5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for producing aminolevulinic acid and bacterial strains, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation, and can solve the problems of poor overall effect and the production of ALA by recombinant engineering bacteria fermentation that has not been seen yet.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
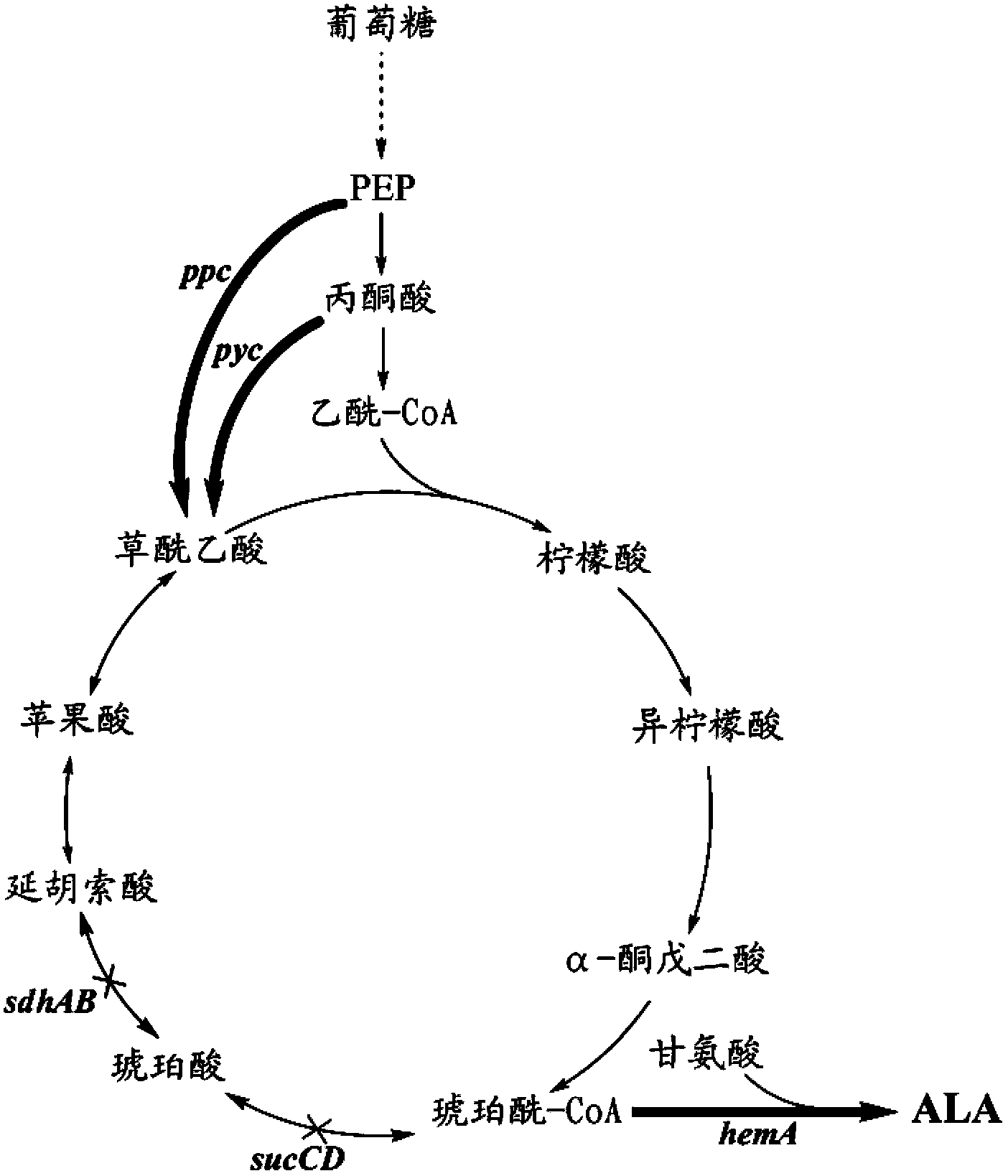
[0090] Example 1. Construction of succinyl-CoA synthase deletion mutants and succinate dehydrogenase deletion mutants
[0091] The E. coli gene knockout was carried out using the classic Red recombination method, referring to the relevant literature. The specific operations are as follows: For the knockout of the succinyl-CoA synthase structural gene sucCD gene, firstly, according to the genome sequence and auxiliary vector of E. coli MG1655 published by NCBI The primers sucCD-1 and sucCD-2 were designed for the sequence of pKD13. The specific sequence is shown in the primer sequence table. The Kan resistance gene fragment with the upstream and downstream homology arms of the sucCD gene was amplified with pKD13 as the template. PCR amplification parameters were 94°C for 2 min; 94°C for 20s, 64°C for 20s, 72°C for 1min, cycle 30 times; 72°C for 5min extension. After gel recovery of the PCR product, the MG1655 / pKD46 strain was electro-transformed. For the preparation and transfo...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Example 2. Construction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase ppc and ALA synthase co-expression plasmid
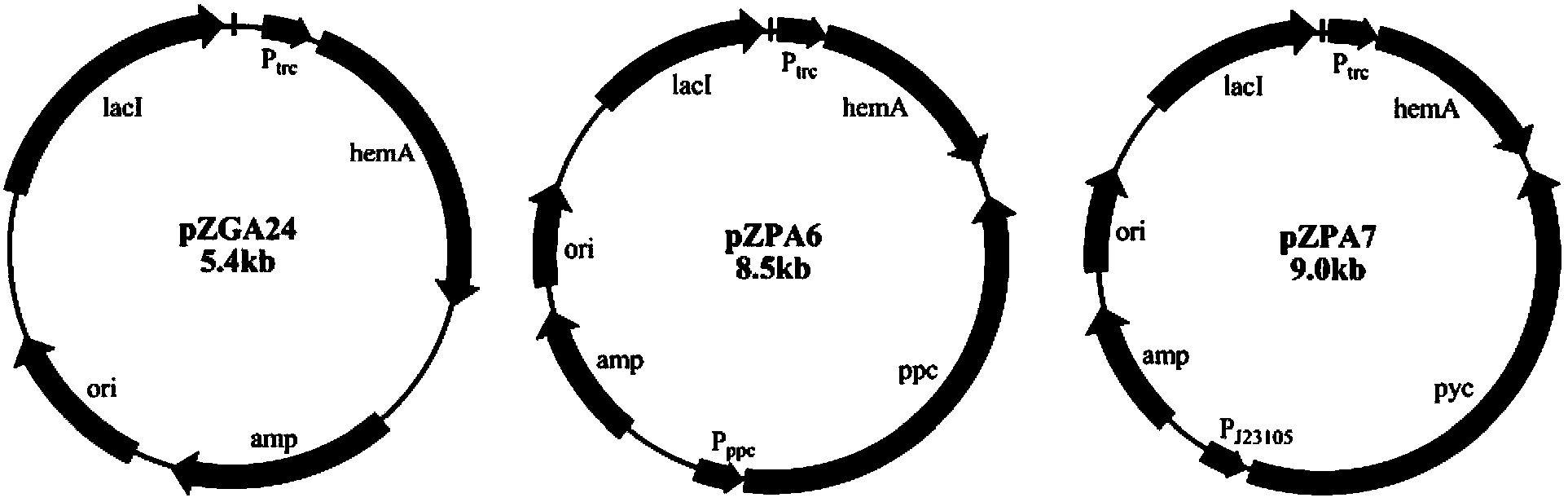
[0094] According to the genome sequence of Escherichia coli MG1655 published by NCBI, primers ppc-F and ppc-R were designed, and the ppc gene fragment with its own promoter was obtained by PCR amplification with the genome of Escherichia coli MG1655 as a template. The PCR amplification parameter was 94℃ for 2min; 94°C for 20s, 60°C for 20s, 72°C for 1.5min, cycle 30 times; extension at 72°C for 5min. The ppc gene fragment was recovered and treated with HindIII. At the same time, the plasmid pZGA24 carrying ALA synthase (for the construction of pZGA24, see reference: Guo Xiaofei et al.) was used to synthesize 5-aminolevulinic acid using recombinant Escherichia coli lacking 5-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase. , Journal of Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2012, 27(4): 1-6) was also treated with this enzyme, the vector and fragment were recovered and then liga...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3. Construction of pyruvate carboxylase pyc and ALA synthase co-expression plasmid
[0096]Primers pyc-1 and pyc-2 were designed according to the sequence of the promoter BBa_J23105 in BioBrick and the genome sequence of Rhizobium CFN42 published by NCBi, and the pyc gene fragment with the constitutive promoter sequence was obtained by PCR amplification with the genome of Rhizobium CFN42 as a template , PCR amplification parameters are 94°C for 2 min; 94°C for 20s, 60°C for 20s, 72°C for 2min, cycle 30 times; 72°C for 5min extension. The target fragment was recovered and treated with phosphorylase. At the same time, the pWSK29 vector was treated with restriction endonuclease PvuII and then treated with dephosphorylase. The obtained vector fragment and the phosphorylated pyc gene fragment were ligated with T4 ligase and transformed. DH5α competent cells were coated with Amp-containing LB plates, positive clones were picked to extract plasmids and verified by enzy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com