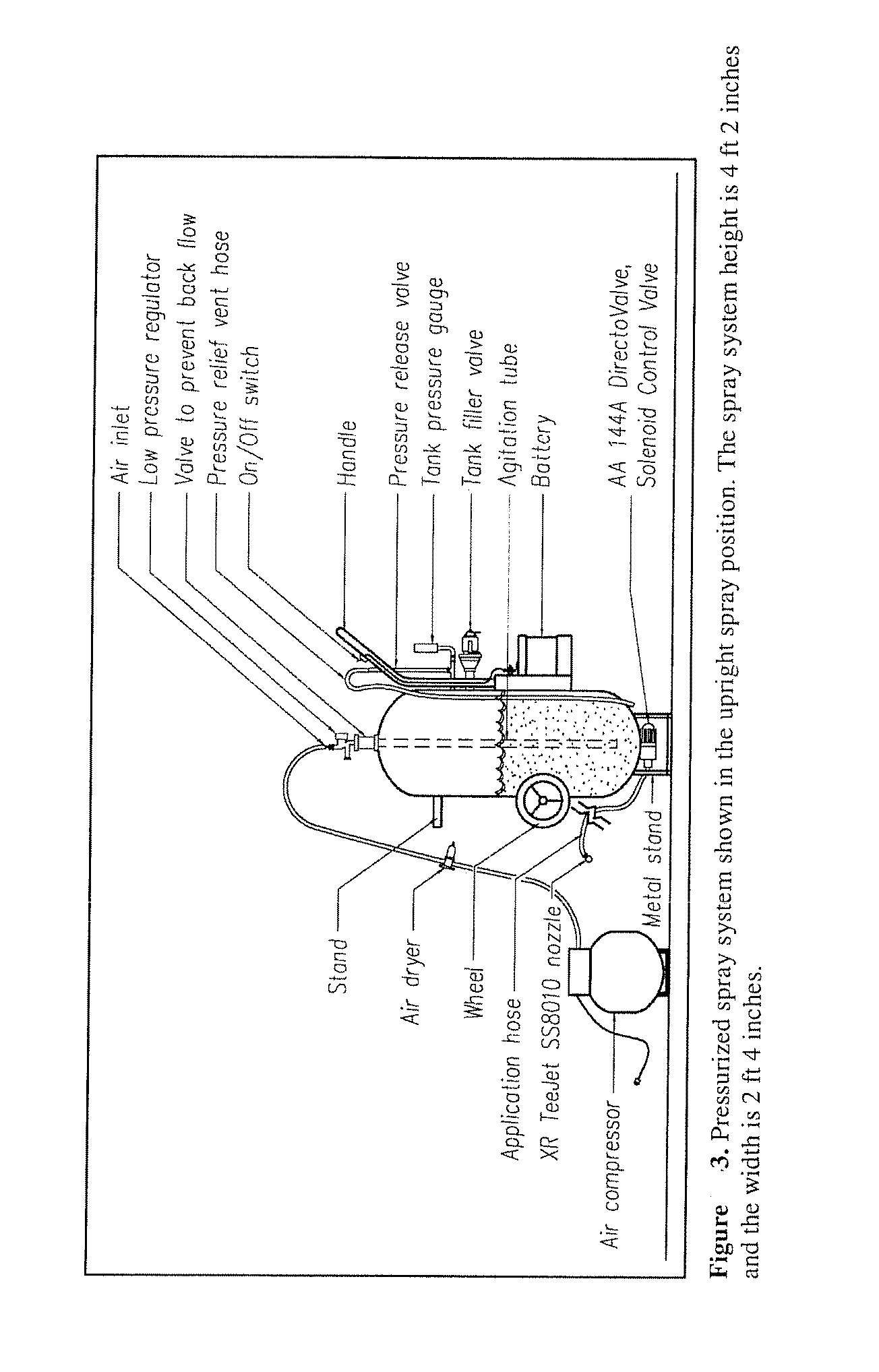
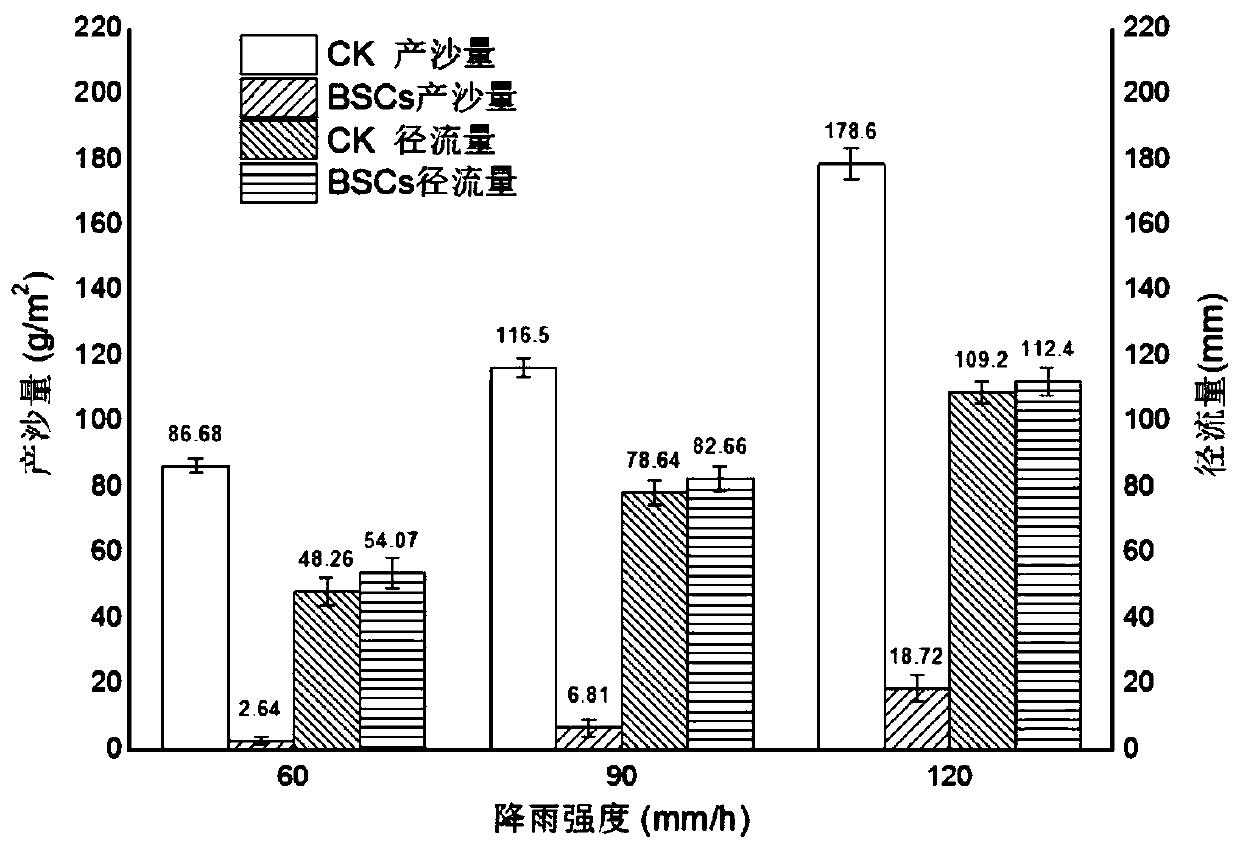
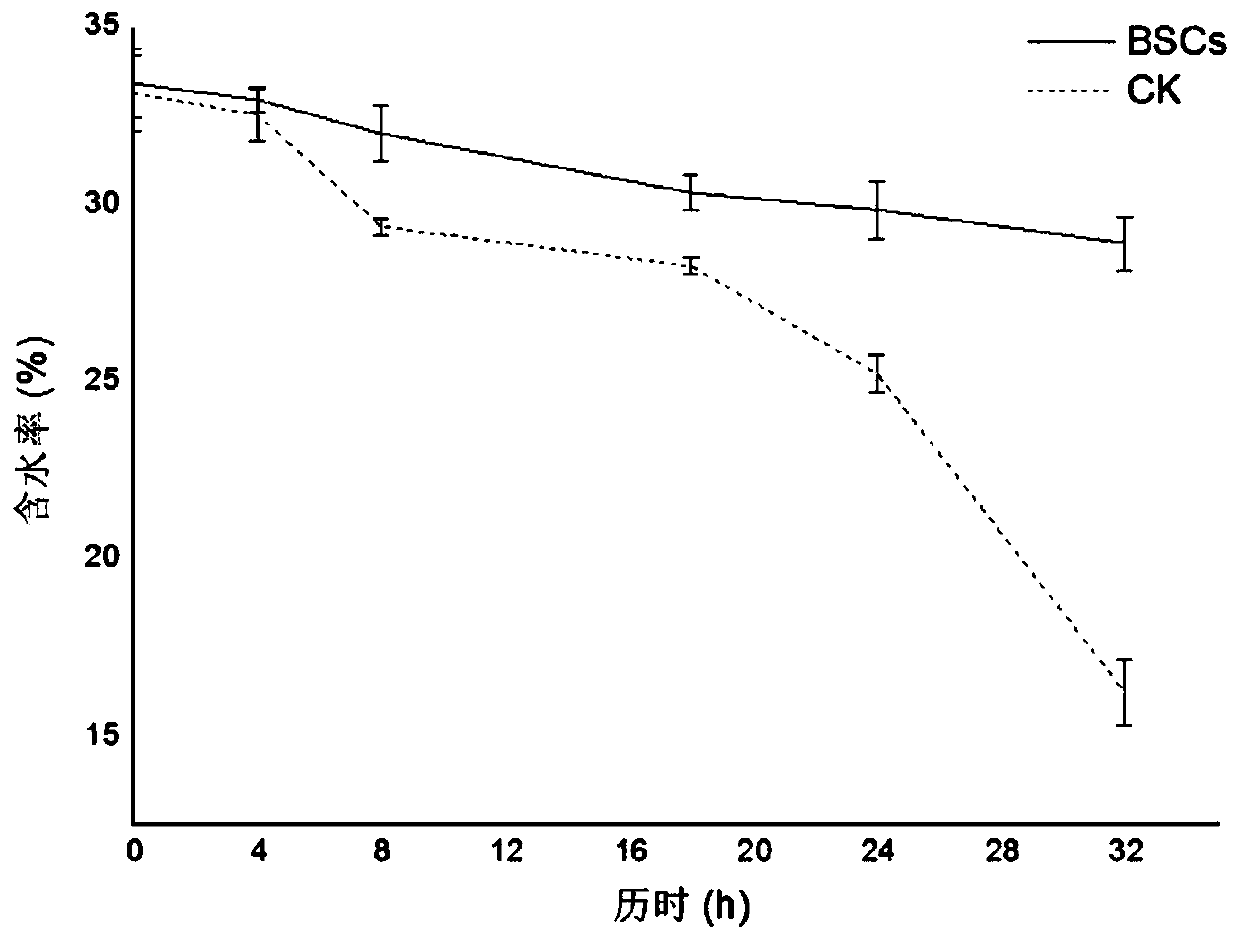
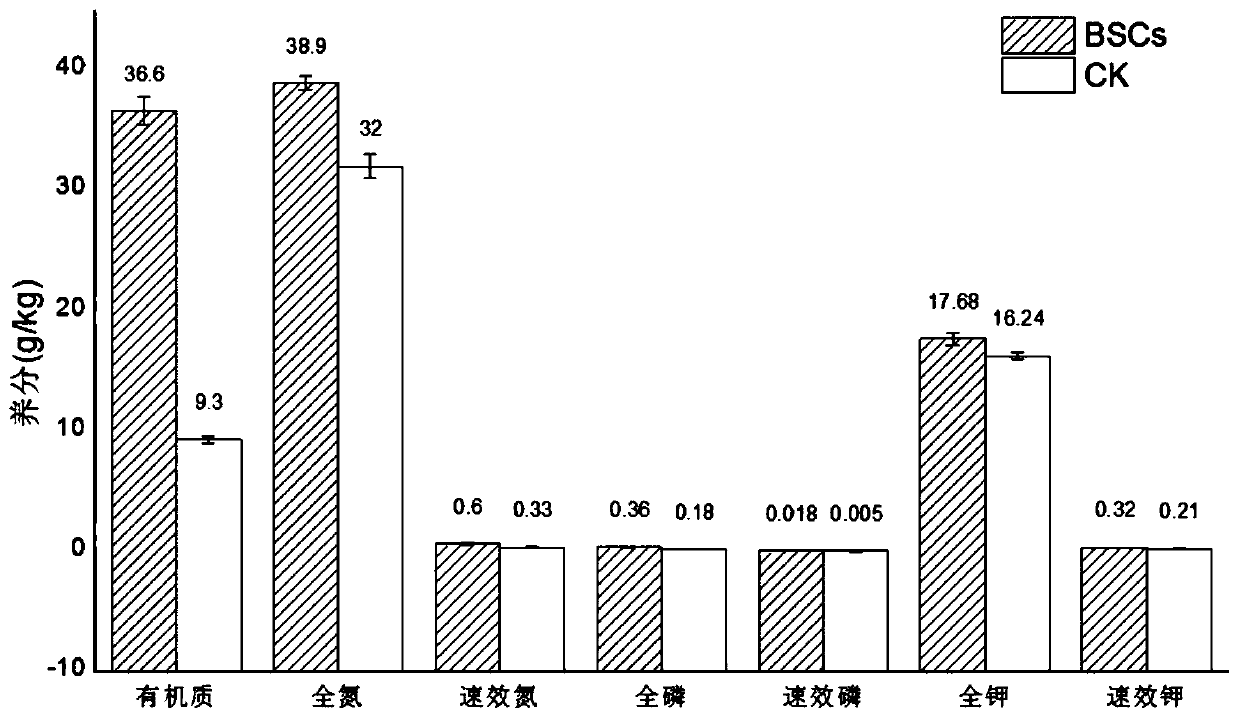
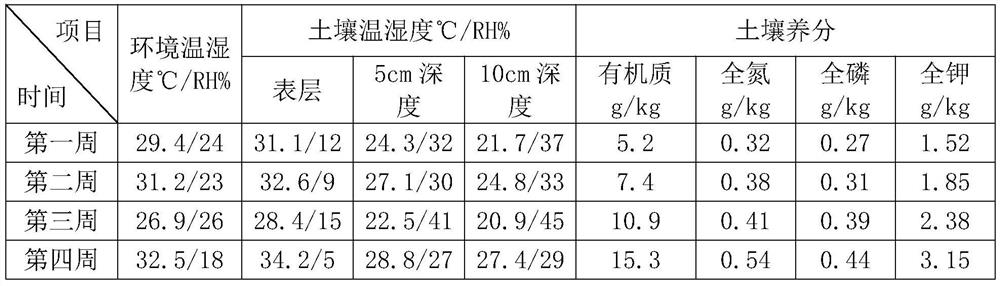
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Biological soil crust" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
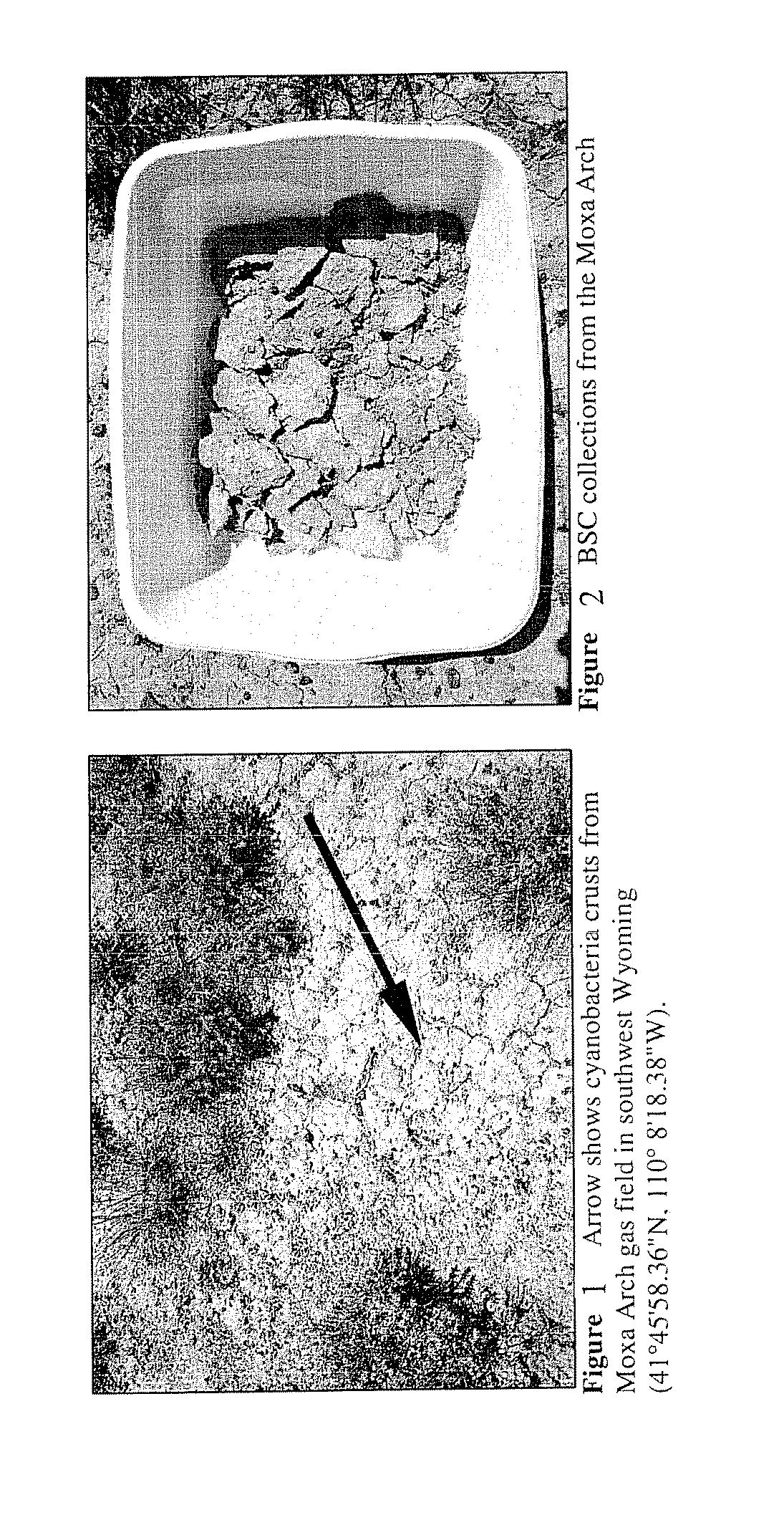
Biological soil crusts are communities of living organisms on the soil surface in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. They are found throughout the world with varying species composition and cover depending on topography, soil characteristics, climate, plant community, microhabitats, and disturbance regimes. Biological soil crusts perform important ecological roles including carbon fixation, nitrogen fixation and soil stabilization; they alter soil albedo and water relations and affect germination and nutrient levels in vascular plants. They can be damaged by fire, recreational activity, grazing and other disturbances and can require long time periods to recover composition and function. Biological soil crusts are also known as cryptogamic, microbiotic, microphytic, or cryptobiotic soils.
Novel sand fixing method of terraneous nitrogen fixation blue algae
InactiveCN1734021ADrought resistantResistant to barrennessUnicellular algaeSoil preservationMicroorganismSoil organic matter
This invention relates to new consolidation sand method with terraneous nitrogen fixation blue-green algae, which is completed by the following steps: blue-green algae foster, inoculation environment, inoculation time and inoculation quantity, and it uses the microorganism technology such as terraneous nitrogen fixation blue-green algae to achieve the fast consolidation of the flowing sand in the fixed and the half fixed desert area and achieve the ecology rehab in the engineering trouble area of the fixed and half fixed desert area. The applied nitrogen fixation blue-green algae can do photosynthesis by itself by the limited precipitation in desert, it grows up, and produces hull, which achieves the purpose of adding organic matter in soil and improving the structure of the soil and preventing and consolidating sands.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dry desert zone sand binder planting method
ActiveCN104885752AMitigation of wind and sand disasters in the northMitigation of wind and sand disastersClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsSoil sciencePlant species
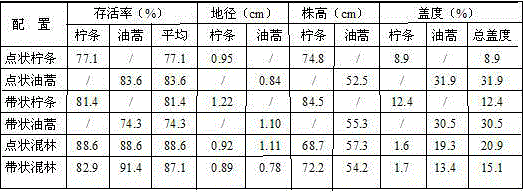
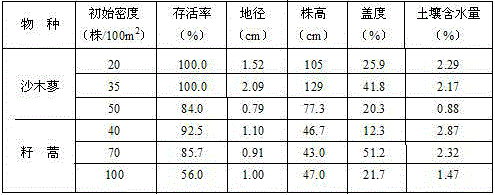
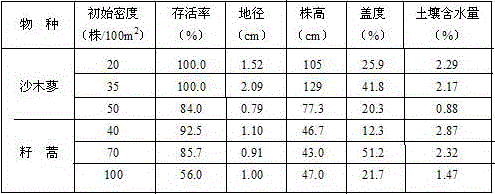
The invention relates to a dry desert zone sand binder planting method. The survival rate of all kinds of sand binders is 70 percent or more in the dry desert regions with the annular precipitation ranging from 100 mm to 250 mm through sand face fixing, plant species selecting, planting density determining, planting mode selecting and seedling managing. The planted sand binders are planted along with deposition of falling dust on the surface of sand dunes, settlement of therophytes and growing of biological soil crusts are promoted, and long-term effective fixing of the sand dunes is guaranteed. By means of the sand binder planting method, the survival rate of the sand binders is guaranteed, the labor and seedling cost is reduced, and the purposes of preventing wind and fixing sand are achieved on the premise of maintaining the water balance.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO-ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Cultivation method of moss and desert algae composite crust
ActiveCN106472281ASpeed up the succession processIncrease diversityUnicellular algaeGrowth substratesProtonemaCarex buchananii
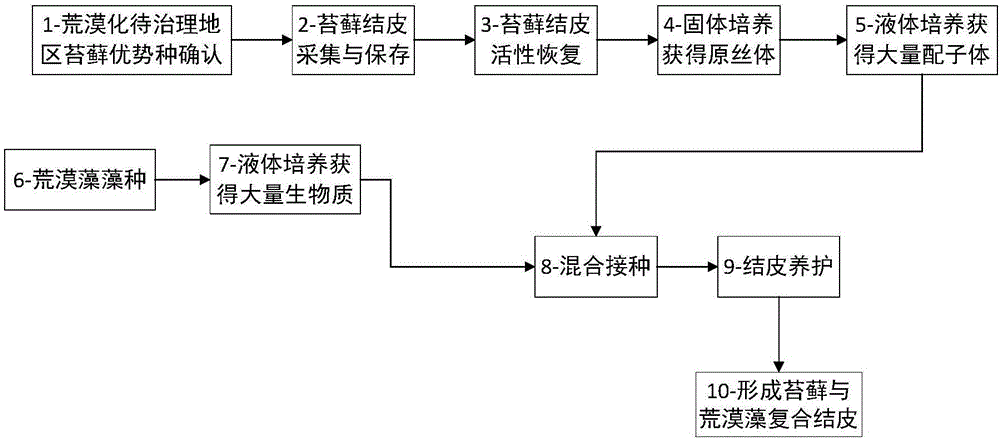
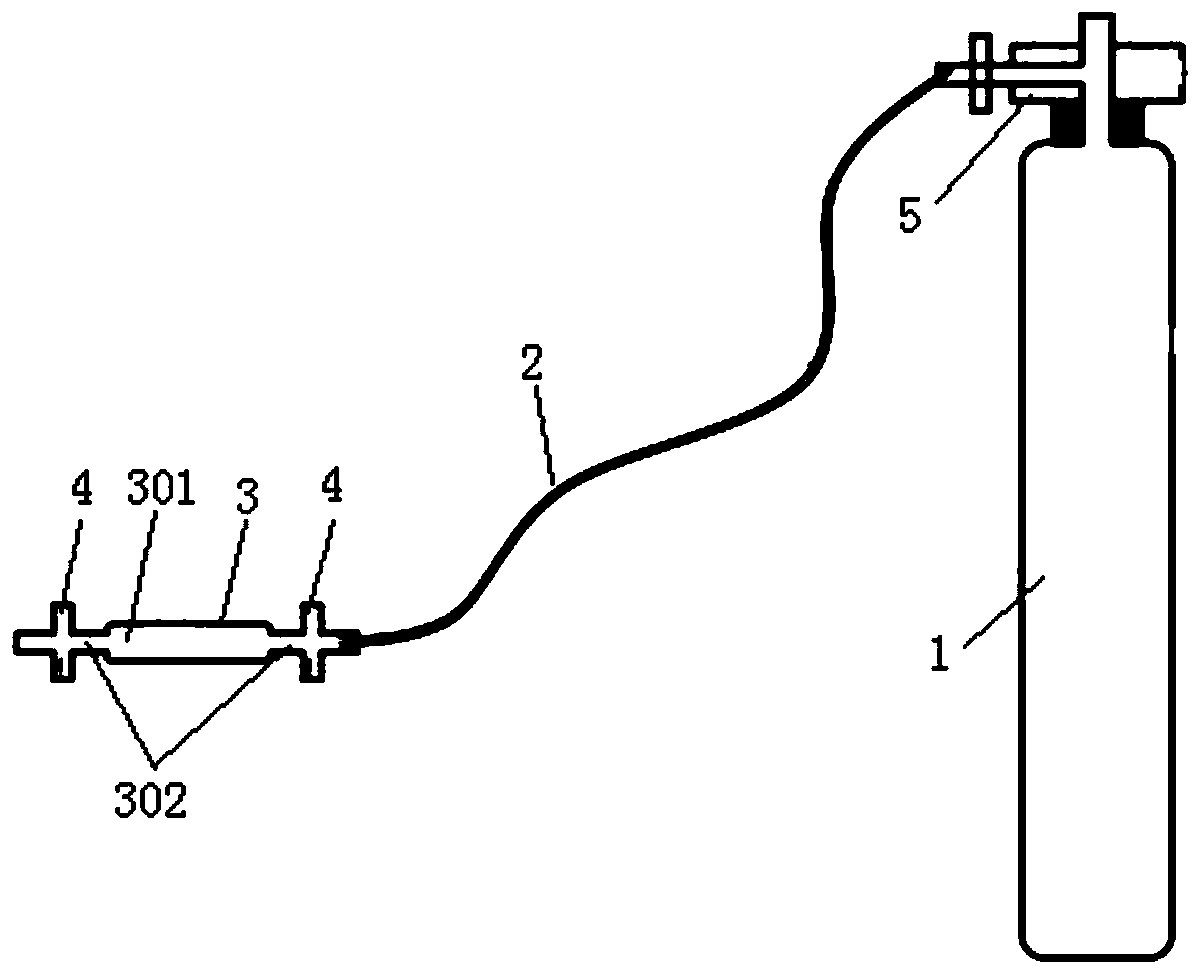
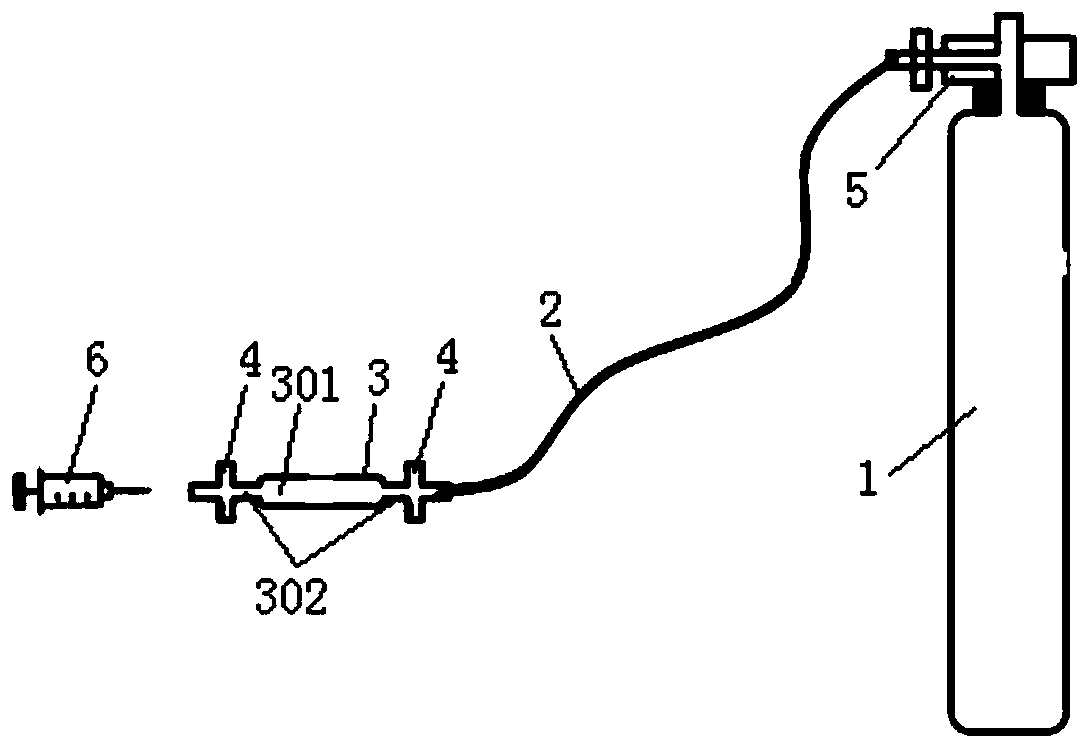
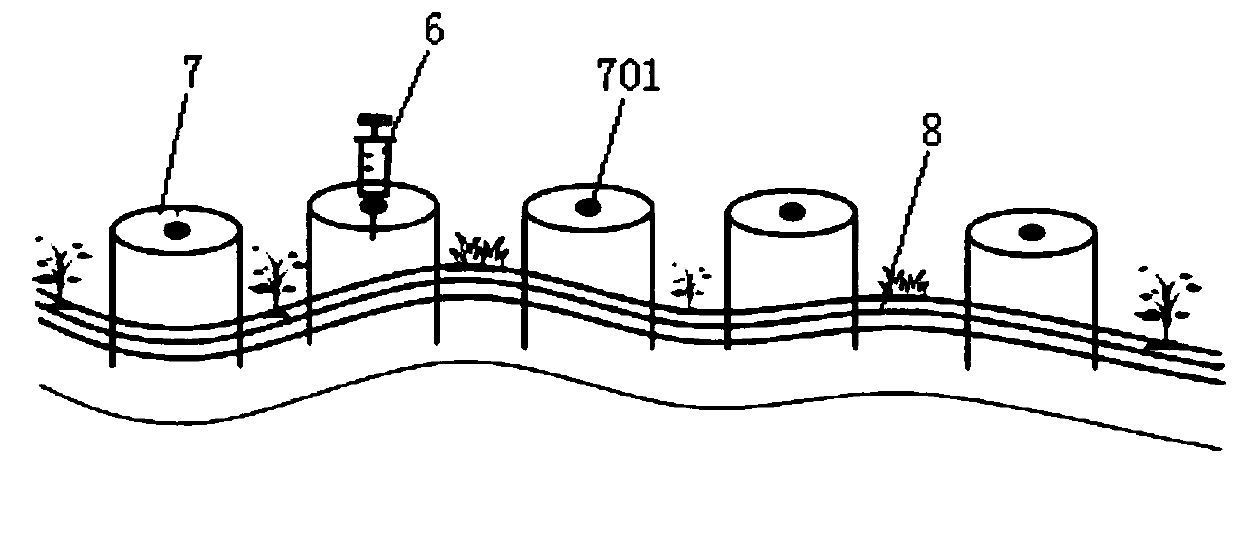
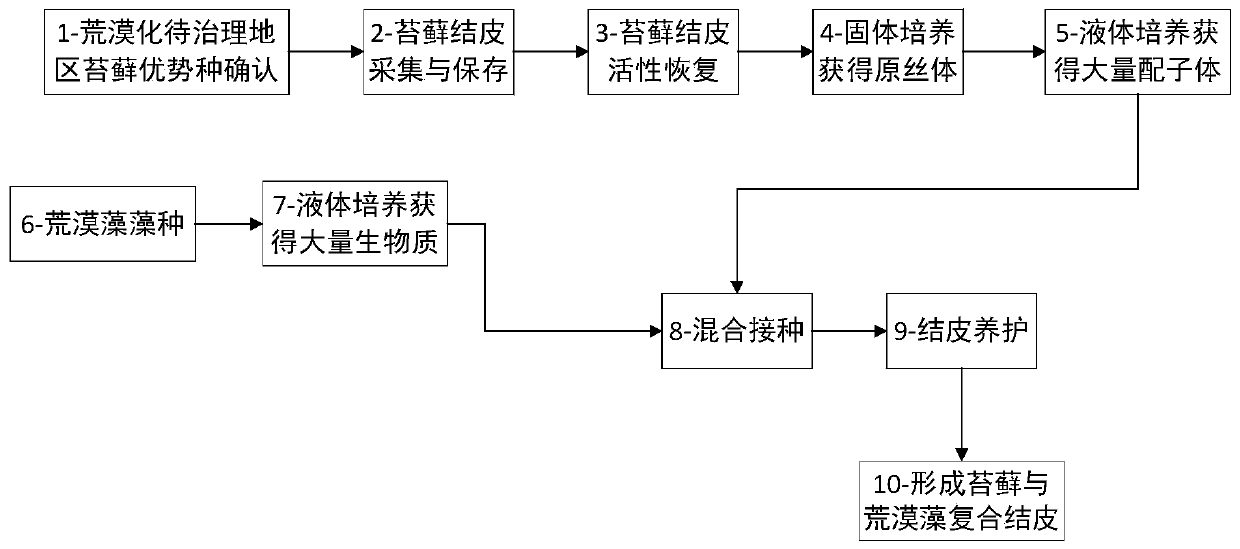
The invention discloses a cultivation method of a moss and desert algae composite crust. The cultivation method comprises the first step of collecting in summer a superior kind of moss in a natural habitat of an area to be restored; the second step of returning activities of the moss; the third step of using distilled water to wash moss crust the activities of which are returned and obtaining moss gametophyte; the fourth step of putting the gametophyte into a solid culture medium to be subjected to cultivation after the gametophyte is subjected to sterilization and obtaining moss protonema; the fifth step of picking the moss protonema and conducting static liquid cultivation to obtain differentiated gametophyte, and putting the gametophyte into a fluid culture medium to conduct aerobic cultivation; the sixth step of conducting aerobic cultivation on the desert algae through the fluid culture medium till a logarithmic growth phase, and obtaining algae thick liquid after removing supernatant; the seventh step of mixing the moss gametophyte with the desert algae thick liquid and afterwards inoculating the moss gametophyte and the desert algae thick liquid to the surface of desertification soil, and cultivating the moss and desert algae composite crust. The cultivation method of the moss and desert algae composite crust is easy to carry out and convenient to operate, evolvement process of biological soil crust in a desert area is accelerated, and fast treatment of desertification soil in arid and semi-arid lands is realized.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Arid land soil crust restoration
InactiveUS20110281331A1Promote recoveryImparts stabilityBacteriaUnicellular algaeOrganismLiquid suspension
The present invention relates to a process for restoring disturbed arid land soil crust. According to the process, site-sourced biological soil crusts (BSC) serve as sources for liquid suspension inoculants onto degraded arid lands. The BSC are gathered from near the disturbed site, and organisms from them are cultured, replicated and multiplied many times, preferably off-site. Then, this inoculant resulting from the indigenous population is distributed live and active in a liquid suspension over the entire area of the disturbed site.
Owner:LIVING EARTH
Measuring method for algae biomass in biological soil crust
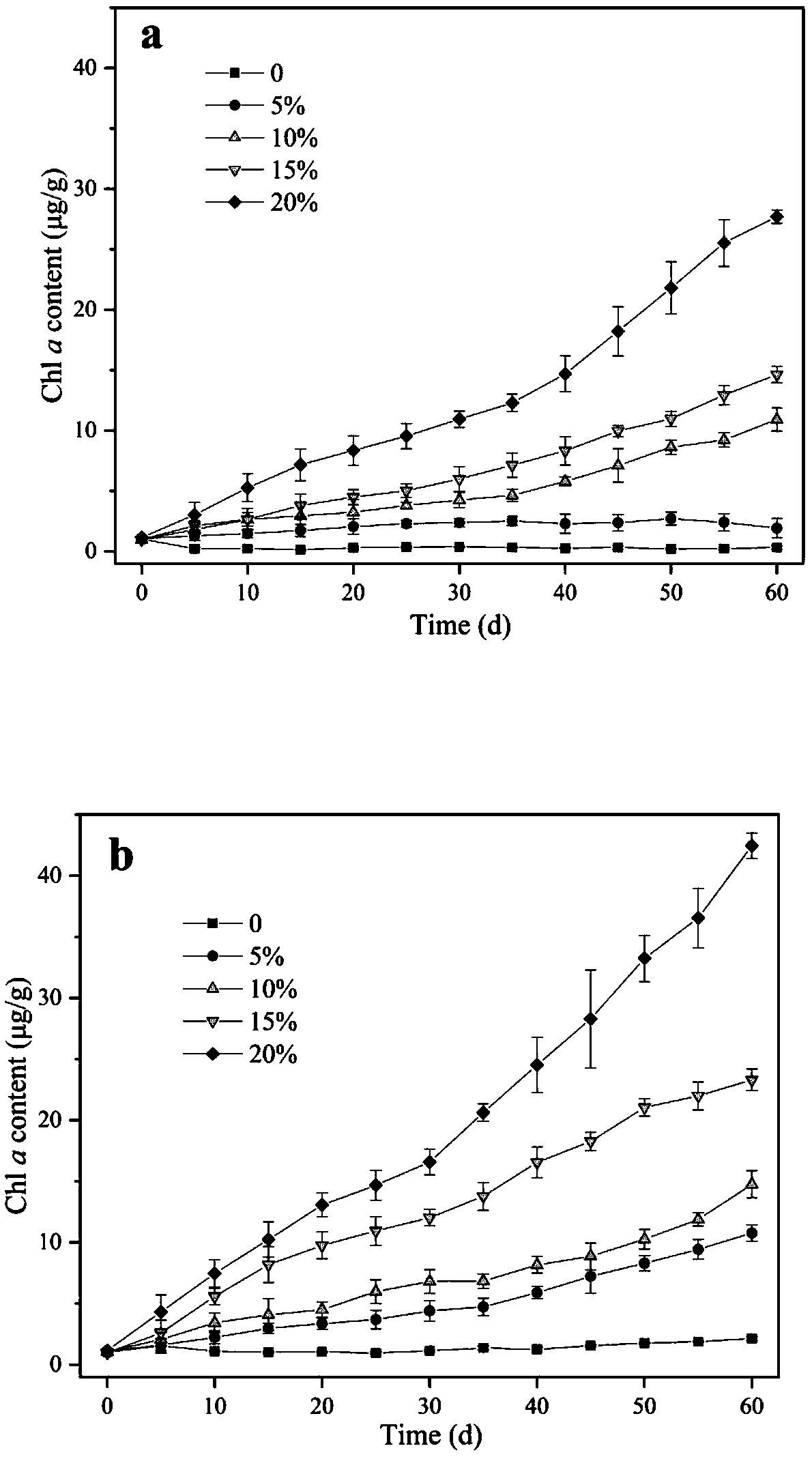
ActiveCN105092495AEasy to collectEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll bNatural development
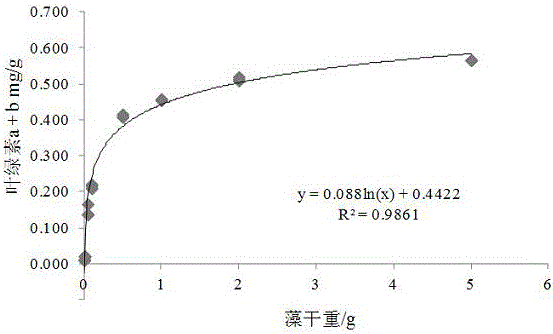
The invention discloses a measuring method for the algae biomass in a biological soil crust, and relates to the field of biology. The method includes the steps of sampling of an algae crust sample, sieving, cleaning, algae cultivating, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b measuring, standard curve drawing and algae biomass measuring (natural development). In the algae cultivating step, cultivating is carried out through BG11 cultivating media, and use algae are mixed algae. In the chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b measuring step, chlorophyll is extracted with a mixed solution method, wherein extracting solutions comprise absolute ethyl alcohol, acetone and water in the ratio of 4.5 to 4.5 to 1. The relationship between the gross of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b of the algae and the algae biomass is regressed through a standard curve. Measuring of the natural developing algae biomass is converted through the standard curve between the gross of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b and the cultivated algae biomass. Direct comparison between the algae crust and the vascular plant biomass is achieved, and a reliable approach is provided for more accurately calculating the productivity of the algae crust and the effect of the productivity in an ecological system.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Fungus and quick cultivation method of fungus-blue algae composite lichen crust
InactiveCN109337826AIncrease carbon and nitrogen contentHigh activityFungiBacteriaSnow moldCalocybe cyanea
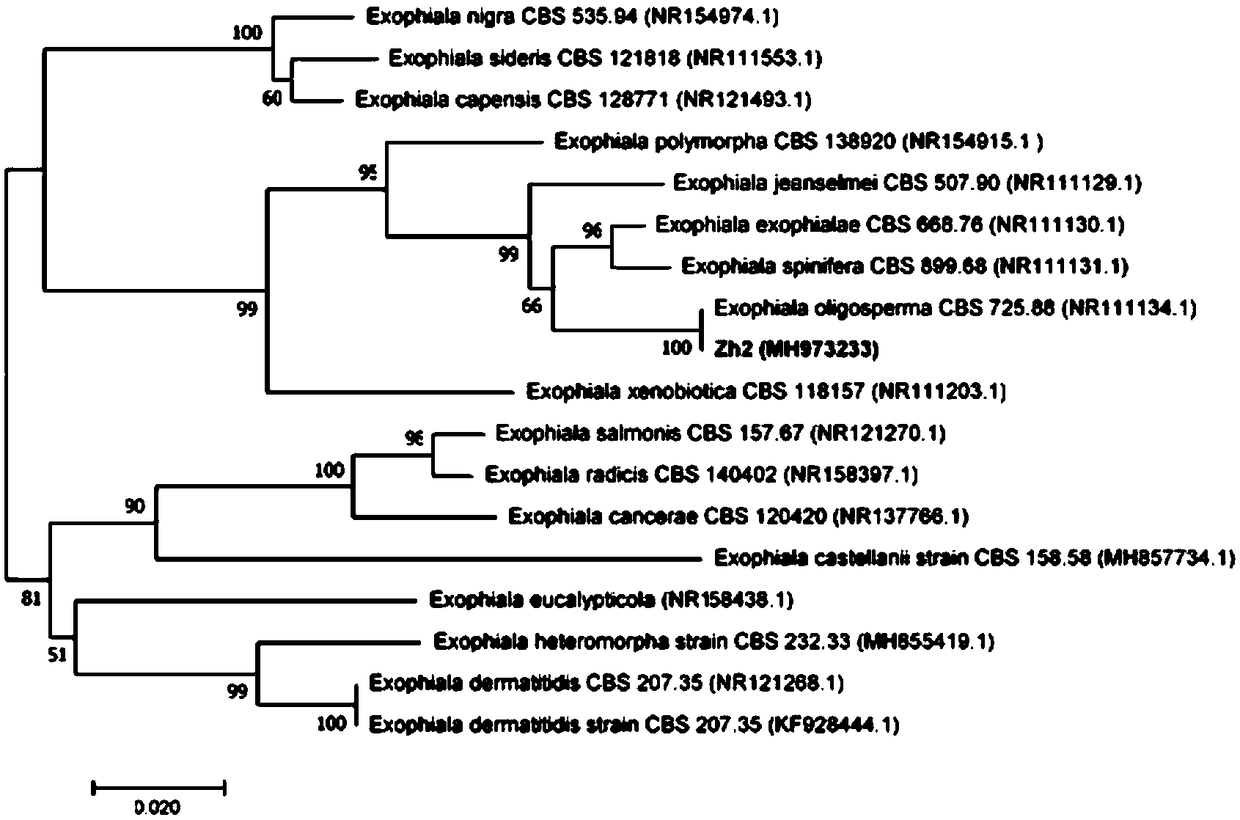
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental biology and specifically relates to a fungus and a quick cultivation method of a fungus-blue algae composite lichen crust. In the invention, exophiala oligosperma Zh2 obtained by screening belongs to a high-yield exopolysaccharides strain; the exophiala oligosperma Zh2 and blue algae are composited and applied to biological soil crust for artificial sand fixing, so that on one hand, the exophiala oligosperma Zh2 can supply a carbon source for growth of the blue algae, on the other hand, grains of sand can be cemented to form a stable aggregate, therefore, the carbon and nitrogen contents of soil and the soil enzyme activity are improved, the physical and chemical properties of the soil are improved, and the nutritional level ofthe soil is remarkably promoted. The fungus and the blue algae are mixed and inoculated on quicksand, so that a stable composite crust can be quickly formed, and the cultivation period is short; meanwhile, the stability of an artificial crust is improved, and the process of succession from an algae crust to the lichen crust is added. The drought resistant ability of the fungus-blue algae compositelichen crust cultivated by adopting the method is obviously higher than that of a single algae crust, which indicates that the composite crust can better adapt to a harsh environment of a drought region.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Composition for ecological restoration using and method for restoring the degraded ecology by them
ActiveCN105521989AIncrease biomassImproved aggregation stabilityUnicellular algaeContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentPlant growth
The invention relates to composition for ecological restoration using of barren land including alga, culture medium of the alga, soil fixing agent and ultra water absorbing materials, and a method for restoring the degraded ecology by them. According to the invention, biological soil crust can be formed in a short time; desertization and yellow sand can be avoided; waste coal mine and oil polluted land are improved into an ecological environment suitable for growth of plants; and ecological and environmental pollution caused by desert, waste coal mine and oil polluted land can be avoided.
Owner:国立顺天大学校产学协力团
Three-dimensional prevention and control method for desertification using biological soil crust-plant system
InactiveCN106538100AReduce formationShorten the timeClimate change adaptationSoil-working methodsVegetationEcological environment
A three-dimensional prevention and control method for desertification using a biological soil crust-plant system. The method comprises following steps: (1) water collecting pipe preparation; (2) supporting layer preparation; (3) functional bacteria composite system suspension preparation; (4) protection layer preparation. The three-dimensional prevention and control method for desertification using a biological soil crust-plant system has the water collecting and water conservation effect, which can reduce the influences of wind erosion and water erosion; the method realizes fast generation and well development of biological soil crust, realizes germination and growth of plants, increases building rate and coverage of vegetation in desert, effectively prevents and controls desertification and promotes ecological environment recovery in desert regions.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
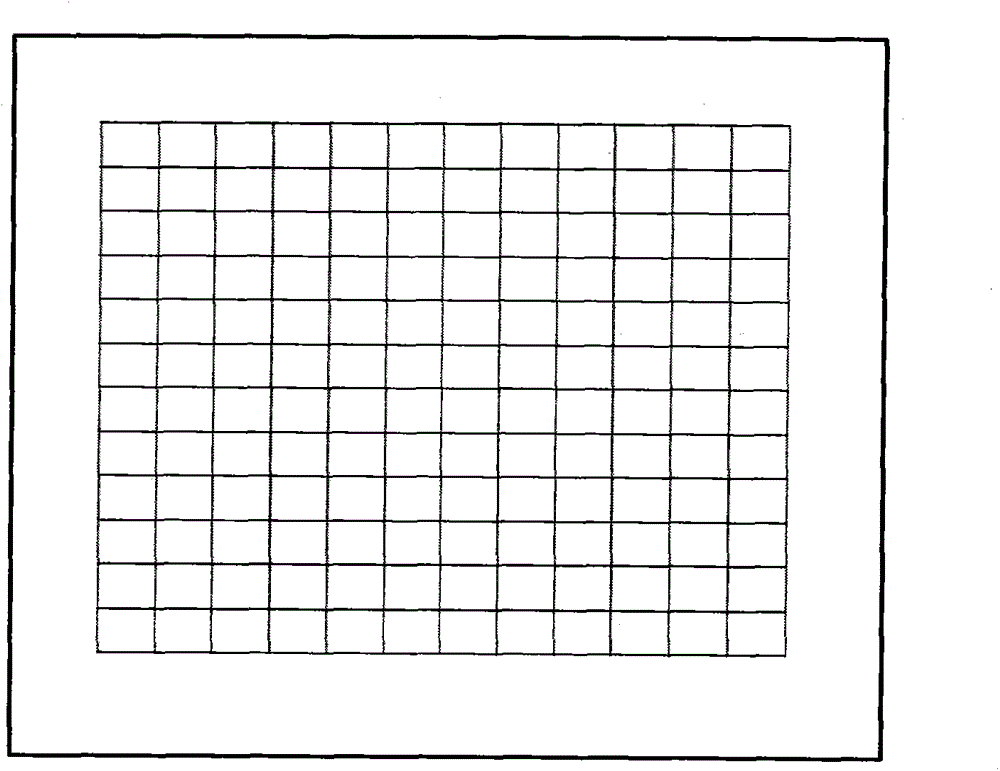
Method for determining biological soil crust coverage
The invention discloses a method for determining biological soil crust coverage. A soft polyvinyl chloride biological crust coverage determination box is made. Soft polyvinyl chloride plastic with the length of 40cm, the width of 40cm and the thickness of 2mm is selected, a square with the length and width of 30cm is drawn as square grids with the side length of 2.5 cm, the width of lines is 1mm, and 169 points are formed by the intersection of the lines. A throwing method is used to randomly select a quadrat in a sample area, distilled water is sprayed to wet biological soil crust, a plastic sample frame is horizontally laid on a quadrat to be measured, and the periphery of the plastic sample frame is pressed and fixed by sandbags or stone. If cryptogam is not covered, the corresponding position of a table remains blank. The recorded number of specific cryptogam specie is counted according to the table. In addition, a digital camera can be used to take picture closely just above the sample frame, a picture is taken to a room to carry out the determination of the biological soil crust coverage in a computer. The method is friendly to the environment, the biological soil crust is not destroyed, and the method is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
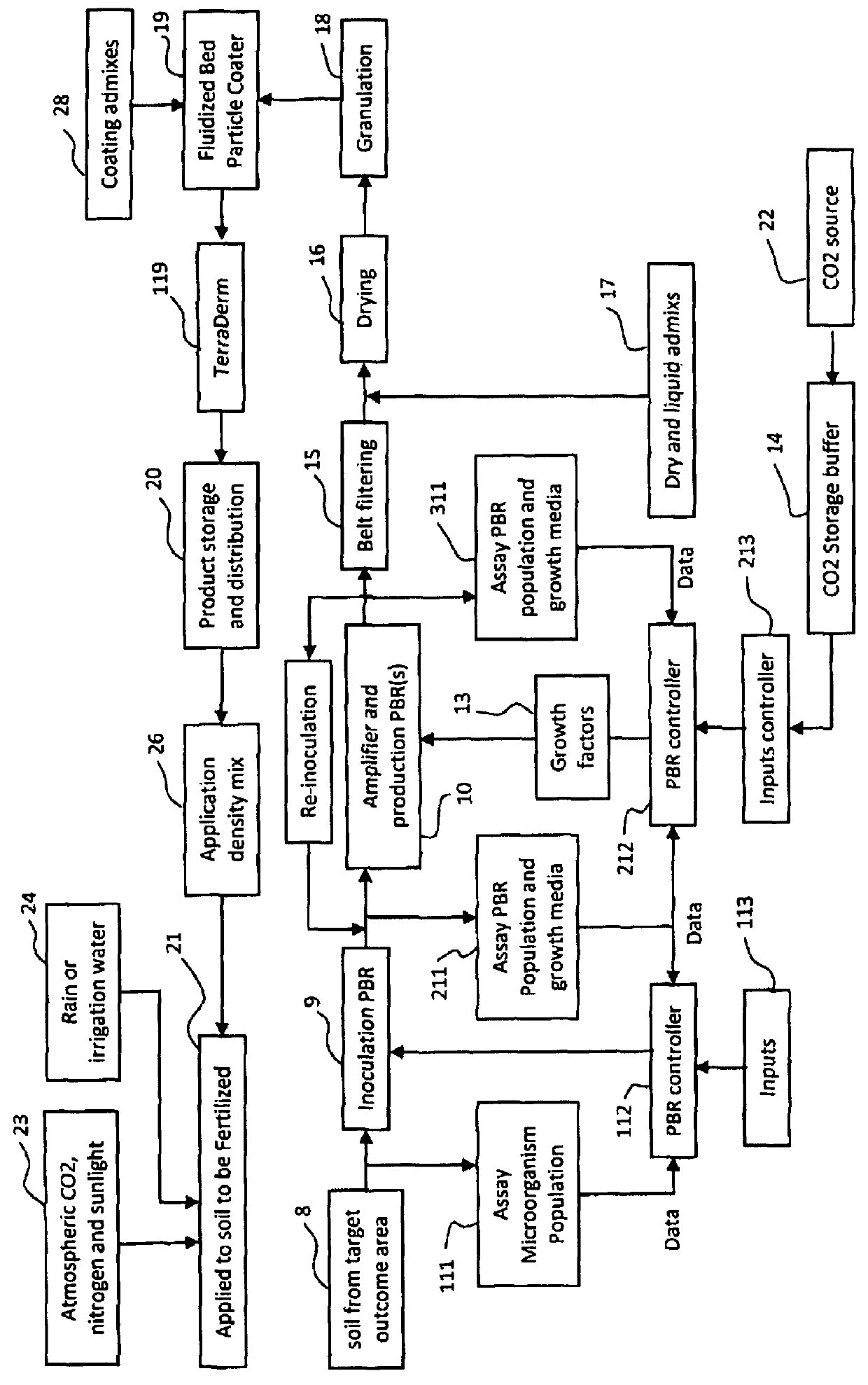
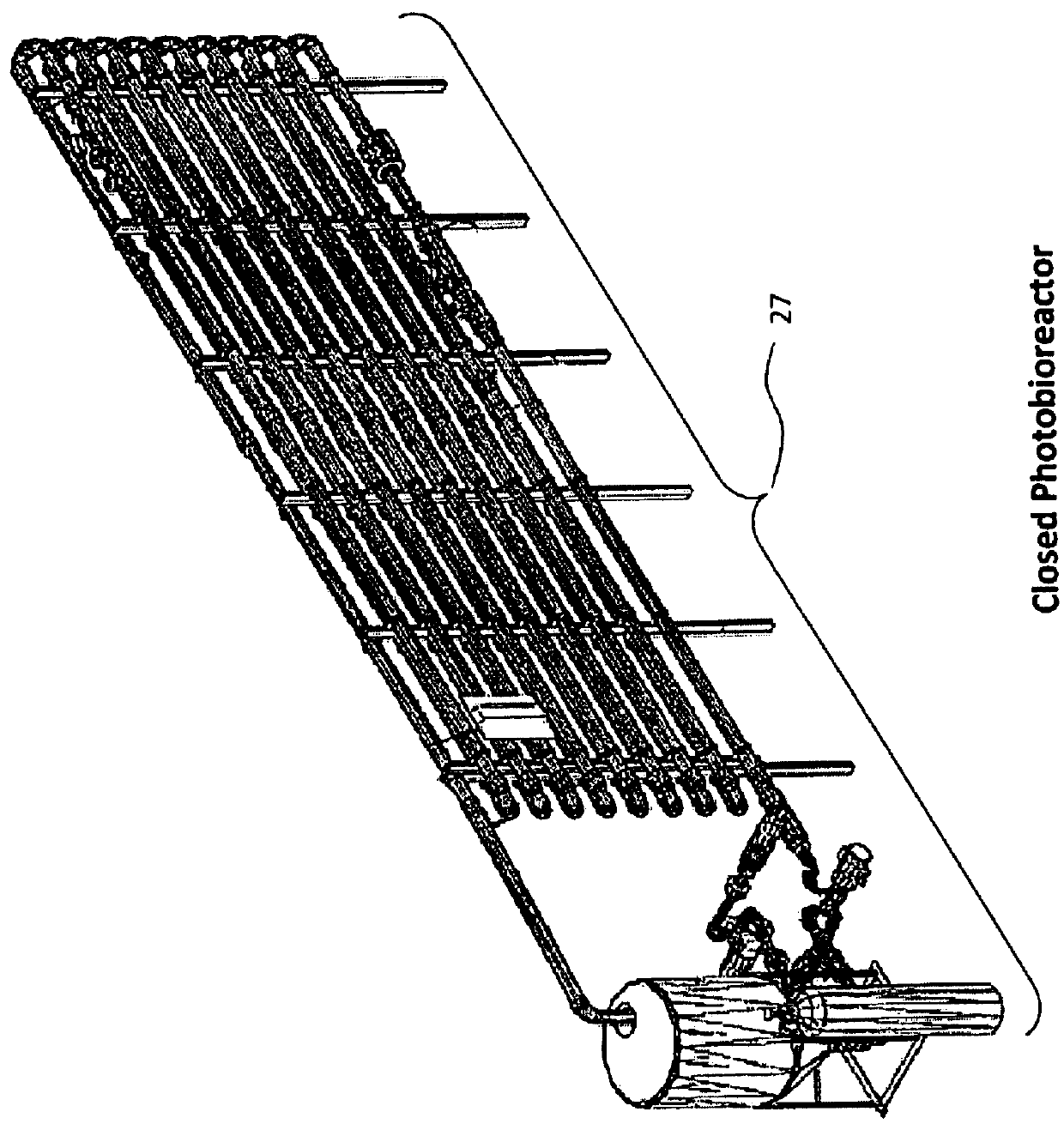
Production and application of an aircraft spreadable, cyanobacterial based biological soil crust inoculant for soil fertilization, soil stablization and atmospheric CO2 drawdown and sequestration
ActiveUSH2271H1Efficient mannerEasy to manufactureBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhylum CyanobacteriaSoil stabilization
Systems and methods are described for the production and application of a cyanobacteria based biological soil crust inoculant for soil fertilization, soil stabilization and the drawing down and sequestering of atmospheric carbon. Inoculant is generated as a dry granulate that can be stockpiled and spread onto soils using standard agricultural spreading practices employing aircraft, ground equipment and irrigation systems. This inoculant will have particular application in stabilizing agricultural and arid land soils to limit their erosion, increasing soil fertility by fixing atmospheric nitrogen and providing nutrients, and drawing down atmospheric carbon dioxide by stimulating the growth and propagation of these biological soil crusts and their associated microorganisms and vascular plants. The effect of this carbon dioxide draw down will further the broad scale application of the soil crust inoculant by industries and nations interested in offsetting their anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions while increasing the fertility of their soils.
Owner:SEARS JAMES THOMAS
Extracellular polysaccharide lysobacter SCSIO 17111 with sand fixation effect and application thereof
The invention discloses an extracellular polysaccharide lysobacter SCSIO 17111 with sand fixation effect and application thereof. The lysobacter SCSIO17111 was collected into Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM ) on August 18th, 2018; the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences at No.3, No.1 Community, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City; the collection number is CGMCC NO.14537. The lysobacter SCSIO17111 has the advantages that the sand particles can be agglomerated and the relative stable stateis maintained, so as to reach the sand fixation effect, and apply to the prevention and control of desertification in arid and semi-arid areas and the construction of reef biological soil crust. Compared with the physical sand fixation, chemical sand fixation and vegetation cultivation methods, the lysobacter SCSIO17111 has the advantages that by using the microorganism crust sand fixation type as the novel sand fixation type, the adaptability is strong, the cost is low, the effect is quick, and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for distinguishing biological soil crust and subsoil basic respiration of biological soil
ActiveCN105004853AEasy to operateNo pollution in the processEarth material testingField conditionsEdaphic
The invention relates to a method for distinguishing biological soil crust and subsoil basic respiration of biological soil to test the contribution of components (biological soil crust and subsoil basic respiration) of soil to the soil respiration. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a biological soil crust layer is carefully separated from the soil surface and arranged in a screen with 150 meshes, the subsoil of the biological soil crust is heated for 3 h at the high-temperature of 160 DEG C, and after the subsoil temperature recovers to the indoor temperature, the screen with the biological soil crust layer is placed in the soil surface layer. The method has the advantages that operation is easy, separation is carried out through a physical method and is thorough, pollution does not exist, and cost is low; according to the method, the soil water content of components of the soil cannot be changed after natural raining, a processed soil sample testing environment is close to natural conditions, and the accuracy of the test result is high; the interference in soil is small, and the measurement result is close to the real value; continuous monitoring can be carried out under the field condition. By means of the method, the soil respiration rate that the biological soil crust covers the components of the soil can be accurately tested.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO-ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Detection method of biological soil crust polysaccharide
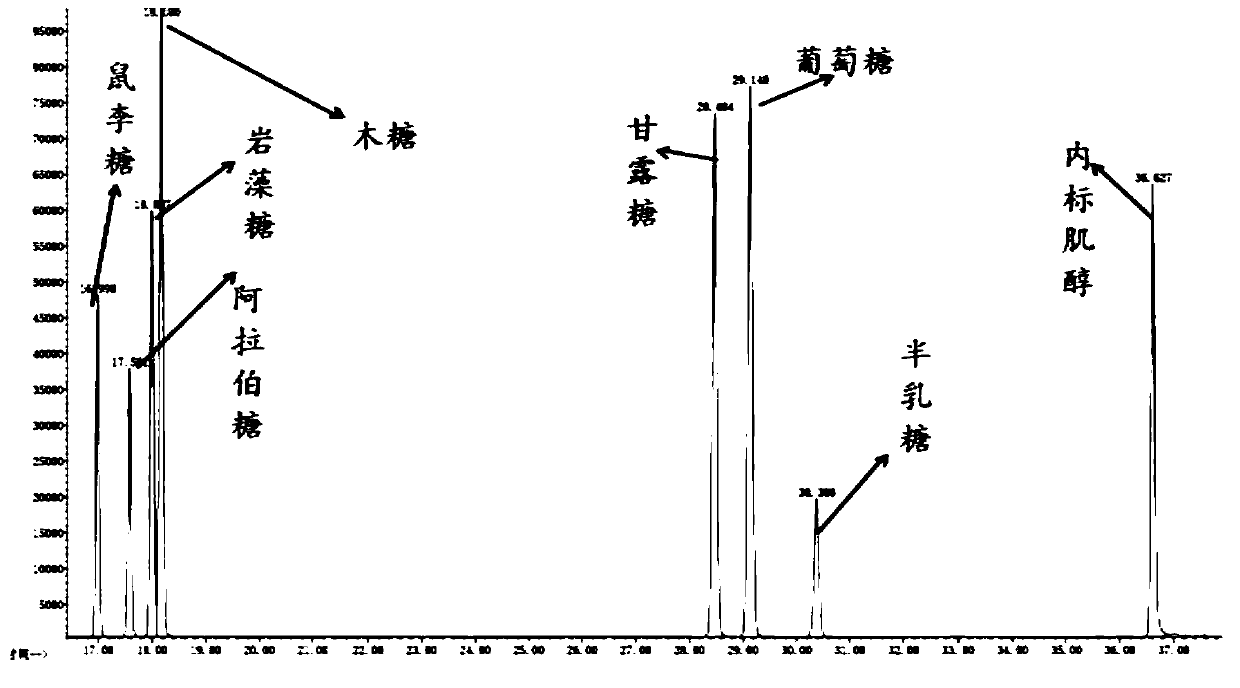
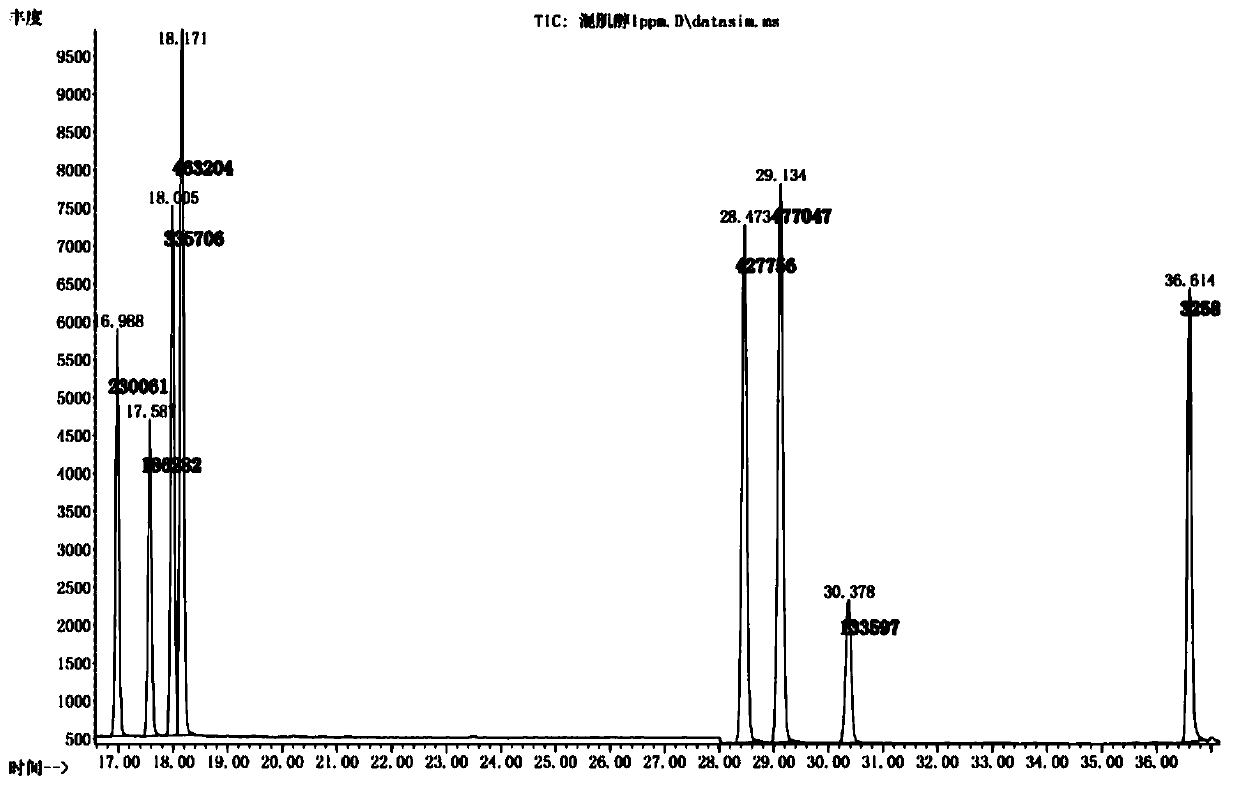
PendingCN110441418AAdvantages of detection methodHigh yieldComponent separationSilanesGas chromatography–mass spectrometry
The invention provides a detection method of biological soil crust polysaccharide. On the one hand, the detection method comprises the step of extracting the biological soil crust exopolysaccharide byadopting water extraction and alcohol precipitation method, wherein the extraction method is economic and convenient, the equipment is simple, and the polysaccharide yield is high; on the other hand,the hydrolyzed polysaccharide after extraction is derivatively treated by adopting saccharin acetate derivatization method and the trimethyl silane derivatization method, the monosaccharide in different types can be detected, and the detection comprehensiveness is ensured; furthermore, the monosaccharide component after derivatization treatment is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by adopting gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis method and an internal standard method, and three are collaboratively used, so that the detection method of the biological coil crust polysaccharidecan detect the polysaccharide with high sensitivity and accuracy; and meanwhile, the detection method disclosed by the invention is easy to realize, and the method is easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Arid land soil crust restoration
The present invention relates to a process for restoring disturbed arid land soil crust. According to the process, site-sourced biological soil crusts (BSC) serve as sources for liquid suspension inoculants onto degraded arid lands. The BSC are gathered from near the disturbed site, and organisms from them are cultured, replicated and multiplied many times, preferably off-site. Then, this inoculant resulting from the indigenous population is distributed live and active in a liquid suspension over the entire area of the disturbed site.
Owner:LIVING EARTH
Remediation method of ionic type rare earth tailings soil
PendingCN113560333AImprove fat retention capacityImprove water holding capacityContaminated soil reclamationFungicideAmmoniacal nitrogen
The invention relates to a remediation method of ionic type rare earth tailings soil. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a biological crust sample of soil to be repaired; separating and purifying the biological crust sample, and culturing to obtain nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria; carrying out propagation culture on nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria to obtain cyanobacteria crust algae liquid; carrying out propagation culture on the AM fungus inoculant; and treating to-be-restored soil through the cyanobacteria crust algae liquid and the AM fungus fungicide subjected to propagation culture, and sowing pioneer plants. The biological soil crust, AM fungi and pioneer plants are combined to improve the soil in the ionic rare earth waste tailing area, enhance the water binding capacity of the soil, reduce the concentration of heavy metals and ammonia nitrogen in the soil and improve the fertilizer retention capacity of the soil.
Owner:天津市滨海新区环境创新研究院
A method for differentiating biological soil crusts from their subsoil basal respiration
ActiveCN105004853BEfficient removalEasy to operateEarth material testingField conditionsSoil surface
The invention relates to a method for distinguishing biological soil crust and subsoil basic respiration of biological soil to test the contribution of components (biological soil crust and subsoil basic respiration) of soil to the soil respiration. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a biological soil crust layer is carefully separated from the soil surface and arranged in a screen with 150 meshes, the subsoil of the biological soil crust is heated for 3 h at the high-temperature of 160 DEG C, and after the subsoil temperature recovers to the indoor temperature, the screen with the biological soil crust layer is placed in the soil surface layer. The method has the advantages that operation is easy, separation is carried out through a physical method and is thorough, pollution does not exist, and cost is low; according to the method, the soil water content of components of the soil cannot be changed after natural raining, a processed soil sample testing environment is close to natural conditions, and the accuracy of the test result is high; the interference in soil is small, and the measurement result is close to the real value; continuous monitoring can be carried out under the field condition. By means of the method, the soil respiration rate that the biological soil crust covers the components of the soil can be accurately tested.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Composition for ecological restoration and ecological restoration method using the same
ActiveCN105521989BIncrease biomassImprove aggregation stabilityUnicellular algaeContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentRestoration method
The invention relates to composition for ecological restoration using of barren land including alga, culture medium of the alga, soil fixing agent and ultra water absorbing materials, and a method for restoring the degraded ecology by them. According to the invention, biological soil crust can be formed in a short time; desertization and yellow sand can be avoided; waste coal mine and oil polluted land are improved into an ecological environment suitable for growth of plants; and ecological and environmental pollution caused by desert, waste coal mine and oil polluted land can be avoided.
Owner:国立顺天大学校产学协力团
Soil restoration system
PendingUS20210269373A1Facilitating plant seed catchment plantFacilitating plant vascular plant germinationBacteriaFertilising methodsPlanting seedCyanobacteria
A soil restoration system including a plurality of dry particles, each particle inoculated with dehumidified biological material including at least one species of cyanobacteria, the cyanobacteria being physically supported by the particles, and the cyanobacteria being activatable by a threshold amount of moisture so that when the cyanobacteria is activated at an application site, the cyanobacteria multiplies to form a biological soil crust capable of facilitating plant seed catchment and vascular plant germination at the application site.
Owner:PROFILE PRODS
Method for preventing microbiotic crusts from cutting off rainfall infiltration in arid desert areas
ActiveCN111567175AReduce lateral penetrationBoth horizontal penetrationBiocideDisinfectantsSoil scienceEngineering
The invention discloses a method for preventing microbiotic crusts from cutting off rainfall infiltration in arid desert areas. The method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting trimmed treebranches, cutting side branches to obtain tree sticks, and drying the tree sticks in the sun; (2) performing hydrophilic diversion treatment on one ends of the tree sticks, and performing hydrophobicsterilization treatment on the other end of the tree sticks to obtain the tree sticks with hydrophilic diversion ends and hydrophobic sterilization ends; and (3) downwards inserting the hydrophilic diversion ends of the tree sticks into the stratum, and enabling the length of the hydrophobic sterilization ends exposed out of the ground to be at least 5 cm. According to the method, the water content of the sandy soil layer below the biological soil crusts can be effectively increased under the condition of not damaging the biological soil crusts in a large area.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rapid cultivation method for forming biological soil crusts from ionic rare earth abandoned mine soil and application of rapid cultivation method
PendingCN111492744AAccelerate cultivationShorten the production cycleAgriculture gas emission reductionSoil-working methodsSoil scienceSoil surface
The invention provides a rapid cultivation method for forming biological soil crusts from ionic rare earth abandoned mine soil and an application of the rapid cultivation method, and belongs to the field of environmental biotechnology. The rapid cultivation method comprises the following steps of 1) selecting a plurality of different types of biological soil crusts, and performing impurity removal, air drying and crushing to obtain different types of crushed crusts; 2) inoculating the different types of crushed crusts obtained in the step (1) to the surface of soil, and carrying out constant-temperature illumination cultivation for 7-9 weeks to obtain different types of candidate artificially cultivated biological soil crusts; and 3) with the crust coverage as a first screening index and the plant height as a second screening index, performing screening to obtain the most dominant artificially cultivated biological soil crusts. Cultivation is continued for 240-260 days, and the influence of the development of the artificially cultivated biological soil crusts on the physicochemical and hydrological properties of the ionic rare earth abandoned mine soil is researched. The artificialbiological soil crusts provided by the invention has good effects of improving the ionic rare earth abandoned mine soil and preventing and treating water and soil loss.
Owner:江西离子型稀土工程技术研究有限公司
Desertified soil treatment method
PendingCN113853863AGuaranteed living conditionsRestore partial consolidationProtective constructionClimate change adaptationCelluloseSoil treatment
The invention relates to the technical field of soil treatment, in particular to a desertified soil treatment method. The method comprises the steps of data collection, environment measurement, soil layer remediation, inspection maintenance and process analysis. Due to the fact that an existing desertified soil treatment mode is single, and meanwhile, a simple accumulated comprehensive treatment mode is carried out, the treatment effect of the mode is still limited; and therefore, the survival condition for treating initial biological soil crust is ensured through spraying and water supplementing measures in inspection maintenance, partial consolidation and water storage performance of the soil layer is recovered by matching with laid sunshade nets and sand barriers and assisting the modification effect of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose on the soil layer, then the engineering sand stabilization method and the chemical sand stabilization method are combined, the success rate of biological desertification control is increased, continuously covered vegetation is formed in the desertified soil, and optimal treatment measures are deployed by combining water supplementing in inspection maintenance and recording and analysis in the treatment process, so that the application effect of the desertified soil treatment method is stabilized.
Owner:李攀
Device used for collecting biological crust soil layer, and application thereof in the wild
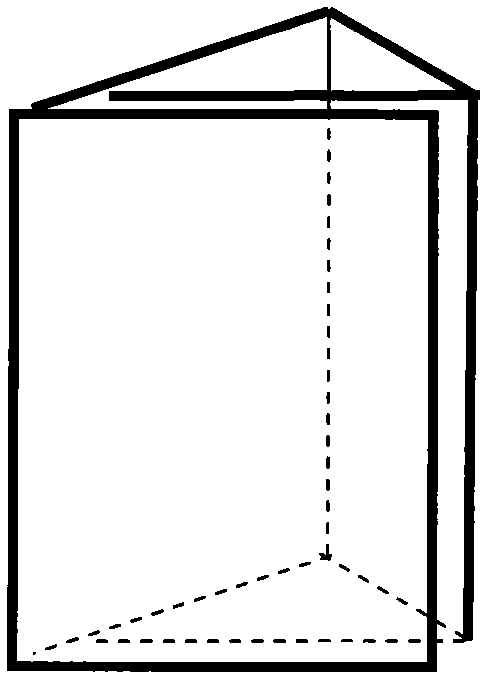
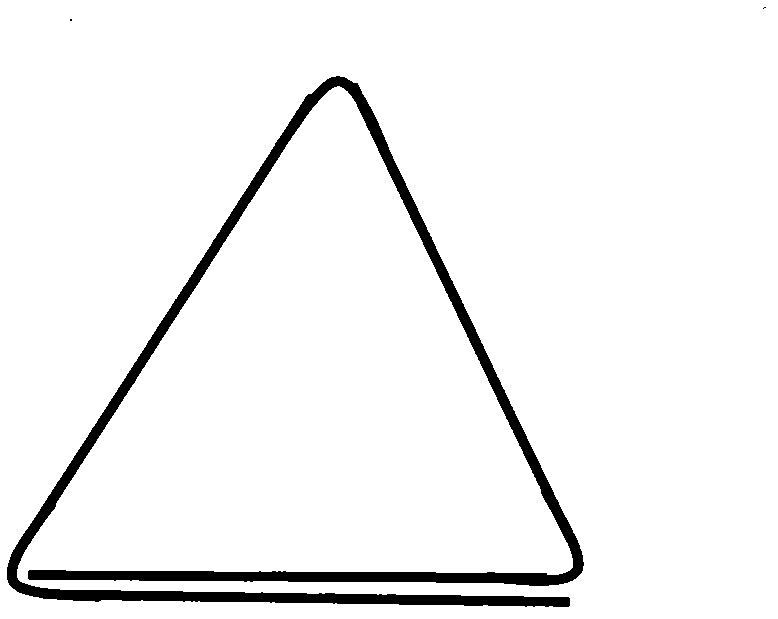
InactiveCN102840998ASimple structureProcess stabilityWithdrawing sample devicesRigid containersEngineeringApplication areas
The invention discloses a device used for collecting biological crust soil layers, and applications thereof in the wild. In one embodiment, the device for collecting samples is a triangular prismoid having a height of 5cm and a side length of 3cm, wherein one surface of the triangular prismoid is composed of two overlapped layers; and the device is made by a sheet of plastic board having a thickness of 0.5-1mm. The plastic board is cut into plastic strips having a length of 9cm and a width of 5cm, and each plastic strip is folded into a triangular prismoid, with the surface of the opening side composed of two overlapped layers. Another embodiment is a storage device for the sample-collecting device. Planks having a length of several times of 20cm, a thickness of 8cm and a width of 19.5cm are used as the pedestal for the storage device. A plurality of rectangular grooves are made inside the pedestal as sample grooves, each sample groove has a length of 14cm, a width of 2.5cm and a depth of more than 5cm and less than 8cm, and the space between the sample grooves is 3cm. The sample collector and a method for wild operation are successfully designed in the invention, which ensure the integrity of the biological soil crust, prevent the separation of the crust layer and soil of the lower layer, and can be applied in various fields.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method utilizing biological soil crust to prepare coagulant aids
InactiveCN103159308BReduce usageIncrease in sizeWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSoil scienceSewage
The invention provides a method utilizing biological soil crust to prepare coagulant aids. According to the method, the biological soil crust is utilized as main raw material, and a series of processing is conduced to the biological soil crust to obtain the coagulant aids used for sewage treatment. The method has the advantages of being environment-friendly and obvious in coagulation aid effect.
Owner:溧阳市天目湖保健品有限公司
A method for planting sand-fixing plants in arid sandy areas
ActiveCN104885752BAvoid harmIncrease roughnessClimate change adaptationPlant cultivationWater balanceBiology
The invention relates to a dry desert zone sand binder planting method. The survival rate of all kinds of sand binders is 70 percent or more in the dry desert regions with the annular precipitation ranging from 100 mm to 250 mm through sand face fixing, plant species selecting, planting density determining, planting mode selecting and seedling managing. The planted sand binders are planted along with deposition of falling dust on the surface of sand dunes, settlement of therophytes and growing of biological soil crusts are promoted, and long-term effective fixing of the sand dunes is guaranteed. By means of the sand binder planting method, the survival rate of the sand binders is guaranteed, the labor and seedling cost is reduced, and the purposes of preventing wind and fixing sand are achieved on the premise of maintaining the water balance.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Method utilizing biological soil crust to prepare coagulant aids
InactiveCN103159308AReduce usageIncrease in sizeWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSoil scienceSewage
The invention provides a method utilizing biological soil crust to prepare coagulant aids. According to the method, the biological soil crust is utilized as main raw material, and a series of processing is conduced to the biological soil crust to obtain the coagulant aids used for sewage treatment. The method has the advantages of being environment-friendly and obvious in coagulation aid effect.
Owner:溧阳市天目湖保健品有限公司
A kind of assay method of algal biomass in biological soil crust
ActiveCN105092495BEasy to collectEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsVascular bundleChlorophyll b
The invention discloses a method for measuring algal biomass in biological soil crusts, and relates to the field of biology. The method comprises the steps of algae crust sample sampling, sieving, cleaning, algae cultivation, determination of chlorophyll a and b, standard curve drawing and algae biomass (natural growth) determination. Among them, the algae culture is cultivated with BG11 medium, and the algae used are mixed algae; the determination of chlorophyll a and b adopts the mixed solution method to extract chlorophyll (extraction solution: absolute ethanol: acetone: water = 4.5:4.5:1); standard curve The relationship between the total amount of chlorophyll a and b and algae biomass was regressed; the determination of the biomass of naturally growing algae was converted by the standard curve between the total amount of chlorophyll a and b and the biomass of cultured algae. The invention realizes the direct comparison between the algae crust and the vascular plant biomass, and provides a reliable way for more accurate calculation of the algae crust productivity and its function in the ecosystem.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Sand fixing method of terraneous nitrogen fixation blue algae
This invention relates to new consolidation sand method with terraneous nitrogen fixation blue-green algae, which is completed by the following steps: blue-green algae foster, inoculation environment, inoculation time and inoculation quantity, and it uses the microorganism technology such as terraneous nitrogen fixation blue-green algae to achieve the fast consolidation of the flowing sand in the fixed and the half fixed desert area and achieve the ecology rehab in the engineering trouble area of the fixed and half fixed desert area. The applied nitrogen fixation blue-green algae can do photosynthesis by itself by the limited precipitation in desert, it grows up, and produces hull, which achieves the purpose of adding organic matter in soil and improving the structure of the soil and preventing and consolidating sands.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantitative analysis method for soil microplastics in biological soil crust layer
PendingCN113720844AAvoid interferenceImprove accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationSoil scienceChemical composition
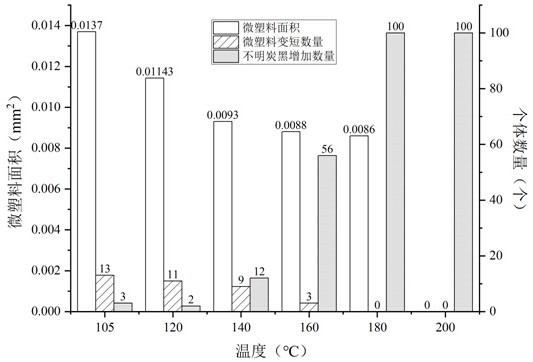
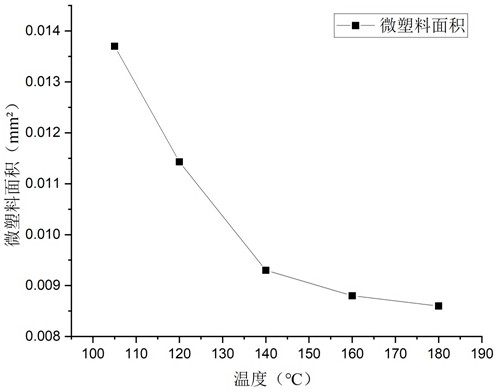
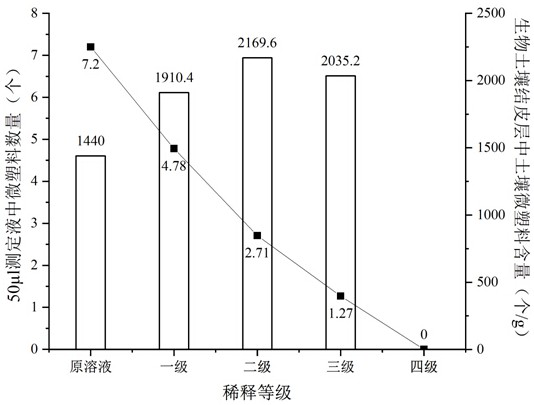
Biological soil crust is a common complex formed by cementation of tiny organisms and soil particles on the earth surface of an arid and semi-arid region, and the biological soil crust is extremely easy to adsorb organic substances and micro-plastics due to the special physical structure and chemical composition of the biological soil crust. Due to the fact that the organic matter and the micro-plastic have similar properties and structures, the micro-plastic is not prone to being separated from the biological soil crust layer with the concentrated organic matter content in the detection process, and quantitative analysis is not prone to being carried out. The invention relates to a method for extracting soil micro-plastics in a biological soil crust layer according to the proportion of 2 ml corn germ oil / g biological soil crust, gradually diluting an extracting solution according to three stages, namely two times of each stage, and heating by using a high-temperature probe to promote the structure and form of the micro-plastics to change, so the problem that organic matters in the crust layer interfere with quantitative analysis of the microplastics is effectively solved, and the quantitative analysis precision and efficiency of the soil microplastics in the biological soil crust layer are improved. The method is simple to operate, low in cost and high in accuracy.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO-ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Field environment nitrogen fixation activity ARA determination method and device
PendingCN111413426ASolve the problem that it cannot accurately reflect the actual situation of complex environmental changes in the fieldAccurate field in situ measurement resultsComponent separationGlass coverExperimental laboratory
The invention discloses a field environment nitrogen fixation activity ARA determination method and device. The field environment nitrogen fixation activity ARA determination method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting biological soil crusts (hereinafter referred to as biological crusts) with nitrogen fixation activity under a field environment condition; s2, spraying distilled water to the biological crust, and then covering the biological crust with a glass cover to form a closed space; S3, injecting acetylene gas into the glass cover by using an acetylene injection device, and thenculturing for more than 3 hours; S4, after the culture is finished, extracting the gas in the glass cover by using an extraction device, then analyzing the gas by using a gas chromatographic analysisinstrument, and finally performing measurement to obtain data. A field in-situ observation and research mode is adopted; the field in-situ measurement result is obtained by matching with a self-designed simple and convenient scientific research instrument, the measurement result better conforms to the actual situation of the field environment, and the problems that an existing ARA measurement method can only perform measurement in a laboratory and the measurement result cannot accurately reflect the actual situation of field complex environment change are solved.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO-ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
A kind of cultivation method of compound crust of moss and desert algae
ActiveCN106472281BSpeed up the succession processIncrease diversityUnicellular algaeGrowth substratesComposite skinProtonema
The invention discloses a cultivation method of a moss and desert algae composite crust. The cultivation method comprises the first step of collecting in summer a superior kind of moss in a natural habitat of an area to be restored; the second step of returning activities of the moss; the third step of using distilled water to wash moss crust the activities of which are returned and obtaining moss gametophyte; the fourth step of putting the gametophyte into a solid culture medium to be subjected to cultivation after the gametophyte is subjected to sterilization and obtaining moss protonema; the fifth step of picking the moss protonema and conducting static liquid cultivation to obtain differentiated gametophyte, and putting the gametophyte into a fluid culture medium to conduct aerobic cultivation; the sixth step of conducting aerobic cultivation on the desert algae through the fluid culture medium till a logarithmic growth phase, and obtaining algae thick liquid after removing supernatant; the seventh step of mixing the moss gametophyte with the desert algae thick liquid and afterwards inoculating the moss gametophyte and the desert algae thick liquid to the surface of desertification soil, and cultivating the moss and desert algae composite crust. The cultivation method of the moss and desert algae composite crust is easy to carry out and convenient to operate, evolvement process of biological soil crust in a desert area is accelerated, and fast treatment of desertification soil in arid and semi-arid lands is realized.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com