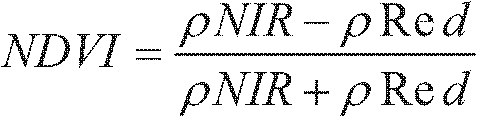Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Vascular plant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vascular plants (from Latin vasculum: duct), also known as tracheophytes (from the equivalent Greek term trachea), form a large group of plants (c. 308,312 accepted known species) that are defined as those land plants that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers) and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida sensu lato.
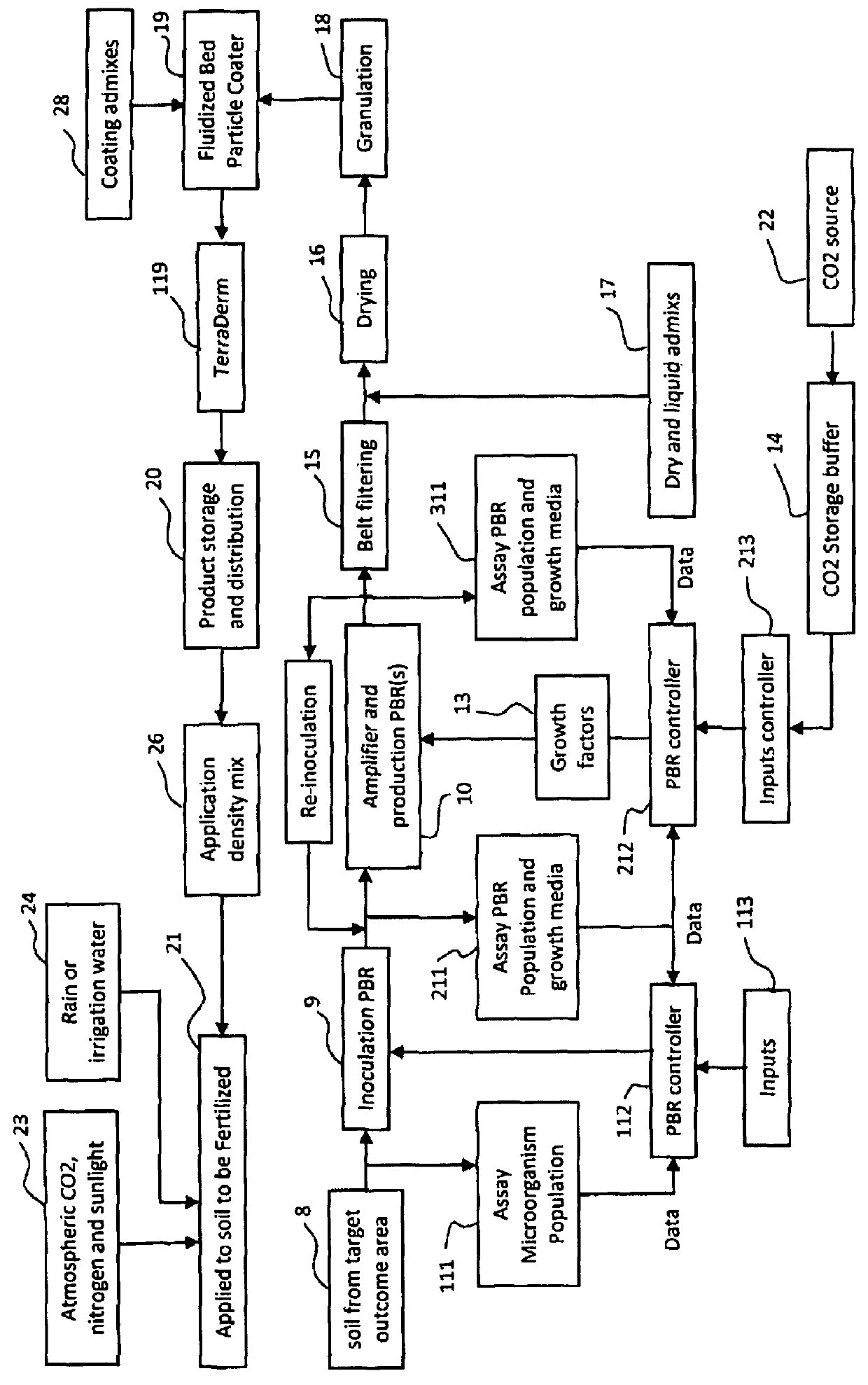
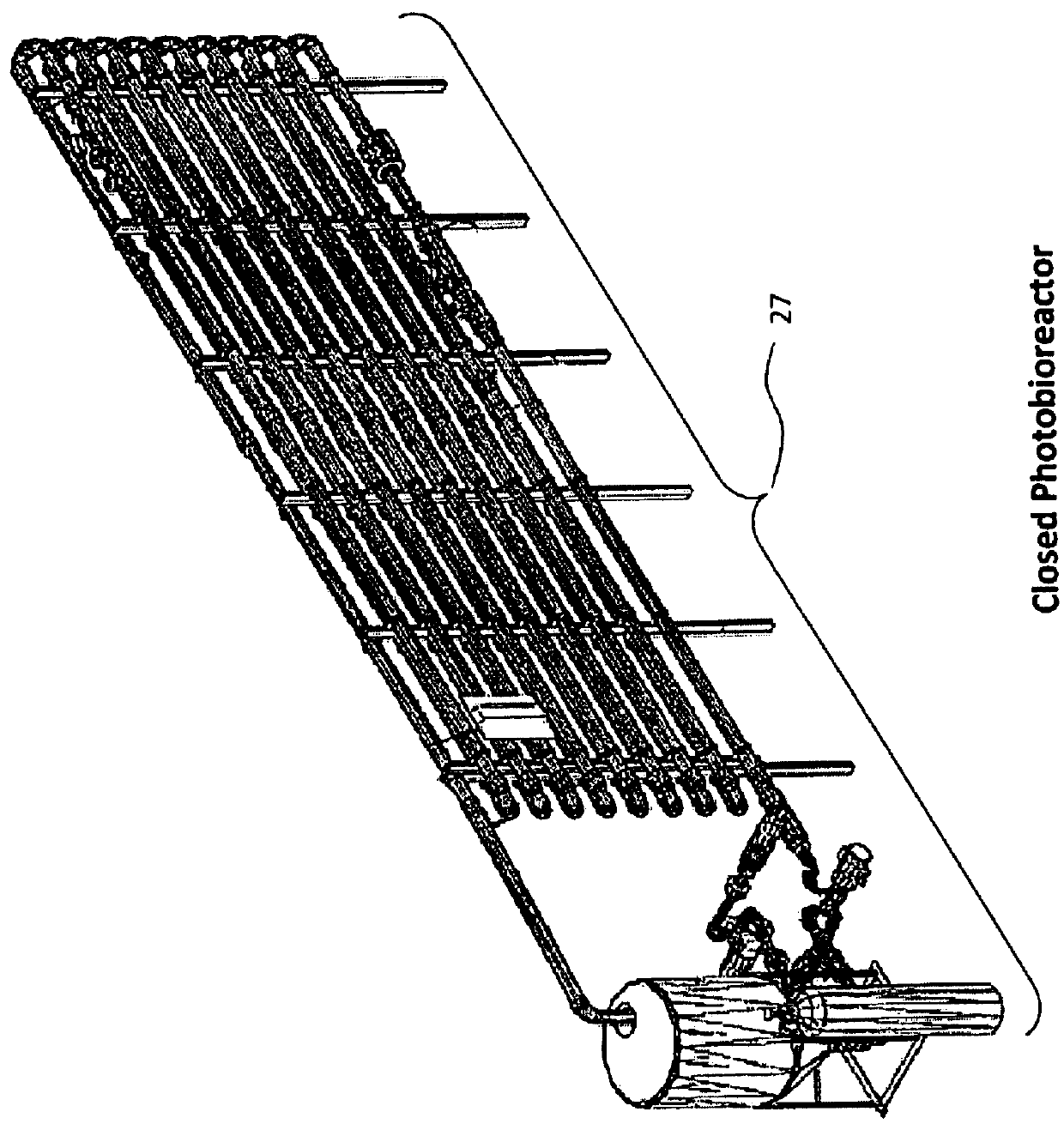
Dry land erosion control using photosynthetic nitrogen-fixing microorganisms
InactiveUS20080236227A1Good curative effectInhibit seed germinationBio-organic fraction processingEfficient propulsion technologiesPhylum CyanobacteriaArid
In mesic environments, erosion control measures usually employ the establishment of vegetative cover by vascular plants in order to hold the soil in place. The current art often includes the application of seeds, chemical fertilizers, tackifiers, and mulches to promote the growth of vascular plants. However, arid environments so not support dense vegetative cover, but are instead dominated by photosynthetic microorganisms, primarily cyanobacteria and lichens. The cyanobacteria not only hold the soil in place, but also are the primary source of fixed nitrogen in arid environments. Disclosed herein, is a description of an apparatus and methods for the production and preservation of a photobiofertilizer as a means for repairing disturbed arid soils.
Owner:FLYNN TIMOTHY M
Evaluation method for botanical-integrity of vascular plant, irrigating method to vascular plant, film electret sensor and film ecm array
InactiveUS20110288689A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidCavitationVascular tissue
A method includes measuring an occurrence frequency of elastic waves generated by cavitations in vascular tissues in vascular plant, before and after a change in water stress to the vascular plant, respectively by an elastic wave reception sensor fixed to an axis of the vascular plant, calculating a change rate of the occurrence frequency, from the occurrence frequency of the elastic wave measured before and after the change, respectively, and determining whether or not an embolism in the vascular tissue arrives at an unrecoverable level of the embolism, from the calculated change rate. And then, one can determine irrigation timing and quantity to the vascular plant, using an index based upon the above-determined result.
Owner:SAITAMA UNIVERSITY
Technique for restraining grass and controlling sludge by using cinder
InactiveCN101811782ASolve environmental problemsCause secondary pollutionSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentVascular bundleSludge
The invention aims to solve the problems of over spread of large-sized vascular plants in grass-type lakes and over-strong biological deposit-promoting effect and provide a technique and a method for restraining grass and controlling sludge for improving the growing water quality condition of aquatic plants and accelerating bottom sludge decomposition. Iron, aluminum and calcium oxides in cinder can strongly adsorb phosphate radical in the water body, the loose and porous surface of the cinder is favorable for the fixation and growth of soil microbes, and a formed biological membrane can effectively remove organic substances and ammonia nitrogen from the water body and accelerate the biological decomposition of the lake bottom sludge. The cinder is filled in a nylon bag and the nylon bag is fixed in a ground cage for facilitating reclamation and preventing physical deposition at the lake bottom. By using the existing resources in rural areas of China and using the local materials, the method is convenient and feasible, and has strong operability and wide application; and the implementation of the technique does not affect the primary ecological function of the ecosystem of the lake and has significance for maintaining the ecological health of the grass-type lakes for long term.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Measuring method for algae biomass in biological soil crust
ActiveCN105092495AEasy to collectEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll bNatural development
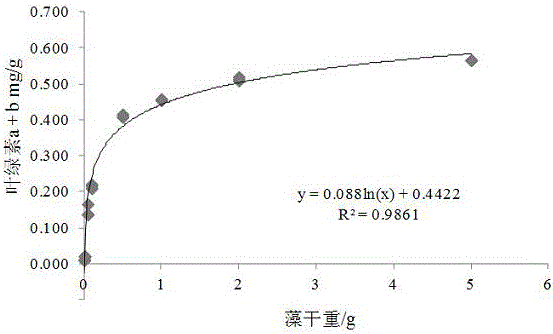
The invention discloses a measuring method for the algae biomass in a biological soil crust, and relates to the field of biology. The method includes the steps of sampling of an algae crust sample, sieving, cleaning, algae cultivating, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b measuring, standard curve drawing and algae biomass measuring (natural development). In the algae cultivating step, cultivating is carried out through BG11 cultivating media, and use algae are mixed algae. In the chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b measuring step, chlorophyll is extracted with a mixed solution method, wherein extracting solutions comprise absolute ethyl alcohol, acetone and water in the ratio of 4.5 to 4.5 to 1. The relationship between the gross of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b of the algae and the algae biomass is regressed through a standard curve. Measuring of the natural developing algae biomass is converted through the standard curve between the gross of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b and the cultivated algae biomass. Direct comparison between the algae crust and the vascular plant biomass is achieved, and a reliable approach is provided for more accurately calculating the productivity of the algae crust and the effect of the productivity in an ecological system.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Fungus-algae symbiosis-based high-efficiency biogas liquid purifying method
ActiveCN106630483AImprove use valueImprove responseMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationSludgeVascular plant
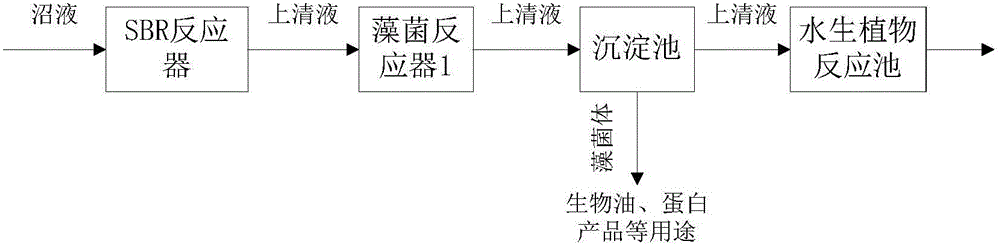
The invention provides a fungus-algae symbiosis-based high-efficiency biogas liquid purifying method. The fungus-algae symbiosis-based high-efficiency biogas liquid purifying method comprises the following steps: a, taking biogas liquid, inoculating active sludge, performing aeration treatment until the pH falls to 6.5 to 7.0 and naturally settling to obtain supernate 1; b, inoculating microalgae into the supernate 1 obtained in the step a, culturing and naturally settling to obtain precipitate and supernate 2, wherein the precipitate is microalgae bacteria; c, discharging the supernate 2 obtained in the step b into a vascular plant reaction tank and standing for 5 to 10 days.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Method for quickly growing bryophyte crust on cross section of expressway slope
InactiveCN107094468AImprove soil and water micro-ecologyAvoid erosionExcavationsPlant cultivationFiberBryophyte
The invention discloses a method for quickly growing a bryophyte crust on the cross section of an expressway slope. The method comprises the following steps: performing natural air drying on crust bryophytes together with very thin crust soil, and then smashing; uniformly spraying with water to wet fiber grid cells on an expressway slope, uniformly spreading the smashed soil-mixed bryophyte fragments on the cross section of a fiber grid, compacting the bryophytes with a flat tool, and covering with a plastic film; and pricking a certain number of pinholes in the film, and performing shading treatment on the film with a shading net to ensure that scattered light is received. According to the invention, the crust bryophytes are taken as basic materials, and the quick bryophyte propagation method is used for the cross section of an expressway, the cross section of mining area exploitation and other places where ecological environment of soil is destroyed, so that a bryophyte crust is formed on the surface of the soil, and the bryophyte crust can achieve the effects of rainfall interception and soil organic nutrient accumulation improvement, thereby laying a foundation for survival of advanced vascular plants in the later period.
Owner:LULIANG UNIV
Selective control of lignin biosythesis in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20030005481A1Enhancing lignificationLignification is enhancedBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesLignin biosynthesisGene product
The present invention provides methods of selectively controlling lignin biosynthesis in plants such that lignification is reduced or enhanced, as desired. The invention provides, for example, a method of reducing lignification in a vascular plant by ectopically expressing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an AGL8-like gene product in the plant, whereby lignification is reduced due to ectopic expression of the nucleic acid molecule. An AGL8-like gene product useful in the invention can have, for example, substantially the amino acid sequence of an AGL8 ortholog such as Arabidopsis AGL8 (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Production and application of an aircraft spreadable, cyanobacterial based biological soil crust inoculant for soil fertilization, soil stablization and atmospheric CO2 drawdown and sequestration
ActiveUSH2271H1Efficient mannerEasy to manufactureBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhylum CyanobacteriaSoil stabilization
Systems and methods are described for the production and application of a cyanobacteria based biological soil crust inoculant for soil fertilization, soil stabilization and the drawing down and sequestering of atmospheric carbon. Inoculant is generated as a dry granulate that can be stockpiled and spread onto soils using standard agricultural spreading practices employing aircraft, ground equipment and irrigation systems. This inoculant will have particular application in stabilizing agricultural and arid land soils to limit their erosion, increasing soil fertility by fixing atmospheric nitrogen and providing nutrients, and drawing down atmospheric carbon dioxide by stimulating the growth and propagation of these biological soil crusts and their associated microorganisms and vascular plants. The effect of this carbon dioxide draw down will further the broad scale application of the soil crust inoculant by industries and nations interested in offsetting their anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions while increasing the fertility of their soils.
Owner:SEARS JAMES THOMAS
Age Authentication For Longer-Lived Vascular Herbal Plants
InactiveUS20160283649A1Testing plants/treesSpecial data processing applicationsMedicineVascular plant
Owner:MACAU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method or system for identification of a causative mutation causing a phenotype of interest in a test sample
A method for identifying a mutation associated with a phenotype of interest in a non- vascular plant, wherein the method comprises (a) aligning the DNA sequence of a reference DNA sequence and identifying a first set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; wherein the test sample is from a mutagenized non-vascular plant; (b) aligning the DNA sequence of at least one comparison sample to the reference DNA sequence and identifying a second set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; (c) filtering the first set of mismatches with respect to the second set of mismatches to identify a subset of mismatches that are unique to the first set of mismatches, wherein the subset of mismatches are candidate mutations for the causative mutation; wherein the test sample is from a non-vascular plant exhibiting the phenotype of interest and wherein the at least one comparison sample is from an independent non- vascular plant of the same genus that does not exhibit the phenotype of interest; and wherein the reference DNA sequence is a known reference sequence for a non-vascular plant of the genus. In addition, a method for identifying a mutation associated with a phenotype of interest in a non-vascular plant, wherein the method comprises a) aligning the DNA sequence of a reference DNA sequence and identifying a first set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; wherein the test sample is from a mutagenized non-vascular plant; (b) aligning the DNA sequence of at least one comparison sample to the reference DNA sequence and identifying a second set of sequence mismatches between the two sequences; (c) filtering the first set of mismatches with respect to the second set of sequence mismatches to identify a subset of mismatches that are common to the first and second sets of sequence mismatches wherein the test sample and the comparison sample(s) are from independent non-vascular plants exhibiting the phenotype of interest and wherein the independent non-vascular plants are the same genus; and wherein the reference DNA sequence is a known reference sequence or a non-vascular plant of the genus or a non-vascular plant of the genus.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Selective control of lignin biosynthesis in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20020129403A1Delayed lignificationSuppressed AGL and AGLOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationLignin biosynthesisGene product
The present invention provides methods of selectively controlling lignin biosynthesis in plants such that lignification is reduced or enhanced, as desired. The invention provides, for example, a method of reducing lignification in a vascular plant by ectopically expressing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an AGL8-like gene product in the plant, whereby lignification is reduced due to ectopic expression of the nucleic acid molecule. An AGL8-like gene product useful in the invention can have, for example, substantially the amino acid sequence of an AGL8 ortholog such as Arabidopsis AGL8 (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Vascular plants expressing Na+ pumping ATPases
The present invention relates to a vascular plant including cells expressing a Na<+> pumping ATPase.
Owner:植物功能基因组PTY澳大利亚中心有限公司
Hyperspectral remote sensing method for estimating species richness of vascular plants
ActiveCN110967300AImprove Quantitative AnalysisHigh precisionScattering properties measurementsEngineeringGrassland
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing method for estimating the species richness of a vascular plant, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining remote sensing data, carrying out the radiation correction, geometric correction and terrain correction, and extracting spectral data; correcting and checking the obtained spectral data to ensure that no data error exists; smoothing the obtained spectral data, and obtaining the mean value of intermediate data on the basis of four adjacent data; calculating a first-order spectral derivative; calculating the first-order derivative ratio of each waveband; and calculating a species diversity index estimated value. According to the method, the diversity of the plant species can be rapidly estimated, and the method can be widely applied to rapid evaluation of the abundance of the vascular plant species in grassland, grassland, shrubs, farmlands, nursery lands and the like; different from a large amount of manpower and material resources consumed by on-site quadrat investigation or a large amount of expenditure for purchasing remote sensing images, the diversity index of the plant species can be rapidly determined, a large amount of manpower and material resource investment is not needed, and the method has the advantages of efficient information processing and investment cost saving.
Owner:MINZU UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
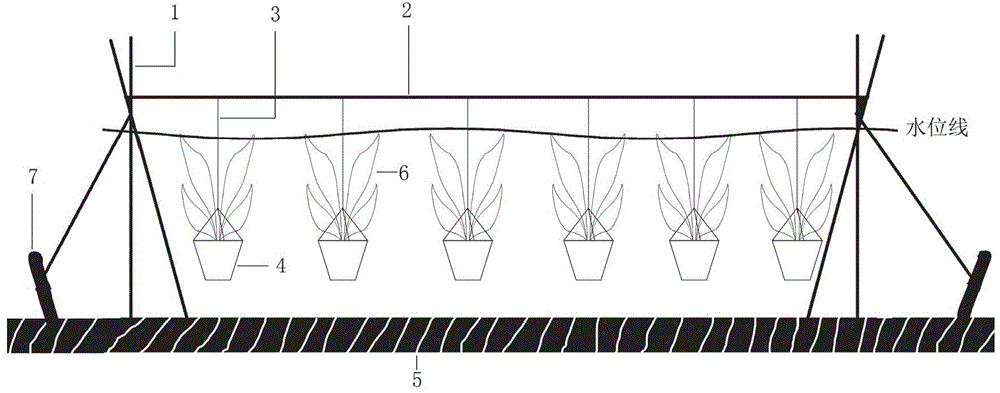
Device for planting submerged vascular plants and floating plants in suspension manner
InactiveCN102907277ASimple structureLow costSustainable biological treatmentReceptacle cultivationEutrophicationSludge
The invention relates to a device for planting submerged vascular plants and floating plants in a suspension manner, belonging to the construction field of ecological restoration engineering and landscape water. The device consists of a support frame (1), a horizontal cable (2), cables (3) and a planting pot (4), wherein the lower end of the support frame is inserted in substrate sludge (5), both ends of the horizontal cable are respectively arranged on the support frame, the cables are vertically suspended on the horizontal cable at equal intervals and the lower end of the cable is provided with a fixed sleeve, and plants (6) are planted in the planting pot arranged inside the fixed sleeve (3); the support frame 1 is composed of four support rods and two sway rods (7); and the fixed sleeve is a rope loop fixed by three ropes. The device is prepared from conventional marketing materials according to a conventional method. The device has the following advantages: firstly, the device is simple in structure, low in cost, high in stability and resistance to storm; secondly, the position of the planting pot is convenient to adjust, which is beneficial to photosynthesis of plants and ensures high survival rate; and thirdly, the plants absorb enriched nutritional substances in the water so that the water quality is efficiently improved, and the device is particularly suitable for ecological water management of eutrophic plateau lakes.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
On-line dynamic monitoring method for biomass of large vascular plant in small area range
InactiveCN102679958AImprove real-time performanceImprove conveniencePhotogrammetry/videogrammetryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight energyDynamic monitoring
The invention provides an on-line dynamic monitoring method for biomass of a large vascular plant in a small area range. The method comprises the steps as follows: a demonstration site for area characteristics is established, and spectrogram of the large vascular plant is shot; the result obtained by shooting with a multi-spectrum camera is converted through an NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) conversion formula to obtain the NDVI of the large vascular plant within the range of the demonstration site; the NDVI is converted into NPP (net primary productivity) through a light energy conversion model; the relationship between NDVI and the biomass within the range of the demonstration site is obtained according to the biomass obtained through actual sampling; area TM image data with lower precision are regressed and adjusted respectively to obtain a function equation between the NDVI and the area TM image data; and the area NPP is obtained through the light energy conversion model again. Compared with traditional manual sampling and monitoring, the online dynamic monitoring method provided by the invention improves real-time performance and convenience of biomass monitoring, facilitates scientific management of small-area environment and ecology, improves precision of biomass monitoring in a whole area, is simple and convenient in data processing, and is high in operability.
Owner:程红光
Evaluation method for botanical-integrity of vascular plant, irrigating method to vascular plant, film electret sensor and film ECM array
InactiveUS8806942B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCavitationWave measure
Owner:SAITAMA UNIVERSITY
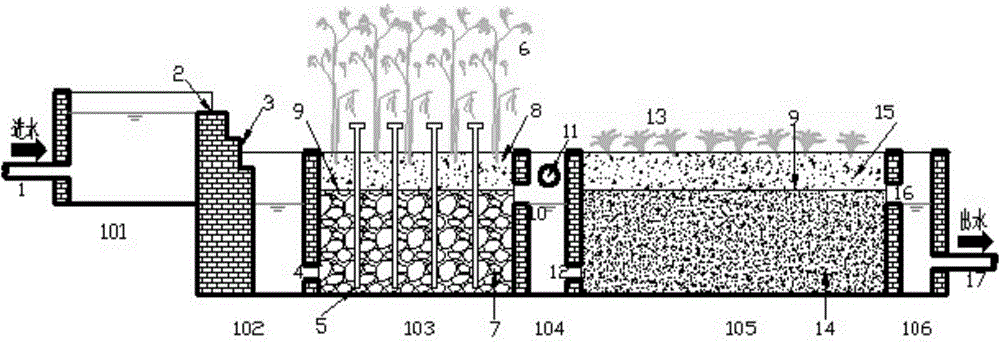
Black and odorous water treatment system based on constructed wetland
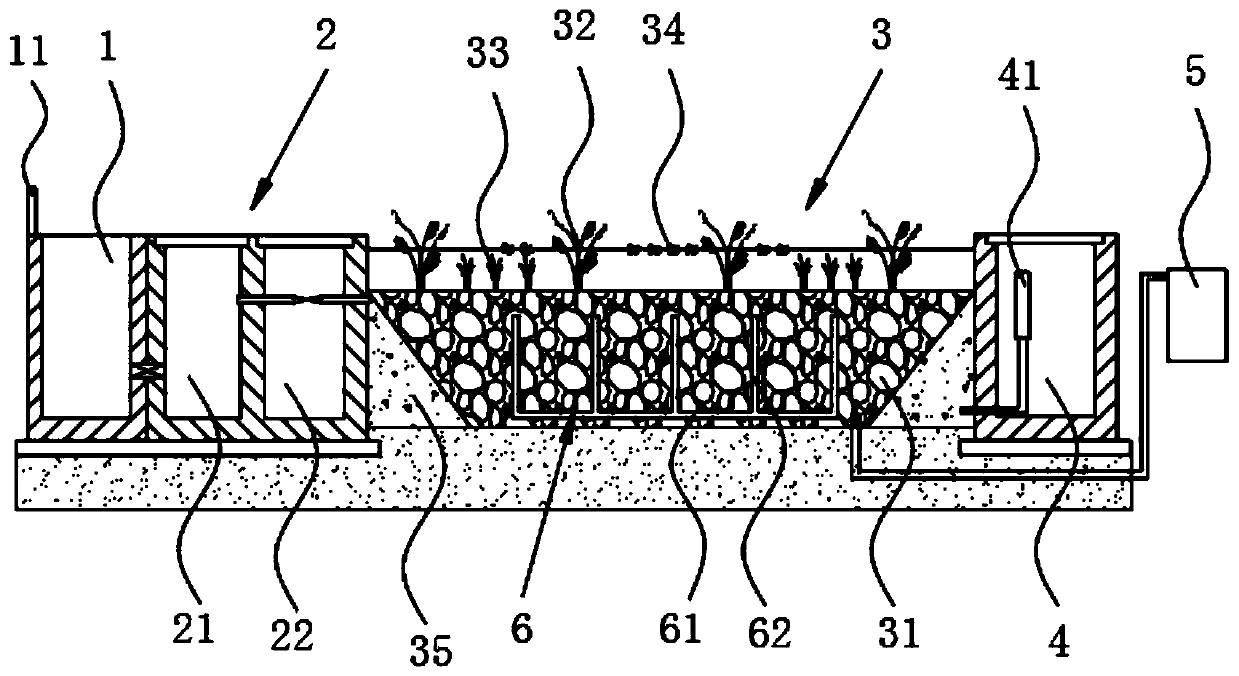
PendingCN110104894AEasy to handleSmall footprintSpecific water treatment objectivesMultistage water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandExpanded clay aggregate
The invention discloses a black and odorous water treatment system based on a constructed wetland. The black and odorous water treatment system includes a coagulative precipitation pool, a water inletarea, a constructed wetland pool, a water collection channel and monitoring equipment; the coagulative precipitation pool is communicated with the water inlet area, the water inlet area is communicated with the constructed wetland pool, the constructed wetland pool is communicated with the water collection channel, and the water inlet of the monitoring equipment is communicated with the constructed wetland pool; a filter medium and aquatic vascular plants are arranged inside the constructed wetland pool, wherein the aquatic vascular plants are located on the filter medium; the filter mediumis prepared from, by weight, 10-20 parts of gravel, 5-15 parts of coarse sand, 15-30 parts of limestone, 10-15 parts of zeolite and 40-50 parts of ceramic granules. By adopting the black and odorous water treatment system based on the constructed wetland, nitrogen and phosphorus in a water body are absorbed, the adsorption performance is high, the treating performance of the constructed wetland isensured, the COD removal rate reaches 70%, the TN removal rate reaches 60%, the TP removal rate reaches 50%, the content of dissolved oxygen is greater than 4 gm / L, and index parameters are monitoredonline.
Owner:JIANGSU YIYUJING ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
Vegetated Canopy Apparatus, System, and Method
InactiveUS20200275613A1Promote healthEasy to grow plantsSelf-acting watering devicesRenewable energy machinesVascular plantVegetation canopy
A vegetated canopy is provided with a support structure and a vegetation support assembly including a plurality of soil containers supported by a plurality of brackets, a plurality of ribs supported by a plurality of supporting members, and a plurality of connecting members forming a trellis structurally configured to support the vegetation of vascular plants growing in the soil containers. The vegetated canopy includes plant- and vine-friendly support structures and may include irrigation and drainage systems, including a ‘smart’ irrigation system powered by solar energy, to support plant and foliage growth and health. The vegetated system provides a shade canopy that may block the sun's rays, lower the surrounding temperature through plant transpiration and ecosystem evaporation, and facilitate ease of use, transportation, and maintenance through automation and modularity.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Soil restoration system
PendingUS20210269373A1Facilitating plant seed catchment plantFacilitating plant vascular plant germinationBacteriaFertilising methodsPlanting seedCyanobacteria
A soil restoration system including a plurality of dry particles, each particle inoculated with dehumidified biological material including at least one species of cyanobacteria, the cyanobacteria being physically supported by the particles, and the cyanobacteria being activatable by a threshold amount of moisture so that when the cyanobacteria is activated at an application site, the cyanobacteria multiplies to form a biological soil crust capable of facilitating plant seed catchment and vascular plant germination at the application site.
Owner:PROFILE PRODS
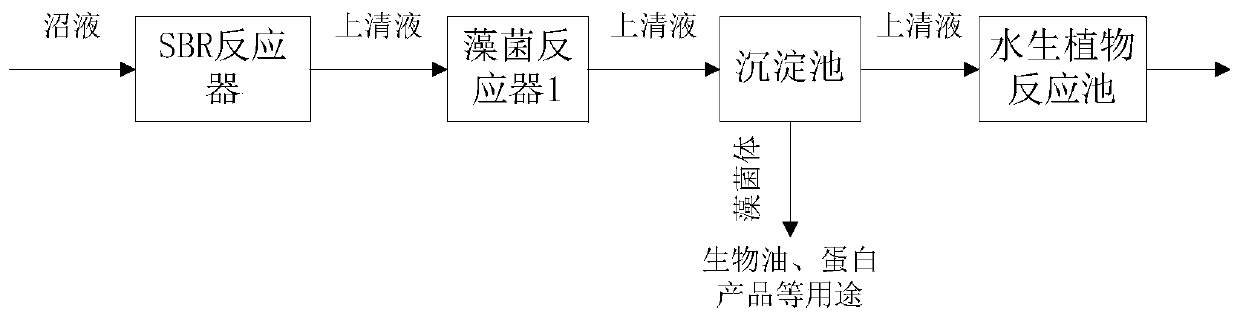
A method for efficient purification of biogas slurry based on algae-bacteria symbiosis
ActiveCN106630483BImprove use valueImprove responseMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationActivated sludgeSlurry
The invention provides a fungus-algae symbiosis-based high-efficiency biogas liquid purifying method. The fungus-algae symbiosis-based high-efficiency biogas liquid purifying method comprises the following steps: a, taking biogas liquid, inoculating active sludge, performing aeration treatment until the pH falls to 6.5 to 7.0 and naturally settling to obtain supernate 1; b, inoculating microalgae into the supernate 1 obtained in the step a, culturing and naturally settling to obtain precipitate and supernate 2, wherein the precipitate is microalgae bacteria; c, discharging the supernate 2 obtained in the step b into a vascular plant reaction tank and standing for 5 to 10 days.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
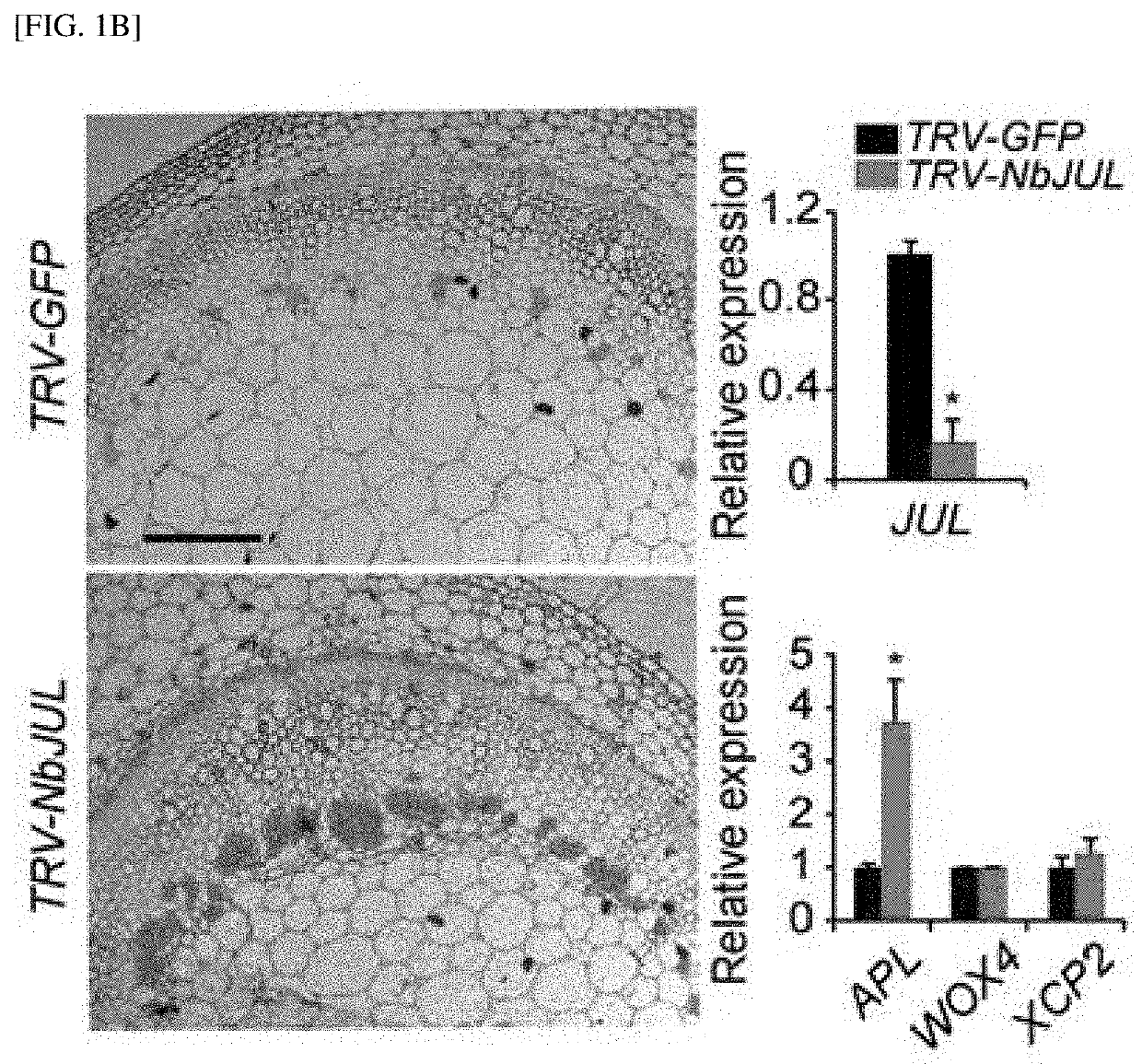
Composition for increasing nutrient storage capacity of plant nutrient storage tissues, containing julgi protein expression or activity inhibitor
InactiveUS20210115458A1Negative developmentImprove developmentPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyVascular plant
The present invention relates to a composition for increasing the sink strength of sink tissues, containing an inhibitor of the expression or activity of a JULGI protein or a protein having 80% or more homology with the JULGI protein; a method for increasing the sink strength of sink tissues of plants by using the composition; and a plant body of which the sink strength is increased through the method. A plant body is treated with a composition containing an inhibitor of the expression or activity of a JULGI protein or a protein having 80% or more homology with the JULGI protein, according to the present invention, such that the development of the phloem, which is an organ serving the most important role in the movement of photosynthates and eventual storage thereof in sink tissues in starch and sugar forms in plants, can be enhanced so as to increase the sink strength of sink tissues in plants, and thus the productivity of various crops including vascular plants in which JULGI is conservatively expressed can be promoted. In addition, unlike conventional methods, a method for increasing the sink strength of plants, according to the present invention, can overcome conventional limitations by being a method that produces higher value-added crops into which no exogenous gene is introduced and which are free of GMO problems.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
A Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Method for Estimating Species Richness of Vascular Plants
ActiveCN110967300BQuick estimate of richnessRapid Determination of Diversity IndexScattering properties measurementsInformation processingGrassland
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing method for estimating species richness of vascular plants. The method comprises: acquiring remote sensing data, performing radiation correction, geometric correction and terrain correction, and then extracting spectral data; correcting and Check to ensure that there is no data error; smooth the acquired spectral data, and obtain the mean value of the intermediate data based on the adjacent 4 data; calculate the first-order spectral derivative; calculate the ratio of the first-order derivative of each band; calculate species diversity Index estimates. The present invention can quickly estimate the diversity of plant species, and can be widely applied to the rapid assessment of the species richness of vascular plants in grasslands, grasslands, shrubs, farmlands and nurseries; Or the large cost of purchasing remote sensing images can quickly determine the diversity index of plant species without requiring a lot of manpower and material resources, and has the advantages of efficient information processing and saving input costs.
Owner:MINZU UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
A method and system for synthesizing apparent texture of leaves of parallel venation plants
ActiveCN104732583BClear contextIn line with the actual apparent structural characteristics3D modellingPattern recognitionVascular plant
The invention relates to a synthesizing method and system for representation texture of parallel venation plant leaves. According to the method, the leaves are divided into a plurality of basic structure units according to texture characteristics; an image of the representation texture of each basic structure unit is obtained according to representation parameters of the parallel venation plant leaves; the images of the representation texture of the basic structure units are arranged so that the representation texture structure of a parallel venation plant can be formed. Through the method and system, not only can the generated representation texture structure of the parallel venation plant meet characteristics of an actually representation structure of the leaves, but also representation texture with any resolution ratio can be generated in theory; by controlling the difference of representation parameters of the units in the same column, the venation of the constructed representation texture structure of the parallel venation plant can be clearer.
Owner:INTELLIGENT EQUIP TECH RES CENT OF BEIJING ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Preparation method and application of a vascular plant-based porous oxidative polymeric chelate adsorption material
ActiveCN105664864BLarge specific surface areaRich in poresOther chemical processesWater contaminantsHydroxylamineAcrylonitrile
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a vascular plant based porous oxidative polymerization chelating adsorption material. The adsorption material takes a porous vascular plant as the carrier, and is grafted with a lot of amidoxime groups. The preparation method includes: subjecting the vascular plant to oxidation treatment, then conducting coupling with a double-bond equipped silane coupling agent, then carrying out free radical polymerization reaction with acrylonitrile under the action of an initiator, and finally converting part of a nitrile group into an amidoxime group through hydroxylamine, thus obtaining the adsorption material. The adsorption material has strong hydrophilicity, abundant porous structure and numerous amidoxime groups, and can be applied to removal of heavy metals or radioactive metallic elements from wastewater. The adsorption material shows the characteristics of high adsorption capacity, strong adsorption ability, reproducibility and reusability, and good reuse effect, and is especially suitable for adsorption removal of lead, cadmium, uranium and other metals from wastewater.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
On-line dynamic monitoring method for biomass of large vascular plant in small area range
InactiveCN102679958BImprove real-time performanceImprove conveniencePhotogrammetry/videogrammetryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight energyPrimary productivity
The invention provides an on-line dynamic monitoring method for biomass of a large vascular plant in a small area range. The method comprises the steps as follows: a demonstration site for area characteristics is established, and spectrogram of the large vascular plant is shot; the result obtained by shooting with a multi-spectrum camera is converted through an NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) conversion formula to obtain the NDVI of the large vascular plant within the range of the demonstration site; the NDVI is converted into NPP (net primary productivity) through a light energy conversion model; the relationship between NDVI and the biomass within the range of the demonstration site is obtained according to the biomass obtained through actual sampling; area TM image data with lower precision are regressed and adjusted respectively to obtain a function equation between the NDVI and the area TM image data; and the area NPP is obtained through the light energy conversion model again. Compared with traditional manual sampling and monitoring, the online dynamic monitoring method provided by the invention improves real-time performance and convenience of biomass monitoring, facilitates scientific management of small-area environment and ecology, improves precision of biomass monitoring in a whole area, is simple and convenient in data processing, and is high in operability.
Owner:程红光
Vascular plants expressing Na+ pumping ATPases
InactiveUS20080020464A1Improve responseDecreased level of necrosisBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesATPaseVascular plant
Owner:AUSTRALIAN CENT FOR PLANT FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS
Fertilizer for transplanting vascular plants and covering for preparing fertilizer
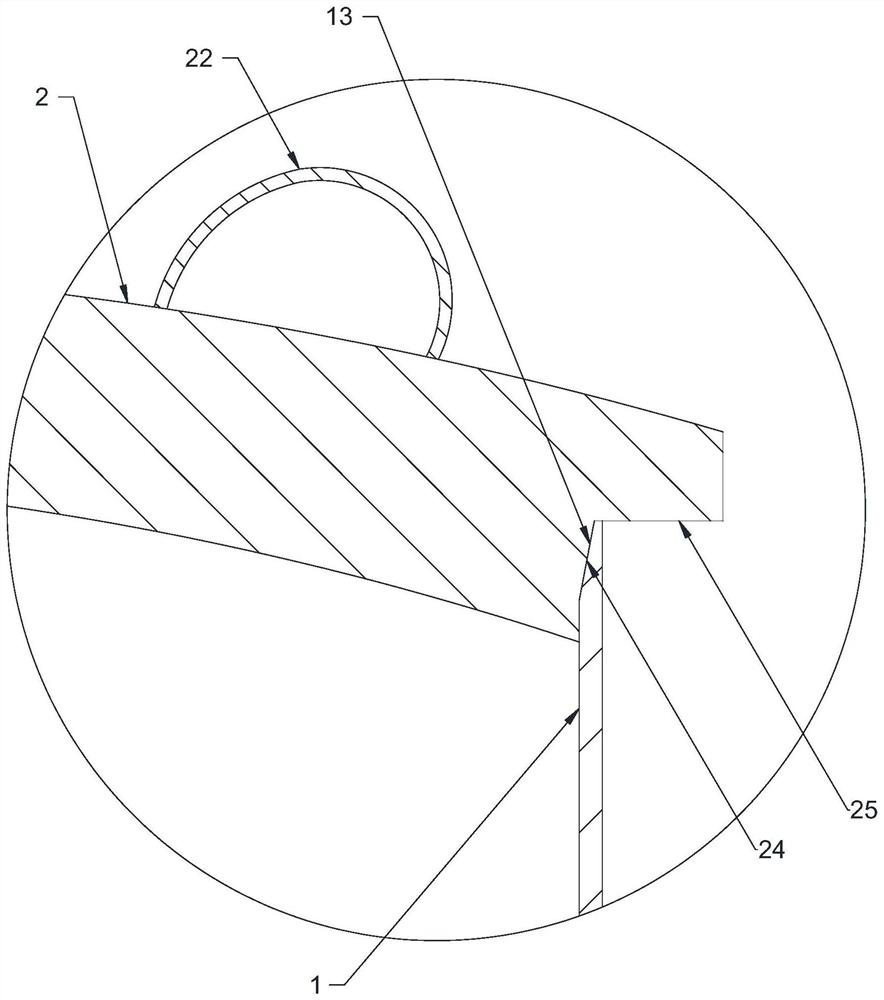
PendingCN112661544AAvoid pollutionDoes not affect extensionBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser apparatusTree rootWoody plant
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of transplanting of vascular plants, in particular to a fertilizer for transplanting vascular plants and a covering for preparing the fertilizer. A transplanting cylinder is provided with an accommodating chamber capable of accommodating culture soil and roots of the vascular plants, and the transplanting cylinder is of a rotary structure; the transplanting cover covers the upper opening of the accommodating chamber in an openable and closable manner, is provided with a penetrating hole through which the neck of the vascular plant penetrates, and is of a rotary structure; both the transplanting cylinder and the transplanting cover are prepared by crushing, fermenting, airing and pressing crop straws in sequence. The embodiment of the invention has the beneficial effects that the fertilizer can be degraded quickly (for example, two years) to serve as a fertilizer, the extension of tree roots to the surrounding and underground is not influenced, and the fertilizer is not needed any more wen the tree grows up; the structure is simple, and mounting and dismounting are convenient; and the survival rate of transplanting is high, especially the survival rate of woody plants transplanted on mountaintops and upslopes is extremely high, and the fertilizer is resistant to wind, freeze-proof, warm-keeping, moisture-preserving and breathable.
Owner:晋中市青林绿化有限公司
Compositions and methods for systemic delivery of cagos in vascular plants
Compositions and methods for systemic delivery of at least one cargo in a vascular plant. Compositions may include at least one cargo delivery particle, having a core and a shell; and at least one cargo disposed on the shell. The core may include at least one micronutrient. The shell may include a coating material. The at least one cargo delivery particle may have a size of less than about 10 nanometers. Methods may include administering an effective amount of the compositions to a plant.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
A kind of assay method of algal biomass in biological soil crust
ActiveCN105092495BEasy to collectEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsVascular bundleChlorophyll b
The invention discloses a method for measuring algal biomass in biological soil crusts, and relates to the field of biology. The method comprises the steps of algae crust sample sampling, sieving, cleaning, algae cultivation, determination of chlorophyll a and b, standard curve drawing and algae biomass (natural growth) determination. Among them, the algae culture is cultivated with BG11 medium, and the algae used are mixed algae; the determination of chlorophyll a and b adopts the mixed solution method to extract chlorophyll (extraction solution: absolute ethanol: acetone: water = 4.5:4.5:1); standard curve The relationship between the total amount of chlorophyll a and b and algae biomass was regressed; the determination of the biomass of naturally growing algae was converted by the standard curve between the total amount of chlorophyll a and b and the biomass of cultured algae. The invention realizes the direct comparison between the algae crust and the vascular plant biomass, and provides a reliable way for more accurate calculation of the algae crust productivity and its function in the ecosystem.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com