Application of inhibiting accumulation of xantheins and accumulating lycopene and anthocyanin in preparation of Brassica plants with red pedals
A kind of Brassica, petal technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
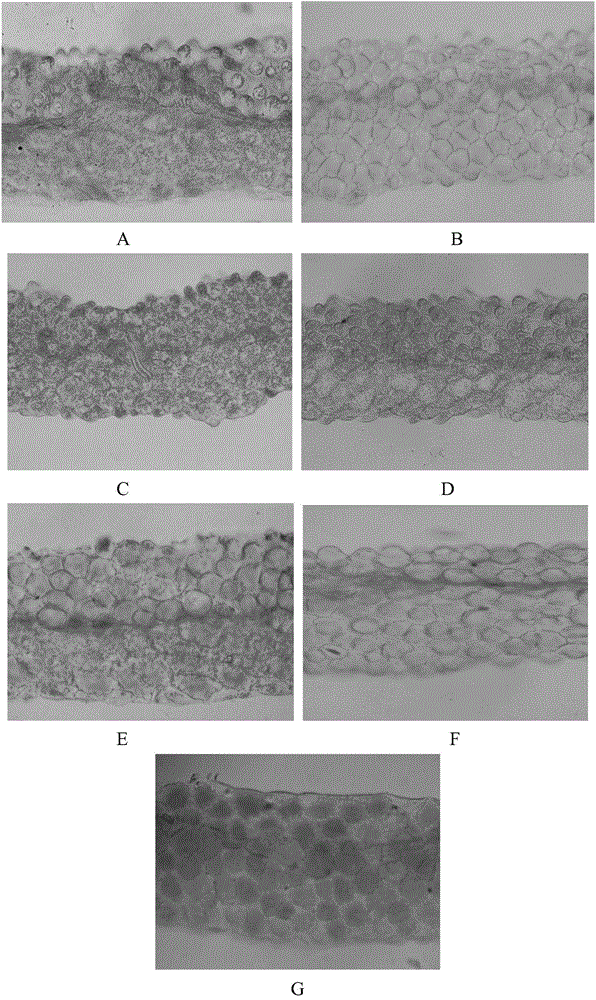
[0041] Example 1. Microscopic observation of chromogenic subcellular organelles in Brassica and radish petals
[0042] Take fresh Brassica napus yellow petals (BnY); Brassica napus milk petals (BnW); Brassica napus yellow petals (BjY); Brassica napus yellow petals (BrY); White petals (BoW) and radish red petals (RsR) were stored on ice and shipped back to the laboratory, then sliced by hand, observed with a low-power lens for quick screening, and qualified slices were selected for careful observation and photography. The results are as follows figure 1 shown. The results showed that the yellow substances in the yellow petals of several species of Brassica appeared as numerous small granules in one cell, distributed unevenly in the cell, and were squeezed to the wall-adhering position by the vacuoles, indicating that the yellow petals The chromogenic organelles are chromoplasts, whose pigments are yellow carotenoids. There are also some cells in the milky petals of Brassica...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2, detect brassica and radish petal pigment
[0044] In the morning of the full flowering period, the newly opened Brassica napus yellow petals (BnY); Brassica napus milk petals (BnW); Brassica napus yellow petals (BjY); BoY), kale white petals (BoW) and radish red petals (RsR), immediately transported back to the laboratory in a cool and fresh place, dried at 50-60°C, ground into powder, passed through a 60-mesh sieve, and stored in a dry place away from light.
[0045] 1. Test results of petroleum ether, hydrochloric acid and ammonia water
[0046] Weigh 0.100g of preserved petal powder, put them into numbered stoppered test tubes, add about 10mL of petroleum ether, 10% hydrochloric acid, and 30% ammonia water, mix gently, filter, and observe the color change. The results are as follows :
[0047] (1) Petroleum ether reaction: Brassica napus, Chinese cabbage rape, and mustard rape all show bright yellow, indicating that the content of carotenoids is high;...
Embodiment 3
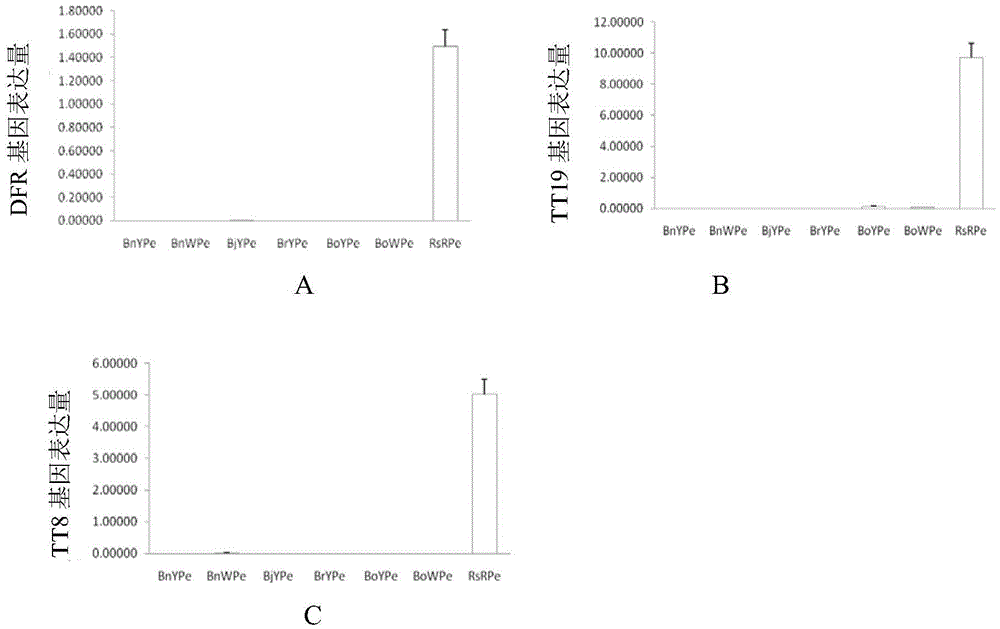
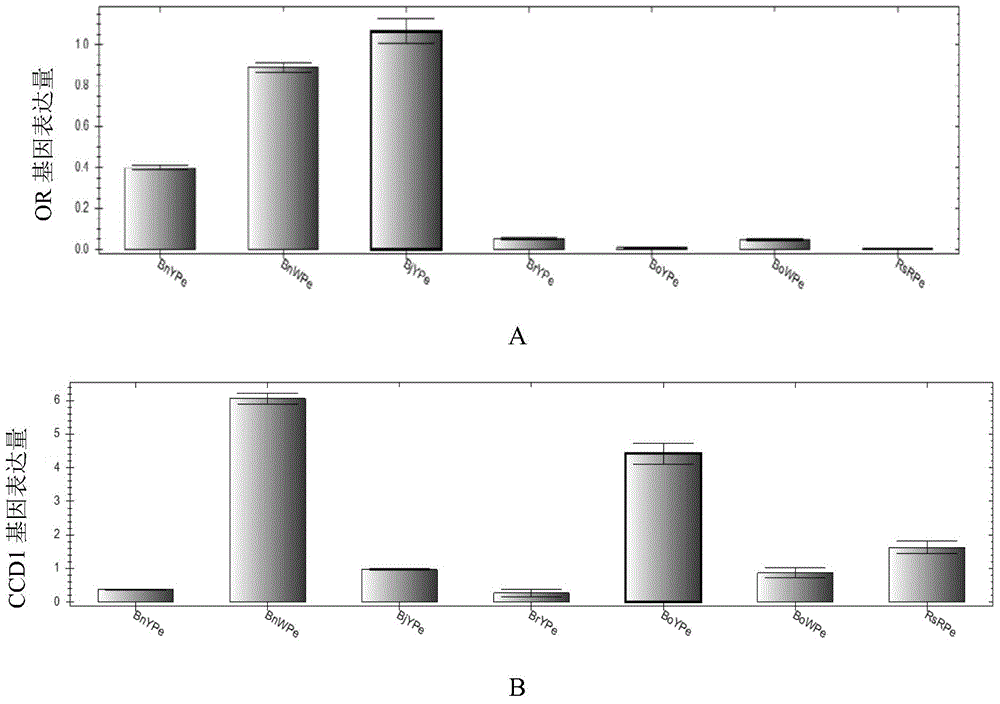
[0067] Example 3. Molecular Identification of Brassica and Radish Petal Pigment Biosynthetic Pathways
[0068] (1) Expression characteristics of flavonoid pathway genes in Brassica and radish petals
[0069] In order to study the molecular mechanism of the difference in petal pigments between Brassica and radish, RT-PCR detection primers for the flavonoid pathway genes of Brassica and radish were designed, and 5SrRNA was used as an internal reference, as shown in Table 1:
[0070] Table 1. Primers for RT-PCR detection of flavonoid pathway
[0071]
[0072]
[0073]In the morning of the full flowering period, the newly opened Brassica napus yellow petals (BnY); Brassica napus milk petals (BnW); Brassica napus yellow petals (BjY); BoY), kale with white petals (BoW) and red radish petals (RsR), transported frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored in a -80°C refrigerator for later use. Then use the RNAprep Pure Plant Total RNA Extraction Kit to extract the total RNA, after el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com