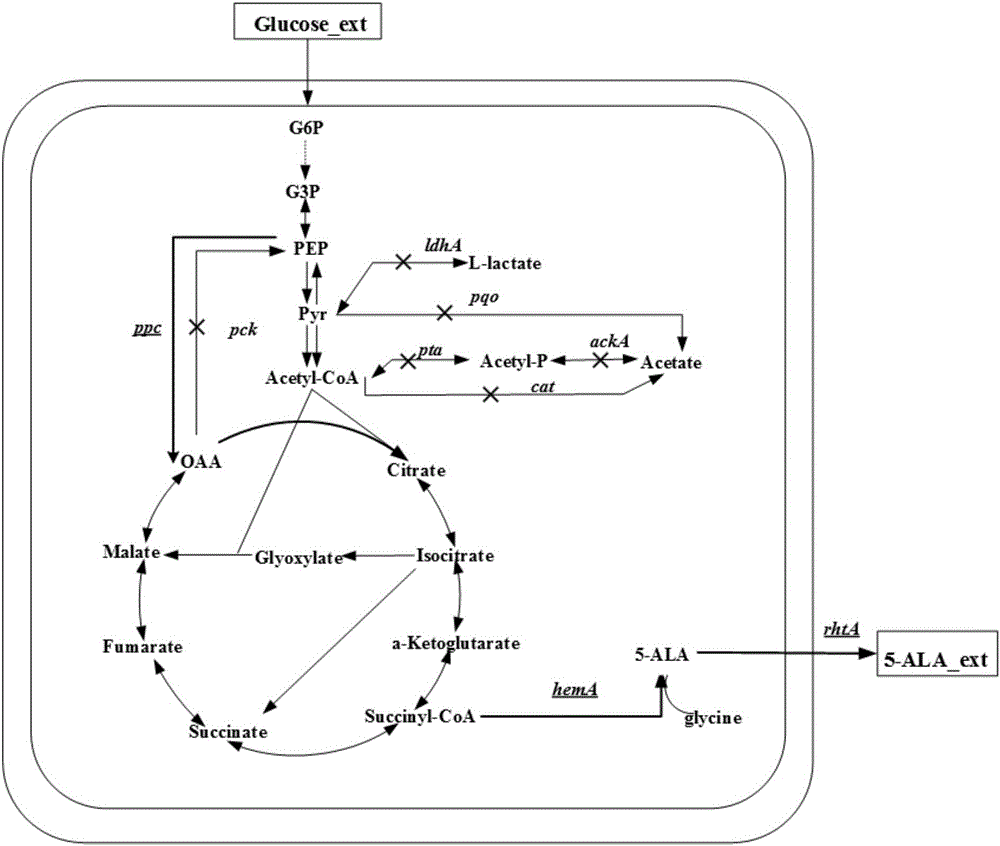
Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain
A technology of Corynebacterium glutamicum and aminolevulinic acid, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low yield and yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid, complicated pathways, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: Construction of knockout plasmid pD-sacB
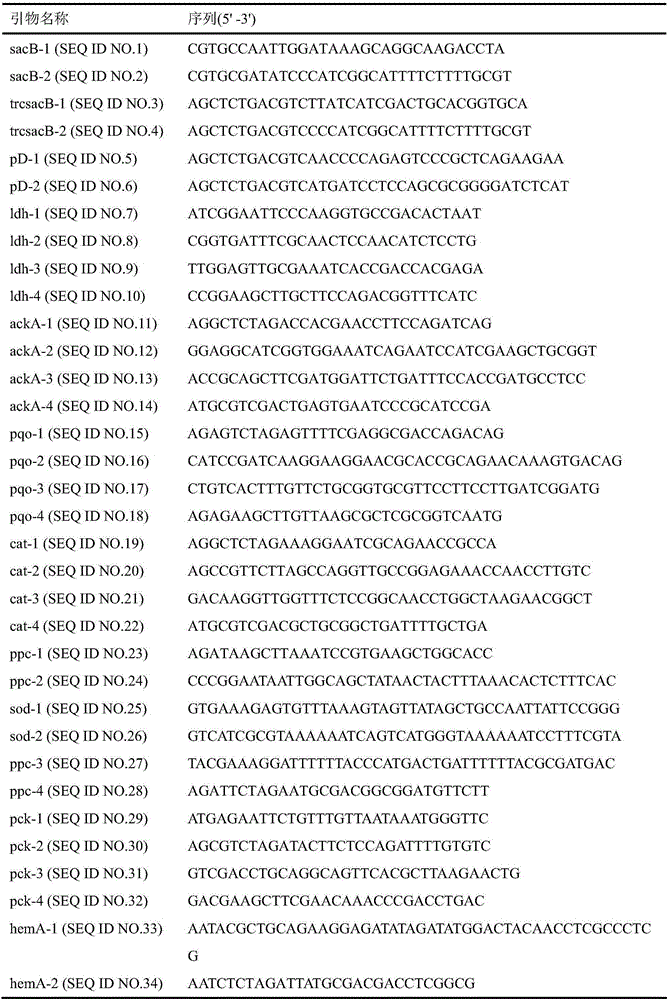
[0025] Firstly, the linear fragment of pK18mobsacB cut by HindIII was used as a template, and the sacB gene was amplified with the following primers sacB-1 (SEQ ID NO.1) / sacB-2 (SEQ ID NO.2). The sacB gene fragment was ligated with the plasmid pEC-XK99E after the MunI / EcoRV double digestion and the EcoRI / SmalI double digestion to obtain the plasmid pEC-XK99E-sacB. The following primers trcsacB-1 (SEQ ID NO.3) / trcsacB-2 (SEQ ID NO.4) were used to amplify the trcsacB fragment containing the trc promoter using the pEC-XK99E-sacB plasmid as a template.
[0026] Use the following primers pD-1 (SEQ ID NO.5) / pD-2 (SEQ ID NO.6), use the pK18mobsacB plasmid as a template to amplify the pD fragment containing kanamycin resistance and the Escherichia coli replicon, and finally The fragment trcsacB digested by AatII was ligated with the pD fragment digested by the same restriction enzyme to obtain plasmid pD-sacB.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: Knockout of the lactate dehydrogenase encoding gene ldhA and knockout of the acetate production pathway genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat
[0028] Knockout of the gene ldhA encoding lactate dehydrogenase:
[0029] Using Corynebacterium glutamicum (C.glutamicum) ATCC 13032 genome as a template, using ldh-1 (SEQ ID NO.7) / ldh-2 (SEQ ID NO.8) as primers to amplify the upstream fragment of gene ldhA, ldh- 3(SEQ ID NO.9) / ldh-4(SEQ ID NO.10) are primers for amplifying the downstream fragment of gene ldhA. After the two fragments were recovered by gel cutting, the fusion product of the two fragments was amplified using the equimolar proportion of the fragments as a template and ldh-1 / ldh-4 as primers. The fused fragment was digested with EcoRI / HindIII and ligated with pD-sacB after the same double digestion to obtain plasmid pD-ldhA.
[0030] Transform the pD-ldhA plasmid into Corynebacterium glutamicum (C.glutamicum) ATCC 13032, use kanamycin to screen the positive clon...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Insertion of a strong sod promoter in front of the ppc gene and knockout of the pck gene, the gene encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
[0045] A strong sod promoter was inserted in front of the ppc gene
[0046] C. glutamicum ATCC13032 genome was used as a template, and ppc-1 (SEQ ID NO. 23) / ppc-2 (SEQ ID NO. 24) was used as primers to amplify the upstream fragment of gene ppc. sod-1 (SEQ ID NO.25) / sod-2 (SEQ ID NO.26) was used to amplify the promoter of sod gene. ppc-3 (SEQ ID NO.27) / ppc-4 (SEQ ID NO.28) is used to amplify the downstream fragments of the ppc gene. After the three fragments are gel-cut and recovered, the equimolar ratio fragments are used as templates. Using ppc-1 / ppc-4 as primers, the fusion product of the three fragments was amplified. The fused fragment was digested with XbaI / HindIII and ligated with the plasmid vector pD-sacB after the same double digestion. The plasmid pD-ppc was obtained.
[0047] The constructed plasmid was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com