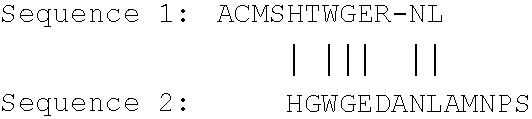Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Regulon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular genetics, a regulon is a group of genes that are regulated as a unit, generally controlled by the same regulatory gene that expresses a protein acting as a repressor or activator. This terminology is generally, although not exclusively, used in reference to prokaryotes, whose genomes are often organized into operons; the genes contained within a regulon are usually organized into more than one operon at disparate locations on the chromosome. Applied to eukaryotes, the term refers to any group of non-contiguous genes controlled by the same regulatory gene.
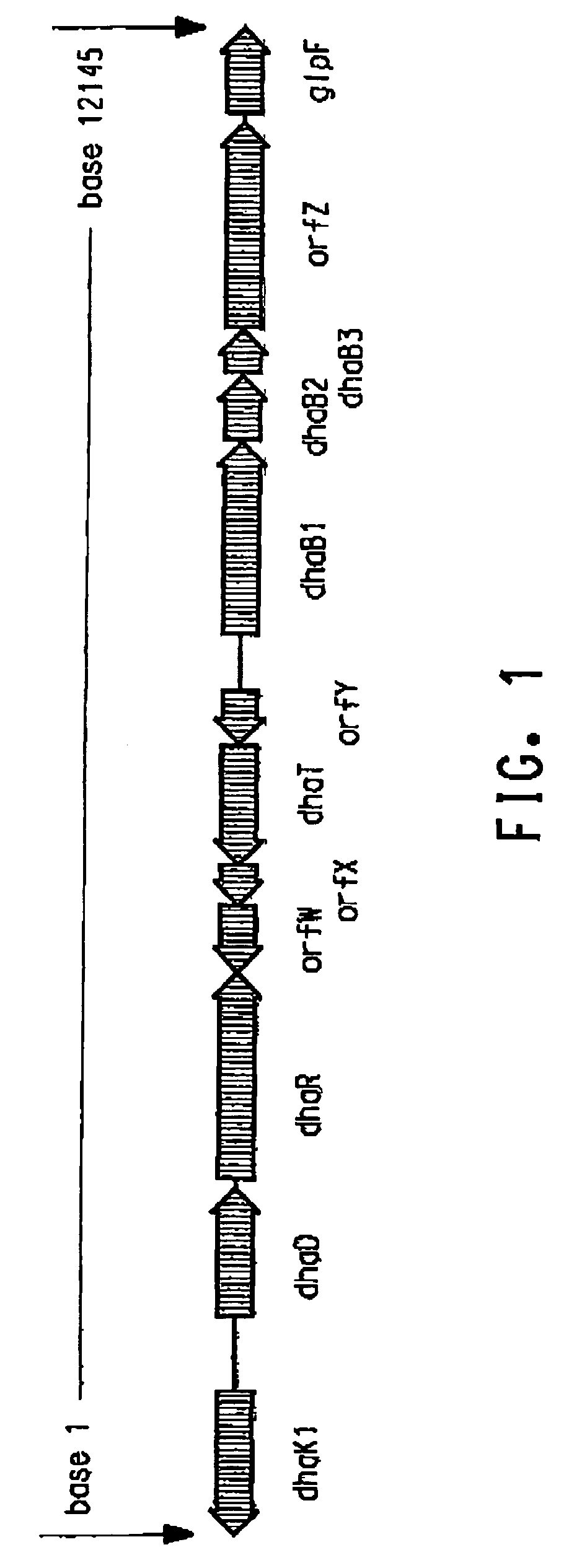
Process for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol with high titer
The present invention provides an improved method for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol from a fermentable carbon source in a single microorganism. In one aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the conversion of glucose to 1,3-propanediol is achieved by the use of an E. coli transformed with the Klebsiella pneumoniae dha regulon genes dhaR, orfY, dhaT, orfX, orfW, dhaB1, dhaB2, dhaB3, and orfZ, all these genes arranged in the same genetic organization as found in wild type Klebsiella pneumoniae. In another aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the production of 1,3-propanediol from glucose using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, and a dehydratase reactivation factor compared to an identical process using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, a dehydratase reactivation factor and a 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase (dhaT). The dramatically improved process relies on the presence in E. coli of a gene encoding a non-specific catalytic activity sufficient to convert 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde to 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
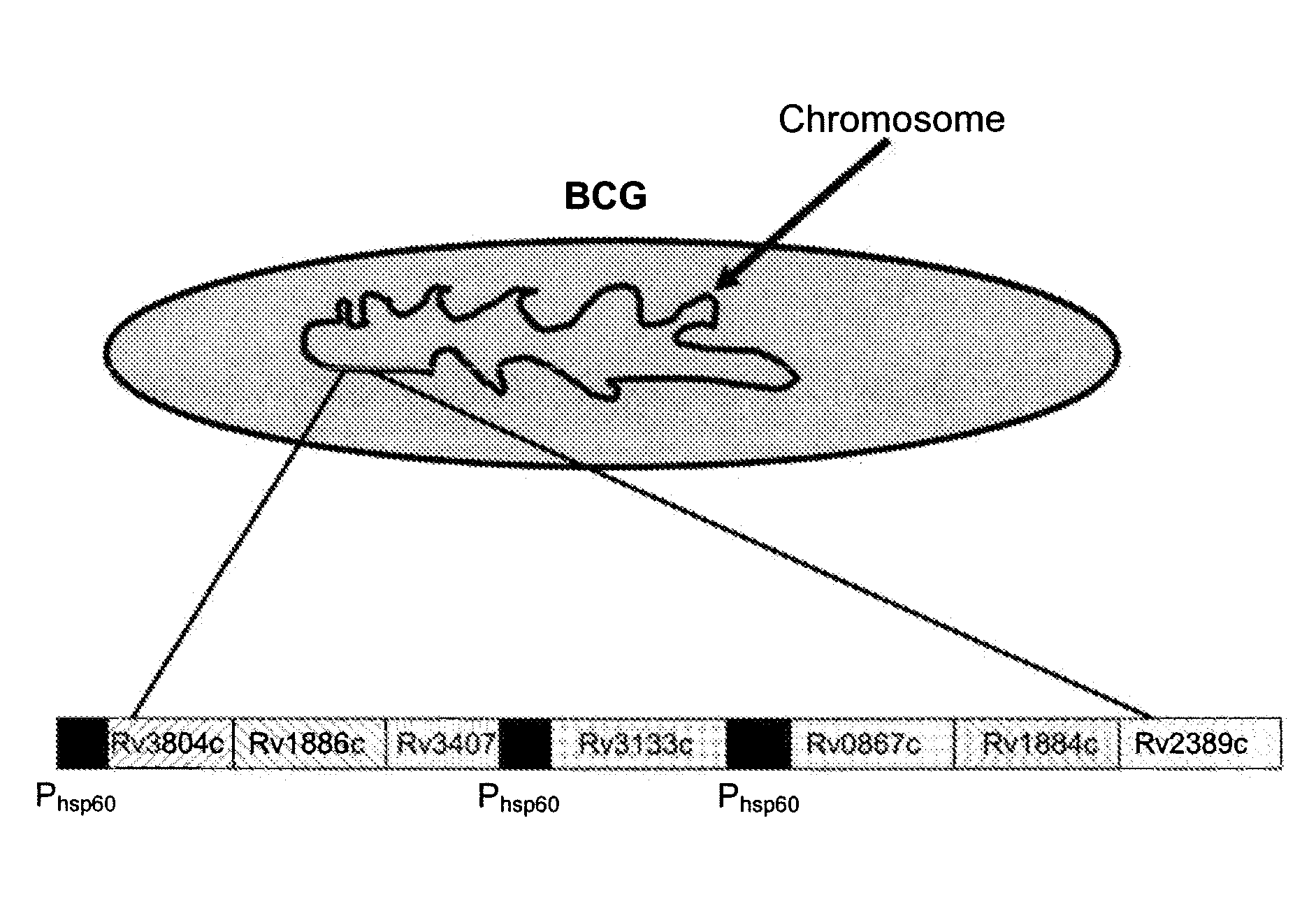
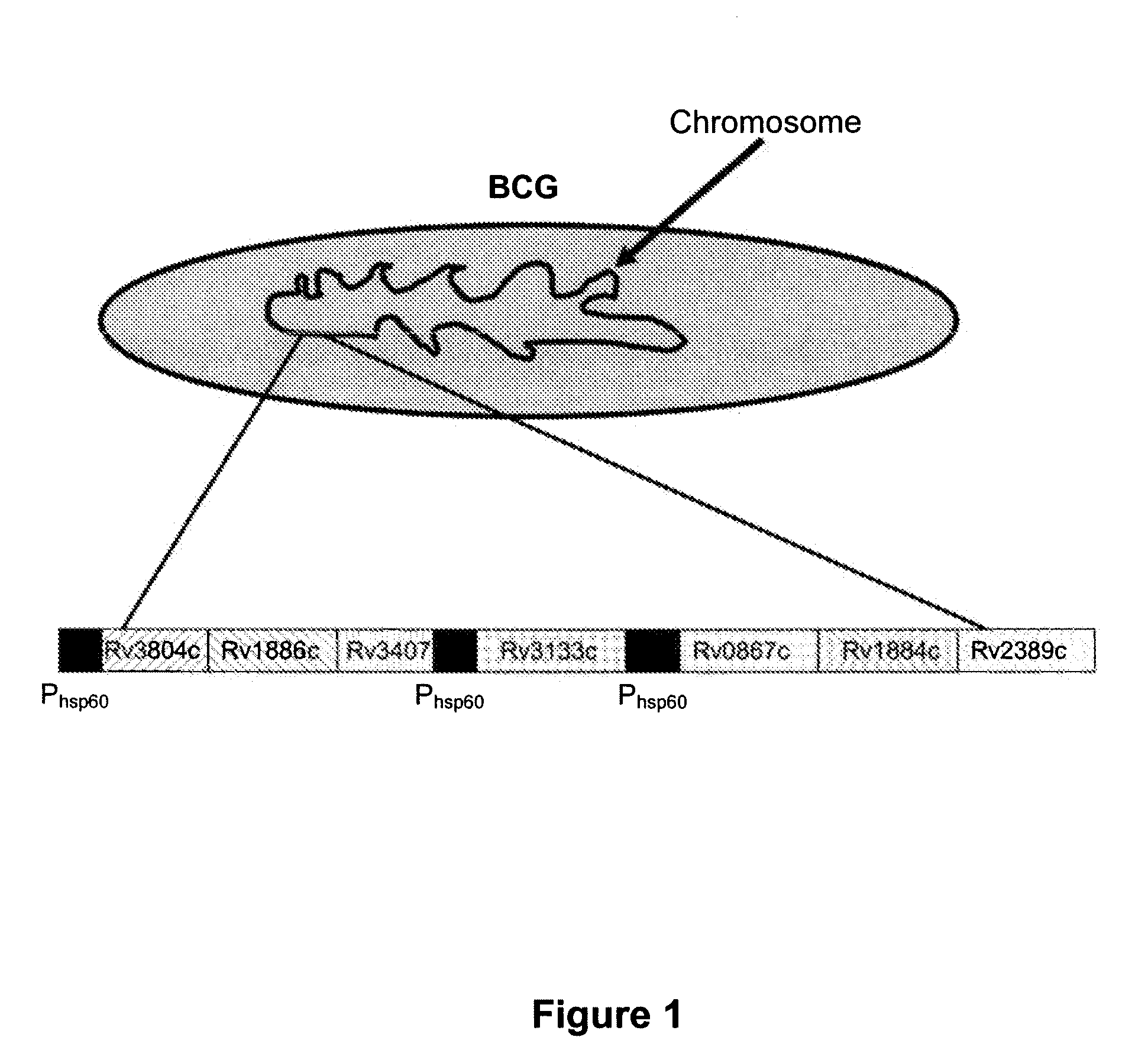
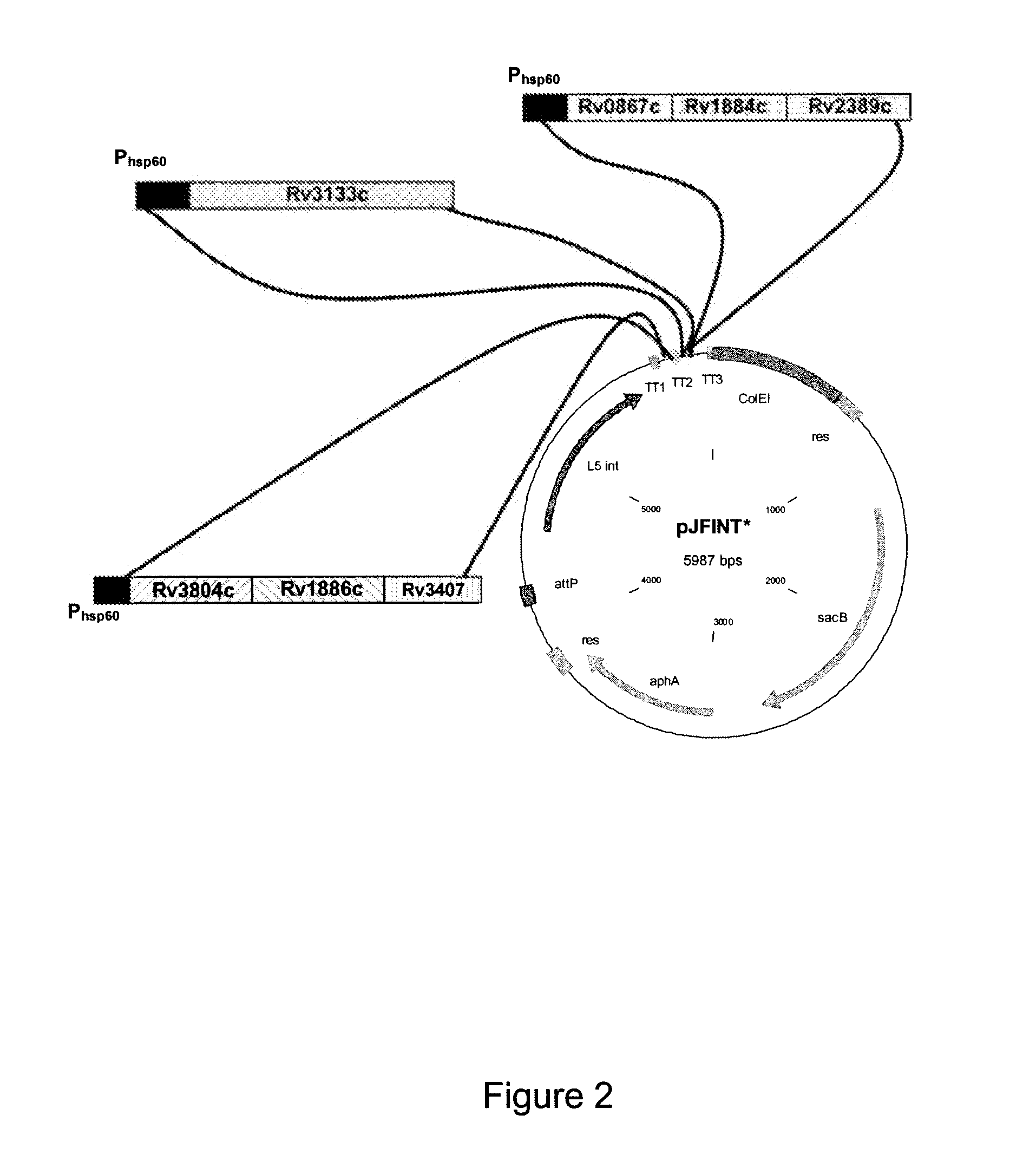
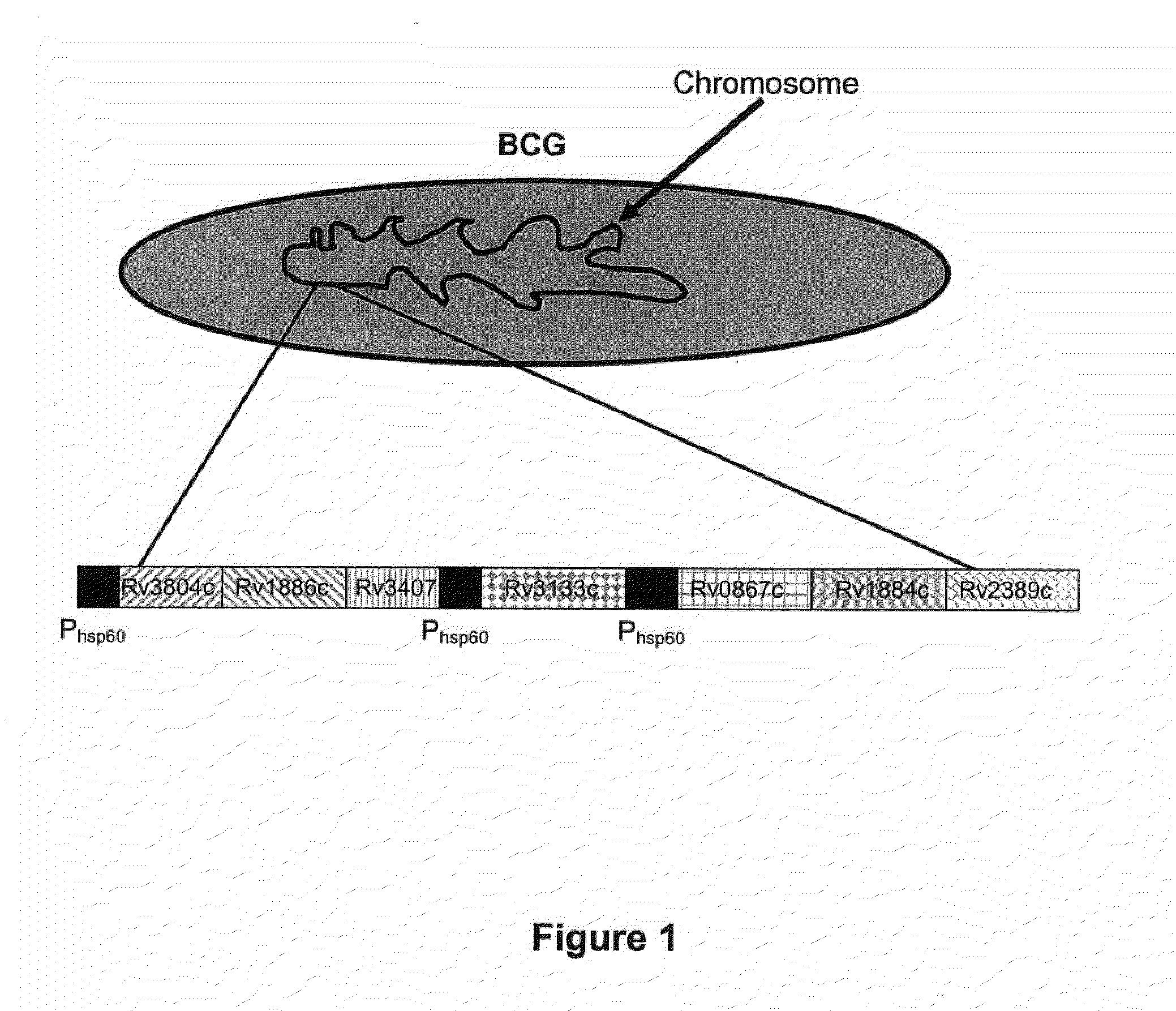
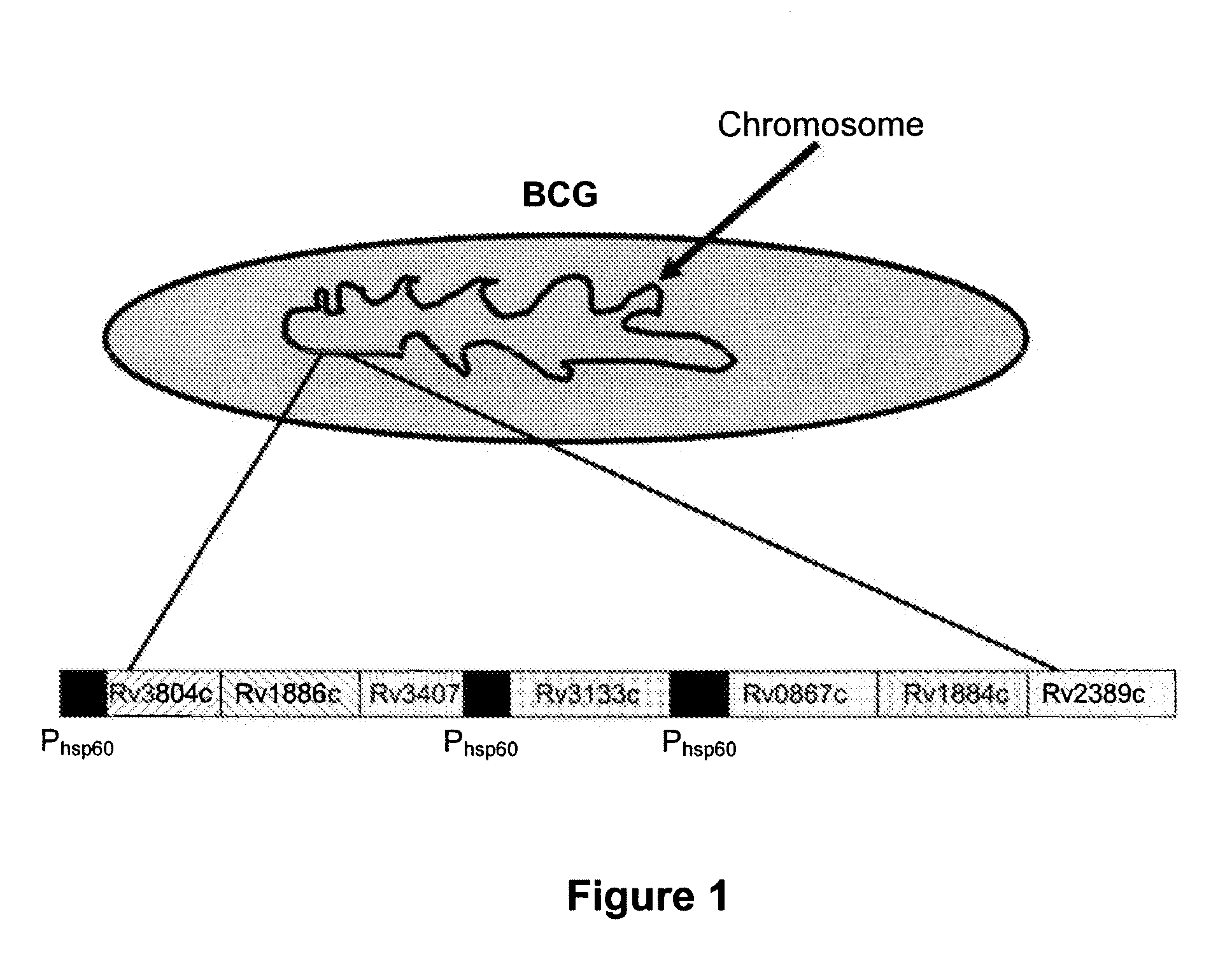
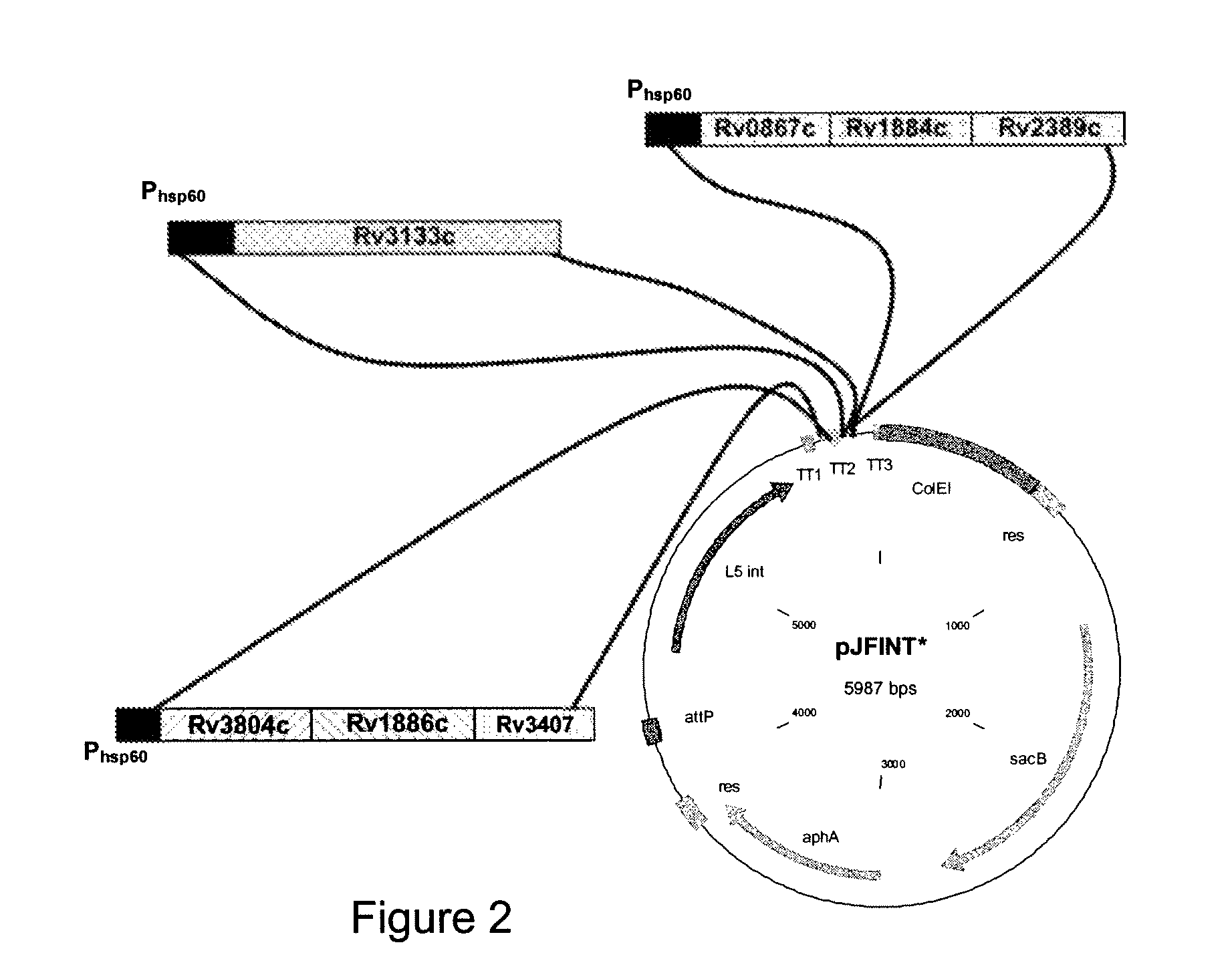
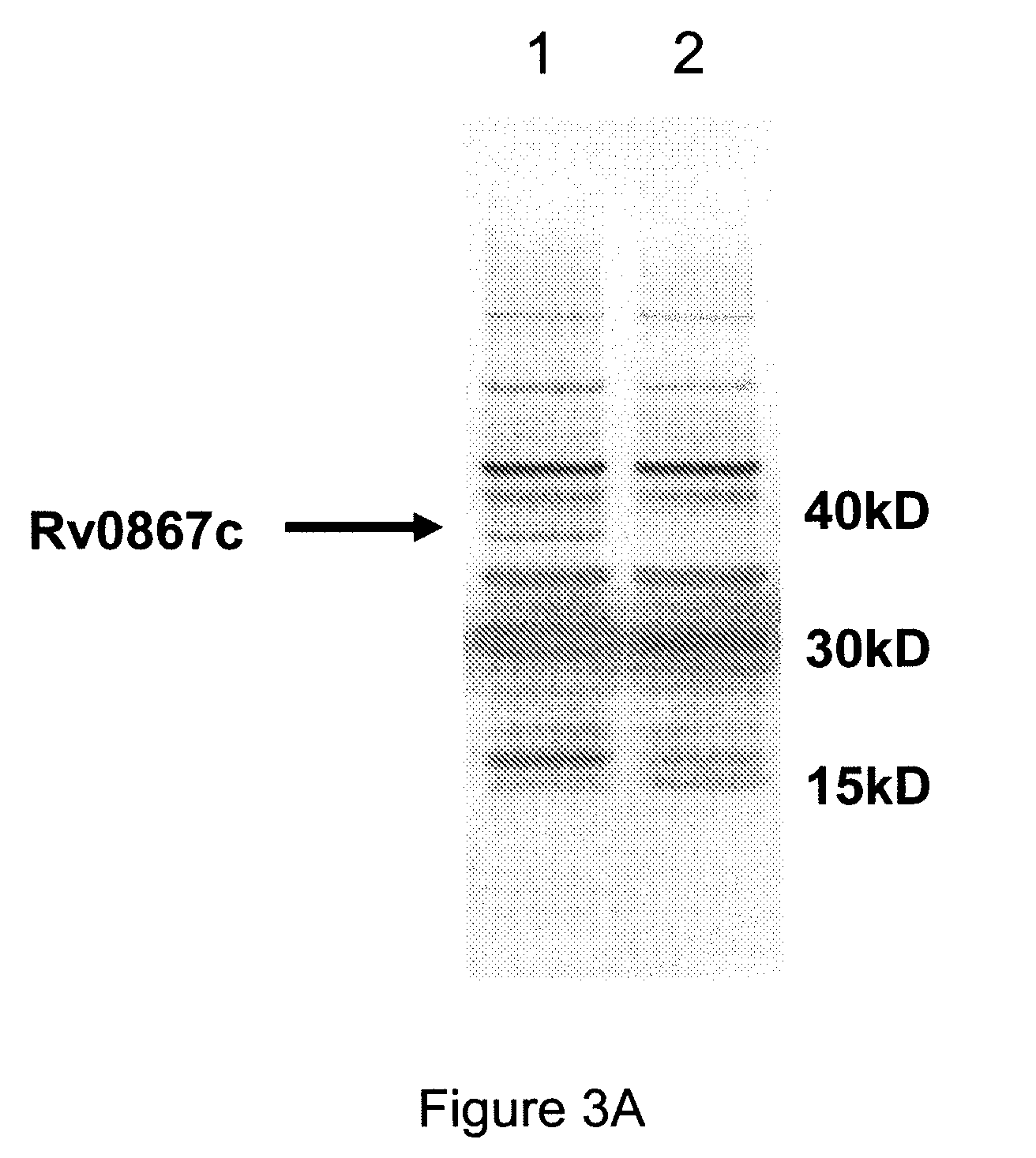
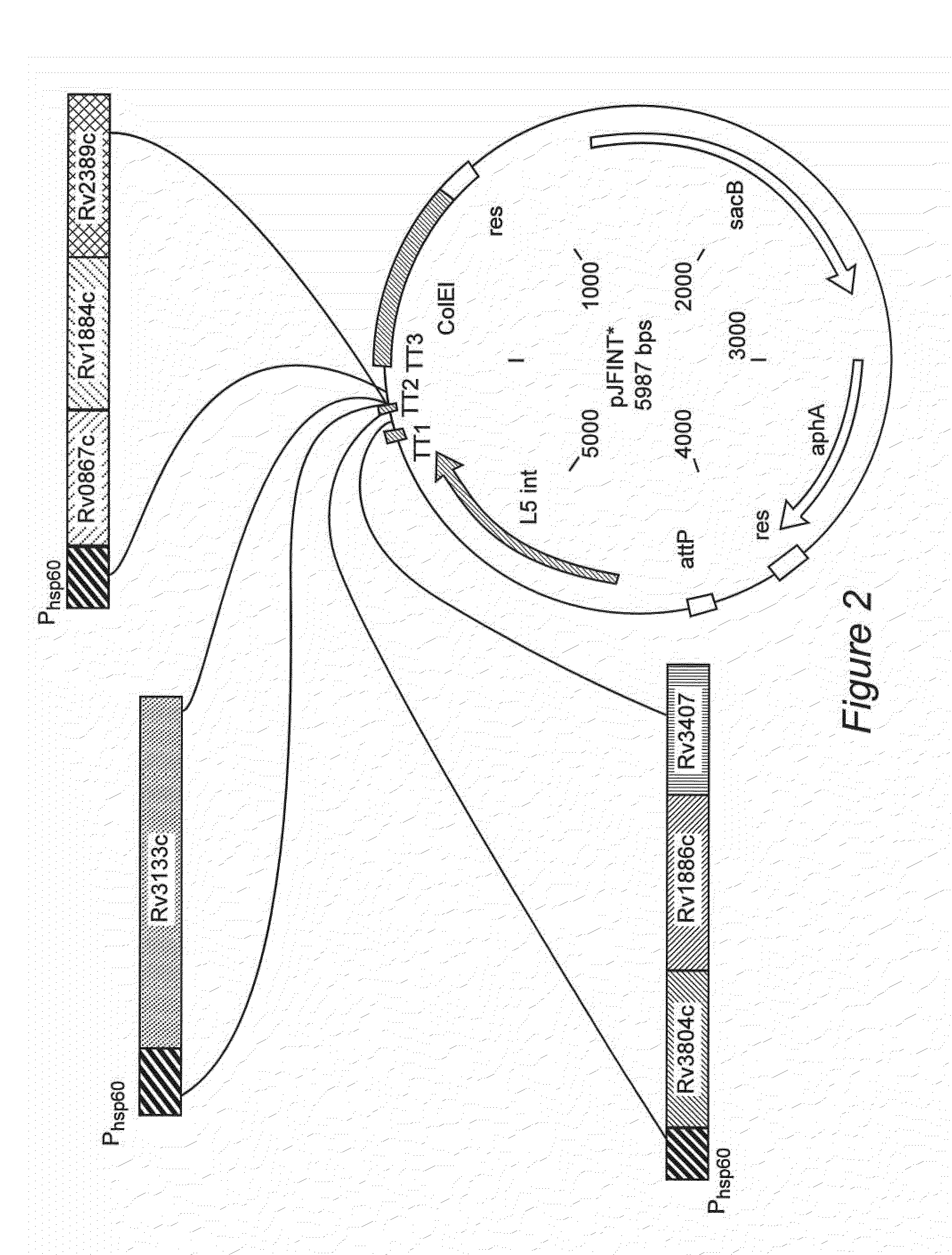
Novel recombinant bcg tuberculosis vaccine designed to elicit immune responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis in all physiological stages of infection and disease
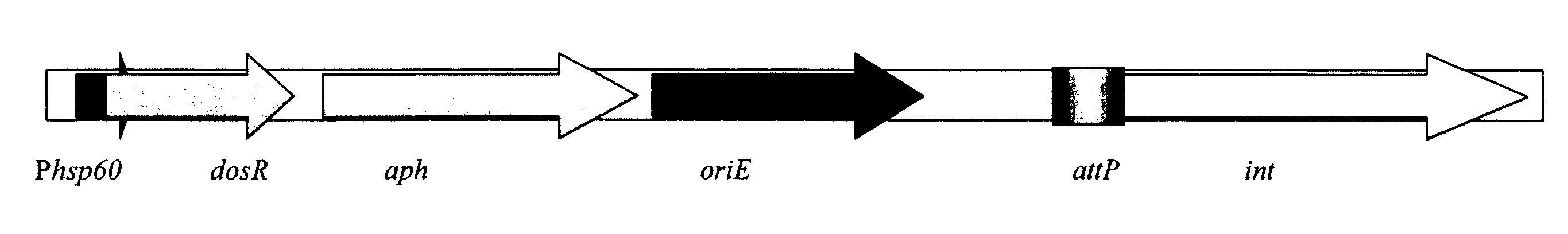
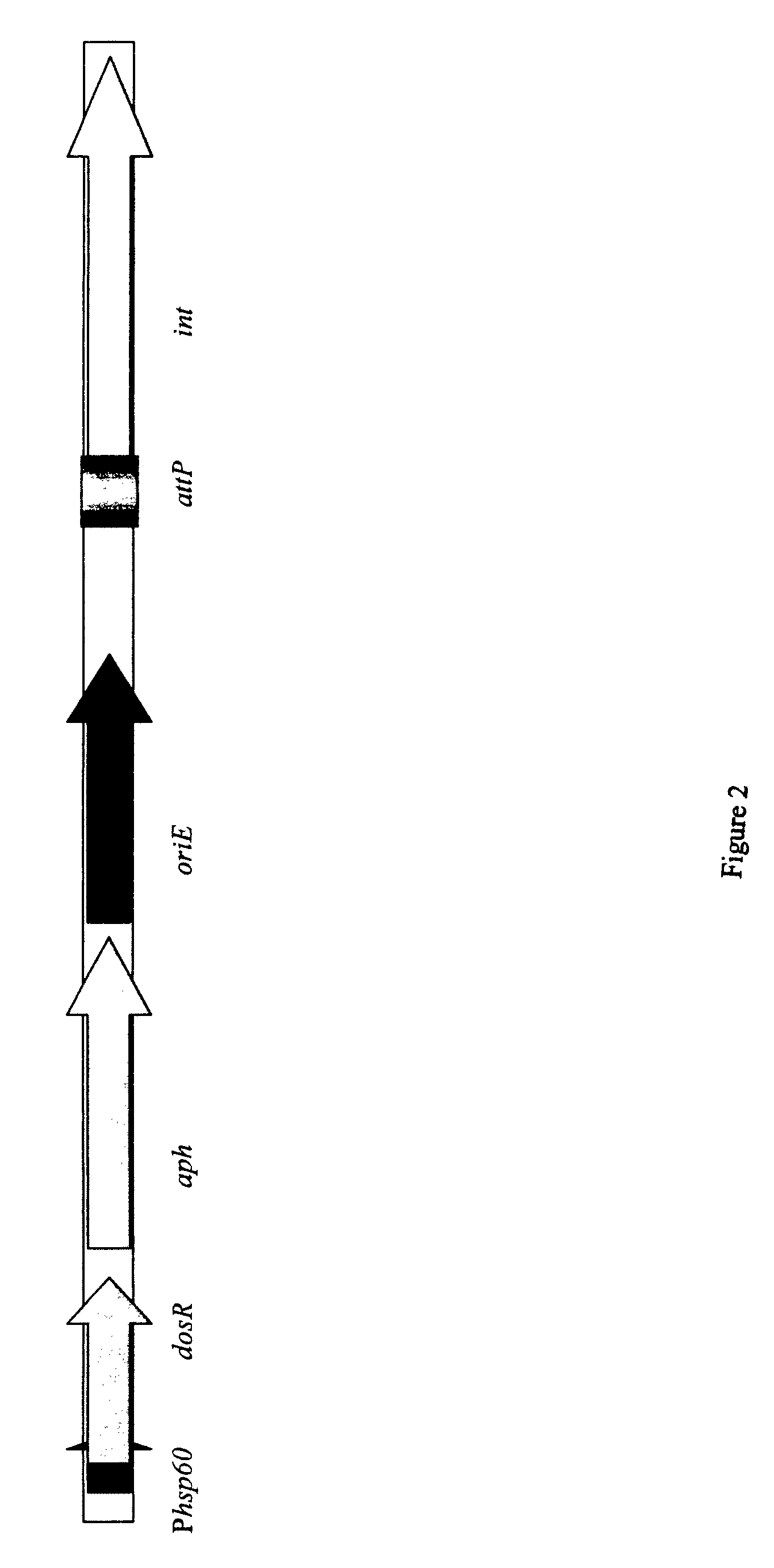
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
Novel Recombinant BCG Tuberculosis Vaccine Designed to Elicit Immune Responses to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in all Physiological Stages of Infection and Disease
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
Recombinant BCG tuberculosis vaccine designed to elicit immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in all physiological stages of infection and disease
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
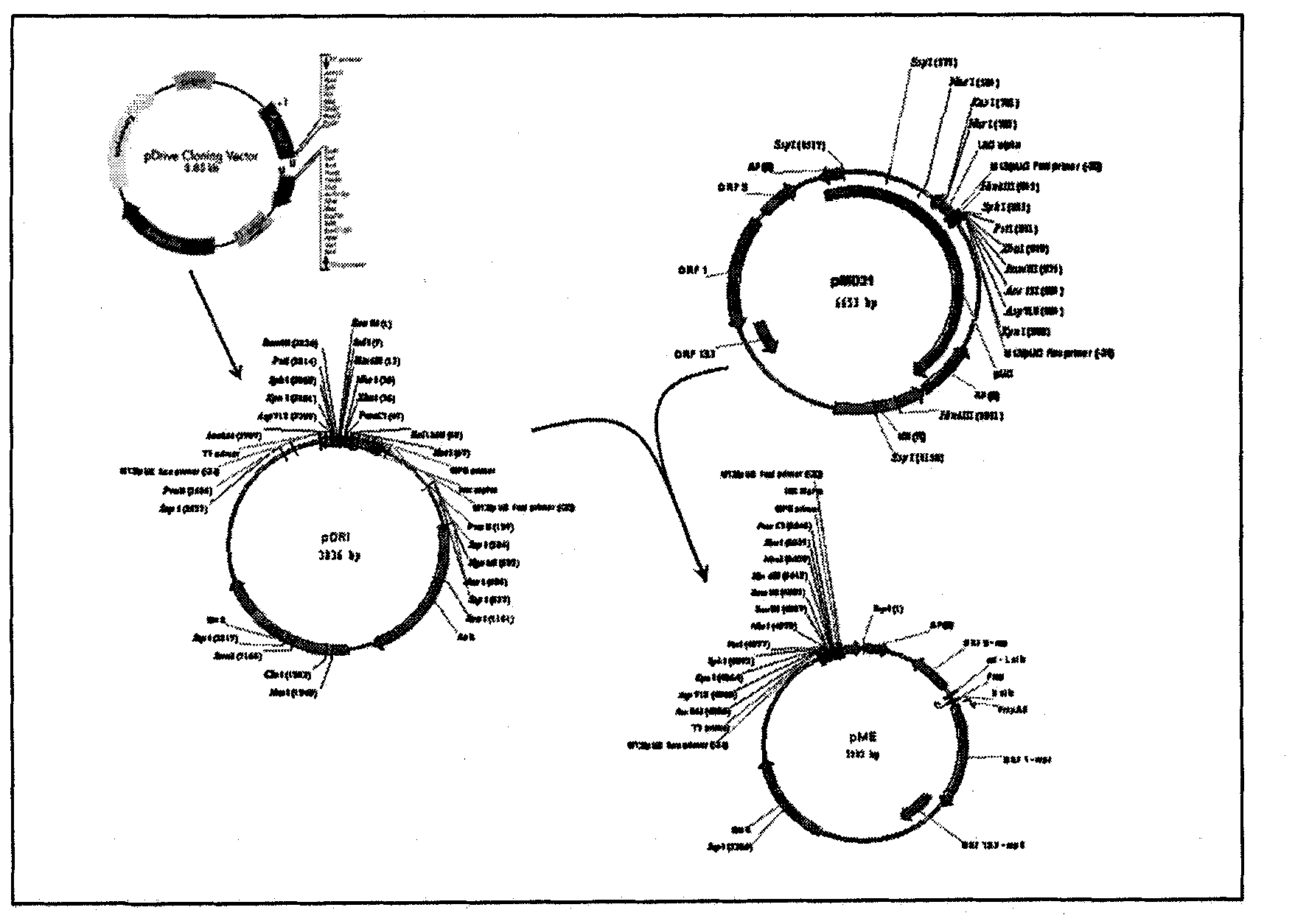
Method for identifying genes that are upstream regulators of other genes of interest
InactiveUS7125664B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenetic MaterialsRegulon
There is provided a method for identifying genes that regulate the expression of other genes, by placing a sample containing genetic material in a section of a grid, silencing expression of at least one predetermined gene in the sample, grown in the section of the grid, so that in each section of the grid at least one predetermined gene is silenced, determining the amount of genetic material of interest is present in each section of the grid, and identifying the sections of the grid in which the silencing was maximal thereby identifying genes that regulate the expression of other genes and the genes of interest identified by the method. Also provided by the present invention is a kit for performing the above method, the kit having a grid for holding a sample, inactivating agents for inactivating genetic material in the sample, and a measuring device for measuring the inactivation of the genetic material.
Owner:MINC GOLOMB DAHLIA
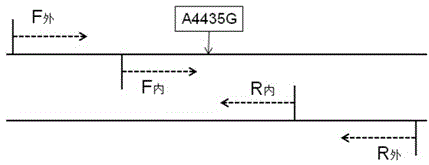
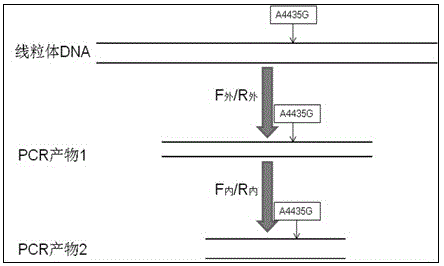
Kit for detecting regulon of Leber disease and use thereof
InactiveCN102747152ARelieve painSolve the problem of extracting DNAMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlMitophagy
The invention provides a kit for detecting mitochondrial DNA mutation related to a regulon of a Leber disease, wherein the kit consists of primer sequences, reagents for extracting genome DNA of samples, reagents for PCR amplification reaction, a positive control sample, a negative control sample and an instruction, restrictive endonucleases comprise a restrictive endonuclease Nla III, and the positive control sample is a restriction enzyme digested sample in which 4435th site of a mitochondrial sequence occur A to G mutation. The kit provided by the invention can be applied in the detection of mitochondrial DNA mt DNAA4435G mutation related to the regulon of the Leber disease. According to the kit, specificity and stability of detection results can be ensured, cost is lower than that of other detection methods, and the detection process is simple, quick, accurate and economic, and thus is suitable for detecting LHON-related gene mutation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and compositions for promoting thermogenic potential
ActiveUS20180362623A1Decrease weightReduce weightOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsOn cellsUncoupling protein
The invention provides methods and compositions relating to molecular targets identified as being capable of increasing or decreasing thermogenic potential in cells, including preadipocytes. Included in the invention are methods and compositions relating to inhibiting or suppressing the activity of an uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) negative regulator, such as cardiac actin 1 (ACTC1), somatostatin receptor 1 (SSTR1), FAT atypical cadherin 1 (FAT1), and protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type B (PT-PRB). Also included in the invention are methods and compositions relating to activating a UCP1 positive regulator, such as phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (PREX1), cortactin binding protein 2 (CTTNBP2), doublesex and mab-3-related transcription factor-like family A1 (DMRTA1), and endothelin receptor type B (ENDRB). The invention also provides methods and compositions relating to enrichment of cells having thermogenic potential based on cell surface markers, e.g., CD29, identified as being predictive of such.
Owner:JOSLIN D ABETES CENTER INC
Method for methanol independent induction from methanol inducible promoters in Pichia
The present invention relates to a method for producing a polypeptide in a methylotrophic yeast host cell, wherein expression of the polypeptide is controlled by a methanol inducible promoter, comprising: i) expression of a positive regulator from a non-native promoter, said positive regulator activating transcription from the methanol inducible promoter, and ii) no addition of methanol.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Generation of new bcg vaccine strains protecting against the establishment of latent mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and reactivation from the latent or persistent state
InactiveUS20090123492A1Ability of to to attenuatedShorten the progressBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesADAMTS ProteinsBCG vaccine
A vaccine for treating or preventing the establishment of latent tuberculosis infections is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant mycobacterium that overexpresses the transcription factor DosR, at a level sufficient to induce production of the dosR regulon genes or proteins. A host to whom the vaccine is administered mounts an immune response to the dosR regulon proteins and is thus protected from the establishment, persistence or reactivation of latent tuberculosis.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC +1
Process for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol with high titer
The present invention provides an improved method for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol from a fermentable carbon source in a single microorganism. In one aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the conversion of glucose to 1,3-propanediol is achieved by the use of an E. coli transformed with the Klebsiella pneumoniae dha regulon genes dhaR, orfY, dhaT, orfX, orfW, dhaB1, dhaB2, dhaB3, and orfZ, all these genes arranged in the same genetic organization as found in wild type Klebsiella pneumoniae. In another aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the production of 1,3-propanediol from glucose using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, and a dehydratase reactivation factor compared to an identical process using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, a dehydratase reactivation factor and a 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase (dhaT). The dramatically improved process relies on the presence in E. coli of a gene encoding a non-specific catalytic activity sufficient to convert 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde to 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Tuberculosis vaccines including recombinant bcg strains overexpressing phop, and/or phop regulon protein(s)
A live recombinant Mycobacterium bovis-BCG strain comprising a nucleic acid encoding PhoP protein and / or one or more phoP regulon proteins is provided, in which the nucleic acid is capable of being overexpressed. A vaccine or immunogenic composition comprising the live recombinant Mycobacterium bovis-BCG strain and a method for treatment or prophylaxis of a mammal against challenge by Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Mycobacterium bovis are also provided.
Owner:成都安永鼎业生物技术有限公司
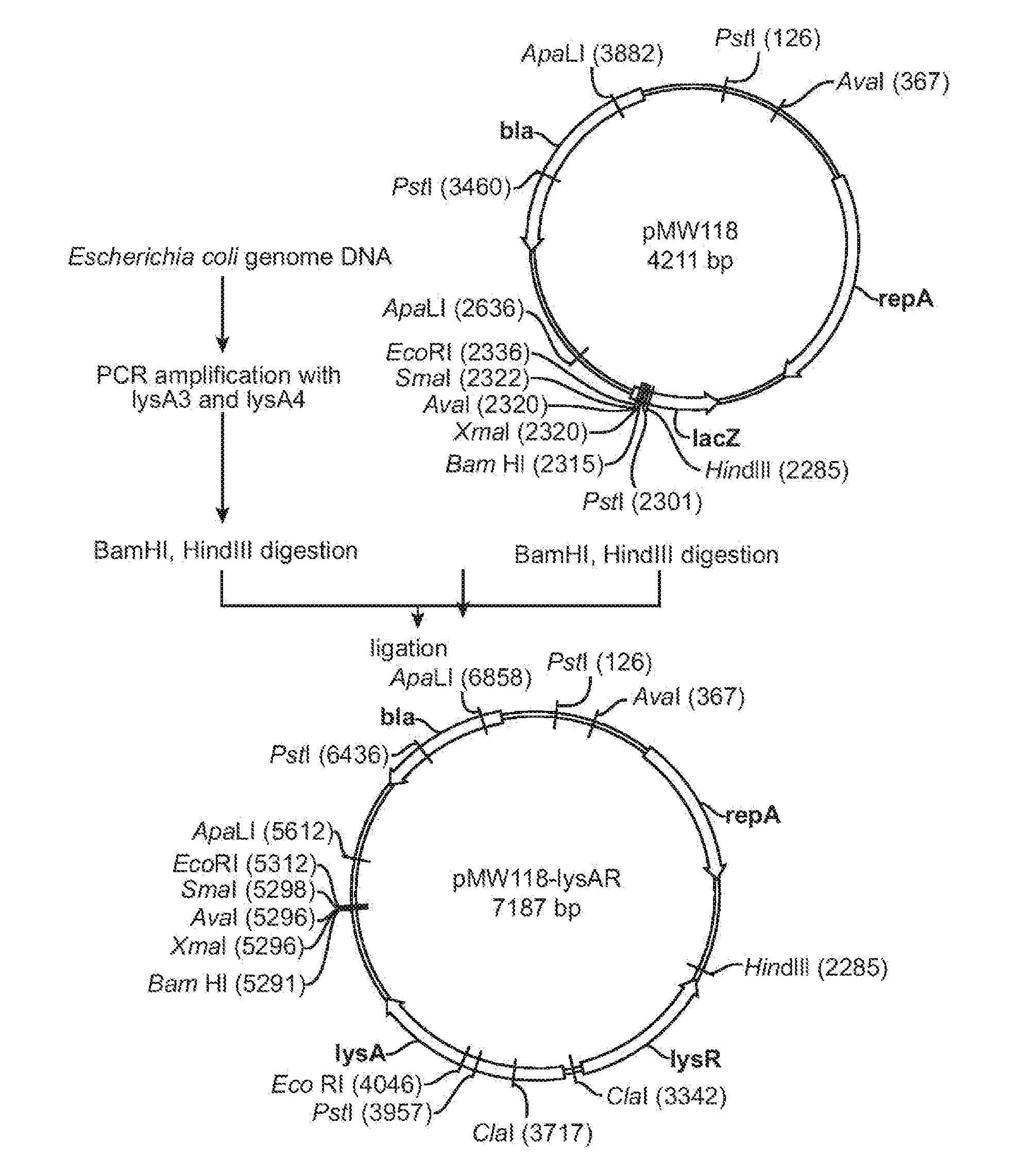
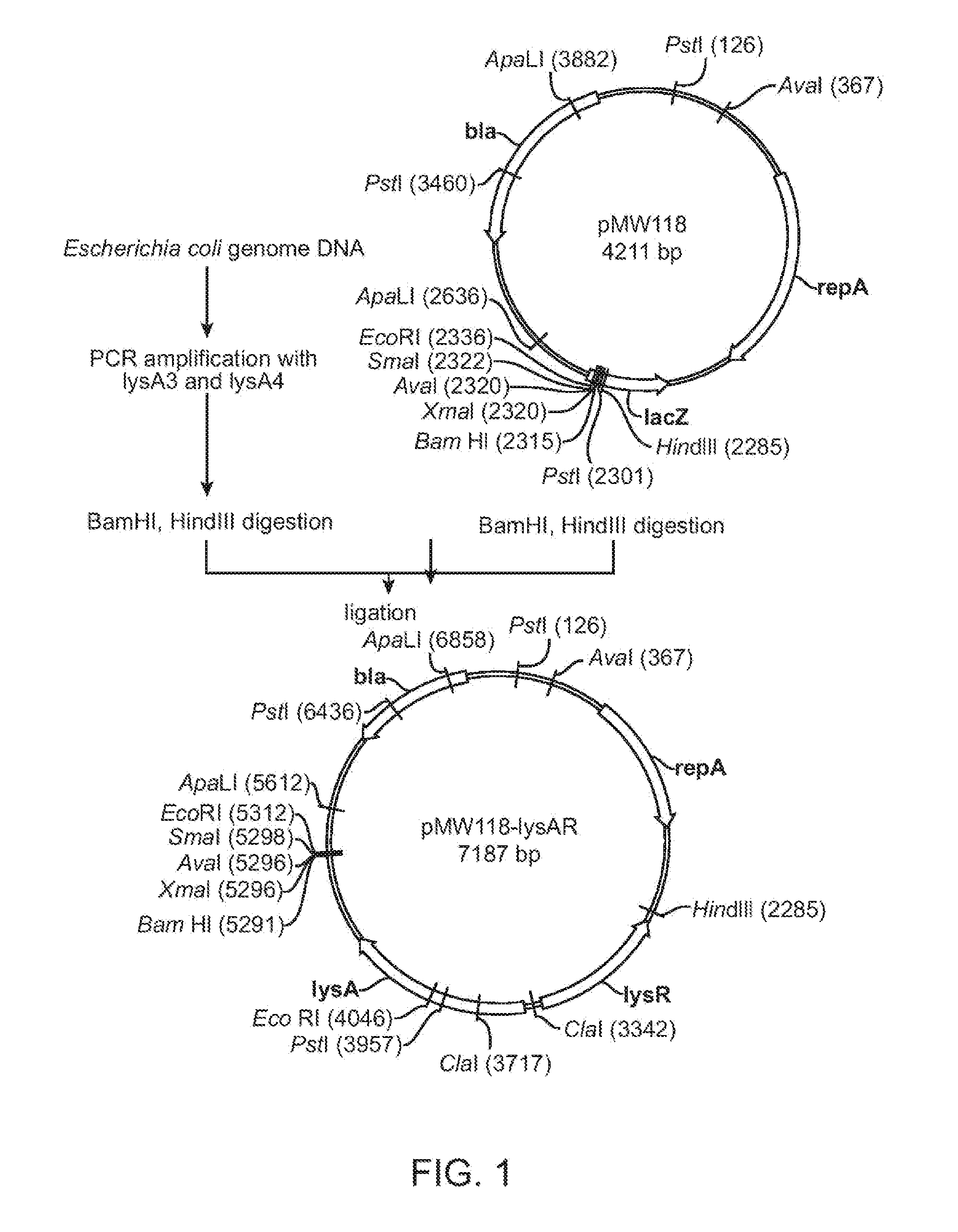
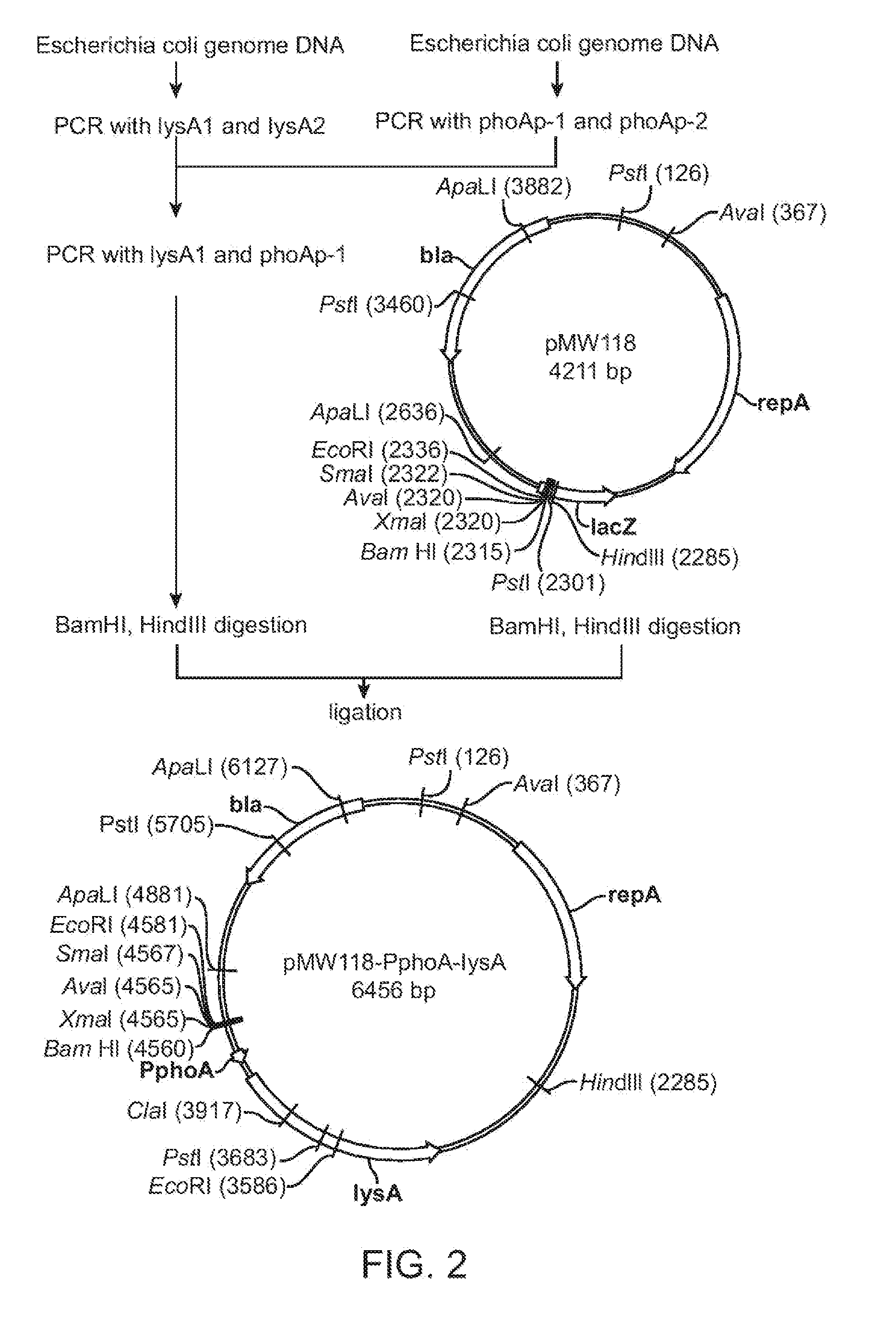
Method for production of an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20100184162A1Improve productivityHigh yieldFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismDNA fragmentation
A method is provided for producing an L-amino acid by culturing a microorganism belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family and having the ability to produce an L-amino acid, in a medium to produce and accumulate the L-amino acid in the medium. The microorganism has been modified by introduction of a DNA fragment which includes a pho regulon promoter and a structural gene encoding an L-amino acid biosynthetic enzyme, which is ligated downstream of the promoter so that the gene is expressed by the promoter, and so that the activity of the L-amino acid biosynthetic enzyme is increased by the expression of the gene by the promoter. In this way, the L-amino acid that is produced in the medium can be collected. Furthermore, the phosphorus concentration in the medium is such that the expression of the gene by the promoter is induced.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombinant BCG tuberculosis vaccine designed to elicit immune responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis in all physiological stages of infection and disease
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
Secreted campylobacter flagella coregulated proteins as immunogens
The invention relates to an immunogenic composition composed of secreted polypeptides derived from Campylobacter jejuni non-flagellar proteins that are coordinately expressed with the flagellar regulon. The invention also relates to a method of inducing an immune response to the non-flagellar protein polypeptides.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Haemophilus influenzae type IV pili
The invention described herein relates to a Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) regulon encoding type IV pili. In particular, the invention relates to type IV pili from nontypeable H. influenzae (NTHi) and from H. influenzae strains a, b, c, e and f. The invention provides isolated H. influenzae pilus polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides as well as polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides involved in the assembly / disassembly of the structure. The invention also relates to uses of these polynucleotides and / or polypeptides including methods for eliciting an immune response to H. influenzae and methods of treating and preventing H. influenzae related pathological conditions.
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Regulators involved in mushroom formation
The invention relates to a fungus or a mushroom and to a method of producing it wherein the fungus / mushroom has an increased expression level of a polypeptide and / or has a decreased expression level of a polypeptide, wherein the polypeptide comprises an amino acid sequence that has at least 40% amino acid identity or similarity with a sequence selected from SEQ ID NO:1-200 and / or that has at least 50% amino acid identity or similarity with a sequence selected from SEQ ID NO:201-208.
Owner:UTRECHT UNIVERSITY +1
Methods for the identification of inhibitors of an isoprenoid metabolic pathway
InactiveUS7078169B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological pathwayBiological activation
The present invention relates to methods of identifying genes whose expression is indicative of activation of a particular biochemical or metabolic pathway or a common set of biological reactions or functions in a cell (“regulon indicator genes”) The present invention provides an example of such an indicator gene. The present invention also relates to methods of partially characterizing a gene of unknown function by determining which biological pathways, reactions or functions its expression is associated with, thereby placing the gene within a functional genetic group or “regulon”. These partially characterized genes may be used to identify desirable therapeutic targets of biological pathways of interest (“regulon target genes”) The present invention provides examples of such target genes. Methods for identifying effectors (activators and inhibitors) of regulon target genes are provided. The present invention also provides examples of regulon target gene inhibitors.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Oxidation and high salt stress resistant artificially synthesized sRNA and application thereof
ActiveCN104593361AImprove salt stress resistanceBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPseudomonas stutzeri
A core sequence fragment from a pseudomonas stutzeri non-coding sRNA gene is discovered and determined for the first time by the invention, and the core sequence fragment is combined with the transcriptional regulon Hfq of an escherichia coli non-coding RNA to synthesize a novel sRNA artificially. Experiments show that the artificially synthesized sequence endows a host cell with an oxidation and high salt stress resisting function.
Owner:北京绿氮生物科技有限公司
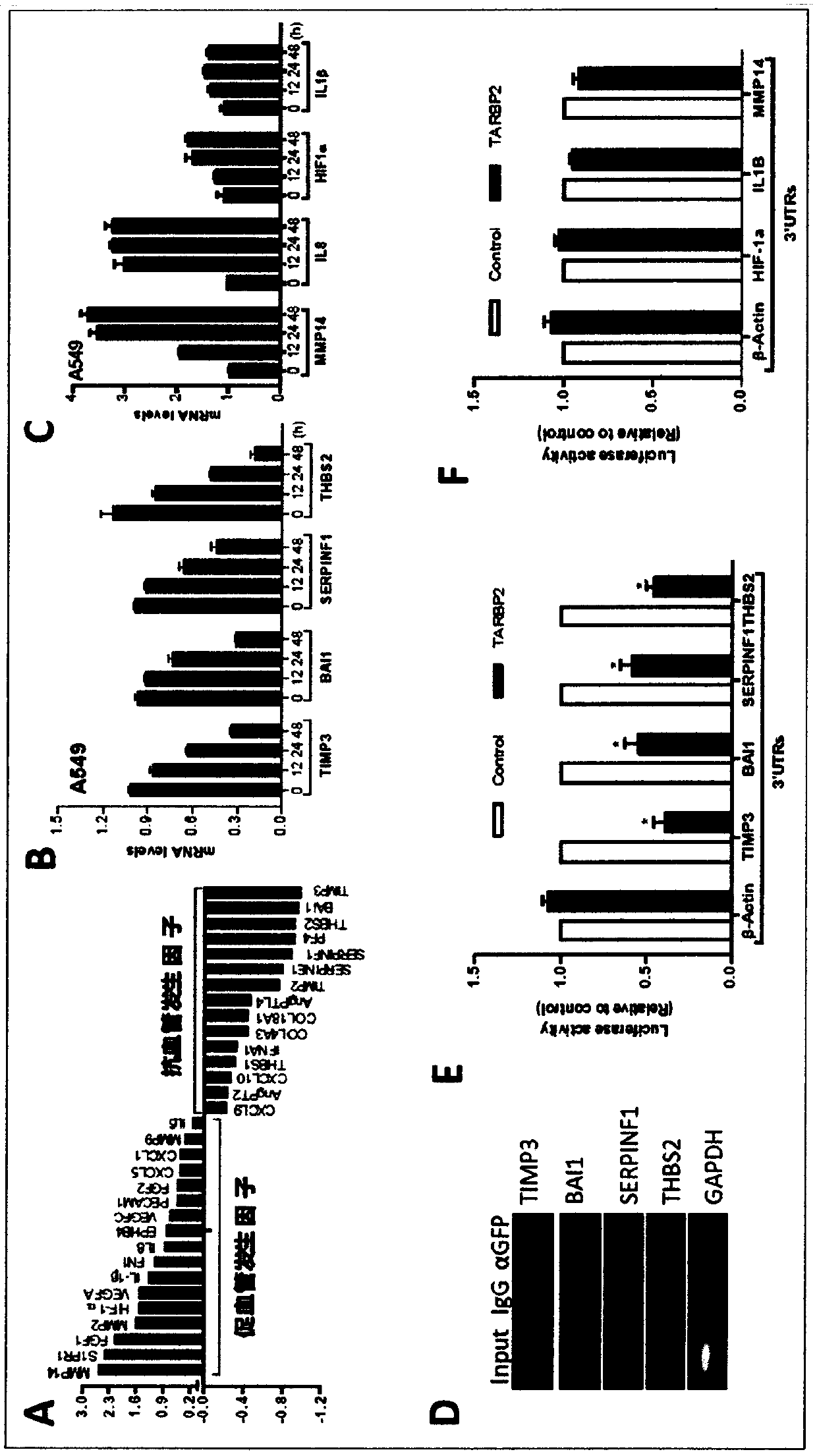
Tumor angiogenesis regulatory protein TARBP2, and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN111333717AEasy transferGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsStable introduction of DNATumor angiogenesisAngiogenesis Factor
According to the invention, with tumor angiogenesis as a starting point, a protein TARBP2 and a coding gene thereof are identified to be novel tumor angiogenesis regulators and can specifically degrade mRNAs of anti-angiogenesis factor genes to induce tumor angiogenesis and promote tumor metastasis. The adenovirus vector expressing shRNA targeting TARBP2 is used for treating tumors and can significantly inhibit tumor angiogenesis, metastasis and growth. The tumor angiogenesis regulatory protein and the encoding gene thereof provided by the invention provide a novel molecular target for targeting tumor angiogenesis to treat tumors, and have important theoretical and practical significance for clinically resisting angiogenesis to treat the tumors in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROCIRCULATION CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Method for production of an L-amino acid
ActiveUS8394612B2Increase productionHigh activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismDNA fragmentation
A method is provided for producing an L-amino acid by culturing a microorganism belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family and having the ability to produce an L-amino acid, in a medium to produce and accumulate the L-amino acid in the medium. The microorganism has been modified by introduction of a DNA fragment which includes a pho regulon promoter and a structural gene encoding an L-amino acid biosynthetic enzyme, which is ligated downstream of the promoter so that the gene is expressed by the promoter, and so that the activity of the L-amino acid biosynthetic enzyme is increased by the expression of the gene by the promoter. In this way, the L-amino acid that is produced in the medium can be collected. Furthermore, the phosphorus concentration in the medium is such that the expression of the gene by the promoter is induced.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
An L-amino acid-producing bacterium and a method for producing an L-amino acid
ActiveCN101273054AImproved ability to produce L-amino acidsBacteria peptidesFermentationBacteroidesMicroorganism
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a microorganism of the family Enterobacteriaceae which has the ability to produce an L-amino acid and which has been modified so as to increase the amount of expression of one or more genes selected from the evgA gene, gadE gene, or ydeO gene that encodes a transcription factor involved in the EvgAS two-component system regulon in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or in cells, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium or cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Haemophilus influenzae type IV pili
ActiveUS20090041774A1Improve efficiencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHaemophilusPilus
The invention described herein relates to a Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) regulon encoding type IV pili. In particular, the invention relates to type IV pili from nontypeable H. influenzae (NTHi) and from H. influenzae strains a, b, c, e and f. The invention provides isolated H. influenzae pilus polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides as well as polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides involved in the assembly / disassembly of the structure. The invention also relates to uses of these polynucleotides and / or polypeptides including methods for eliciting an immune response to H. influenzae and methods of treating and preventing H. influenzae related pathological conditions.
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
New expression system from rhodococcus
Owner:NV ORGANON
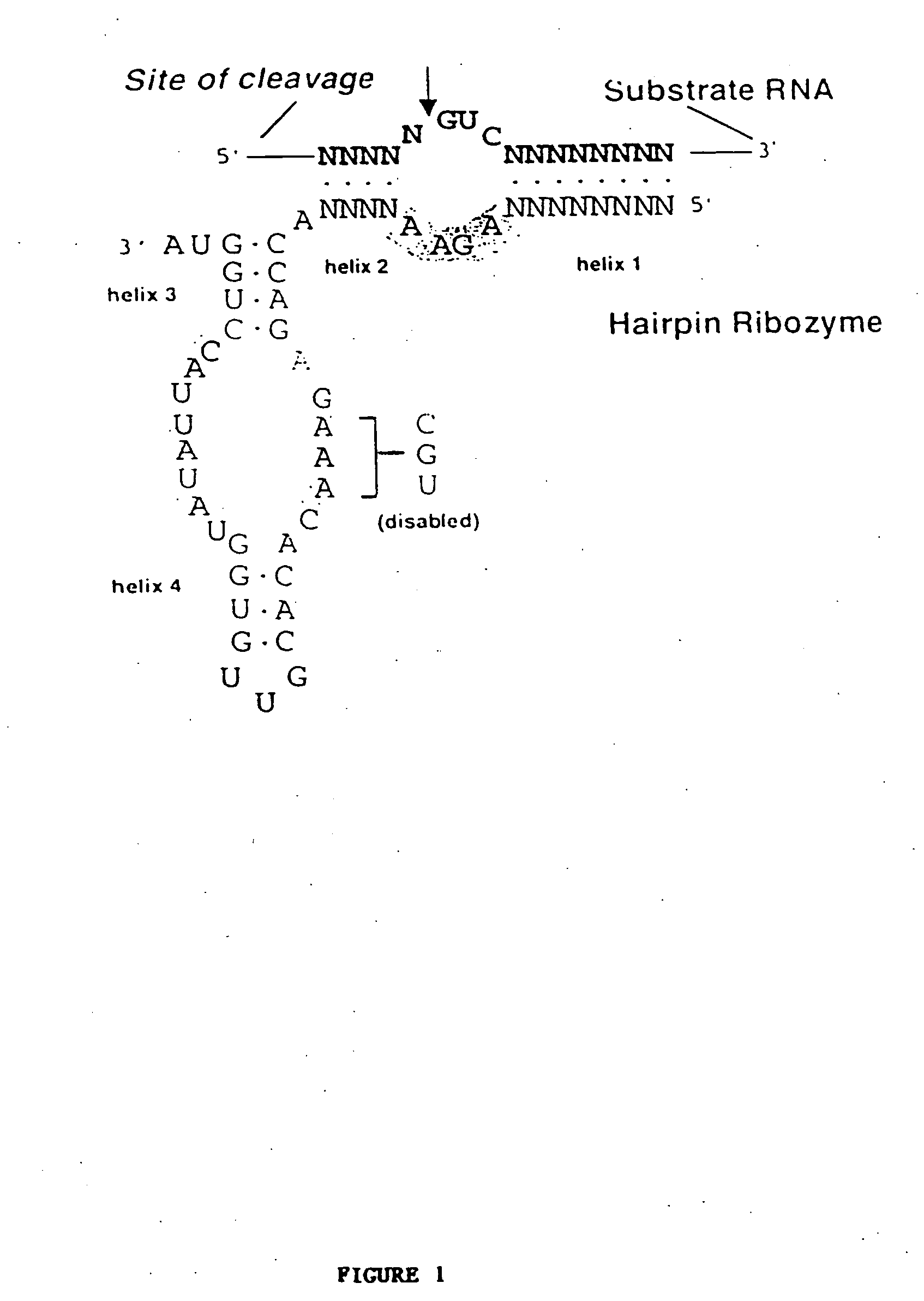
Brca-1 regulators and methods of use
InactiveUS20050208486A1Increase propensityUpregulation or downregulation of BRCA-1TransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellRecognition sequence
The invention provides ribozymes and encoding nucleic acids having target recognition sequences that allow the ribozyme to target and cleave BRCA-1 regulators, resulting in upregulation of BRCA-1 in a cell. Also provided are nucleic acids encoding BRCA-1 regulators that contain the target sequences recognized by the ribozymes of the invention. Fragments of these nucleic acid and protein sequences also are provided. Further provided is a method for identifying a gene where the expression level is affected by a BRCA-1 regulator and the identity of several such affected genes. Still further provided is a method of identifying a compound that modulates the activity of a BRCA-1 regulator. Also provided is a method of treating cancer, comprising introducing a ribozyme selectively reactive with an RNA encoding a BRCA-1 regulator into a cancerous cell. The invention further comprises a method of detecting a neoplastic cell in a sample.
Owner:IMMUSOL
Generation of new BCG vaccine strains protecting against the establishment of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and reactivation from the latent or persistent state
InactiveUS7935354B2Ability of to to attenuatedShorten the progressBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaBCG vaccineLatent tuberculosis
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC +1
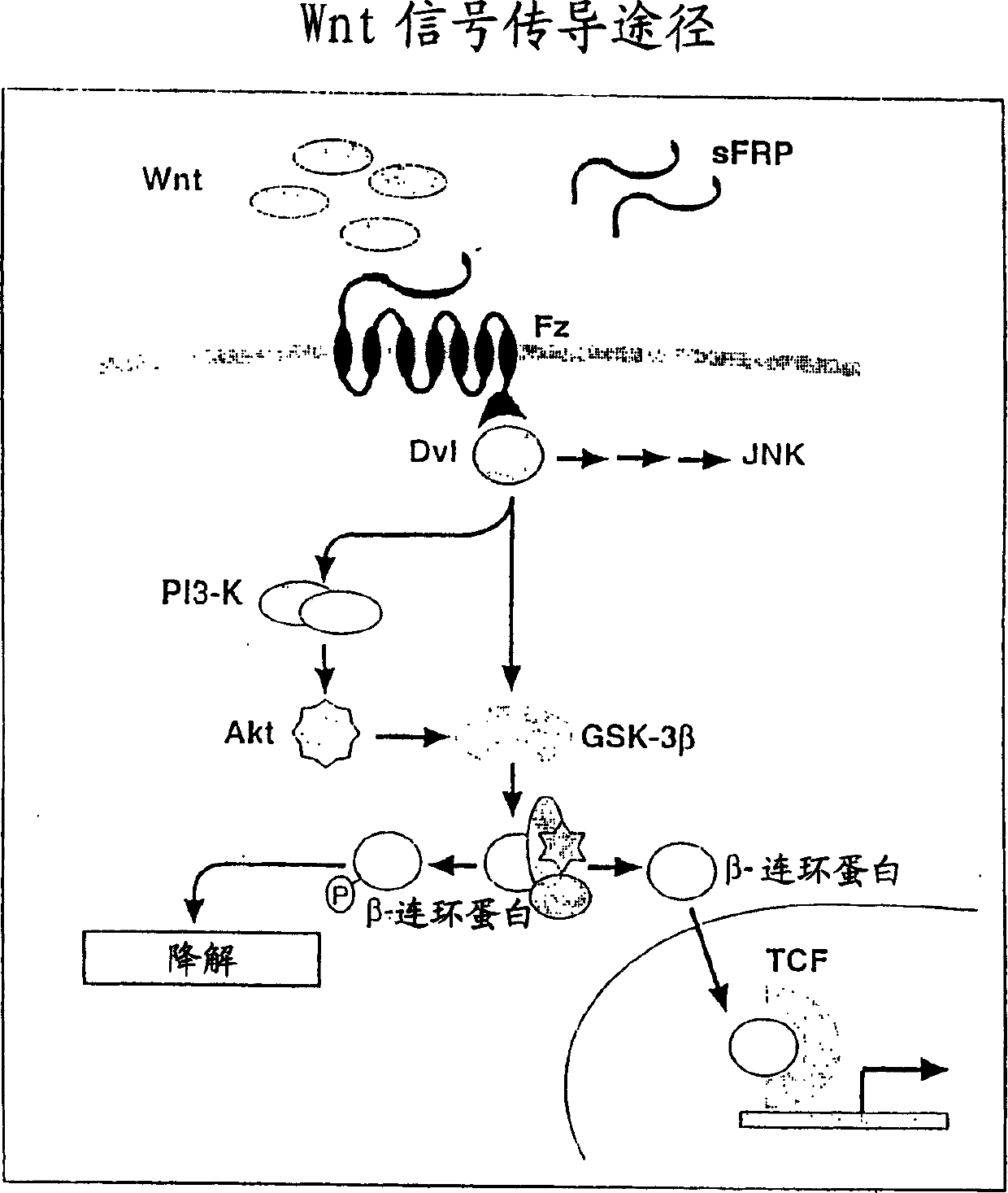
Nucleic protein 'Shoca'-a component of wnt signal transmission channel
An isolated Shoca polypeptide comprising: (i) the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 or SEQ ID NO: 4; or (ii) a variant thereof which is capable of interacting with a polypeptide of the wnt signalling pathway; or (iii) a fragment of (i) or (ii) which is capable of interacting with a polypeptide of the wnt signalling pathway, a polypeptide encoding said polypeptide, a method for identifying a modulator of the wnt signalling pathway utilising said polypeptide or polynucleotide and methods of diagnosing and treating cancer.
Owner:THE UNIV CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF BOTH CANTONS OF BASEL
Application of eif4g protein in regulation of plant tolerance to ABA
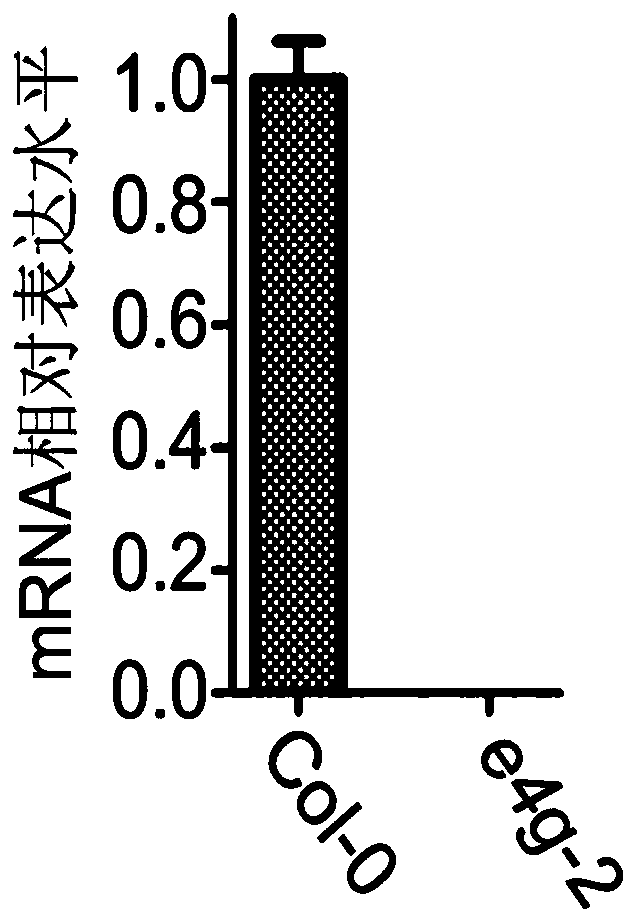
InactiveCN110079547BReduced toleranceImprove food qualityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyAbscisic acid
The invention discloses application of eIF4G protein to regulation and control of the tolerance of plants on ABA (abscisic acid). The application required for protecting substances used for inhibitingspecific gene expression in the plants comprises the following steps of regulating and controlling the tolerance of the plants on the ABA; breeding plant varieties with reduced tolerance on the ABA;regulating and controlling vivipary resistance of the plants; breeding plant varieties with increased vivipary resistance, wherein a specific gene is a gene encoding the eIF4G protein. The conditionsthat the eIF4G protein is an important negative regulator in ABA signal conduction, and the tolerance of the plants on the ABA can be obviously reduced by knocking out the eIF4G gene are found. The sustainable agriculture development requirement is conformed; important practical values and market prospects are realized in aspects of culturing new efficient ABA and adversity stress resistant varieties and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cyclic AMP response element activator proteins and uses related thereto
The present invention discloses newly identified cyclic AMP response element activator proteins (CREAP proteins). It is mentioned herein that the protein is a suitable drug target for developing new therapeutic agents to prevent, treat or alleviate pathological conditions related to abnormal activation of CRE-dependent gene expression or abnormal activation of chemokines. The present invention relates to a method for preventing, treating or alleviating said pathological conditions and a pharmaceutical composition comprising a regulator having an inhibitory effect on CREAP protein activity and / or CREAP gene expression. The present invention also relates to methods of identifying compounds useful in the treatment of said pathological conditions, comprising identifying compounds capable of inhibiting CREAP protein activity and / or CREAP gene expression.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Application of eifiso4g1 protein in regulation of plant tolerance to ABA
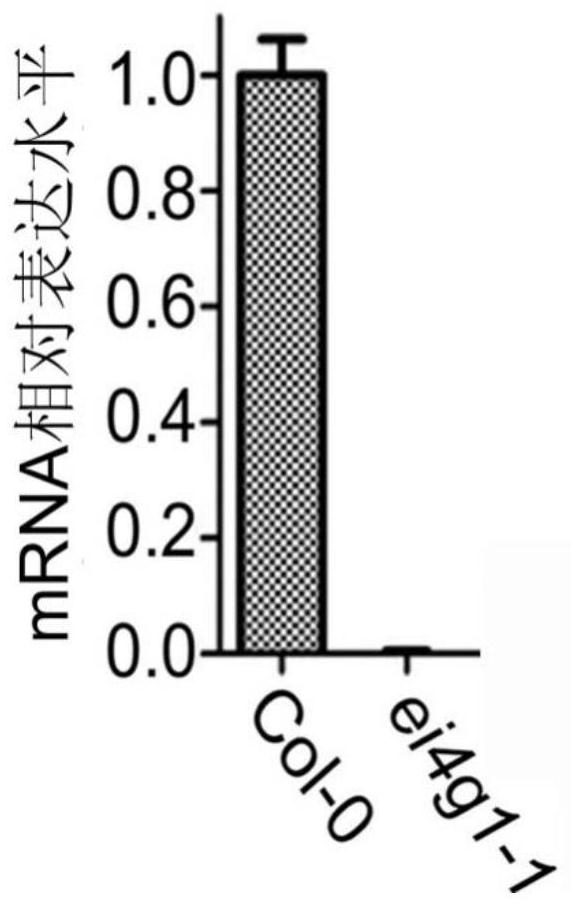
InactiveCN109988232BReduced toleranceInhibition of premature germinationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPlant peptidesBiotechnologyAbscisic acid
The invention discloses the application of the eIFiso4G1 protein in regulating the tolerance of plants to ABA. The present invention claims to protect the application of substances used to inhibit the expression of specific genes in plants: regulating the tolerance of plants to abscisic acid; breeding plant varieties with reduced tolerance to abscisic acid; regulating the embryonic resistance of plants; breeding A plant variety with increased fetal germination resistance; the specific gene is the gene encoding eIFiso4G1 protein. The present invention finds that the eIFiso4G1 protein is an important negative regulator in ABA signal transduction, and knocking out the eIFiso4G1 gene can significantly reduce the tolerance of plants to ABA. The invention meets the requirement of sustainable agricultural development, and has important practical value and market prospect for cultivating new varieties with high efficiency and tolerance to ABA and adversity stress.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Single-stranded antimicrobial oligonucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveCN101076589AInhibitionGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsOligonucleotideGrowth function
The current invention is directed to oligonucleotide sequences isolated from a sequence designated rbl-1 [SEQ ID NO. 19] that either kill or inhibit growth, or prevent the production of endogenously expressed toxin, of microorganisms. These ssDNA sequences, identified through use of a screening method, appear to act as modulators of essential growth functions which may act at the level of triplex formation, antisense inhibition, or as aptamers that alter gene function. The sequences, referred to as minimum functional regions, or MFRs, are useful inter alia as therapeutic agents for treatment of sepsis and other pathologies caused by microorganisms such as sepsis and / or in which microorganisms are contributory agents.
Owner:CYTOGENIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com