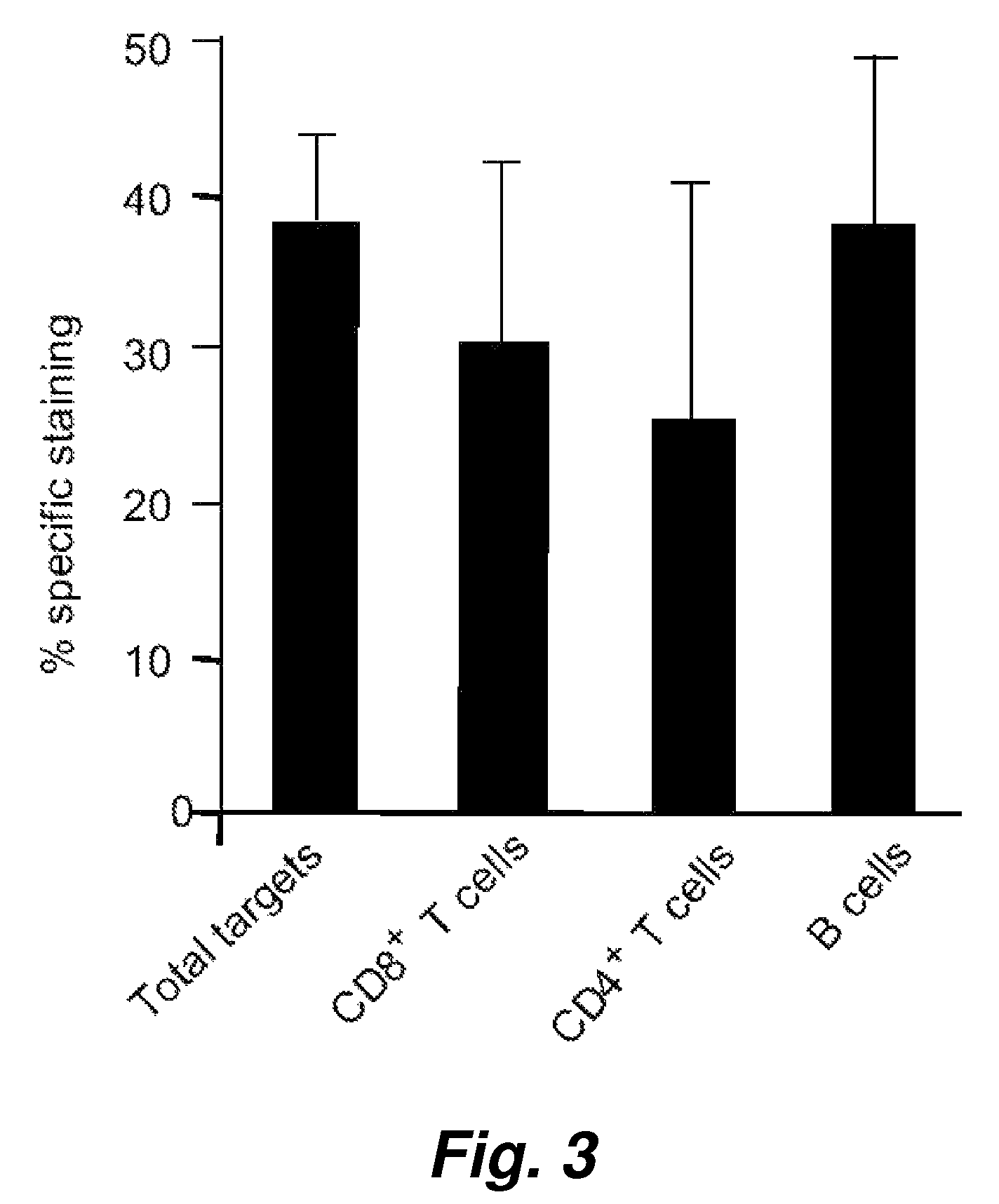
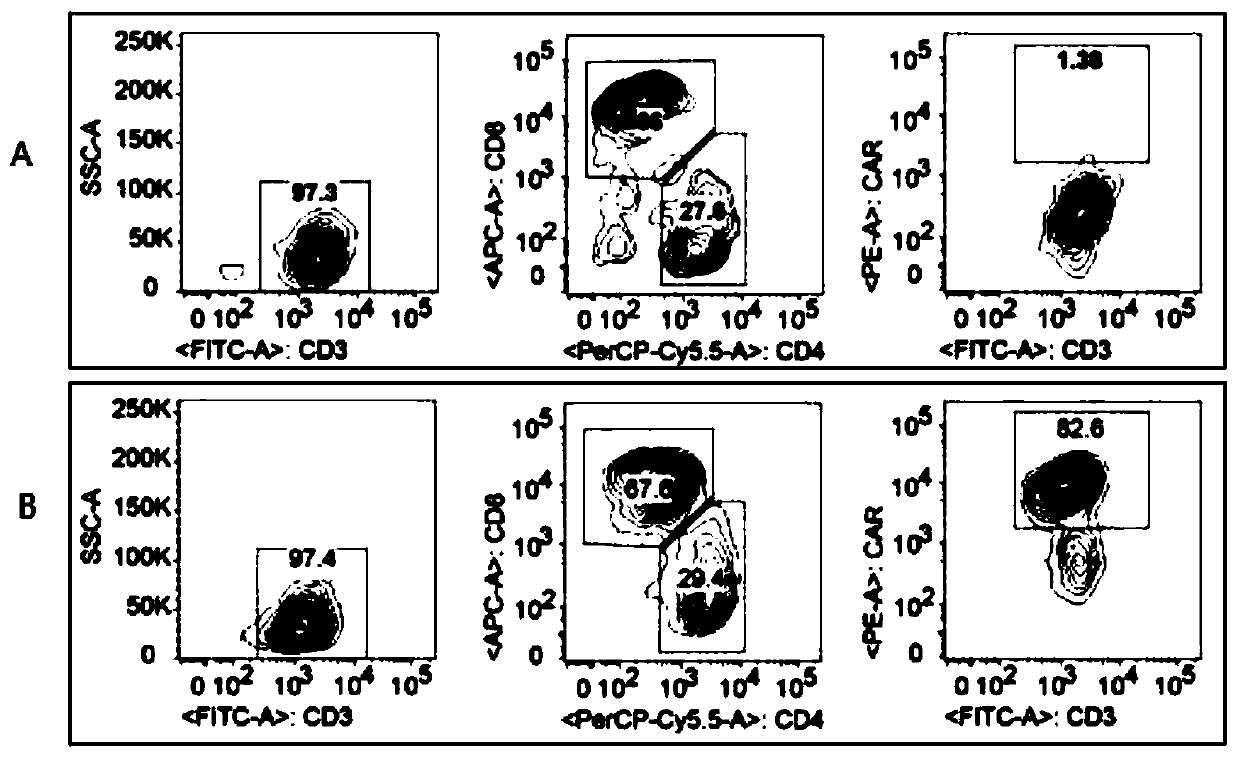
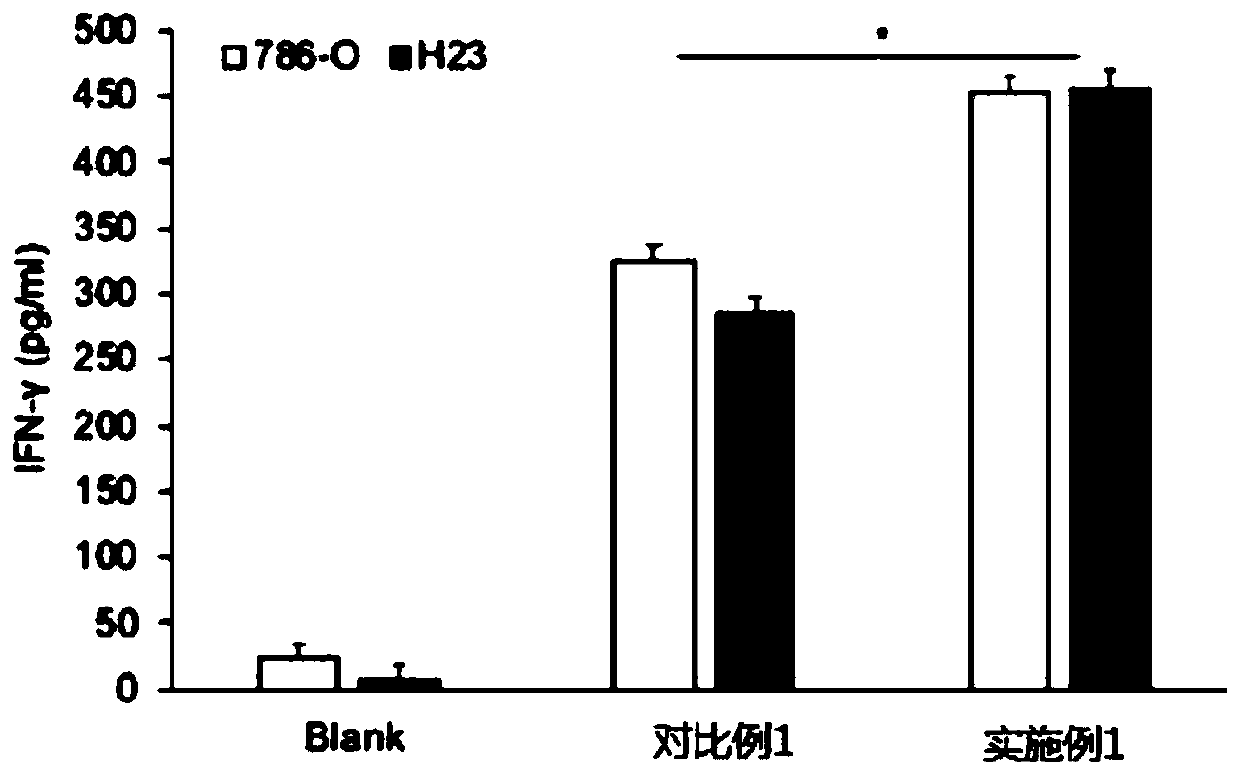
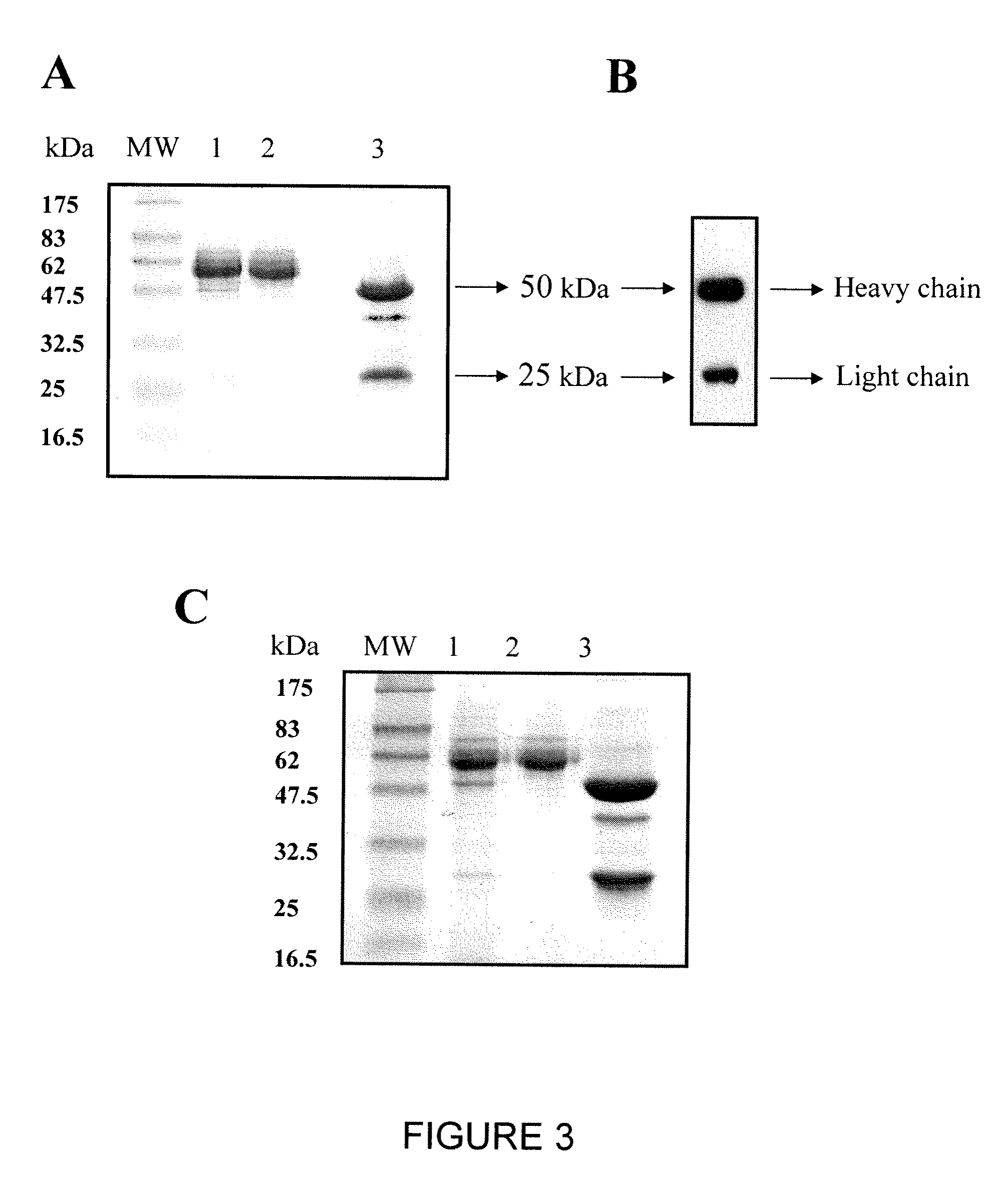
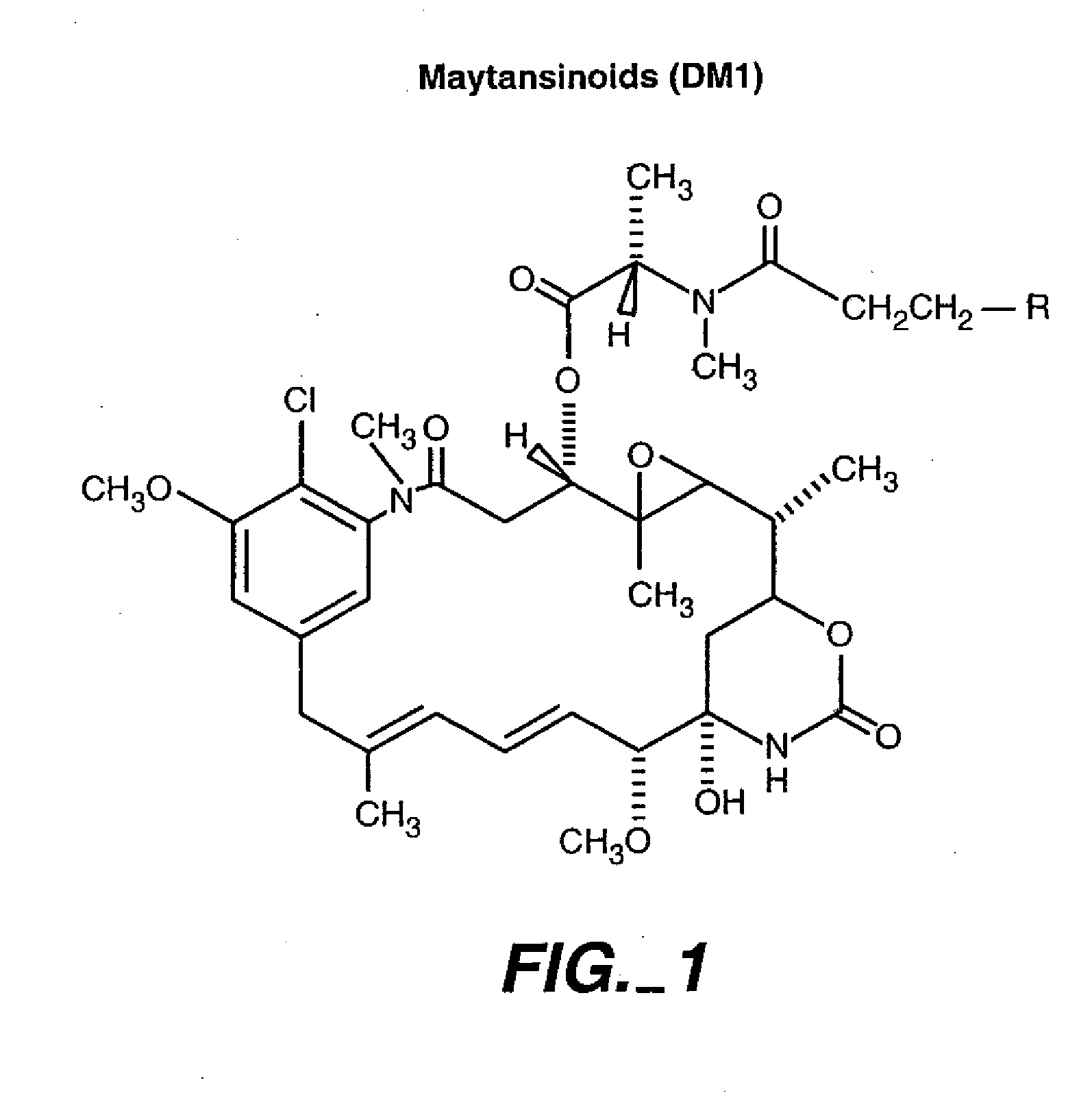
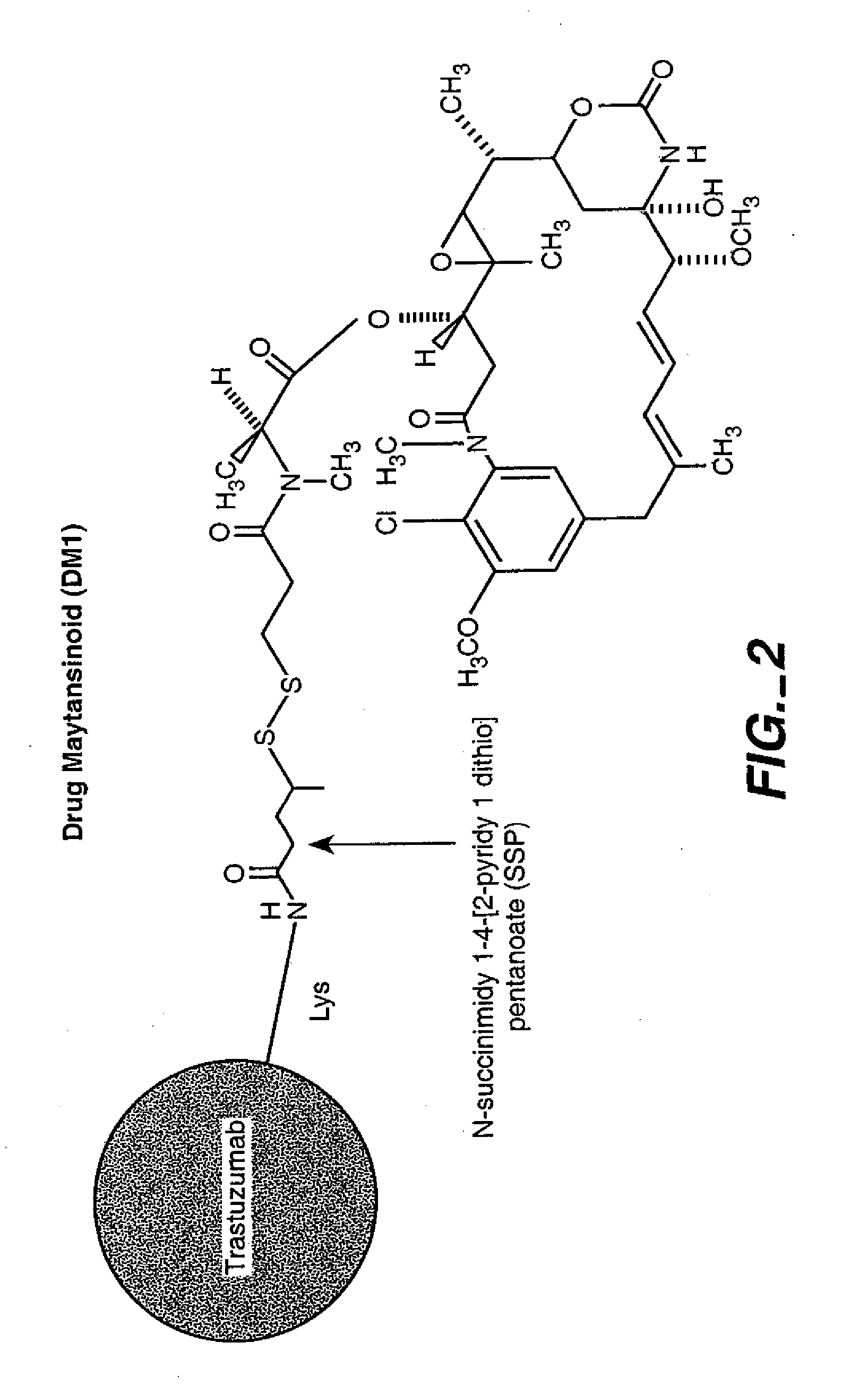
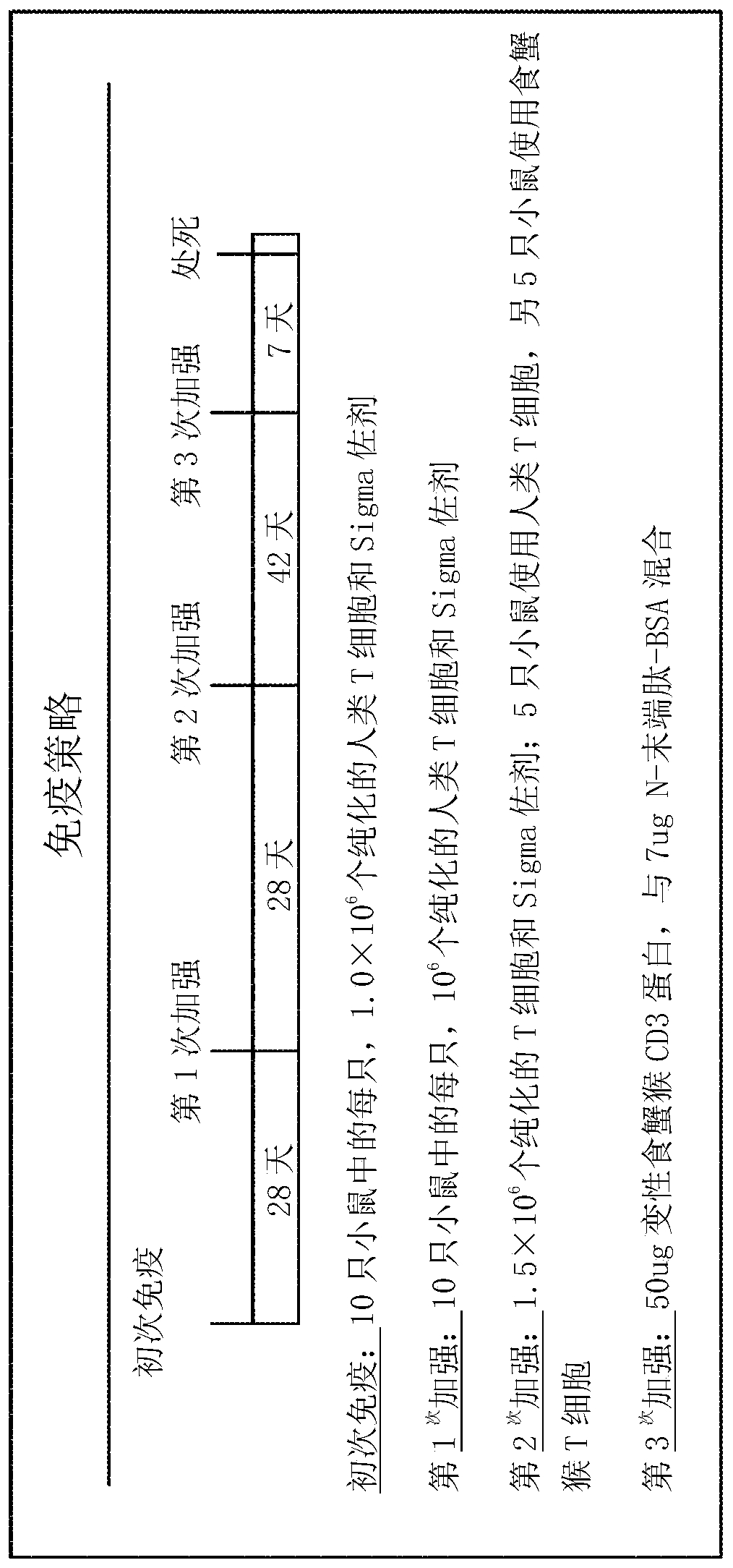
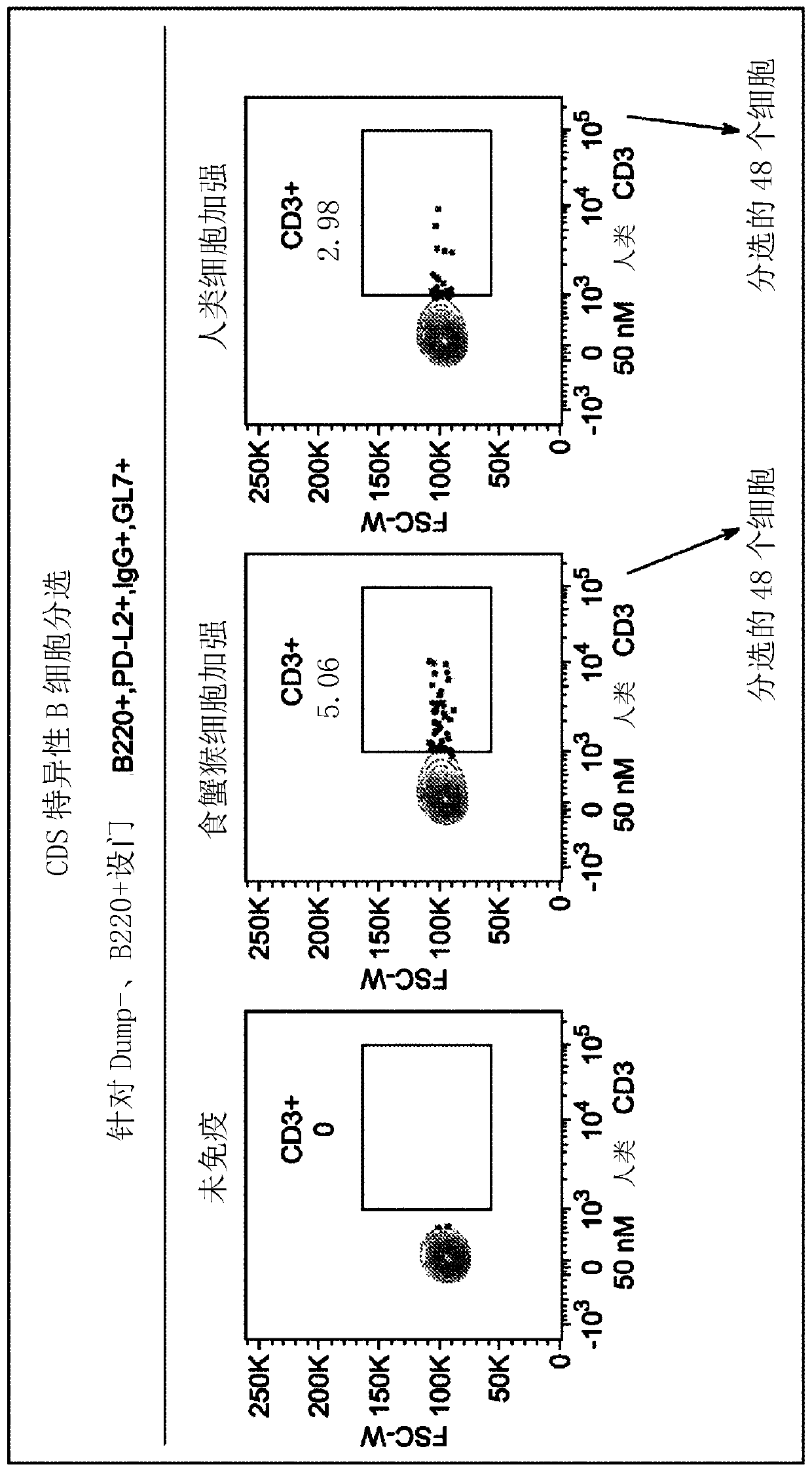
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
160 results about "Cell kill" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for assaying for natural killer, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte and neutrophil-mediated killing of target cells using real-time microelectronic cell sensing technology
ActiveUS7468255B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEffector cellNeutrophil granulocyte
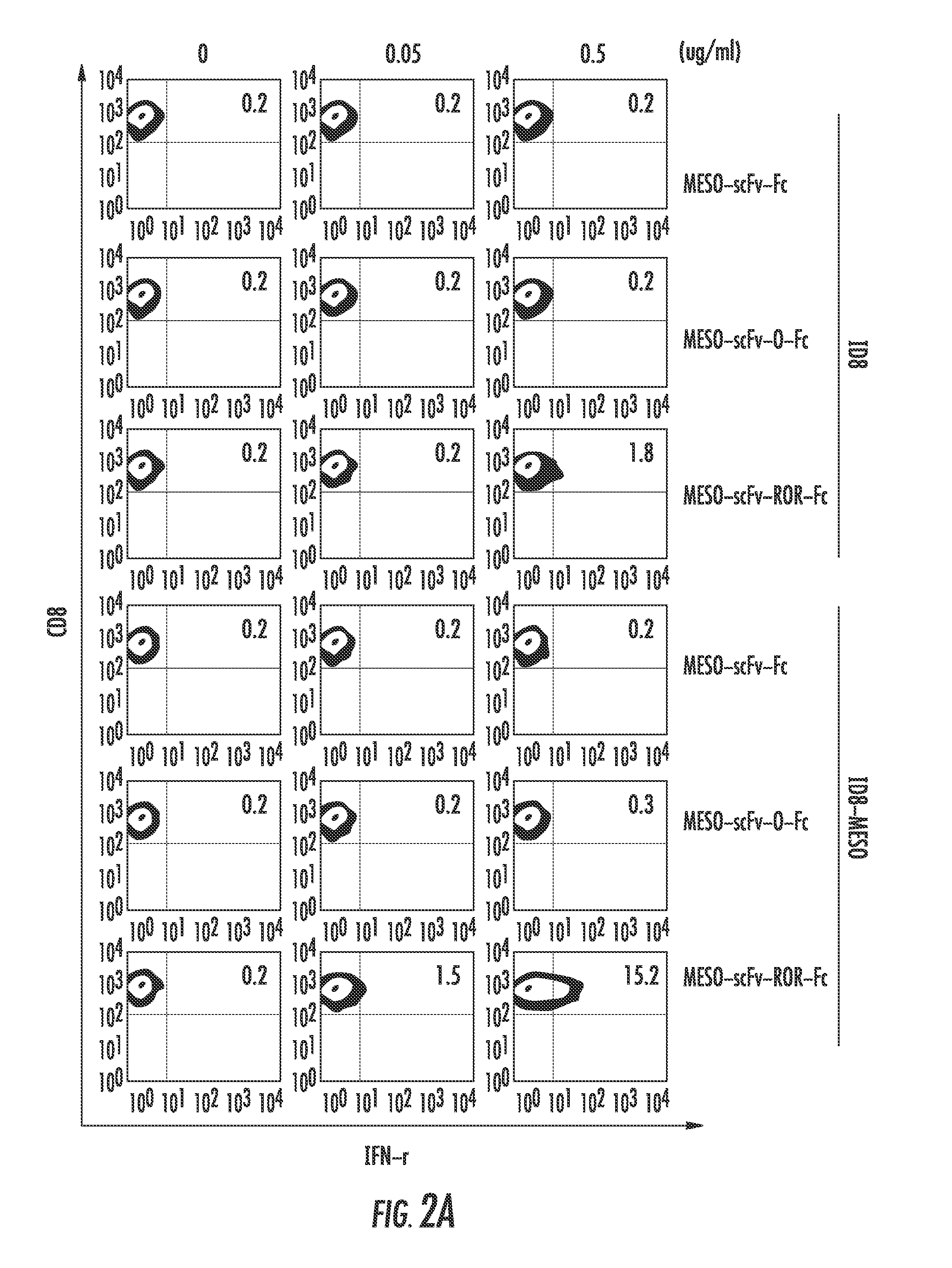
The present invention includes a method of measuring cytolytic activity including providing a device capable of monitoring cell-substrate impedance operably connected to an impedance analyzer, adding target cells to at least one well of the device, adding effector cells to the at least one well, monitoring impedance of the at least one well and optionally determining a cell index from the impedance, wherein monitoring impedance includes measuring impedance during at least one time point before and at least one time point after adding effector cells, and determining viability of said target cells after adding effector cells by comparing the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point after adding effector cells to the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point before adding effector cells.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods for the identification of polypeptide antigens associated with disorders involving aberrant cell proliferation and compositions useful for the treatment of such disorders
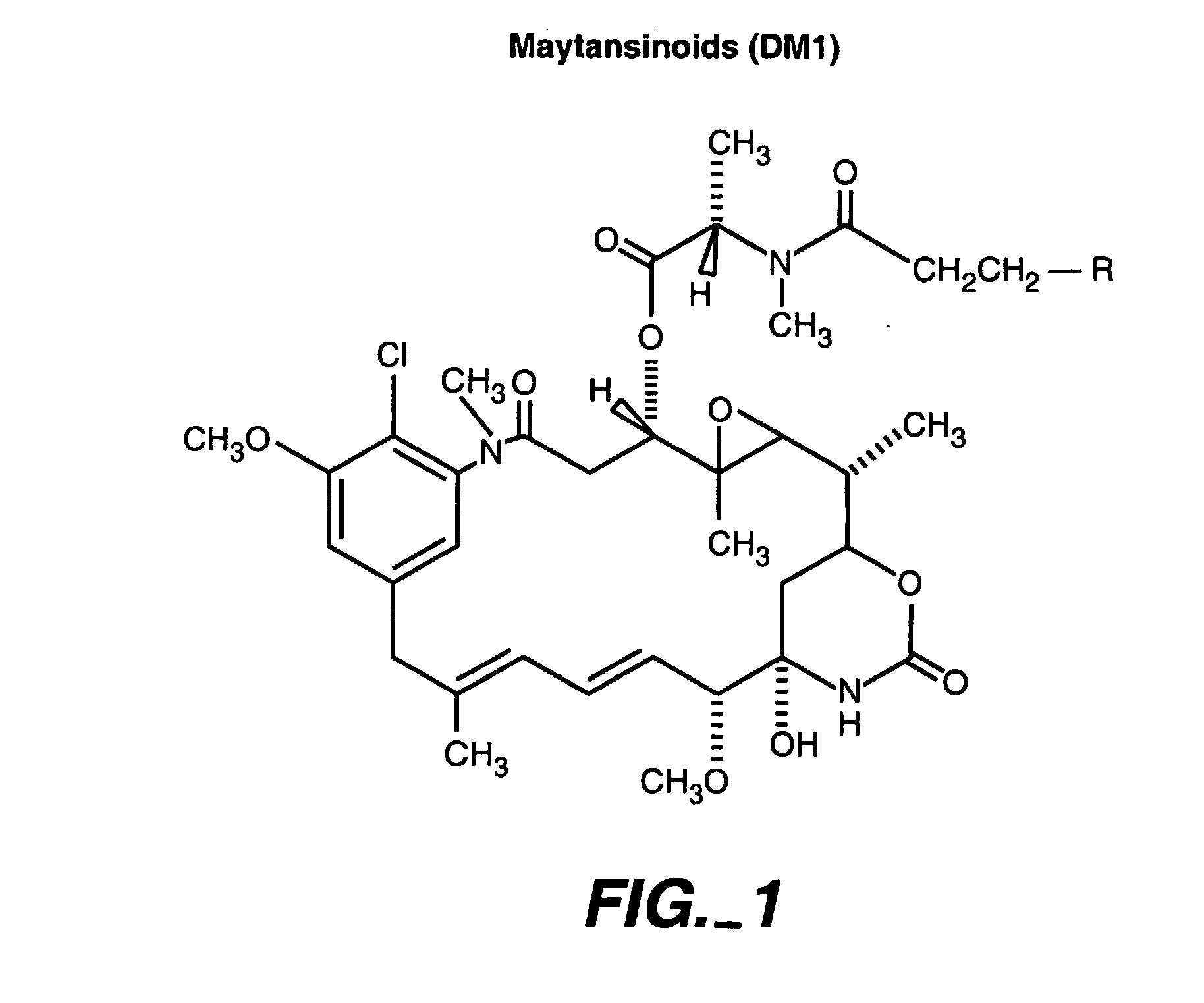
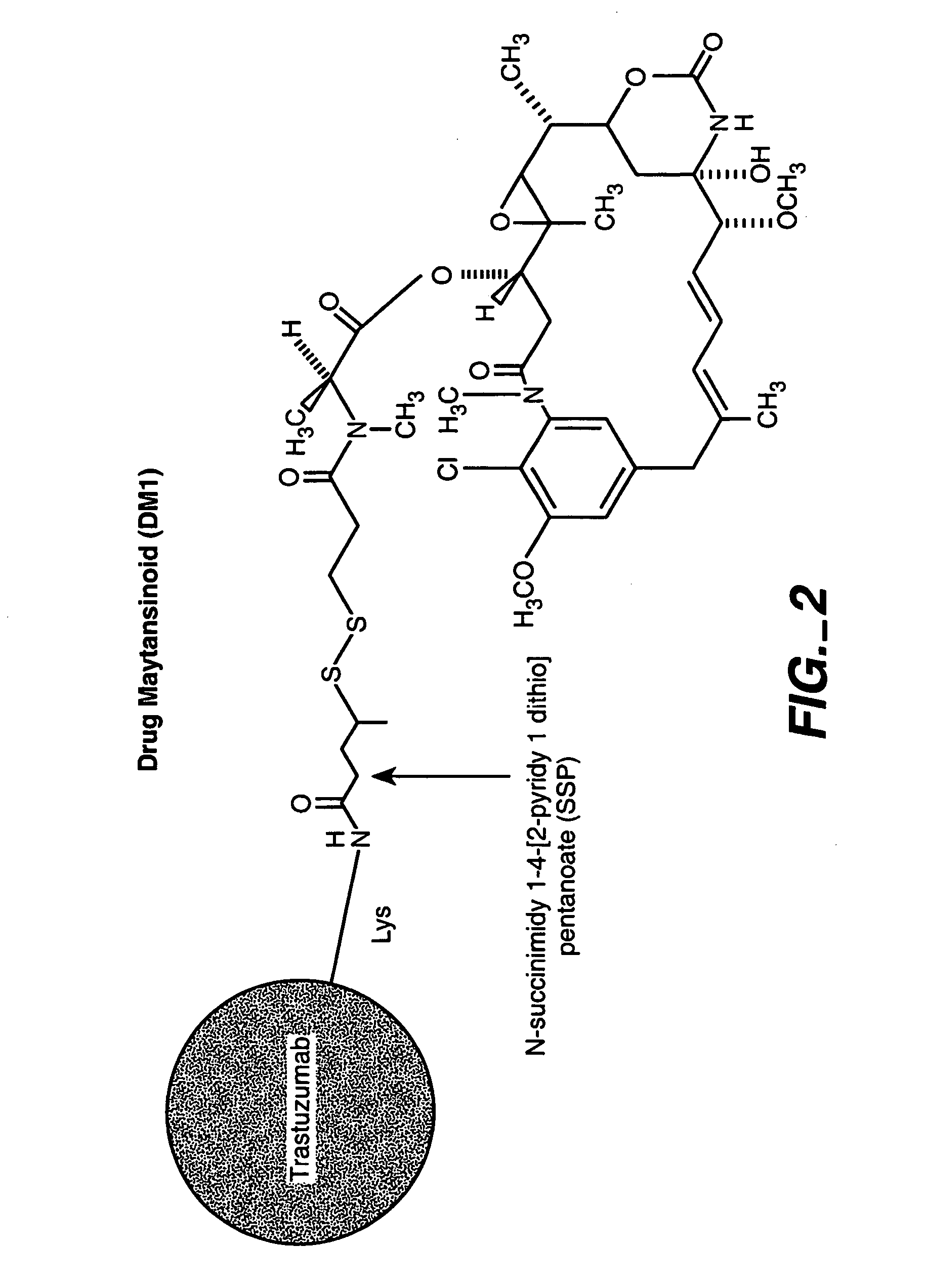
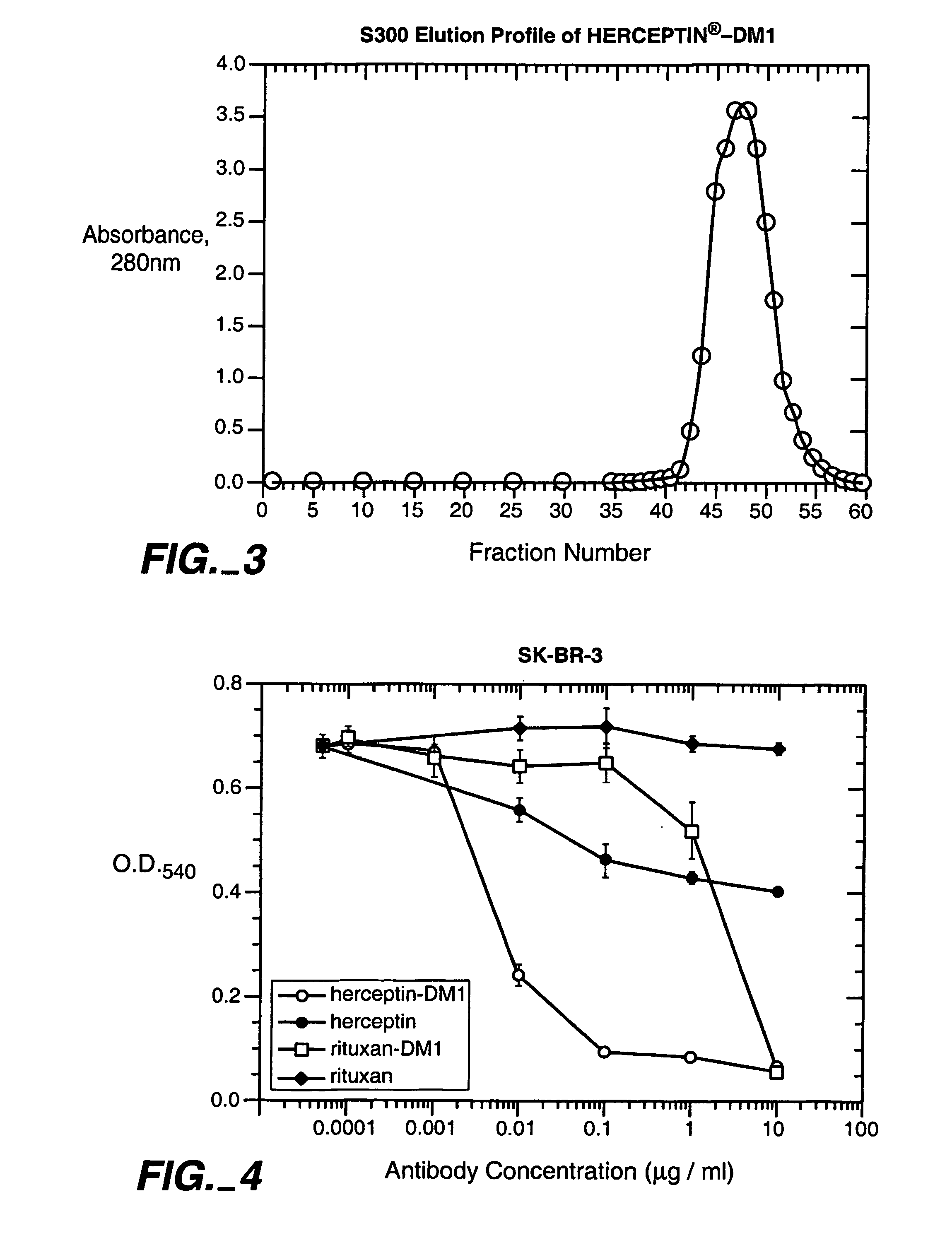
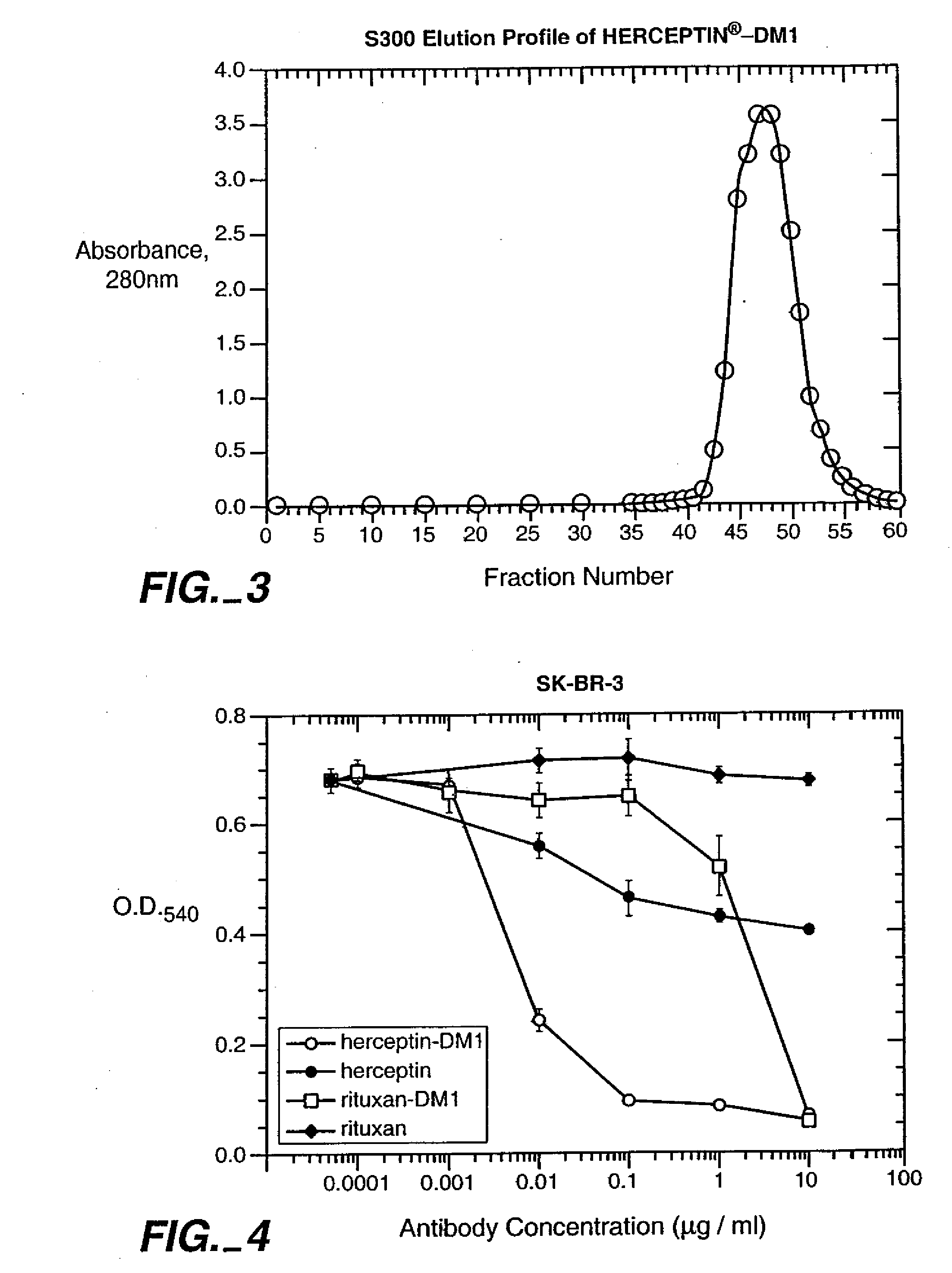
Methods and compositions for the development of effective cancer therapies using mitotic inhibitors which have limited general toxicity to normal, non-cancerous cells and tissues are provided. The methods and compositions utilize cytotoxic compounds comprised of a cell-binding agent (e.g., antibodies) conjugated to an anti-mitotic compound (e.g., maytansinoids). The invention further provides antibodies which are substantially incapable of inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), thereby ensuring that the therapeutic effect is mediated primarily by the anti-mitotic component of the cytotoxic compound, rather than by indirect cell killing via ADCC and / or CDC. The antibodies of the invention further are capable of differentiating between polypeptide antigens which are more highly expressed on proliferating cancer cells as compared to proliferating non-cancer cells.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Visualization and quantitation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
ActiveUS20070184493A1Microbiological testing/measurementTetrapeptide ingredientsFluorescenceApoptosis pathways
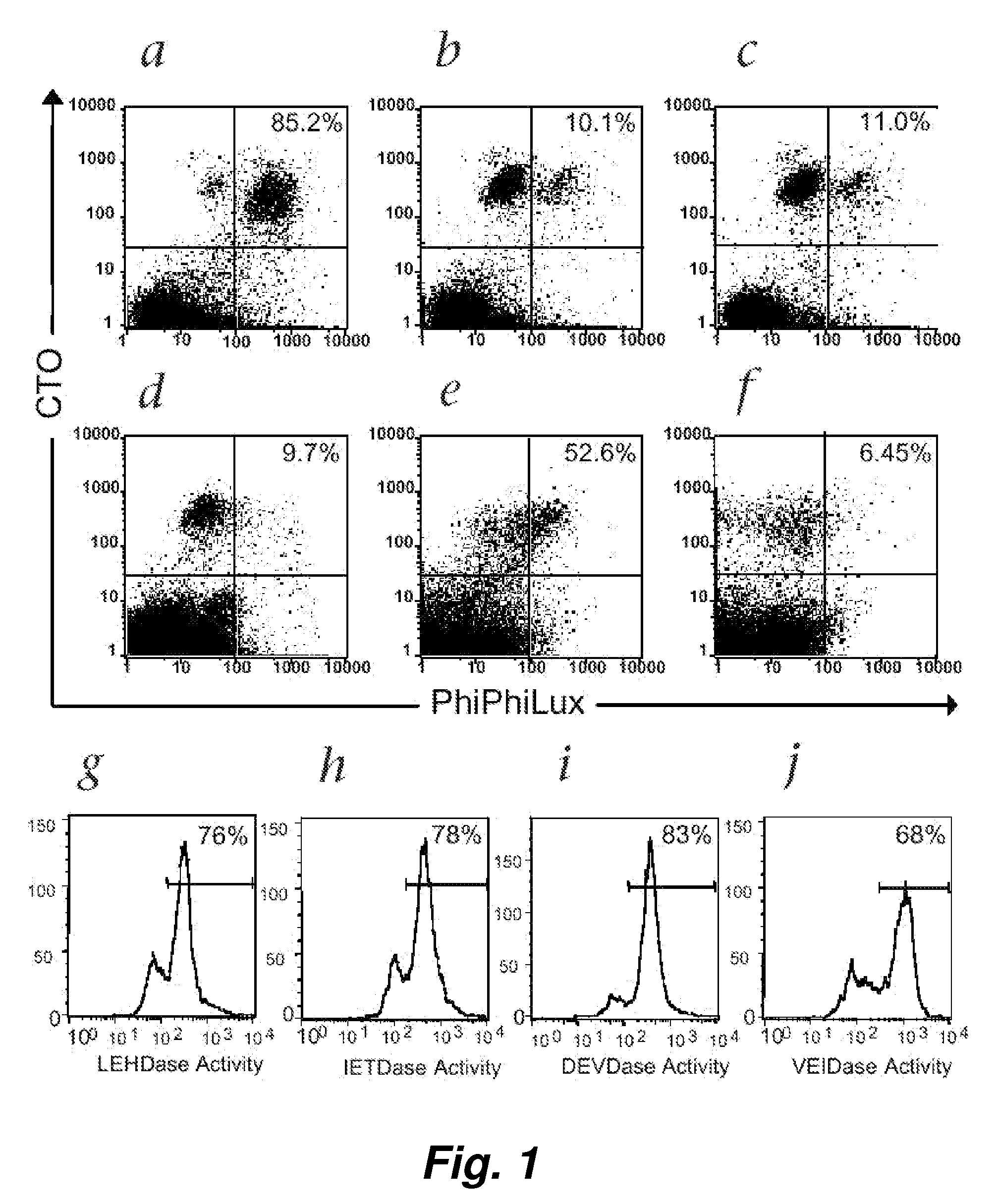
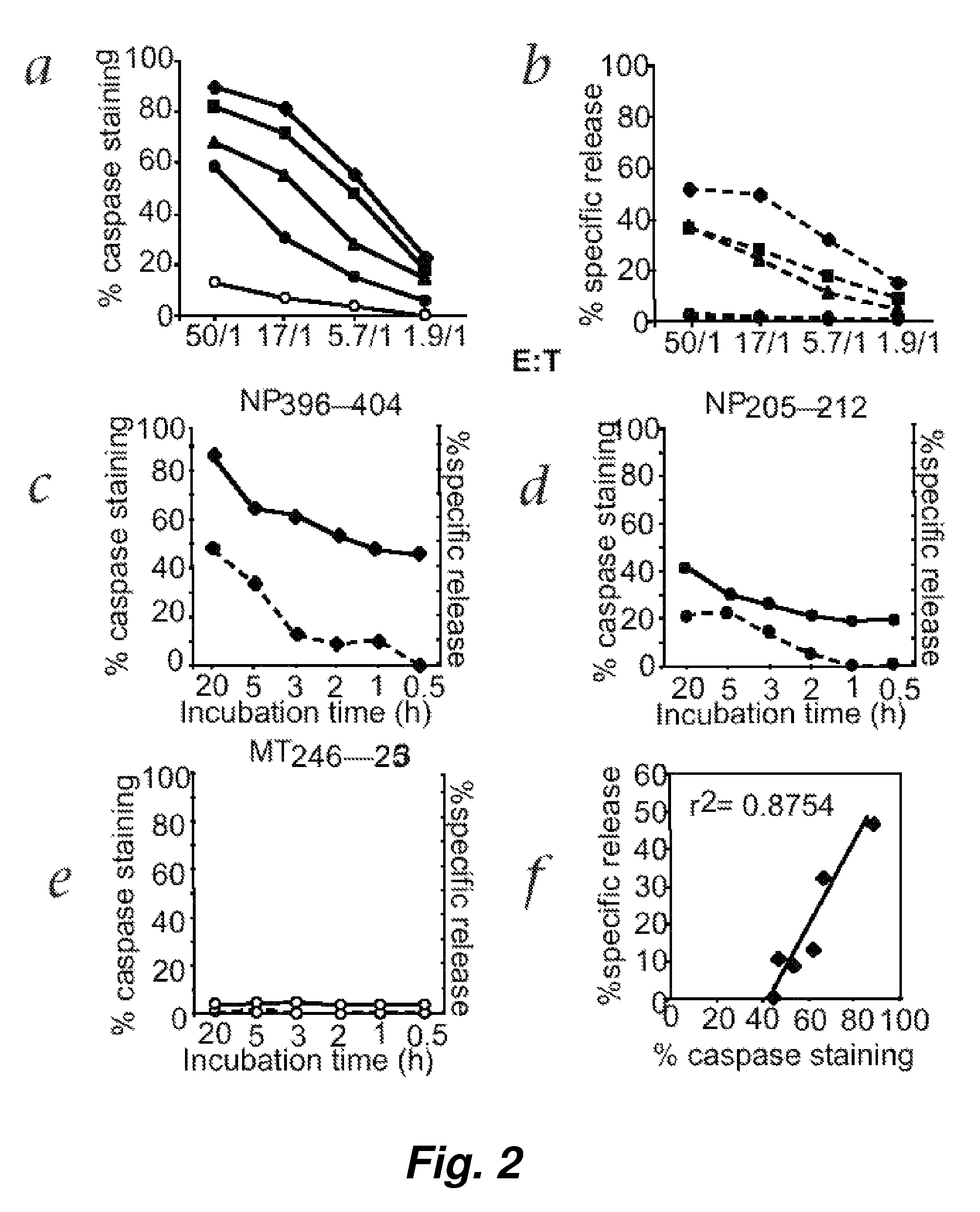
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, granzyme B activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced granzyme B activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic granzyme B substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
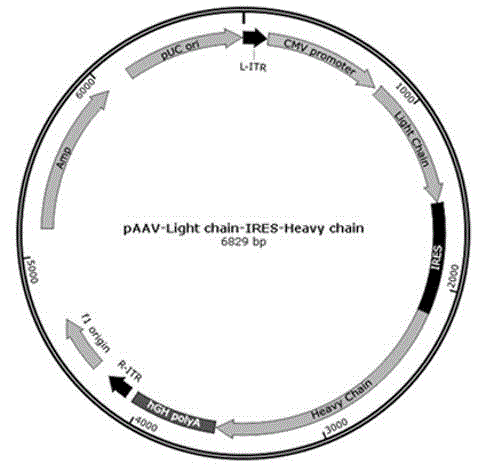
Recombinant lentivirus and application thereof
ActiveCN106749675ASignificant in vivo and in vitro amplificationSignificant tumor killing effectMammal material medical ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAbnormal tissue growthMicro environment
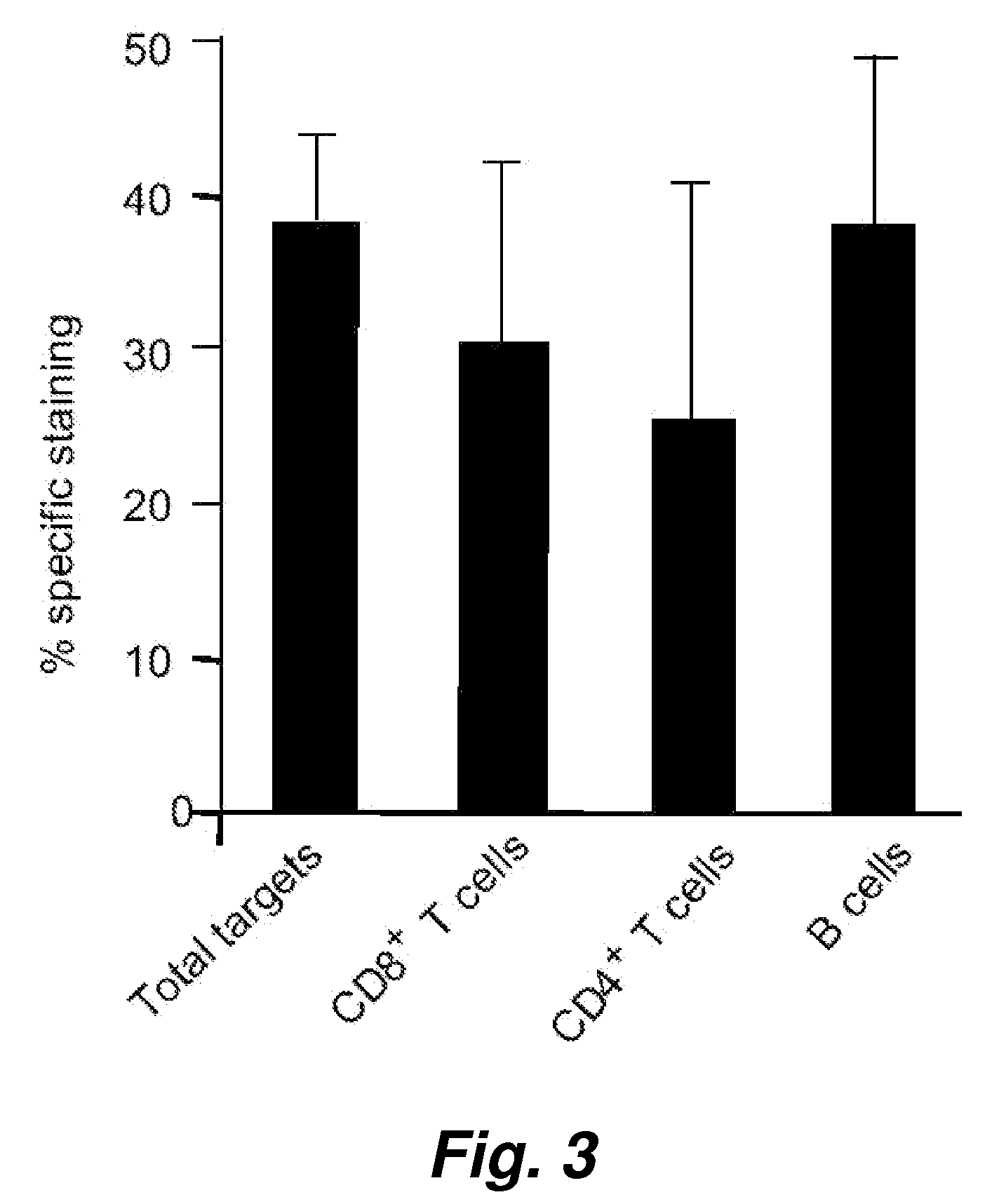
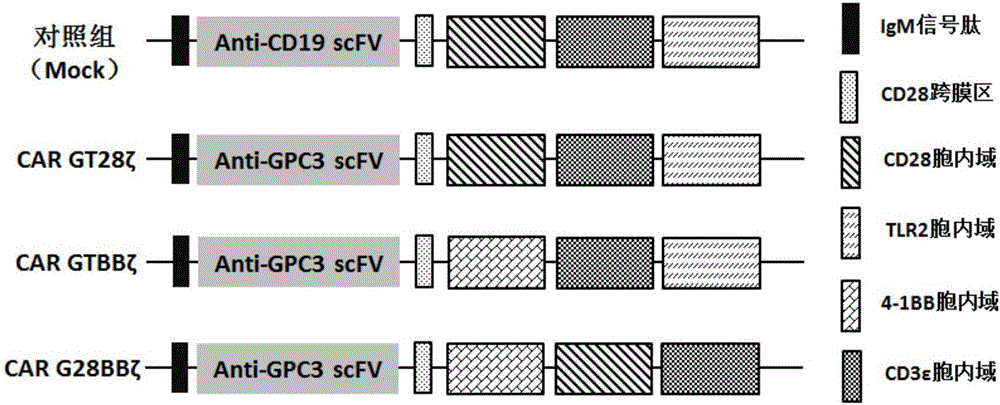
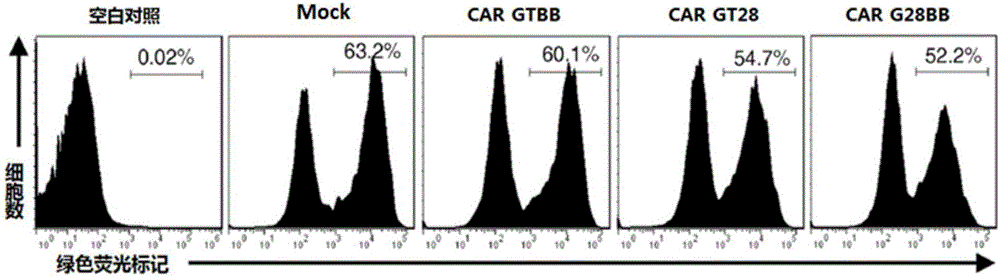
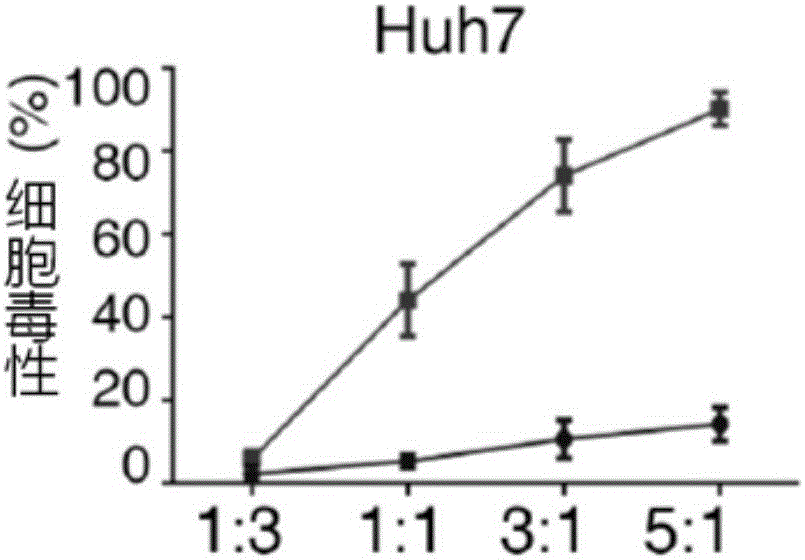
The invention relates to the field of tumor cellular immunotherapy, and in particular relates to a recombinant lentivirus and application thereof. The recombinant lentivirus comprises a chimeric antigen receptor, wherein the chimeric antigen receptor mainly comprises signal peptide, an antigen recognition domain, a transmembrane domain, an intracellular co-stimulation signal transduction domain and a CD3 zeta signal transduction domain which are serially connected; the intracellular co-stimulation signal transduction domain mainly comprises a human TLR2 (Toll Like Receptor 2) intracellular domain. A GPC3 CAT T (Glypican 3 CAT T) cell prepared from the recombinant lentivirus has an intense cell killing effect on liver cancer cells, a Th1 cell factor can be highly expressed, a tumor killing effect caused by non-CAR T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T) cell can be stimulated to the maximum extent, escape and potential reoccurrence risk of GPC 3-tumor cells can be effectively prevented, the tumor cells can be killed by T cells expressing the chimeric antigen receptor, normal tissue can be slightly damaged, a tumor immunosuppression micro environment can be broken through, and thus a relatively good treatment effect on solid tumor can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN IN VIVO BIOMEDICINE TECH LTD
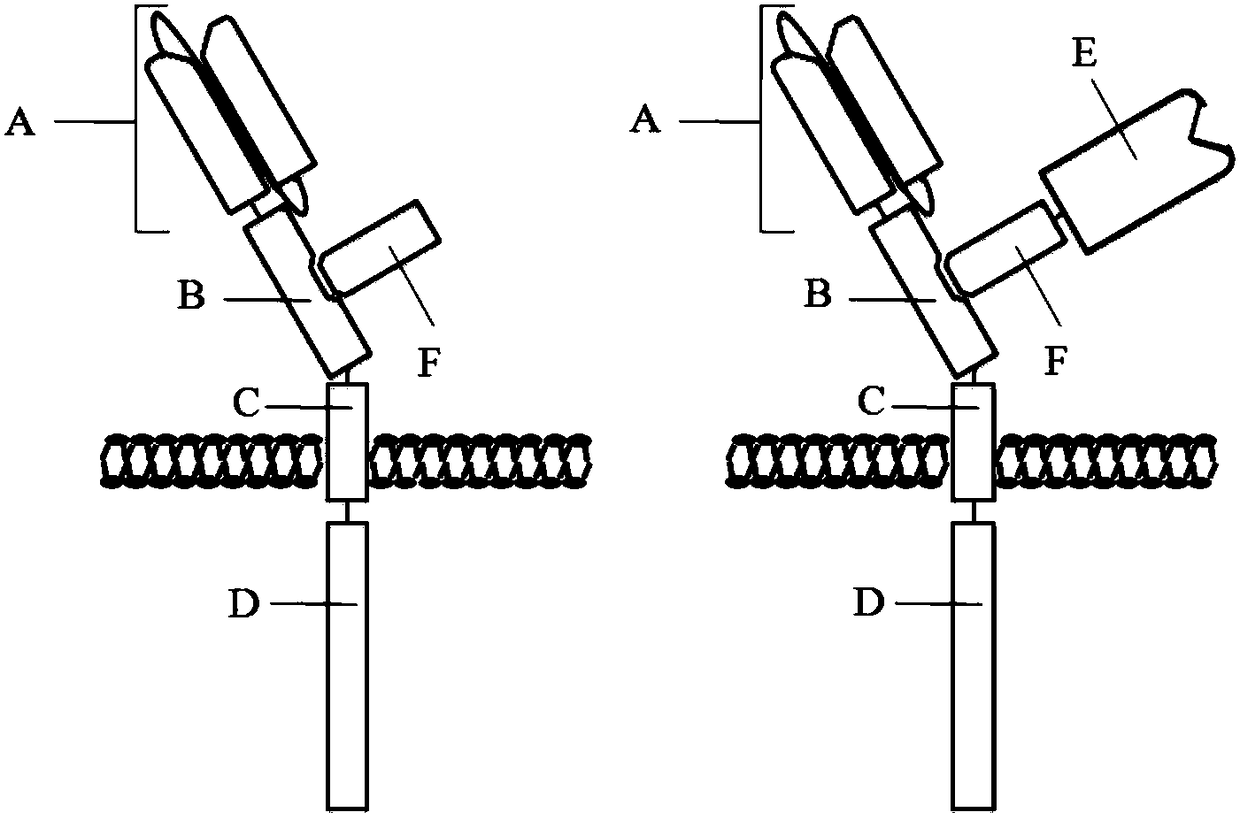
Multi-target chimeric antigen receptor
InactiveCN108250301AEliminate dependenciesReduced activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyTransmembrane domainChimeric antigen receptor
The invention discloses a multi-target chimeric antigen receptor. The multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention consists of a main peptide chain and an assistant peptide chain.The main peptide chain includes an antigen binding domain A, an assistant peptide chain connection domain B, a transmembrane domain C and an intracellular signal conduction domain D. The assistant peptide chain includes a main peptide chain connection domain F. The antigen binding domain A is a polypeptide with antigen-bonding function. The assistant peptide chain connection domain B and the mainpeptide chain connection domain F are mutually combined. The transmembrane domain C is the transmembrane domain of arbitrary membrane binding protein or the transmembrane domain of transmembrane protein. The intracellular signal conduction domain D includes a primary signal conduction region. The multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention can mediate specific cell killing bycombining two antigen binding domains with different antigens. Also a cytokine and cytokine receptor compound are introduced into the multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention and can play the role of cytokines.
Owner:TIMMUNE BIOTECH INC
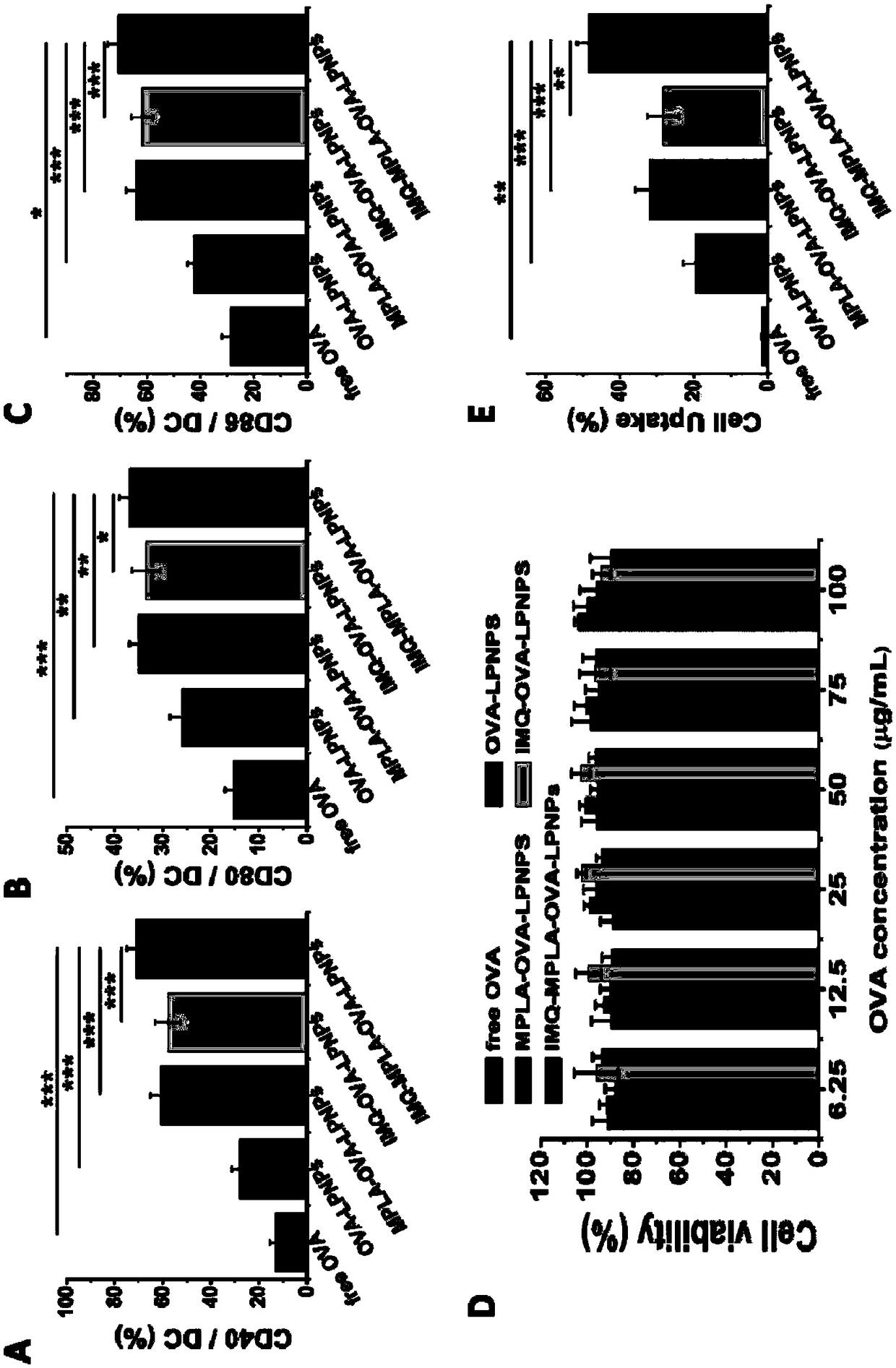
Cationic phospholipid-polymer hybridized nanoparticle vaccine adjuvant of common-carrier antigen, MPLA (Monophosphoryl Lipid A) and IMQ (Imiquimod) as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108743939AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsDendritic cellPhospholipid
The invention relates to a cationic phospholipid-polymer hybridized nanoparticle vaccine adjuvant of a common-carrier antigen, MPLA (Monophosphoryl Lipid A) and IMQ (Imiquimod) as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The vaccine adjuvant is characterized in that the IMQ as a TLR7 agonist is loaded on a hydrophobic core; the MPLA as a TLR4 agonist is loaded in a phopholipid layer;cationic phospholipid DOTAP (1,2-dioleoy-3-trimethylammonium-propane) in the phopholipid layer is used for adsorbing an antigen; the antigen is protected through hybridized nanoparticles, and the ingestion of the antigen by dendritic cells is improved; immune response after antigen stimulation is improved remarkably through the TLR agonist, and cross-presentation of the antigen is improved remarkably. The hybridized nanoparticles as the vaccine adjuvant can load the antigen and different types of TLR agonists simultaneously, can deliver the antigen through a plurality of immune paths, and promotes the DC activation and maturation. The cross-presentation level is raised, a strong and powerful T-cell killing effect is achieved, cell factor secretion is induced, a long-term memory T-cell reaction is generated, and higher prevention capability for tumors is achieved.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
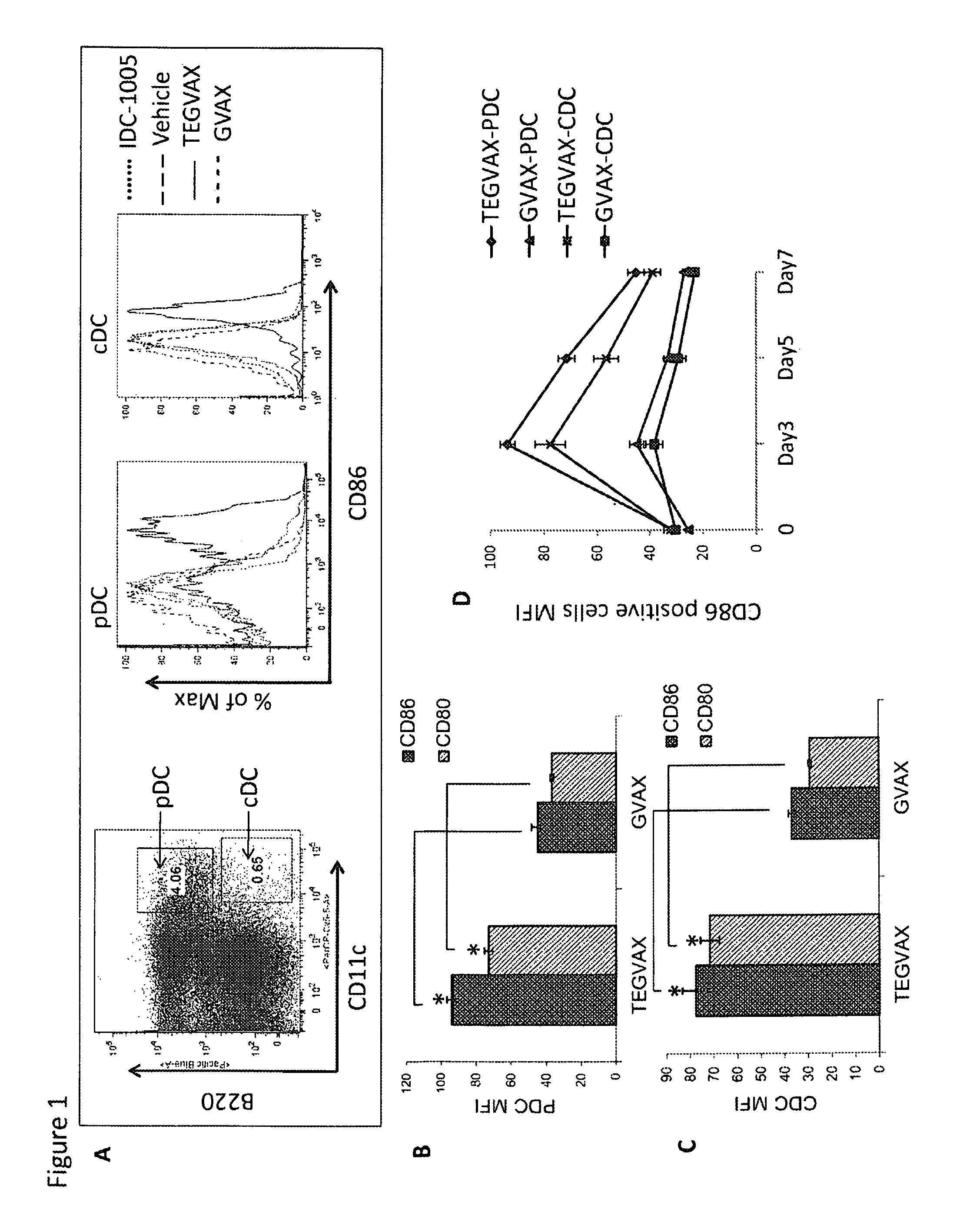
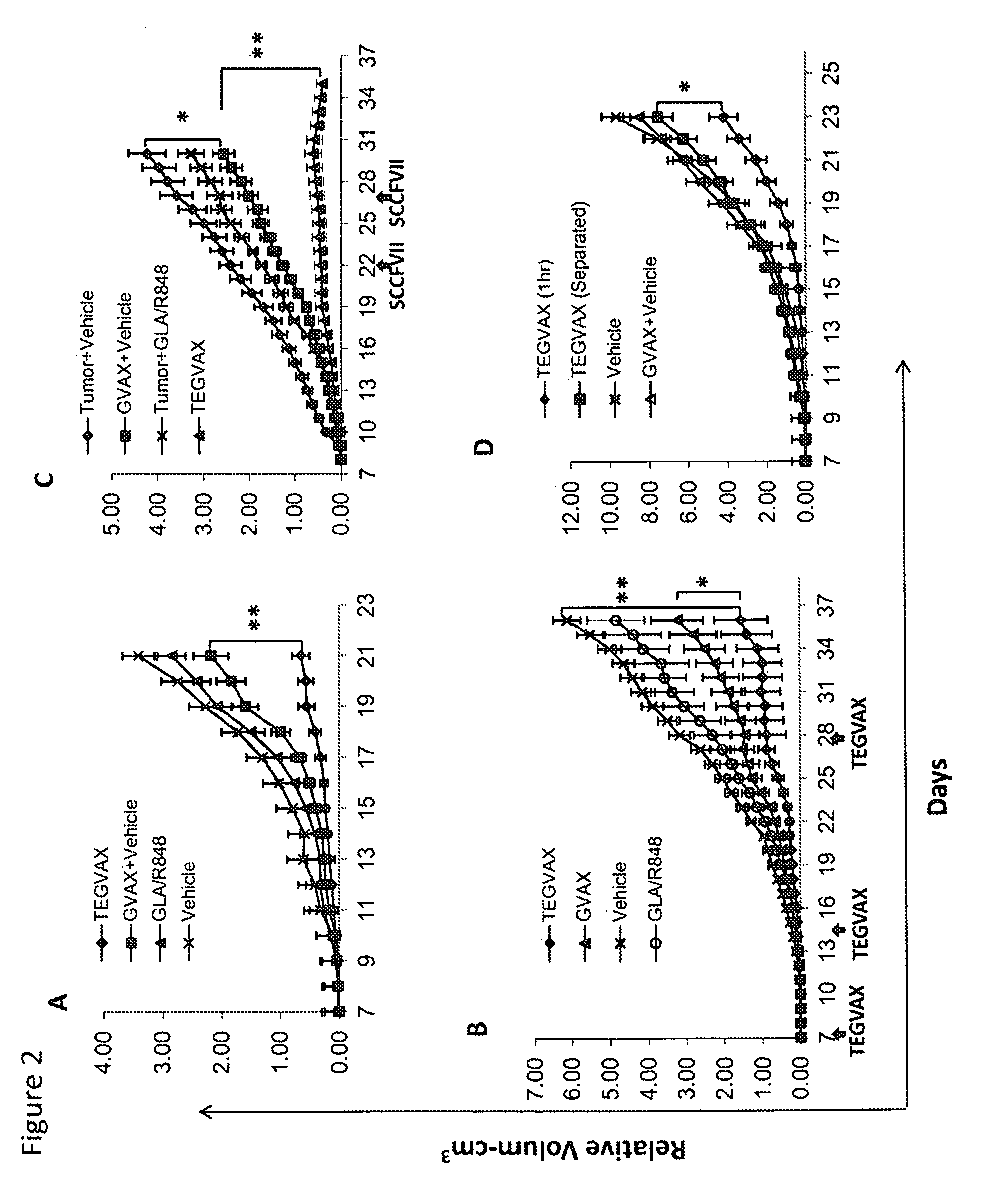
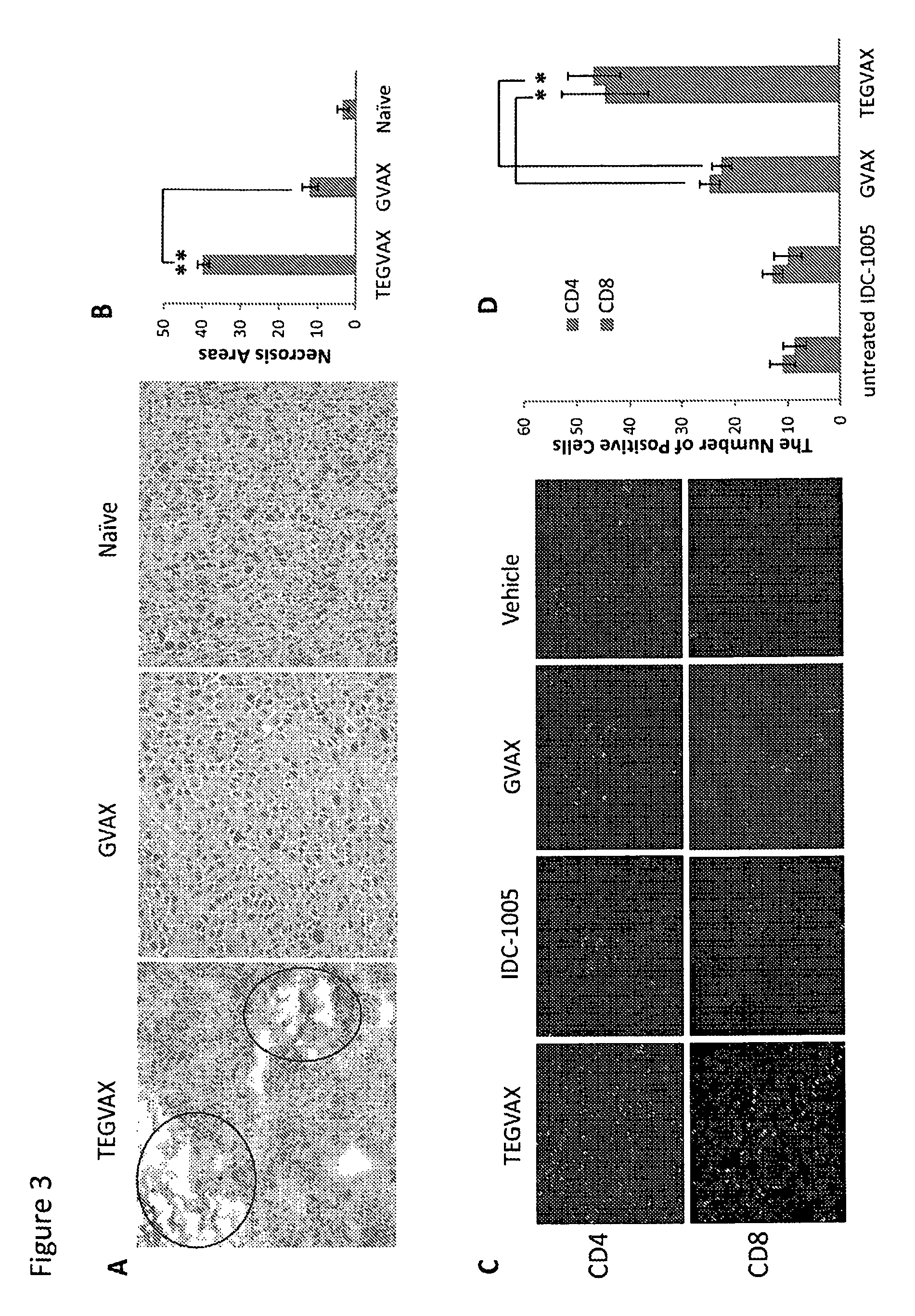
Cancer immunotherapy
We formulated multiple TLR agonists into GVAX (lethally irradiated tumor cell vaccines engineered to secrete GM-CSF). Specifically, GLA and R848, TLR4 and TLR7 / 8 agonists found to be safe in patients, were formulated with GVAX (TEGVAX—for TLR agonists enhanced GVAX), and this formulation was effective in producing anti-tumor responses in 3 different preclinical models, including palpable B16. These anti-tumor responses were correlated with increased CD4 and CD8 T-cells that can secrete IFNγ circulating in the tumor microenvironment as well as significantly higher level of p15E specific CTL mediated cell killing in mice treated with TEGVAX in comparison to controls. When combined with anti-PD-1 antibody, TEGVAX was able to induce regression of established B16 tumors.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for assaying for natural killer, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte and neutrophil-mediated killing of target cells using real-time microelectronic cell sensing technology
ActiveUS20060023559A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEffector cellT lymphocyte
The present invention includes a method of measuring cytolytic activity including providing a device capable of monitoring cell-substrate impedance operably connected to an impedance analyzer, adding target cells to at least one well of the device, adding effector cells to the at least one well, monitoring impedance of the at least one well and optionally determining a cell index from the impedance, wherein monitoring impedance includes measuring impedance during at least one time point before and at least one time point after adding effector cells, and determining viability of said target cells after adding effector cells by comparing the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point after adding effector cells to the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point before adding effector cells
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Serine protease molecules and therapies
ActiveUS20140140976A1Enhanced intracellular activityReduce distractionsNervous disorderHydrolasesResistant cancerCancer research
Cell-targeted serine protease constructs are provided. Such constructs can be used in methods for targeted cell killing such as for treatment cell of proliferative diseases (e.g., cancer). In some aspects, recombinant serine proteases, such as Granzyme B polypeptides, are provided that exhibit improved stability and cell toxicity. Methods and compositions for treating lapatinib or trastuzumab-resistant cancers are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Visualization and quantitation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
ActiveUS7927871B2Microbiological testing/measurementTetrapeptide ingredientsFluorescenceCytotoxicity
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, granzyme B activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced granzyme B activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic granzyme B substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Preparation method and application of CAR-T cell targeting B7H3
ActiveCN109880804AHas a lethal effectEnhance killing activityMammal material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBiologyLung cancer
The invention relates to a preparation method of a CAR-T cell targeting B7H3. The preparation method includes first preparing a PBMC cell; then co-transfecting a 293T cell with a shuttle plasmid LV-B7H3 containing the CAR structure, a helper plasmid psPAX2 and an envelope plasmid VSV-G to obtain a packaged B7H3-CAR virus; then taking a PBMC cell, using anti-human CD3 and anti-human CD28 as activators, culturing and activating for 48 hours and adding the B7H3-CAR virus for infection. By means of the preparation scheme, the expression of IFN-gamma in the CAR-T cell is increased, and the cell killing activity is high. The CAR-T cell targeting B7H3 has a killing effect on various solid tumor cells, has high killing activity, is safe and effective, and can be used for immunotherapy of kidney cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, glioma, ovarian cancer, breast cancer and the like.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
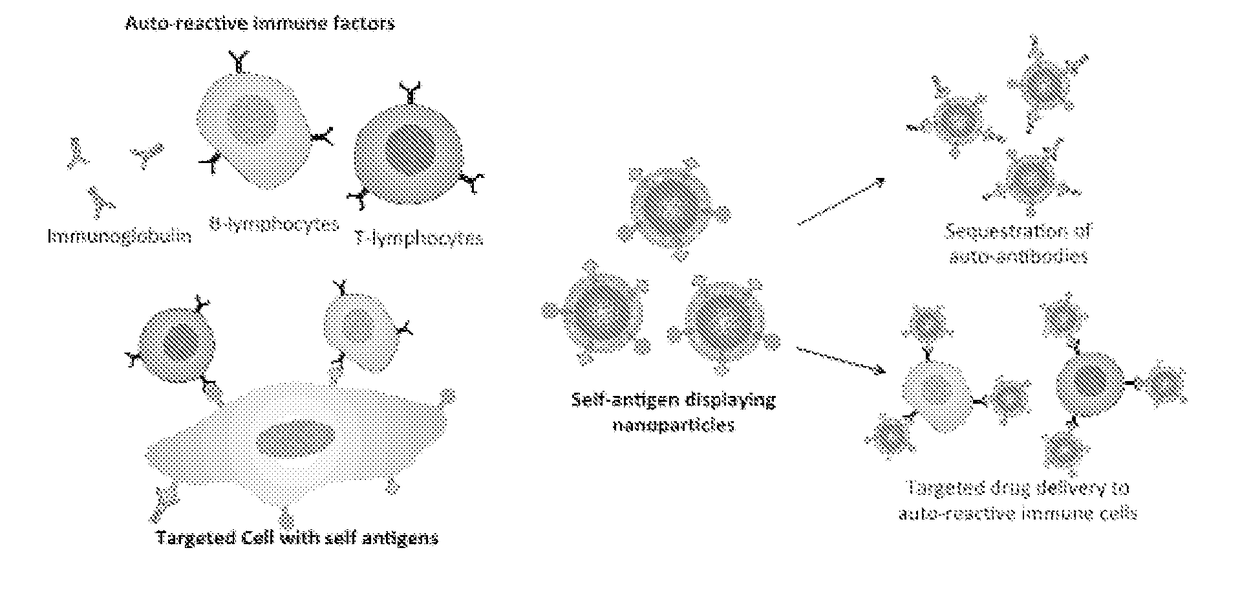
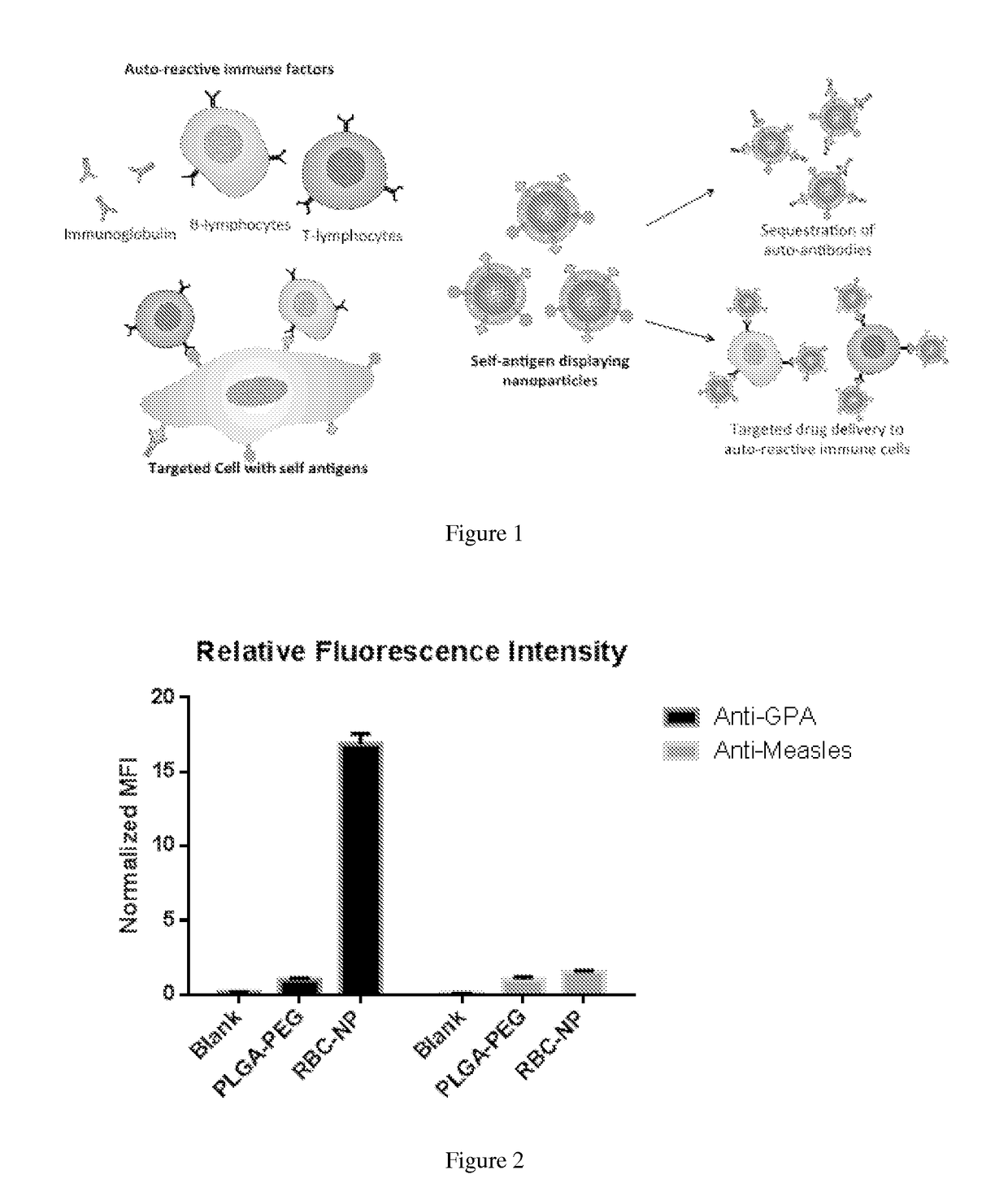
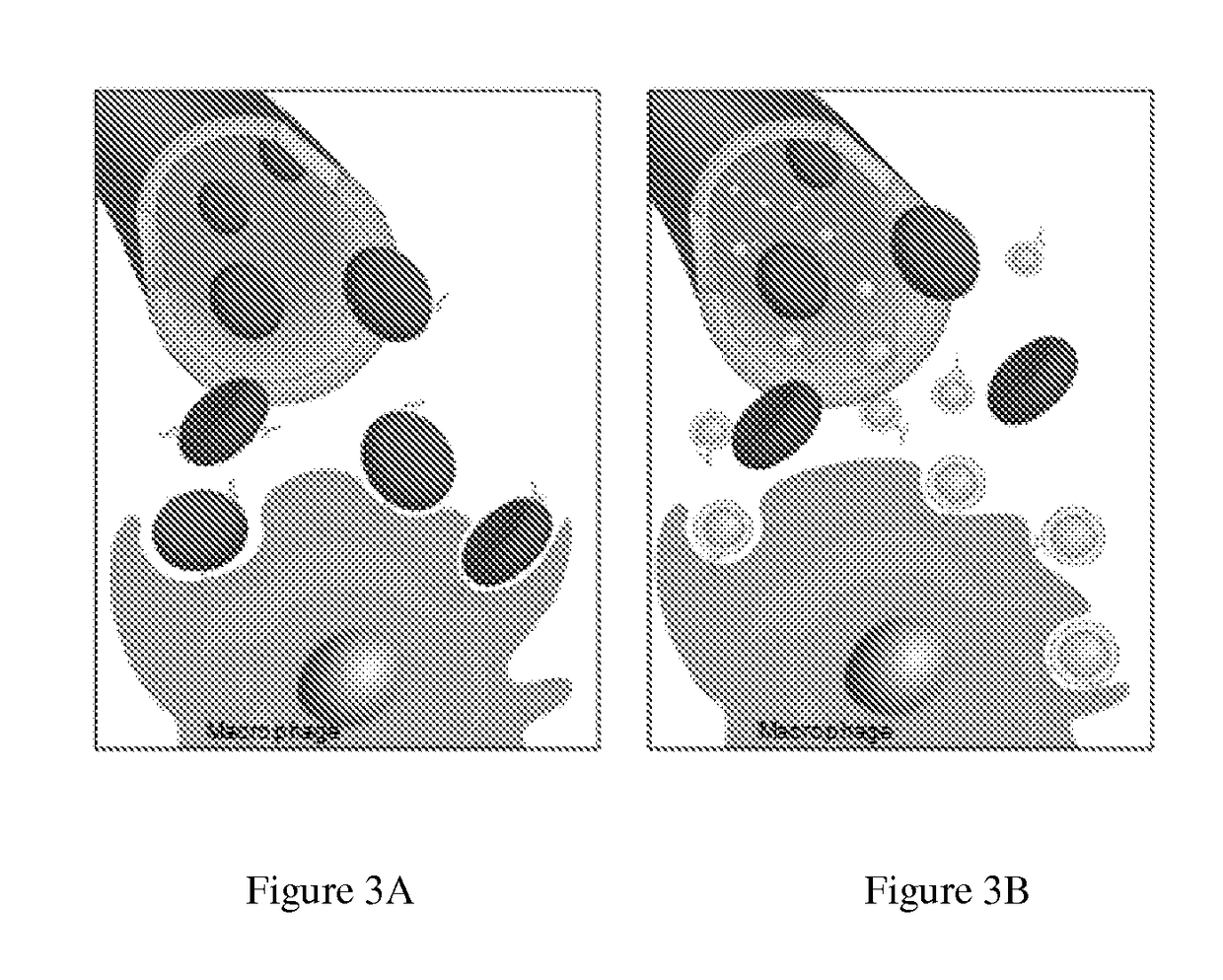
Self-Antigen Displaying Nanoparticles Targeting Auto-Reactive Immune Factors and Uses Thereof
PendingUS20170274059A1Normalize the immune regulationRelieve symptomsMammal material medical ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsNanoparticleCytotoxic drug
The invention provides a composition, and method of use thereof, comprising self-antigen displaying nanoparticles to target auto-reactive immune components for treating and / or preventing the autoimmune diseases associated therewith. The nanoparticles can also be loaded with cytotoxic drugs for targeted cell killing or with immune-tolerizing compounds to normalize the immune regulation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Recombinant fusion protein and polynucleotide construct for immunotoxin production
The present invention relates to a polynucleotide construct encoding a fusion protein consisting of a domain which binds the immunoglobulin Fc region, genetically fused to a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE). In particular, the invention discloses the fusion protein, ZZ-PE38, and further provides immunotoxins, formed from complexes of the fusion protein with antibodies for targeted cell killing.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Anti-tumor NK cell, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110964697AStrong cytotoxicityGood effectImmunoglobulinsBlood/immune system cellsSingle-Chain AntibodiesNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The invention provides an anti-tumor NK cell, and a preparation method and application thereof. The anti-tumor NK cell is an NK cell edited by a chimeric antigen receptor. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular domain fragment of PD-1, an F2A peptide fragment, the extracellular region of a CD8a signal peptide, the extracellular variable region of a single-chain antibody capable of recognizing and binding to HER2 protein, a CD8 alpha Linker region, a CD28 transmembrane and intracellular synergistic co-stimulation region, and a CD3 zeta fragment for intracellular signal transmission. The NK cell disclosed by the invention can express a CAR element targeting HER2 on a cell membrane and express secretory PD-1 protein at the same time, so the binding of PD-1 and PD-L1 is blocked, and the killing function of the NK cell is increased; and the anti-tumor NK cell is used for preparing anti-tumor drugs, can target tumor cells and enhance cytotoxic effect, is low in immunogenicity, easily realizes response and activation and can achieve allogeneic reinfusion, and the tumor killing effect of the NK cell is remarkably improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
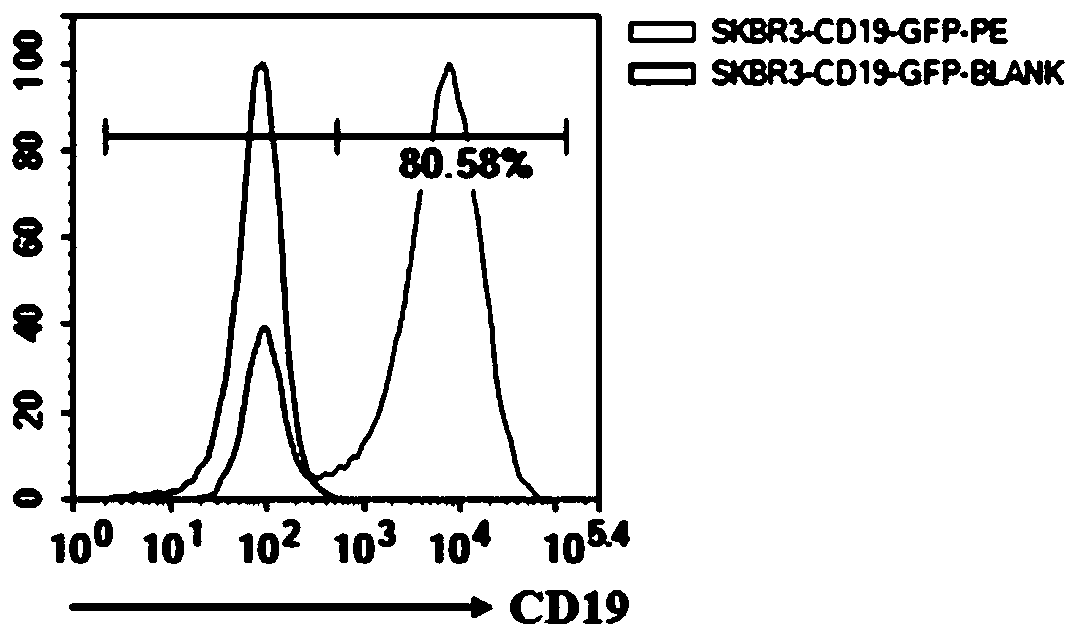
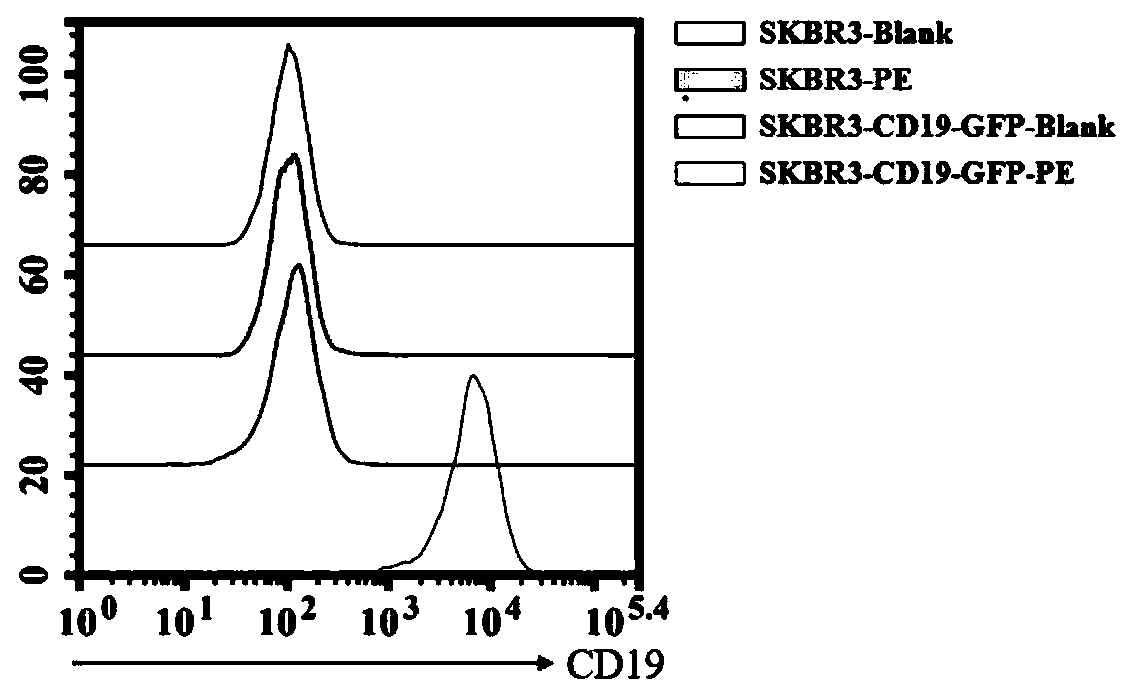
Preparation and application of CD19-targeting humanized chimeric antigen receptor
PendingCN111733186AIncrease lethalityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCell phenotypeCell kill
The invention relates to preparation and application of a CD19-targeting humanized chimeric antigen receptor, and concretely relates to construction of a human CD19-antigen-targeting humanized lentiviral vector expression plasmid. The human CD19-antigen-targeting humanized lentiviral vector expression plasmid is applied to the preparation of chimeric antigen receptor T cells; and then, the effectsare verified through the chimeric antigen receptor T cells in in-vitro proliferation tests, cell phenotype tests and cell killing tests. A CAR sequence of the invention consists of a leader peptide sequence, a human CD19-antigen-targeting single-chain scFv sequence, a hinge region, a transmembrane region structure domain and an intracellular signal conduction structure domain sequence. The chimeric antigen receptor is built into a lentivirus system expression vector, and immune cells are infected; the human CD19-antigen-targeting chimeric antigen receptor can be expressed on the surface of the immune cells; the effects of killing tumor cells can be achieved by recognizing the CD19 antigen expressed on tumor tissues; the goal of tumor treatment is achieved; and a novel measure is providedfor cancer treatment.
Owner:天津英科赛奥科技有限公司
Methods for the identification of polypeptide antigens associated with disorders involving aberrant cell proliferation and compositions useful for the treatment of such disorders
Methods and compositions for the development of effective cancer therapies using mitotic inhibitors which have limited general toxicity to normal, non-cancerous cells and tissues are provided. The methods and compositions utilize cytotoxic compounds comprised of a cell-binding agent (e.g., antibodies) conjugated to an anti-mitotic compound (e.g., maytansinoids). The invention further provides antibodies which are substantially incapable of inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), thereby ensuring that the therapeutic effect is mediated primarily by the anti-mitotic component of the cytotoxic compound, rather than by indirect cell killing via ADCC and / or CDC. The antibodies of the invention further are capable of differentiating between polypeptide antigens which are more highly expressed on proliferating cancer cells as compared to proliferating non-cancer cells.
Owner:LEVINSON ARTHUR D
Viral vector driven mutant bacterial cytosine deaminase gene and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070225245A1Low efficiencyGreat fold substrate preferenceVectorsHydrolasesCytosine deaminaseHuman glioma
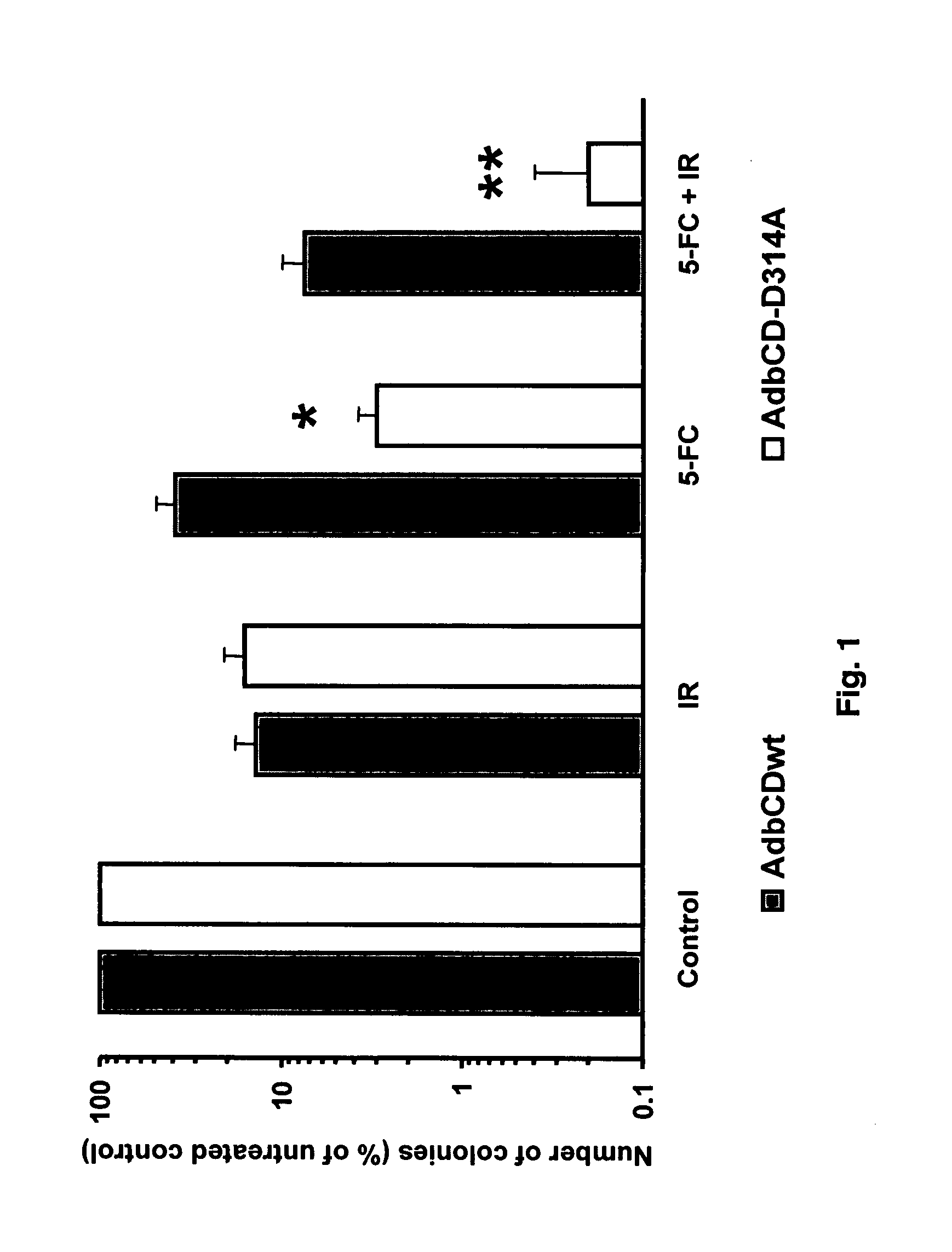
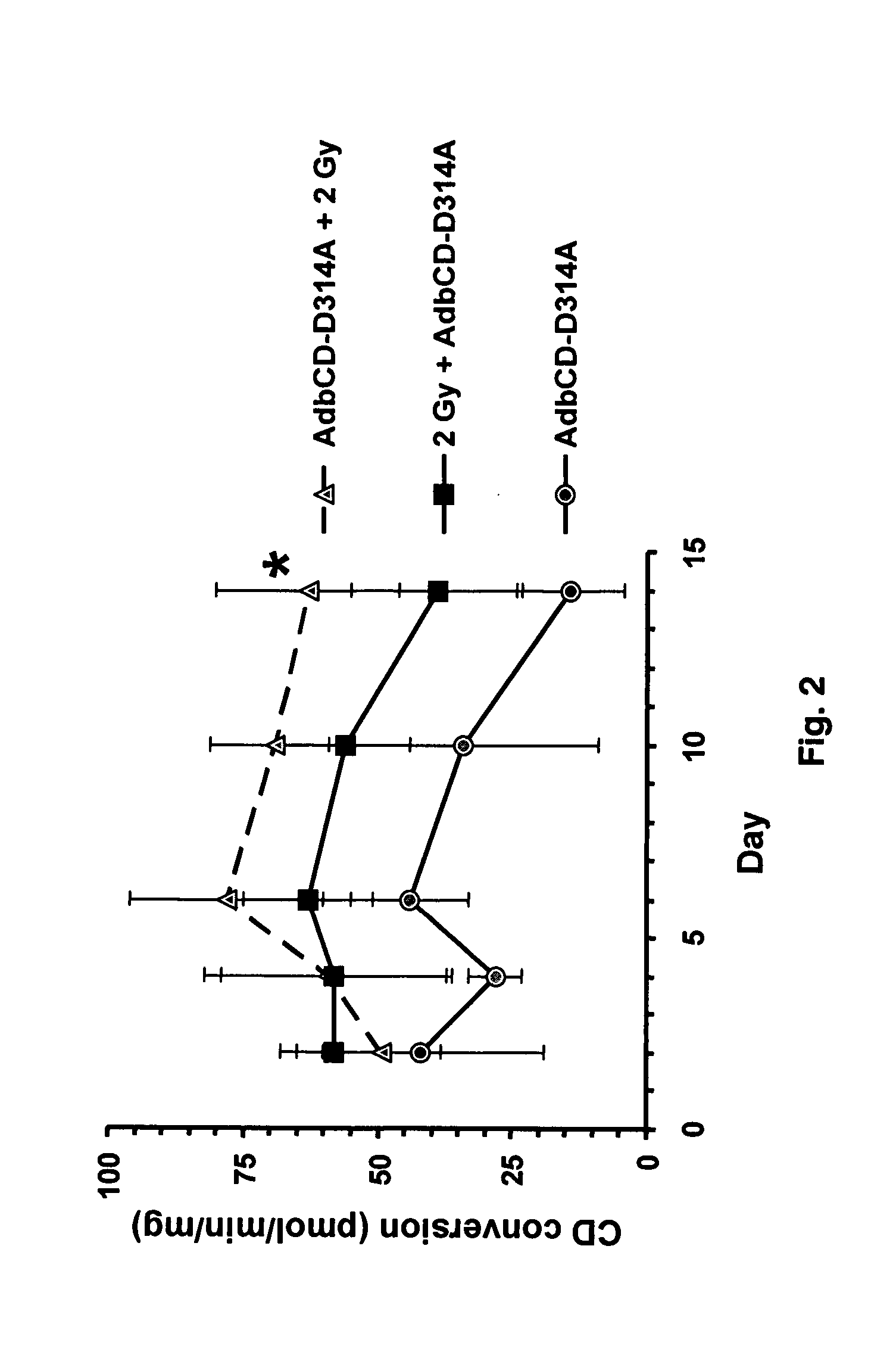
The instant invention has developed viral vectors encoding a mutant bacterial cytosine deaminase (bCD) gene, which have a higher affinity for cytosine than wild type bCD (bCDwt). The purpose of the present invention was to evaluate cytotoxicity in vitro and therapeutic efficacy in vivo of these vectors in combination with the prodrug 5-FC and ionizing radiation against human glioma. The present study demonstrates that infection with the viral vector expressing the mutant cytosine deaminase gene resulted in increased 5-FC-mediated cell killing, compared with vectors expressing the wild-type gene. Furthermore, a significant increase in cytotoxicity following infection with viral vector expressing the mutant cytosine deaminase gene and radiation treatment of glioma cells in vitro was demonstrated as compared to infection with viral vector expressing the wild-type gene. Animal studies showed significant inhibition of subcutaneous or intracranial tumor growth of D54MG glioma xenografts by the combination of AdbCD-D314A / 5-FC with ionizing radiation as compared with either agent alone, and with AdbCDwt / 5-FC plus radiation. These data indicate that combined treatment with this mutant enzyme / prodrug therapy and radiotherapy provides a promising approach for cancer therapy.
Owner:BUCHSBAUM DONALD J +3
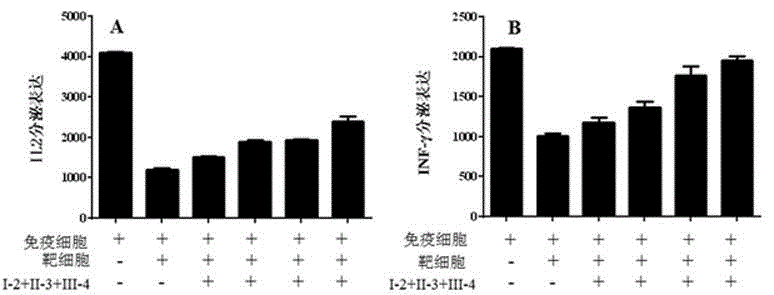
Immunity enhancing reagent
ActiveCN104887717APromote activationIncreased proliferationViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsAntibody ingredientsReceptorT lymphocyte
The invention discloses an immunity enhancing reagent comprising AAVs carrying molecule encoding genes of antibodies at immunodetection points, wherein the immunodetection points are one or several from PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4. The AAVs carrying the molecule encoding genes of the antibodies at different immunodetection points are combined with each other, T cells, natural killer cells, cytotoxic T lymphocytes or cell factor induced killer cells and other immune cells are infected in vitro, and the antibodies at the immunodetection points are expressed and secreted after the infected immune cells are fed back to bodies of patients suffering from tumors, so that the combination of receptors at the immunodetection points and ligands of the receptors is blocked, the transfer of an immunosuppression signal is effectively blocked, the immune tumor suppression microenviroment is destroyed, the immune cell killing capacity is improved, and furthermore the curative effect of adoptive immune therapy is improved.
Owner:ICARTAB BIOMEDICAL
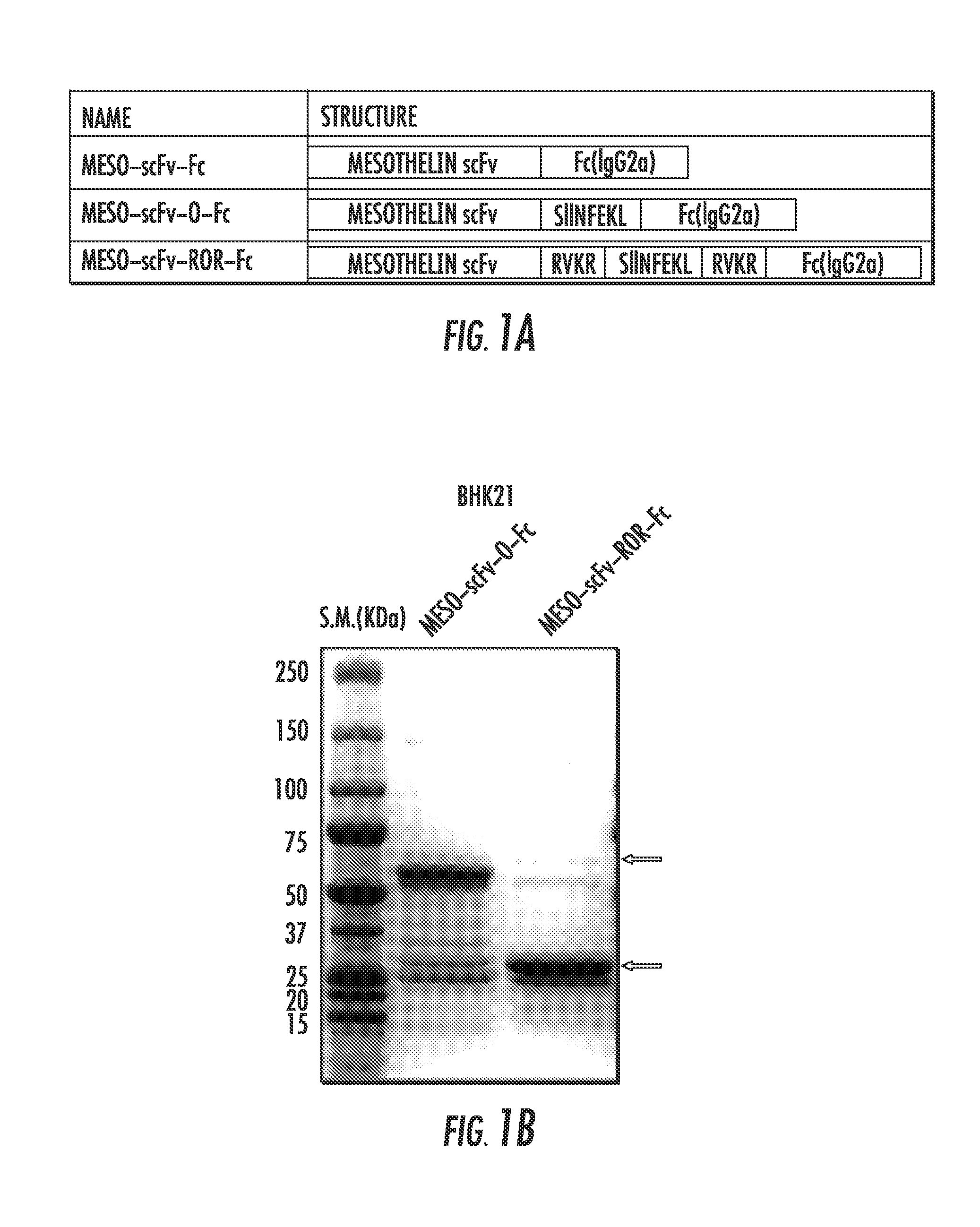
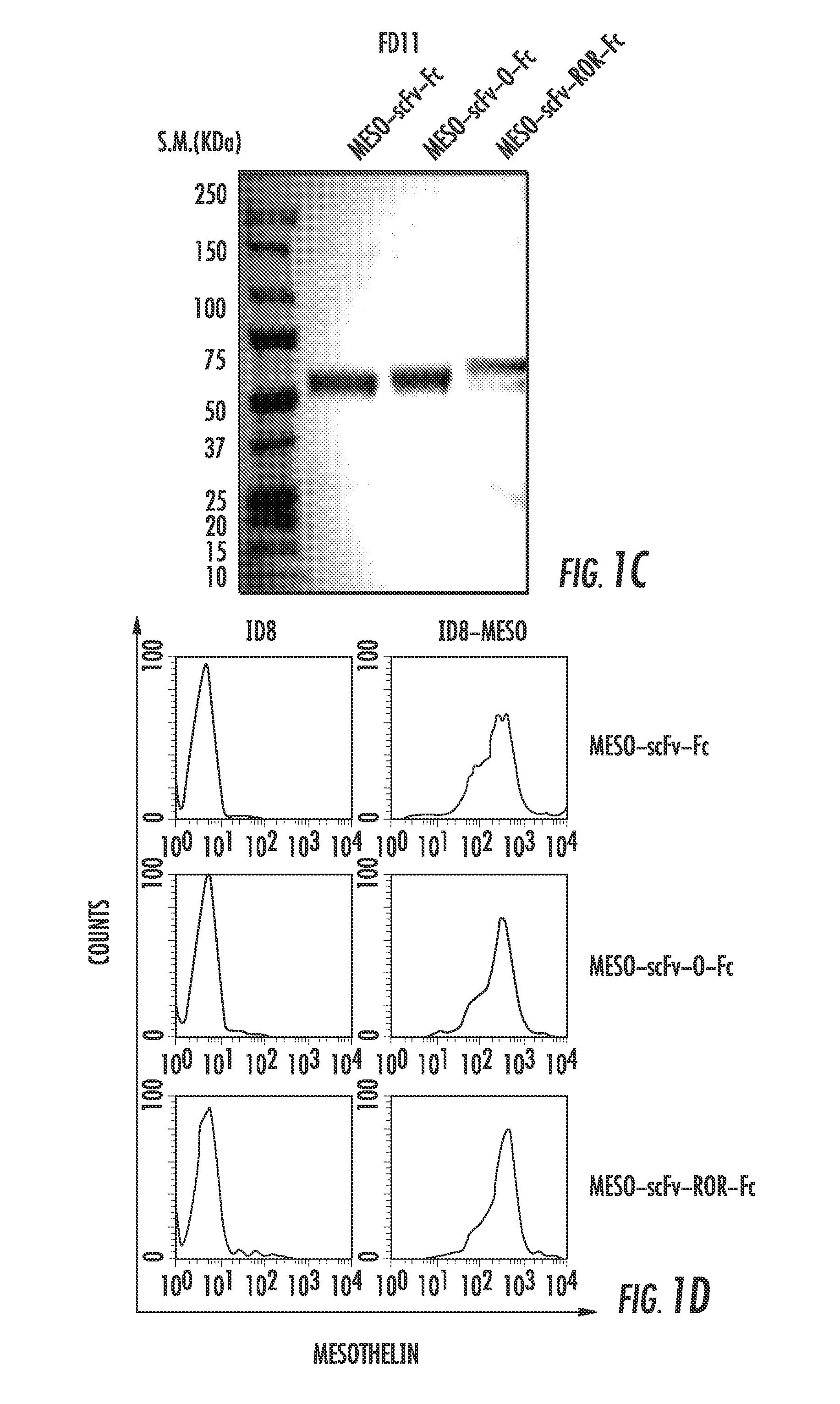
Compositions and methods for rendering tumor cells susceptible to CD8+ t cell-mediated killing
The present invention provides an immunoconjugate having the formula: T-c-En-c-Fcn or T-c-Fcn-c-En; wherein, T is a single chain variable portion fragment of a monoclonal antibody (scFv) directed to a target protein, polypeptide, or fragment thereof, which is highly expressed on cancer cells; E is two or more foreign immunogenic CD8+ T cell antigenic epitopes; c is a peptide or polypeptide fragment thereof, capable of being cleaved by a specific protease; and Fc is two or more Fc portions of an IgG antibody. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the same and vectors containing said nucleic acid sequences are also provided. Methods of making the immunoconjugate, along with methods of making target cells susceptible to CTL mediated cell killing, and methods for treatment of cancers are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Apparatus and method for cell kill confirmation
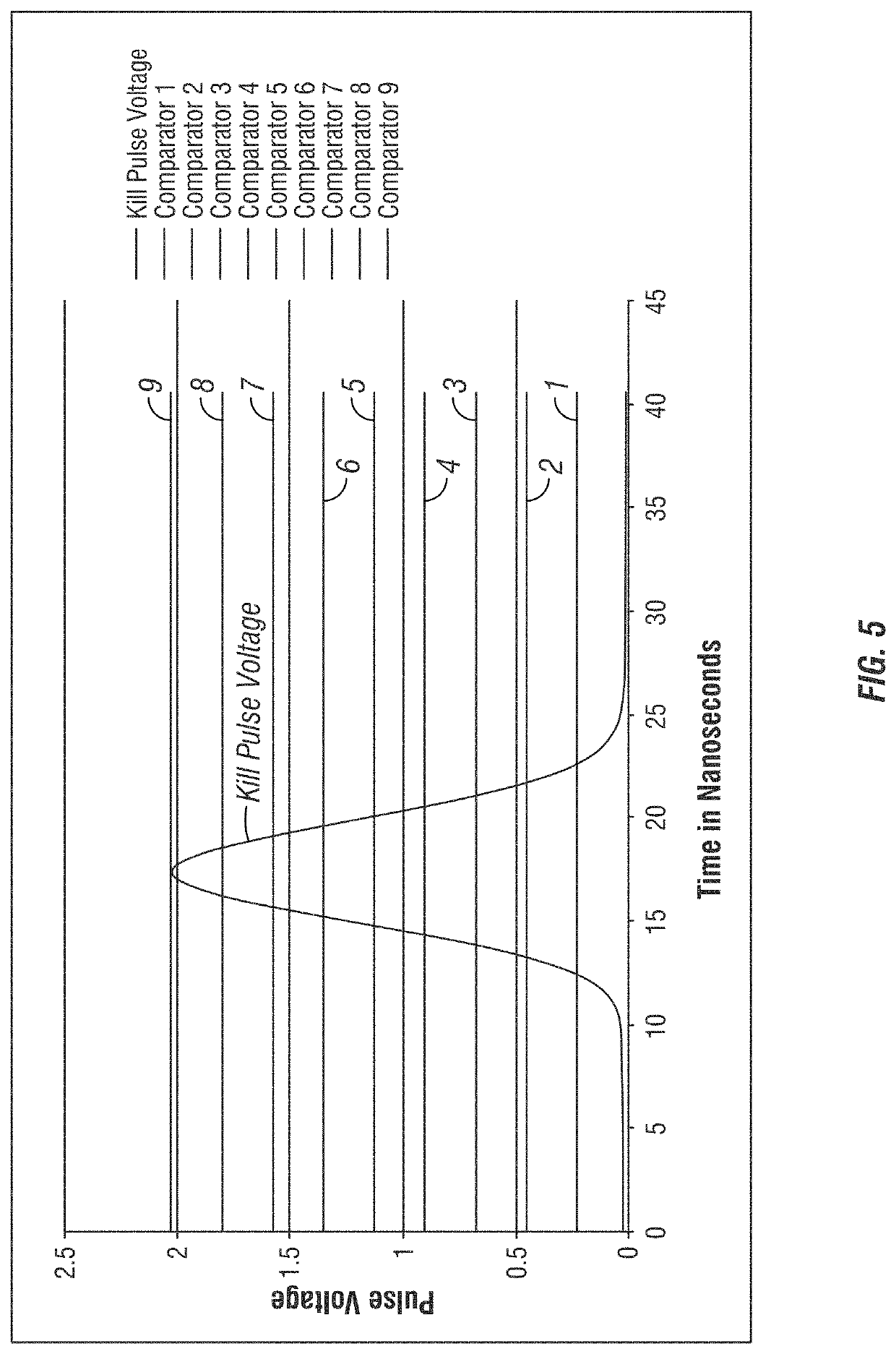
ActiveUS20190382720A1Improve on and overcome deficiencyHigh purity productMicroscopesIndividual particle analysisFluorescenceCell based
A method and related apparatus for confirming whether a kill laser successfully destroys an undesired population of cells includes introducing fluorescent dye into cells, exciting the cells with a detection laser or a light emitting diode to cause the cell to fluoresce for a first time, measuring the amount of fluorescence in the cells with a detector capable of emitting a detection pulse, classifying the cells via embedded processing as undesired or desired cells based on the amount of fluorescence, firing a kill beam with a kill laser at any undesired cells, measuring the amount of fluorescence in the cells a second time to determine whether a fluorescent event was generated from the kill beam striking the cells, and providing feedback to an operator of the kill laser as to whether any fluorescent events were generated from the kill beam striking the cells.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
Method and system for detecting cell killing efficacy and application of method and system
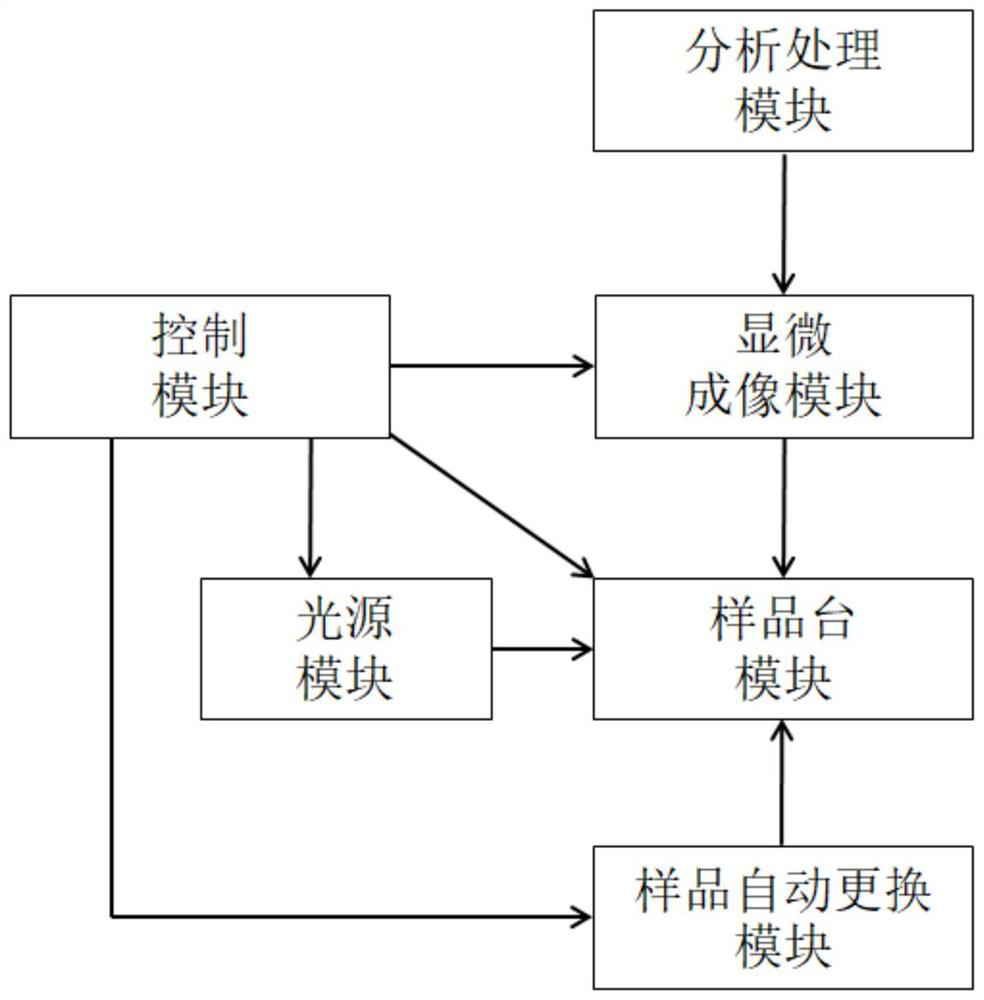
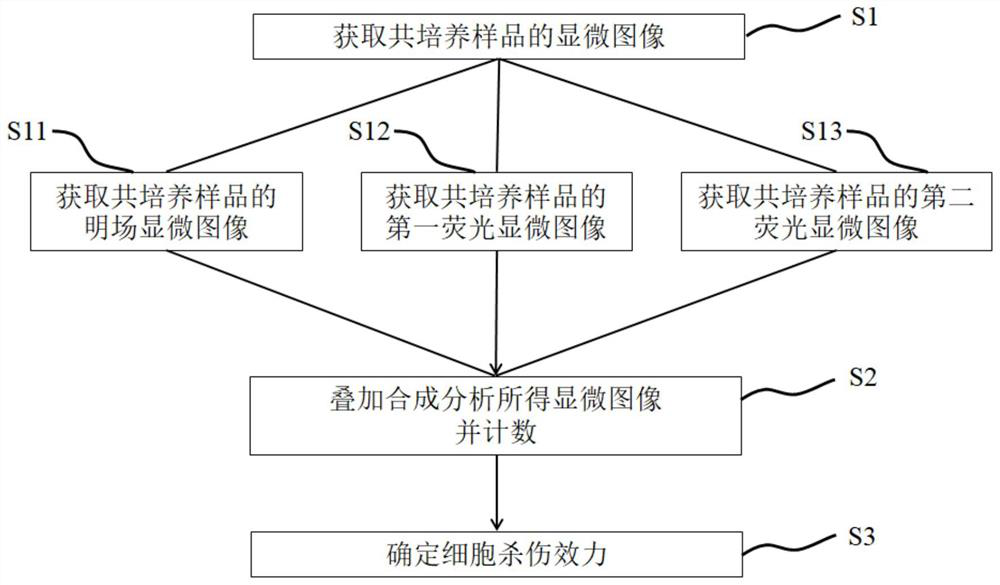
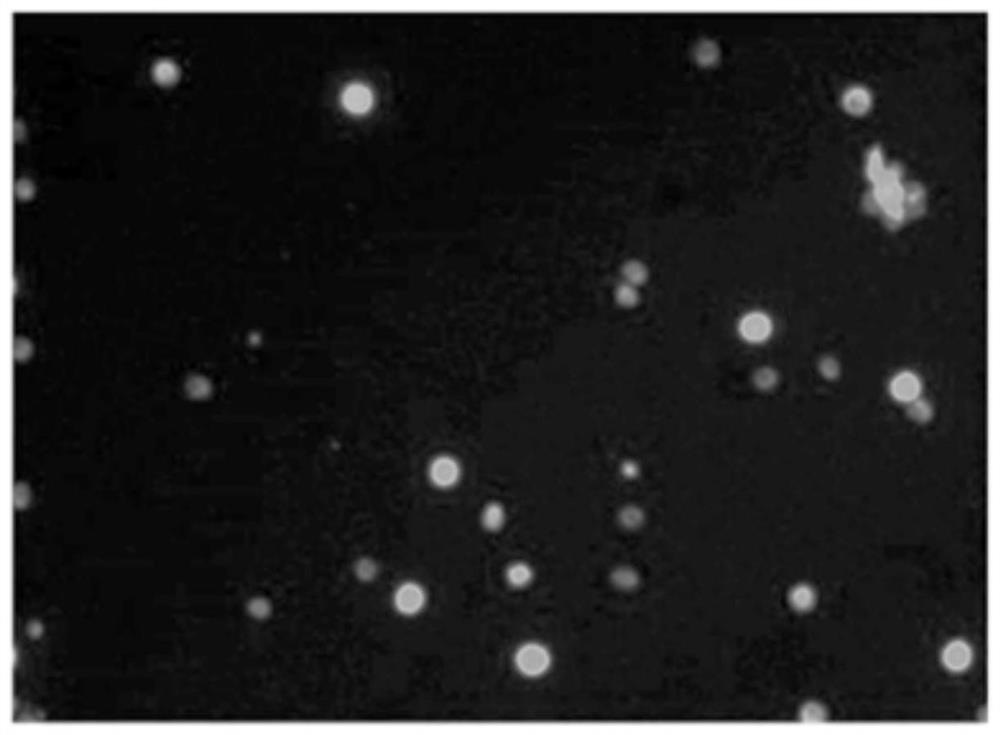
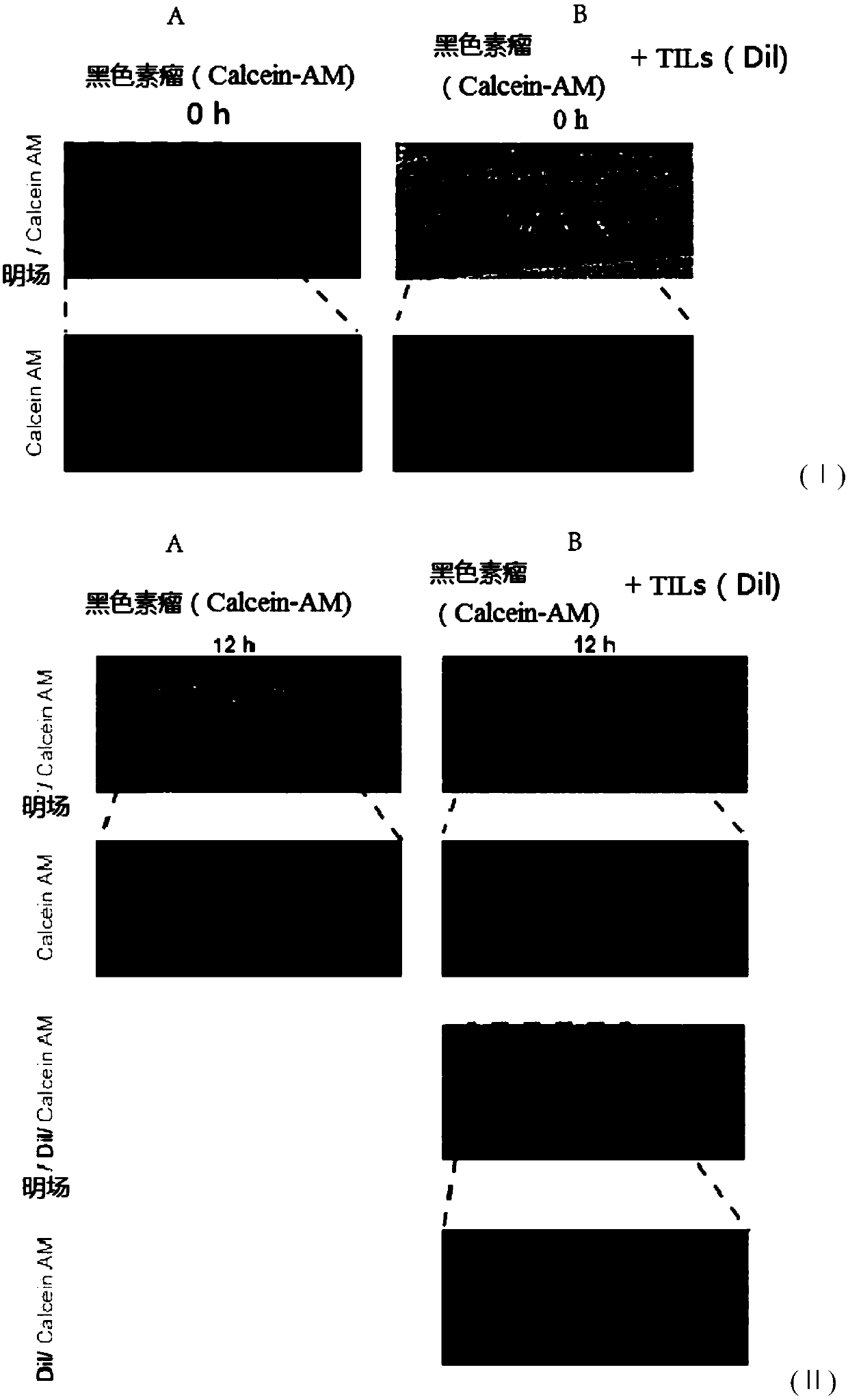
ActiveCN112813133AReduce detection stepsImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageStaining
The invention provides a method and a system for detecting cell killing efficacy and application of the method and the system. The method for detecting cell killing efficacy comprises the following steps: microscopic images of a co-culture sample on a cell counting slide are acquired, the co-culture sample is a cell sample obtained by co-culturing a target cell and an effector cell, the target cell carries a first fluorescent label, the co-culture sample at least uses a second fluorescent label for dyeing labeling, the microscopic images include a bright field microscopic image, a first fluorescent microscopic image and at least one second fluorescent microscopic image, and then the bright field microscopic image, the first fluorescent microscopic image and the at least one second fluorescent microscopic image are subjected to to superposing synthetic analysis and counted, and a detection result of the cell killing efficacy is obtained. According to the detection method, the image information and the data processing result of the to-be-detected cell can be simultaneously obtained, the obtained result is more direct, few detection steps are needed, and the detection efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUIYU BIOTECH
Method for evaluating cell killing efficacy
ActiveCN112285083AIntuitive and accurate test resultsIntuitive test resultsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageMicro imaging
The invention provides a method for evaluating cell killing efficacy. The evaluation method comprises the following steps: (1) co-culturing a target cell carrying a fluorescence label A and an effector cell, and dyeing and labeling dead cells generated after co-culture by using a fluorescence label B, wherein the excitation light wavelengths corresponding to the fluorescence label A and the fluorescence label B are different; (2) respectively using a bright field, a fluorescence channel matched with the fluorescence label A and a fluorescence channel matched with the fluorescence label B to perform microscopic imaging on the dyed and labeled cells to obtain a microscopic image; and (3) carrying out superposition synthesis analysis on the obtained microscopic image, and evaluating the cellkilling efficacy of the effector cells according to an analysis result. According to the invention, the fluorescent reagent A and the fluorescent label B are respectively used for staining and markingthe target cells and dead cells, and then fluorescence microscopic imaging and image synthesis analysis are carried out, so that the evaluation result of the cell killing efficacy can be quickly, intuitively and accurately obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUIYU BIOTECH
Anti-cd3-binding domains and antibodies comprising them, and methods for their generation and use
PendingCN110913895AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesBinding domain
Anti-CD3 binding domains and antibodies comprising them, including multispecific antibodies, with, inter alia, desirable T-cell activation and (re)directed target cell killing potency and developability, profiles are provided, as well as methods for their identification, isolation, and generation, and methods for their preparation and use. Reagents for identifying, isolating, selecting, generatingand characterizing CD3 binding domains and antibodies comprising them are also provided.
Owner:ADIMAB LLC
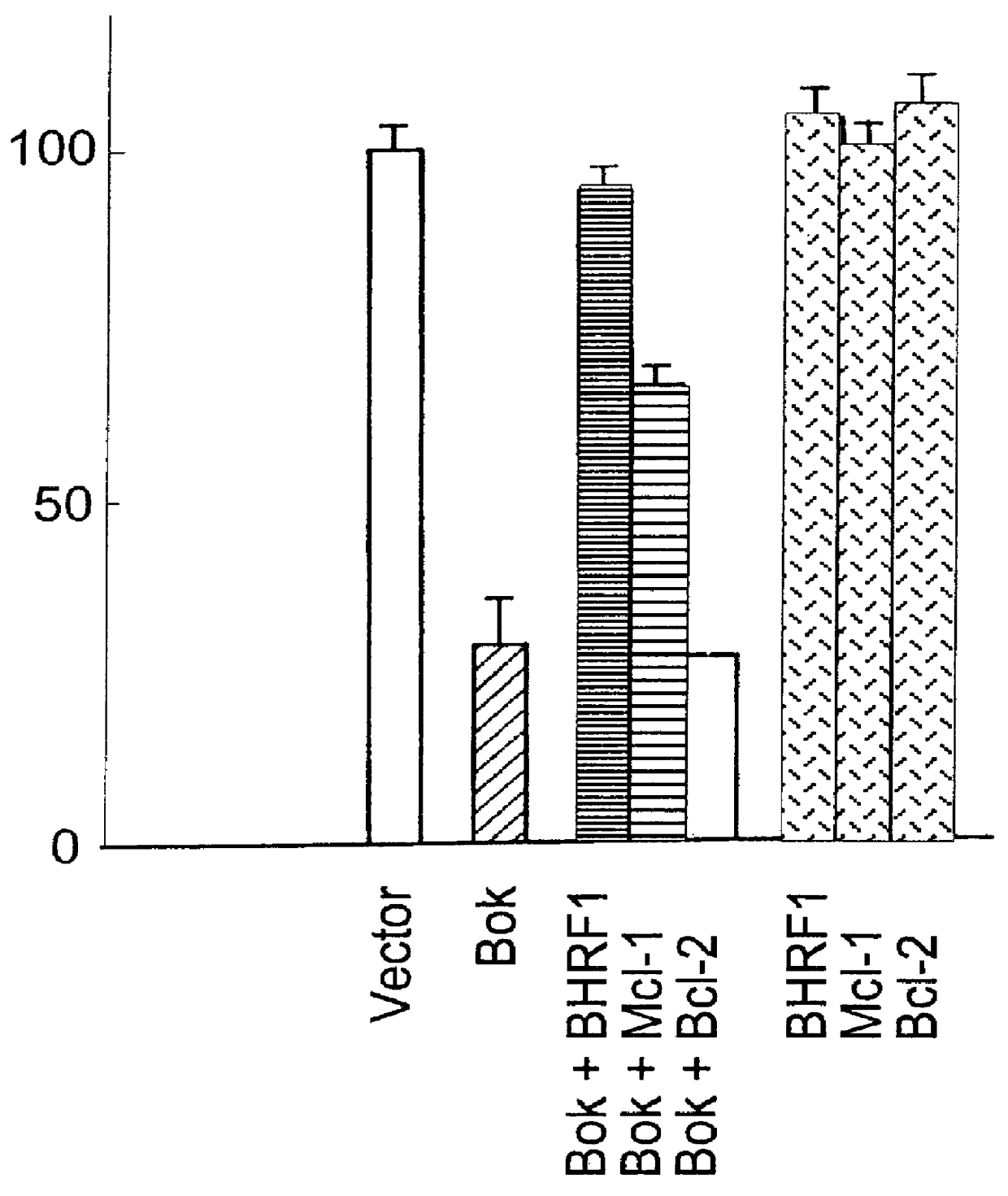
Mammalian pro-apoptotic Bok genes and their uses
Nucleic acid compositions encoding a pro-apoptotic protein, Bok (Bcl-2-related ovarian killer) are identified. Bok has conserved Bcl-2 homology domains 1, 2 and 3 and a C-terminal transmembrane region present in other Bcl-2 related proteins, but lacks the BH4 domain found only in anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Over-expression of Bok induces apoptosis. Cell killing induced by Bok is suppressed by co-expression with selective anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Bok is highly expressed in the ovary, testis and uterus, particularly in granulosa cells, the cell type that undergoes apoptosis during follicle atresia. Identification of Bok as a new pro-apoptotic protein with wide tissue distribution and hetero-dimerization properties facilitates elucidation of apoptosis mechanisms in reproductive and other tissues, and provides a means for manipulating apoptosis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Construction method and application of NKG2D-ACE2 CAR-NK cell secreting super IL 15
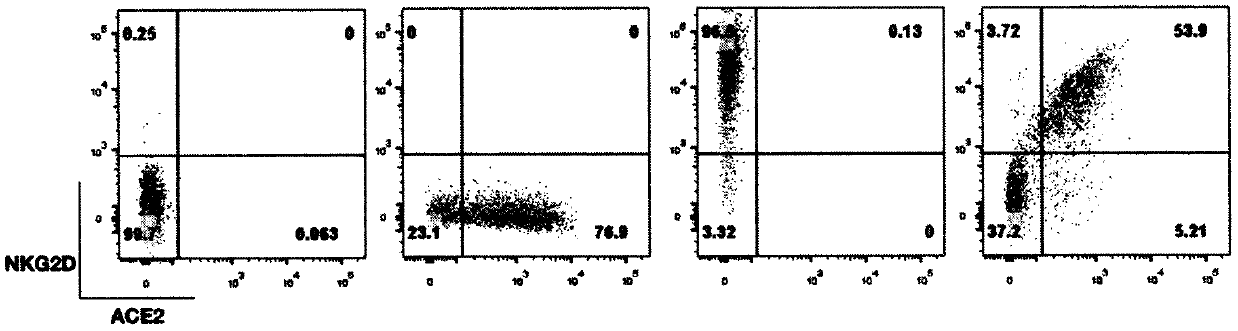
PendingCN111454372AImprove securityVersatilityImmunoglobulin superfamilyLectin superfamilyInfected cellSide effect
The invention discloses a construction method and application of an NKG2D-ACE2 CAR-NK cell secreting super IL 15. An expression vector mainly comprises an NKG2D extracellular segment, an ACE2 extracellular segment, 4-1BB, CD3[zeta] and IL15R[alpha]-IL15 thawing protein. NKG2D is an activation receptor of the NK cell and is used for identifying ligands (MICA, MICB, ULBP1-6) on the surfaces of virusinfected cells or tumor cells; ACE2 is a receptor of SARS-CoV-2 and is combined with S protein of a virus envelope; the NK cell modified by CAR is proved to be capable of breaking through the limitation of an inhibitory receptor to activate the NK cell, so that the specific killing effect of the NK cell on target cells is enhanced, and no serious toxic or side effect exists; and the activity of an IL15 super agonist is increased by 20 times compared with that of natural IL15 in the body, and the pharmacokinetic property is improved, so that the CAR-NK cell has enhanced durability and target cell killing activity. Therefore, the ACE2 and the NKG2D respectively target the S protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and NKG2DL on the surfaces of the infected cells, and the powerful synergistic effectof the super IL15 is achieved, so that the NKG2D-ACE2 CAR-NK cell can specifically remove SARS-CoV-2 virus particles and the infected cells, and a safe and effective cell therapy is provided for COVID-19.
Owner:温州启星生物技术有限公司
Method for evaluating CAR-T killing activity in vitro
InactiveCN111041064AImmunoglobulin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementEngineeringTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a method for evaluating CAR-T killing activity in vitro. IN the prior art, the existing CAR-T cell in-vitro killing activity detection method relates to isotope safety, operation is tedious and other problems exist. Based on the problems in the prior art, in order to conveniently and simply realize the detection of in vitro killing activity of CAR-T cells, a cell strain capable of evaluating the CAR-T killing function in vitro is constructed, and a method for detecting the CAR-T in-vitro killing activity through RTCA is provided, wherein the CAR-T cell killing activitycan be efficiently, sensitively and continuously detected in vitro through the method so as to provide the guarantee for the subsequent treatment effect of CAR-T cells.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Immune cell tumor killing capability detection model and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110402853AShort build cycleImprove unityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaStainingCell tumor
The invention provides a construction method of an immune cell tumor killing capacity detection model. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) 24 after egg membranes of embryos of zebrafish fertilized for 24-96 hours are removed, injecting tumor cells labeled by a first living cell staining agent into zebrafish bodies, then executing culturing in culture water containing a melanin inhibitor, and screening out the zebrafish with the tail parts labeled by the first living cell staining agent; (2) after the collected zebrafish is anesthetized, the zebrafish is divided into an immune cell injection group and a control group, injecting immune cells labeled by a second living cell staining agent into the immune cell injection group in a microinjection mode, injecting a carriersolution into the control group, and then putting the zebrafish in the culture water containing the melanin inhibitor for continuous culture. Short period, time saving, labor saving and low modelingcost are achieved by adopting the construction method, and a constructed detection model can accurately and objectively evaluate the effect of tumor immunotherapy. The invention also provides a detection model prepared based on the method and application thereof.
Owner:义慧科技(深圳)有限公司
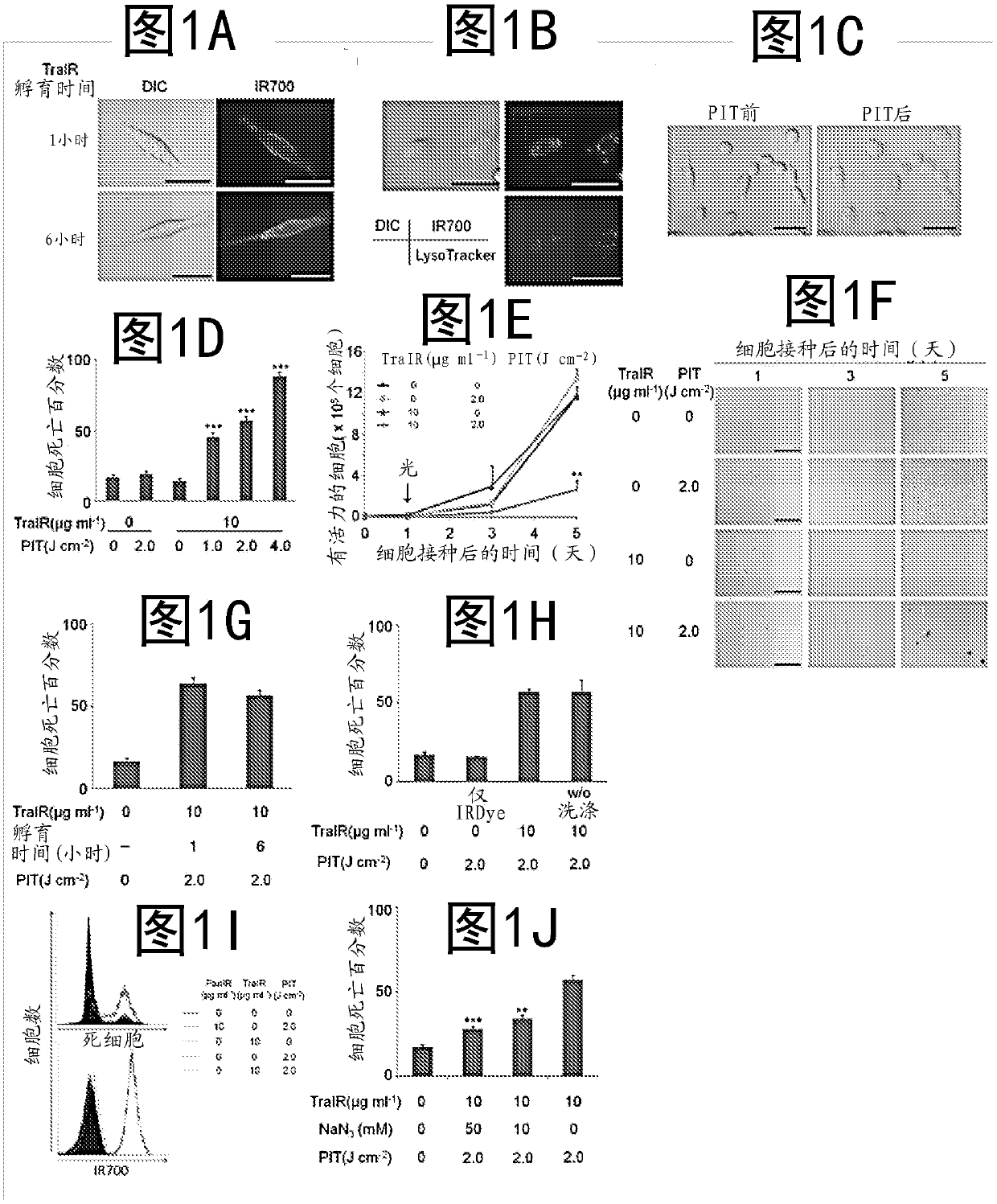
Photosensitizing antibody-fluorophore conjugates
PendingCN107929733AAllow treatmentGarment special featuresEnergy modified materialsAnticarcinogenAntiendomysial antibodies
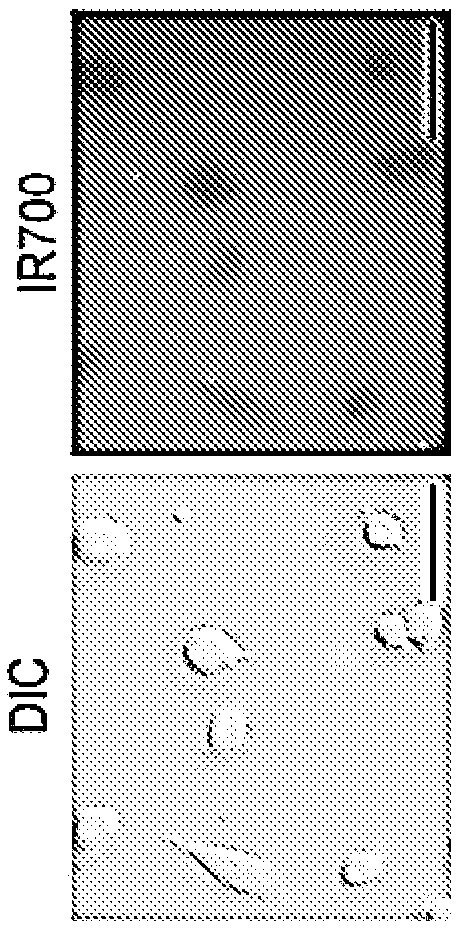
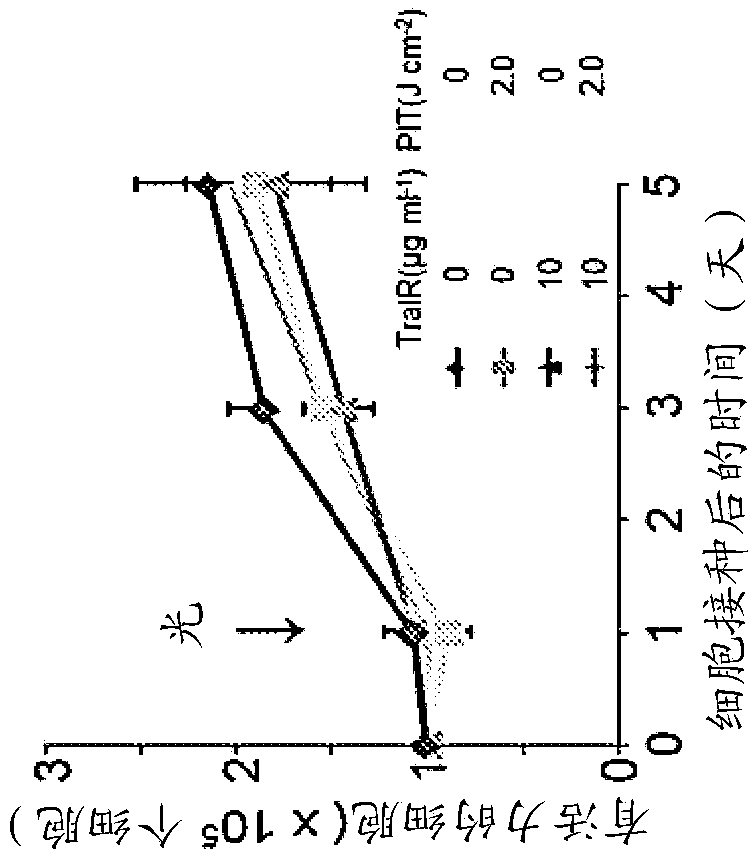
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods of killing cells. In particular examples, the method includes contacting a cell having a cell surface protein with a therapeutically effective amount of an antibody-IR700 molecule, wherein the antibody specifically binds to the cell surface protein, such as a tumor-specific antigen on the surface of a tumor cell. The cell is subsequently irradiated, such as at a wavelength of 660-740 nm at a dose of at least 1 J cm<-2>. The cell is also contacted with one or more therapeutic agents (such as an anti-cancer agent), for example about 0 to8 hours after irradiating the cell, thereby killing the cell. Also provided are methods of imaging cell killing in real time, using fluorescence lifetime imaging. Also provided are wearable devices that include an article of clothing, jewelry, or covering; and an NIR LED incorporated into the article, which can be used with the disclosed methods.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Cell killing efficacy detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN112285081AEasy to rule outEfficient exclusionFluorescence/phosphorescenceAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicroscopic imageStaining
The invention provides a cell killing efficacy detection method and application thereof. The detection method comprises the following steps: carrying out mixed co-culture on target cells carrying a fluorescence label A and effector cells, then adding a fluorescence label B to label the target cells and the effector cells, and adding a fluorescence label C to carry out dyeing labeling on dead cellsgenerated after co-culture; and then respectively carrying out microscopic imaging on the cells by using different fluorescence channels, identifying and analyzing the cells in the same region in a microscopic image by combining an image synthesis analysis method, and obtaining the cell killing efficacy of effector cells according to an analysis result. Therefore, the detection method can effectively eliminate the interference of impurities and cell debris, can directly obtain a plurality of data such as cell death rate, cell self-injury rate and cell specific killing rate from the image, andhas the advantages of intuitive and visible detection result, high accuracy and high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUIYU BIOTECH
Method for efficient in-vitro amplification and culture of natural killer T cells with high killing capacity
PendingCN110283786AEasy to obtainHigh Effector Cell PurityMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsAbnormal tissue growthSide effect
The invention discloses a method for efficient in-vitro amplification and culture of natural killer T cells with high killing capacity. The method comprises the following steps: a, taking fresh human peripheral blood and obtaining mononuclear cells with a gradient centrifugation method; b, pre-stimulating mononuclear cells in an in vitro medium; c, expanding culture of peripheral blood derived mononuclear cells, detecting the proportion of various cells, and judging amplification efficiency and activity of the target NK / NKT cells; d, detecting the proportion of NK / NKT cells to the cell population after culture for 3-4 weeks, and detecting cell killing efficiency; e, further purifying the NK / NKT cells. The method is simple to operate, the NK cell population rich in NKT cells with high killing activity is obtained and contains no impurity cells, immunogenicity caused by the impurity cells is avoided, and side effects in clinical application are lower. Besides, the method has the advantages that materials are easily available, the cells are suitable for large-scale culture, damage to the body is small and the like, and is more suitable for adjuvant treatment of tumor patients.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com