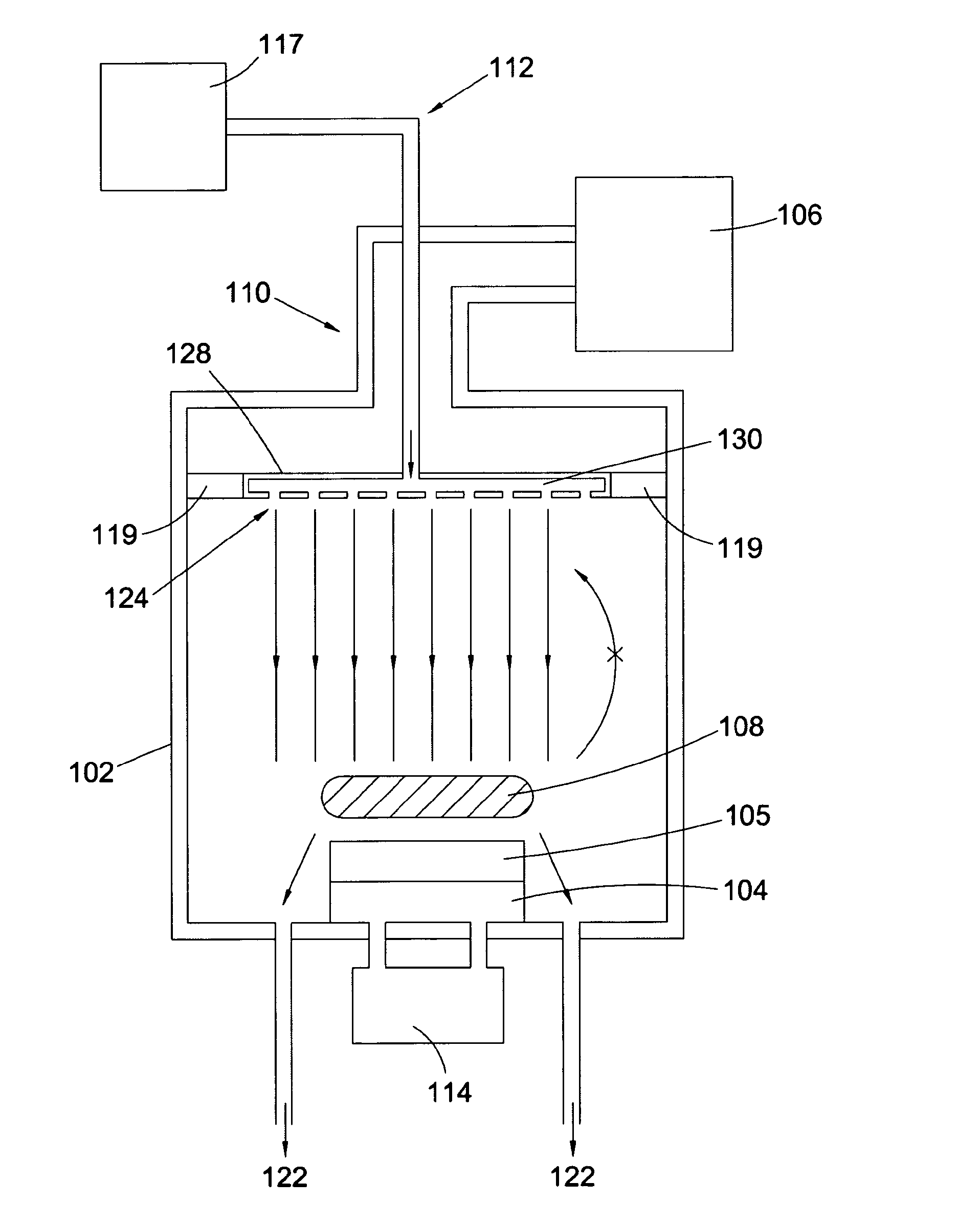
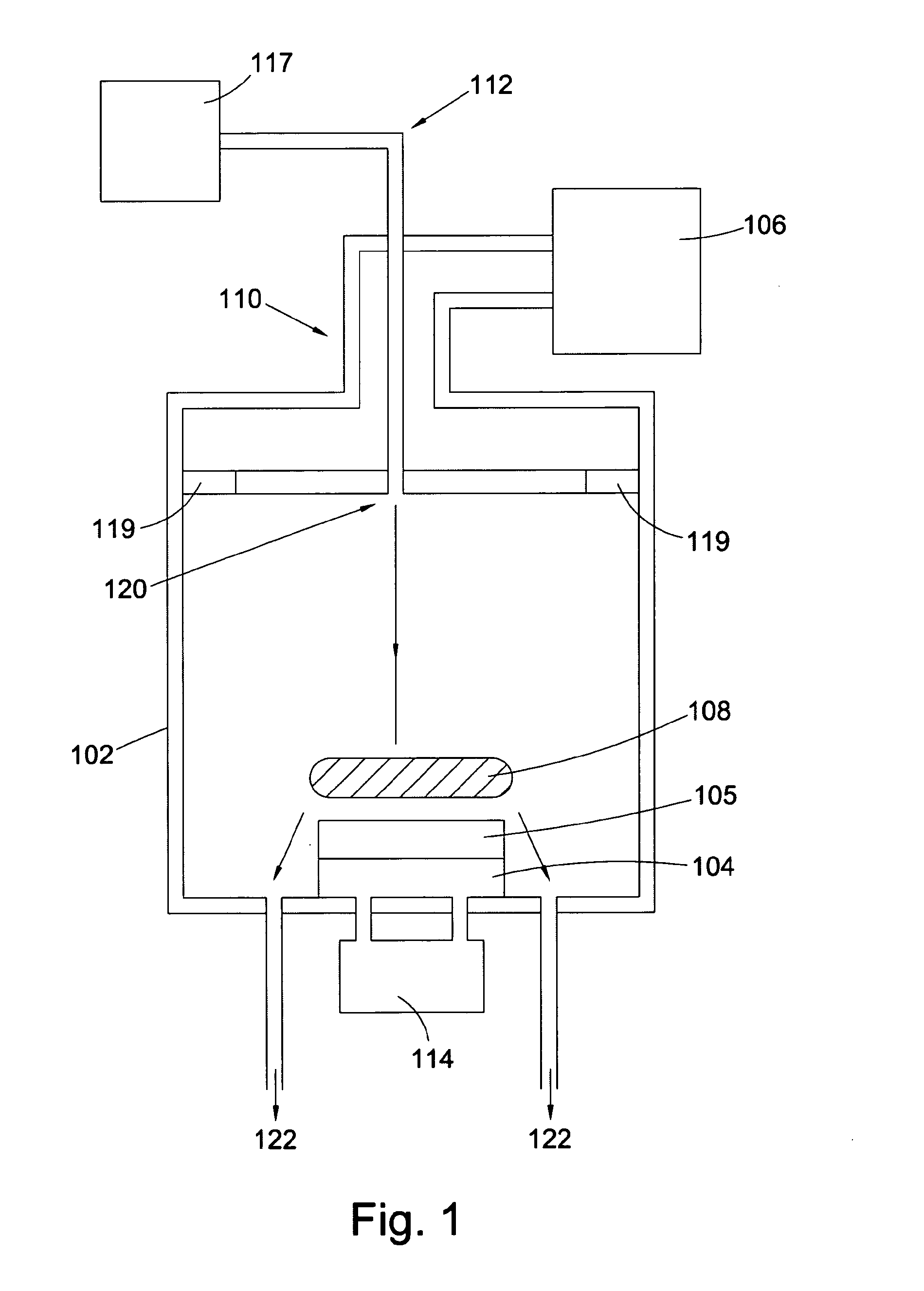
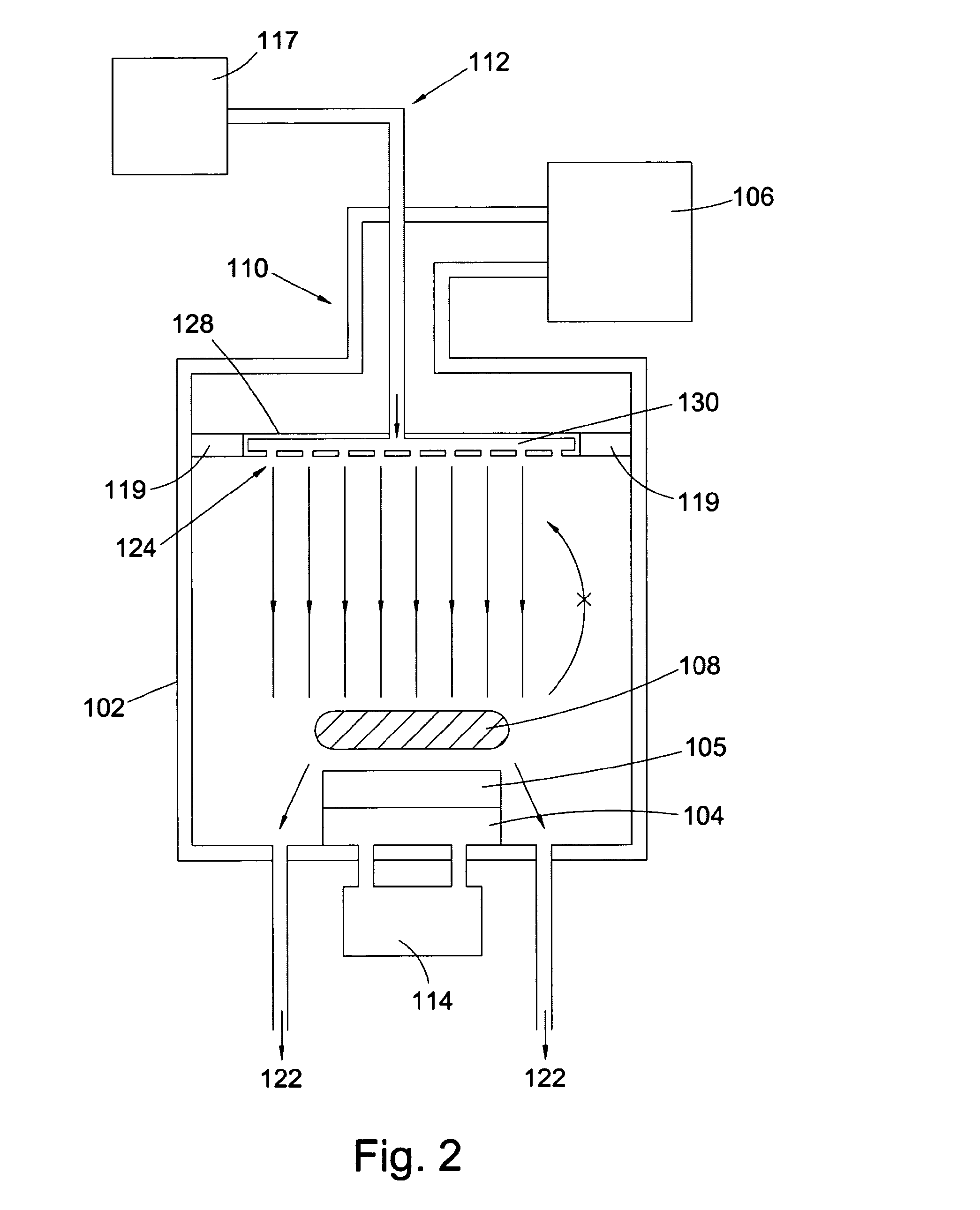
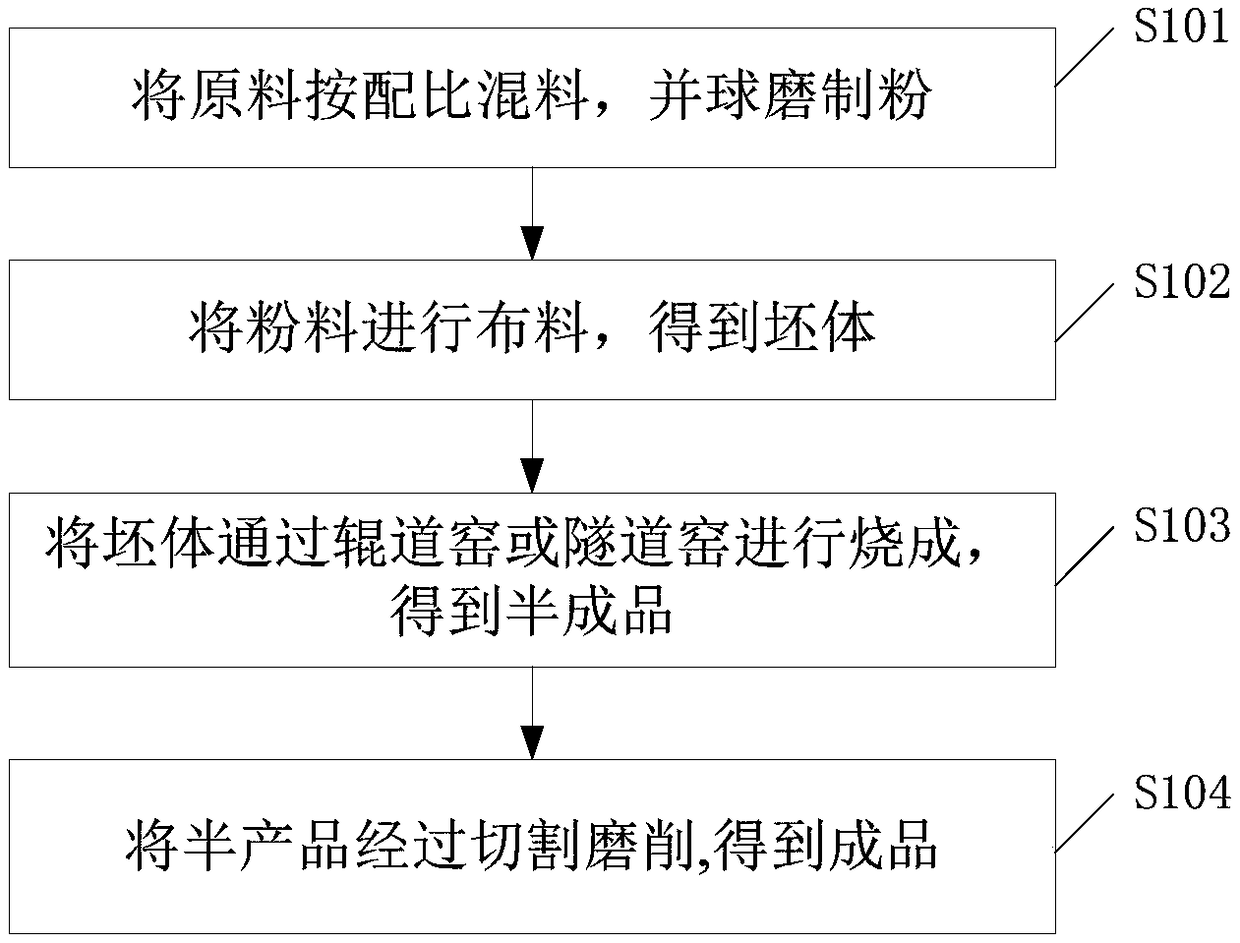
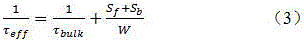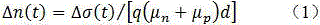Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169results about How to "Improve material quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
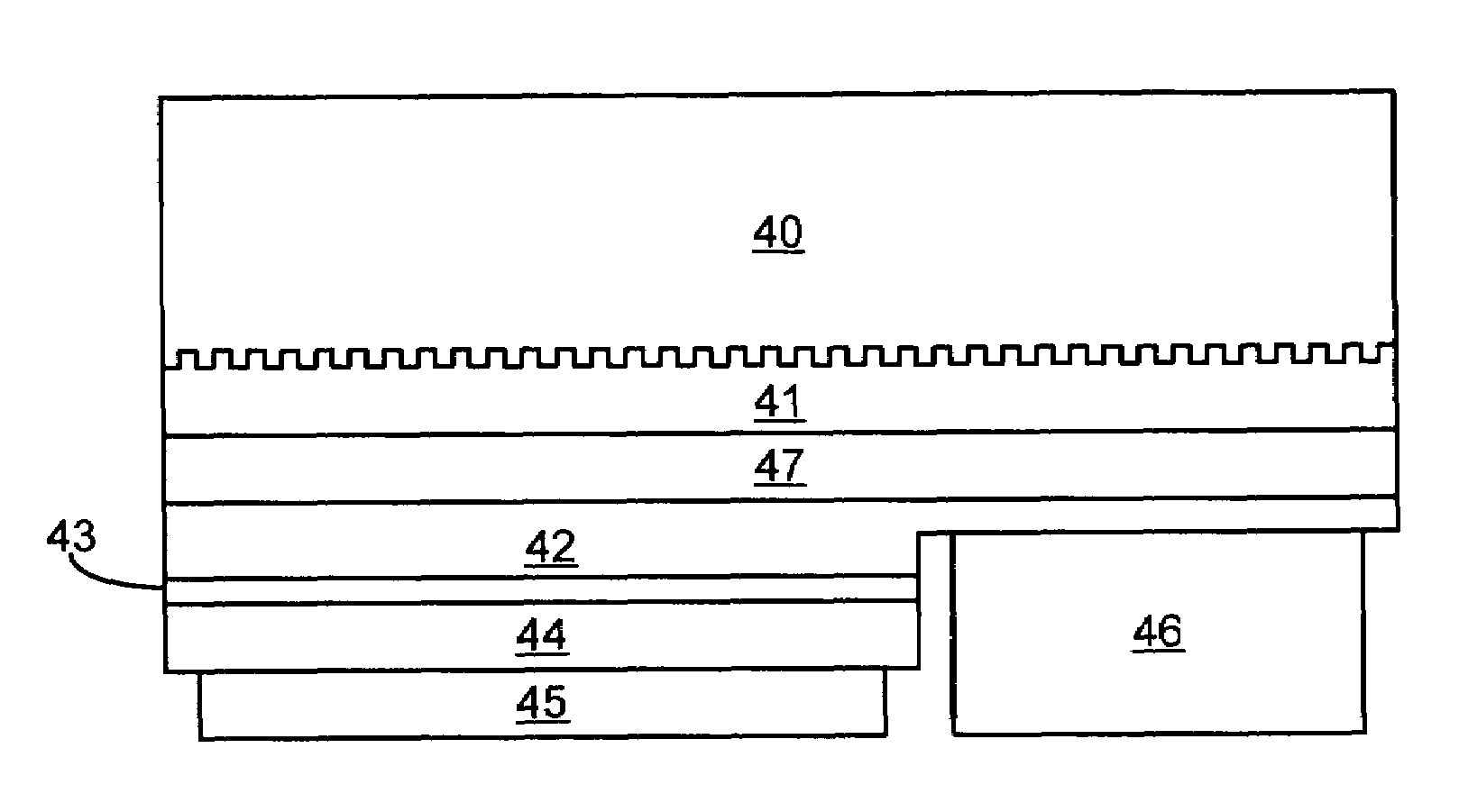
III-V Nitride homoepitaxial material of improved MOVPE epitaxial quality (surface texture and defect density) formed on free-standing (Al,In,Ga)N substrates, and opto-electronic and electronic devices comprising same
InactiveUS20030213964A1Improve material qualityReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCelsius DegreeSource material
A III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structure comprising a III-V nitride homoepitaxial epi layer of improved epitaxial quality deposited on a III-V nitride material substrate, e.g., of freestanding character. Various processing techniques are described, including a method of forming a III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer on a corresponding III-V nitride material substrate, by depositing the III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer by a VPE process using Group III source material and nitrogen source material under process conditions including V / III ratio in a range of from about 1 to about 10<5>, nitrogen source material partial pressure in a range of from about 1 to about 10<3 >torr, growth temperature in a range of from about 500 to about 1250 degrees Celsius, and growth rate in a range of from about 0.1 to about 10<2 >microns per hour. The III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structures are usefully employed in device applications such as UV LEDs, high electron mobility transistors, and the like.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
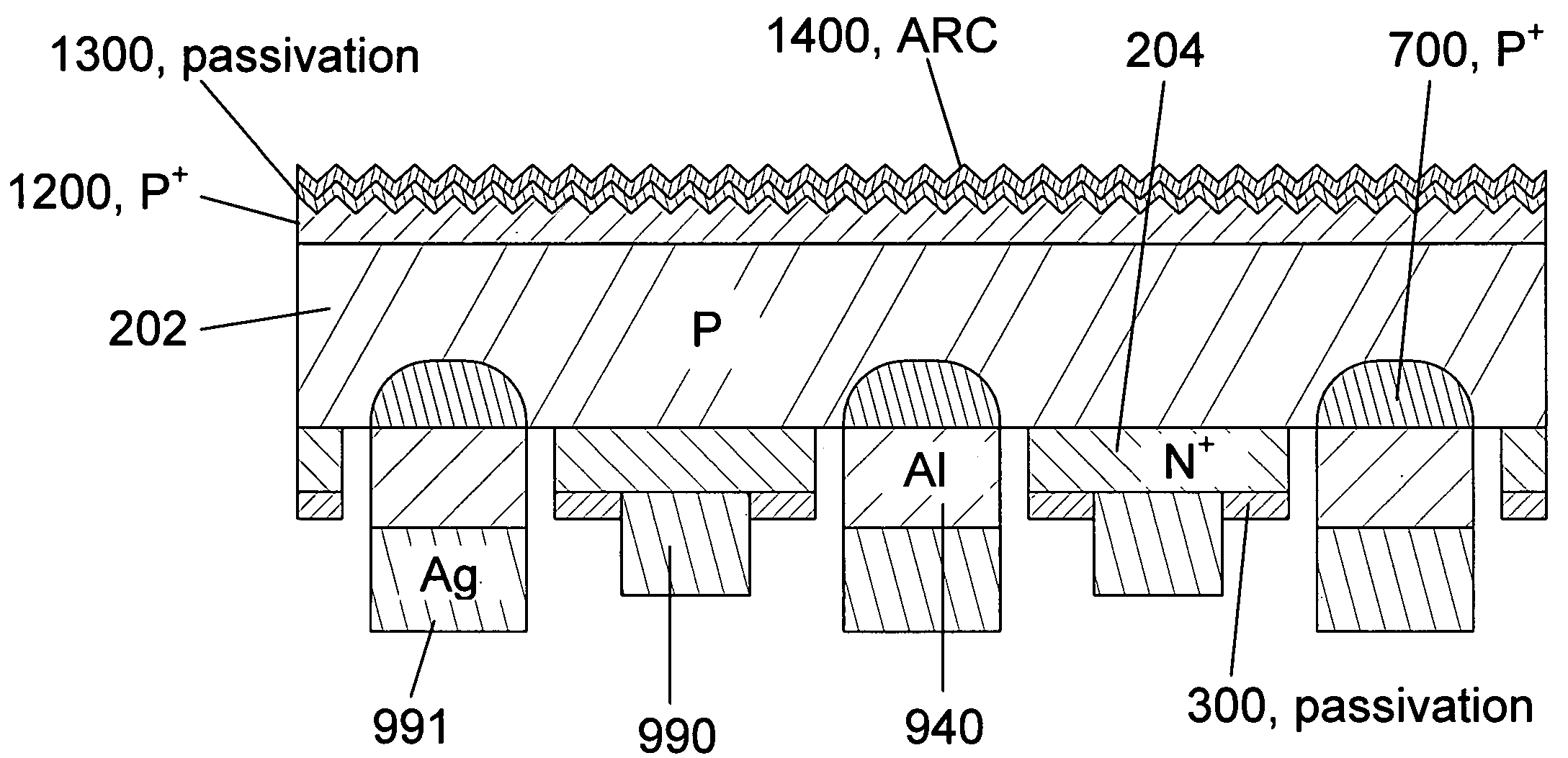
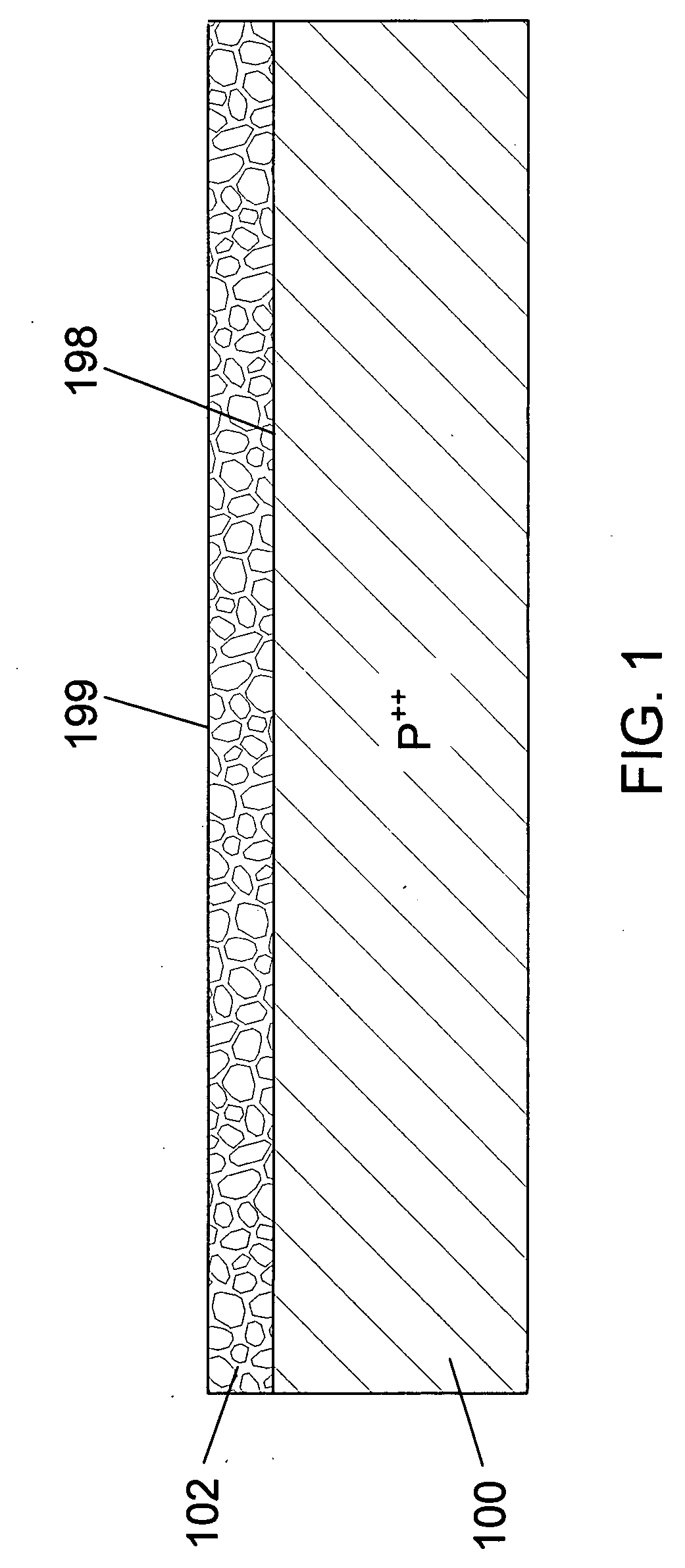
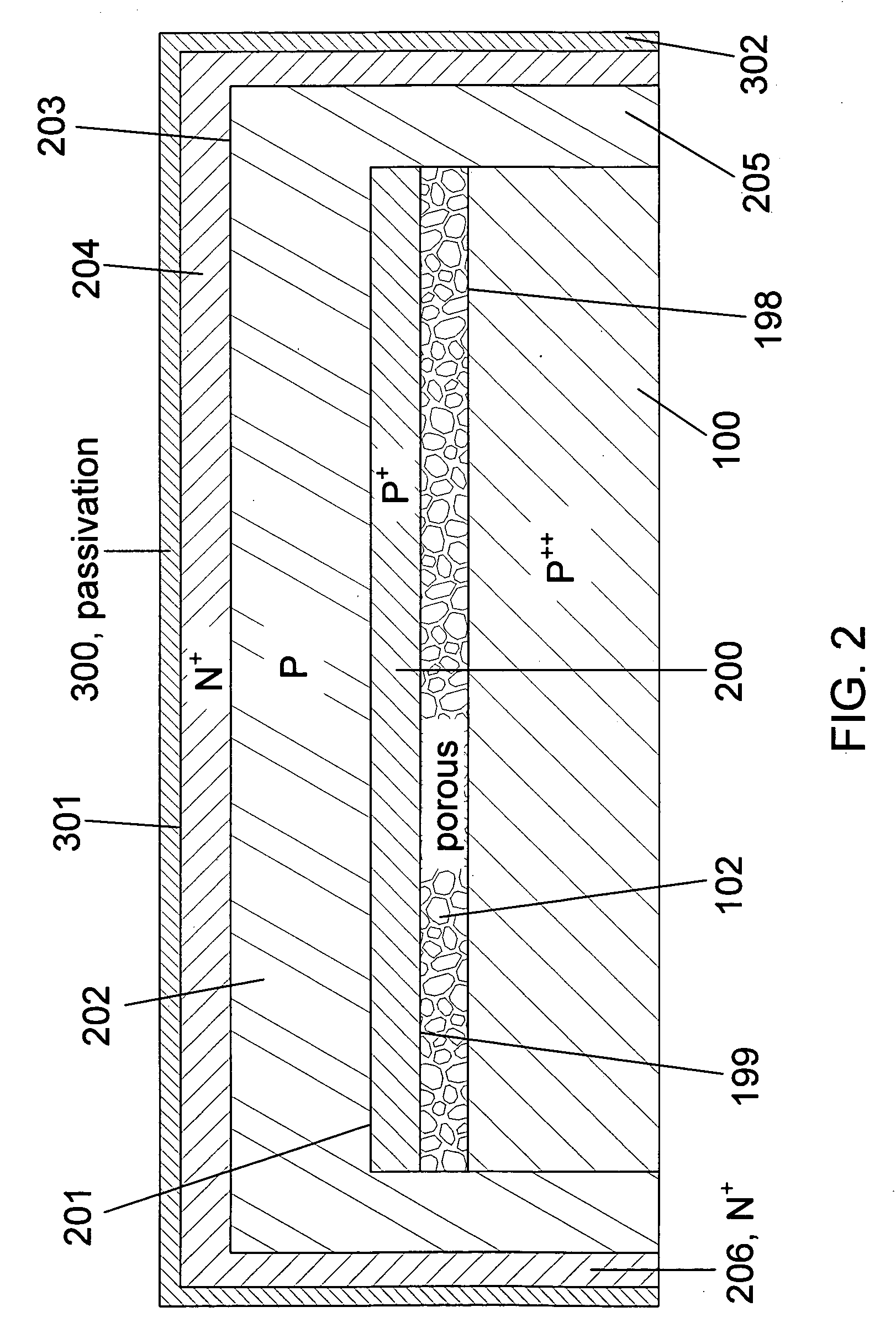
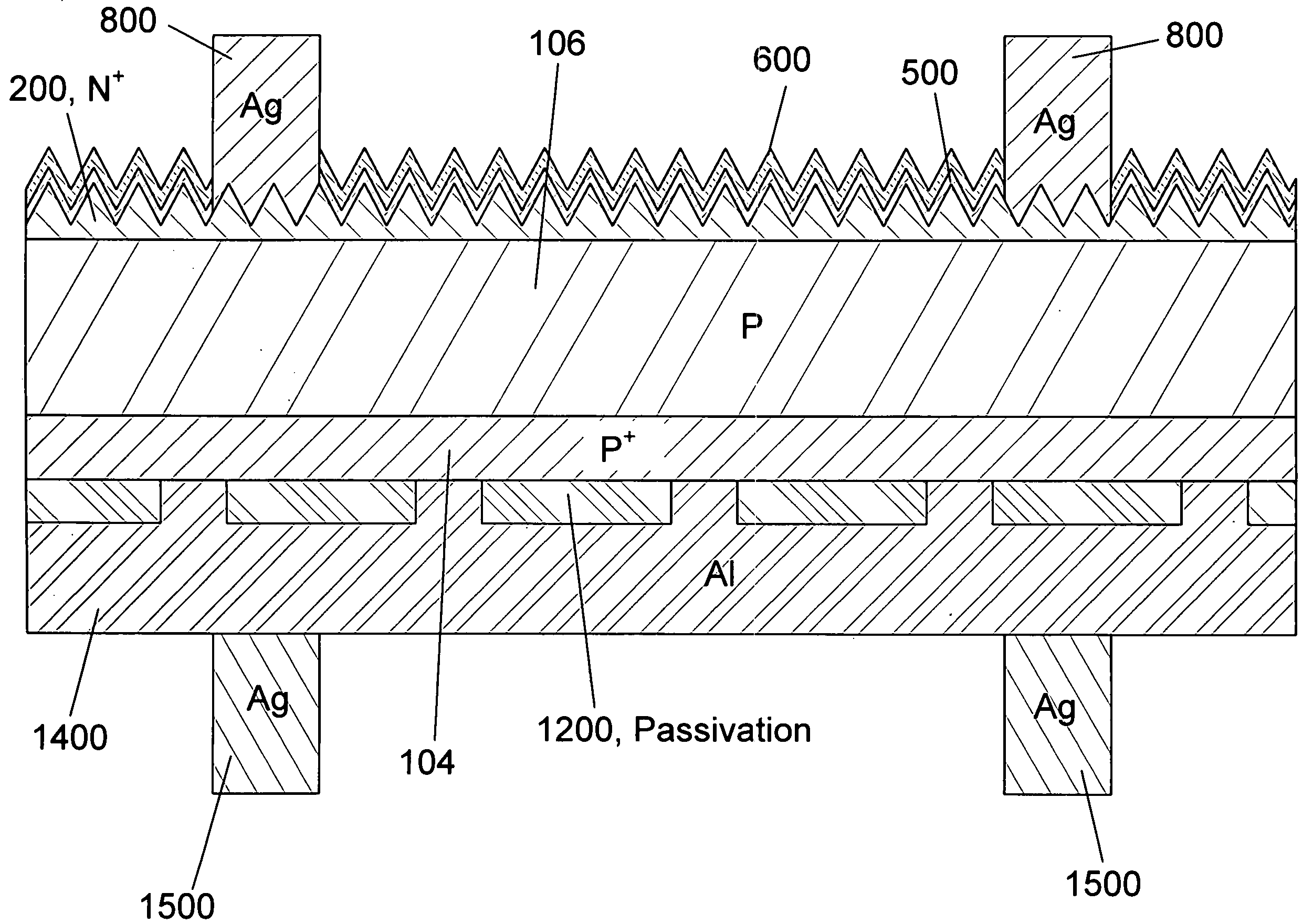
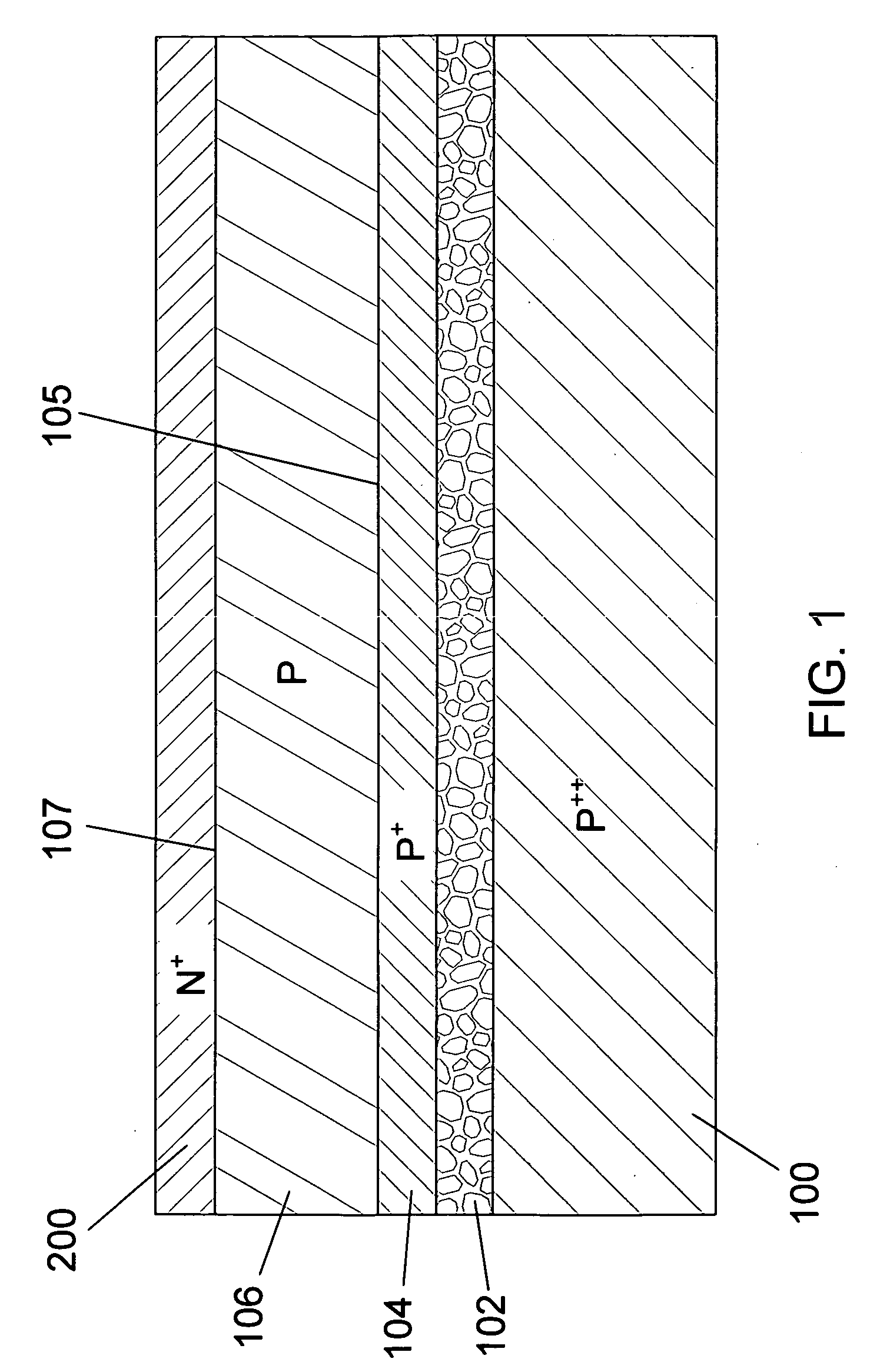
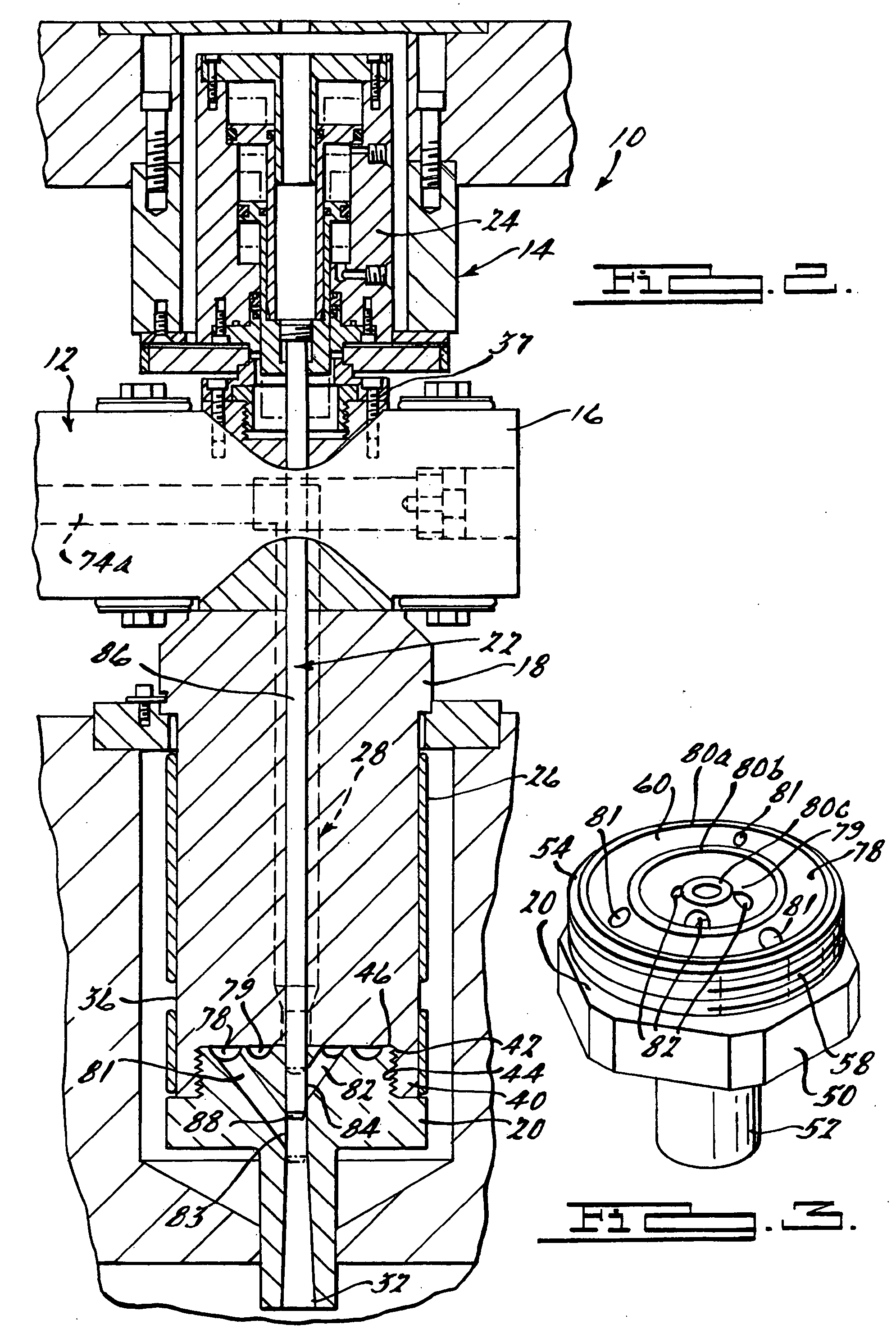
Thin Interdigitated backside contact solar cell and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveUS20100108130A1Material quality is stableControl wellSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPorous layerSolar cell
A design and manufacturing method for an interdigitated backside contact photovoltaic (PV) solar cell less than 100 μm thick are disclosed. A porous silicon layer is formed on a wafer substrate. Portions of the PV cell are then formed using diffusion, epitaxy and autodoping from the substrate. All backside processing of the solar cell (junctions, passivation layer, metal contacts to the N+ and P+ regions) is performed while the thin epitaxial layer is attached to the porous layer and substrate. After backside processing, the wafer is clamped and exfoliated. The front of the PV cell is completed from the region of the wafer near the exfoliation fracture layer, with subsequent removal of the porous layer, texturing, passivation and deposition of an antireflective coating. During manufacturing, the cell is always supported by either the bulk wafer or a wafer chuck, with no processing of bare thin PV cells.
Owner:CRYSTAL SOLAR INC
Thin two sided single crystal solar cell and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveUS20100108134A1High quality epitaxial growthImprove material qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationAnti-reflective coatingPorous layer
A design and manufacturing method for a photovoltaic (PV) solar cell less than 100 μm thick are disclosed. A porous silicon layer is formed on a wafer substrate. Portions of the PV cell are then formed using diffusion, epitaxy and autodoping from the substrate. All front side processing of the solar cell (junctions, passivation layer, anti-reflective coating, contacts to the N+-type layer) is performed while the thin epitaxial layer is attached to the porous layer and substrate. The wafer is then clamped and exfoliated. The back side of the PV cell is completed from the region of the wafer near the exfoliation fracture layer, with subsequent removal of the porous layer, passivation, patterning of contacts, deposition of a conductive coating, and contacts to the P+-type layer. During manufacturing, the cell is always supported by either the bulk wafer or a wafer chuck, with no processing of bare thin PV cell
Owner:CRYSTAL SOLAR INC
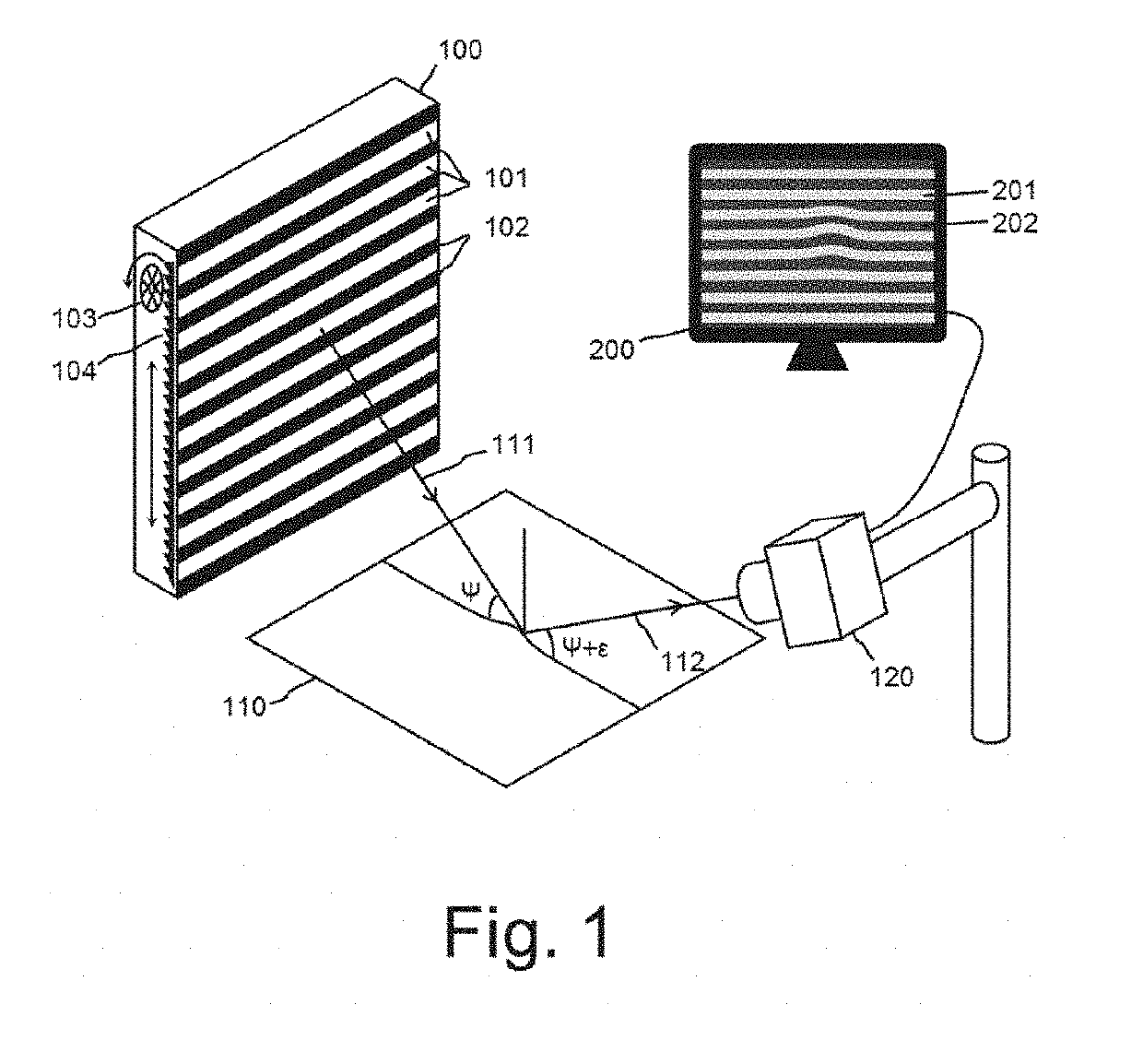
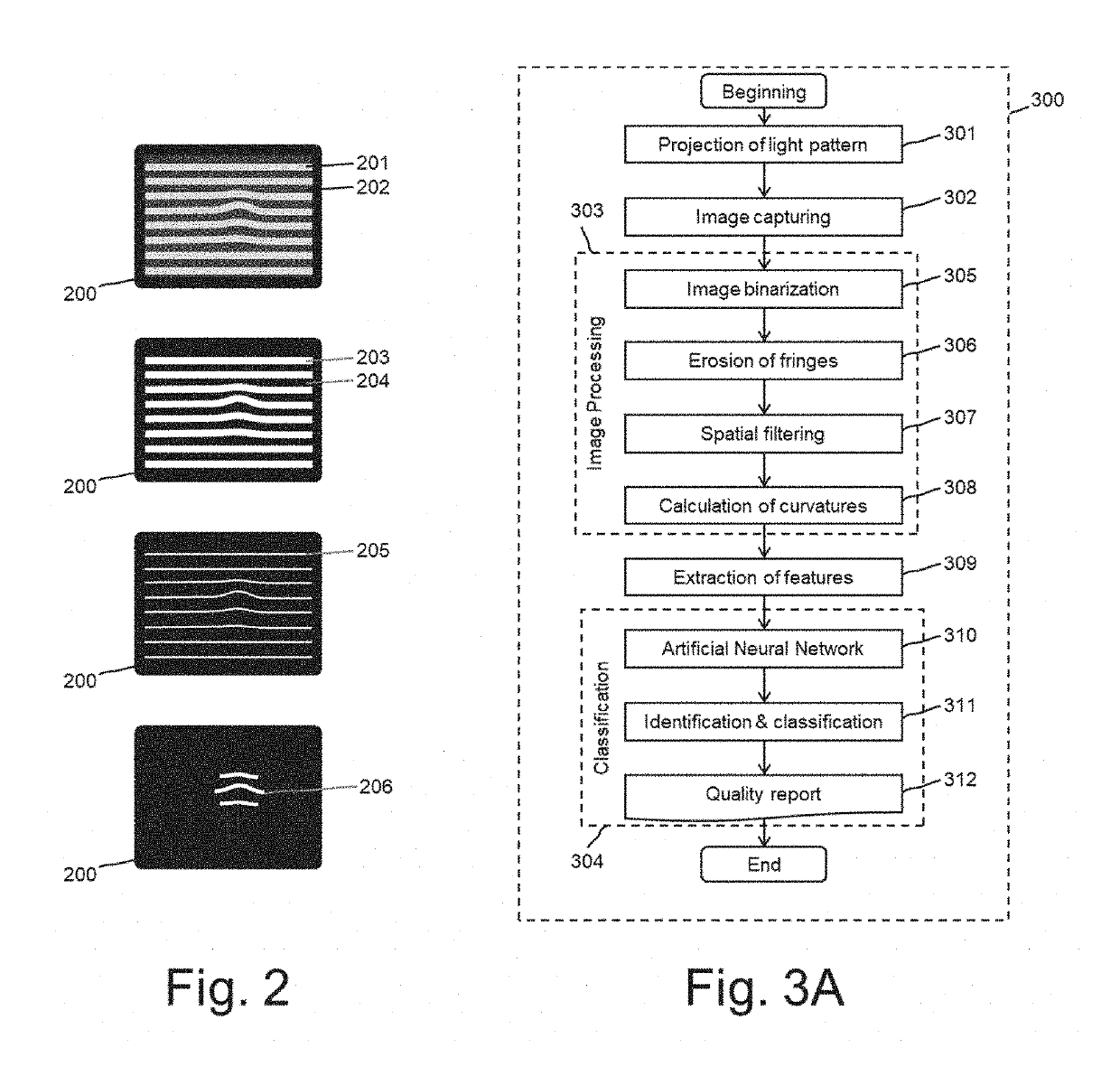
Method and system for automatic quality inspection of materials and virtual material surfaces
ActiveUS20190287237A1Improve objectivityGood reproducibilityImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionDistortion
The present document describes methods and systems for the automatic inspection of material quality. A set of lights with a geometric pattern is cast on a material to be analyzed. Depending on the material being inspected, same may act as a mirror and the reflected image is captured by a capture device, or the light passes through the material being inspected and the image is captured by a capture device. Defects in the material can be detected by the distortion caused by same in the pattern of the reflected image or passing through. Finally, software is used to identify and locate these distortions, and consequently the defects in the material. This classification of defects is carried out using artificial intelligence techniques.
Owner:AUTAZA TECH SA
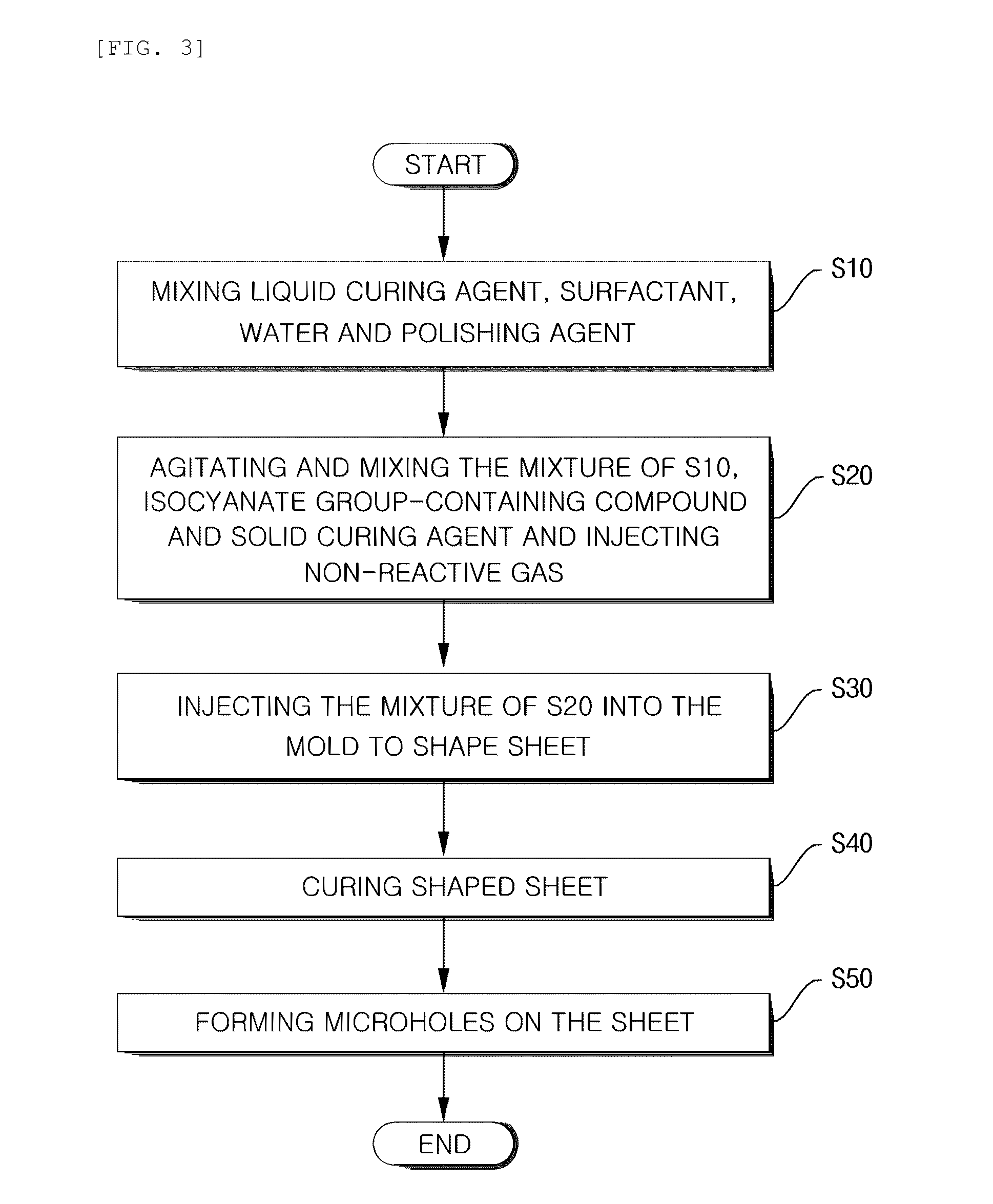
Polyurethane porous product and manufacturing method thereof and polishing pad having polyurethane porous product
InactiveUS20100247868A1Improve stabilityImprove uniformitySynthetic resin layered productsAbrasion apparatusIn planeHardness
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a polyurethane porous product, a polyurethane porous product according to the manufacturing method, and a polishing pad having the polyurethane porous product. According to the present invention, it is possible to manufacture a polishing pad that has excellent polishing efficiency and has a minimal difference in the polishing characteristic during a polishing process and improves uniformity in plane of material that will be polished because the polyurethane porous product of the present invention has small density difference, small hardness difference, and the stabilized quality of material.
Owner:CHA YOON JONG +1
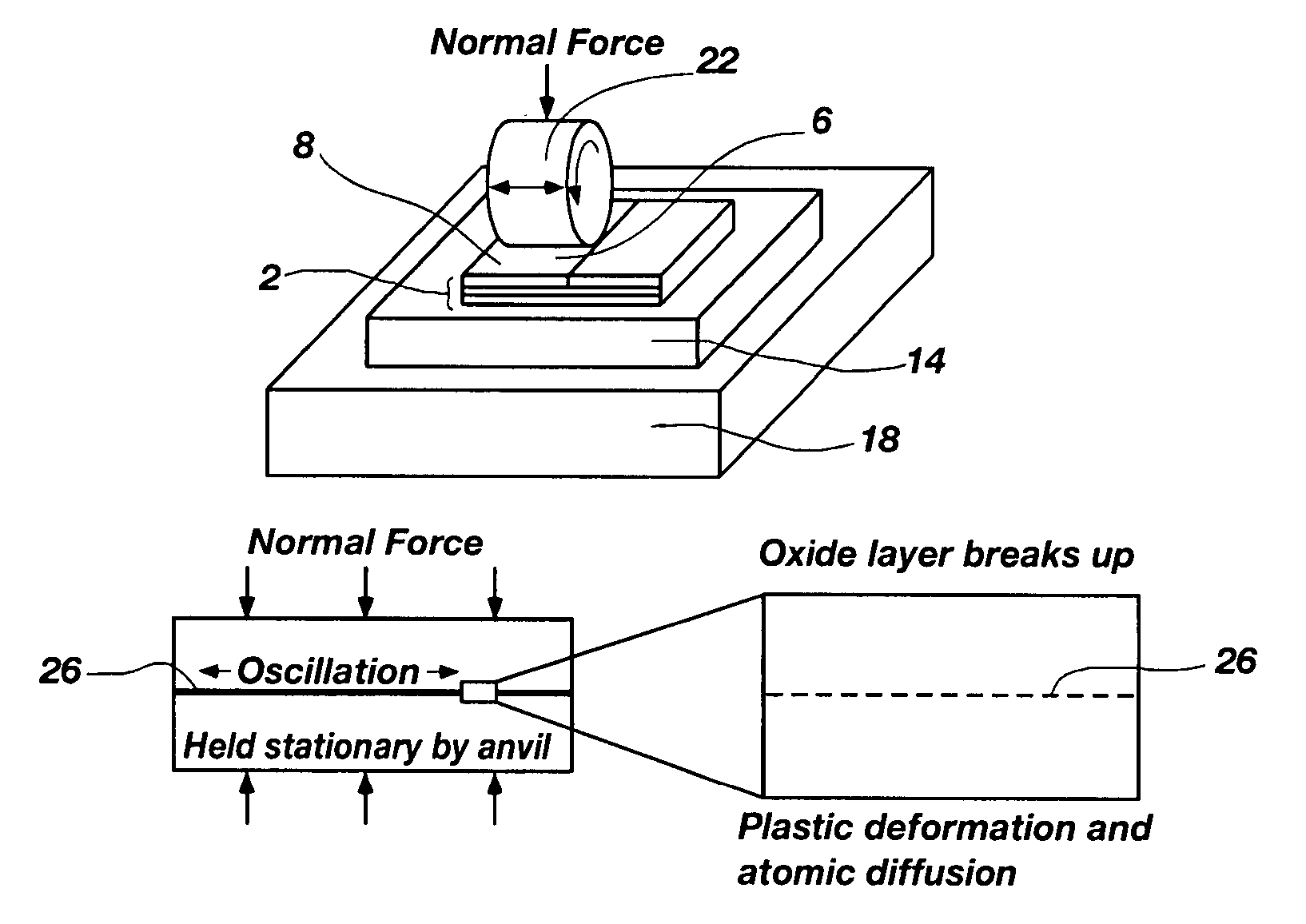
Surface roughness reduction for improving bonding in ultrasonic consolidation rapid manufacturing
InactiveUS20070295440A1Efficient manufacturingReduce contact surfaceAdditive manufacturing apparatusLaminationMetallurgySurface roughness
A method for enhancing the bonding and linear weld density along the interface of material layers deposited in accordance with an ultrasonic consolidation manufacturing process, the method comprising: initiating an ultrasonic consolidation manufacturing process; depositing a first material layer having a contact surface; reducing surface roughness of the contact surface to prepare the contact surface to receive a subsequent material layer, the step of reducing facilitating an increased percentage and quality of material contact between the first and subsequent material layers; and bonding a subsequent material layer to the contact surface of the first material layer, as prepared.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
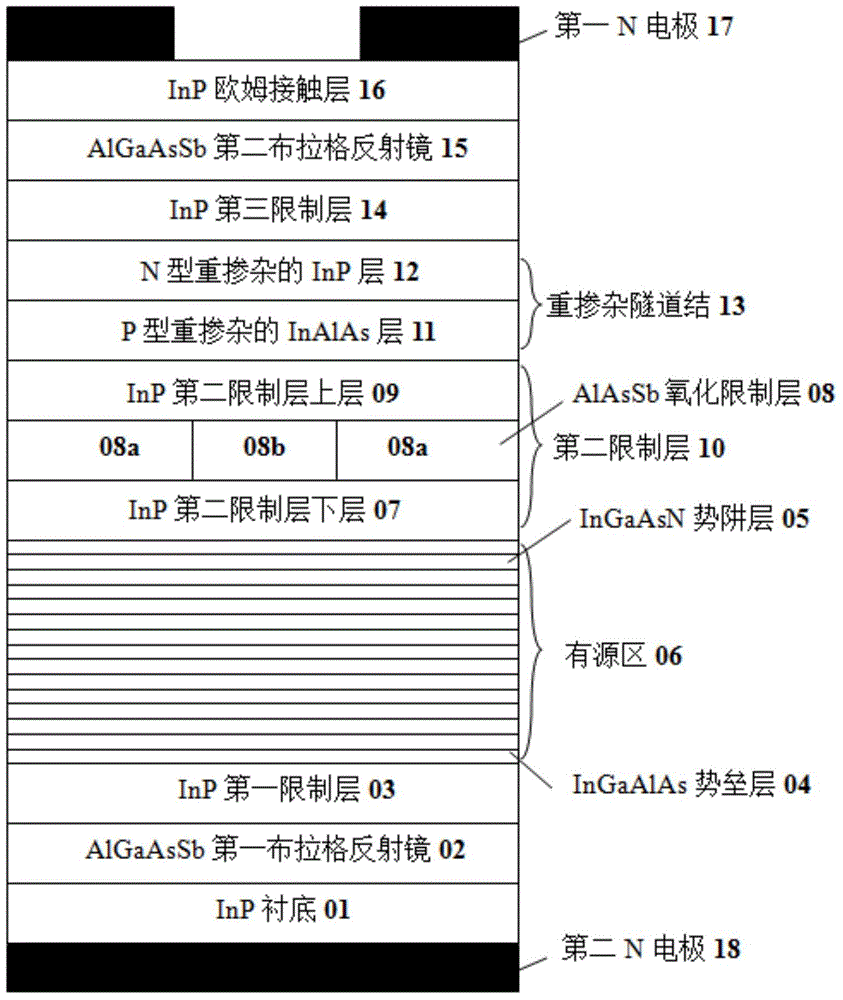
Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104577711AHigh gainEffective limitLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPotential well
The invention discloses a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser which comprises a substrate, a first Bragg reflector, a first limiting layer, an active region, a second limiting layer, a second Bragg reflector and an Ohmic contact layer which are arranged in a laminated manner, wherein the active region adopts a quantum well structure, a potential barrier layer is made of InGaAlAs, and a potential well layer is made of InGaAsN; a heavily-doped tunnel junction and a third limiting layer are also arranged between the second limiting layer and the second Bragg reflector; an oxidized limiting layer is also arranged in the second limiting layer. The invention also provides a preparation method of the laser. The laser has the advantages that the laser uses an InGaAsN / InGaAlAs material system as the active region, has large conduction band order ratio and can effectively limit injected carriers, so that the threshold current is reduced, and the laser gain is improved; on an isometric wavelength band of 1550 nm, the content of N required by an active region material is lower, and devices with high material quality are easy to obtain.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
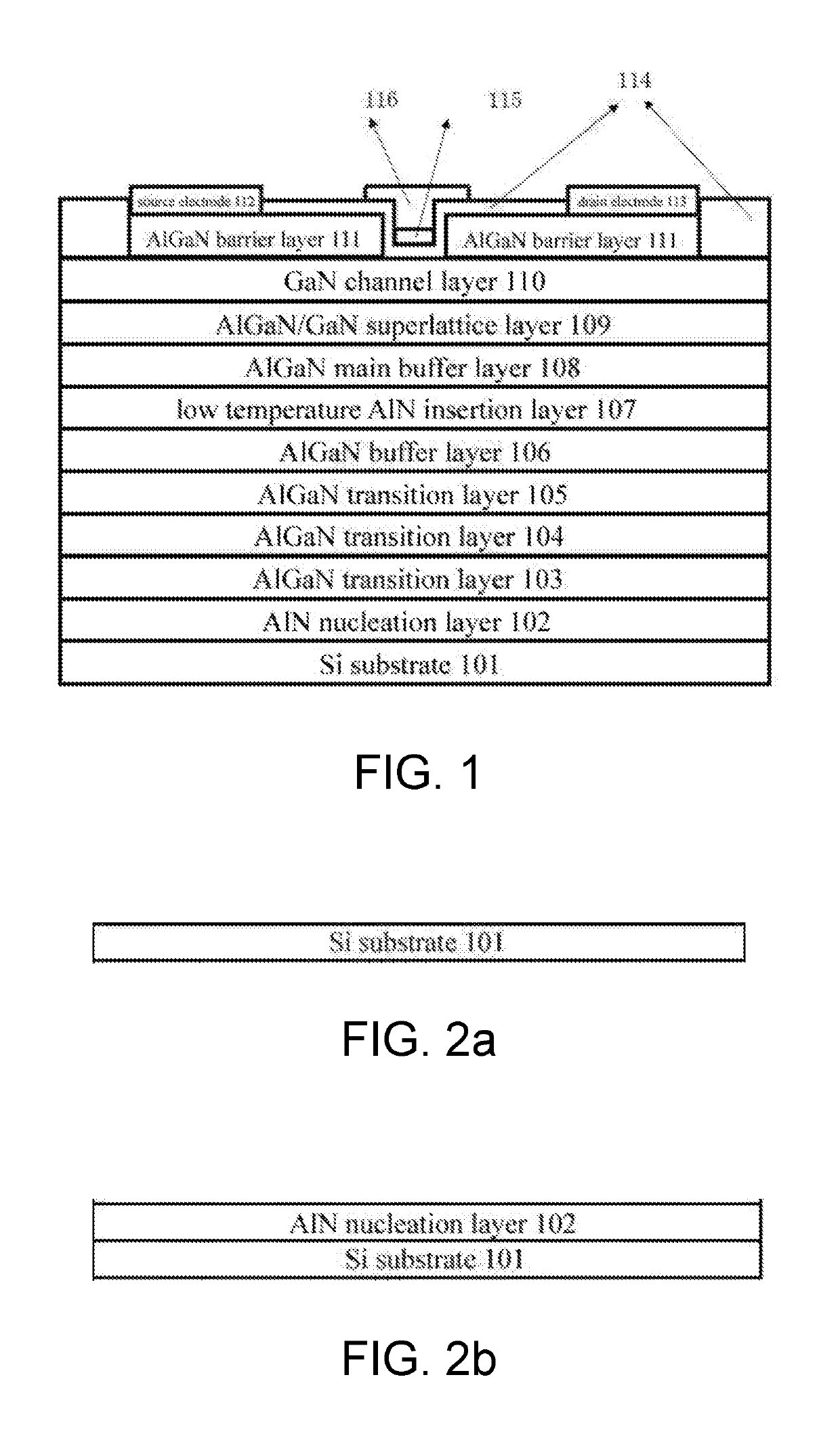
Enhancement-mode gan-based HEMT device on si substrate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20190109208A1Easy to achieve CMOS-compatibleSuppresses material failureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricEngineering
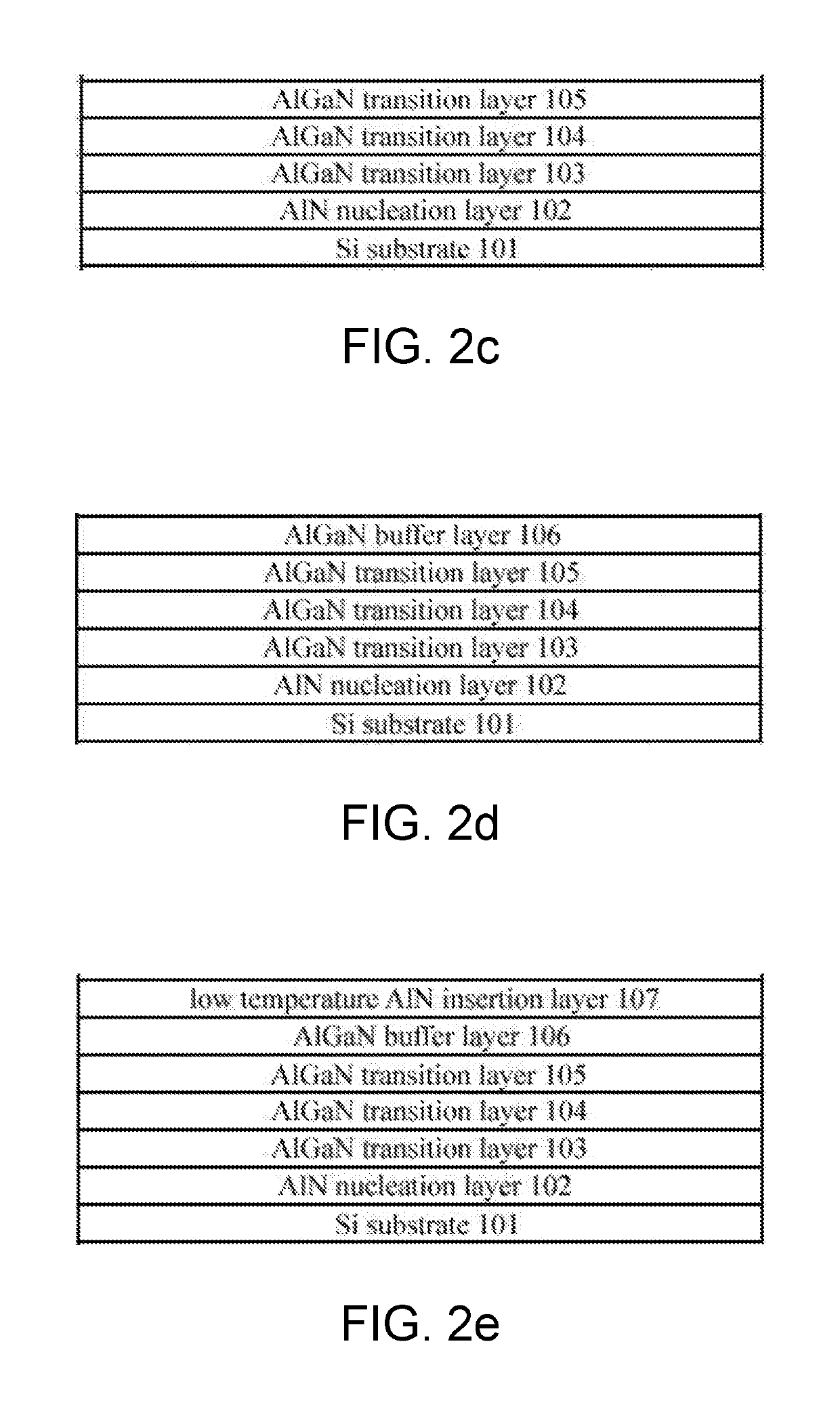
An enhancement-mode GaN-based HEMT device on Si substrate and a manufacturing method thereof. The device includes a Si substrate, an AlN nucleation layer, AlGaN transition layers, an AlGaN buffer layer, a low temperature AlN insertion layer, an AlGaN main buffer layer, an AlGaN / GaN superlattice layer, an GaN channel layer), and an AlGaN barrier layer. Both sides of a top end of the HEMT device are a source electrode and a drain electrode respectively, and a middle of the top end is a gate electrode. A middle of the AlGaN barrier layer is etched through to form a recess, and a bottom of the recess is connected to the GaN channel layer. A passivation protective layer and a gate dielectric layer are deposited on the bottom of the recess, and the gate electrode is located above the dielectric layer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Silicon carbide power devices having increased voltage blocking capabilities
InactiveUS6734462B1Reduce processing stepsLow costThyristorSolid-state devicesContact positionVoltage
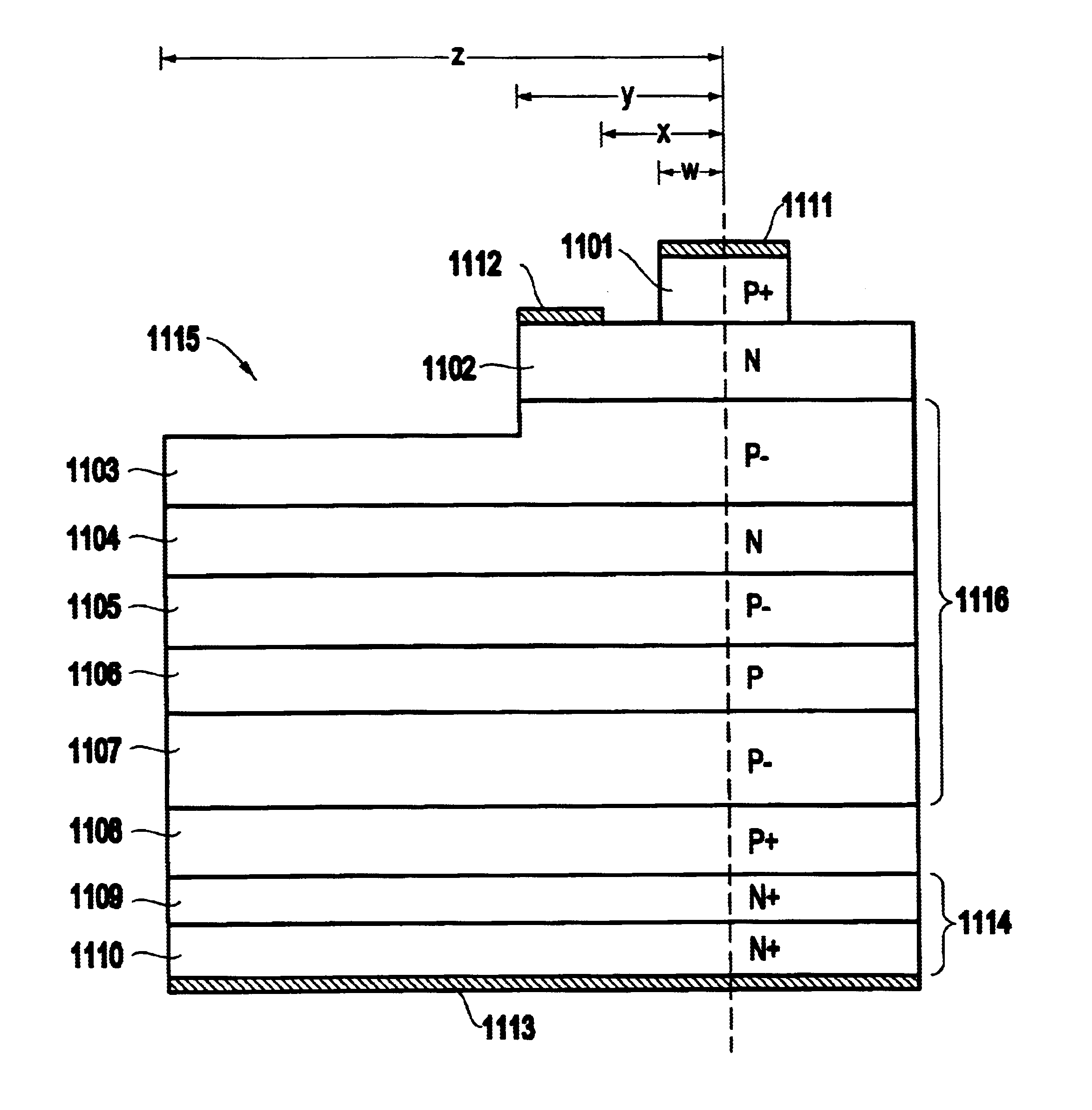
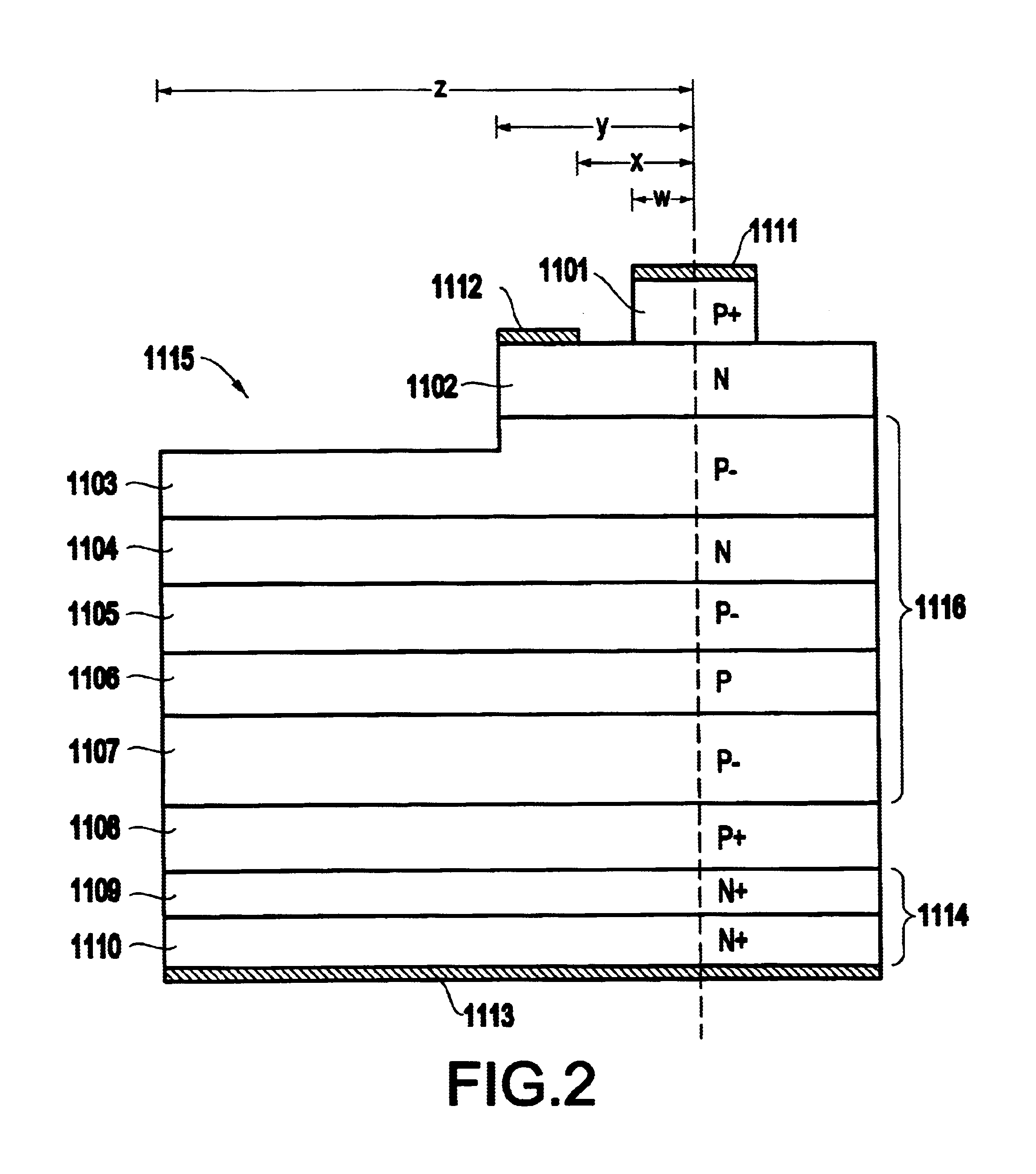
A structure and method for a voltage blocking device comprises a cathode region, a drift region positioned on the cathode region, a gate region positioned on the drift region, an anode region positioned on the gate region and a plurality of contacts positioned on each of the cathode region, the gate region, and the anode region, wherein the drift region comprises multiple epilayers having first doped type layers surrounding second doped type layers, wherein dopant concentrations of the first doped type layers are lower than dopant concentrations of the second doped type layers. The epilayers comprise at least one i-n-i layer and / or at least one i-p-i layer. Moreover, the multiple epilayers are operable to block voltages in the device.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
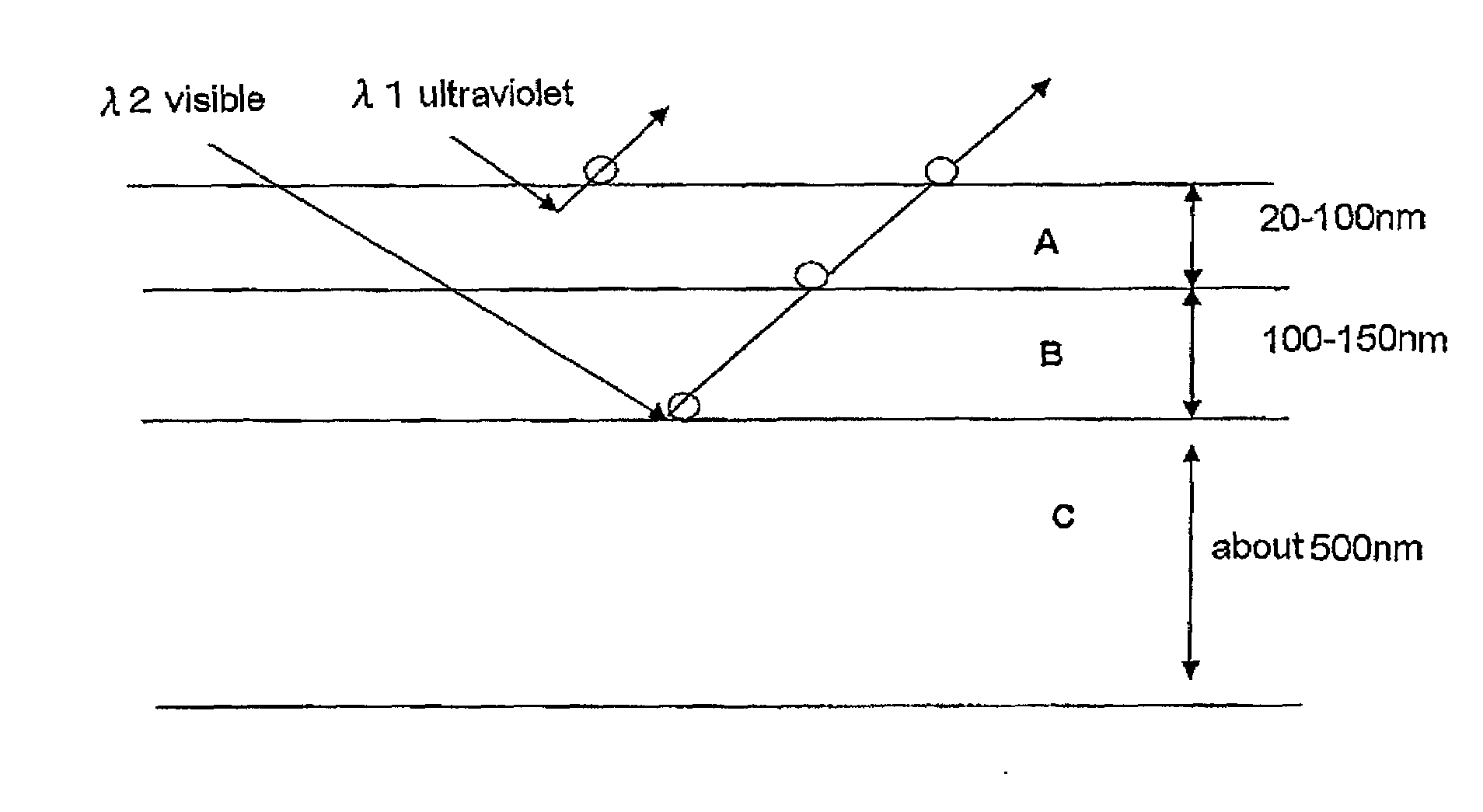
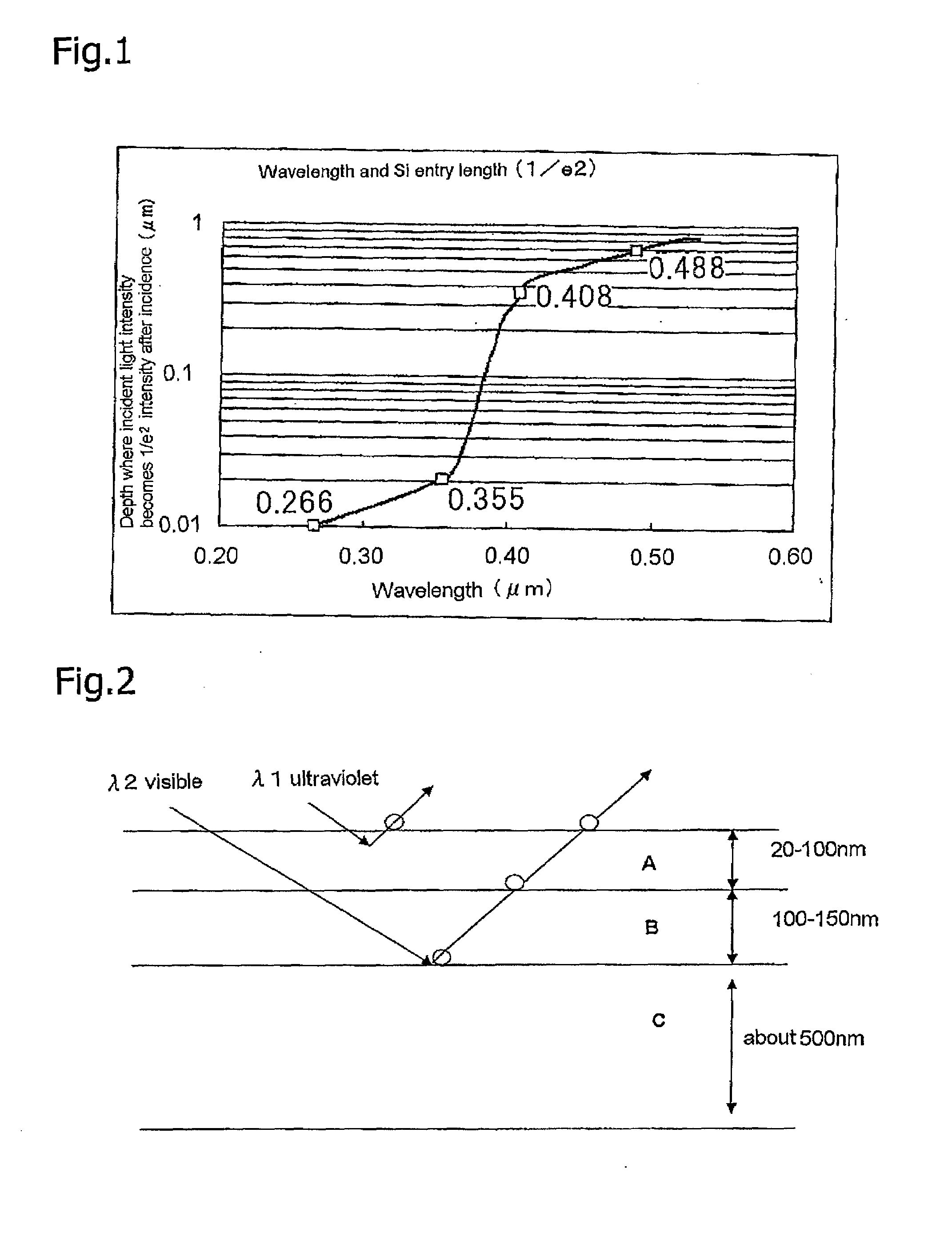
Surface inspecting method and device
InactiveUS20100007872A1Accurate measurementIncrease productionRadiation pyrometrySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLight beamLuminous flux
A light source section outputs optical flux having two types of wavelength, which are a short wavelength and a long wavelength, while the intensity is made variable. The optical flux is made incident to a detected surface of a body to be detected at a predetermined incident angle simultaneously or alternatively. Based on a type of optical flux outputted from the light source section and an output from a first light intensity detecting section, at least the intensity of the optical flux having a long wavelength outputted from the light source section is adjusted. The output from the first light intensity detecting section in irradiating the optical flux having a short wavelength is compared with the output from the first light intensity detecting section in irradiating the optical flux having a long wavelength. A signal that appears only in the output from the first light intensity detecting section in irradiating the optical flux having a long wavelength is identified as a detected signal from an internal subject. The intensity of optical flux having a long wavelength is adjusted. A disappearance level near a point where the detected signal from the internal subject disappears is calculated. The first intensity of optical flux having a long wavelength is set to level higher than the disappearance level. Based on the output from the first light intensity detecting section obtained by the optical flux having a long wavelength of the first intensity, a subject inside the body to be detected is measured.
Owner:KK TOPCON
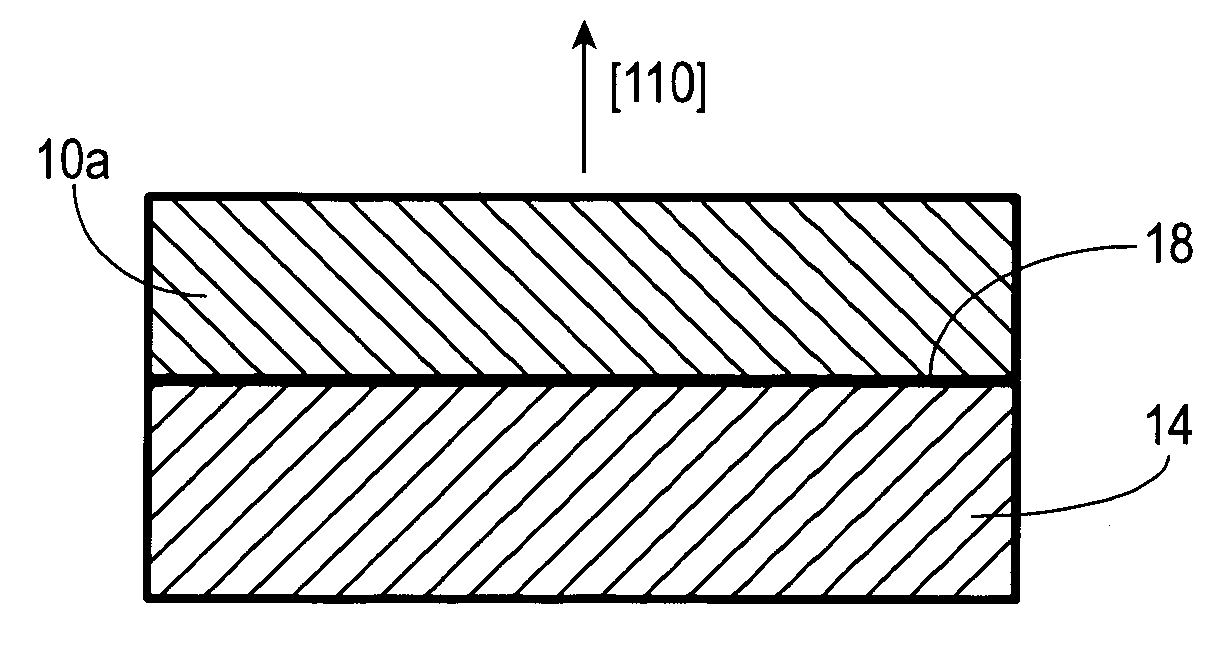
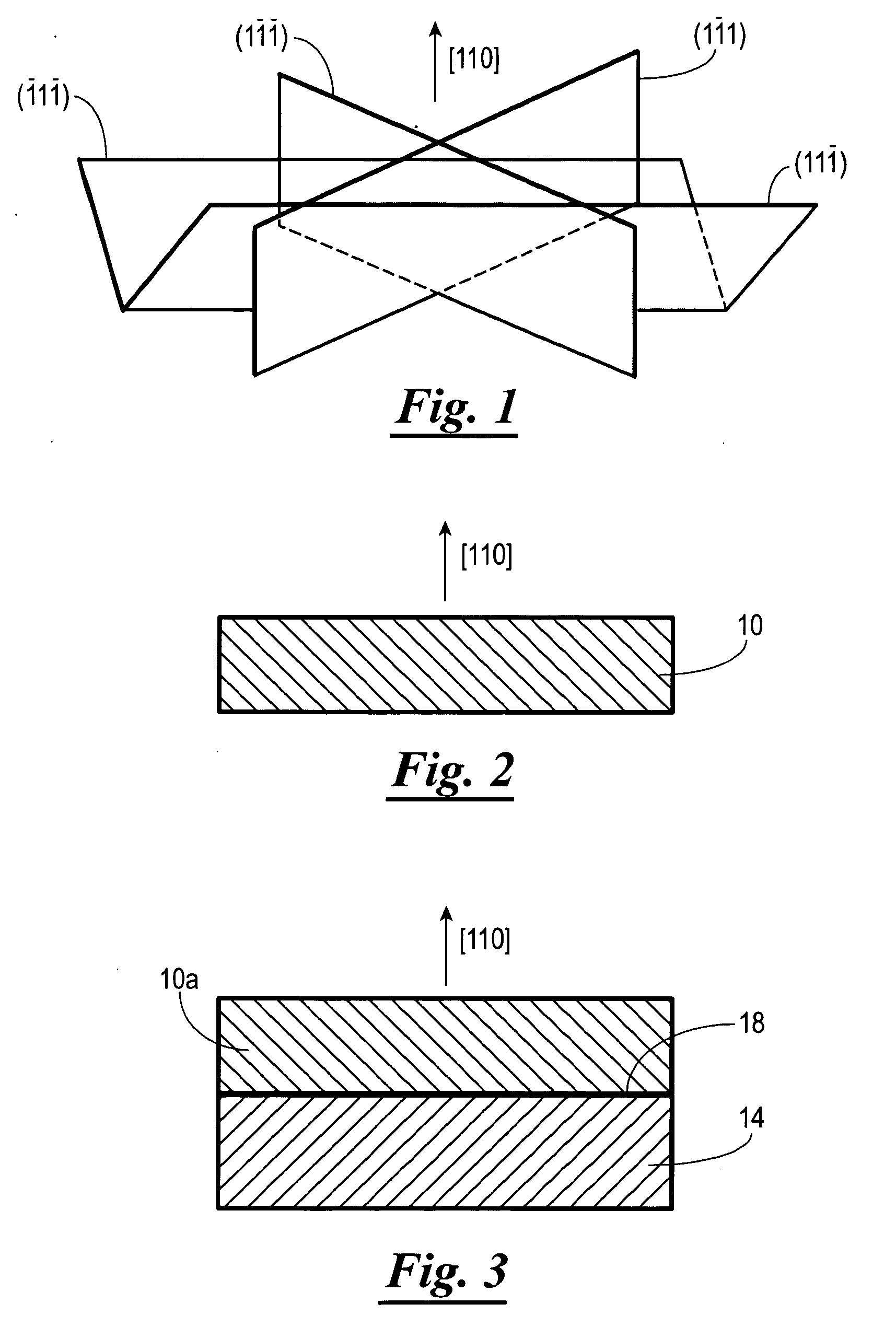
Orientated group IV-VI semiconductor structure, and method for making and using the same
InactiveUS20050199869A1High material gainExpected material qualityLaser active region structureBulk negative resistance effect devicesPresent methodSemiconductor structure
A method of growing and fabricating a group IV-VI semiconductor structure, for use in fabricating devices. In one embodiment, the group IV-VI semiconductor structure produced by the method of the present invention includes a group IV-VI material grown on a selected orientation of [110]. The devices fabricated can be a laser, detector, solar cell, thermal electrical cooling devices, etc. A laser device produced according to the present method will have a low threshold due to the lift-off of the energy degeneracy and low defect density. Growth on the [110] orientation also allows epitaxial growth of the semiconductor structure on a dissimilar substrate, which could improve the thermal dissipation and thus increase the operating temperature of the laser device.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
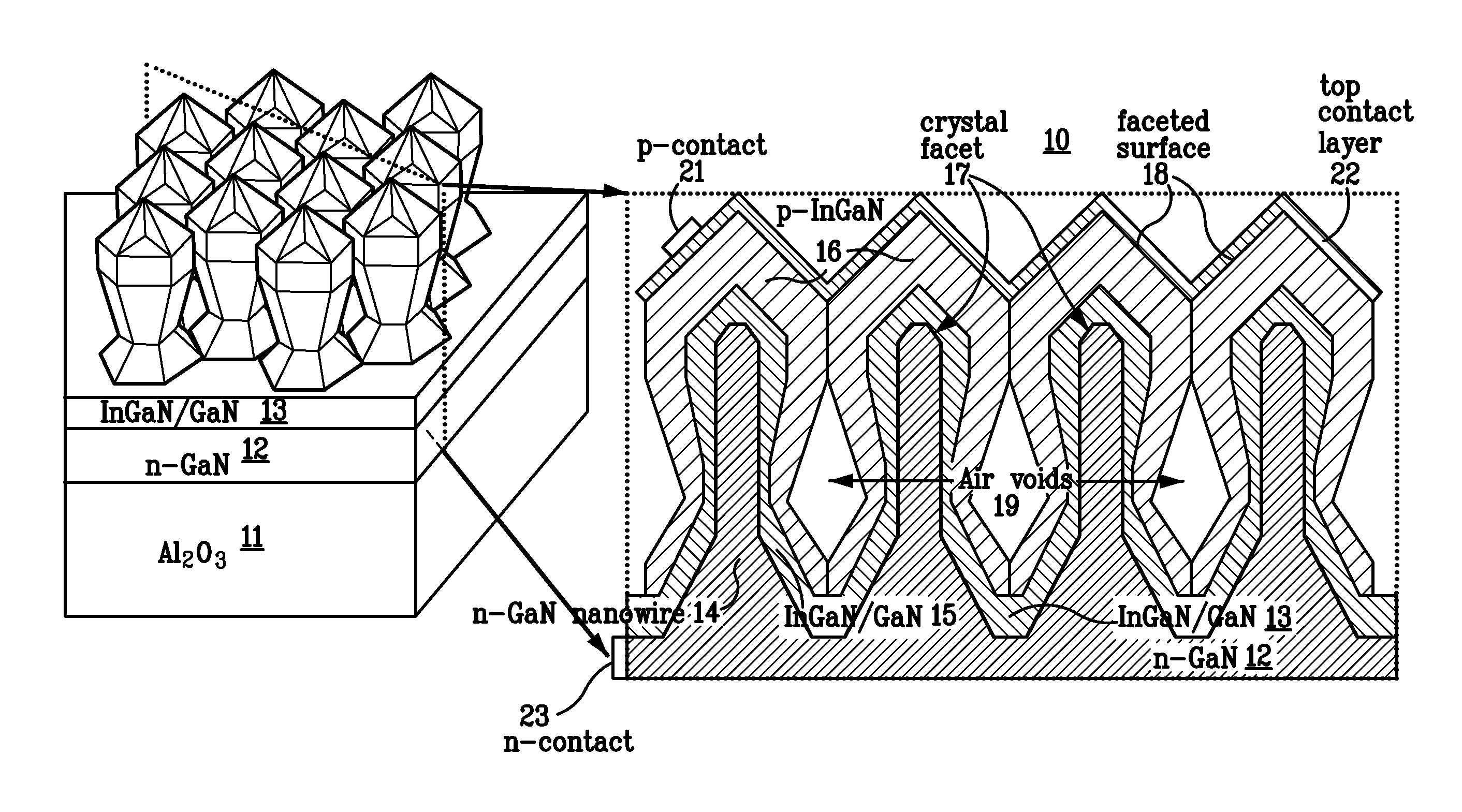
Amber light-emitting diode comprising a group III-nitride nanowire active region
ActiveUS8785905B1Improve material qualityImprove quantum efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor devicesNanowireIndium
A temperature stable (color and efficiency) III-nitride based amber (585 nm) light-emitting diode is based on a novel hybrid nanowire-planar structure. The arrays of GaN nanowires enable radial InGaN / GaN quantum well LED structures with high indium content and high material quality. The high efficiency and temperature stable direct yellow and red phosphor-free emitters enable high efficiency white LEDs based on the RGYB color-mixing approach.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Foaming ceramic light sheet material prepared from granite scraps and preparation method thereof
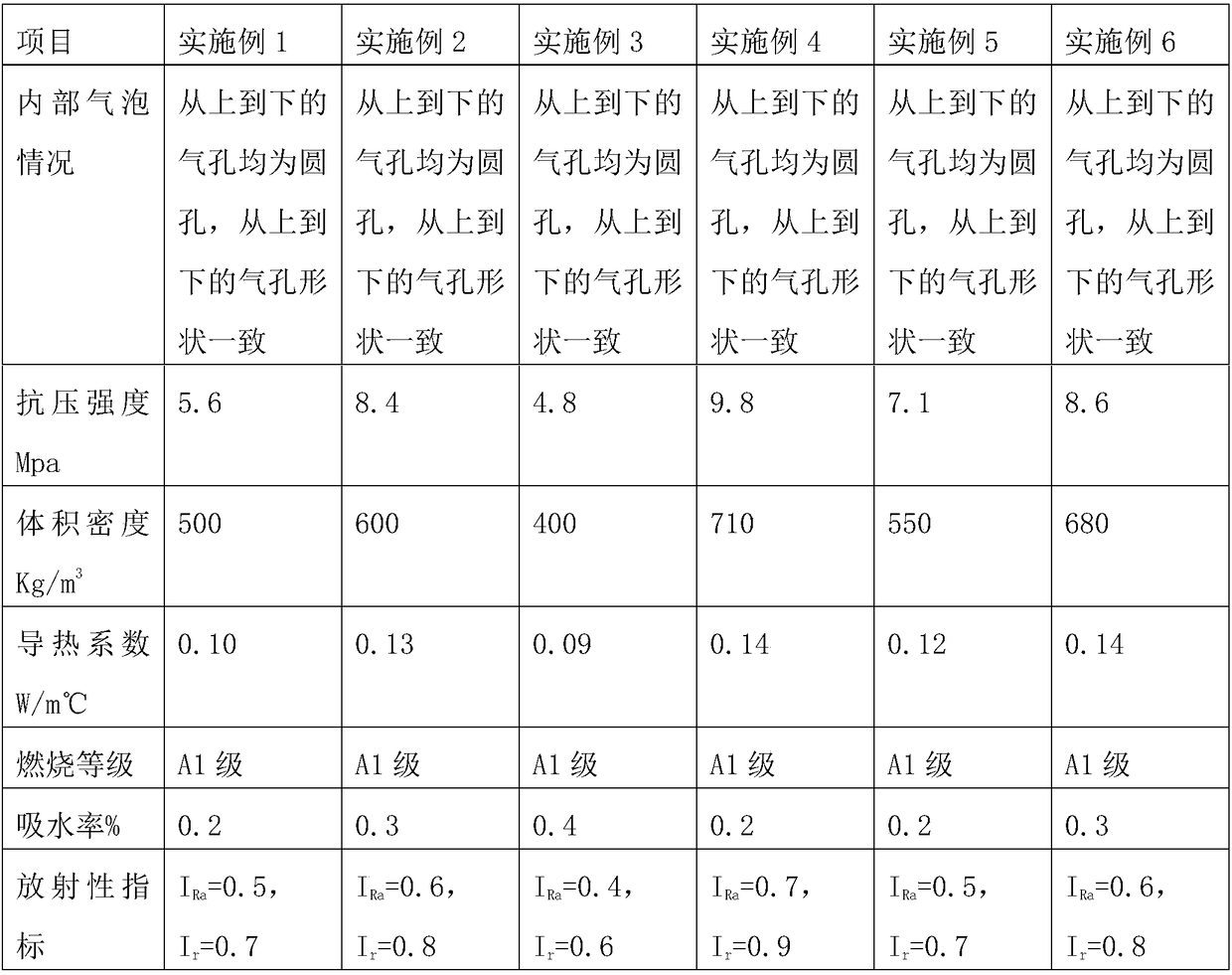
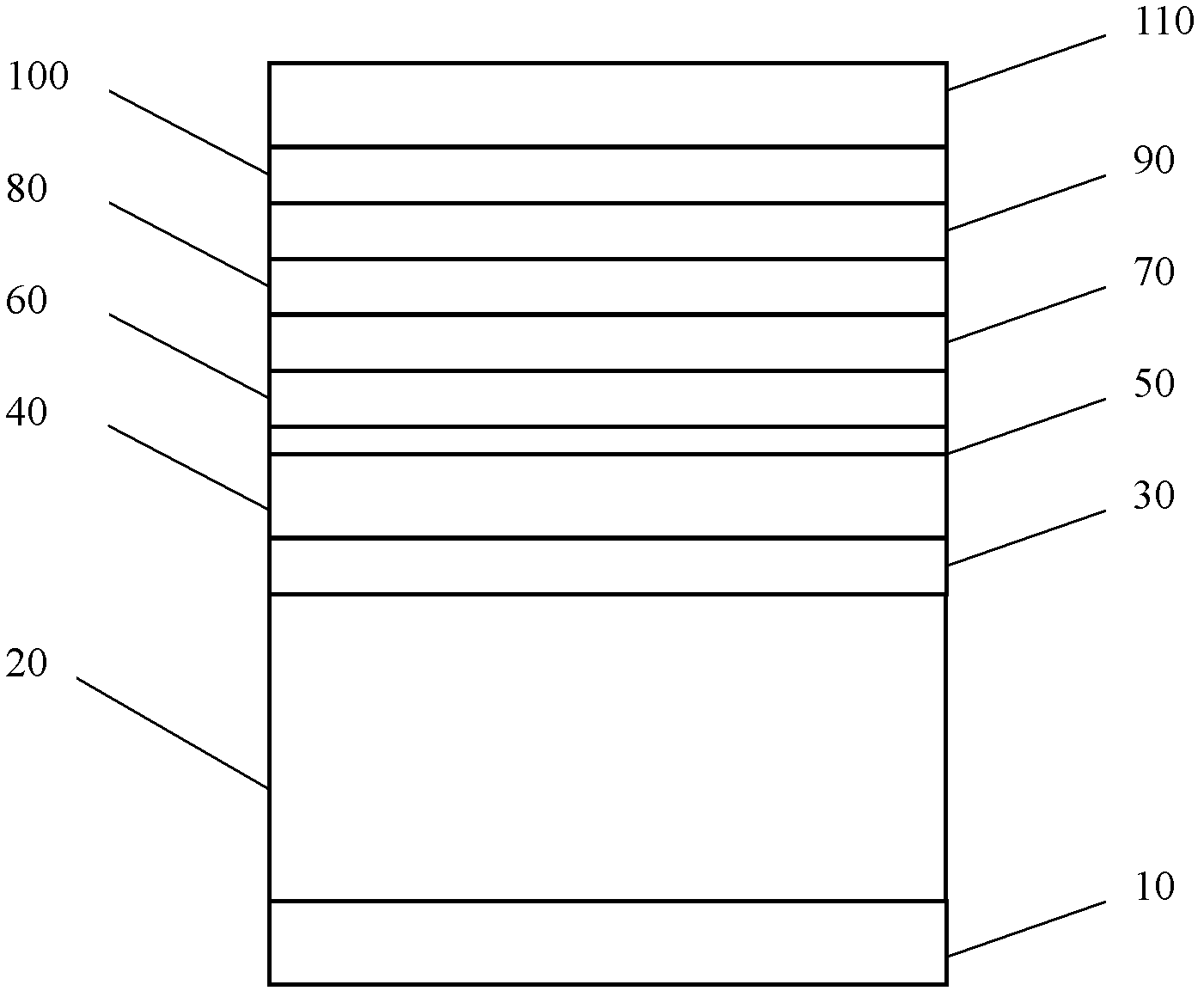
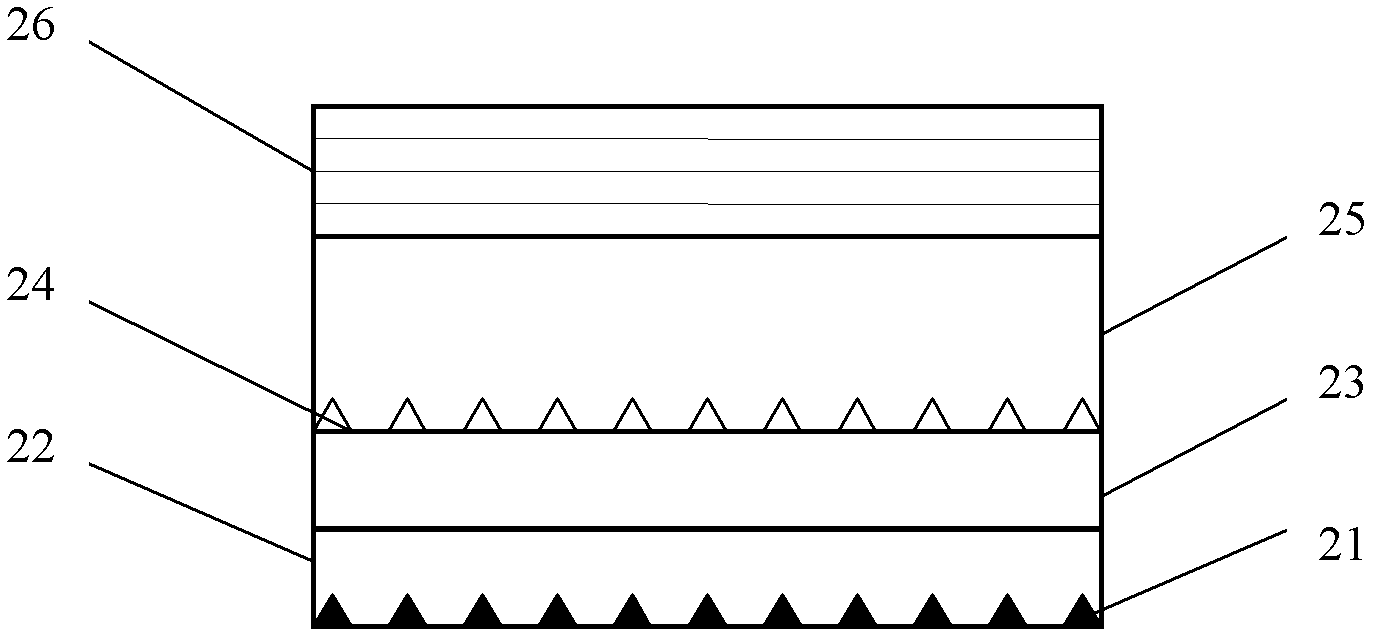
InactiveCN108752035AImprove uniformityOrdinary firing fastCeramic materials productionCeramicwareSpray GranulationTunnel kiln
The invention discloses a method of using granite scraps to prepare a foaming ceramic light sheet material. The method comprises following steps: (1) weighing following raw materials in percentage byweight: 70 to 90% of granite scraps, 5 to 20% of clay, 0.01 to 5% of foaming agent, and 0.1 to 5% of manganese dioxide; (2) ball-milling raw materials; (3) after ball milling, sieving raw materials bya sieving facility; (4) after sieving, spray-granulating sieved raw materials; (5) after spray granulation, distributing the raw materials to obtain a green body; and (6) burning the green body in aroller kiln or a tunnel kiln to obtain a finished product. Correspondingly, the invention also discloses a foaming ceramic light sheet material prepared by the method mentioned above. The air holes ina cross section of the foaming ceramic light sheet material are uniform from top to bottom; the air hole uniformity is high, and the sheet material can be prepared by a tunnel kiln or a roller kiln.
Owner:KEDA INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
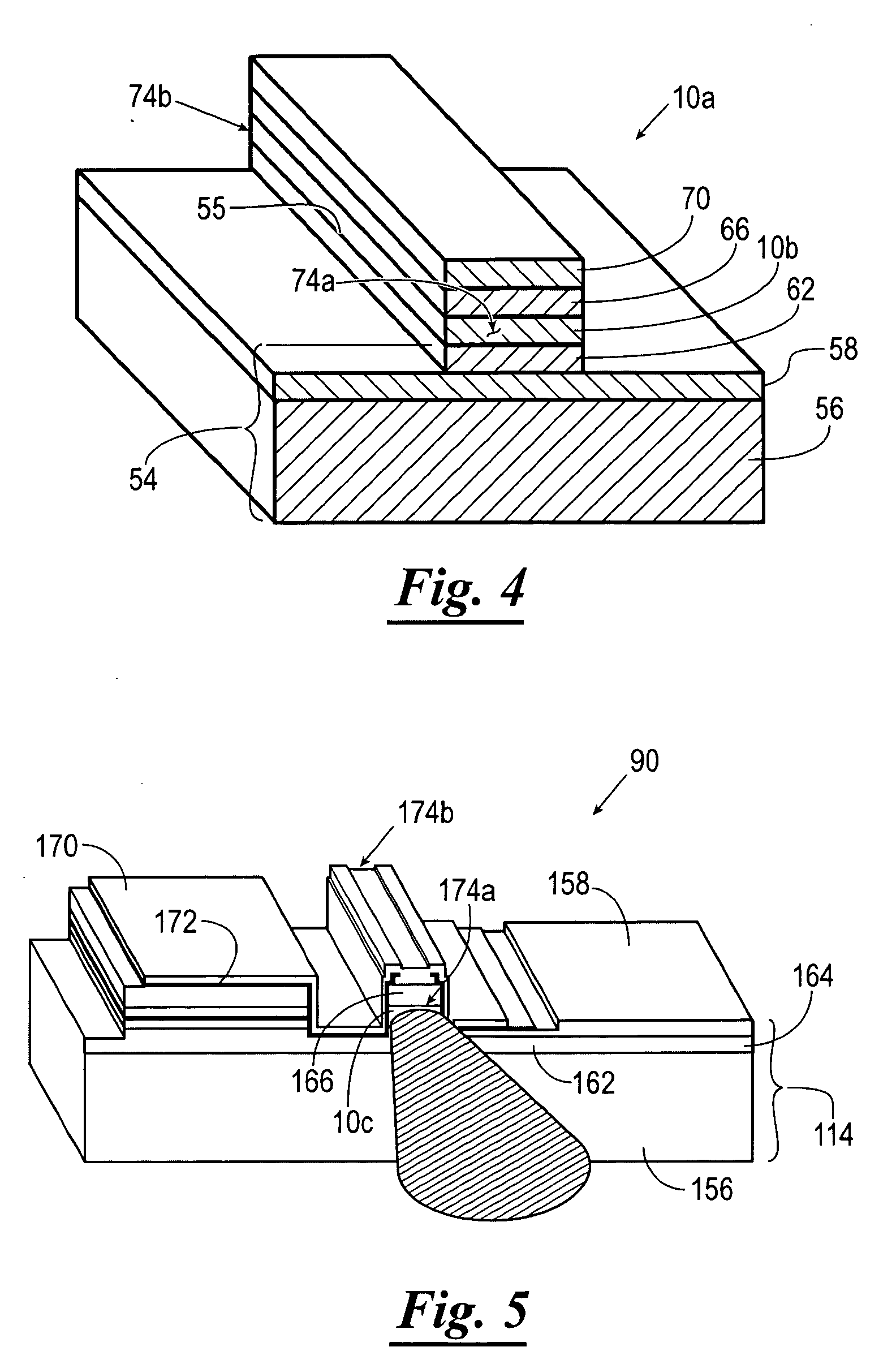
Method for fabricating a semi-polar nitride semiconductor
InactiveUS20110045658A1Quality improvementReduce quality problemsPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitride semiconductorsOxide
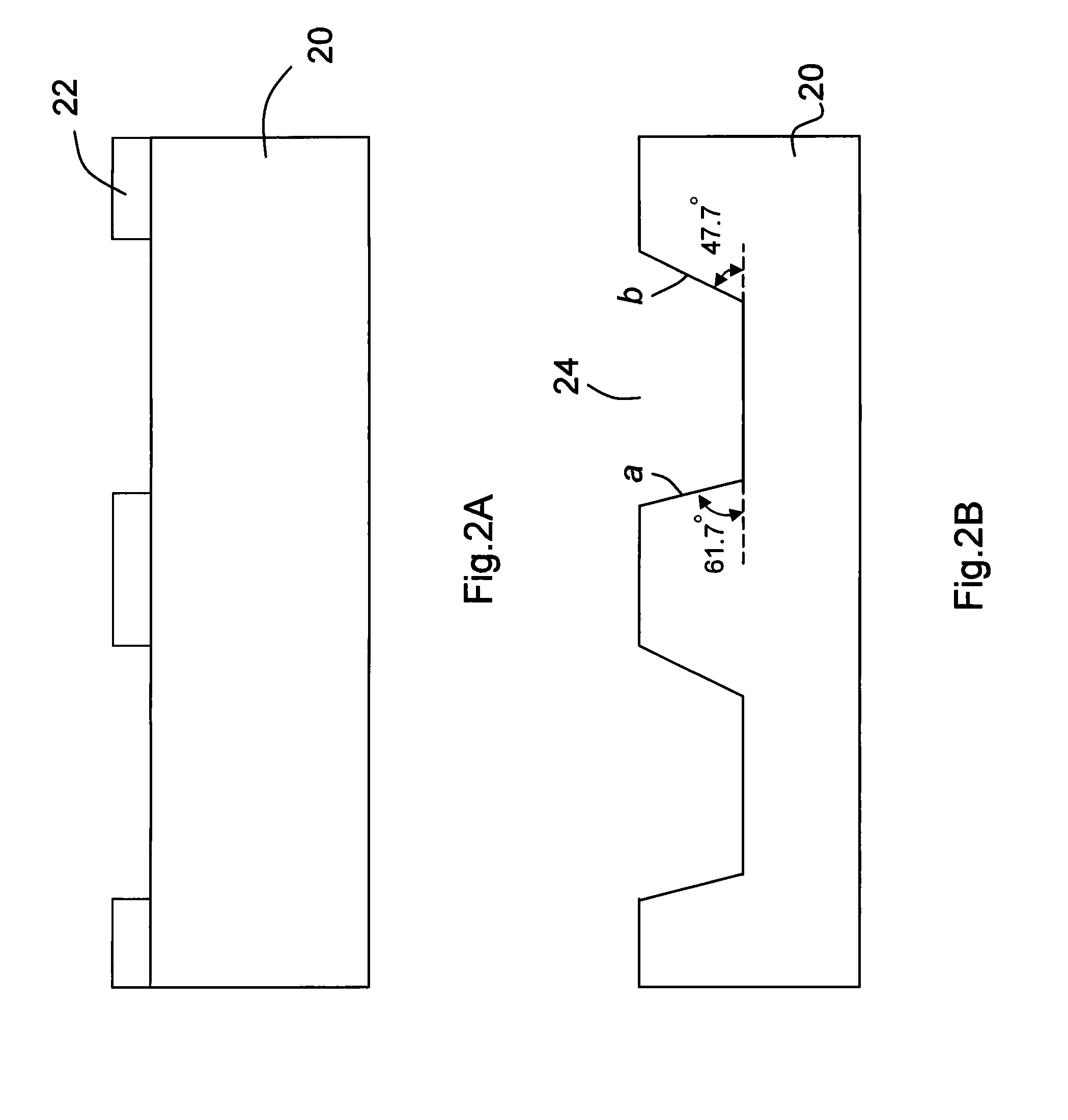
A method for fabricating a semi-polar nitride semiconductor is disclosed, comprising following steps: firstly, a (001) substrate tilted at 7 degrees and having a plurality of V-like grooves is provided, and tilted surfaces of the V-like groove are a (111) surface at 61.7 degrees and a ( 111) surface at 47.7 degrees; next, a surface of said substrate is cleaned by using a deoxidized solution, and then a buffer layer is formed on said substrate to cover said V-like grooves; then, said buffer layer is covered with an oxide layer except for said buffer layer formed on said (111) surface at 61.7 degrees; and finally, said semi-polar nitride semiconductor is formed on said buffer layer having (111) surface at 61.7 degrees to enhance the quality of said semi-polar nitride semiconductor.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Extruder system and cutting assembly
ActiveUS20100143520A1Improve throughputImprove usabilityFeeding-stuffAuxillary shaping apparatusPolymer scienceMechanical engineering
An extruder system for extruding material through a die / extrude insert in an opening in an extruder plate.
Owner:JMP INDS
Controlling doping of synthetic diamond material
ActiveUS20140150713A1Reliably and consistently processedQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge tubesPlasma reactorPlasma chamber
A method of manufacturing synthetic CVD diamond material, the method comprising: providing a microwave plasma reactor comprising: a plasma chamber; one or more substrates disposed in the plasma chamber providing a growth surface area over which the synthetic CVD diamond material is to be deposited in use; a microwave coupling configuration for feeding microwaves from a microwave generator into the plasma chamber; and a gas flow system for feeding process gases into the plasma chamber and removing them therefrom, injecting process gases into the plasma chamber; feeding microwaves from the microwave generator into the plasma chamber through the microwave coupling configuration to form a plasma above the growth surface area; and growing synthetic CVD diamond material over the growth surface area, wherein the process gases comprise at least one dopant in gaseous form, selected from a one or more of boron, silicon, sulphur, phosphorous, lithium and beryllium at a concentration equal to or greater than 0.01 ppm and / or nitrogen at a concentration equal to or greater than 0.3 ppm, wherein the gas flow system includes a gas inlet comprising one or more gas inlet nozzles disposed opposite the growth surface area and configured to inject process gases towards the growth surface area, and wherein the process gases are injected towards the growth surface area at a total gas flow rate equal to or greater than 500 standard cm3 per minute and / or wherein the process gases are injected into the plasma chamber through the or each gas inlet nozzle with a Reynolds number a Reynolds number in a range 1 to 100.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
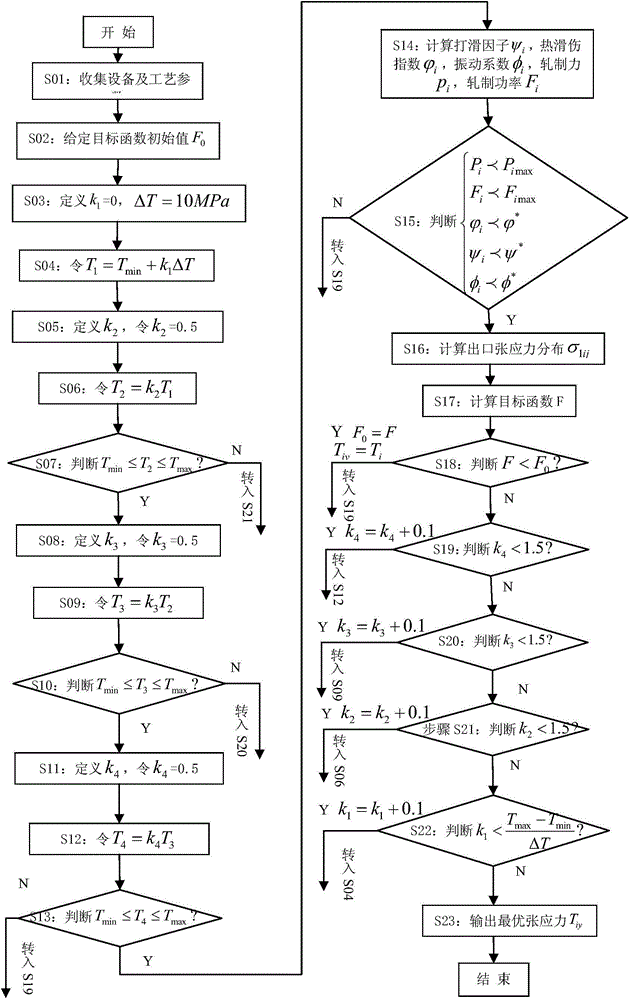
Method for optimizing tension system for rolling of ultra thin steel strip of cold continuous rolling mill
ActiveCN104785537AStrip quality improvementImprove material qualityTension/compression control deviceStress distributionControl system
The invention discloses a method for optimizing a tension system for rolling of an ultra thin steel strip of a cold continuous rolling mill, and relates to control equipment or method special for metal rolling mills or machining products of the metal rolling mills, in particular to optimization of a comprehensively-controlled tension system in the rolling process of ultra thin materials of the cold continuous rolling mill. The cold continuous rolling mill is used for controlling existing equipment parameter and technological parameter data of equipment; according to inlet tensile stress, outlet tensile stress, deformation resistance, the rolling speed, the width of a strip material, the inlet thickness, the output thickness and the working roller diameter of all racks, slipping factors, hot slip indexes, vibration coefficients, rolling force and rolling power of all the racks under the current working condition are calculated; through program control of a computer, optimization control over the tension system is achieved; the depressing capacity, the rolling efficiency and outlet strip shapes and tensile stress distribution of all the racks are considered while the rolling stability, slippage, heat slippage and vibration are considered; and the tail rack output strip shape which represents the strip quality is obviously reduced, and the strip quality is obviously improved than that of a traditional method.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
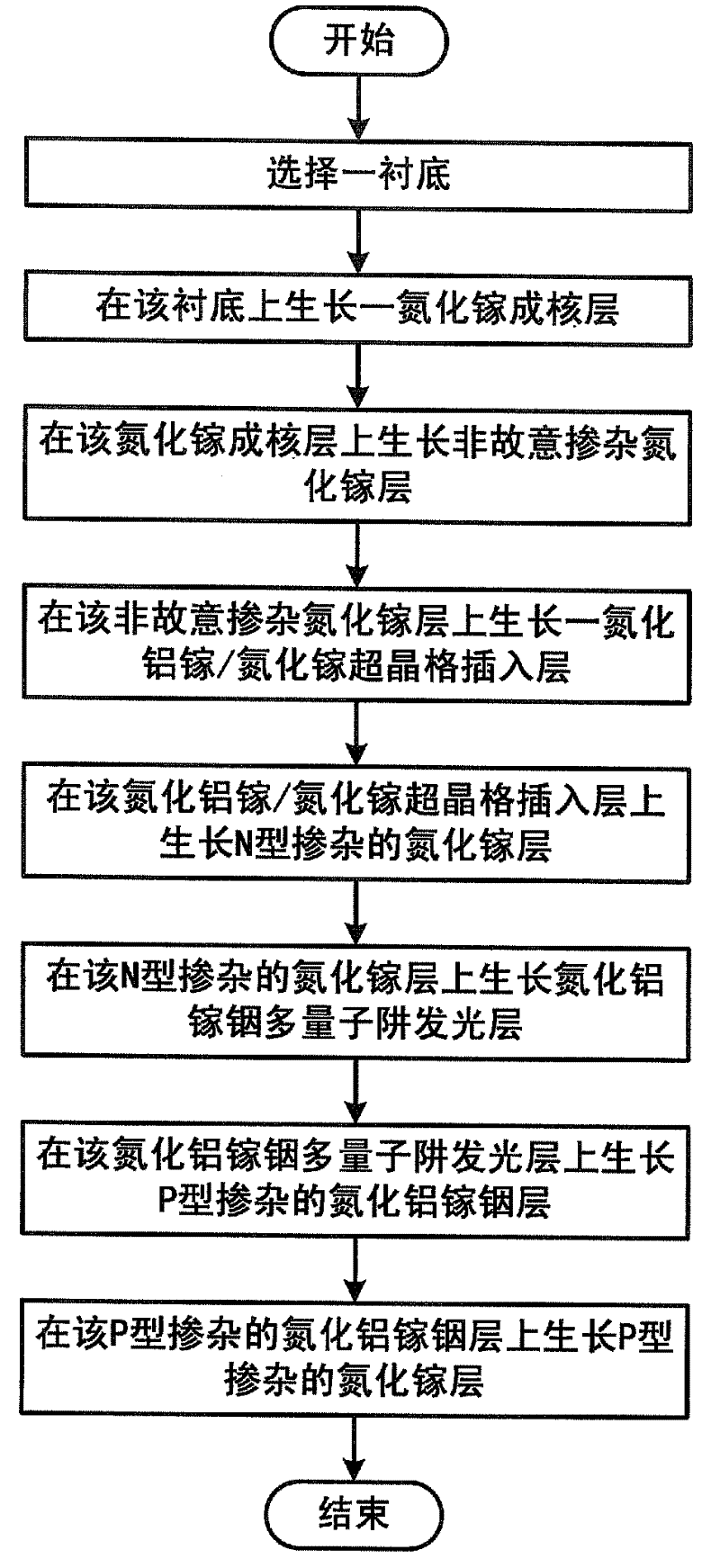
Method for improving antistatic capability of gallium nitride based light emitting diode
InactiveCN102214740AImprove material qualityImprove antistatic performancePolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsIndiumLattice mismatch
The invention discloses a method for improving antistatic capability of a gallium nitride based light emitting diode. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a substrate; growing a gallium nitride nucleating layer on the substrate; growing an involuntary doped gallium nitride layer on the gallium nitride nucleating layer; growing an aluminum gallium nitride / gallium nitride superlattice insertion layer on the involuntary doped gallium nitride layer; growing an N-type doped gallium nitride layer on the aluminum gallium nitride / gallium nitride superlattice insertion layer; growing an indium gallium aluminum nitride multiple quantum-well light-emitting layer on the N-type doped gallium nitride layer; growing a P-type doped indium gallium aluminum nitride layer on the indium gallium aluminum nitride multiple quantum-well light-emitting layer; and growing a P-type doped gallium nitride layer on the P-type doped indium gallium aluminum nitride layer. By utilizing the method provided by the invention, the stress caused by lattice mismatch in an epitaxial layer can be modulated, simultaneously the dislocation in the epitaxial layer of the GaN (gallium nitride) can be deflected and combined, thus the density of threading dislocation in the epitaxial layer developed subsequently is reduced, the material quality is improved, and the antistatic capability of the light emitting diode is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
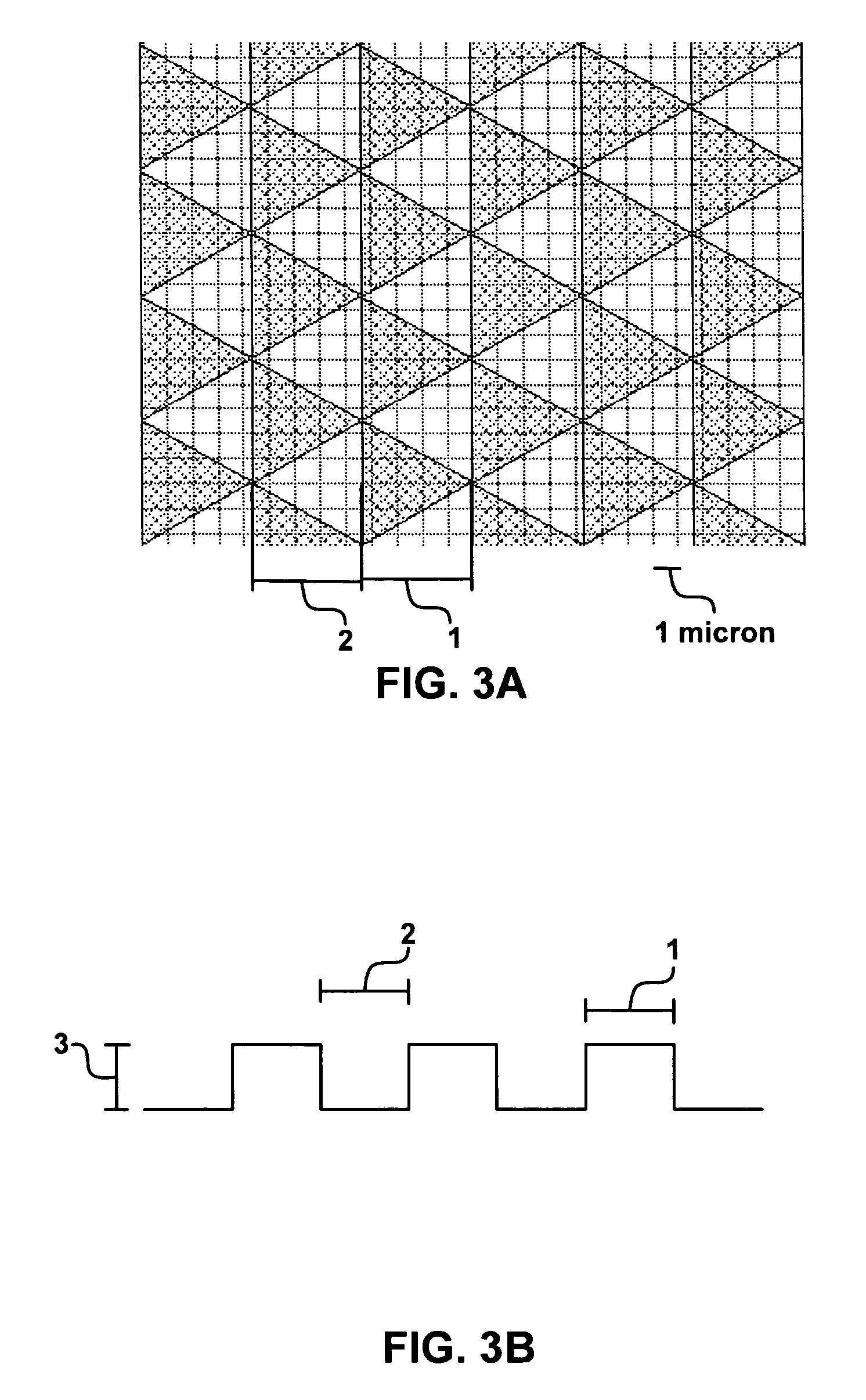
Growth of III-nitride light emitting devices on textured substrates
ActiveUS7633097B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove material qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTotal internal reflectionNitride
A III-nitride light emitting device is grown on a textured substrate, in order to reduce the amount of total internal reflection at the interface between the substrate and the III-nitride layers. In some embodiments, the device includes a first growth region substantially free of voids, and a second growth region that improves the material quality such that high quality layers can be grown over the first and second regions.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Injection molding system for injection molding a plurality of materials
An injection molding system for injection molding a plurality of molten materials into a mold cavity includes a nozzle, a drop tip supported by the nozzle, and a central bore extending through the nozzle and drop tip. The injection molding system also includes a first and second flow passage each extending through the nozzle, so as to define a first and second nozzle flow passage, and drop tip, so as to define a first and second drop tip flow passage. The first and second drop tip flow passages each include a plurality of branching portions each defining a junction at which the respective flow passage communicates fluidly with the central bore.
Owner:PLASTIC ENG & TECHN SERVICES
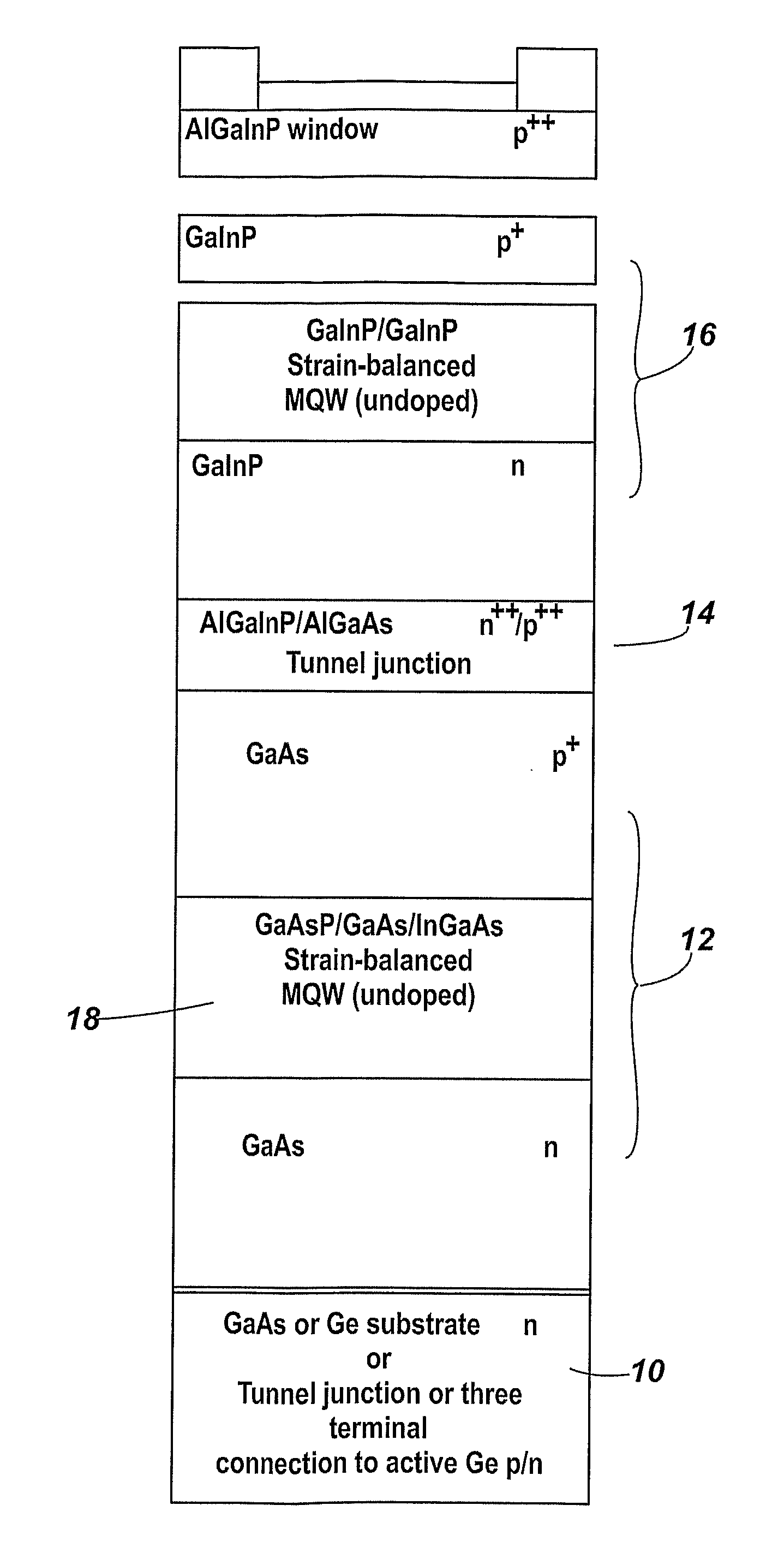
Photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20110180129A1Improve material qualityEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsSolar cellQuantum
The disclosure relates to multiple quantum well (MQW) structures for intrinsic regions of monolithic photovoltaic junctions within solar cells which are substantially lattice matched to GaAs or Ge. The disclosed MQW structures incorporate quantum wells formed of quaternary InGaAsP, between barriers of InGaP.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Large area optical quality synthetic polycrystalline diamond window
ActiveUS20140342122A1Precise design toleranceImprove optical qualitySynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageDielectric lossPolycrystalline diamond
A polycrystalline chemical vapour deposited (CVD) diamond wafer comprising: a largest linear dimension equal to or greater than 125 mm; a thickness equal to or greater than 200 μm; and one or both of the following characteristics measured at room temperature (nominally 298 K) over at least a central area of the polycrystalline CVD diamond wafer, said central area being circular, centred on a central point of the polycrystalline CVD diamond wafer, and having a diameter of at least 70% of the largest linear dimension of the polycrystalline CVD diamond wafer: an absorption coefficient≦0.2 cm−1 at 10.6 μm; and a dielectric loss coefficient at 145 GHz, of tan δ≦2×10−4.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
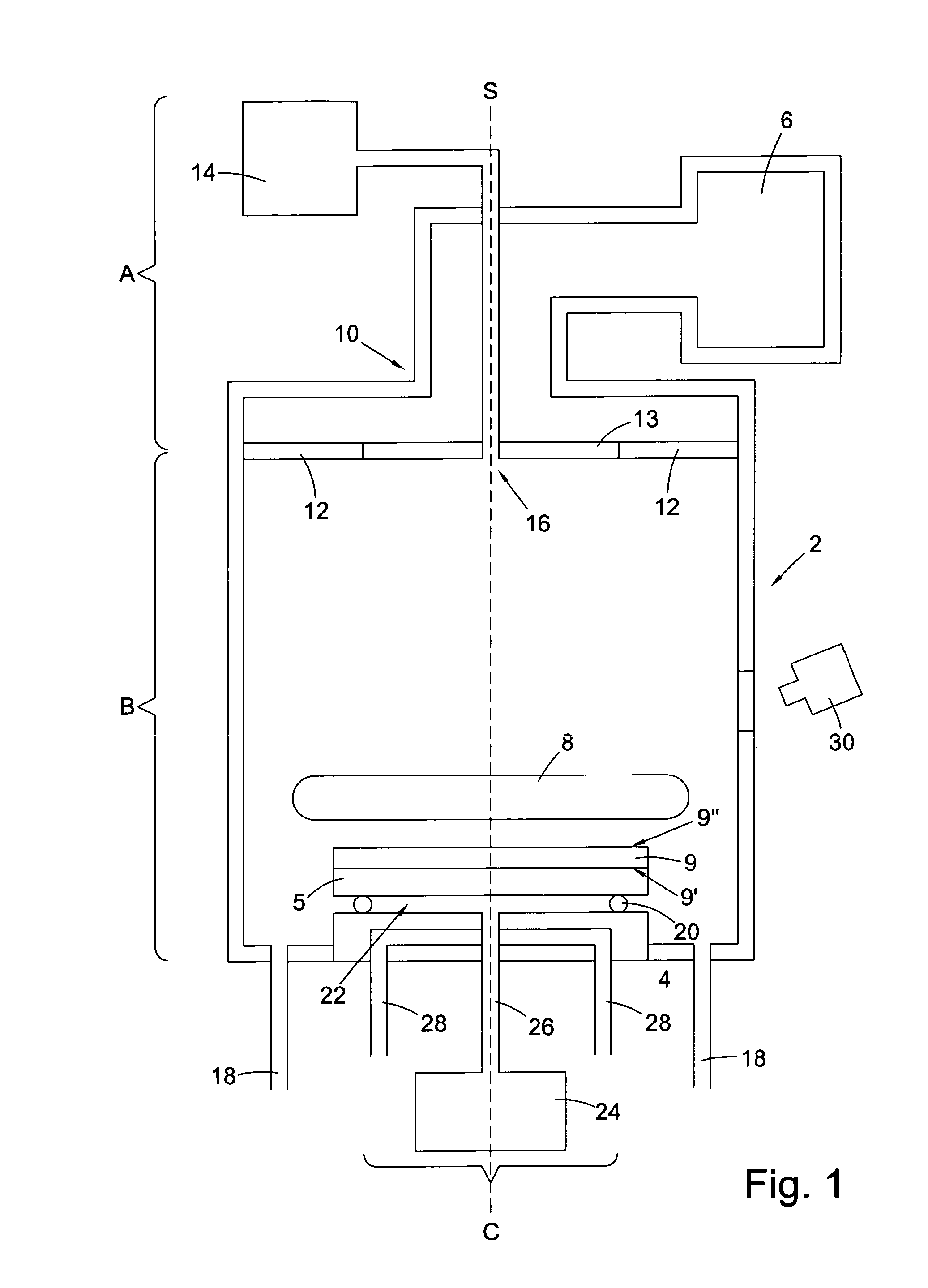
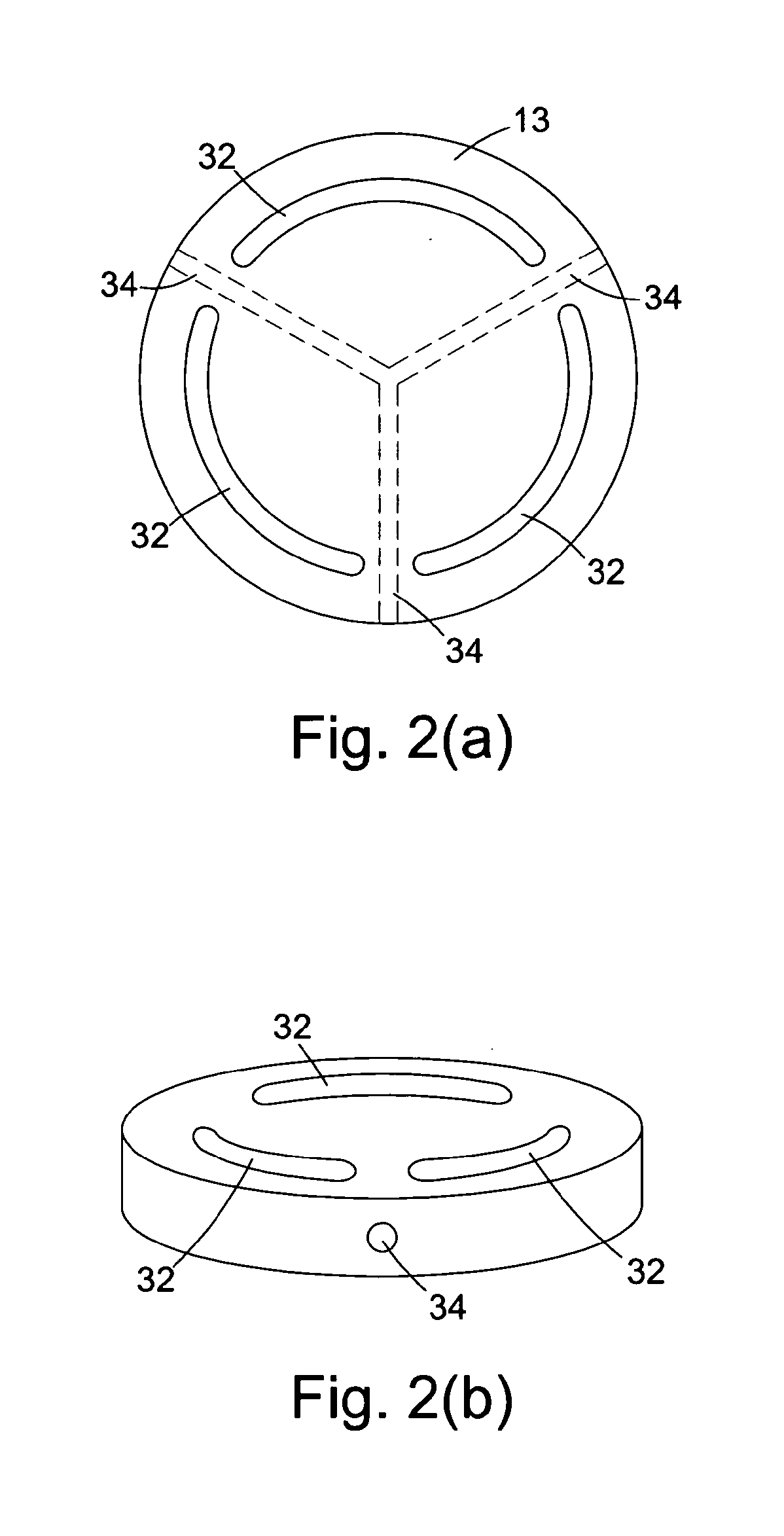
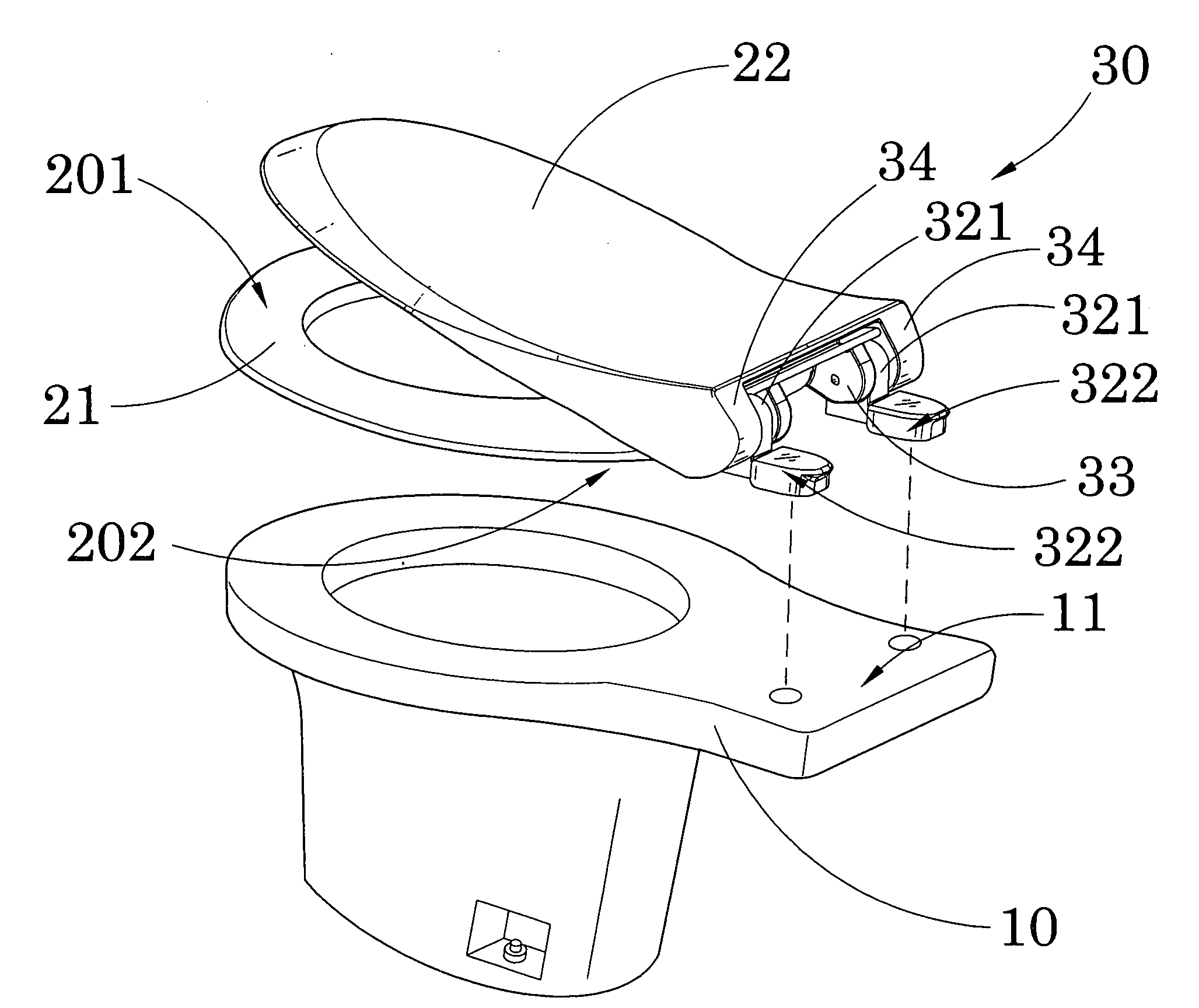
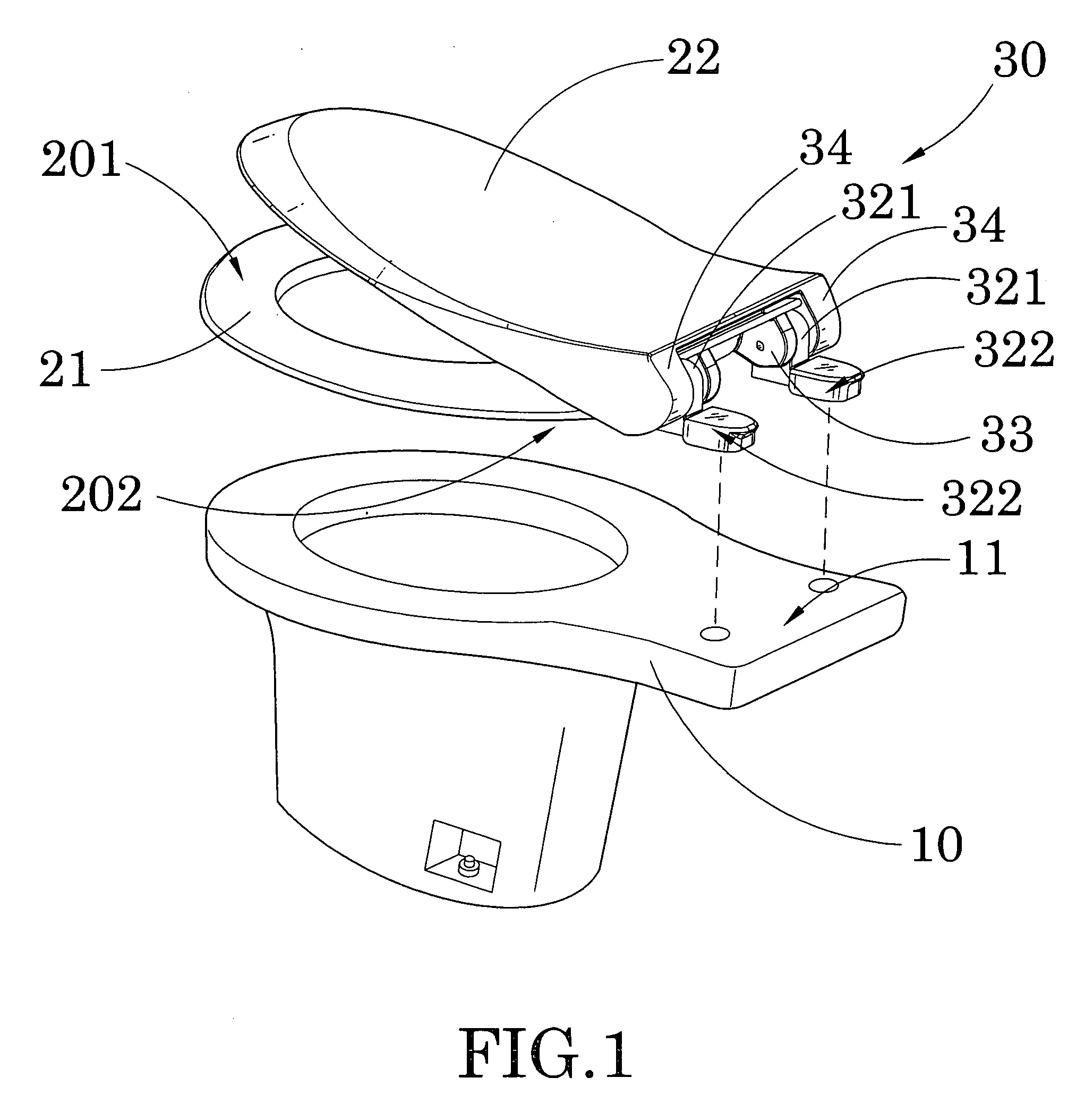
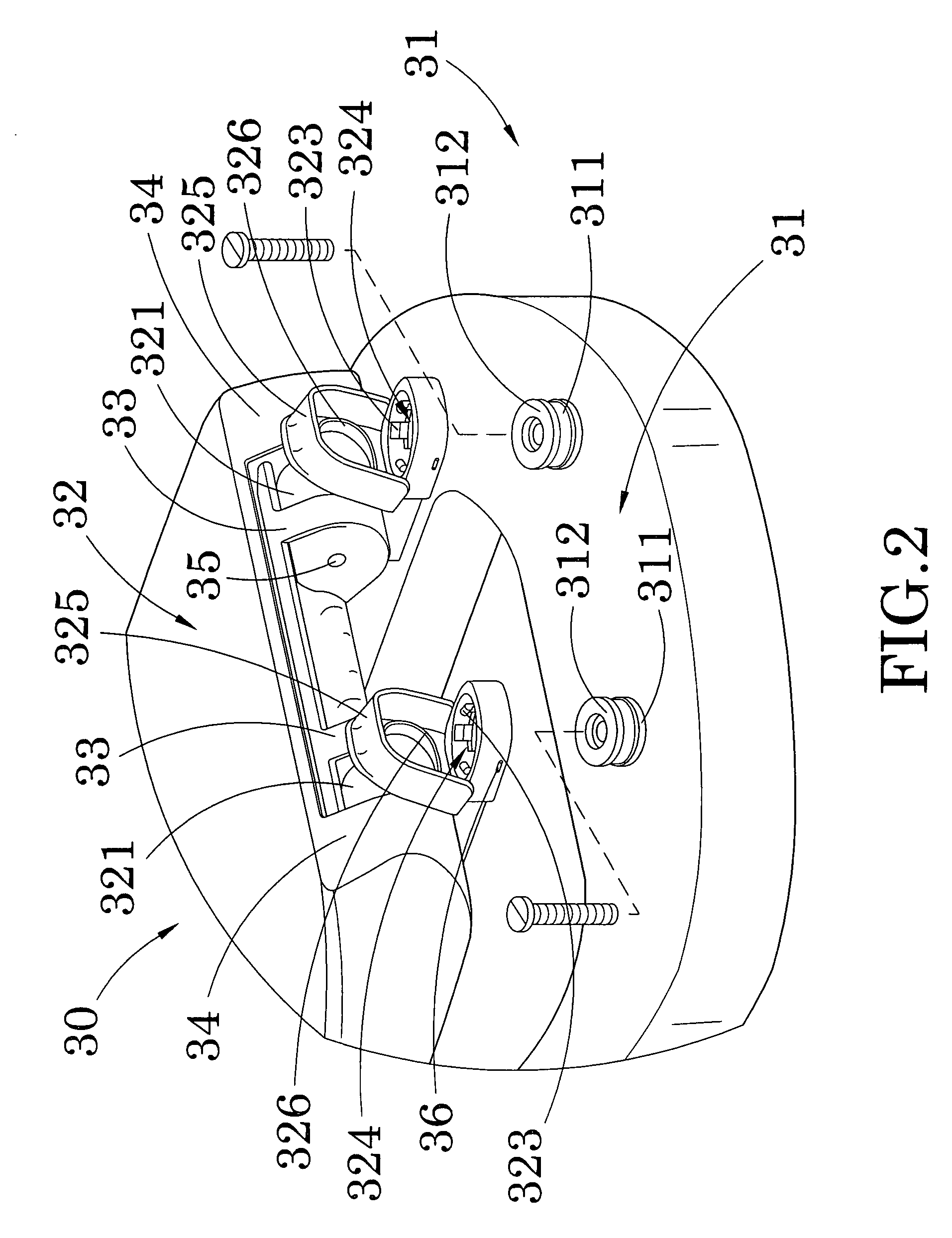
Hinge for toilet seat
A toilet seat includes a toilet bowl and a toilet platform. A toilet platform includes a bowl seat having a seating portion and a mounting portion. A seat hinge mechanism includes two spaced apart retention bases adapted for securely mounting at the toilet platform of the toilet bowl wherein the joint members are detachably engaged with the retention bases respectively for detachably mounting bowl seat on the toilet platform of the toilet bowl in a tool-less manner.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN MEITU PLASTIC IND
Laser devices using a semipolar plane
ActiveUS8971370B1Improve device performanceLower resistanceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsQuantum wellNitrogen
An optical device includes a gallium and nitrogen containing substrate comprising a surface region configured in a (20-2-1) orientation, a (30-3-1) orientation, or a (30-31) orientation, within + / −10 degrees toward c-plane and / or a-plane from the orientation. Optical devices having quantum well regions overly the surface region are also disclosed.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
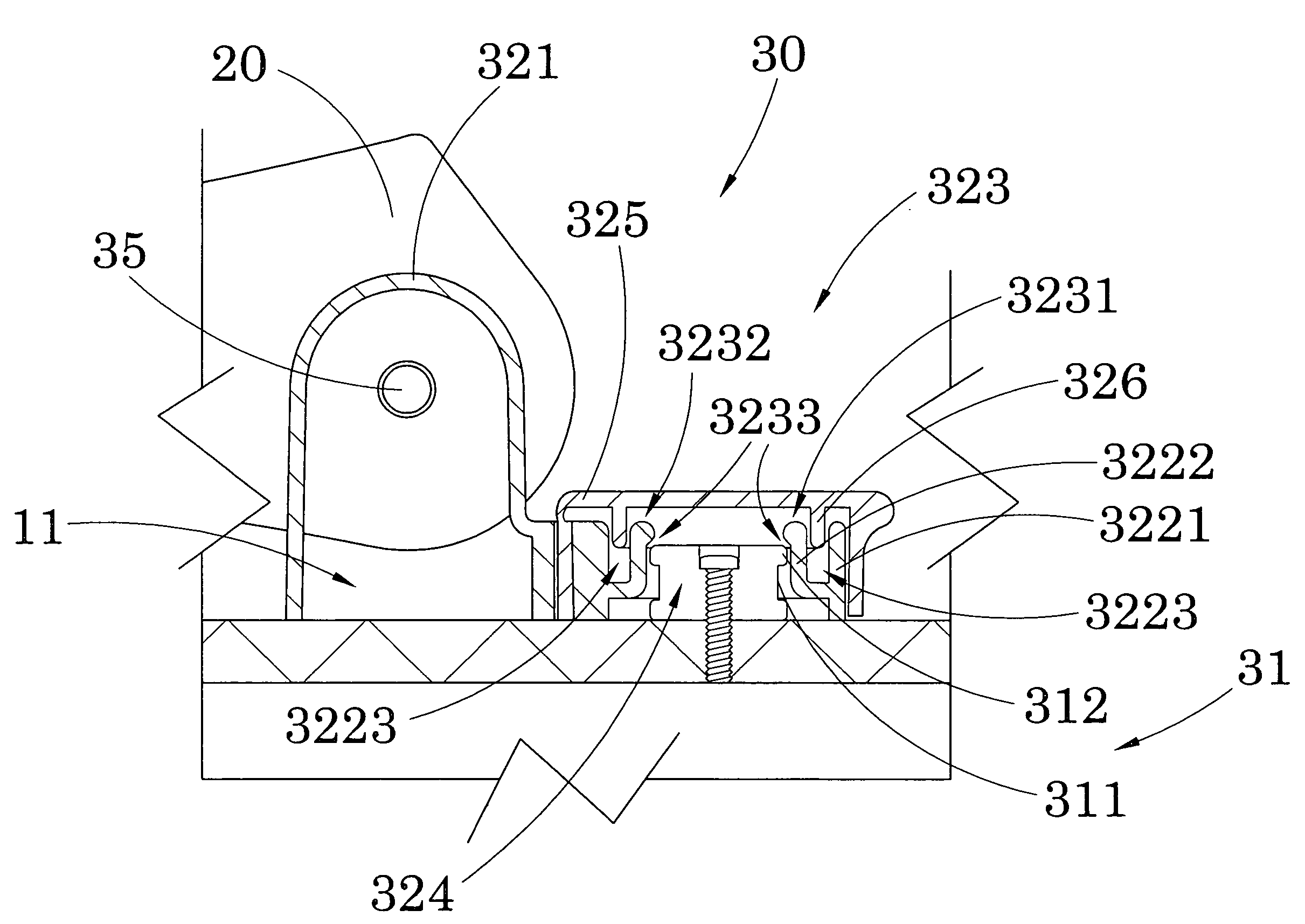
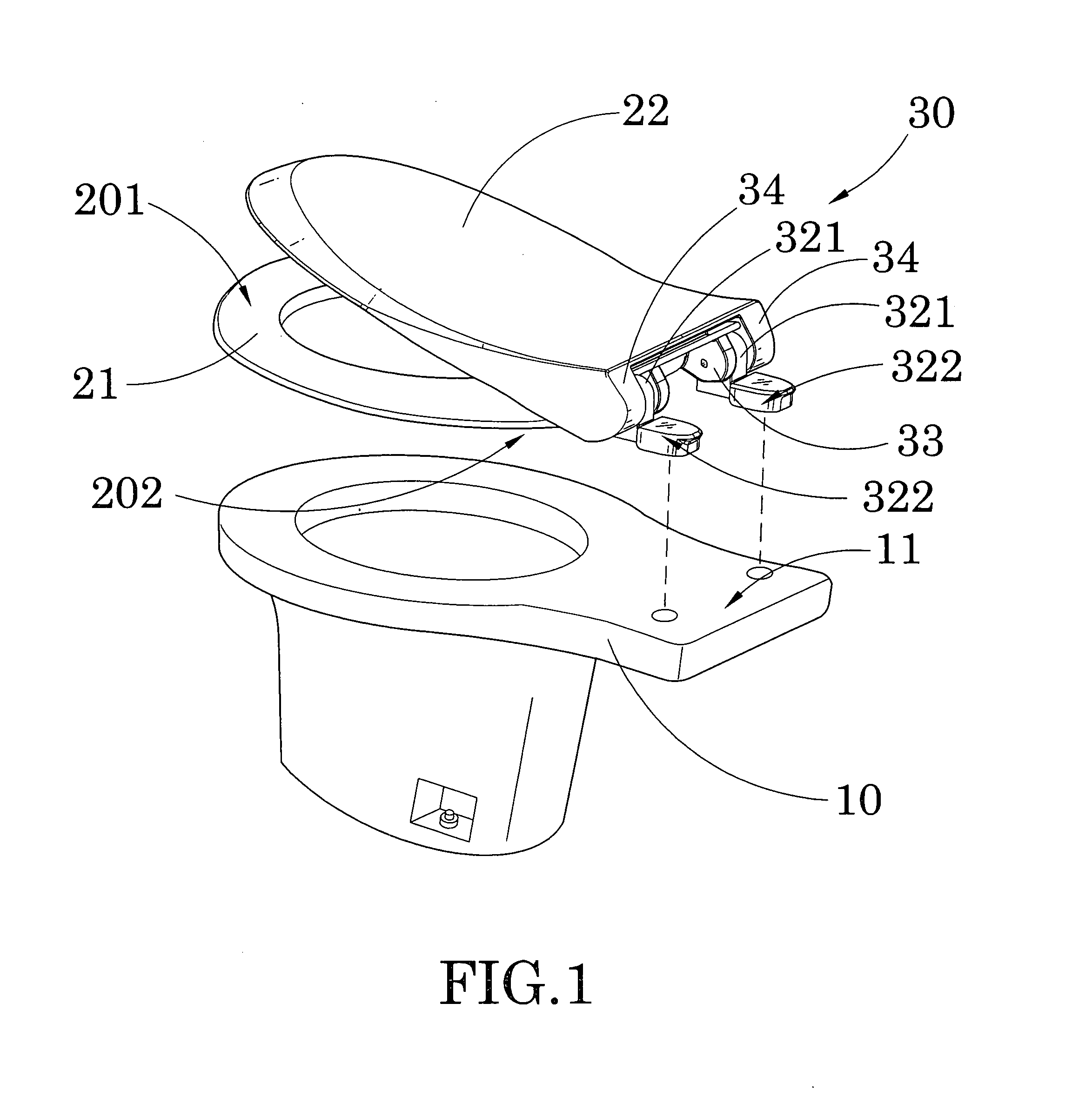
Hinge for toilet seat
A toilet seat includes a toilet bowl and a toilet platform. A toilet platform includes a bowl seat having a seating portion and a mounting portion. A seat hinge mechanism includes two spaced apart retention bases adapted for securely mounting at the toilet platform of the toilet bowl wherein the joint members are detachably engaged with the retention bases respectively for detachably mounting bowl seat on the toilet platform of the toilet bowl in a tool-less manner.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN MEITU PLASTIC IND
Foam ceramic light-weight plate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108863302AOrdinary firing fastFire fastCeramic materials productionCeramicwareSlagCeramic tiles
The invention discloses a foam ceramic light-weight plate, which is mainly prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 70 to 96 percent of ceramic tile polished waste slag, 0 to10 percent of clay, 0 to 20 percent of feldspar, 0.01 to 0.6 percent of foaming agents and 0.1 to 4 percent of stabilizing agents, wherein the stabilizing agents are manganese dioxide. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a preparation method of the foam ceramic light-weight plate. By using the foam ceramic light-weight plate and the preparation method, air holes are identical from top tobottom at the same cross section of the foam ceramic light-weight plate; the bubble uniformity is high; a tunnel kiln can be used for firing; a roller kiln can also be used for firing.
Owner:KEDA INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Large-mismatch silicon-based substrate antimonide transistor with high electron mobility and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102324436AImprove output characteristicsLow Power FeaturesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDelta dopingIsolation layer
The invention provides a large-mismatch silicon-based substrate antimonide transistor with high electron mobility. The large-mismatch silicon-based substrate antimonide transistor comprises a substrate, a composite buffering layer growing on the substrate, an insert layer growing on the composite buffering layer, an AlSb isolation layer growing on the insert layer, a sub channel layer growing on the AlSb isolation layer, an antimonide lower potential barrier layer growing on the sub channel layer, an InAs channel layer growing on the antimonide lower potential barrier layer, an antimonide isolation layer growing on the InAs channel layer, a doping layer growing on the antimonide isolation layer, wherein the doping layer is InAs doped with a Si plane or delta doping of Te; an upper potential barrier layer growing on the doping layer, wherein the upper potential barrier layer is a composite potential barrier layer consisting of an AlSb layer and an InAlAs layer; and an InAs cap layer growing on the upper potential barrier layer, wherein the InAs cap layer is an unintentionally doped InAs or n type doped InAs.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Precise measuring method of crystalline silicon body lifetime
InactiveCN106680687AImprove material qualityReduce the effects of noiseSemiconductor operation lifetime testingSemiconductor characterisationPhotoconductive decayCrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a precise measuring method of crystalline silicon body lifetime. The precise measuring method of the crystalline silicon body lifetime comprise the steps that minority carrier lifetime is measured through a quasi-steady-state photoelectric conduction method, a true value of the silicon wafer minority carrier lifetime can be obtained accurately and quickly through a quasi-steady-state minority carrier lifetime measuring method, the effective minority carrier lifetime comprises a body lifetime and a surface recombination lifetime, on the precise of the same silicon wafer recombination conditions, the true body lifetime of the silicon wafer is obtained by calculating through formulas, and the calculated true body lifetime of the silicon wafer is similar to the body lifetime measured through the photoconductive decay method. The method for measuring the minority carrier lifetime through the quasi-steady-state photoelectric conduction method and obtaining the true body lifetime through calculation has the advantages of being simple, fast, free of contamination and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
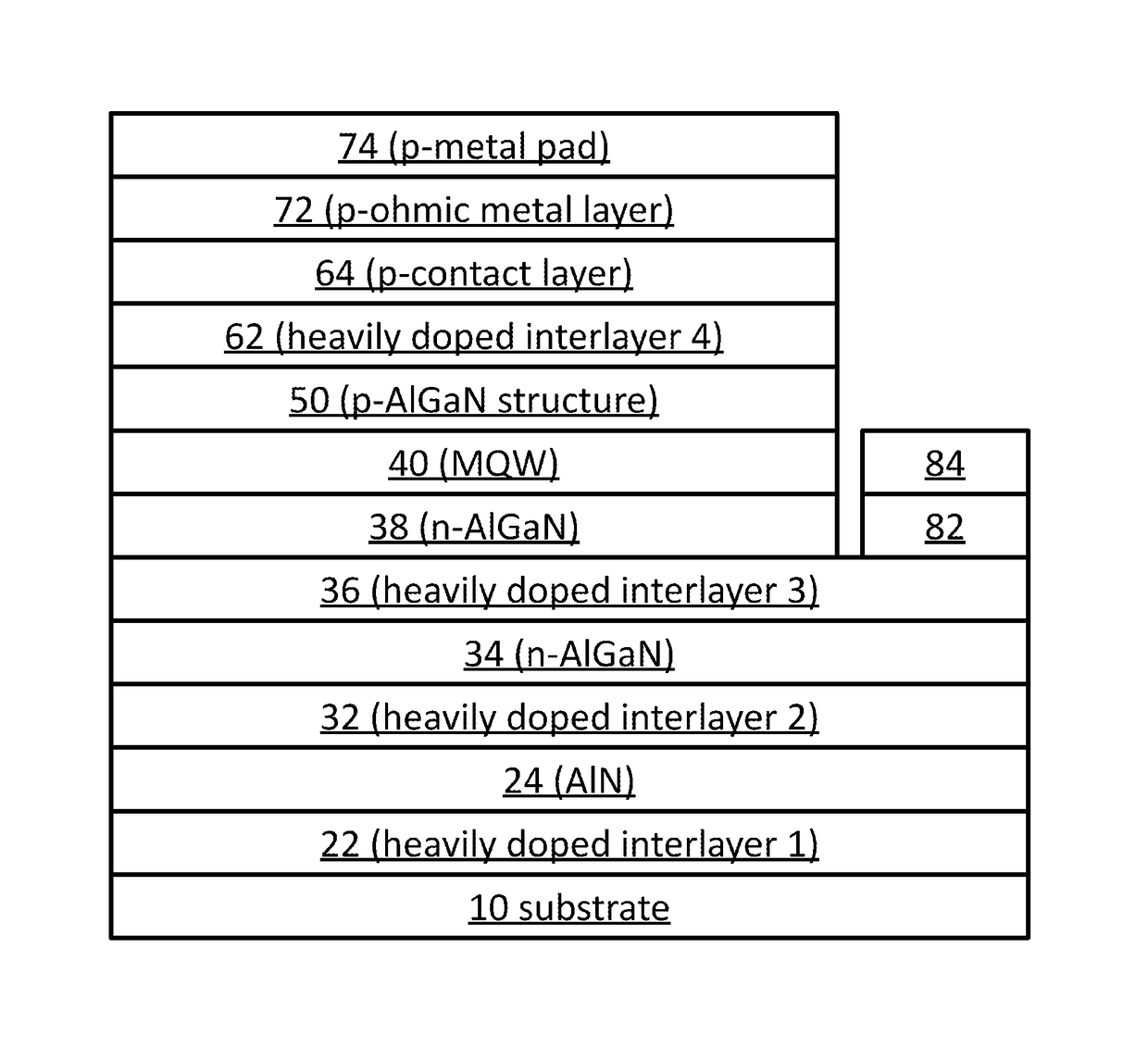
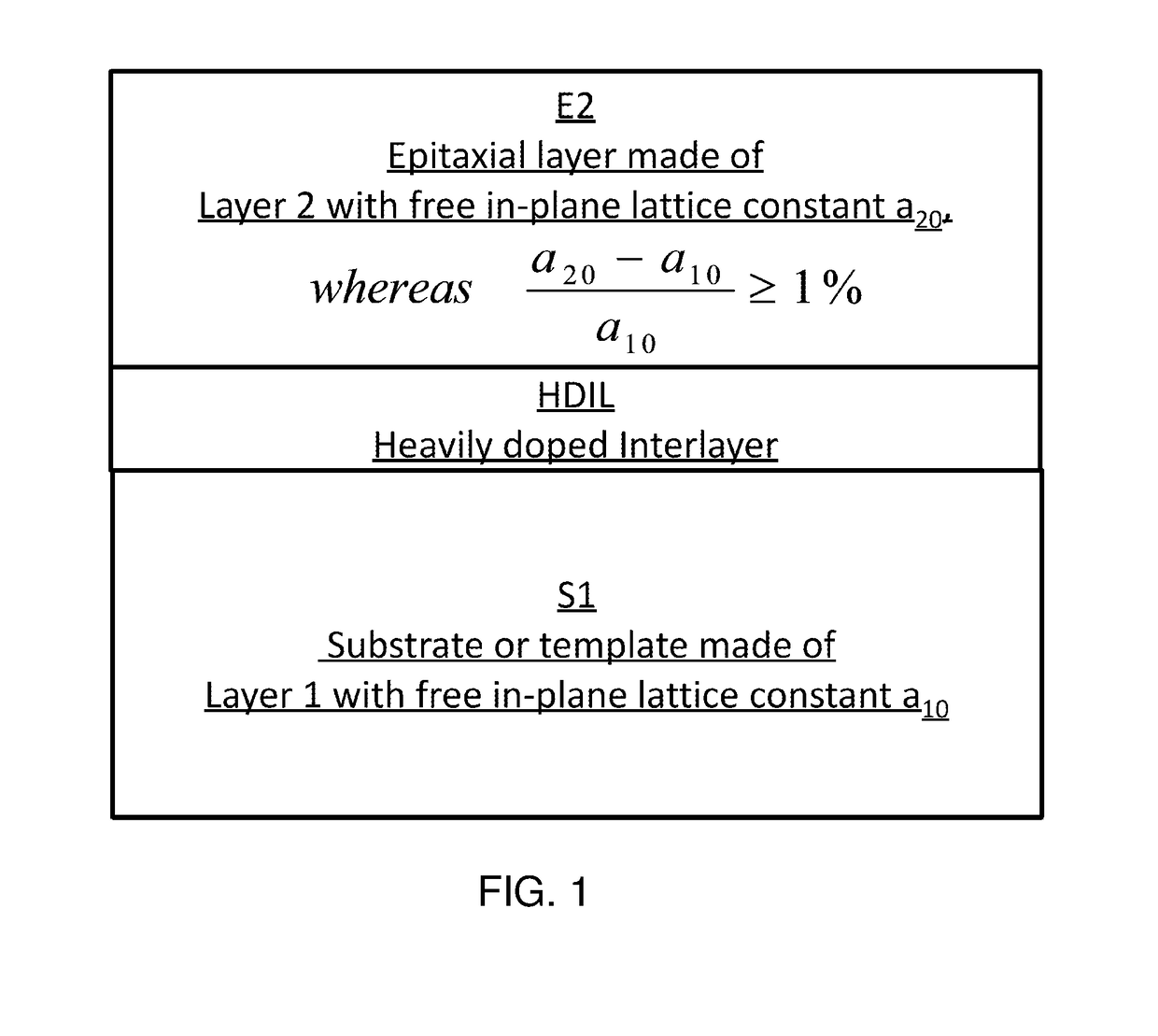
Ultraviolet light-emitting device with a heavily doped strain-management interlayer
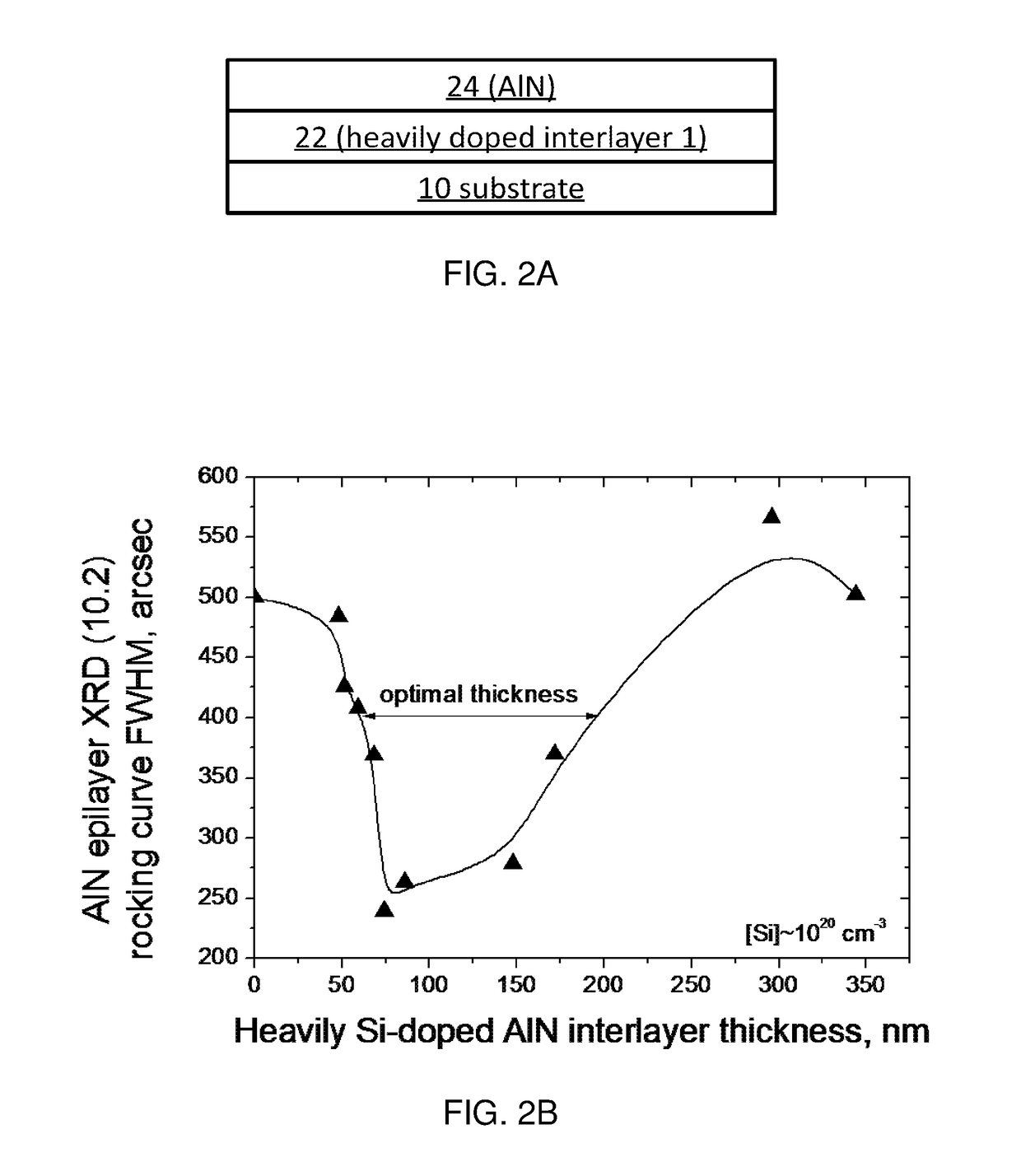
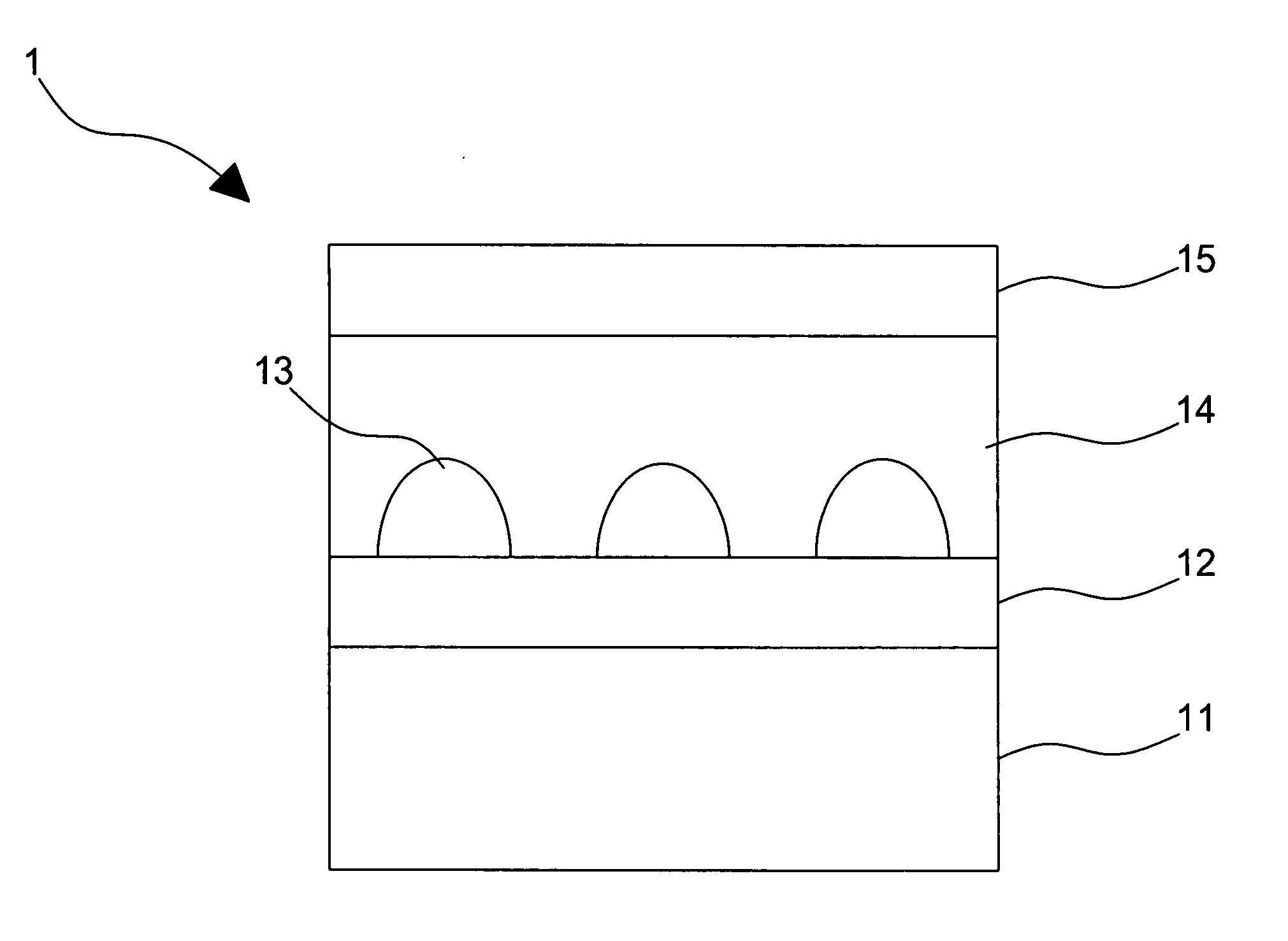
ActiveUS9680056B1Efficient and cost-effective approachImprove device performanceSemiconductor devicesIn planeUltraviolet lights
A heteroepitaxy strain-management structure for a light emitting device includes: a substrate or template; an epitaxial layer to be epitaxially formed over the substrate or template, wherein a calculated in-plane compressive strain to be exerted by the substrate or template to the epitaxial layer is equal to or larger than 1%; and a heavily doped interlayer inserted in-between the epitaxial layer and the substrate or template; wherein the heavily doped interlayer is of substantially the same material composition as that of the epitaxial layer, with a thickness of 40-400 nm, and doped at a doping level in the range of 5×1019 to 5×1020 cm−3. Also provided is an ultraviolet light emitting device having a heteroepitaxy strain-management structure.
Owner:BOLB
Quantum dot optoelectronic device having an sb-containing overgrown layer
InactiveUS20080258132A1Improve quality and carrier confinementEnhance it optical characteristic and thermal stabilityNanoinformaticsSemiconductor devicesQuantum dotCharge carrier
A quantum dot optoelectronic device has an overgrown layer containing antimony (Sb). The optical characteristics and thermal stability of the optoelectronic device are thus greatly enhanced due to the improved crystal quality and carrier confinement of the quantum dot structure.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com