Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Negative regulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Negative Regulation. The binding of a specific protein (repressor) inhibits transcription from occurring. DNA bound repressors often act to prevent RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter, or by blocking the movement of RNA polymerase.
Methods of using combinations of siRNAs for treating a disease or a disorder, and for enhancing siRNA efficacy in RNAi
InactiveUS20080081791A1Good effectImprove efficacyOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseNegative regulator
The present invention provides methods for treating diseases or disorders, and methods for enhancing siRNA efficacy in RNAi, including administering to a subject or a biological system one or more siRNAs capable of down regulating the expression of one or more target genes and one or more siRNAs capable of down regulating the expression of one or more negative regulators of RNAi. The present invention also provides compositions including one or more siRNAs, or precursors thereof, capable of down regulating the expression of one or more target genes and comprising one or more siRNAs, or precursors thereof, capable of down regulating the expression of one or more negative regulators of RNAi.
Owner:SHANGHAI HENGDA SCI & TECH DEV
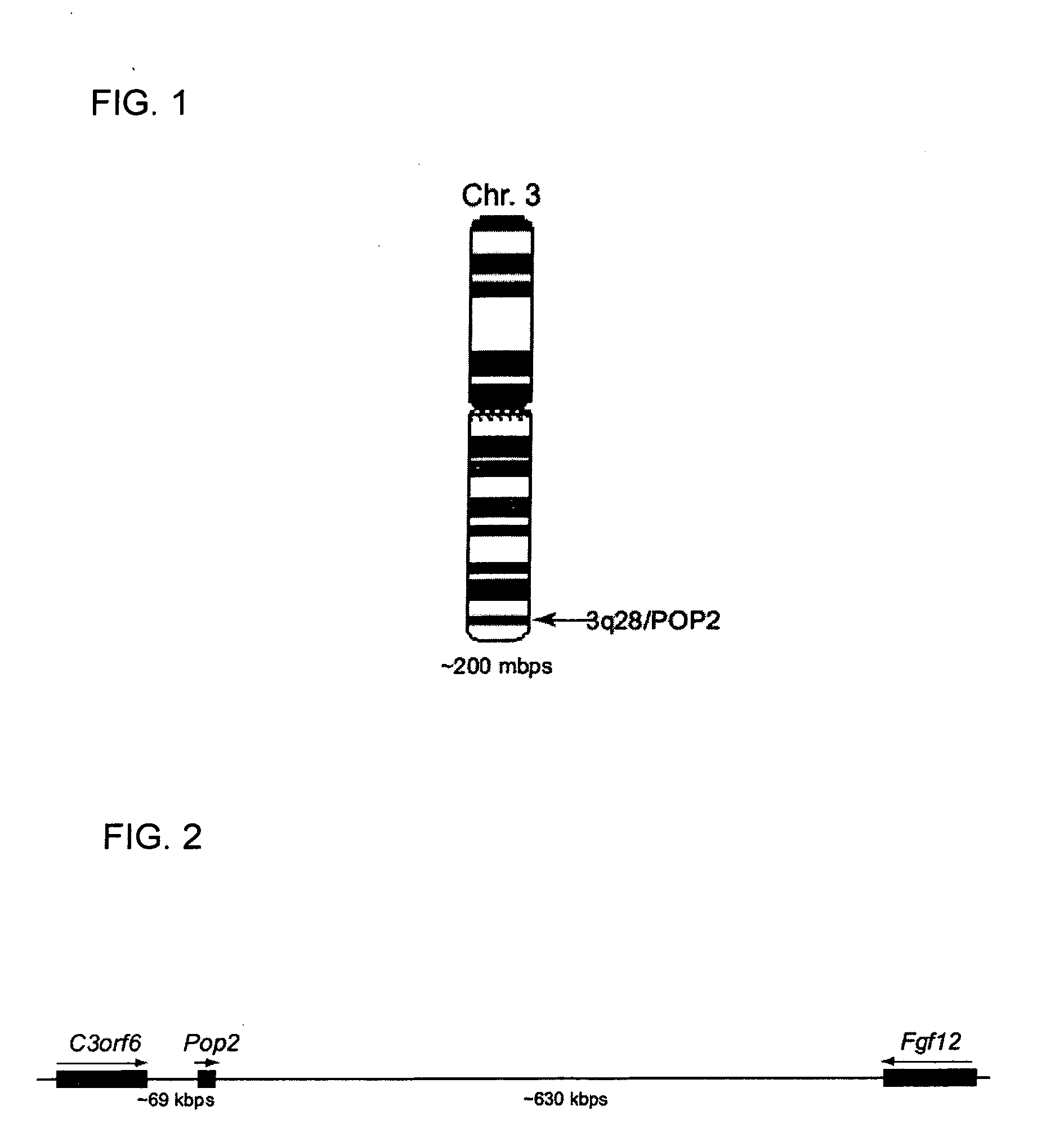
POP2: NFkB - Inhibiting Polypeptides, Nucleic Acids and Methods of Use
This invention provides a novel pyrin-only protein (POP2), polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them. The polypeptides of this invention have nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) modulating activity. NF-κB is pivotal for transactivation of cell-cycle regulatory, cytokine and adhesion molecule genes and is dysregulated in many cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory diseases. Proteins with Pyrin and / or caspase recruitment (CARD) domains have roles in apoptosis, innate immunity, and inflammation. Many pyrin domain proteins modulate NF-KB activity as well as participate in assembling both the perinuclear “apoptotic speck” and the pro-IL1β / IL-18 converting inflammasome complex. ‘Pyrin-only’ proteins are attractive as negative regulators of pyrin domain-mediated functions and one such protein, POP1, has been reported. We teach a second Pyrin-only protein (POP2). POP2 is a 294 nt single exon gene located on human chromosome 3 encoding a 97 amino acid protein with sequence and predicted structural similarity to other pyrin domains. Highly similar to pyrin domains in CATERPILLER (CLR, NLR, NALP) family proteins, POP2 is less like the prototypic Pyrin and ASC pyrin domains. POP2 is expressed principally in peripheral blood leukocytes and displays both cytoplasmic and nuclear expression patterns in transfected cells. TNFα-stimulated and p65 (RelA) induced NF-KB-dependent gene transcription is inhibited by POP2 in vitro by a mechanism involving changes in NF-κB nuclear import or distribution. While colocalizing with ASC in perinuclear specks, POP2 also inhibits the formation of specks by the CLR protein CIAS1 / NALP3. Together these observations indicate that POP2 is a negative regulator of NF-KB activity that may influence the assembly of pyrin-domain dependent complexes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Modulation of T cell signaling threshold and T cell sensitivity to antigens
ActiveUS20080200416A1High outputHigh expressionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPeptide antigenDUSP6
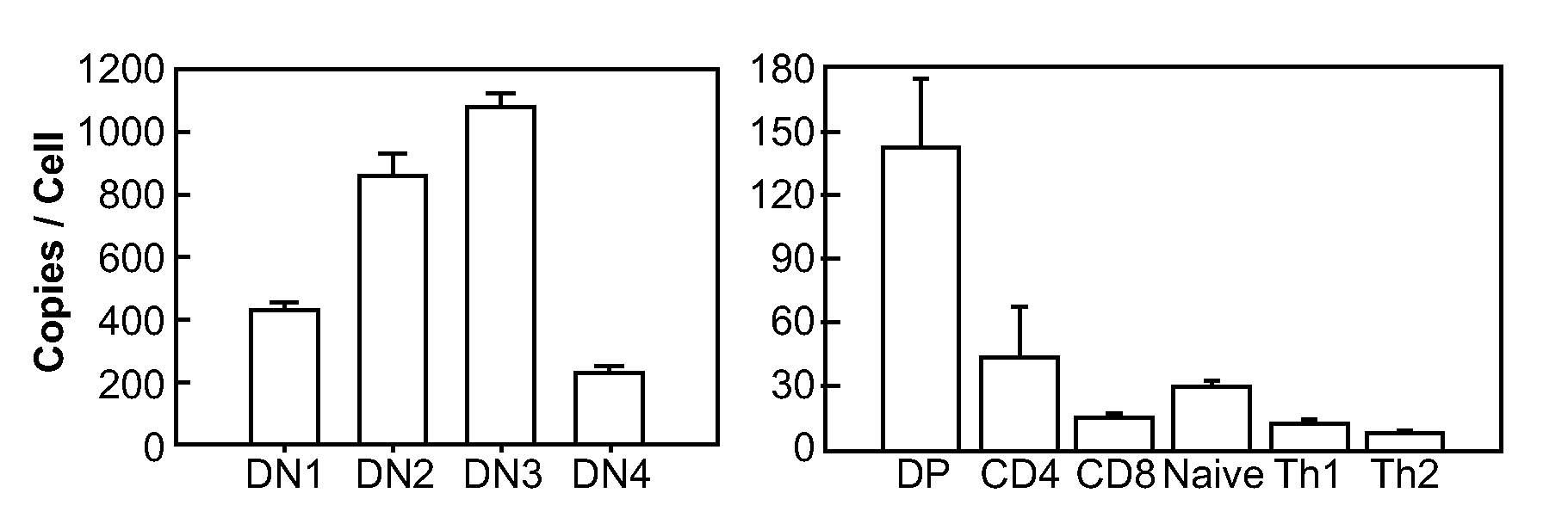
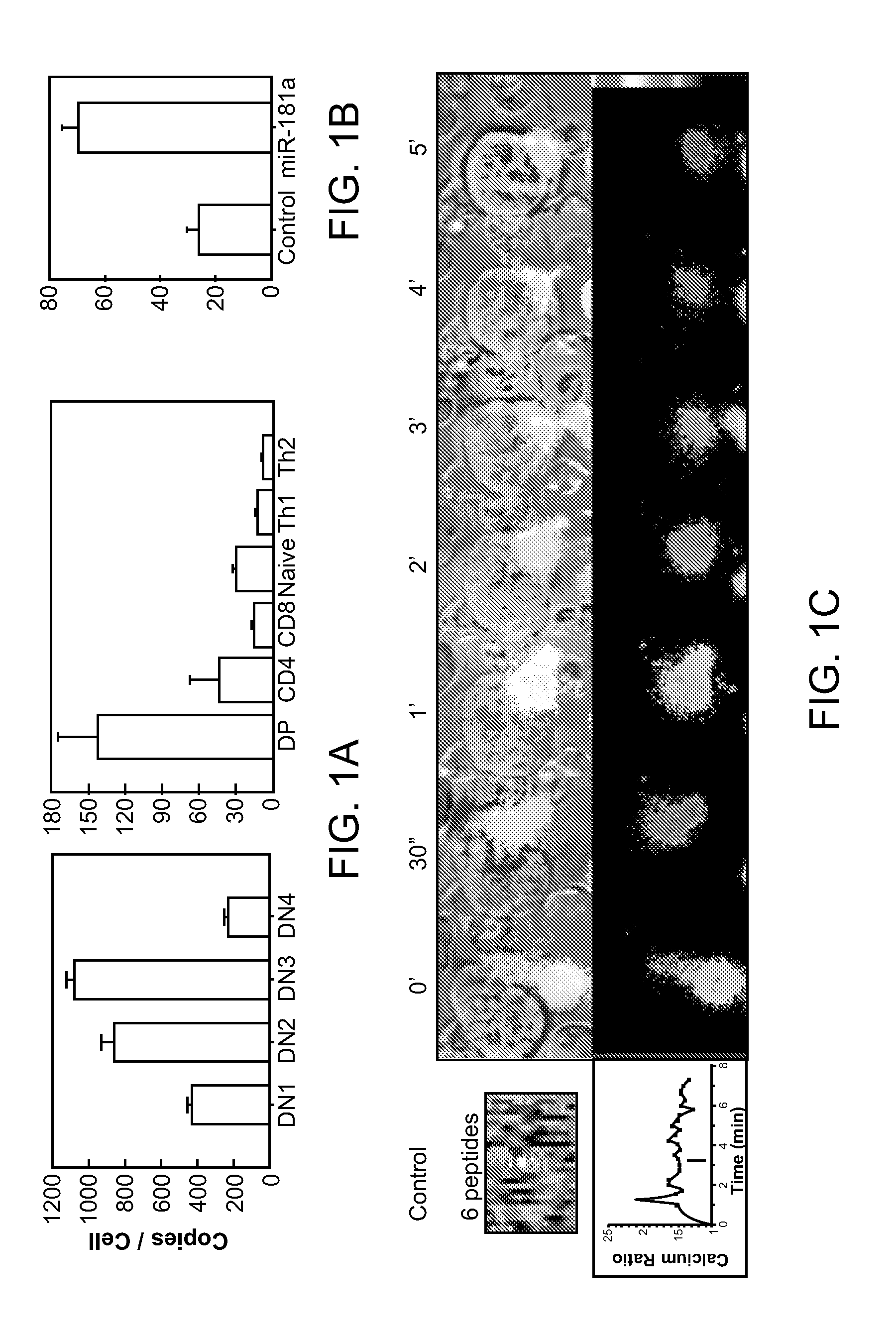
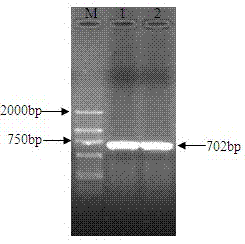
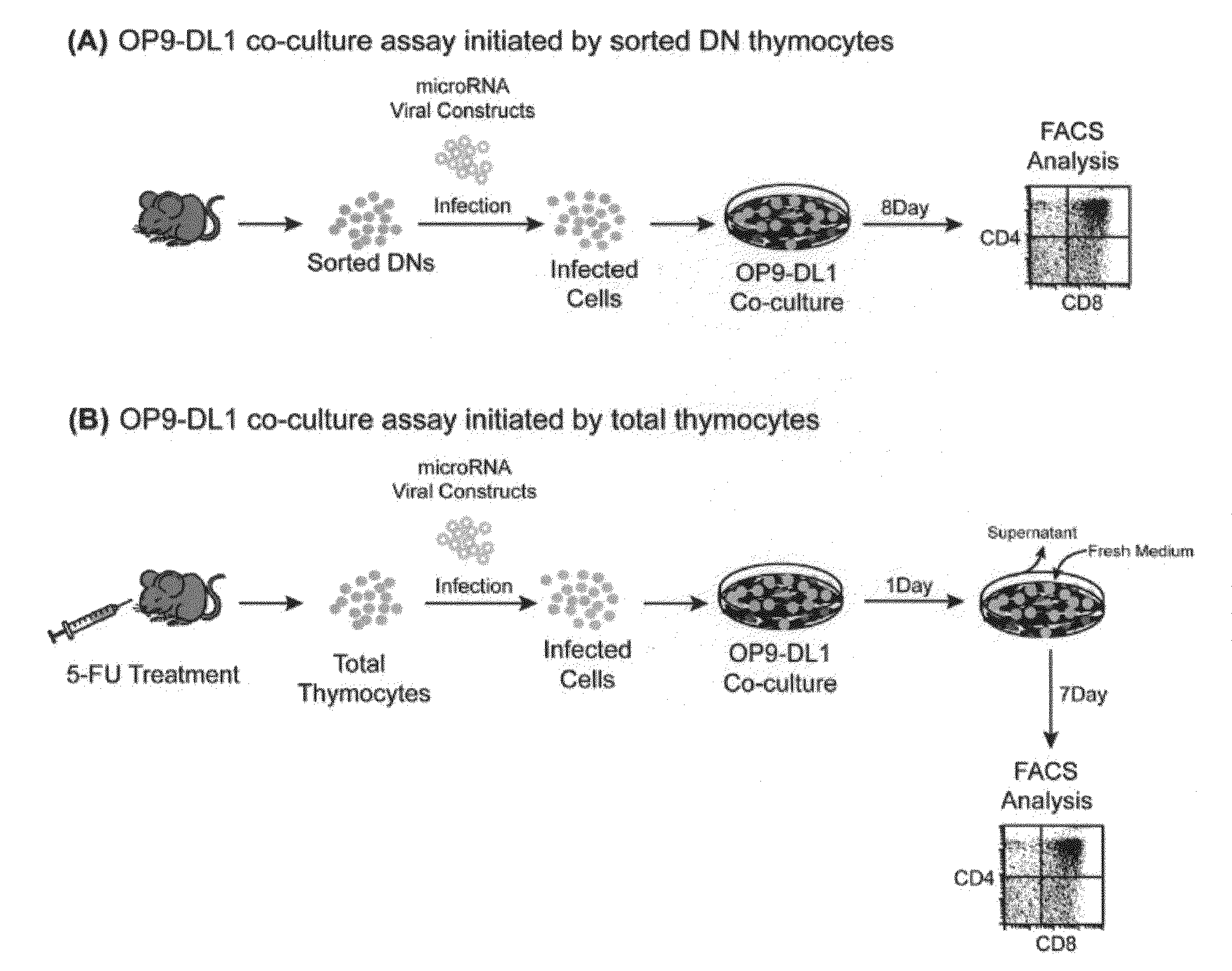
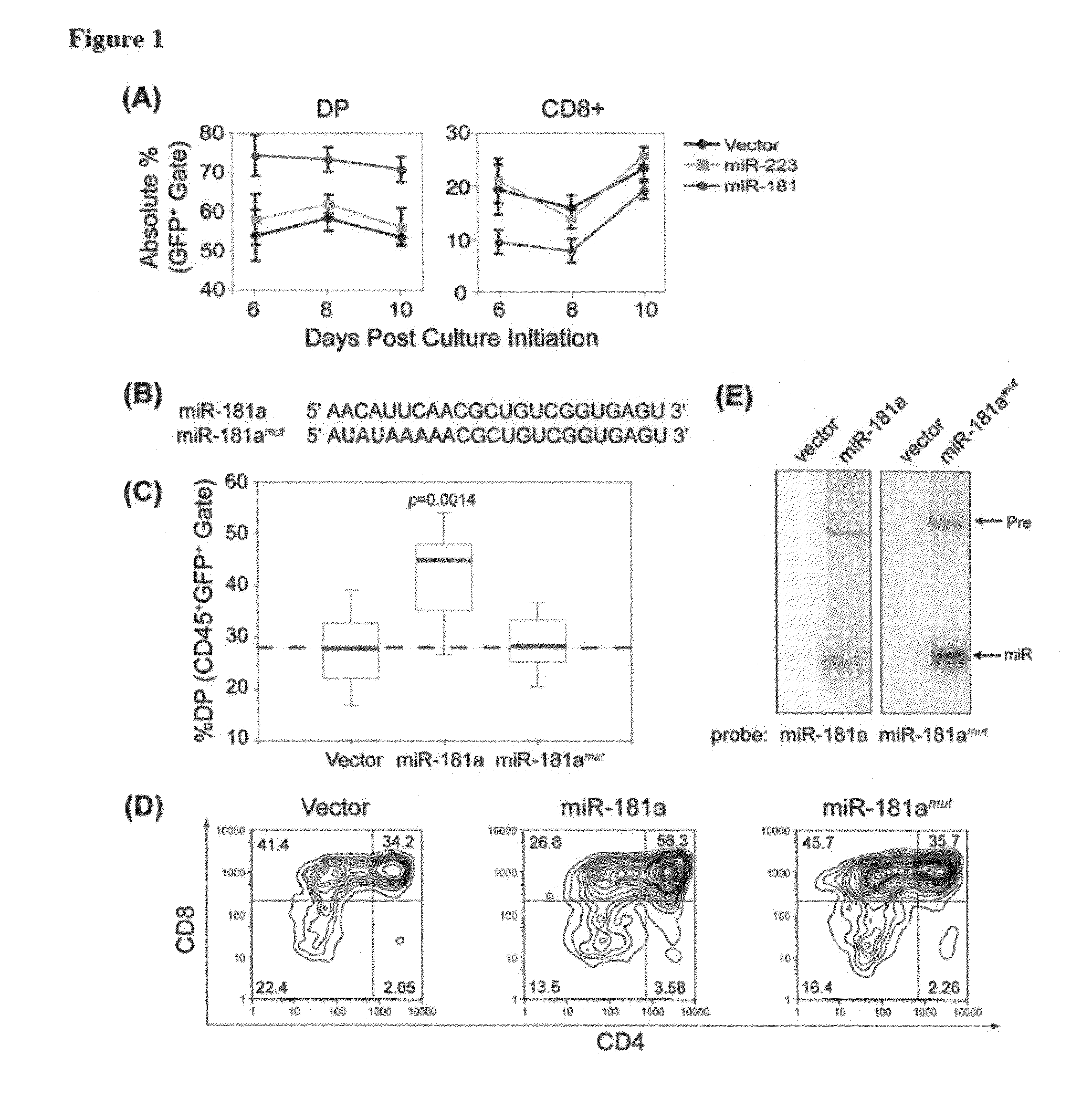
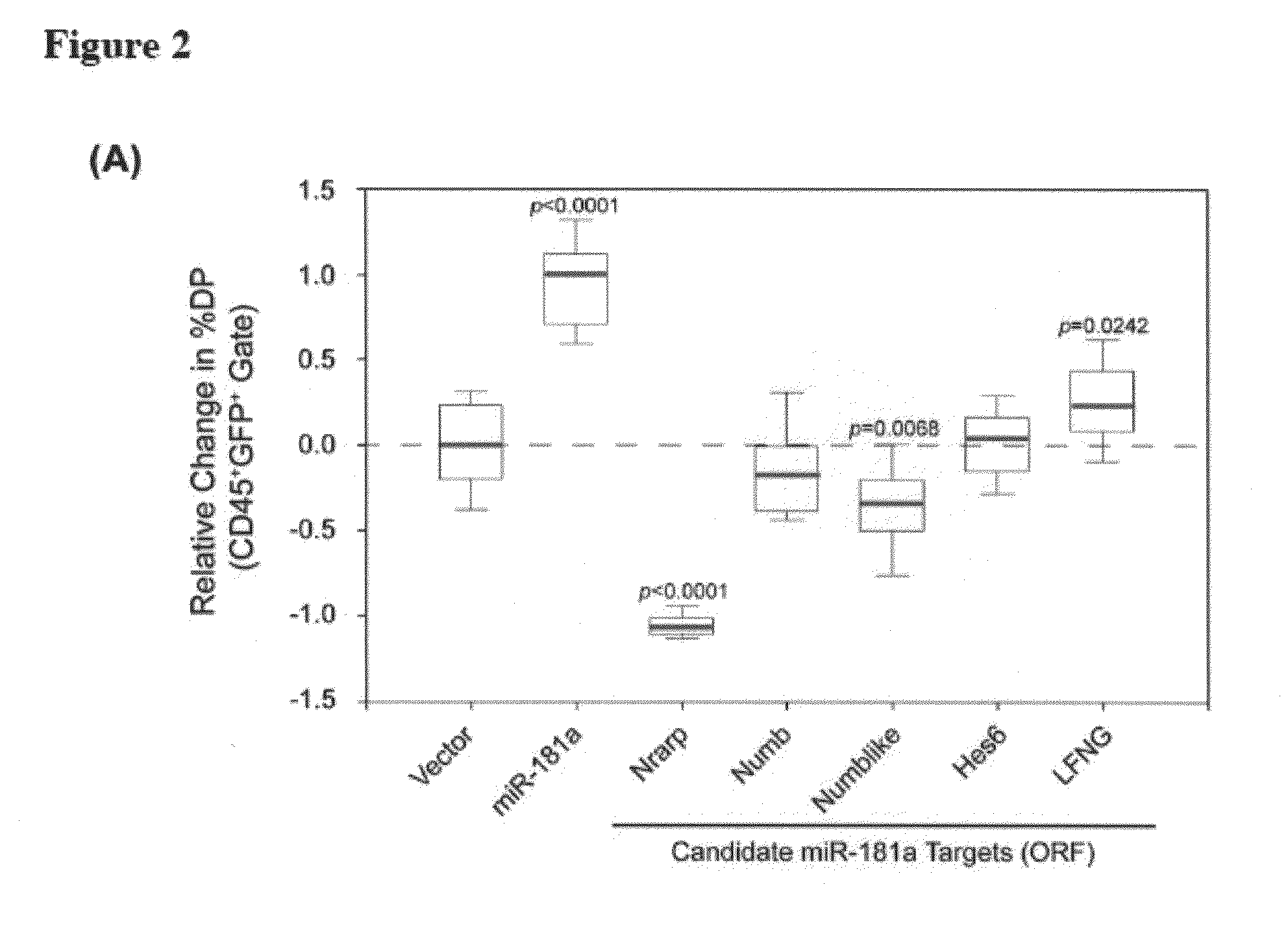
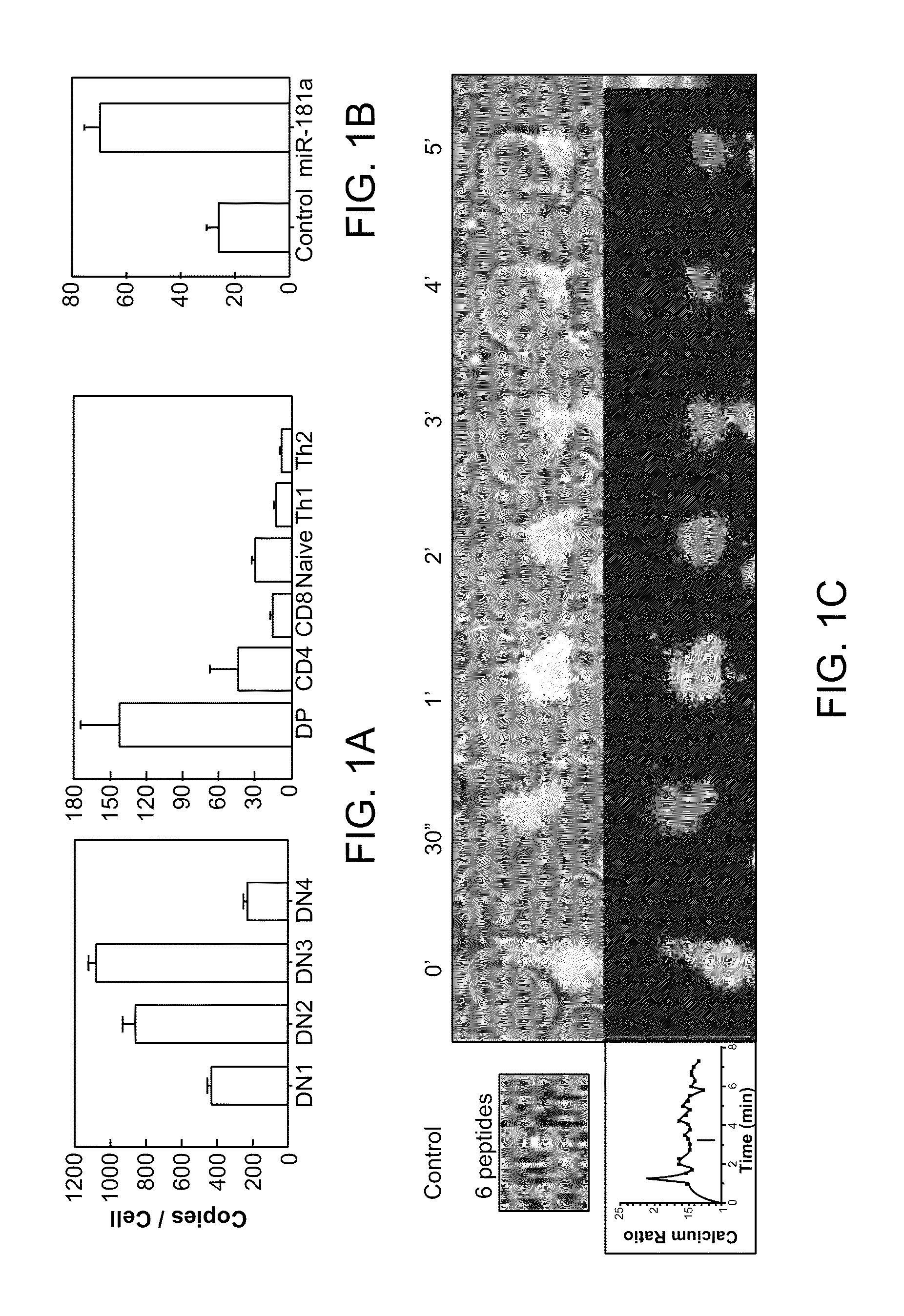
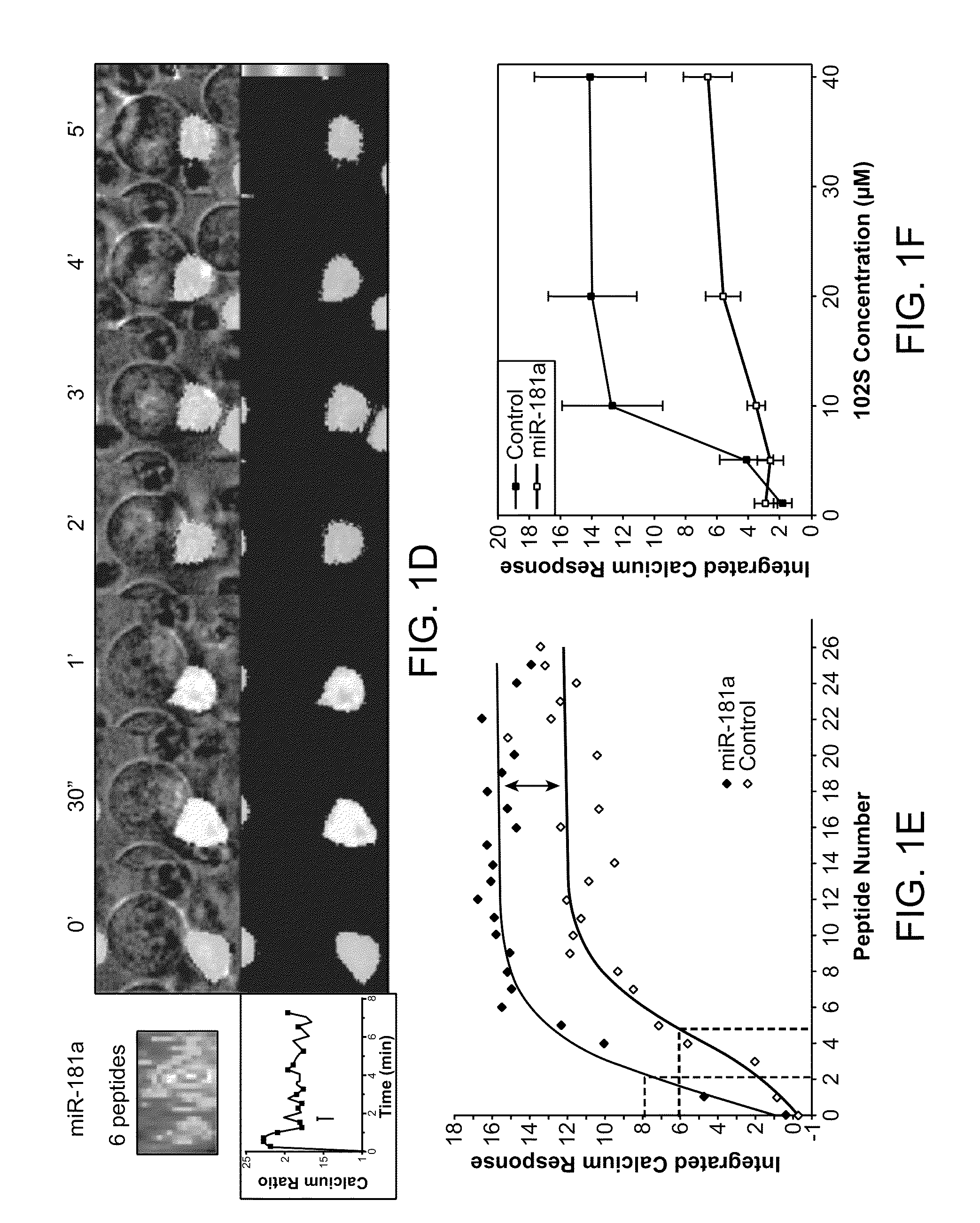
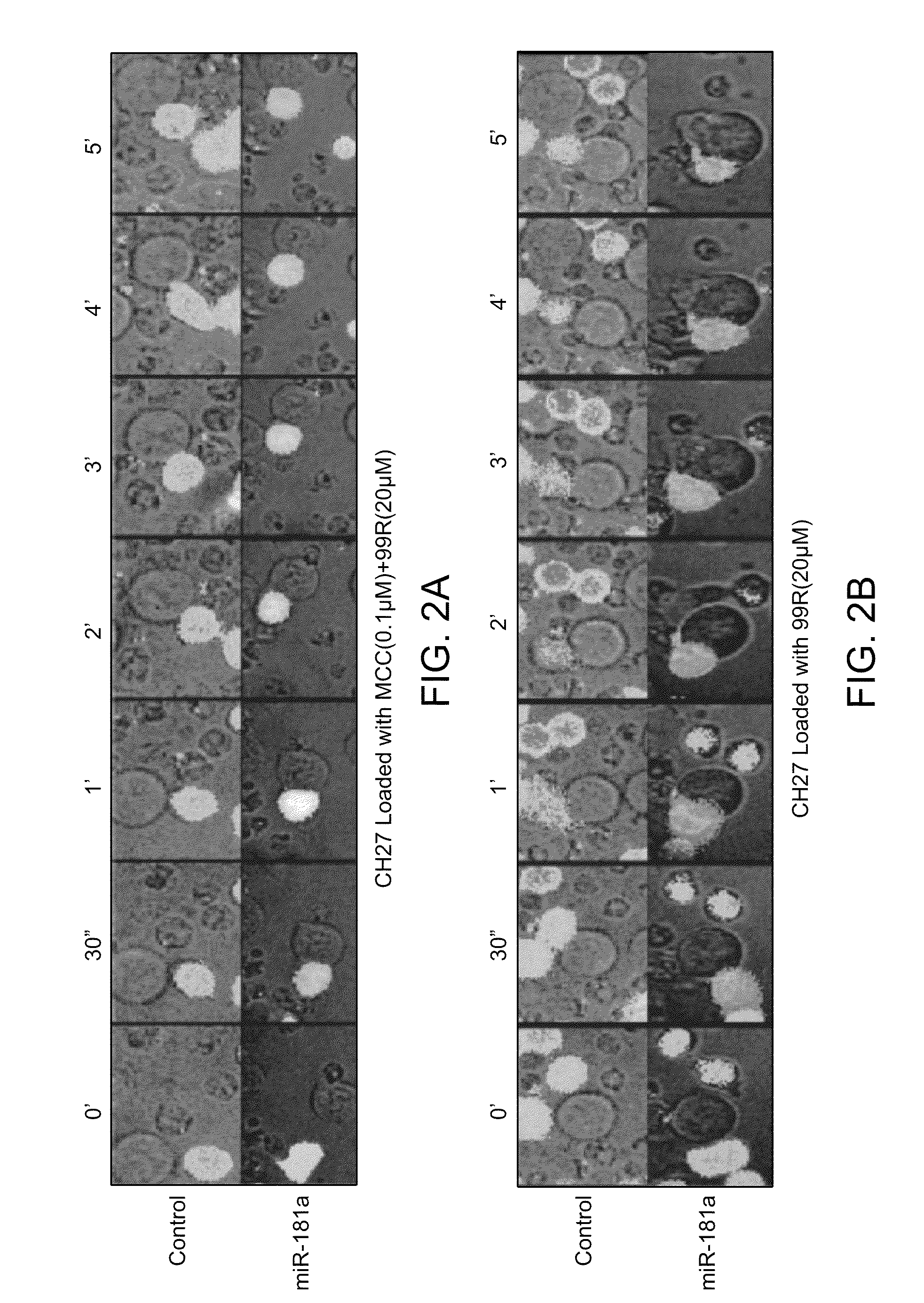
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a diverse and abundant class of ˜22-nucleotide (nt) endogenous regulatory RNAs that play a variety of roles in animal cells by controlling gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Increased miR-181a expression in mature T cells is shown to cause a marked increase in T cell activation and augments T cell sensitivity to peptide antigens. Moreover, T cell blasts with higher miR-181a expression become reactive to antagonists. The effects of miR-181a on antigen discrimination are in part achieved by dampening the expression of multiple negative regulators in the T cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway, including PTPN22 and the dual specificity phosphatases DUSP5 and DUSP6. This results in a reduction in the TCR signaling threshold, thus quantitatively and qualitatively enhancing T cell sensitivity to antigens.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
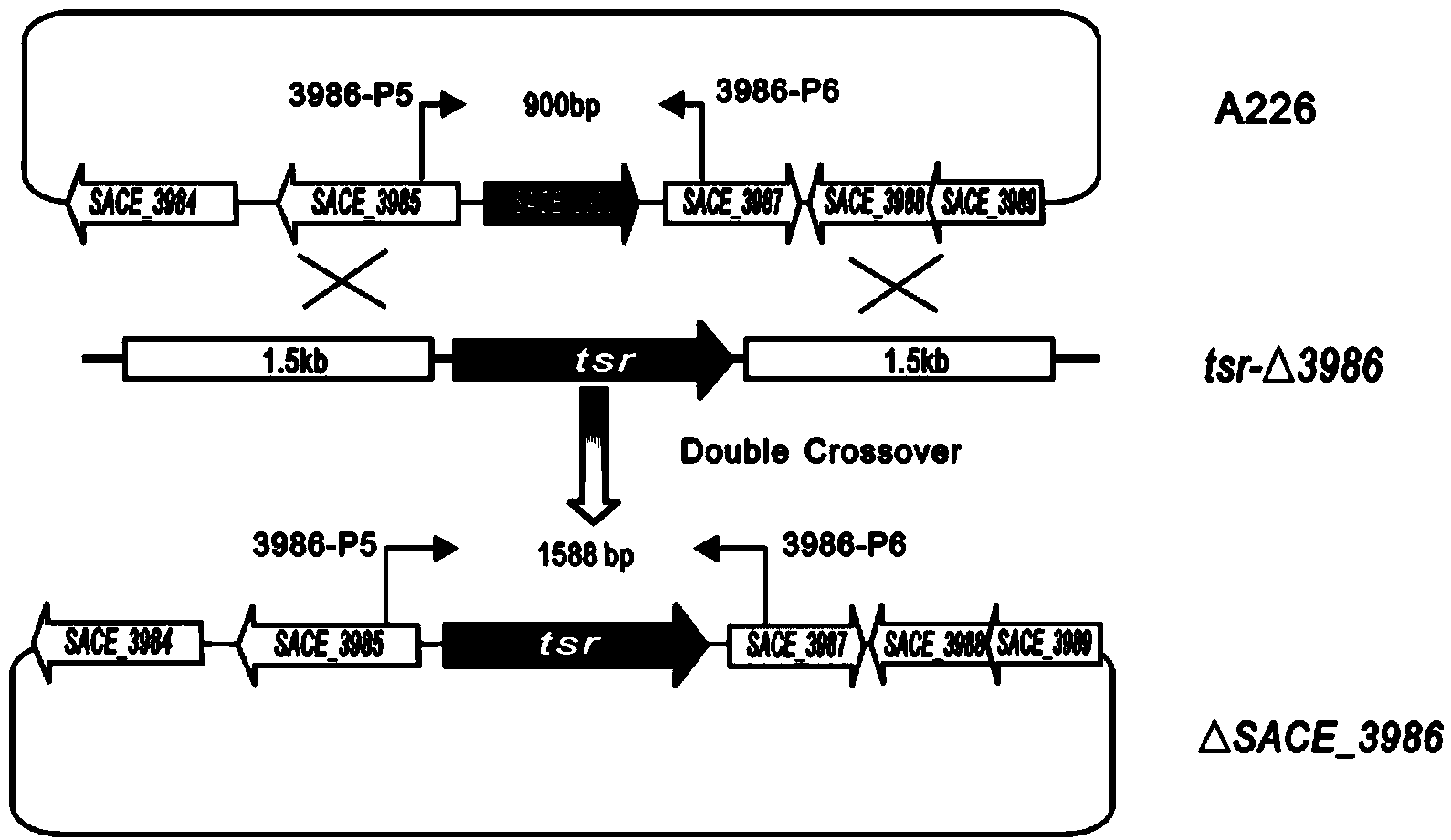
Method for increasing yield of erythromycin by virtue of saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3986 gene
ActiveCN103849642AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses a method for increasing yield of erythromycin by virtue of a saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3986 gene. The method for increasing the yield of erythromycin by virtue of the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3986 gene is that a saccharopolyspora erythraea erythromycin high yield engineering strain is obtained by virtue of an SACE_3986 gene with saccharopolyspora erythraea deleted in a genetic engineering way, the obtained bacterial strain can increase the yield of erythromycin when being used for fermentation, an erythromycin biosynthesis negative regulator SACE_3986 is screened under study, and an erythromycin high yield bacterial strain can be obtained by copying the SACE_3986 gene on a chromosome with saccharopolyspora erythraea deleted in the genetic engineering way, so that technical support is provided for increasing fermentation yield of erythromycin in industrial production.
Owner:阜阳天祥食品科技有限公司
TGFbeta signaling inhibitors
InactiveUS20050136043A1Peptide/protein ingredientsChemical treatment enzyme inactivationKinase activityNegative regulator
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Method and composition for increasing insulin sensibility
InactiveCN101176786AIncreased sensitivityHigh biosecurityHydroxy compound active ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseInsulin signalling
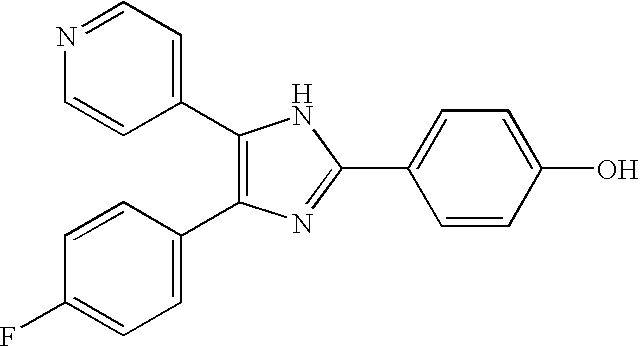
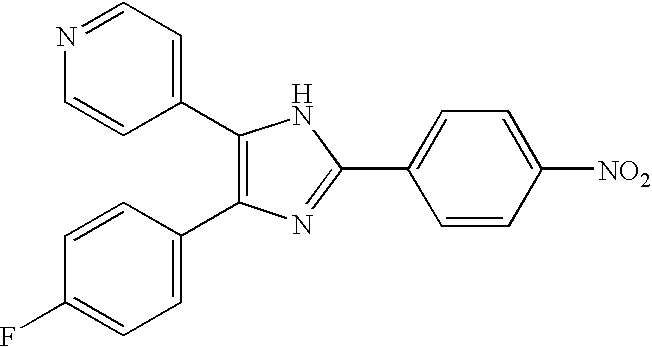
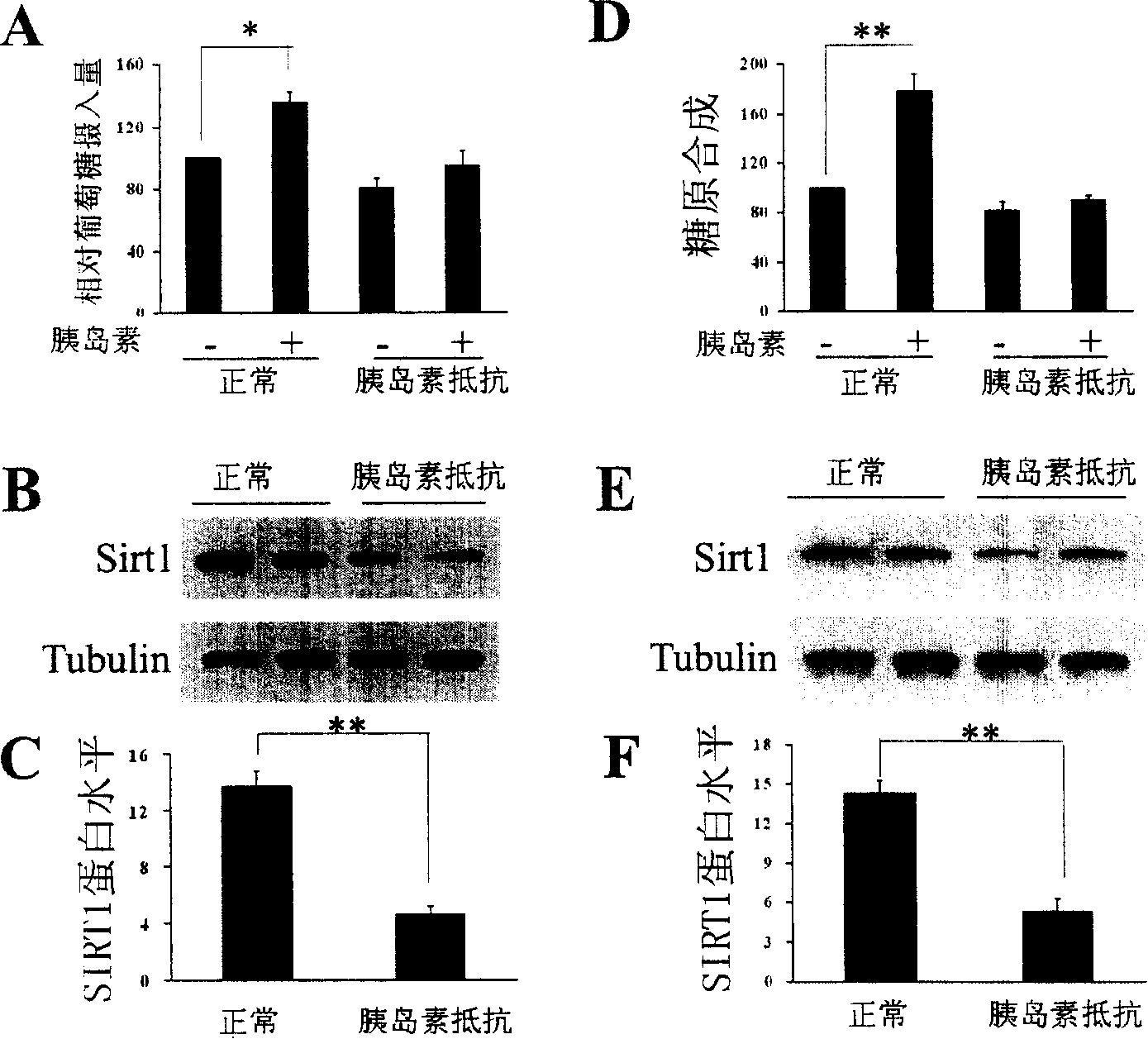
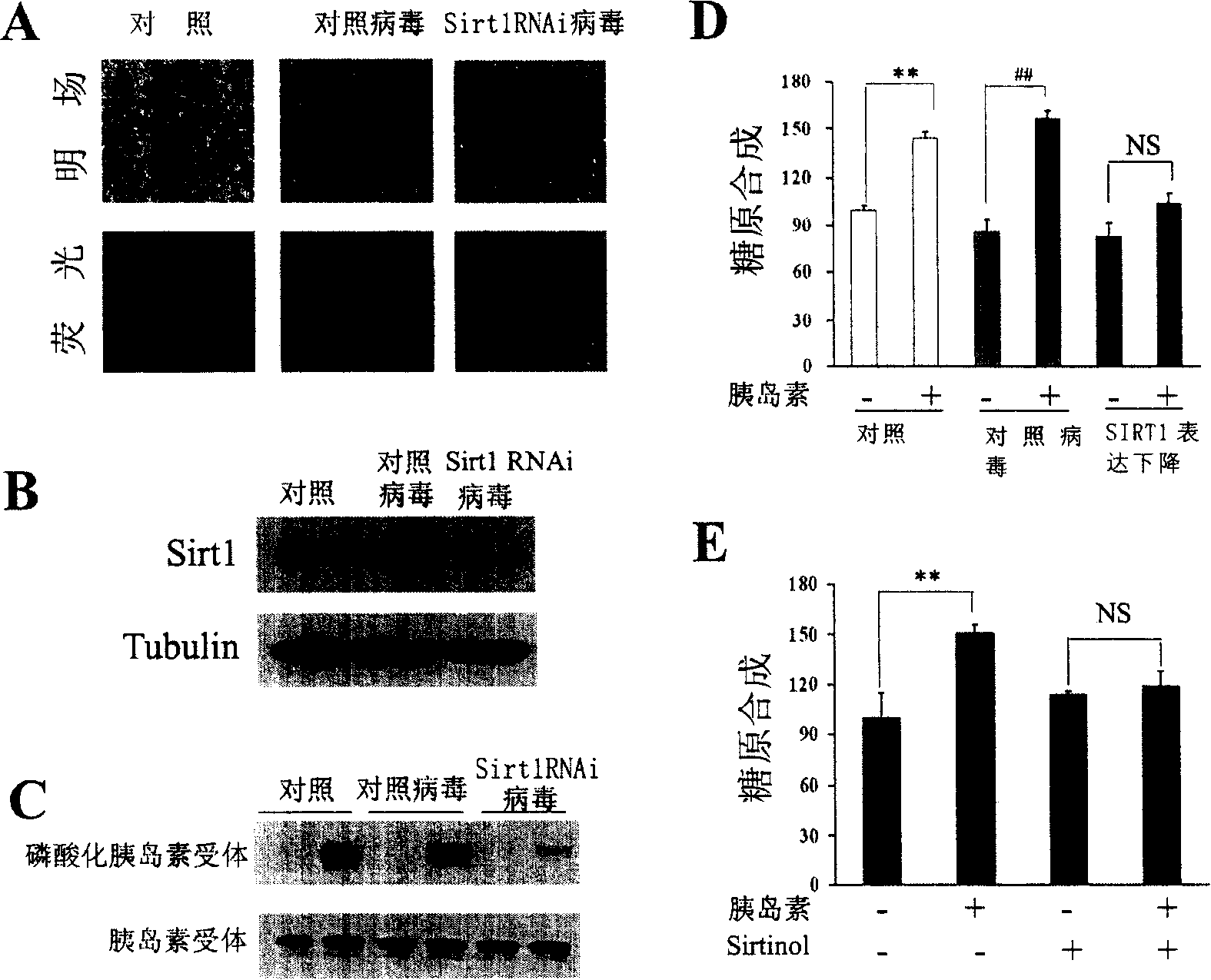
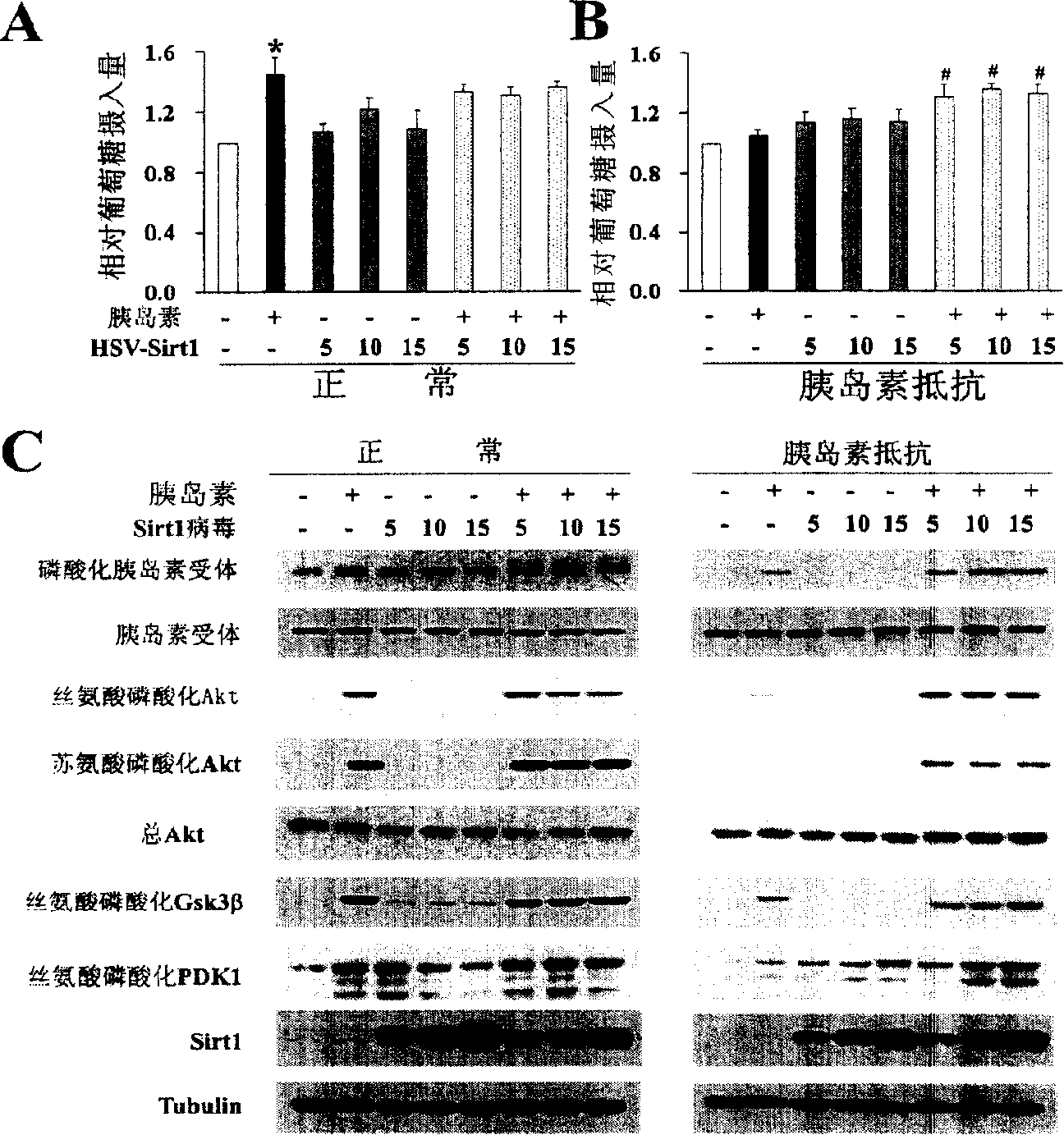
The present invention provides a use of SIRT1 protein or agonists or up-regulators thereof for manufacturing a composition which can increase insulin sensitivity. SIRT1 can be used to increase insulin sensitivity by down-regulating expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, a negative regulator of insulin action.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antisense IAP oligonucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7294713B2Enhanced cellular uptakeImprove stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNegative regulatorApoptosis pathway
The present invention feature antisense IAP oligonucleotides and other negative regulators of the IAP anti-apoptotic pathway, and methods for using them to enhance apoptosis.
Owner:OTTAWA UNIV OF +1
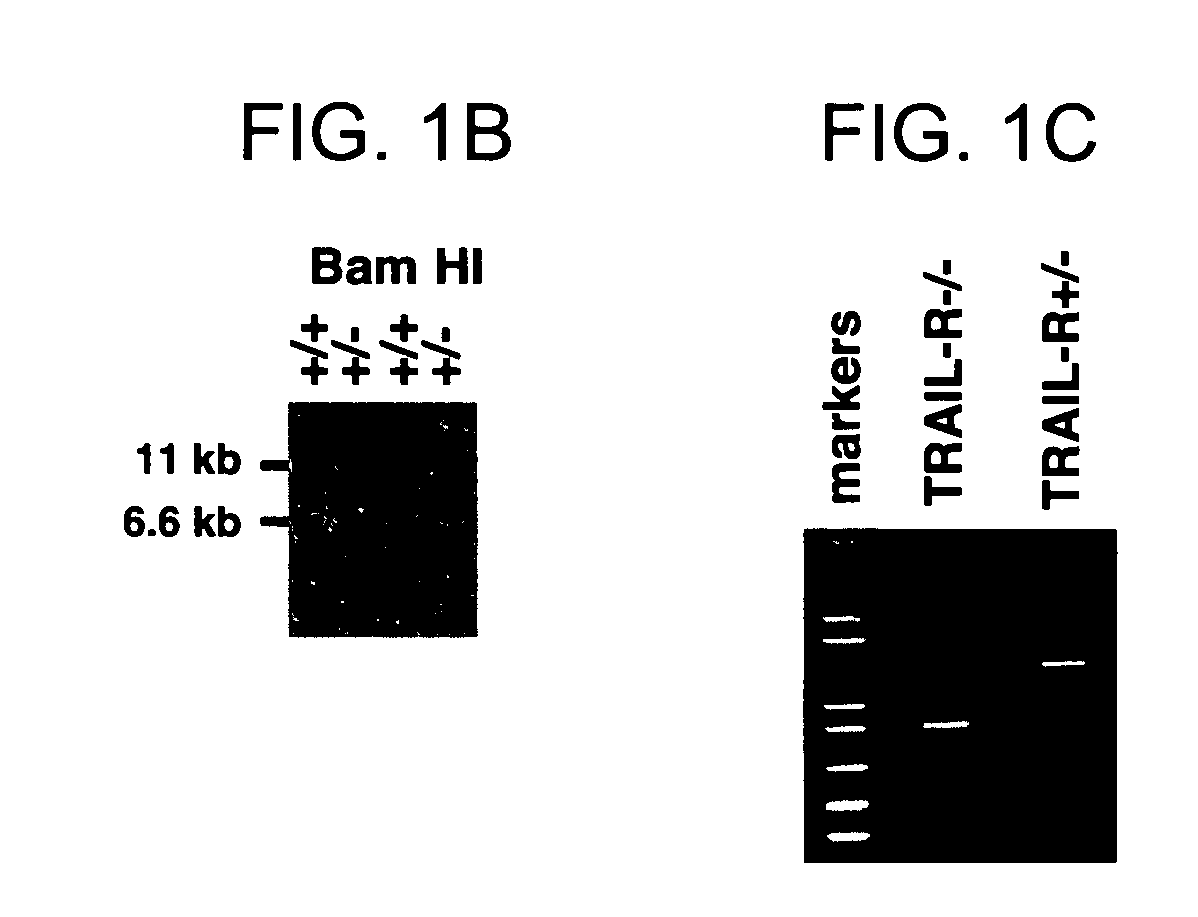
TRAIL-R as a negative regulator of innate immune cell responses
InactiveUS20050216960A1Inhibitory responseIncreasing and decreasing activity of cellCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellTRAIL Receptors
Methods and composition are provided for modulating innate immunity by modulating activation of the TRAIL receptor. Signaling through the TRAIL-R inhibits the responsiveness of cells including dendritic cells, macrophages, and the like. The activity of these cells is increased or decreased by the administration of agents that inhibit or activate TRAIL-R signaling. Innate immunity includes the production of cytokines that act on the immune system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for regulating osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption using LRRc17
Provided is a purified, negative regulator of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption, specifically LRRc17. Further provided are methods and compositions for treating degenerative bone disorders, and treatments and prophylactic approaches for regulating bone resorption, and for decreasing or inhibiting the excessive bone loss associated with abnormal or excessive generation of or activity of osteoclasts.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
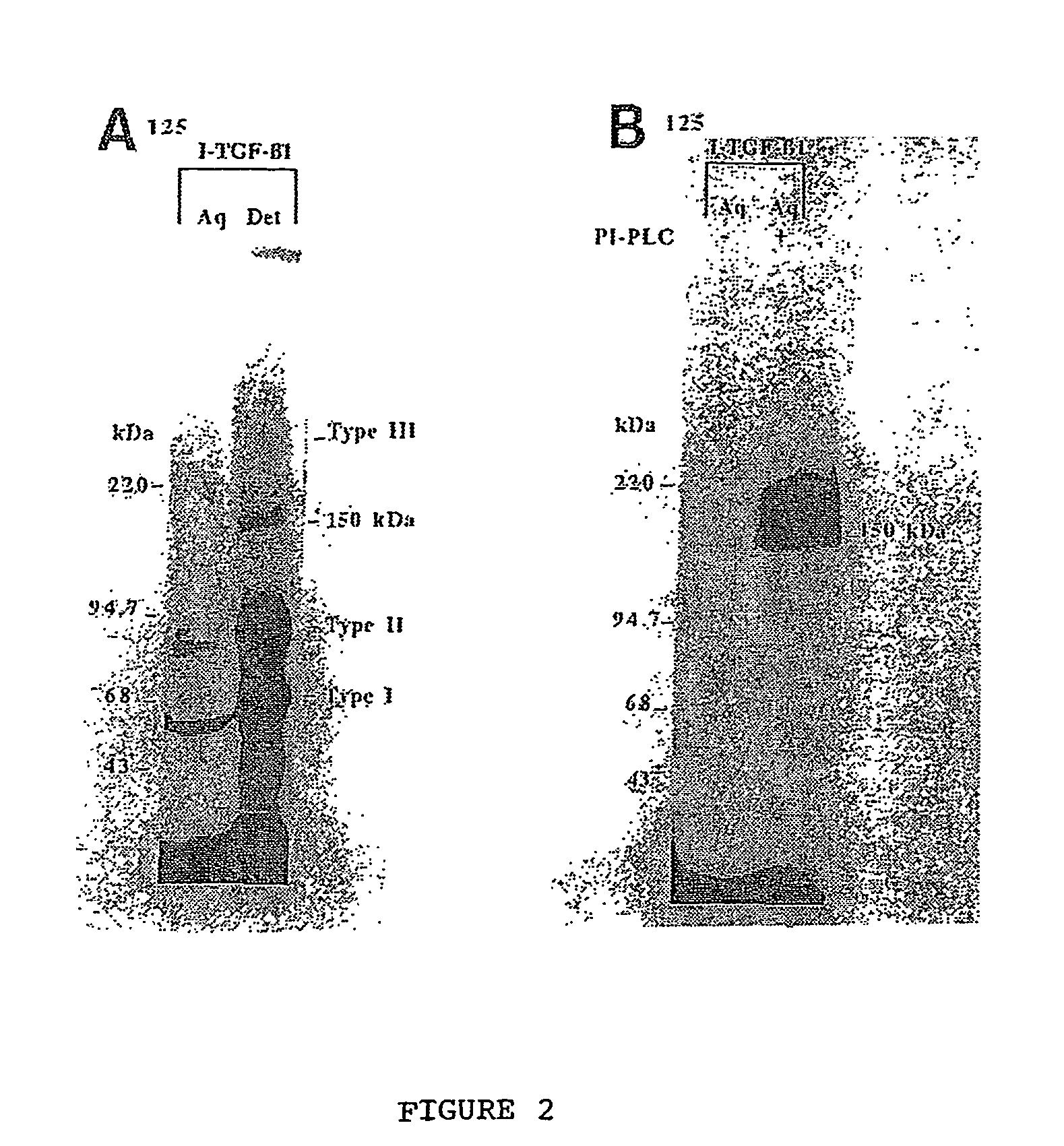
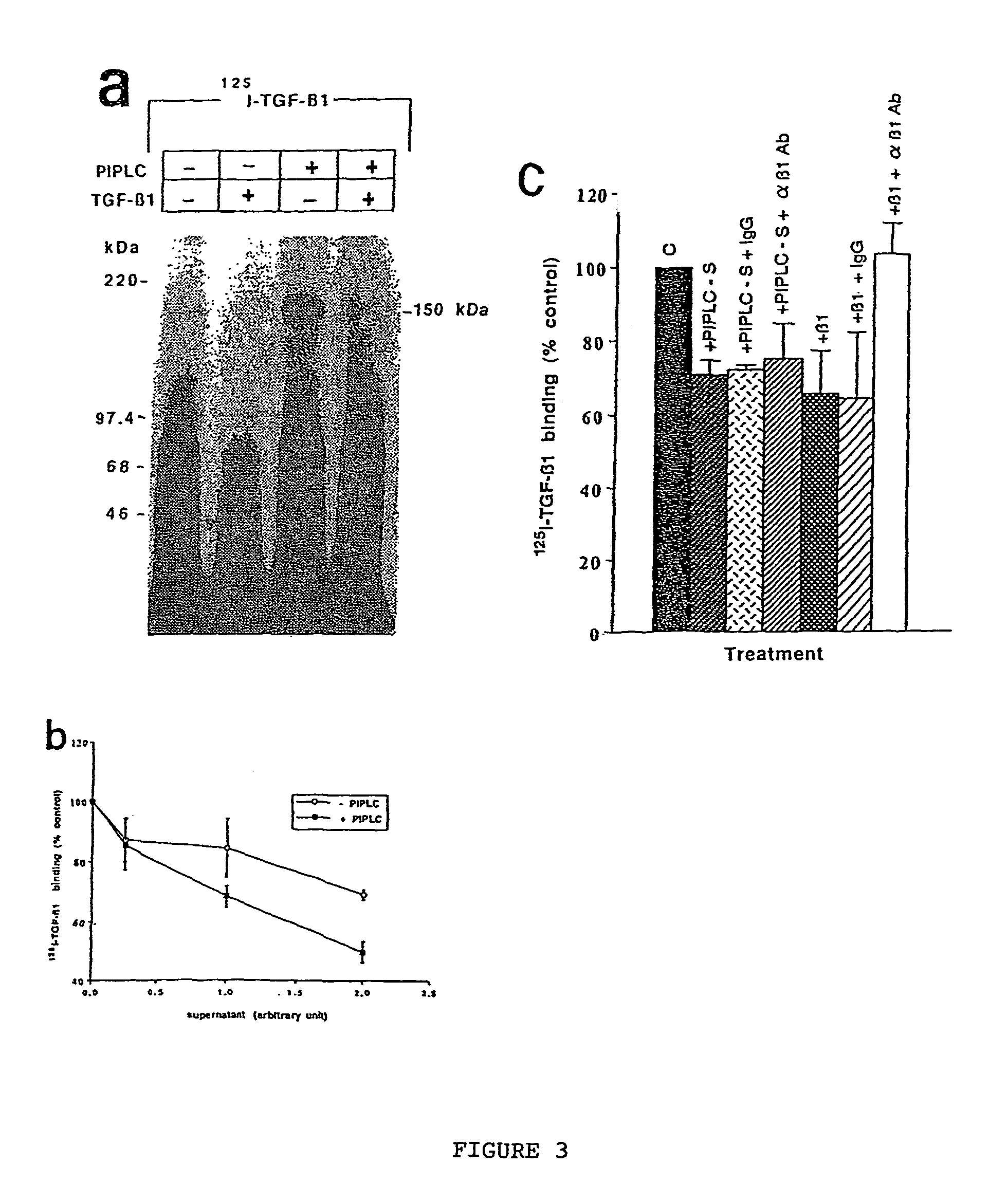
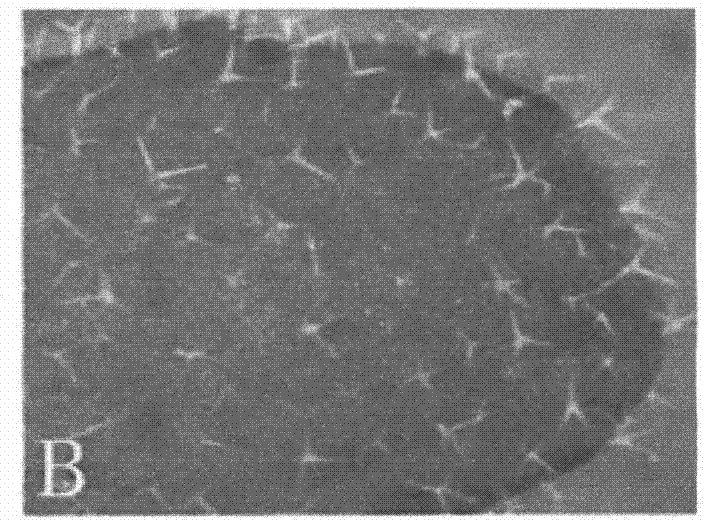
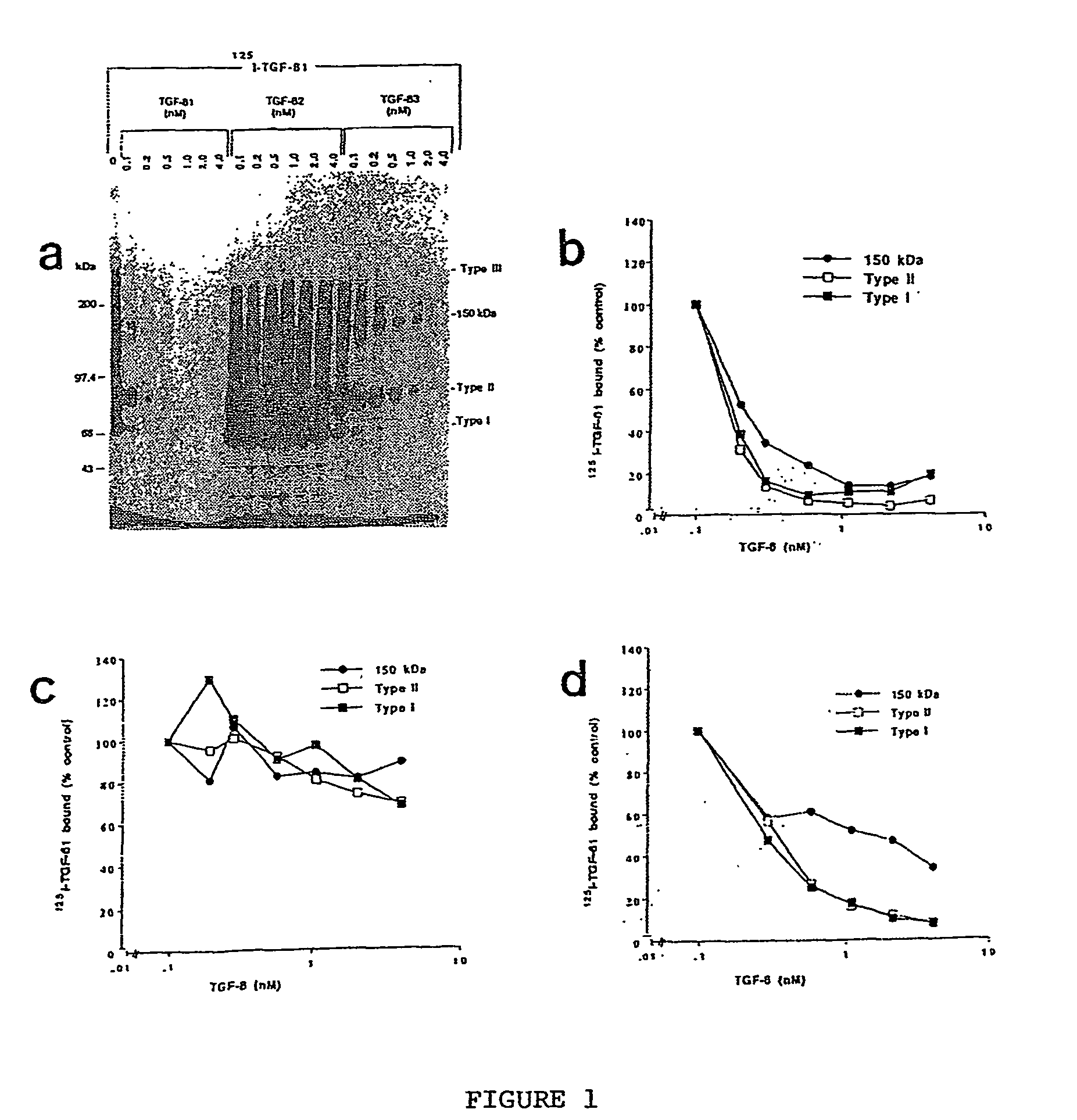
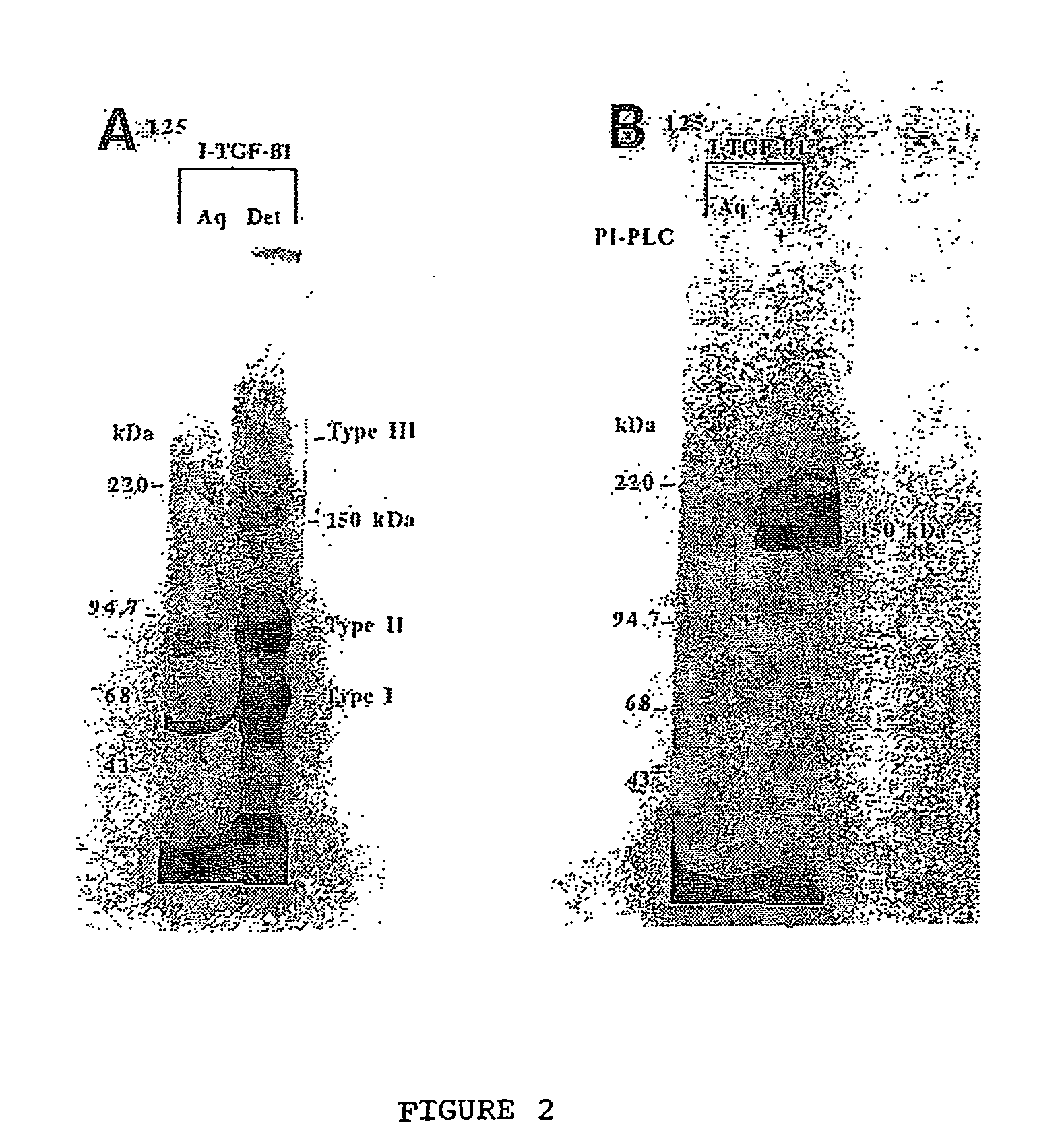
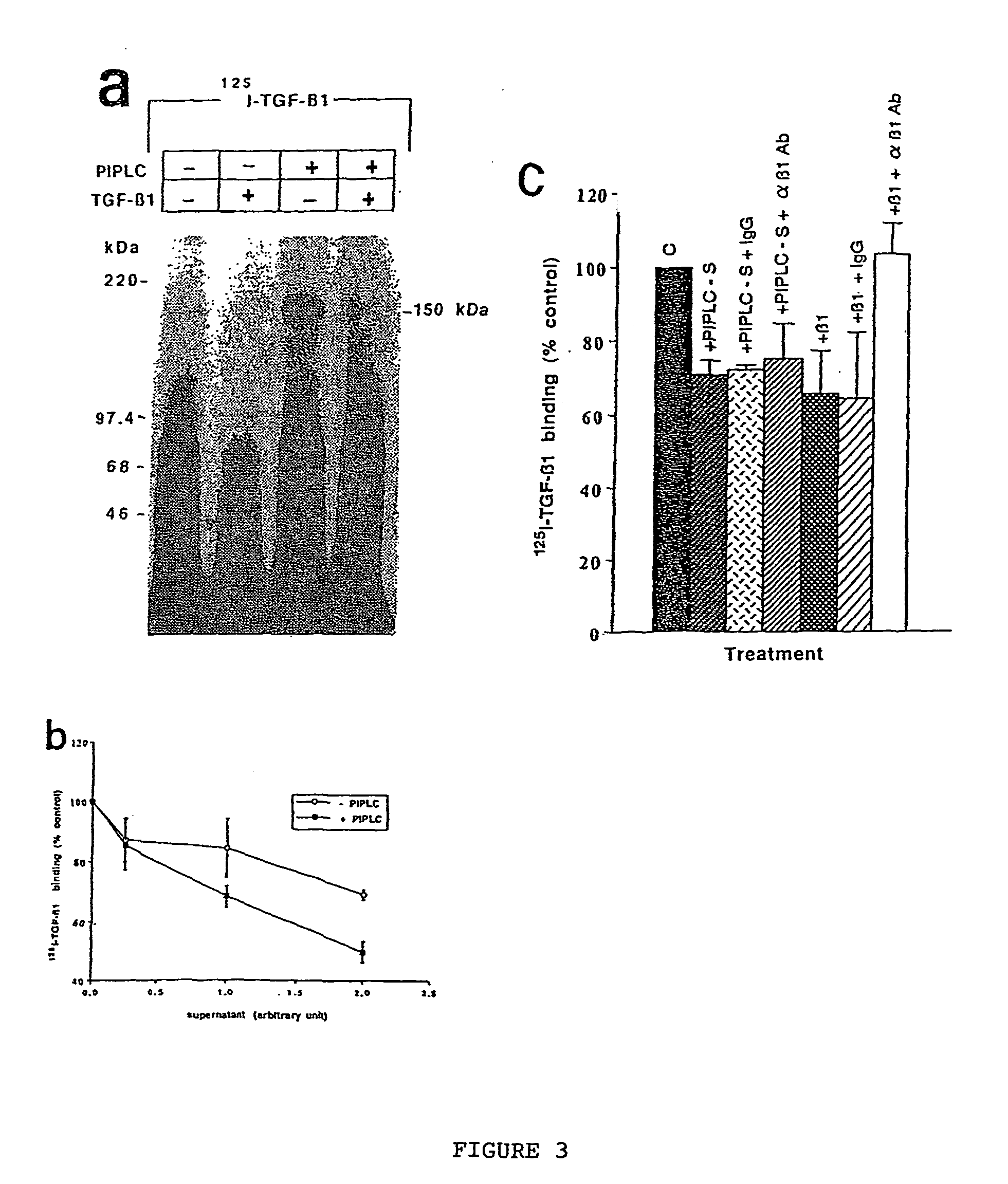
150 KDA TGF-B1 accessory receptor acts a negative modulator of TGF-B signaling
The present invention relates to a TGF-β1 binding protein called r150. This protein has a GPI-anchor contained in r150 itself and not on a tightly associated protein and that it binds TGF-β1 with an affinity comparable to those of the signaling receptors. Furthermore, the released (soluble) form of this protein binds TGF-β1 independent of the types I and II receptors. Also, the soluble form inhibits the binding of TGF-β to its receptor. In addition, evidence that r150 is released from the cell surface by an endogenous phospholipase C is provided. Also, the creation of a mutant human keratinocyte cell line with a defect in GPI synthesis which displays reduced expression of r150 is described. Our results using these mutant keratinocytes suggest that the membrane anchored form of r150 is a negative modulator of TGF-beta responses. These findings, taken together with the observation that r150 forms a heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors, suggest that this accessory receptor in either its membrane anchored or soluble form may antagonize TGF-β responses in human keratinocytes. Experiments with mutants confirmed that TGFβ1 activity can be modulated when the expression of the accessory receptor r150 is silenced. The complete nucleic acid and deduced amino acid sequences are now provided. The r150 cloned nucleic acid was used to study overexpression of r150. When r150 gene is overexpressed, TGFβ responses are increased. r150 and its derivatives or precursors (fragments, variants and nucleic acids encoding the same) will find a broad clinical utility, knowing that TGFβ1 is an important cytokine.
Owner:9406 2668 QUEBEC INC
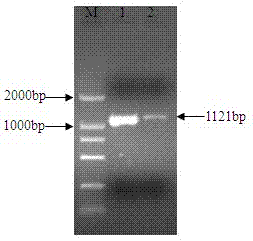
Negative regulator gene of streptomyces roseofulvus as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to an nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. In the invention, primers Ns8F and Ns8R are designed by utilizing an important negative regulator gene nsdB sequence in a Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) antibiotic metabolic pathway, and genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 is amplified to obtain a 1121bp segment; and two ends of a target sequence are extended by utilizing a primer anchoring polymerase chain reaction) (NPA-PCR ) method by a non-specific primer, thus obtaining the nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63. The preparation of the nsdBmgh gene provides an important basis for further researching and verifying the Streptomyces roseoflavus antibiotic metabolic pathway and regulatory mechanism, and establishes an important base for obtaining high-yield antibiotic gene engineering strains.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Role of miRNA in T cell leukemia
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
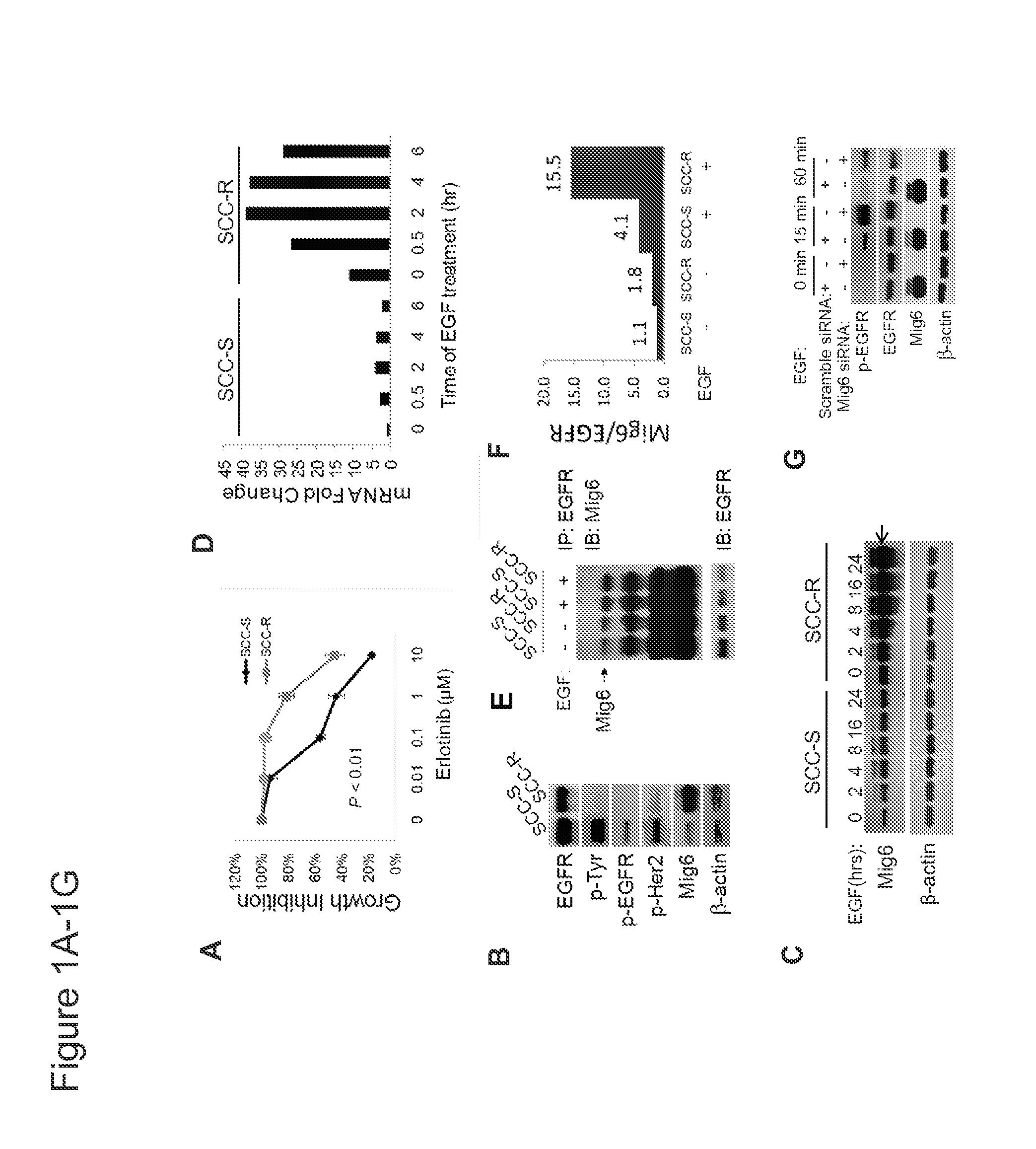
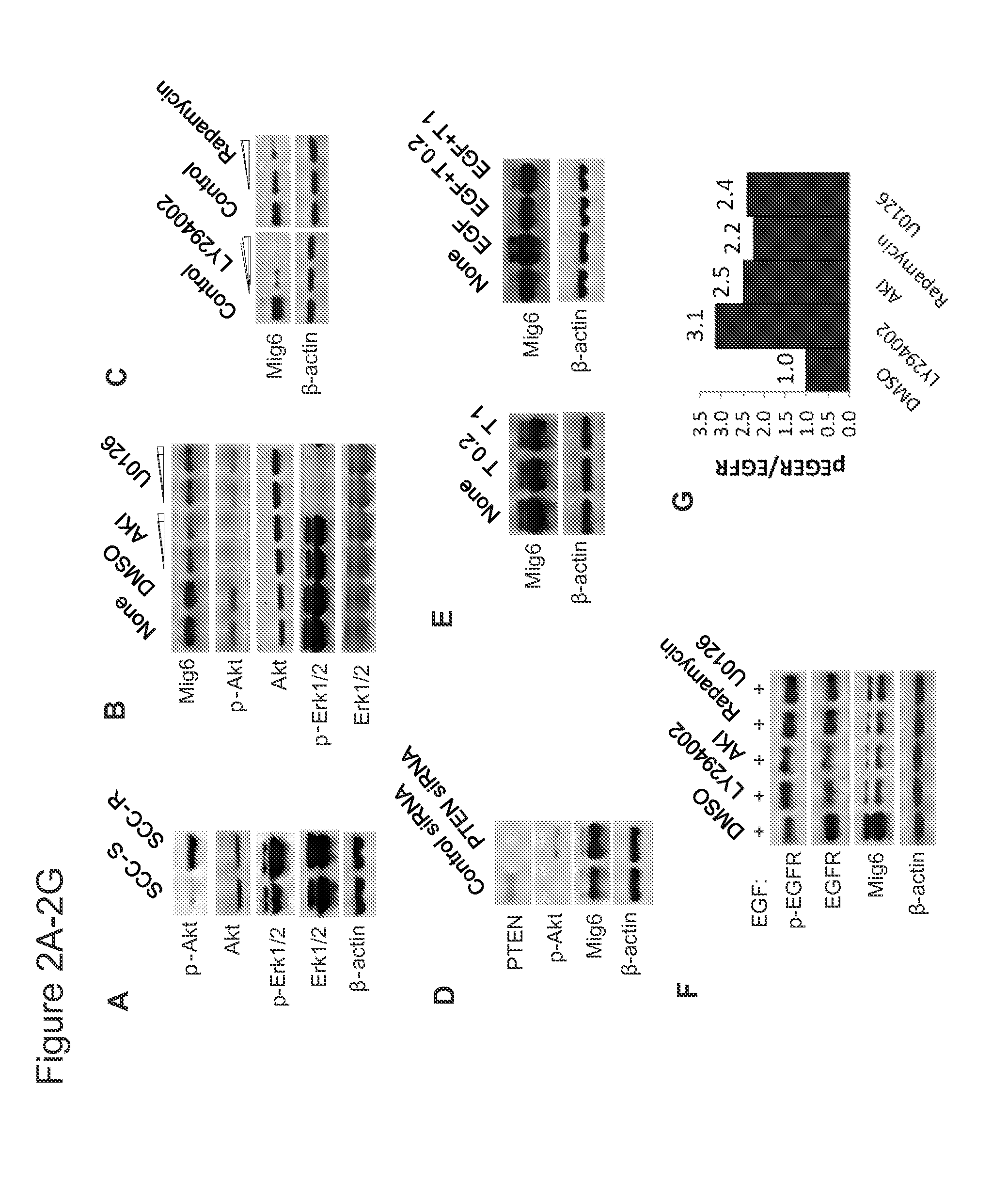
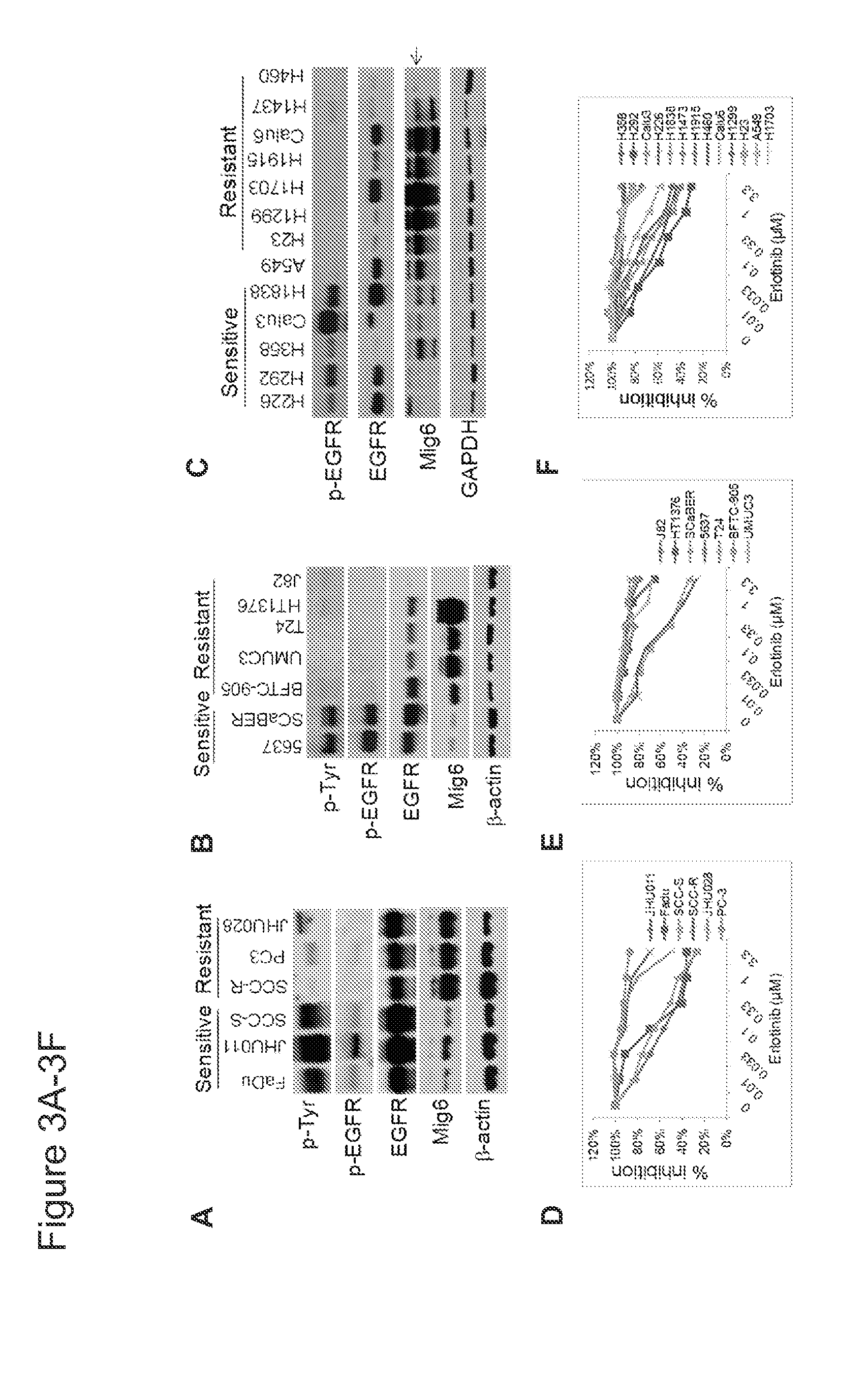
Mig6 and therapeutic efficacy
We identify markers capable of guiding the decision to incorporate epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors, in particular EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), into chemotherapeutic regimens. Mitogen-inducible gene 6 (Mig6), a negative regulator of EGFR, is selectively upregulated during the development of resistance to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) erlotinib, resulting in decreased EGFR phosphorylation. The ratio of Mig6 / EGFR expression highly correlates with erlotinib sensitivity. A low Mig6 / EGFR ratio correlates with a high response rate to gefitinib and a marked increase in progression-free survival for patients. The ratio of Mig6 to EGFR is a major predictor of biologic and clinical responses to EGFR inhibitors.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
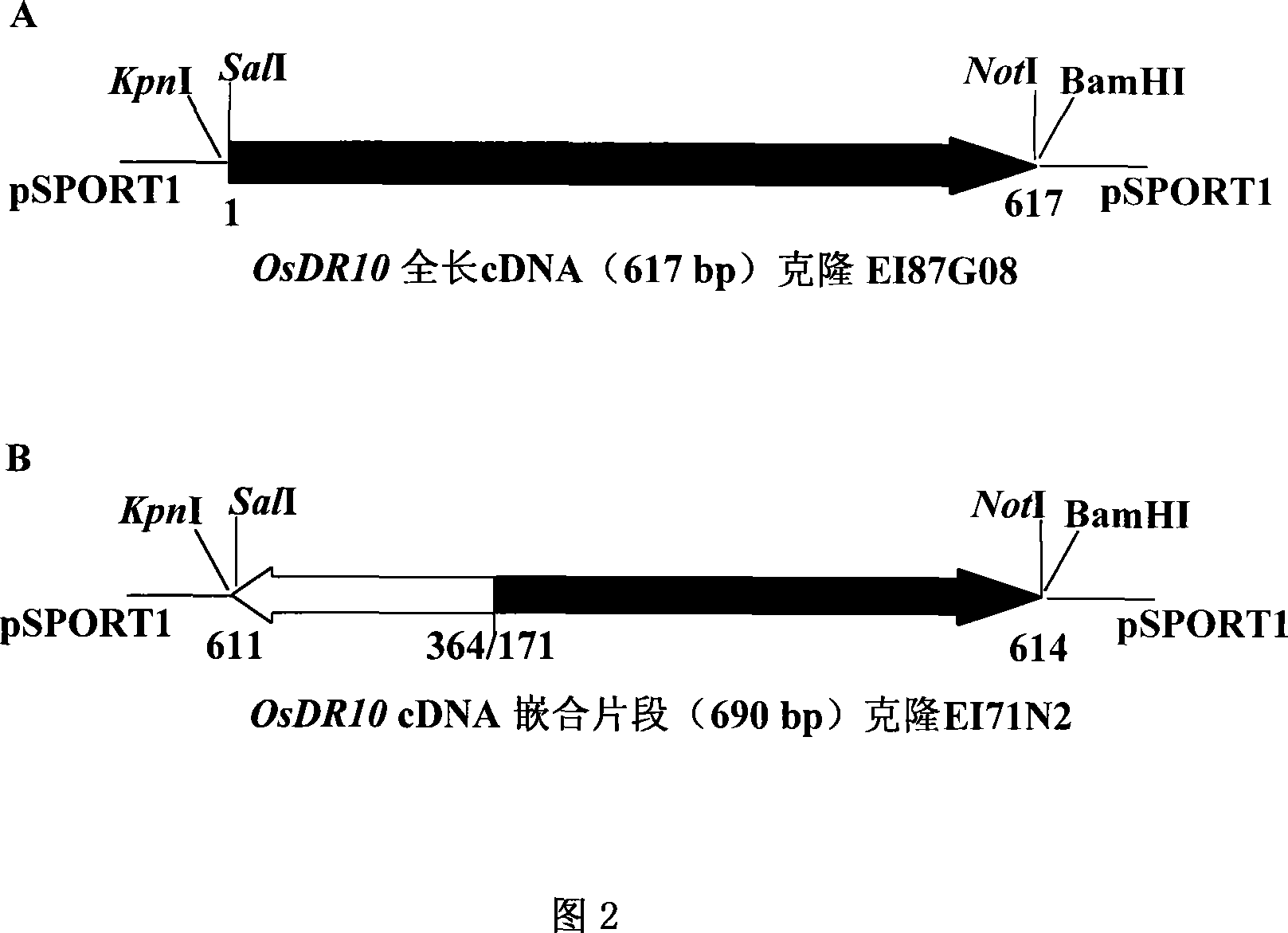
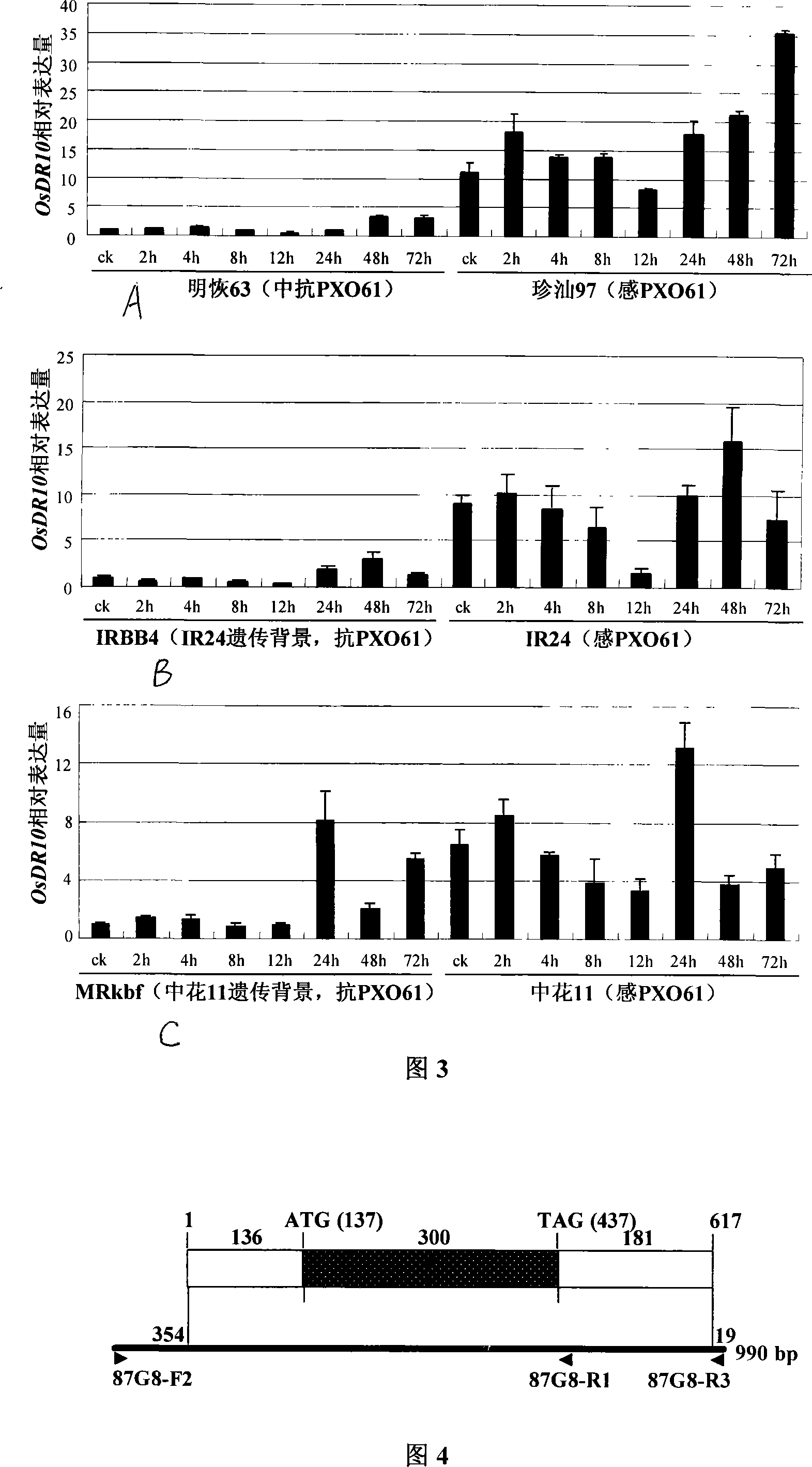
Rice disease-resistant related gene OsDR10 and its application in rice disease resistance
The invention relates to plant genetic engineering technical field, in particular to separation and clone of DNA sequence containing rice disease resistance related gene OsDR10 and function identification. A part of the DNA fragment of OsDR10 gene is connected with carriers expressing double strands RNA and further transferred into rice species to inhibit the expression of OsDR10 gene of rice species by transgenic technology based on RNA interference (RNAi). Genetic transformation rice with significant decreasing of OsDR10 gene enhances resistance to white leaf blight bacteria and proves that OsDR10 gene is the negative regulator in rice anti-white leaf blight reaction.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
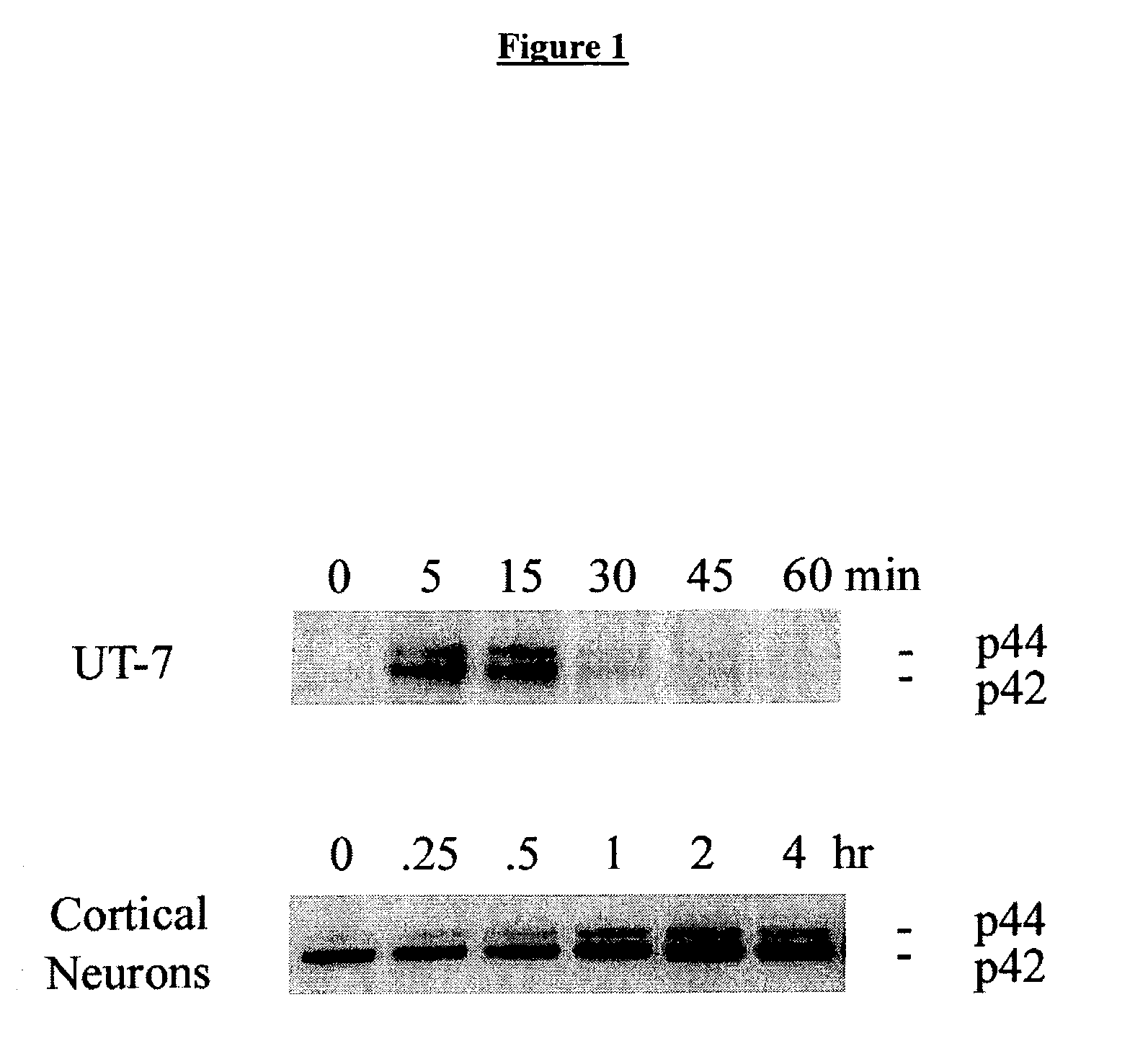
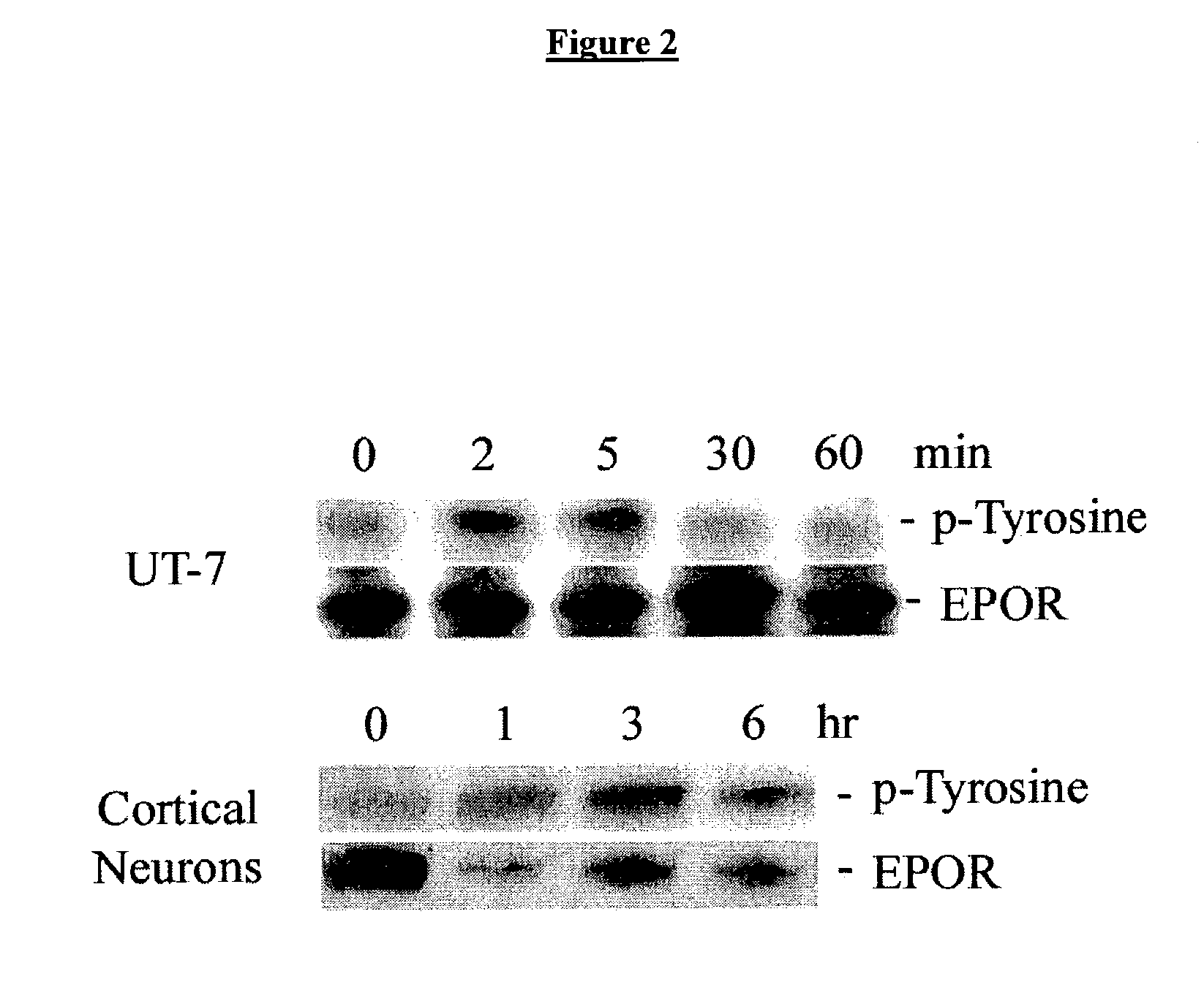
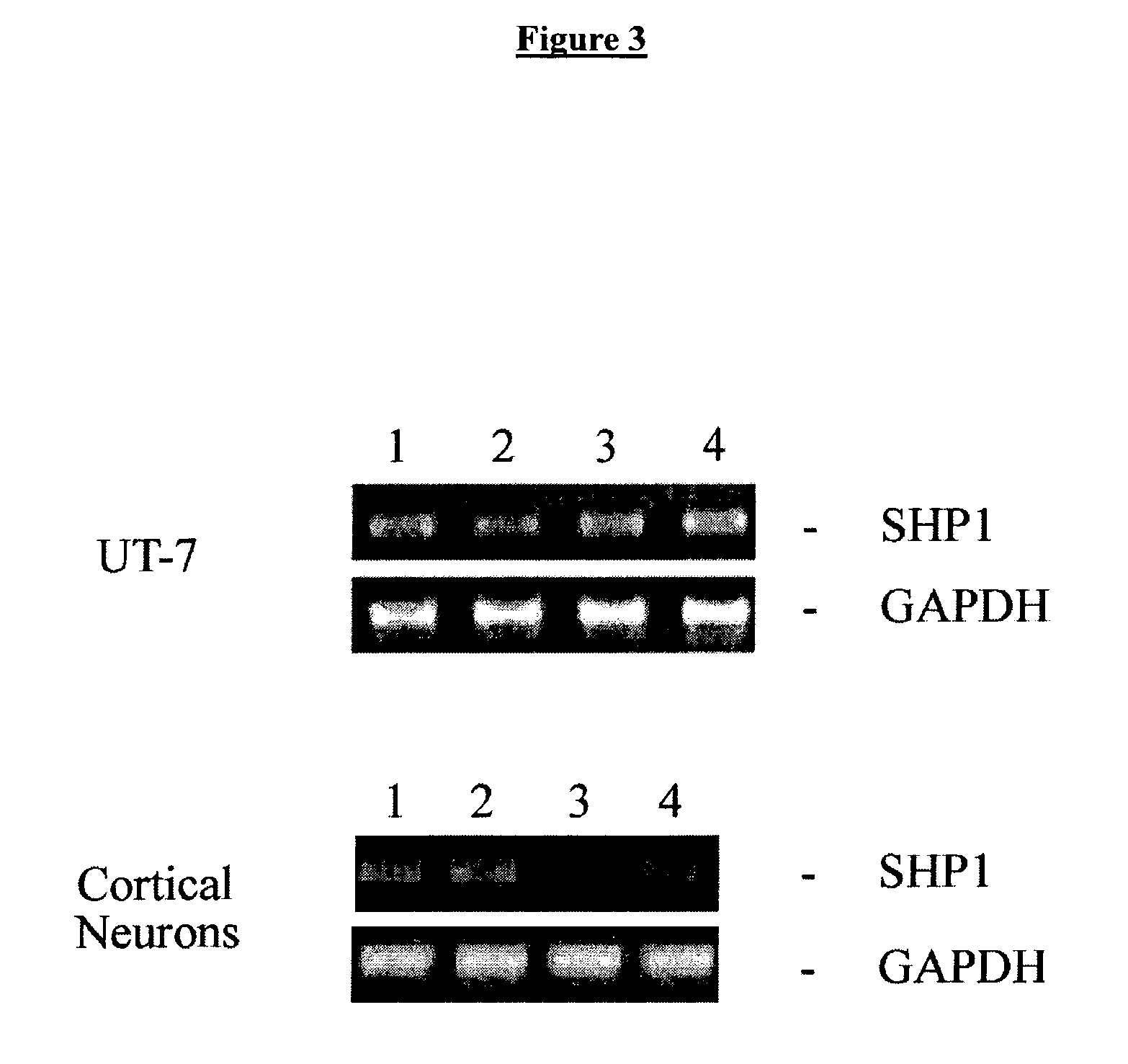
Methods for SHP1 mediated neuroprotection
InactiveUS7129267B2Reduce expressionPrevents the timely dephosphorylation of the EPORCompound screeningBiocidePhosphorylationNeural cell
The effect of EPO on the phosphorylation of the EPO receptor, the activation of the MAP Kinase pathway, and the expression of SHP-1 were analyzed. EPO was observed to cause a decrease in the expression of its negative regulator SHP-1. The decrease observed at both the mRNA and protein level was dose dependent and persisted as long as 24 hr following EPO treatment. EPO can down regulate the expression of its own negative regulator as a means for increased potency in neurons. Assays were generated to identify compounds that are useful in regulating SHP1 activity in neural cells.
Owner:ORTHO MCNEIL PHARM INC
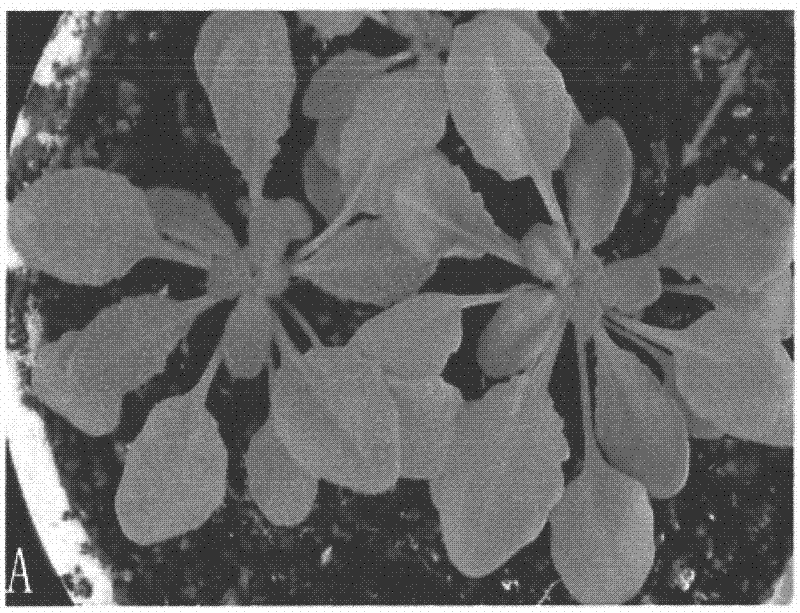
Gene for controlling arabidopsis trichome development and coded protein and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of plant gene engineering, in particular to a gene for controlling arabidopsis trichome development and a coded protein and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene has the sequences as shown in the SEQ ID NO:1, and the amino acid sequence has the sequences as shown in the SEQ ID NO:2. The gene plays an important role in regulating leaf and stem trichome development and is a negative regulator in trichome development. A mutant B11 with leaf and stem trichomes deleted is screened by a method of activating indexes. The T-DNA is found to be inserted between the No.4 chromosomes At4g01050 and At4g01060 of arabidopsis after the T-DNA flanking sequence is subjected to amplification, sequencing and database comparison by a TAIL-PCR (thermal asymmetric interlaced-polymerase chain reaction) method. The phenotype of the mutant is caused by overexpression of At4g01060, and the overexpression can cause reduction of leaf and stem trichomes. The study further perfects the regulation mode of trichome development, lays the theoretical and production practice foundations for cultivating new species of genetically modified crops and has important practical significance for agricultural production and crop improvement.
Owner:SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI GARDENING RES INST
150 Kda accessory receptor for tgf-beta
InactiveUS20040191860A1Good effectPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsMutant
The present invention relates to a TGF-.beta.1 binding protein called r150. This protein has a GPI-anchor contained in r150 itself and not on a tightly associated protein and that it binds TGF-.beta.1 with an affinity comparable to those of the signaling receptors. Furthermore, the released (soluble) form of this protein binds TGF-.beta.1 independent of the types I and II receptors. Also, the soluble form inhibits the binding of TGF-.beta. to its receptor. In addition, evidence that r150 is released from the cell surface by an endogenous phospholipase C is provided. Also, the creation of a mutant human keratinocyte cell line with a defect in GPI synthesis which displays reduced expression of r150 is described. Our results using these mutant keratinocytes suggest that the membrane anchored form of r150 is a negative modulator of TGF-beta responses. These findings, taken together with the observation that r150 forms a heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors, suggest that this accessory receptor in either its membrane anchored or soluble form may antagonize TGF-.beta. responses in human keratinocytes. Experiments with mutants confirmed that TGF.beta.1 activity can be modulated when the expression of the accessory receptor r150 is silenced. The complete nucleic acid and deduced amino acid sequences are now provided. The r150 cloned nucleic acid was used to study overexpression of r150. When r150 gene is overexpressed, TGF.beta. responses are increased. r150 and its derivatives or precursors (fragments, variants and nucleic acids encoding the same) will find a broad clinical utility, knowing that TGF.beta.1 is an important cytokine.
Owner:9406 2668 QUEBEC INC
Modulation of T cell signaling threshold and T cell sensitivity to antigens
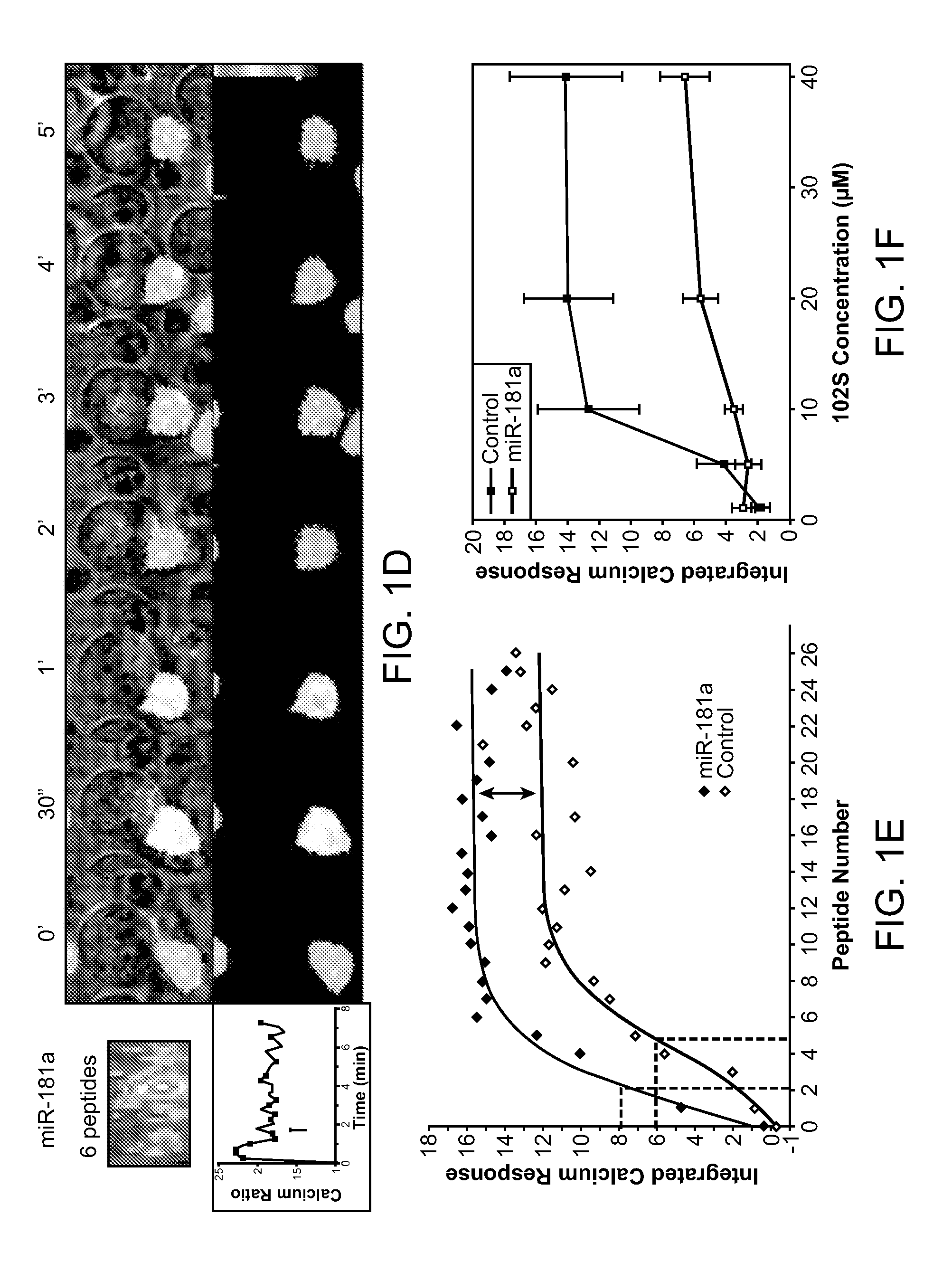
ActiveUS7803784B2Increase volumeLower the thresholdCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPeptide antigenDUSP6
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a diverse and abundant class of ˜22-nucleotide (nt) endogenous regulatory RNAs that play a variety of roles in animal cells by controlling gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Increased miR-181a expression in mature T cells is shown to cause a marked increase in T cell activation and augments T cell sensitivity to peptide antigens. Moreover, T cell blasts with higher miR-181a expression become reactive to antagonists. The effects of miR-181a on antigen discrimination are in part achieved by dampening the expression of multiple negative regulators in the T cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway, including PTPN22 and the dual specificity phosphatases DUSP5 and DUSP6. This results in a reduction in the TCR signaling threshold, thus quantitatively and qualitatively enhancing T cell sensitivity to antigens.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant strain for regulating expression activity of GRE3 genes and application of recombinant strain
InactiveCN105985915AImprove enduranceIncrease growth rateFungiBiofuelsBiotechnologyGlucose utilization
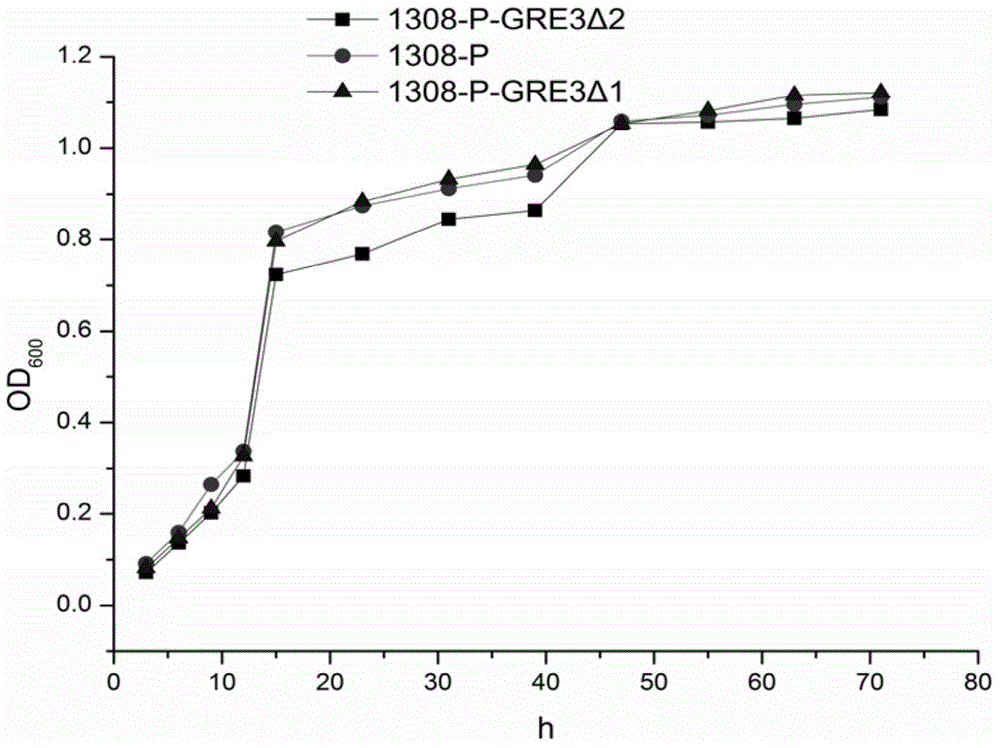
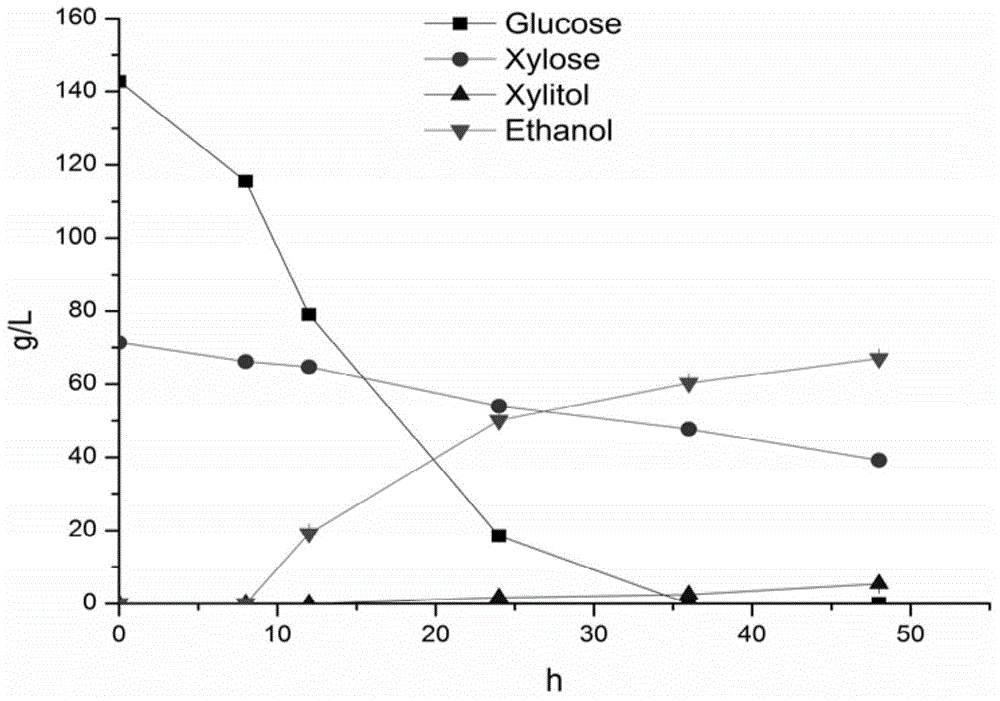
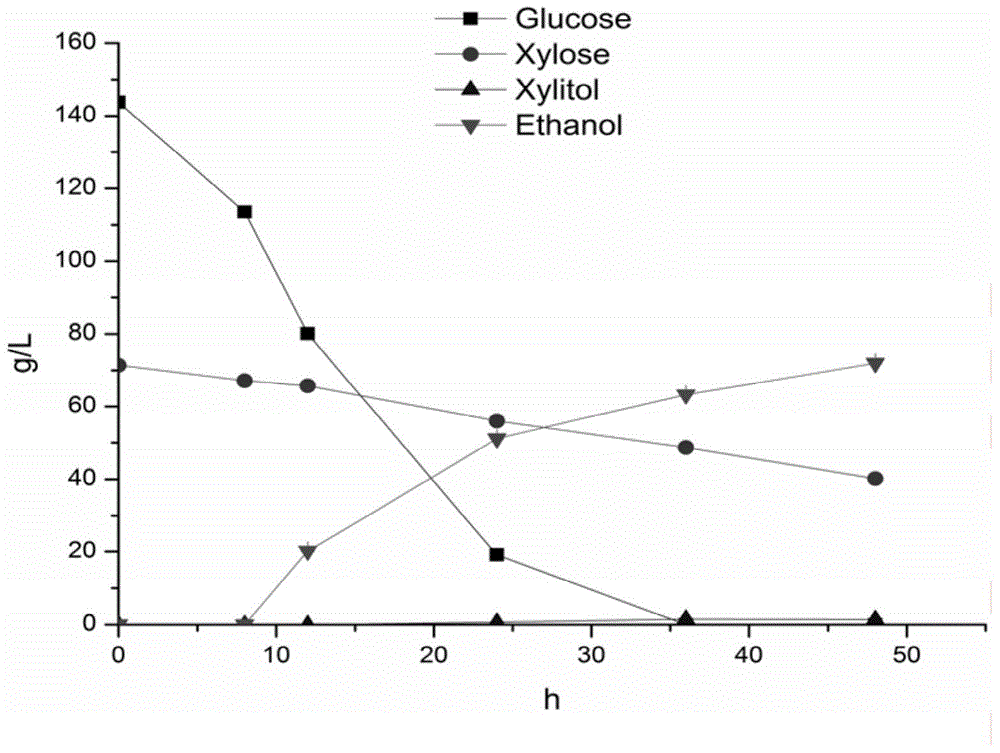
The invention relates to a genetic engineering strain for regulating expression activity of GRE3 genes in saccharomyces cerevisiae 1308-P. According to the invention, it discovers that the GRE3 genes in the saccharomyces cerevisiae can induce the generation of a by-product, namely xylitol, from xylose metabolism, and the generation of the xylitol is related to tolerance in a xylose fermenting process. It also discovers that the GRE3 genes, which are although negative regulator genes, cannot be completely knocked out. Experiments prove that the engineering strain, which is obtained by knocking out one of the GRE3 genes in the 1308-P, can improve the efficiency of fermenting ethanol by virtue of the xylose and reduce the generation of the by-product, namely the xylitol. Moreover, the modified bacterium also has the advantages that the original glucose utilization rate of an original strain, an inhibitor is high in tolerance and the like.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Osmotic stress-inducible protein functioning as a negative regulator in osmotic stress signaling pathway of plants
InactiveUS20050054831A1Improve plant resistanceImprove productivitySugar derivativesTransferasesProtein isolateStress signaling
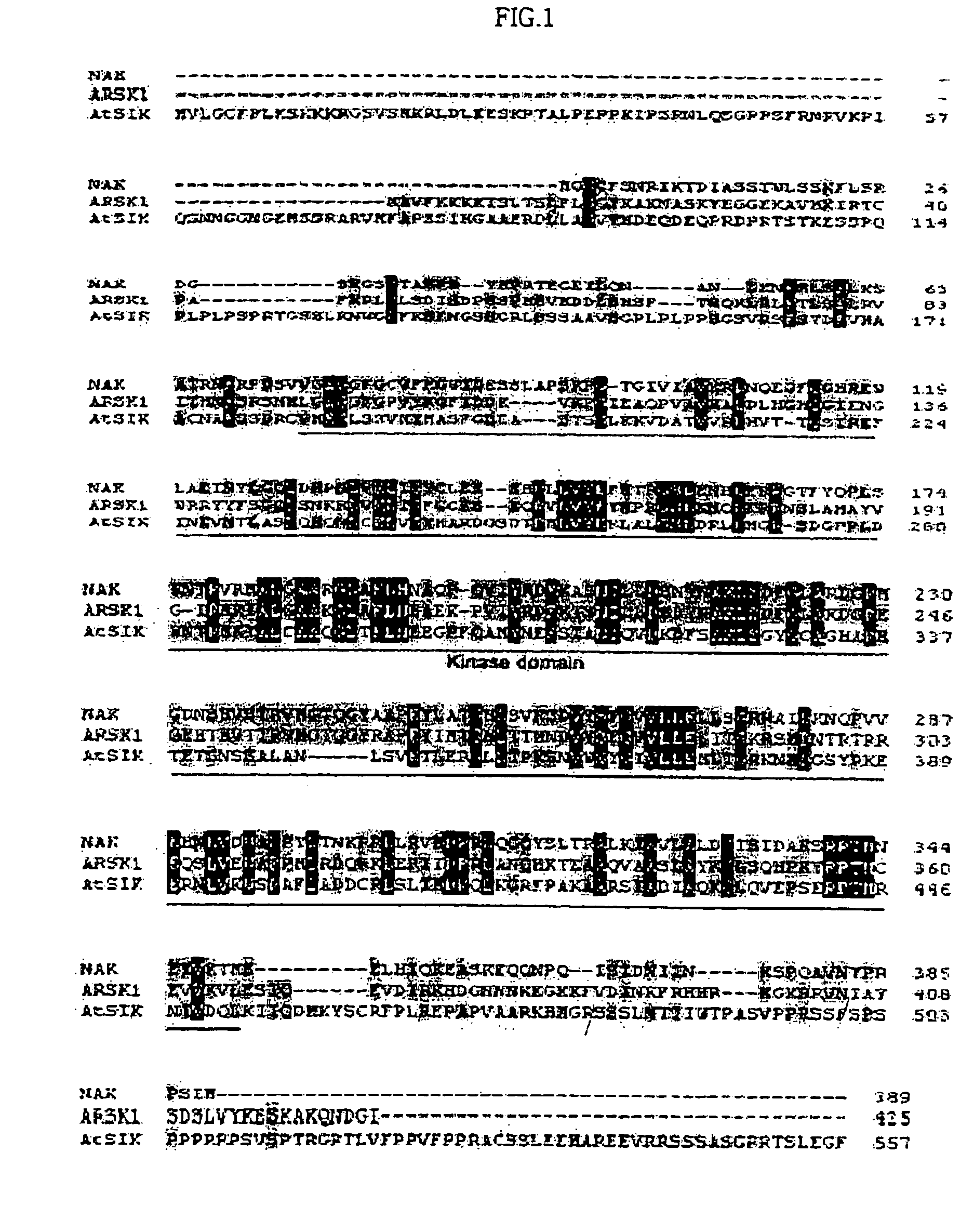
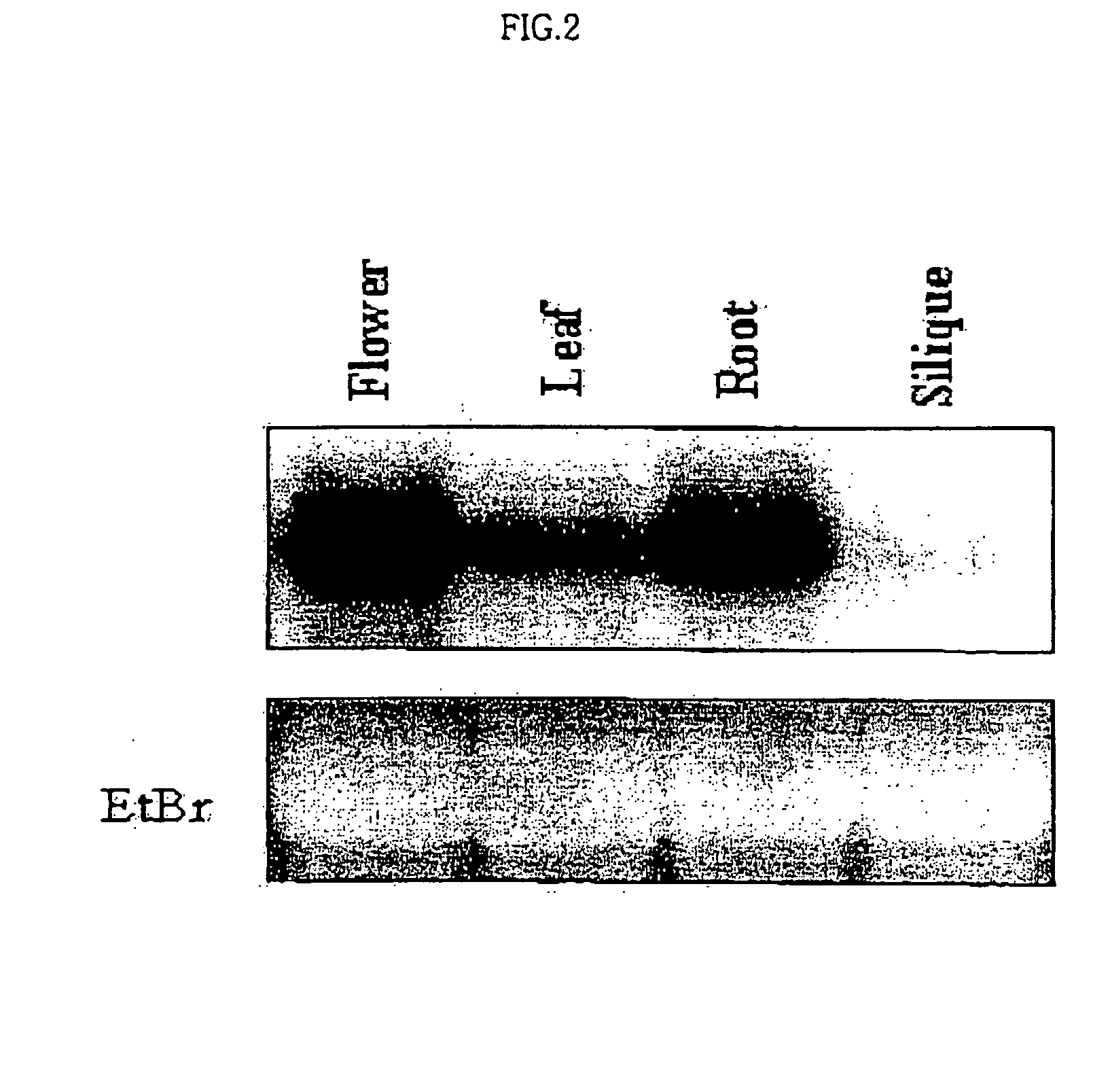
The present invention relates to an AtSIK protein functioning as a negative regulator to the osmotic stress-inducible gene and more particularly to a gene encoding said protein. Said AtSIK protein isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana acts as a negative regulator to the osmotic stress-inducible gene. Therefore, a plant having enhanced resistance to osmotic stress can be produced by inhibiting expression of AtSIK and consequently, the productivity of the plant can be increased.
Owner:GENOMINE
Medicine composition for preventing and treating diabetes mellitus and its use
ActiveCN1935261APromote proliferationFunction increaseMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsCTLA4 ProteinProinsulin
The present invention relates to a medicine composition for preventing and curing diabetes type I and its application. Said medicine composition includes (1), polypeptide capable of curing diabetes type I and (2), nucleic acid vaccine possesses the polypeptide which has 50% of homology respectively with proinsulin, GAD65 and B7-1 wa polypeptide which can be combined with T cell negative regulator CTLA-4. The invented medicine composition can effectively prevent and cure diabetes type I.
Owner:KUNMING INNOGEN PHARM TECH CO LTD +1
Use of trim72 as a target for muscle and heart enhancer
ActiveUS20110251256A1Simple designOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMyogenesisEccentric hypertrophy
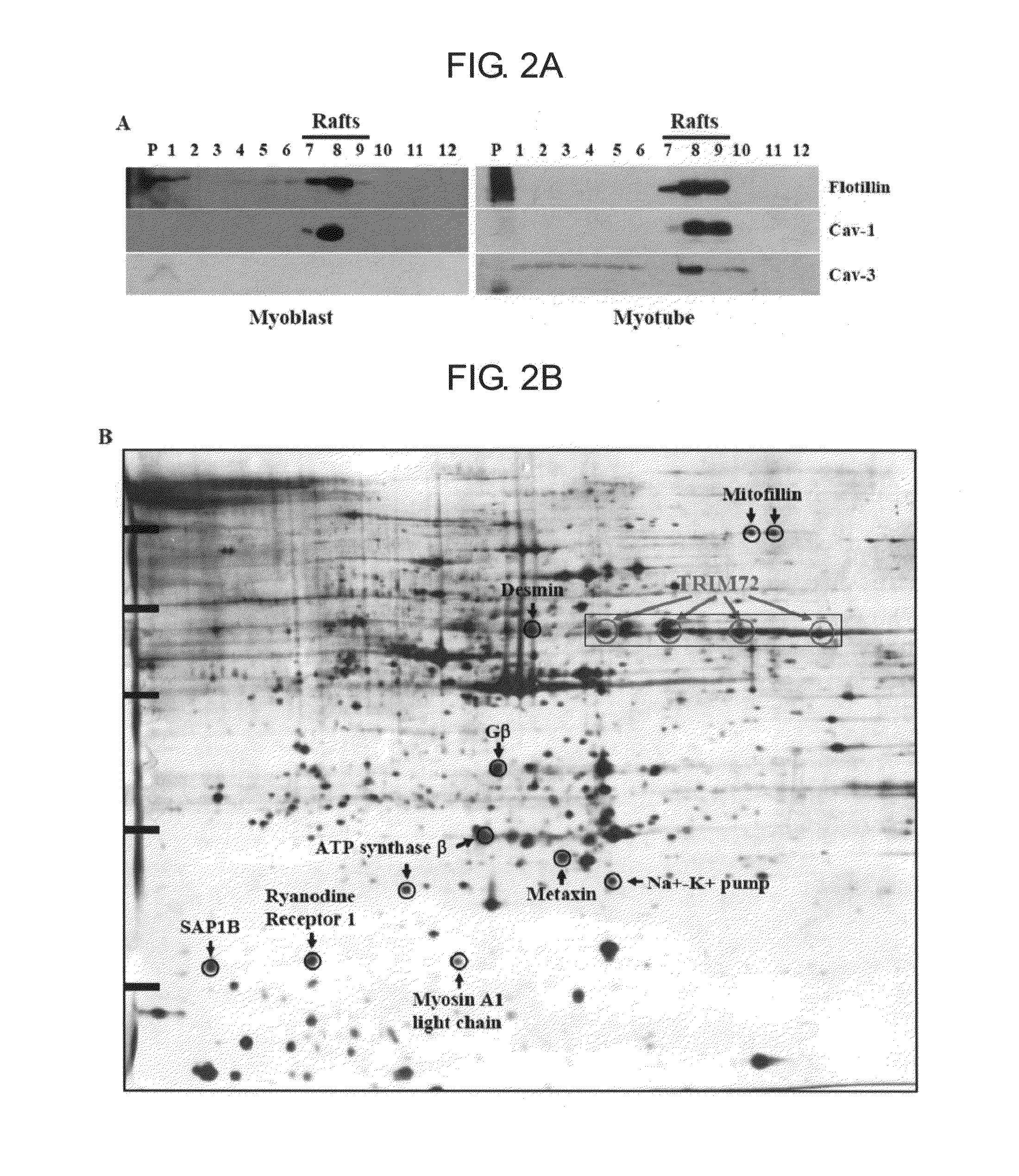
The present invention relates to a new use of TRIM72 as a target for muscle enhancer and heart enhancer, more particularly to a composition for enhancing muscle or heart comprising an expression or action inhibitor of TRIM72 protein. The present invention further relates to a new TRIM mutant protein inducing muscle differentiation and hypertrophy and its gene. The inventors of the present invention have identified that TRIM72 overexpression inhibits myogenesis whereas TRIM72 knockdown enhances myogenesis, and first elucidated that TRIM72 is a negative regulator of skeletal muscle differentiation. Accordingly, the inhibition of TRIM72 acts exclusively on skeletal muscle and heart muscle, but does not affect IGF-I signaling pathway in other tissues. Therefore, a drug or gene therapy using TRIM72 as a target may be helpful in treating obesity and type 2 diabetes by promoting skeletal muscle differentiation, hypertrophy and energy consumption in adipose tissue and inducing strong muscle by promoting physiological hypertrophy of heart muscle, without cancer or other side effects.
Owner:KOREA UNIV IND ACADEMIC COLLABORATION FOUND
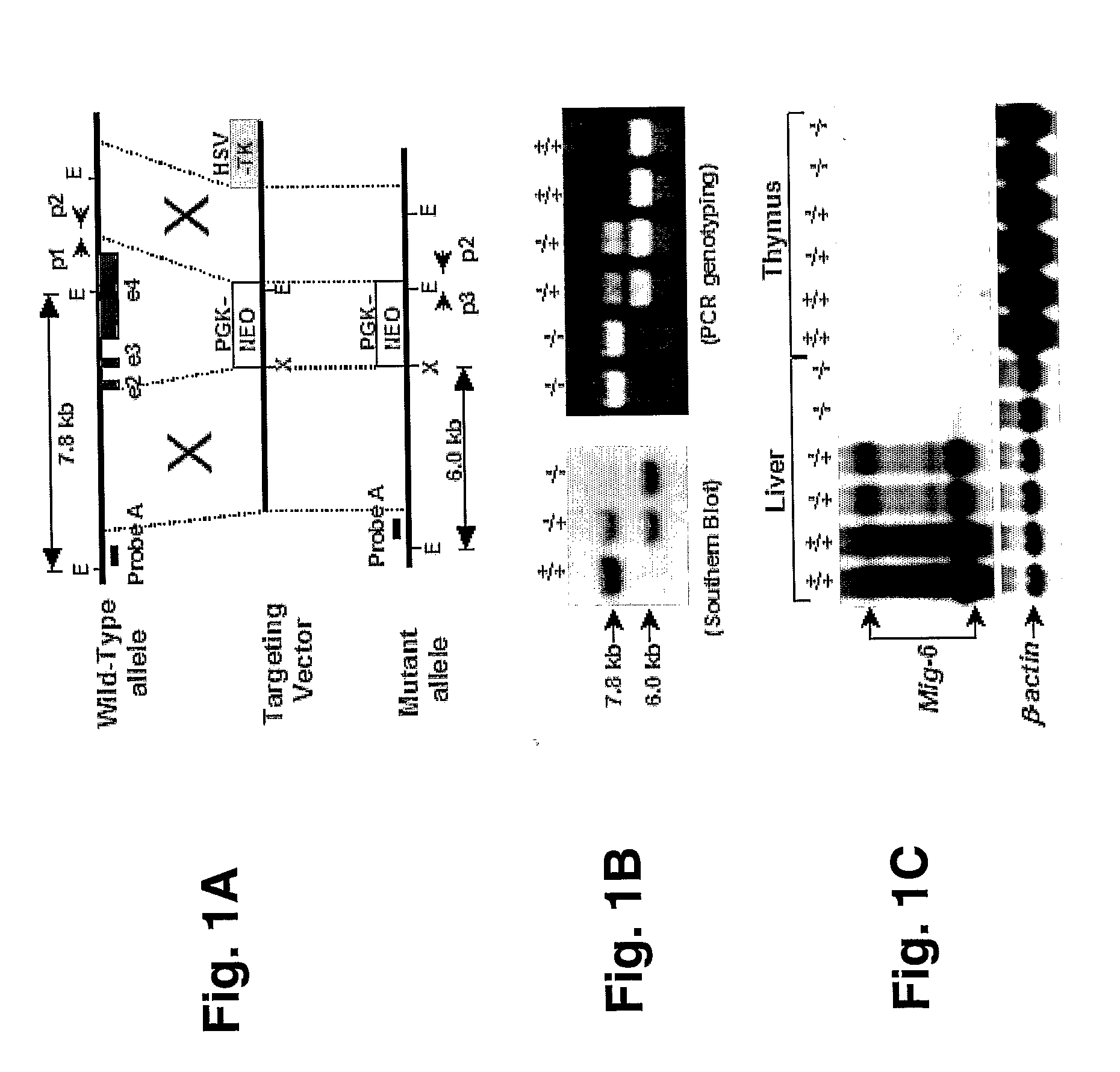
Mig-6 knockout mice and elucidation of association of mig-6 with early onset degenerative joint disease and role as a tumor suppressor
InactiveUS20110099644A1Reduce developmentIncreased tumorigenesisAnimal cellsSugar derivativesProgenitorDisease
The molecular mechanism underlying degenerative joint disease, also known as osteoarthritis (OA), is not fully understood. Disruption of mitogen inducible gene 6 (Mig-6) in mice by homologous recombination (KO mice) led to early onset OA as revealed by simultaneous enlargement and deformity of multiple joints, degradation of articular cartilage and the development of bony outgrowths or osteophytes within the joint space. The latter appeared to be derived from proliferation of mesenchymal progenitor cells followed by differentiation into chondrocytes. Because of the striking similarity to human OA, Mig-6 KO mice are a useful animal model for studying the mechanism of this disease and for testing new drugs or therapies for treating OA. These KO mice also developed epithelial hyperplasia, adenoma, and adenocarcinoma in organs such as lung, gallbladder, and bile duct. Mig-6 is therefore a tumor suppressor gene and is a candidate gene for the frequent Ip36 genetic alterations found in lung cancer. It can be used as a tumor biomarker as well as a target for cancer therapy. Mig-6 is located in human chromosome Ip36, a locus frequently associated with human lung cancer. Mig-6 is a negative regulator of EGF signaling, and like EGF, was induced by HGF / SF in human lung cancer cell lines. Frequently the receptors EGFR and Met were co-expressed, and Mig-6 was induced by both EGF and HGF / SF in a MAPK-dependent fashion. Not all tumor lines express Mig-6 in response to either EGF or HGF / SF. In these cases, missense and nonsense mutations in the Mig-6 coding region were found, as was evidence for Mig-6 transcriptional silencing.
Owner:VAN ANDEL RES INST
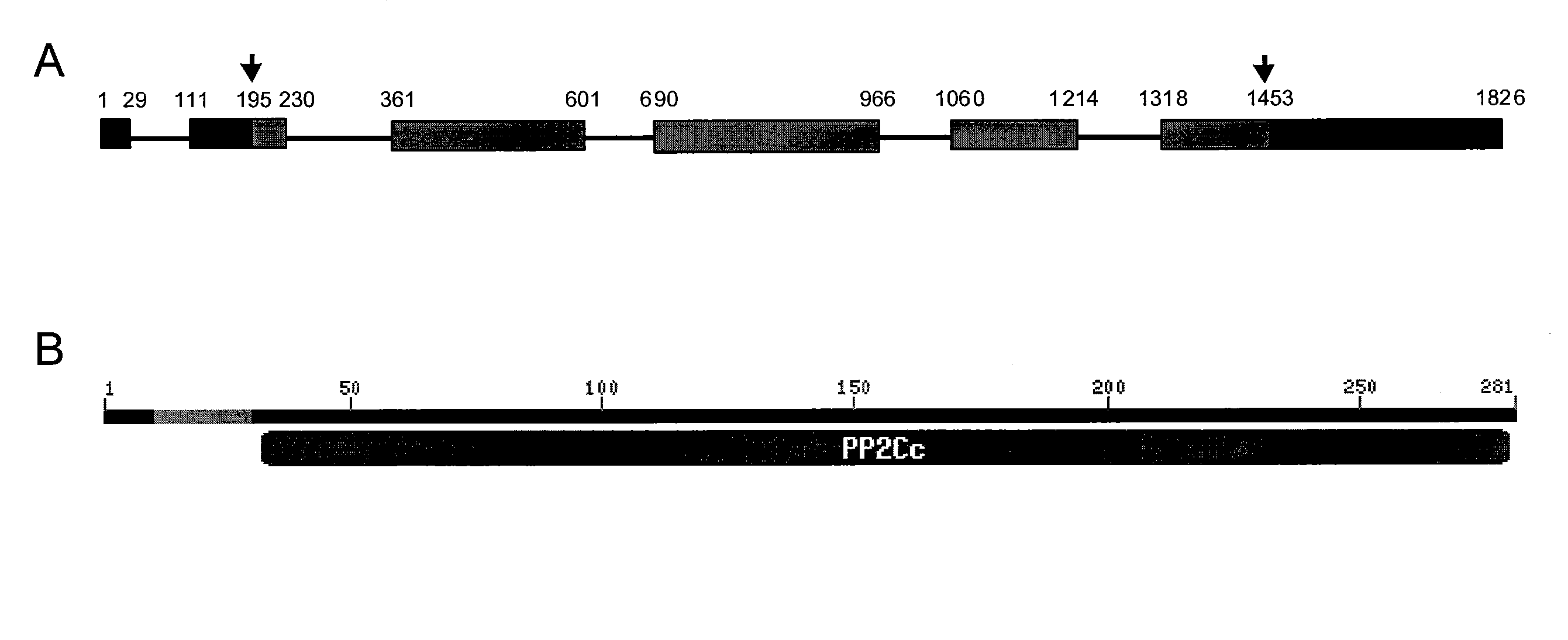
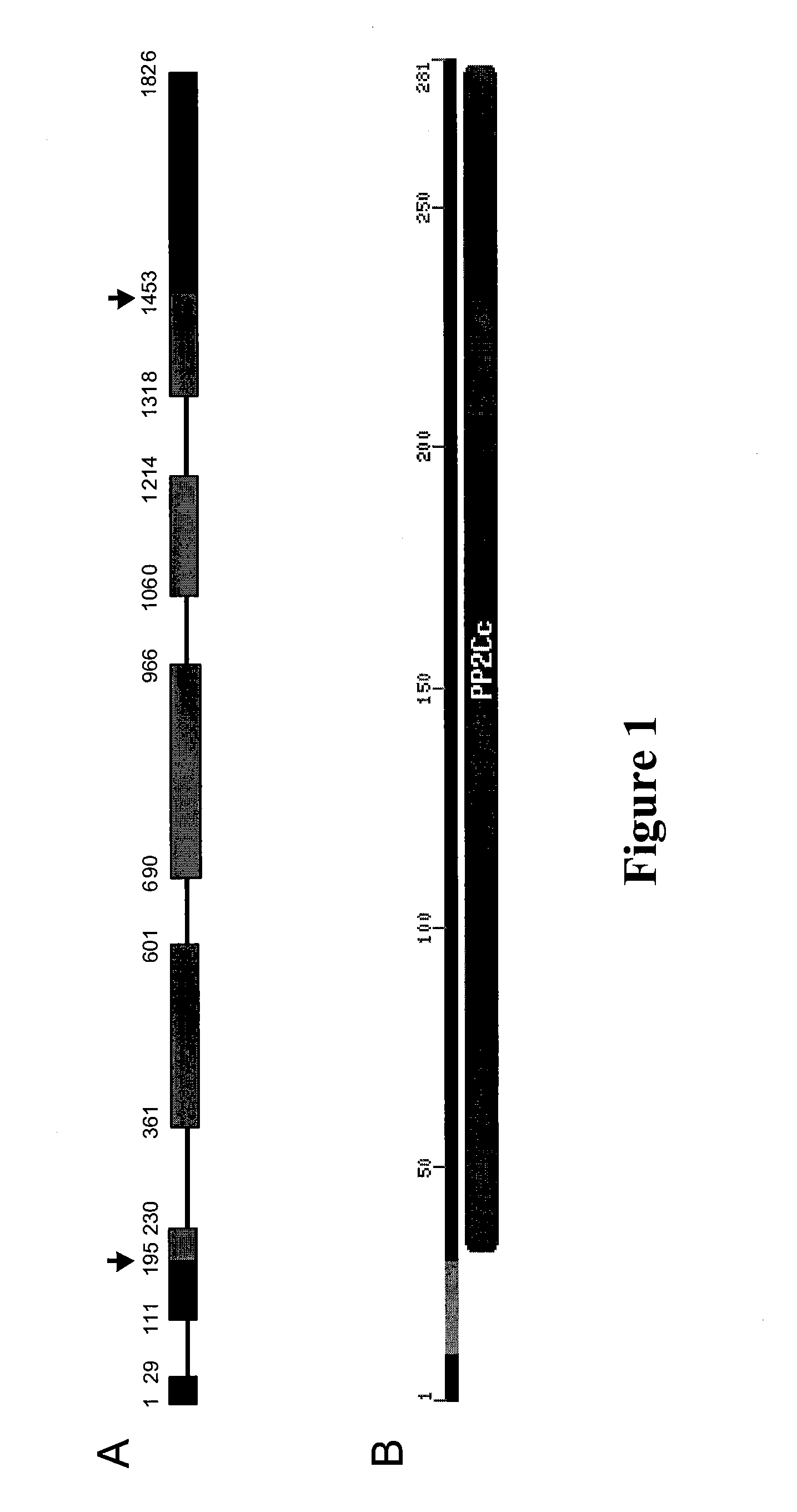
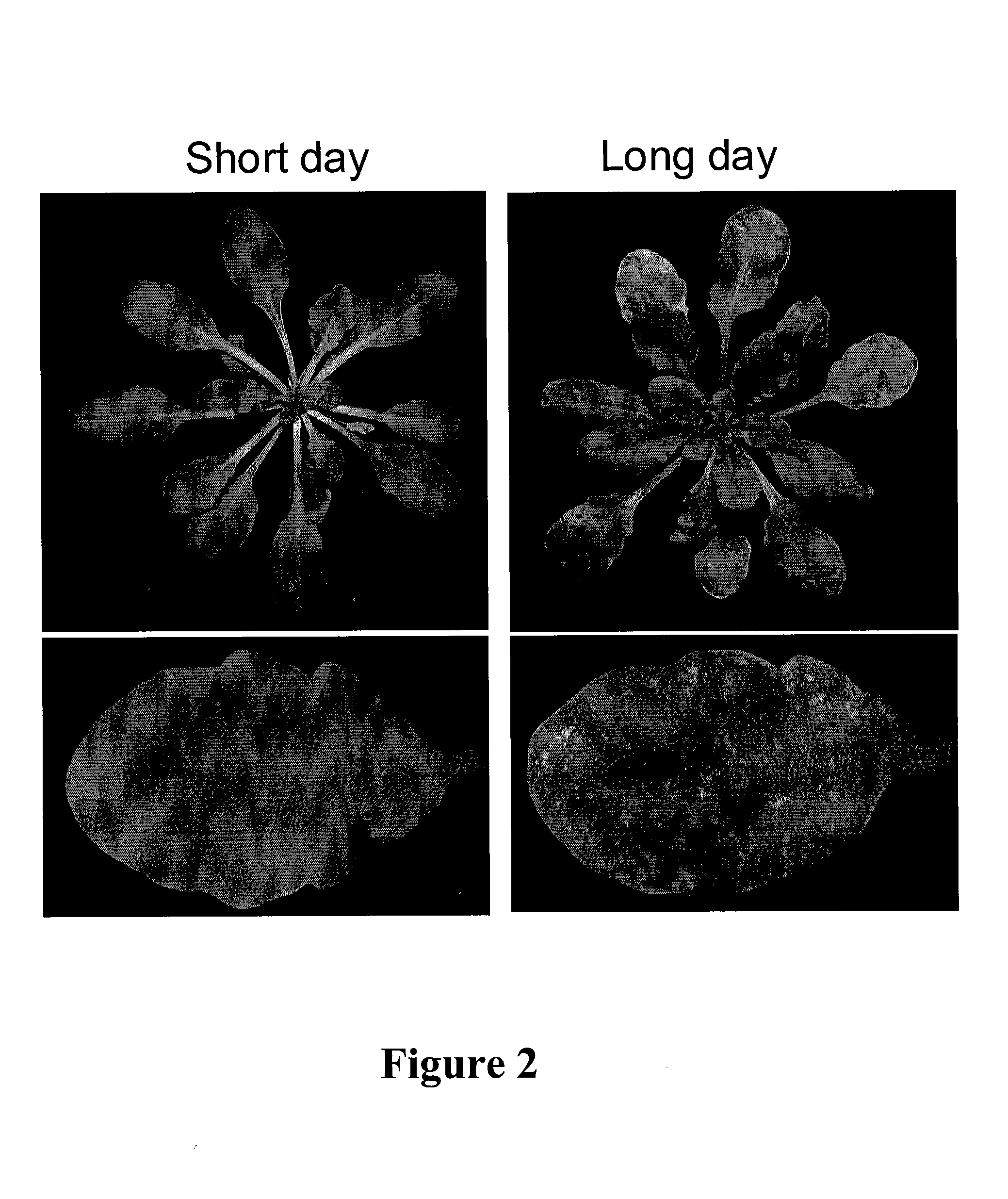
Plants with reduced expression of phosphatase type 2c gene for enhanced pathogen resistance
InactiveUS20070256193A1Improve disease resistanceTight regulationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationDiseaseR gene
The present invention relates to a method for down regulating an Arabidopsis protein phosphatase type 2C gene, referred to as “defense-associated protein phosphatase type 2C one” (DAPP1) that functions as a negative regulator of a plant defense pathway by contacting the gene or gene mRNA with an interfering nucleotide sequence that interacts with the gene and reducing expression thereof. Plants including such interfering nucleotide sequence exhibit increased disease resistance to pathogen even in the absence of R genes. Close homologs of DAPP1 exist in multiple crop species, and as such, the controlled down-regulation of homologous genes in a variety of crop species will enhance disease resistance of target crop species to pathogens.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
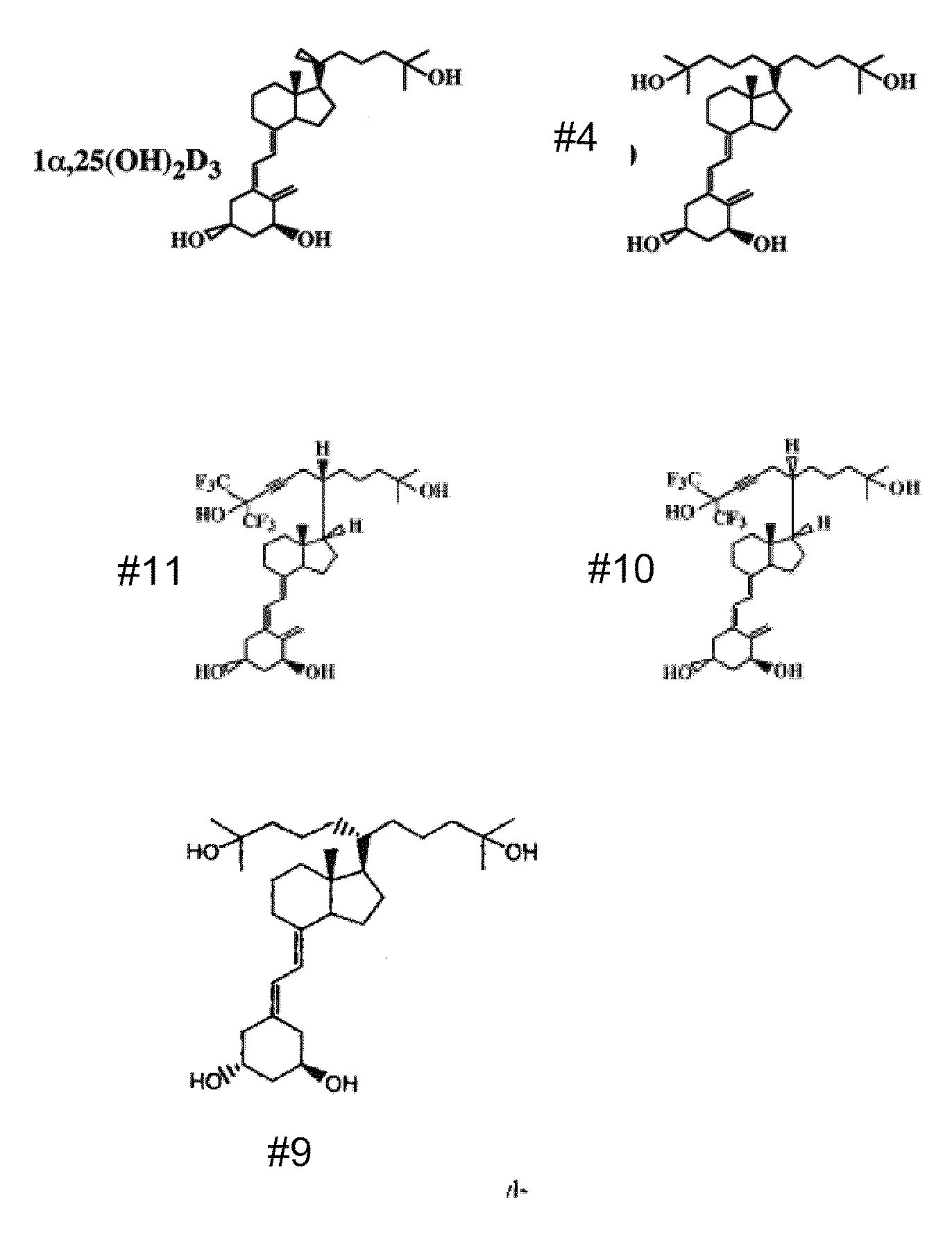
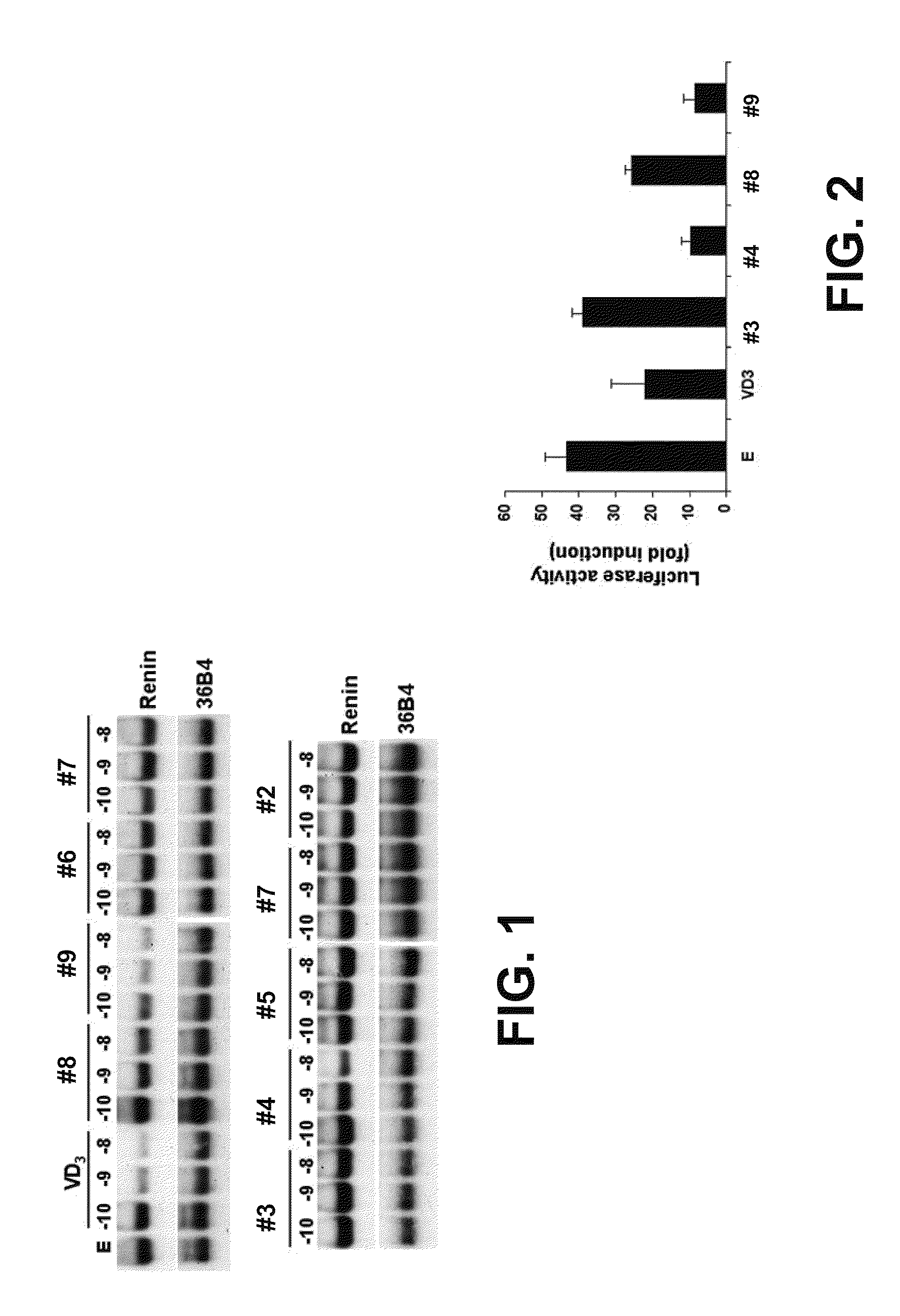
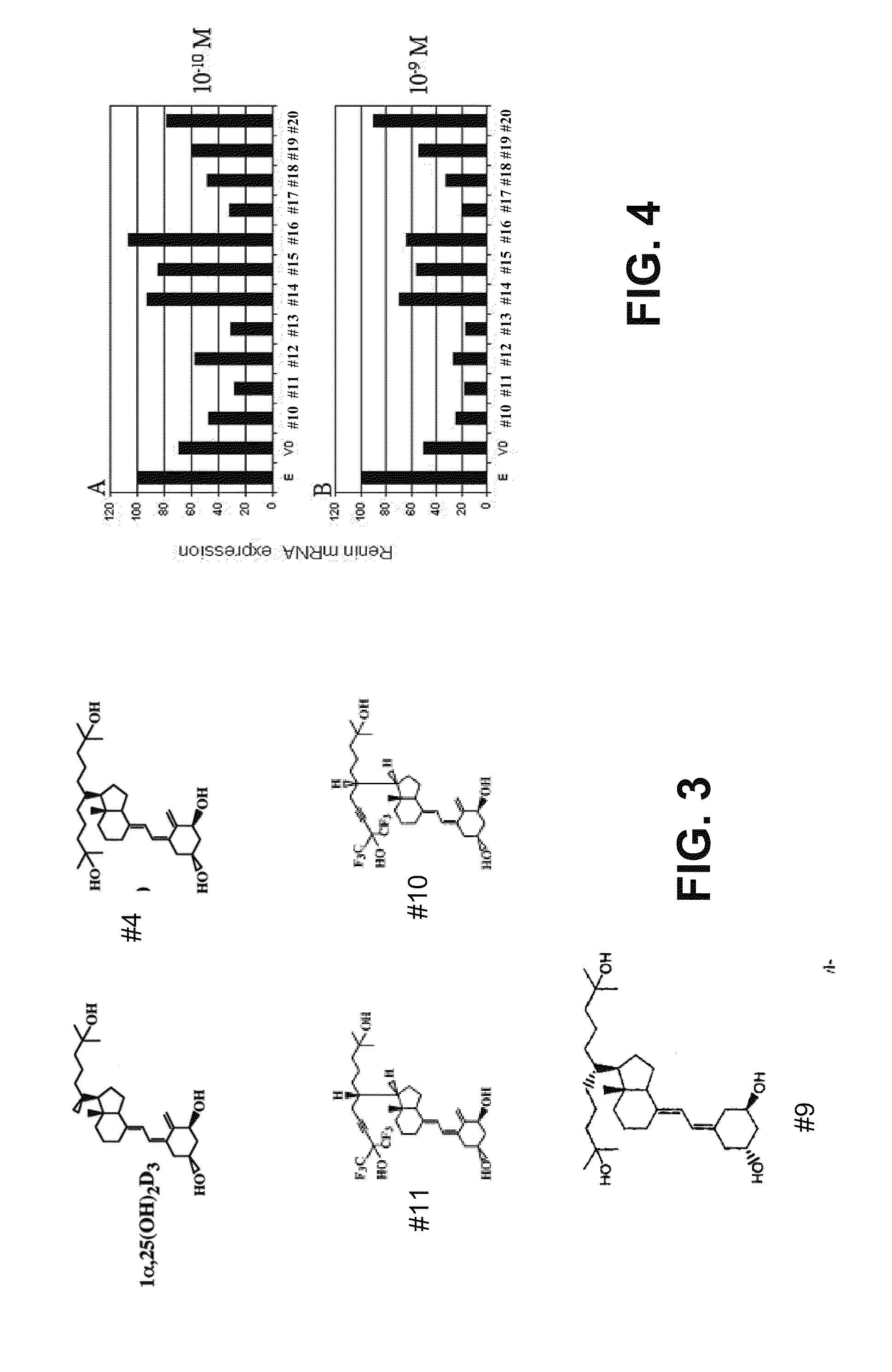
Vitamin d and vitamin d analogs or derivatives as new Anti-hypertensive agents
InactiveUS20100222307A1Less calcemic effectImprove performanceCompound screeningBiocideCalcium metabolismHypertension medications
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
SKIN gene silencing plasmid and transformed plant cell containing plasmid
ActiveCN104805114AClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellDNA fragmentation
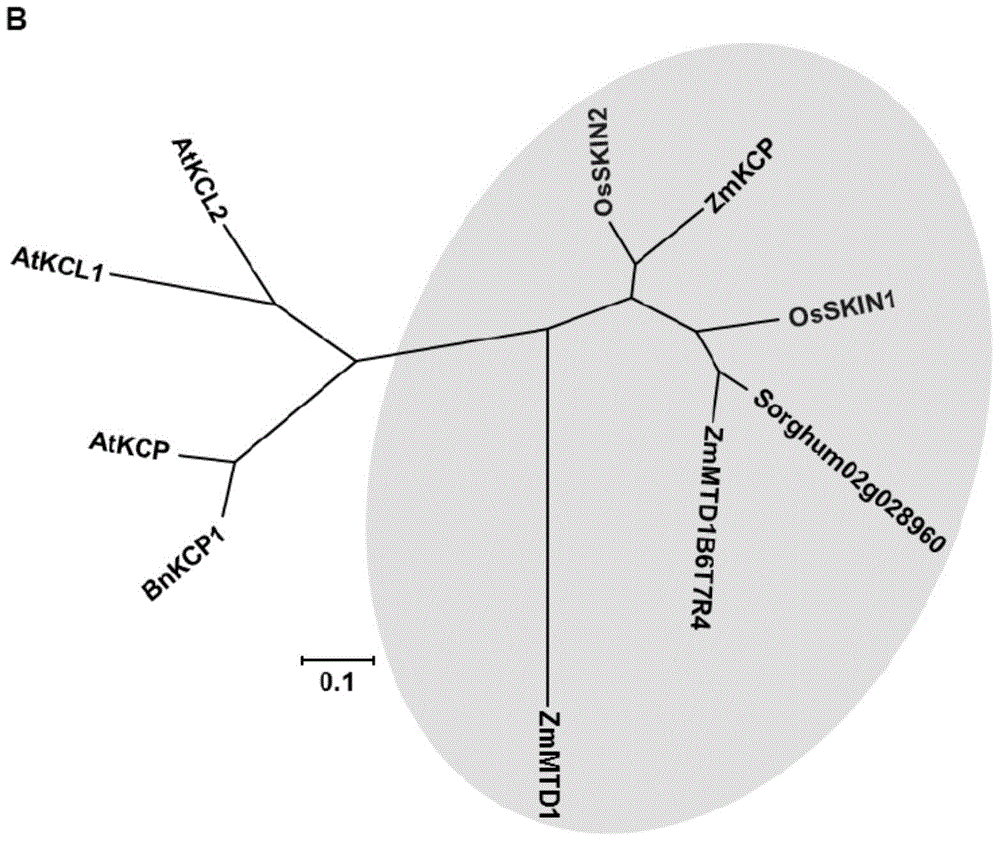
The present invention relates to a SKIN gene silencing plasmid and a transformed plant cell containing the plasmid. The SKIN gene silencing plasmid comprises a promoter, two DNA fragments derived from one DNA segment of the cDNA of the SKIN1 or the cDNA of the SKIN2 in the positive-sense direction and in the negative-sense direction respectively, and a third DNA fragment inserted between the two DNA segments. The SKIN1 is in the form of a negative regulator for regulating the growth and the yield of rice. The expression of the endogenous SKIN reduces the yield of rice. The invention also relates to a transformed plant cell containing the SKIN gene silencing plasmid and a transgenic plant.
Owner:ACAD SINICA
Methods for Identifying Modulators of Pyrimidine Tract Binding Protein
InactiveUS20100144838A1Inhibit and induce PTB activityOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningADAMTS ProteinsNegative regulator
Provided herein are methods and materials for identifying compounds that modulate polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB), a protein that functions as a negative regulator of pre-mRNA splicing by blocking the inclusion of numerous alternative exons into mRNA.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Rice disease-resistant related gene OsDR9 and its use in improving rice disease resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and in particular relates to isolation cloning and functional verification of a DNA fragment which contains rice disease resistance related genes OsDR9. The resistance of rice to rice blast and brown spot disease is intensified through inhibiting expression of the OsDR9 genes in the rice, the OsDR9 genes are proved to be negative regulators in reaction that the rice resists fungous diseases, and disease-resistant rice varieties are cultured through inhibiting the expression of the OsDR9 genes.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
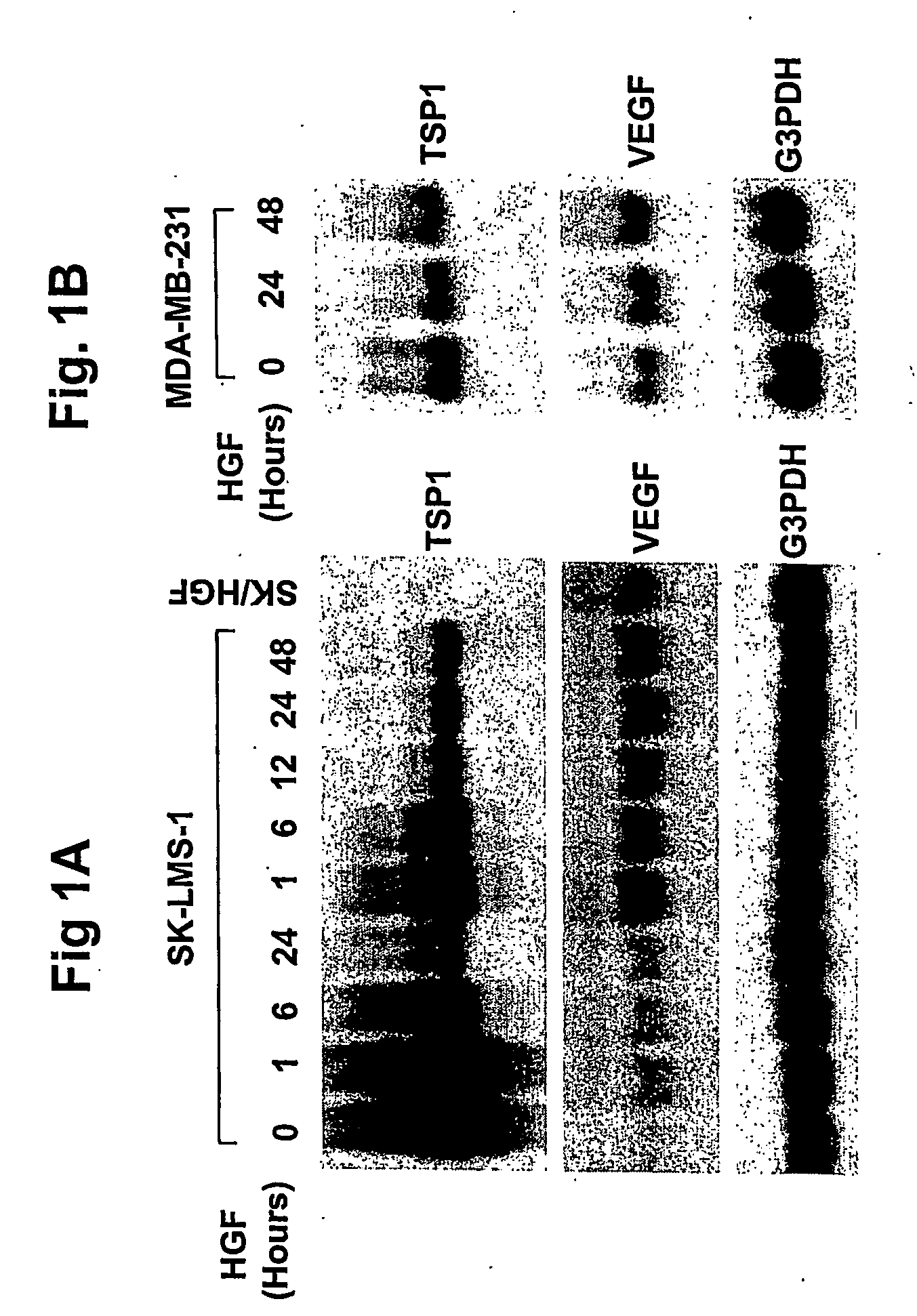
Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by combination of thrombospondin-1 and inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor
InactiveUS20070020234A1Prevent and inhibitSuppression problemOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEctopic expressionAgonist peptide
Hepatocyte growth factor / scatter factor (HGF / SF), acting through the Met receptor, plays an important role in most human solid tumors and inappropriate expression of this ligand-receptor pair is often associated with poor prognosis. The molecular basis for the malignant activity imparted by signaling of HGF / SF-Met in cancer cells has been attributed to its mitogenic and invasive properties. However, HGF / SF also induces angiogenesis, but the signaling mechanism has not been understood, nor has this activity been directly associated with HGF / SF-Met mediated tumorigenesis. HGF / SF induces expression in vitro of VEGF, a key agonist of tumor angiogenesis. By contrast, thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) is a negative regulator of angiogenesis. This application discloses that, in the very same tumor cells, in addition to inducing VEGF expression, HGF / SF dramatically down regulates TSP-1 expression. TSP shut off plays an important, extrinsic role in HGF / SF-mediated tumor development, as ectopic expression of TSP-1 markedly inhibited tumor formation through the suppression of angiogenesis. While VEGF induced expression is sensitive to inhibitors of several pathways, including MAP kinase, PI3 kinase and Stat3, TSP-1 shut off by HGF / SF is prevented solely by inhibiting MAP kinase activation. Thus HGF / SF is a “switch” for turning on angiogenesis. TSP-1 is a useful antagonist to tumor angiogenesis, and therefore TSP-1 and agonist peptides and mimics, as well as inducers of TSP-1, have therapeutic value when used in conjunction with inhibitors of VEGF.
Owner:VAN ANDEL RES INST
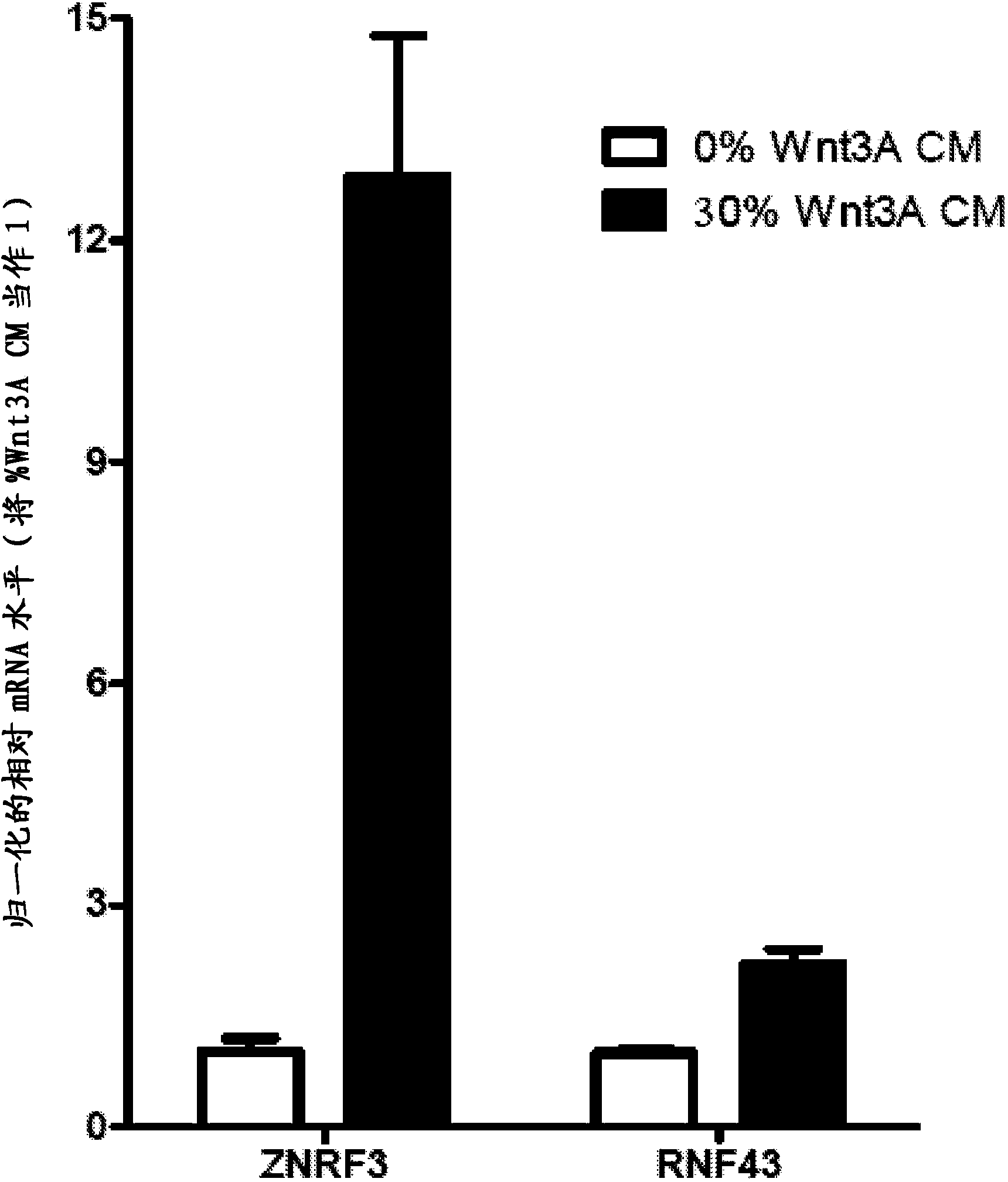
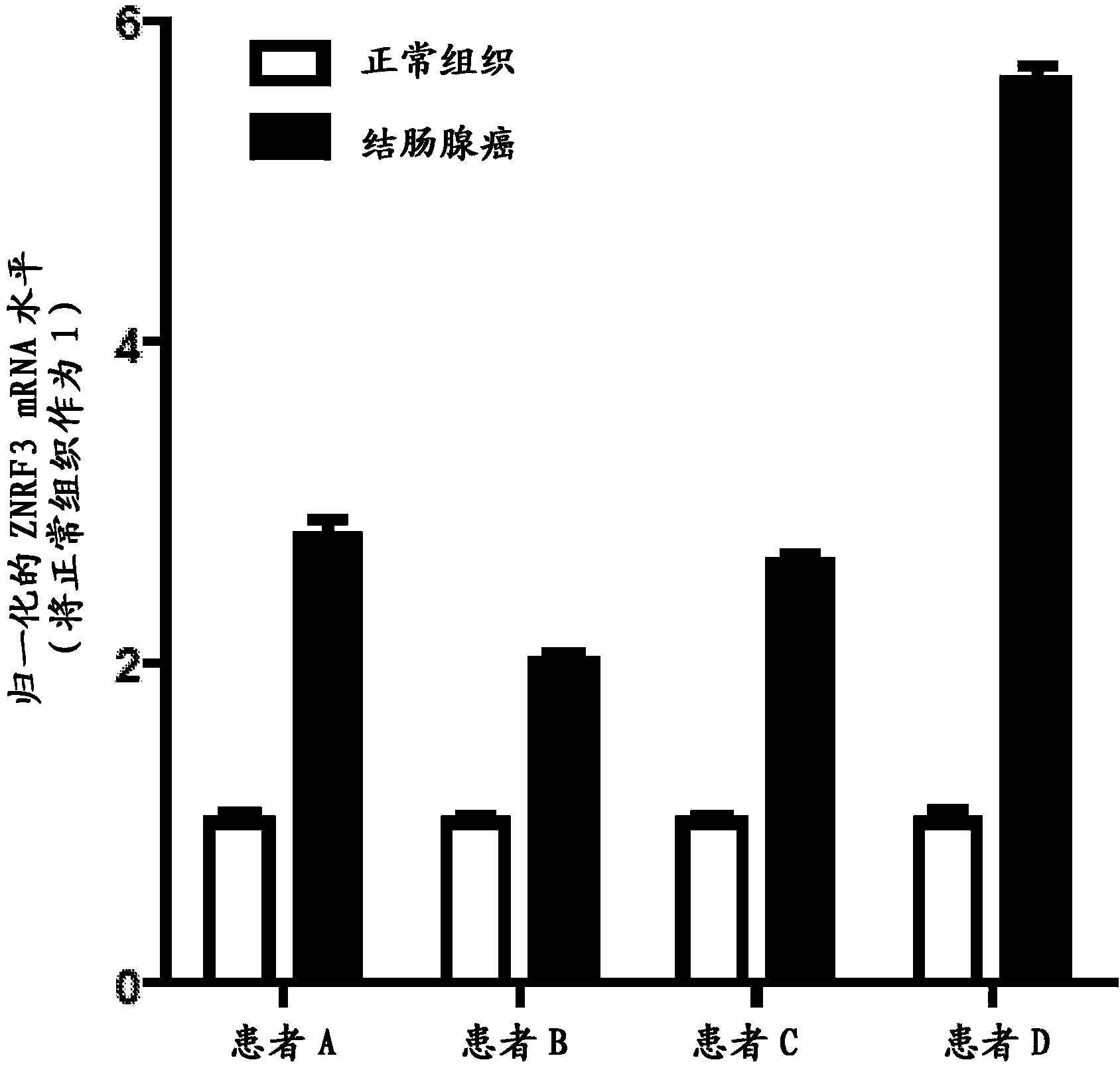
Antibodies and methods for Wnt pathway-related diseases
The transmembrane E3 ubiquitin ligases ZNRF3 and RNF43 are negative regulators of [beta]-catenin and the Wnt signaling pathway in eukaryotic cells. The activity of ZNRF3 can be modulated by antibody binding to its extracellular domain, thus causing an increase in Wnt signaling. The ZNRF3 antagonizing antibodies can be used to treat diseases with low Wnt signaling, such as short bowel syndrome, osteoporosis, diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and mucositis. In addition, the antagonizing antibodies of the invention can be used to enhance Wnt signaling for tissue repair and wound healing.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com