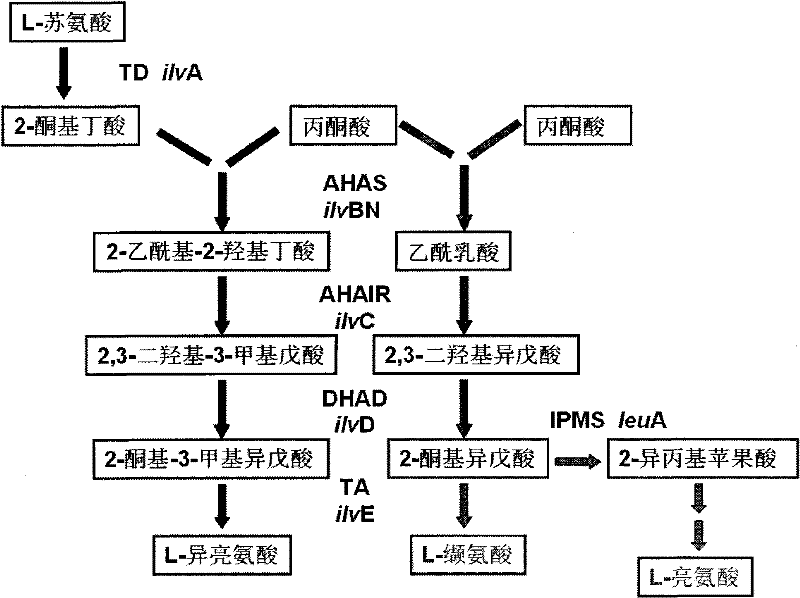
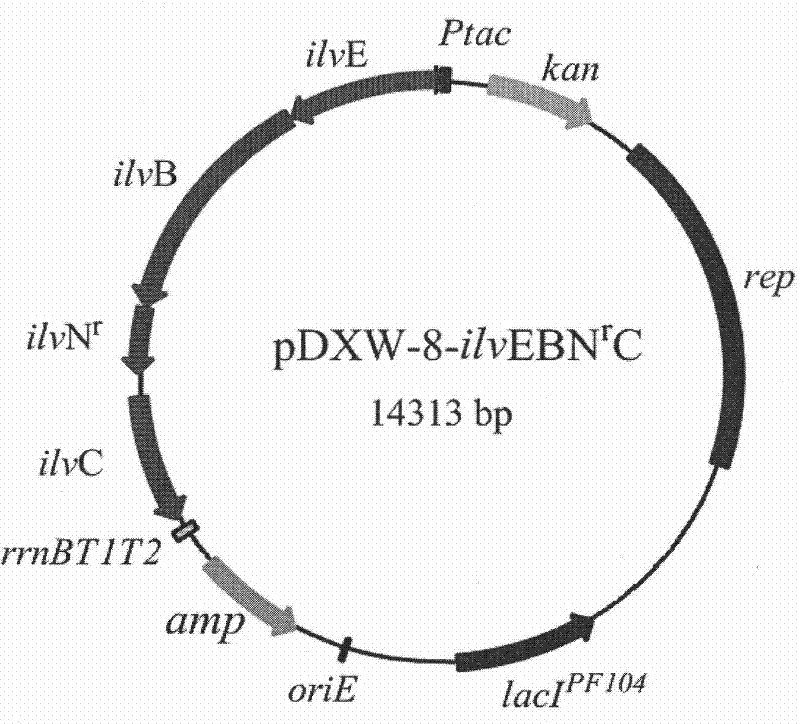
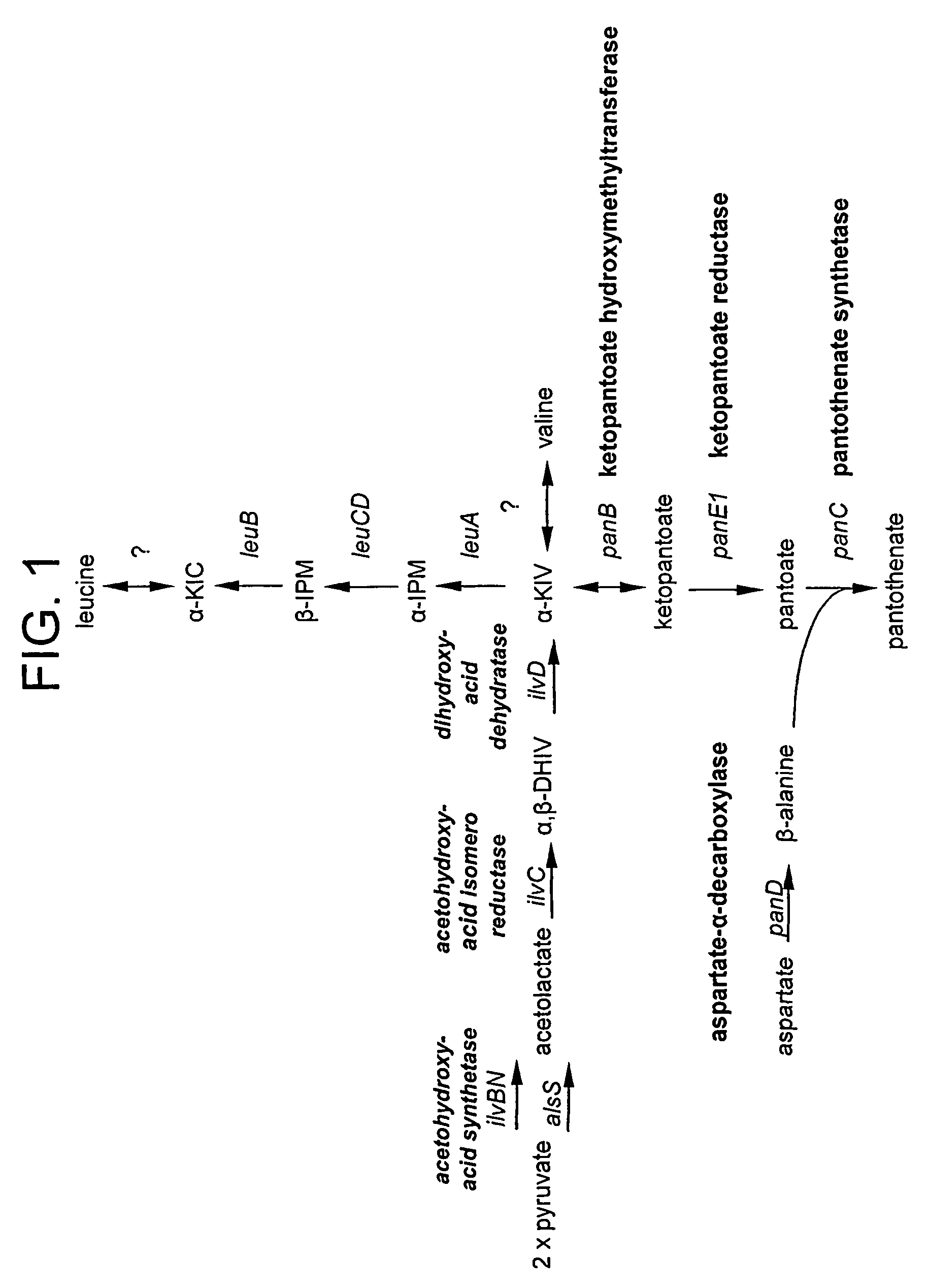
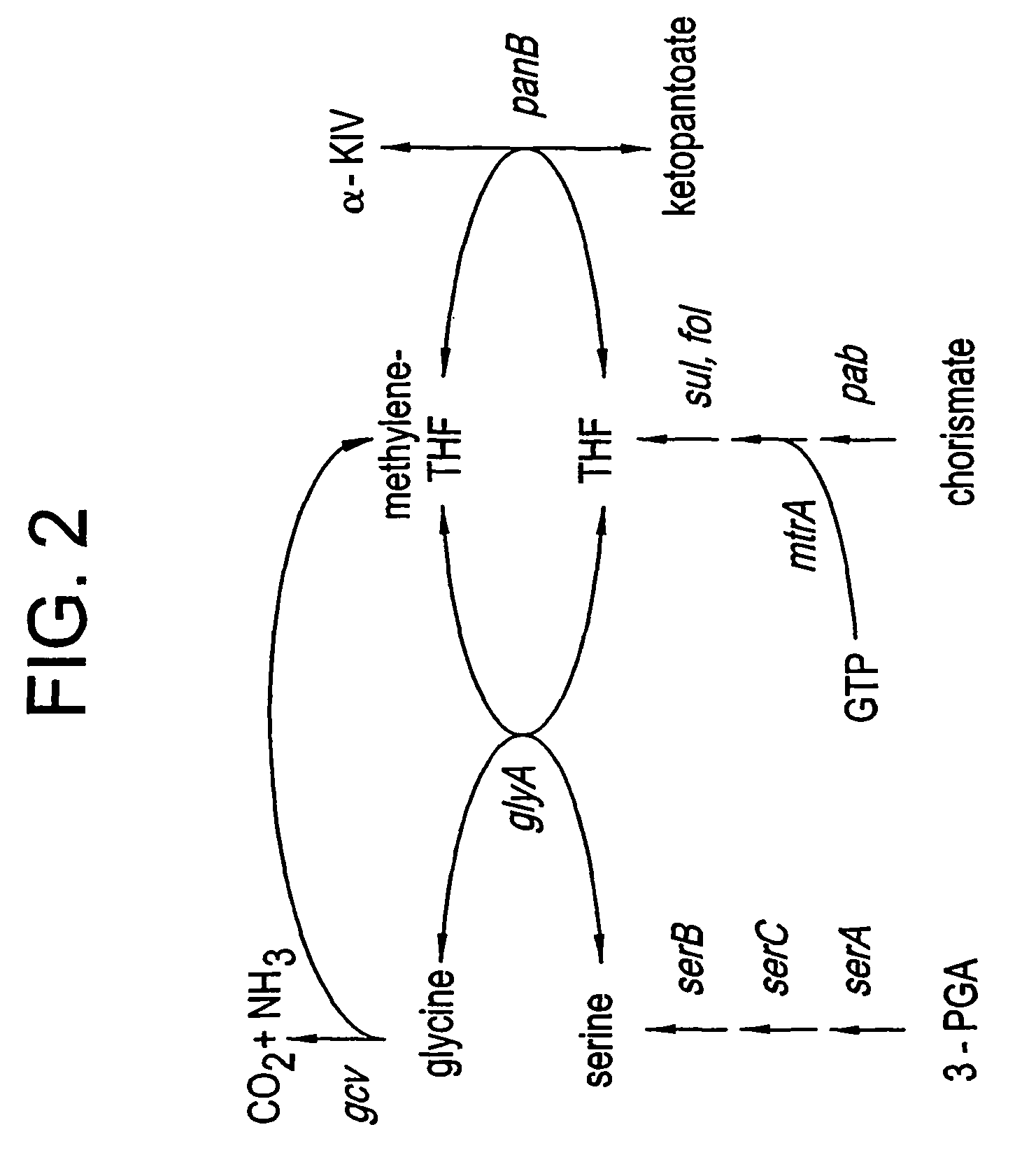
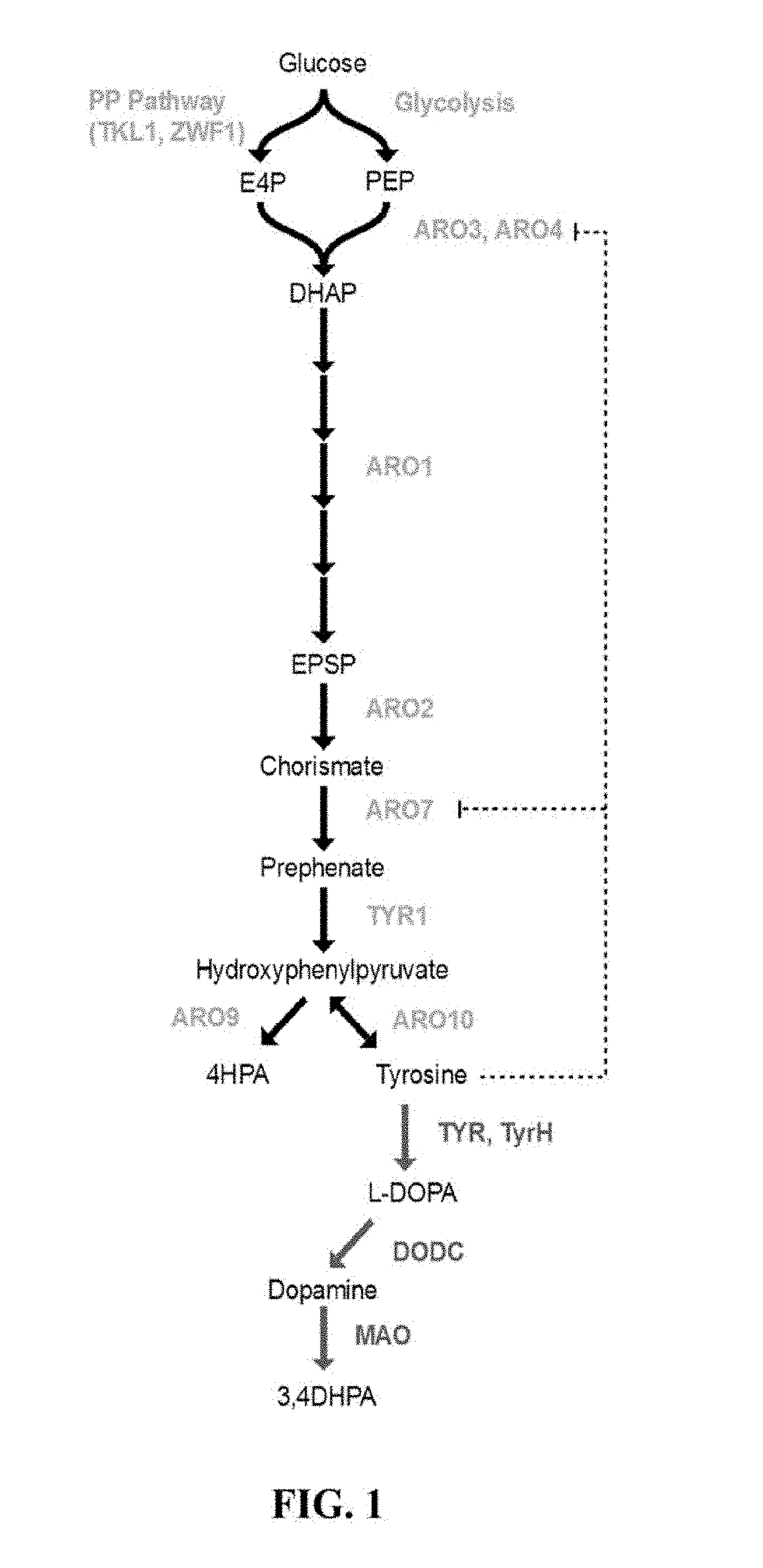
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Biosynthetic enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Uridine monophosphate biosynthesis involves an enzyme that is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and multifunctional enzymes that are located in the cytosol. The first step involves the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthase combining glutamine with CO2 in an ATP dependent reaction to form carbamoyl phosphate.
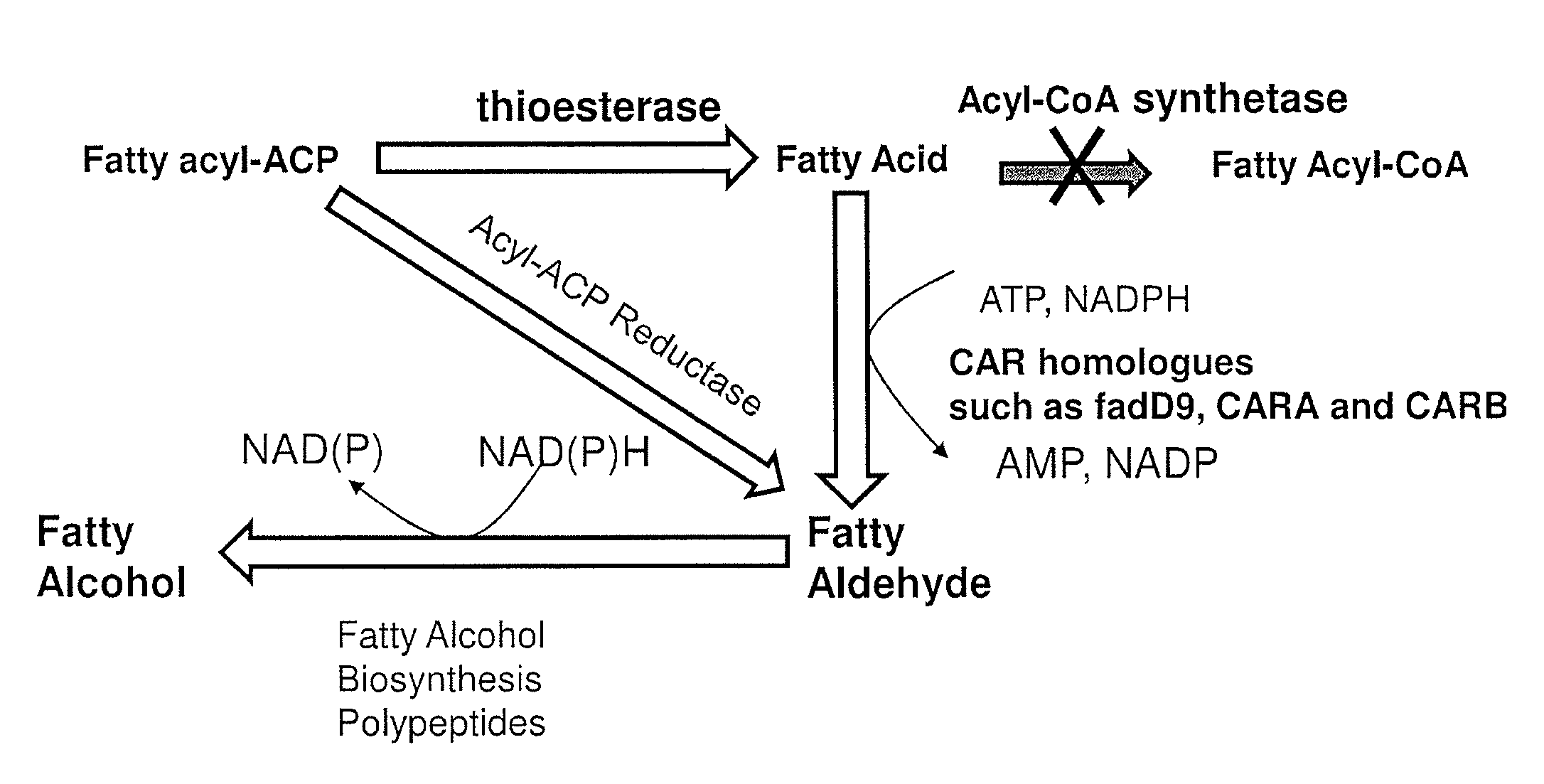
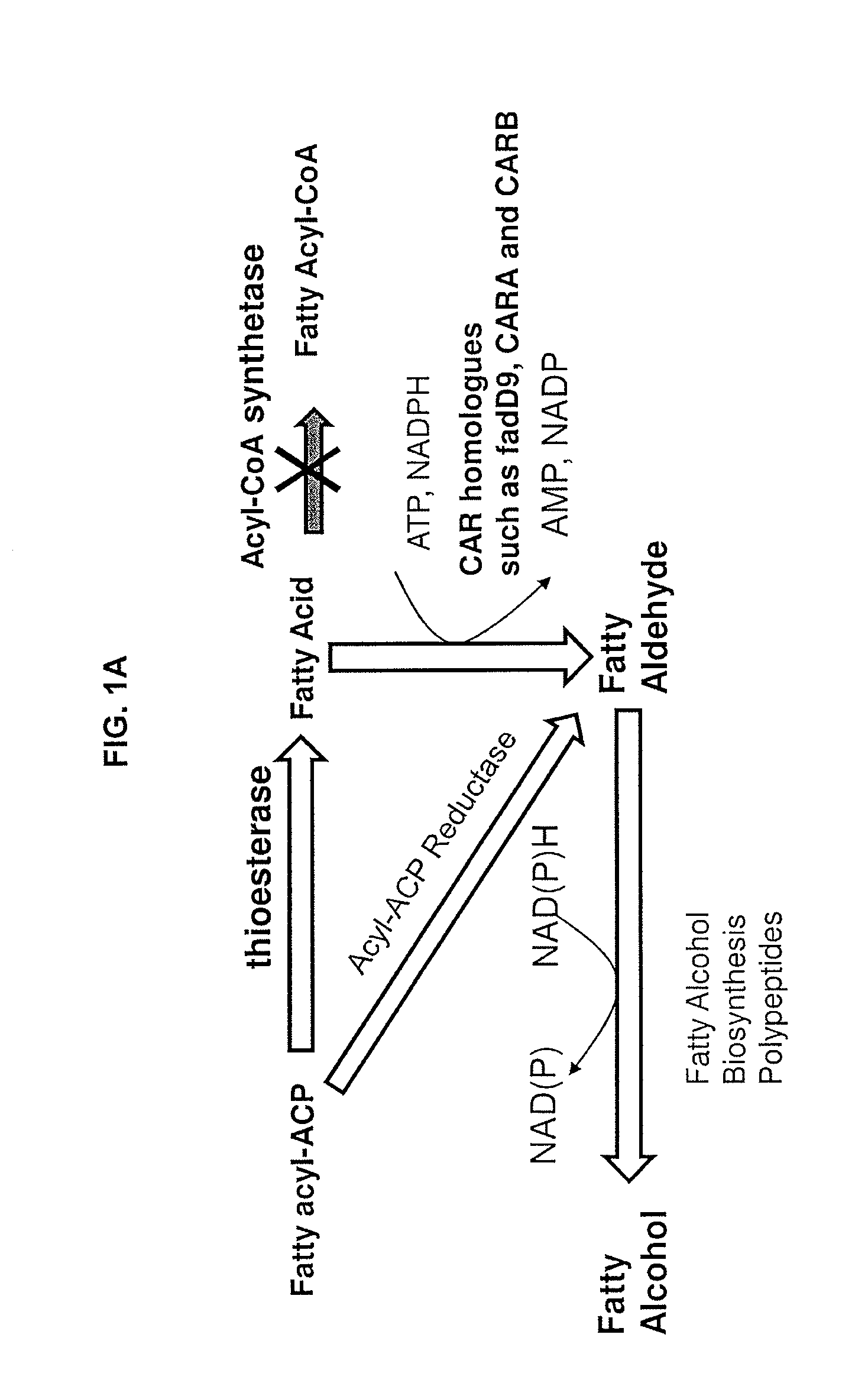
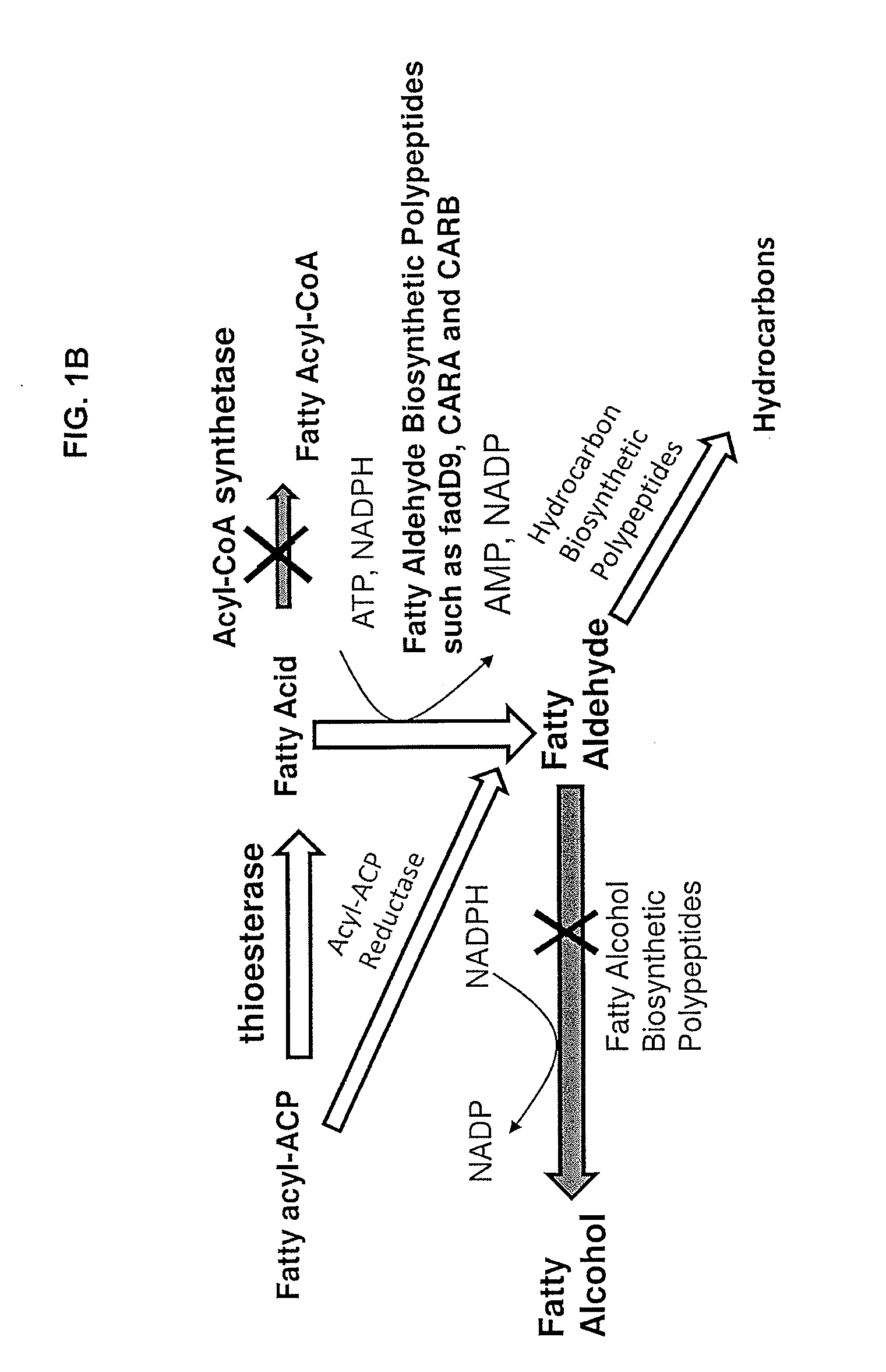
Methods and compositions related to fatty alcohol biosynthetic enzymes
InactiveUS20110250663A1High potencyOrganic chemistryMicroorganismsFatty alcoholFatty acid derivatives
Compositions and methods for producing fatty acid derivatives using recombinant microorganisms are described herein.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
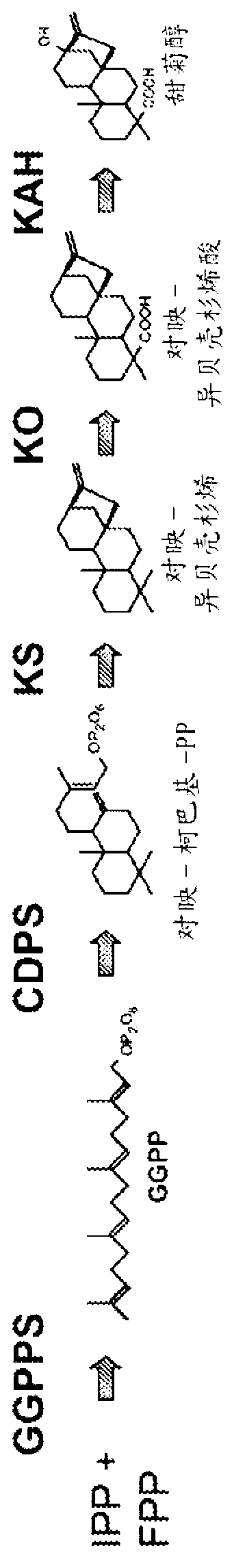
Recombinant production of steviol glycosides
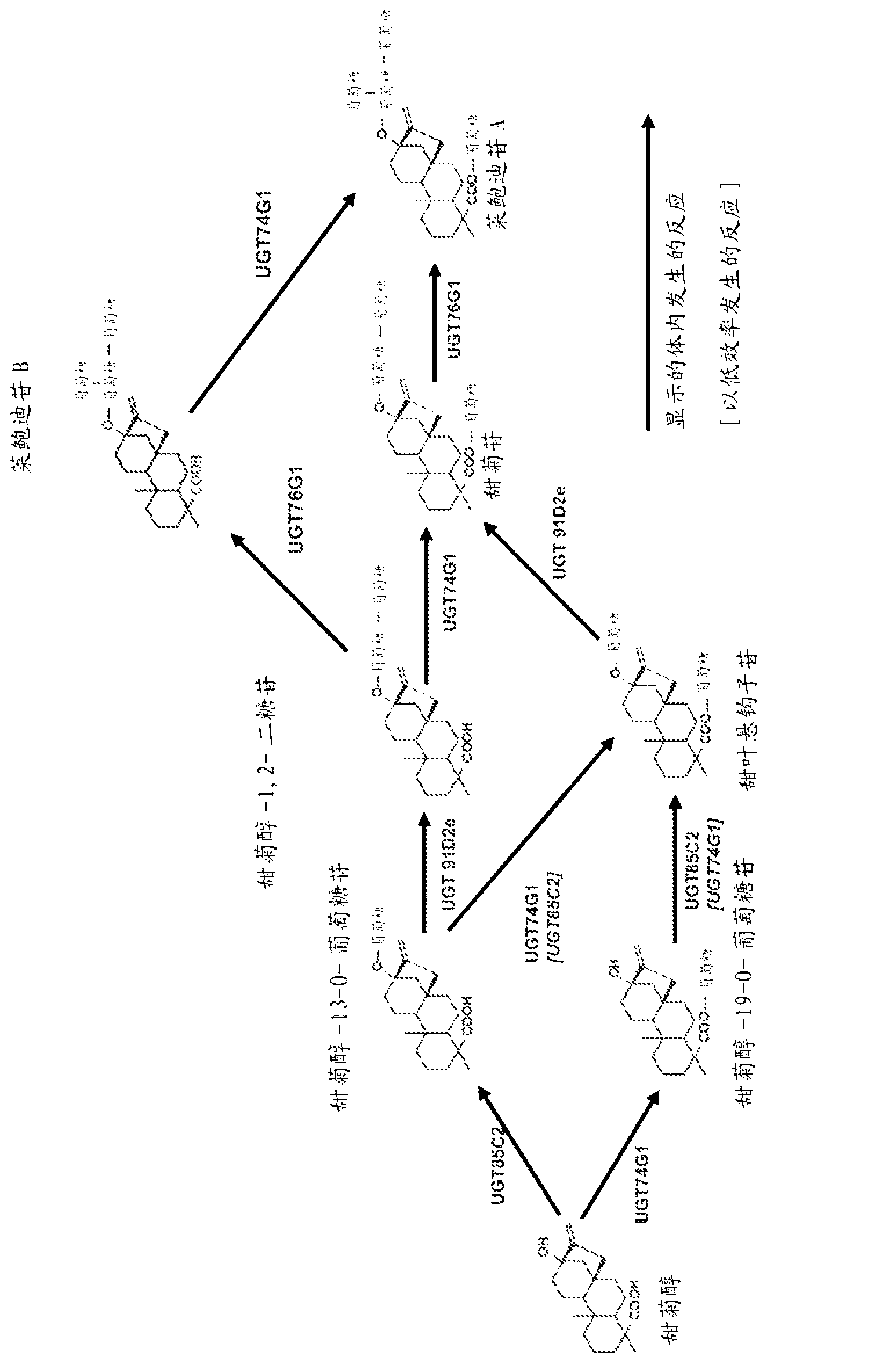
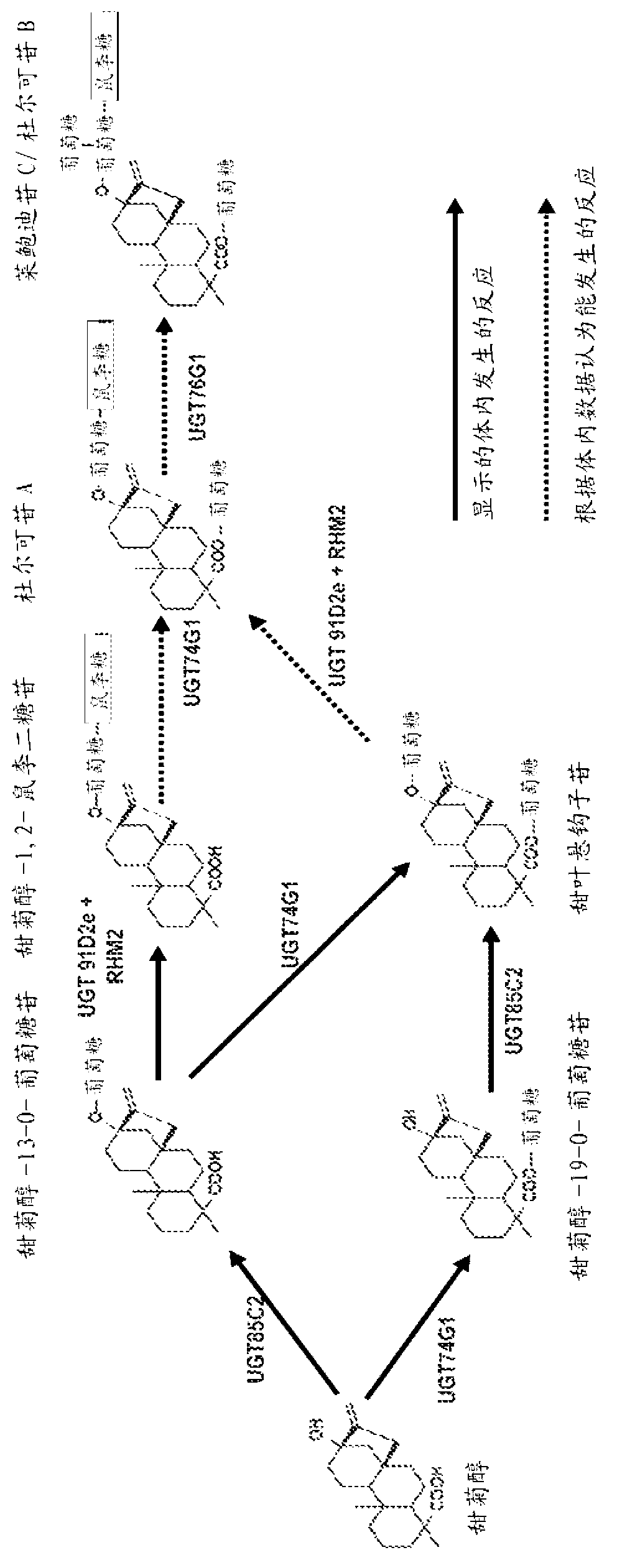
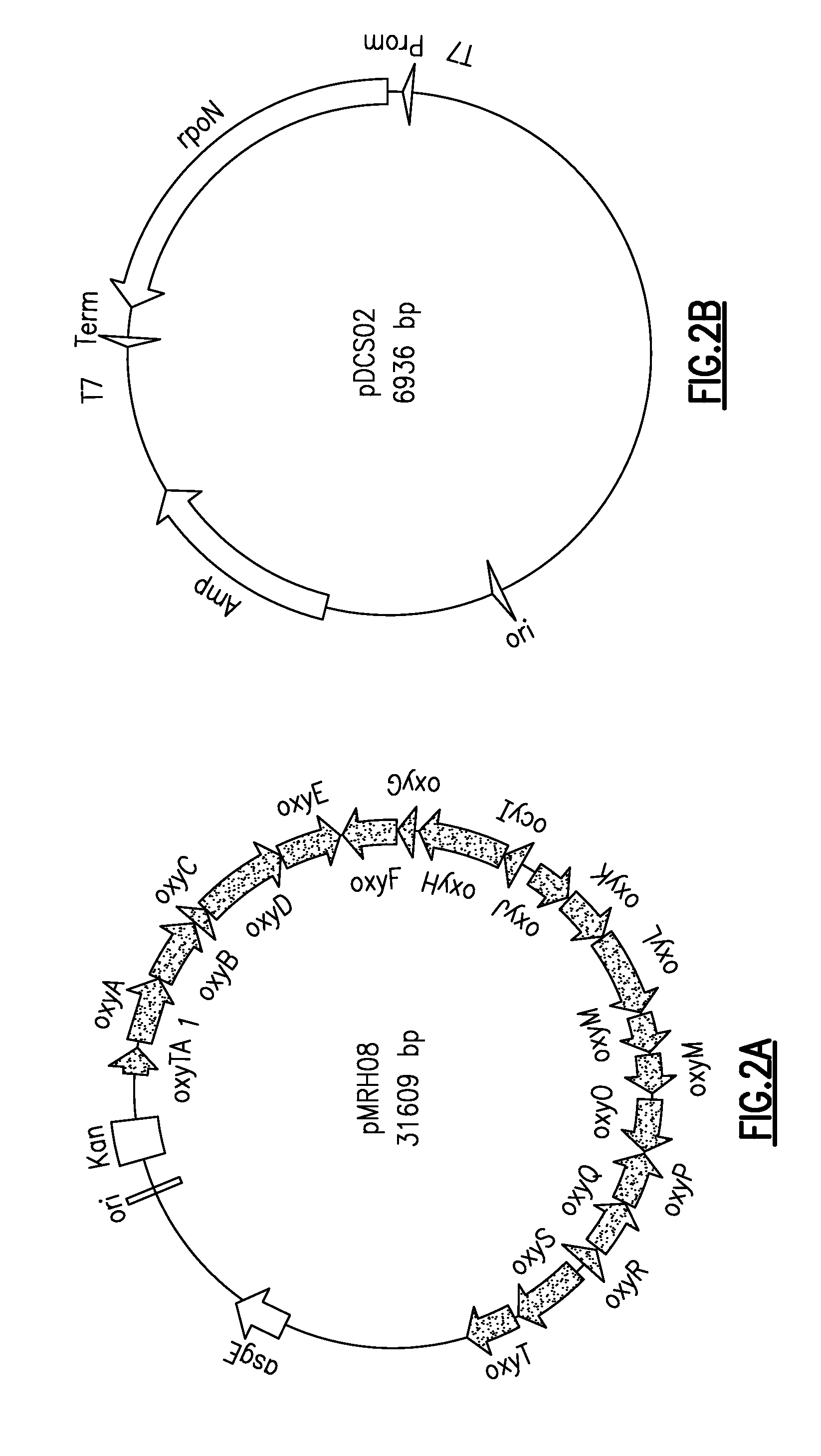
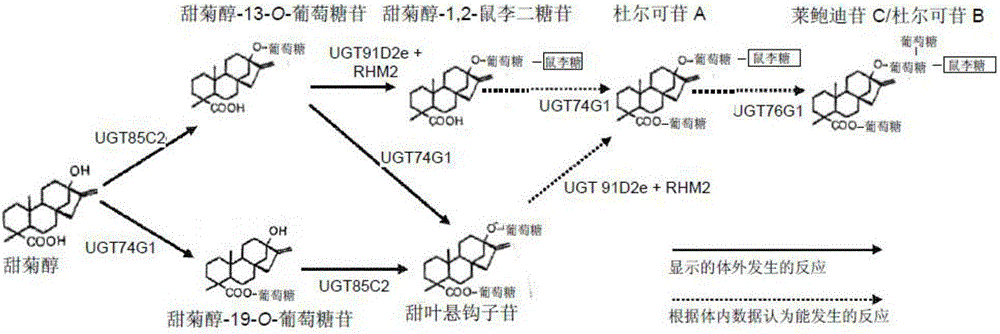
Recombinant microorganisms, plants, and plant cells are disclosed that have been engineered to express novel recombinant genes encoding steviol biosynthetic enzymes and UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs). Such microorganisms, plants, or plant cells can produce steviol or steviol glycosides, e.g., rubusoside or Rebaudioside A, which can be used as natural sweeteners in food products and dietary supplements.
Owner:沃维公司
Method for producing biodegradable polyester
Owner:RIKEN
Recombinant dna, bacterial strain and method for fermentative production of l-valine
InactiveCN102286505AHigh activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
The invention relates to a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), strain and method for producing L-valine by fermentation. The recombinant DNA comprises DNA sequence for coding acetohydroxy acid synthetase free of feedback inhibition of three branched-chain amino acids to acetohydroxy acid synthetase, DNA sequence for coding dihydroxy reduction isomerase, and DNA sequence for coding branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. The strain is corynebacterium or brevibacterium transformed by introducing the recombinant DNA. The method is implemented by culturing the strain to produce the L-valine. In the invention, the expression L-valine is used for producing the bacterium L-valine biosynthetic gene, so the yield of the L-valine can be greatly increased; and the fermentation model, especially the high-temperature short-time fermentation model, is constructed according to the optimum temperature of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme, so that the metabolism intensity of the strain is enhanced, the activity of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme is enhanced, and the yield of the L-valine and the conversion rate of the sugar acid can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Prenylation inhibitors reduce host cell permissiveness to viral replication
InactiveUS20050085529A1Reducing permissivenessConfirming a resultant reduction in permissiveness of the cellsBiocideAnimal repellantsHMG-CoA reductaseHuman cell
Permissiveness of human cells to replication of susceptible pathogenic human viruses is reduced by treating the cells with a selective inhibitor of prenylation of a host cell protein. Target viruses, especially Flaviviridae, are predetermined to lack a CXXX box and prenylated viral protein, and to be replication-dependent on host protein prenylation. The general method comprises (a) contacting human cells subject to infection by the virus with an effective amount of a selective inhibitor of a prenylation enzyme of the cells; and (b) confirming a resultant reduction in permissiveness of the cells to replication of the virus. Targeted enzymes include prenyl biosynthetic enzyme like HMG CoA reductase farnesyl and / or geranylgeranyl transferase enzymes.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Microorganisms and processes for enhanced production of pantothenate
InactiveUS7244593B2Improve the level ofIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesMicroorganismMicrobiology
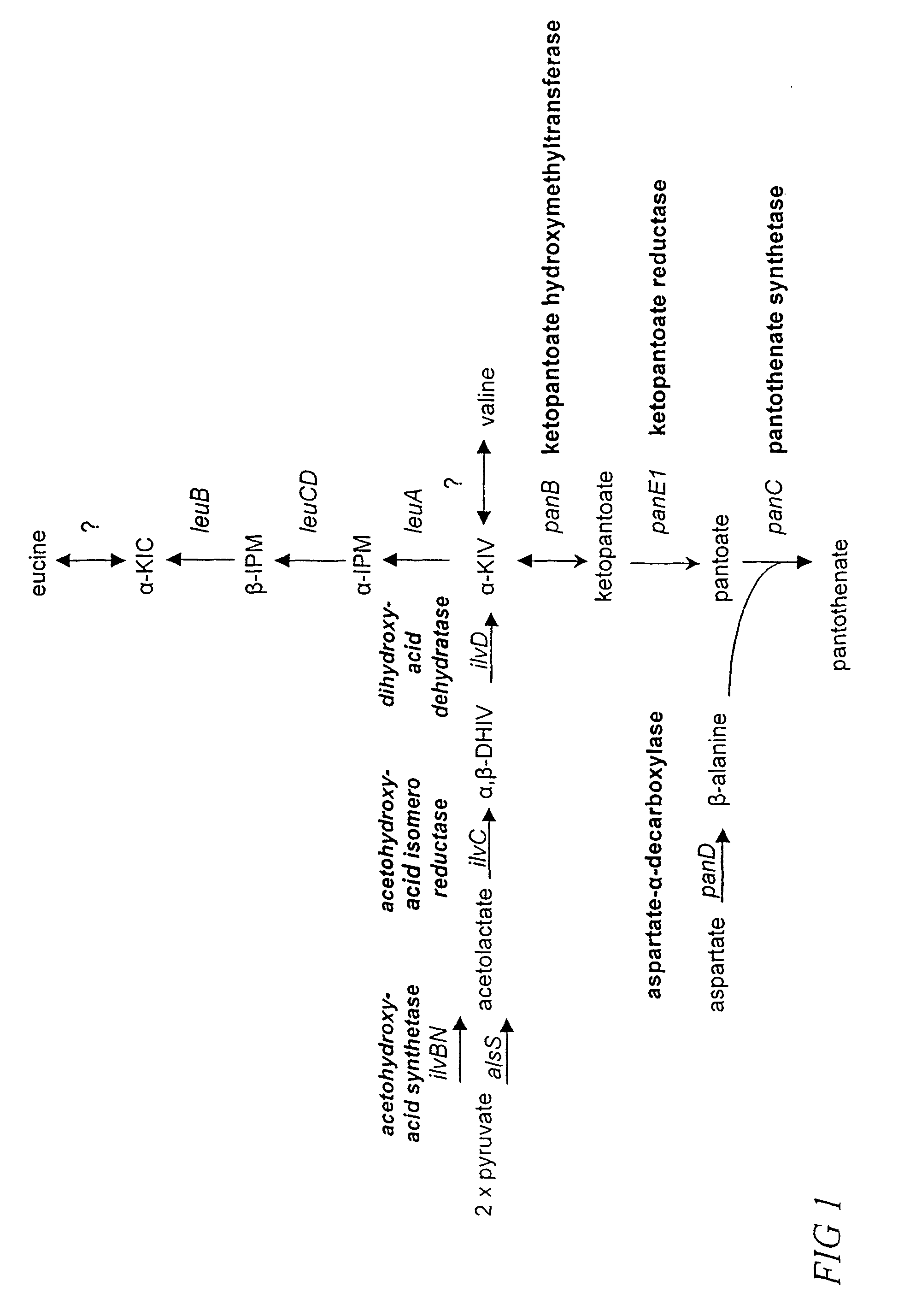
The present invention features improved methods for the enhanced production of pantoate and pantothenate utilizing microorganisms having modified pantothenate biosynthetic enzyme activities and having modified methylenetetrahydrofolate (MTF) biosynthetic enzyme activities. In particular, the invention features methods for enhancing production of desired products by increasing levels of a key intermediate, ketopantoate by enzymes that contribute to its synthesis. Recombinant microorganisms and conditions for culturing same are also are featured. Also featured are compositions produced by such microorganisms.
Owner:BASF AG
Plant raffinose saccharide biosynthetic enzymes
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a galactinol synthase. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the galactinol synthase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the galactinol synthase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Gene for coding glutamine dipeptide biosynthetic enzyme and application thereof
ActiveCN106754985AImprove conversion efficiencyResolve separabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDipeptide
The invention discloses a gene for coding a glutamine dipeptide biosynthetic enzyme and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses an amino acid sequence coded by the gene, and provides a recombinant vector containing the gene, recombinant escherichia coli, and a method for performing biotransformation to synthesize the glutamine dipeptide by using the gene. The gene and the application of a recombinant bacterial strain of the gene have the advantages of high mol conversion rate, high reaction speed, easy separation, low cost and the like. In the synthesis method, the maximum mol conversion rate of the glutamine dipeptide can reach 83.3 percent; meanwhile, the thalli can be applied to the catalytic synthesis of the glutamine dipeptide again after the circulation recovery; in addition, the catalytic activity is stable. Therefore high market competitive power and application values are realized; a foundation is laid for the industrial production of the glutamine dipeptide.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
Metal resistant plants and phytoremediation of environmental contamination
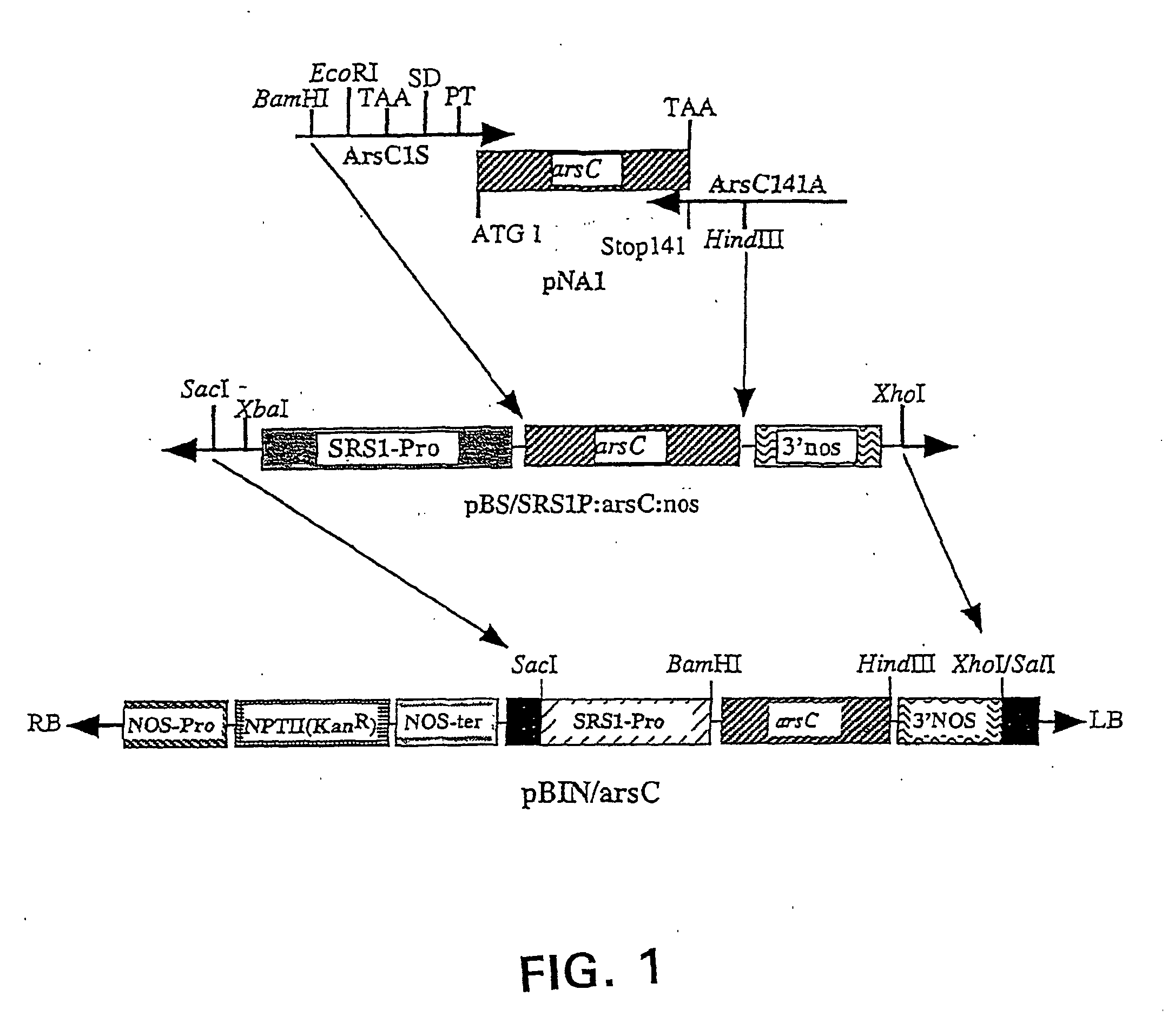
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic plant cells, plant tissue and plants which contain and express at least one phytochelatin biosynthetic coding sequence under the regulatory control of the strong ACT2 constitutive promoter or the light-inducible SRS1 promoter and / or a plant-expressible arsenate reductase coding sequence. Optionally the plant expressing the at least one phytochelatin biosynthetic enzyme coding sequence can also express a mercuric ion reductase coding sequence. The transgenic plants are tolerant of heavy metal ions, e.g., cadmium, arsenate and / or mercury, and can accumulate those ions from a contaminated environment, to thus, effect phytoremediation of a contaminated soil or water environment which contains mercury, cadmium and / or arsenate ions.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
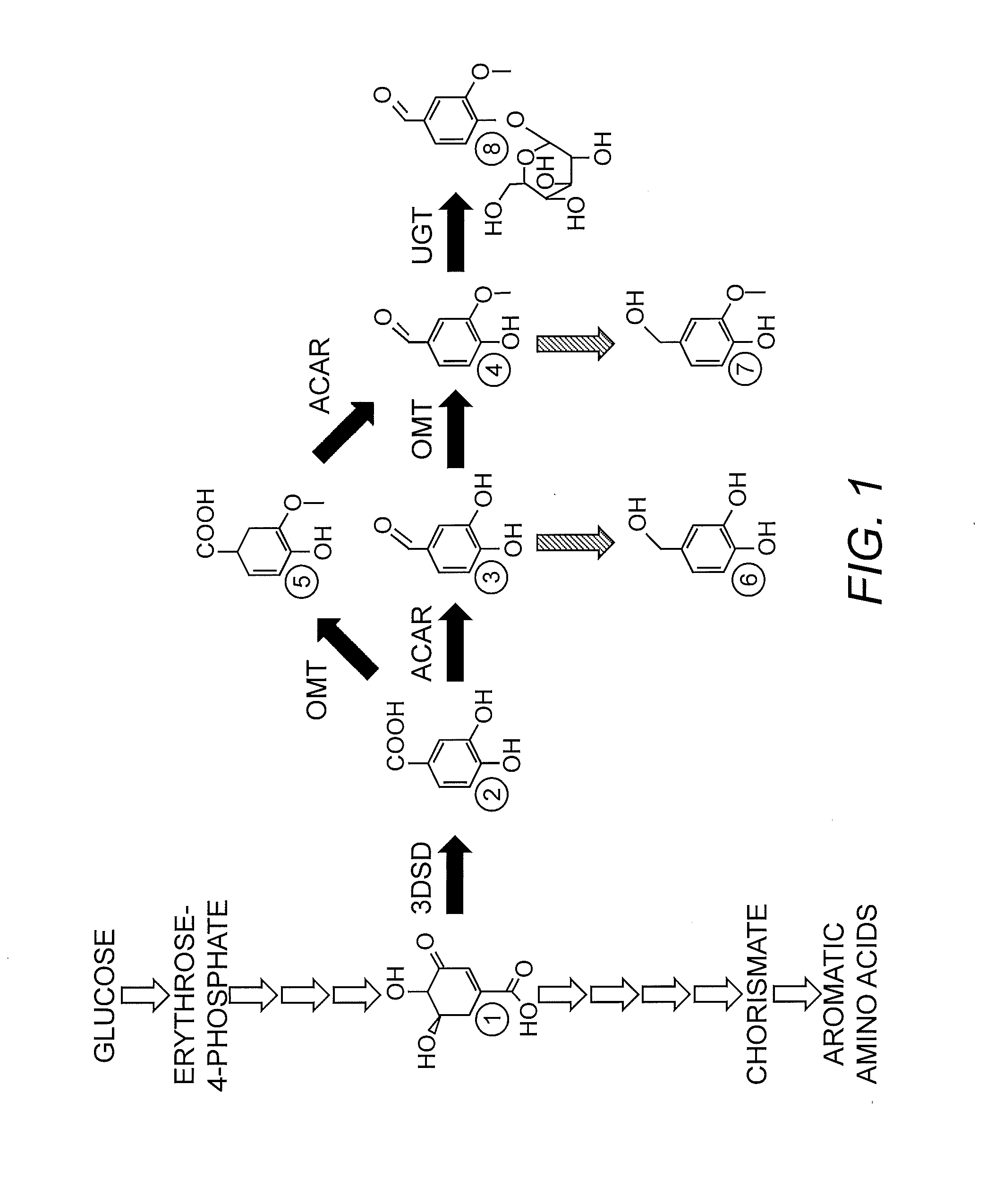
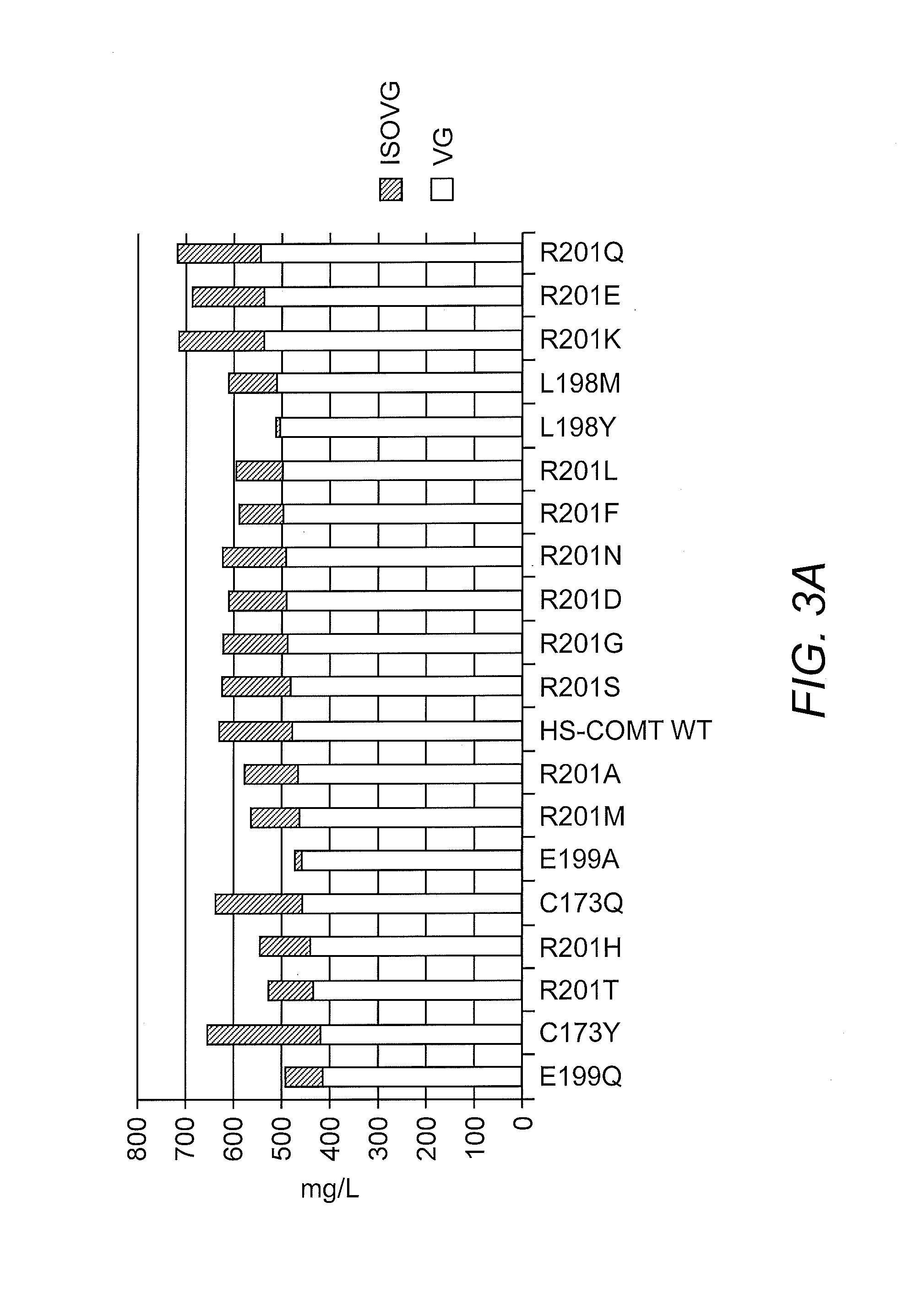
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of vanillan or vanillin beta-d-glucoside
Recombinant microorganisms, plants, and plant cells are disclosed that have been engineered to express a mutant AROM polypeptide and / or mutant catechol-O-methyltransferase polypeptide alone or in combination with one or more vanillin biosynthetic enzymes or UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs). Such microorganisms, plants, or plant cells can produce vanillin or vanillin beta-D-glucoside.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES +1
Methods and organisms for production of b6 vitamers
InactiveUS20050164335A1Biosynthesis of vitamers by an organism can be increasedExcessive levelFungiBacteriaMicroorganismBiological body
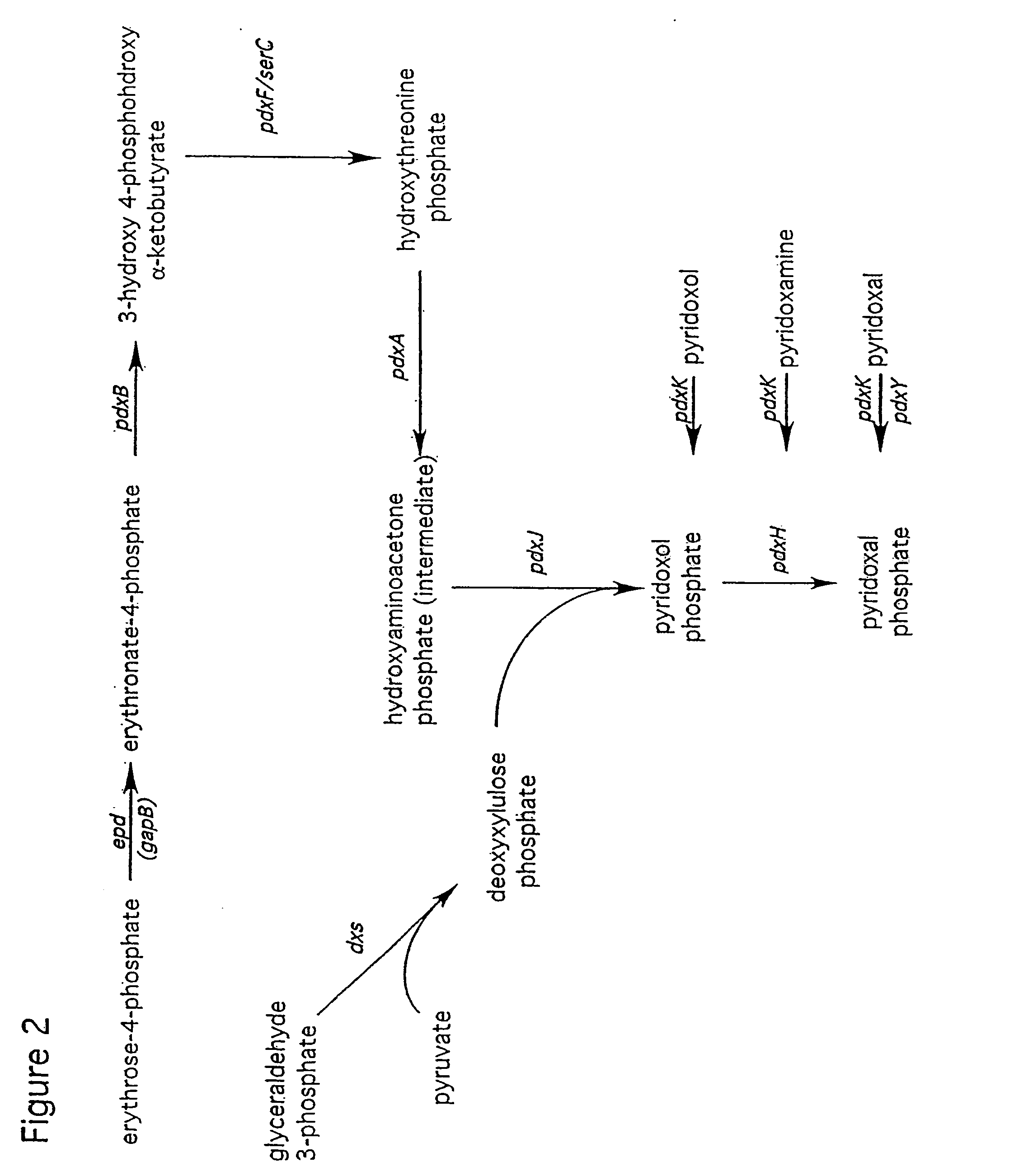
The present invention features methods of producing B6 vitamers that involve culturing an organism overexpressing an enzyme that catalyzes a step in the biosynthesis of a B6 vitamer under conditions such that a B6 vitamer is produced. The present invention further features methods of producing B6 vitamers that involve culturing recombinant microorganisms having increased activity of at least one B6 vitamer biosynthetic enzyme, e.g., YaaD or YaaE, or a homologue thereof, or Epd, PdxA, PdxJ, PdxF, PdxB, PdxH, and / or Dxs, or a homologue thereof.
Owner:OMNIGENE BIOPRODS
Processes for enhanced production of pantothenate
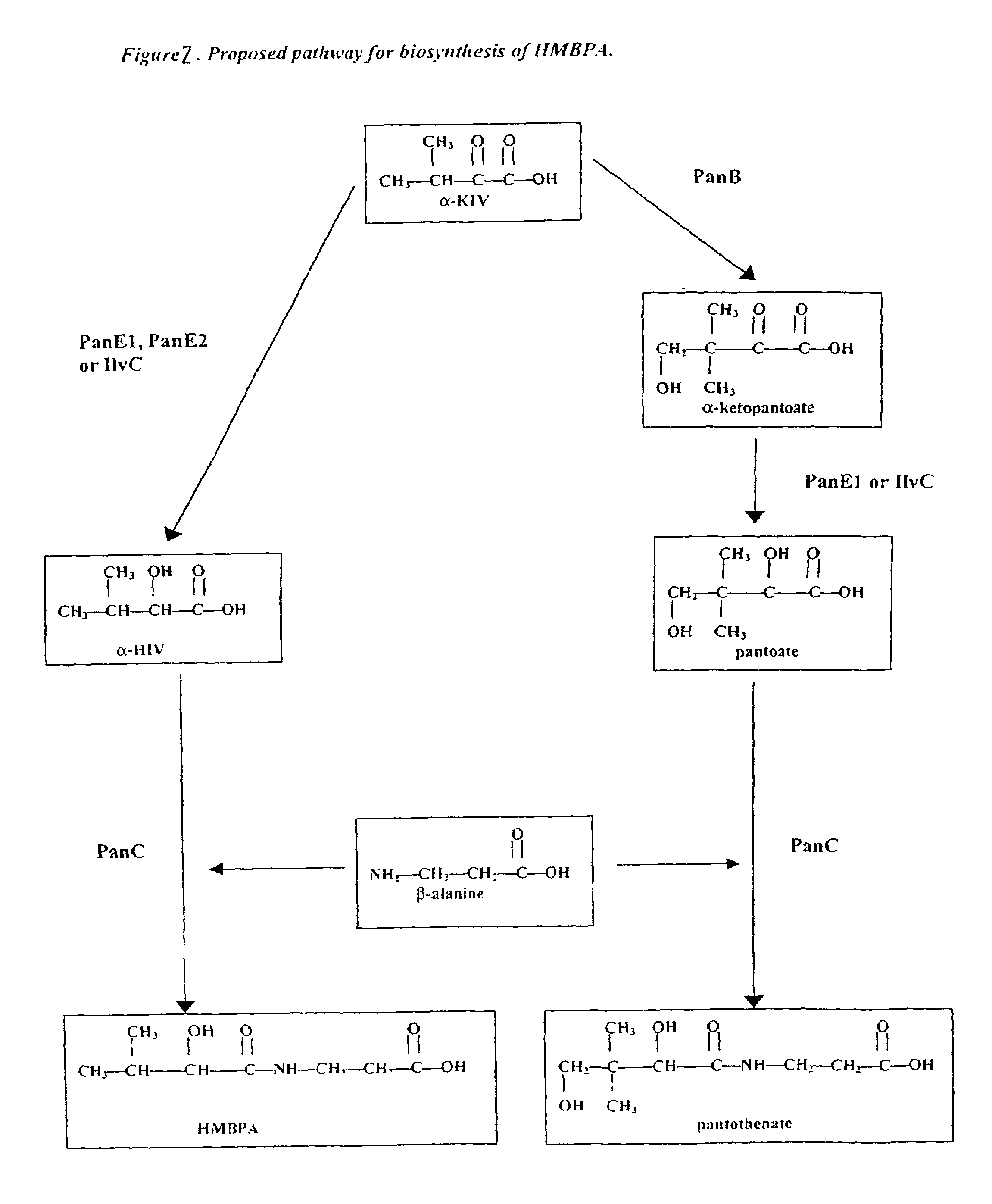
ActiveUS7220561B2Increased pantoateDecrease and eliminate HMBPA biosynthesisOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMicroorganismPantothenic acid
The present invention features improved methods for producing pantoate and pantothenate utilizing microorganisms having modified pantothenate biosynthetic enzyme activities. In particular, the invention features methods for reducing byproduct formation and increasing yields and purity of desired product. Recombinant microorganisms and conditions for culturing same are also are featured. Also featured are compositions produced by such microorganisms.
Owner:BASF AG
Protein having glycoalkaloid biosynthetic enzyme activity and gene encoding the same
ActiveUS20130167271A1Low costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySolanum tuberosum
Disclosed is the provision of a DNA for a glycoalkaloid biosynthetic enzyme in a plant belonging to the family Solanaceae such as potatoes. Also disclosed is a protein having the enzymatic activity of a glycoalkaloid biosynthetic enzyme of a plant belonging to the family Solanaceae such as potatoes and a method for producing and examining a novel organism using a gene encoding this protein.
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
Preparation of allophycocyanin fluorescent protein
InactiveCN101440370ASmall molecular weightSingle ingredientBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFluorescence
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing low molecular weight heparin with high activity
InactiveCN101591401AHigh coagulation activityLow costBlood disorderExtracellular fluid disorderHeparin biosynthesisSulfate
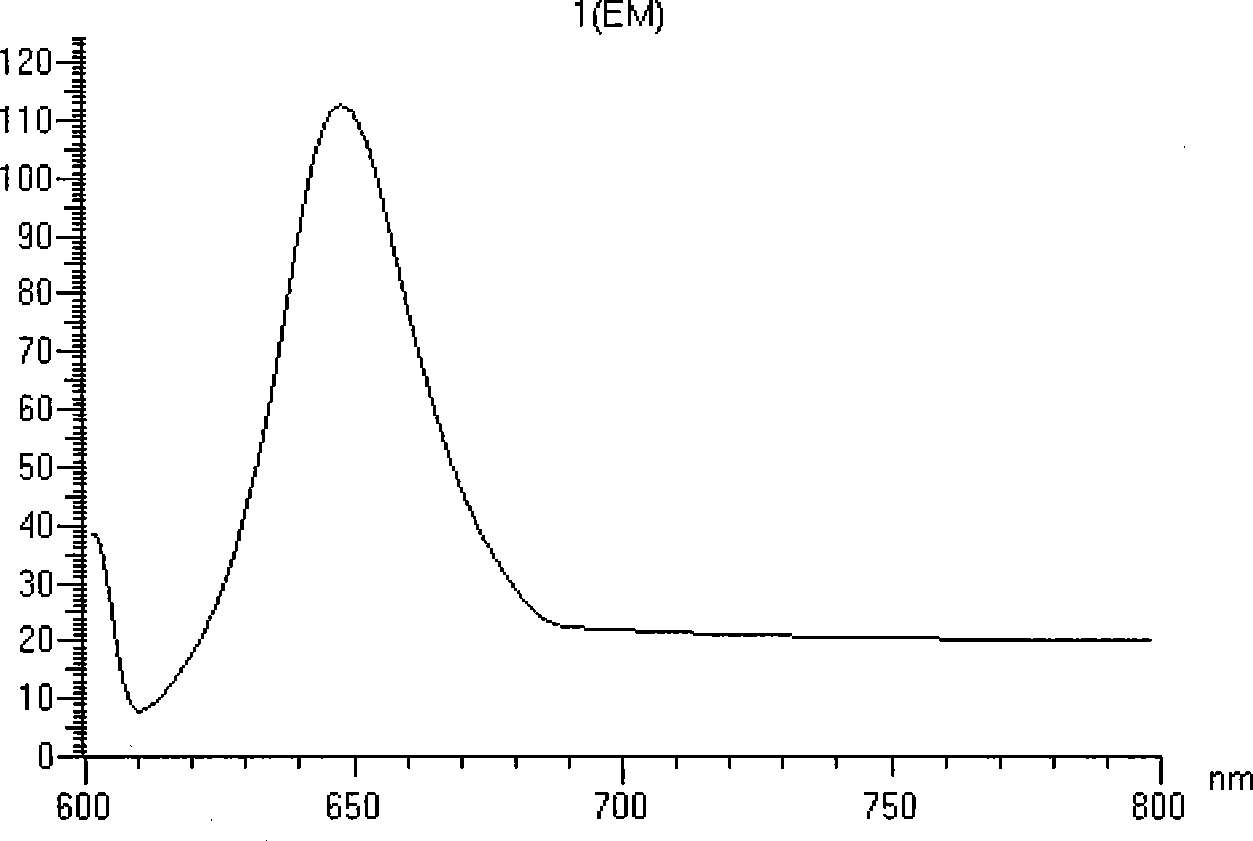
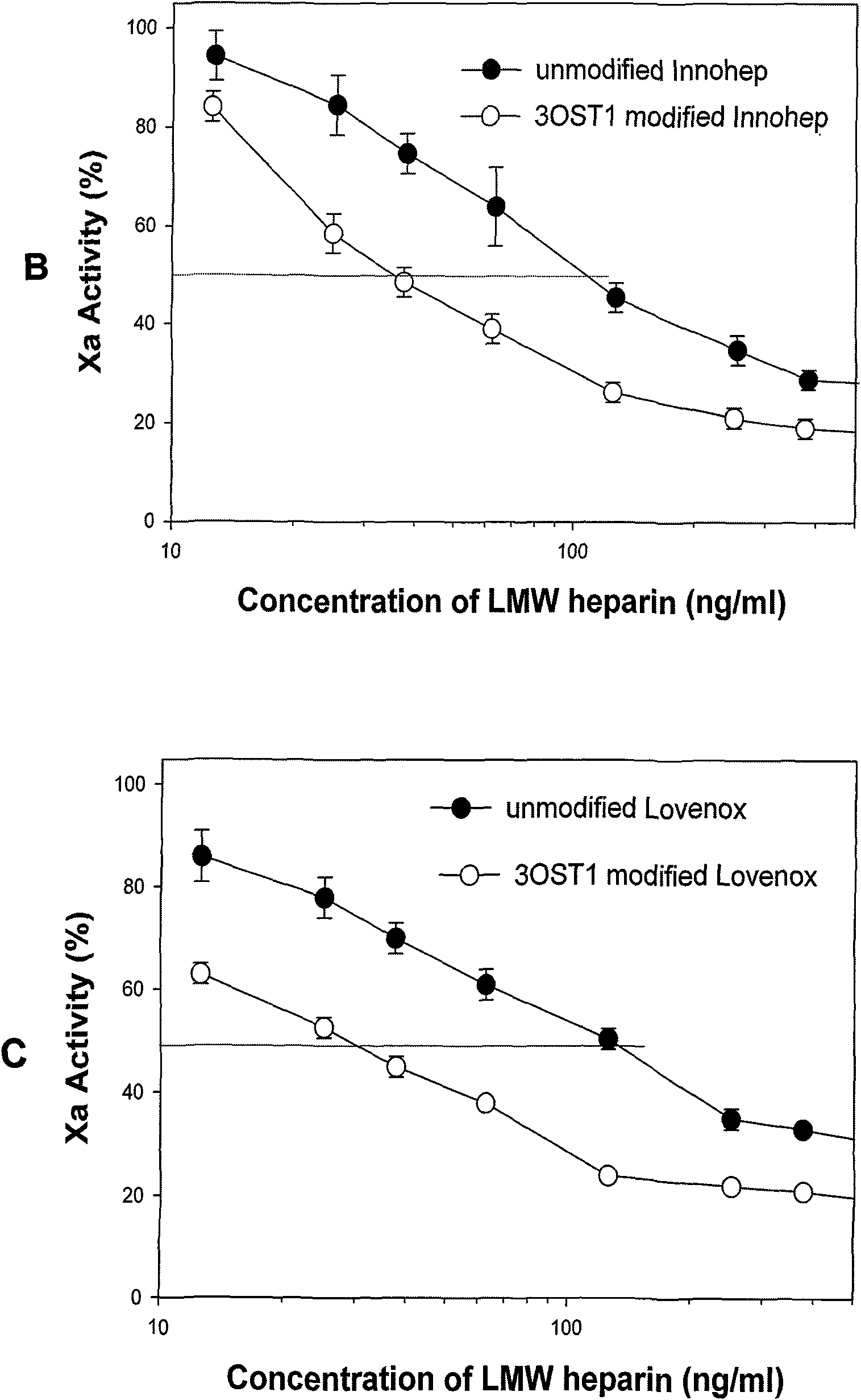
The invention discloses a method for preparing low molecular weight heparin with high activity, which is characterized in that the prior low molecular weight heparin with low anticoagulant activity is used as a substrate, a PAPS (3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphoric acid sulfuric acid) regeneration system is adopted, and a heparin biosynthetic enzyme 3-O-sulfate-transferase is used for modifying the substrate to obtain the low molecular weight heparin with high anticoagulant activity; and the PAPS regeneration system can use extremely cheap PNPS (p-nitryl potassium phenolsulfonate) as an enzyme-modified reactive sulfate donor to further save the cost and make the industrialization possible. The method adopts the 3-O-sulfate-transferase with high enzyme activity to combine with the PAPS regeneration system, performs selective modification on the low molecular weight heparin, and increases the number of anticoagulant activity centers so as to greatly improve the anti-thrombosis activity of the heparin. The method provides a path for the enzymatic industrial production of the low molecular weight heparin with high activity.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
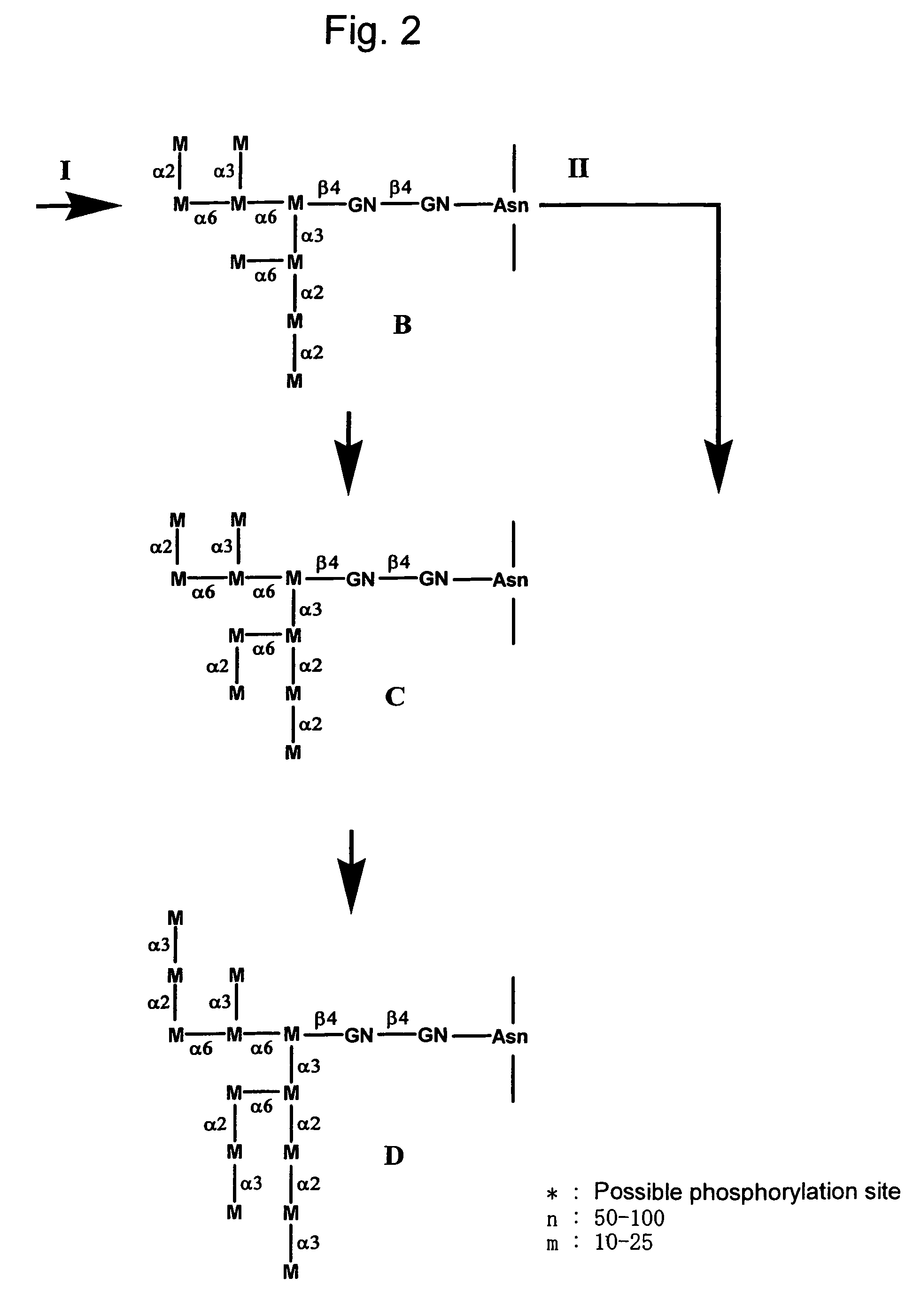
Methylotrophic yeast producing mammalian type sugar chain
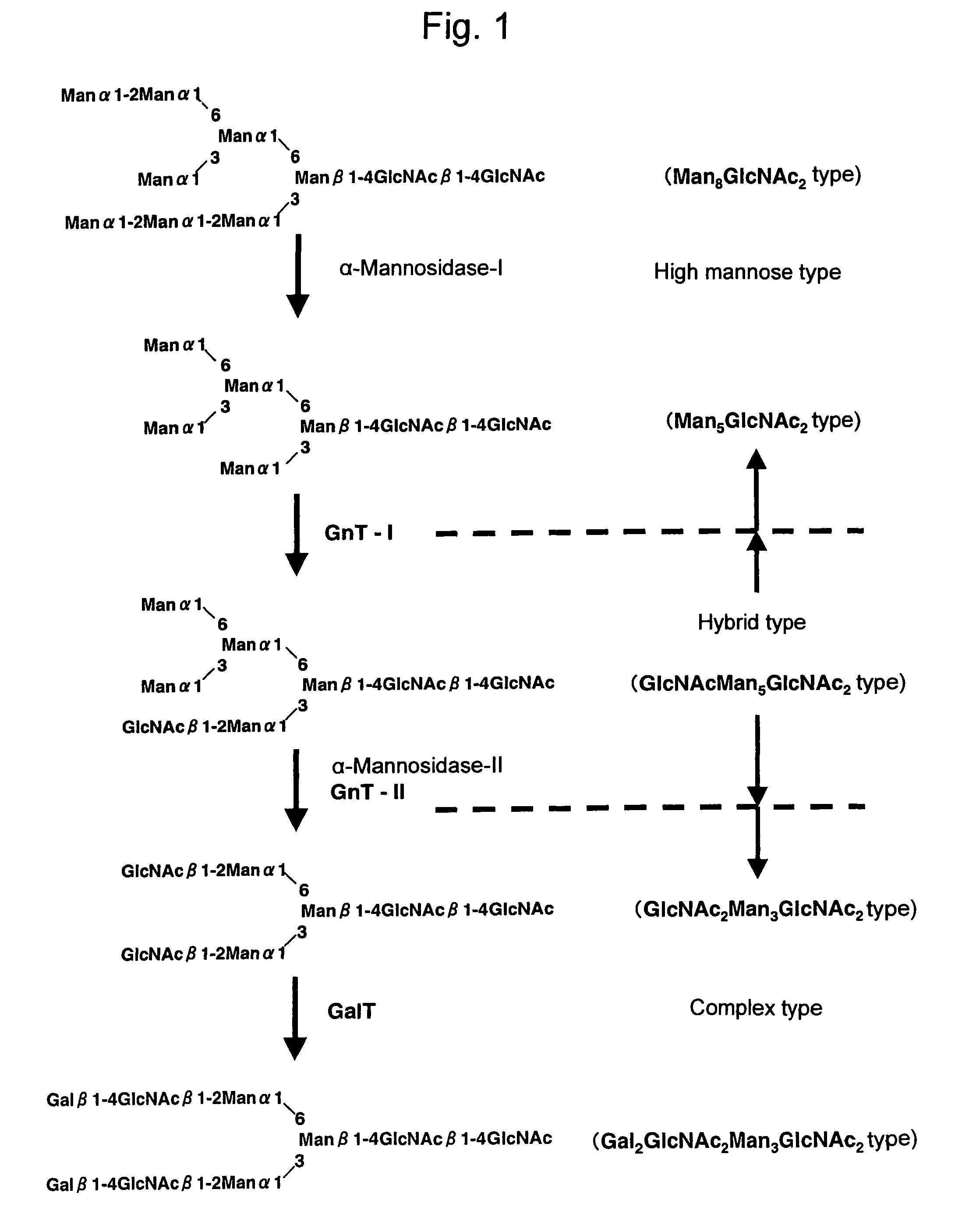
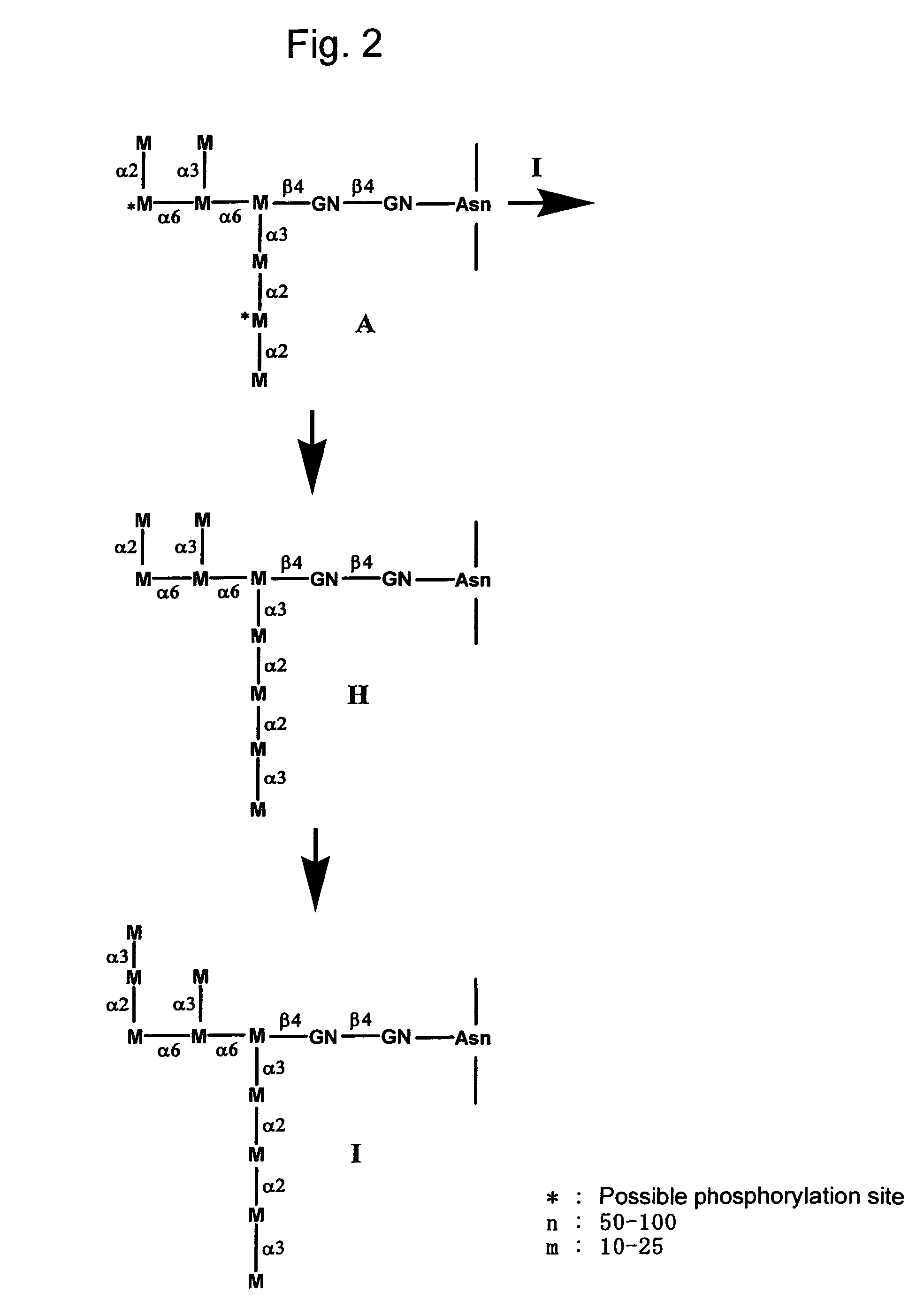
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Genes of strain DC413 encoding enzymes involved in biosynthesis of carotenoid compounds
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
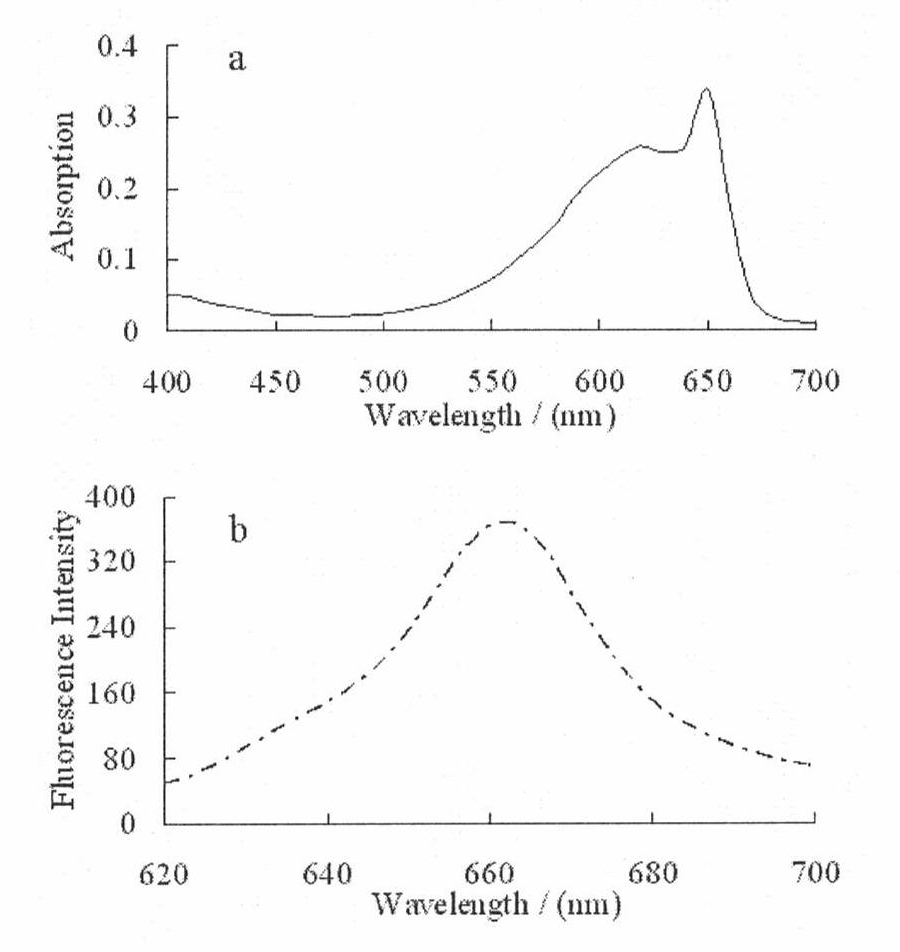
Preparation method of high fluorescence intensity recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer
ActiveCN106916839AAvoid mutual interferenceHigh fluorescence intensityNucleic acid vectorHybrid peptidesEscherichia coliLyase
The present invention belongs to the field of fluorescent proteins in biotechnology, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a high fluorescence intensity recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer. According to the preparation method, a streptavidin gene is linked to an allophycocyanin alpha subunit gene through a linker sequence; on the basis, one or a plurality of allophycocyanin alpha subunit genes are connected in series through linker sequences to form a fusion gene; and the fusion gene, a phycobiliprotein lyase gent and a phycoerythrobilin biosynthetic enzyme gene co-express in Escherichia coli to obtain the recombinant allophycocyanin concatermer with characteristics of biotin binding ability and high fluorescence intensity. According to the present invention, tn the immunofluorescence assay, the recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer can achieve the strong fluorescent signal compared to the recombinant phycobiliprotein monomer; and the prepared recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer can be adopted as the fluorescent marker for immunofluorescence detection in the field of biology and biomedicine.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
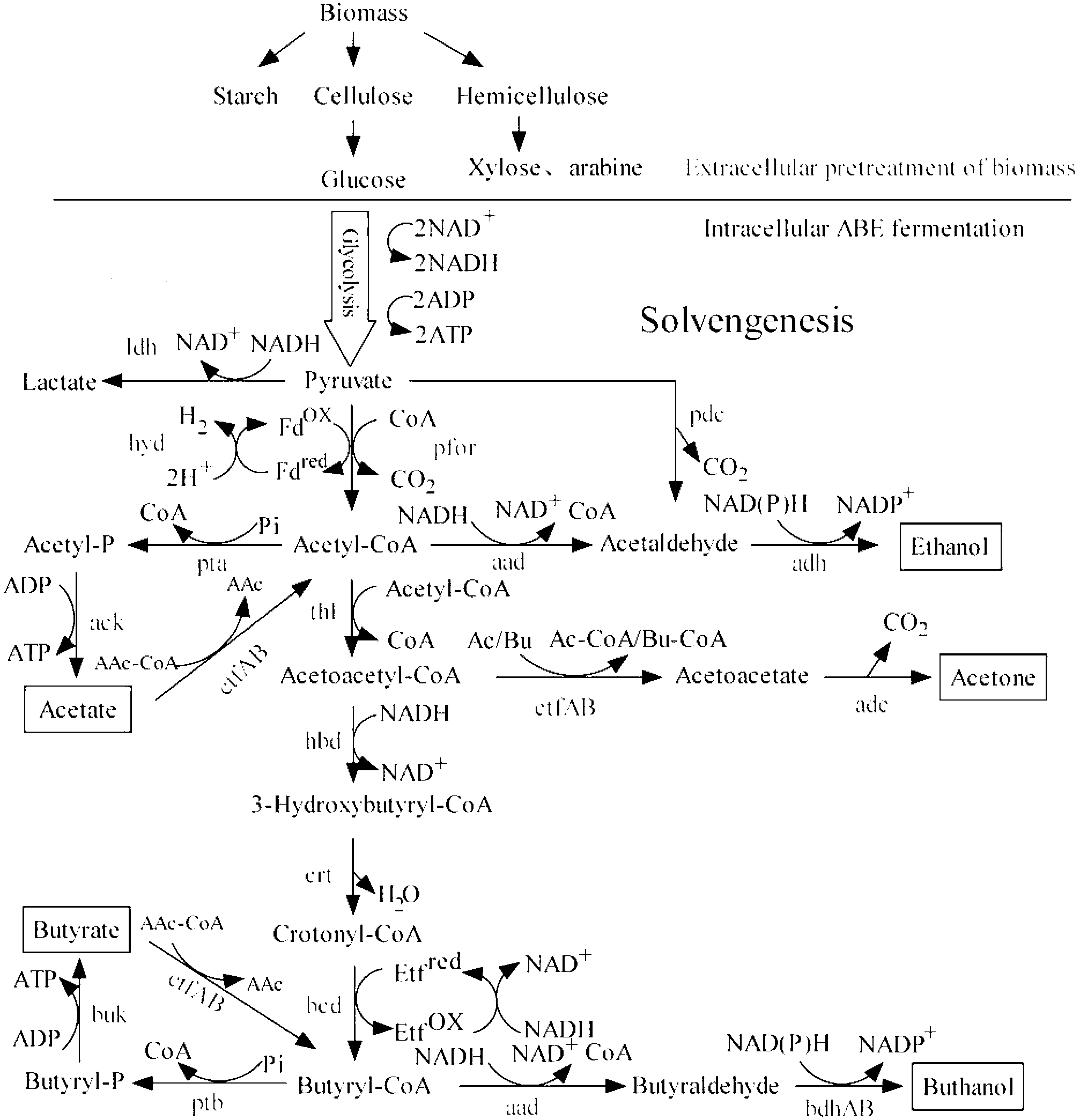
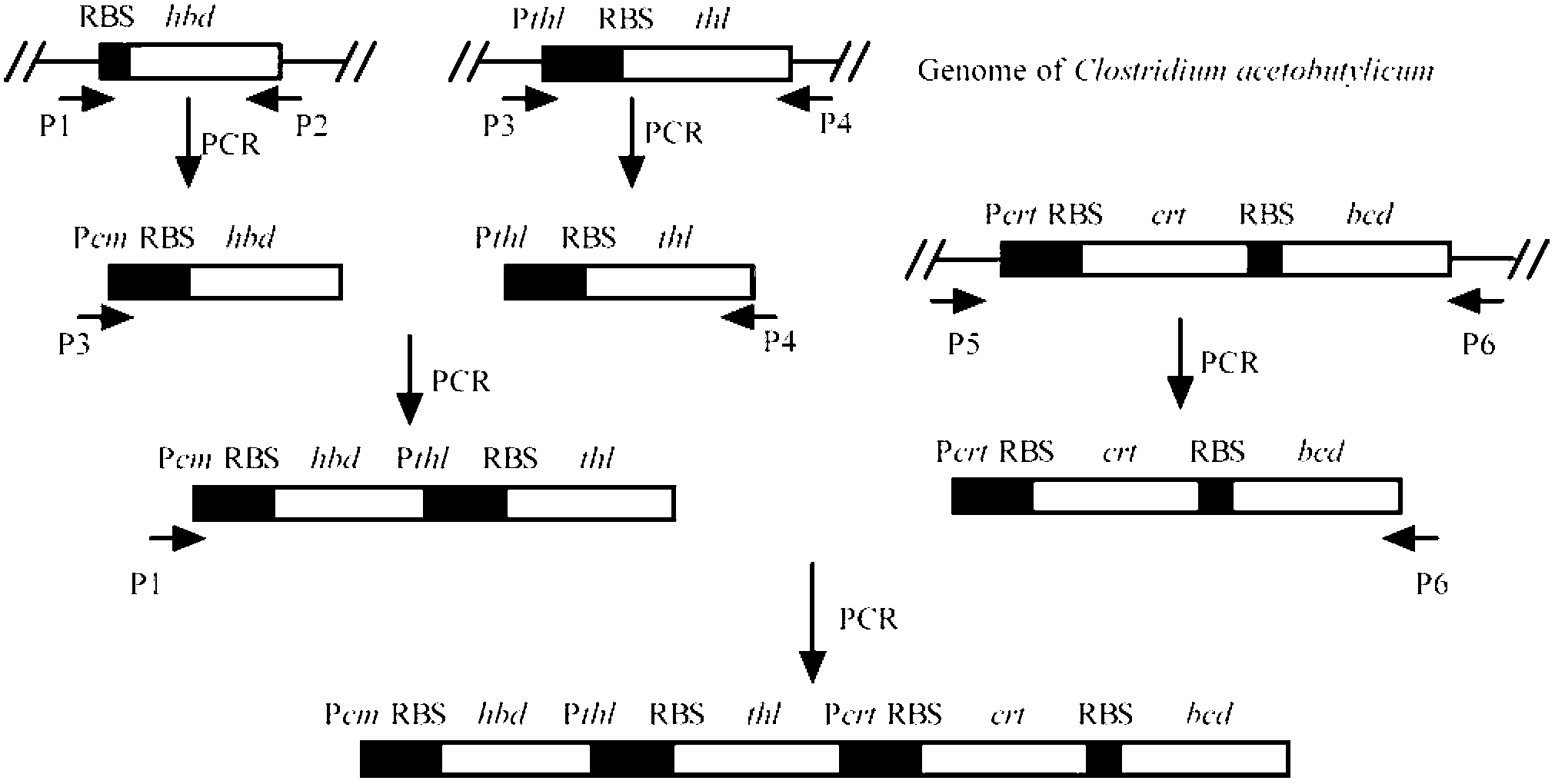
Recombinant strain for high yield of butanol and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102703493AIncrease metabolic strengthIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiosynthetic genesNucleotide
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for the high yield of butanol and a construction method thereof. The construction method is characterized in that an objective segment is connected with an expression vector to obtain a recombination expression plasmid, and then the recombination expression plasmid is transformed to enter clostridium acetobutylicum, thereby obtaining the recombinant strain for the high yield of the butanol; the objective segment is an expression cassette EC, butanol dehydrogenase gene bdh, or a combination of two or three of the expression cassette EC, the butanol dehydrogenase gene bdh or an operon Sol; the nucleotide sequence of the expression cassette EC is shown in SEQ ID NO.11; the nucleotide sequence of the operon Sol is shown in SEQ ID NO.16; and the nucleotide sequence of the butanol dehydrogenase gene bdh is shown in SEQ ID NO.20. The recombinant strain provided by the invention can be used for expressing butanol biosynthetic enzymes coded by butanol producing strain butanol biosynthetic genes, thereby enabling the activity of the butanol biosynthetic enzymes and the metabolism degree of the strain to be increased; and the yield and conversion rate of the butanol can be further increased so that the industrial production of the butanol is facilitated.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and Method For the Heterologous Expression of Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters
ActiveUS20100184038A1Sufficient quantityEfficient productionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousEscherichia coli
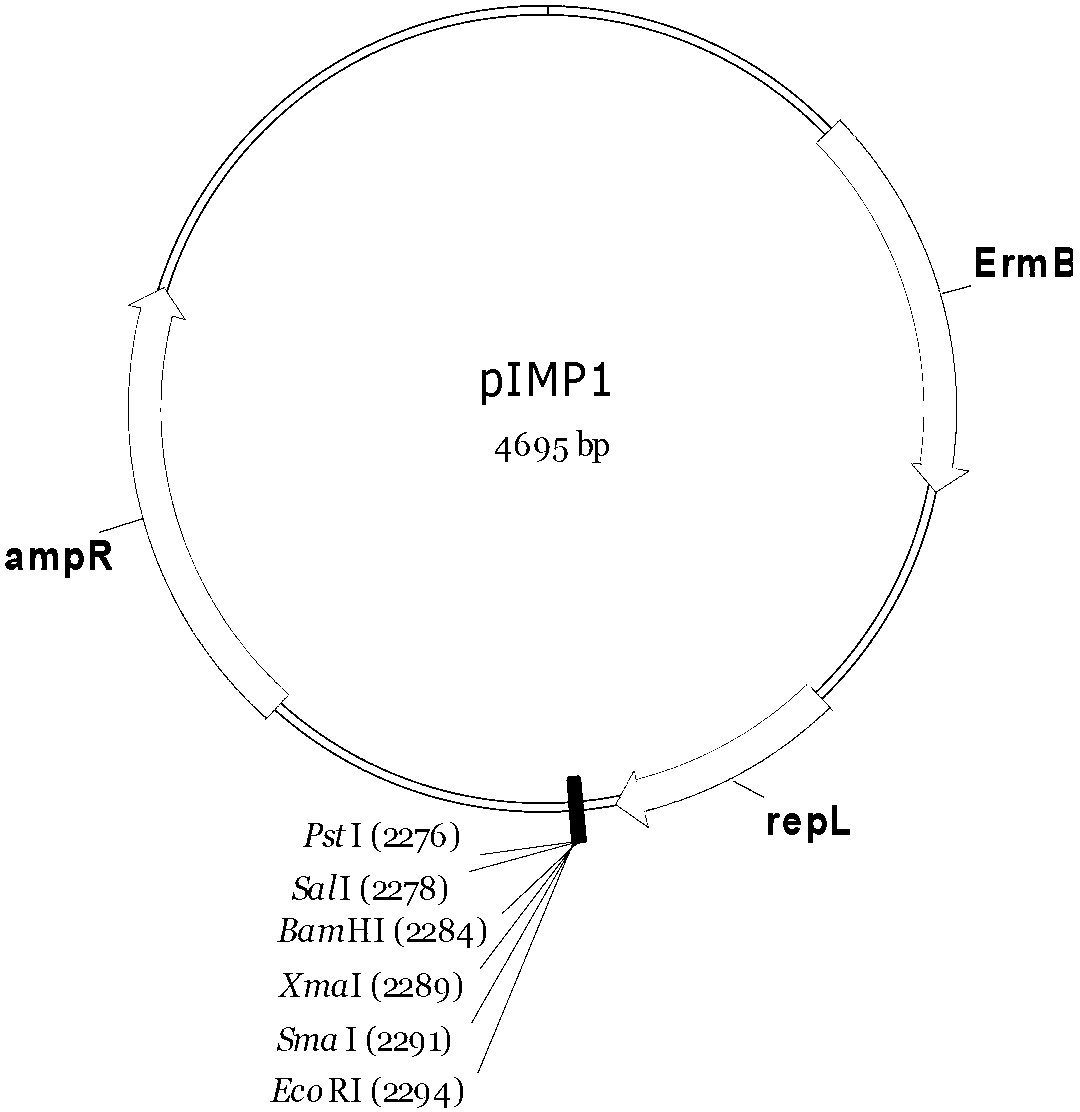
A system and method for heterologous expression of polyketide biosynthetic pathways from streptomycetes hosts in Escherichia coli for the production and discovery of secondary metabolites. Genomic DNA from Streptomyces rimosus encoding the oxytetracycline biosynthetic pathway is inserted into the genome of the surrogate host Myxococcus xanthus. The M. xanthus transcriptional machinery recognizes and uses the streptomycetes promoter regions to express the biosynthetic enzymes. Co-expression in E. coli of S. rimosus oxytetracycline biosythensis enzymes and M. xanthus σ54, a key piece of the M. xanthus transcriptional machinery, enables E. coli to recognize and use the promoters from the S. rimosus oxytetracycline biosynthetic pathway, facilitating production of oxytetracycline.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Recombinant production of steviol glycosides
PendingCN105671108ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismUdp glycosyltransferase
Recombinant microorganisms, plants, and plant cells are disclosed that have been engineered to express novel recombinant genes encoding steviol biosynthetic enzymes and UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs). Such microorganisms, plants, or plant cells can produce steviol or steviol glycosides, e.g., rubusoside or Rebaudioside A, which can be used as natural sweeteners in food products and dietary supplements.
Owner:沃维公司
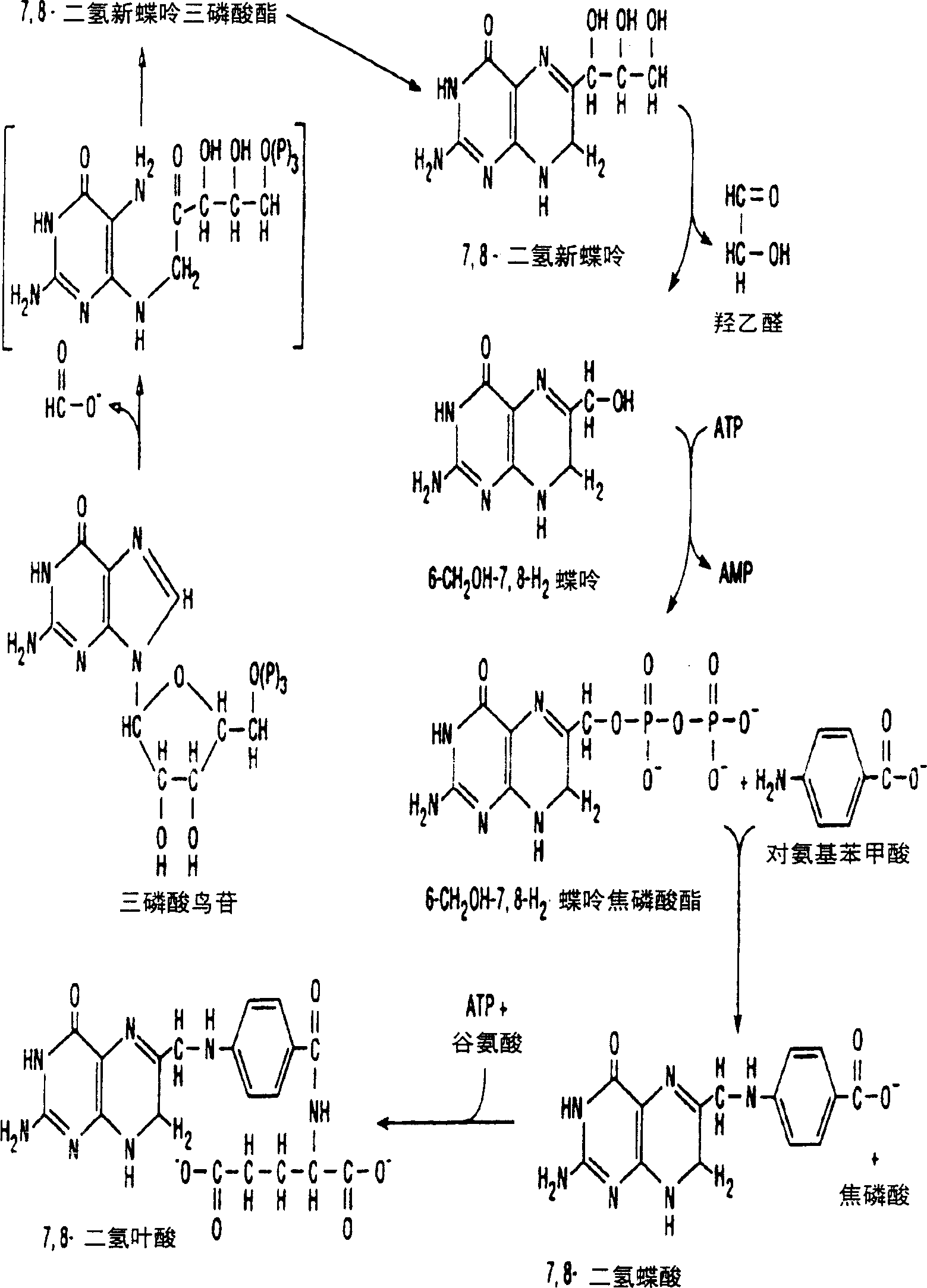
Production of bioarailable folic acid
InactiveCN1513056APromote secretionOrganic active ingredientsFood genetic modificationHeterologousMicroorganism
The invention provides a process of producing bio-available folate, i.e. folic acid having an increased proportion of monoglutamyl folate and a decreased proportion of polyglutamyl folate, by culturing micro-organisms containing an active heterologous or homologous polyglutamyl hydrolase activity or containing increased activities of folate biosynthesis enzymes. The genes encoding the polyglutamyl hydrolase and the folate biosynthesis enzymes may be of various origin, e.g. from rodents or other mammals including man. Also provided is a foodstuff, especially a dairy product containing such monoglutamyl folate-producing micro-organisms.
Owner:CAMPINA BV
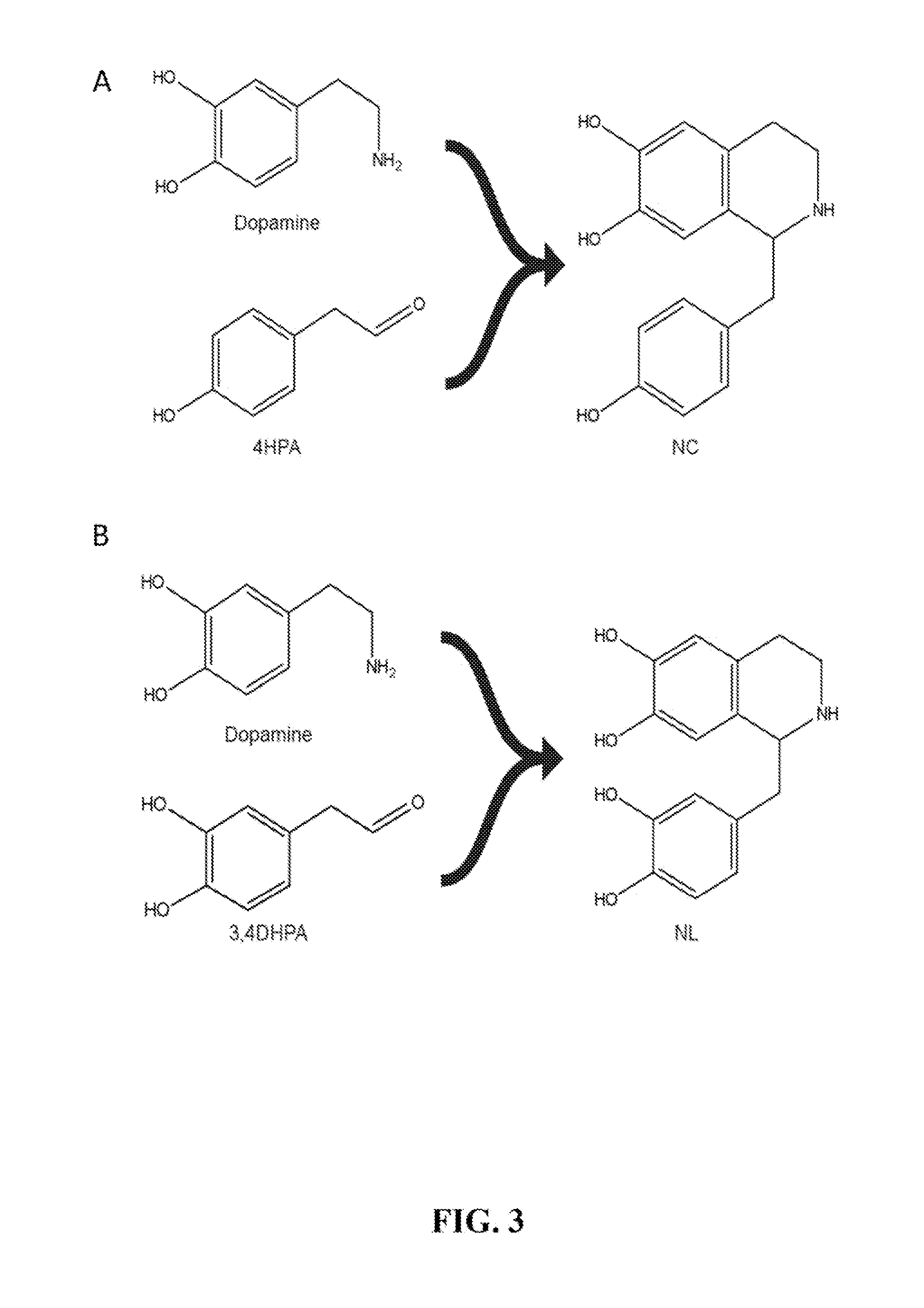
Benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) precursor producing microbes, and methods of making and using the same
Host cells that are engineered to produce benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIAs) precursors, such as norcoclaurine (NC) and norlaudanosoline (NL), are provided. The host cells may have one or more engineered modifications selected from: a feedback inhibition alleviating mutation in a enzyme gene; a transcriptional modulation modification of a biosynthetic enzyme gene; an inactivating mutation in an enzyme; and a heterologous coding sequence. Also provided are methods of producing a BIA of interest or a precursor thereof using the host cells and compositions, e.g., kits, systems etc., that find use in methods of the invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
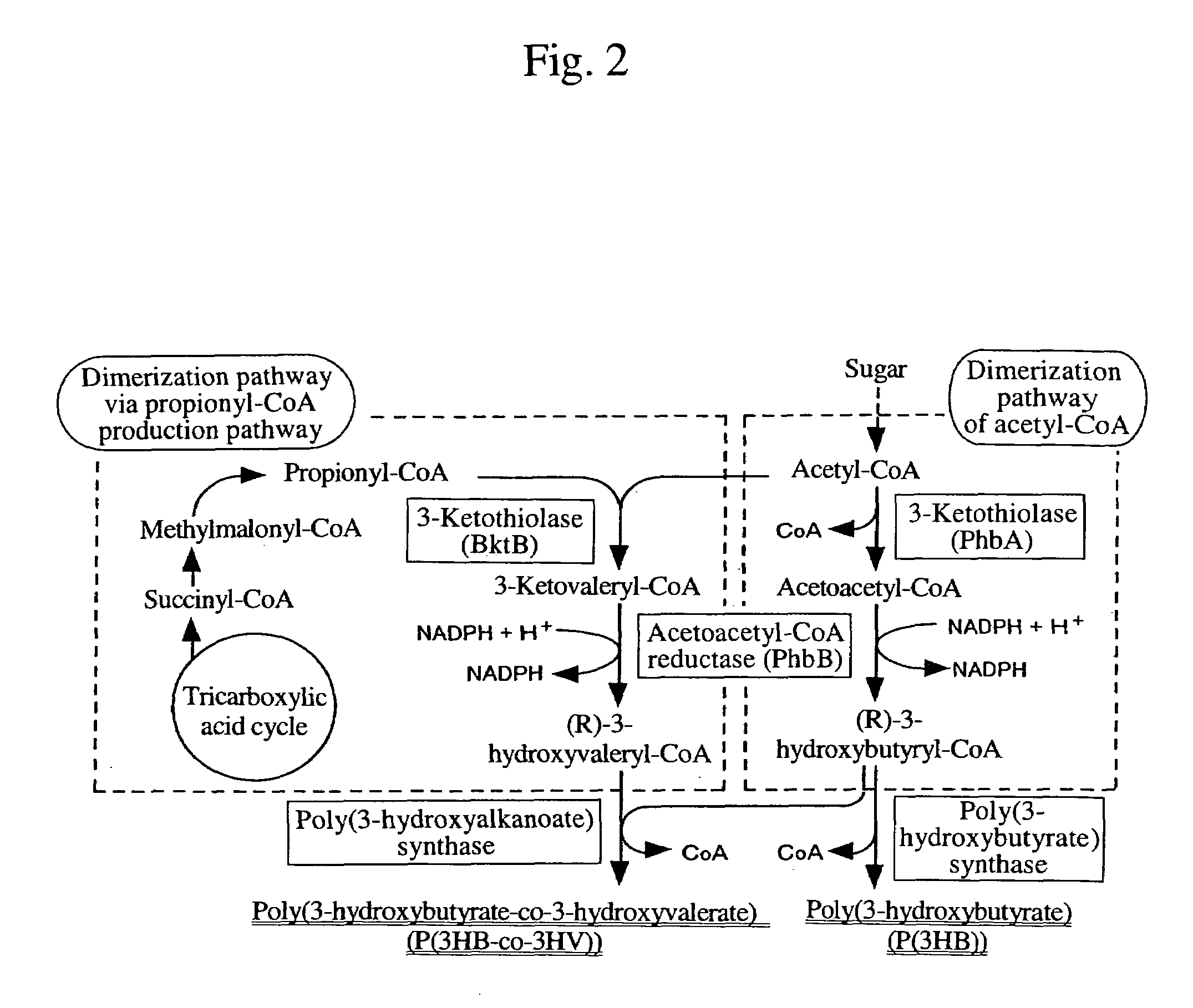
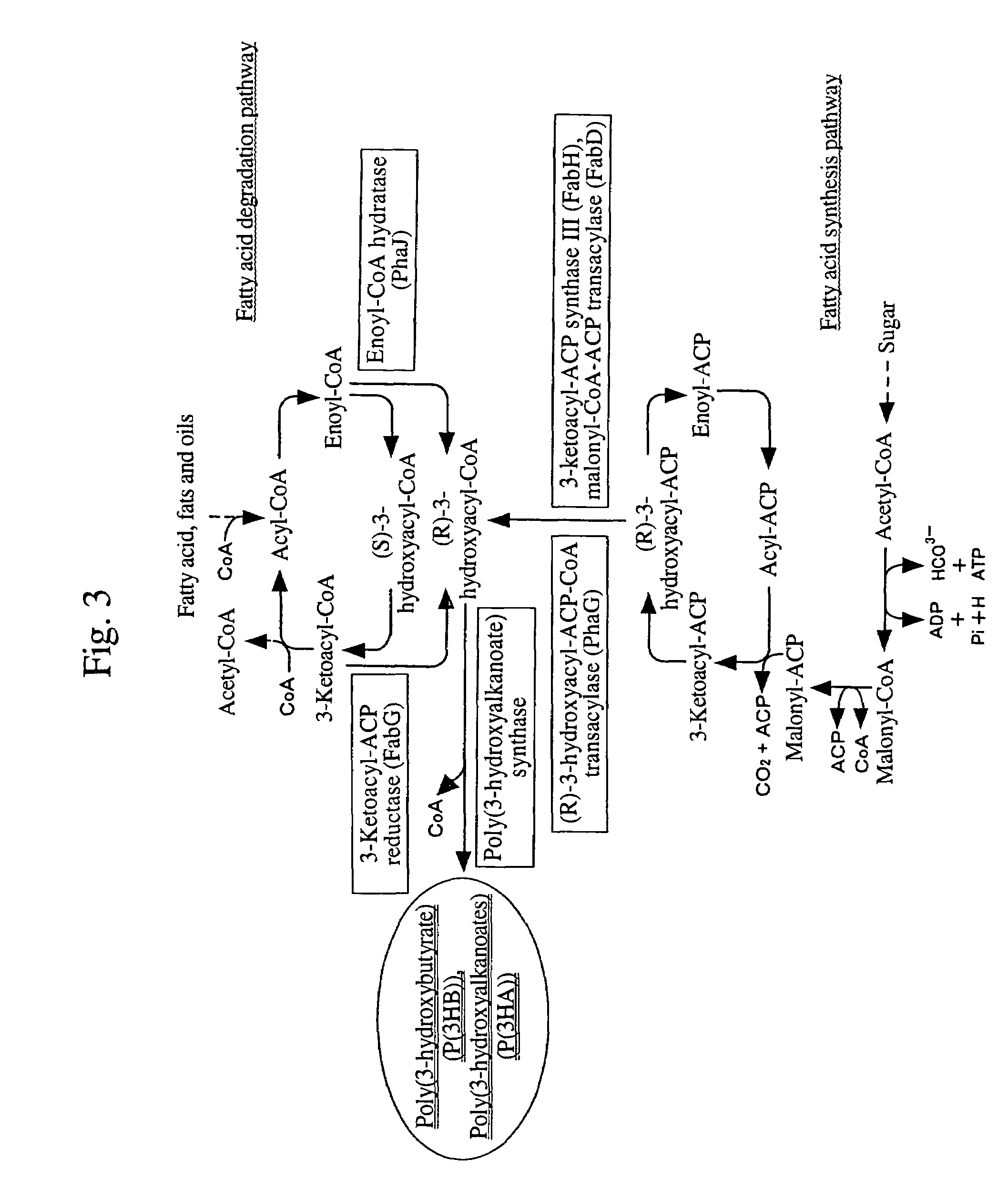
Process for producing biodegradable polyester
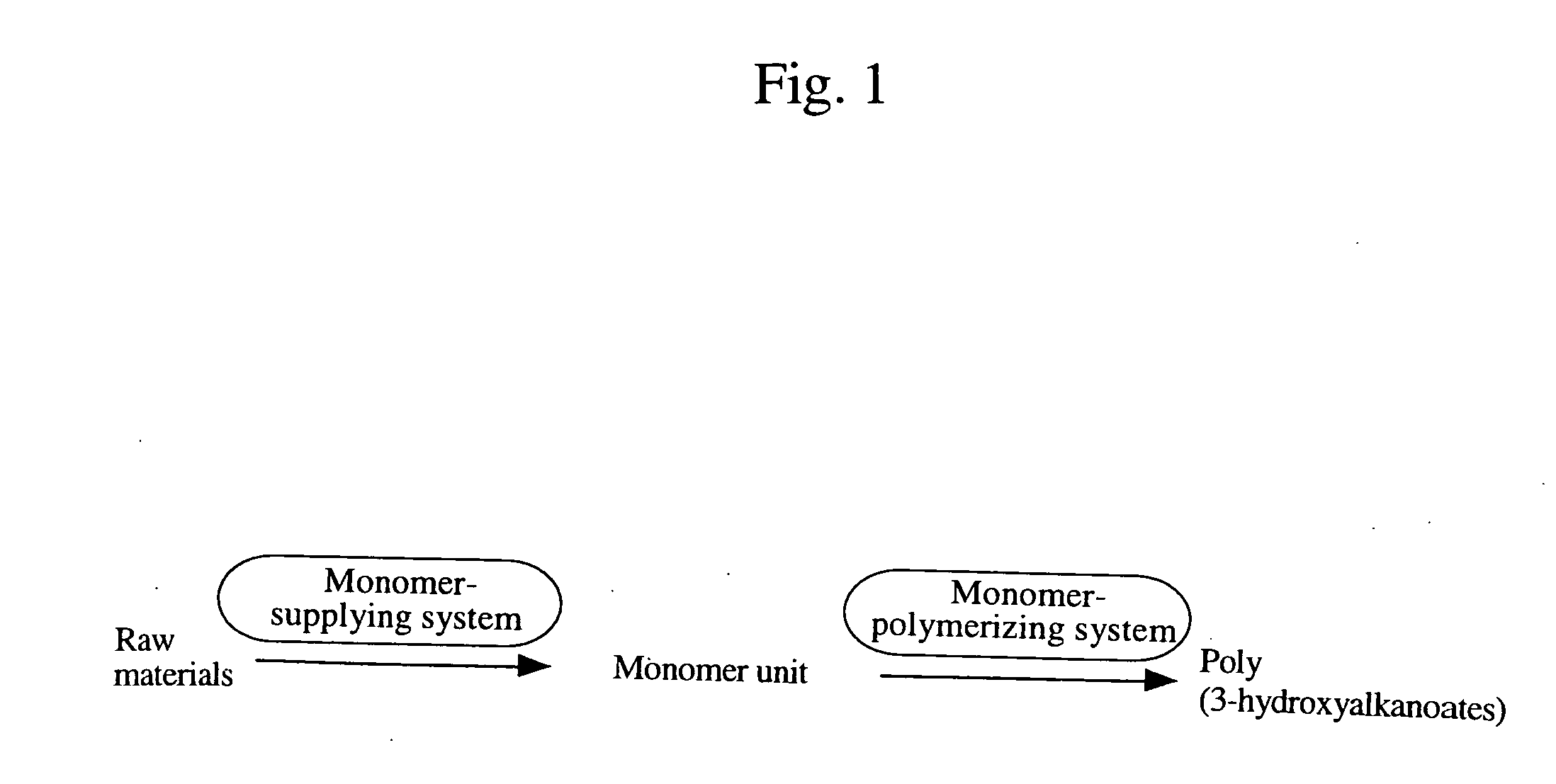
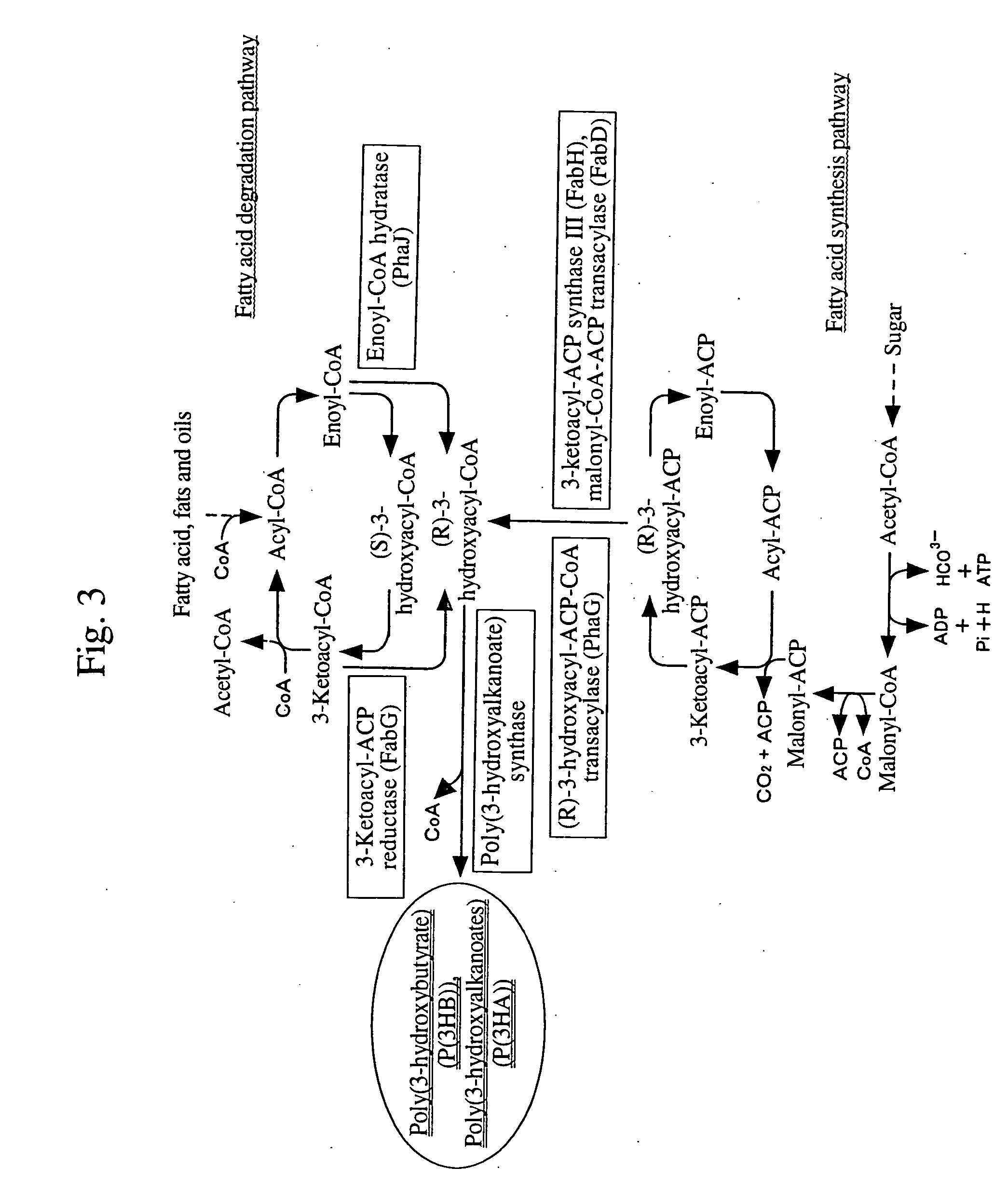
There is provided a method for producing a biodegradable polyester capable of controlling various physical properties of the biodegradable polyester. A poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate) biosynthetic enzyme is altered by an evolutionary-engineering technique, and the poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate) biosynthetic enzyme is expressed in a host to synthesize various copolymers in the host.
Owner:RIKEN
Plant amino acid biosynthetic enzymes
An isolated polynucleotide encoding a plant cysteine synthase is disclosed. Also disclosed is the construction of a recombinant construct comprising all or part of a coding or non-coding region of the isolated polynucleotide for use in co-suppression or antisense suppression of endogenous nculeic acid sequences encoding polypeptides having cysteine synthase activity. In another aspect, use of this construct to alter levels of cysteine synthase in a plant is disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for preparing fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles with streptavidin combination function
InactiveCN102010872AGood water solubilitySmall side effectsInorganic material magnetismAlgae/lichens peptidesEscherichia coliFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano materials and particularly relates to a method for preparing fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles with streptavidin combination function. The method comprises the following specific steps of: respectively connecting a Strep II label gene to N ends of alpha and beta sub-gene apoprotein genes to obtain Strep II-apcA and Strep II-apcB gene segments; embedding the Strep II-apcA gene segment to the downstream of a 6*His gene, and cloning to one expression vector together with a phycobilin biosynthetic enzyme gene; embedding the Strep II-apcB gene segment to the downstream of the 6*his gene, cloning to another vector together with a chromphore lyase gene, simultaneously converting the two expression vectors into escherichia coli, screening engineering bacteria, separating and purifying the engineering bacteria by protein, and oscillating and mixing the purified double-label recombinant APC fluorescent protein and zinc ion modified superparamagnetism silicon shell nanoparticles to obtain the fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles with the streptavidin combination function. The obtained double-label recombinant protein can biologically combine streptavidin without being modified chemically.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of vanillan or vanillin beta-D-glucoside
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES +1
Method for production of an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20100184162A1Improve productivityHigh yieldFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismDNA fragmentation
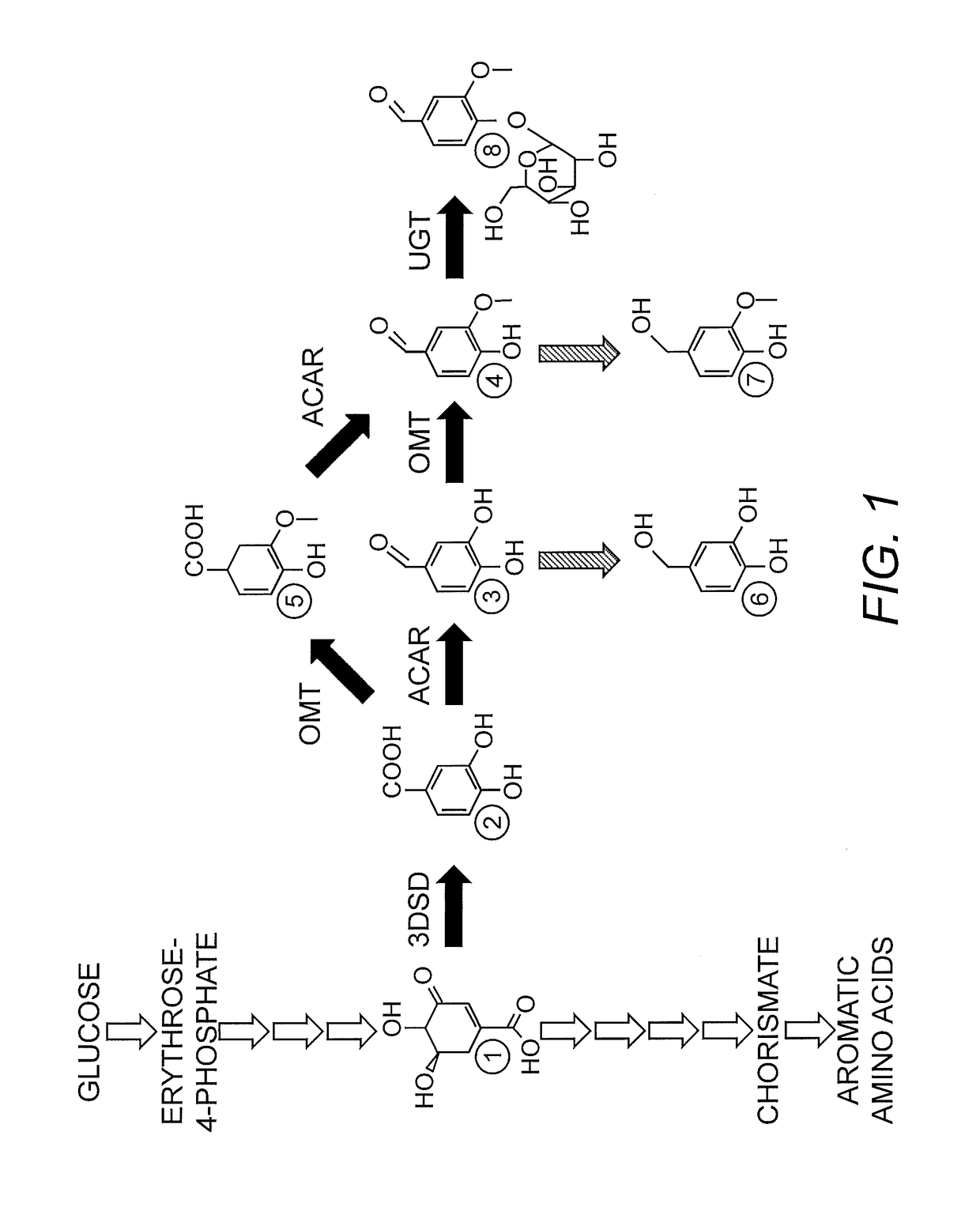
A method is provided for producing an L-amino acid by culturing a microorganism belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family and having the ability to produce an L-amino acid, in a medium to produce and accumulate the L-amino acid in the medium. The microorganism has been modified by introduction of a DNA fragment which includes a pho regulon promoter and a structural gene encoding an L-amino acid biosynthetic enzyme, which is ligated downstream of the promoter so that the gene is expressed by the promoter, and so that the activity of the L-amino acid biosynthetic enzyme is increased by the expression of the gene by the promoter. In this way, the L-amino acid that is produced in the medium can be collected. Furthermore, the phosphorus concentration in the medium is such that the expression of the gene by the promoter is induced.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloid (BIA) Precursor Producing Microbes, and Methods of Making and Using the Same
Host cells that are engineered to produce benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIAs) precursors, such as norcodaurine (NC) and norlaudanosoline (NL), are provided. The host cells may have one or more engineered modifications selected from: a feedback inhibition alleviating mutation in a enzyme gene; a transcriptional modulation modification of a biosynthetic enzyme gene; an inactivating mutation in an enzyme; and a heterologous coding sequence. Also provided are methods of producing a BIA of interest or a precursor thereof using the host cells and compositions, e.g., kits, systems etc., that find use in methods of the invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
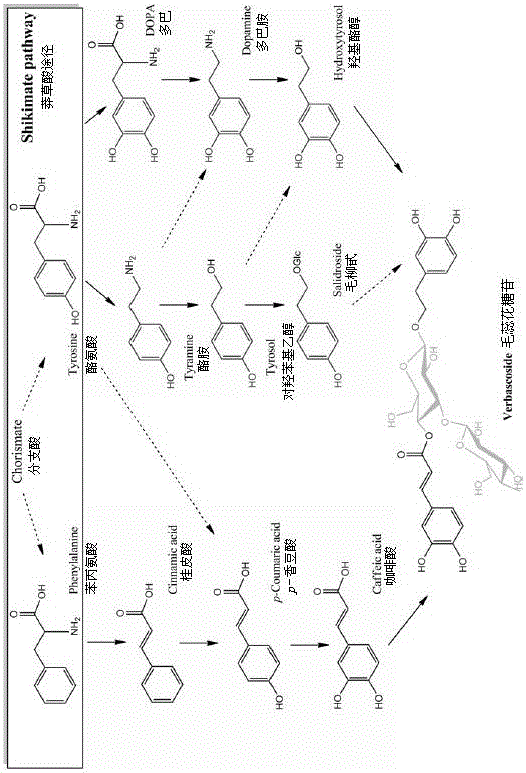
Verbascoside biosynthesis pathway and verbascoside biosynthesis enzyme related genes
InactiveCN106498009AIncreased glycoside contentIncrease contentOxidoreductasesLigasesTotal rnaMetabolism pathway
The invention discloses a verbascoside biosynthesis pathway and verbascoside biosynthesis enzyme related genes. Tuberous roots of rehmannia at six different development stages serve as materials, overall RNA (ribonucleic acid) is extracted and detected, combined transcriptome sequencing is performed by an Illumina HiSeq2500 platform to obtain 149.8 million reads, and head assembly is performed to obtain 96961 Unigenes sequences. The Unigenes sequences are compared with a KEGG (Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes) database to perform metabolism pathway analysis and obtain 280 KEGG pathways, a metabolism pathway is compared with a supposed verbascoside biosynthesis pathway, and 5 candidate KEGG pathways are screened. The supposed verbascoside biosynthesis pathway is compared with the screened 5 candidate KEGG pathways, 19 gene coding enzyme catalysis verbascoside biosynthesis pathways are built, the Unigenes sequences and the database are subjected to Blast X comparison, and ESTscan software functions are added to obtain 13 candidate verbascoside biosynthesis enzyme related genes. A foundation is laid for illuminating the complete verbascoside biosynthesis pathway and producing verbascoside by secondary metabolism engineering or synthetic biology.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com