Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Apoptosis pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular Apoptosis Pathway Apoptosis is a naturally occurring process by which a cell is directed to programmed cell death. ... The intrinsic apoptosis pathway begins when an injury occurs within the cell. Intrinsic stresses such as oncogenes, direct DNA damage, hypoxia, and survival factor deprivation, can activate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. p53 is a sensor of cellular stress and is a critical activator of the intrinsic pathway.
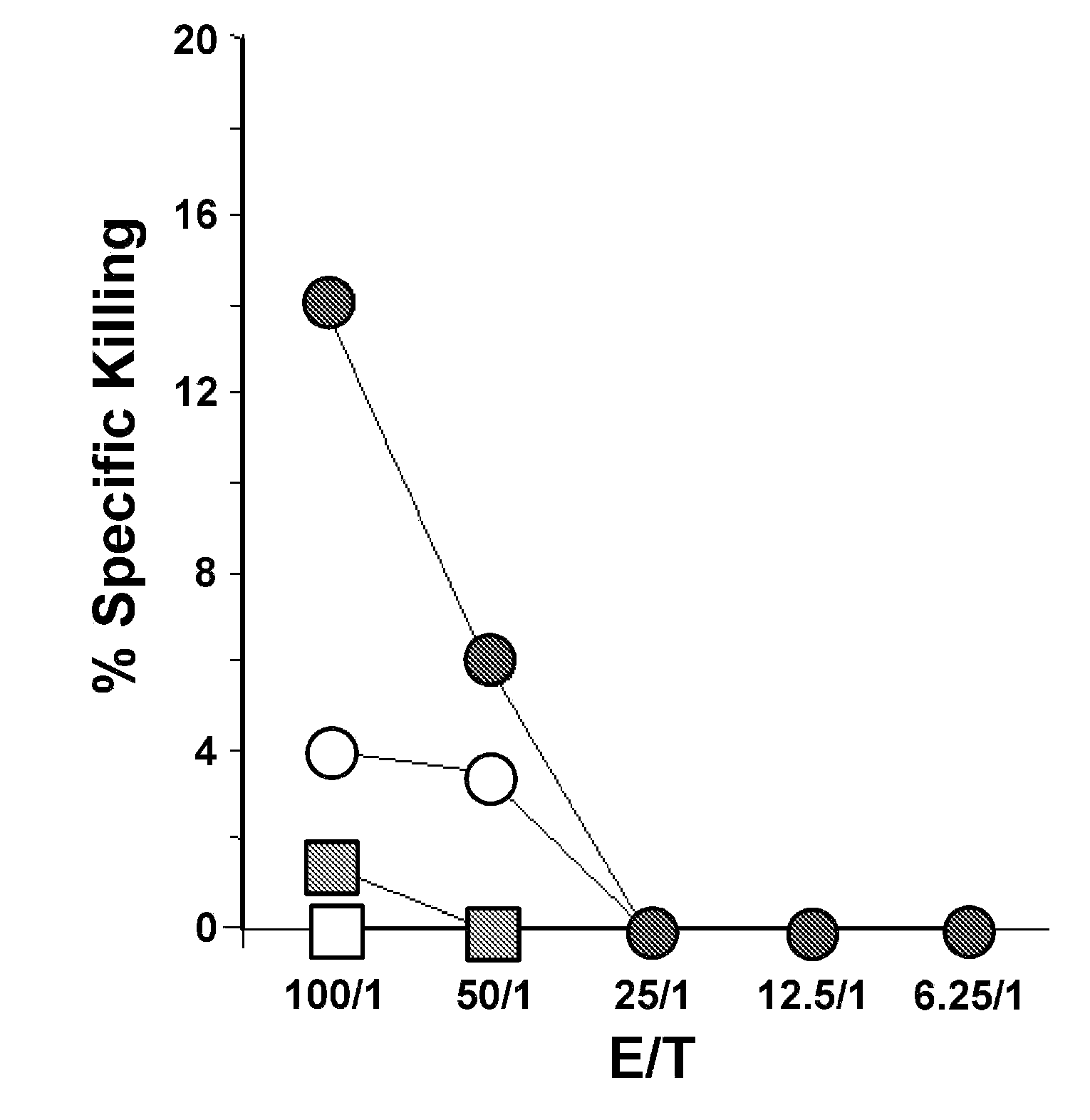
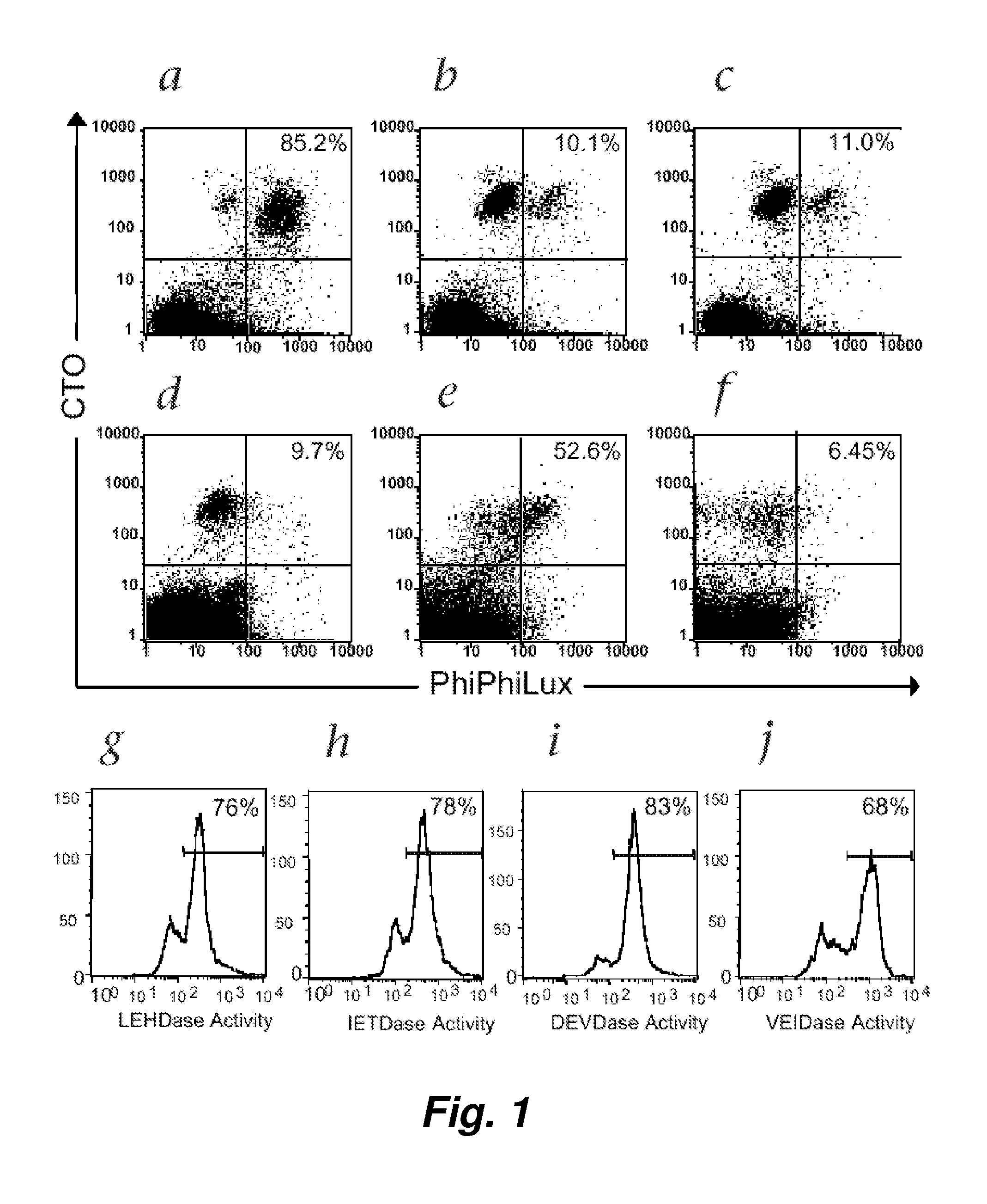
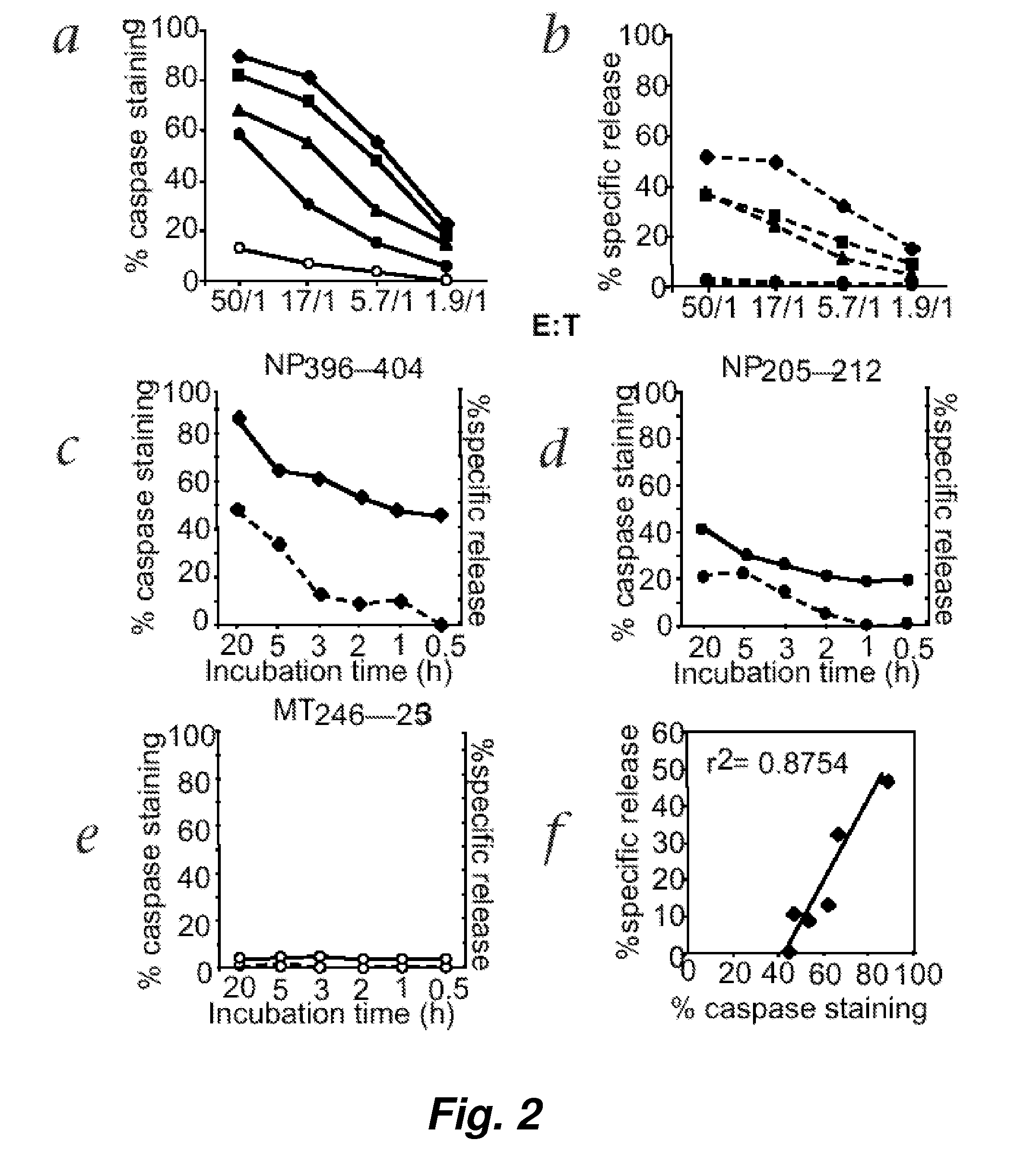
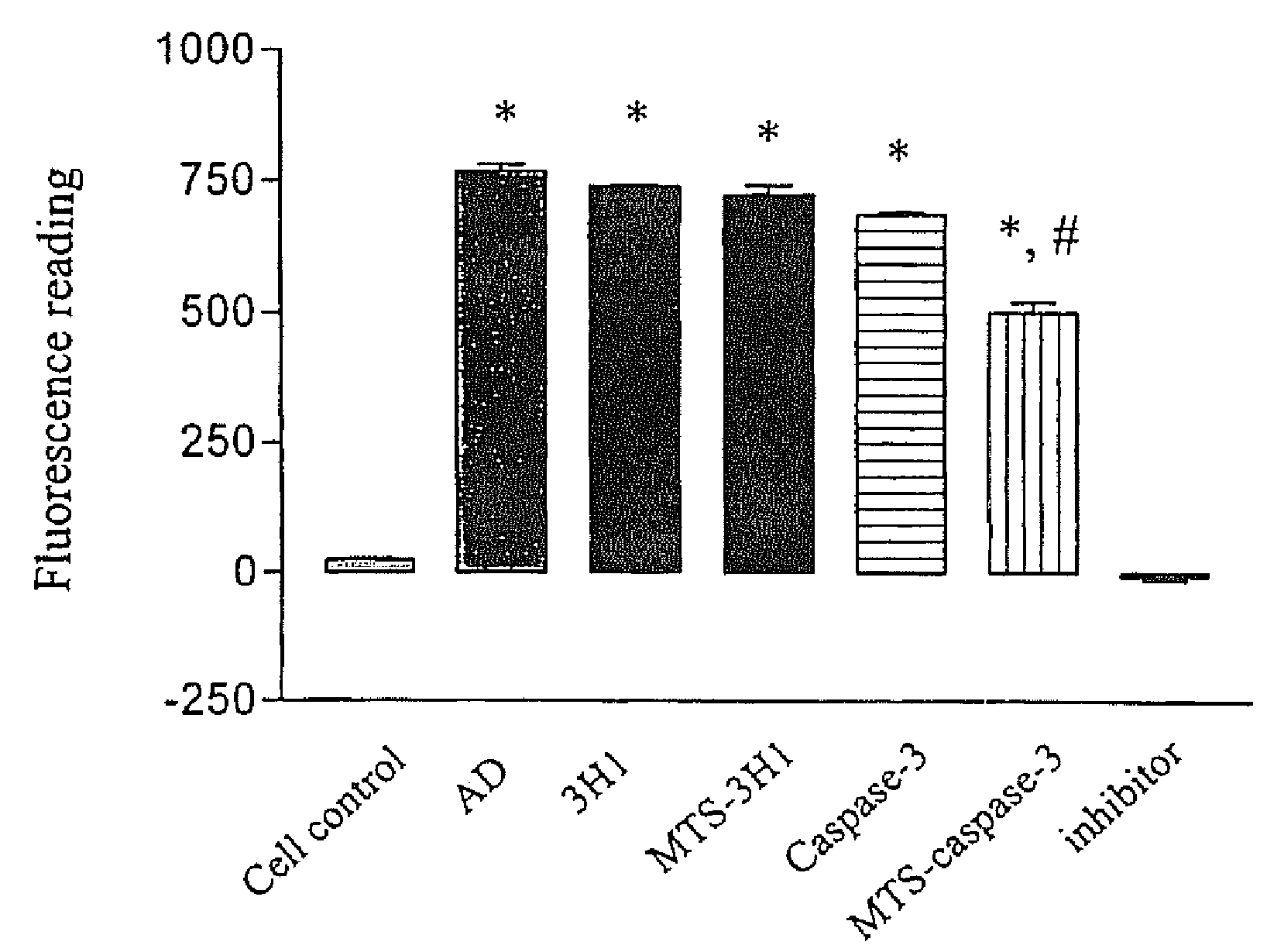
Visualization and quantitation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
ActiveUS20070184493A1Microbiological testing/measurementTetrapeptide ingredientsFluorescenceApoptosis pathways
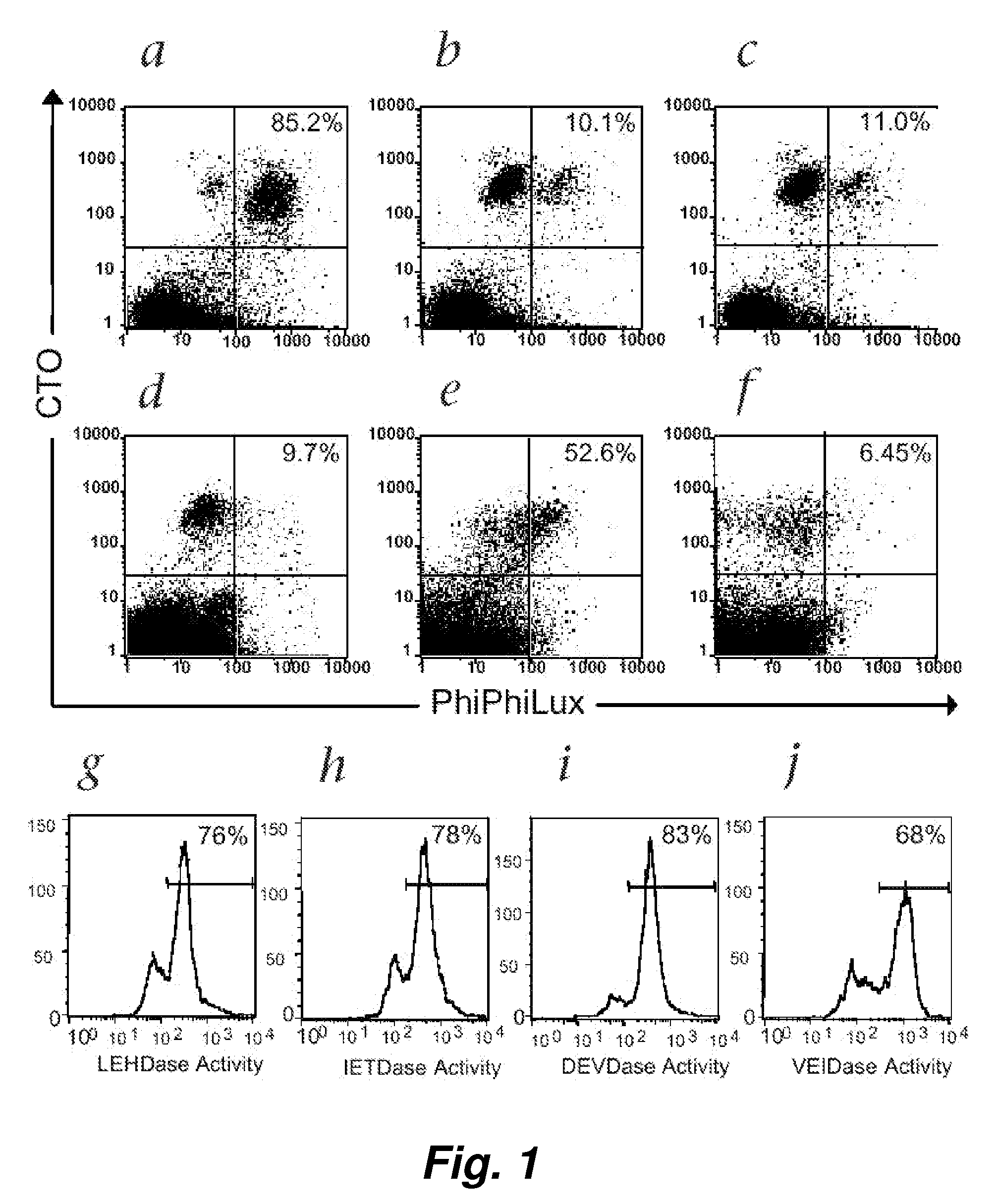
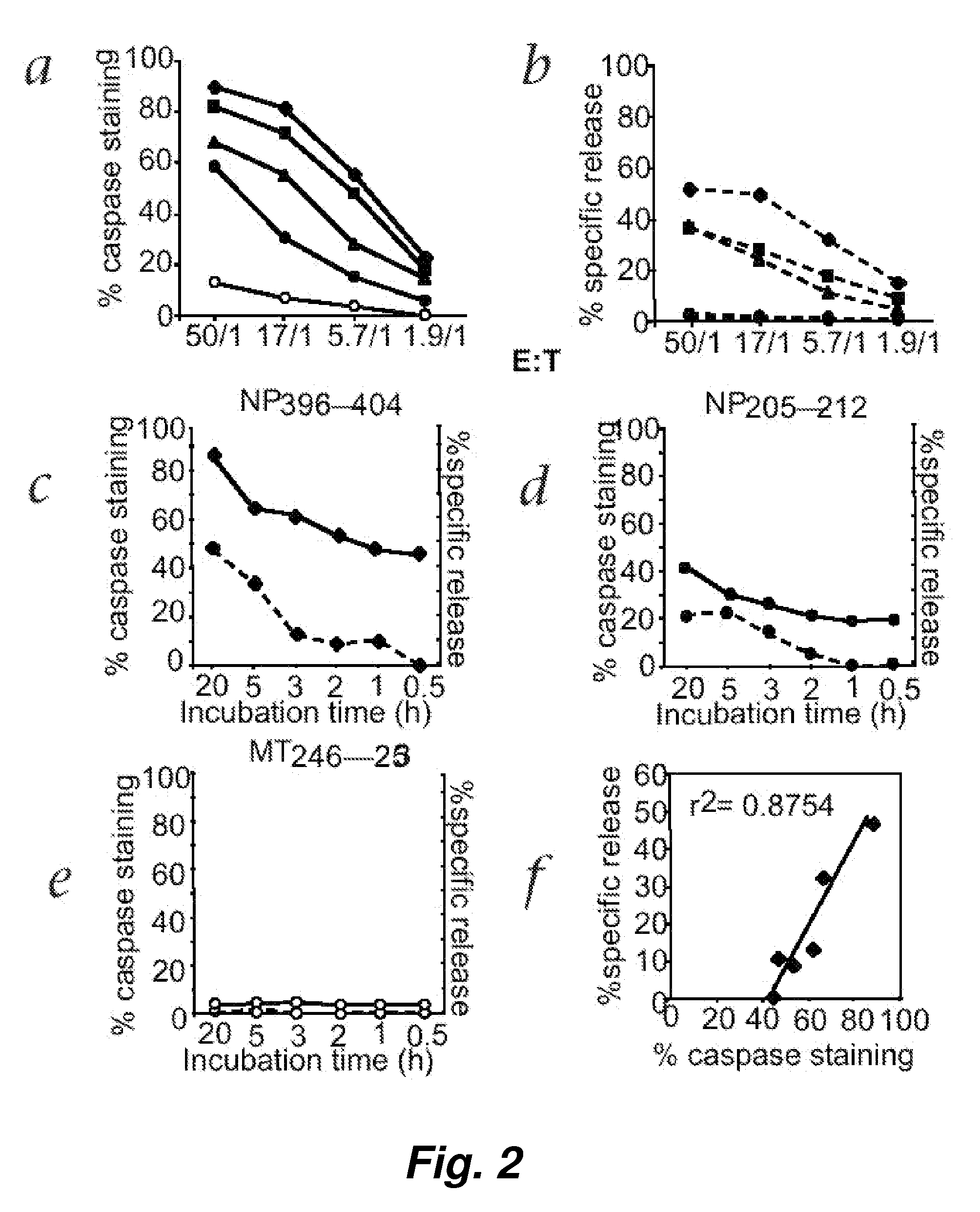
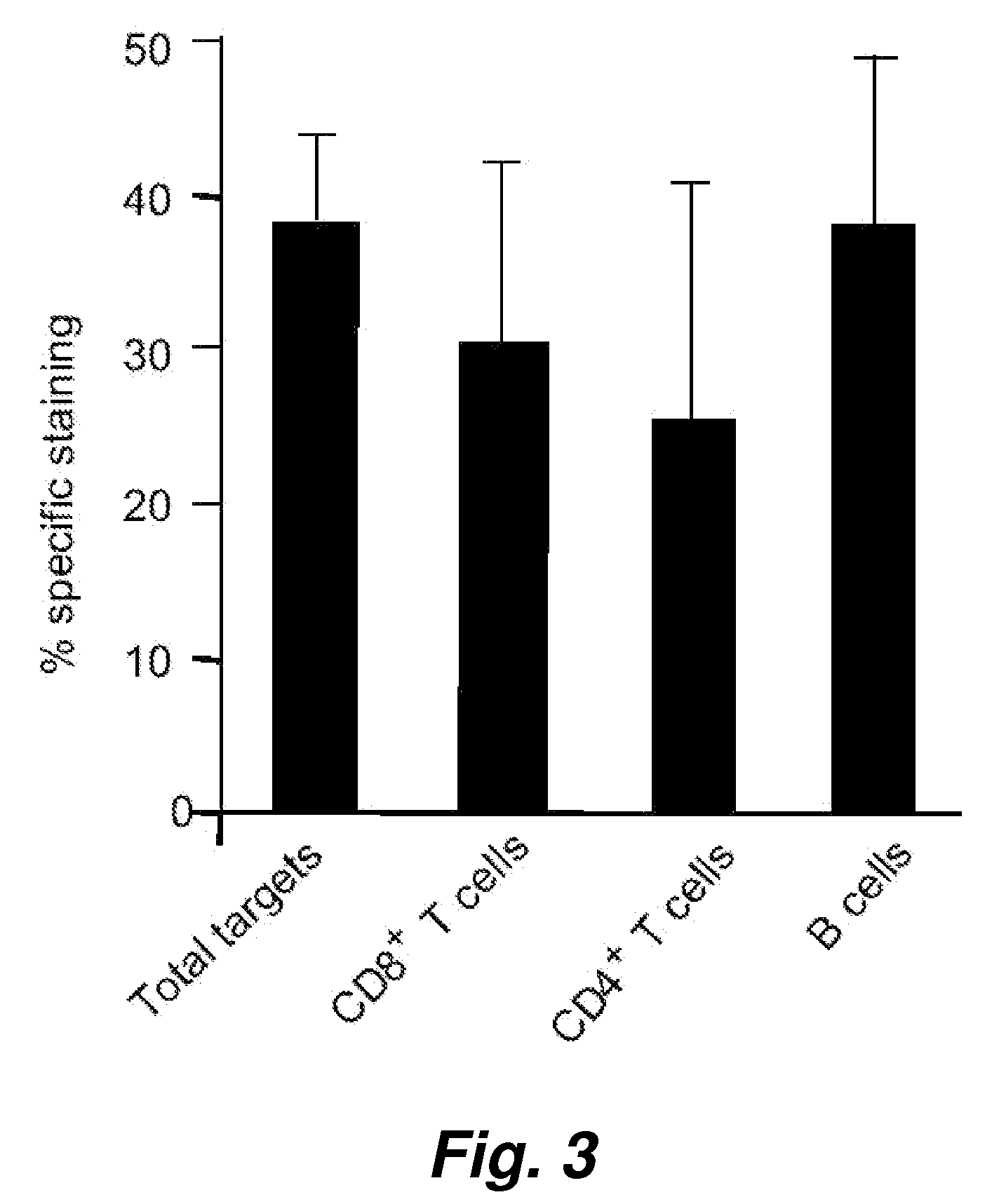
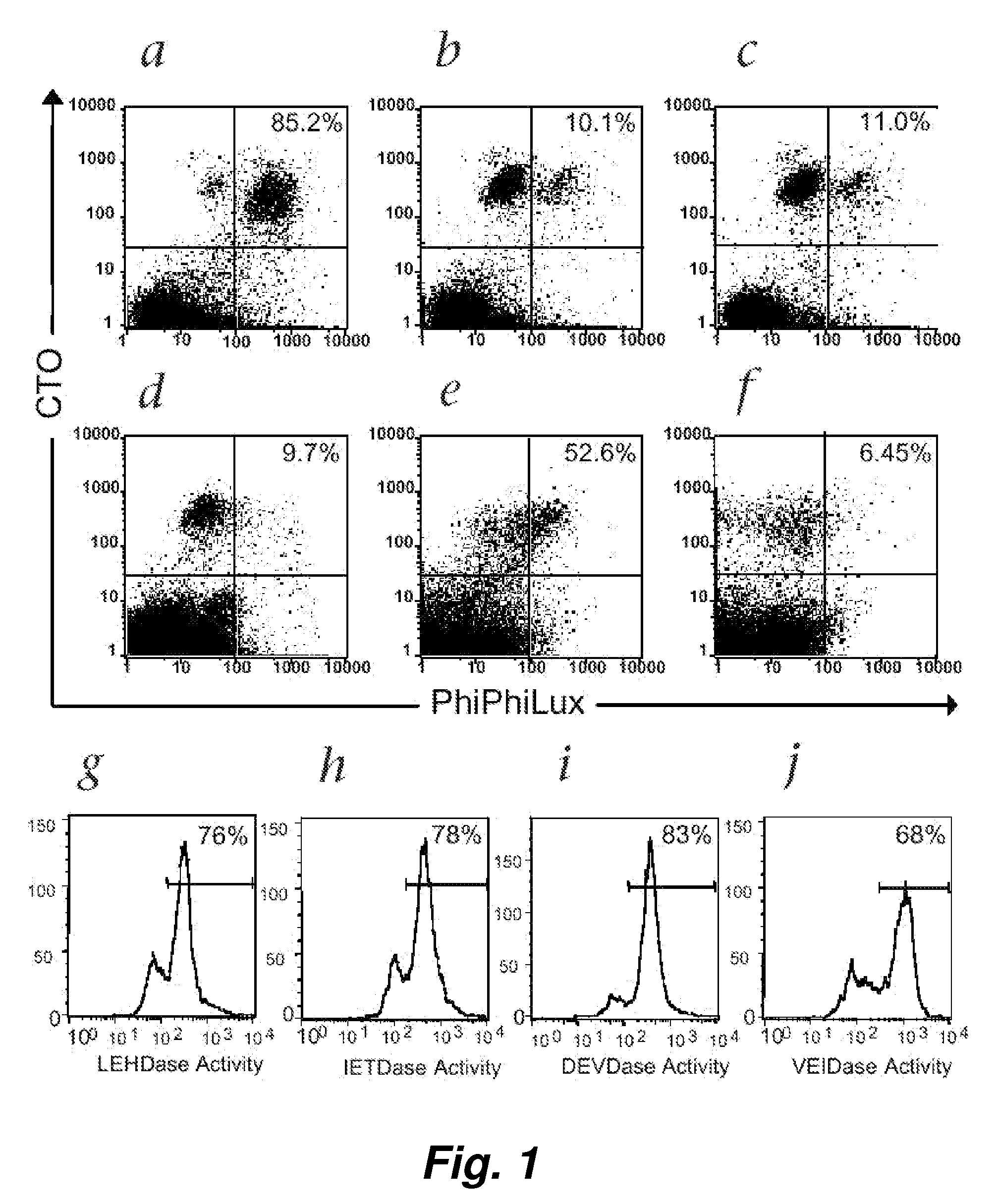
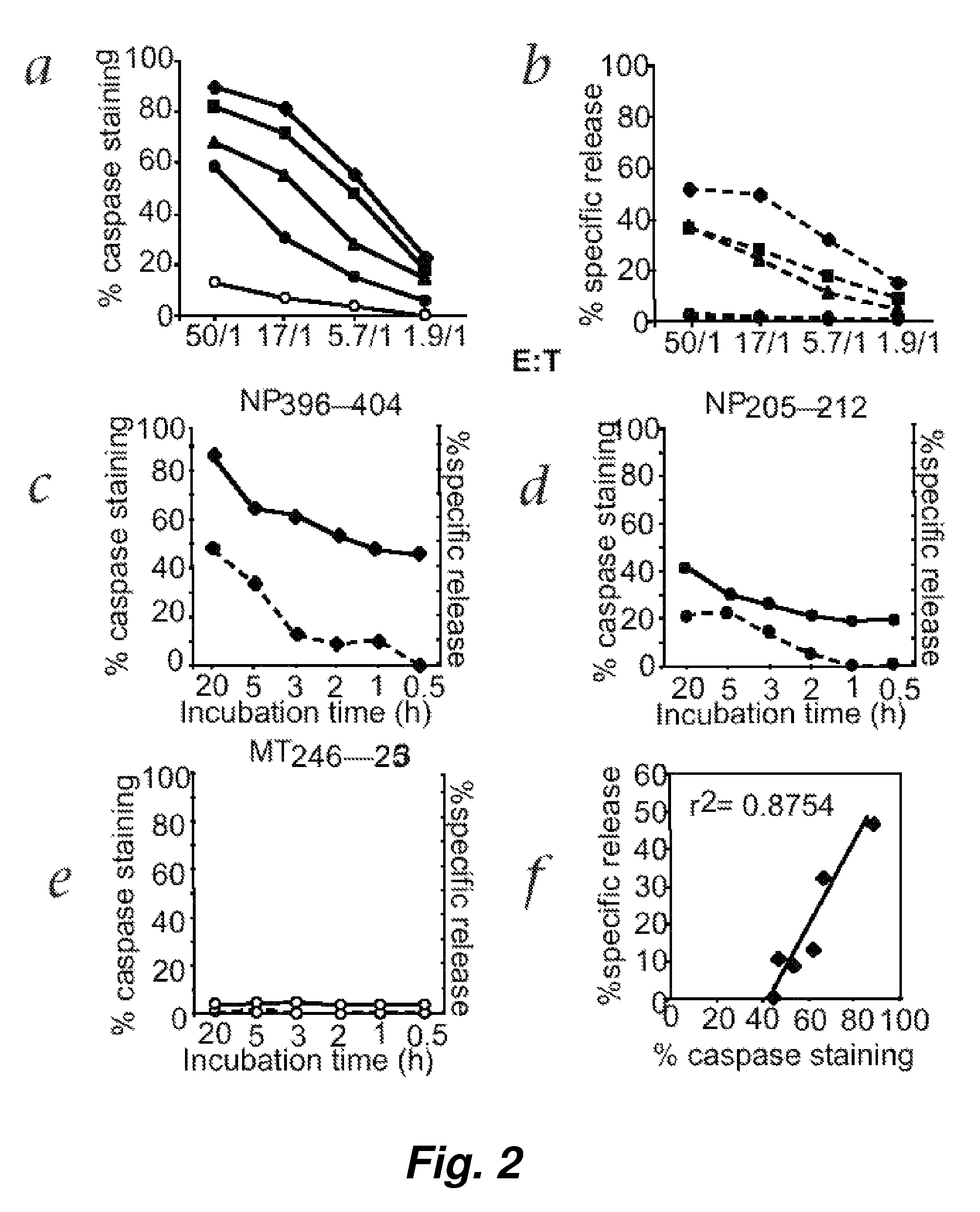
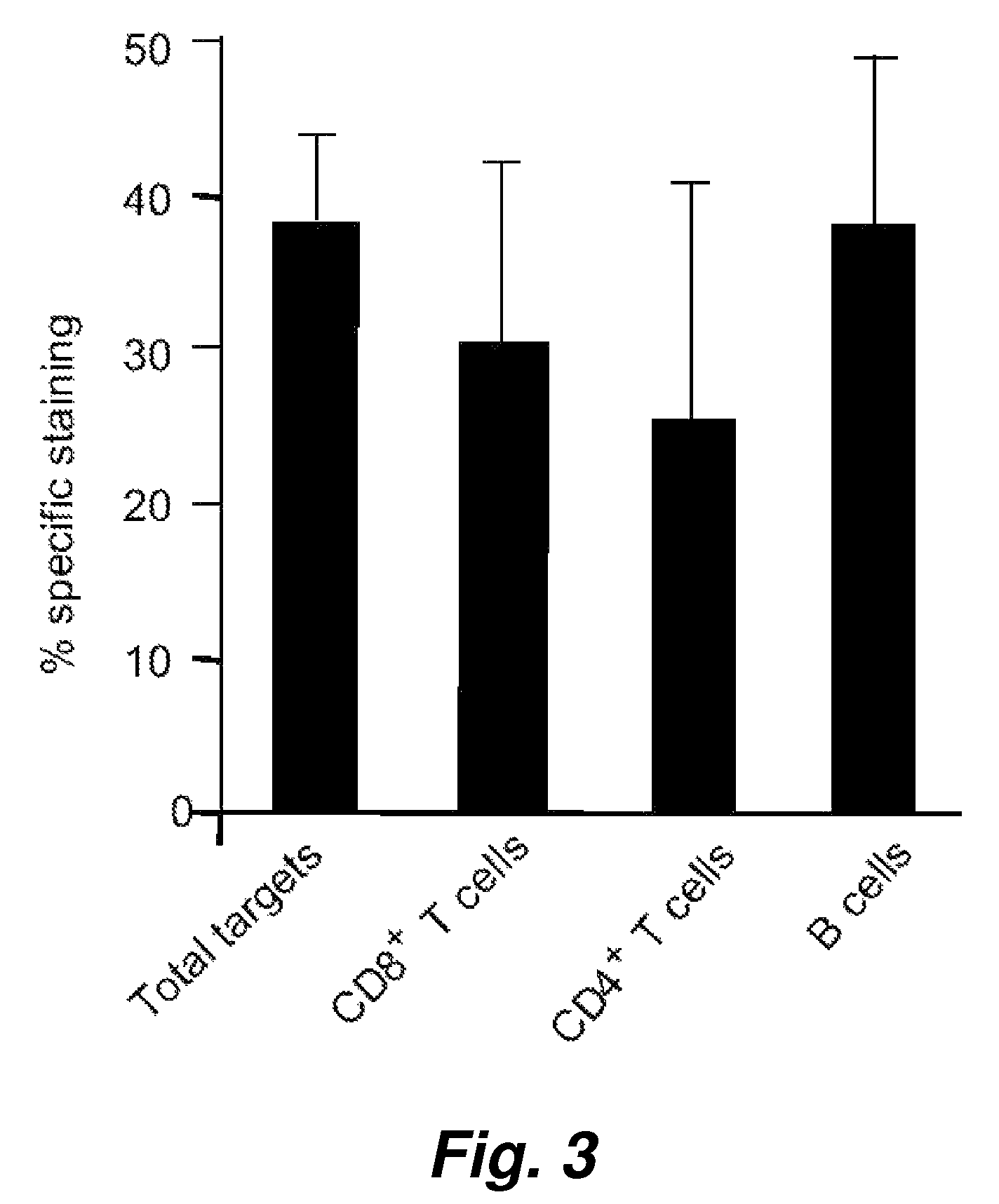
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, granzyme B activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced granzyme B activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic granzyme B substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Visualization and quantitation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
ActiveUS7927871B2Microbiological testing/measurementTetrapeptide ingredientsFluorescenceCytotoxicity
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, granzyme B activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced granzyme B activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic granzyme B substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
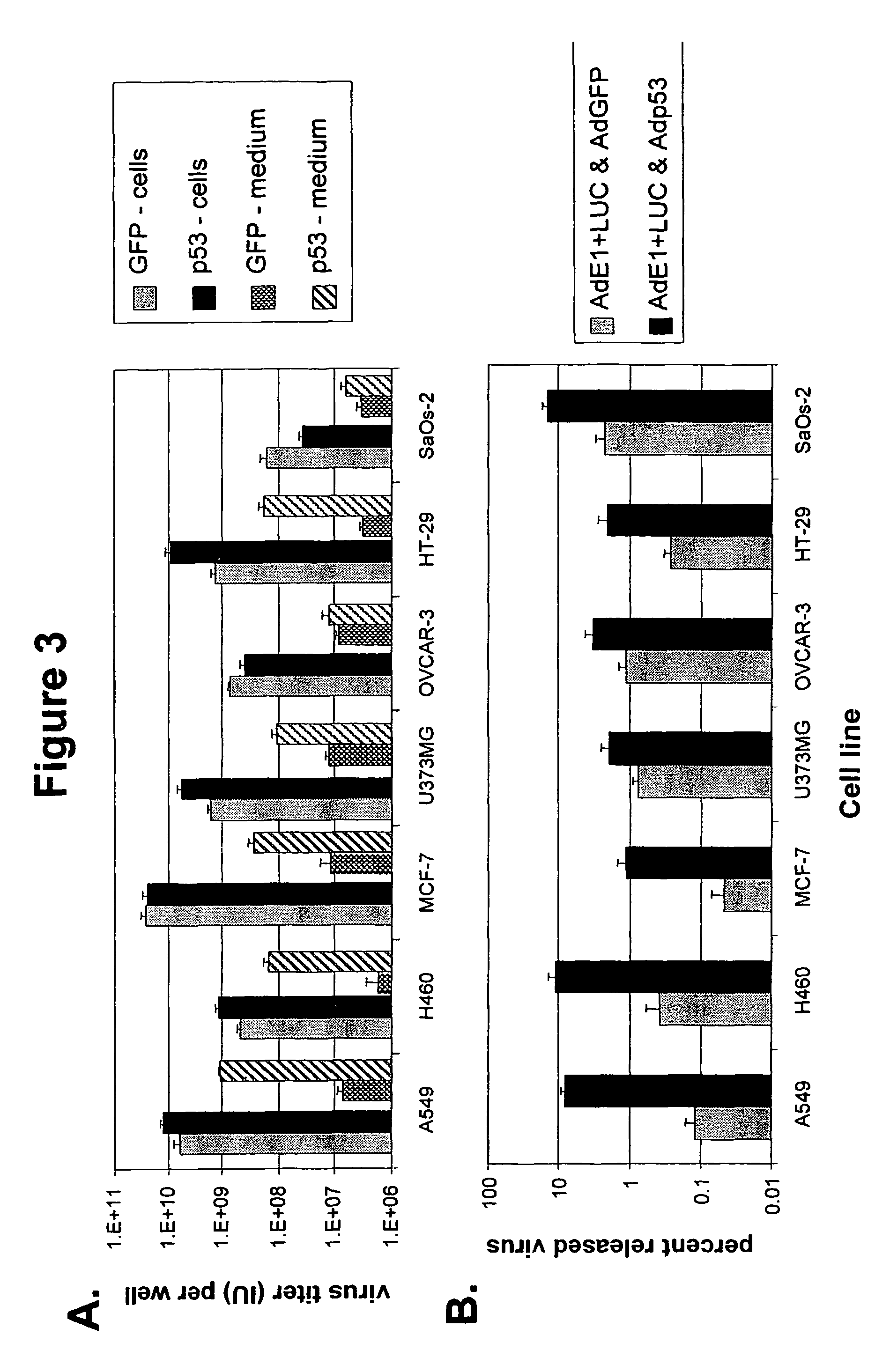
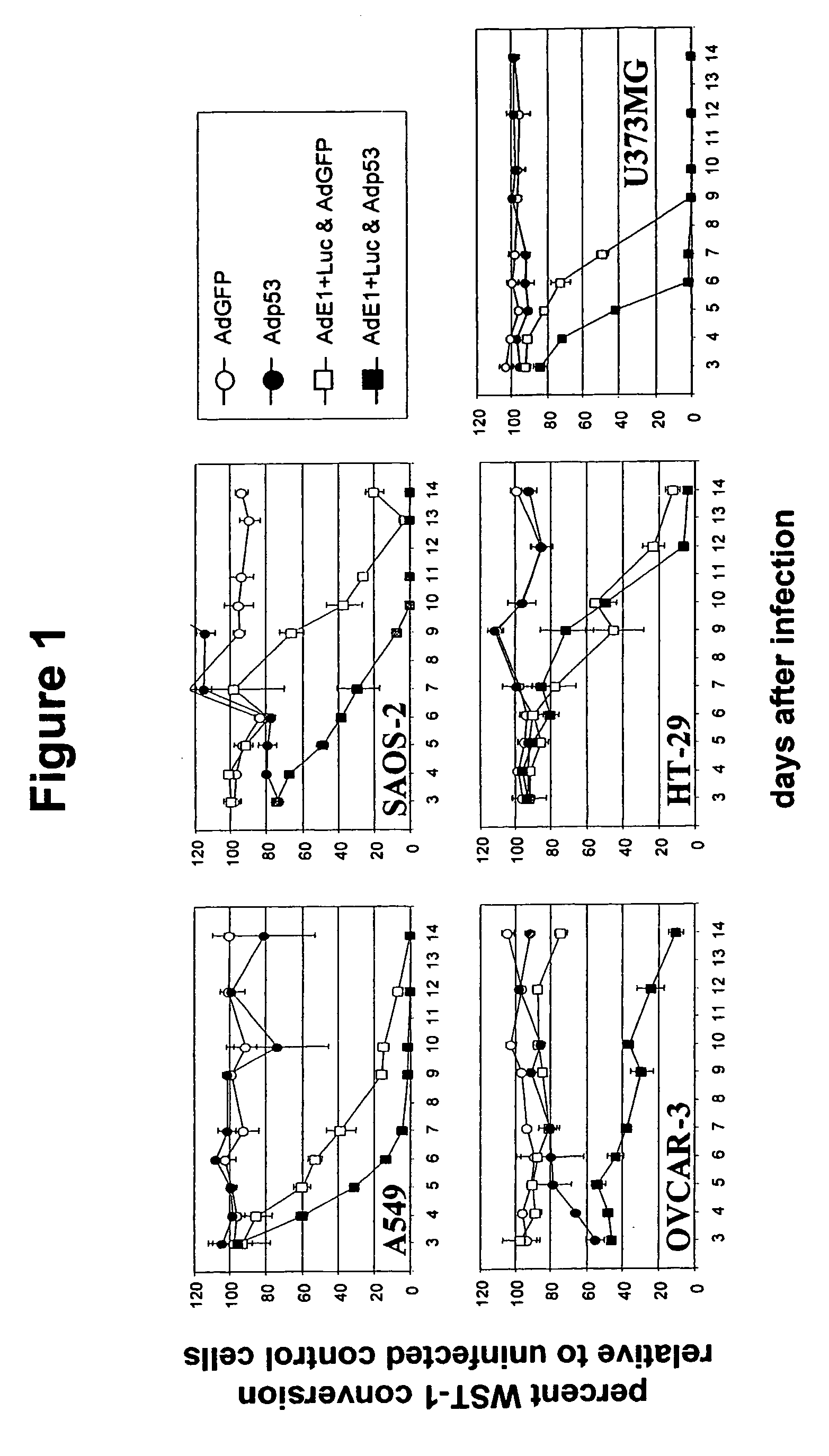
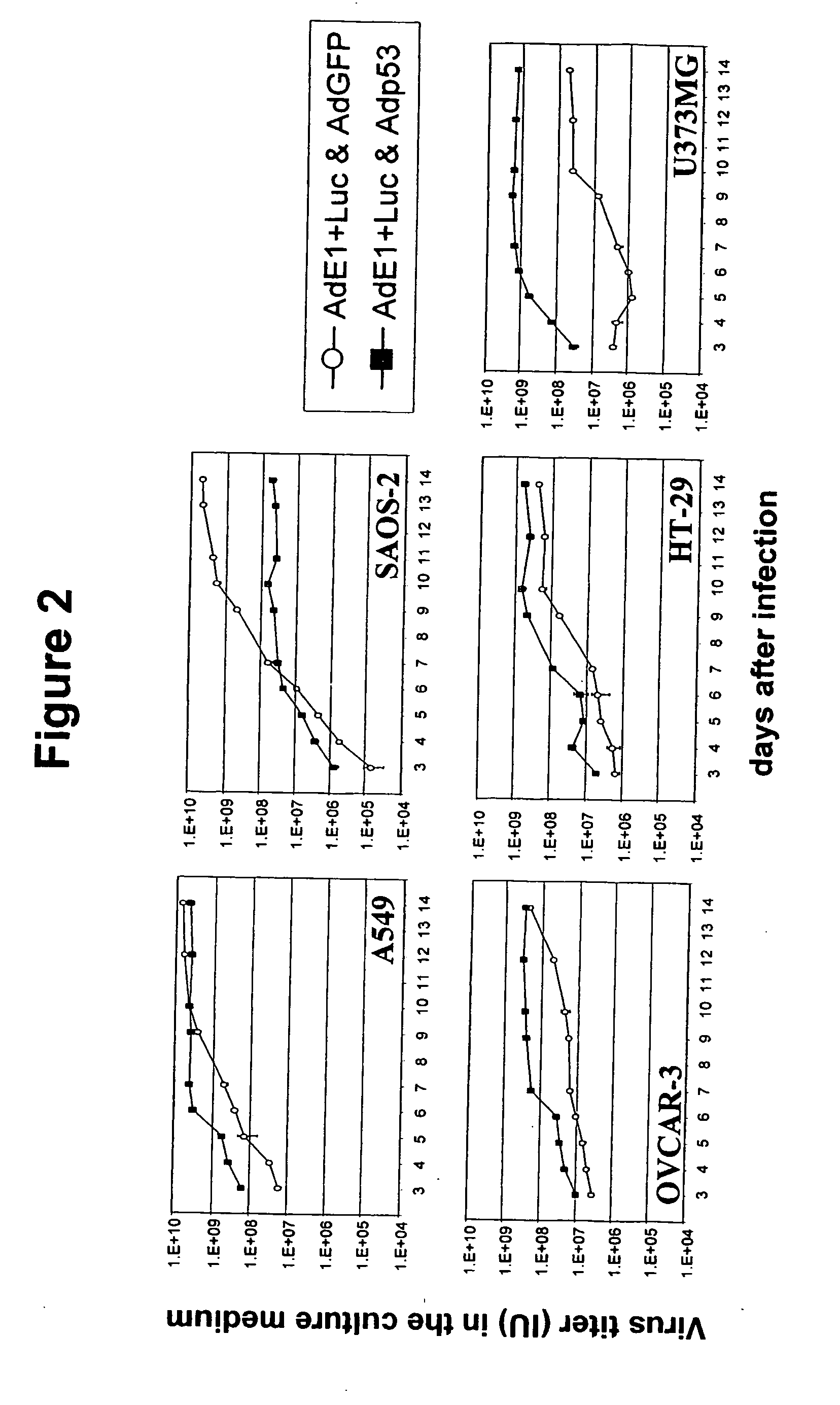
Viruses with enhanced lytic potency
InactiveUS8052965B2Limited durationProcessing speedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsApoptosis pathwaysCell growth
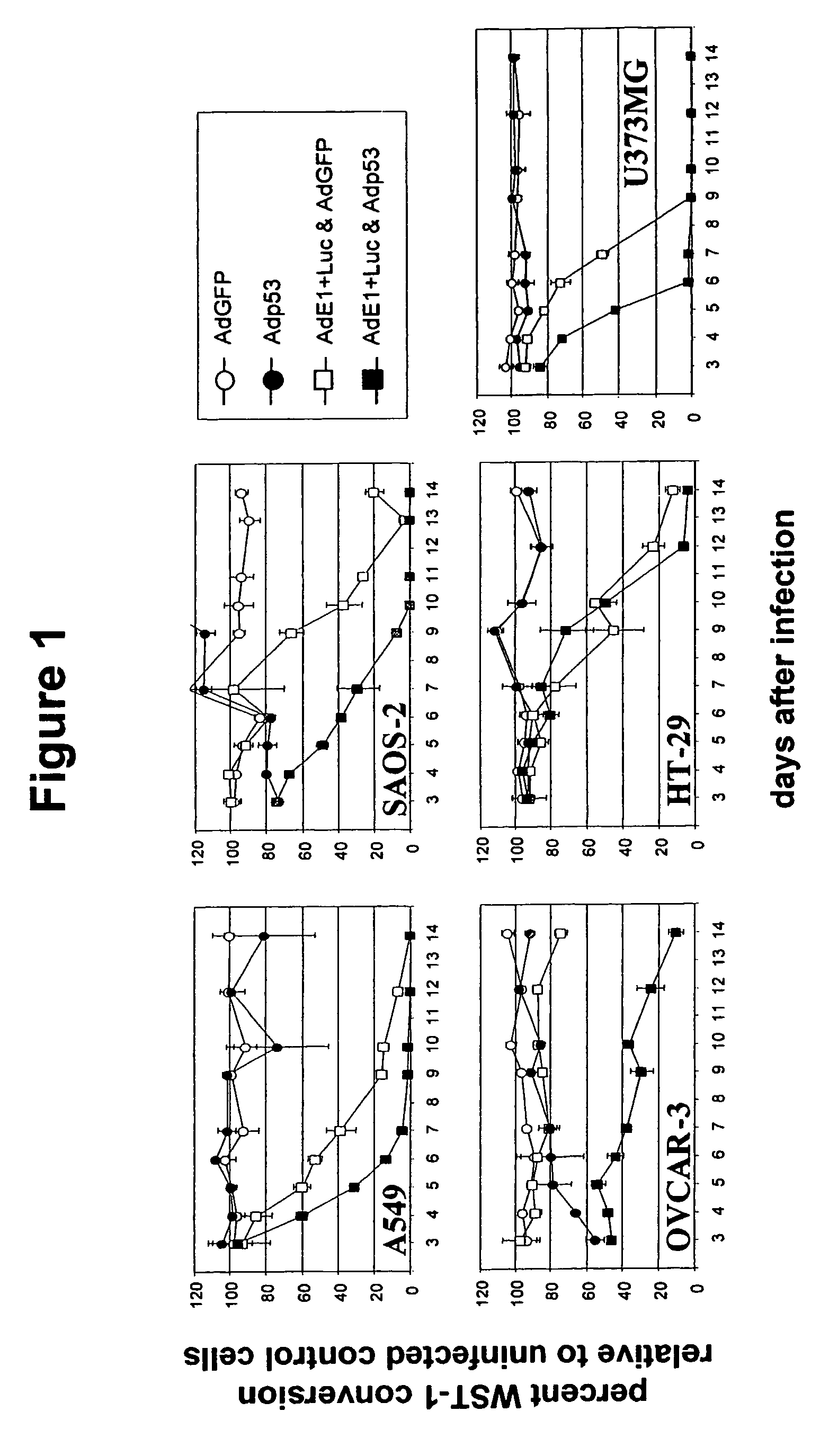
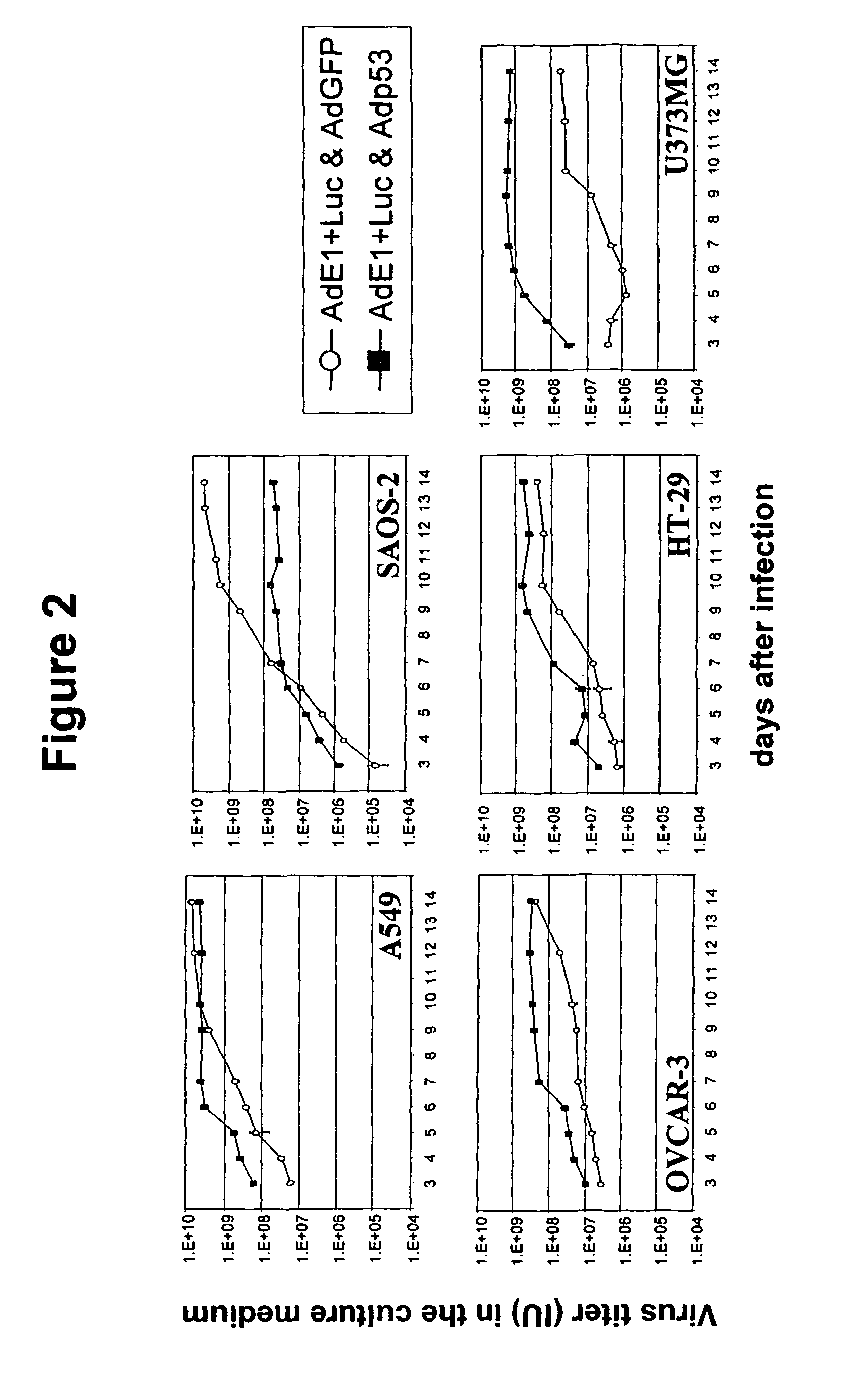
Described is a replication competent recombinant virus, being capable to replicate and having lytic capacity in target cells, the said cell being hampered in the p53 dependent apoptosis pathway, the virus including in the genome thereof, the coding sequence of at least one restoring factor functional in restoring the p53 apoptosis pathway in the said target cells, operably linked to one or more expression control sequences, functional in the said target cells, as well as the use thereof in the preparation of a medicament, in particular for suppressing uncontrolled cell growth.
Owner:STICHTING VUMC
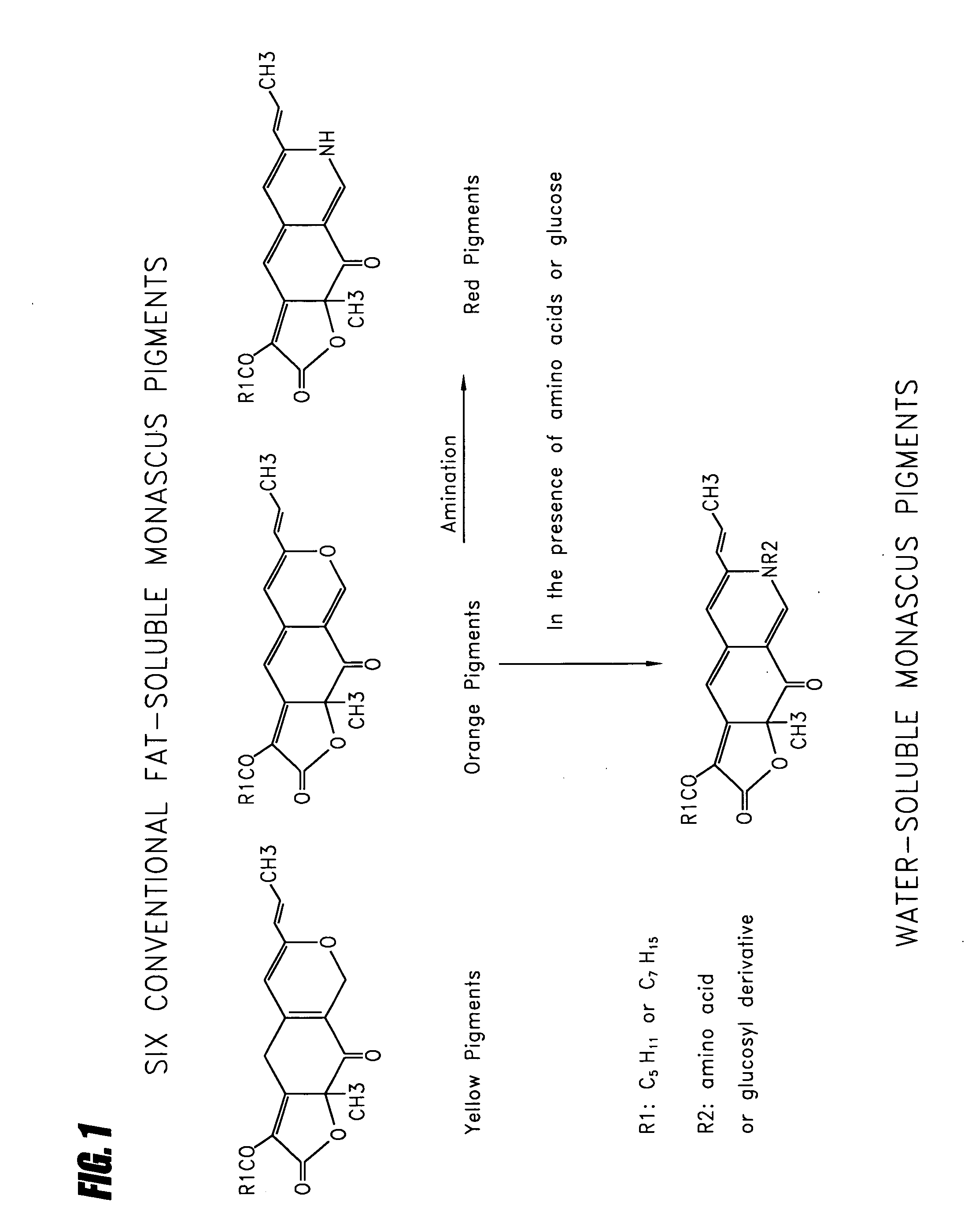
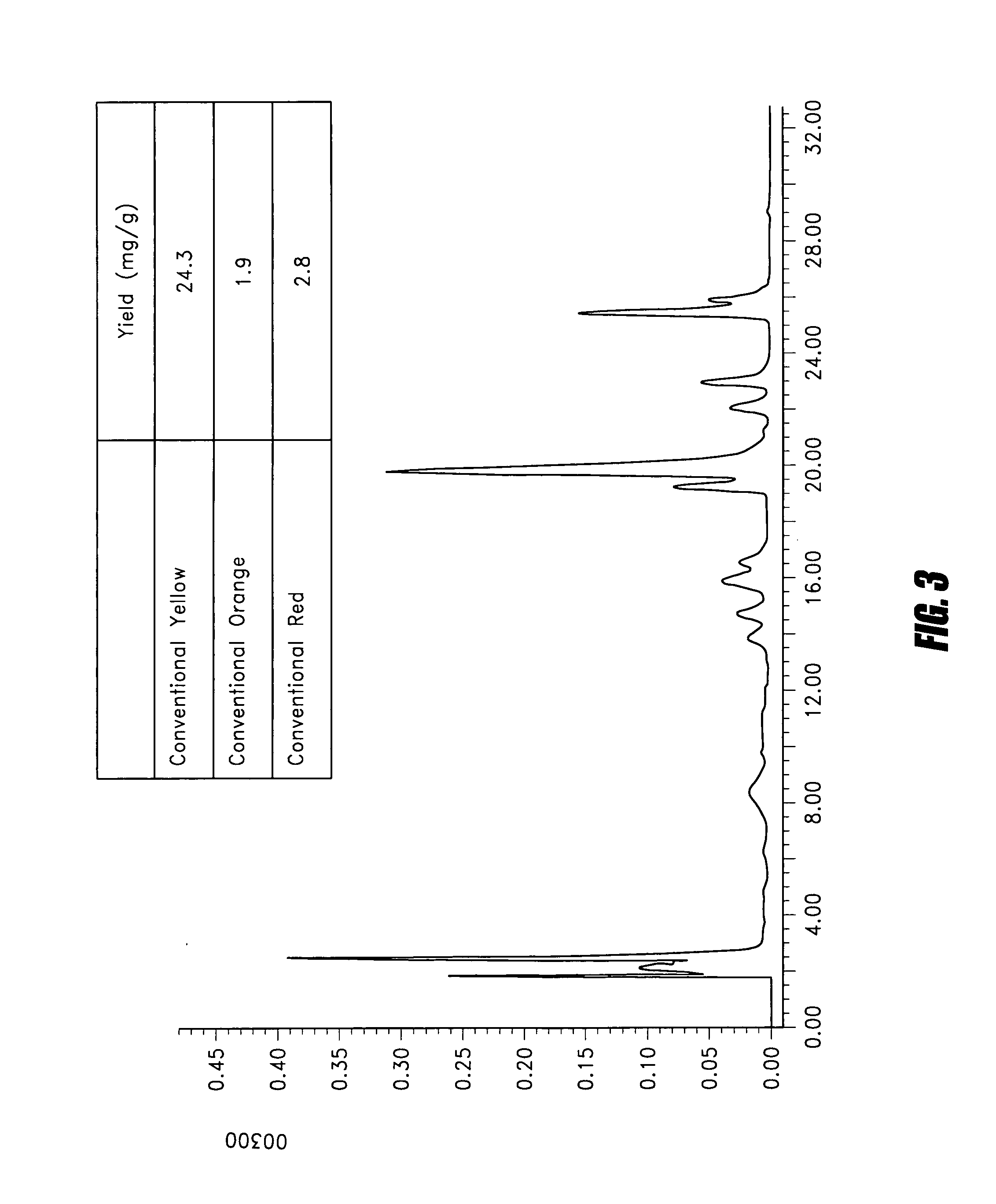
Method for preparing citrinin-free Monascus biomass and use of citrinin-free Monascus biomass
Disclosed is a method for preparing a citrinin-free Monascus biomass. Also disclosed are a pharmaceutical and a functional food comprising a preparation by the method. The Monascus biomass possesses anti-oxidation property, and shows anti-proliferation property on cancer cells via apoptosis pathway.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Antisense IAP oligonucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7294713B2Enhanced cellular uptakeImprove stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNegative regulatorApoptosis pathway
The present invention feature antisense IAP oligonucleotides and other negative regulators of the IAP anti-apoptotic pathway, and methods for using them to enhance apoptosis.
Owner:OTTAWA UNIV OF +1
Viruses with enhanced lytic potency
InactiveUS20050220765A1Processing speedLimited durationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsApoptosis pathwaysCell growth
Described is a replication competent recombinant virus, being capable to replicate and having lytic capacity in target cells, the said cell being hampered in the p53 dependent apoptosis pathway, the virus including in the genome thereof, the coding sequence of at least one restoring factor functional in restoring the p53 apoptosis pathway in the said target cells, operably linked to one or more expression control sequences, functional in the said target cells, as well as the use thereof in the preparation of a medicament, in particular for suppressing uncontrolled cell growth.
Owner:STICHTING VUMC
Multifunctional nano-biomaterial transfection reagent with effect of treating parkinsonism by gene, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104043132ATreatment reachedInhibition of apoptosisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsApoptosis pathwaysCell
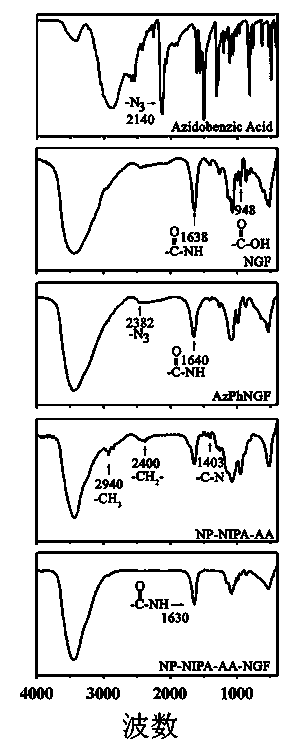
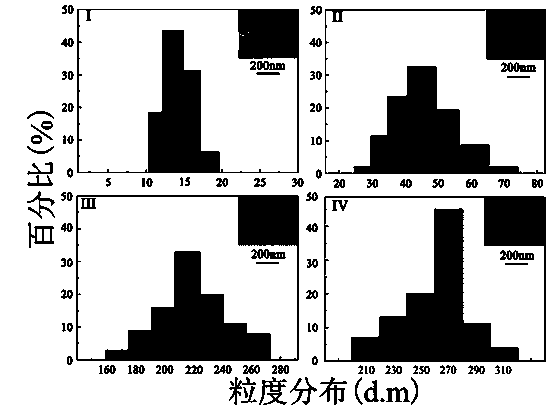
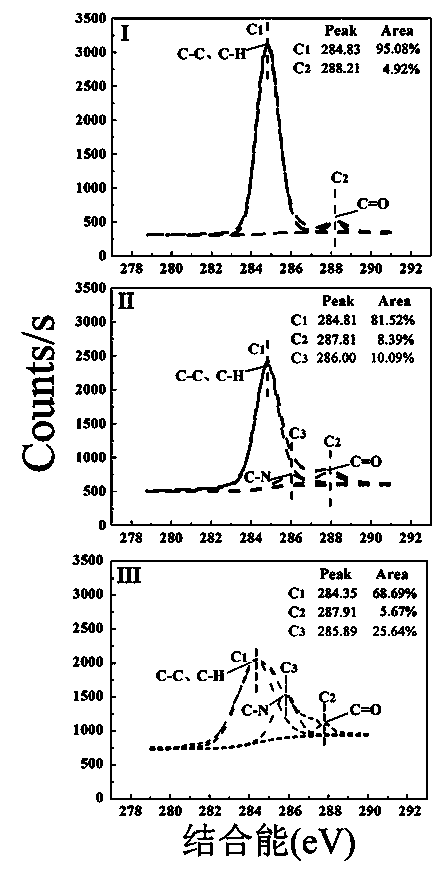
The invention provides a multifunctional nano-biomaterial transfection reagent with an effect of treating parkinsonism by gene, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the method, a nerve growth factor (NGF) is immobilized on the surface of a hydrogel coated ferroferric oxide nano-particle (Fe3O4-OA-NAPI-AA) by virtue of a photo-grafting method, and plasmid DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) capable of interfering with alpha-synuclein synthesis is adsorbed. The nano-material transfection reagent acts on the cell of an MPP+ (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium) induced in-vitro parkinsonism model PC12, and cell apoptosis is remarkably inhibited, wherein expression of the nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR) is up-regulated, expression of alpha-synuclein is down-regulated, and classic apoptosis pathway of BAX, P53 and Bcl-2 is influenced so as to achieve the aim of treating parkinsonism. The nano-material transfection reagent is non-toxic and less in side effects, can smoothly carry a gene to enter cells, is remarkable in action, and is worthy of popularization and application of parkinsonism treatment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
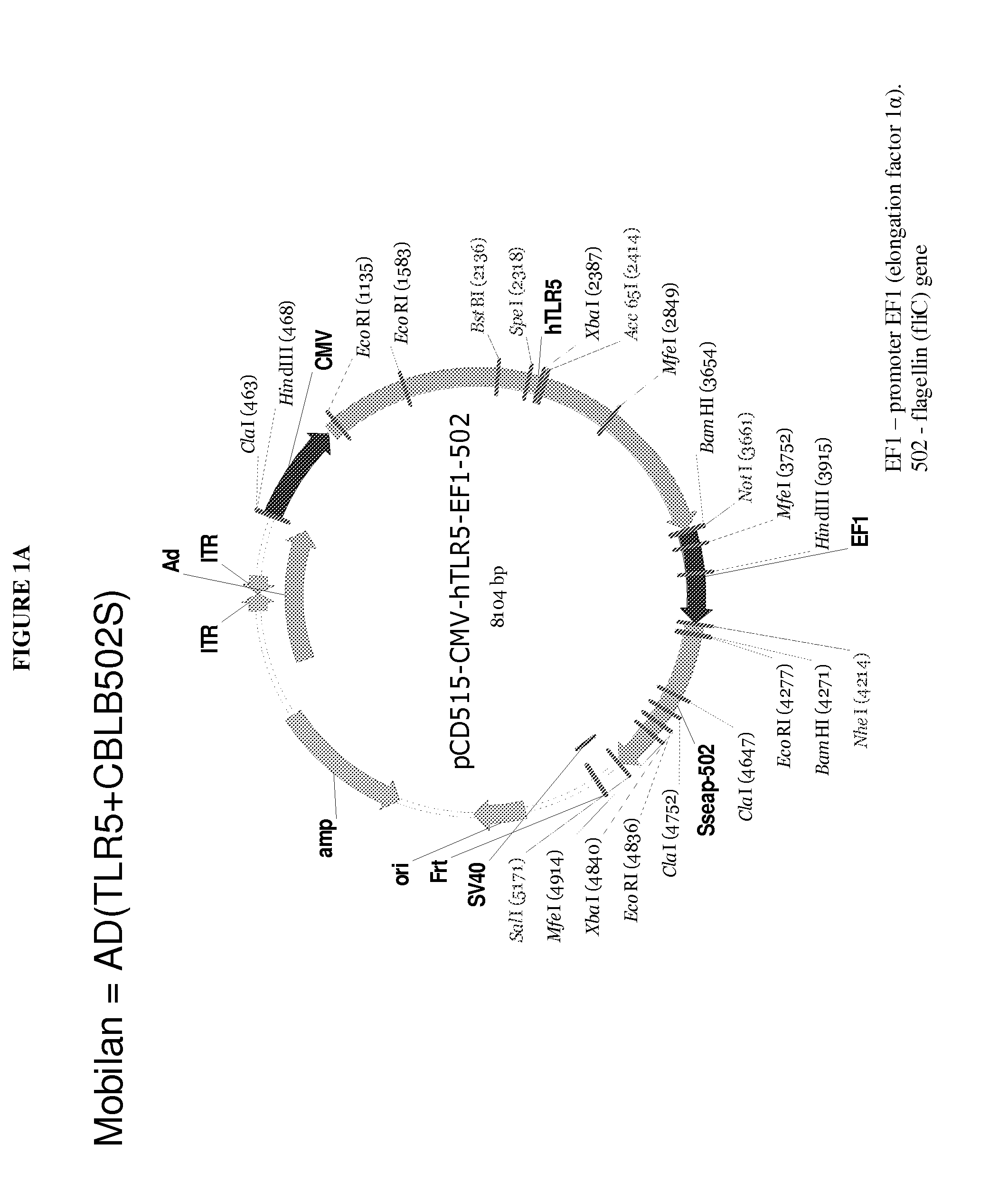
Use of toll-like receptor and agonist for treating cancer
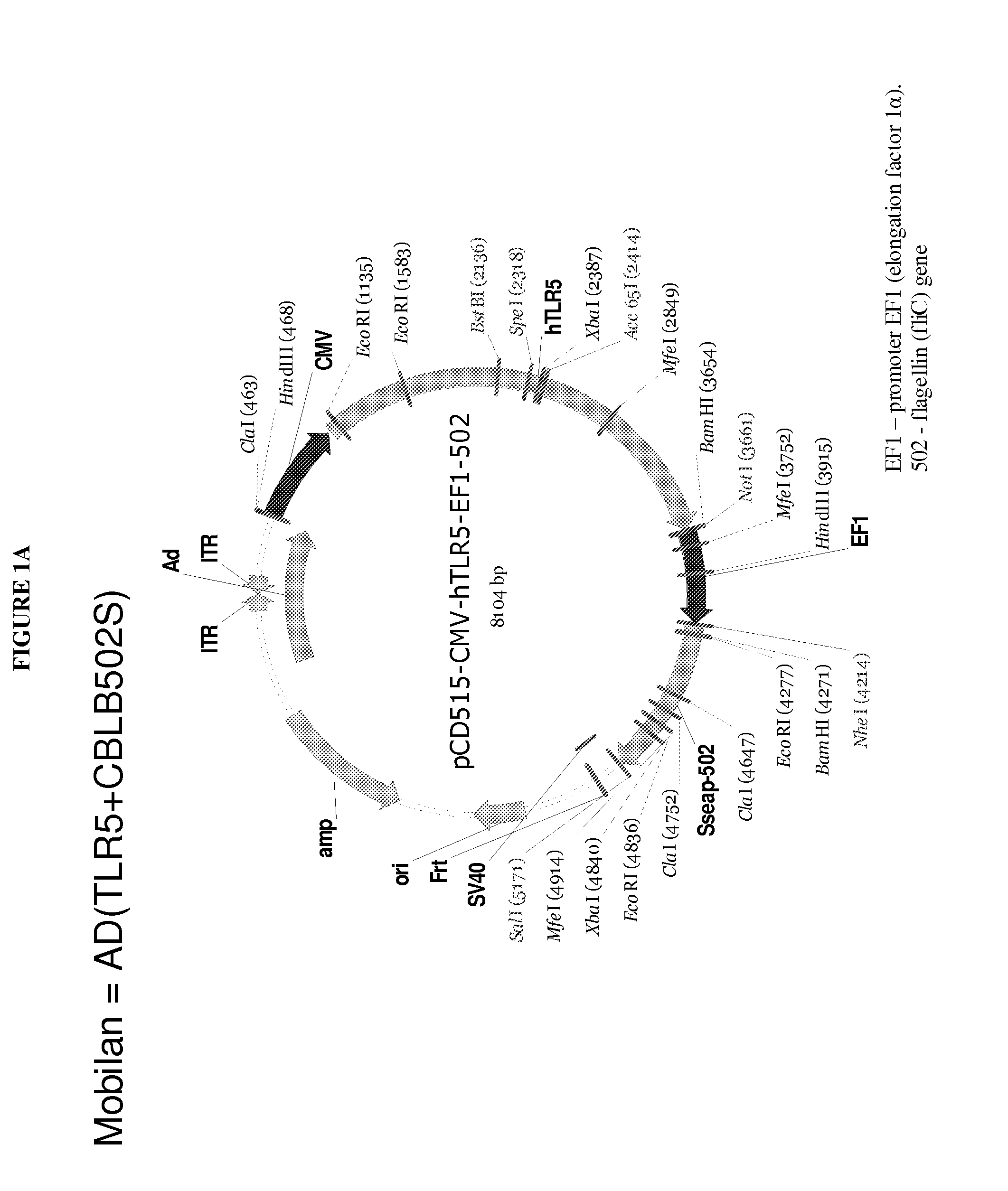
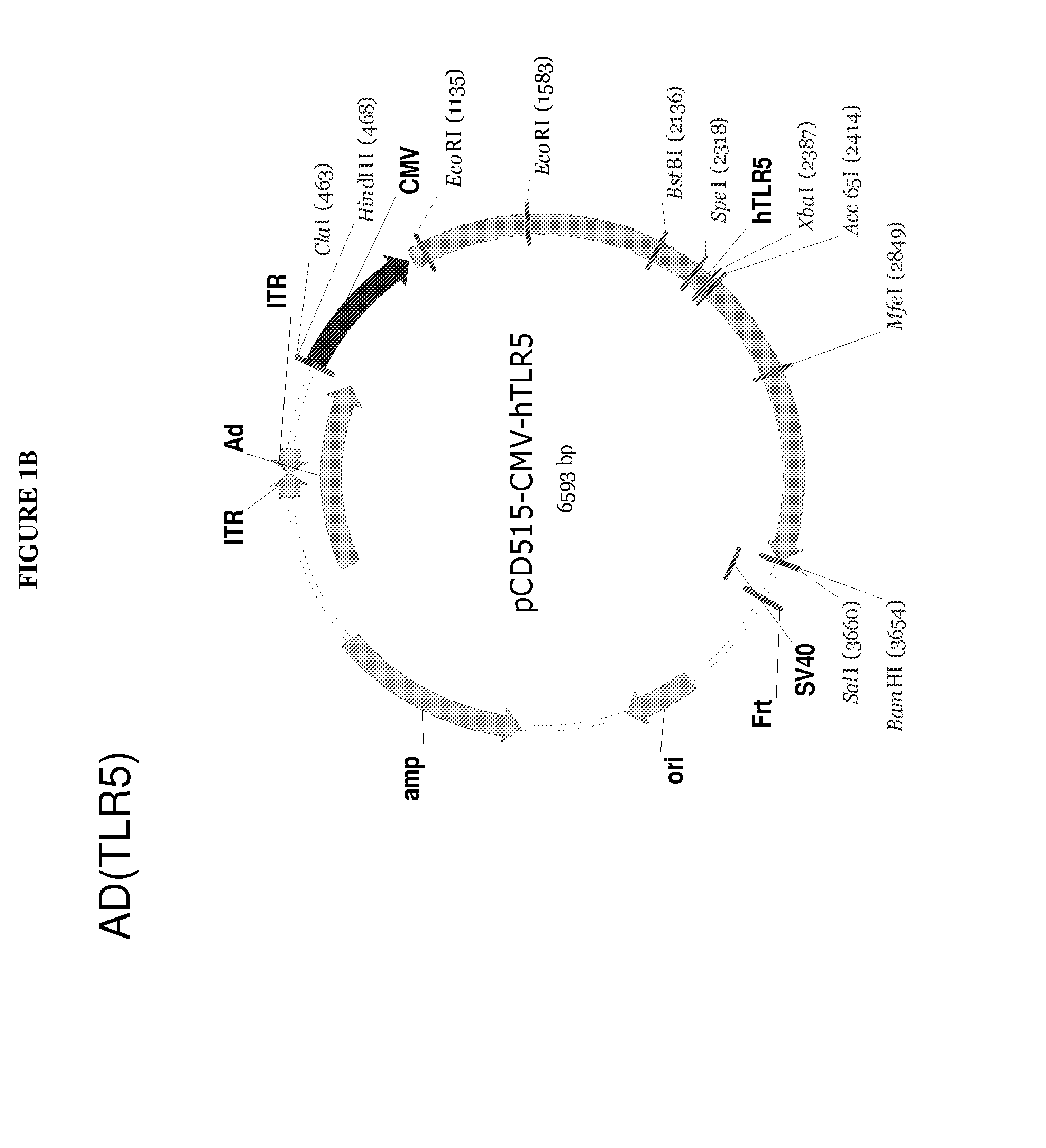
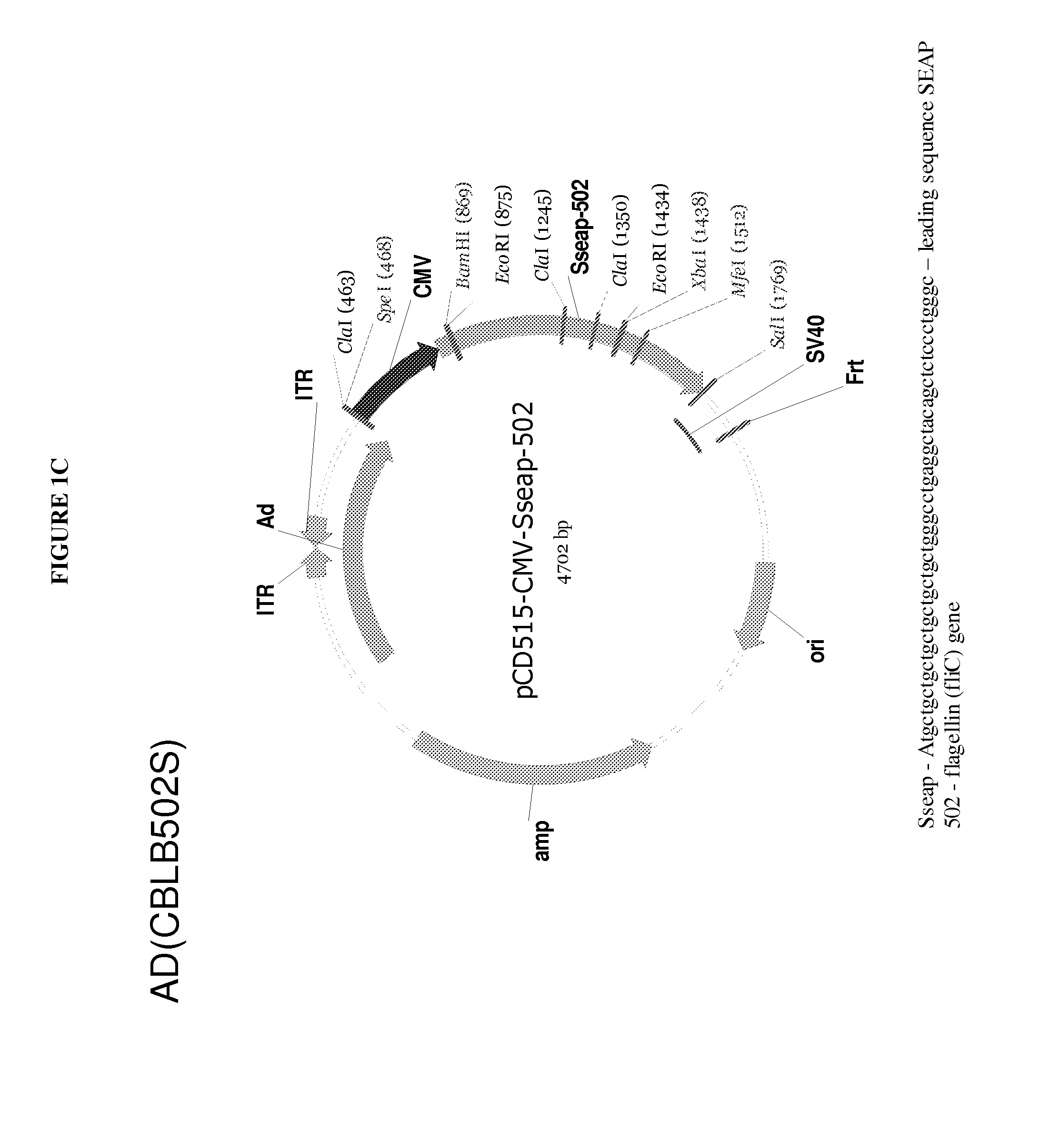
The present invention is directed to methods and agents used for treating cancer or infectious diseases by providing toll-like receptors such as toll-like receptor 5 (TLR-5) in combination with providing a toll-like receptor agonists such as flagellin resulting in a cis and intrans effect that recruits cells involved in both the innate (cis effect) and adaptive (trans effect) immune response to specifically kill cancer cells and cells infected with a pathogen via the NF-κB apoptosis pathway.
Owner:ROSWELL PARK CANCER INST +1
Method for preventing skin-cellular injury by using green algae extract and cosmetic composition containing green algae extract
InactiveUS20090142369A1Irreparable damage can be preventedPreventing UV-induced skin injuryBiocideAlgae medical ingredientsFiberApoptosis pathways
A method for preventing UV-induced skin-cellular injury by using a green algae extract and a cosmetic composition containing the green algae extract are disclosed. An effective dose of the green algae extract is used to protect fibroblasts from UV-induced apoptosis. The mechanism of the disclosed method is using the green algae extract to inhibit interaction between apoptosis pathway molecules Fas / FasL so as to inhibit an adapter protein (FADD) in a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) and in turn to inhibit caspase-3 activation and cleaved polymerase (PARP) such that irreparable damage to DNA can be prevented. The green algae extract can be mixed with a skin permeable cosmetic composition so that the cosmetic composition possesses the function of preventing skin from UV-induced injury.
Owner:SHIH MENG HAN +1
Methods for selectively modulating survivin apoptosis pathways
The present invention, based on the discovery of a new biological phenomena, provides methods and compositions for use in identifying agents that modulate the phosphorylation of survivin, the interaction between survivin and p34cdc2-cyclin B1 kinase complex, and the interaction between survivin and caspase-9. Related methods and compositions can be used to modulate survivin regulated apoptosis.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Bad phosphorylation determines ovarian cancer chemo-sensitivity and patient survival
Despite initial sensitivity BAD-protein phosphorylation were evaluated in patient samples and cell lines as determinants of chemo-sensitivity and / or clinical outcome, and as therapeutic targets. Induced in-vitro OVCA cisplatin-resistance was associated with BAD-pathway expression. Expression of the pathway was also associated with resistance of 7 different cancers cell-types to 8 chemotherapeutic agents. Phosphorylation of the BAD-protein was associated with platinum-resistance in OVCA cells and primary OVCA specimens, and also overall patient survival. Targeted modulation of BAD-phosphorylation levels influenced cisplatin-sensitivity. A 47-gene BAD-pathway signature was associated in-vitro phospho-BAD levels and with survival of 838 patients with ovarian, breast, colon, and brain cancer. The survival advantage associated with both BAD-phosphorylation and also the BAD-pathway signature was independent of surgical cytoreductive status. The BAD apoptosis pathway influences human cancer chemo-sensitivity and overall survival. The pathway is useful as a biomarker of therapeutic response, patient survival, and therapeutic target.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
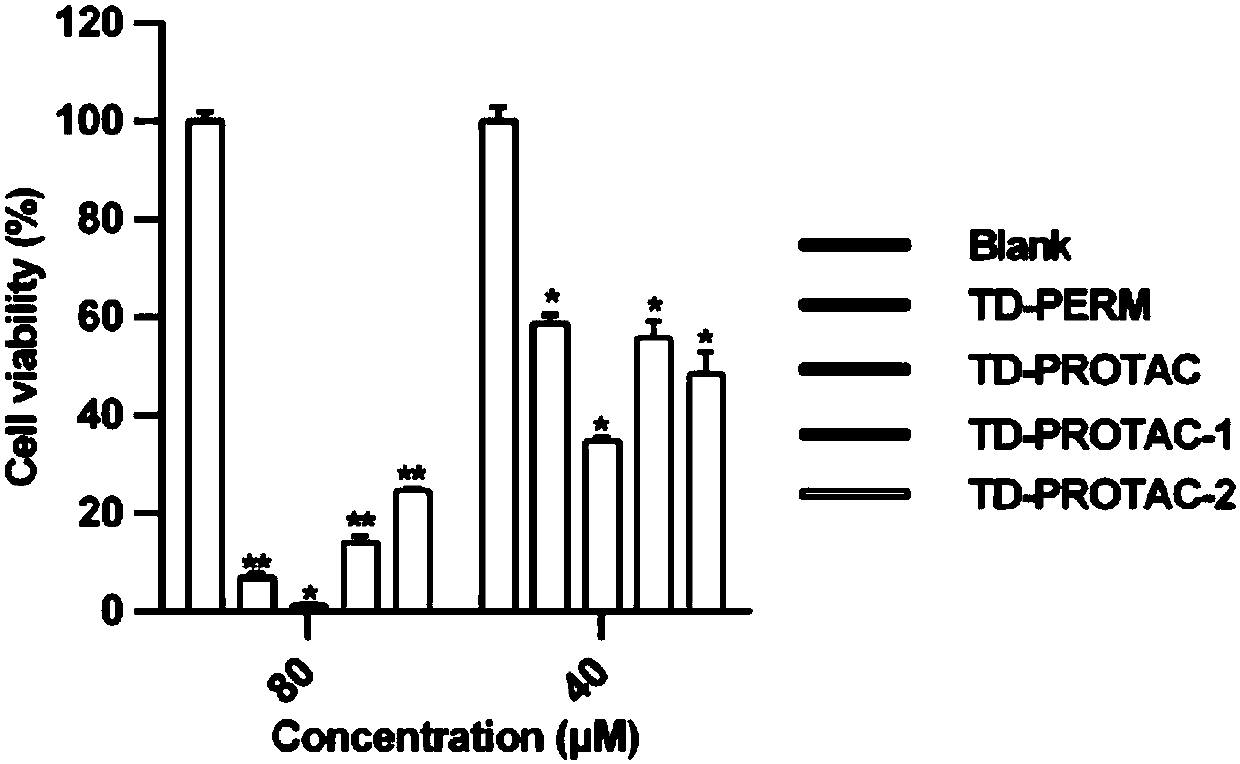
Stable polypeptide protein-targeted chimeric molecule, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108047312AImprove bindingGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesProtein targetApoptosis pathways
The invention provides a stable polypeptide protein-targeted chimeric molecule with an amino-acid sequence structure being described in the specification. The invention also provides an application ofthe stable polypeptide protein-targeted chimeric molecule in degrading ERalpha protein. The invention also provides an application of the stable polypeptide protein-targeted chimeric molecule in preparing a medicine for treating breast cancer. The invention also provides a preparation method of the stable polypeptide protein-targeted chimeric molecule. Proved by a fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) experiment, the stable polypeptide protein-targeted chimeric molecule provided by the invention has the advantage that the expression of downstream genes of the ERalpha can beinhibited. Also proved by a cell proliferation experiment and cell apoptosis experiment, the polypeptide can kill breast cancer cells by a apoptosis pathway.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Visualization and quantitiation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
InactiveUS20090263830A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingApoptosis pathwaysT lymphocyte
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, caspase activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced caspase activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic caspase substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
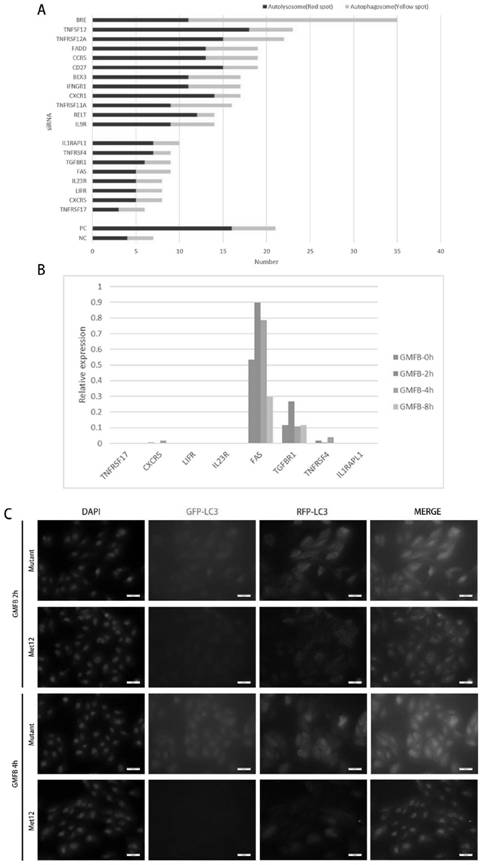
Inhibitor for autophagy and apoptosis of retinal pigment cells RPE and application of inhibitor
InactiveCN112043833AReduce apoptosisReduced responsePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseDiabetes retinopathy
The invention provides an inhibitor for autophagy and apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelial cells RPE and application of the inhibitor, and relates to the technical field of biological medicines. The invention relates to an inhibitor for autophagy and apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelial cells RPE. The inhibitor comprises an antagonist Met of a tumor necrosis factor superfamily receptor FAS.It is verified that the tumor necrosis factor superfamily receptor FAS can serve as a receptor of GMFB to activate downstream autophagy and apoptosis pathways, the antagonist Met of the tumor necrosisfactor superfamily receptor FAS can inhibit activation of the FAS and downstream related pathways of the FAS, cell apoptosis and autophagy reactions are reduced, and therefore the morbidity process of diabetic retinopathy is delayed. The inhibitor can be used for preparing medicines for delaying and / or treating diabetic retinopathy in the early stage of disease.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
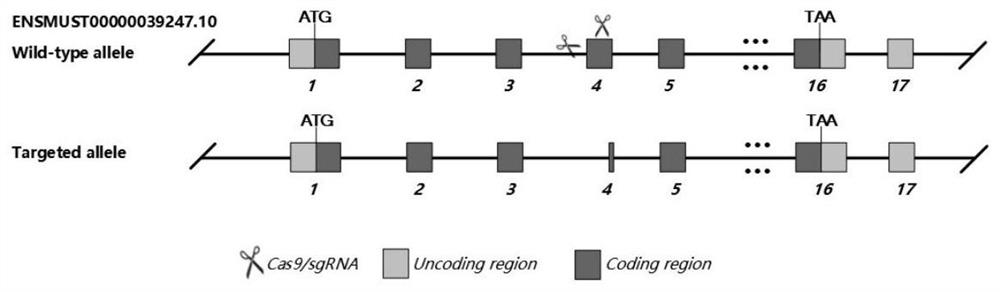
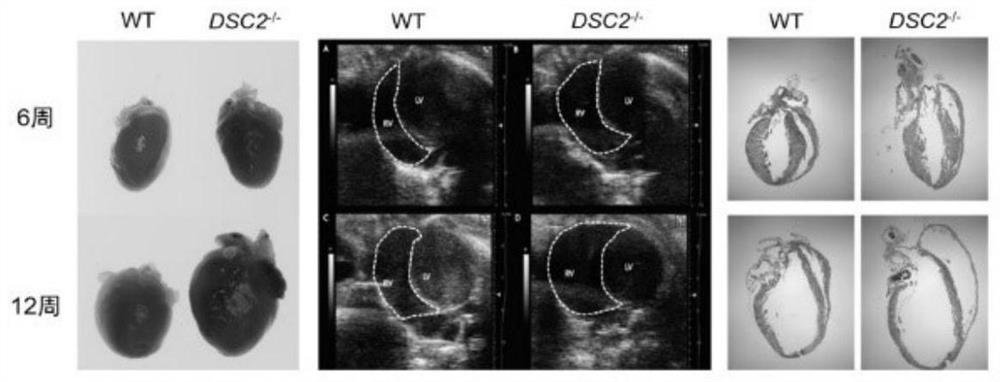
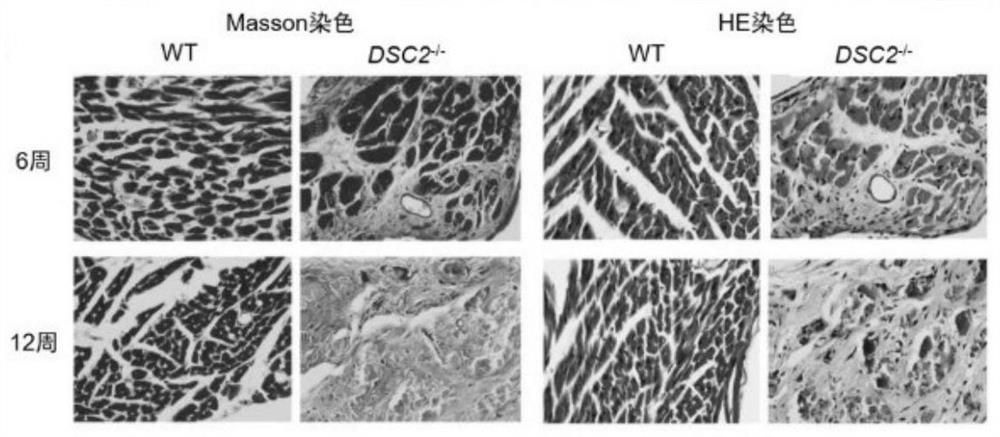
Construction method and application of DSC2 gene knockout mouse model
The invention provides a construction method and application of a DSC2 gene knockout mouse model, and particularly relates to application of the DSC2 gene knockout mouse model in preparation of a reagent and a medicine for preventing and treating right heart disease, monitoring right ventricular diastole and contraction, and preparing an apoptosis pathway regulation reagent and a medicine or preparing a fibrosis pathway regulation reagent and a medicine. A DSC2 deletion mutant mouse is constructed on the basis of a C57BL / 6J mouse through a CRISPR-Cas9 technology, and the DSC2 knockout mouse can effectively induce right ventricular cardiomyopathy and can be used for a mouse model for right ventricular cardiomyopathy research; after the DSC2 gene is simply knocked out, along with the increase of the age of the mouse, the mouse has the expression of right ventricular cardiomyopathy such as right ventricular enlargement, right ventricular myocardial fibrosis and middle and advanced right ventricular heart failure, so that the mouse model can be used as an effective model in subsequent molecular mechanism research on the right ventricular cardiomyopathy.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Application of triclabendazole in preparation of drugs for treating breast cancer
InactiveCN110840887AHighlighting the role of cancer treatmentHighlight its role in the treatment of cancerOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellApoptosis pathways
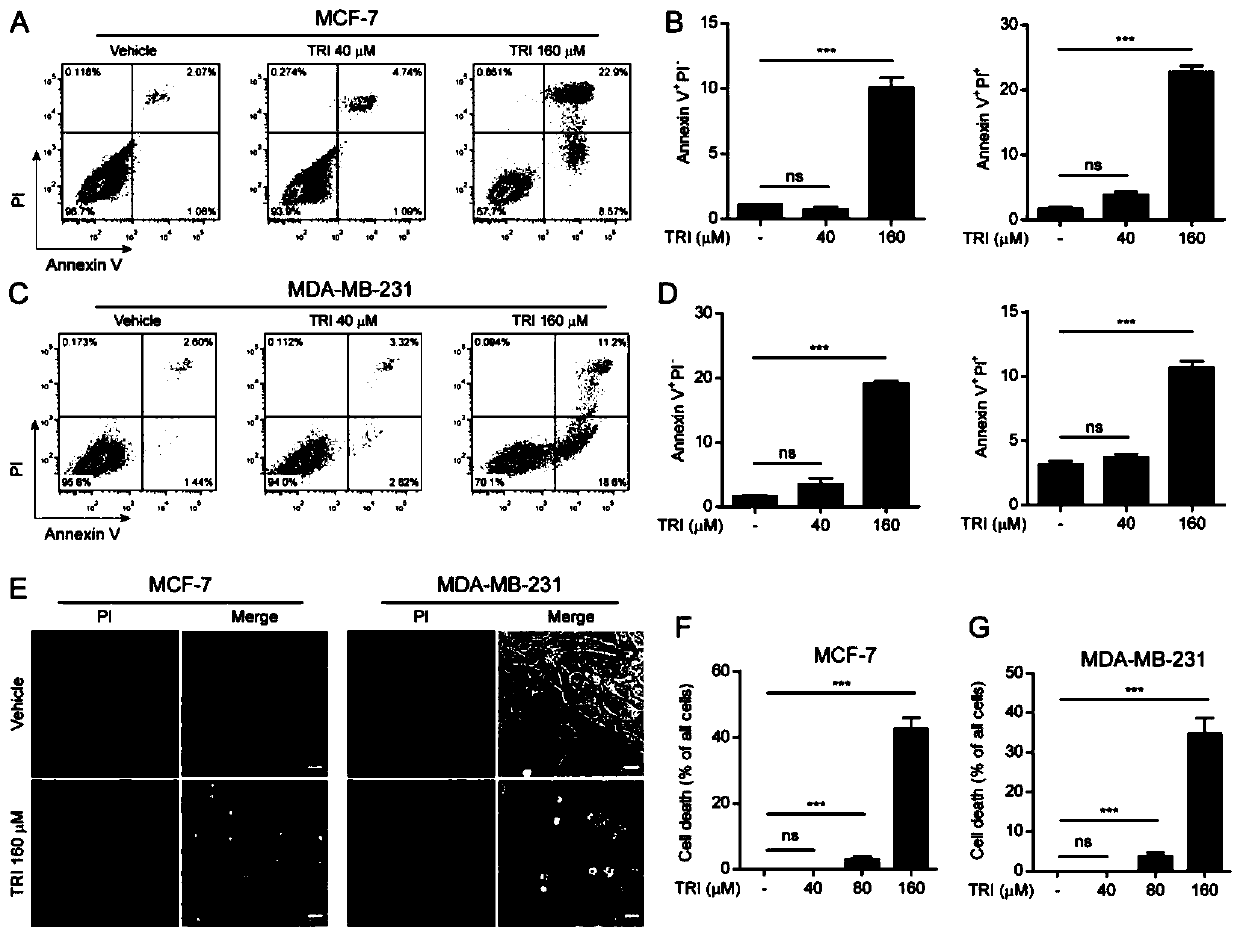
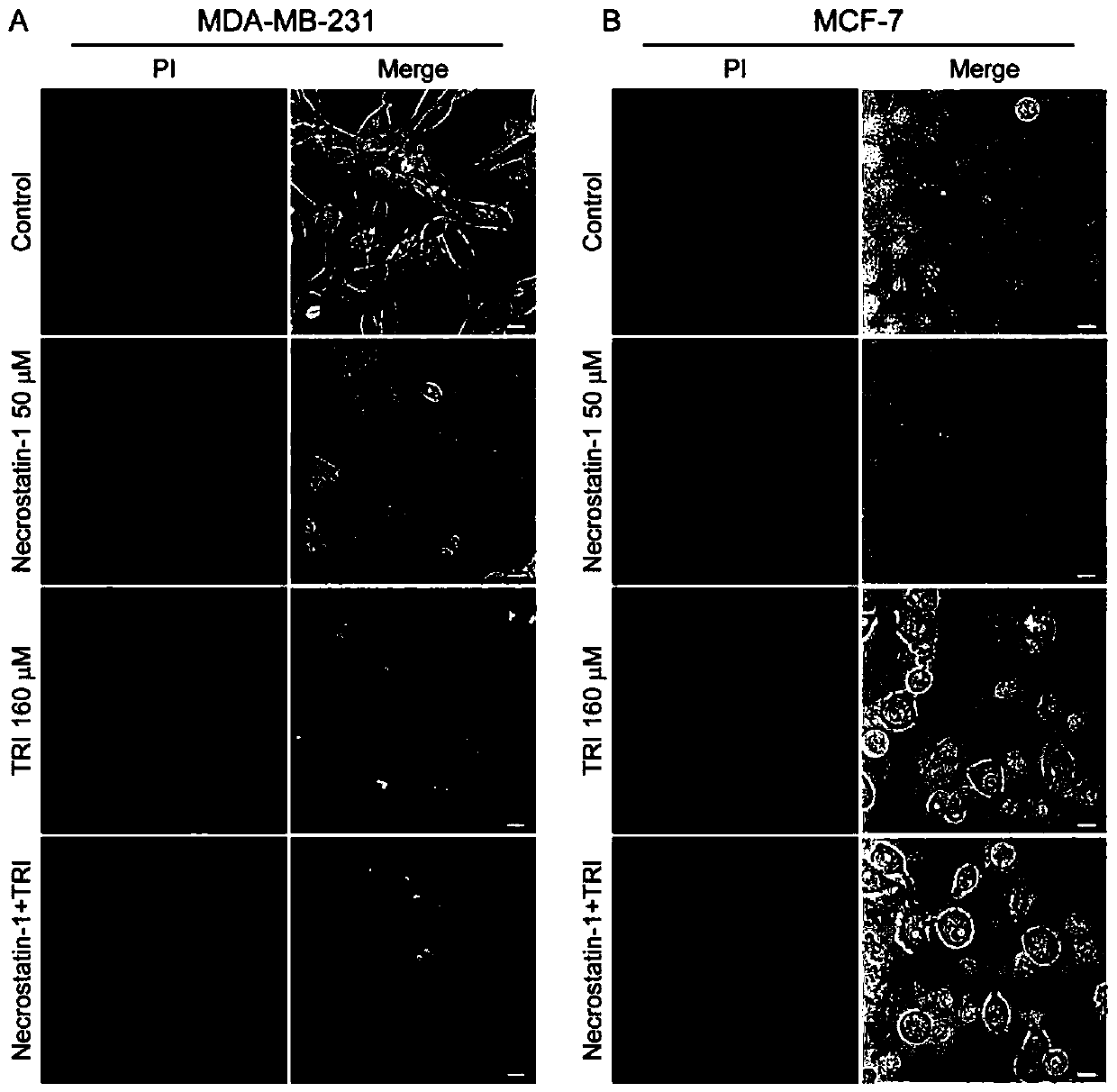
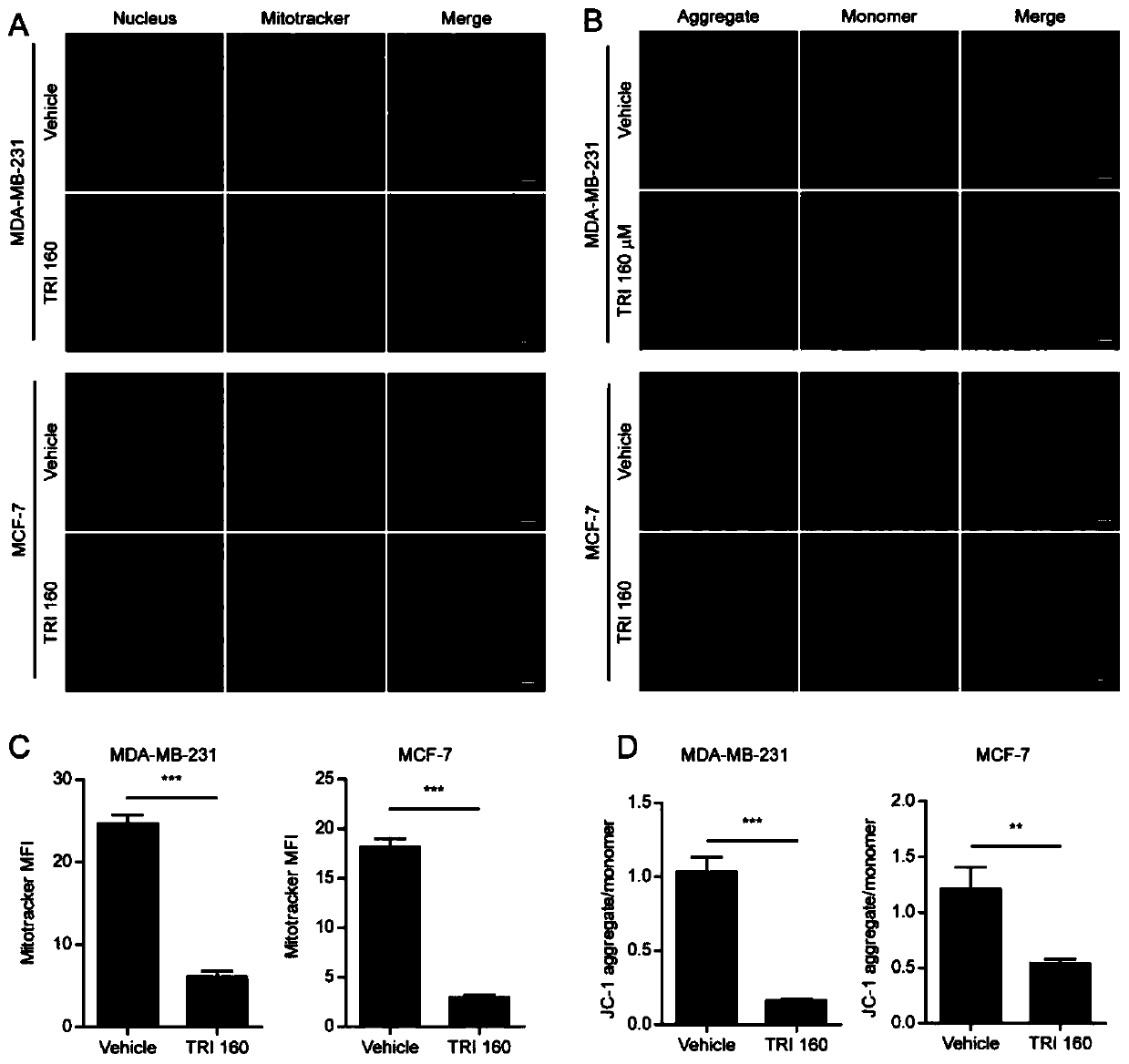
The invention relates to application of triclabendazole in preparation of drugs for treating breast cancer. According to the application of the triclabendazole in the preparation of the drugs for treating the breast cancer, the drugs for treating the breast cancer are tablets, granules, pills or capsules. Application of a triclabendazole composition in the preparation of the drugs for treating thebreast cancer is also included. Cancer cells of the to-be-treated breast cancer are MCF-7 or MDA-MB-231. The application has the advantages that the triclabendazole can induce apoptotic pyroptosis invitro and in vivo, and GSDME is cut by activated caspase-3 to generate GSDME-NT that take effects and forms vacuoles; the discovery suggests that the triclabendazole plays a role in cancer treatmentby inducing apoptosis of the cancer cells, specifically inducing GSDME-dependent apoptosis through the activated caspase-3 and at least partially through enhanced ROS / JNK / bax mitochondrial apoptosis pathways.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUIBO SCI & TECH CO LTD
NiPS3 nano-drug with tumor targeting, preparation method thereof and application of NiPS3 nano-drug
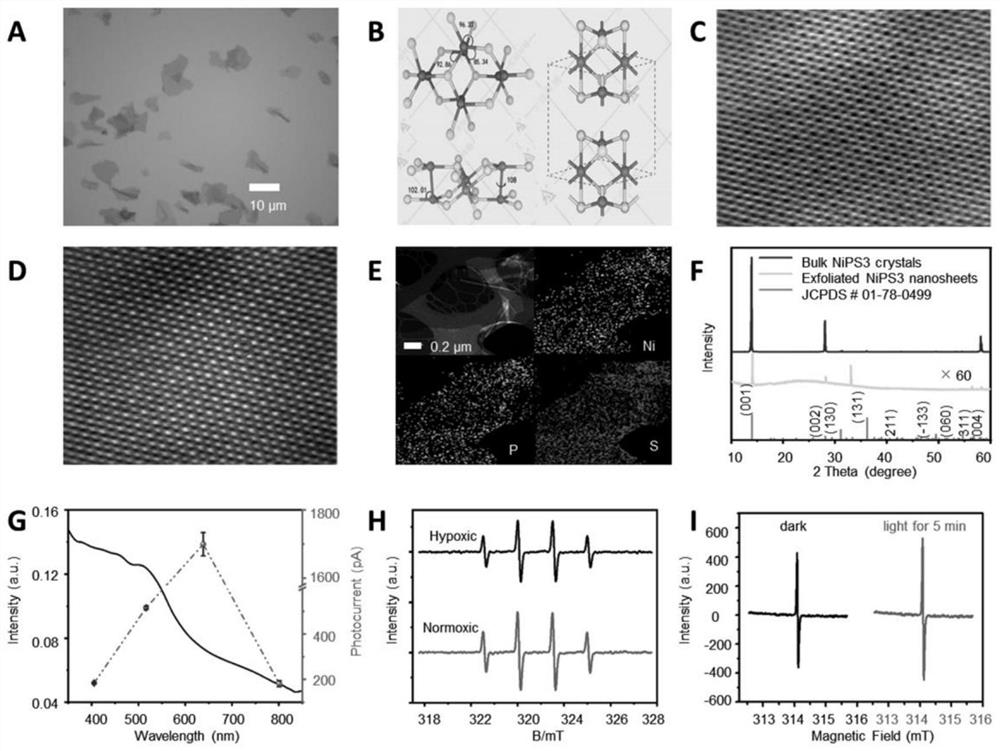
InactiveCN112057615AGood photodynamic effectGood biocompatibilityPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsTumor targetingApoptosis pathways
The invention provides an NiPS3 nano-drug with tumor targeting. The NiPS3 nano-drug comprises a two-dimensional NiPS3 nano-sheets and triphenylphosphine, wherein the two-dimensional NiPS3 nano-sheetsare each coated with the triphenylphosphine. According to the NiPS3 nano-drug with tumor targeting provided by the invention, in an anaerobic pathway, holes generated by optical excitation in the two-dimensional NiPS3 nano-sheets can oxidize OH<-> in water to generate .OH, which represents the possibility of anaerobic photodynamics. Therefore, an NiPS3 semiconductor photosensitive nano-material can be applied to the anaerobic condition to generate active free radicals to further start a cell apoptosis pathway. The two-dimensional NiPS3 nanosheets have an obvious photodynamic effect, high chemical stability, low toxicity and good biocompatibility, and have a wide application prospect in the field of photothermal therapy, photodynamics therapy and drug-loaded therapy. The invention further discloses a preparation method for and application of the NiPS3 nano-drug with tumor targeting.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANGUANG TECH CO LTD
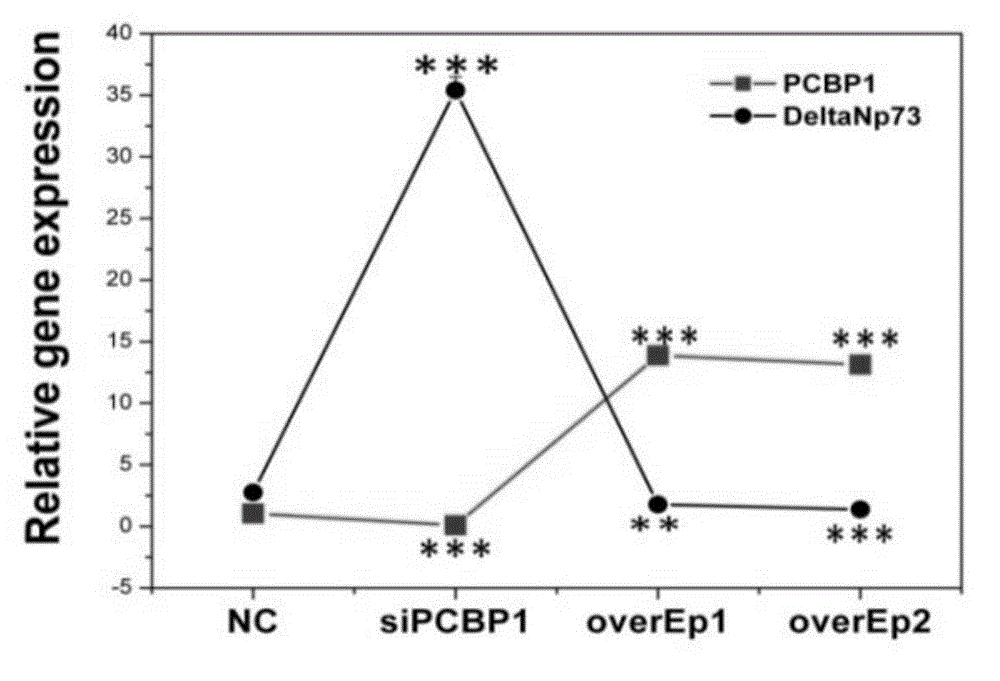
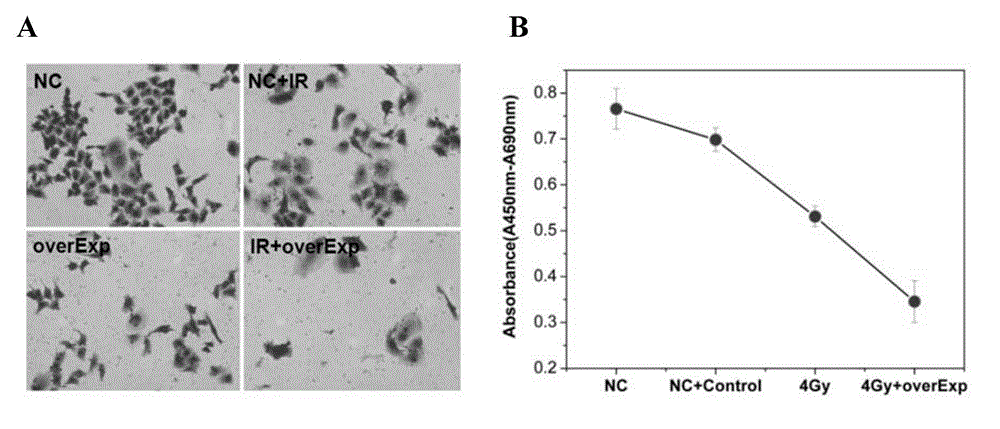
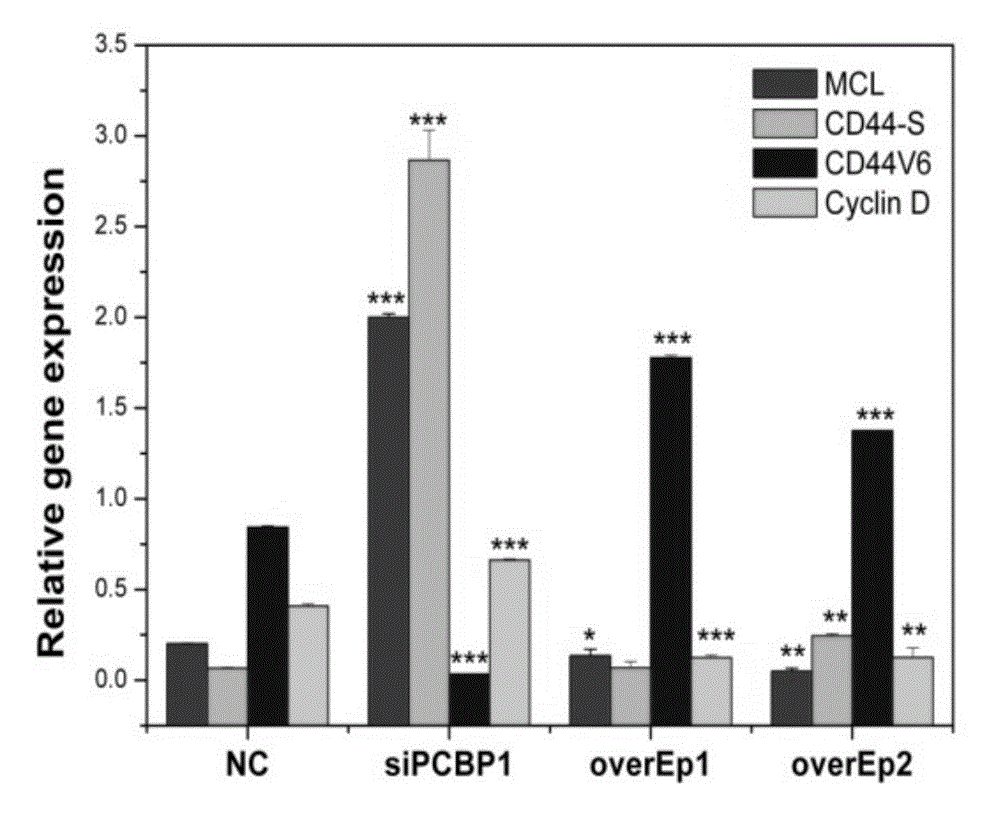
Application of PCBP1 gene in preparing radiotherapy sensitivity enhancing kit
InactiveCN104338150ASignificant radiosensitization synergistic effectPrevent proliferationGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCyclin D1Lymphatic Spread
The invention discloses application of a PCBP1 gene in preparing a radiotherapy sensitivity enhancing kit, and in particular relates to application of the PCBP1 gene in preparing a sensitivity enhancing kit for tumor radiotherapy utilizing ionizing radiation including heavy ion rays. The nucleotide sequence of the PCBP1 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and the PCBP1 gene is established in eukaryotic expression plasmid. Together with heavy ion beams, the PCBP1 gene regulates and controls expression of the CD44v6 gene related to tumor metastasis and invasion, inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of HeLa tumor cells, remarkably down-regulates the cell cycle regulatory protein Cyclin D1, prompts cells to generate G0 / G1 retardation, enhances the radiotherapy sensitivity of HeLa cells, up-regulates pro-apoptotic protein Tap73 and expression of the mitochondria apoptosis pathway MCL, down-regulates the apoptosis inhibition DelNp73 protein, and induces apoptosis of many HeLa cells.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Polypeptide binding with tumor necrosis factor, and applications thereof
ActiveCN104829697ALow cost of treatmentInhibit apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticApoptosis pathwaysMitophagy
The present invention relates to a polypeptide binding with tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha), and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the polypeptide and TNF-alpha have high affinity, and the polypeptide can be bound with the excess TNF-alpha to make the apoptosis promoting protein Bid in the apoptosis-related mitochondrion apoptosis pathway be down-regulated while make the anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2 be up-regulated in the apoptosis-related mitochondrion apoptosis pathway so as to inhibit the apoptosis caused by TNF-alpha, such that the polypeptide can be used for preparation of TNF-alpha-related disease treating drugs. The present invention further provides a method for screening at the molecular and cellular level and researching the influence of the polypeptide antagonist on the TNF-alpha physiological effect, and applications thereof so as to provide the effective method for development of the low-cost anti-TNF-alpha drug.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Application of ciona intestinalis linnaeus peptides
ActiveCN102172394ANovel structureHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsStainingTumor cell apoptosis
The invention belongs to the fields of biochemistry and biomedicines, in particular to application of ciona intestinalis linnaeus peptides in preparation of antineoplastic medicaments. In vitro methods such as MTT assay, scanning electron microscopy, nucleus staining, mitochondrial membrane potential changing and the like prove that the ciona intestinalis linnaeus peptides have a significant antineoplastic effect and can induce apoptosis of tumor cells. The induction mechanism of the ciona intestinalis linnaeus peptides is based on apoptosis, which indicates novel functions and means of cionaintestinalis linnaeus peptides in prevention and treatment of tumors.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of evodiamine in preparation of preparation for resisting white spot syndromevirus
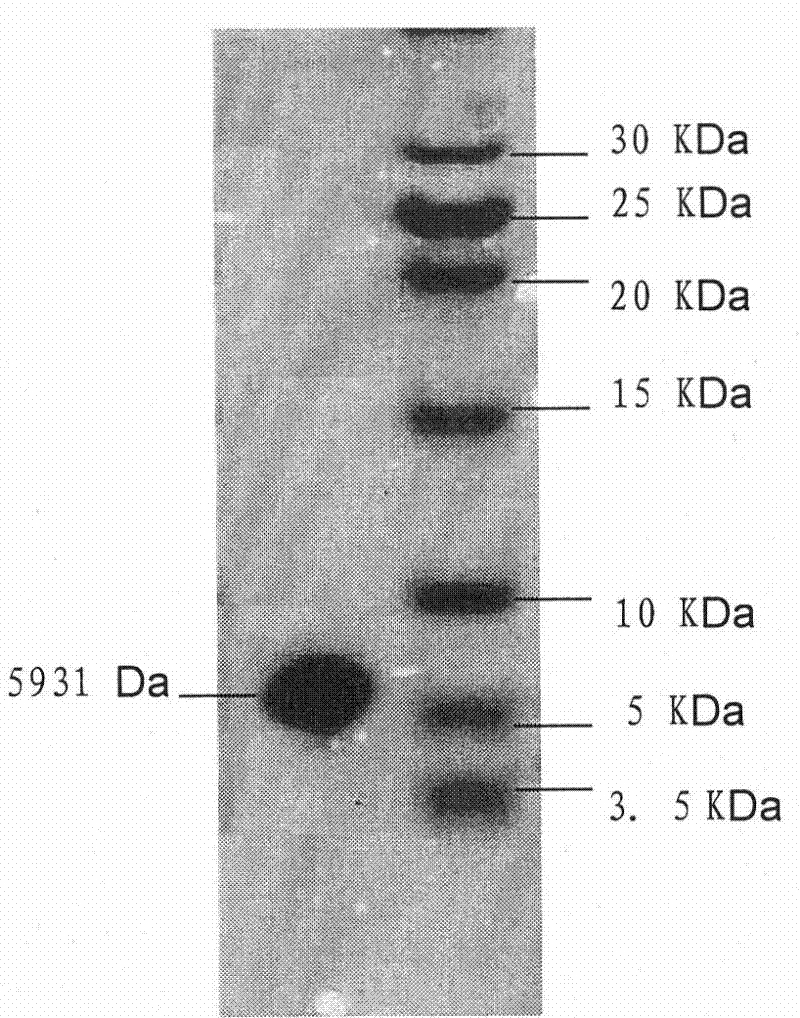
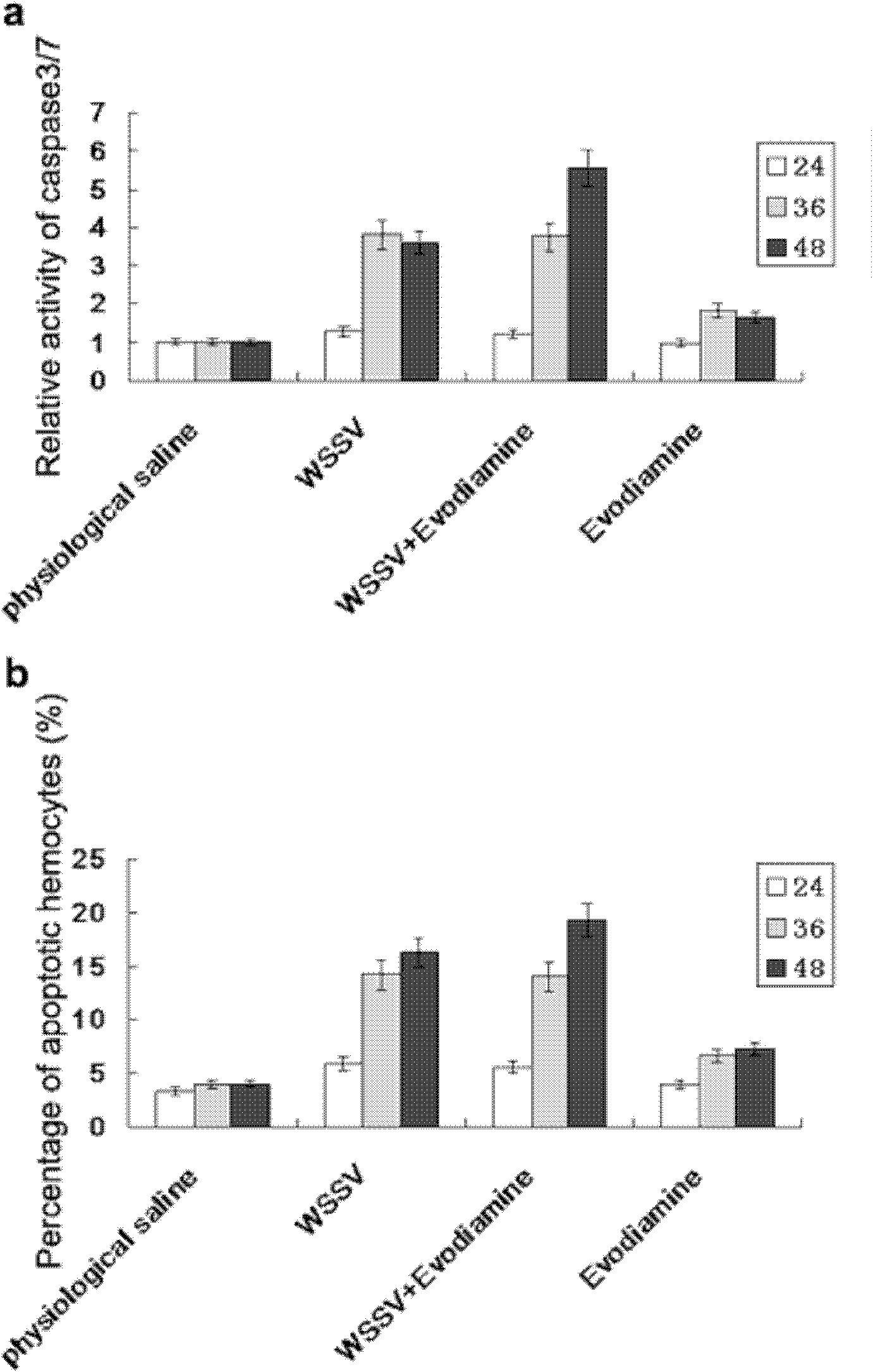
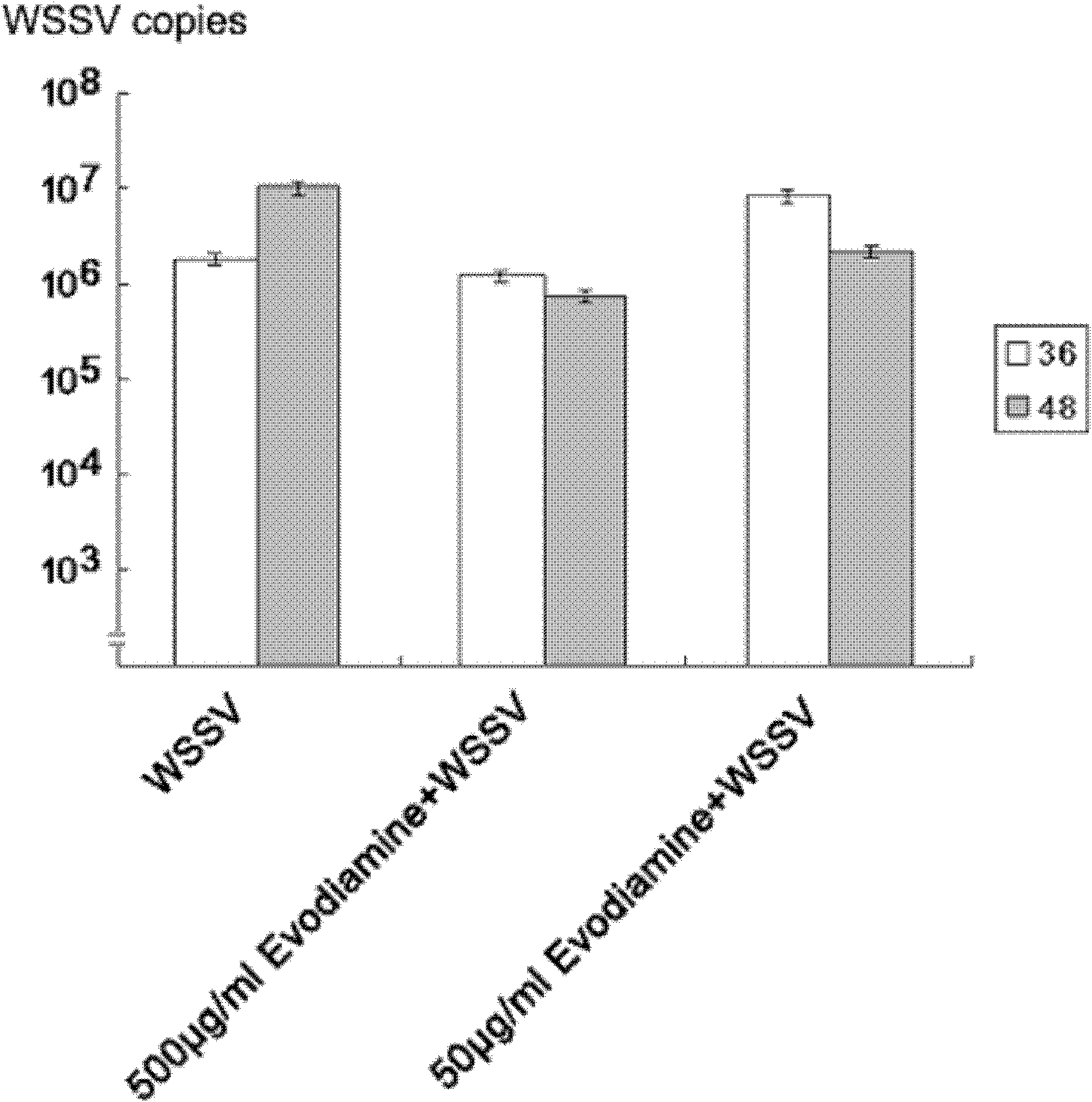
InactiveCN101862334AEffective induction of activationImprove immunityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsEvodiamineDrug metabolism
The invention provides application of evodiamine in the preparation of a preparation for resisting white spot syndromevirus. Evodiamine can act on the protein essential for the apoptosis pathway of prawns, so the small molecules can be utilized to prepare the preparation for resisting the white spot syndromevirus so as to greatly enhance the resistance of the prawns to the white spot syndromevirus (WSSV) and reduce the fatality rate. The advantages of the invention are mainly embodied in that: the evodiamine can effectively induce activation of the PjCaspase, greatly enhance the resistance of the prawns to the white spot syndromevirus (WSSV) and reduce the fatality rate; and because the evodiamine is the medicament which is widely used in human body for improving the immunity, the evodiamine has no toxicity to the human body, and the prawns using the evodiamine can be enjoyed with safety no matter whether the medicament is completely metabolized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Composition Of Dietary Supplements Based On Apoptosis that Support Optimal Health
InactiveUS20170035789A1Reduce or prevent post-menopausal problems currently experienced by womenLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsFood preparationEnlarged breastsMale gender
This invention clearly identifies the current agriculture-based diseases facing United States citizens such as, heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes and other degenerative diseases that did not exist in our hunter-gatherer ancestors. The United States government has established the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) to solve the problem. The DGAC's approach includes exercise, better agricultural based food choices plus vitamins-mineral supplements that are sex and age adjusted. We designed supplement compositions composed of unmodified dried fruits, herbs, including roots and tubers, many of which contain a lot of phytoestrogens. Currently, the medical profession has a bias against phytoestrogens, based on science that we believe is incorrectly interpreted. Today, women are afraid of getting breast cancer, and men are afraid of getting enlarged breasts from phytoestrogens. We will reinterpret the pre-clinical medical studies to alleviate these accepted concerns. Our supplement ingredients are chosen based on the different apoptosis pathways, which they stimulate, modulate or inhibit.
Owner:MCANALLEY BILL H +2
Viral vector encoding a toll-like receptor and encoding a toll-like receptor agonist
The present invention is directed to methods and agents used for treating cancer or infectious diseases by providing toll-like receptors such as toll-like receptor 5 (TLR-5) in combination with providing a toll-like receptor agonists such as flagellin resulting in a cis and in-trans effect that recruits cells involved in both the innate (cis effect) and adaptive (trans effect) immune response to specifically kill cancer cells and cells infected with a pathogen via the NF-κB apoptosis pathway.
Owner:ROSWELL PARK CANCER INST +1
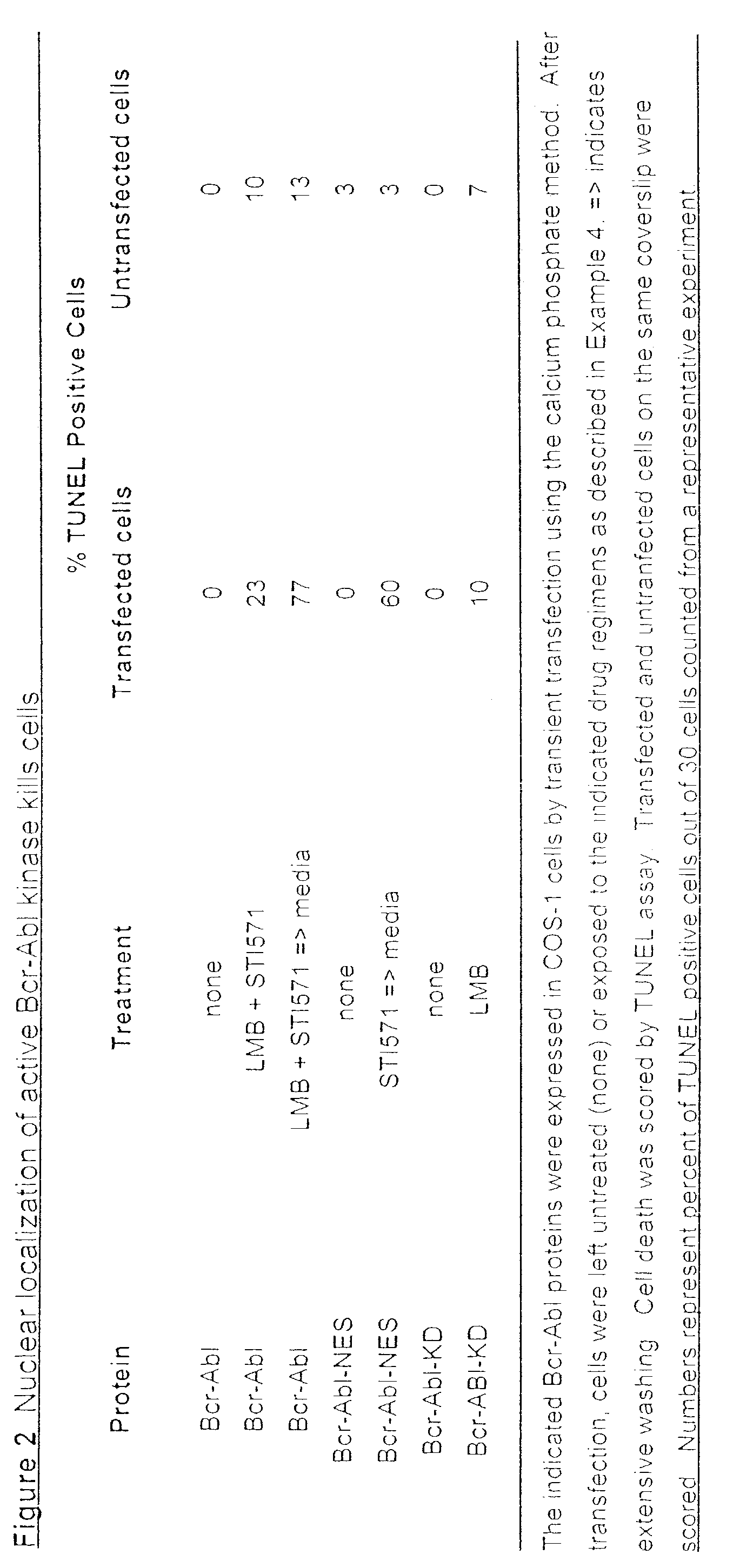
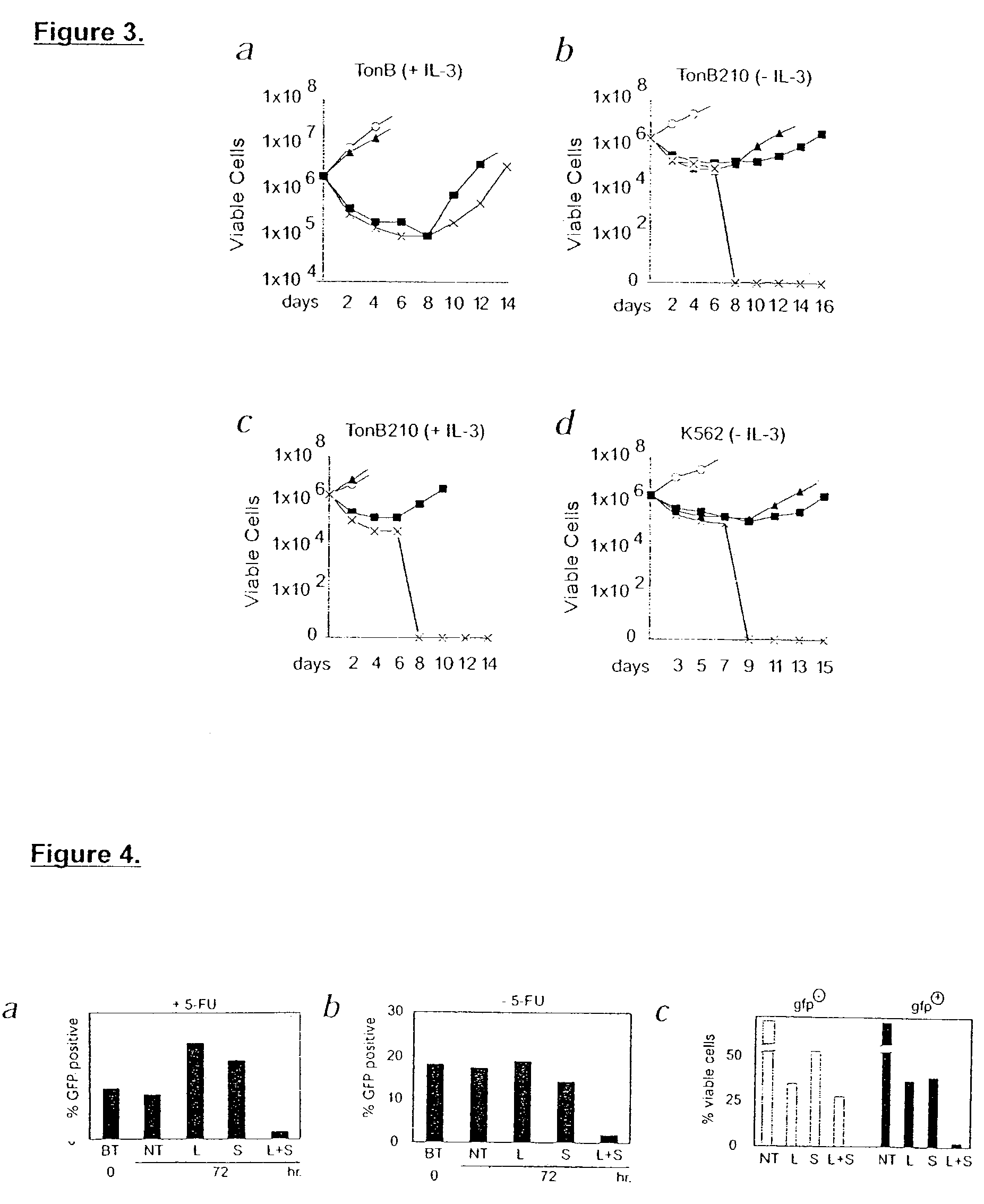
Strategy for leukemia therapy
InactiveUS7238525B2Improve the quality of lifeReduce chanceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCancer cellProtein translocation
The chimeric Bcr-Abl oncoprotein is the molecular hallmark of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). In the cytoplasm, the protein transduces a growth signal that is responsible for overexpansion of cells. In the nucleus, the protein induces apoptosis. The invention is a method of treating cancer / killing Bcr-Abl expressing cells by inducing the translocation of Bcr-Abl to the nucleus to activate the apoptotic pathway in cancer cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Protein nano-drug for cancer targeted therapy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111905105AImprove delivery efficiencyMaintain membrane protein integrityNanomedicineMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCancer cellApoptosis pathways
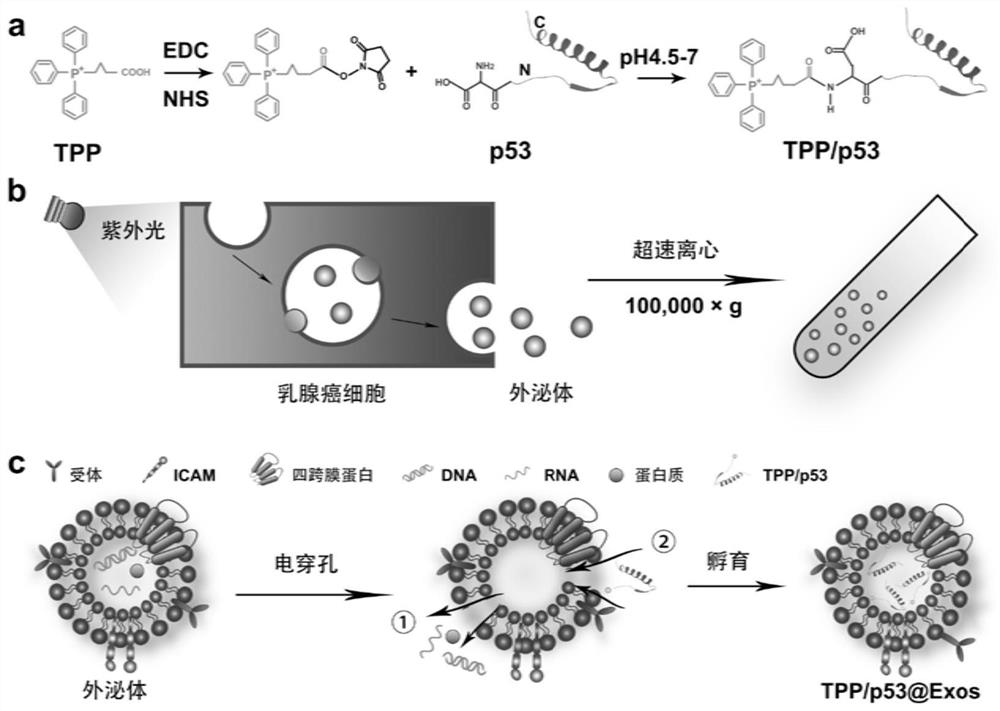
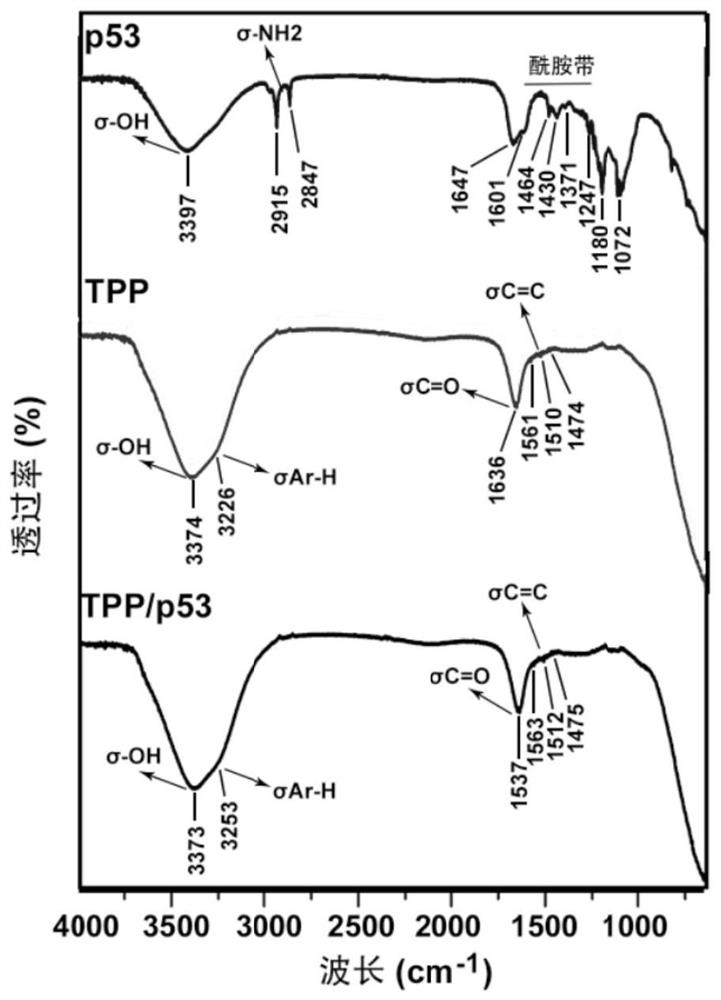
The invention discloses a protein nano-drug for cancer targeted therapy and a preparation method thereof. The protein nano-drug is an exosome of humanized p53 protein transferred with covalent cross-linked triphenylphosphine (TPP). A protein nano-drug delivery system TPP / p53@Exos developed by the invention can recognize specific cancer cells in a targeted manner, efficiently inhibits the growth ofthe cancer cells by activating endogenous apoptosis pathways of the cells, has no toxic or side effect, and provides a new means for cancer treatment. The preparation method of the nano-drug deliverysystem has a high protein loading rate (about 75%), and can also be used for protection and targeted delivery of other protein drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
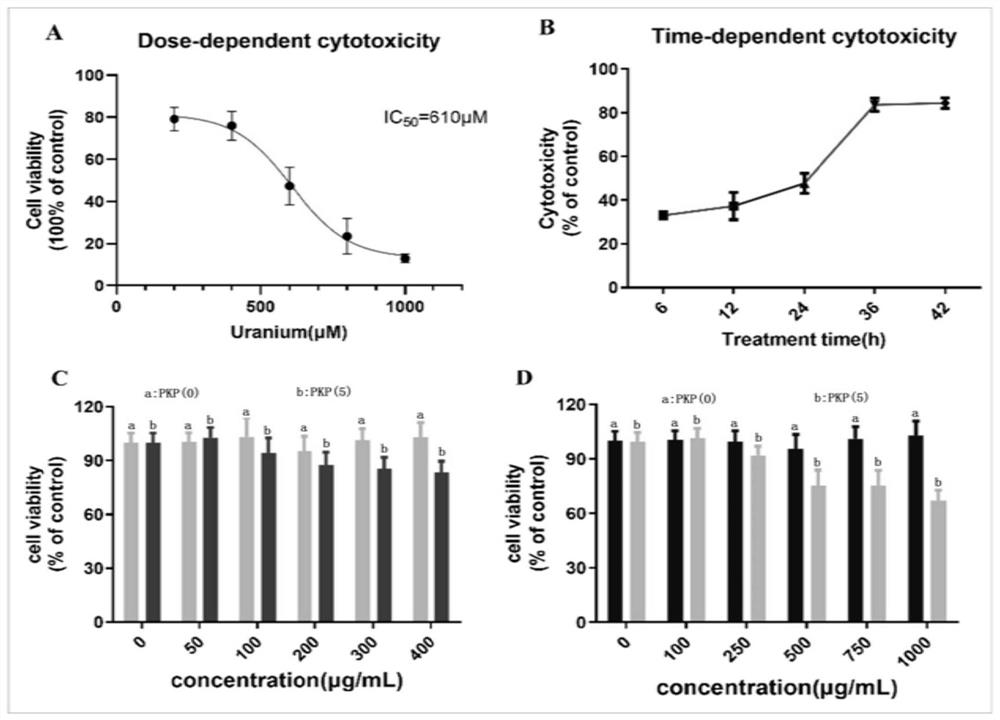
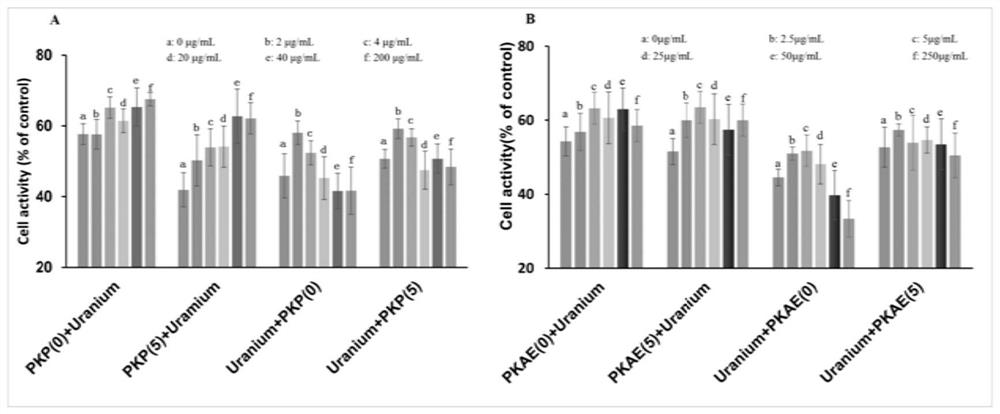
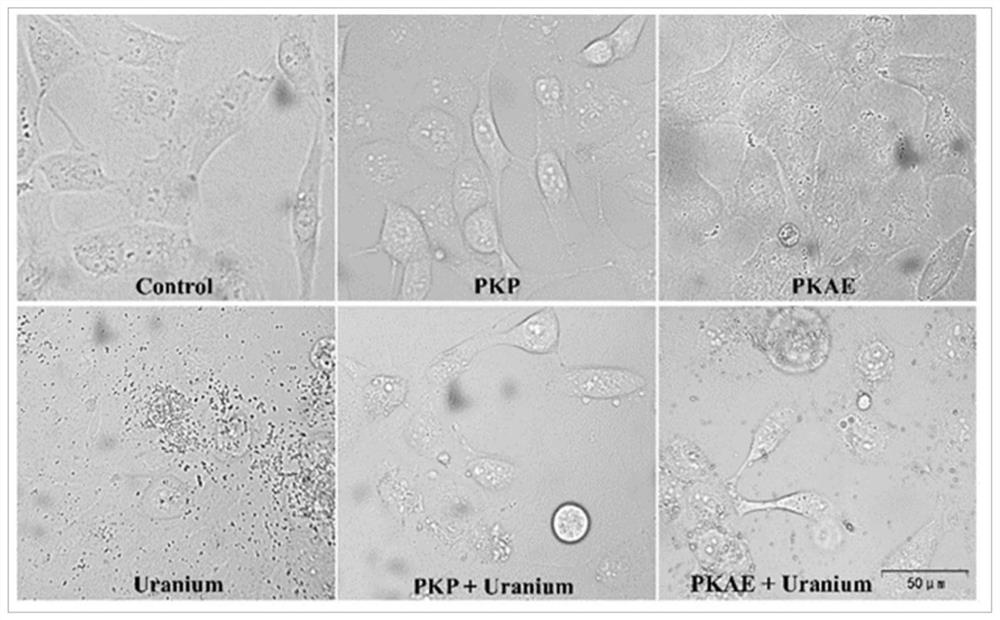
Application of rhizoma polygonati in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating low-dose or/and chronic uranium exposure
ActiveCN113101341AIncrease vitalityReduce apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsApoptosis pathwaysPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses application of rhizoma polygonati in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating low-dose or / and chronic uranium exposure, belongs to the technical field of medicines, and solves the technical problems that no low-toxicity and high-efficiency uranium detoxification medicine is available for being administered preventively and taken for a long time. The invention discloses application of rhizoma polygonati in preparation of the medicine for preventing and treating low-dose uranium exposure or / and chronic uranium exposure. The medicine has an inhibiting effect on a mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and has an activating effect on an endogenous antioxidant pathway. The medicine has good effects of preventing and treating low-dose uranium exposure and chronic uranium exposure. Experiments show that the polygonatum polysaccharide and the water extract can significantly improve the activity of HK-2 cells, reduce the apoptosis of the HK-2 cells and improve the mitochondrial function, and the polygonatum polysaccharide and the water extract inhibit the uranium-induced cytotoxic effect by inhibiting a mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and activating an endogenous antioxidant GSK-3beta / Fynin / Nrf2 pathway.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
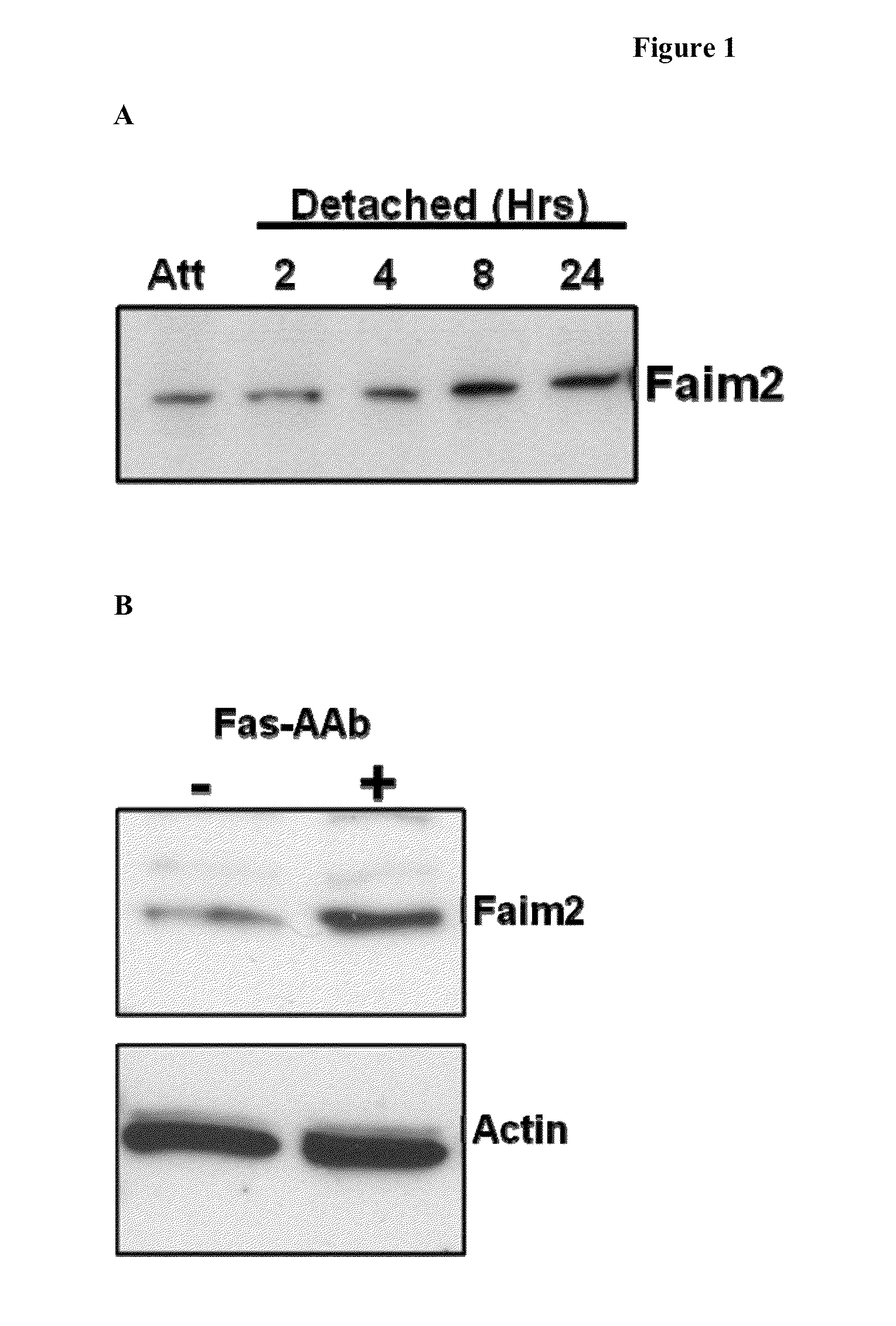
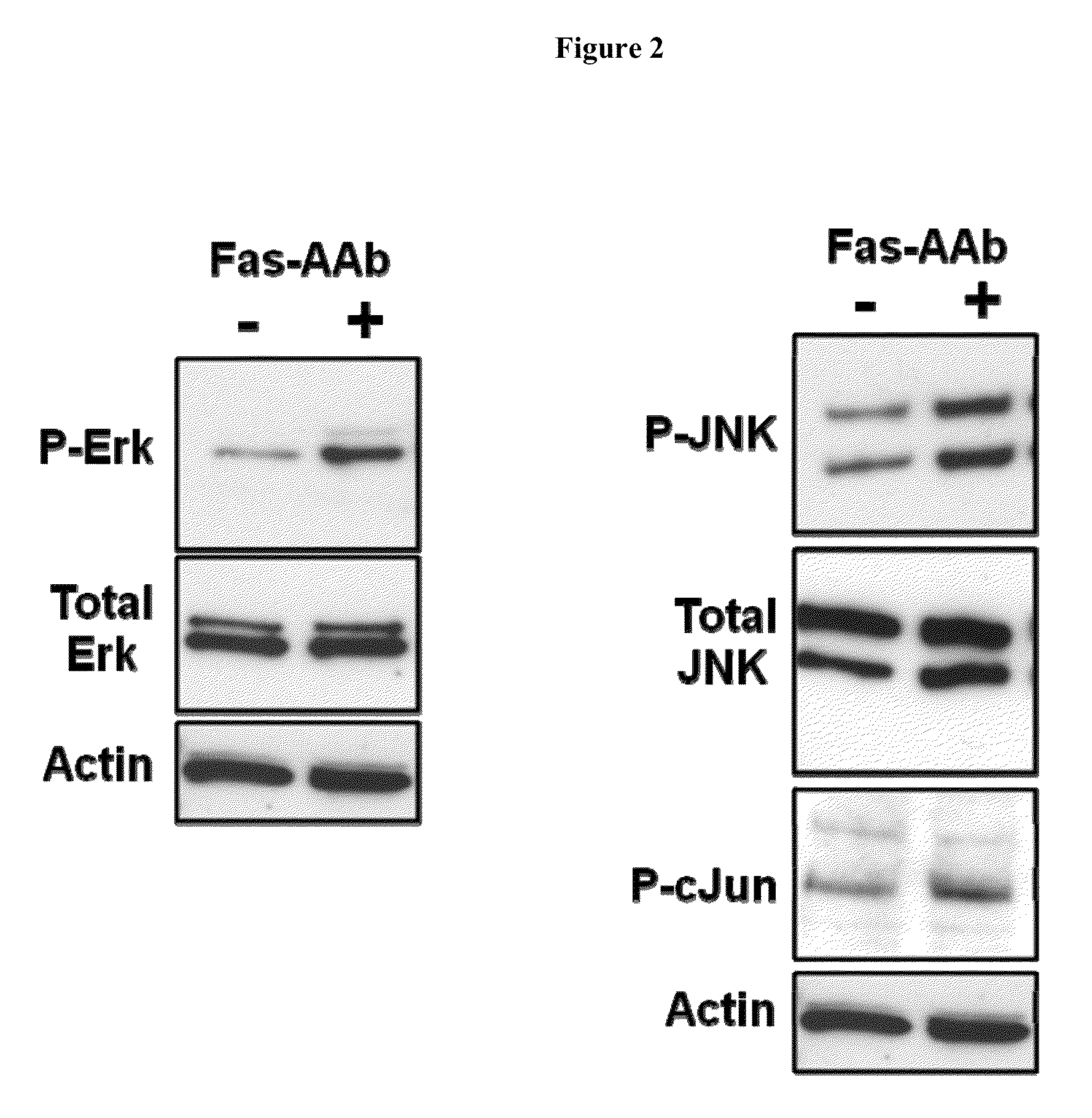
Methods of inhibiting photoreceptor apoptosis by eliciting the Faim2 antiapoptotic pathway
ActiveUS9192650B2Improve survivalInhibiting photoreceptor apoptosisSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyApoptosis pathway
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method for predicting anti-cancer efficacy of compound targeting apoptosis pathway and composition
PendingCN112852959AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementApoptosis pathwaysDual inhibitor
The invention relates to a biomarker for predicting the efficacy of an MDM2 inhibitor or a Bcl-2 / Bcl-xL dual inhibitor or a Bcl-2 inhibitor or a Bcl-xL inhibitor in the treatment of a cancer patient. The invention also provides a composition, e.g. a kit, for assessing the gene levels of biomarkers, and a method for using such gene levels to predict the response of a cancer patient to the MDM2 inhibitor or the Bcl-2 / Bcl-xL dual inhibitor or the Bcl-2 inhibitor or the Bcl-xL inhibitor. The information can be used to determine prognosis and treatment selection for cancer patients.
Owner:ASCENTAGE PHARMA SUZHOU CO LTD +1
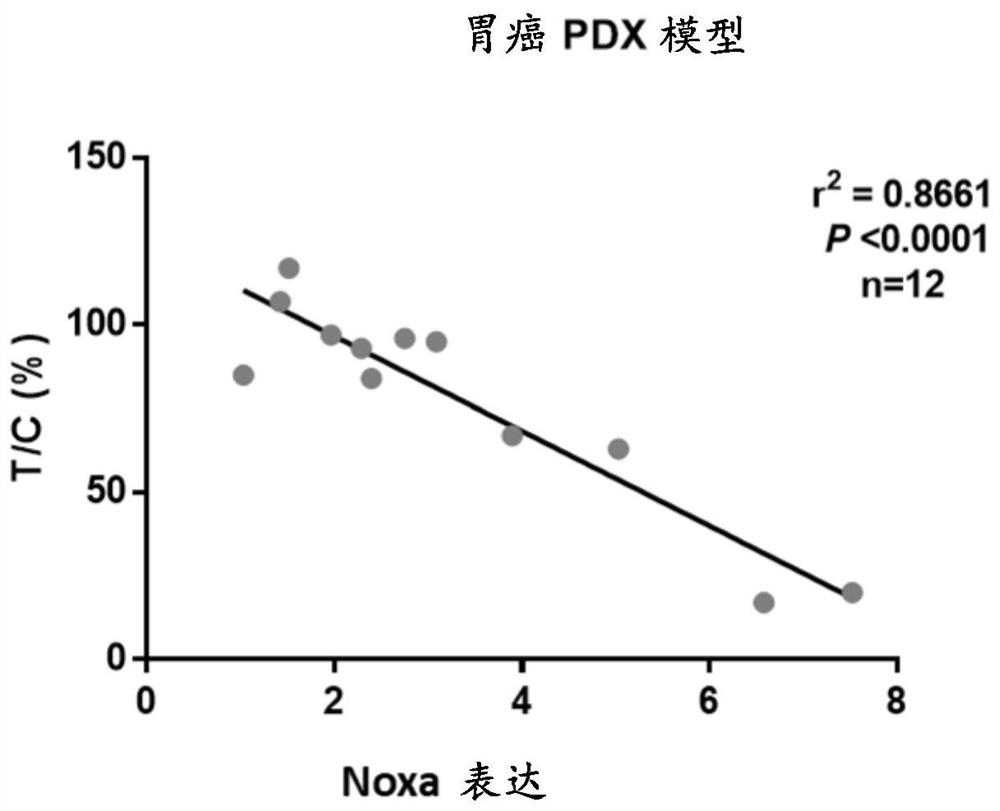
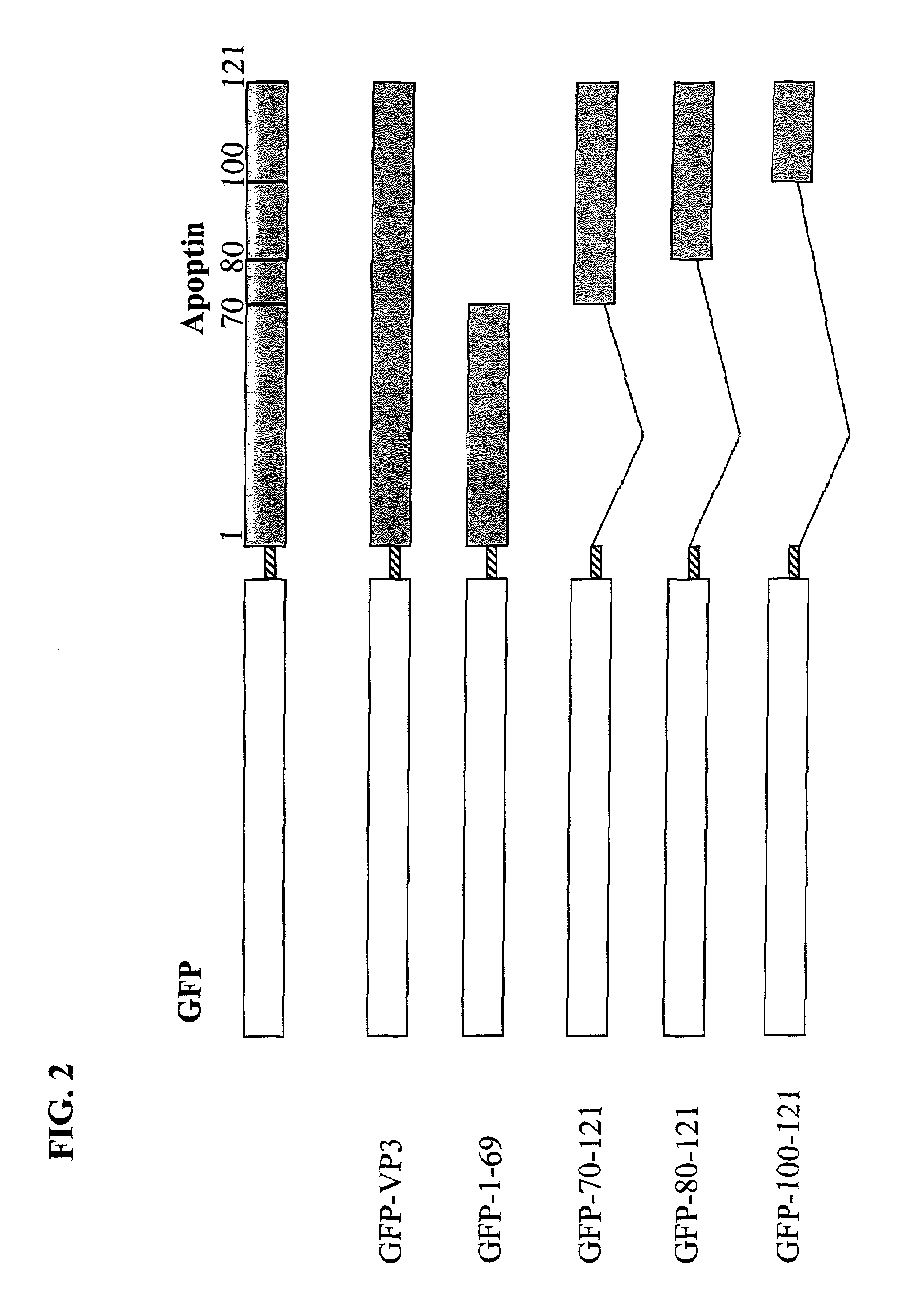
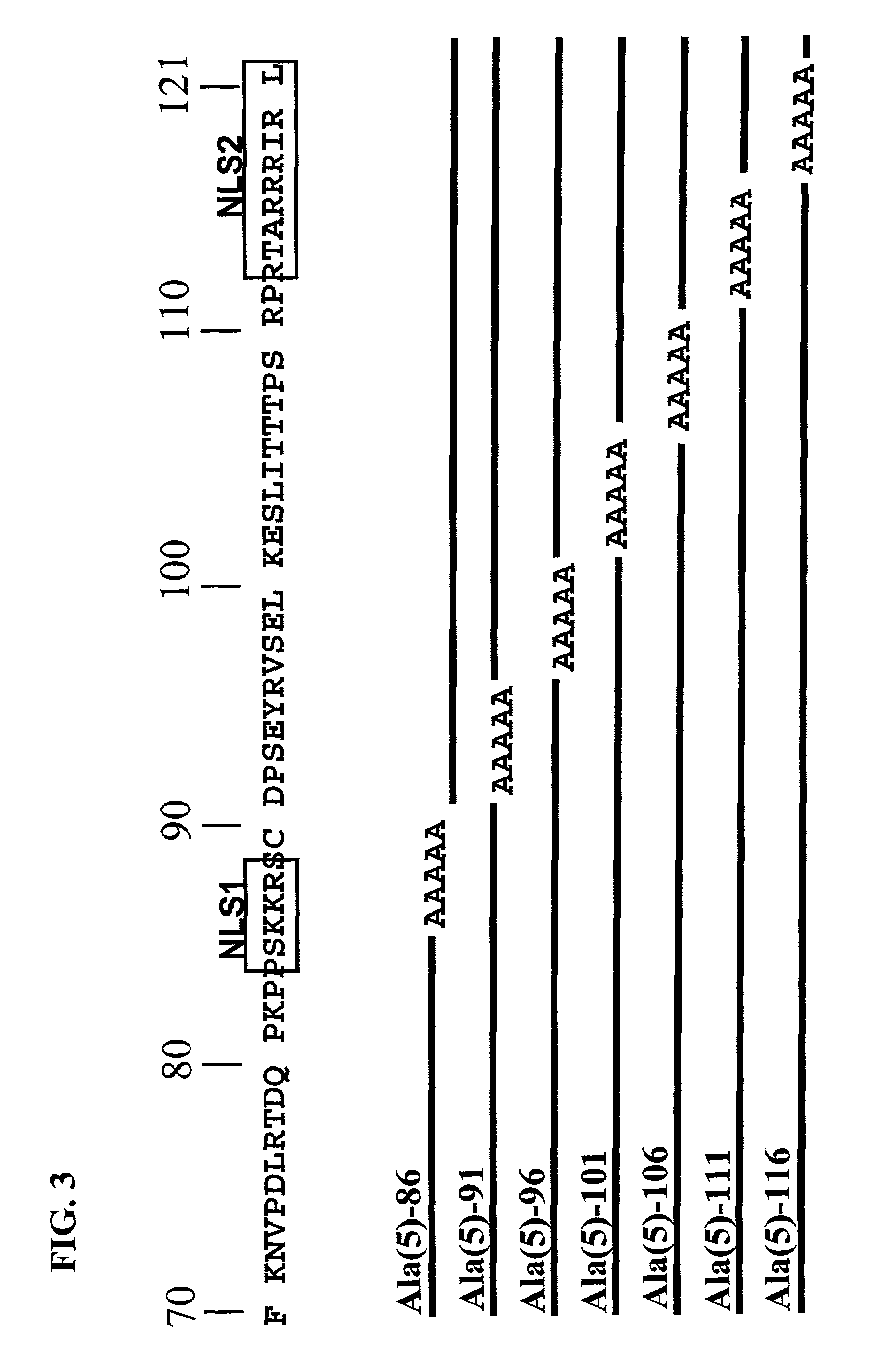
Modifications of apoptin
InactiveUS7319034B2Reduce mortalityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthHuman tumor
Phosphorylated Apoptin is described. Apoptin is tumor-specifically phosphorylated and part of the Apoptin apoptotic pathway in tumor cells is elucidated. New therapeutic possibilities, for example, novel therapeutic compounds that can work alone or, sequentially to, or jointly with other known compounds. Also, the use of tumor-specifically phosphorylation of Apoptin for diagnostic purposes is described. Such a diagnostic purpose can, for example, be a method for detecting the presence of cancer cells or cells that are cancer prone or a method to identify a putative cancer inducing agent or a method for the in vitro treatment effect of Apoptin on tumor cells by testing the phosphorylation state of Apoptin. Even more, the invention provides possibilities to further elucidate the apoptotic pathway and to identify for example crucial mediators of phosphorylation in human tumor cells. Interfering with such a mediator could provide new anti-cancer therapies.
Owner:RIIDO
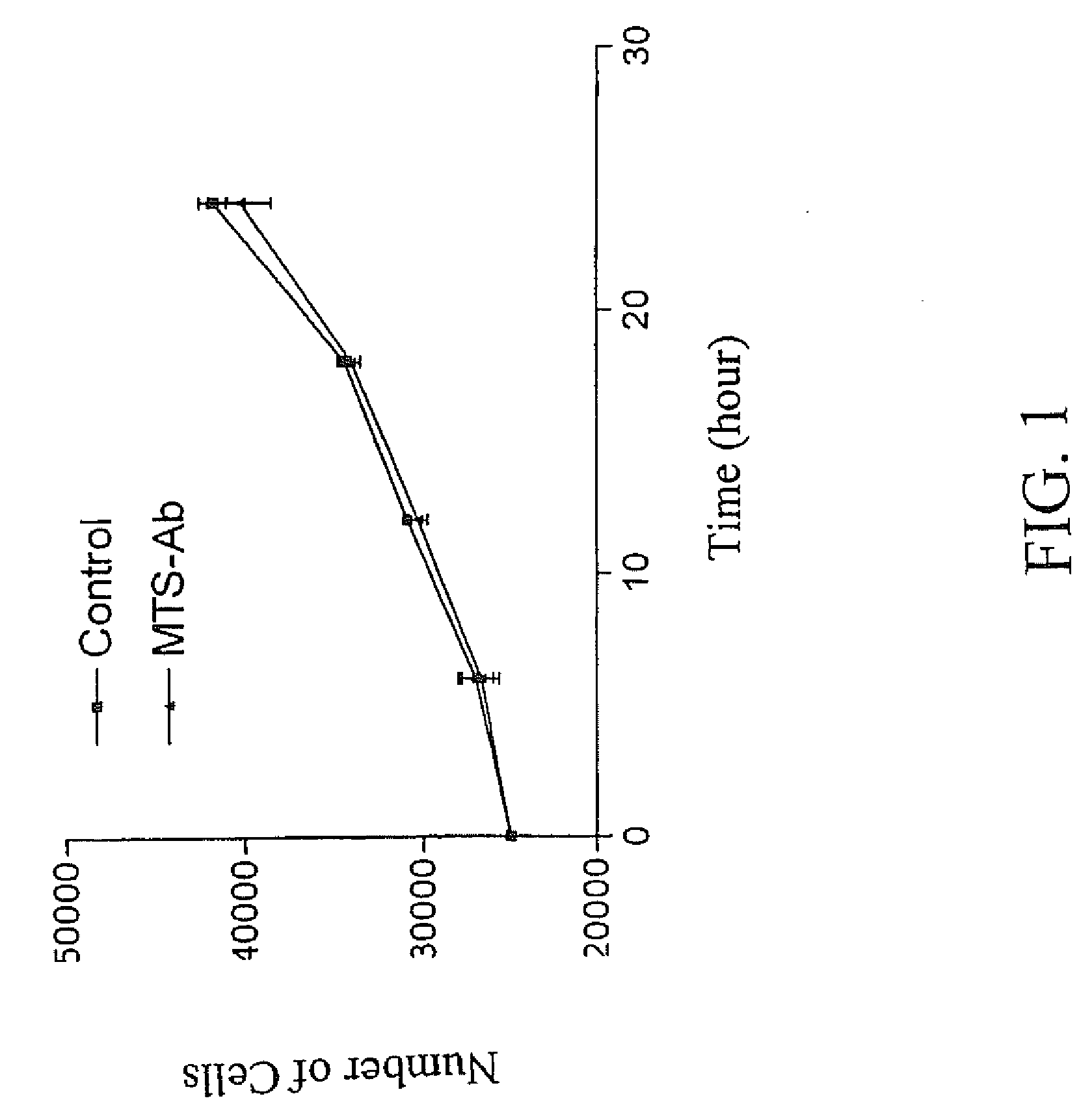
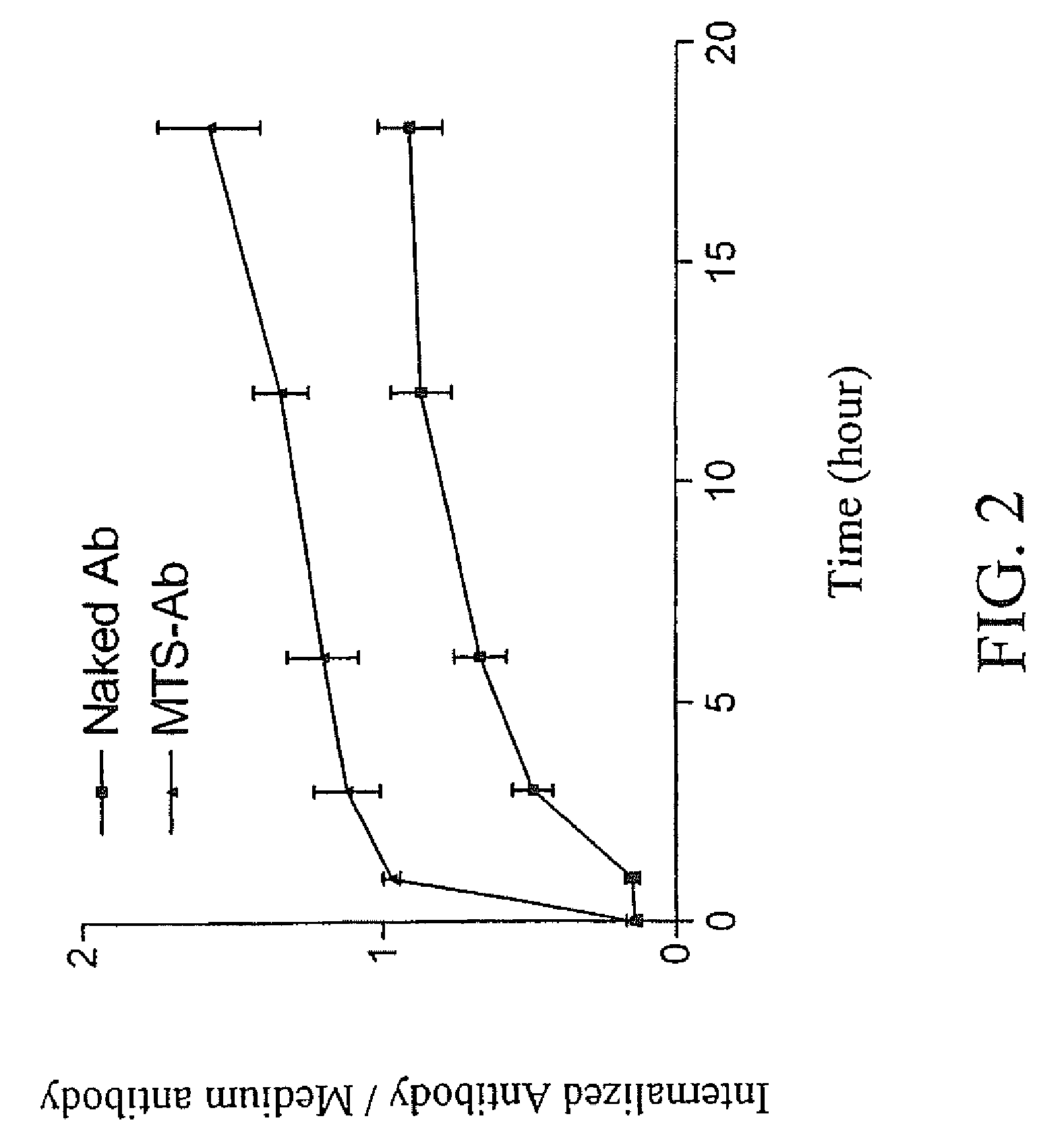
Trans-membrane-antibody induced inhibition of apoptosis
InactiveUS20090274710A1Nervous disorderHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody conjugateMembrane Transporters
Owner:INNEXUS BIOTECHNOLOGY INT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com