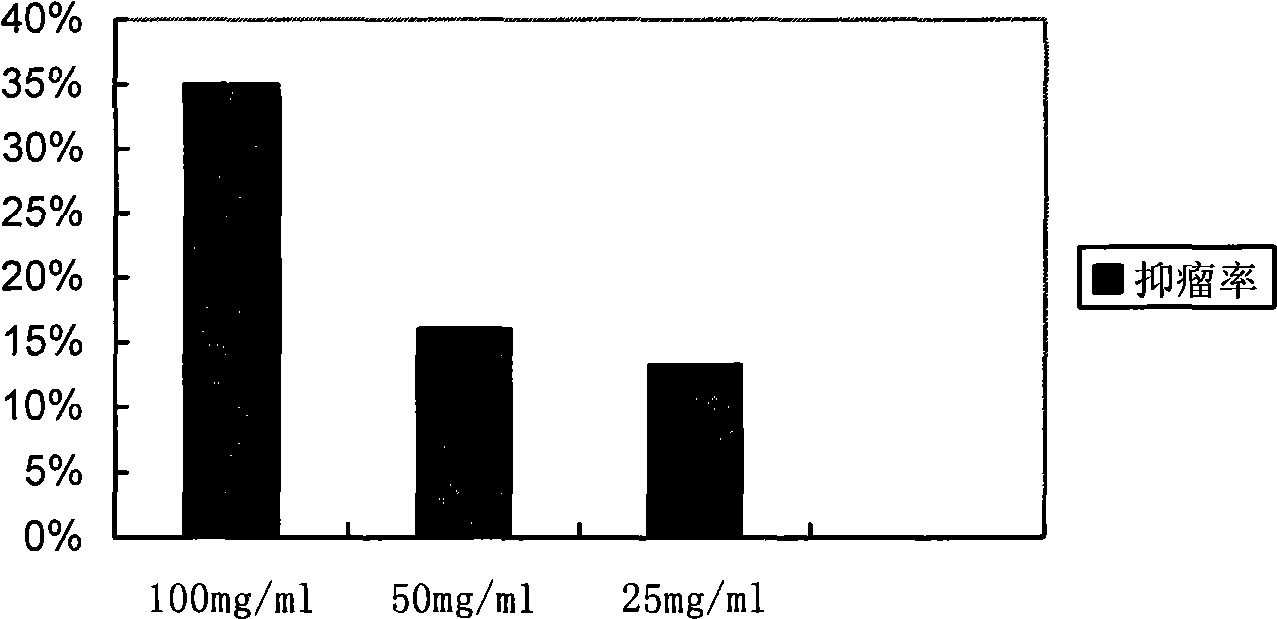
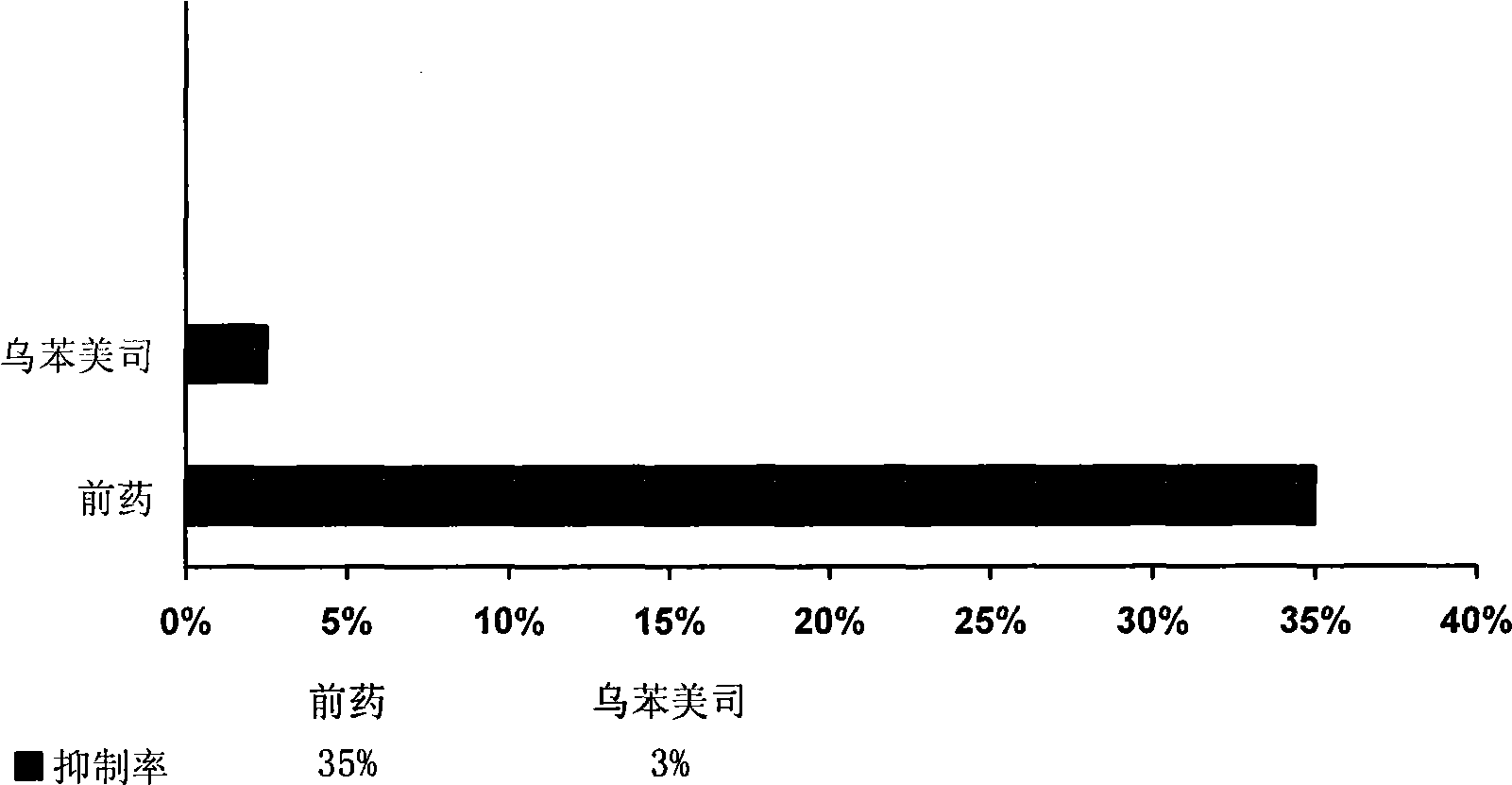
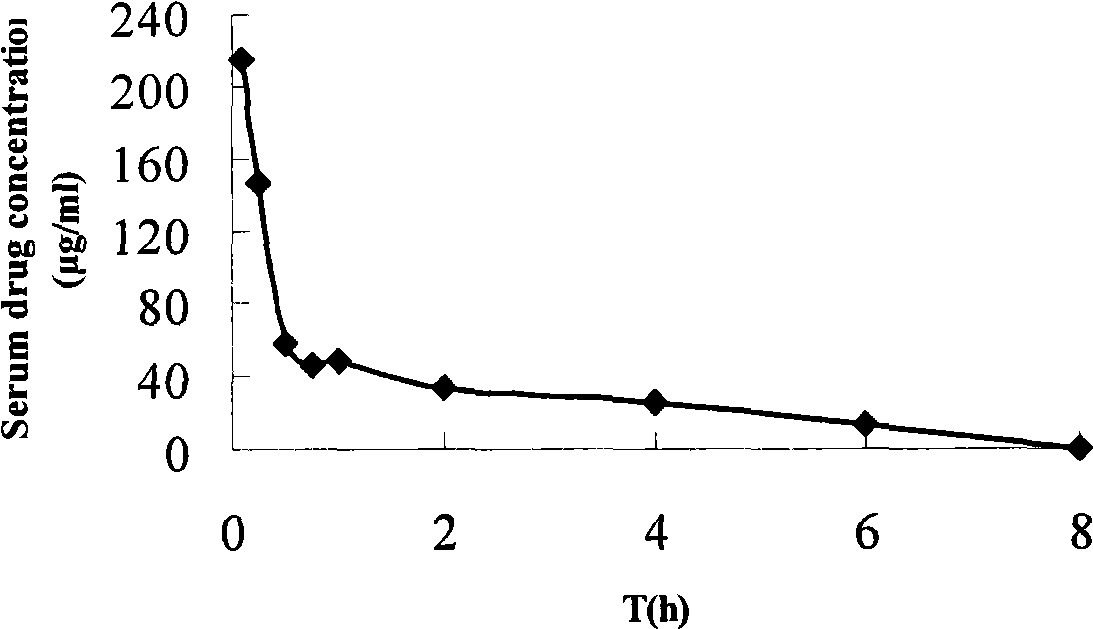
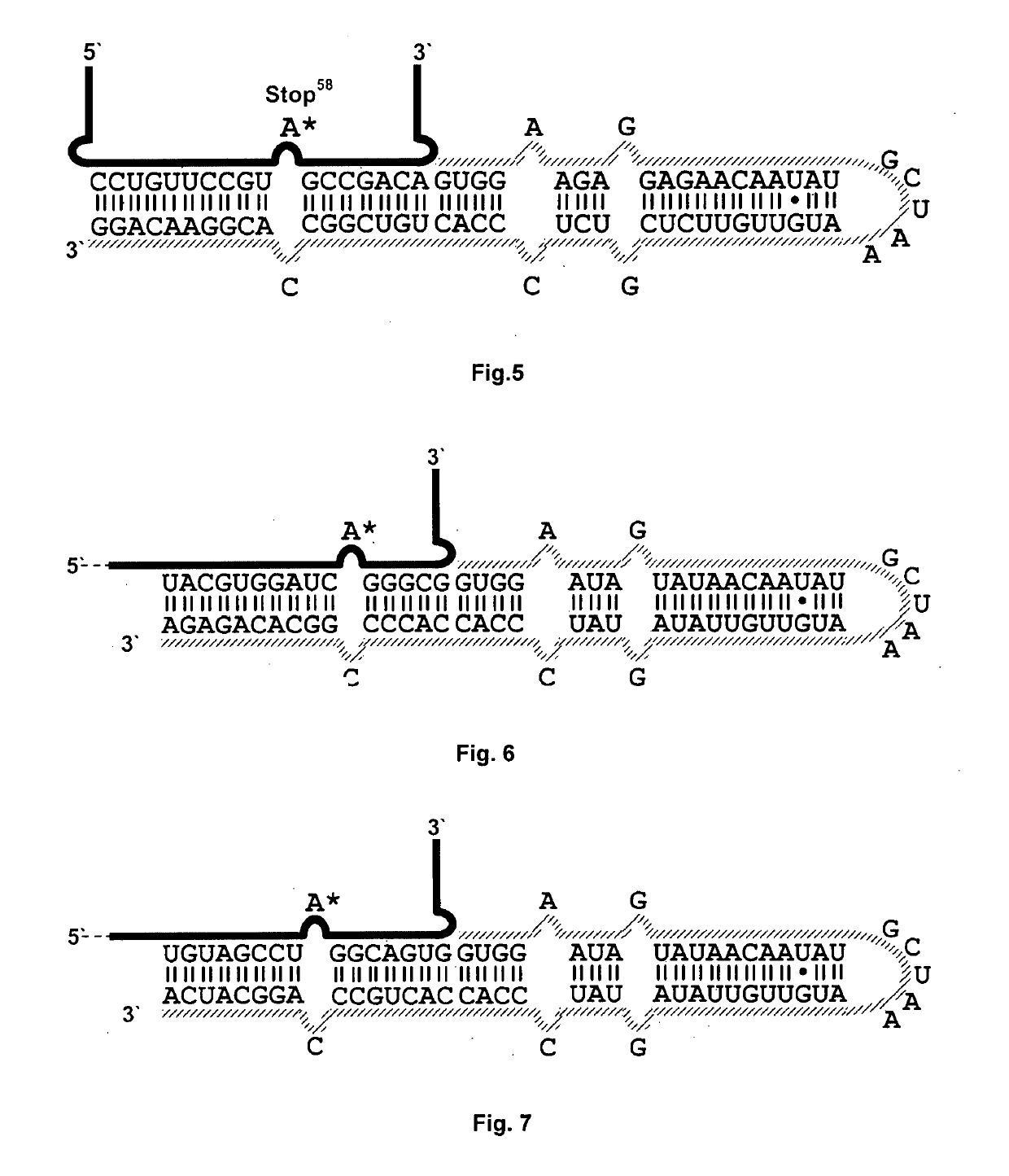
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Ectopic expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ectopic is a word used with a prefix, ecto, meaning “out of place.” Ectopic expression is an abnormal gene expression in a cell type, tissue type, or developmental stage in which the gene is not usually expressed. The term ectopic expression is predominately used in studies using metazoans, especially in Drosophila melanogaster for research purposes.
Biotic and abiotic stress tolerance in plants
InactiveUS20090138981A1Improve the immunityIncreased susceptibilityBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyNucleotide
Transcription factor polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into nucleic acid constructs, including expression vectors, have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these constructs have been shown to be more resistant to disease (in some cases, to more than one pathogen), or more tolerant to an abiotic stress (in some cases, to more than one abiotic stress). The abiotic stress may include, for example, salt, hyperosmotic stress, water deficit, heat, cold, drought, or low nutrient conditions.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Plants with improved water deficit and cold tolerance
The present invention provides nucleic acid constructs, including plasmids, expression vectors or expression cassettes comprising polynucleotides encoding CCAAT-binding transcription factor polypeptides that have the ability to increase a plant's tolerance to abiotic stress. Polynucleotides encoding functional CCAAT-binding transcription factors were incorporated into expression vectors, introduced into plants, and ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention significantly increased the cold and water deficit tolerance of the transgenic plants, as compared to tolerance to these stresses of control plants.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Early flowering in genetically modified plants
InactiveUS20070199107A1Other foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesNucleotideEctopic expression
The present invention provides polynucleotides encoding CCAAT-binding transcription factor polypeptides that modulate the onset of reproductive development in plants. Polynucleotides encoding functional CCAAT-binding transcription factors were incorporated into expression vectors, introduced into plants, and ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention significantly shortened the time to flower development in the transgenic plants, as compared to the flowering time of control plants.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants
ActiveUS20080010703A1Increase productionImprove adverse reactionsClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesIncreased toleranceLow nitrogen
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, greater early season growth, greater canopy coverage, greater stem diameter, greater late season vigor, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low nitrogen tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY) +1
Stress tolerance in plants
Transcription factor polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into nucleic acid constructs, including expression vectors, have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these constructs have been shown to be more resistant to disease (in some cases, to more than one pathogen), or more tolerant to an abiotic stress (in some cases, to more than one abiotic stress). The abiotic stress may include, for example, salt, hyperosmotic stress, water deficit, heat, cold, drought, or low nutrient conditions.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
T cell regulation
InactiveUS20060240024A1Increases magnitudeSimple methodAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderRegulatory T cellAutoimmune responses
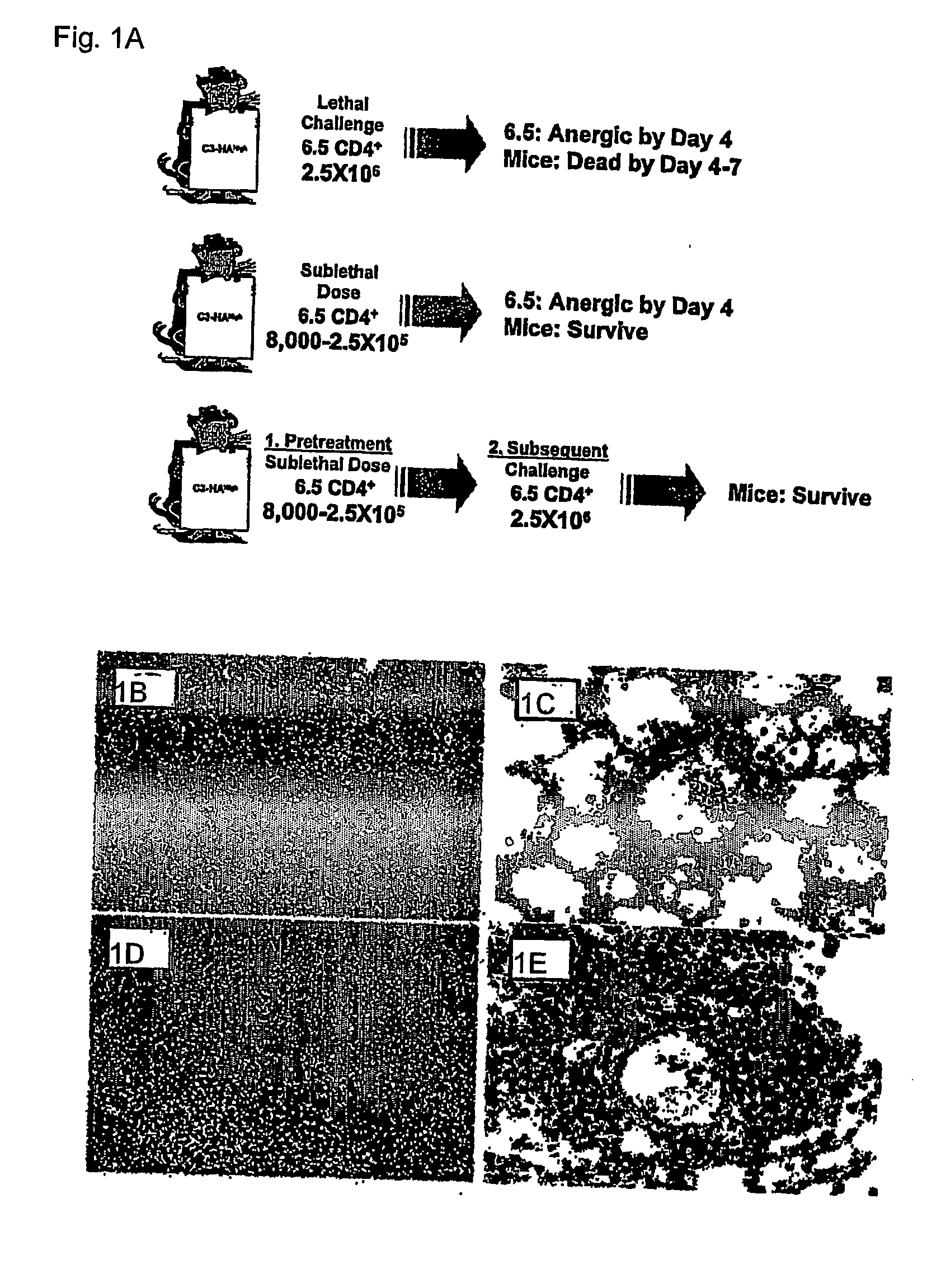
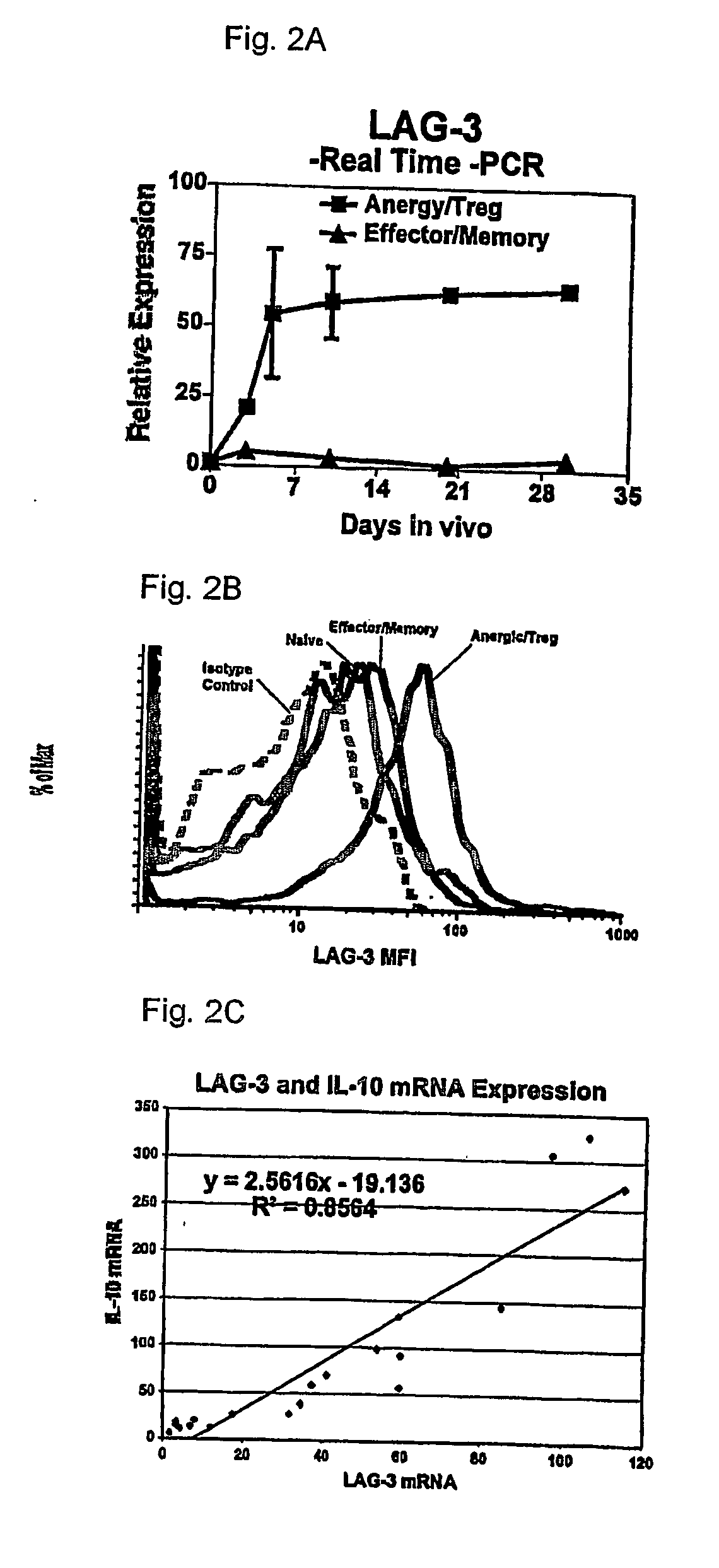
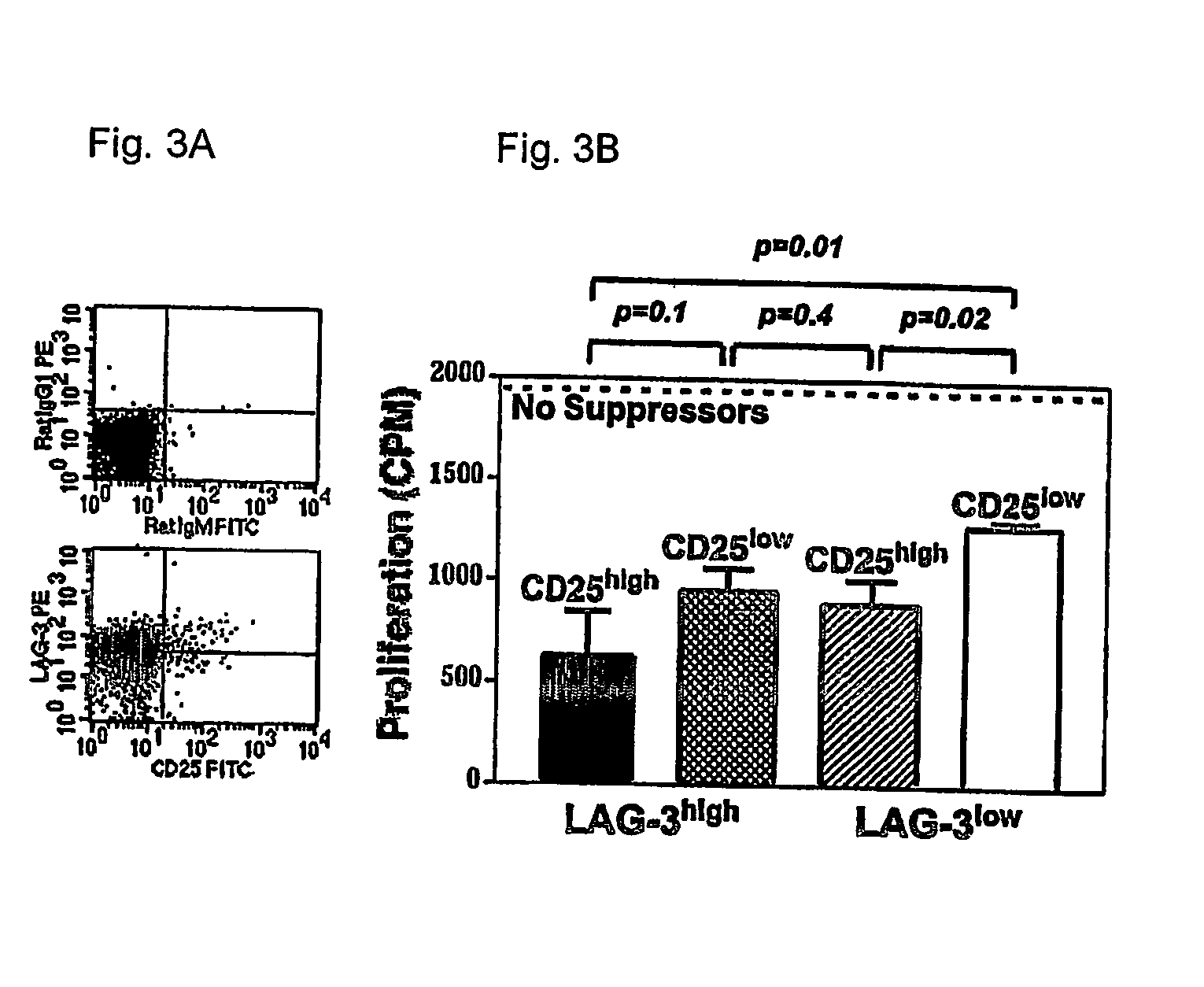
Regulatory T cells (Treg) limit autoimmunity but can also attenuate the magnitude of anti-pathogen and anti-tumor immunity. Understanding the mechanism of Treg function and therapeutic manipulation of Treg in vivo requires identification of Treg selective receptors. A comparative analysis of gene expression arrays from antigen specific CD4+ T cells differentiating to either an effector / memory or a regulatory phenotype revealed Treg selective expression of LAG-3 (CD223), a CD4-related molecule that binds MHC class II. LAG-3 expression on CD4+ T cells correlates with the cells' in vitro suppressor activity, and ectopic expression of LAG-3 on CD4 T cells confers suppressor activity on the T cells. Antibodies to LAG-3 inhibit suppression both in vitro and in vivo. LAG-3 marks regulatory T cell populations and contributes to their suppressor activity.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC +1
Plants with improved yield and stress tolerance
InactiveUS20080301841A1Greater stringencySmall sizeSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationEctopic expressionPolynucleotide
Polynucleotides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer greater size, greater organ size, greater biomass, greater yield, curlier leaves, darker coloration, greater tolerance to water deprivation, delayed flowering, delayed development, delayed senescence, greater tolerance to cold, and / or greater tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Disease-inducible promoters
Disease-inducible promoter sequences have been identified that may be used to produce transgenic plants that are both more resistant to disease than control plants, and are wild-type or nearly wild type in appearance. Any of these disease-inducible promoters may be incorporated into expression vectors that each comprise a defense response protein operably linked to the promoter. The expression vectors can be introduced into plants and the defense response protein then ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these expression vectors have been shown to be more resistant to disease, in some cases, to more than one type of pathogen, and yet are similar to wild type plants in their morphology and development.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Method to produce induced pluripotent stem (IPS) cells from non-embryonic human cells
The invention provides methods for generating induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells from normal and mutant adult cells, as well as the iPS cells so generated from such methods. In some aspects, iPS cells are generated by ectopically expressing SOX2 and OCT4 nucleic acids in such adult cells. Other nucleic acids such as but not limited to MYC may also be ectopically expressed in such adult cells in the methods described herein.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Plants with enhanced size and growth rate
ActiveUS20100223689A1Increase productionHigh yieldClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotideIncrease size
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention regulate transcription in these plants and have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity that results in increased size, biomass, growth rate, and / or yield as compared to a control plan.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Stress tolerance in plants
InactiveUS20170121733A1Climate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
Transcription factor polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into nucleic acid constructs, including expression vectors, have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these constructs have been shown to be more resistant to disease (in some cases, to more than one pathogen), or more tolerant to an abiotic stress (in some cases, to more than one abiotic stress). The abiotic stress may include, for example, salt, hyperosmotic stress, water deficit, heat, cold, drought, or low nutrient conditions.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
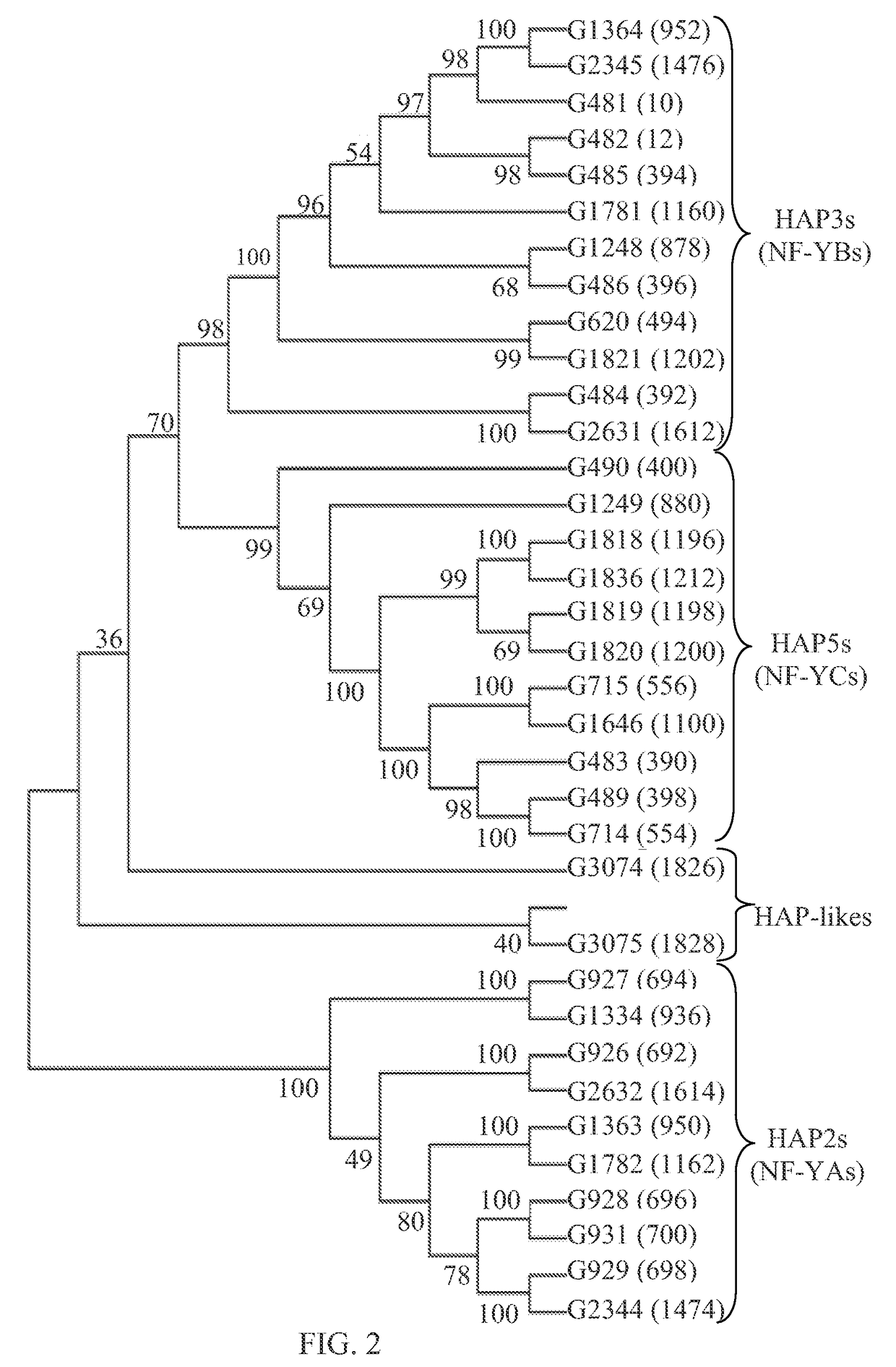
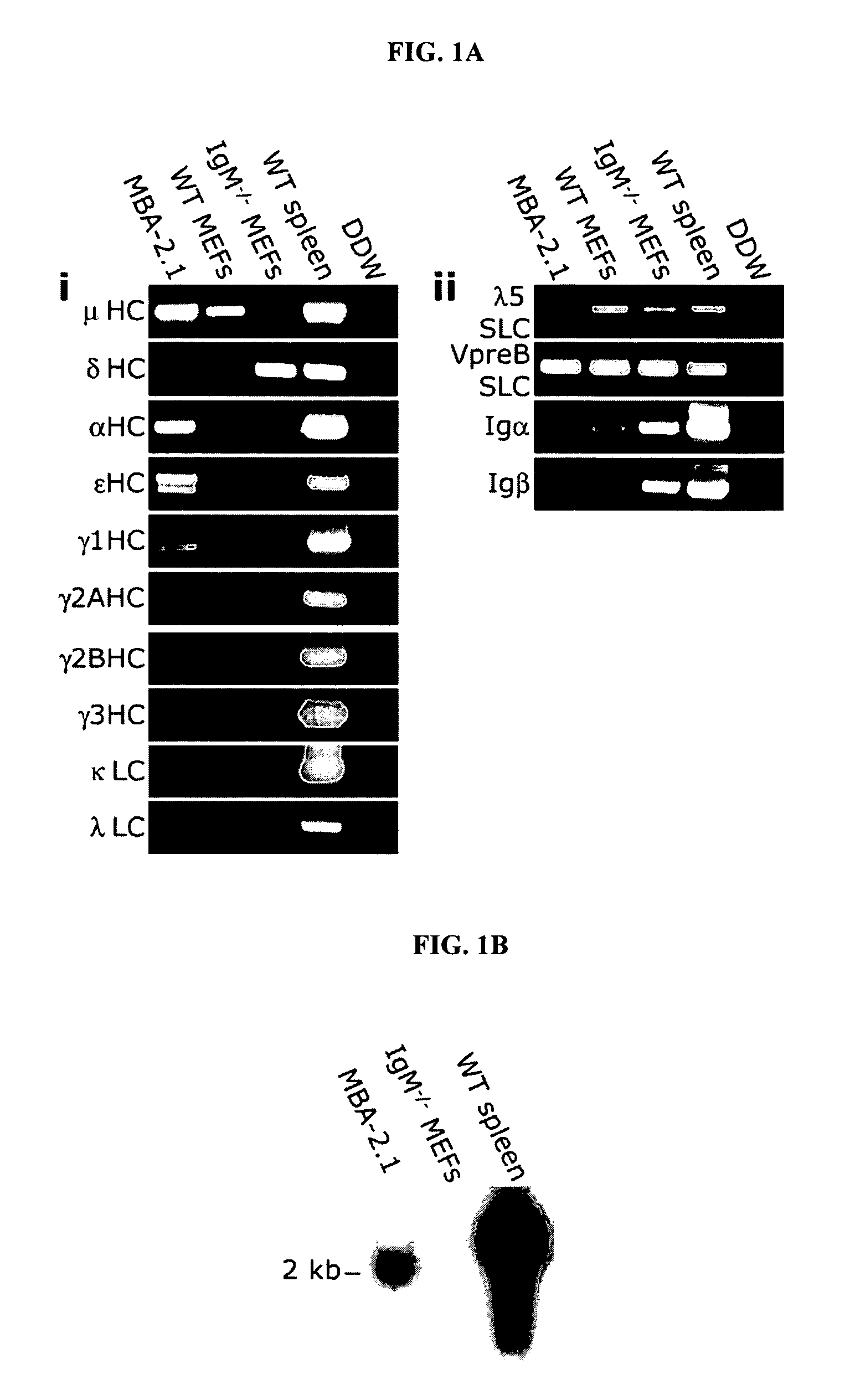
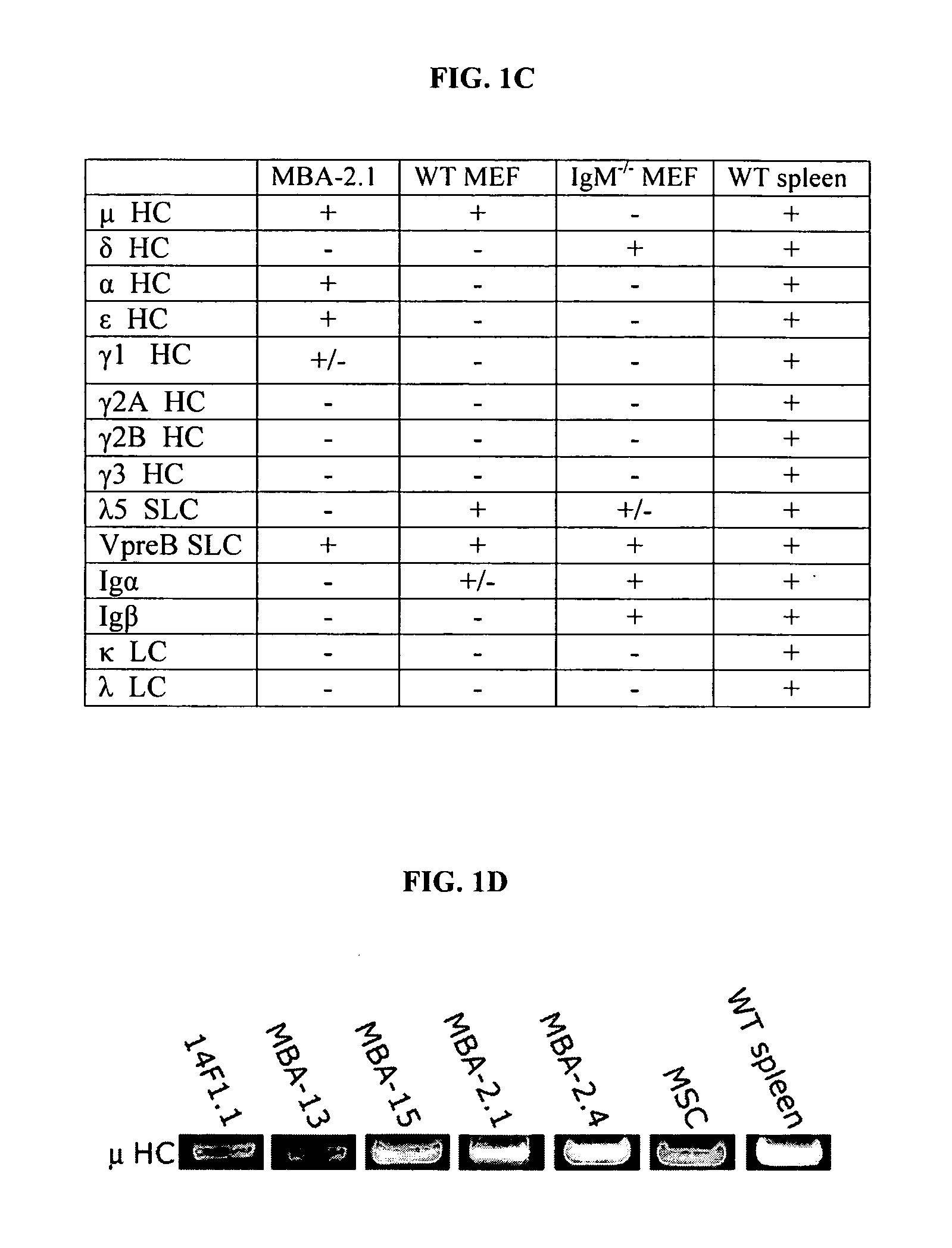
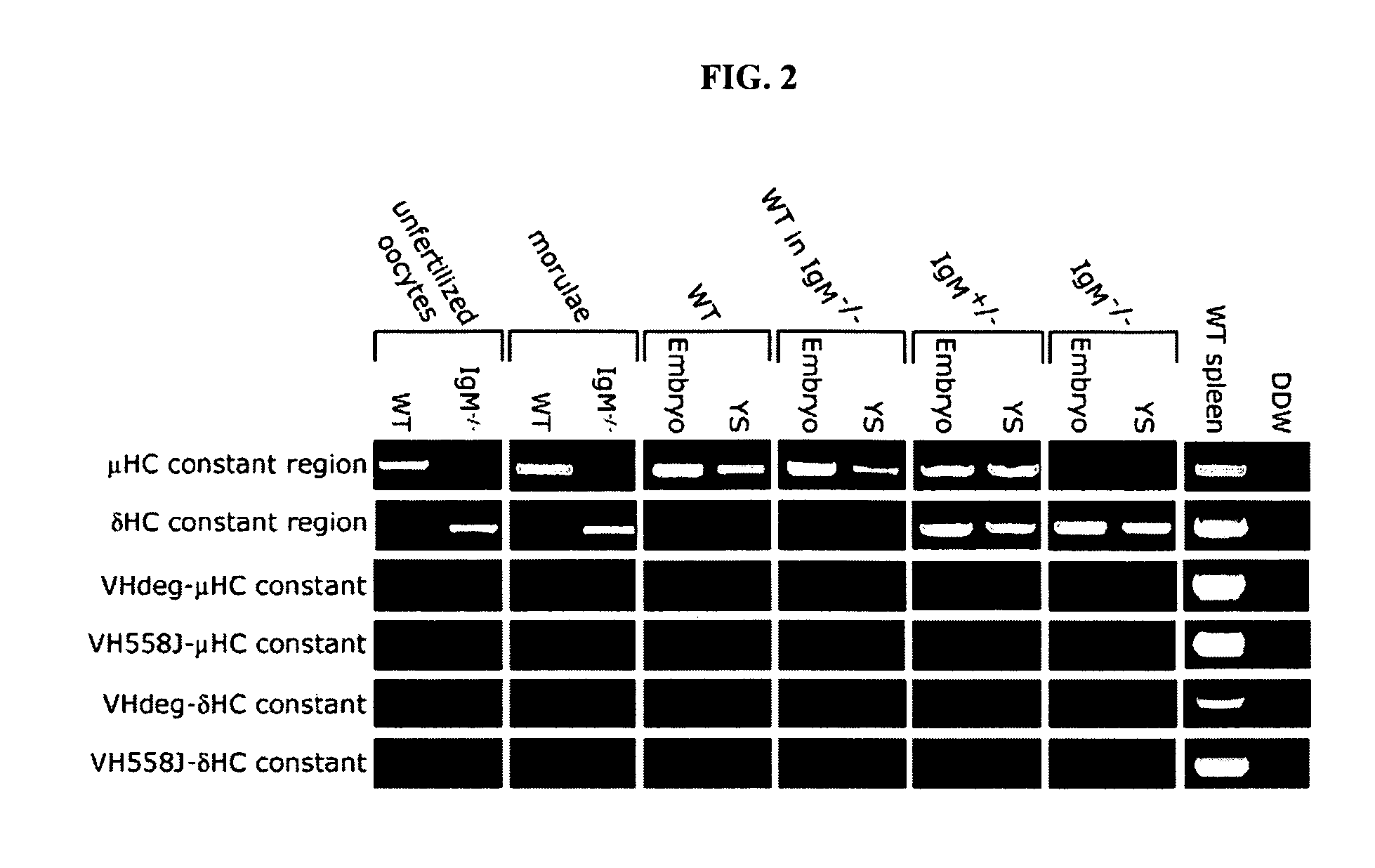
Immunoglobulin heavy chain variants expressed in mesenchymal cells and therapeutic uses thereof
Mesenchymal cells are unexpectedly found to express specific truncated versions of immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily members, Igμ heavy chain and Igδ heavy chain variants. Mesenchymal Ig heavy chain gene products either directly or indirectly control hemopoietic stem cells. Ectopic expression, RNAi or antibody therapy can be used to modulate Ig heavy chain mediated functions.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Aminopeptidase N inhibitor bestatin dino ester, synthesis and application thereof
InactiveCN101531613AStrong noveltySignificantly inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationSolubilityCurative effect
The invention provides an intensive antitumor medicament, namely bestatin deanol ester, a preparation method and application thereof. The bestatin deanol ester not only can effectively inhibit ectopic expression of aminopeptidase N activity, but also greatly improve the water solubility of the parent drug bestatin of the bestatin deanol ester, has slow release effect, is more excellent than the parent drug bestatin either from healing effect or preparation, and has wide application. Particularly, the invention mainly relates to the following three aspects: (1) design and synthesis of the bestatin deanol ester; (2) N'N deanol which is a micromolecule fragment, can be connected with other medicaments containing carboxyl, improves the pharmacokinetic property of the medicaments, and improves water solubility; and (3) a method for synthesizing an ester substance to which the invention relates with wide application and mild condition.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and application thereof
The invention discloses a rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and application thereof.Sequences of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in sequence tables, and amino acid sequences of glutathione S-transferase (GSTs) of an encoding protein of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence tables.As proved by ectopic expression of yeast, the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 has cadmium toxicity tolerant characteristics.The rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and the application have the advantages that knockout lines and over-expression lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are constructed, as discovered in seed germination comparative experiments on the knockout lines, the over-expression lines and wild type rice, the knockout lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are poor under cadmium stress, but the over-expression lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and the wild type rice can germinate, and germination and growth of the over-expression lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37are superior to germination and growth of the wild type rice; important effects of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 in cadmium-tolerant mechanisms can be equivalently described; over-expression vectors of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are constructed, and plants are transformed by the aid of the over-expression vectors, so that cadmium-tolerant plant varieties can be obtained, the cadmium stress resistance of the plants can be improved, and theoretical bases can be provided for breeding novel cadmium-tolerant crop varieties.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods and substances for directed RNA editing
PendingUS20190093098A1Accumulation of mutationAltered levelHydrolasesPolymorphism usesDiseaseNucleotide
The invention relates to methods and substances for the targeted alteration of genetic information on an RNA level. The substances are artificially produced guide RNAs, which are capable of recruiting endogenous editing enzymes, such as hADAR enzymes, in particular hADAR2 and hADAR1, in order to introduce targeted point mutations in selected mRNAs. The guide RNA consists of multiple segments and is constructed in such a way that individual nucleotides from different segments pair to form a double helix, and the nucleotides of a determined segment form a hairpin structure within the guide RNA. The invention also relates to the method for directed RNA editing, wherein the guide RNA is transfected into the cells in which the RNA editing is to be carried out. The substances and the method can be used for repairing individual, e.g. disease-relevant point mutations, such as those leading to premature stop signals. An advantage of the invention is that endogenous editing enzymes are also used in order to introduce targeted point mutations into the RNA. Only the short guide RNA, used for recruiting endogenous editing enzymes, must be artificially produced for each specific problem and ectopically expressed.
Owner:UNIV TUBINGEN
Early flowering in genetically modified plants
InactiveUS7868229B2Other foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesNucleotideEctopic expression
The present invention provides polynucleotides encoding CCAAT-binding transcription factor polypeptides that modulate the onset of reproductive development in plants. Polynucleotides encoding functional CCAAT-binding transcription factors were incorporated into expression vectors, introduced into plants, and ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention significantly shortened the time to flower development in the transgenic plants, as compared to the flowering time of control plants.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Alternative oxidase and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080103088A1Anti agingExtend your lifeNervous disorderVirusesWhole OrganismPhosphorylation
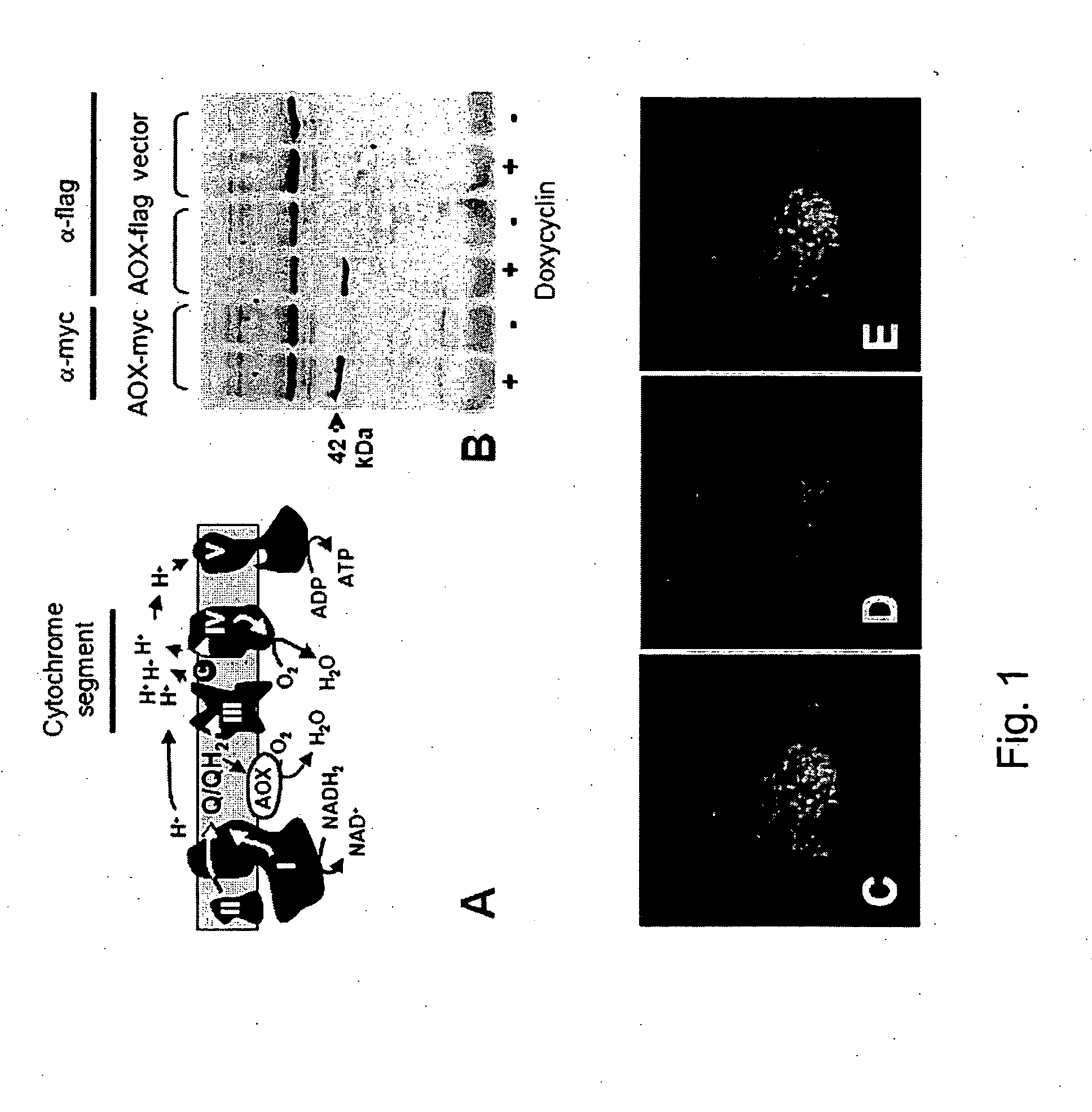
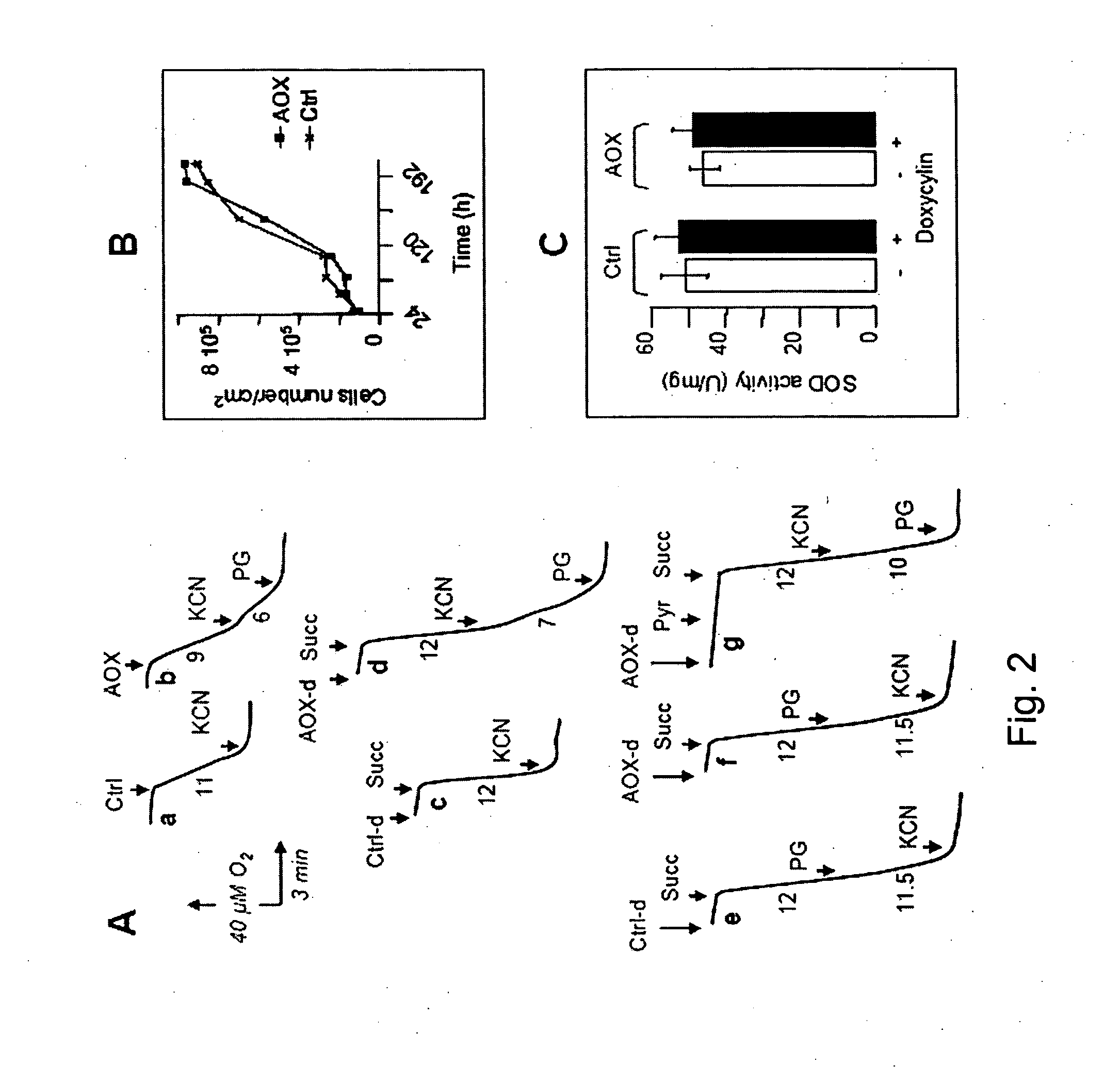
The invention relates to a method for combating disorders affecting the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system by allotopic expression of the cyanide-insensitive alternative oxidase (AOX) in human cells. The successful expression of AOX in human cells and in Drosophila has been shown to confer spectacular cyanide-resistance to mitochondrial substrate oxidation, alleviate oxidative stress, apoptosis susceptibility and metabolic acidosis. AOX is well tolerated when expressed ubiquitously in the whole organism. AOX expression is a valuable tool to limit the deleterious consequences of respiratory chain deficiency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TAMPERE
Compositions and methods for treating cancer by modulating HER-2 and EGF receptors
InactiveUS7396810B1Improved prognosisGrowth inhibitionSaccharide peptide ingredientsDisease diagnosisEctopic expressionOncology
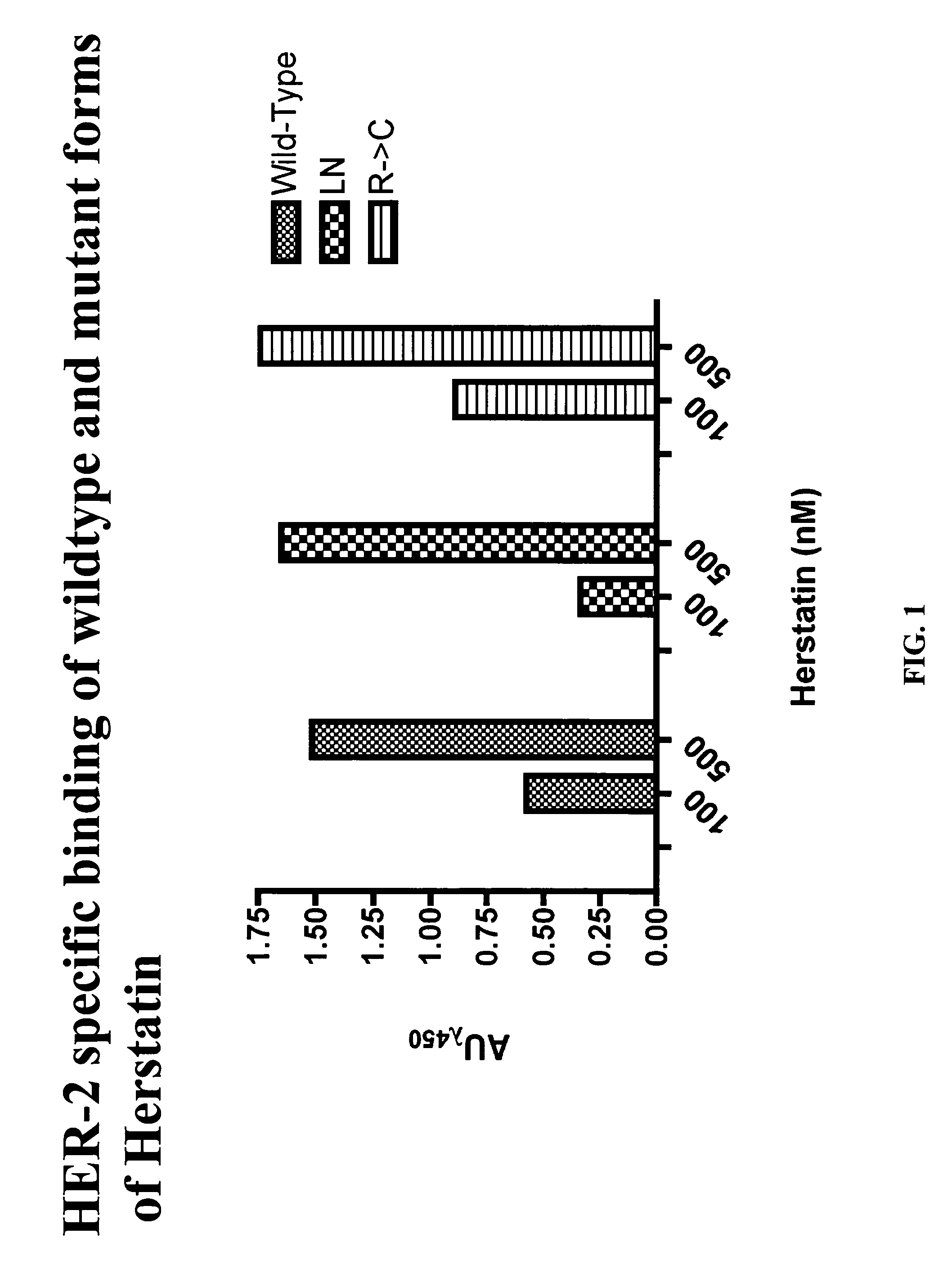
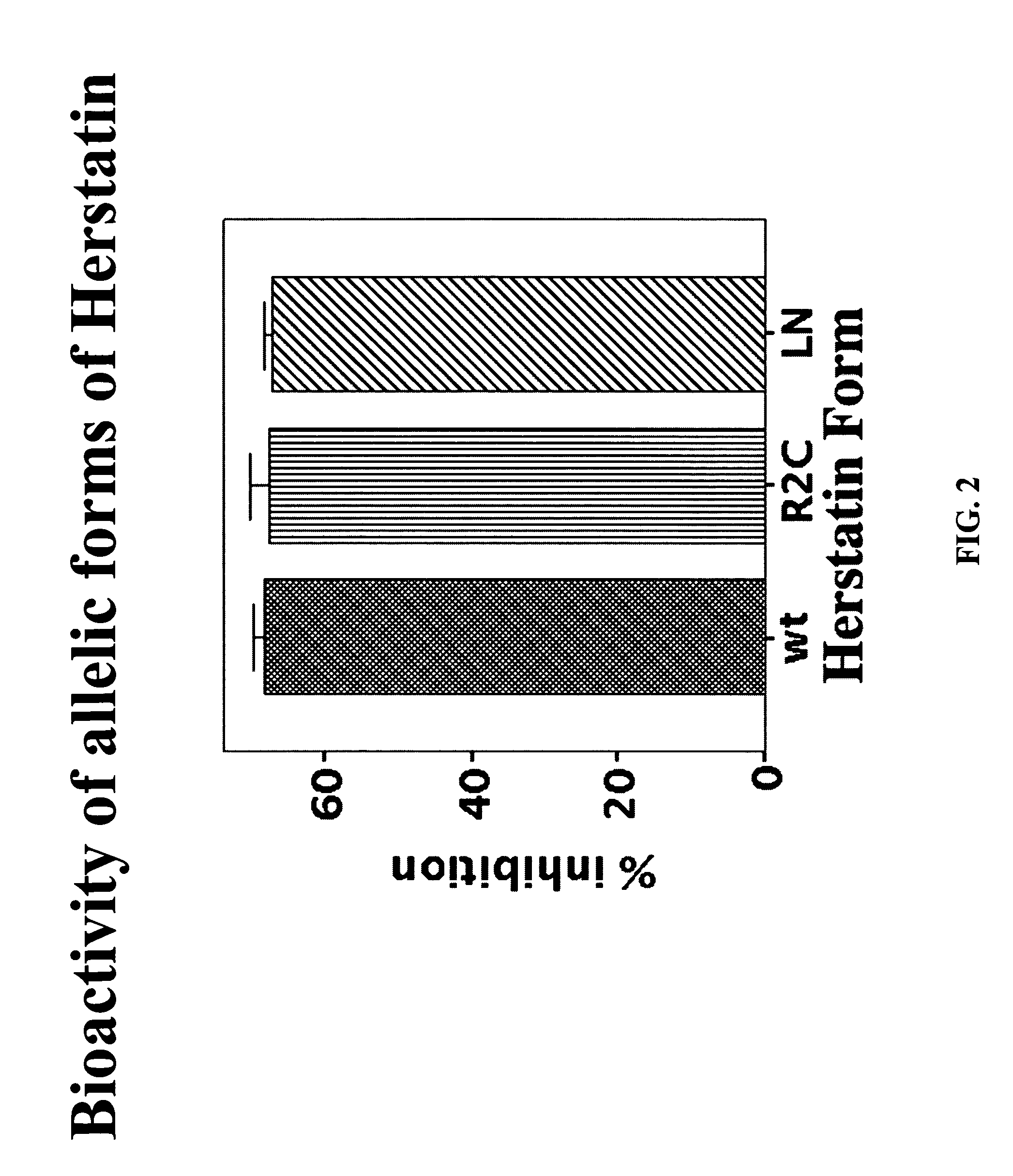
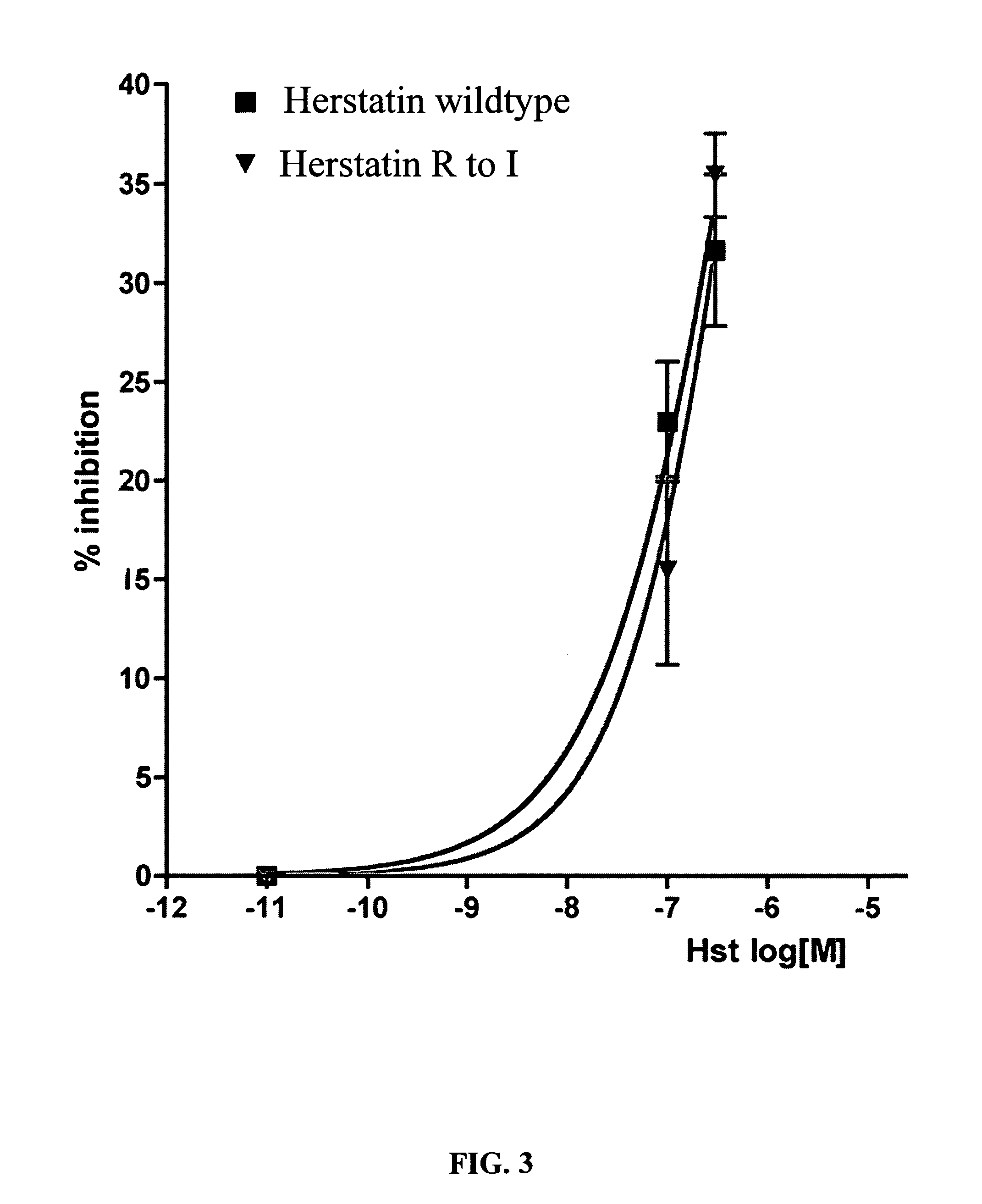
An alternative HER-2 / neu product, herstatin, consists of subdomains I and II from the ectodomain of p185HER-2 and a unique 79 amino acid C-terminus encoded by intron 8. Recombinant herstatin added to cells was found to bind to and inhibit p185HER-2. The effects of ectopic expression of herstatin in combination with either p185HER-2 or with its homolog, the EGF receptor, in several cell lines was studied. Cotransfection of herstatin with HER-2 inhibited p185HER-2 levels and caused an approximate 8 fold reduction in p185 tyrosine phosphorylation. Inhibition of p185HER-2 tyrosine phosphorylation corresponded to a dramatic decline in colony formation by cells that coexpressed p185HER-2 and herstatin. Herstatin also interfered with EGF activation of the EGF receptor in cotransfected cells demonstrated by impaired receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, reduced receptor down-regulation, and growth suppression. For both p185HER-2 and the EGF receptor, the extent of inhibition was affected by the expression levels of herstatin relative to the receptor. Herstatin is an autoinhibitor of p185HER-2 and expands its inhibitory activity to another member of the group I family of receptor tyrosine kinases, the EGF receptor.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Assay for exo-site binding molecules
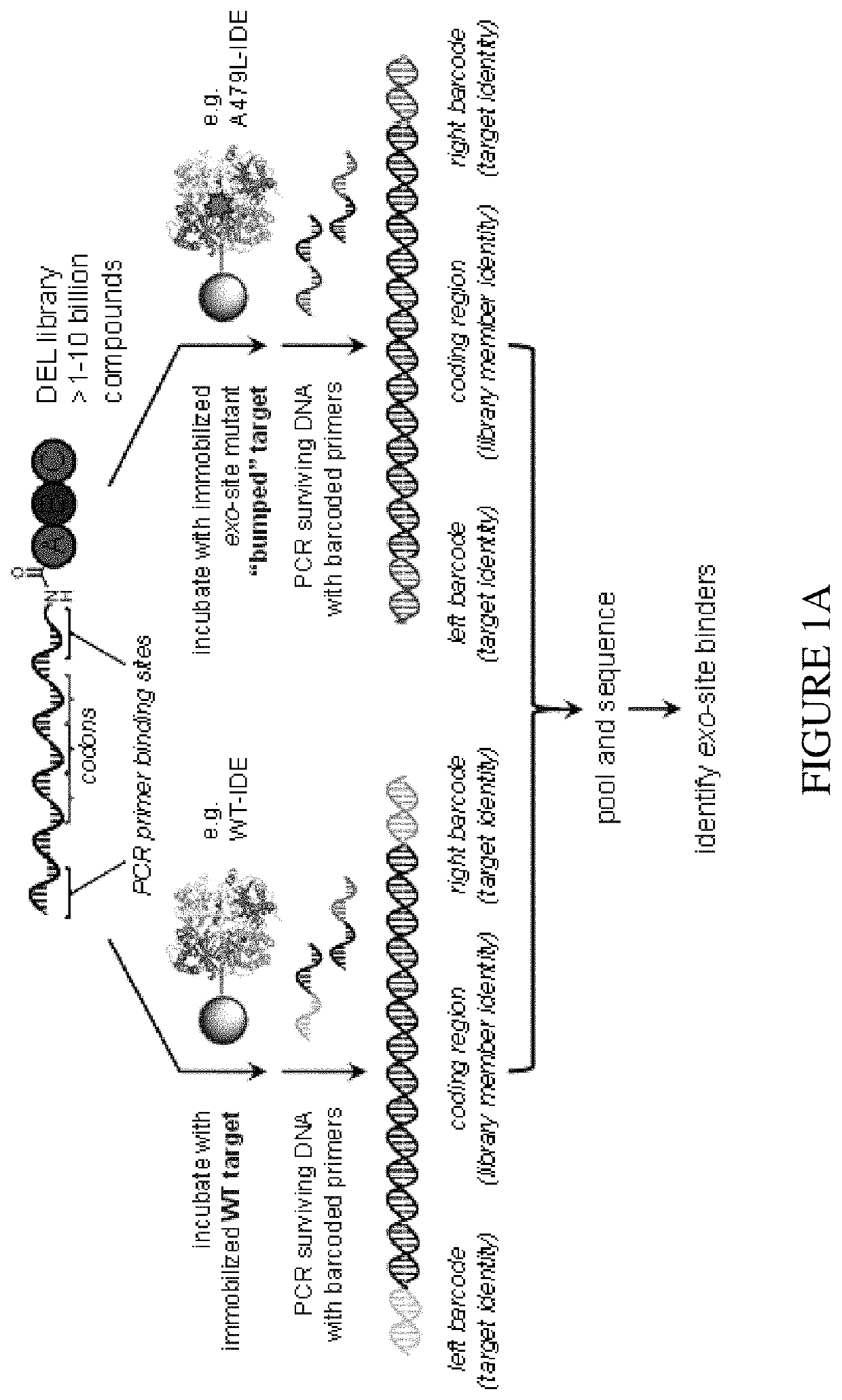
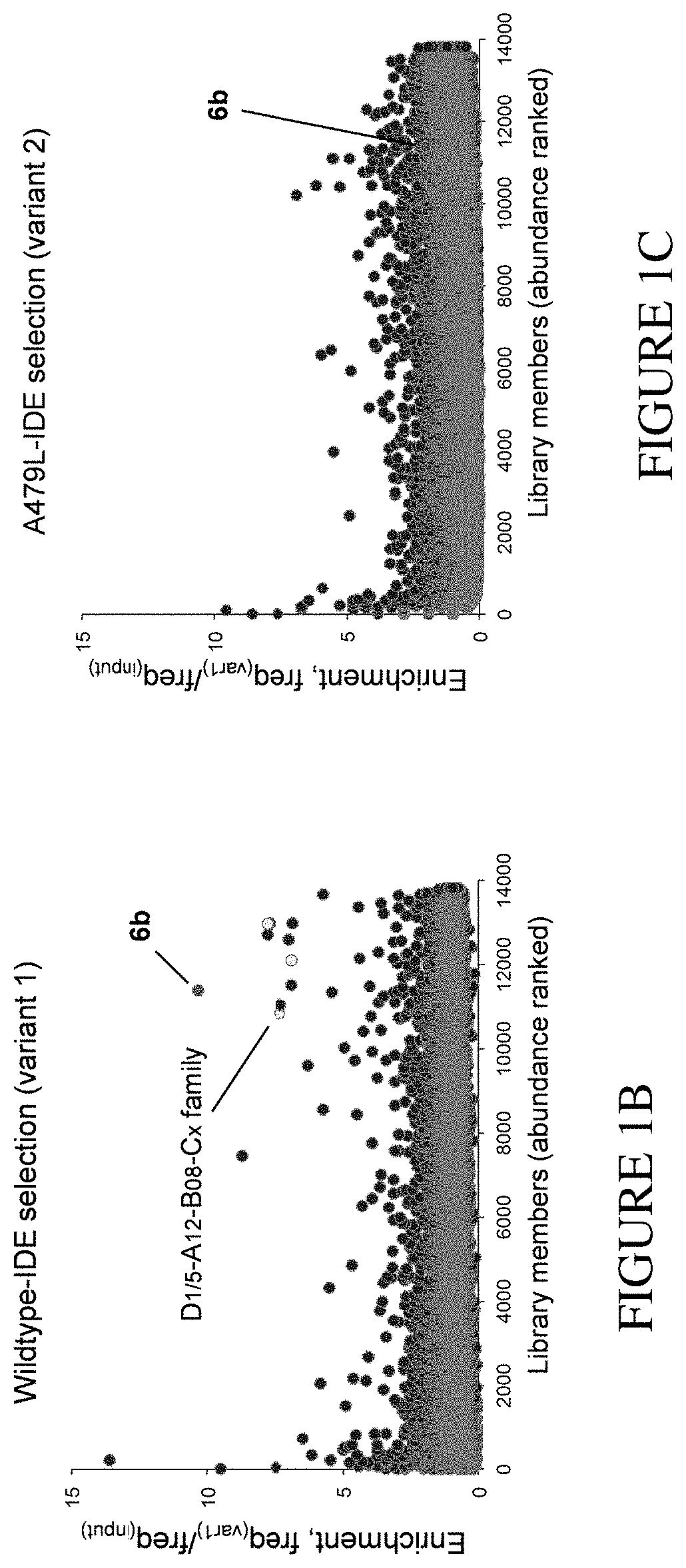
ActiveUS10640767B2Facilitate hit-callingLow signalPeptide librariesMacromolecular librariesDiseaseAssay
Methods for the identification of agents the bind to exo-sites of proteins are provided. Agents identified by the methods described herein and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the identified agents are also provided. Methods of using an identified agent for the treatment or prevention of a disease, disorder, or condition are also provided, including methods of treating or preventing a disease associated with reduced, elevated, or ectopic expression or aberrant activity of a protein comprising an exo-site.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Fusion partner cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS7491530B2Improve the level ofIncrease ratingsGenetically modified cellsTransferasesDiseaseAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides in one aspect novel fusion partner cells that ectopically express one or more genes that alter the phenotype of a hybrid cell made from a fusion of the fusion partner cell and a fusion cell, hybrid cell lines produced using the fusion partner cells. The invention in another aspect provides antibodies produced by certain hybrid cell lines, and compositions containing one or a combination of such antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof. The invention also provides in another aspect methods of using the antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof for diagnosis and treatment of diseases characterized by the antigens specifically bound by the antibodies.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Application of inhibiting accumulation of xantheins and accumulating lycopene and anthocyanin in preparation of Brassica plants with red pedals
InactiveCN104480128AIdentify key differentially expressed gene lociBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBrassicaLycopene
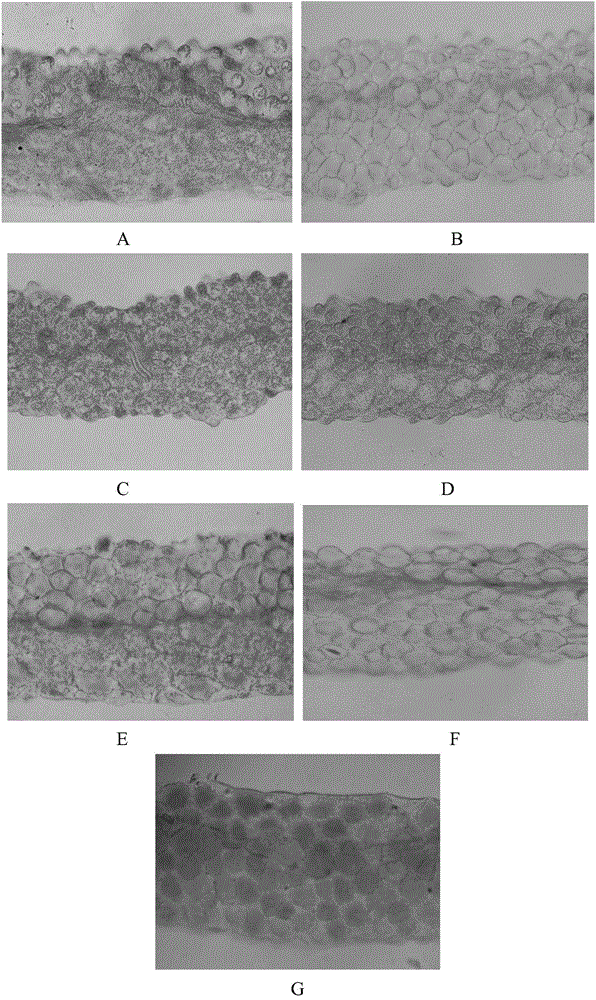
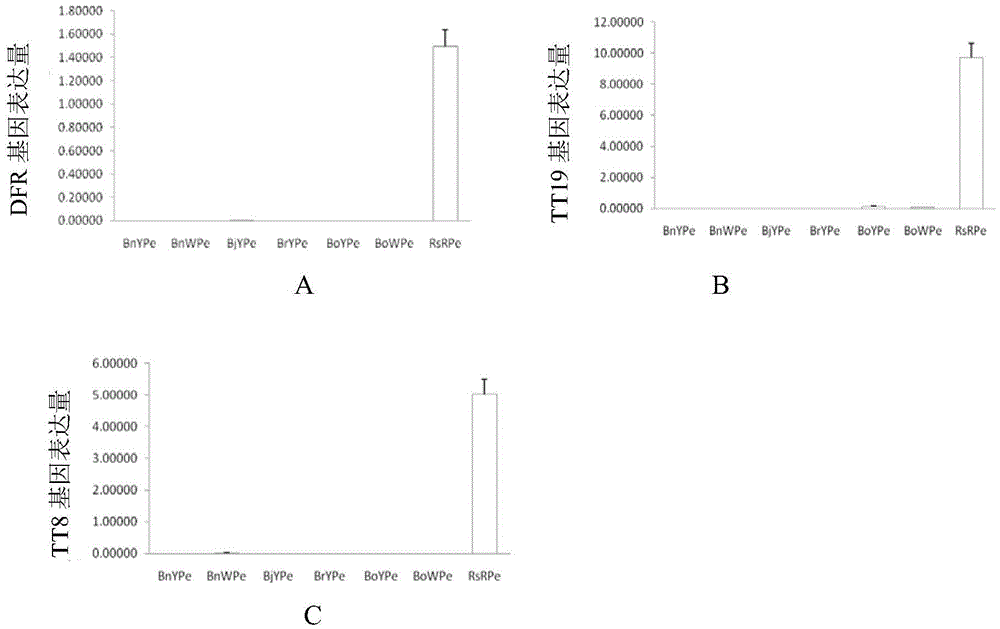
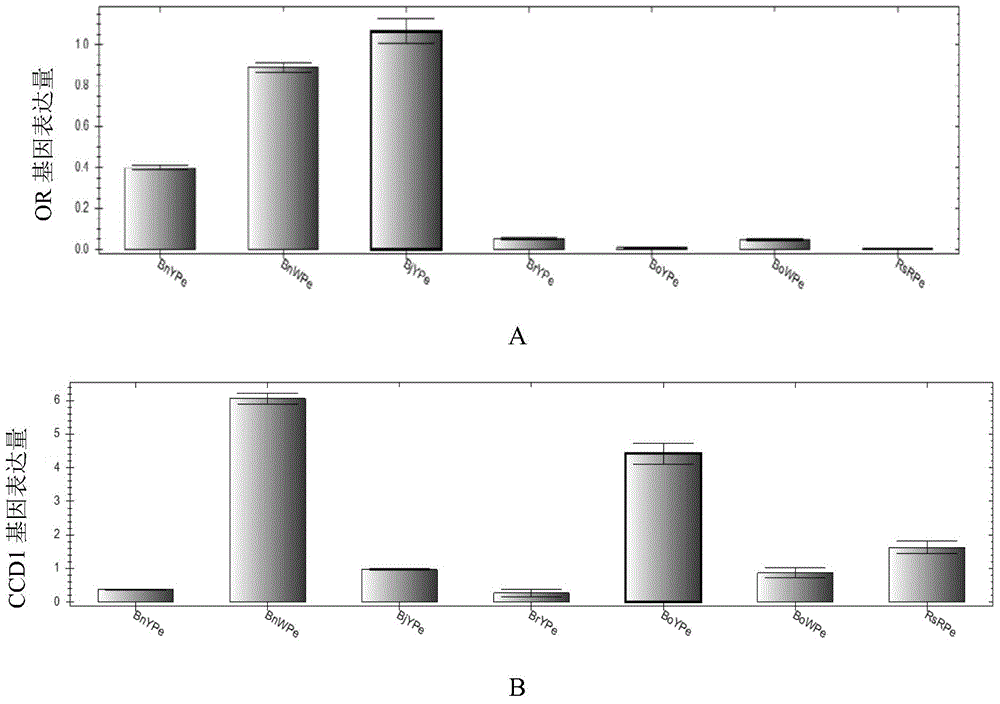
The invention discloses application of inhibiting accumulation of xantheins while accumulating lycopene and anthocyanin in preparation of Brassica plants with red pedals. The application is specifically as follows: interfering with the gene expression of LCYB, LCYE, MYB12 and MYB111 and simultaneously performing ectopic expression of TT8 genes. The invention further discloses a preparation expression vector for interfering with the gene expression of LCYB, LCYE, MYB12 and MYB111 and simultaneously performing ectopic expression of the TT8 genes and a preparation method of the vector. By interfering with the gene expression of LCYB, LCYE, MYB12 and MYB111, the xantheins, namely carotenoid and flavonol are inhibited; and by performing the ectopic expression of the TT8 genes, the accumulation of lycopene and anthocyanin can be promoted, so that the pedals are red, the Brassica plants with the red pedals are successfully prepared, and the flower colors of the Brassica plants are enriched.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
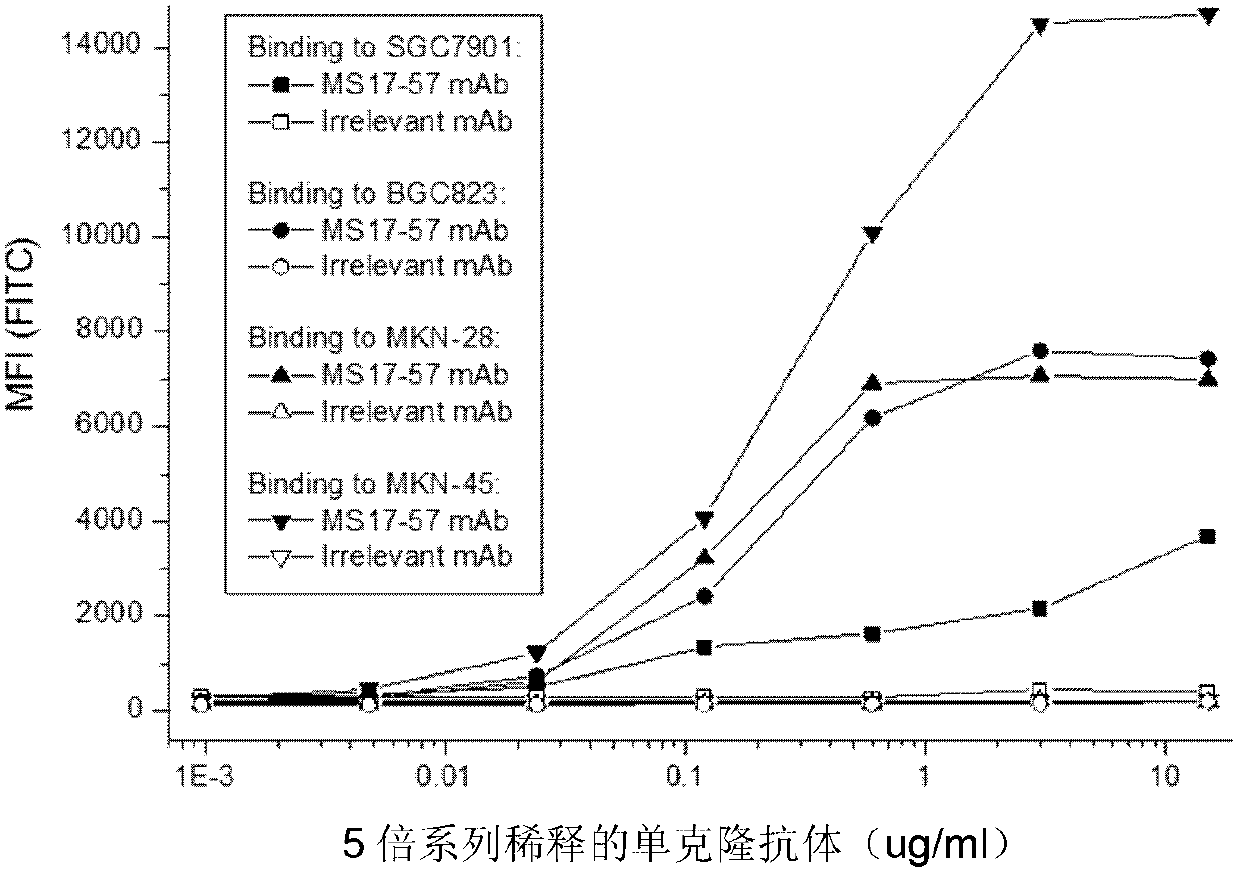
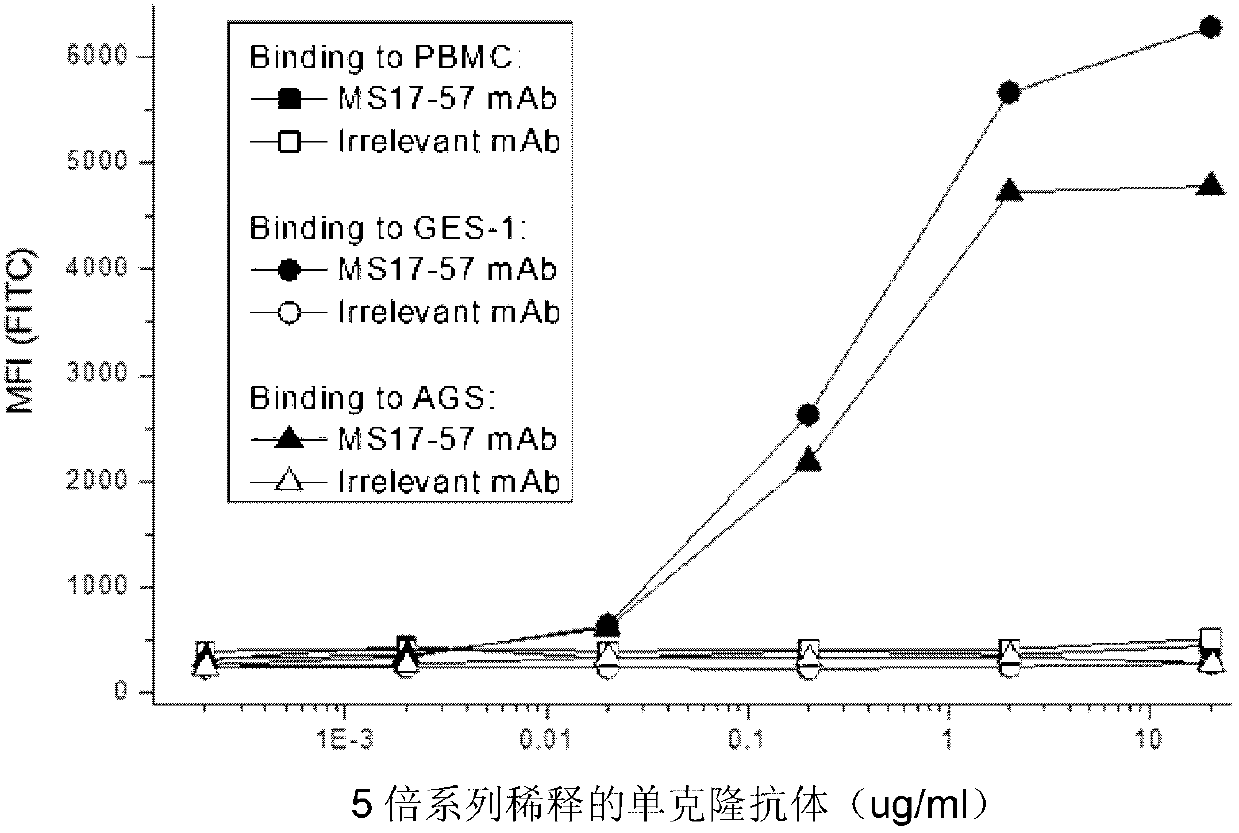
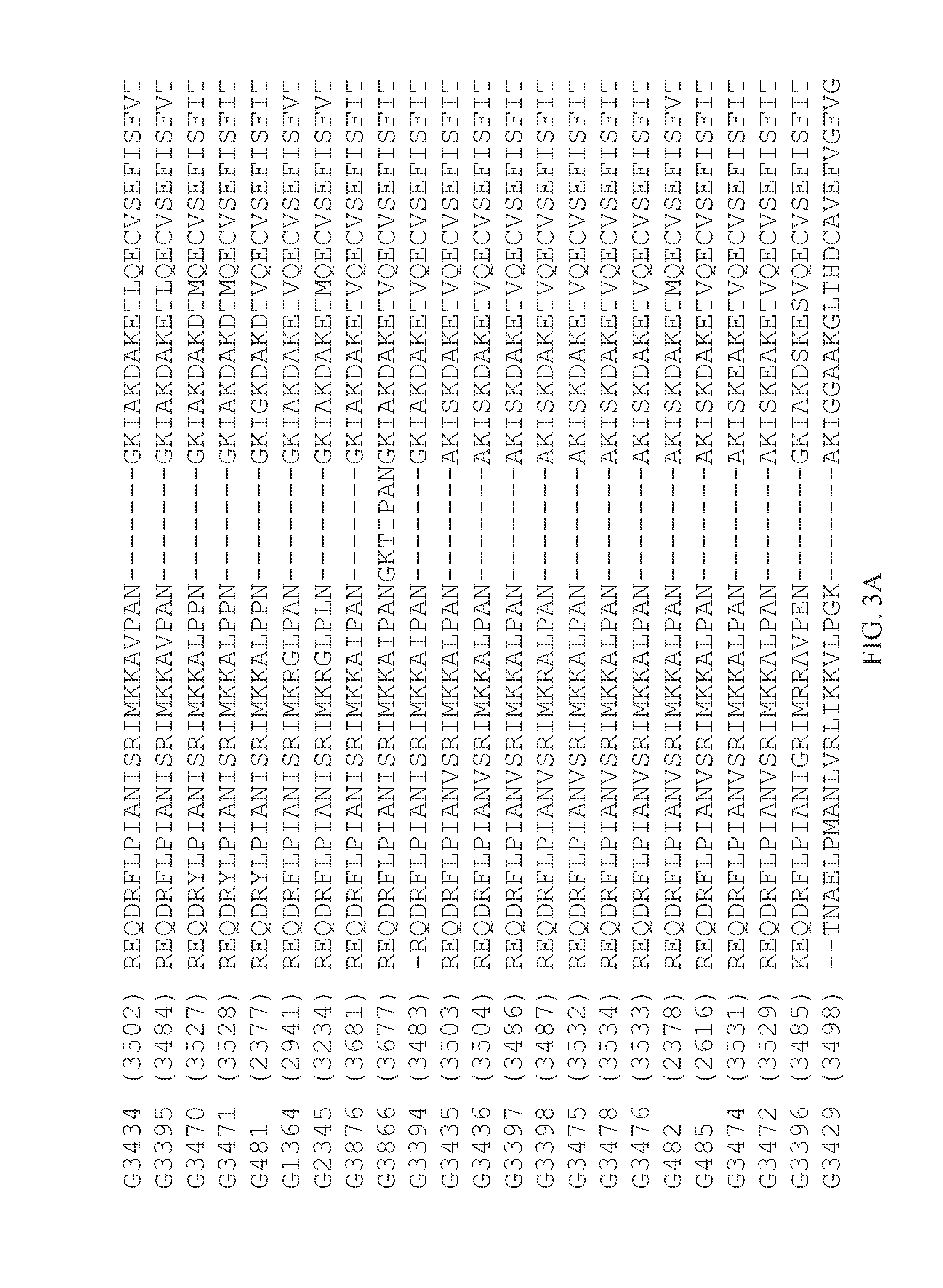
Monoclonal antibody for resisting cell surface ectopic expression, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103130896ASignificant technological progressAntibody ingredientsFused cellsBinding siteIn vitro test
The invention belongs to the field of biological pharmacy and provides a monoclonal antibody for resisting cell surface ectopic expression. The amino acid sequence of a light chain variable region at the Fab fragment antigen-binding site of an antibody molecule is shown as SEQ ID NO:2, and the amino acid sequence of a heavy chain variable region is shown as SEQ ID NO:4. The invention also provides application of the monoclonal antibody in preparation of medicaments for treating and preventing digestive tract tumors or digestive tract tumor metastasis. The invention also provides a detection kit and medicinal composition containing the monoclonal antibody. The invention also provides a preparation method of the monoclonal antibody. A series of in vivo and in vitro tests prove that the purified and degermed monoclonal antibody has high affinity for PALP and / or IALP antigen for resisting extracellular ectopic expression of tumor cells and has a biological activating function of inhibiting growth and migration of tumor cells.
Owner:MABSTAR
Seed plants characterized by delayed seed dispersal
InactiveUS6288305B1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotideGene product
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Stress tolerance in plants
InactiveUS20150135360A1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
Transcription factor polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into nucleic acid constructs, including expression vectors, have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these constructs have been shown to be more resistant to disease (in some cases, to more than one pathogen), or more tolerant to an abiotic stress (in some cases, to more than one abiotic stress). The abiotic stress may include, for example, salt, hyperosmotic stress, water deficit, heat, cold, drought, or low nutrient conditions.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Seed plants characterized by delayed seed dispersal
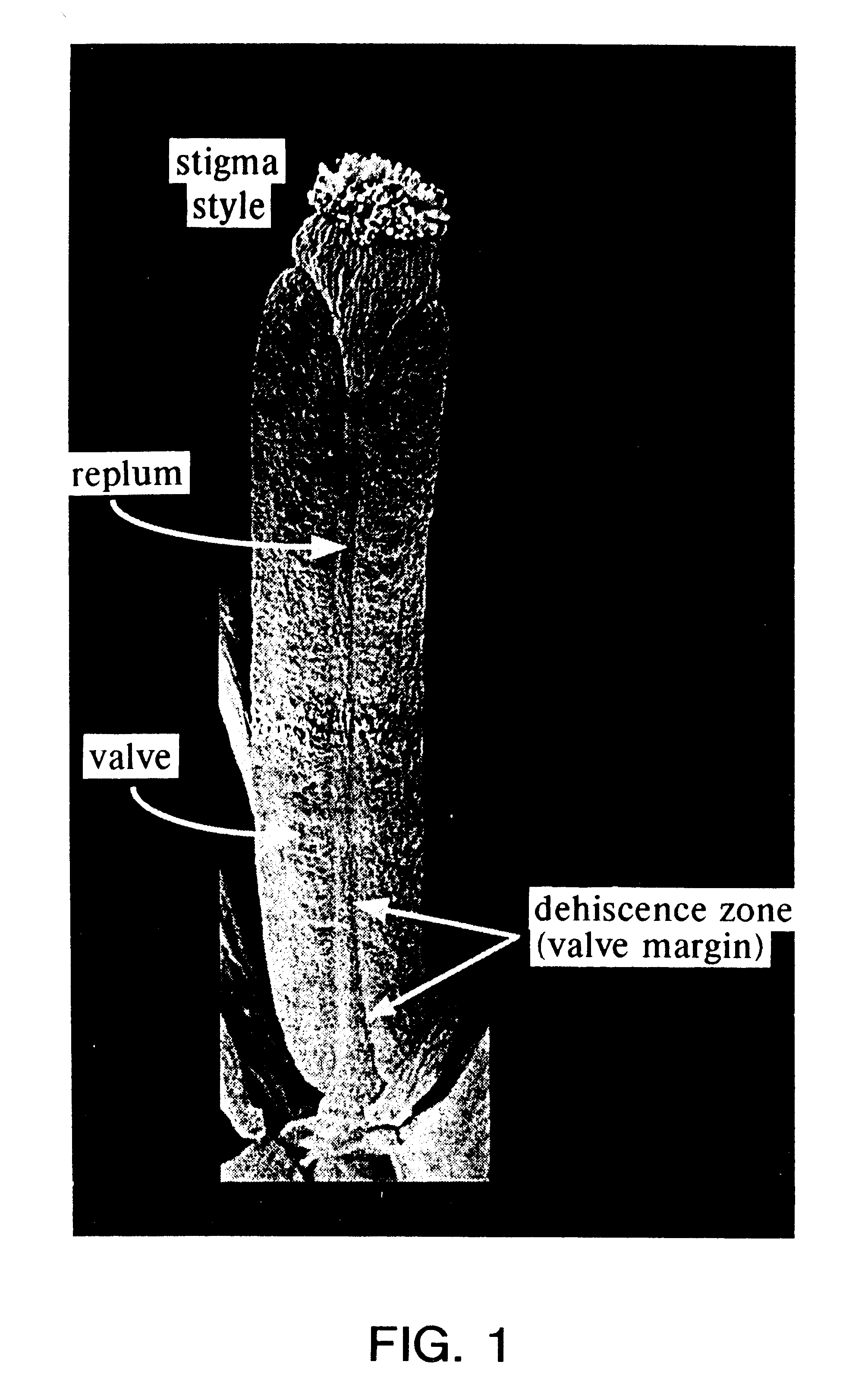
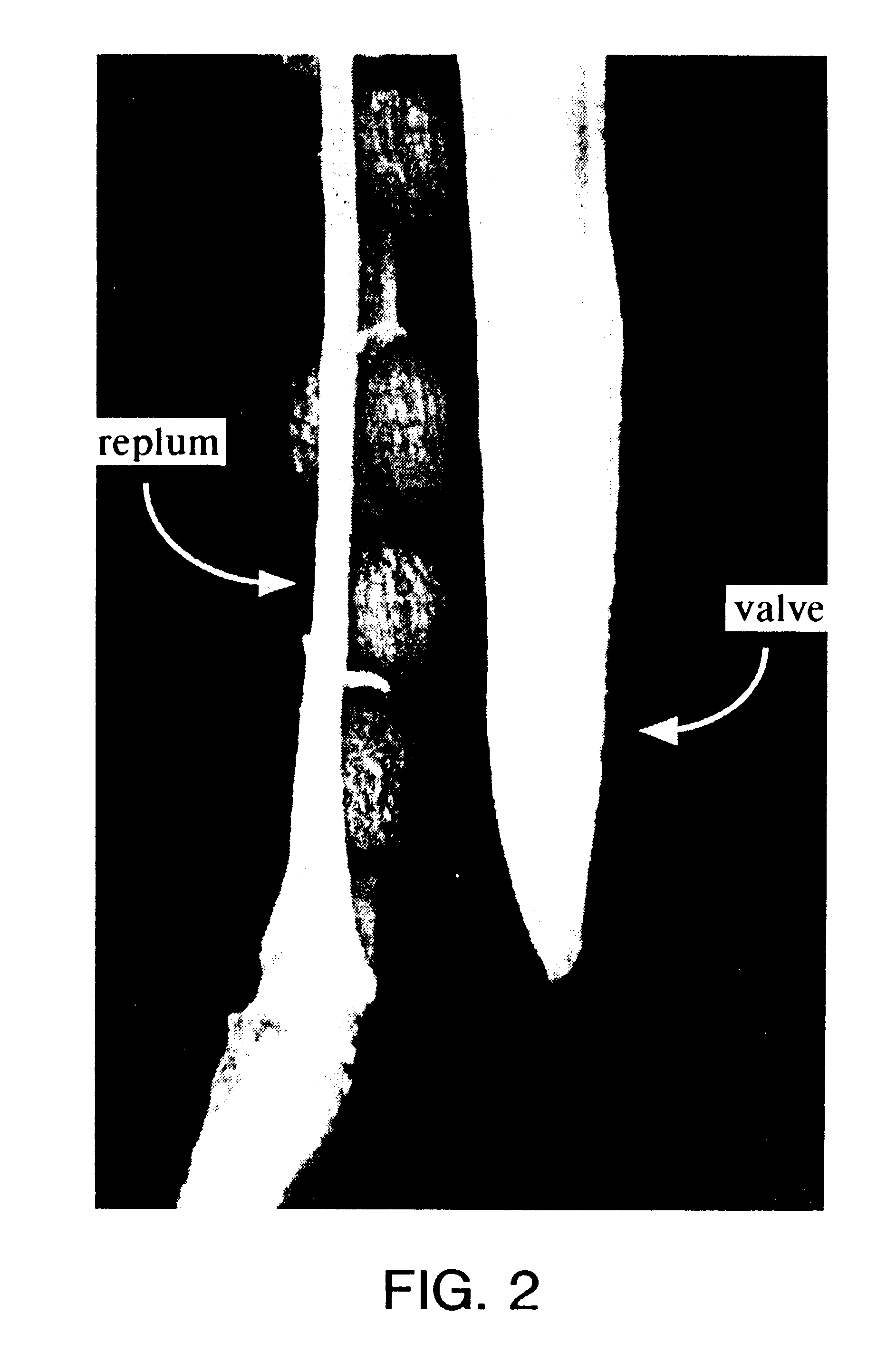
The present invention provides a non-naturally occurring seed plant that is characterized by delayed seed dispersal due to ectopic expression of a nucleic acid molecule encoding an AGL8-like gene product. Further provided herein is a non-naturally occurring seed plant, such as an agl1 agl5 double mutant, that is characterized by delayed seed dispersal due to suppression of AGL1 and AGL5 expression in the seed plant. The invention also provides a substantially purified dehiscence zone-selective regulatory element, which includes a nucleotide sequence that confers selective expression upon an operatively linked nucleic acid molecule in the valve margin or dehiscence zone of a seed plant. Also provided by the invention are kits for producing a transgenic seed plant characterized by delayed seed dispersal, such kits containing a dehiscence zone-selective regulatory element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Development of Very Early Flowering and Normal Fruiting Plum With Fertile Seeds
ActiveUS20110067147A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesPopulus trichocarpaBud
To produce early flowering genotypes, plum (Prunus domestica) was transformed with the poplar (Populus trichocarpa) Flowering Locus T1 (PtFT1) gene. Ectopic expression of 35S::PtFT1 Induced early flowering in vitro from transgenic plantlets within two months of transformation. When the transgenic plum plants were rooted and transferred to soil and grown in posts in the growth chamber, a number of additional lines flowered. Normal flowering and fruiting were observed in the greenhouse within one year of transformation. While dormancy was not necessary for growth or fruiting, FT plums were still winter hardy and floral bud set and flowering responded normally to changes in temperature. By manipulating a single gene, temperate tree crops can be effectively engineered for cultivation in new growing areas and for entirely new modes of agricultural production that are continuous, sustainable, and adaptable to climate change.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Application of gene for interfering expression of LCYB and LCYE and simultaneously ectopically expressing TT8 in preparation of brassica plant having red petals
InactiveCN104531755AIdentify key differentially expressed gene lociFermentationPlant tissue cultureBrassicaLycopene
The invention discloses application of a gene for interfering expression of LCYB and LCYE and simultaneously ectopically expressing TT8 in preparation of a brassica plant having red petals. The invention further discloses an expression vector for preparing the gene for interfering expression of LCYB and LCYE genes and simultaneously ectopically expressing TT8 gene and a preparation method of the vector. Yellow carotenoid is inhibited and red lycopene is accumulated by interfering expression of the LCYB and LCYE genes; accumulation of cyanin can be promoted through ectopic expression of the TT8 gene; therefore, the petals are red; the brassica plant having red petals is successfully prepared; and colours of the brassica plants are enriched.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Novel HIV recombined multi-epitope fusion antigen and application thereof
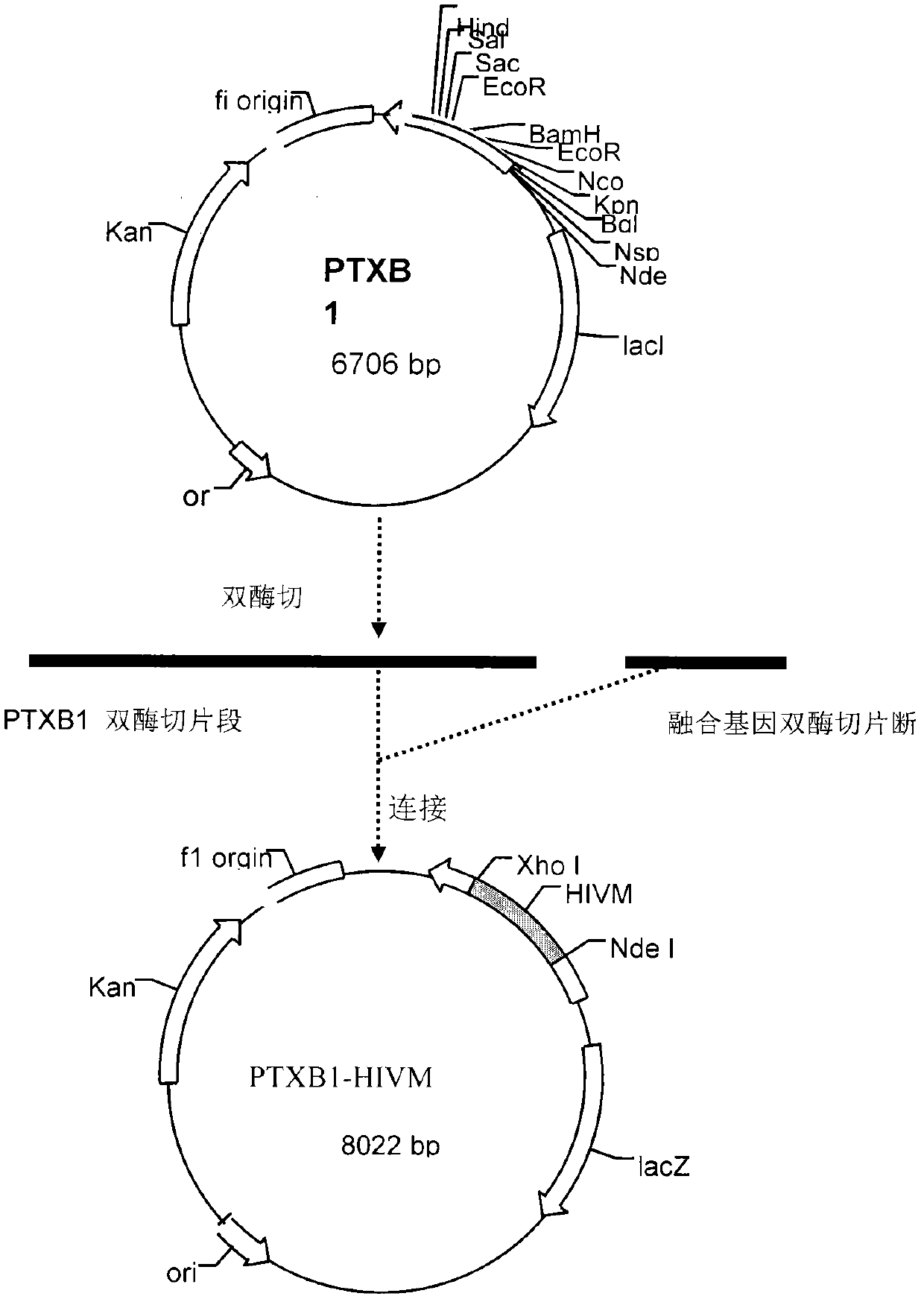
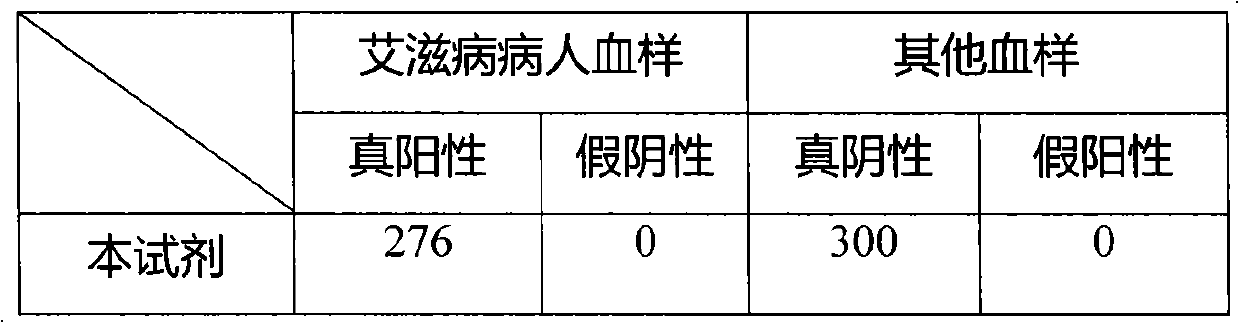
InactiveCN102559724ARapid spreadImprove stabilityBiological testingHybrid peptidesChromatographic separationEctopic expression
The invention provides a novel HIV recombined multi-epitope fusion antigen and a detection kit for preparing through the antigen. Flexible structured genes are added into the main epitope genes of HIV-1 gp41, M group and O group, the main epitope genes of HIV-1gp120 and the main epitope genes of HIV-2gp36, so that all the gene DNA are linked to be an artificial gene sequence. The sequence is cloned to an expression vector for ectopic expression, so as to establish immunocompetent high-expression cell strain, finally the sequence is fermented and induced into efficient expression, and chromatographic separation and purification is performed on the multi-antigen epitope fusion antigen of the HIV. The antigen is applied to the immune detection reagent, as the unnecessary gene sequence is reduced through the fusion antigen, the non-specific action is reduced for more than 50%, and the synergistic effect of the multi-antigen epitope of the same antigen increases the detection sensitivity to be 2 to 3 times.
Owner:北京万达因生物医学技术有限责任公司
Plants with improved water deficit and cold tolerance
The present invention provides nucleic acid constructs, including plasmids, expression vectors or expression cassettes comprising polynucleotides encoding CCAAT-binding transcription factor polypeptides that have the ability to increase a plant's tolerance to abiotic stress. Polynucleotides encoding functional CCAAT-binding transcription factors were incorporated into expression vectors, introduced into plants, and ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention significantly increased the cold and water deficit tolerance of the transgenic plants, as compared to tolerance to these stresses of control plants.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Selective control of lignin biosythesis in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20030005481A1Enhancing lignificationLignification is enhancedBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesLignin biosynthesisGene product
The present invention provides methods of selectively controlling lignin biosynthesis in plants such that lignification is reduced or enhanced, as desired. The invention provides, for example, a method of reducing lignification in a vascular plant by ectopically expressing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an AGL8-like gene product in the plant, whereby lignification is reduced due to ectopic expression of the nucleic acid molecule. An AGL8-like gene product useful in the invention can have, for example, substantially the amino acid sequence of an AGL8 ortholog such as Arabidopsis AGL8 (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com