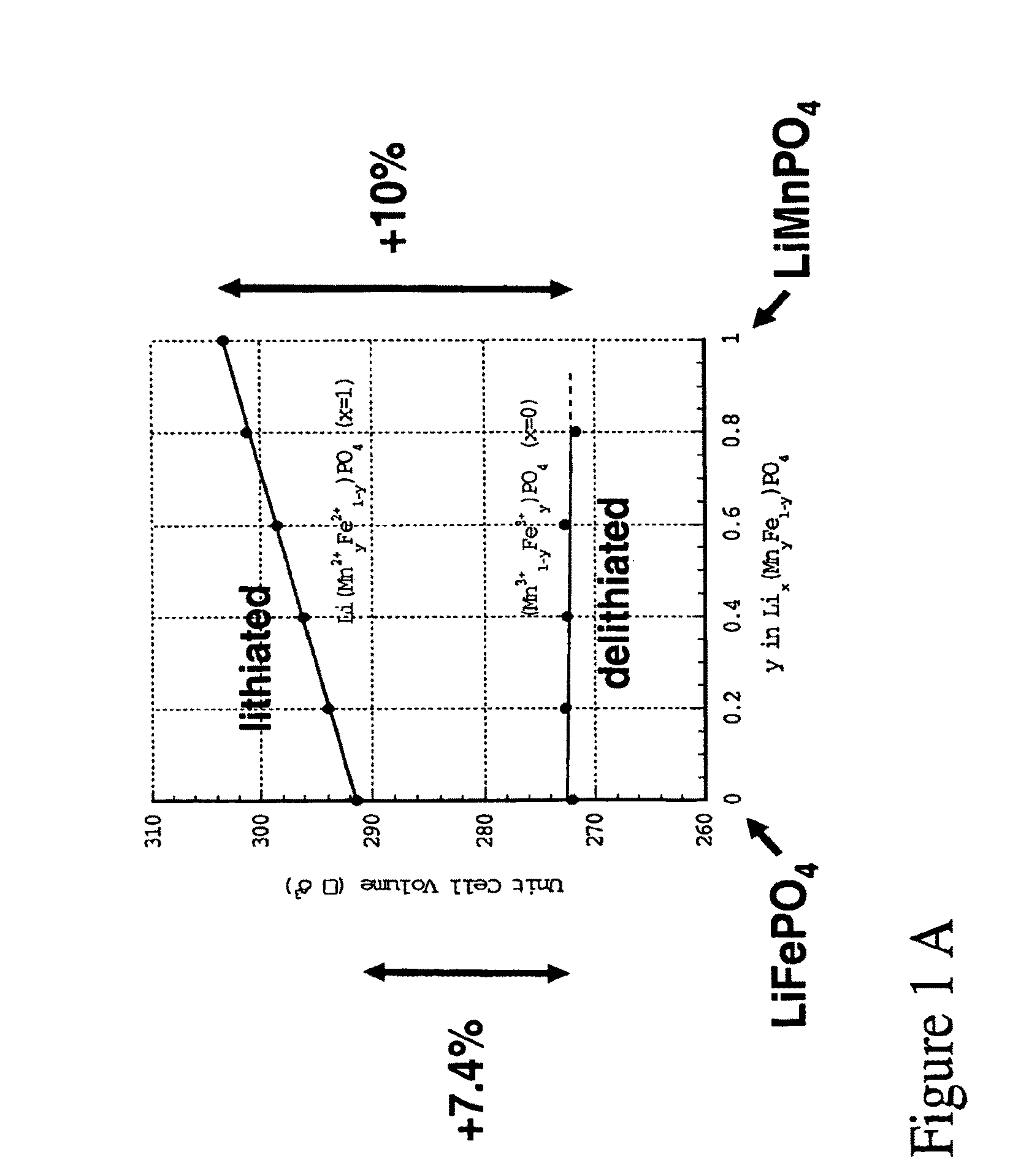
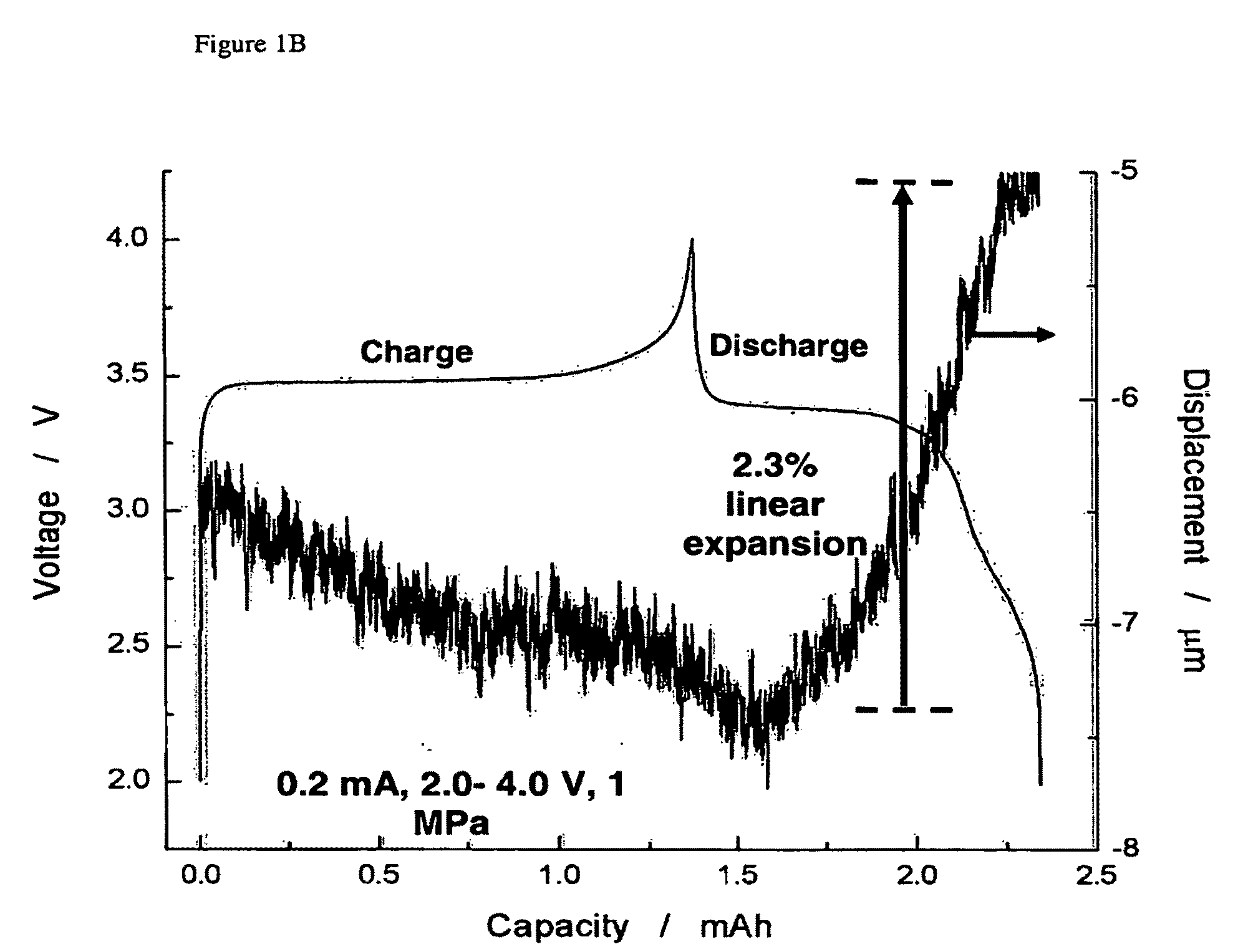
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
611results about How to "Increase strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
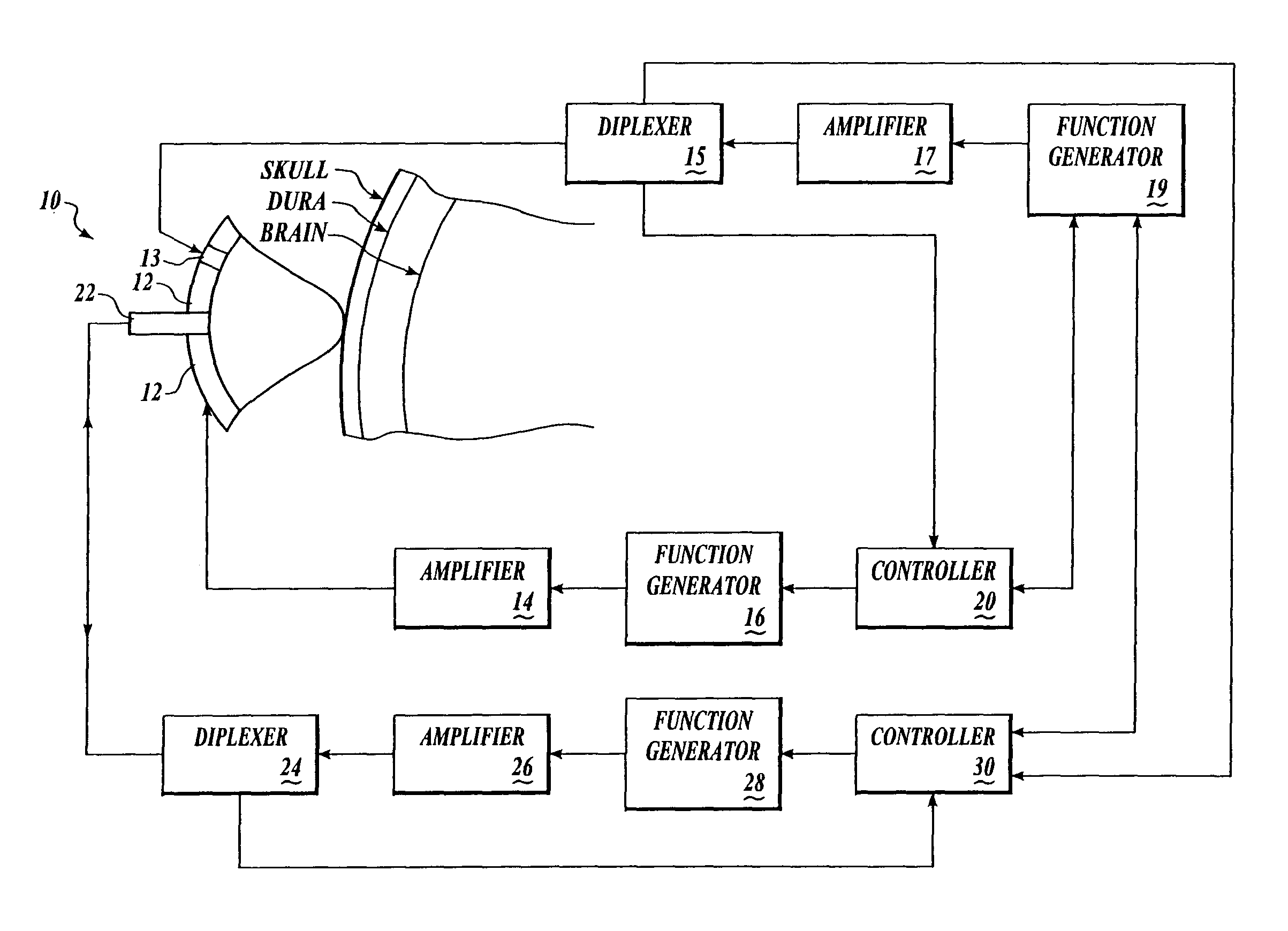
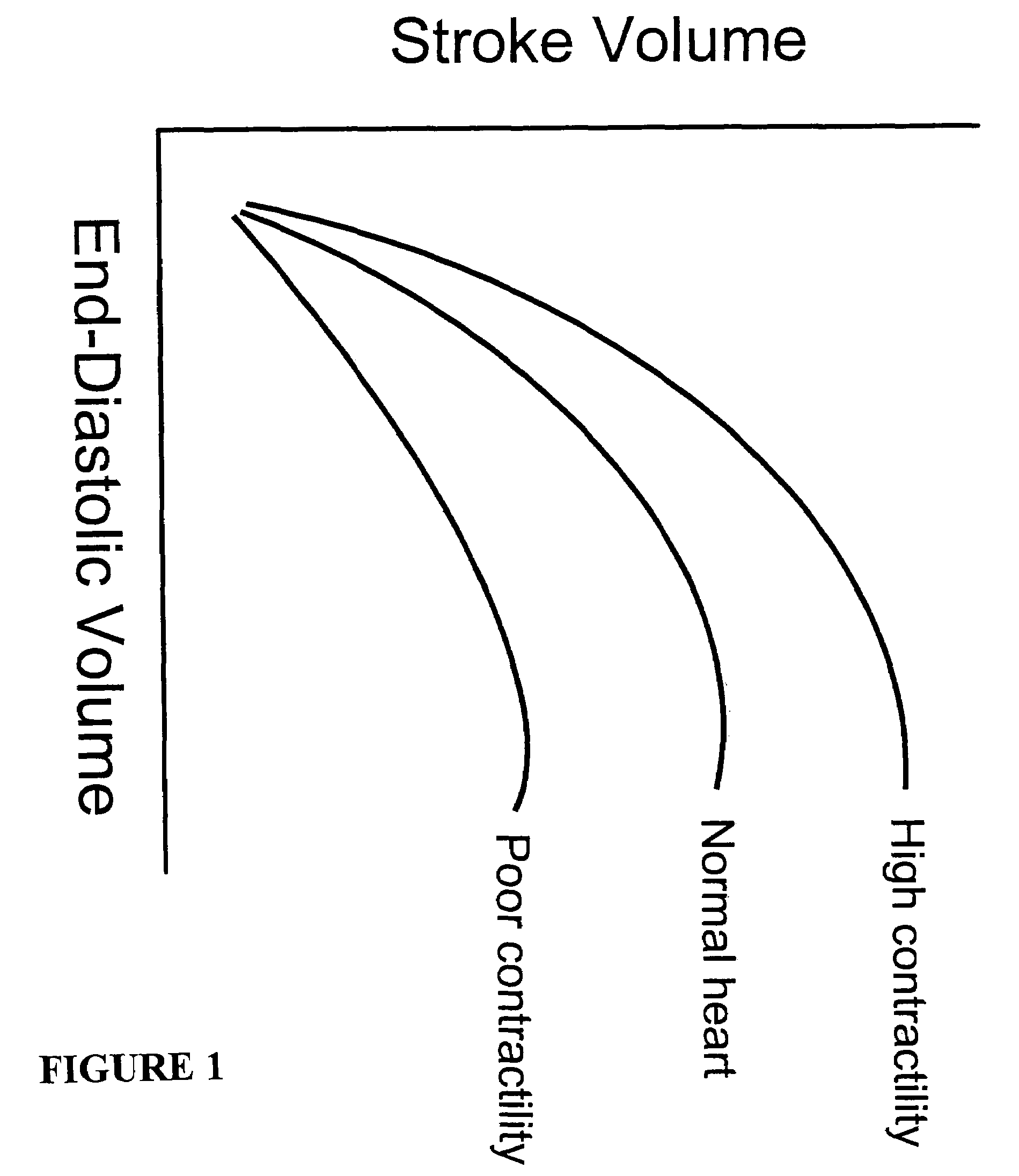
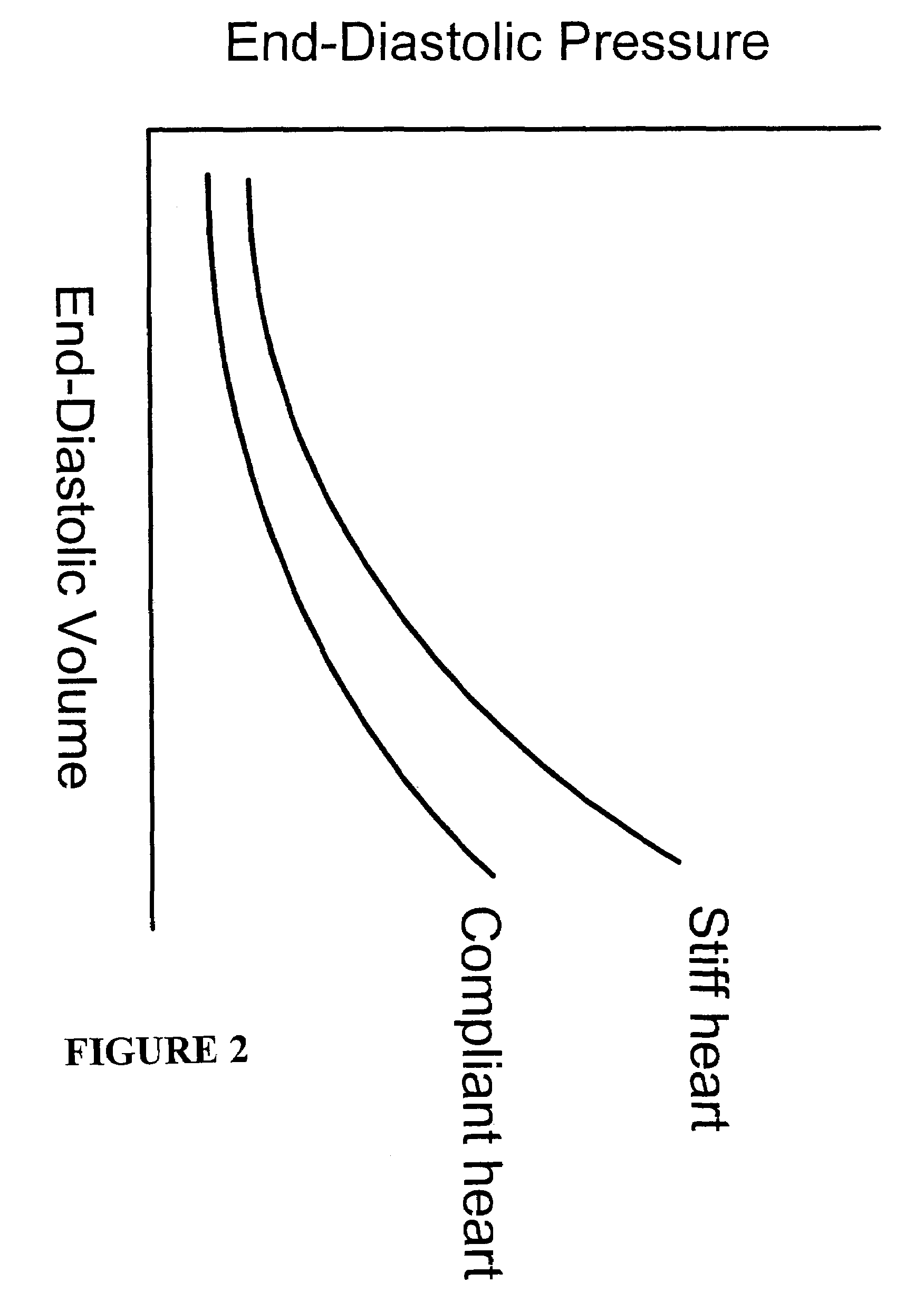
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Dynamic spinal stabilization device
InactiveUS20070288009A1Reduce movementIncrease strainInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsElectrical resistance and conductanceSpinal column
The present invention provides a dynamic stabilization device positionable about a portion of a spinal column. The stabilization device may generally include a first component and a second component, where the first and second components are movably coupled to one another to define an arcuate path of motion. The stabilization device may also include one or more adjustment elements positionable within first and second adjustment openings to affect the path of motion between the first and second components and / or the behavior and characteristics of the movement. In addition, one or more resistive elements may be adjustably positionable within either and / or both of the first and second adjustment openings to provide resistance and / or dampening of the forces experienced as the first and second components move relative to one another. The stabilization device may further define a joint having three degrees of freedom to adapt to movement of a spinal column.
Owner:DISC MOTION TECH
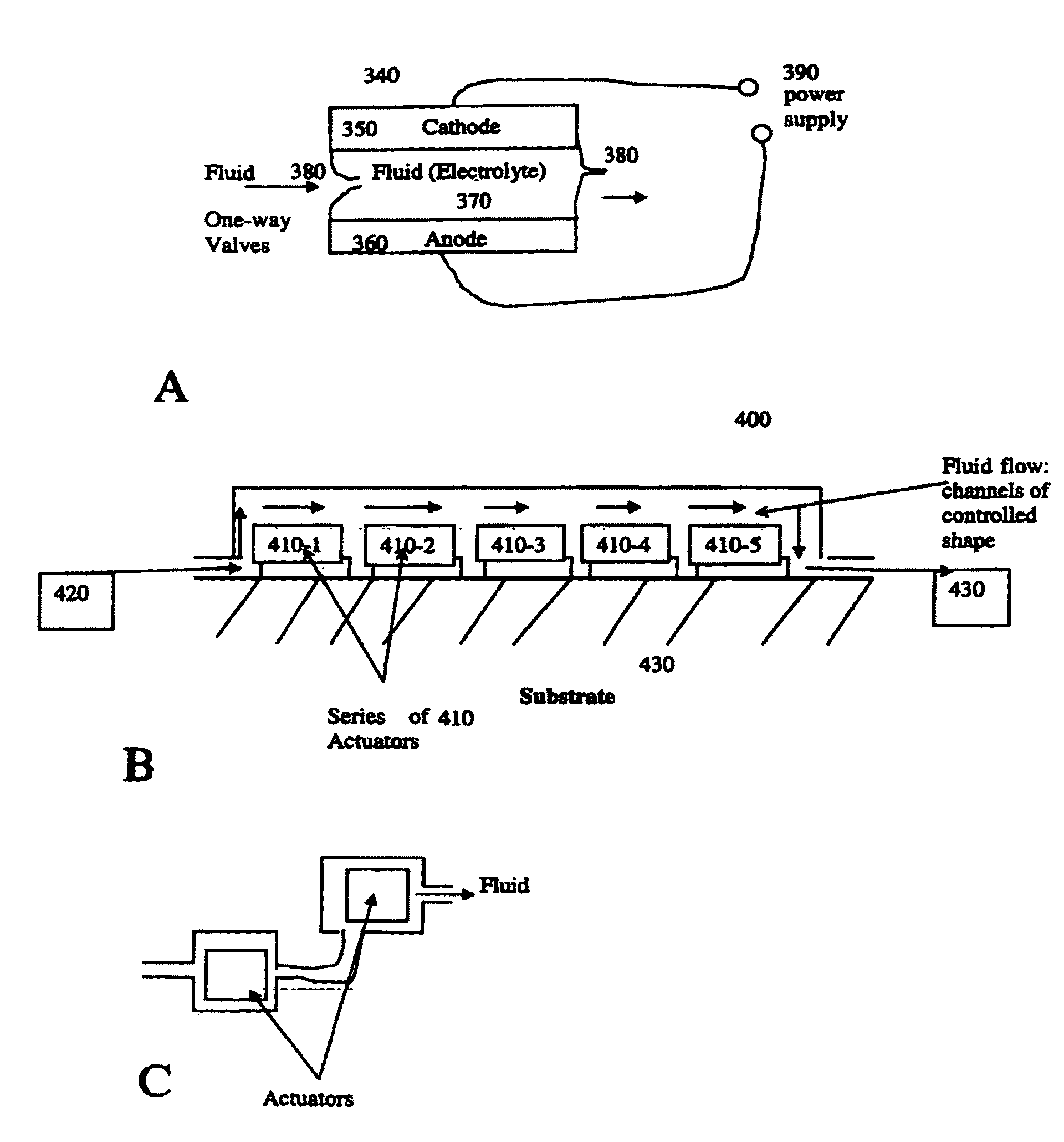
Electrochemical methods, devices, and structures
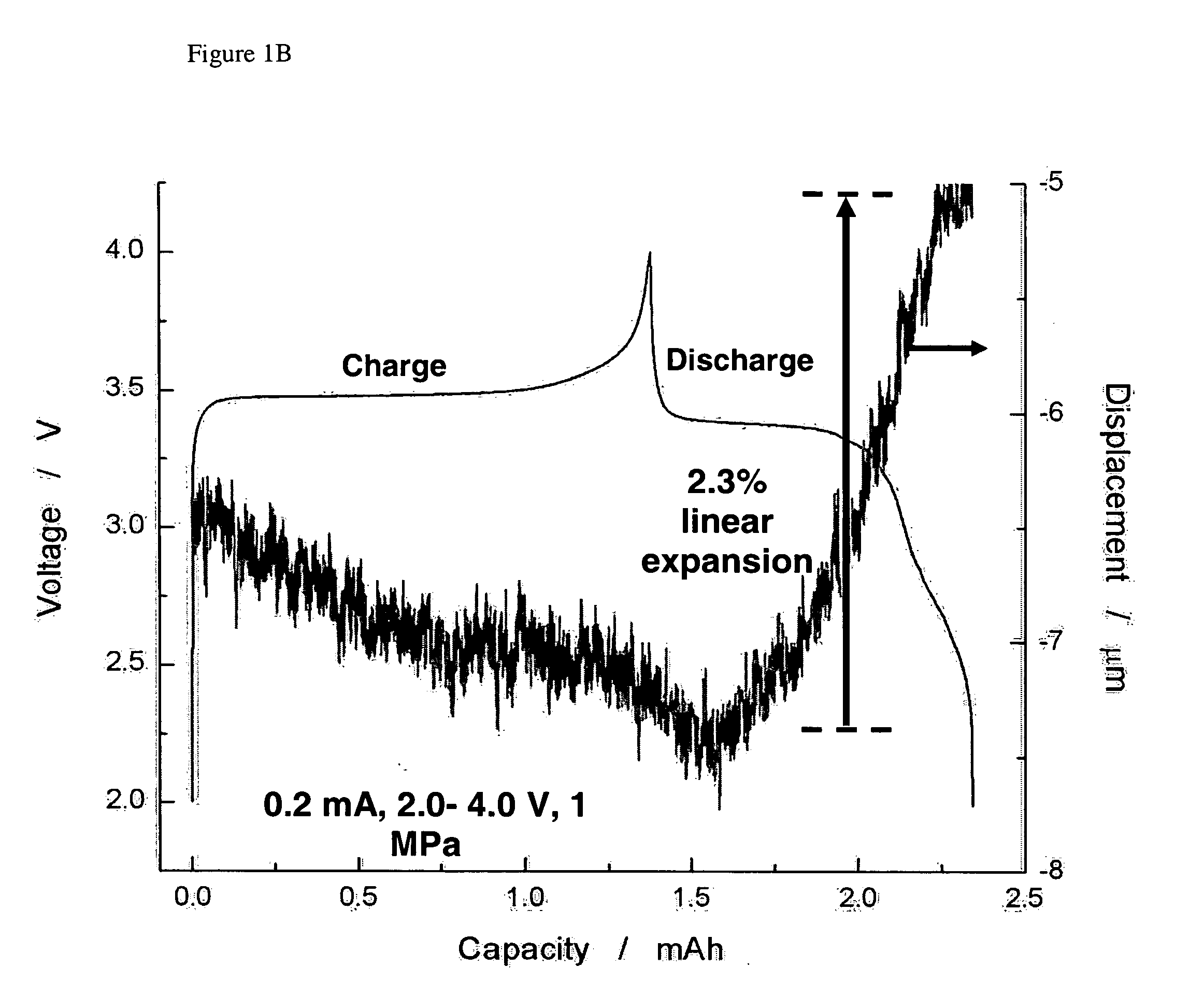
ActiveUS20060102455A1Increase strainDeferred-action cellsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersInorganic compoundElectrochemistry
The present invention provides devices and structures and methods of use thereof in electrochemical actuation. This invention provides electrochemical actuators, which are based, inter-alia, on an electric field-driven intercalation or alloying of high-modulus inorganic compounds, which can produce large and reversible volume changes, providing high actuation energy density, high actuation authority and large free strain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
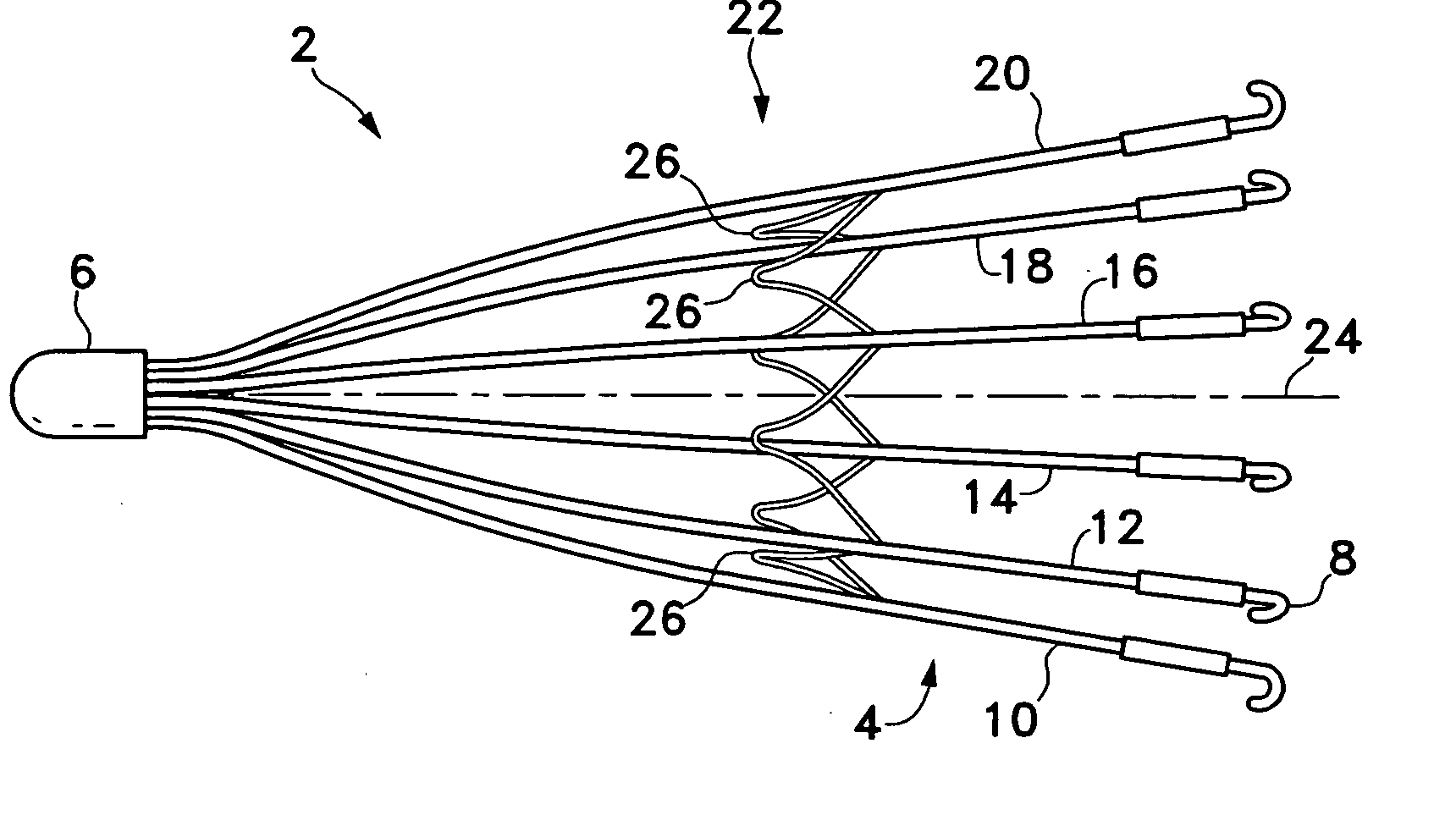
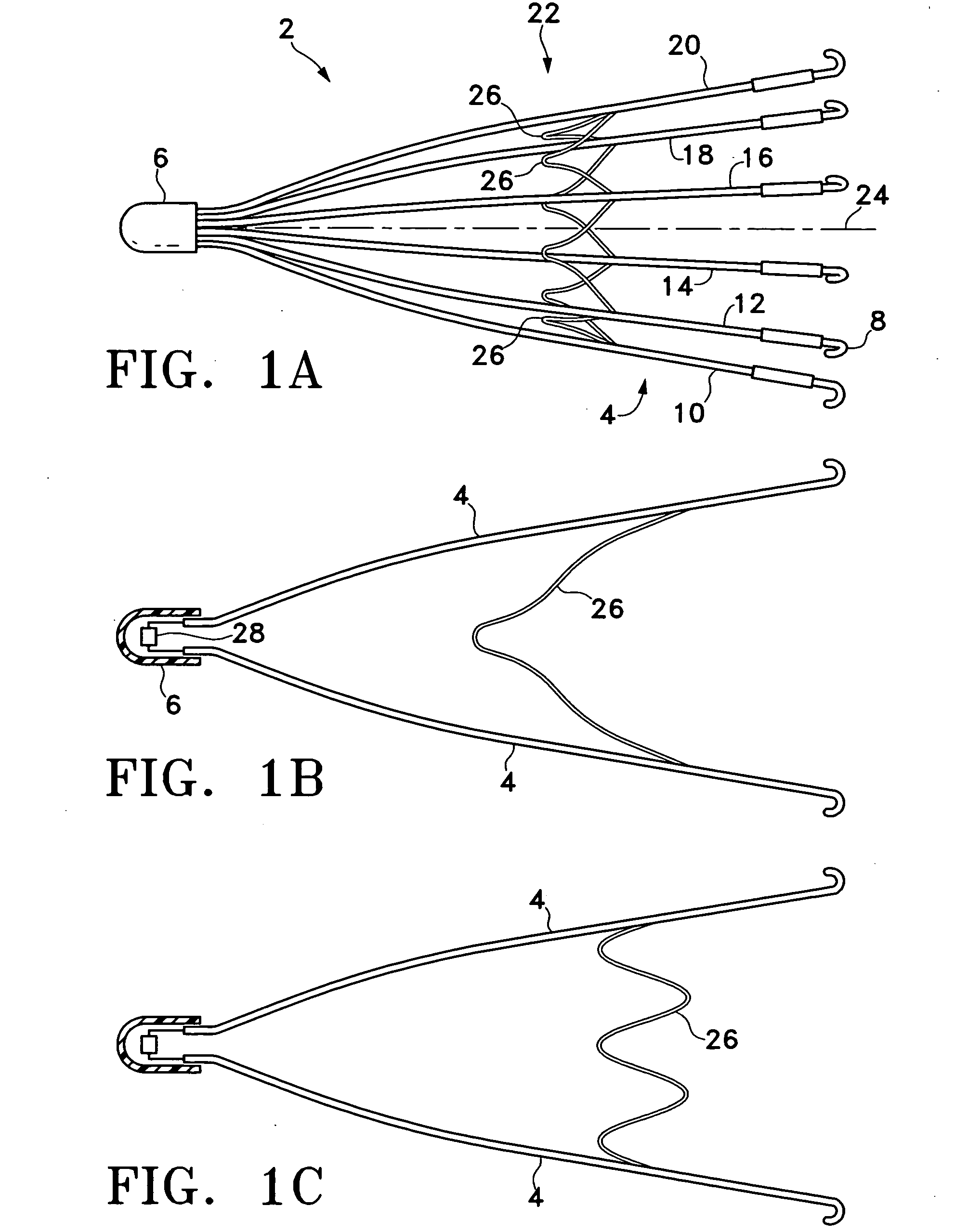
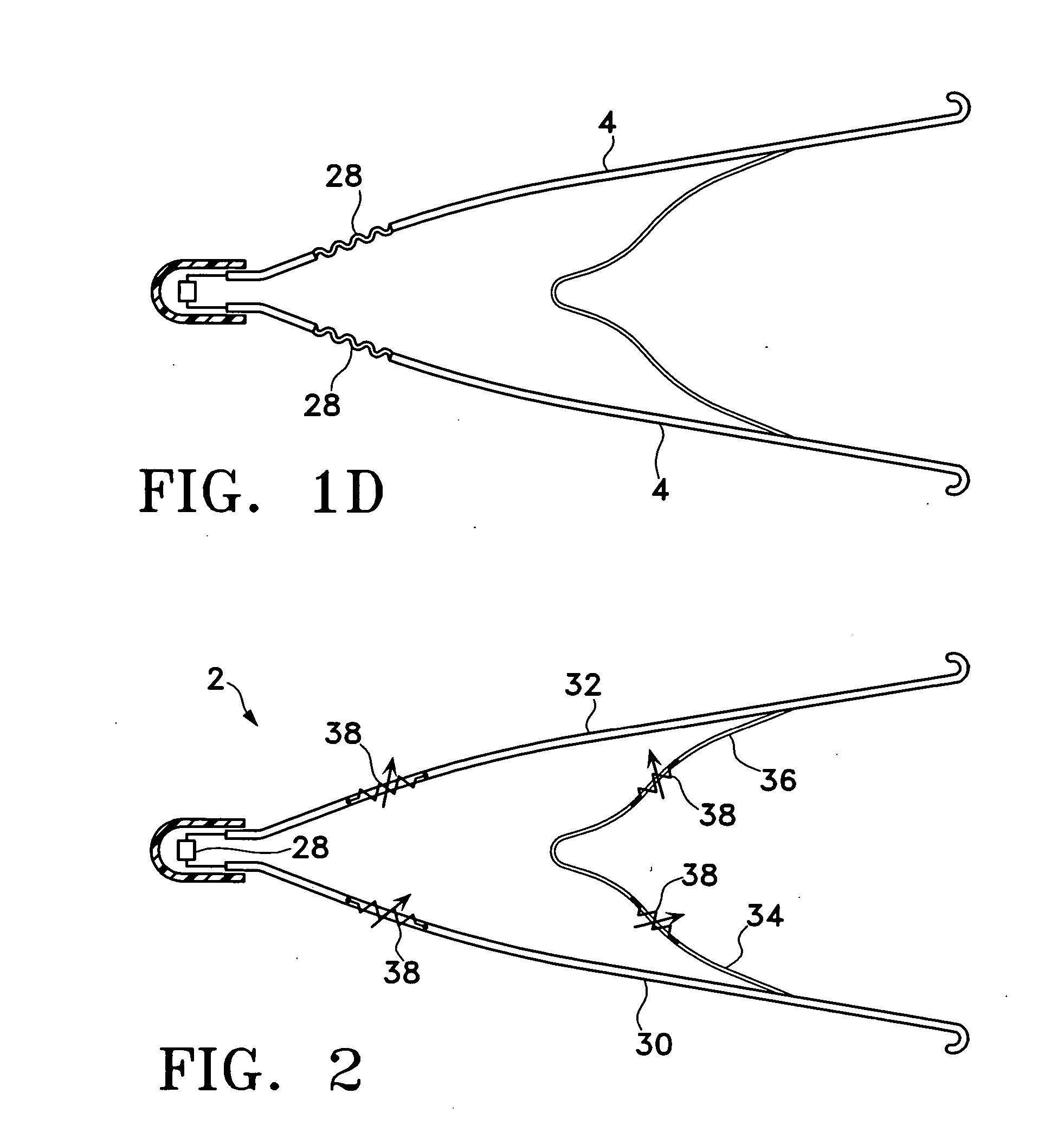
Vascular filter with sensing capability
An implantable vessel filter having an integrated sensing capability for monitoring the condition of the vessel filter. In one variation, the vessel filter comprises a plurality of legs that would themselves perform as a sensor device for detecting distention, which would indicate the presence of a clot or thrombus therein. A passive electrical circuit may be implemented on the vessel filter to receive electromagnetic energy and transmit signals indicative of the condition of the implanted vessel filter. In another variation, a miniaturized sensor is adapted for measuring the strain and / or other physical parameters of the filter legs.
Owner:CR BARD INC
III-V Nitride homoepitaxial material of improved MOVPE epitaxial quality (surface texture and defect density) formed on free-standing (Al,In,Ga)N substrates, and opto-electronic and electronic devices comprising same
InactiveUS20030213964A1Improve material qualityReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCelsius DegreeSource material
A III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structure comprising a III-V nitride homoepitaxial epi layer of improved epitaxial quality deposited on a III-V nitride material substrate, e.g., of freestanding character. Various processing techniques are described, including a method of forming a III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer on a corresponding III-V nitride material substrate, by depositing the III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer by a VPE process using Group III source material and nitrogen source material under process conditions including V / III ratio in a range of from about 1 to about 10<5>, nitrogen source material partial pressure in a range of from about 1 to about 10<3 >torr, growth temperature in a range of from about 500 to about 1250 degrees Celsius, and growth rate in a range of from about 0.1 to about 10<2 >microns per hour. The III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structures are usefully employed in device applications such as UV LEDs, high electron mobility transistors, and the like.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Cardiac motion tracking using cine harmonic phase (HARP) magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6892089B1High speedAccurate operationSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringCircumferential strainFourier transform on finite groups
The present invention relates to a method of measuring motion of an object such as a heart by magnetic resonance imaging. A pulse sequence is applied to spatially modulate a region of interest of the object and at least one first spectral peak is acquired from the Fourier domain of the spatially modulated object. The inverse Fourier transform information of the acquired first spectral-peaks is computed and a computed first harmonic phase image is determined from each spectral peak. The process is repeated to create a second harmonic phase image from each second spectral peak and the strain is determined from the first and second harmonic phase images. In a preferred embodiment, the method is employed to determine strain within the myocardium and to determine change in position of a point at two different times which may result in an increased distance or reduced distance. The method may be employed to determine the path of motion of a point through a sequence of tag images depicting movement of the heart. The method may be employed to determine circumferential strain and radial strain.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
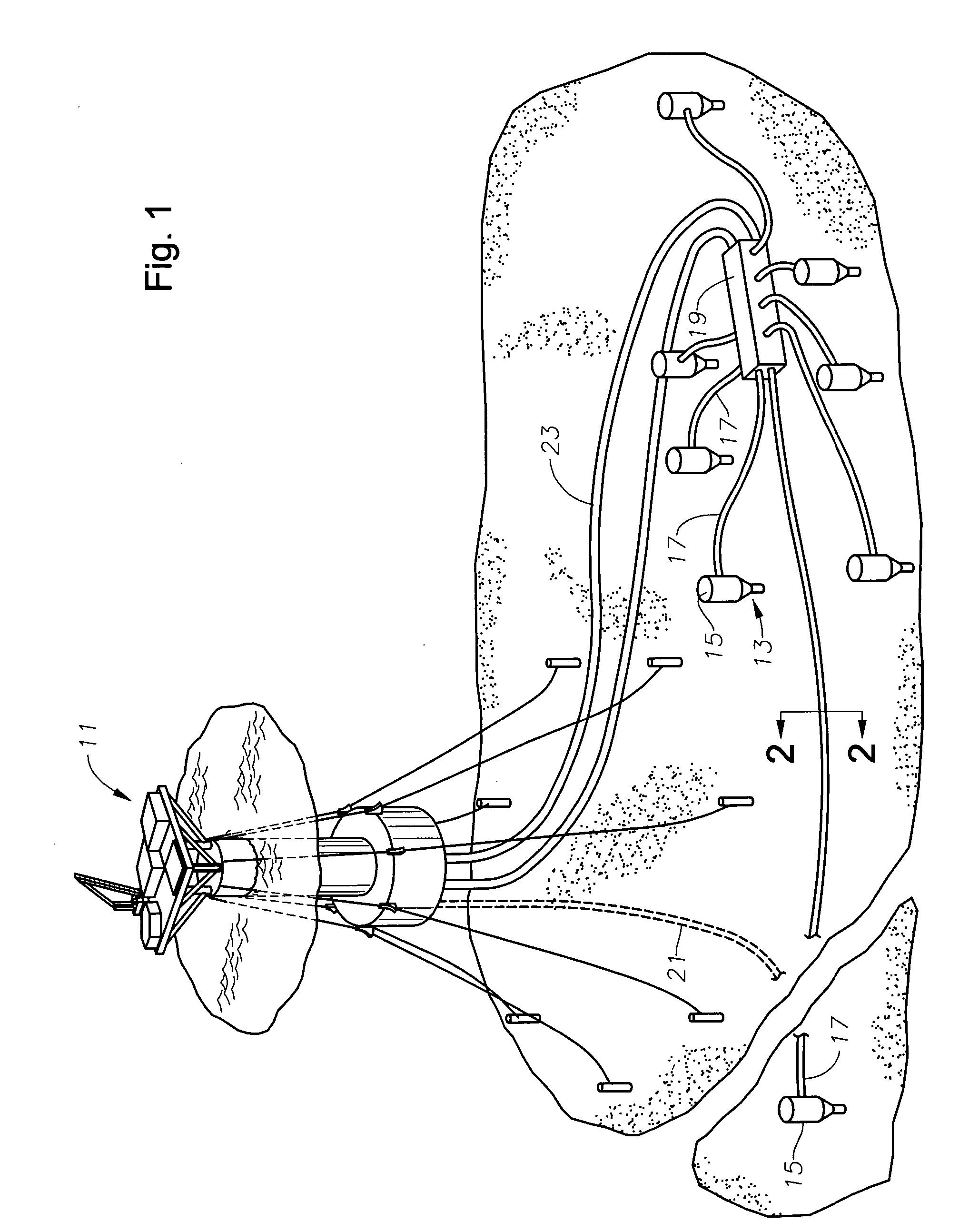
Fiber optic sensor and sensing system for hydrocarbon flow
InactiveUS20060165344A1Improve responsivenessIncrease strainSurveyConstructionsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesEngineering
An assembly senses fluid pressure variations within a passageway along a length of a flowline. A fiber optic cable is disposed axially within the passageway of the flowline. The fiber optic cable experiences a mechanical strain responsive to variations in the fluid pressure of the fluid communicating through the passageway of the flowline along the length of the flowline. The assembly also includes an enhancing layer surrounding the fiber optic cable. The enhancing layer is more responsive to the fluid pressure of the fluid communicating through the passageway of the cable than the fiber optic cable, which enhances the responsiveness of the fiber optic cable to the pressure by magnifying the mechanical strain associated with the fiber optic cable within a particular region of varying fluid pressure. Strain associated with the cable is communicated through back-reflected light.
Owner:GE OIL & GAS UK LTD
AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistor devices
ActiveUS20060006414A1Avoid crackingReduce the appearance of cracksSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMESFETCooling down
The present invention recites a new method for manufacturing Group III-N field-effect devices, such as HEMT, MOSHFET, MISHFET devices or MESFET devices, grown by Metal-Organic Vapor Phase Expitaxy, with higher performance (power), by covering the surface with a thin SiN layer on the top AlGaN layer, in the reactor where the growth takes place at high temperature, prior cooling down the structure and loading the sample out of the reactor, as well as a method to produce some HEMT transistors on those heterostructures, by depositing the contact on the surface without any removal of the SiN layer by MOCVD. The present invention recites also a device.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
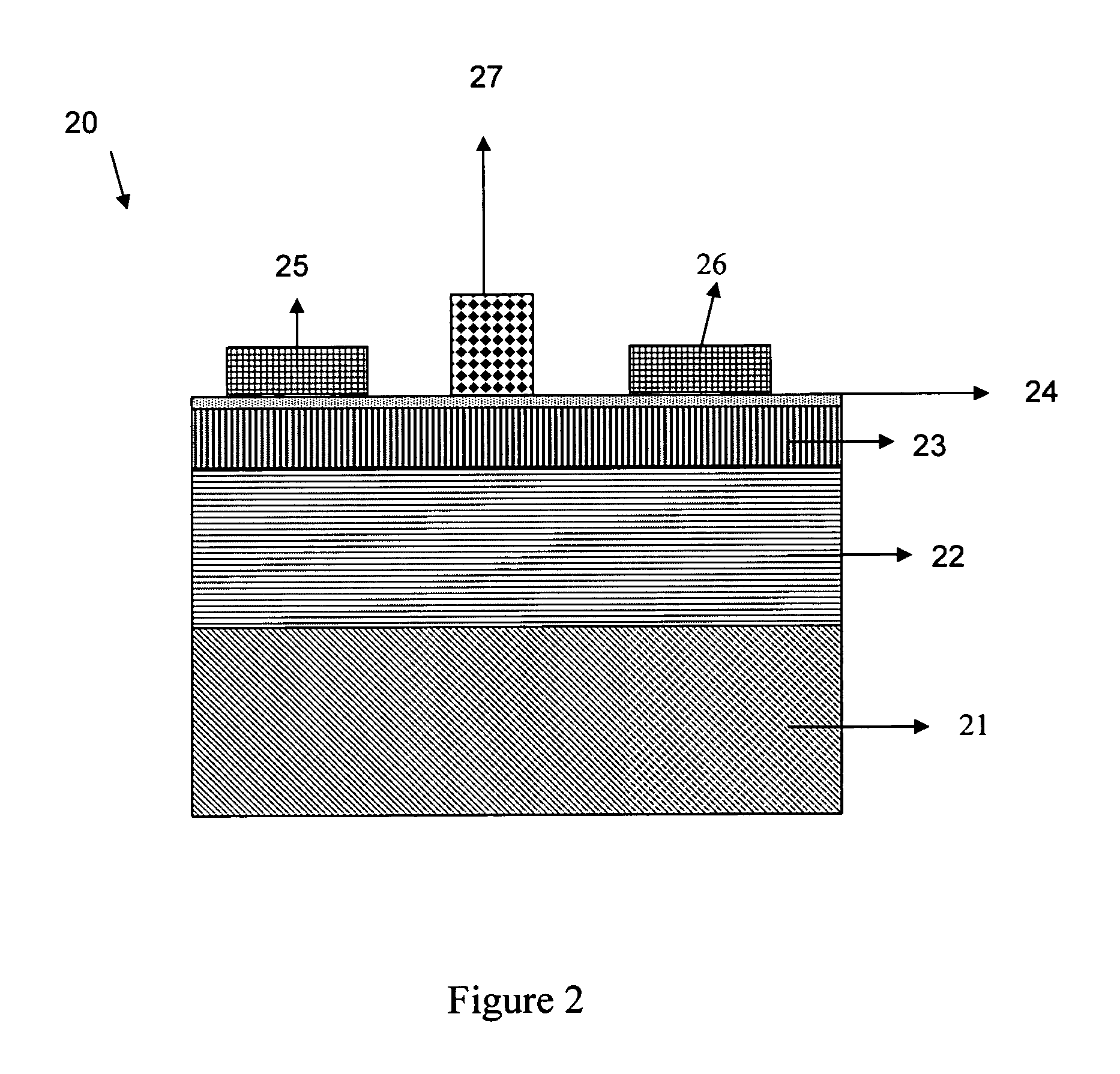
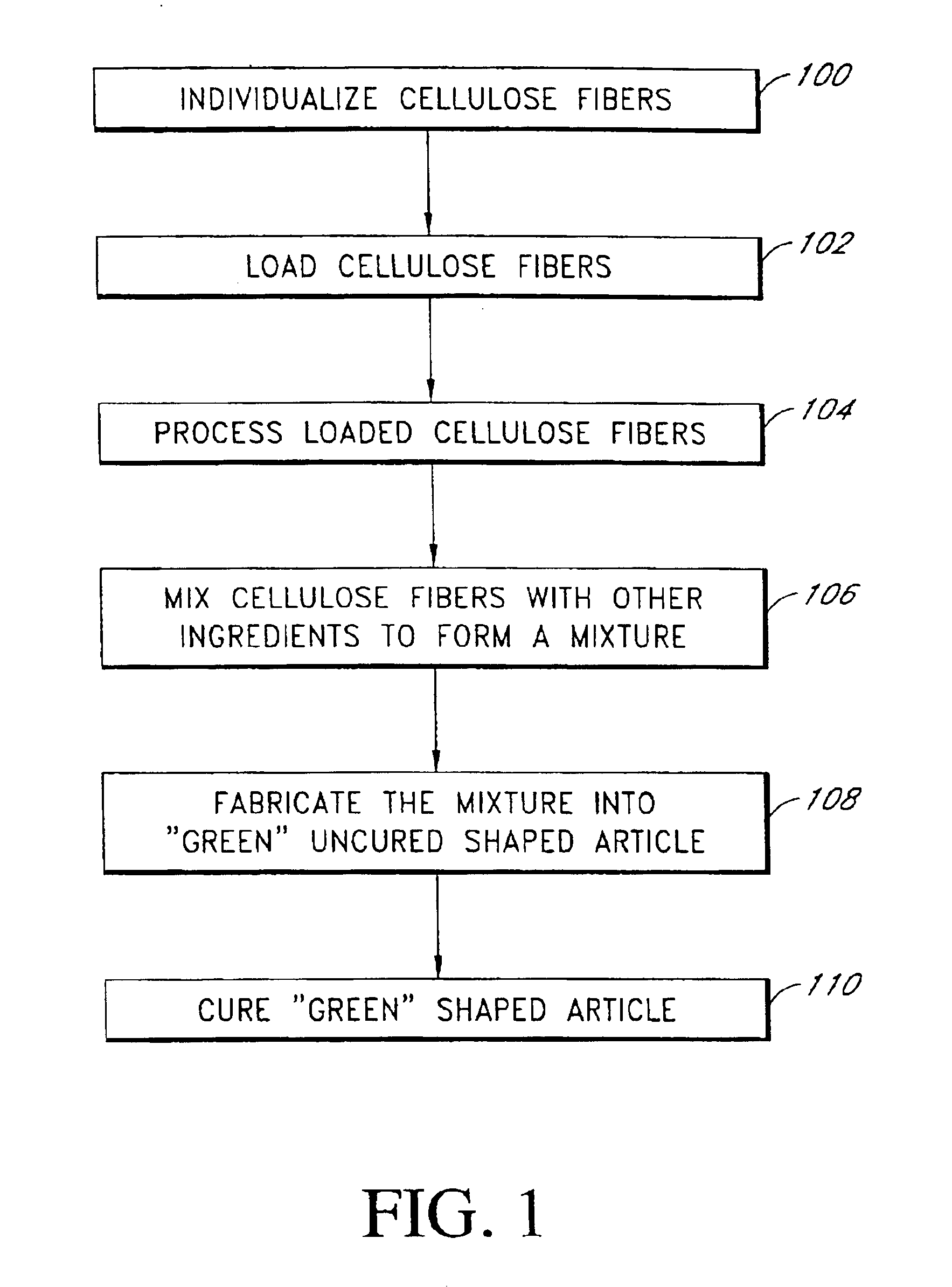
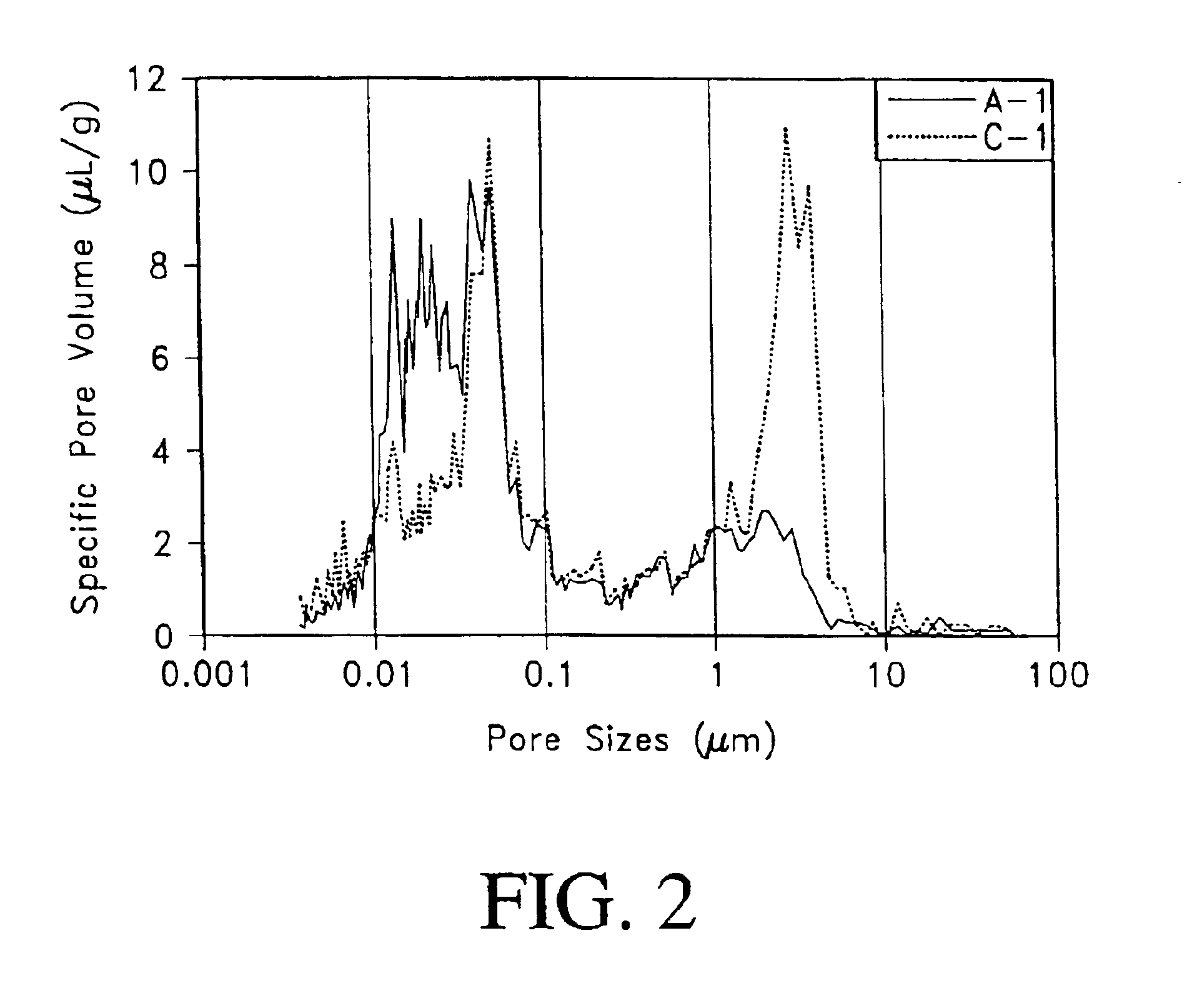
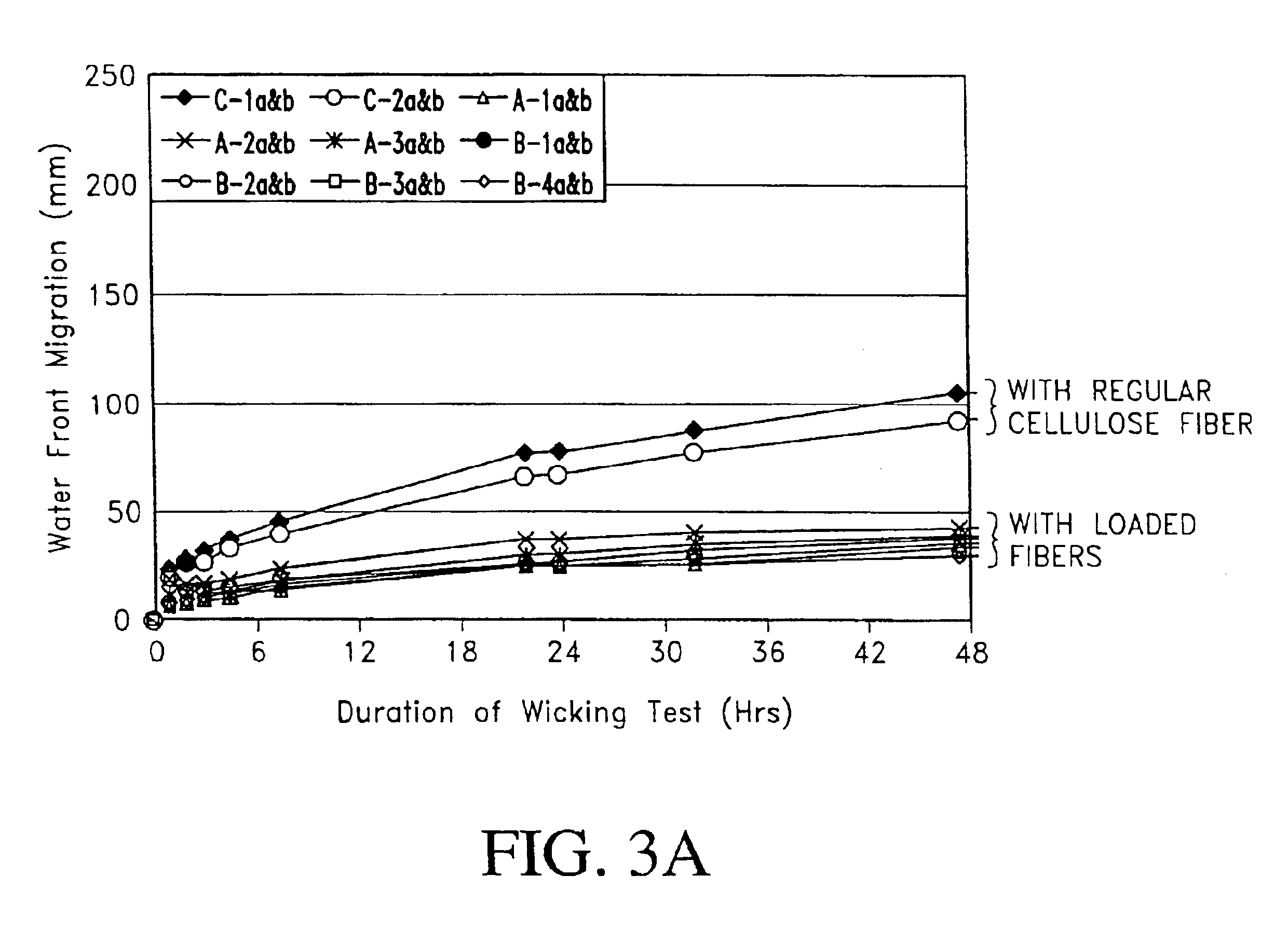
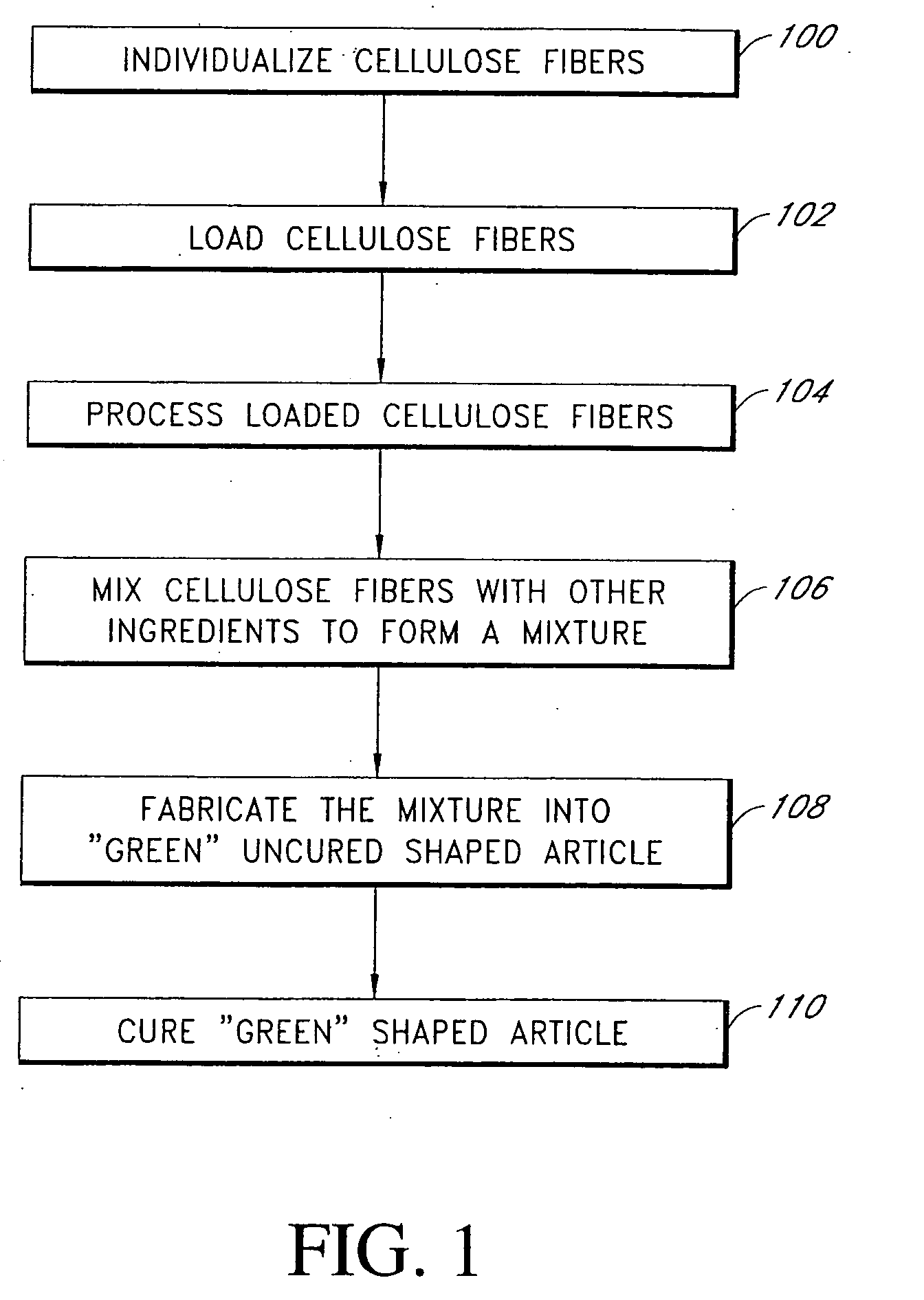
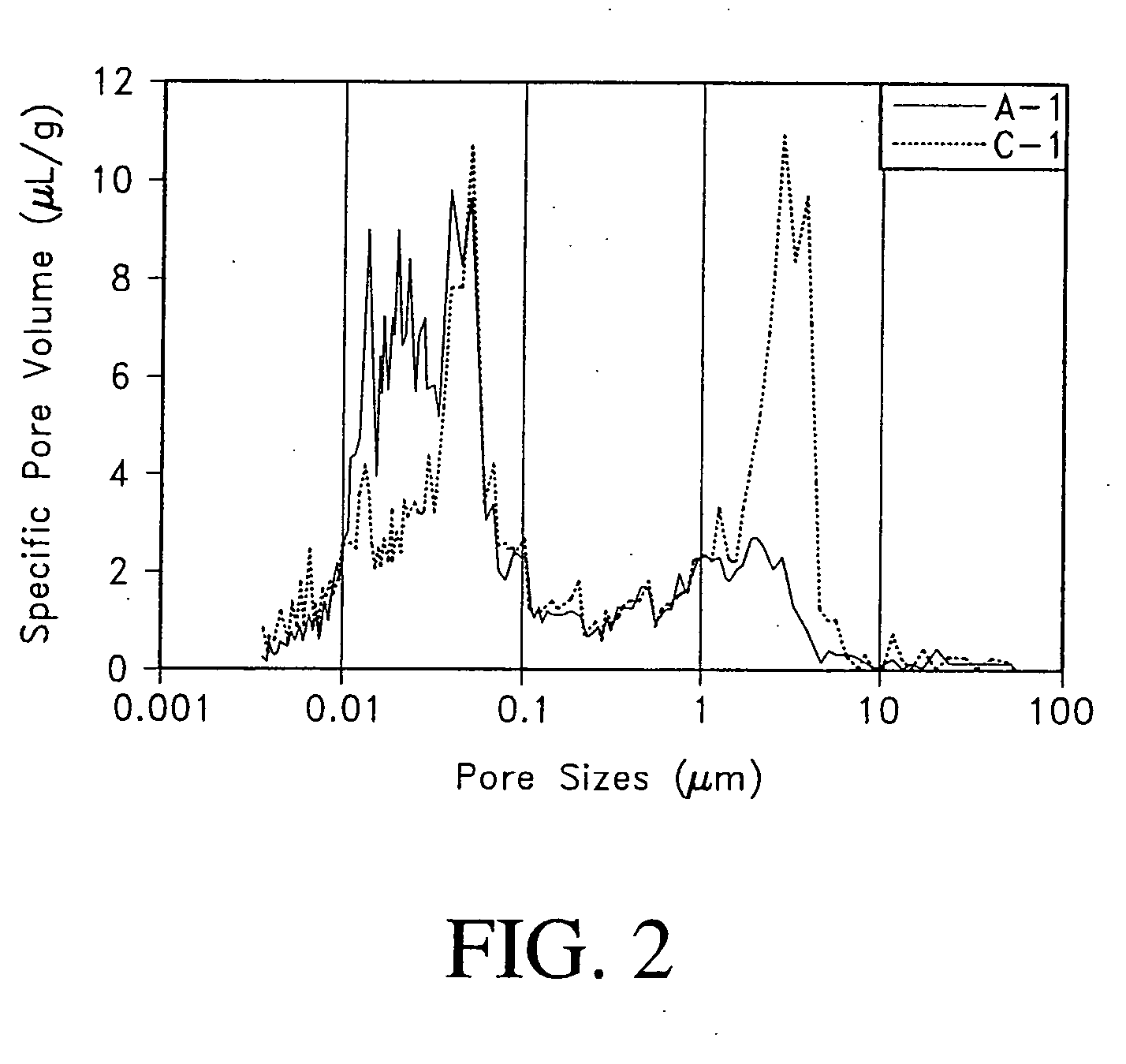
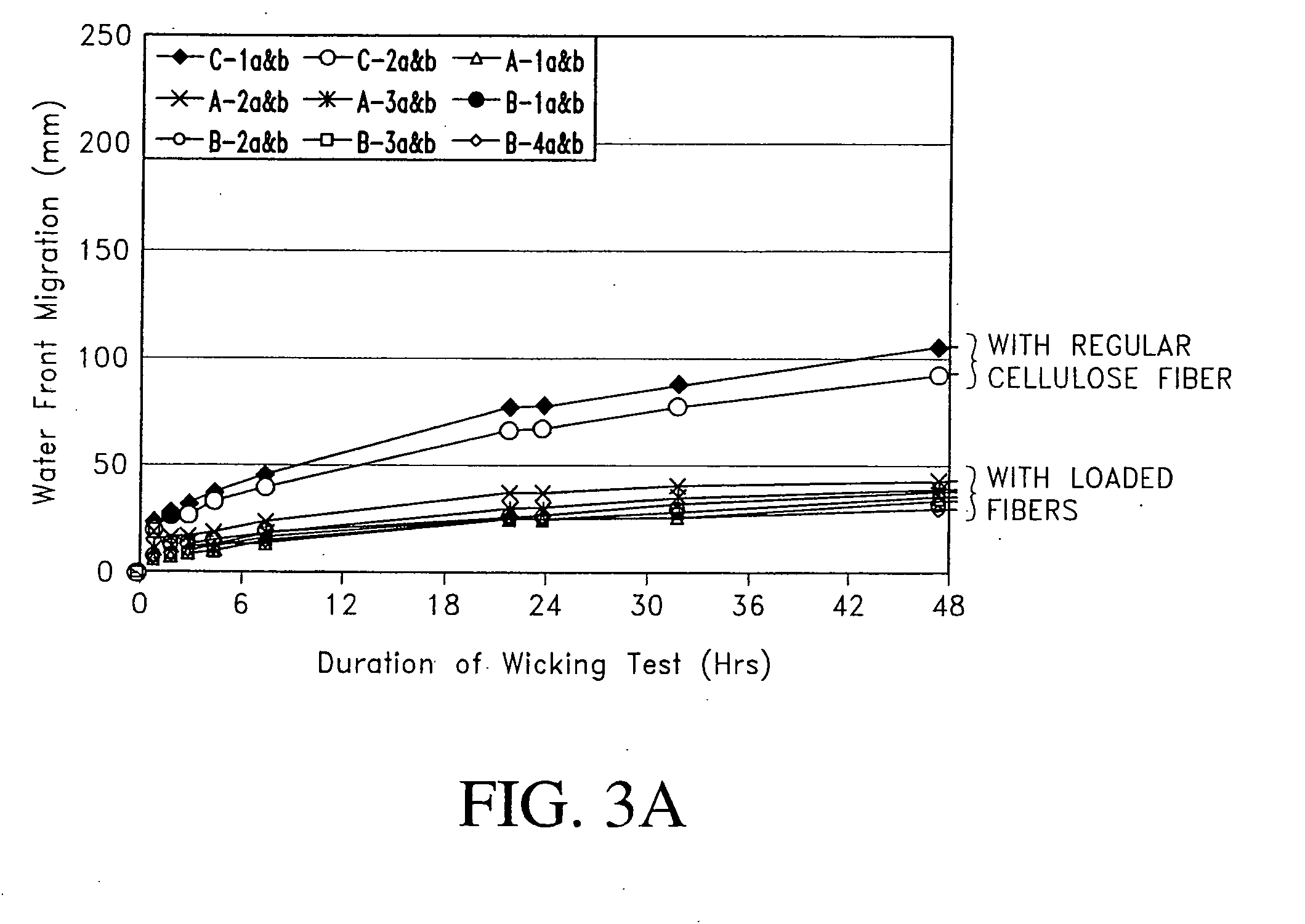
Fiber cement composite materials using cellulose fibers loaded with inorganic and/or organic substances
InactiveUS6872246B2Reduction of it pore volumeIncrease toughnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFreeze thaw resistanceChemical dissolution
This invention discloses a new technology related to cellulose fiber reinforced cement composite materials using the loaded cellulose fibers. This invention discloses four aspects of the technology: fiber treatment, formulation, method and final product. This technology advantageously provides fiber cement building materials with the desirable characteristics of reduced water absorption, reduced rate of water absorption, lower water migration, and lower water permeability. This invention also impart the final products improved freeze-thaw resistance, reduced efflorescence, reduced chemical dissolution and re-deposition, and improved rot and fire resistances, compared to conventional fiber cement products. These improved attributes are gained without loss in dimensional stability, strength, strain or toughness.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH
High strain tear resistant gels and gel composites for use as artificial muscle actuators
InactiveUS6909220B2Improve propertiesImprove tear resistanceCellsSludge treatmentPolymer sciencePlasticizer
Novel gels and articles are formed from one or more copolymers having at least one poly(ethylene) components and high levels of one or more plasticizers, said gels having an amount of crystallinity, glassy components, and selected plasticizers sufficient to achieve improvements in one or more physical properties including improved crack propagation resistance, improved tear resistance, improved resistance to fatigue, resistance to catastrophic failure, and exhibiting high strain under elongations not obtainable in amorphous gels which high strain making the gel suitable for use as film layers for artificial muscles.
Owner:APPLIED ELASTOMERICS
Flexible force or pressure sensor array using semiconductor strain gauge, fabrication method thereof and measurement method thereof
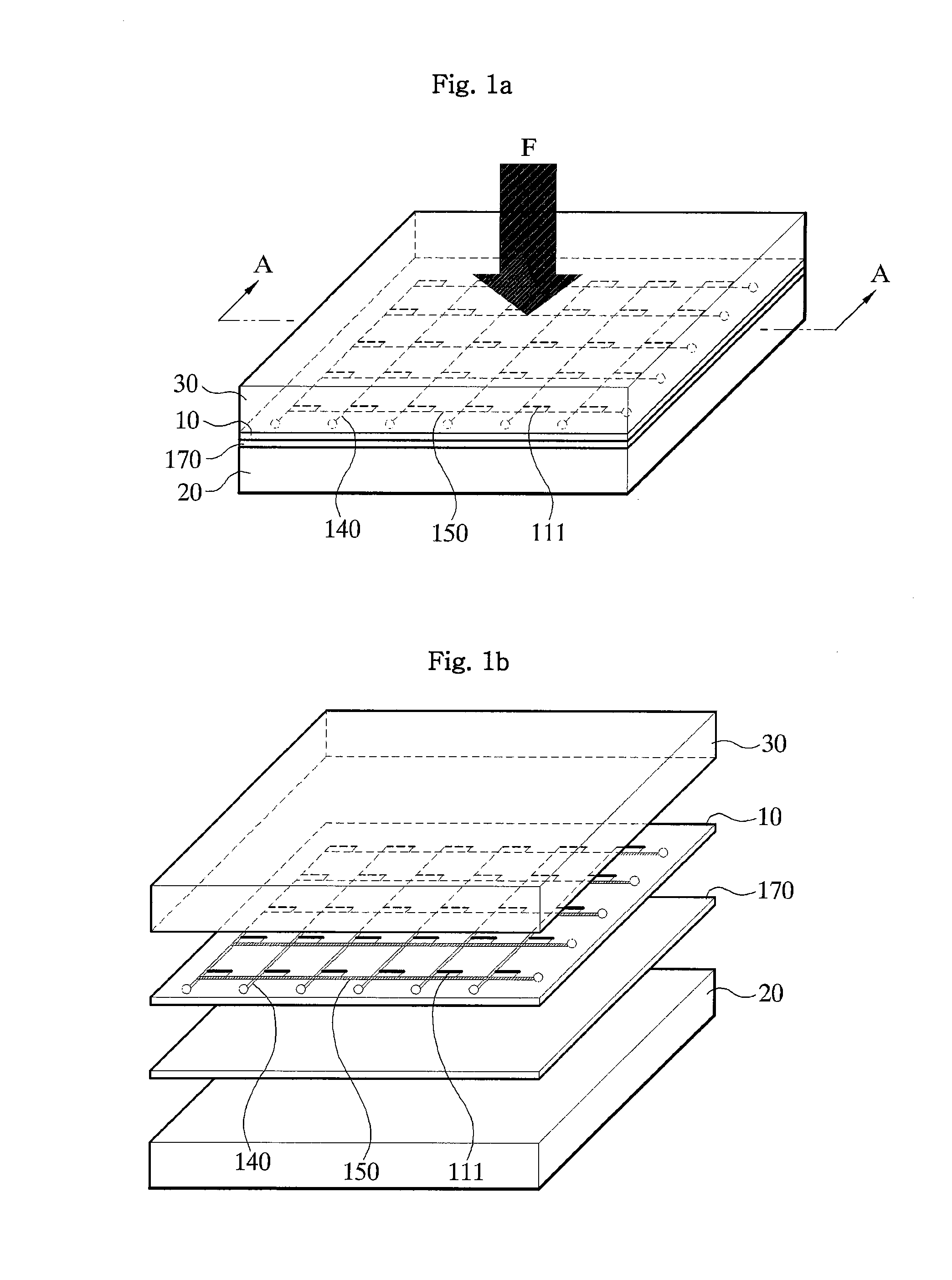
ActiveUS20110226069A1Simple and robust structureIncrease strainForce measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSensor arrayElastomer
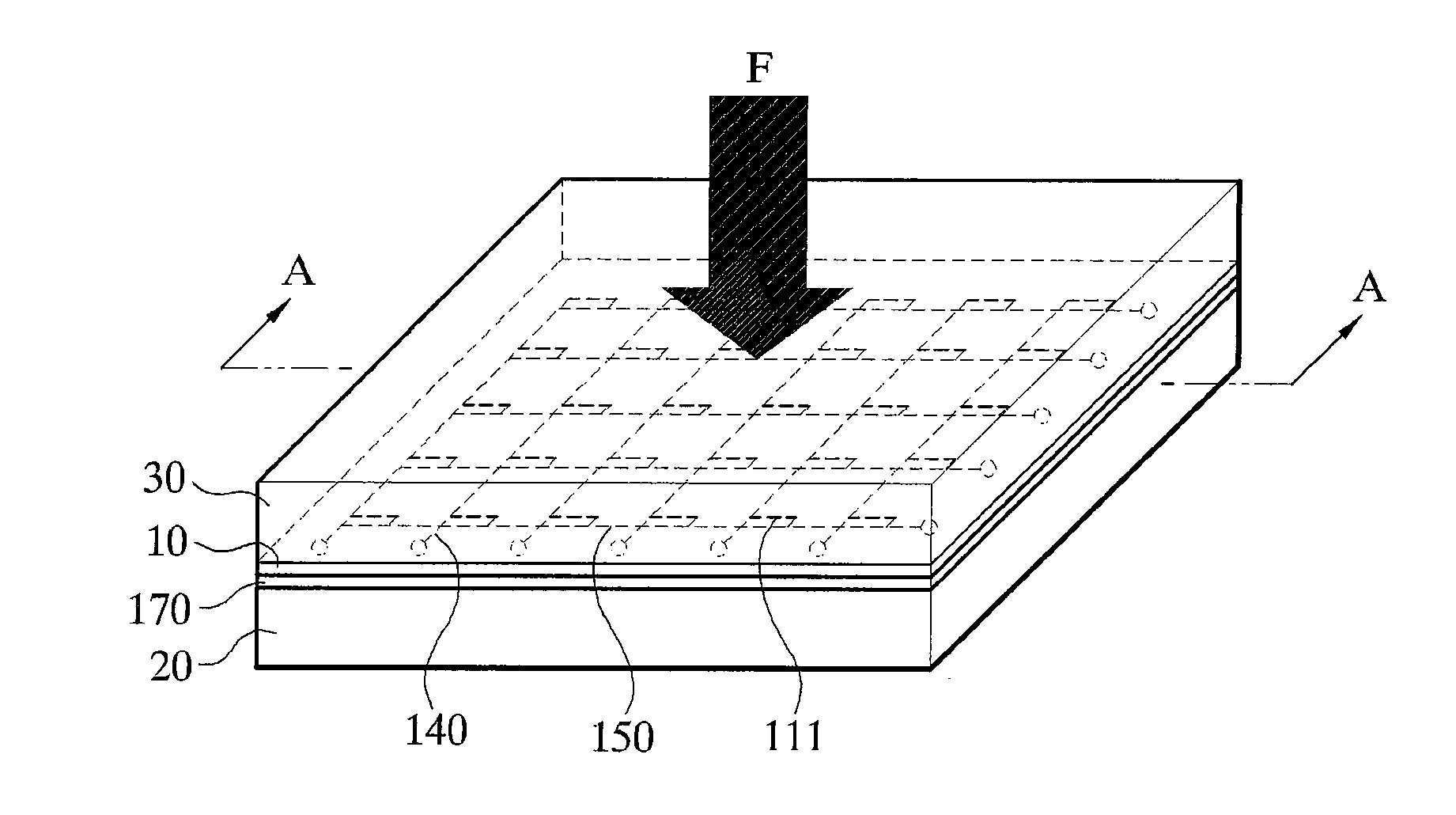
The force or pressure sensor array of the present invention effectively has both flexibility and elasticity. Since the substrate itself is a kind of a polymer material, the substrate can be bent or expanded. Although silicon, which is a material of the semiconductor strain gauge, is easily broken and solid, mechanical flexibility can be secured if it is fabricated extremely thin. To this end, particularly, disclosed is a flexible force or pressure sensor array using semiconductor strain gauges 110, the sensor array comprising: a substrate 10 including: the semiconductor strain gauges 110 in which a plurality of elements formed in a certain array pattern is deformed by force or pressure, a pair of polymer film layers 120 and 130 having film surfaces contacted facing each other and containing the semiconductor strain gauge 110 between the film surfaces contacted with each other, and a pair of signal line layers formed on top and bottom surfaces of an insulating layer using either of the pair of polymer film layers 120 and 130 as the insulating layer and connected to the elements 111 of the array pattern to form electrodes, for fetching deformation signals outputted due to deformation of the elements 111 to outside; and a pair of elastomer layers 20 and 30 formed on both sides of the substrate 10 to contain the substrate 10 inside.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Devices and methods for dressing applicators
ActiveUS20110152738A1Treatment amelioration preventionMechanical advantageNon-adhesive dressingsDiagnosticsElastic skinKeloid
Devices, kits and methods described herein may be for wound healing, including the treatment, amelioration, or prevention of scars and / or keloids by applying and / or maintaining a pre-determined strain in an elastic skin treatment device that is then affixed to the skin surface using skin adhesives to transfer a generally planar force from the bandage to the skin surface. Applicators are used to apply and / or maintain the strains, and some of the applicators are further configured to provide at least some mechanical advantage to the user when exerting loads onto the skin treatment device.
Owner:NEODYNE BIOSCI INC
Dynamic connector for spinal device
InactiveUS20080228227A1Reduce movementIncrease strainInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsElectrical resistance and conductanceSpinal column
The present invention provides a dynamic stabilization device positionable about a portion of a spinal column. The stabilization device may generally include a first component and a second component, where the first and second components are movably coupled to one another to define an arcuate path of motion. The stabilization device may also include one or more adjustment elements positionable within first and second adjustment openings to affect the path of motion between the first and second components and / or the behavior and characteristics of the movement. In addition, one or more resistive elements may be adjustably positionable within either and / or both of the first and second adjustment openings to provide resistance and / or dampening of the forces experienced as the first and second components move relative to one another. The stabilization device may further define a joint having three degrees of freedom to adapt to movement of a spinal column.
Owner:SPINADYNE
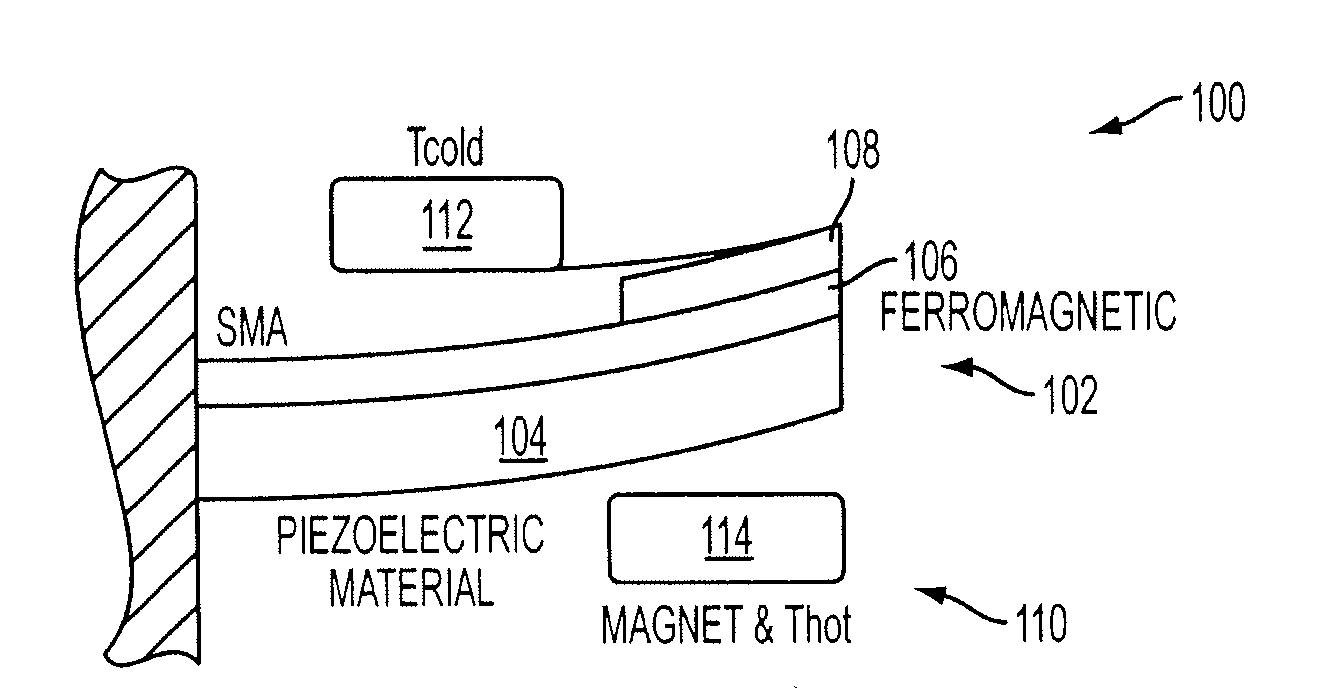
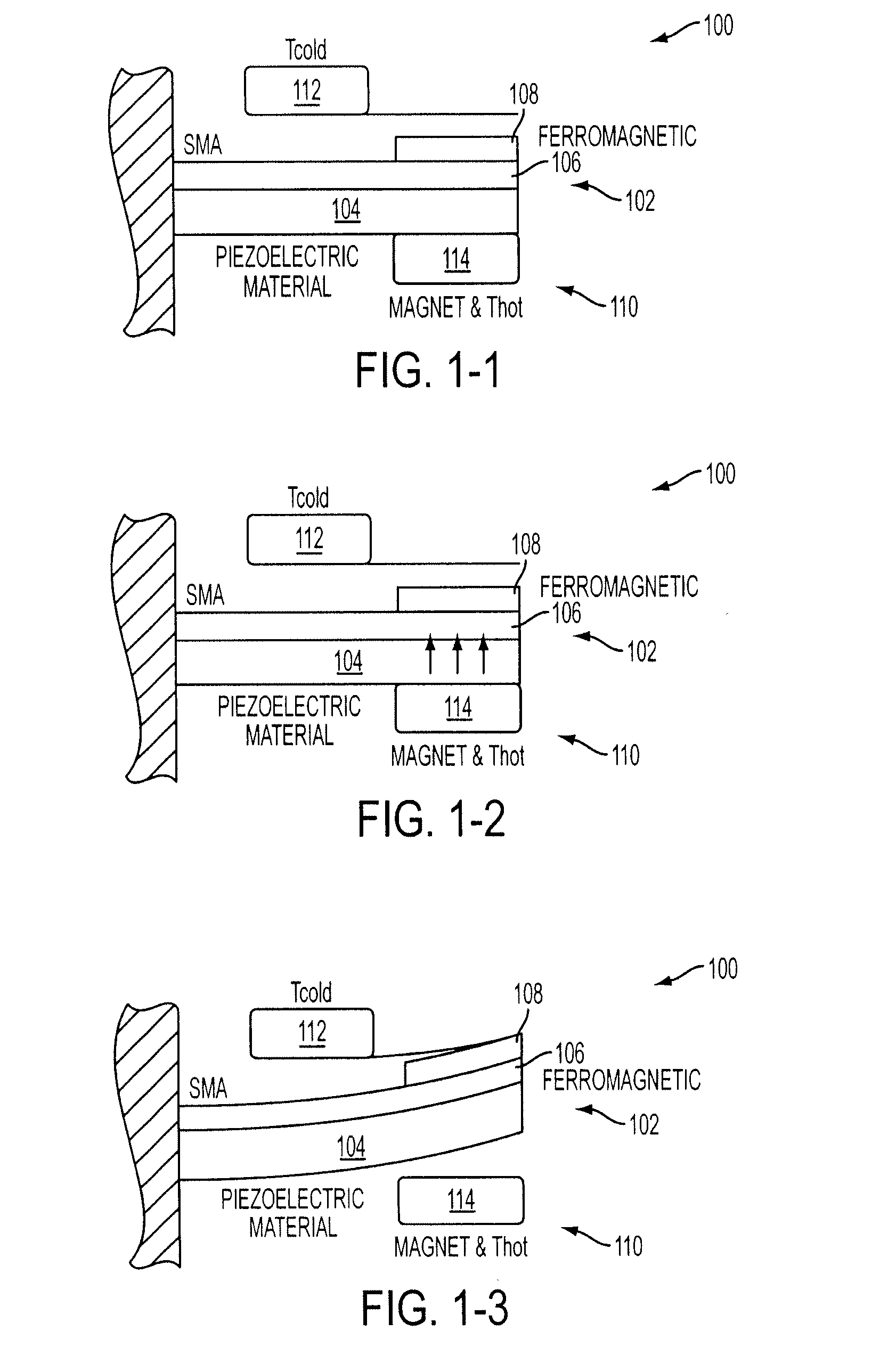
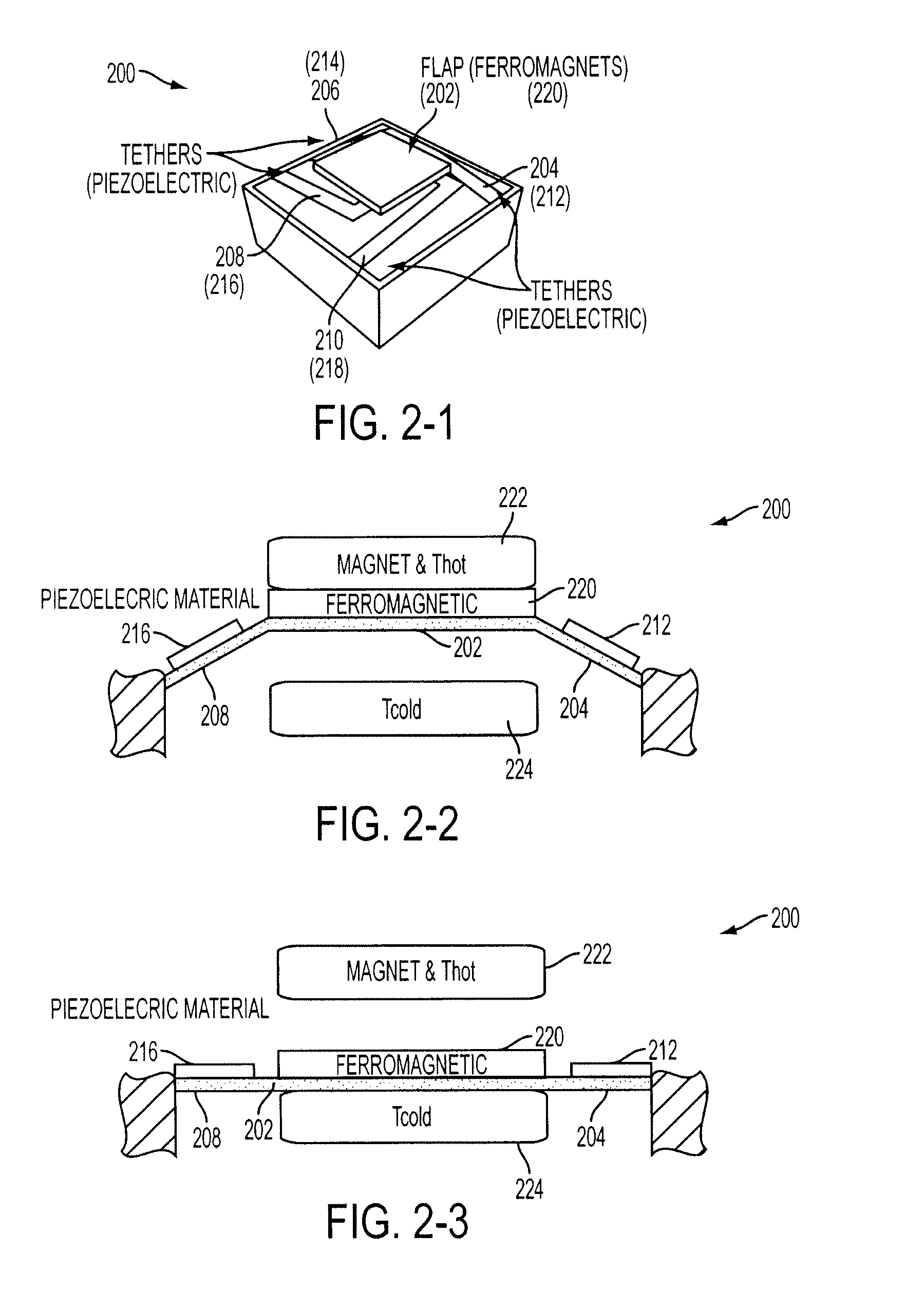
Energy harvesting by means of thermo-mechanical device utilizing bistable ferromagnets
InactiveUS20090315335A1Available energySimple designPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesThermal energyElectricity
An inventive energy harvesting apparatus may include a ferromagnetic material and / or a shape memory alloys to convert thermal energy to mechanical energy to electrical energy. The apparatus is subjected to a thermal gradient to cause beams to bend thus creating stress / strain in a piezoelectric material, or creating magnetic flux in a magnetic path. The charges created in this process can be transferred to electrical batteries.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
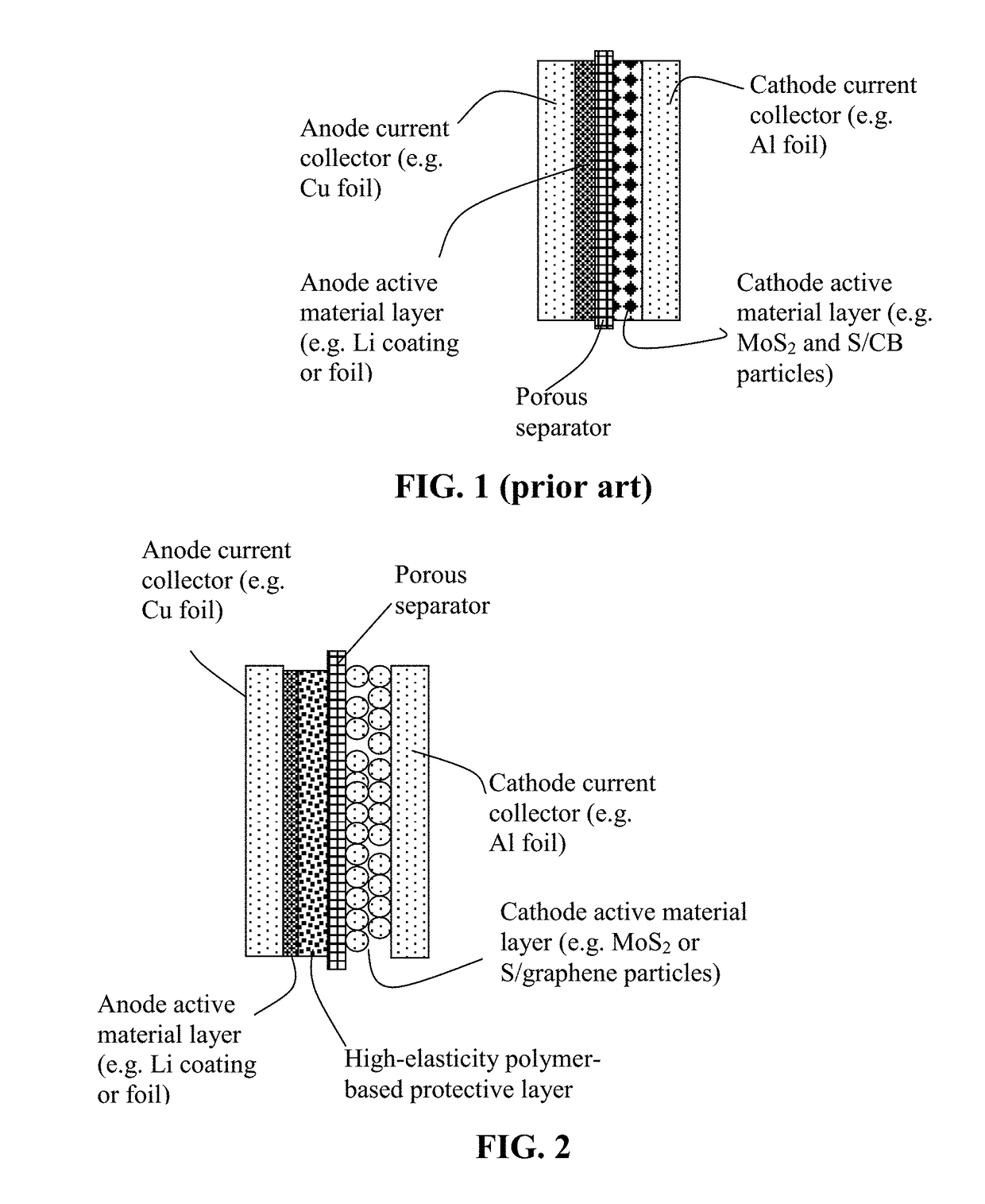
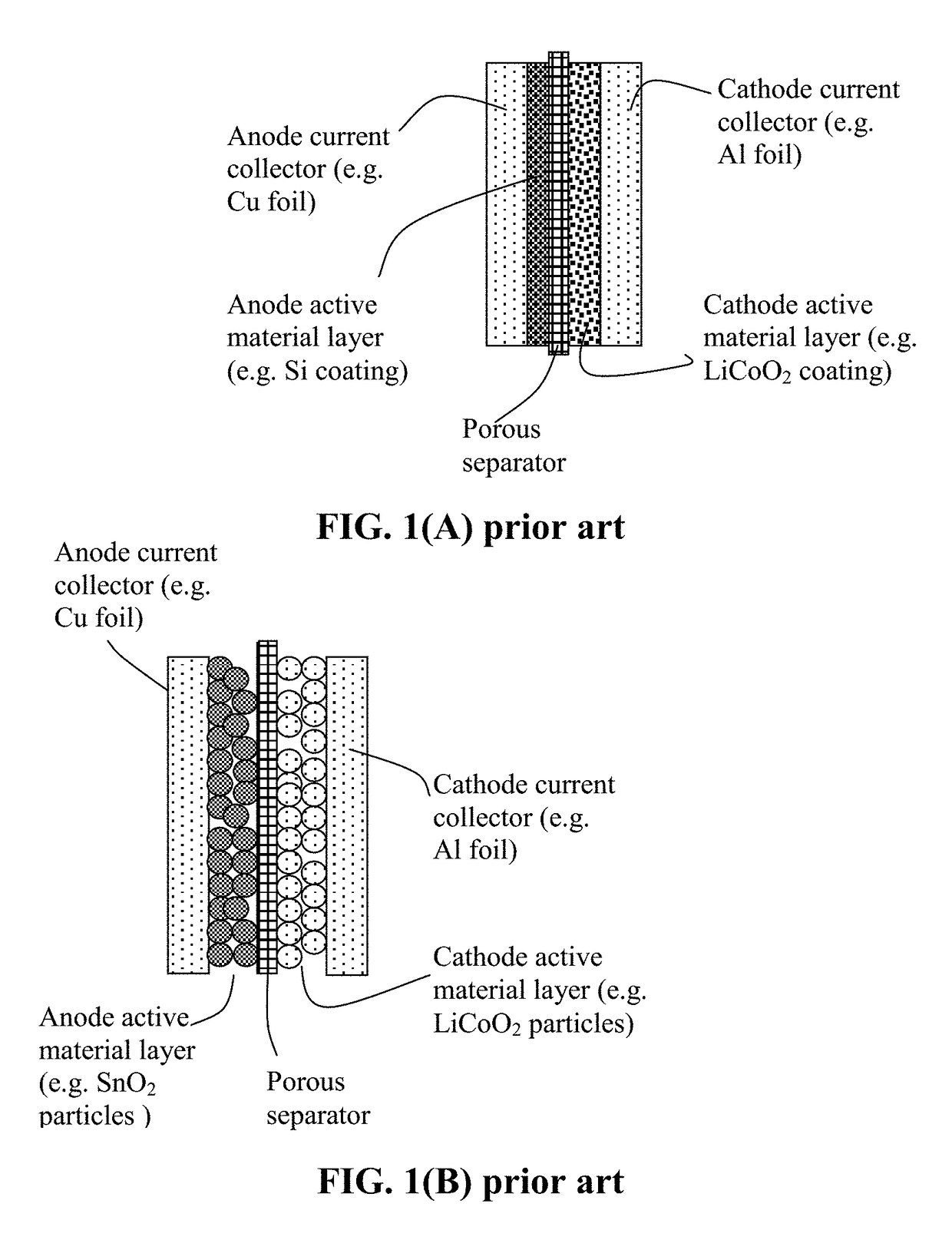
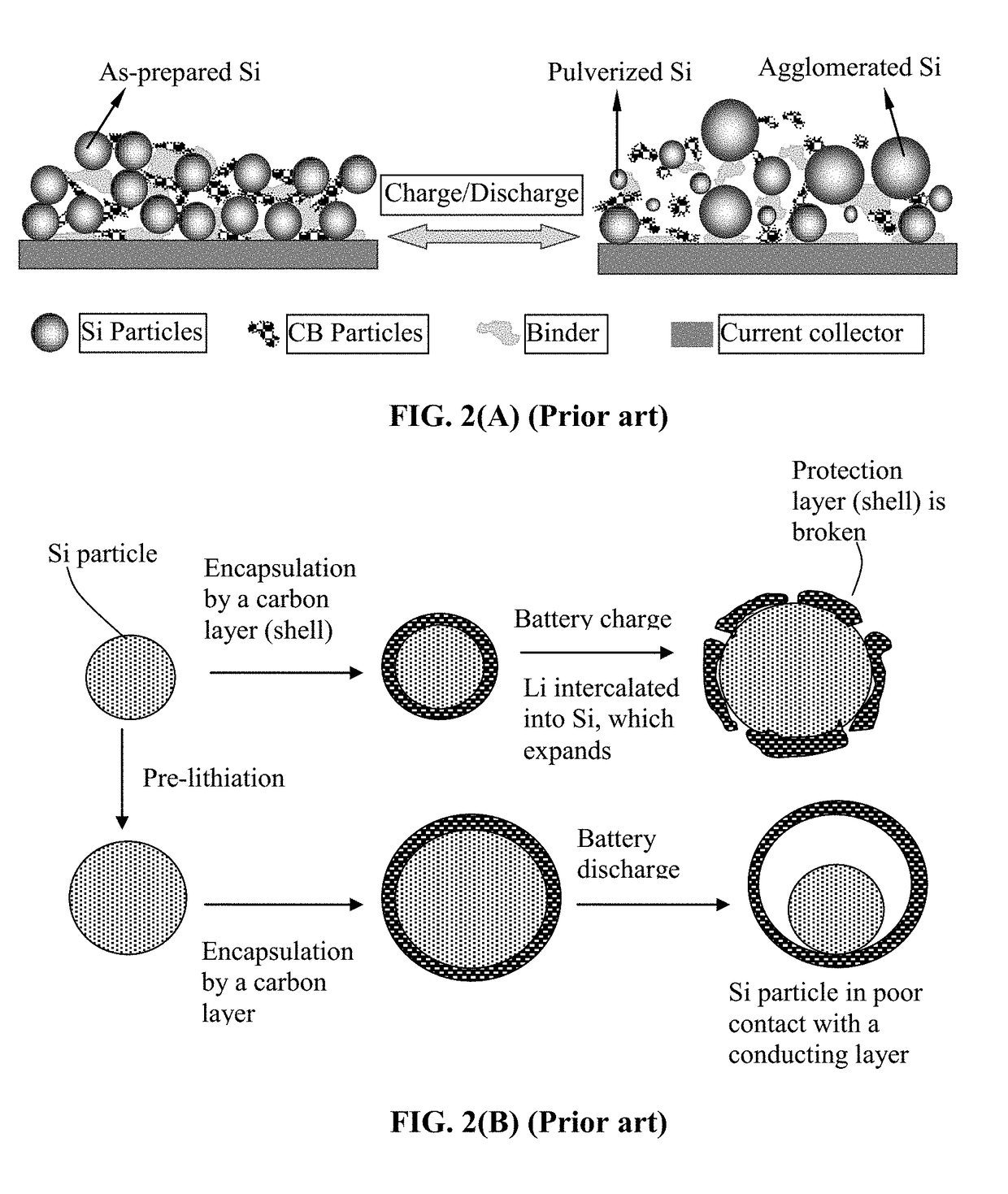
Lithium Anode-Protecting Polymer Layer for a Lithium Metal Secondary Battery and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20180301707A1Improve lithium ion conductivityIncrease elasticityFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesCross-linkLithium metal
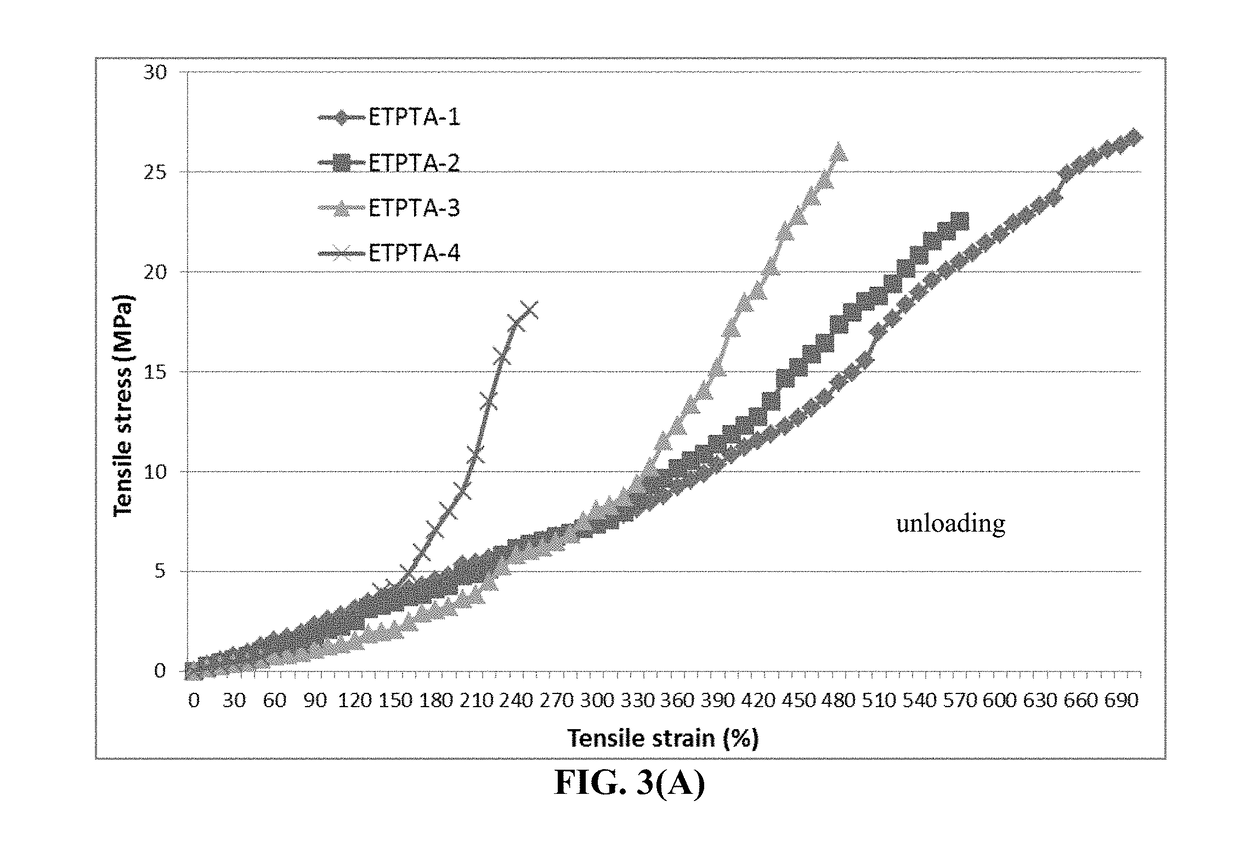
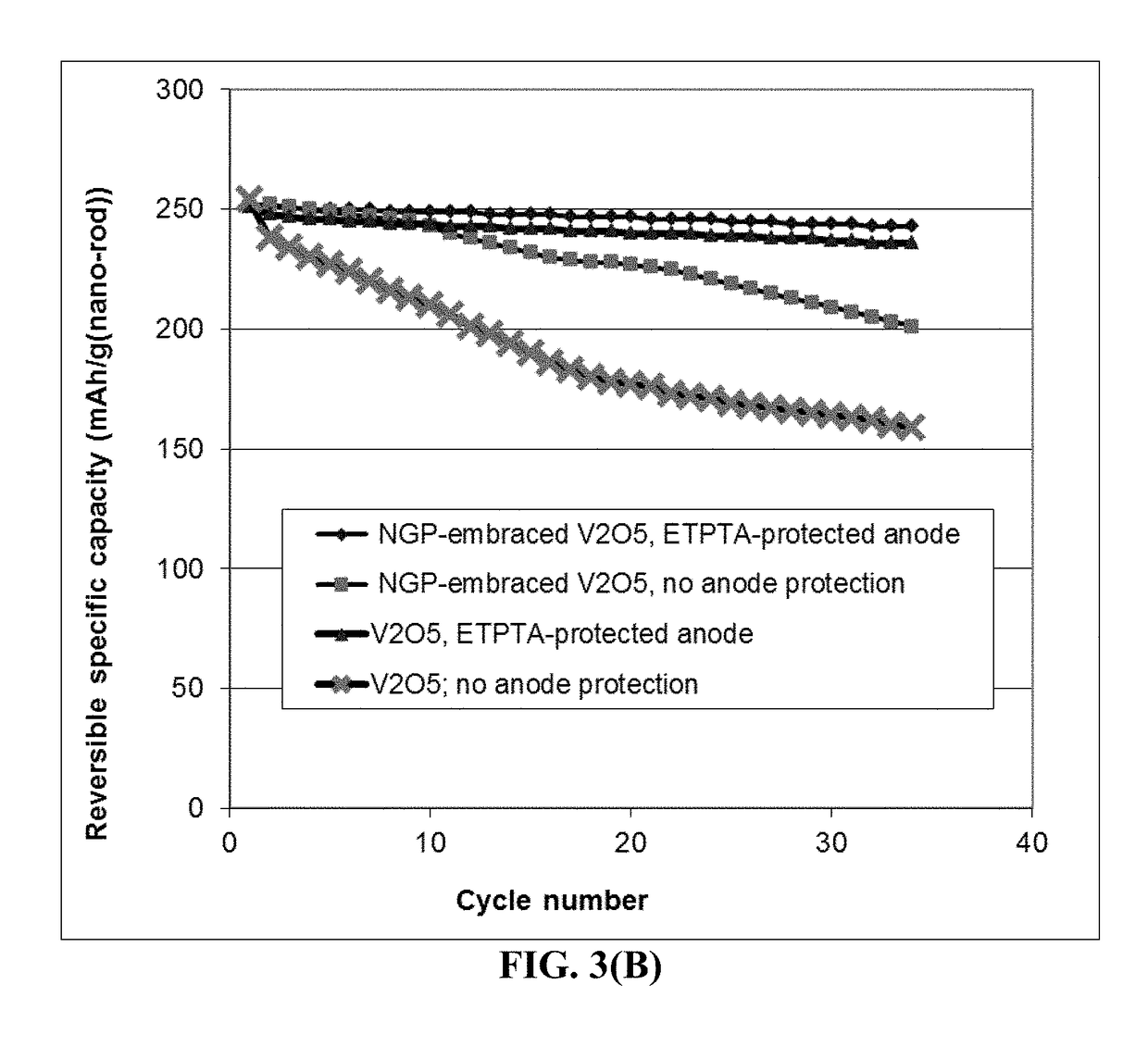
Provided is lithium secondary battery comprising a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte or separator-electrolyte assembly disposed between the cathode and the anode, wherein the anode comprises: (a) a foil or coating of lithium or lithium alloy; and (b) a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer disposed between the foil / coating and the electrolyte (or separator-electrolyte assembly), having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 2%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 1 nm to 10 μm, wherein the high-elasticity polymer contains a cross-linked network of polymer chains having an ether linkage, nitrile-derived linkage, benzo peroxide-derived linkage, ethylene oxide linkage, propylene oxide linkage, vinyl alcohol linkage, cyano-resin linkage, triacrylate monomer-derived linkage, tetraacrylate monomer-derived linkage, or a combination thereof in the cross-linked network of polymer chains.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Method of fabricating strain-silicon CMOS
ActiveUS7429775B1Improve mobilityOptimize strainTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSAnisotropic etching
Owner:XILINX INC
Dynamic spinal stabilization device
InactiveUS20080195154A1Minimum reduction in natural movementIncrease strainInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention provides a dynamic stabilization device positionable about a portion of a spinal column. The stabilization device may generally include a first component and a second component, where the first and second components are movably coupled to one another to define an arcuate path of motion. The stabilization device may also include one or more adjustment elements positionable within first and second adjustment openings to affect the path of motion between the first and second components and / or the behavior and characteristics of the movement. In addition, one or more resistive elements may be adjustably positionable within either and / or both of the first and second adjustment openings to provide resistance and / or dampening of the forces experienced as the first and second components move relative to one another. The stabilization device may further define a joint having three degrees of freedom to adapt to movement of a spinal column.
Owner:SPINADYNE
Method for providing hyaluronic acid
InactiveUSRE37336E1Facilitate easeAbility to controlBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliRecombinant DNA
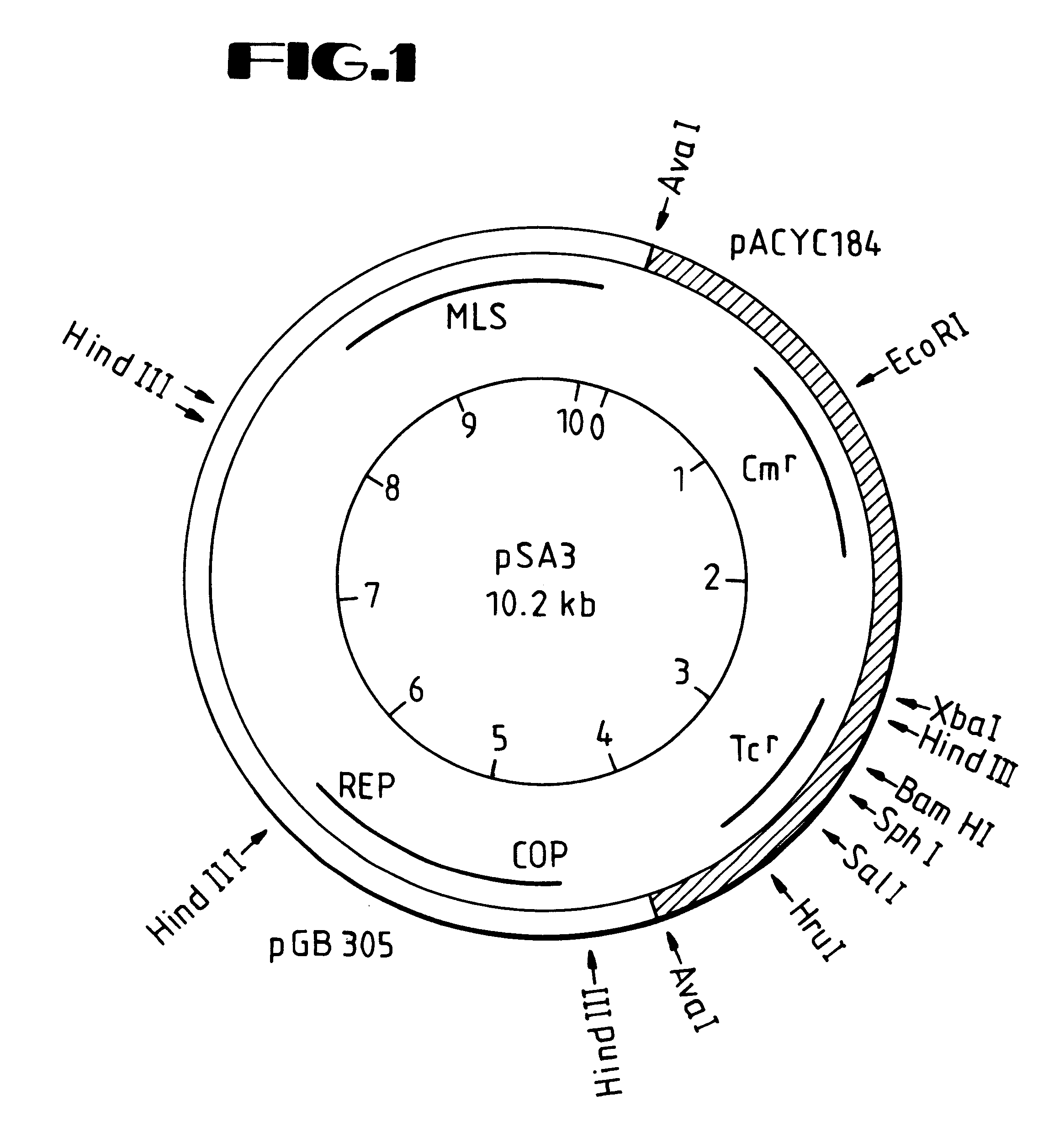
Disclosed are DNA segments encoding <DEL-S DATE="20010821" ID="DEL-S-00001">hyaluronic acid synthase which are employed to construct recombinant cells useful in the production of hyaluronate synthase or hyaluronic acid (HA)<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00001"> <INS-S DATE="20010821" ID="INS-S-00001">the recombinant DNA segment identified in FIG. 5. <INS-E ID="INS-S-00001">In preferred aspects, chromosomal DNA from Streptococcus equisimilis is partially digested with EcoRI and the resultant fragments are ligated to form recombinant vectors. These vectors are useful in the transformation of host cells such as E. coli and or Streptococcal hosts. <DEL-S DATE="20010821" ID="DEL-S-00002">Resultant transformants are screened by the novel screening assays to identify colonies which have incorporated HA synthase DNA in a form that is being actively transcribed into the corresponding HA synthase enzyme. These colonies may be selected and employed in the production of the enzyme itself or its product, HA.<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00002"> <INS-S DATE="20010821" ID="INS-S-00002">The recombinant DNA segment identified in FIG. 5 is then inserted into a recombinant Streptococcal host for the production of hyaluronic acid (HA).<INS-E ID="INS-S-00002">
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Lithium Secondary Batteries Containing Protected Particles of Anode Active Materials and Method of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20180241032A1Improve lithium ion conductivityIncrease elasticityFuel and secondary cellsSecondary cellsParticulatesTensile strain
Provided is anode active material layer for a lithium battery, comprising multiple particulates of an anode active material, wherein a particulate is composed of one or a plurality of particles of a high-capacity anode active material being embraced or encapsulated by a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 10% when measured without an additive or reinforcement, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10-5 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 0.5 nm (or a molecular monolayer) to 10 μm (preferably less than 100 nm), and wherein the high-capacity anode active material has a specific lithium storage capacity greater than 372 mAh / g (e.g. Si, Ge, Sn, SnO2, Co3O4, etc.).
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
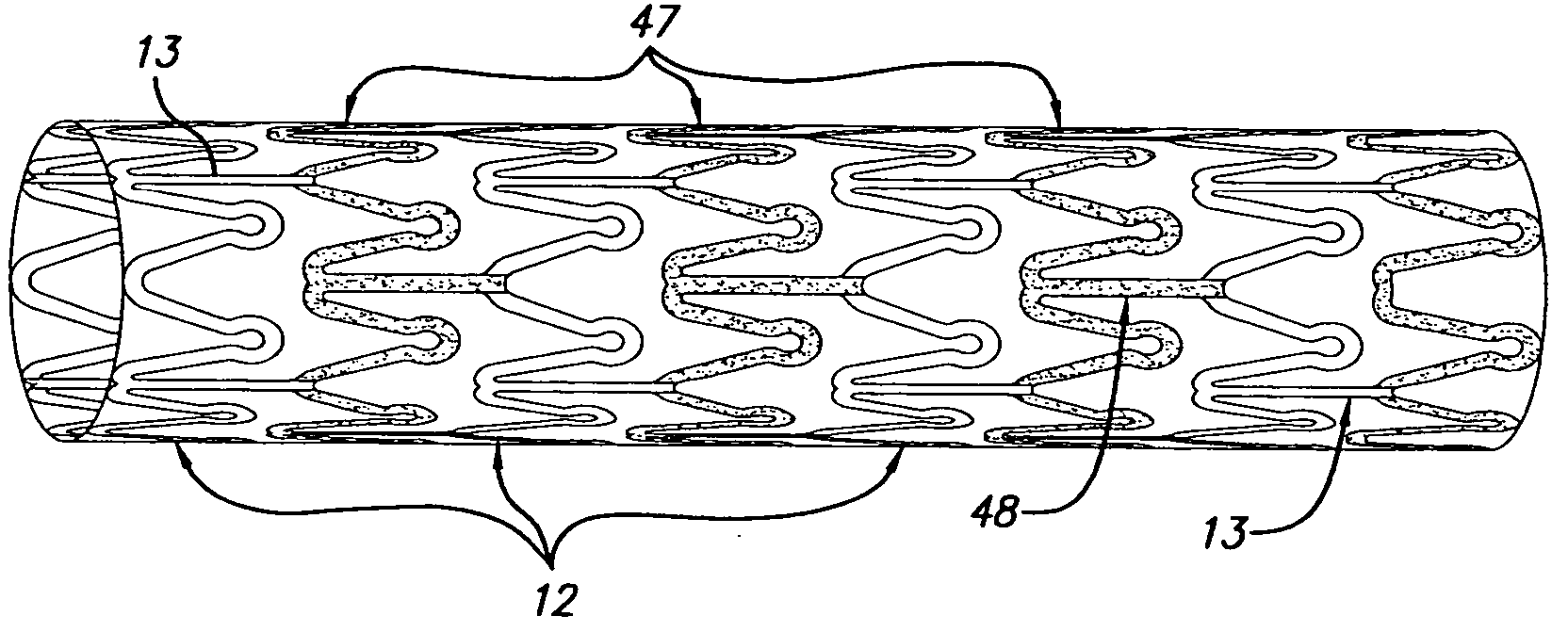
Hybrid intravascular stent
InactiveUS20050107864A1Increase flexibilityImprove radial strengthStentsSurgeryCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Modification of pb-free solder alloy compositions to improve interlayer dielectric delamination in silicon devices and electromigration resistance in solder joints
InactiveUS20090197114A1Good mechanical integrityImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesPrinted circuit manufactureDielectricSilicon
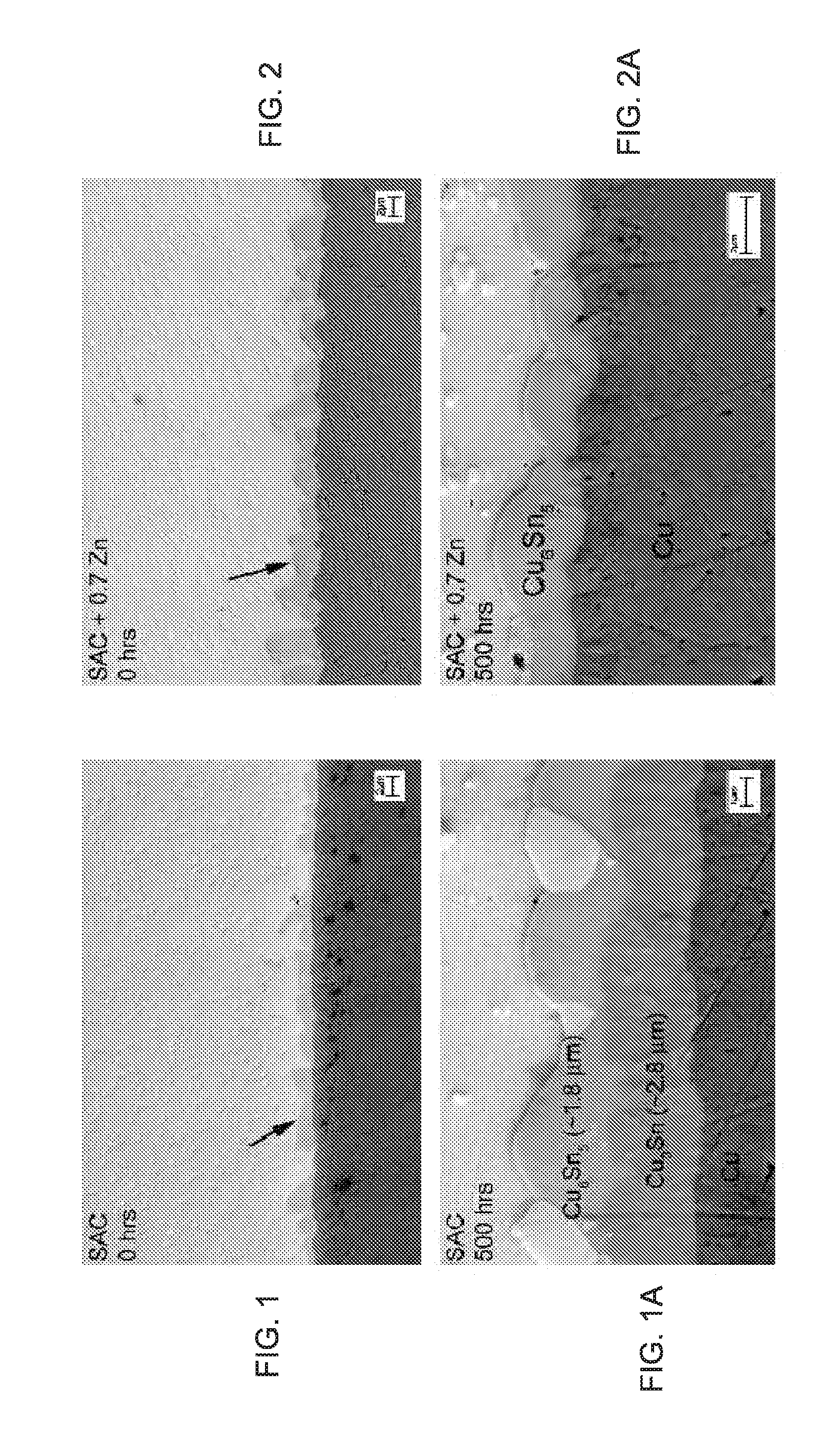
A solder joint comprising a solder capture pad on a substrate having a circuit; and a lead free solder selected from the group comprising Sn—Ag—Cu solder and Sn—Ag solder adhered to the solder capture pad; the solder selected from the group comprising between 0.1 to 2.0% by weight Sb or Bi, and 0.5 to 3.0% Ag. Formation of voids at an interface between the solder and the solder capture pad is suppressed, by including Zn. Interlayer dielectric delamination is suppressed, and electromigration characteristics are greatly improved. Methods for forming solder joints using the solders.
Owner:SHIH YUAN +5
Implantable device formed from polymer blends
A biocompatible material may be configured into any number of implantable medical devices including intraluminal stents. Polymeric materials may be utilized to fabricate any of these devices, including stents. The stents may be balloon expandable or self-expanding. The polymeric materials may include additives such as drugs or other bioactive agents as well as radiopaque agents. By preferential mechanical deformation of the polymer, the polymer chains may be oriented to achieve certain desirable performance characteristics.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
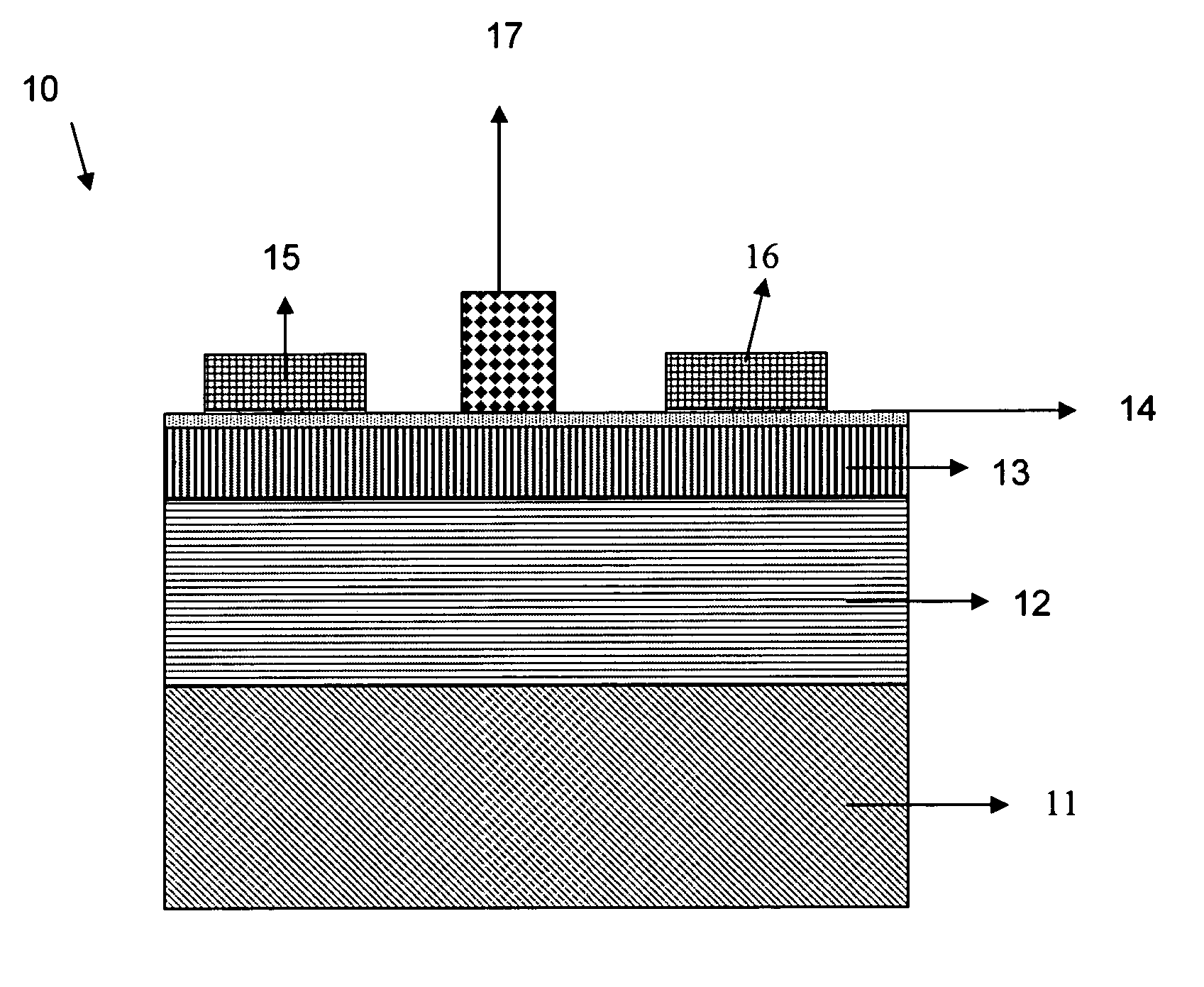
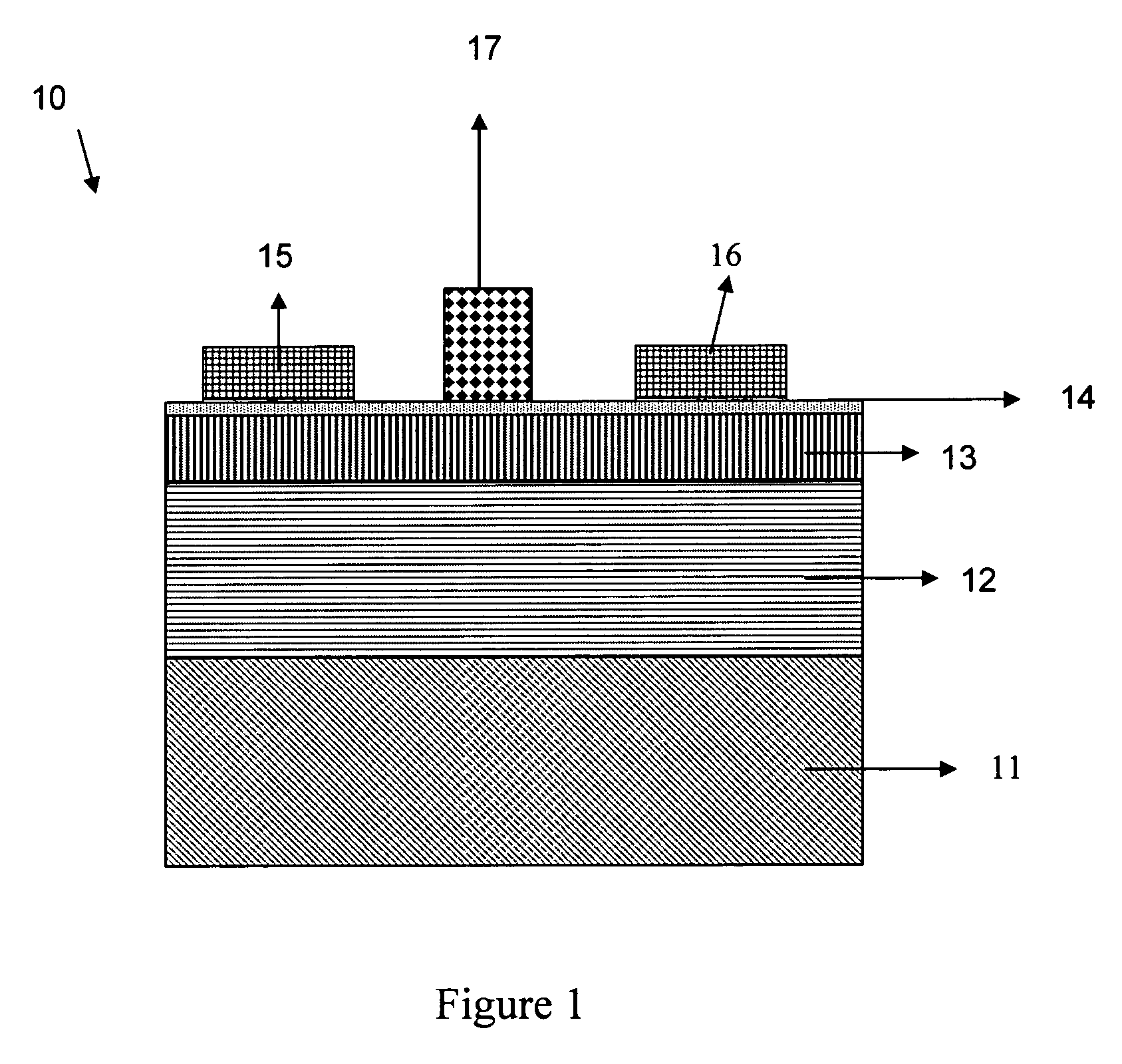
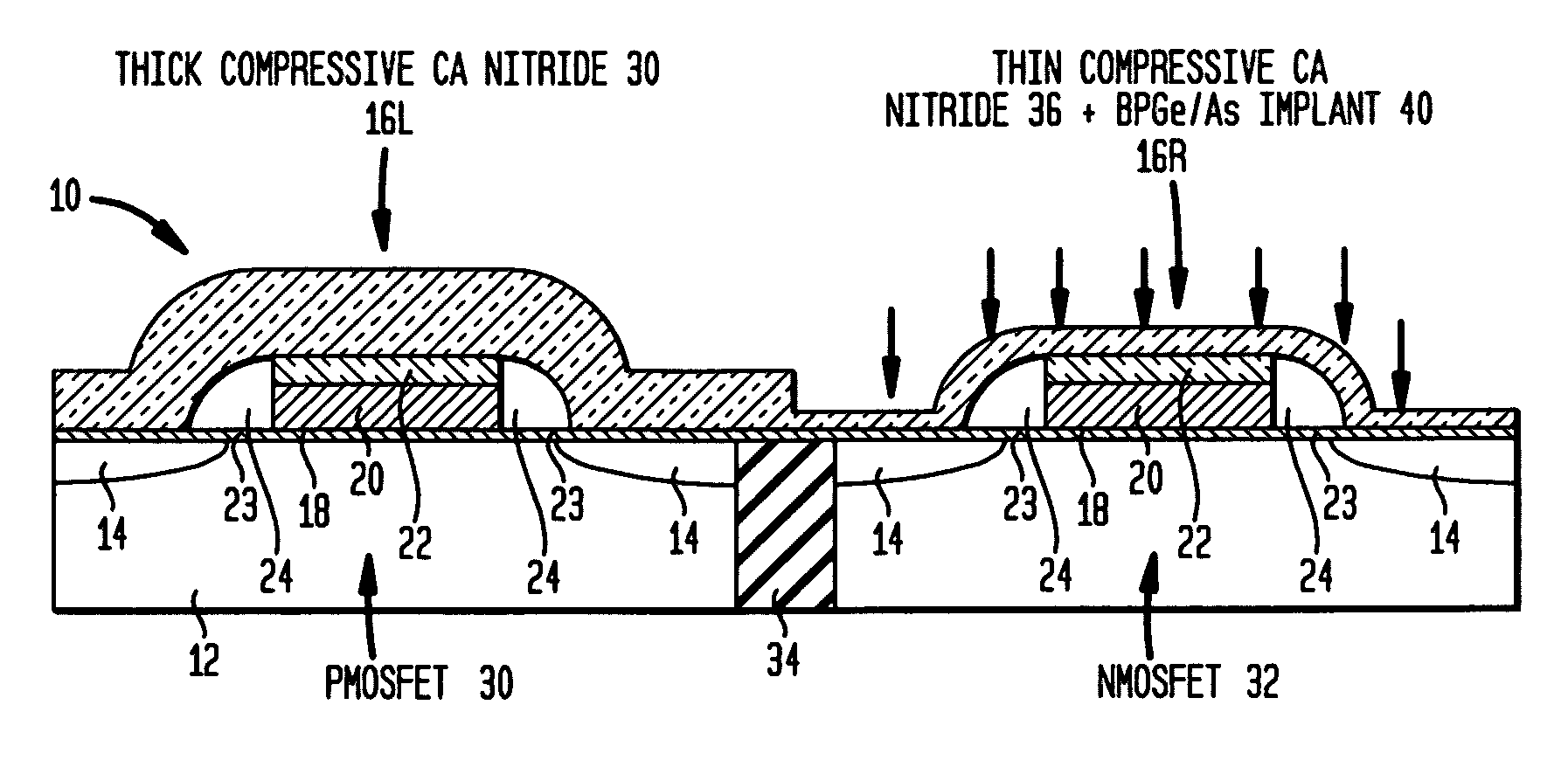
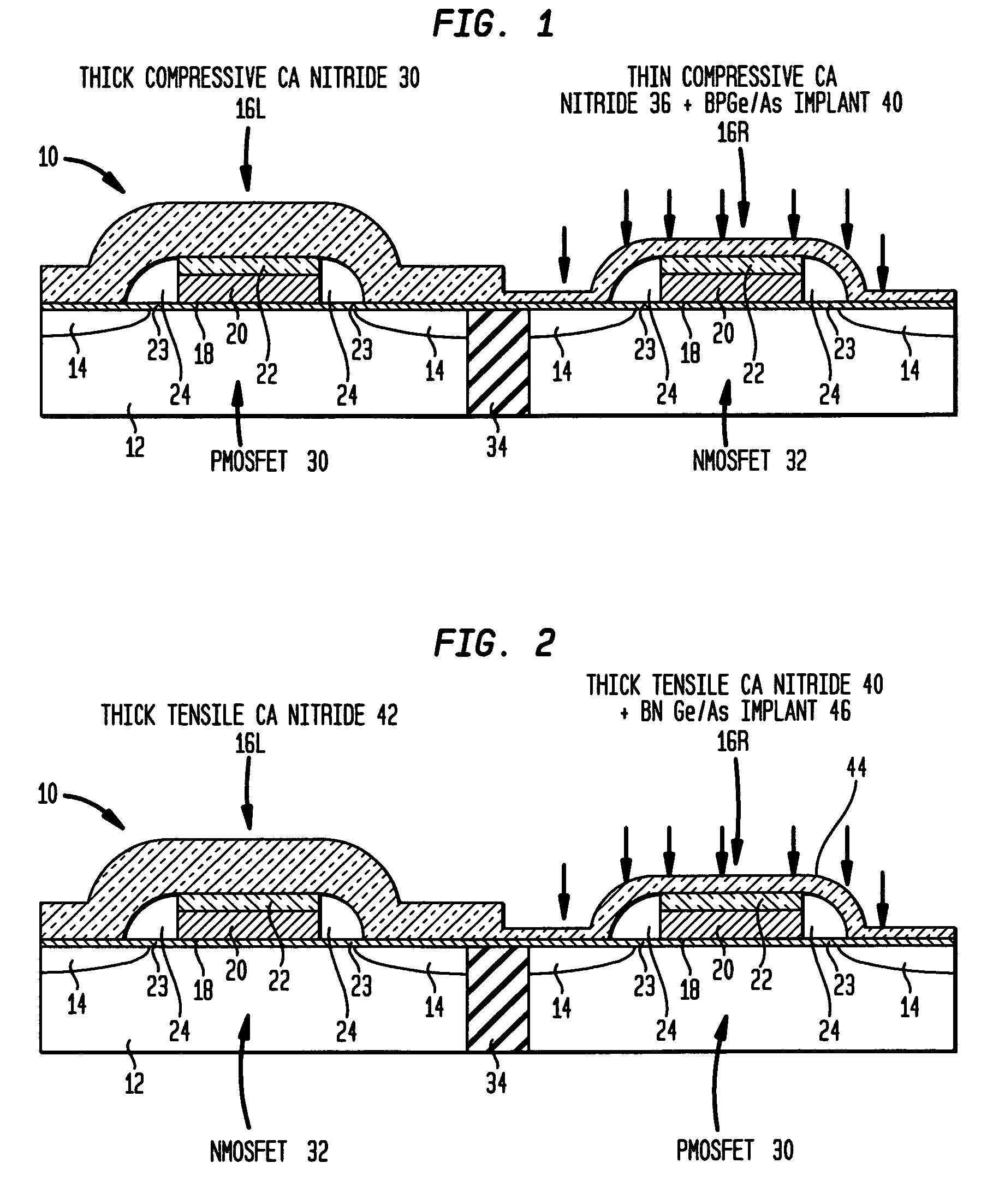
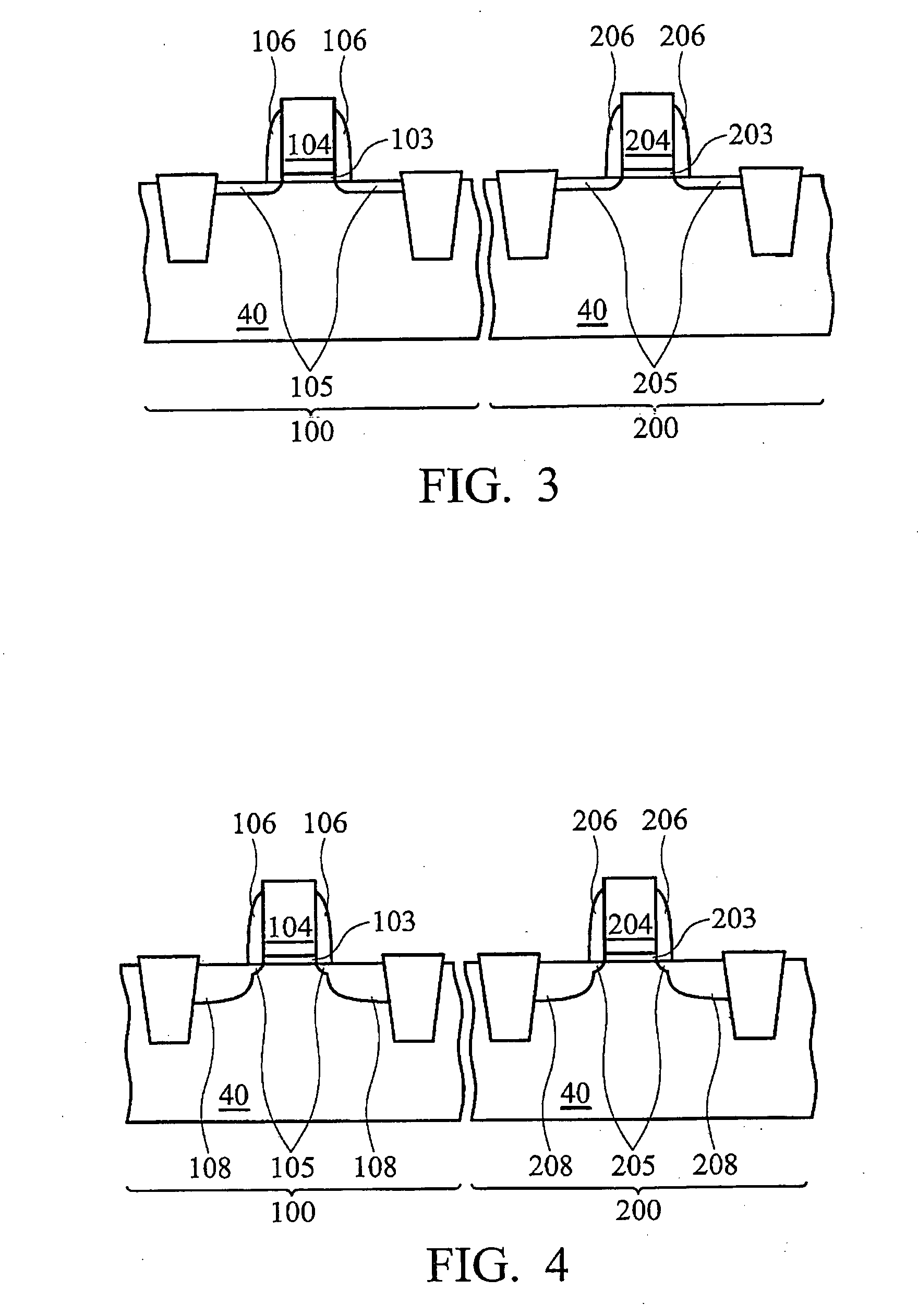
Structure and method to optimize strain in cmosfets
ActiveUS20060157795A1Optimize strainBroad applicabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor structure of strained MOSFETs, comprising both PMOSFETs and NMOSFETS, and a method for fabricating strained MOSFETs are disclosed that optimize strain in the MOSFETs, and more particularly maximize the strain in one kind (P or N) of MOSFET and minimize and relax the strain in another kind (N or P) of MOSFET. A strain inducing CA nitride coating having an original full thickness is formed over both the PMOSFETs and the NMOSFETs, wherein the strain inducing coating produces an optimized full strain in one kind of semiconductor device and degrades the performance of the other kind of semiconductor device. The strain inducing CA nitride coating is etched to a reduced thickness over the other kind of semiconductor devices, wherein the reduced thickness of the strain inducing coating relaxes and produces less strain in the other MOSFETs.
Owner:IBM CORP
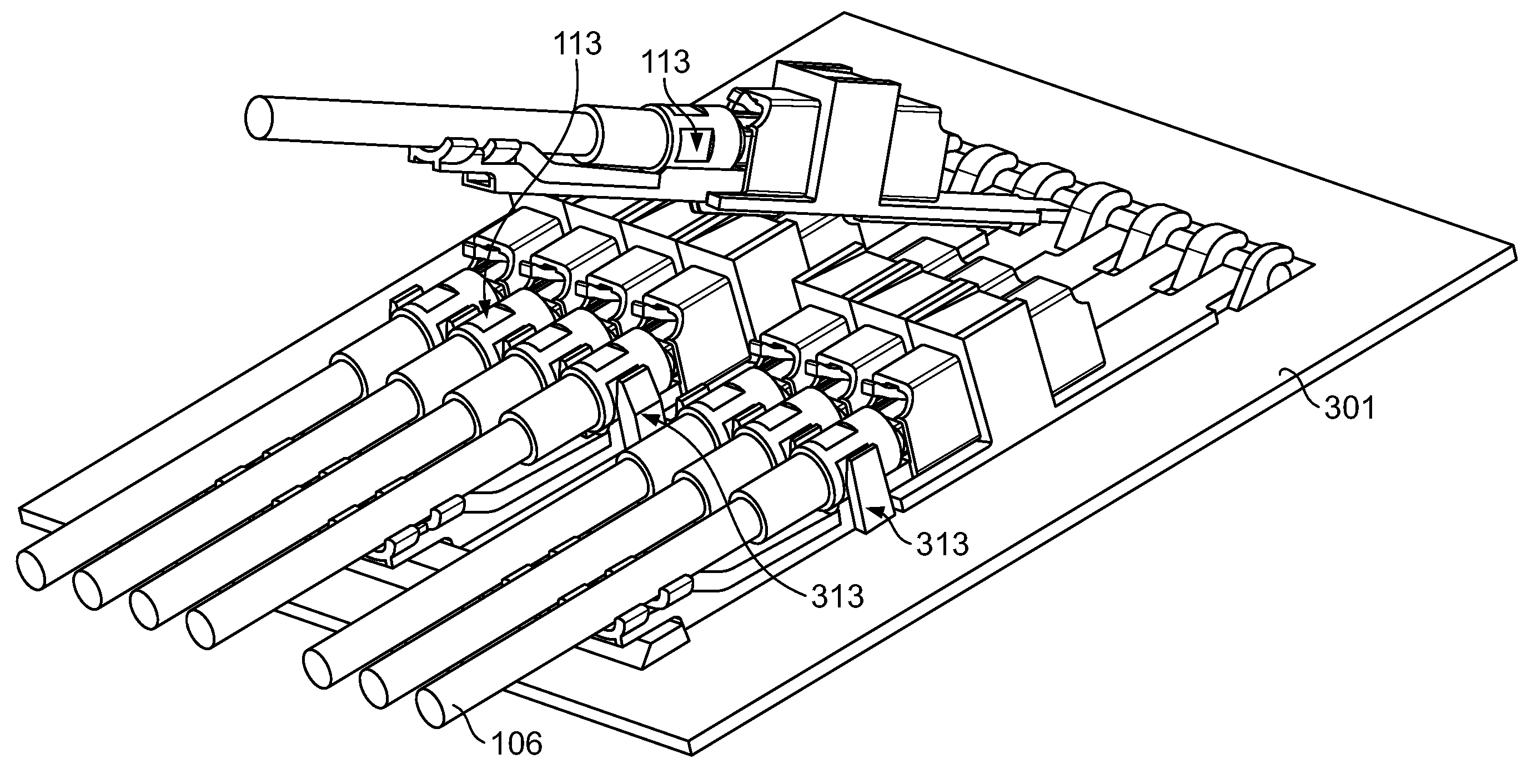
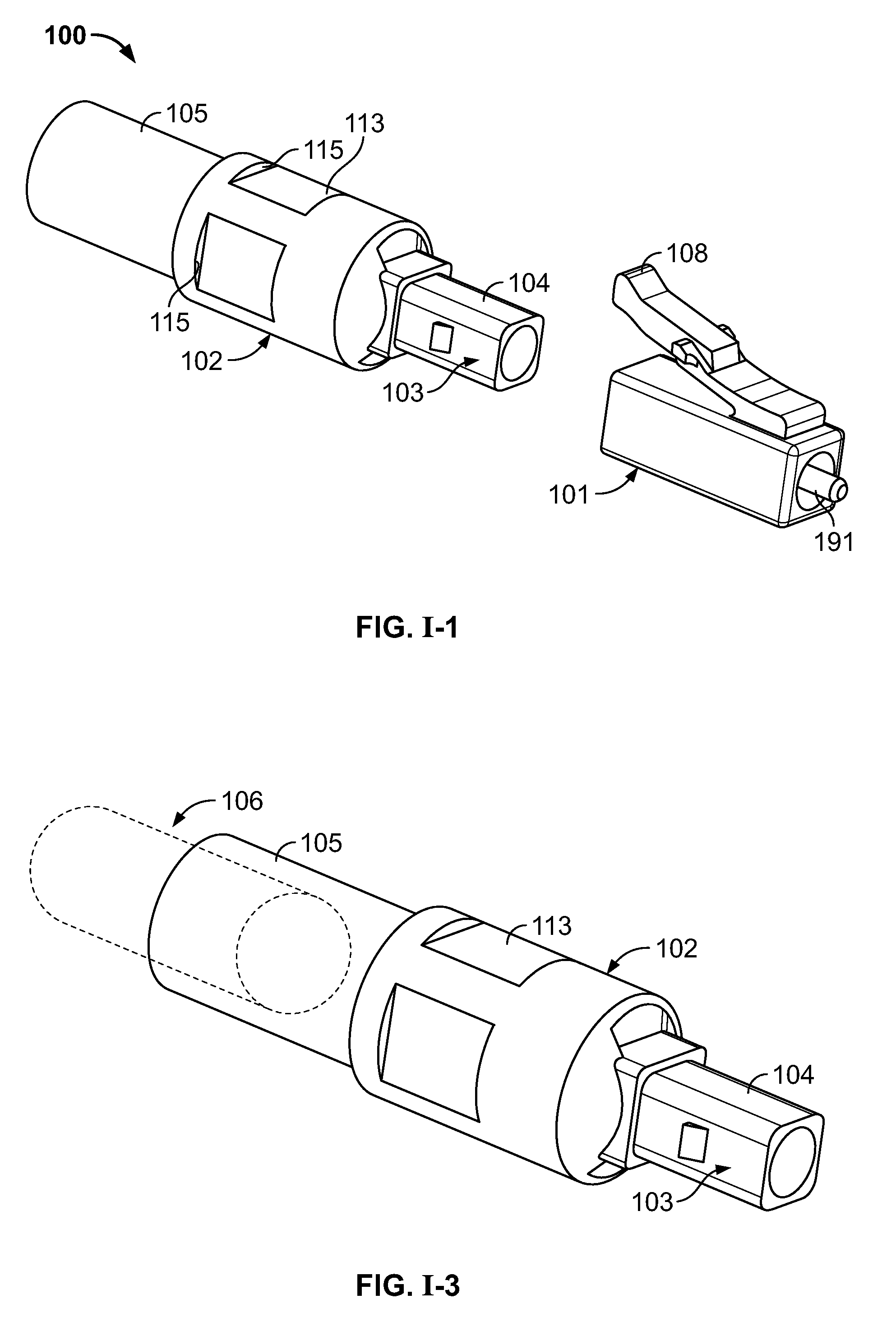
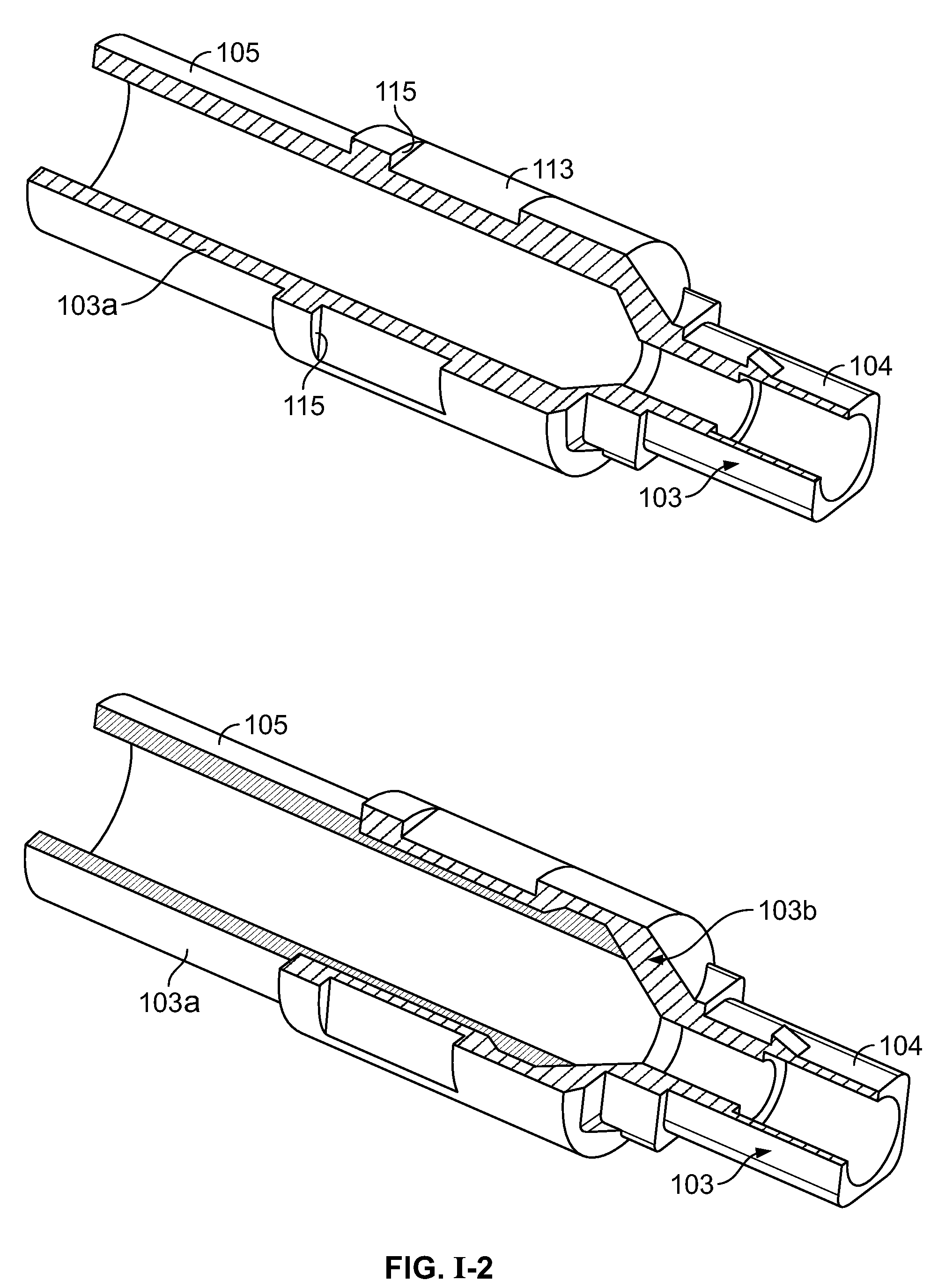
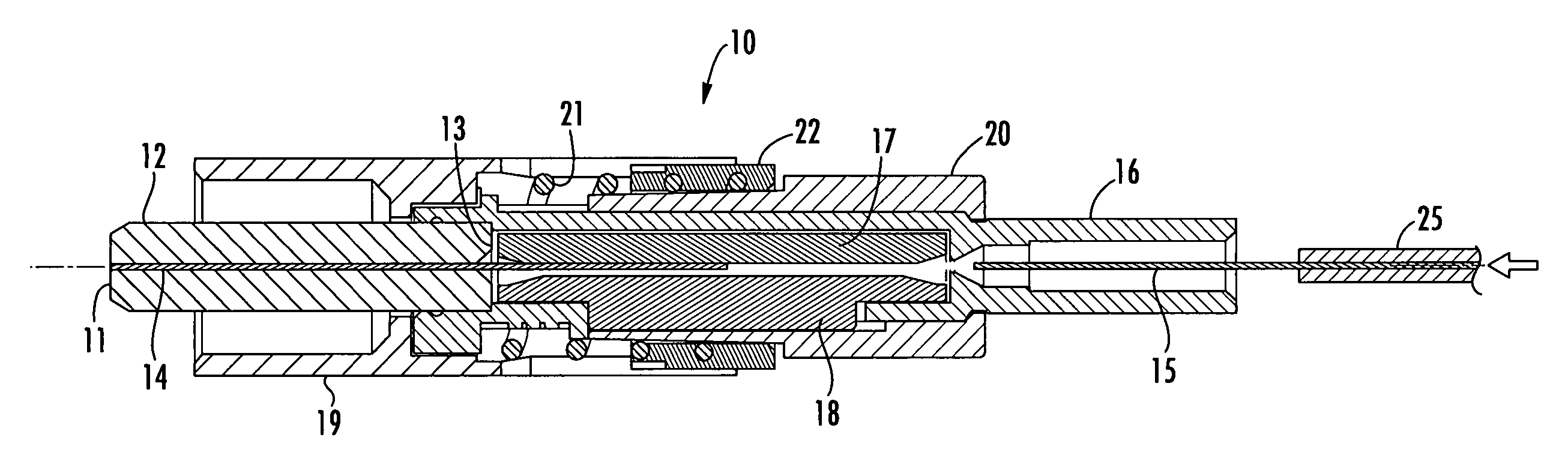
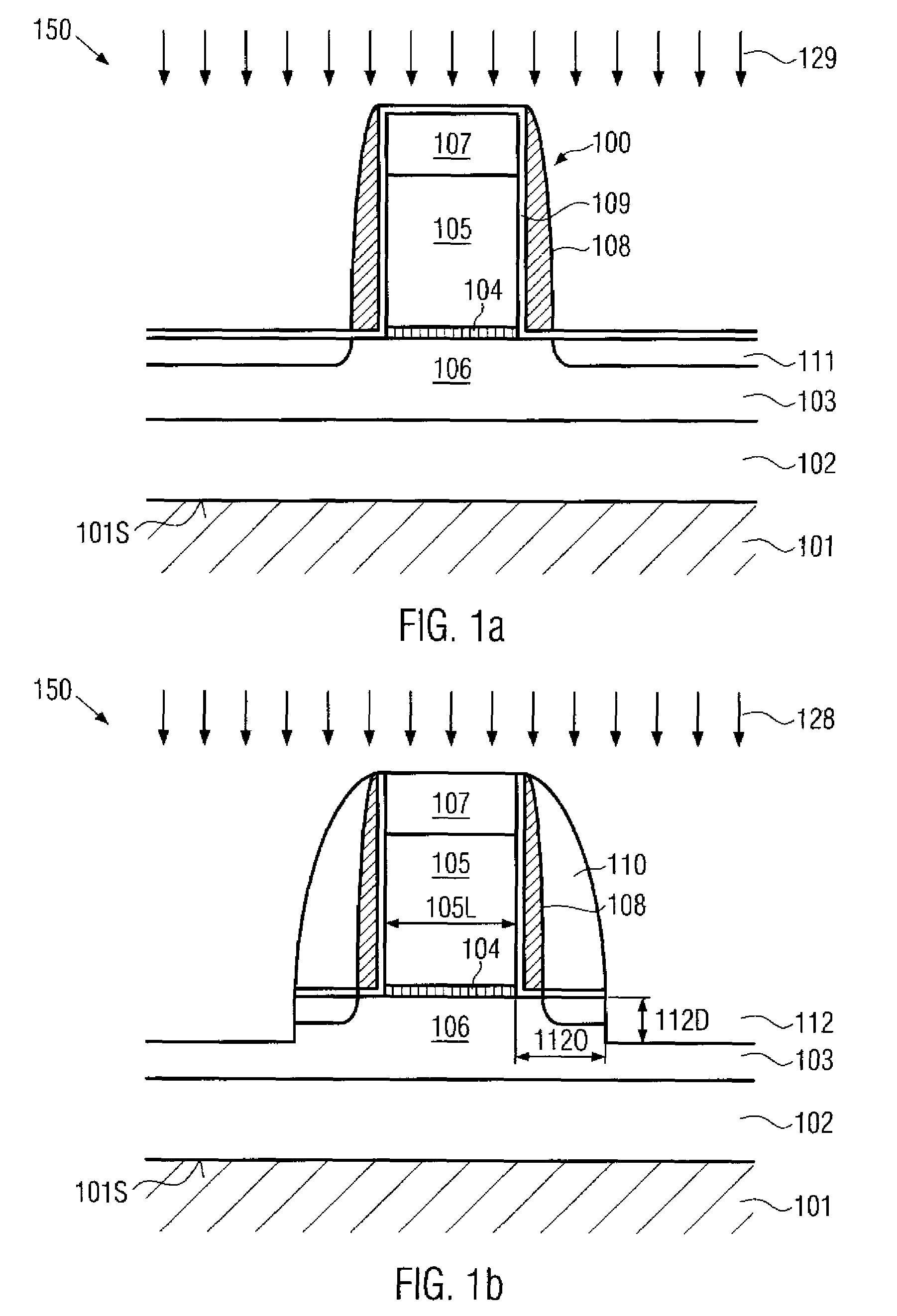
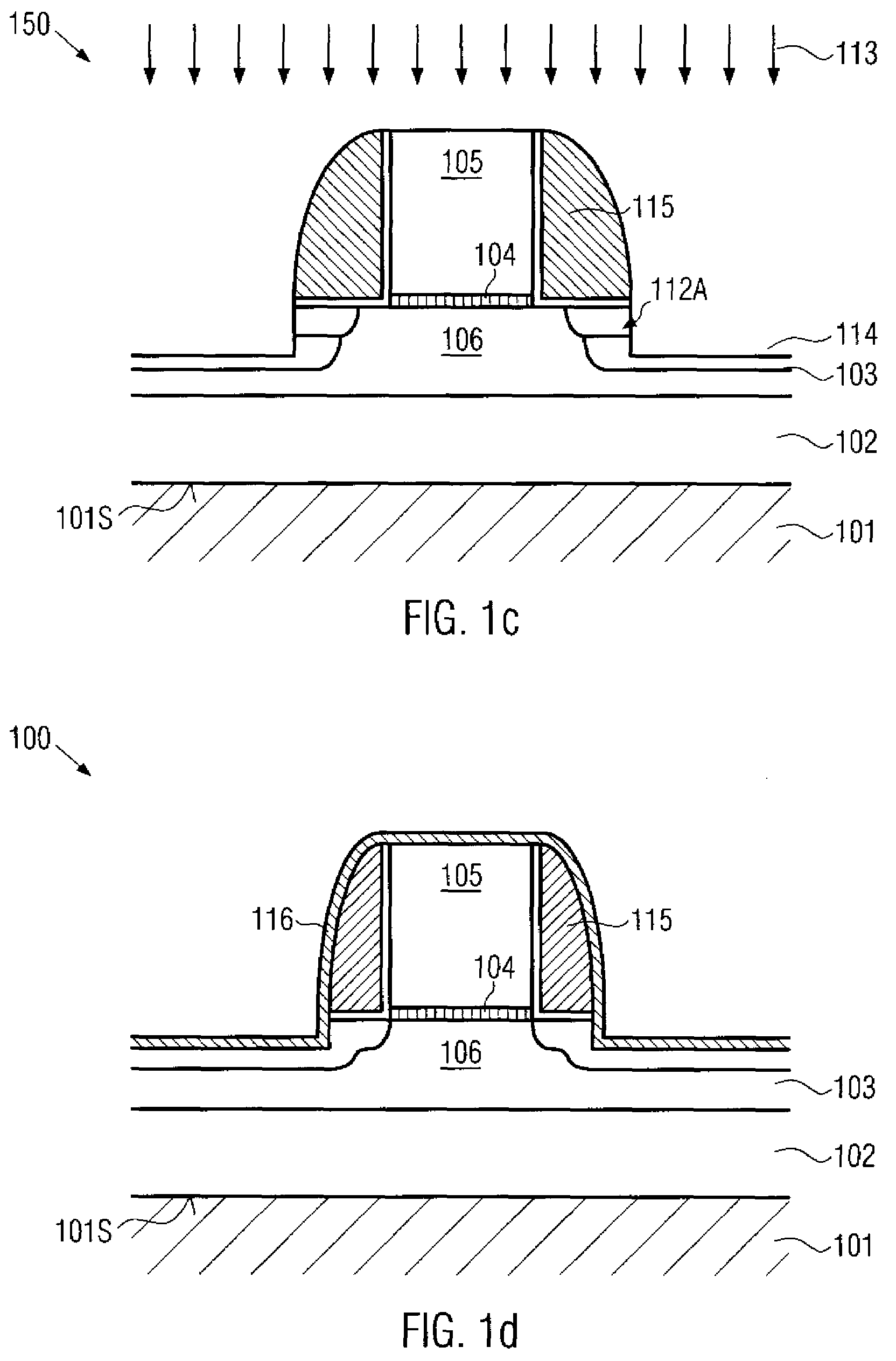
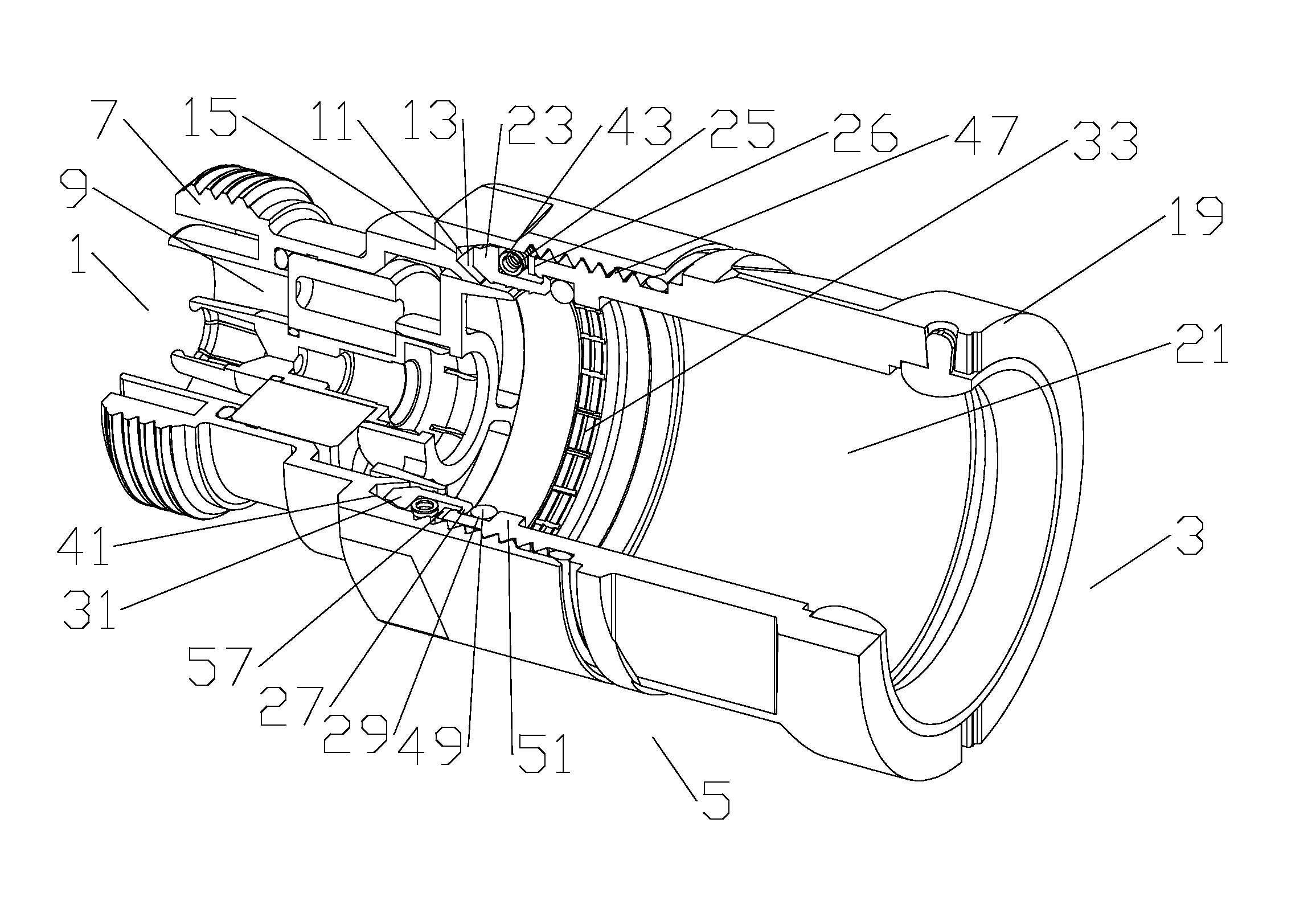
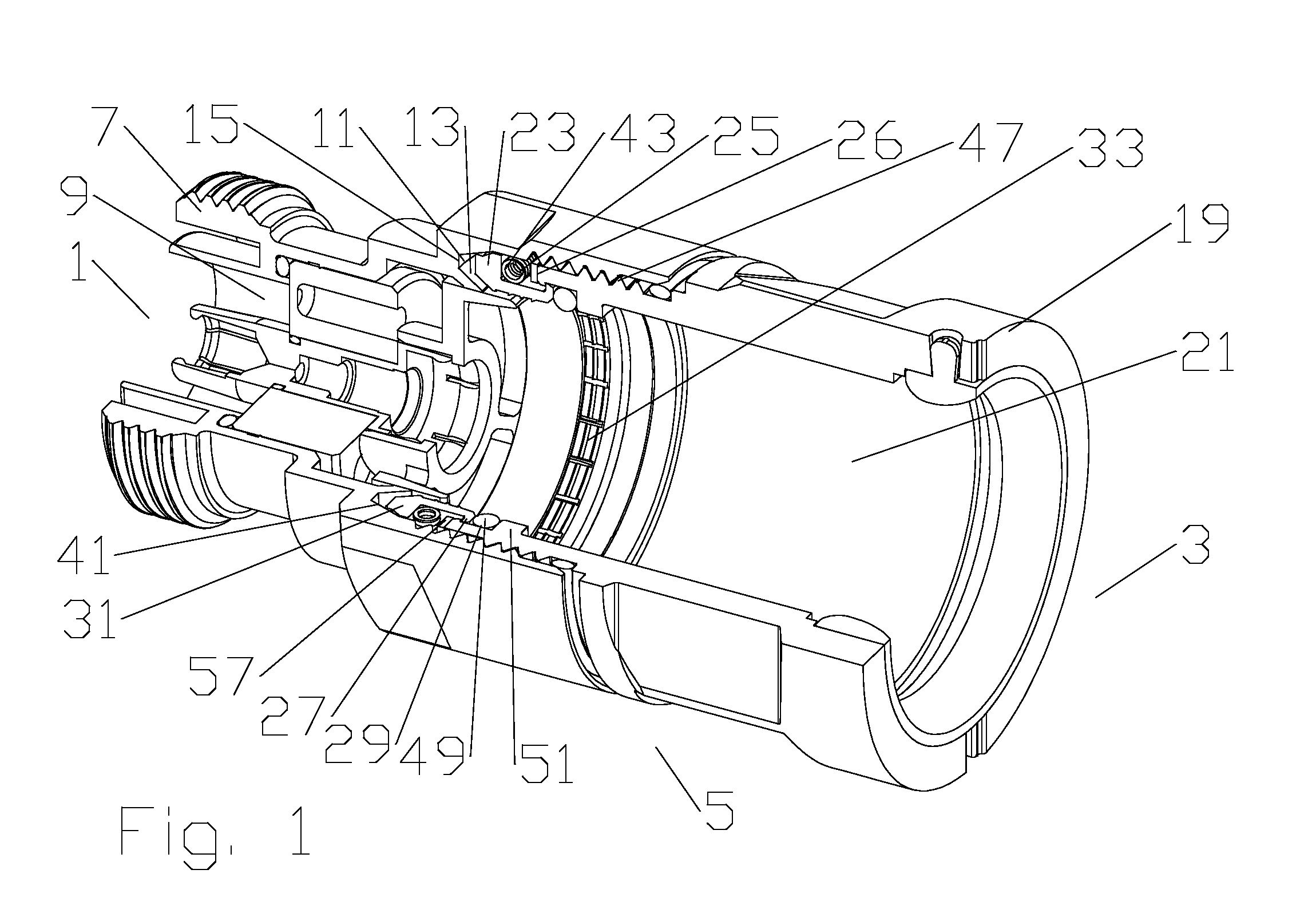
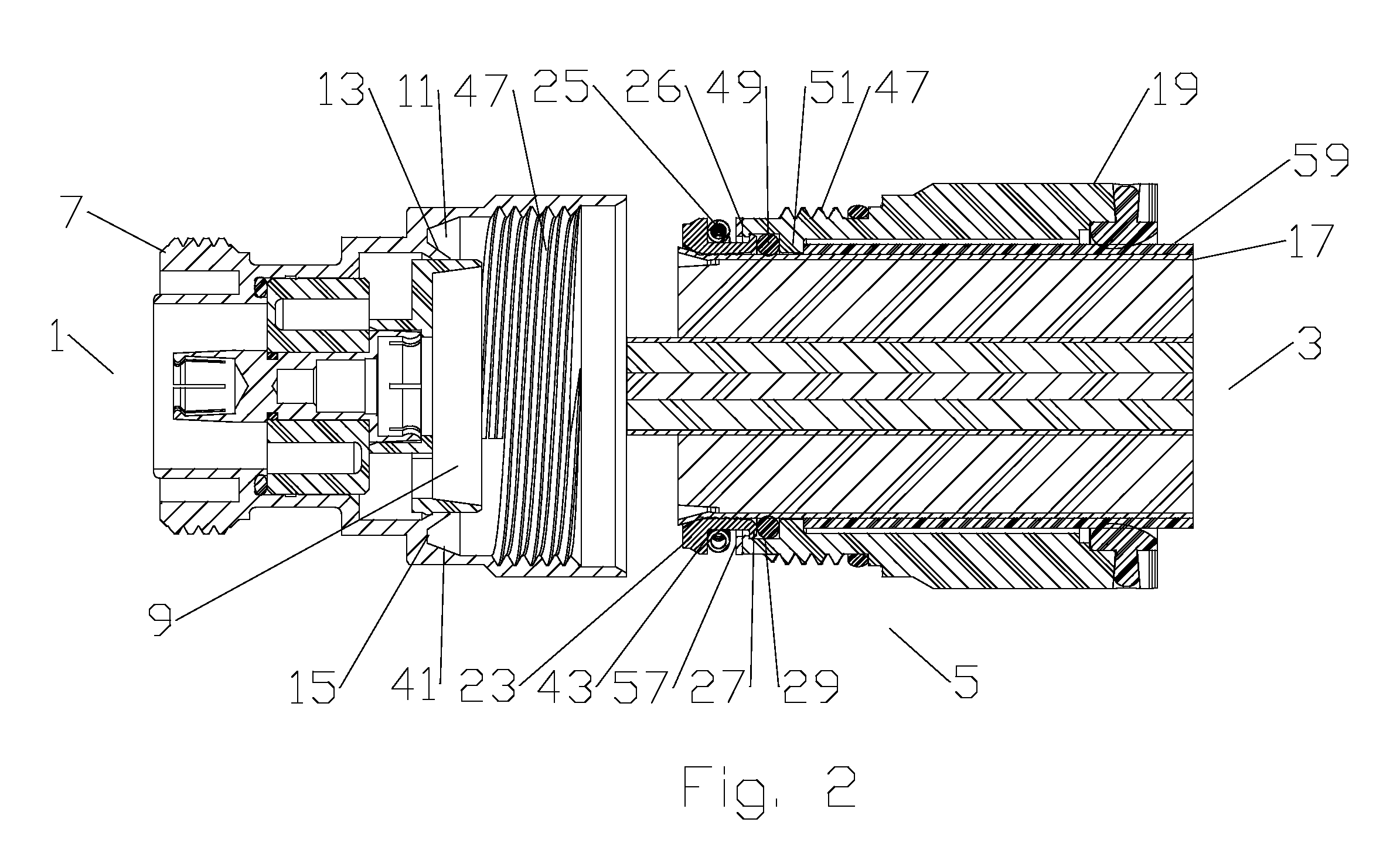
Optical fibre connection device
InactiveUS7802926B2Increase strainRestraint torsionCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringOptical fiber cable
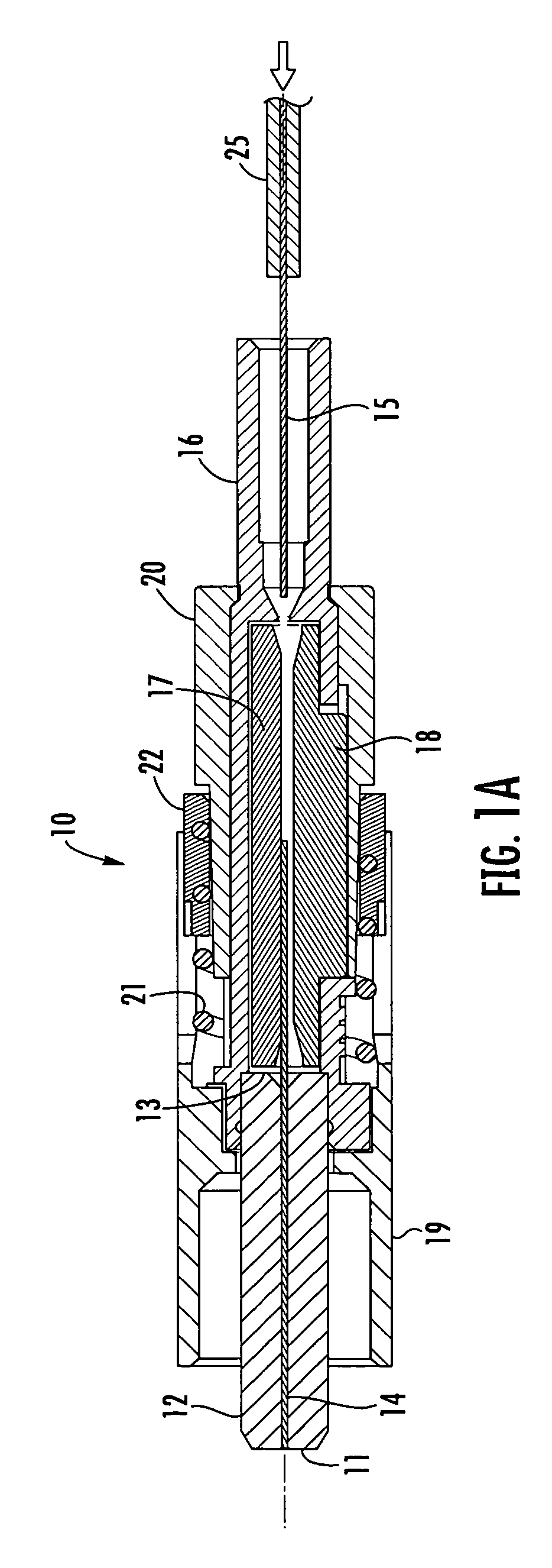
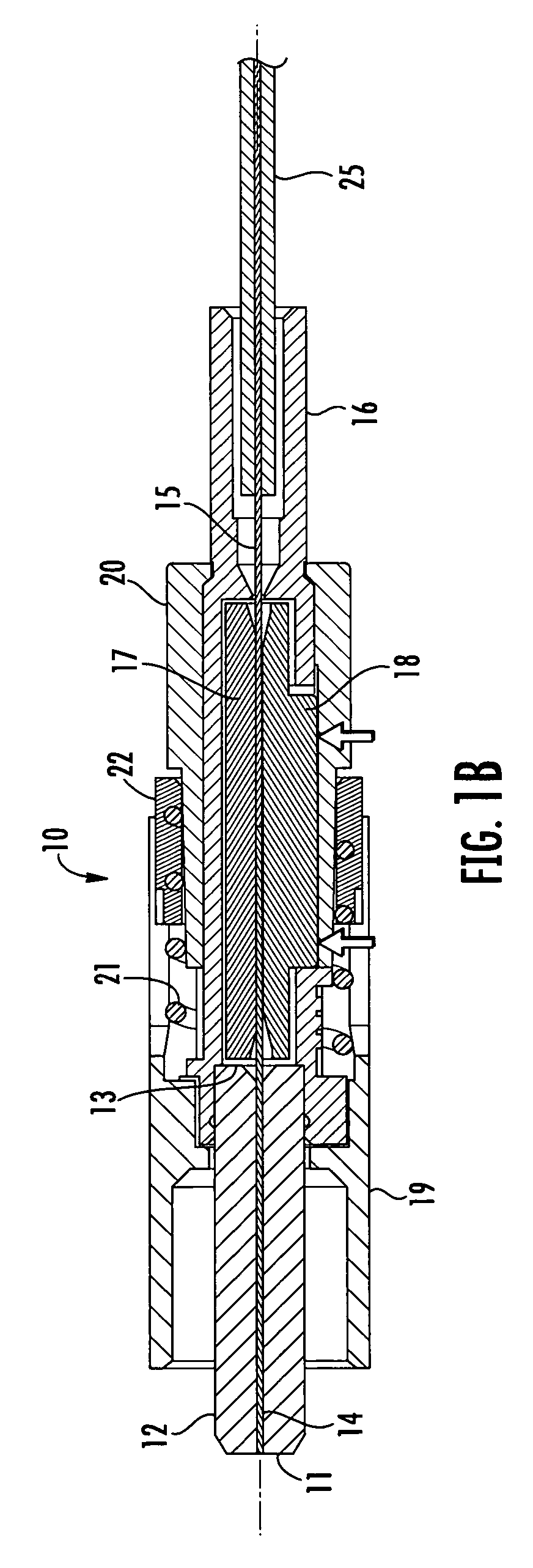
The present invention provides an optical fiber connection device comprising a part (103) of a screw-threadless multi-part (101, 103) optical fiber cable connector (100), the multi-parts (101, 103) of the connector (100) being inter-connectable, the part (103) comprising a body (102), the body (102) comprising: an optical fiber cable connection end (105) for connection with an optical fiber cable (106); a part connection end (104) for connection with another part (101) of the multi-part optical fiber cable connector (100); and one or more formations (113) adapted to co-operate with a retainer (213, 313) in a mounting (200, 300) for the connector (100), the mounting (200, 300) used to retain the optical fiber cable (106) and the connector (100) when the optical fiber cable (106) is connected to the optical fiber cable connection end (105) of the body (102), the formations (113) adapted to co-operate with the mounting retainer (213, 313) to resist rotational and / or axial movement of the connector (100) when the connector (100) is assembled with an optical fiber cable (106) and the other parts (103, 101) of the connector (100) and mounted in the mounting (200, 300).
Owner:COMMSCOPE CONNECTIVITY BELGIUM BVBA
Fiber cement composite materials using cellulose fibers loaded with inorganic and/or organic substances
InactiveUS20050235883A1Low water absorptionLow water migrationConstruction materialWater-repelling agents additionCement compositesCellulose fiber
This invention discloses a new technology related to cellulose fiber reinforced cement composite materials using the loaded cellulose fibers. This invention discloses four aspects of the technology: fiber treatment, formulation, method and final product. This technology advantageously provides fiber cement building materials with the desirable characteristics of reduced water absorption, reduced rate of water absorption, lower water migration, and lower water permeability. This invention also impart the final products improved freeze-thaw resistance, reduced efflorescence, reduced chemical dissolution and re-deposition, and improved rot and fire resistances, compared to conventional fiber cement products. These improved attributes are gained without loss in dimensional stability, strength, strain or toughness.
Owner:MERKLEY DONALD J +1
Installation tool with integrated visual fault indicator for field-installable mechanical splice connector
InactiveUS20070172179A1Improved visual fault locatorMore efficientCoupling light guidesTesting fibre optics/optical waveguide devicesFault indicatorFiber
A mechanical splice fiber optic connector installation tool operable for performing splice terminations and verifying an acceptable splice termination includes a power source, a connector holder, an integrated Visual Fault Locater having an optical transmission element and a display for displaying the status of the termination. An adapter configured to receive the connector and align the connector with the optical transmission element, such that the optical transmission element is spaced apart from the connector at a predetermined distance and is in optical communication with the connector for propagating light energy through the adapter and along the stub optical fiber to a termination area of the connector.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
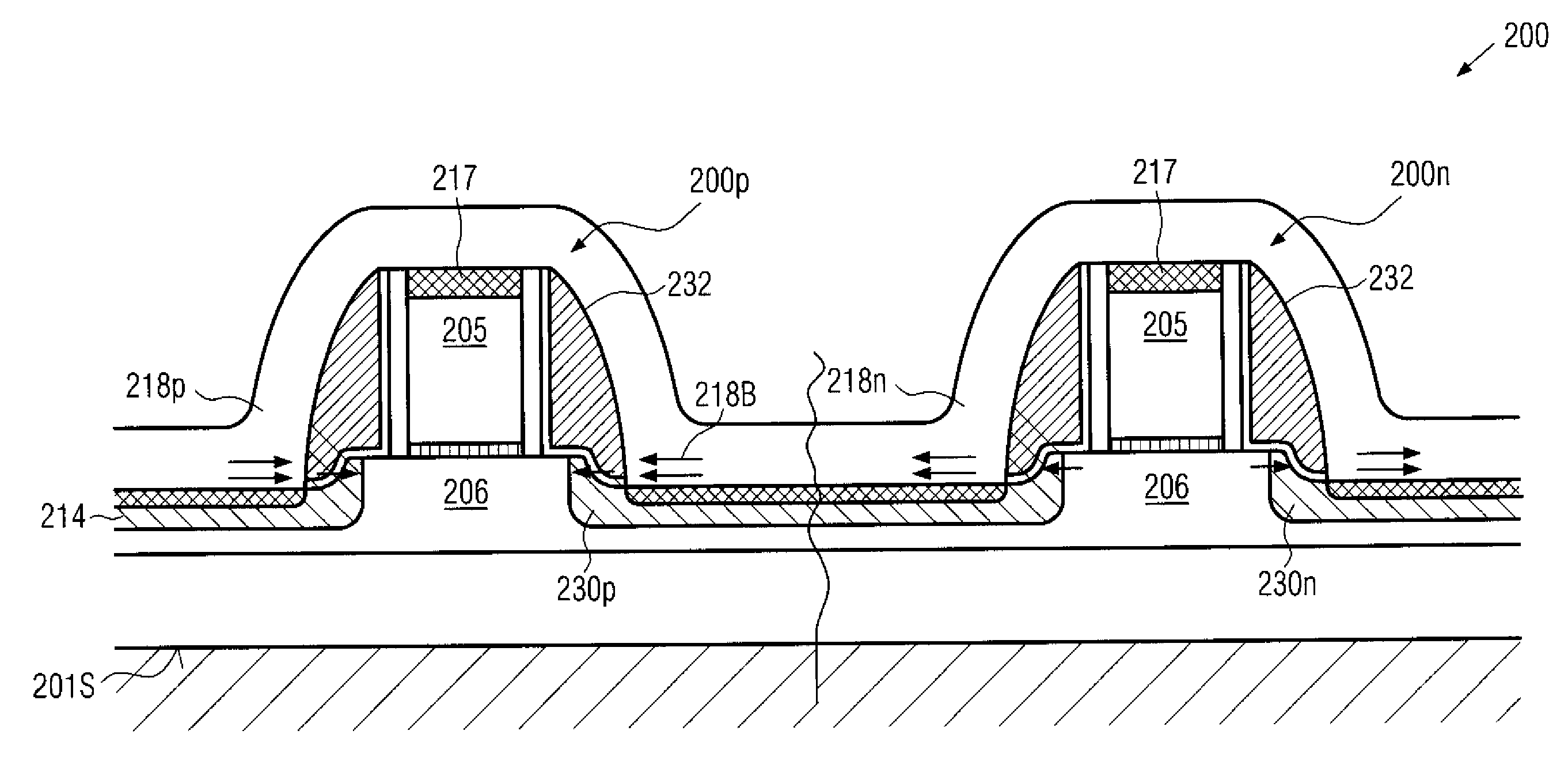
Method of forming a MOS device having a strained channel region
InactiveUS20070010073A1Increase strainIncreasing the thicknessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
A method of forming a semiconductor device comprising providing a substrate comprising a first device region, implanting a source / drain region in the first device region, forming a strained capping layer on the source / drain region, super annealing and crystallizing the source / drain region, and removing substantially all of the strained capping layer is provided. The method further includes pre-amorphizing the source / drain region before the super annealing. The strained capping layer may further be formed on a pre-amorphized gate electrode, and the gate electrode is super annealed. The strain is generated and preserved after the removal of the strained capping layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Technique for providing stress sources in transistors in close proximity to a channel region by recessing drain and source regions
ActiveUS20070228482A1Increase strainEfficient transferSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringField-effect transistor
By recessing drain and source regions, a highly stressed layer, such as a contact etch stop layer, may be formed in the recess in order to enhance the strain generation in the adjacent channel region of a field effect transistor. Moreover, a strained semiconductor material may be positioned in close proximity to the channel region by reducing or avoiding undue relaxation effects of metal silicides, thereby also providing enhanced efficiency for the strain generation. In some aspects, both effects may be combined to obtain an even more efficient strain-inducing mechanism.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC +1
Slip Ring Contact Coaxial Connector
InactiveUS20120064768A1Simple structureReduce the overall diameterElectrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsEngineeringElectrical conductor
A coaxial connector with a connector body is provided with a connector body bore. An annular coupling groove is provided in the connector body bore open to a cable end of the connector body. A clamp sidewall of the coupling grove is angled inward from a bottom of the coupling groove. A slip ring seated within the coupling body bore is provided with a grip surface. An annular compression body is positioned between the slip ring and a compression surface of the coupling body. The connector body and the coupling body are coupled together via threads. The slip ring is dimensioned for axial advancement of the coupling body along the threads to exert a compression force against the compression body to clamp a leading edge of the outer conductor between the slip ring and the clamp sidewall.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Electrochemical methods, devices, and structures
ActiveUS7541715B2Increase strainDeferred-action cellsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesInorganic compoundActuator
The present invention provides devices and structures and methods of use thereof in electrochemical actuation. This invention provides electrochemical actuators, which are based, inter-alia, on an electric field-driven intercalation or alloying of high-modulus inorganic compounds, which can produce large and reversible volume changes, providing high actuation energy density, high actuation authority and large free strain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com