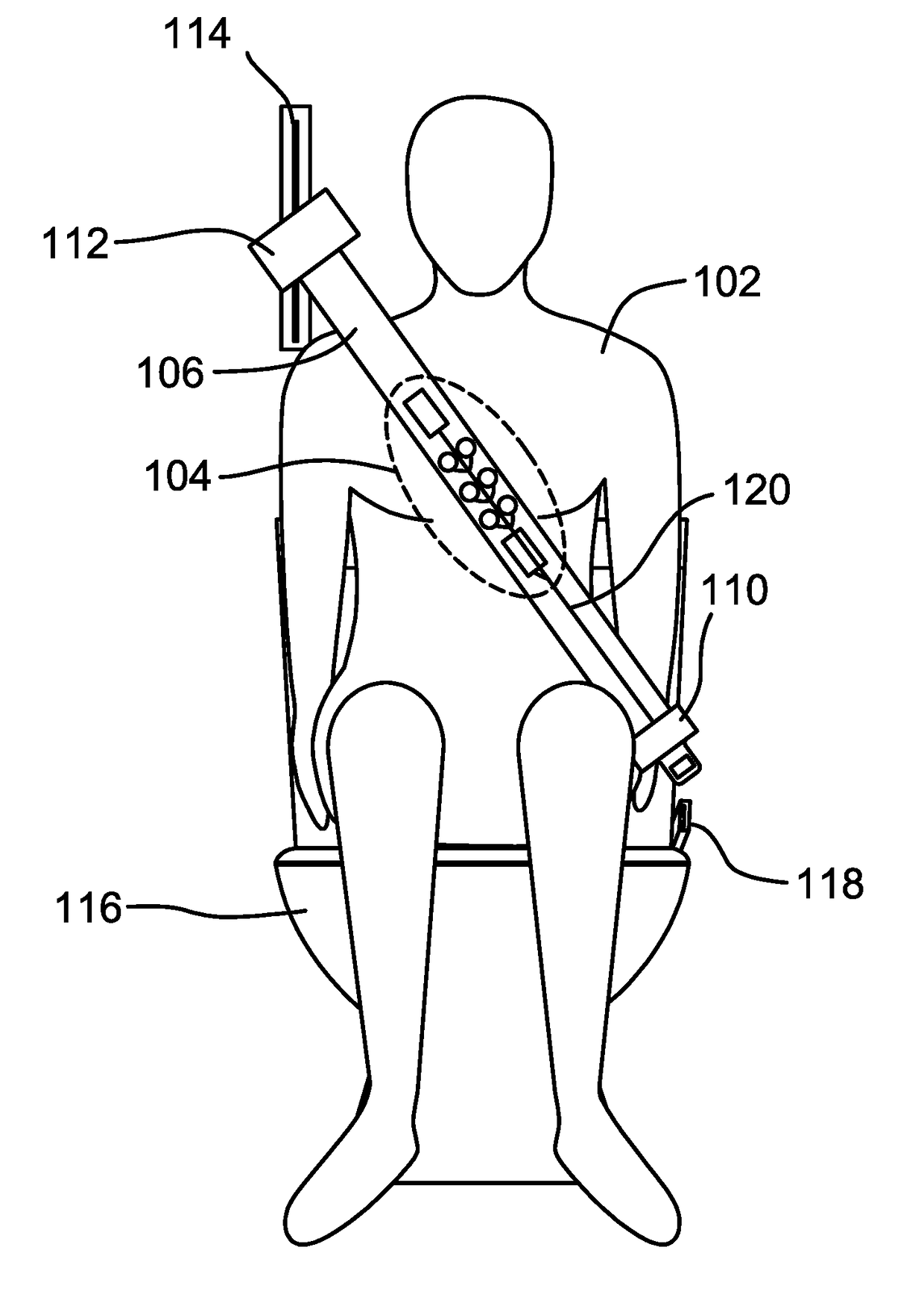
Multifunction health apparatus
InactiveUS20080221404A1Reduce needLow costElectrocardiographySensorsSphygmomanometerGlucose meter device
The present invention provides a multifunction health device, which comprises a meter and a platform. The meter has two electrodes arranged separately at its two sides or both arranged at its one side, and the meter has another electrode arranged in its bottom. The platform has four electrodes arranged in its top face, and a pressure sensor arranged in its inside. With or without some parts assisting, the single use of the meter can function as an ECG detector, a TENS machine, a thermometer, and a first sphygmomanometer. Connecting with the platform, the meter and the platform can function as an ECG detector, a weight scale, and a body composition estimator. Further, the meter can alternatively connect with a chassis thus functioning as a second sphygmomanometer, a stethoscope, a glucose meter, or a pulse oximeter.
Owner:TSO SHUN WUN
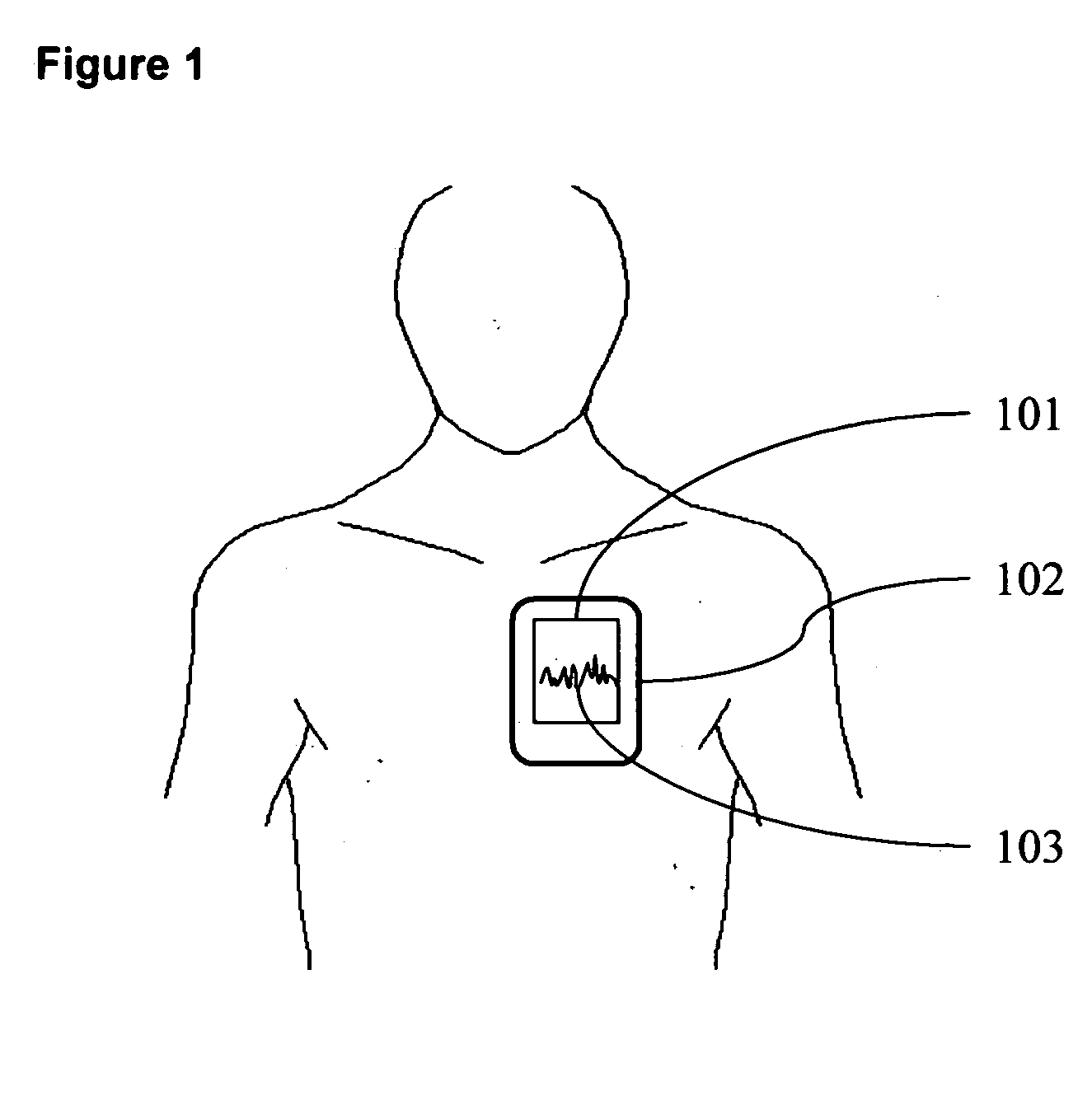
Tele-presence system that allows for remote monitoring/observation and review of a patient and their medical records
A system that includes a mobile platform and a remote station. The remote station may be a personal computer coupled to the remote platform through a broadband network. A user can control movement of the mobile platform through the remote station. A medical monitoring device such as a stethoscope or EKG monitor can be coupled to the mobile platform and used to take patient data. The data can be transmitted to the remote station by the mobile platform. The medical monitoring device(s) may be wirelessly coupled to the mobile platform. The system may include a server that can provide an electronic medical record to the remote station. The remote station may have a monitor that displays the electronic medical record and an image captured by a camera of the mobile platform. The system allows a doctor at the remote station to more fully examine a patient while viewing past medical records.
Owner:INTOUCH TECH
Stethoscope
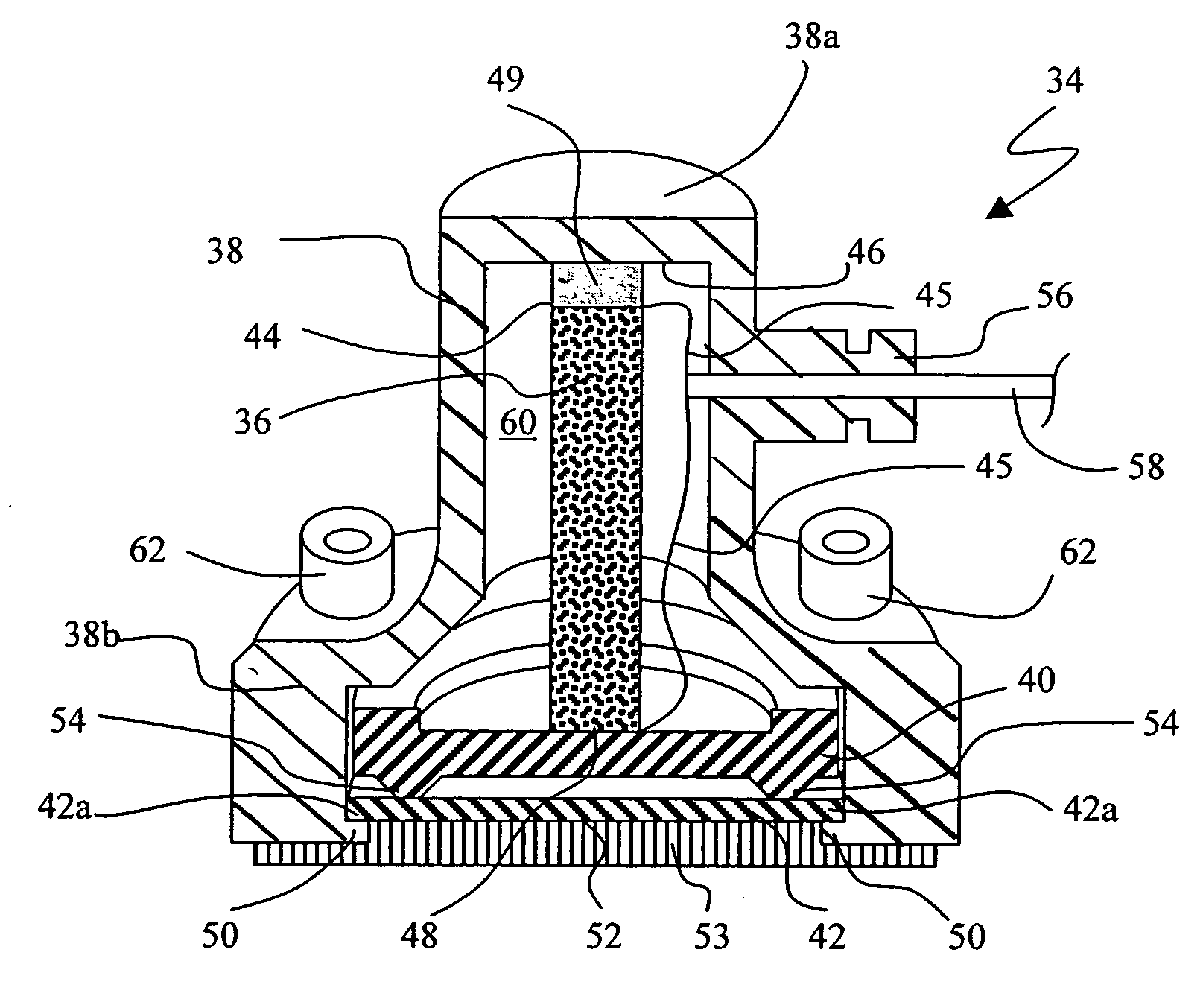
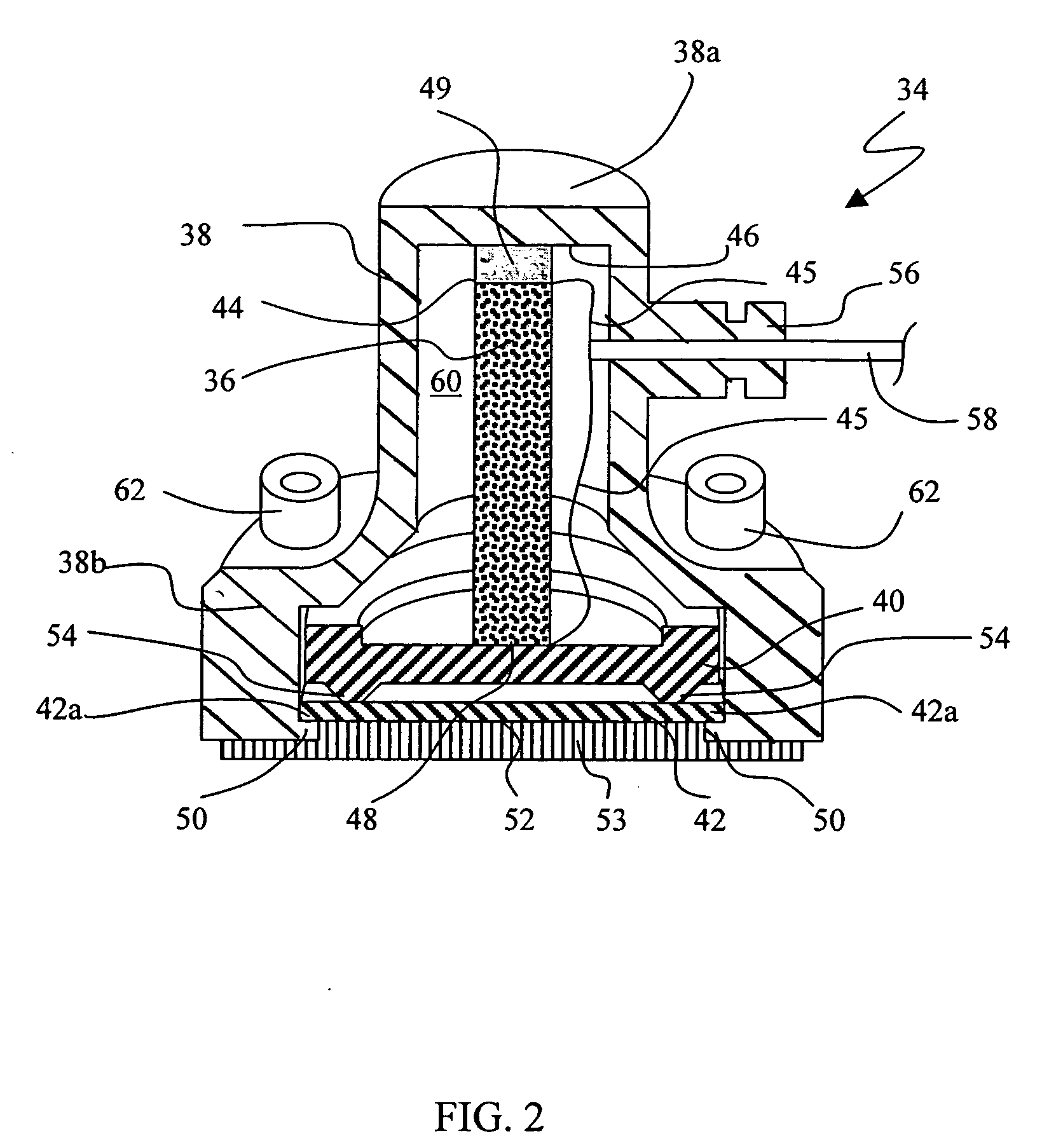
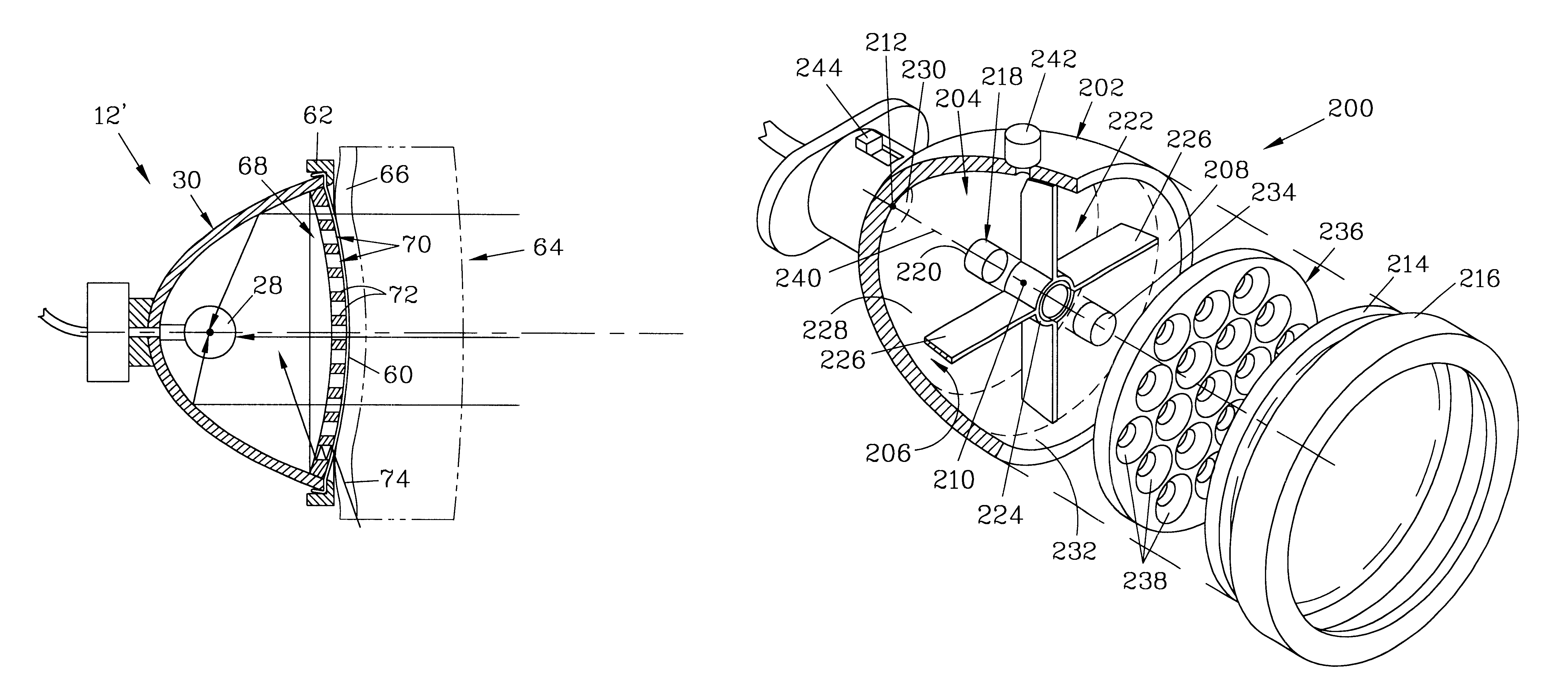
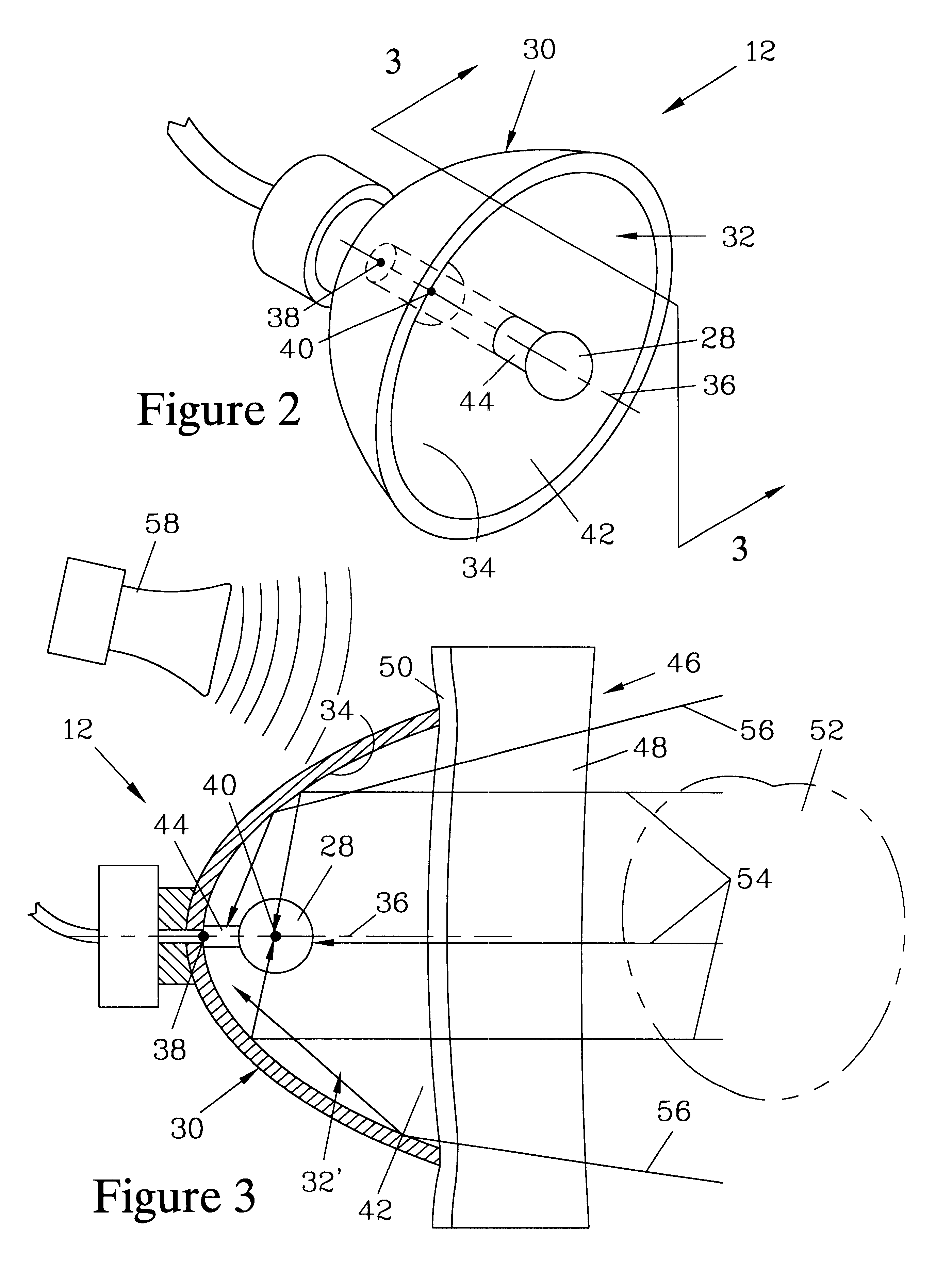
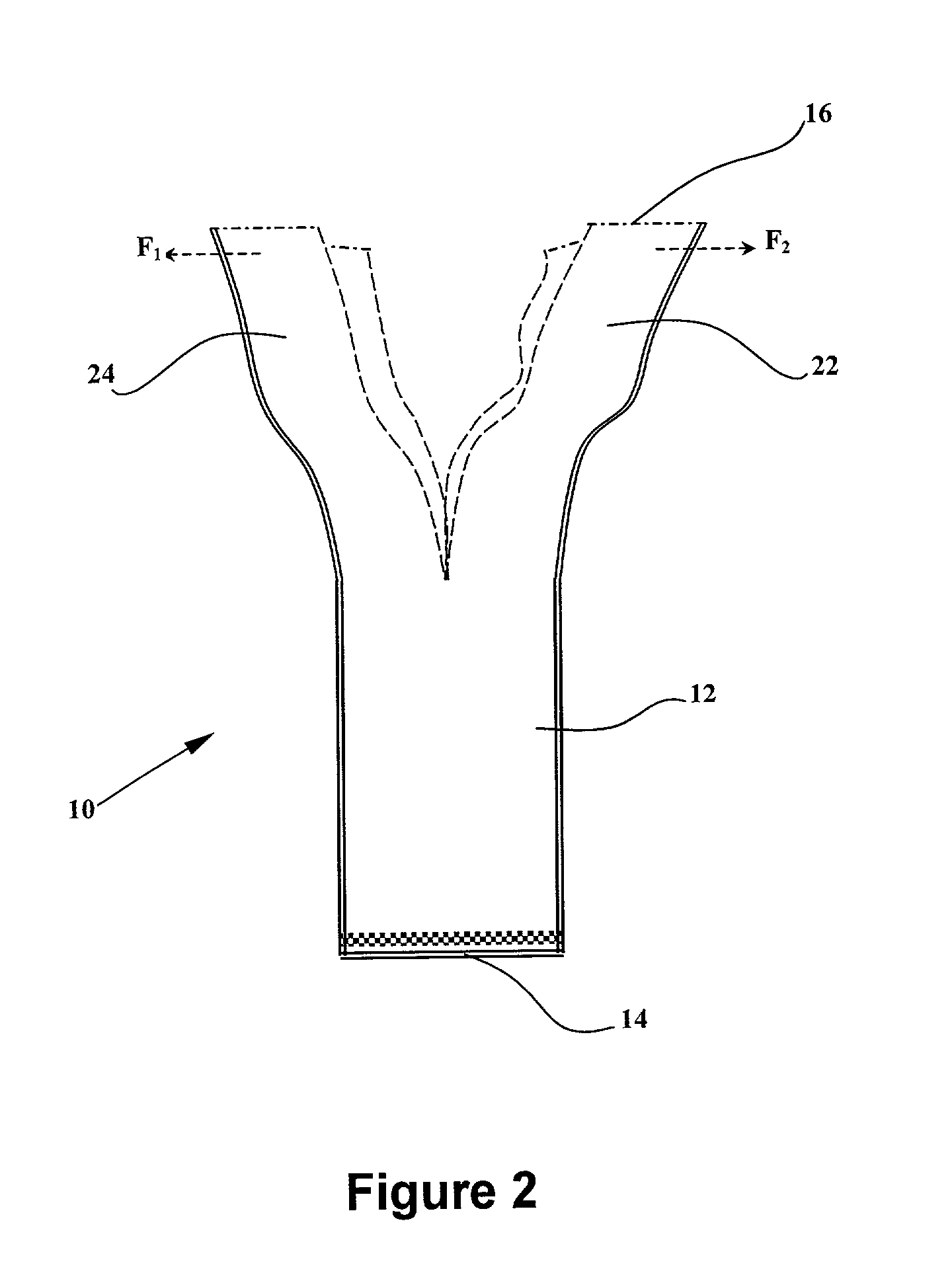
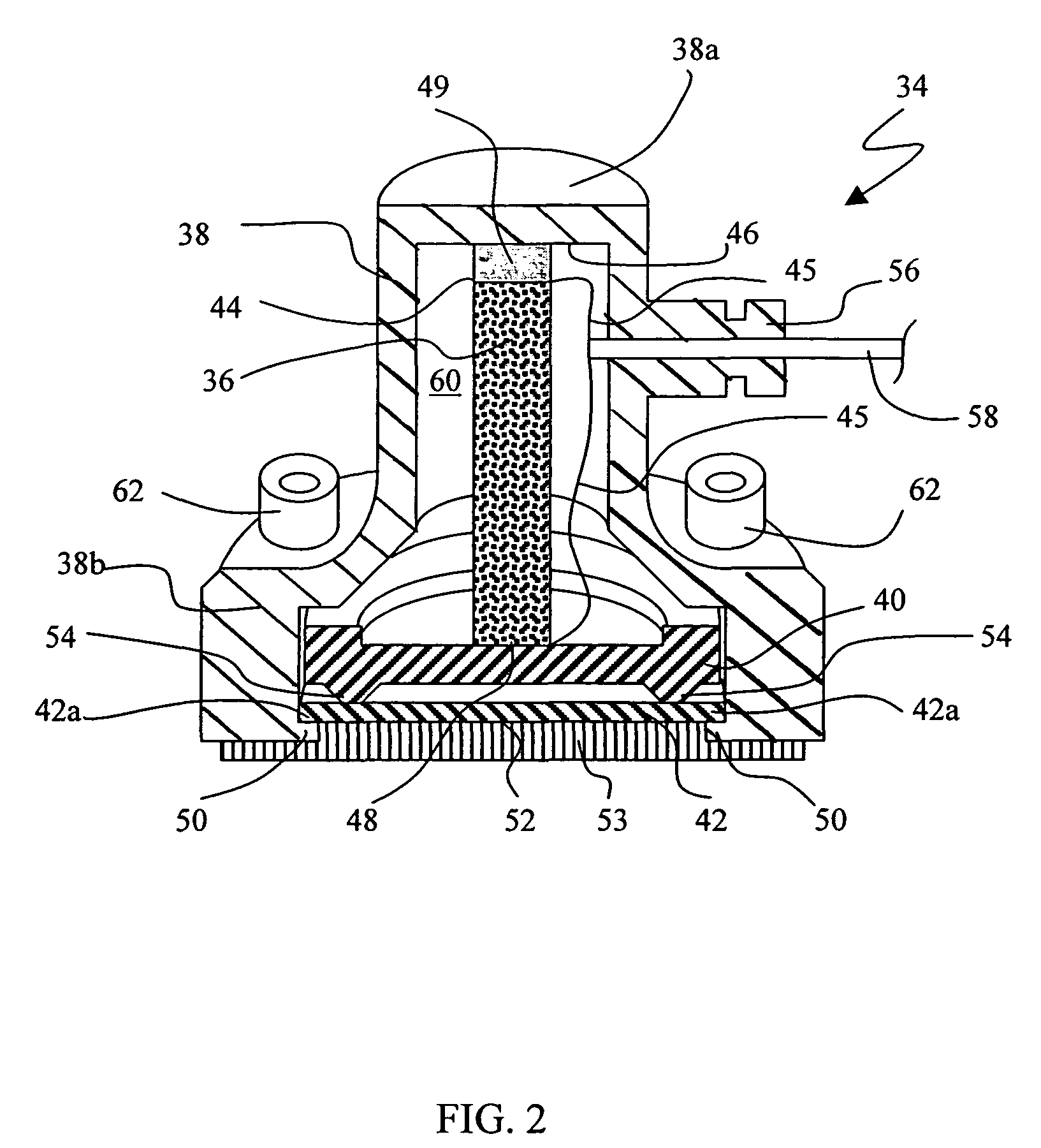
InactiveUS6438238B1Minimize phase differenceImprove directional responseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStethoscopeTransducerAcoustic wave
A chest piece for a stethoscope has a housing with a cavity. The cavity has a cavity surface which is paraboloid in shape, having an apex, an axis, and a focal point. The cavity terminates at the apex and an opening, and the focal point resides in the cavity. A transducer is positioned at the focal point. The parabolic shape of the cavity surface acts to reflect sound waves transmitted normal to the opening to the transducer, while reflecting other sound waves. A mechanical wave guide with a series of parallel passages preferably extends across the opening. Preferably, a membrane with a convex surface covers the opening. The cavity is preferably filled with a liquid or gel having physical characteristics similar to human flesh. To reduce noise from motion of the chest piece across the skin, the stethoscope can be activated by a pressure switch responsive to fluid pressure inside the cavity.
Owner:CALLAHAN MR MATTHEW G
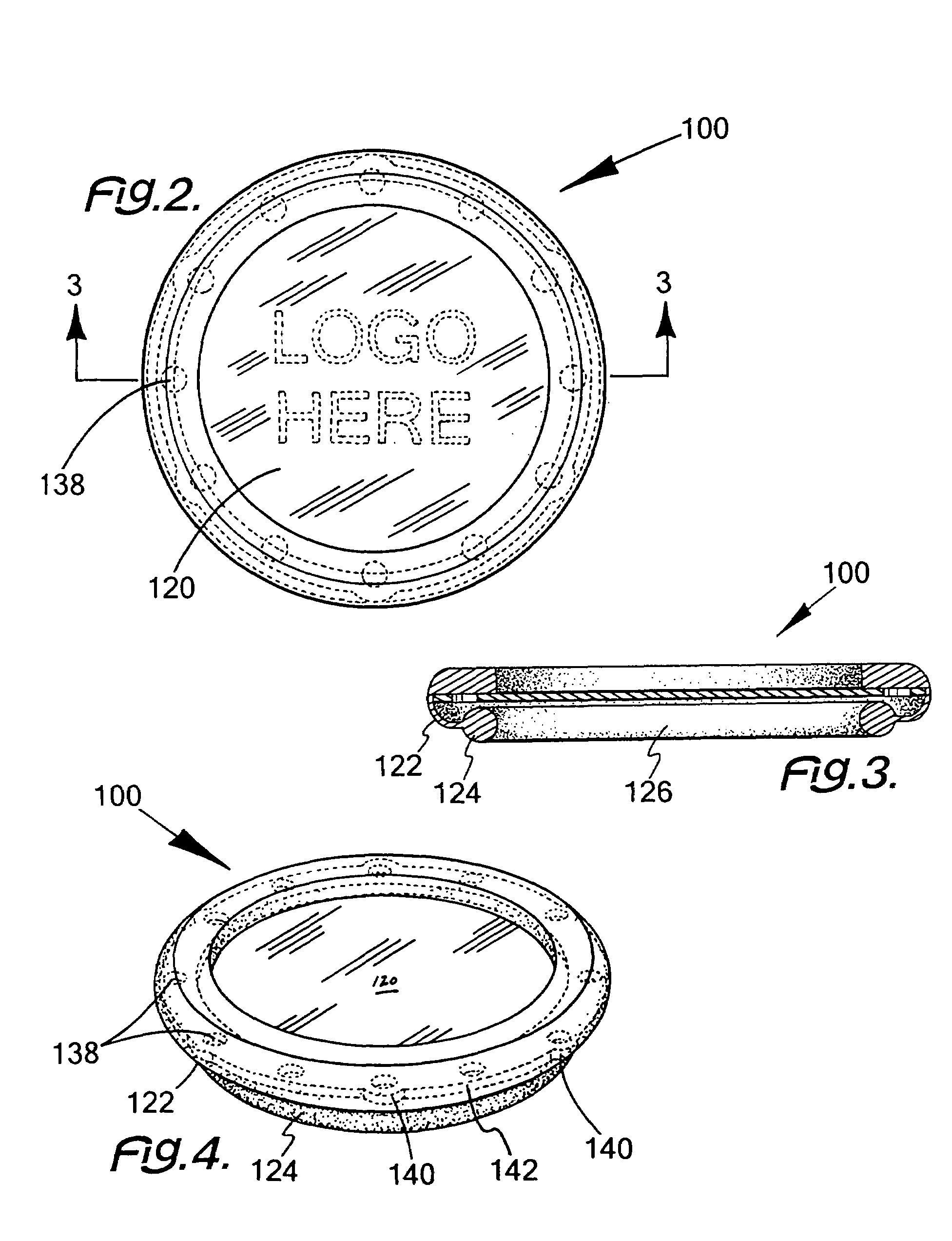
Stethoscope cleansing unit and business method for providing advertising through the use of stethoscope cleansing unit
InactiveUS20050214185A1The process is convenient and fastHighly practicalOther printing matterSurgeryMedical productPatient assessment
The invention is of a stethoscope cleansing unit and of the use of the stethoscope cleansing unit as a novel business method for promoting a marketer's logo and advertisement to medical personnel and patients in the examining room or hospital. The system attaches such advertisements to a useful and conveniently used stethoscope cleansing unit that will be used by medical personnel to sterilize stethoscope diaphragms between patient assessments, thereby preventing the spread of infectious diseases. This apparatus can be utilized in a novel business method as a way for marketers to distinguish their product from the myriad of others by 1) attracting the attention of busy medical personnel during patient examinations, which is the exact time that medical product marketers would benefit most from such attention; and by 2) attracting the attention of the patient through its presence in the examining room at a time when the patient is typically waiting for attention and has time to notice such advertisements.
Owner:CASTANEDA C ROBERT
Transducer for sensing actual or simulated body sounds
InactiveUS20080219464A1Maintenance characteristicChange capacitanceStethoscopeAcoustic sensorsEngineeringMedical treatment
A transducer system is disclosed for detecting actual or simulated body sounds. An audio signal generation and detection system is disclosed for the purposes of simulating the medical examination of a patient or simulating the listening of sounds seeming to emanate from a live or inanimate body. A signal generator sets up a voltage potential at an electrode physically attached to the body, or electrically connected to a body, thereby setting up a voltage potential on a surface area of the body. An electric field potential sensor or a capacitive electrical sensor placed in proximity to the electrode or body surface then detects the voltage potential. The signals produced by the signal generator can represent heart, lung, bowel or other sounds and the electrical sensor can take the physical form of a listening device such as a stethoscope, thereby creating a simulation of listening to body sounds for medical diagnostic purposes.
Owner:SMITH CLIVE LEONARD
Microphone and communication interface system
InactiveUS20050244020A1Avoid damaging the environmentHigh expiratoryMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsSpeech recognitionCultural practiceHuman body
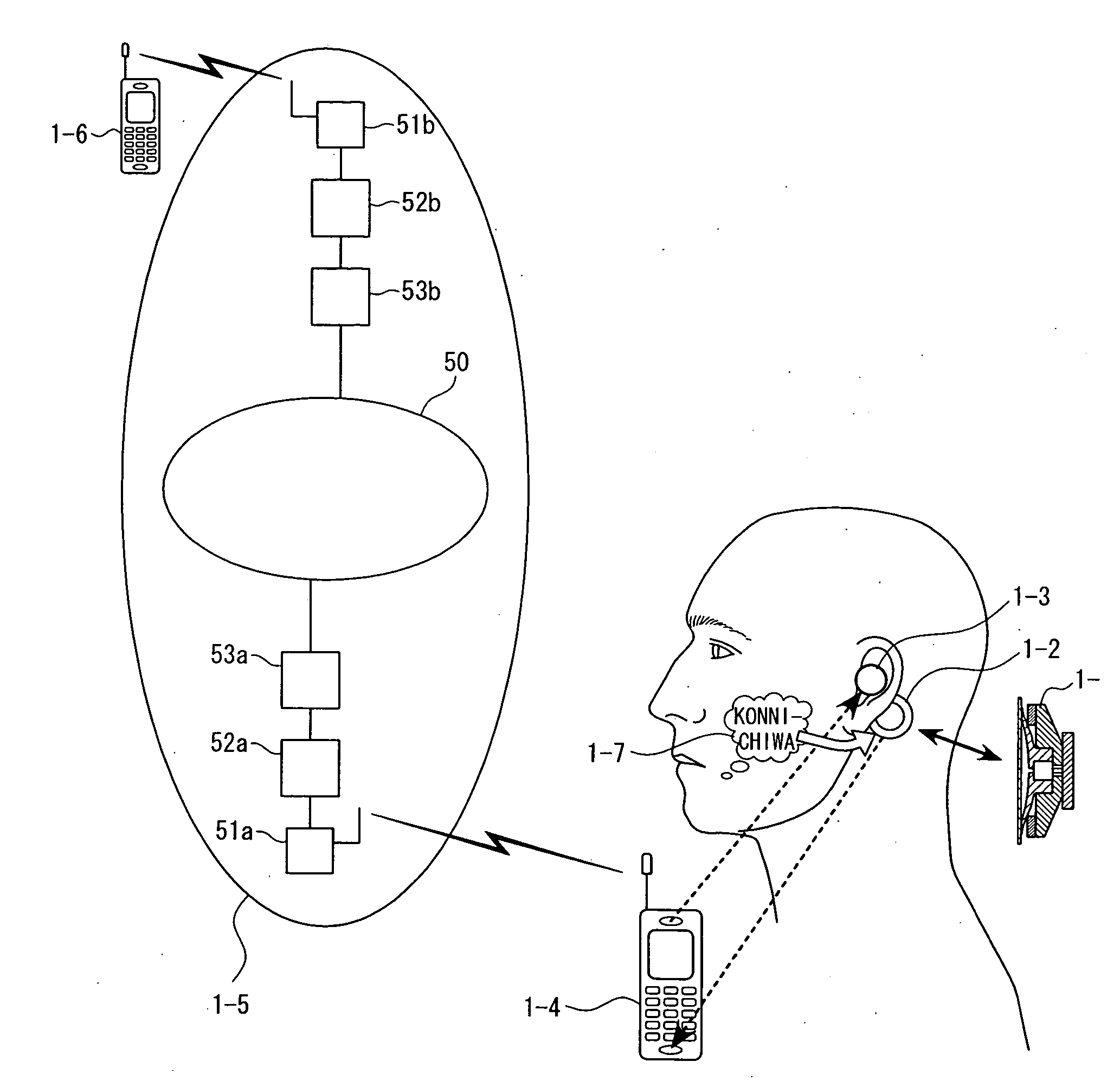
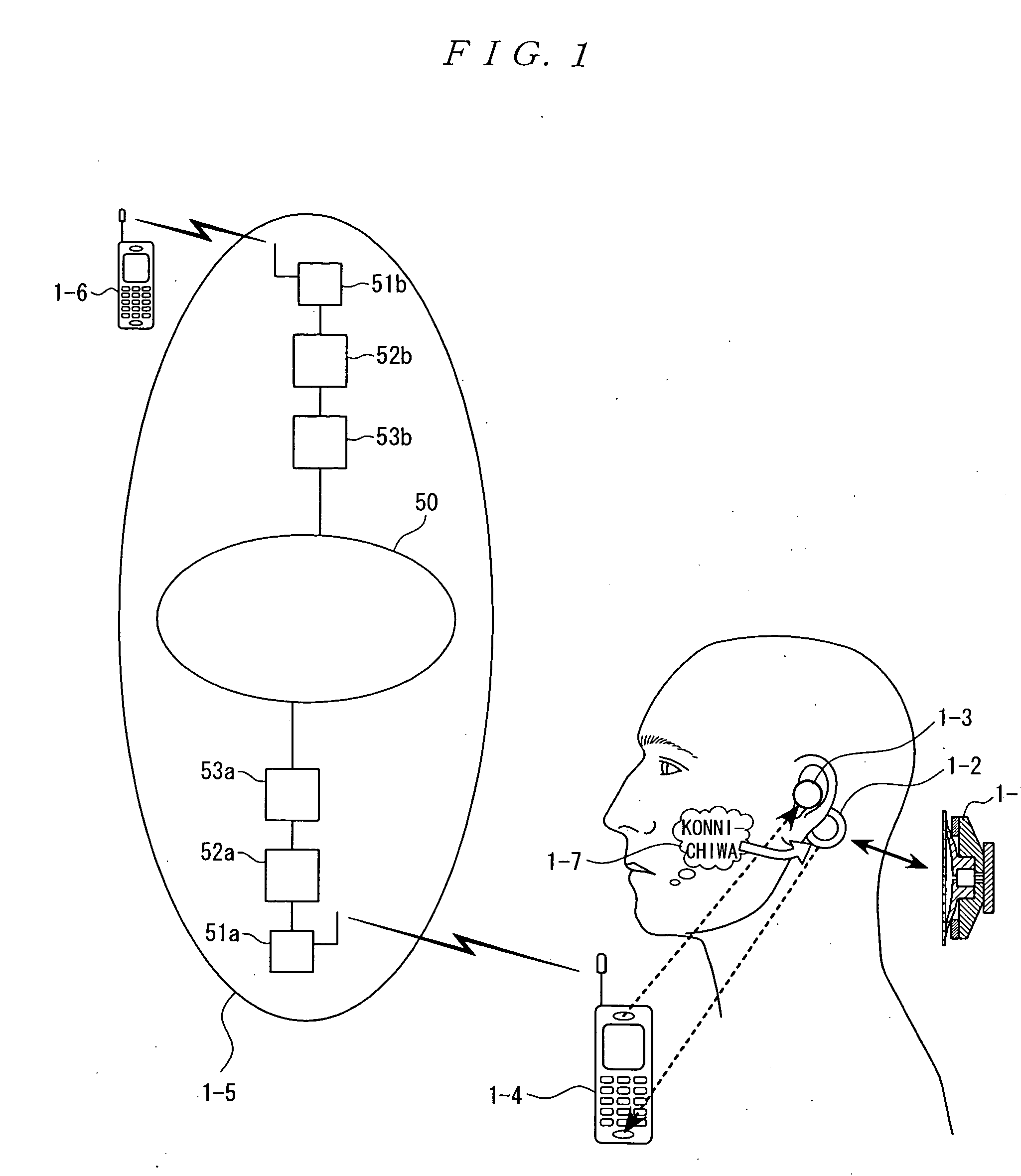
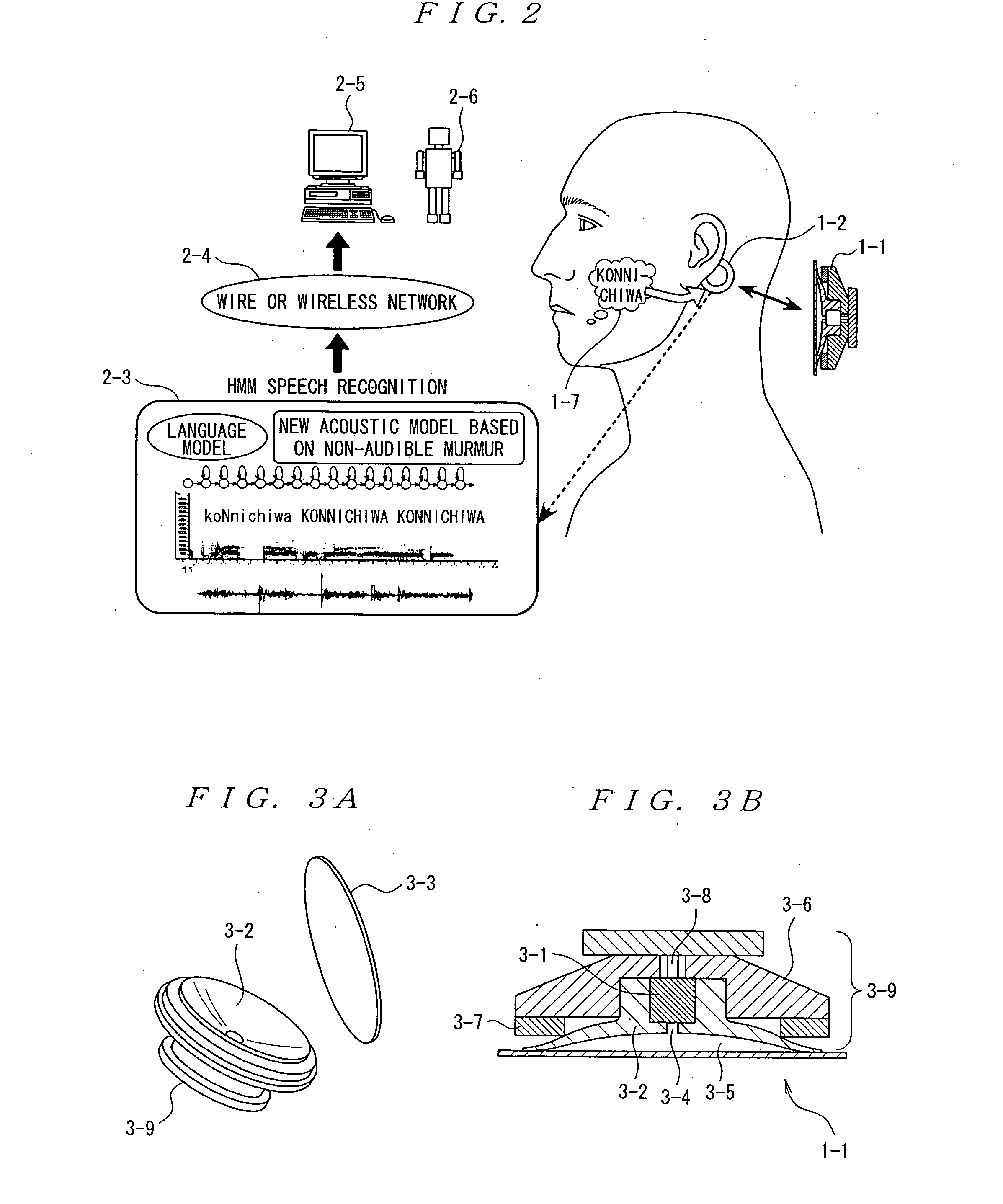
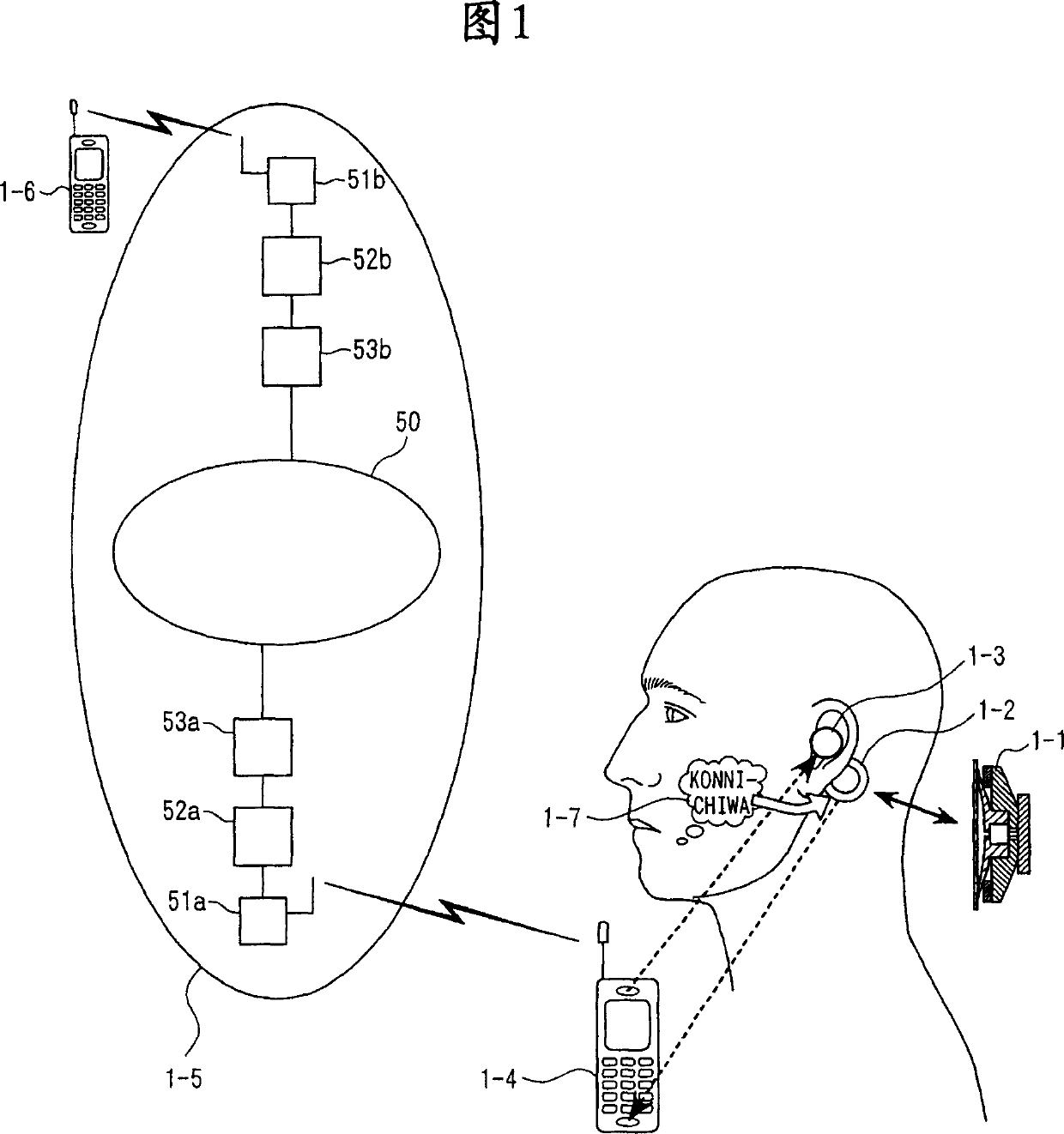
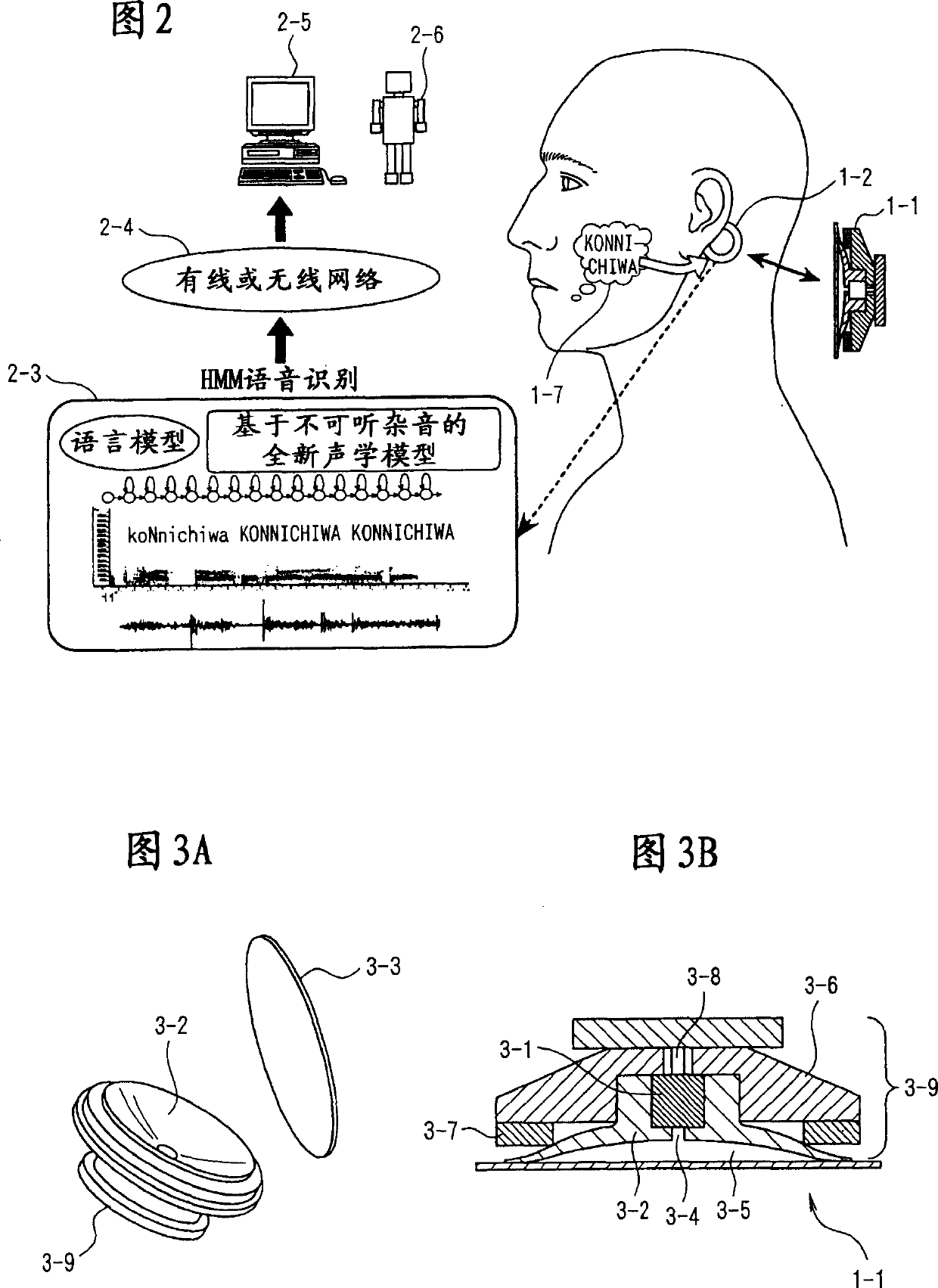
The present invention eliminates the disadvantages of an analysis target used by a cellular phone and speech recognition, that is, a normal sound which is transmitted through the air and which is externally sampled through a microphone, and improves the disadvantages that noise may be mixed or occur in the target, that information may leak, and that corrections are difficult. The present invention also provides a personal portable information terminal realizing new portable terminal communications which do not require training and which conform to the cultural practice of human beings. In the present invention, no apparatus that obtains an analysis target is put off human body, and a normal sound is not an analysis target. A stethoscope-type microphone is installed on the surface of the human skin. Then, a vibration sound is sampled which is obtained when a non-audible murmur articulated in association with speech action (the motion of the mouth) not using the regular vibration of the vocal cords is transmitted through the flesh. A vibration sound obtained when a non-audible murmur amplified is transmitted through the flesh is similar to a whisper. The vibration sound can thus be heard and understood by human beings. Accordingly, the vibration sound can be used for a speech over the cellular phone as it is. Further, when the vibration sound obtained when the non-audible murmur is transmitted through the flesh is analyzed and converted into parameters, a kind of soundless recognition is realized. The present invention replaces the HMM model, conventionally used for speech recognition by an acoustic model created on the basis of a vibration sound obtained when a non-audible murmur is transmitted through the flesh. Therefore, the present invention provides a new method of inputting data to the personal portable information terminal.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
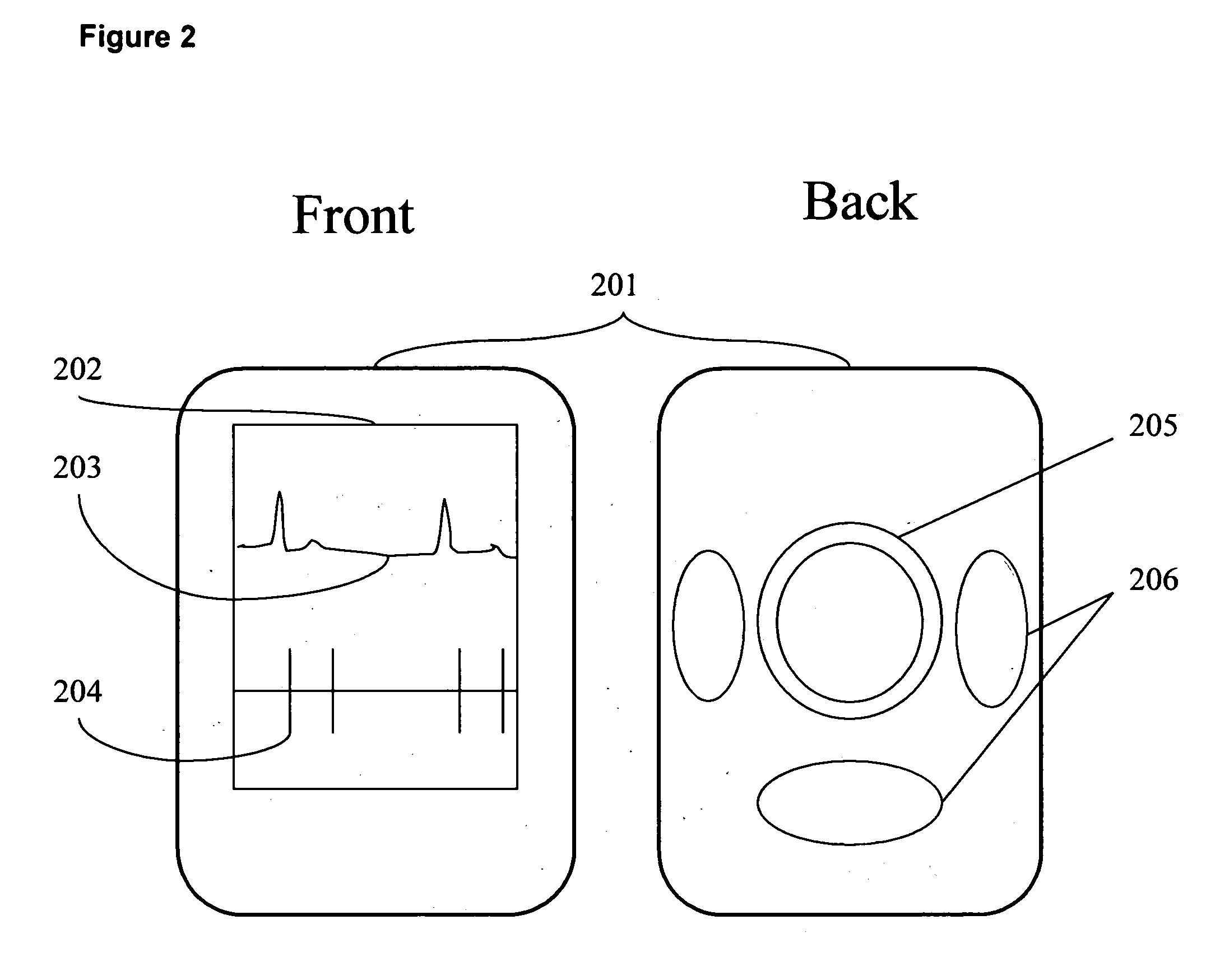
Biometric front-end recorder system
ActiveUS20130116584A1Easy to installEasy to removeElectrocardiographyStethoscopeStethoscopeBiosensor
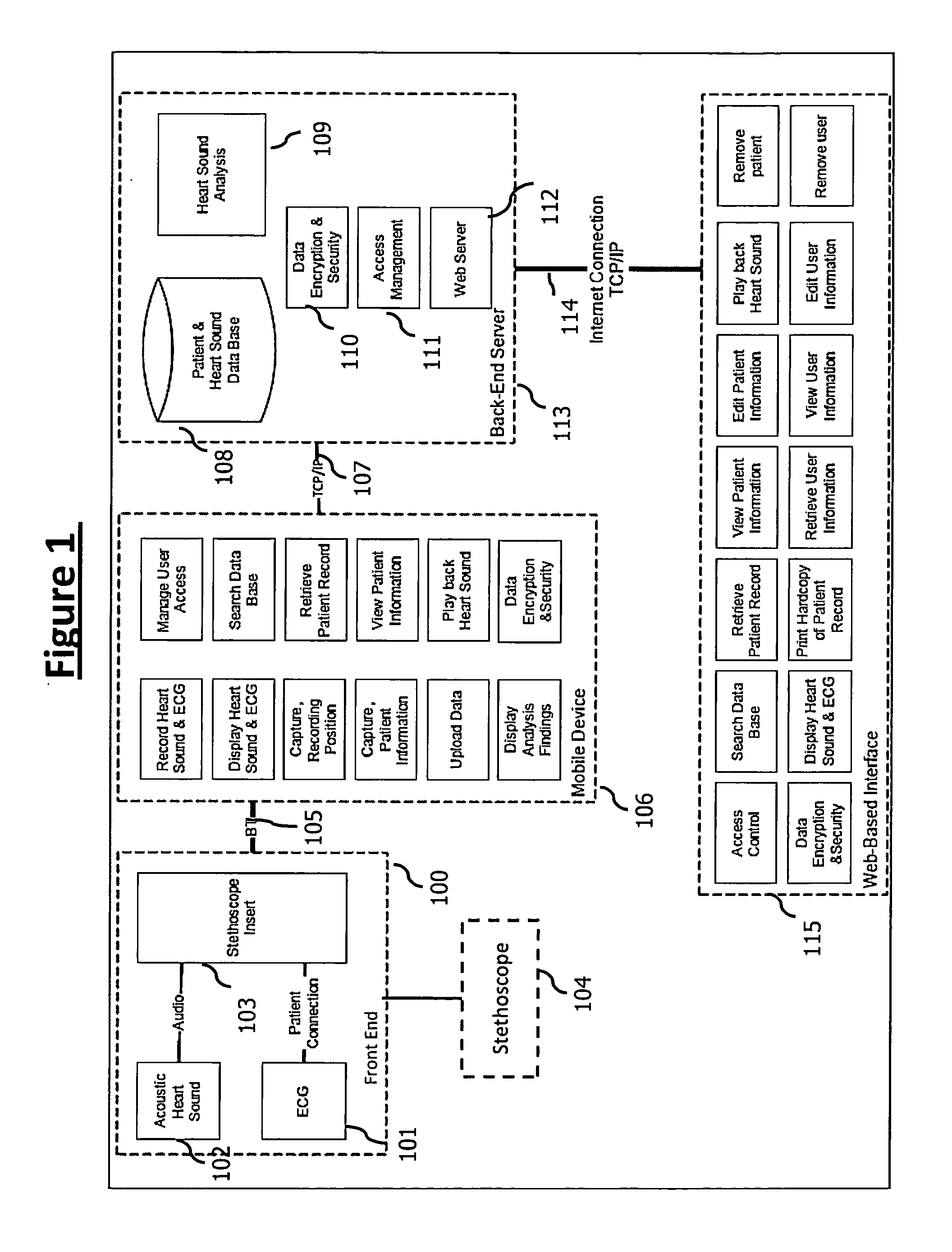
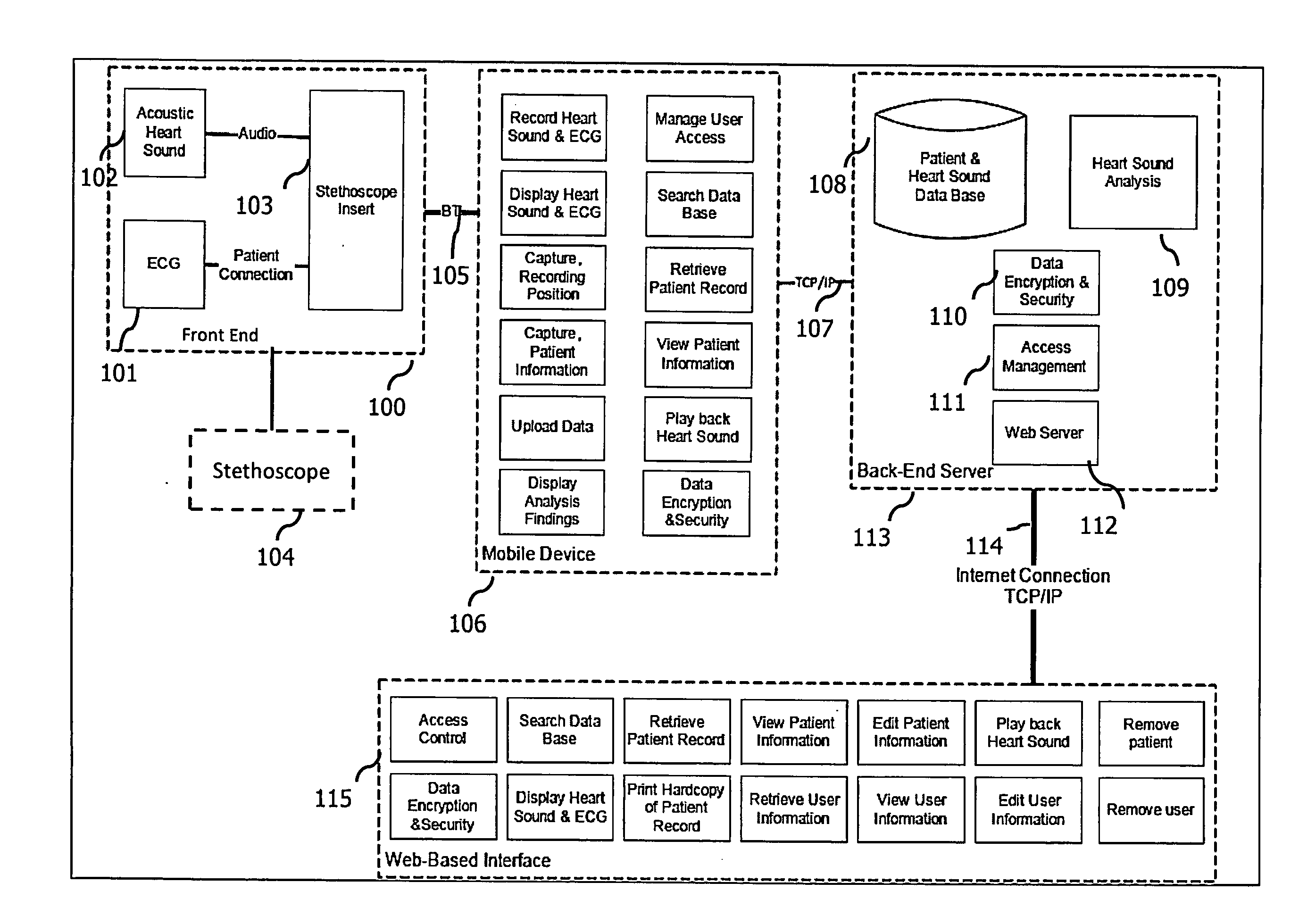
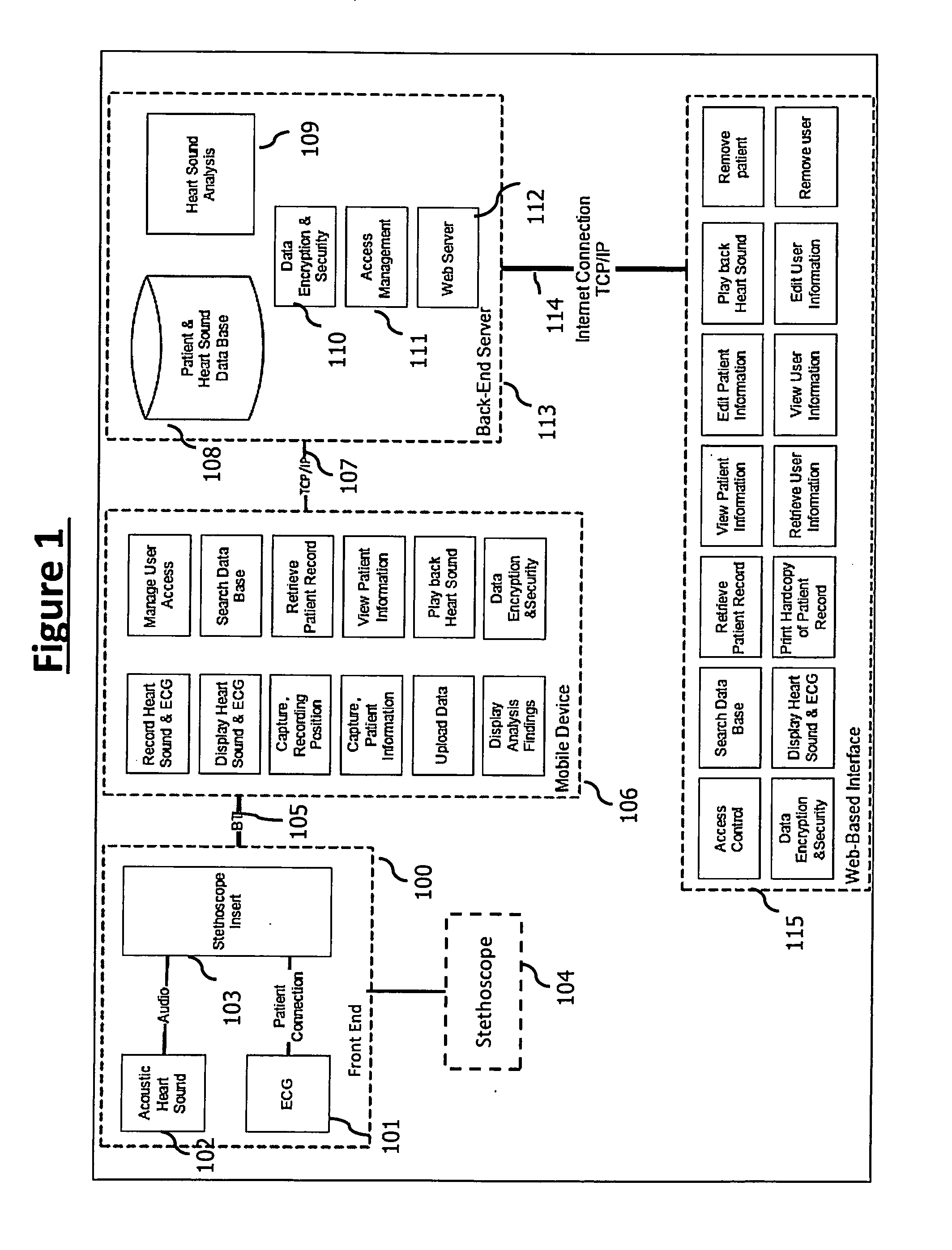
A stethoscope front-end recorder device (also referred to as Sleeve) for the chest piece of a stethoscope, which is easily installed and removed. The Sleeve covers the circumference of the chest piece of a stethoscope. The Sleeve contains sensors for acquiring biosensor parameters such as electrocardiogram, body temperature, heartbeat, heart rhythm, heart rate variability, heart rate turbulence, heart sounds, respiration, cardiac index and blood flow. The Sleeve has Bluetooth interface communicating with a mobile device with software component, interfacing with a back-end server with the capability to capture, analyze and save patient information.
Owner:RIJUVEN
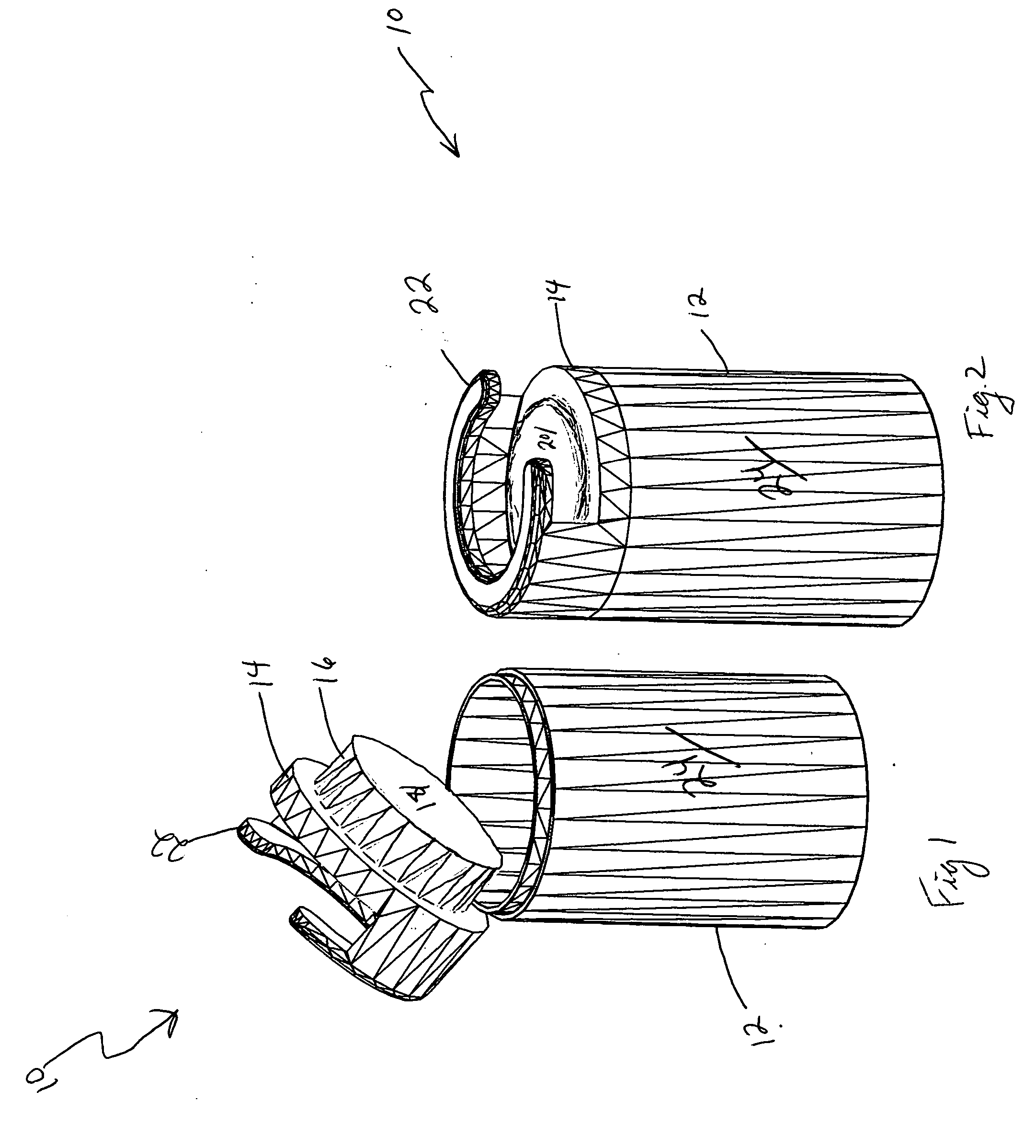
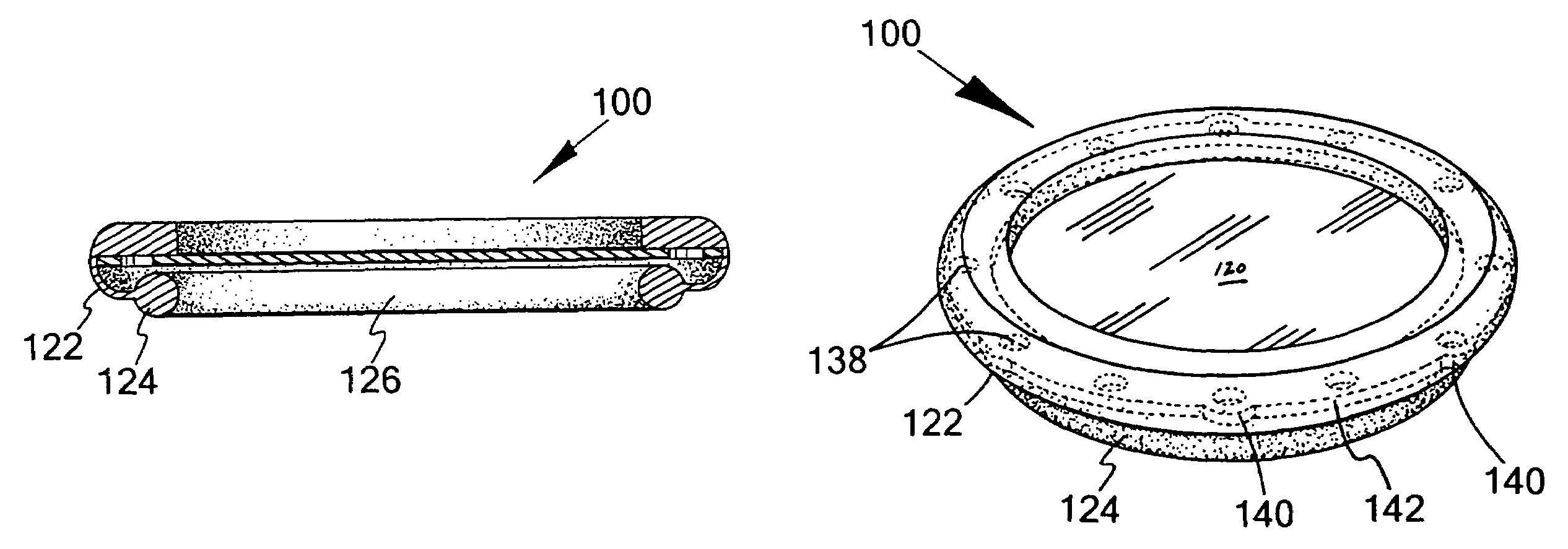
Cover for a bell or a diaphragm of a stethoscope
A cover for a stethoscope, and in particular the bell or diaphragm of a stethoscope, has a semi rigid center portion with a flexible skirt extending therefrom. The skirt and the semi rigid center portion terminates in an expandable binding ring, thereby permitting the cove to be applied thereto. The cover may a unitary or a multiple piece.
Owner:STETHOCAP
Physiological data recording apparatus for single handed application
InactiveUS20050078533A1Broaden applicationAuscultation of heart sounds is greatly facilitatedStethoscopeDigital storageHeadphonesHeart disease
The invention disclosed herein simplifies application of physiological sensors to the body. In the preferred embodiment the plurality of physiological sensors are physically attached to the back of a personal digital assistant (PDA). An operator presses the PDA single-handedly against patient's chest in such a manner that sensors are in contact with patient's skin and the PDA display faces the operator. Physiological signals are then visualized on the PDA screen. The sensors include EKG electrodes and acoustic sensors. The “EKG Stethoscope” is used to simultaneously record the audio signal from an acoustic sensor and the corresponding electrical EKG signal from EKG electrodes. The PDA analyzes EKG and acoustic signals. Further, sound from one acoustic sensor is amplified and transmitted to operator's headphones for simultaneous auscultation. Concurrent audio and visual experience greatly enhances the operator's ability to diagnose lung and heart disease. A plurality of acoustic sensors is used to localize intrathoracic sound origin. The operator looks at the PDA display for cues on abnormal sound location and sound characteristics.
Owner:VYSHEDSKIY ANDREY +2
Stethoscope
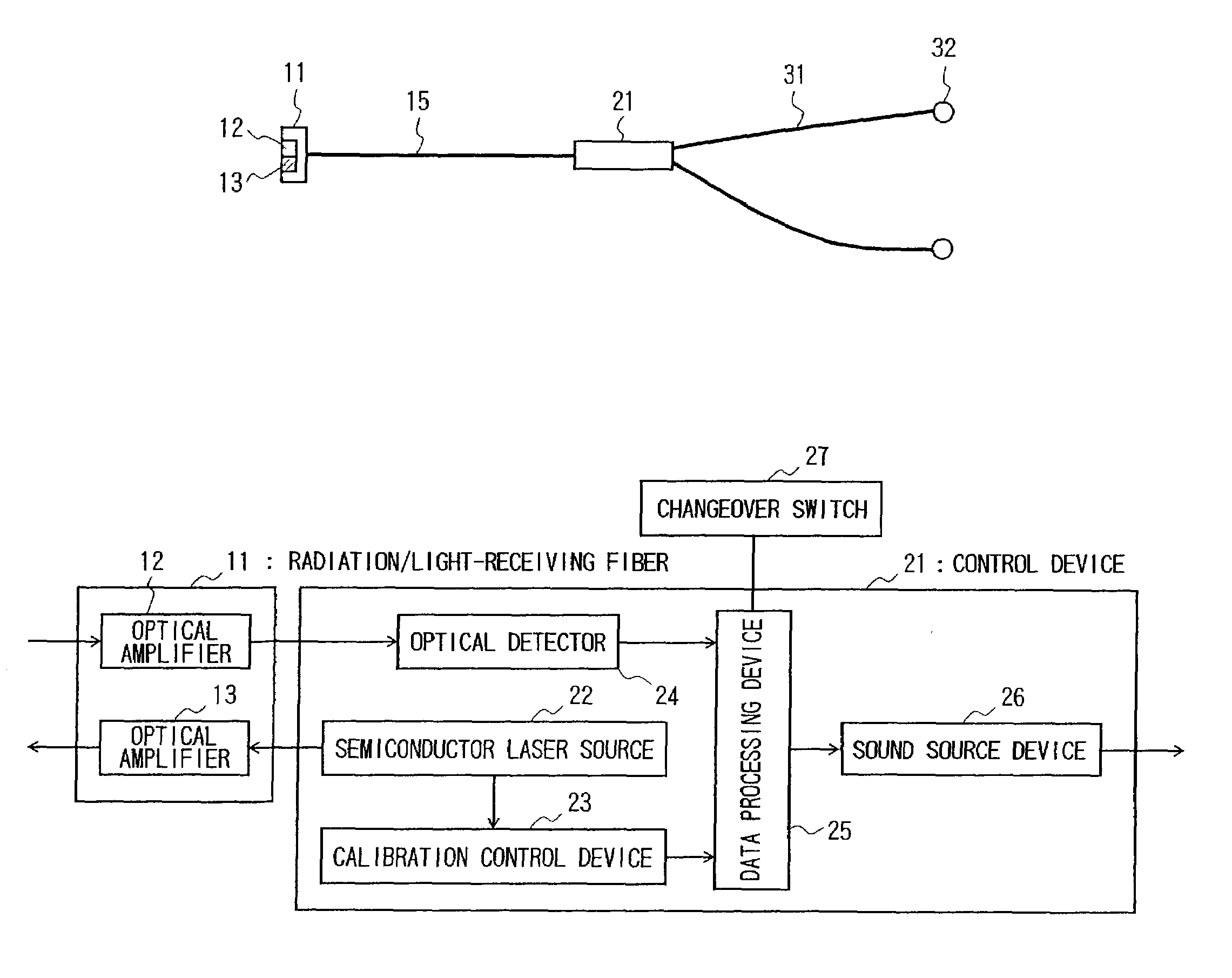
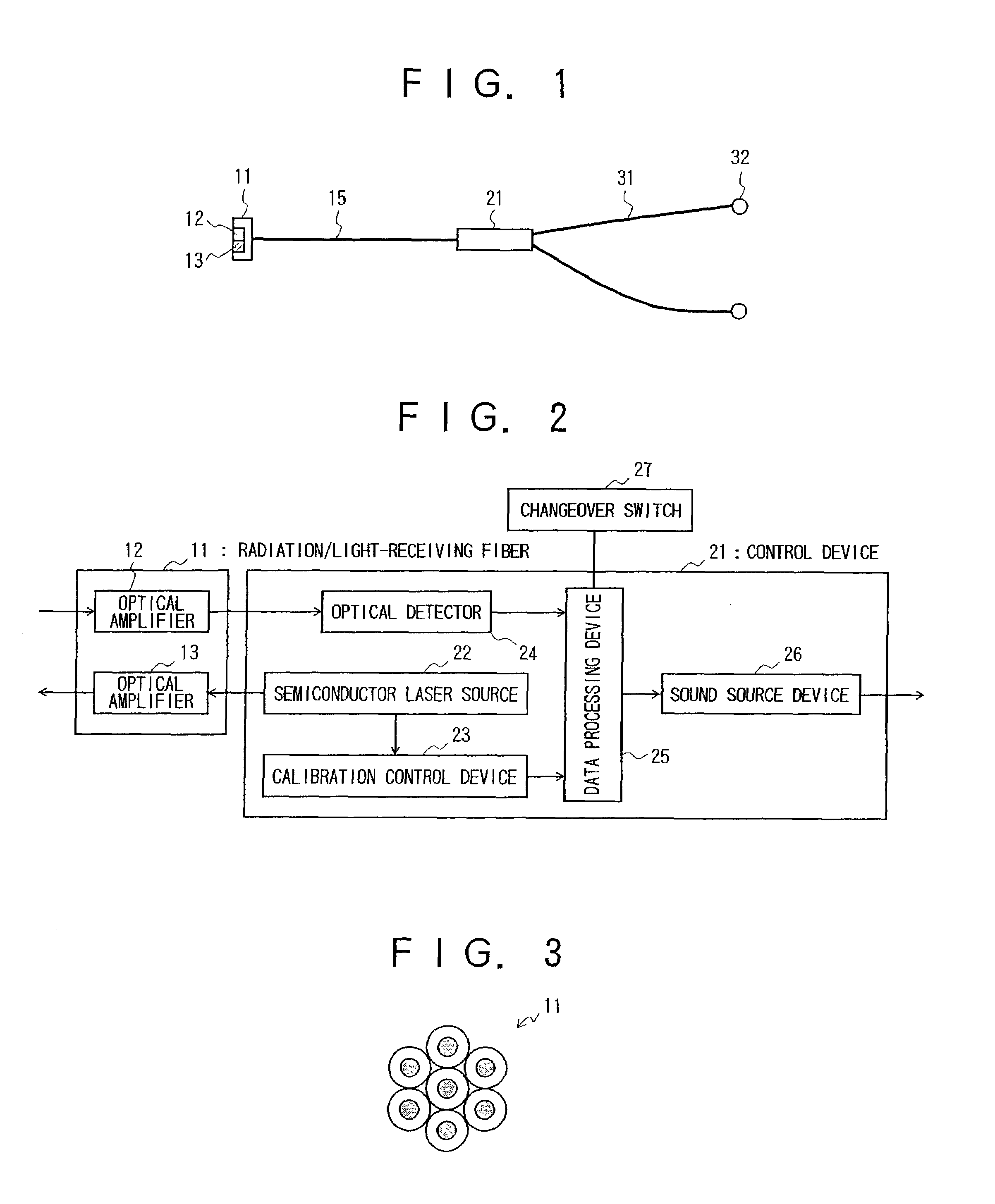
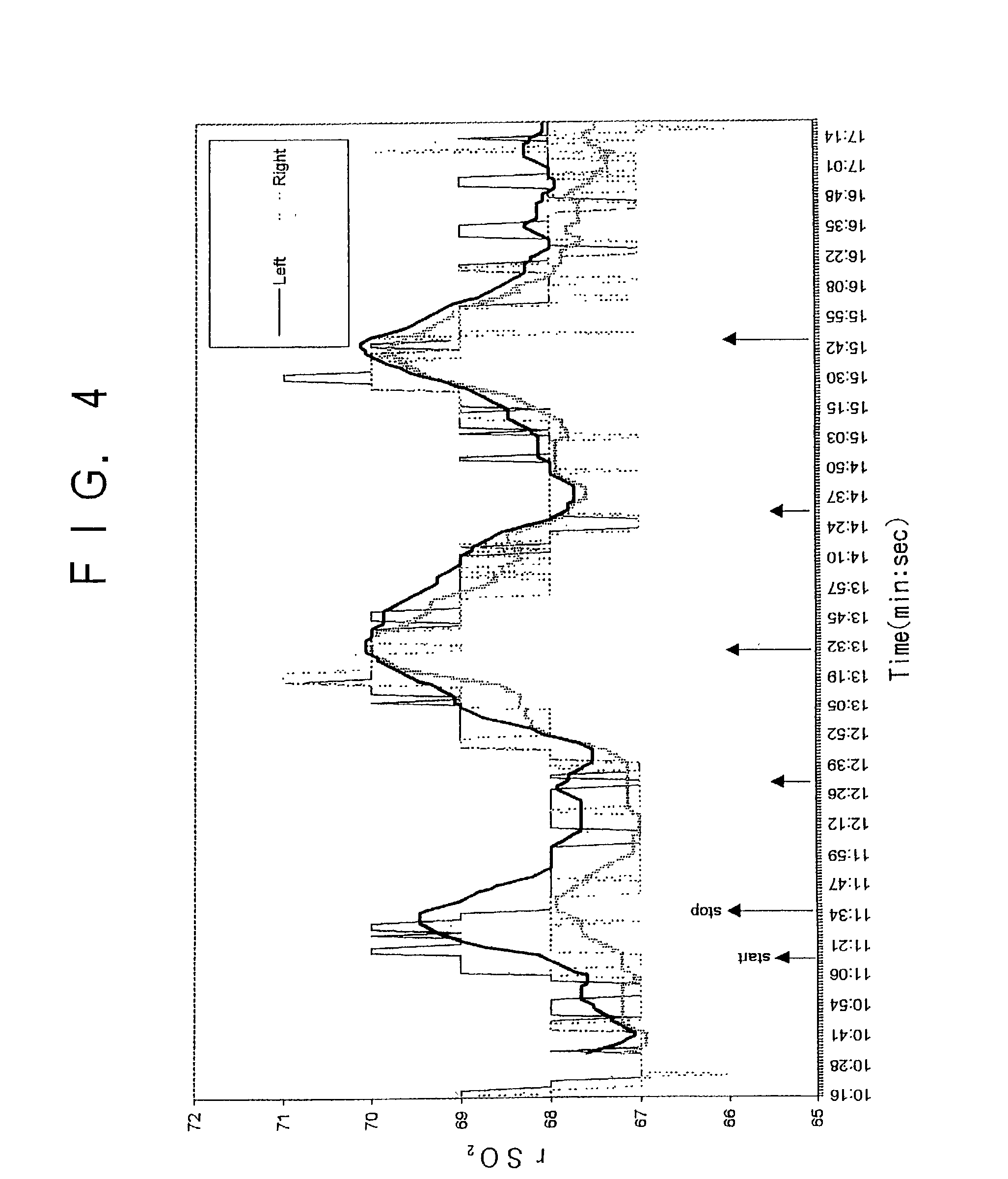
A simple always-portable stethoscope for enabling accurate diagnosis. A radiation / light-receiving fiber (11) serving as a probe part for noninvasively irradiating a diseased part with near-infrared light is applied to the diseased part so as to measure, e.g., a change of the cerebral circulation blood flow. The change is hard as sound pulse modulation to examine the change of the cerebral function. For example, a light beam of three wavelengths λ=760, 800, 830 nm from a semiconductor laser light source (22) is applied to the diseased part, the reflection data from the diseased part is processed by a control device (21), and the doctor can make a diagnosis with the doctor's ears by hearing with a receiver (32) the change as the change of the frequency of the sound the pitch and volume of which are constant.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Auscultation training device
InactiveUS20050048455A1Improve teaching efficiencyEffective instructionSpeech analysisAuscultation instrumentsAuscultationStethoscope
The auscultation training device enables a trainee to experience and learn various case studies without feeling the difference from the actual auscultatory action using the actual stethoscope in order to obtain the auscultatory technique. The auscultation training device 1 mainly comprises the model human body 4, which is an imitation of a human body upper torso; the stethoscope simulator 2 that the trainee 5 uses to perform the simulation of the auscultatory action on the model human body 4; an auscultatory sensor 8 which detects the auscultatory action by the trainee 5 with the stethoscope simulator 2; and the controller 3 which is connected to the stethoscope simulator 2 and the auscultatory sensor 8 respectively, whereby the controller receives the detected signals 9 of the auscultatory action transmitted from the auscultatory sensor 8, and then controls and processes signals for reproduction of vital sounds including those such as cardiac sounds and breathing sounds of the human body by a vital sound player 11 installed in ear piece 10 of the stethoscope simulator 2.
Owner:GIFU UNIVERSITY
Protective cover for stethoscope, and dispensing assembly comprising same
A protective cover for an article such as a stethoscope, comprising a bag member of elongate form, closed at a first end and fully or partially open at a second, opposite end to form an enclosed volume for retention of the head and elongate connector body of a stethoscope. The two longitudinal sides of such bag member can be seamless; alternatively, such longitudinal sides can comprise two seam lines. The bag member is longitudinally, medially severable at an end portion that include the second, open end, to yield two free end segments for covering respective ear tubes of the stethoscope. The protective cover may further include retention means for positionally retaining the free end segments of the bag member in protective covering relationship to the ear tubes of the stethoscope, e.g., adhesive and / or compressive clips, or a transverse heat seal at marginal extremities of the free end segments.
Owner:INFECTION CONTROL SOLUTIONS
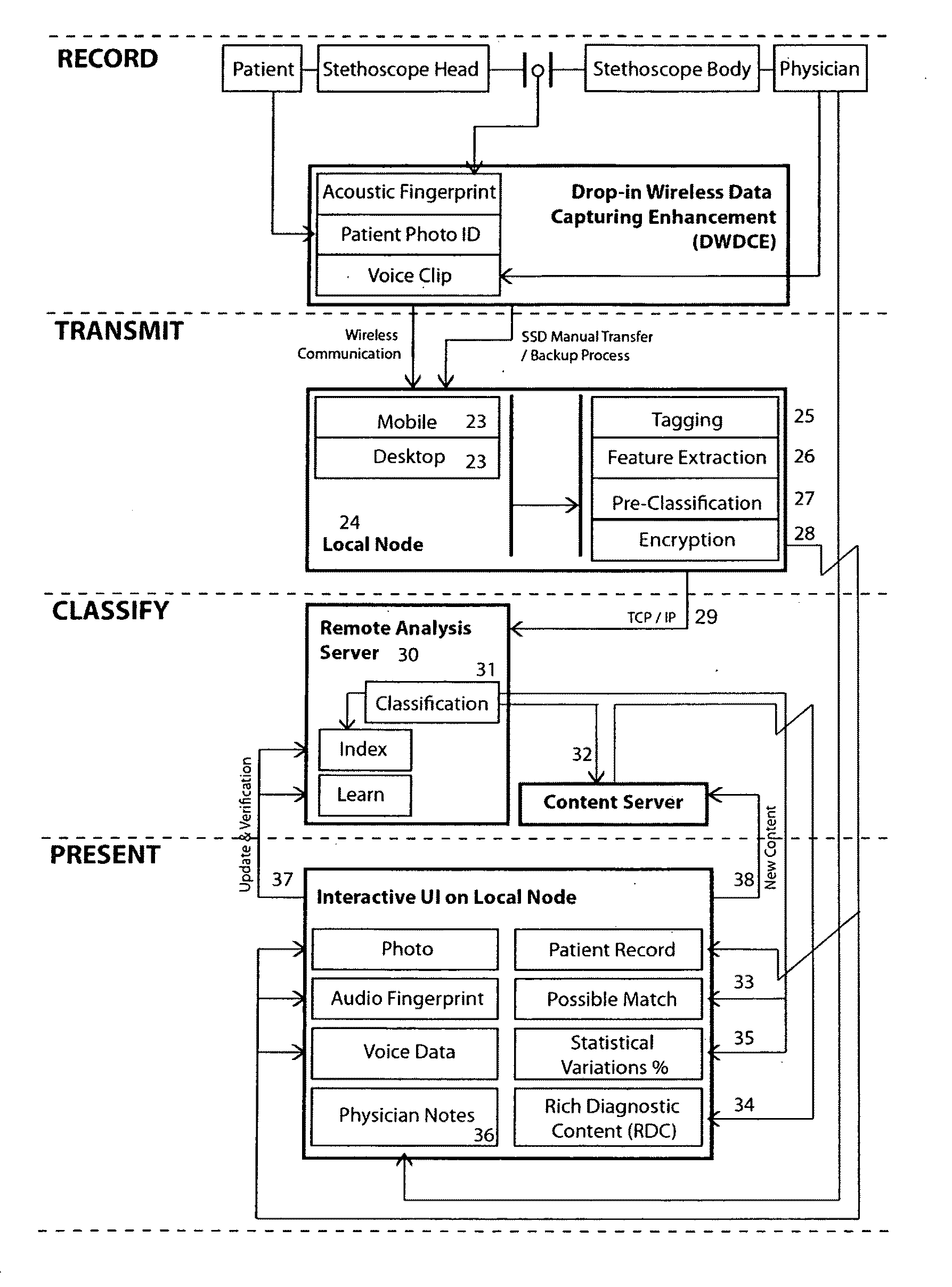
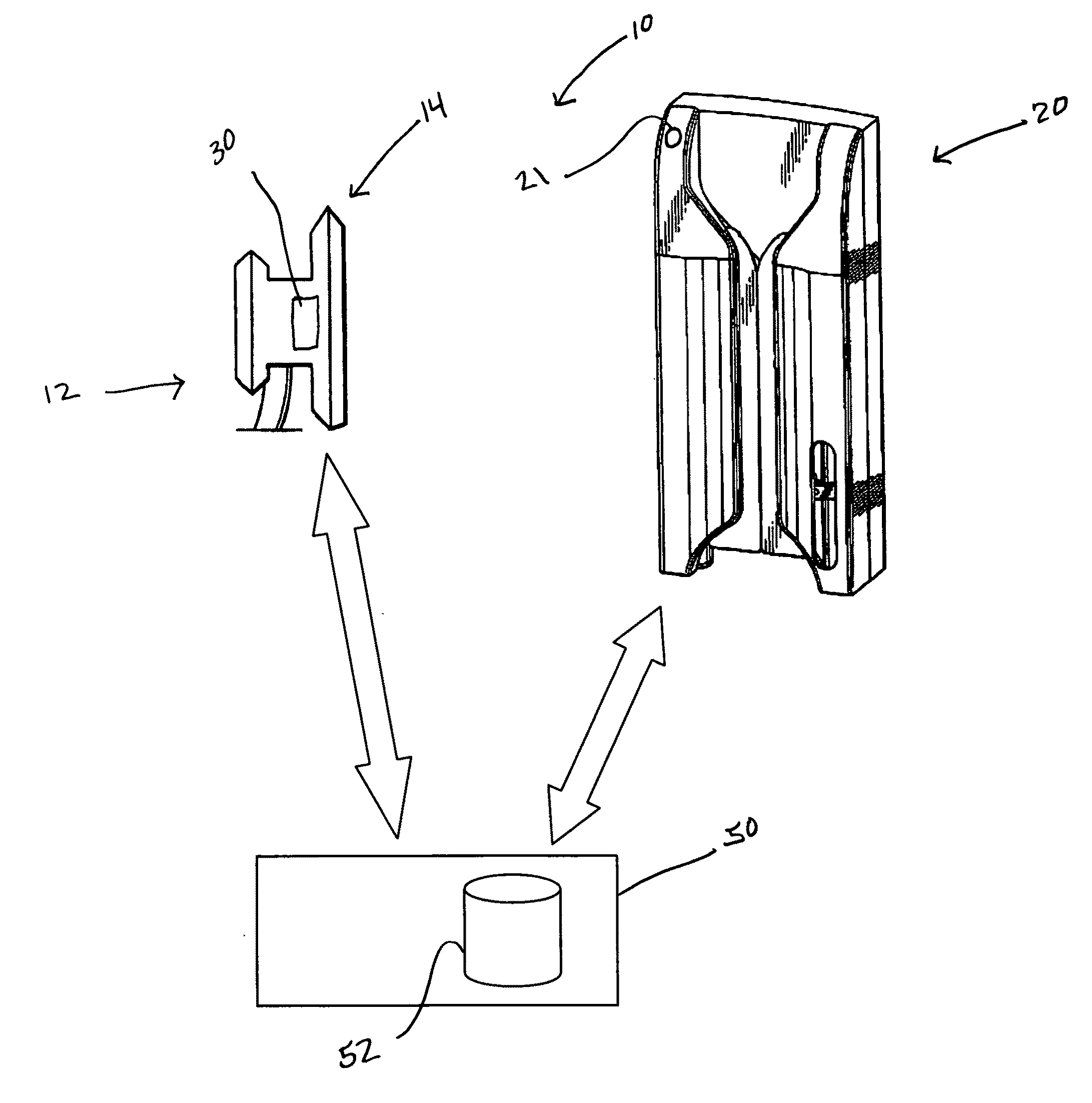
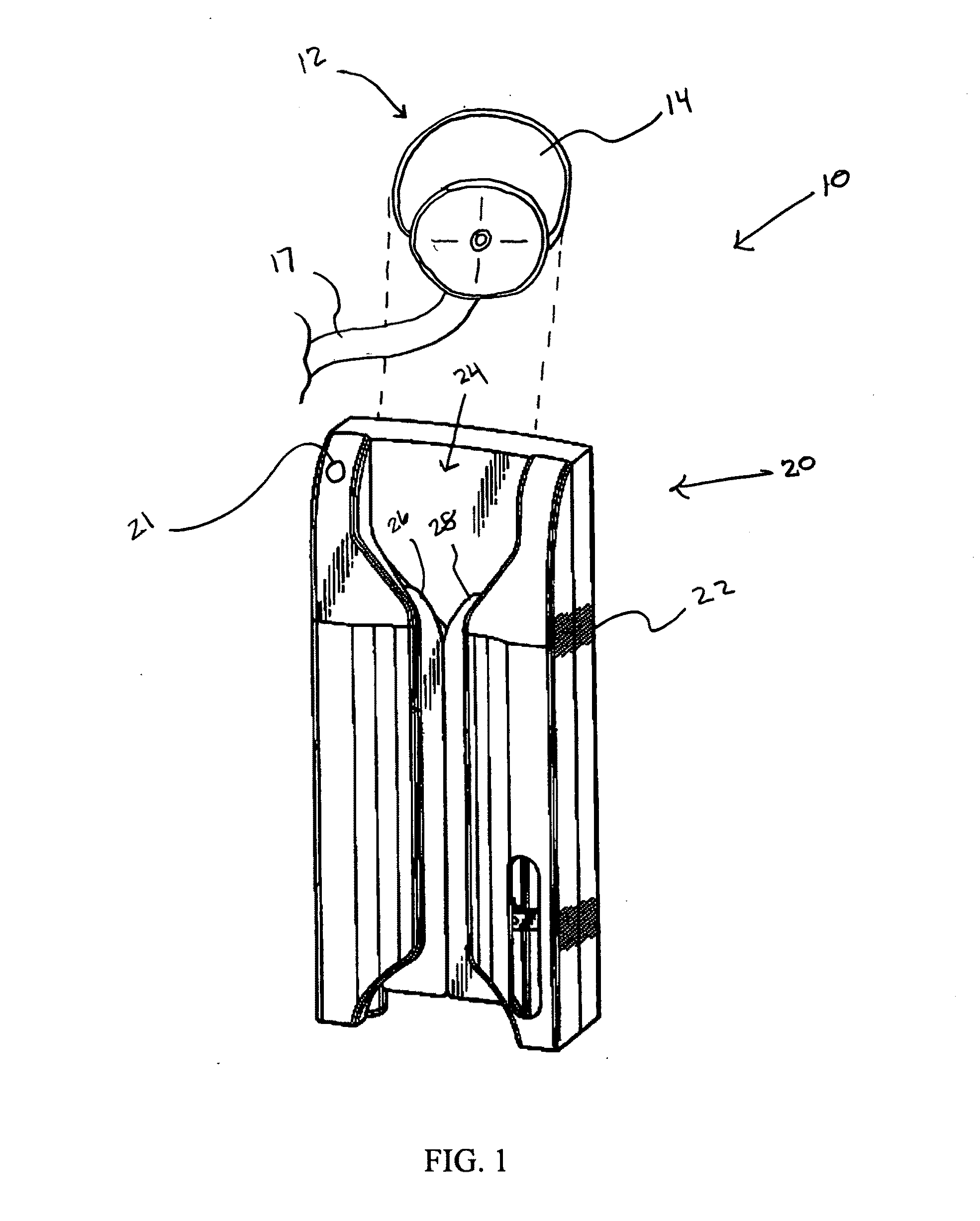
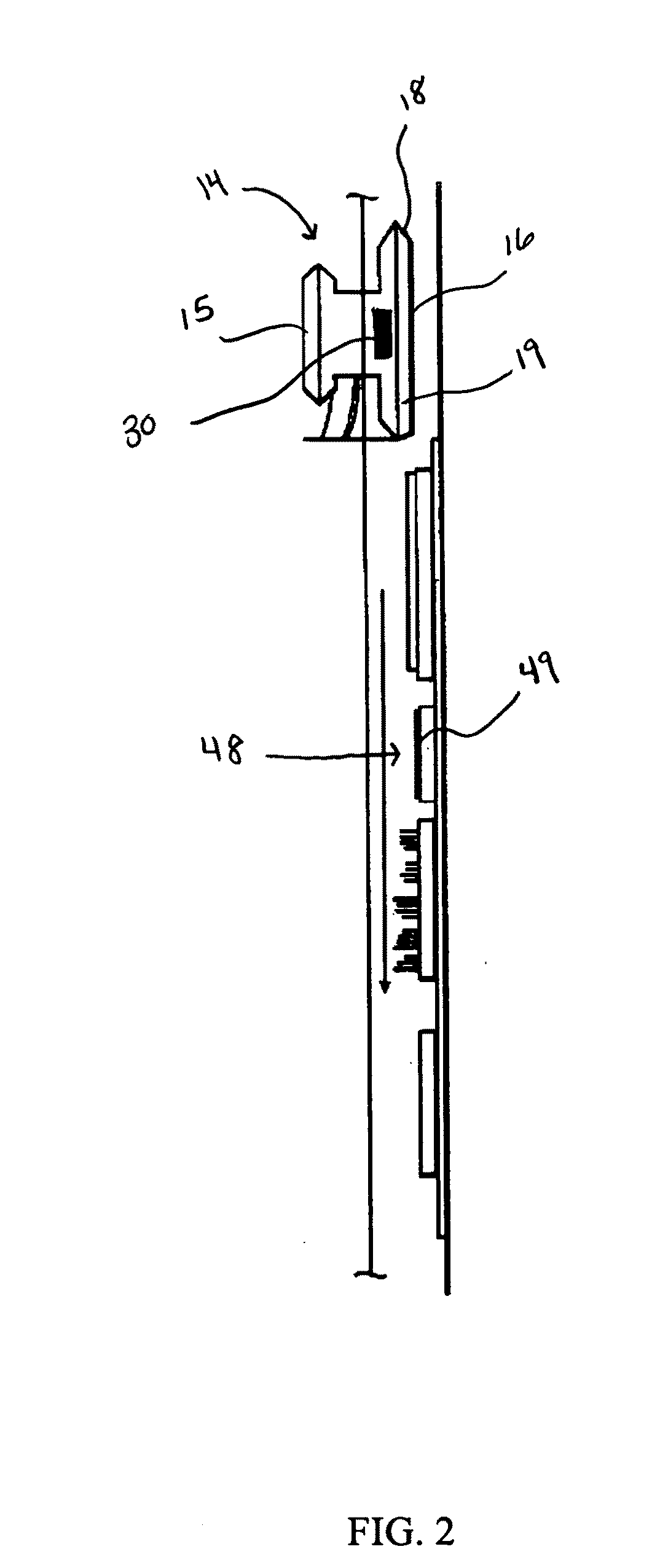
Stethoscope, stethoscope attachment and collected data analysis method and system
ActiveUS20110087135A1Convenient rechargeEasy to integrateMagnetic measurementsStethoscopeDigital dataRemote system
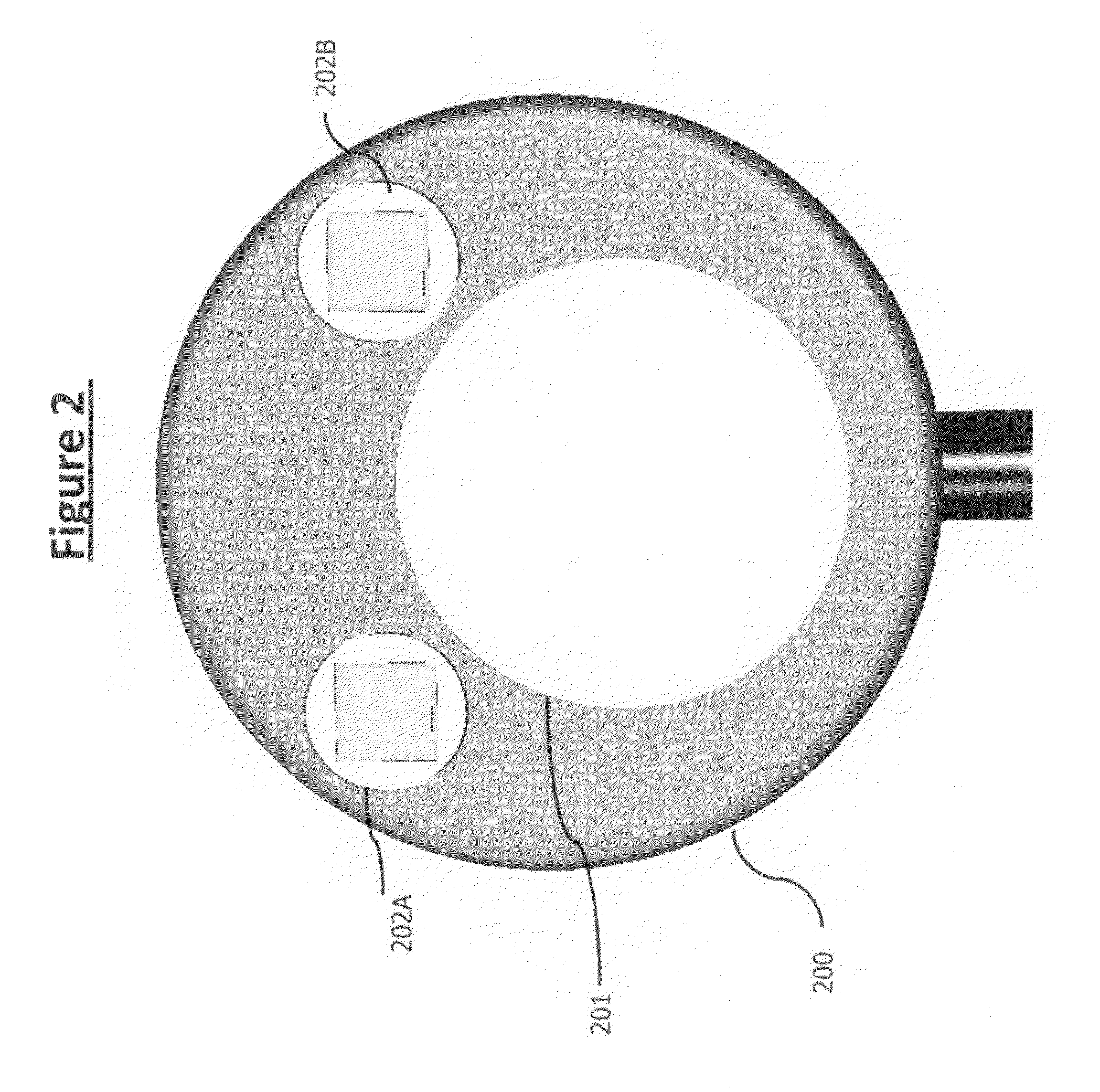
A device for converting acoustic data collected by a stethoscope into digital data for transmission to a processor for storage and / or comparison with data stored in a database, and to optionally provide computer generated suggestions for diagnosis, is provided in the form of an in-line device interposable between a head of the stethoscope and an acoustic transmission portion of the stethoscope, or is integral with the head, and advantageously has the appearance of an icon of pleasing appearance, for example, a butterfly, in which are incorporated the structural requisites of a functioning stethoscope and / or capabilities for receiving and transmitting to a diagnostician, audio signals gathered from patient examination, and optionally also other data collected at examination and / or following the examination. The butterfly-shaped device, includes a central body advantageously serving as a conduit for transmitting sound received from the patient to the physician or a remote system for analysis and diagnosis.
Owner:FERZLI GEORGE S +1
Microphone and communication interface system
It is possible to improve a defect of an analysis object itself of a mobile telephone and speech recognition which is an air propagating normal speech taken from outside by a microphone and realize a new mobile terminal communication based on the human cultural habit in the personal mobile information terminal without requiring training. A stethoscope type microphone is mounted on a human skin surface so as to take a meat-propagating vibration sound of un-hearable murmur articulated by a speech act (mouth movement) without using vocal cord regular vibration. The meat-propagating vibration sound of the amplified non-hearable murmur is like a whisper and the whisper itself can be heard and understood by a human. Accordingly, it can be used for communication via a mobile telephone. Moreover, by making the meat-propagating vibration sound of the un-hearable murmur an object of analysis / parameterization, it is possible to realize a kind of soundless recognition as a new input method of a personal mobile information terminal.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
High sensitivity noise immune stethoscope
ActiveUS8265291B2Improvement factorEnhanced couplingTransducer detailsStethoscopeAir coupledEngineering
A physiological sensing stethoscope suitable for use in high-noise environments is disclosed. The stethoscope is designed to be substantially matched to the mechanical impedance of monitored physiological activity and substantially mismatched to the mechanical impedance of air-coupled acoustic activity. One embodiment of the stethoscope utilizes a passive acoustic system. Another embodiment utilizes an active Doppler system. The passive and active systems can be combined in one stethoscope enabling switching from a passive mode to an active mode suitable for use in very high-noise environments. The stethoscope is suitable for use in environments having an ambient background noise of 100 dBA and higher. The passive includes a head having a housing, a flexural disc mounted with the housing, and an electromechanical stack positioned between the housing and the flexural disc in contact with the skin of a patient. The active system detects Doppler shifts using a high-frequency transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ACTIVE SIGNAL TECH
Method of ultrasound non-contact early detection of respiratory diseases in fowls and mammals
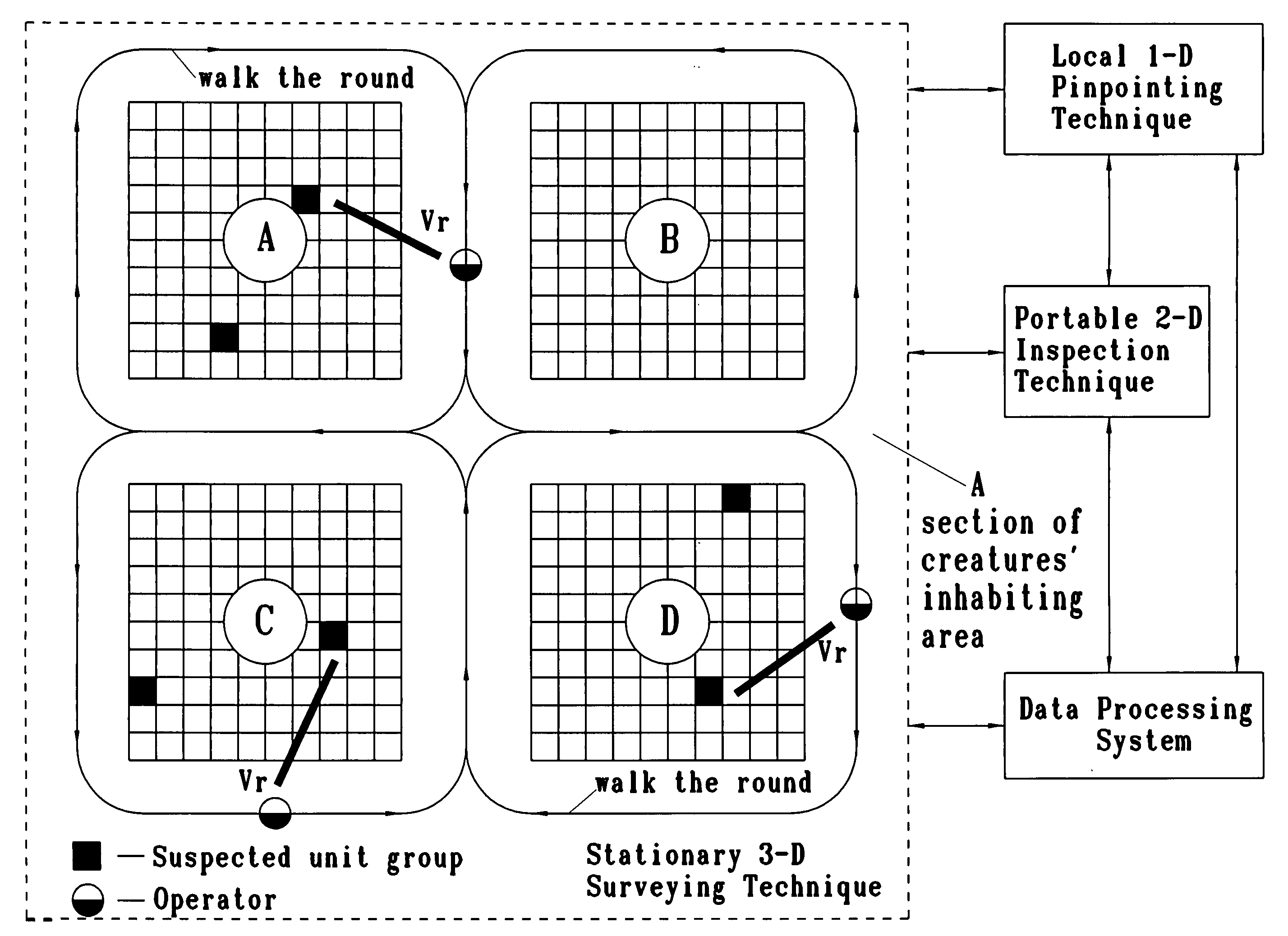
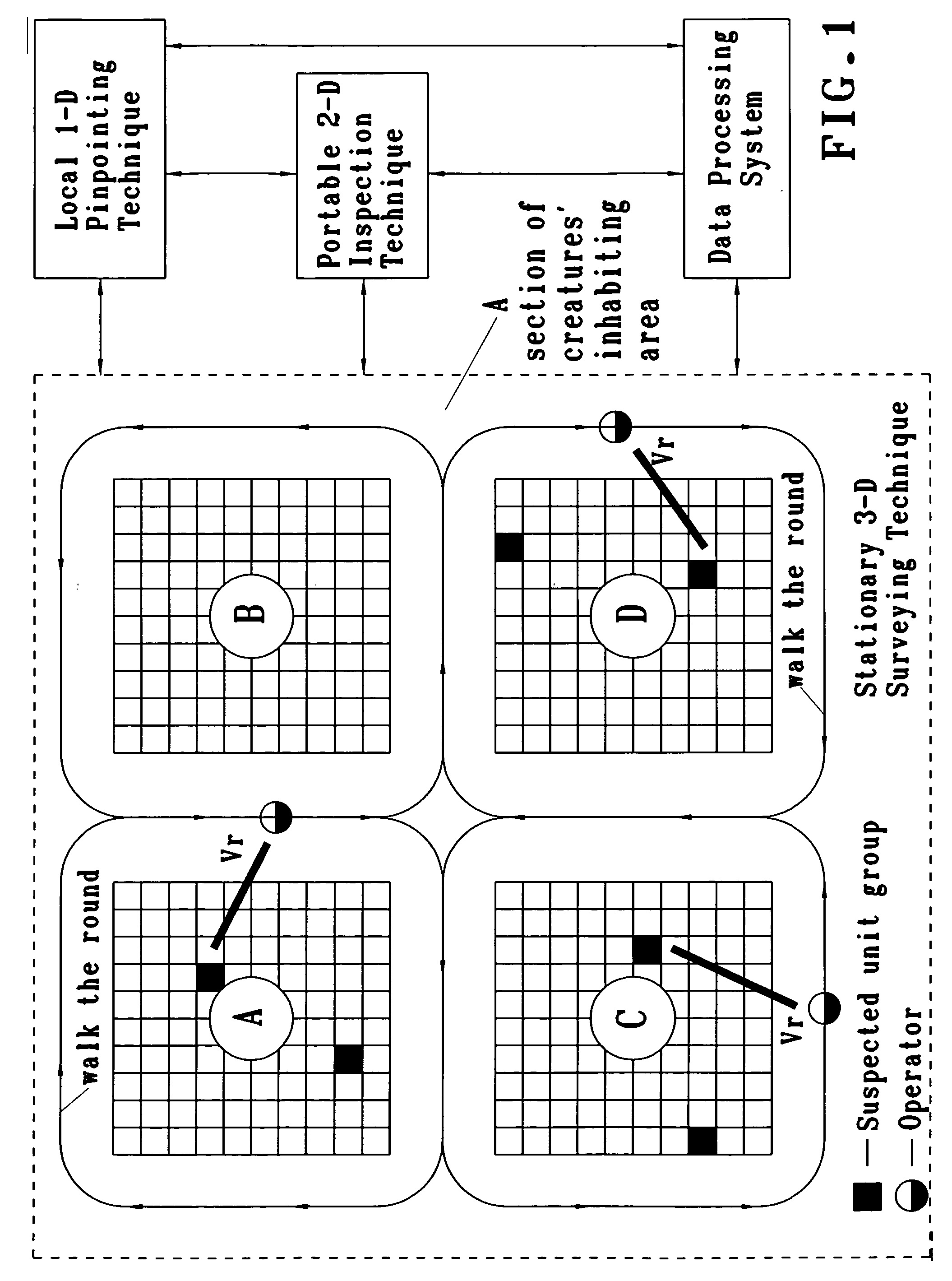
InactiveUS20050049498A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAuscultation instrumentsDiseaseBovine respiratory disease
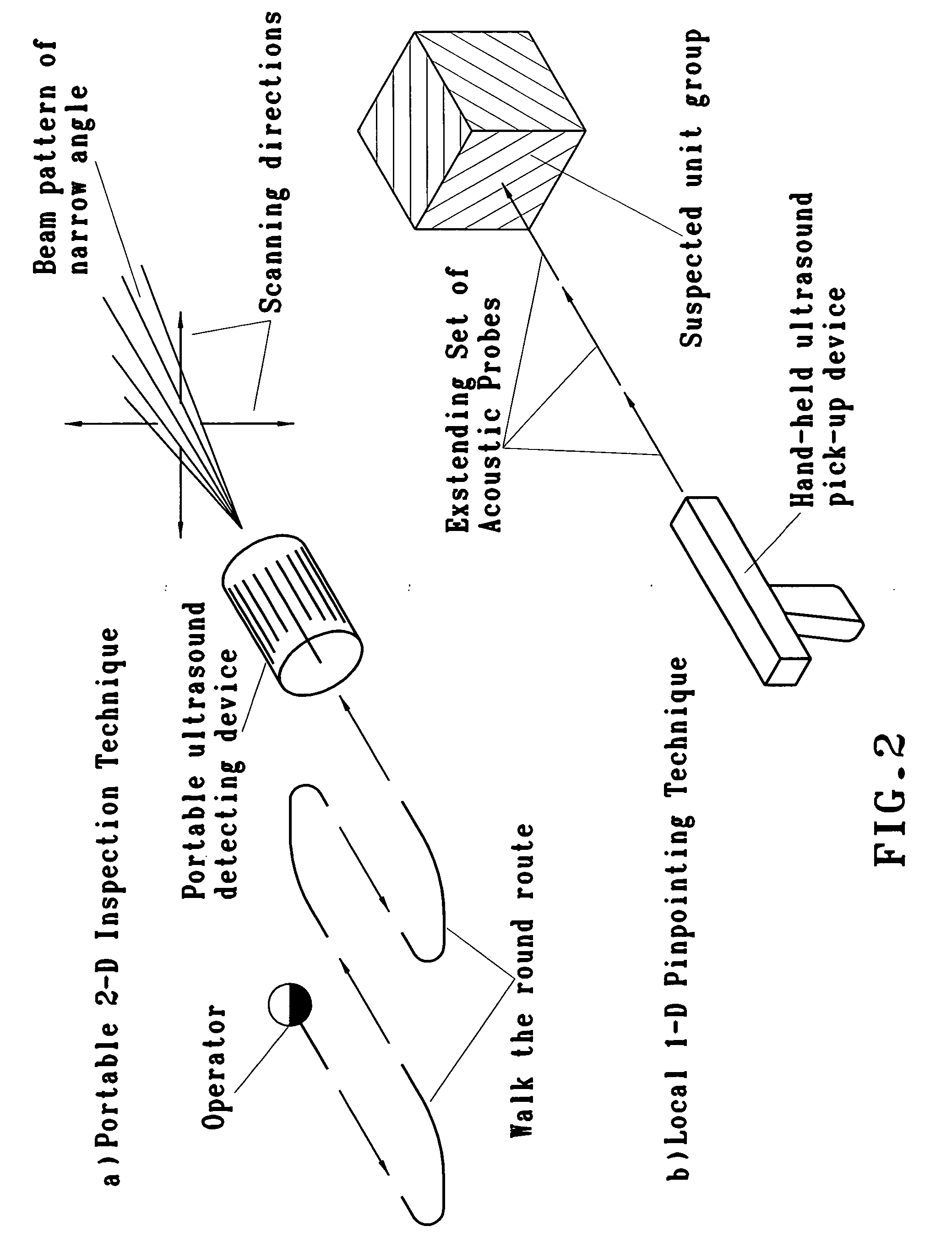
In the case of disease in the respiratory organs of creatures, which especially inhabit in terms of overcrowding, the danger of spreading a disease throughout the entire breeding farm is perfectly evident. The use of traditional methods, such as the stethoscope, for examining the respiratory organs of each creature, in the mode of their direct contact listening, is impossible in most due to the specific spatial arrangement of creatures in breeding farms and / or infectious danger to a veterinary. Moreover, the acoustic signs of the said illness at its early stage cannot be heard audibly with use of traditional methods. The present invention provides a novel method of ultrasound non-contact early detection of respiratory diseases in fowl and mammals, and other breathing creatures of animate nature, wherein innovative technology is applied for revealing the suspected minimal unit group with sick creature(s); wherein the said technology includes at least the following interrelated techniques: I-Stationary 3-D Surveying Technique that enables to identify vectored direction(s) to suspected sections in total creatures' inhabiting area by electronically scanning the said total area with 3-D array of ultrasonic transducers. II-Portable 2-D Inspection Technique that permits to verify disposition of perfect suspected sectional area by locating around each suspected inhabiting section with portable and hand-held ultrasonic detecting devices. III-Local 1-D Pinpointing Technique that provides for pinpointing a distinct suspected unit group, being inside an infected inhabiting sector, by a hand-held ultrasound pick-up device, equipped with extending acoustic probes for veterinary safety. Portable and Local Techniques optionally provides for use of wireless processing with Data Processing System. Spatio-Temporal compliance in applying the said techniques is being considered by operational algorithm of Data Processing System.
Owner:CTRL SYST
System for outputting acoustic signal from a stethoscope
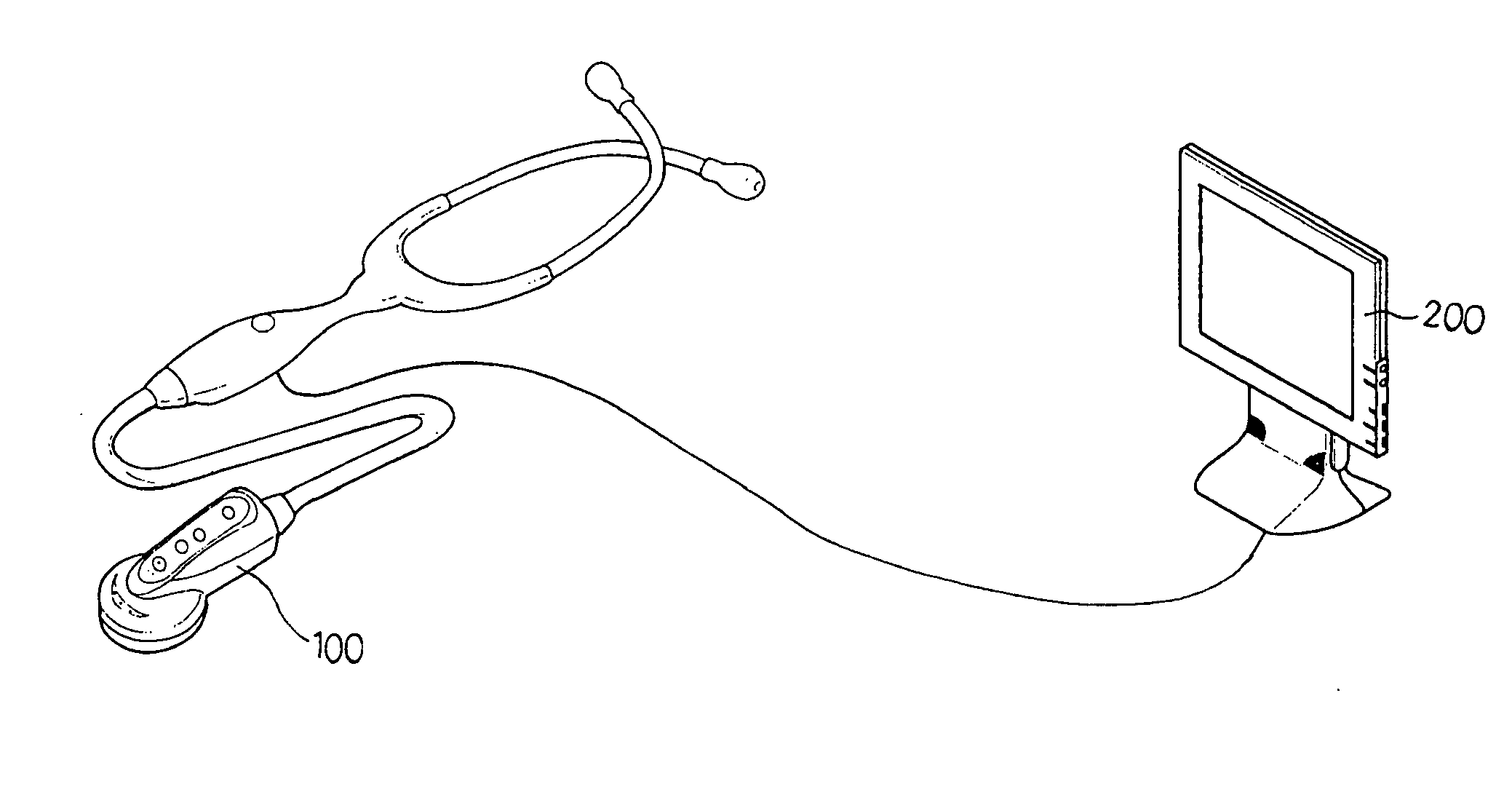
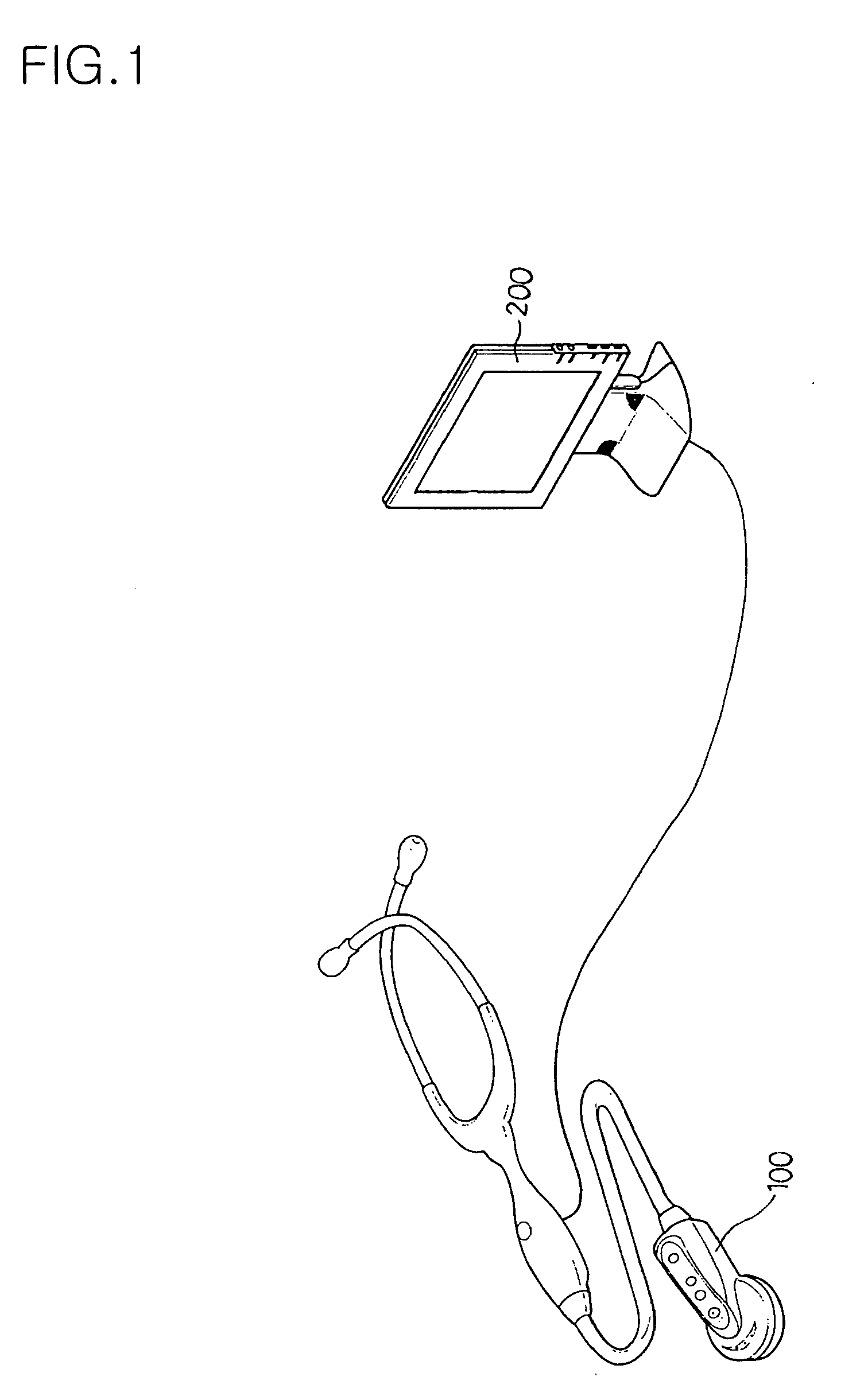
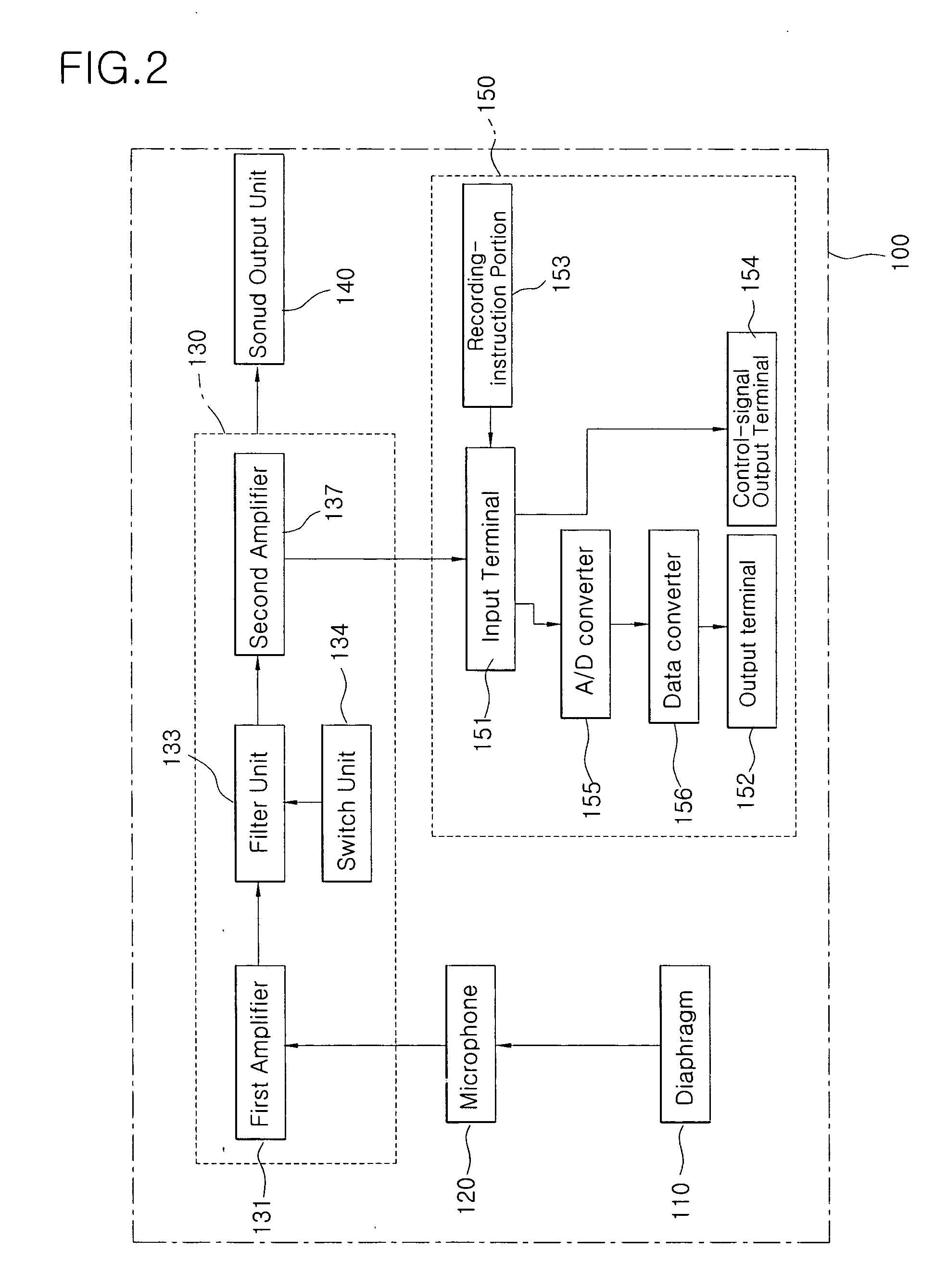
InactiveUS20050157887A1Objective diagnosisObjective managementStethoscopeCatheterEngineeringBreathy voice
Disclosed is an output system for displaying an auscultatory sound signal such as heartbeat or respiratory sounds generated from the interior of a body in real time. The output system includes a stethoscope and a computer. The stethoscope includes at least a) a diaphragm to he brought into contact with a specific portion of a human body so as to vibrate according to a sound generated from the body, b) a microphone for converting the vibration of the diaphragm to an electrical sound signal, c) a signal process unit adjusting an auscultatory frequency band of the electrical sound signal from the microphone and outputting an auscultatory sound signal, d) a sound output unit for outputting a sound input from the signal process unit, and c) a signal output unit for transmitting the auscultatory sound signal output from the signal process unit to the outside. The computer displays an output signal received from the stethoscope, together with a standard sound pattern a user selects from standard sound patterns stored in a database.
Owner:GS TECH
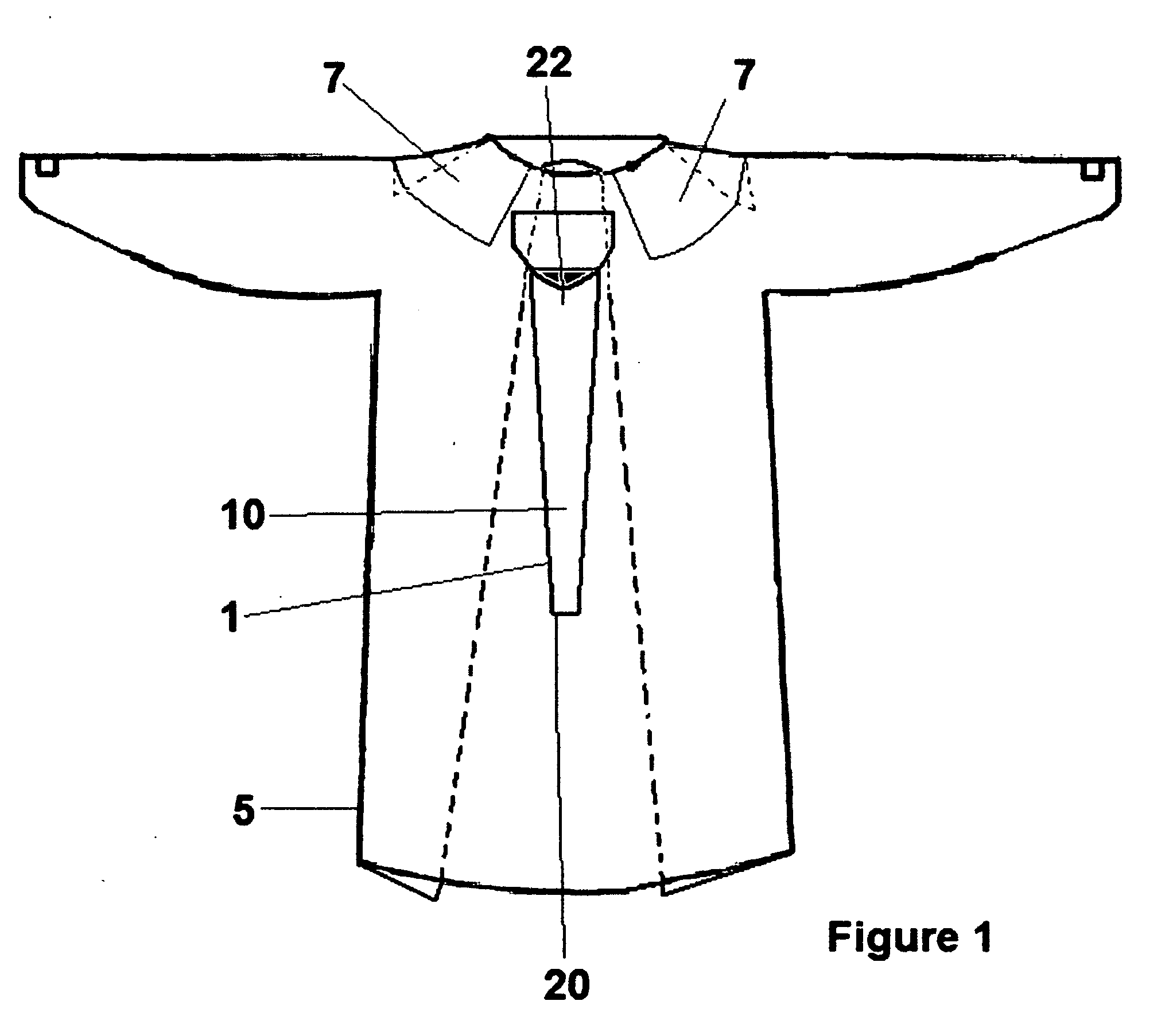
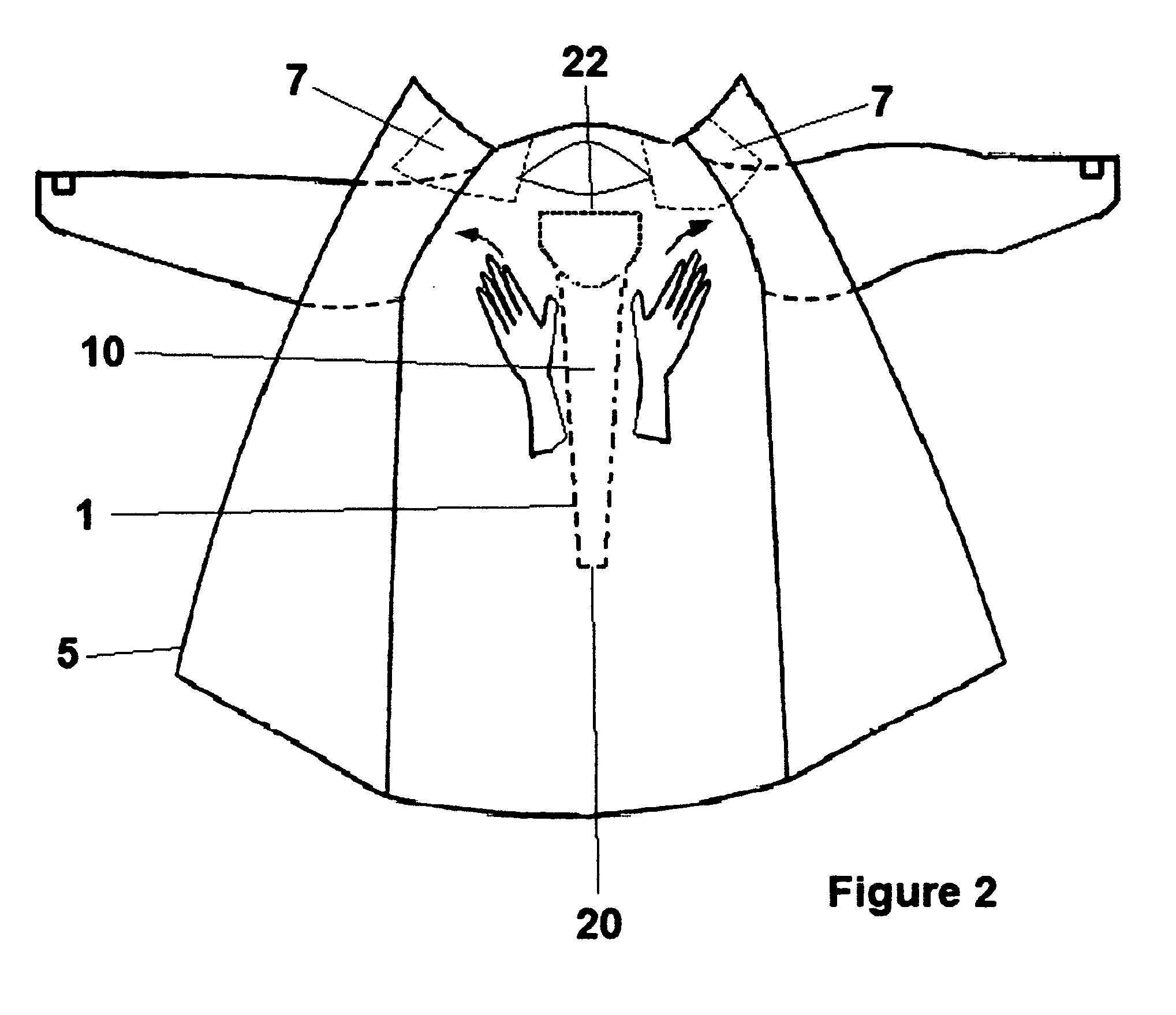
Disposable hospital gown with stethoscope protector/cover
InactiveUS20090165186A1Reduce transmissionImprove hygieneStethoscopePyjamasIntensive care medicineHospital patients
A disposable hospital patient's gown with a stethoscope protector or cover for preventing the stethoscope of healthcare provider from being contaminated, so as to prevent transmission of infectious diseases to the patients.
Owner:MIJARES DANIEL +1
Method and Device for Ultraviolet Light Sterilizing
ActiveUS20120261593A1Maximize irradiation rateEffectively and efficiently usRadiation therapyChemical conversion by chemical reactionUltraviolet lightsUltraviolet A Radiation
In accordance with the present invention, a device and method is provided for covering and sterilizing a stethoscope or other medical instrument for safer use. The device comprises a closed housing for shielding the object to be sterilized, a means for receiving the object, a power supply, an ultraviolet light source within the housing, and a switch for controlling that lamp.
Owner:NOORI GILDA
Stethoscope disinfection monitoring and reporting system
ActiveUS20110197921A1Easily removed and discardedDiagnosticsSurgeryMonitor equipmentWaste management
A stethoscope disinfection monitoring and reporting system structured and configured to track, monitor and report the cleaning, disinfecting, and / or sterilizing of the head portion of a stethoscope is presented. The system comprises a stethoscope cleaning assembly cooperatively structured and configured to clean the head portion of the stethoscope, for instance, via the application of a cleaning fluid or solution thereto. The system further comprises a monitoring device and a cooperatively structured and disposed reader assembly. The monitoring device may be unique to, or otherwise serve to identify, the stethoscope. The reader assembly is structured and disposed to detect, identify, and record data pertaining to the monitoring device and / or stethoscope upon cleaning the head portion, or otherwise upon disposition of the head portion into a cleaning relation with the stethoscope cleaning assembly.
Owner:SEEDLINGS LIFE SCI VENTURES
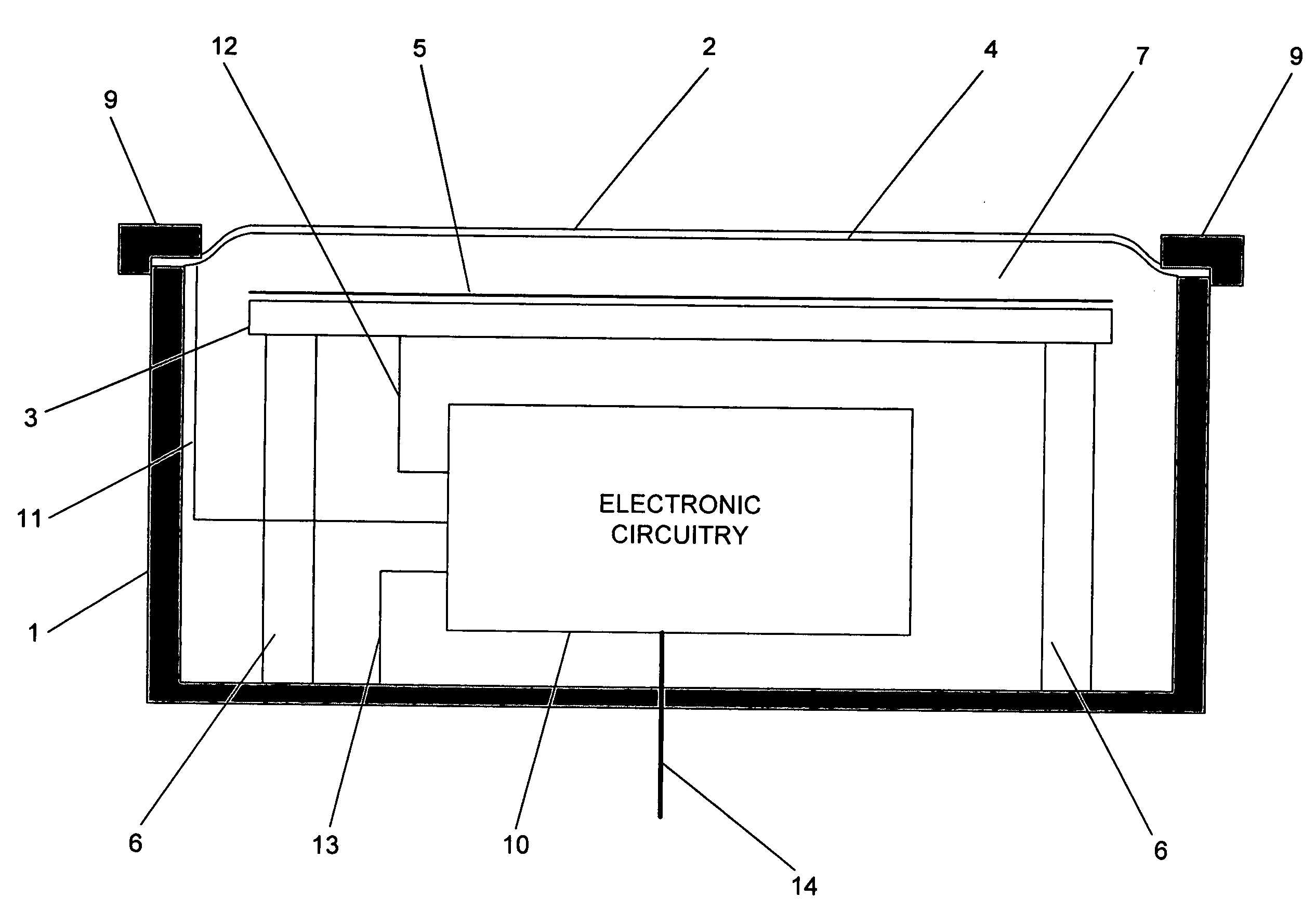
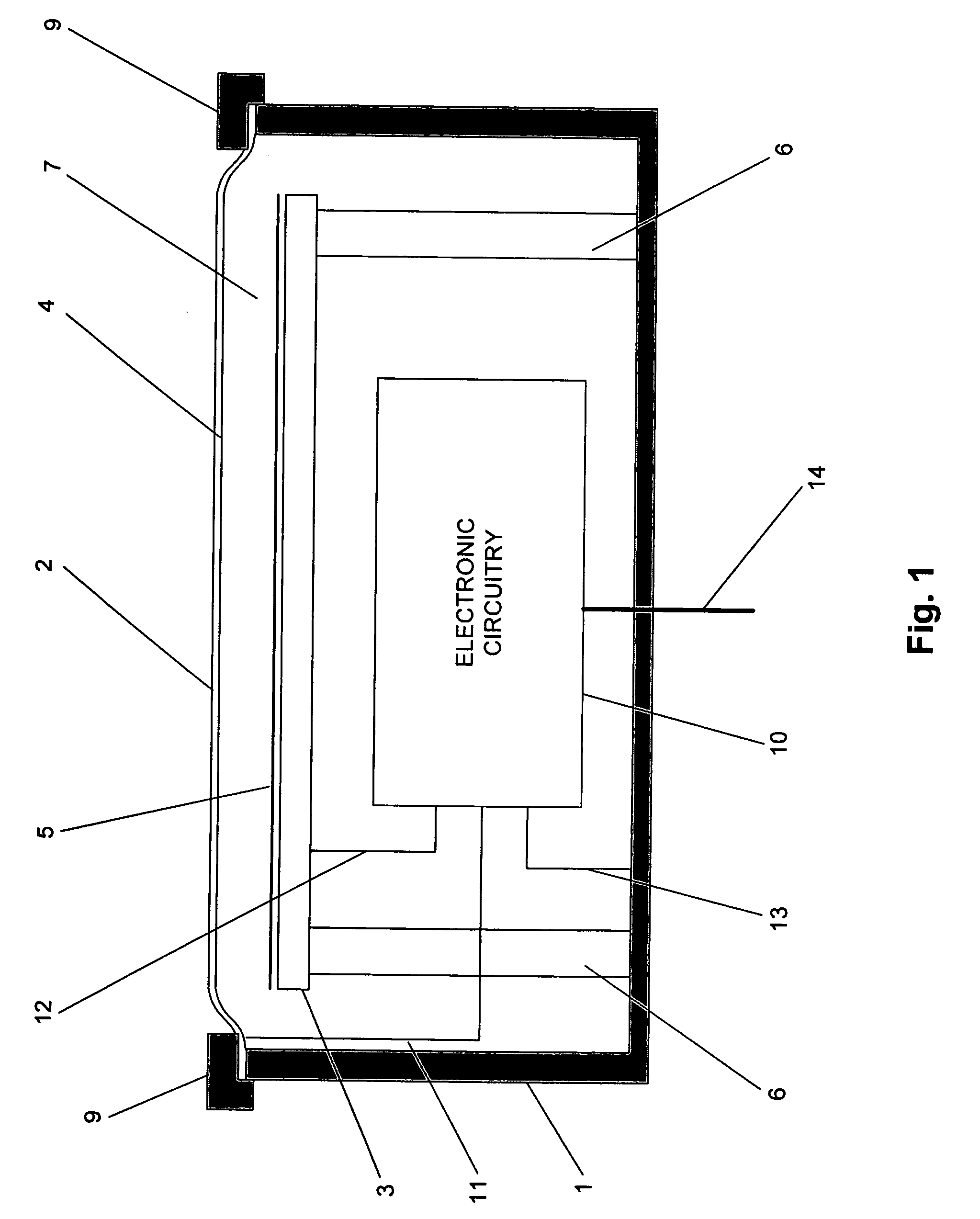
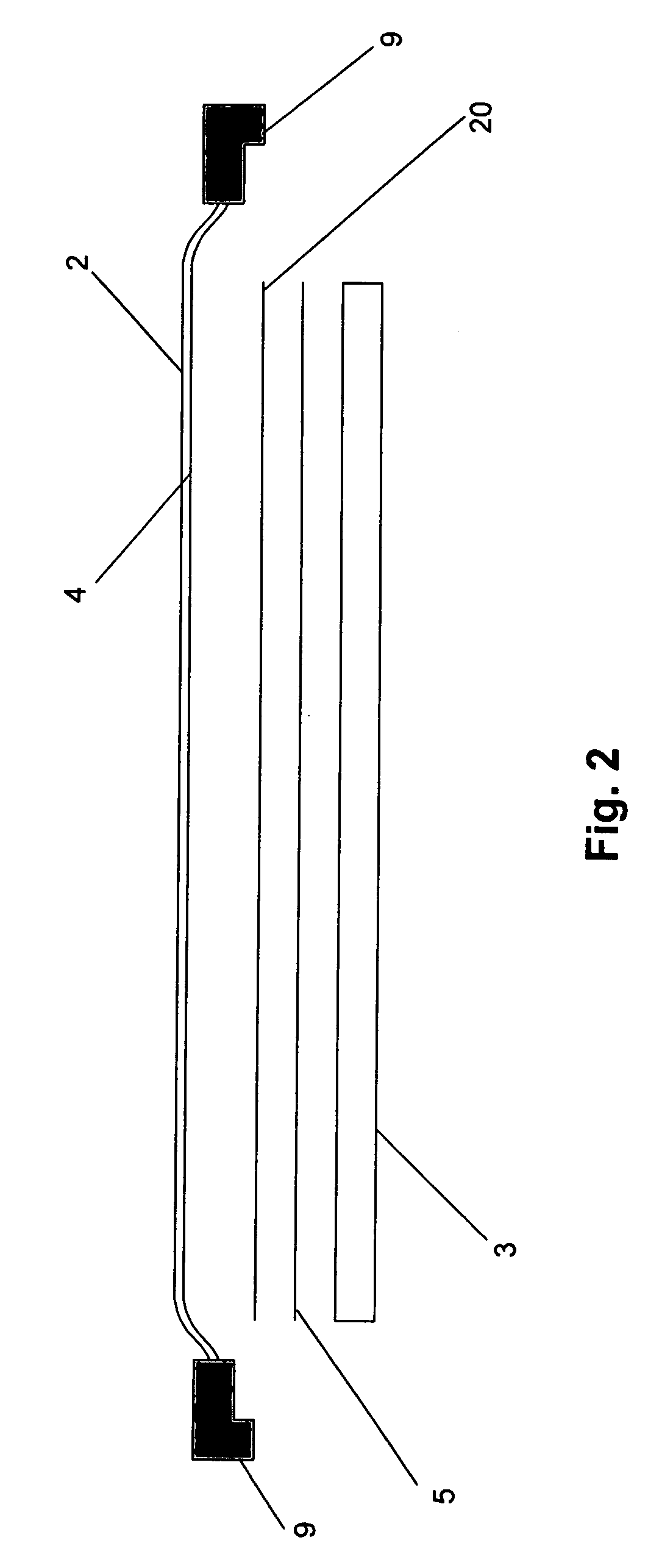
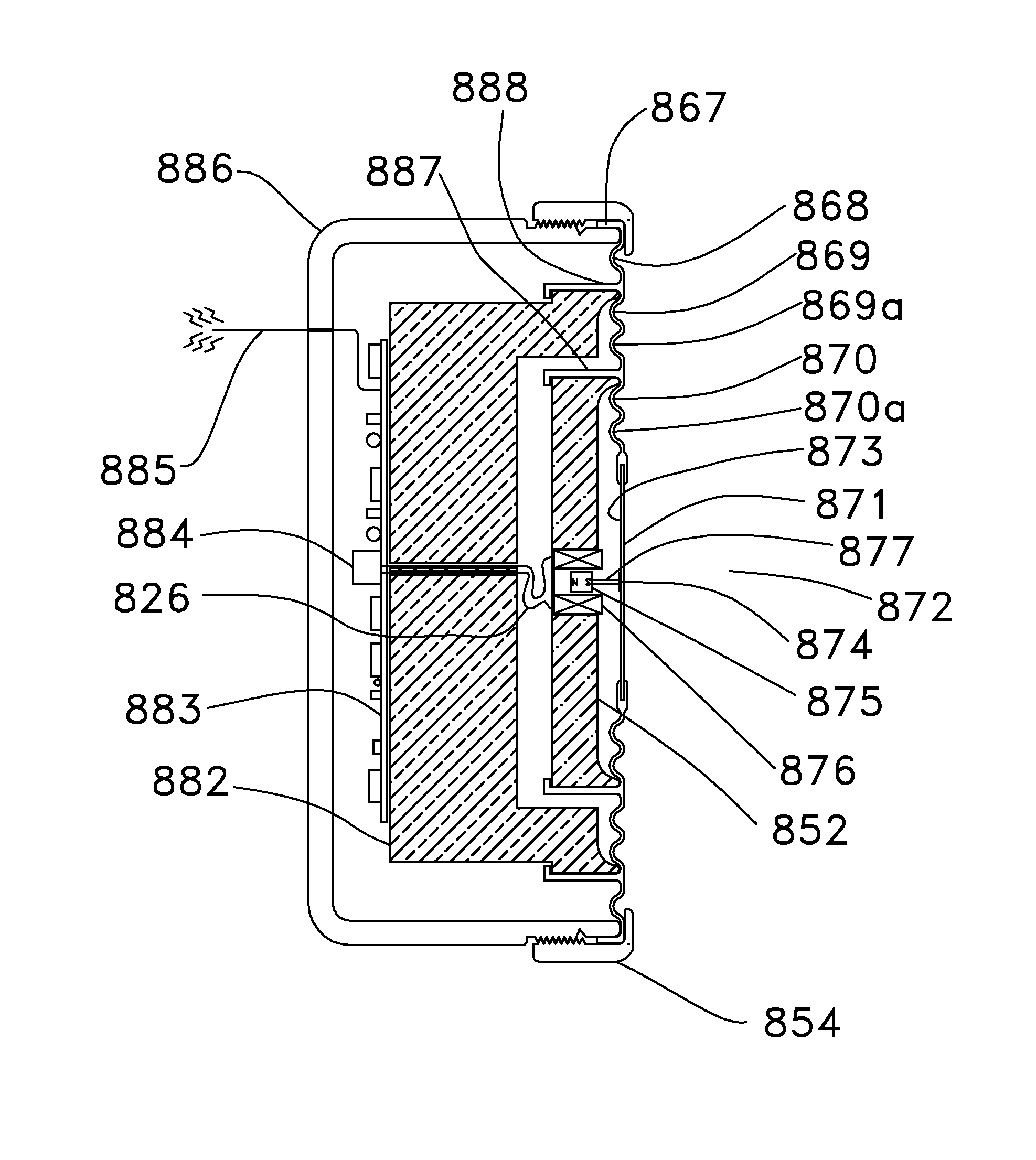
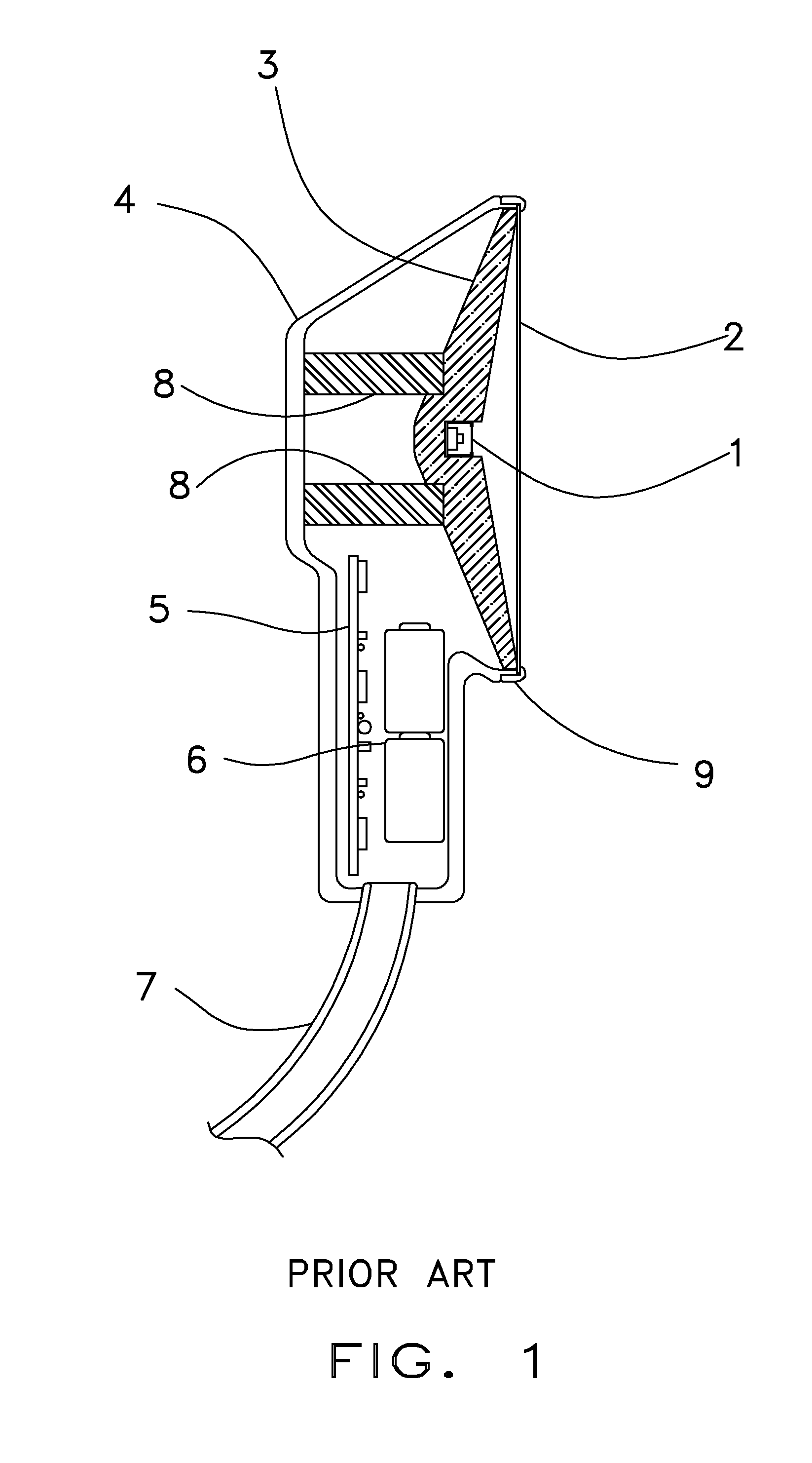
Floating ballast mass active stethoscope or sound pickup device
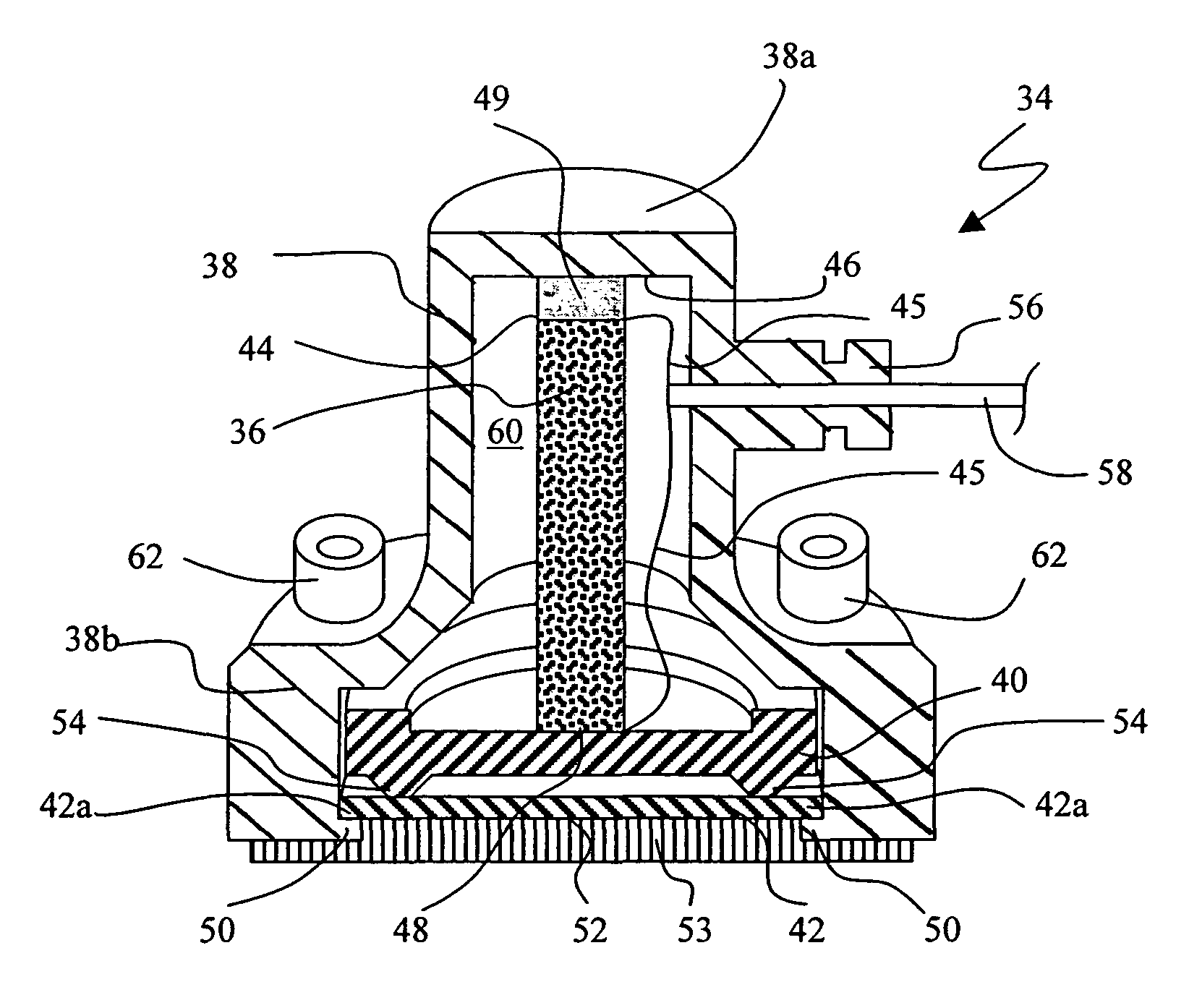
ActiveUS8396228B2Reduce noiseReducing and preventing transmissionStethoscopeCapacitanceSound detection
An active stethoscope or other sound detection device, including a diaphragm, at least one floating mass mounted to the diaphragm (at at least one coupling point of the diaphragm), and an acoustic transducer mounted to the floating mass. Preferably, each floating mass is configured and mounted so that as each floating mass and each coupling point of the diaphragm move in sympathy with acoustic waves (to be detected) that impinge on the diaphragm, the acoustic transducer rides with and is stabilized by the floating mass to which it is mounted and the diaphragm is stabilized by each floating mass. The acoustic transducer can be of any of many different types. For example, it can be a microphone, or an optical, capacitive, or inductive transducer. The diaphragm can have an isolating portion which absorbs acoustic surface wave energy incident thereon, or otherwise prevents or reduces transmission of acoustic surface waves through the isolating portion between regions of the diaphragm.
Owner:STETHOSCOPE TECH
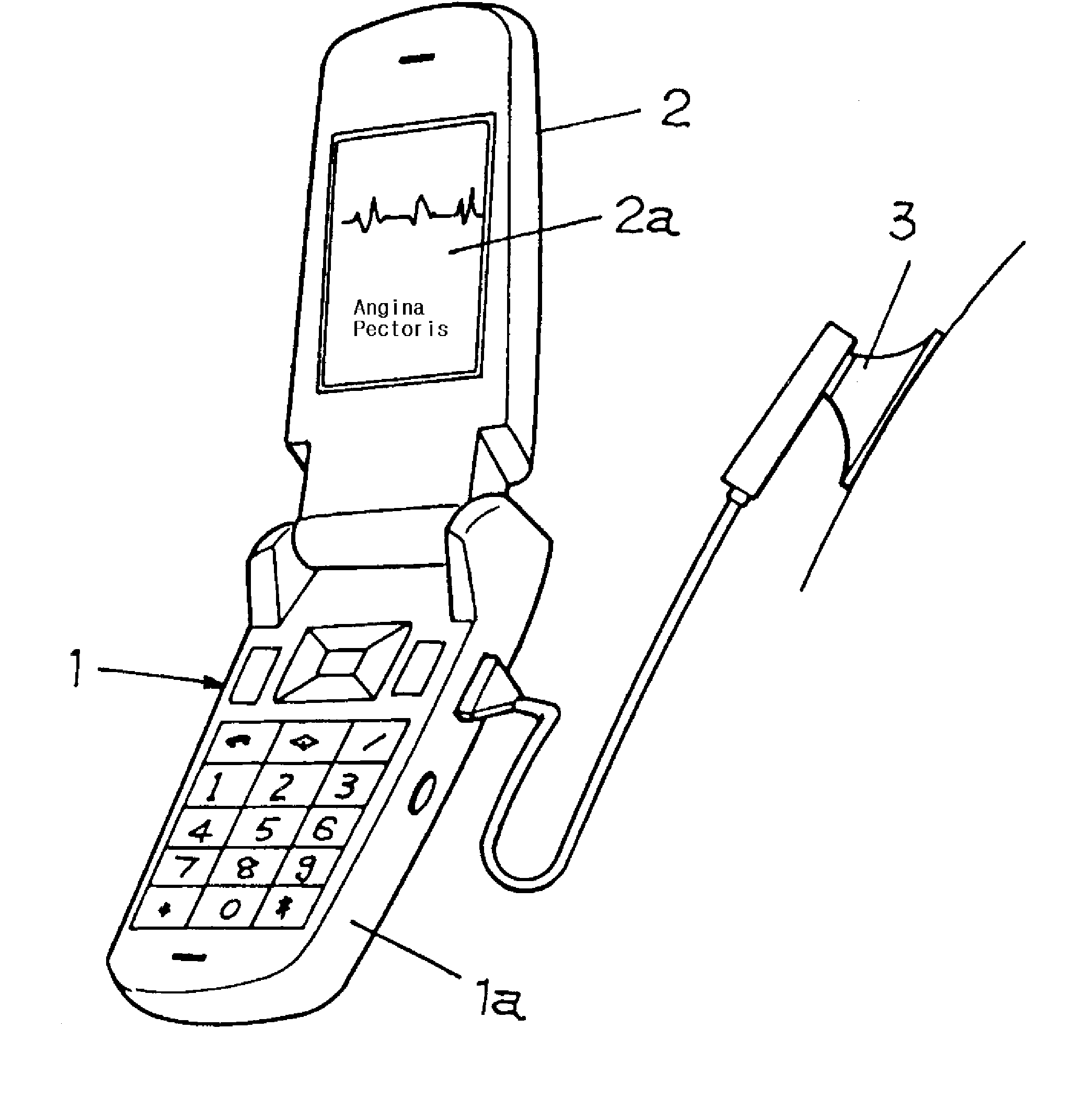
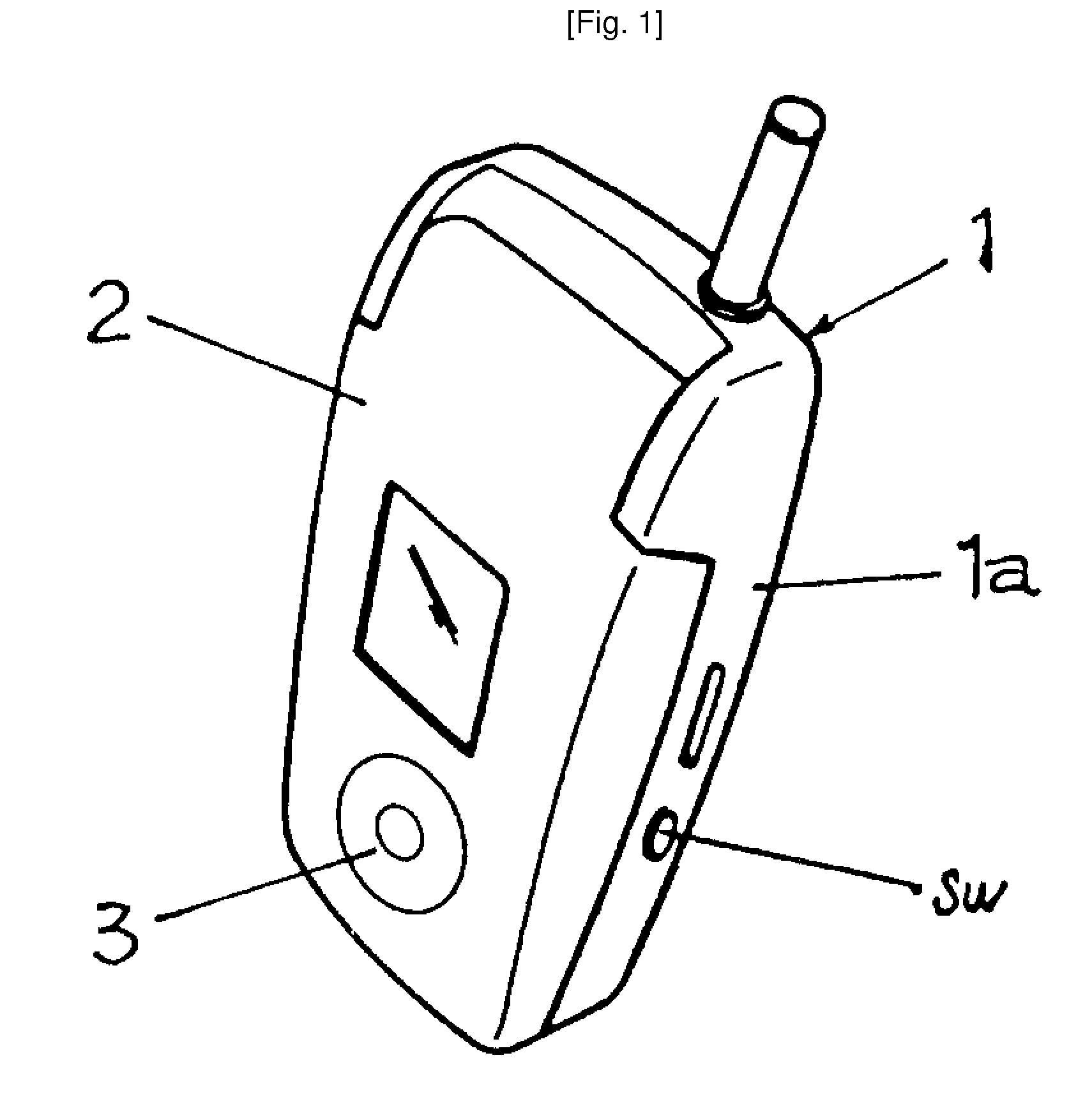
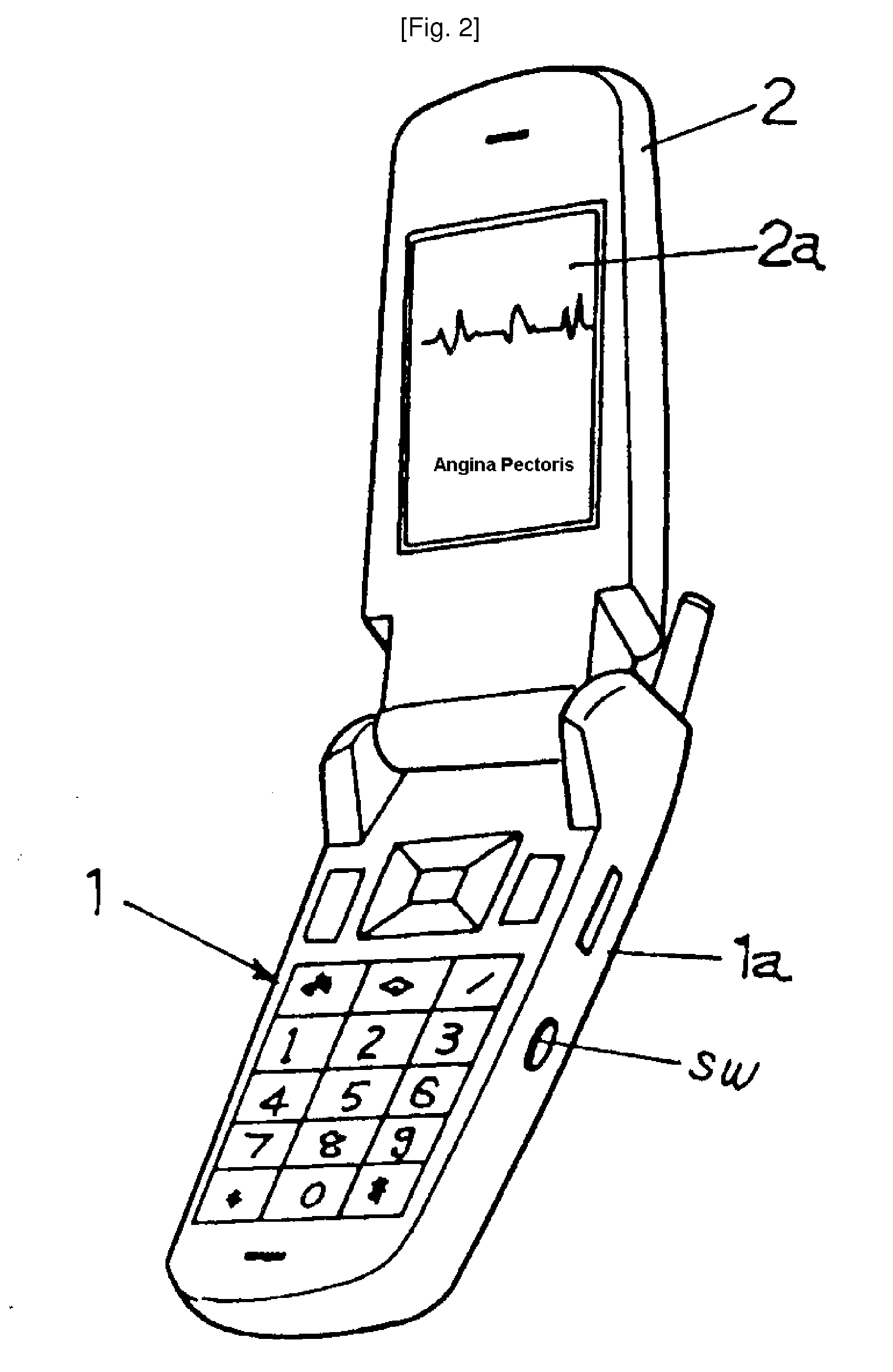
Mobile Phone With A Stethoscope
ActiveUS20080146276A1Improve physical healthFunction increaseStethoscopeSensorsDiagnostic dataData error
Disclosed herein is a mobile phone with a stethoscopic function. The mobile phone with a stethoscopic function, of which the mobile phone has communication data processing functions, comprises a stethoscopic microphone which is arranged in a body of the mobile phone; and a stethoscopic system which is embedded in the body of the mobile phone. The auscultated sound data obtained from the medical examination made on the part of a human body where the stethoscopic microphone is contacted are converted into digital auscultated sound data. The digital auscultated sound data identifies corresponding sound data in the pre-stored standardized digital auscultating sound data through search and comparison within allowable errors of data. With the identified data, a diagnostic data is made available. The diagnostic data may be stored and transmitted to a physician using the communication function of the mobile phone.
Owner:LEE BYUNG HOON
Mobile front-end system for comprehensive cardiac diagnosis
ActiveUS20150065814A1Easy to install and removeConnection is requiredUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStethoscopeHeart soundsBack end server
A stethoscope front-end recorder device (also referred to as Sleeve) for the chest piece of a stethoscope, which is easily installed and removed. The Sleeve is attached to the chest piece of a stethoscope for comprehensive diagnosis of heart issues. The Sleeve contains sensors for acquiring biosensor parameters such as electrocardiogram, body temperature, heartbeat, heart rhythm, heart rate variability, heart rate turbulence, heart sounds, respiration, cardiac index and blood flow. The Sleeve has Bluetooth interface communicating with a mobile device with software component, interfacing with a back-end server with the capability to capture, analyze and save patient information.
Owner:RIJUVEN
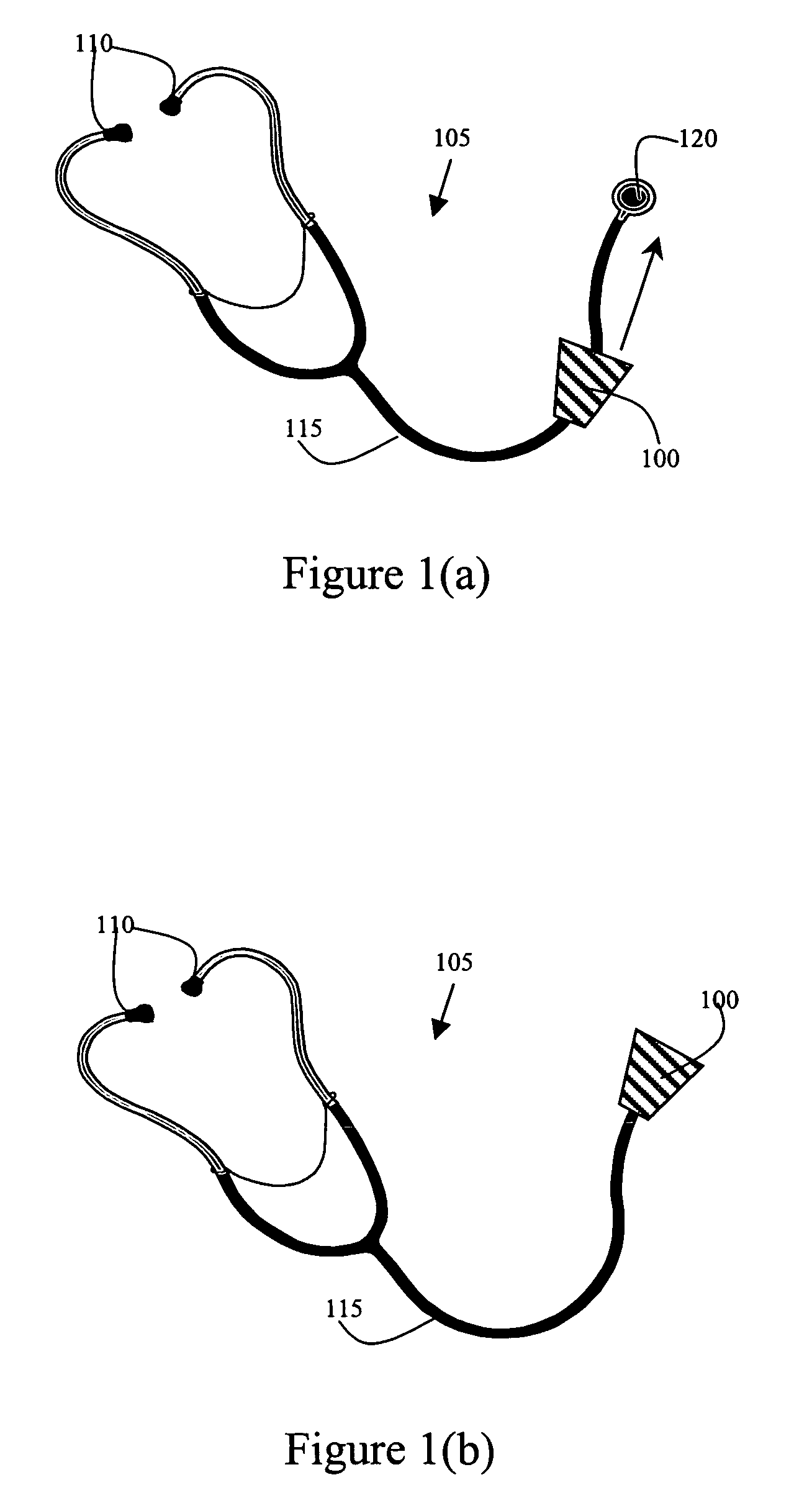
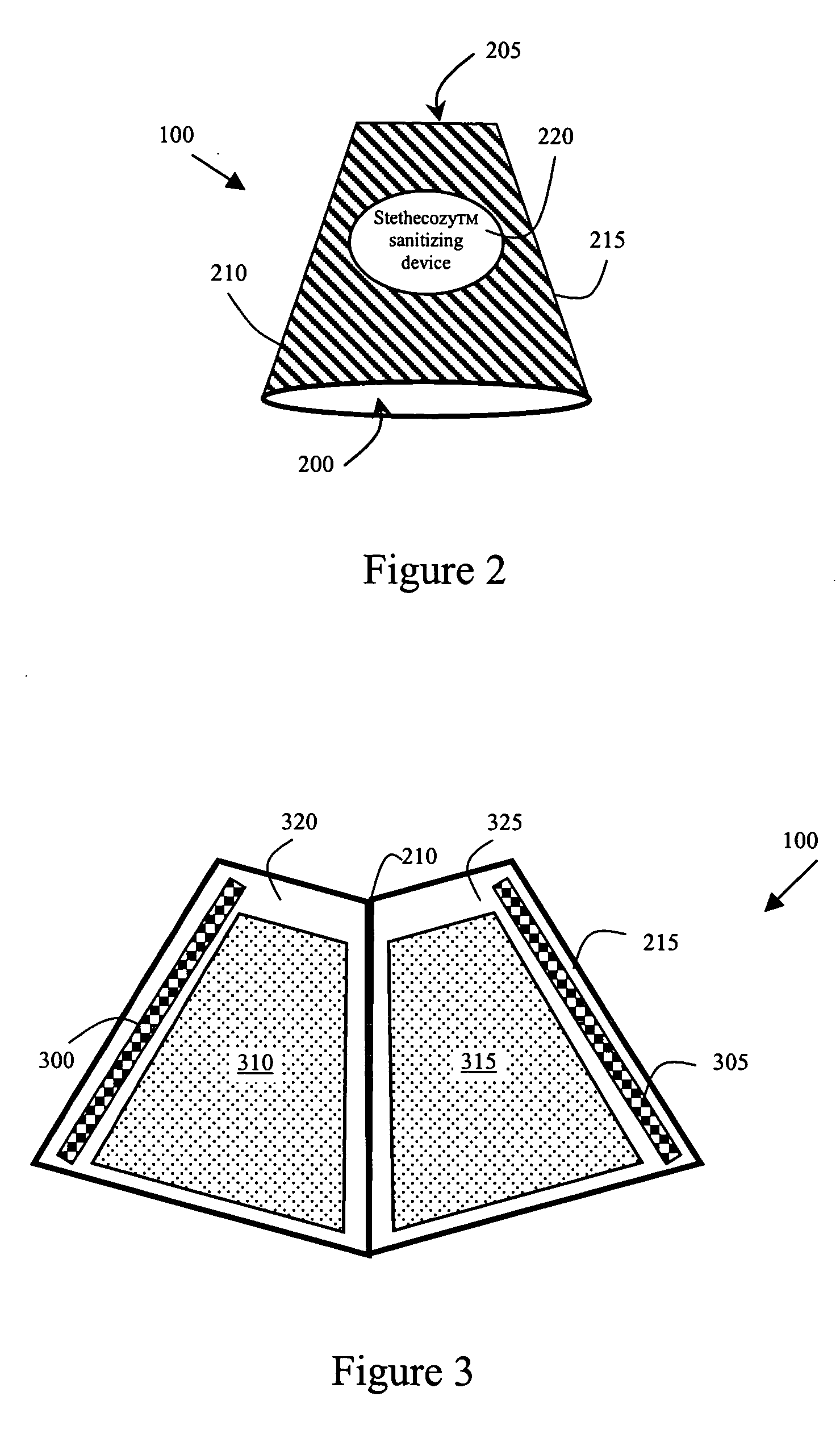
Wearable stethoscope sanitizing device
InactiveUS20070080017A1Little effortSurface cleaningStethoscopeLavatory sanitoryBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
A small, lightweight sanitizing device that is adapted for attachment to a stethoscope. When the stethoscope is not being used the device covers the diaphragm and bell portions of the stethoscope with sanitizing pads that kill germs and prevent the spread of disease between patients that are examined with the stethoscope. When the health care provider needs to use the stethoscope, the device can be slid up a length of the stethoscope to a desired location so that the diaphragm is exposed for use. The device is advantageously produced with a narrow top that frictionally engages with the tube of the stethoscope so that the sanitizing device stays at the desired location until the user pulls the device back down over the diaphragm. The present sanitizing device can be used with both adult and pediatric stethoscopes. In an alternative embodiment, the sanitizing device is designed to be held within the front pocket of a health care provider's shirt or lab coat so that sterilization of the diaphragm and bell are achieved by simply placing the head portion of the stethoscope in the front pocket.
Owner:STICKLEY ROBERT F
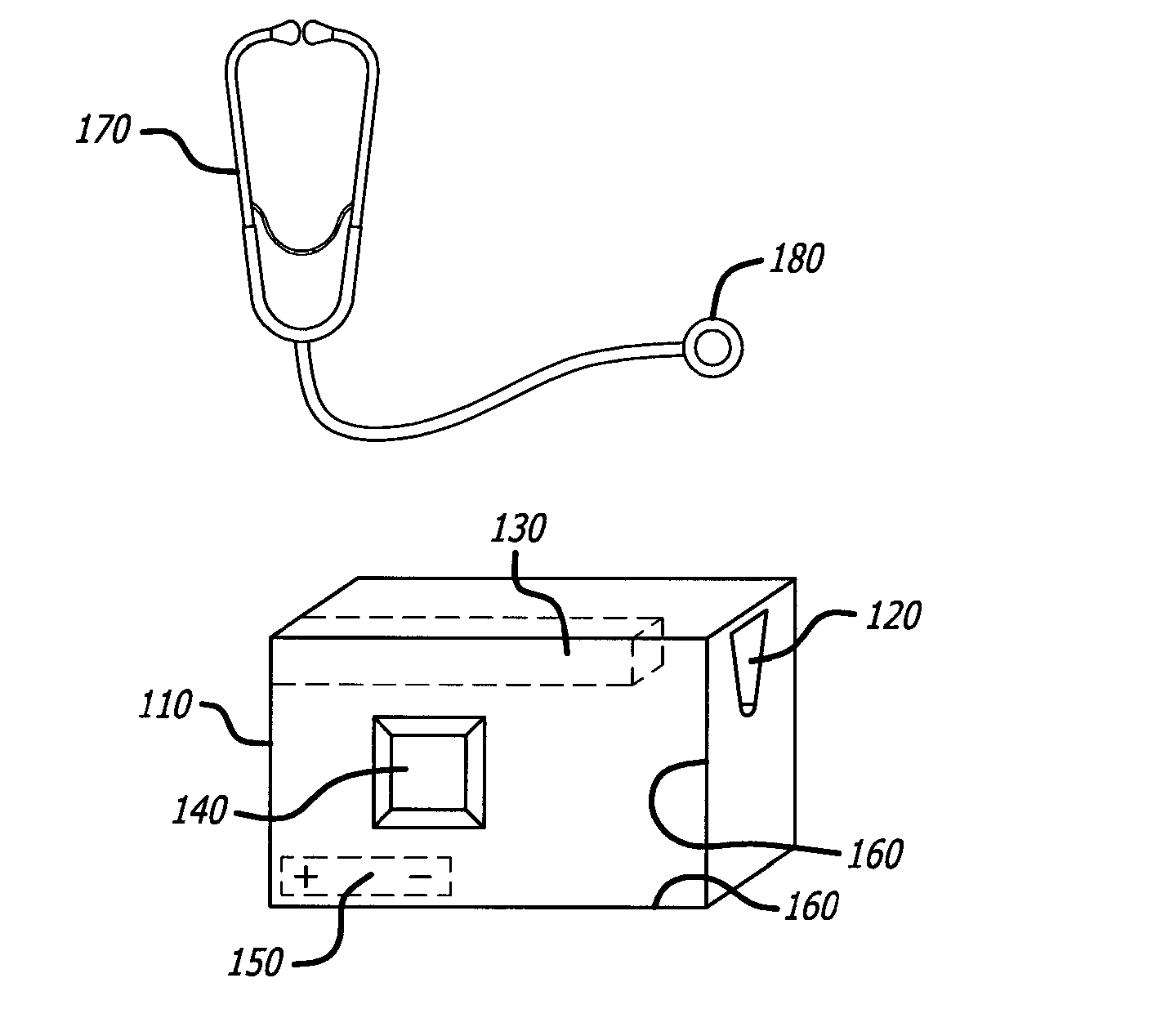
Telemedical stethoscope
The present invention relates to a telemedical stethoscope, which automatically diagnoses a disease, and records visually and auditorily, and stores the stethoscope data on a screen. The present invention enhances primary diagnosis and treatment effect for a patient by transmitting / receiving the data to / from a doctor at a medical center and by receiving a telemedicine service. In addition, the present invention transmits the data to a health management program so as to be used for personal healthcare and disease prognosis decision of a patient.
Owner:LEE BYUNG HOON +1
Arterial endothelial function measurement method and apparatus
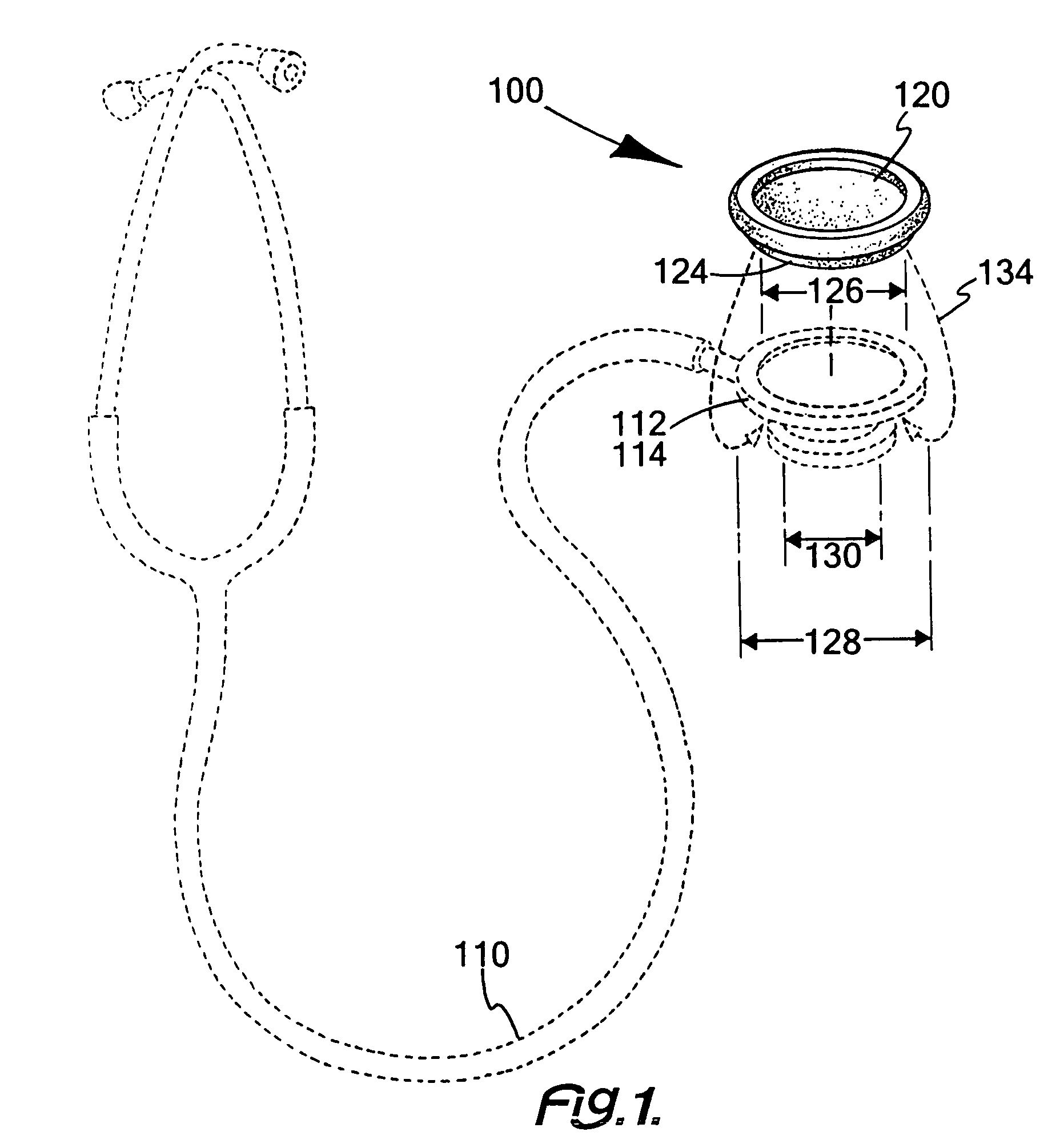
ActiveUS20060264755A1High outputEasy to detectOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsArteriolar VasoconstrictionArterial diameter
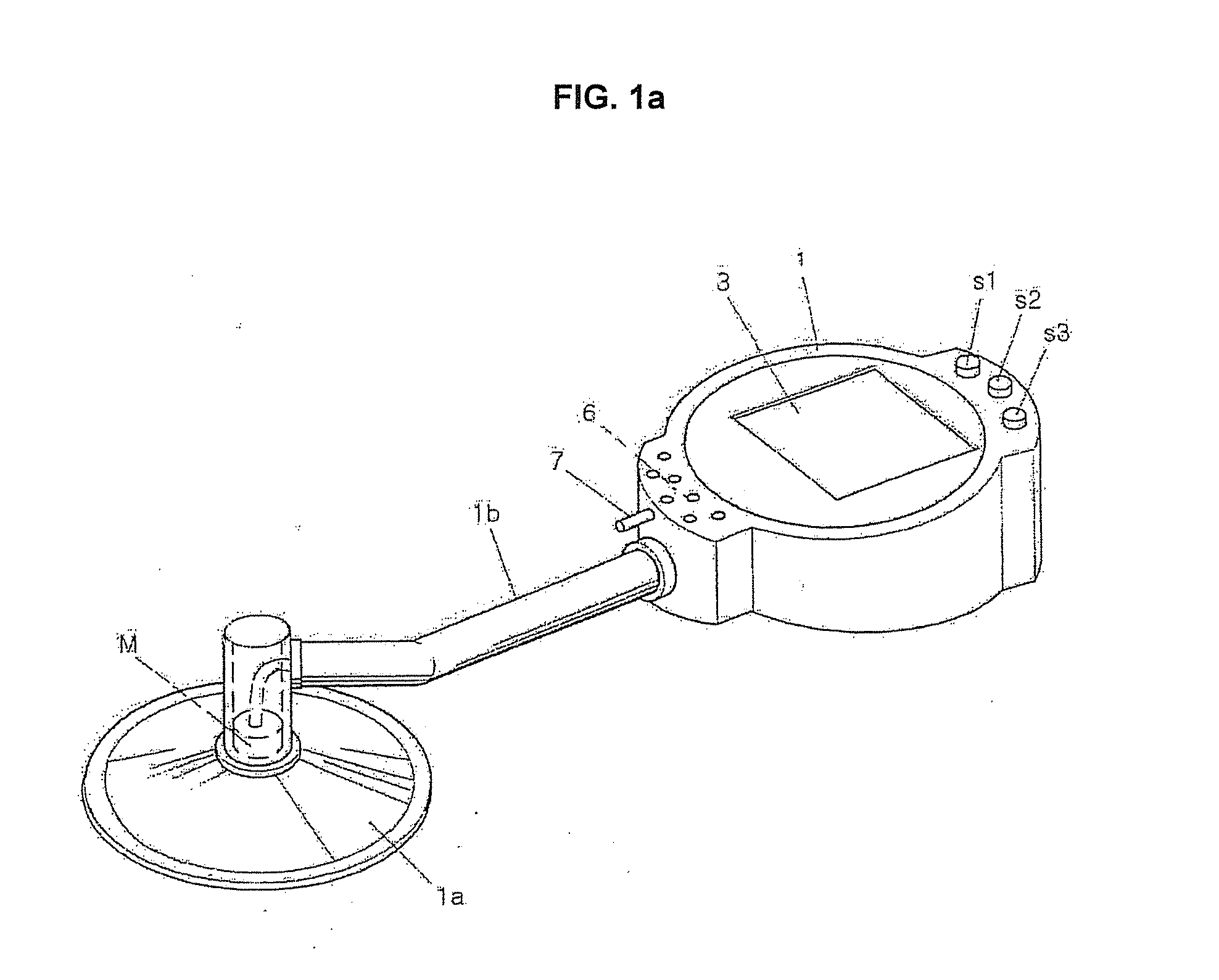
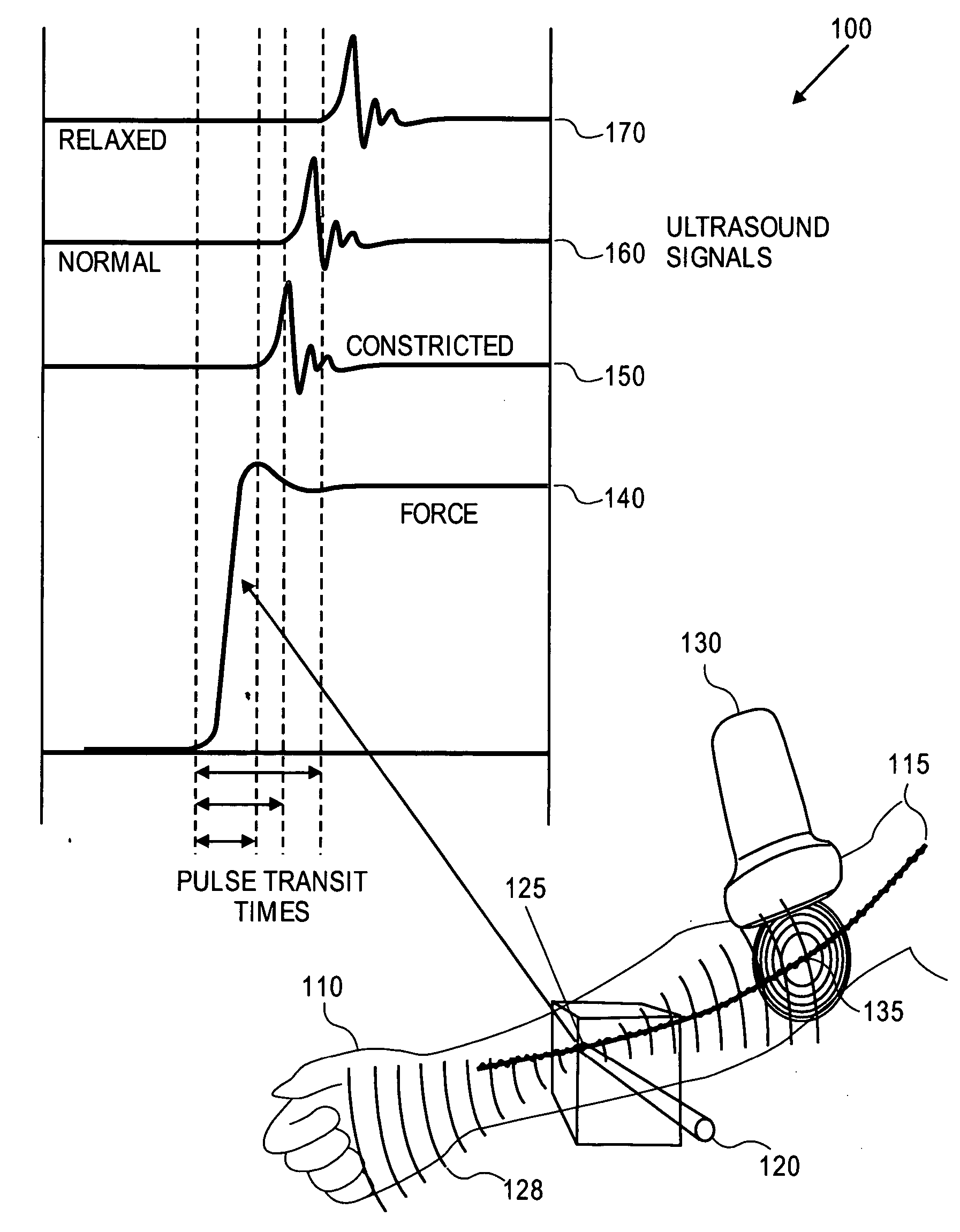
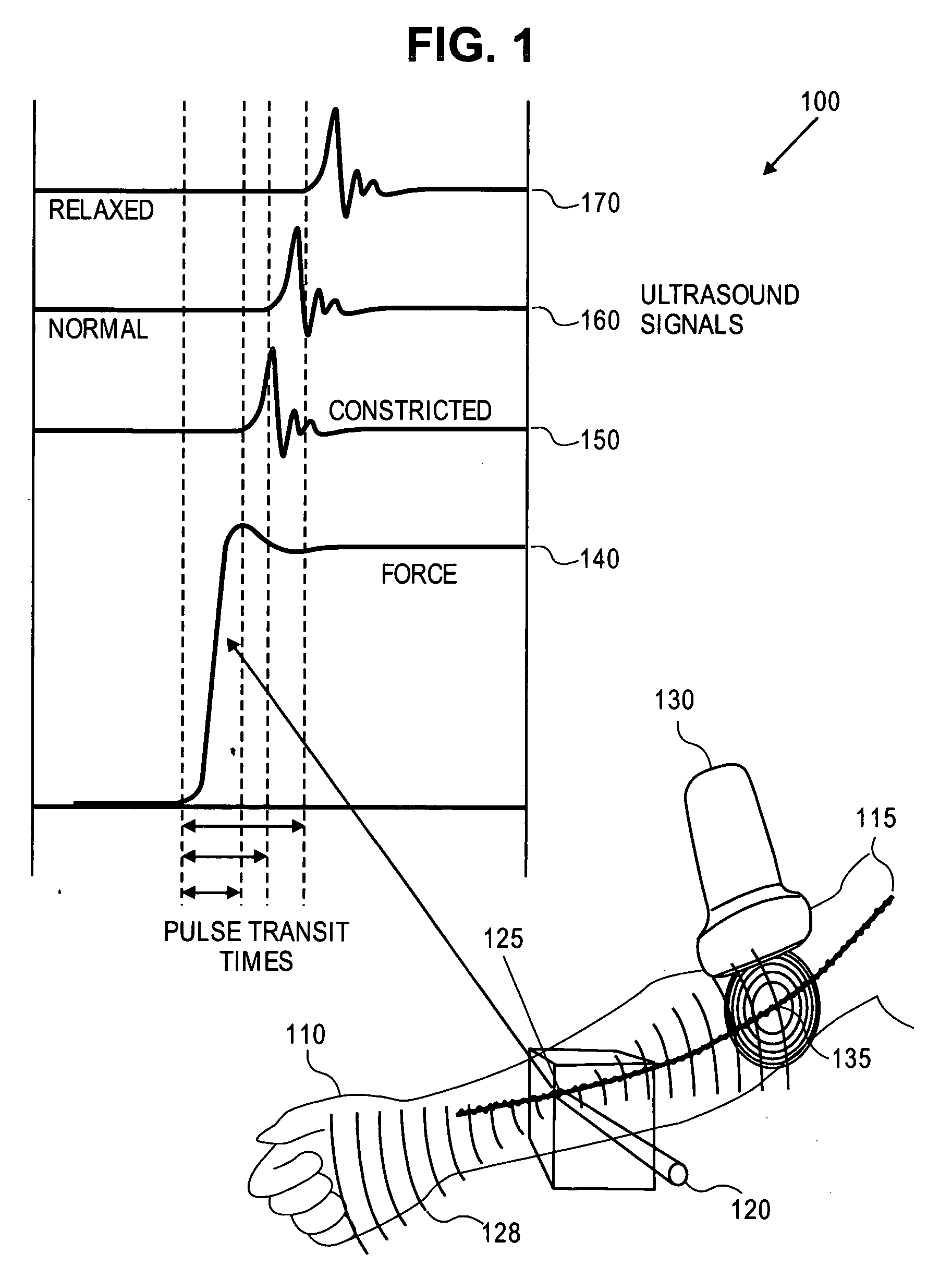
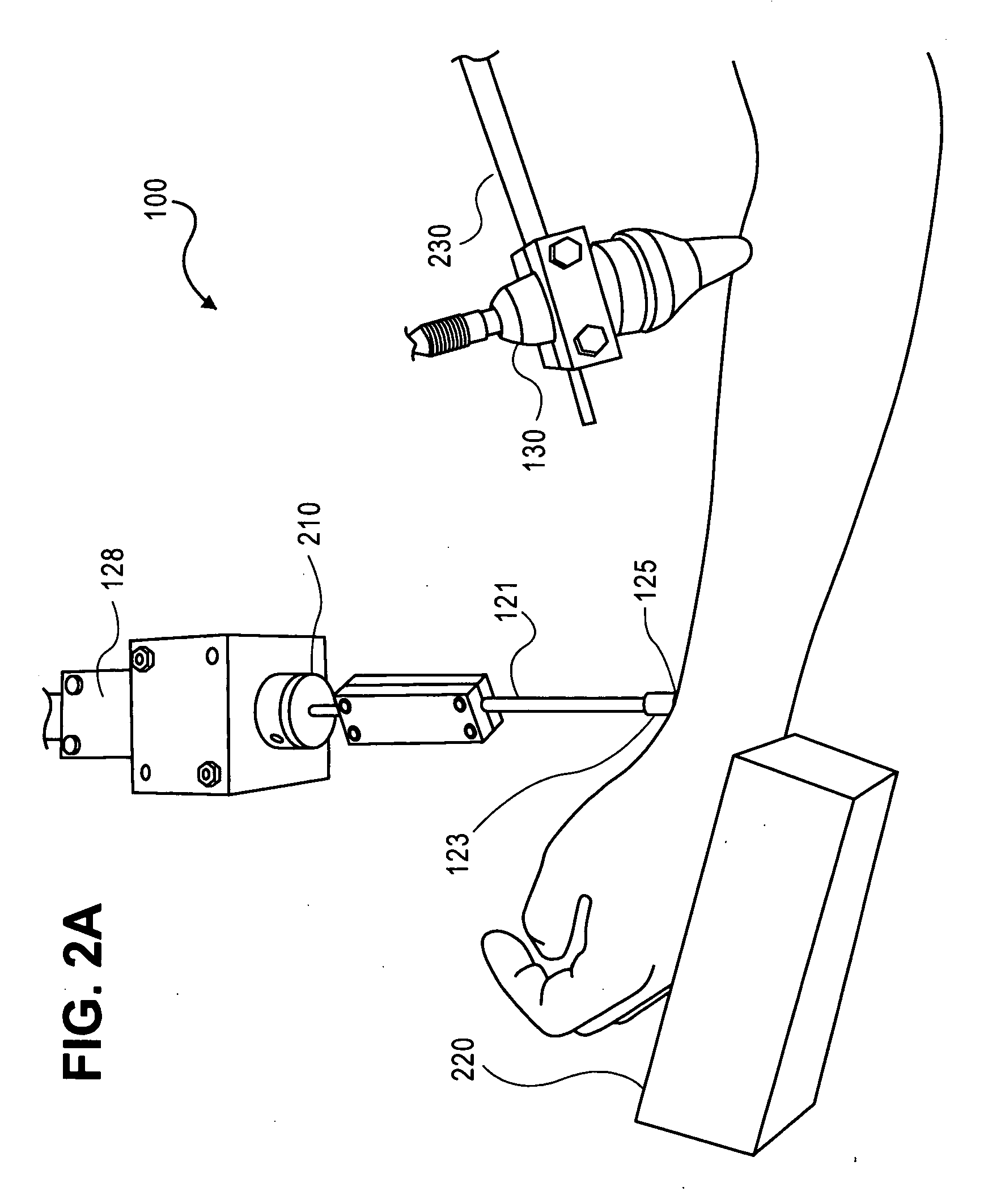
A “relaxoscope” (100) detects the degree of arterial endothelial function. Impairment of arterial endothelial function is an early event in atherosclerosis and correlates with the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease. An artery (115), such as the brachial artery (BA) is measured for diameter before and after several minutes of either vasoconstriction or vasorelaxafion. The change in arterial diameter is a measure of flow-mediated vasomodification (FMVM). The relaxoscope induces an artificial pulse (128) at a superficial radial artery (115) via a linear actuator (120). An ultrasonic Doppler stethoscope (130) detects this pulse 10-20 cm proximal to the point of pulse induction (125). The delay between pulse application and detection provides the pulse transit time (PTT). By measuring PTT before (160) and after arterial diameter change (170), FMVM may be measured based on the changes in PTT caused by changes in vessel caliber, smooth muscle tone and wall thickness.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multifunction health apparatus
The present invention provides a multifunction health device, which comprises a meter and a platform. The meter has two electrodes arranged separately at its two sides, and another electrode arranged in its bottom. The platform has four electrodes arranged in its top face, and a pressure sensor arranged in its inside. With or without some parts assisting, the single use of the meter can function as an ECG detector, a TENS machine, a thermometer, and a first sphygmomanometer. Connecting with the platform, the meter and the platform can function as an ECG detector, a weight scale, and a body composition estimator. Further, the meter can alternatively connect with a chassis thus functioning as a second sphygmomanometer, a stethoscope, a glucose meter, or a pulse oximeter.
Owner:TSO SHUN WUN
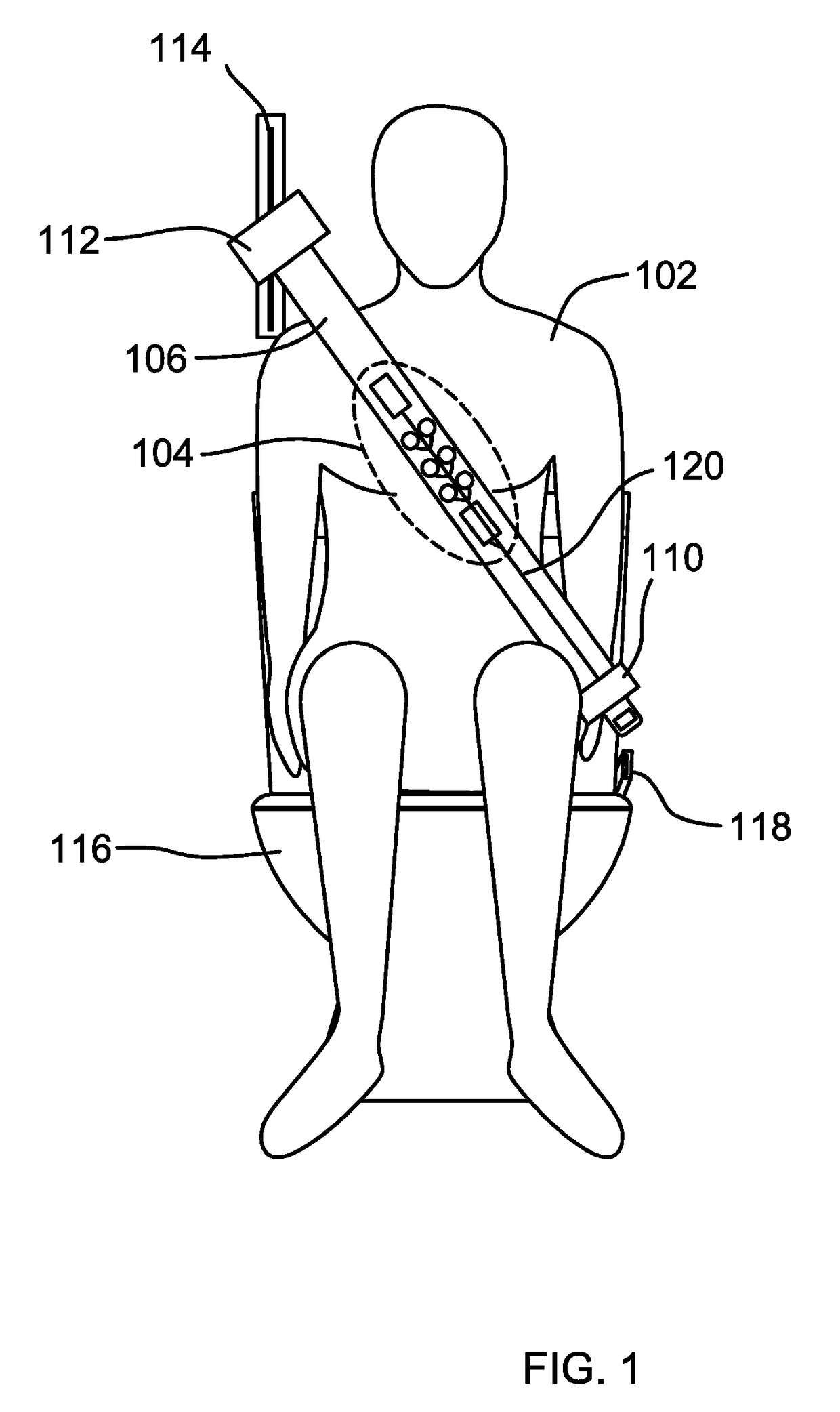
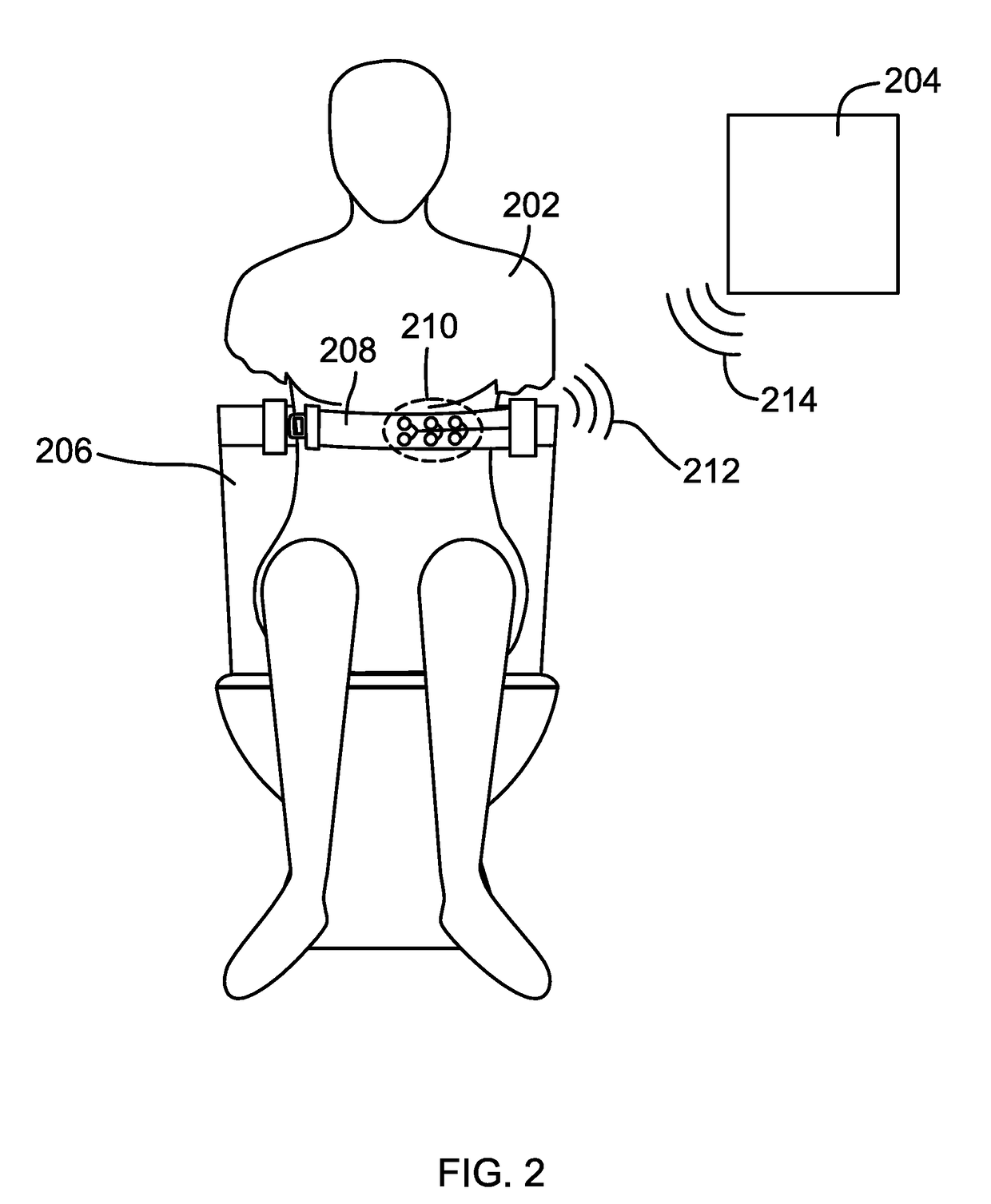
Method of Monitoring Health While Using a Toilet
ActiveUS20180020984A1Different heightUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyEnvironmental healthLatrine
A method of obtaining health data of a toilet user using one or more sensors is disclosed. One or more sensors are used by a toilet user while the toilet user is using the toilet to take health measurement readings of the user. Dynamic heart stress readings may be obtained and monitored over weeks, months and years. Rolling averages of heart function and heart health may be determined and deviations from the rolling averages may trigger notifications. Other health related measurements and functions such as temperature, respirations, heart rate, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and stethoscope sounds are also recorded and stored for trending and data analysis.
Owner:MEDIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com