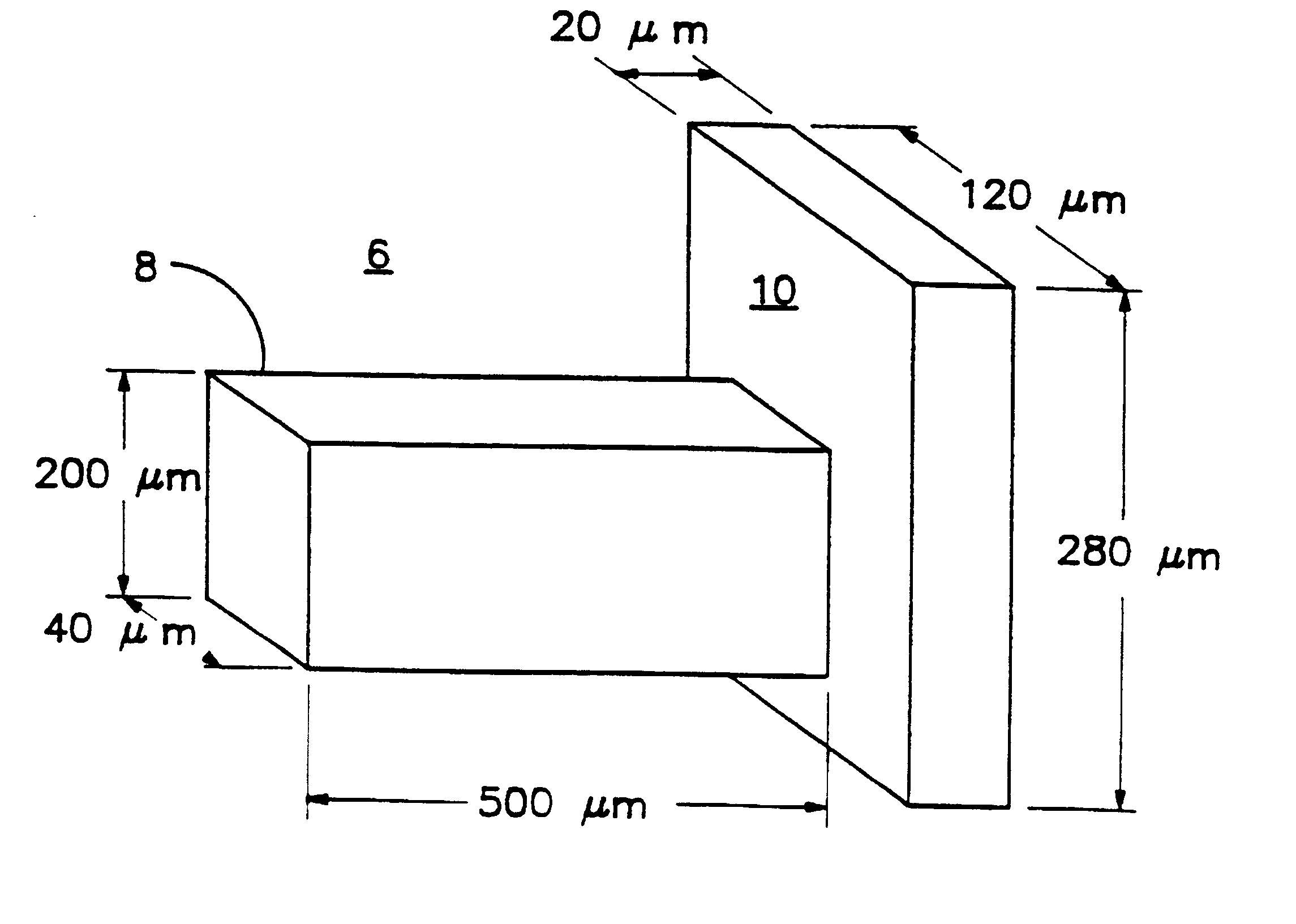
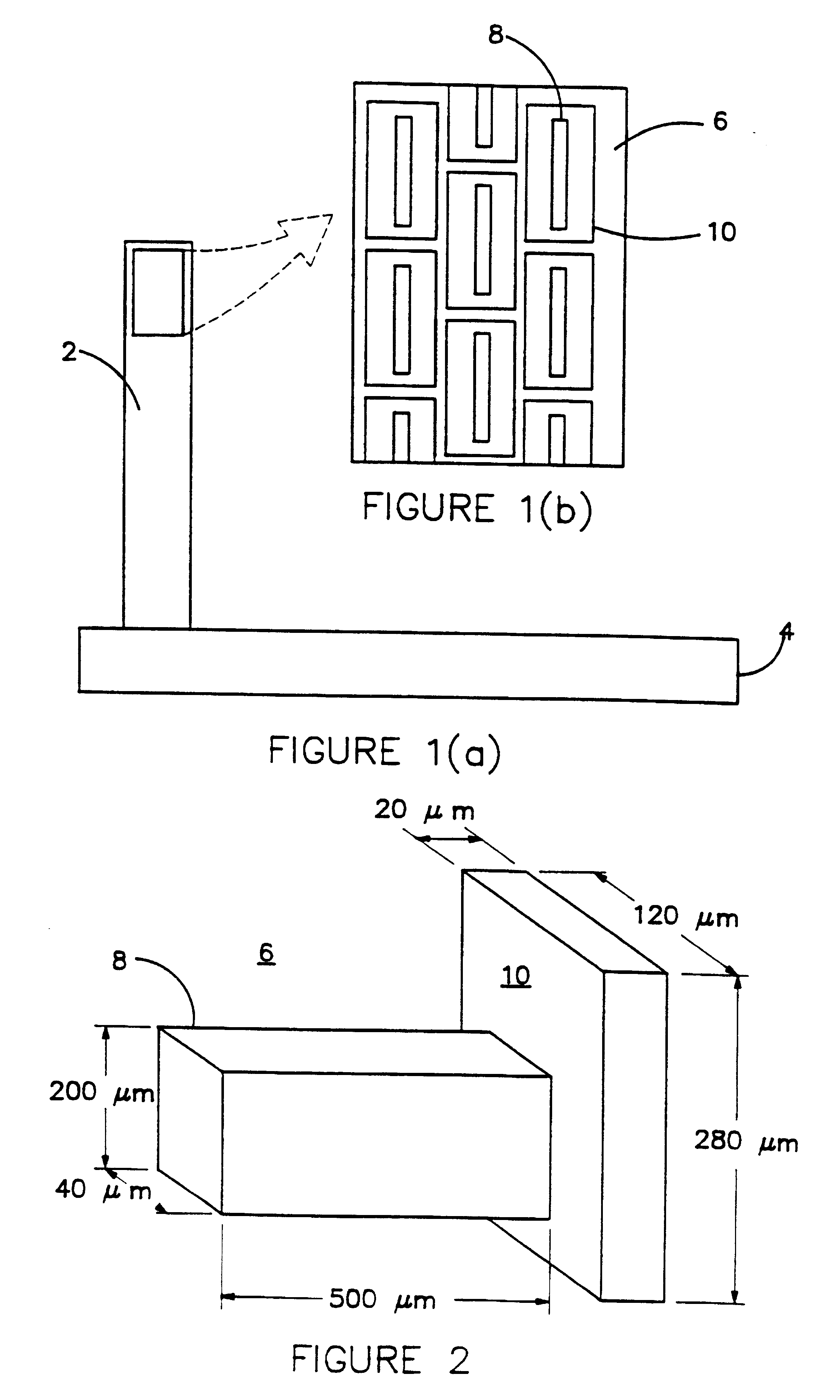
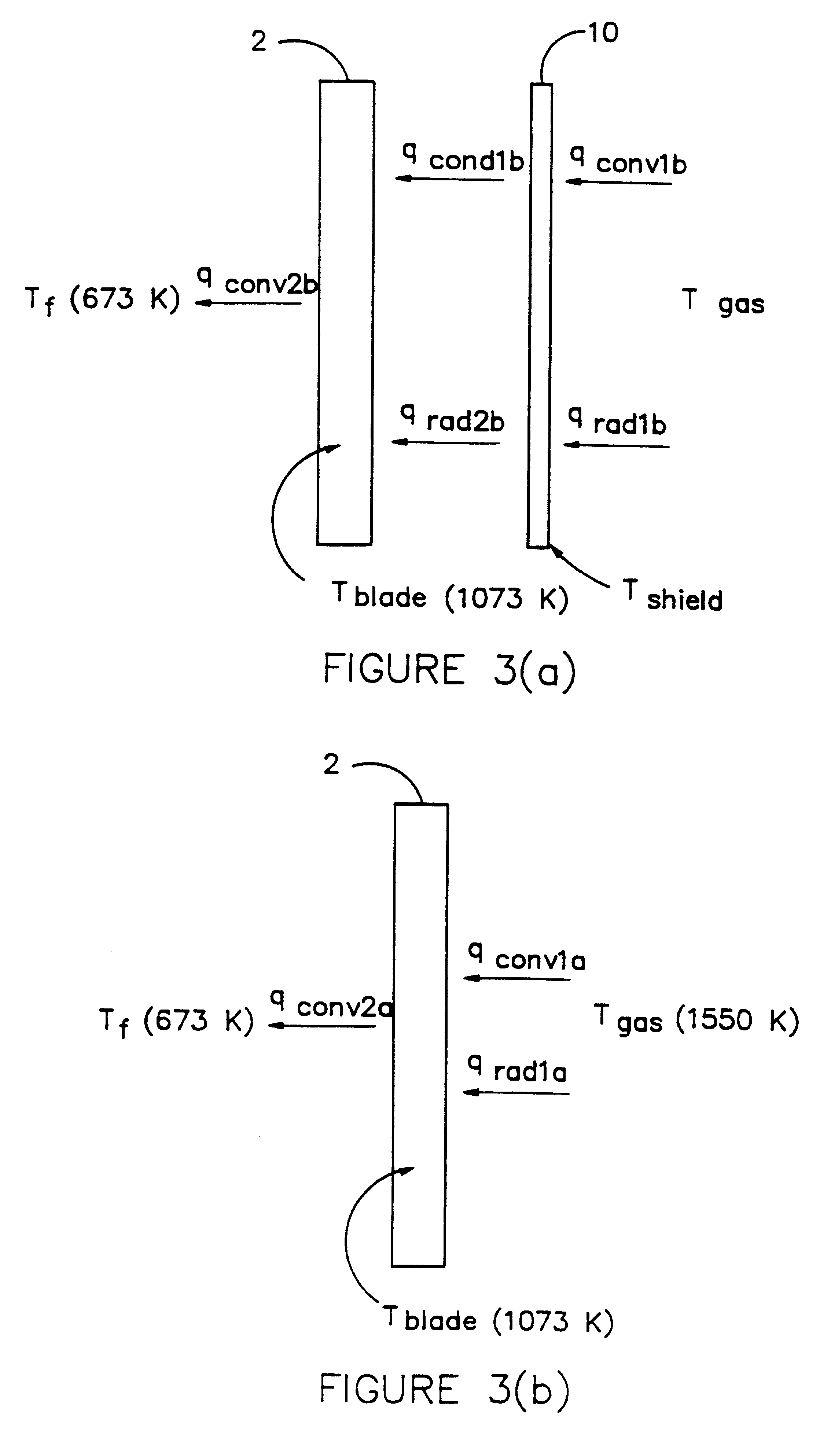
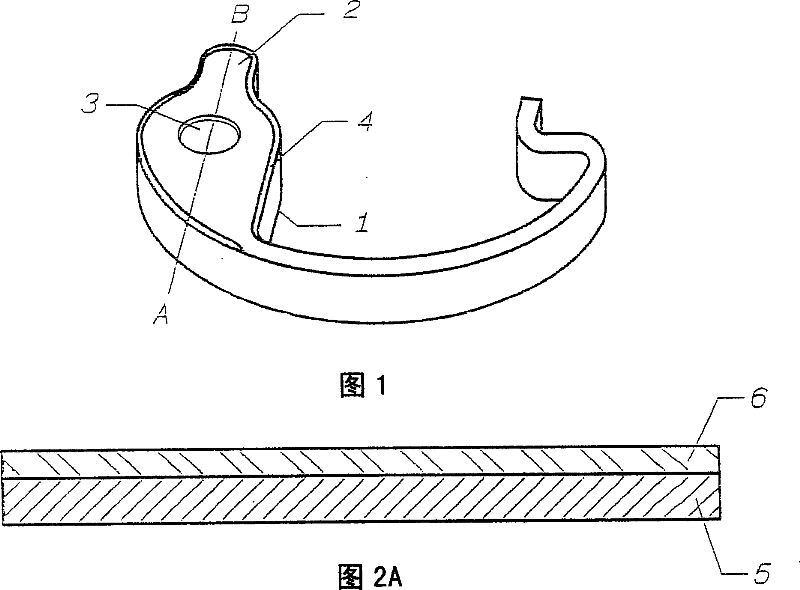
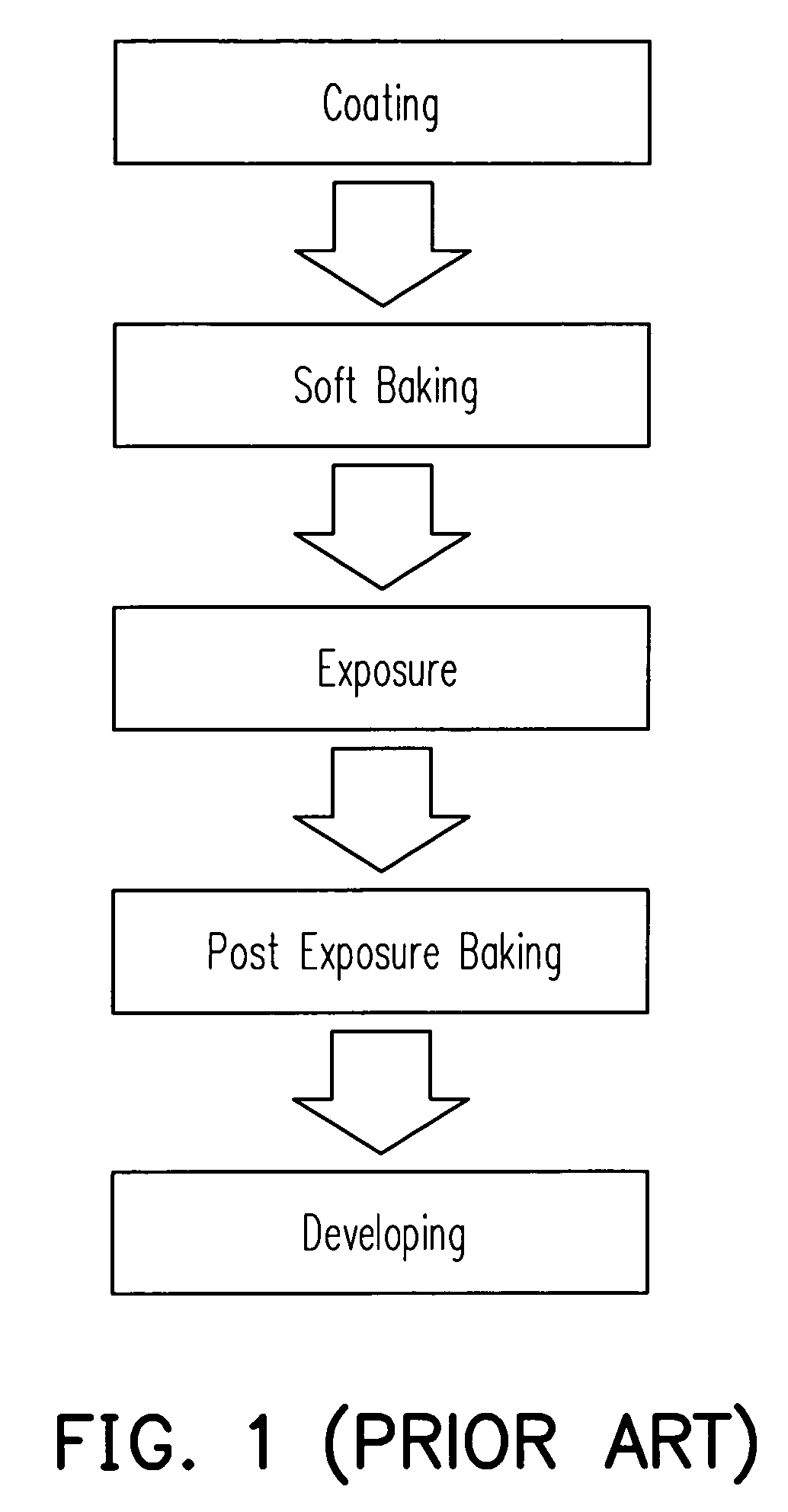
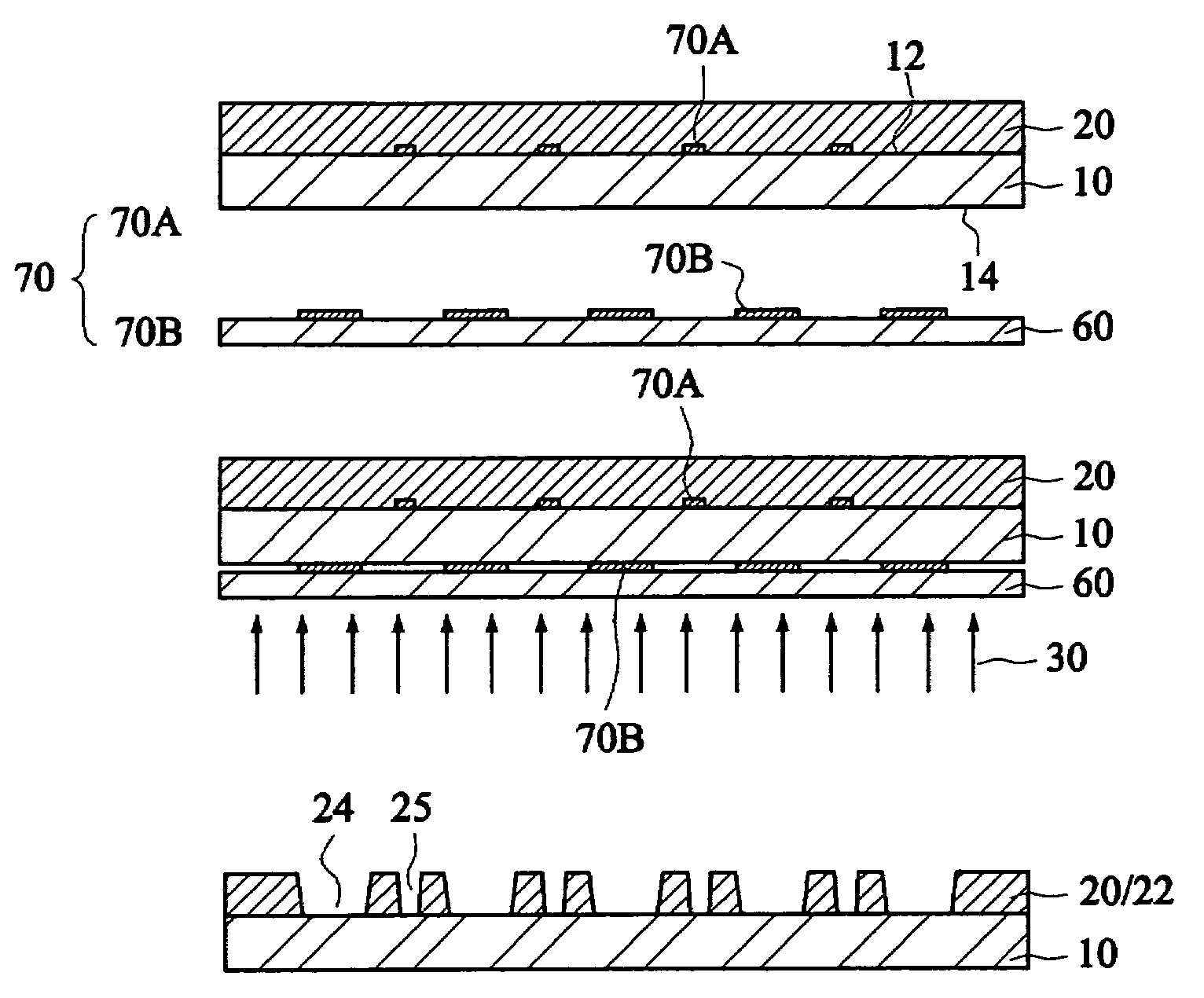
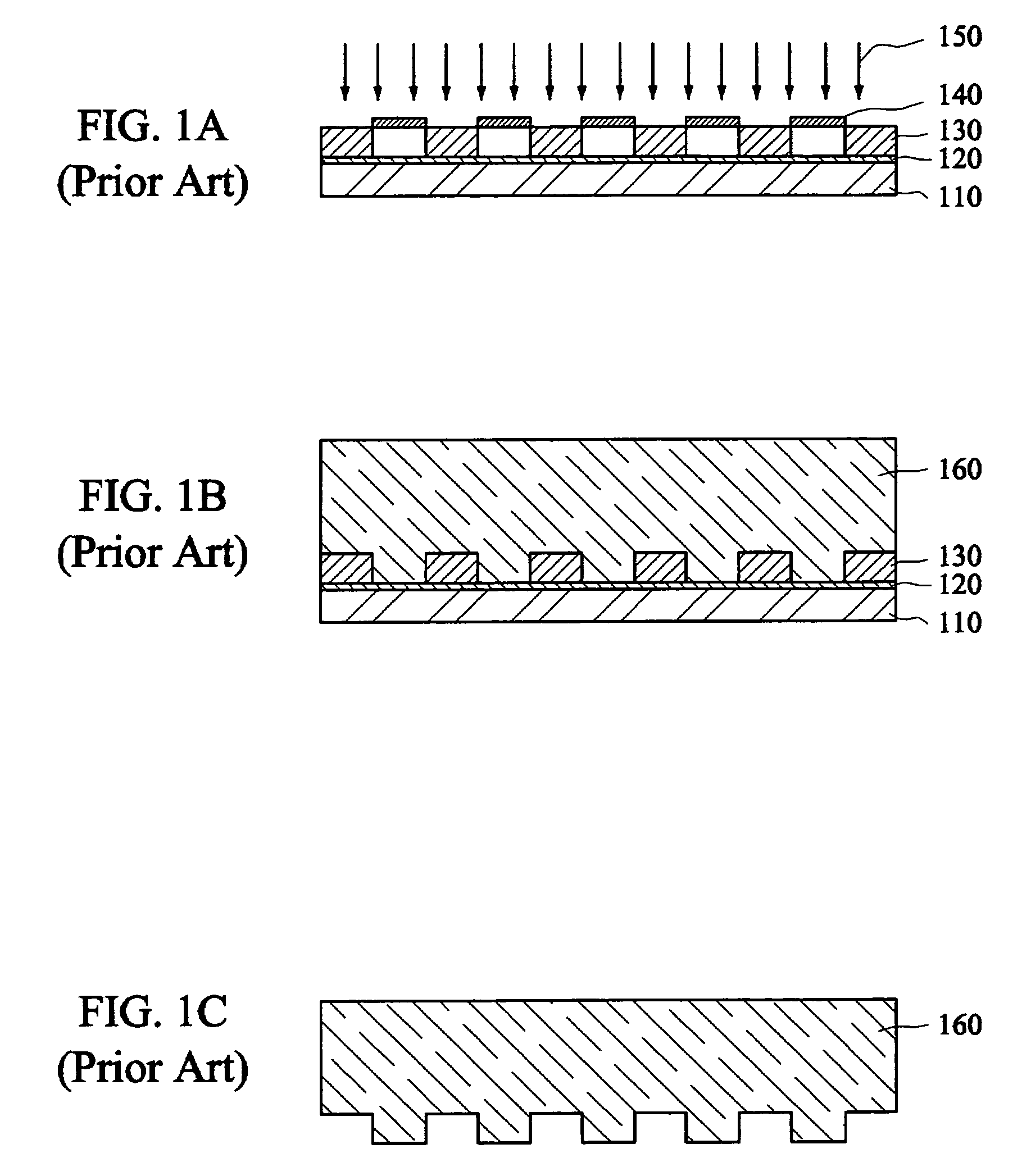
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "LIGA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
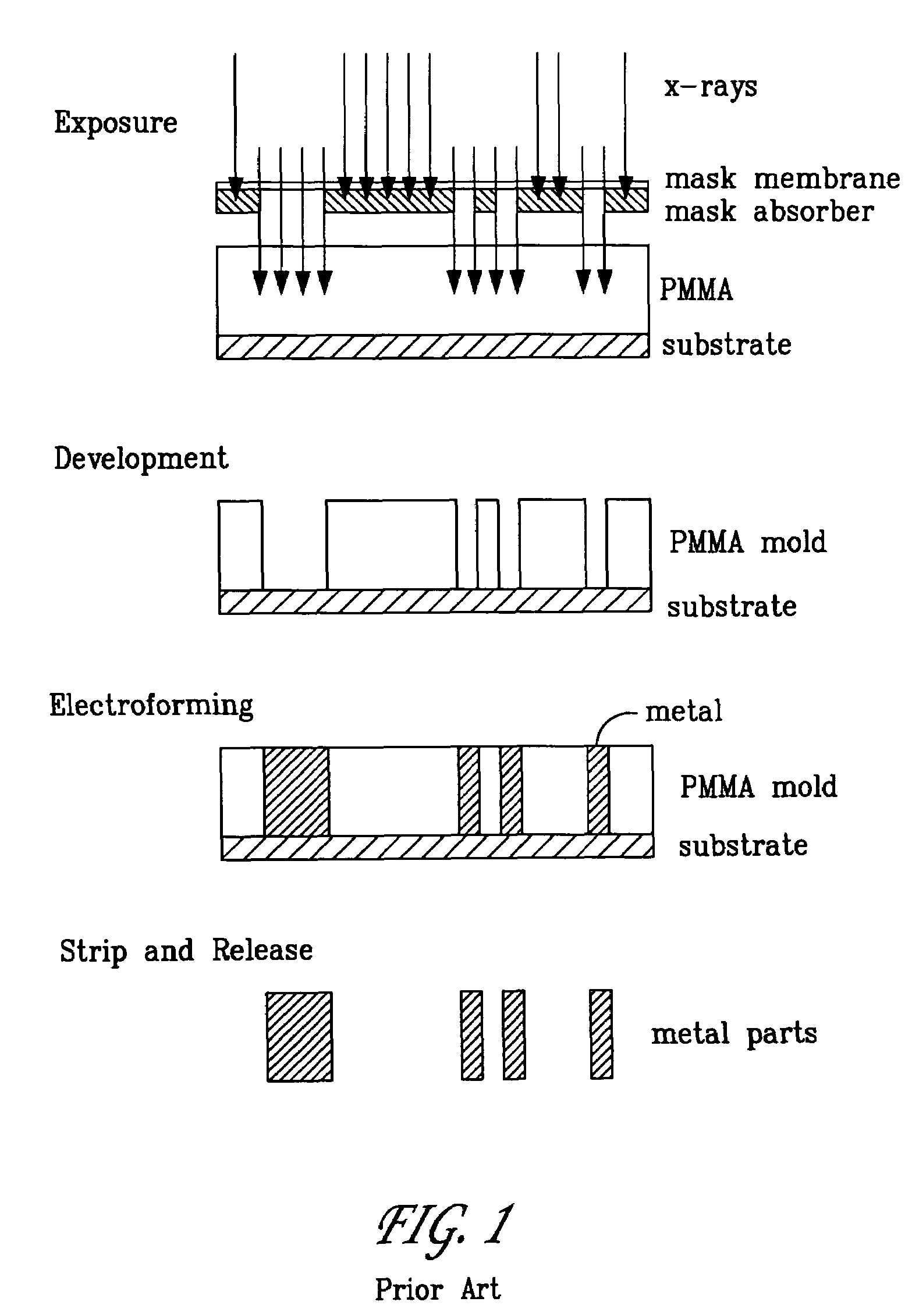
LIGA is a German acronym for Lithographie, Galvanoformung, Abformung (Lithography, Electroplating, and Molding) that describes a fabrication technology used to create high-aspect-ratio microstructures.
High aspect ratio, microstructure-covered, macroscopic surfaces
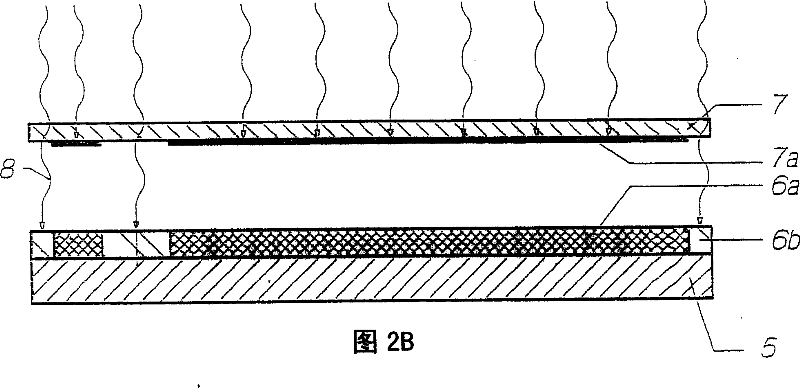
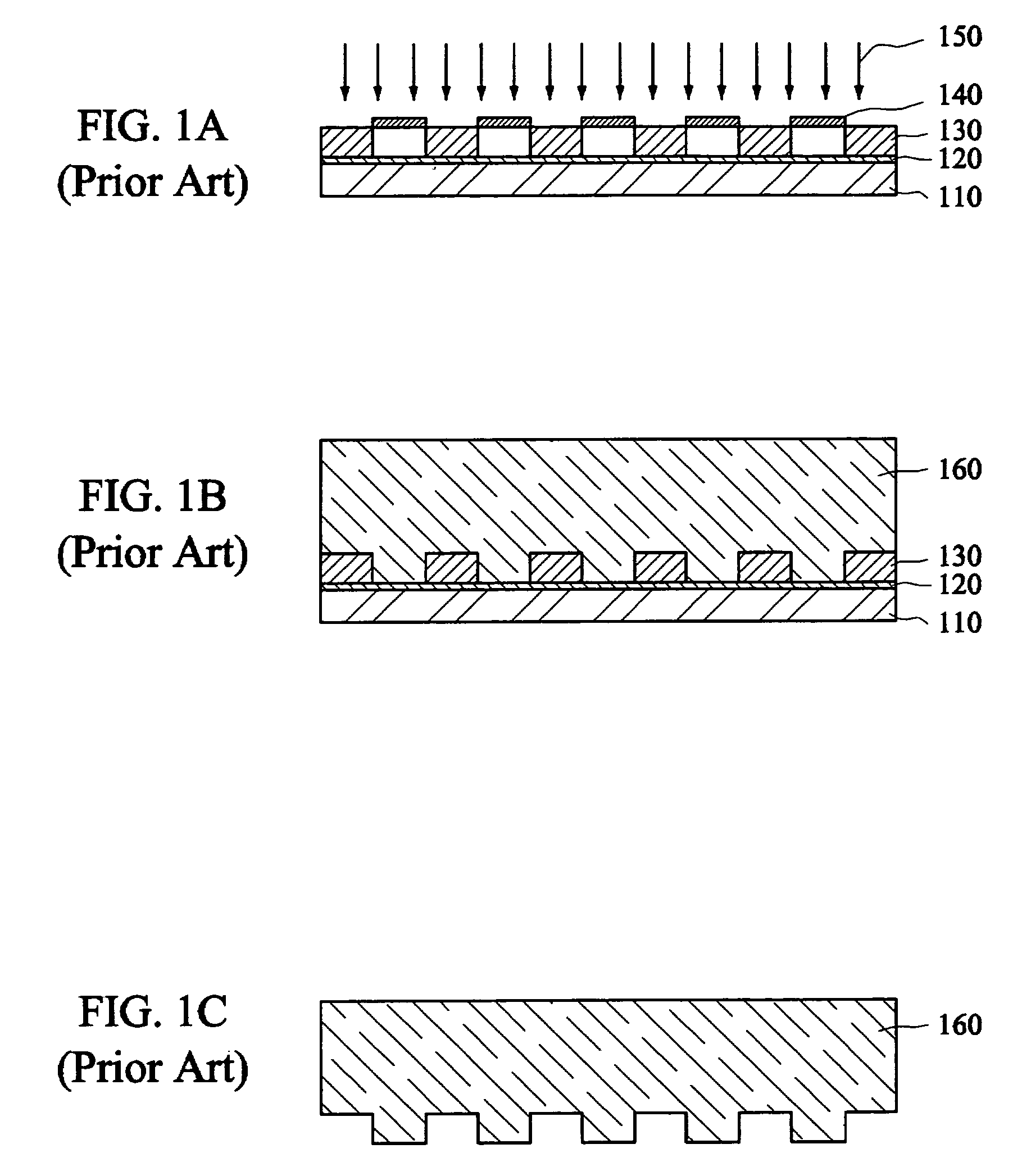
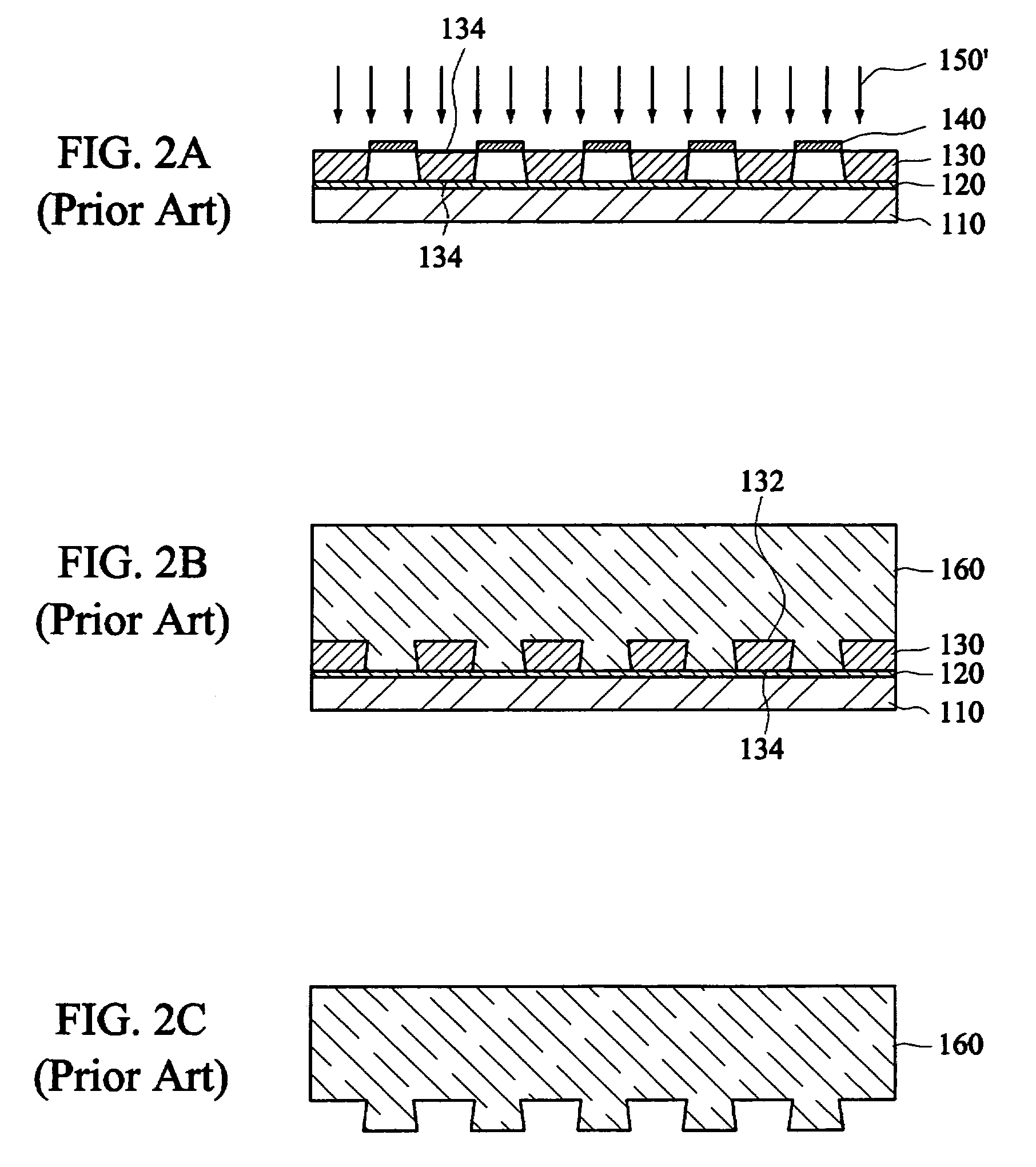
InactiveUS6197180B1Improve performanceDecorative surface effectsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMicrofabricationLIGA
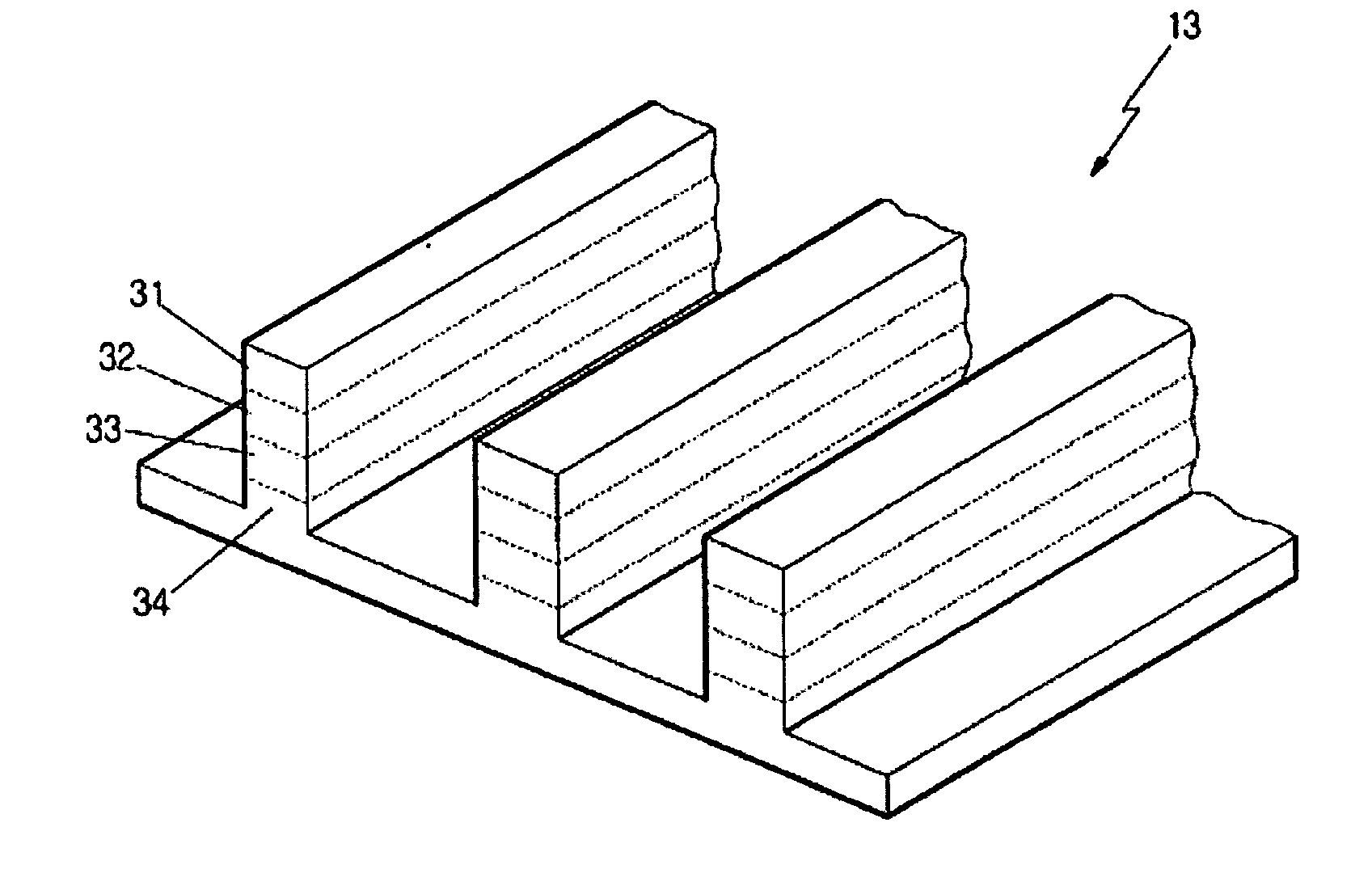
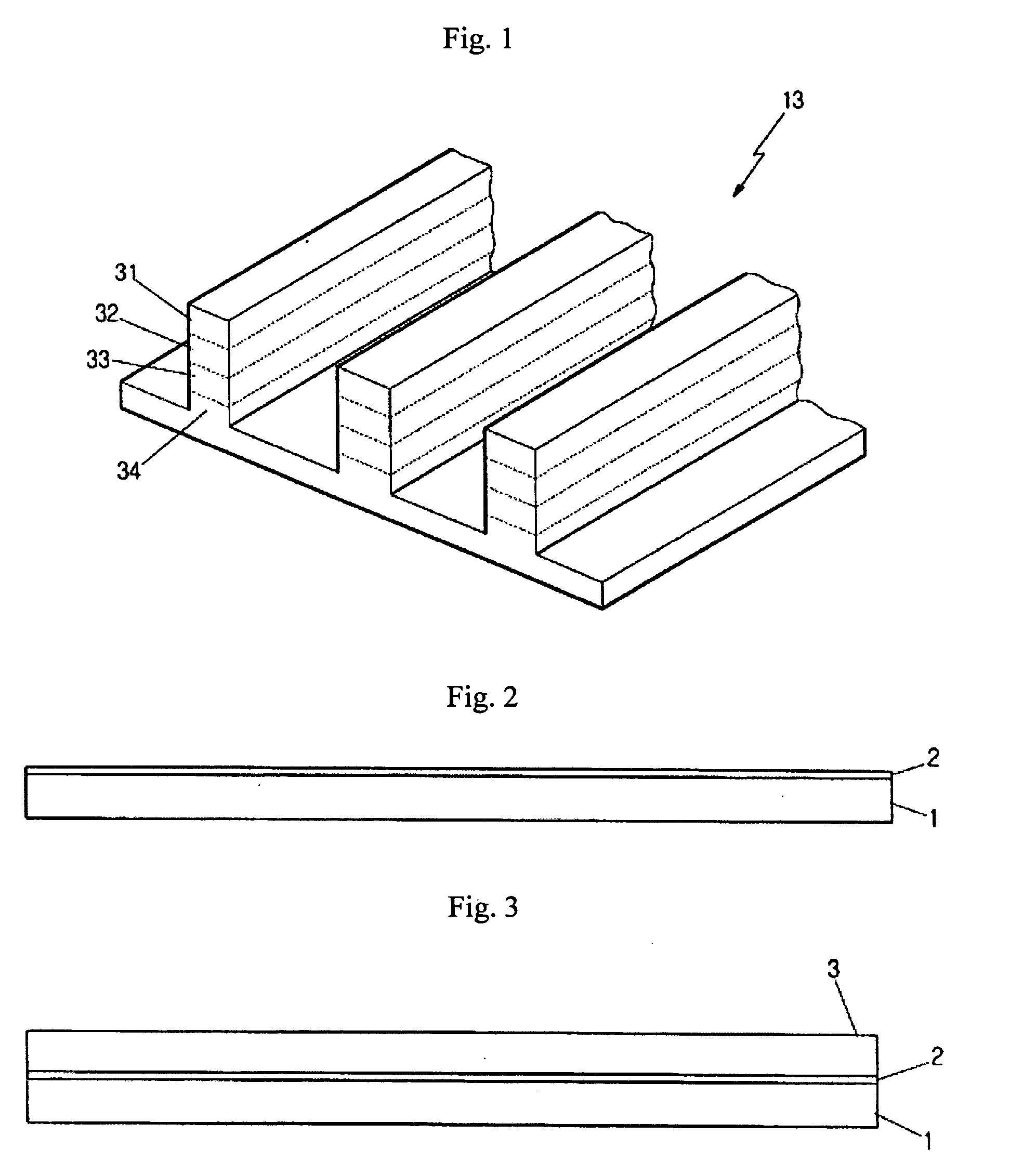
The performance of many macroscopic structures (those whose dimensions are on the order of centimeters, meters, or even larger) can be greatly improved by covering their surfaces with microstructures. There are several applications in which "large," microstructure-covered sheets are useful. An apparatus and method are disclosed for forming high aspect ratio microstructures ("HARMs") on planar and non-planar surfaces, using a modification of the LIGA microfabrication process. A free-standing polymer sheet is lithographically patterned with through-holes. The polymer sheet is then pressed against, clamped to, or otherwise attached to a conductive substrate in such a way that the patterned holes in the sheet are not blocked. Subsequent electroplating produces well-defined HARM structures on the planar or non-planar surface, in shapes that are complementary to the lithographically patterned through-holes in the polymer. The polymer may then be removed (e.g., by melting, dissolution, or burning). Various planar and non-planar surfaces have been covered with microstructures. Where the metal surface is non-planar, the polymer sheet may be heated or otherwise made sufficiently flexible to conform to the metal surface, preferably by heat-shrinking to assure firm contact. The process may be used to electroplate microstructures directly onto metal surfaces generally-not just onto metal surfaces that have been specially prepared for LIGA processes, as has previously been the case.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
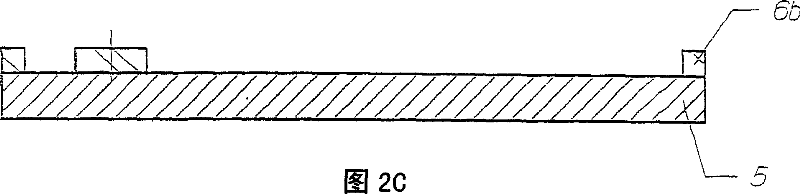
Process for fabricating a monolayer or multilayer metal structure in LIGA technology, and structure obtained
ActiveCN101038440AImprove qualityEasy thickness controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusResistIon bombardment
The invention relates to a process for fabricating a monolayer or multilayer metal structure in LIGA technology, in which a photoresist layer is deposited on a flat metal substrate, a photoresist mold is created by irradiation or electron or ion bombardment, a metal or alloy is electroplated in this mold, the electroformed metal structure is detached from the substrate and the photoresist is separated from this metal structure, wherein the metal substrate is used as an agent involved in the forming of at least one surface of the metal structure other than that formed by the plane surface of the substrate.
Owner:ROLEX SA
Method of manufacturing a LIGA mold by backside exposure
InactiveUS20060275711A1Low costPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLIGAThermal compression
A method of manufacturing a LIGA mold by backside exposure includes the steps of: disposing a mask layer at a side of a first substrate, wherein the first substrate is transparent to a predetermined light source and has a front side and a backside; forming a photoresist layer on the front side of the first substrate; providing the predetermined light source to illuminate the backside of the first substrate so as to expose the photoresist layer to form an exposed portion and an unexposed portion; removing the unexposed portion to form a patterned structure on the photoresist layer; forming a metal layer on the patterned structure of the photoresist layer and the first substrate; and removing the photoresist layer and the first substrate to remain the metal layer as the LIGA mold, which is good in a de-molding procedure of a hot embossing process.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
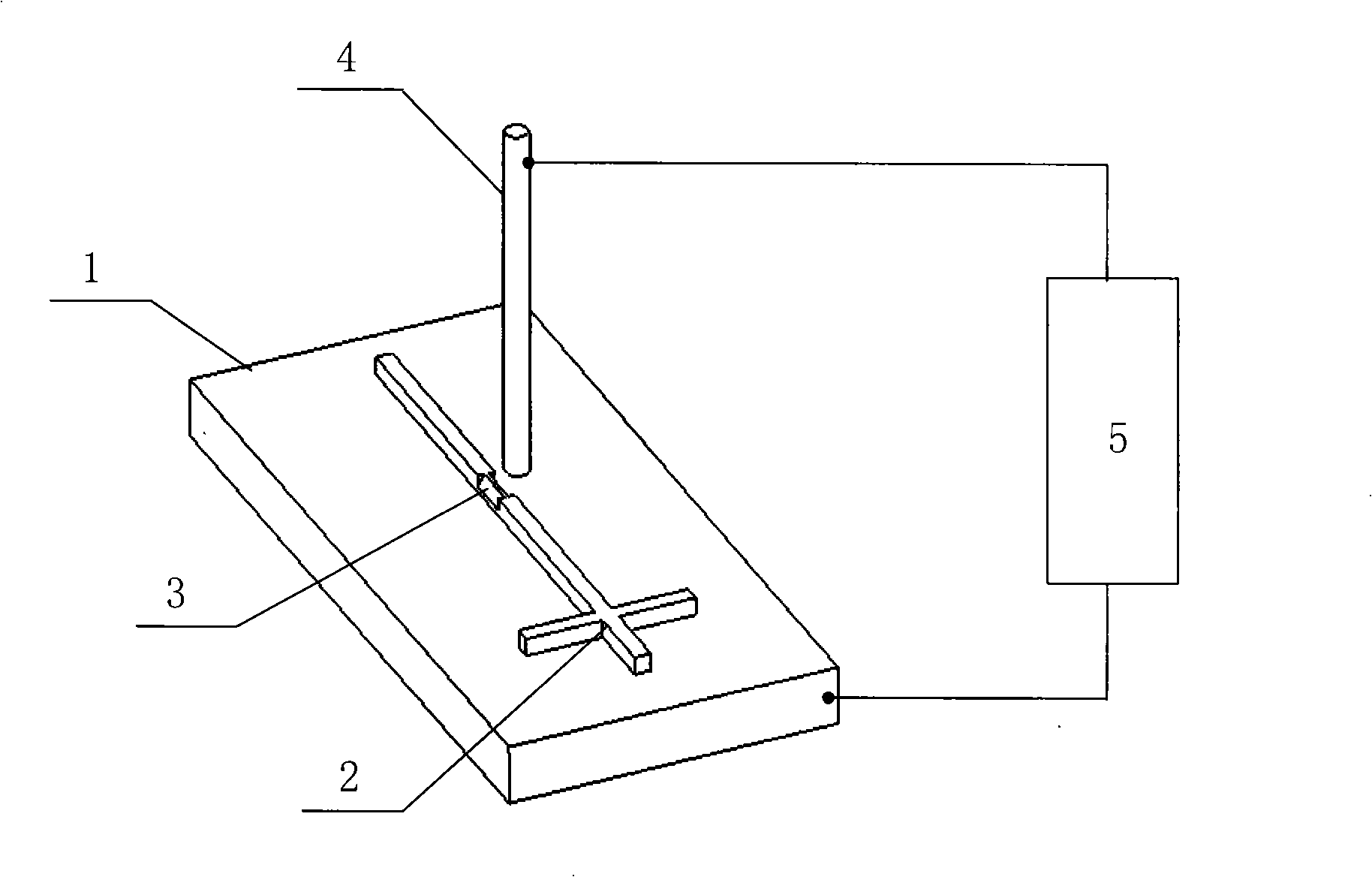
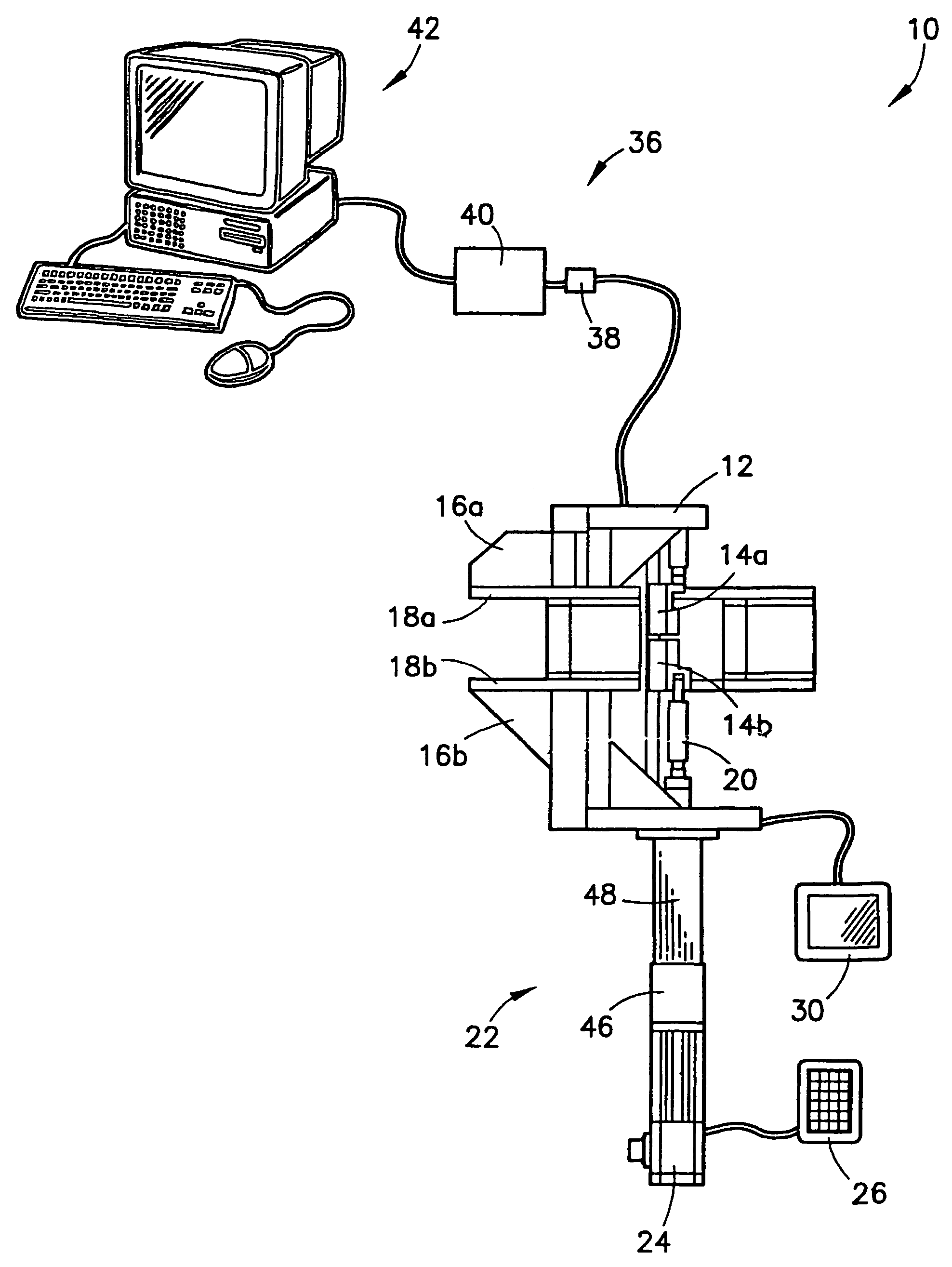
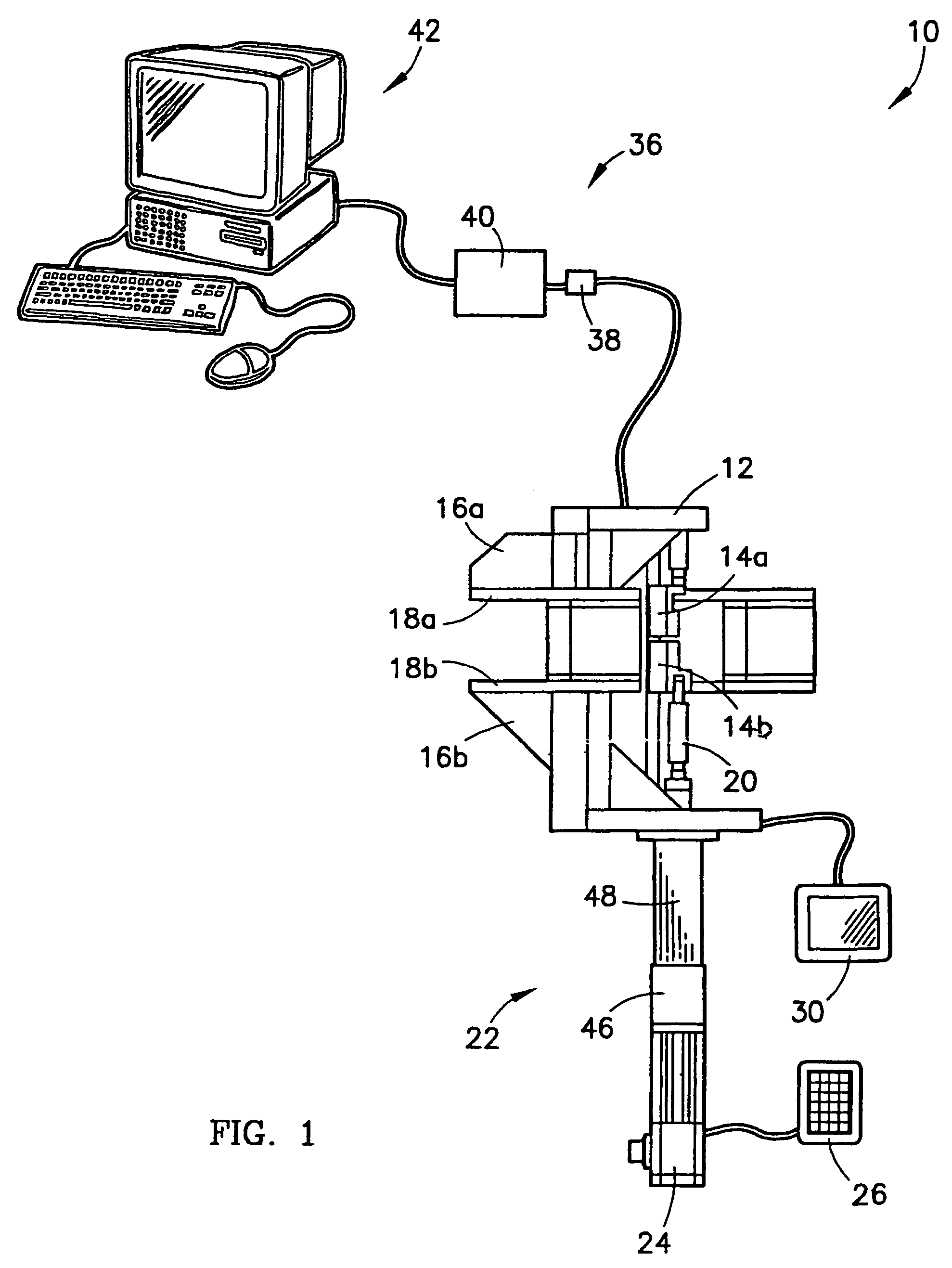
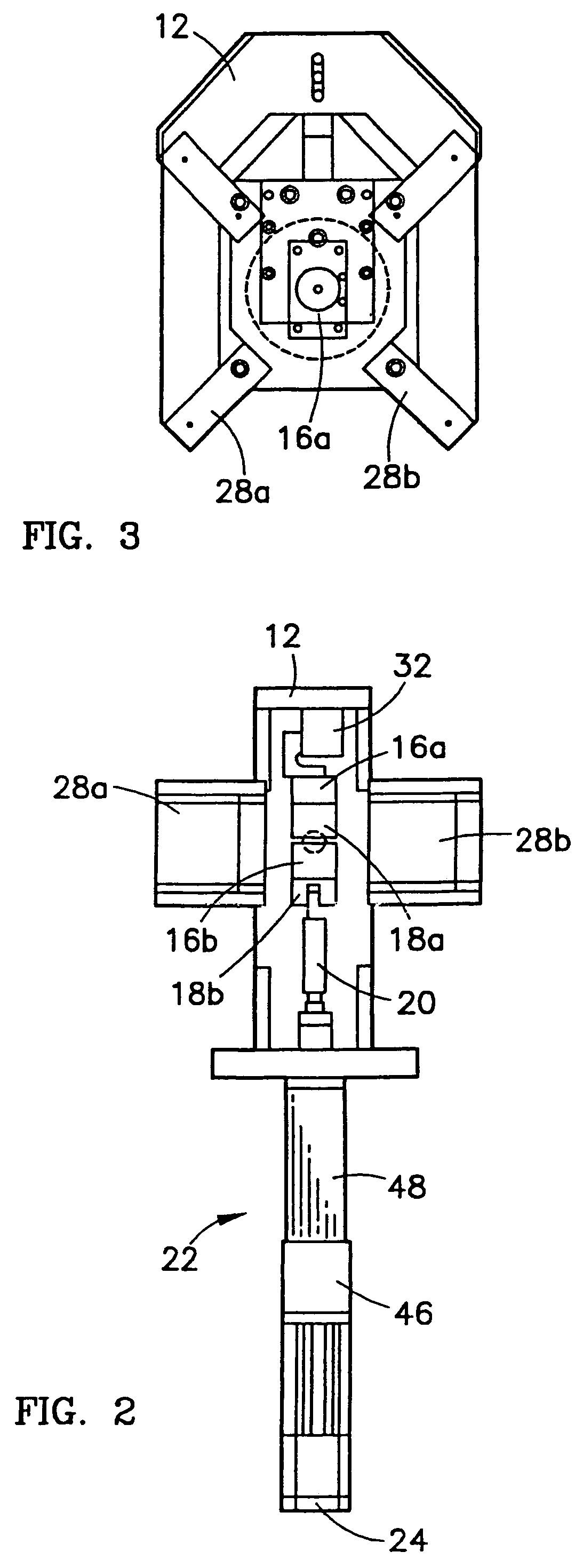
Micro-tensile testing system
InactiveUS20060096385A1Error minimizationMinimize measurement errorForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCyclic testMicrometer
A micro-tensile testing system providing a stand-alone test platform for testing and reporting physical or engineering properties of test samples of materials having thicknesses of approximately between 0.002 inch and 0.030 inch, including, for example, LiGA engineered materials. The testing system is able to perform a variety of static, dynamic, and cyclic tests. The testing system includes a rigid frame and adjustable gripping supports to minimize measurement errors due to deflection or bending under load; serrated grips for securing the extremely small test sample; high-speed laser scan micrometers for obtaining accurate results; and test software for controlling the testing procedure and reporting results.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Method for making a conductive film and a probe card using the same
InactiveUS20090091343A1Large area detection abilityEasy maintenanceLine/current collector detailsElectrical measurement instrument detailsDielectricProbe card
A method for manufacturing a conductive film as well as the structure thereof and a probe card using the same are provided in the invention. The conductive film is substantially a stacked structure of a specific thickness formed by the adhering and stacking of at least an substrate in a vacuum environment by the use of surface processing and mechanical healing whereas each substrate has an array of metal micro-threads formed thereon, in which the plural metal micro-threads, each being wrapped in an insulating film, are arranged on the substrate to form the array in a unidirectional and single-layered manner by the use of a LIGA process and polymer thin film technology. In an exemplary embodiment, the insulating film can be a polymer thin film of high dielectric constant, being made of a material such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMA) or polyimide (PI); and the metal micro-thread is made of a high conductivity and high strength Ni—Co alloy. Moreover, the so-formed conductive film can be cut into any desired dimensions by the use of an energy beam, such as laser beam, ion beam and plasma beam, etc. while combining the conductive film with a panel so as to be used for forming a probe card with large area detection ability that is low-cost, ease-to-maintain and capable of being adapted for wafers of various bonding pad arrangements.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
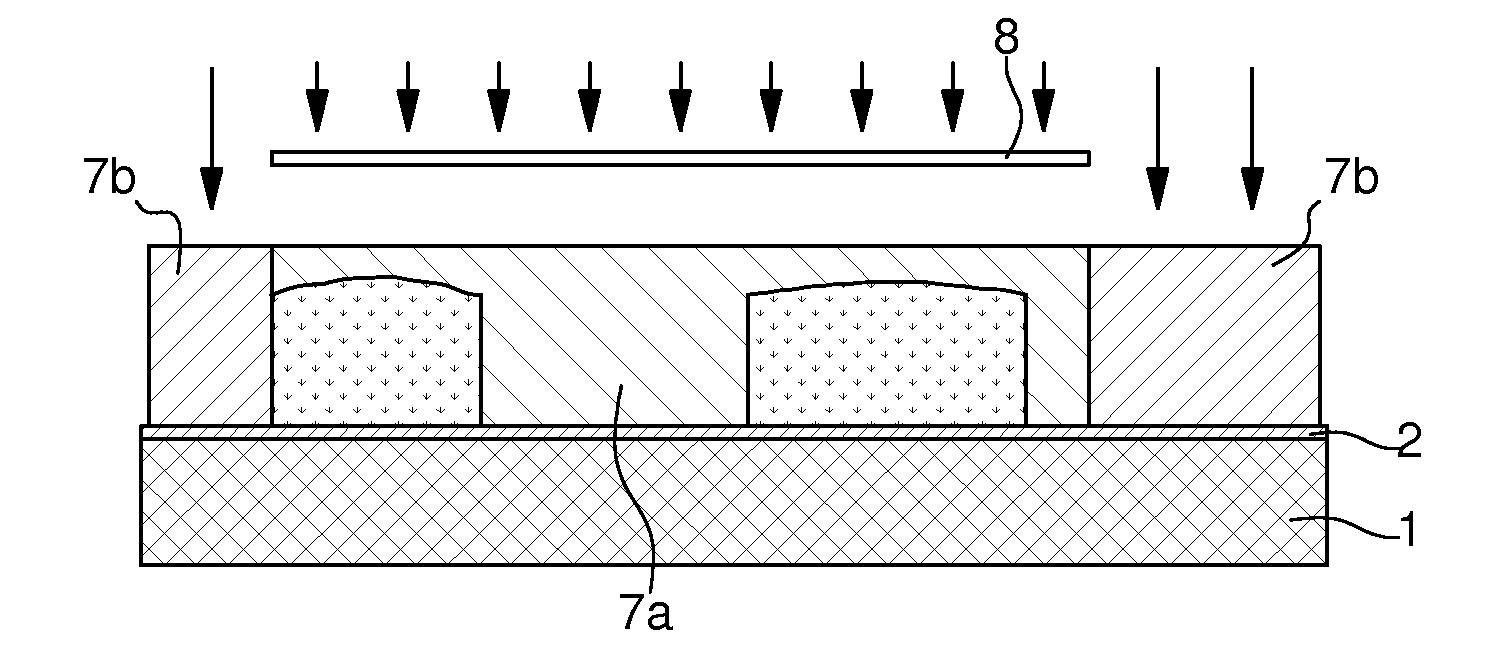
Heterogeneous liga method
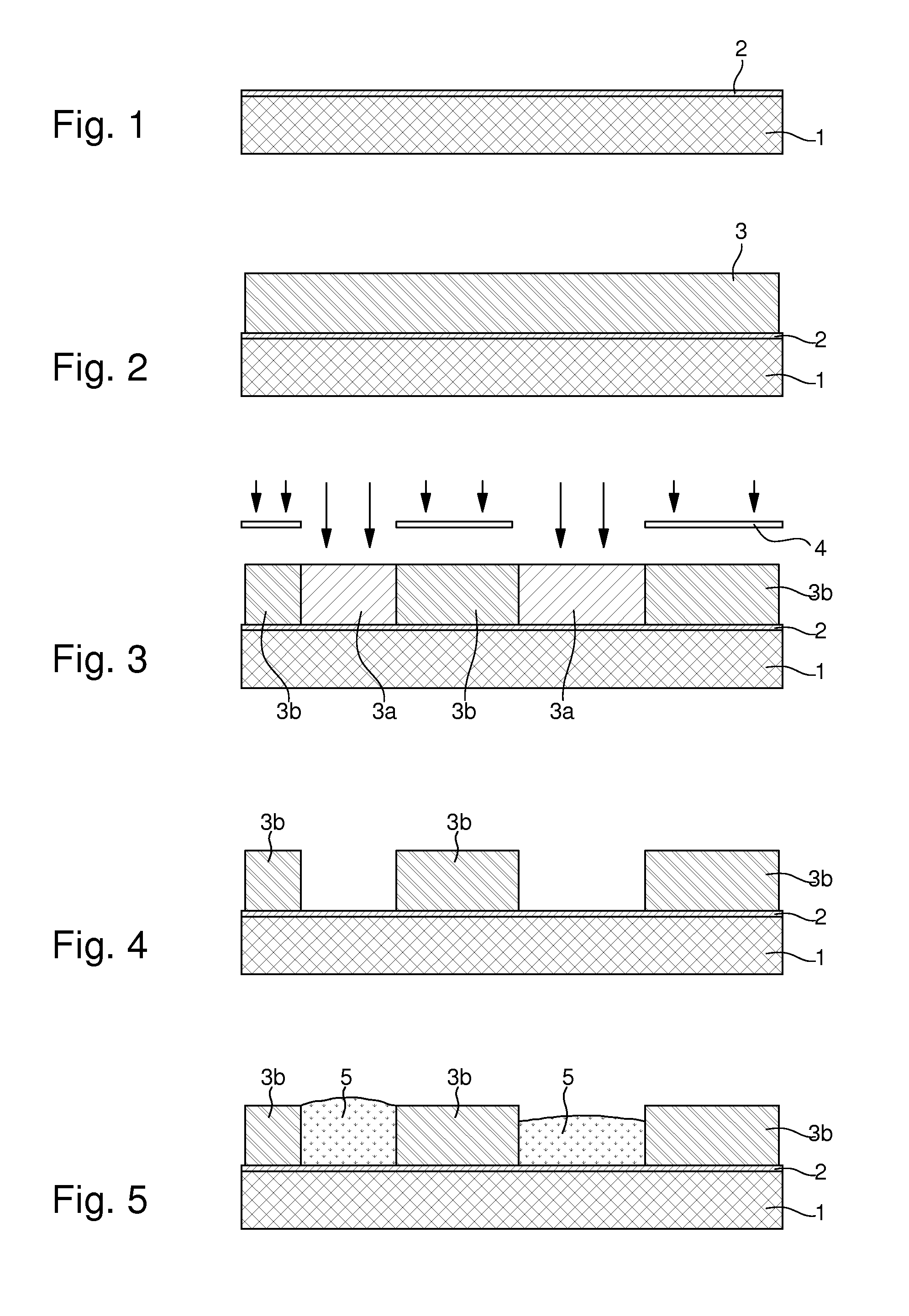
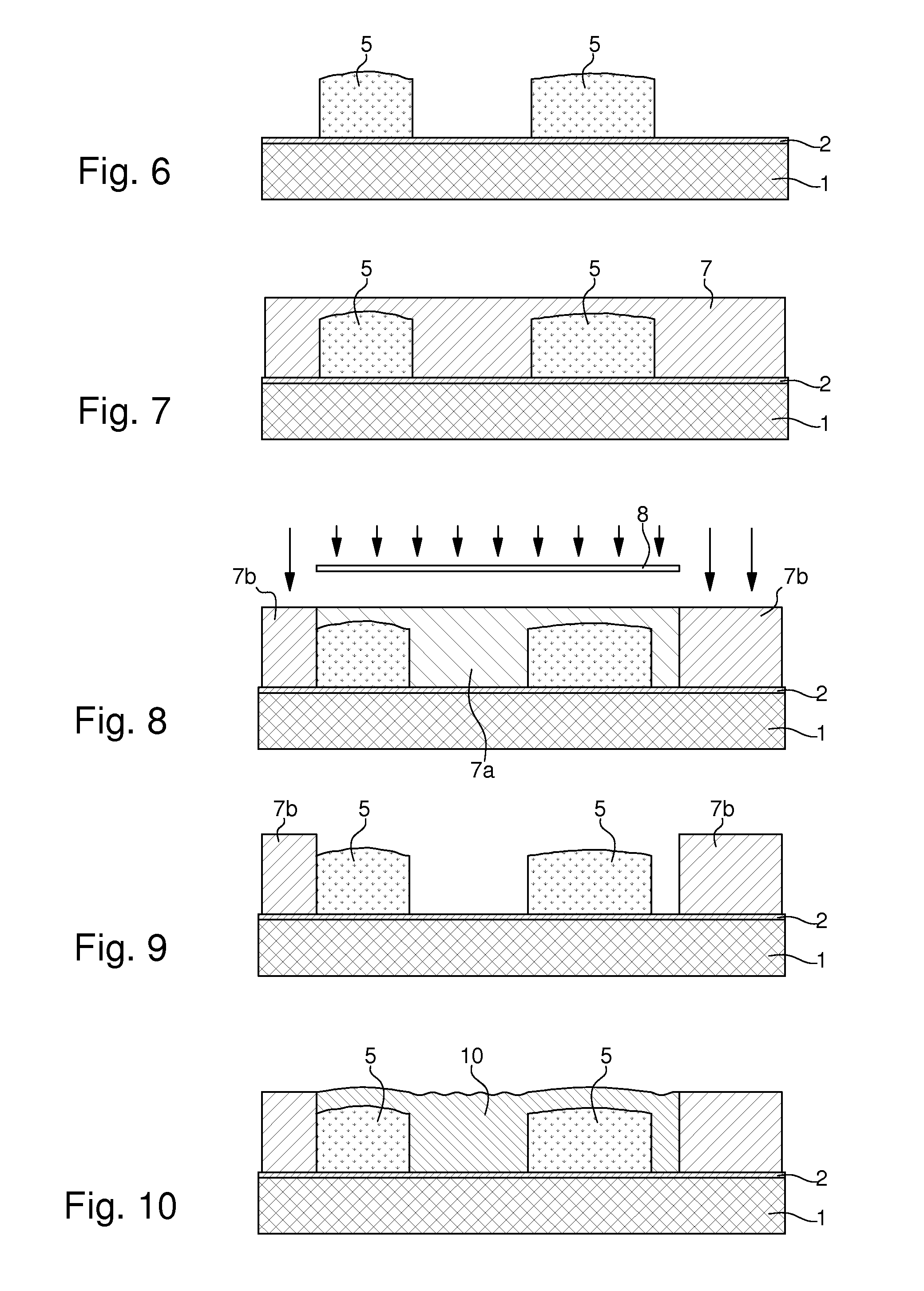
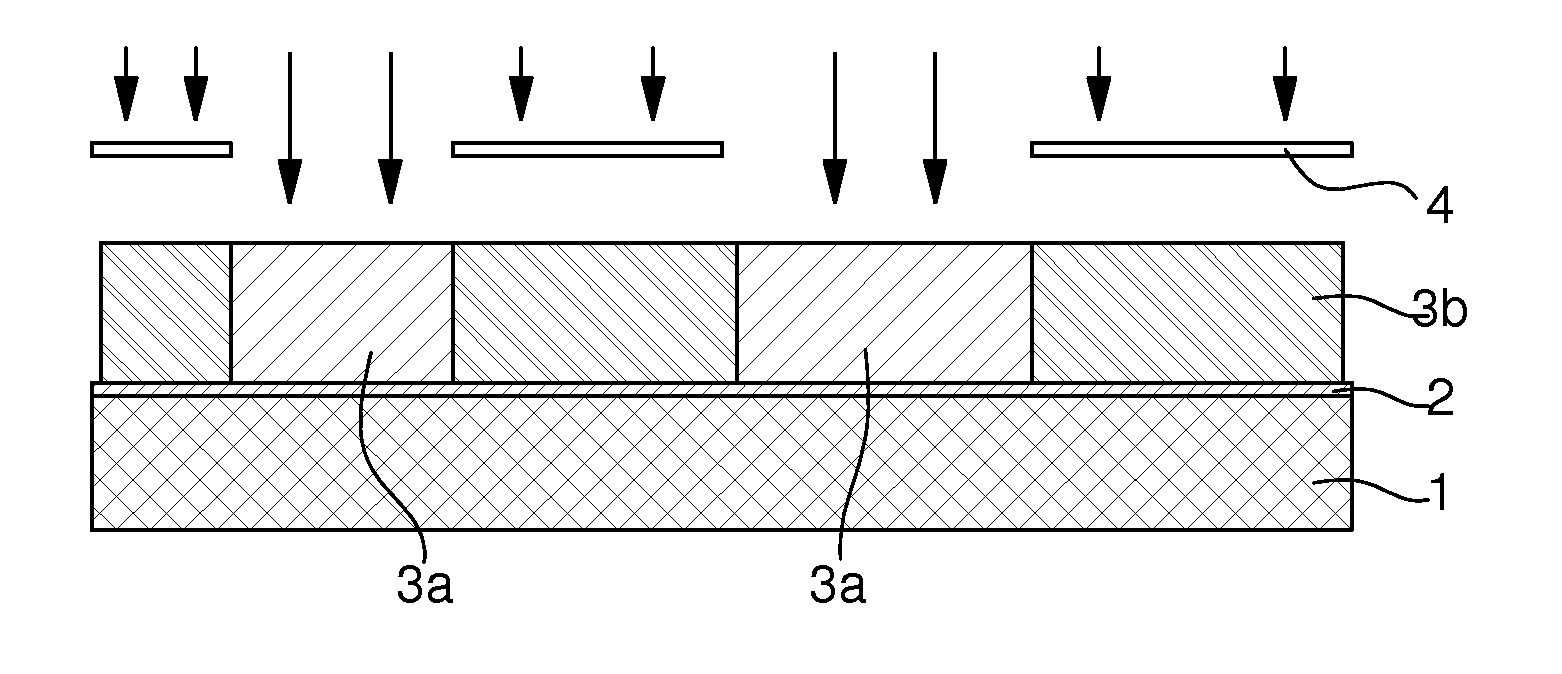
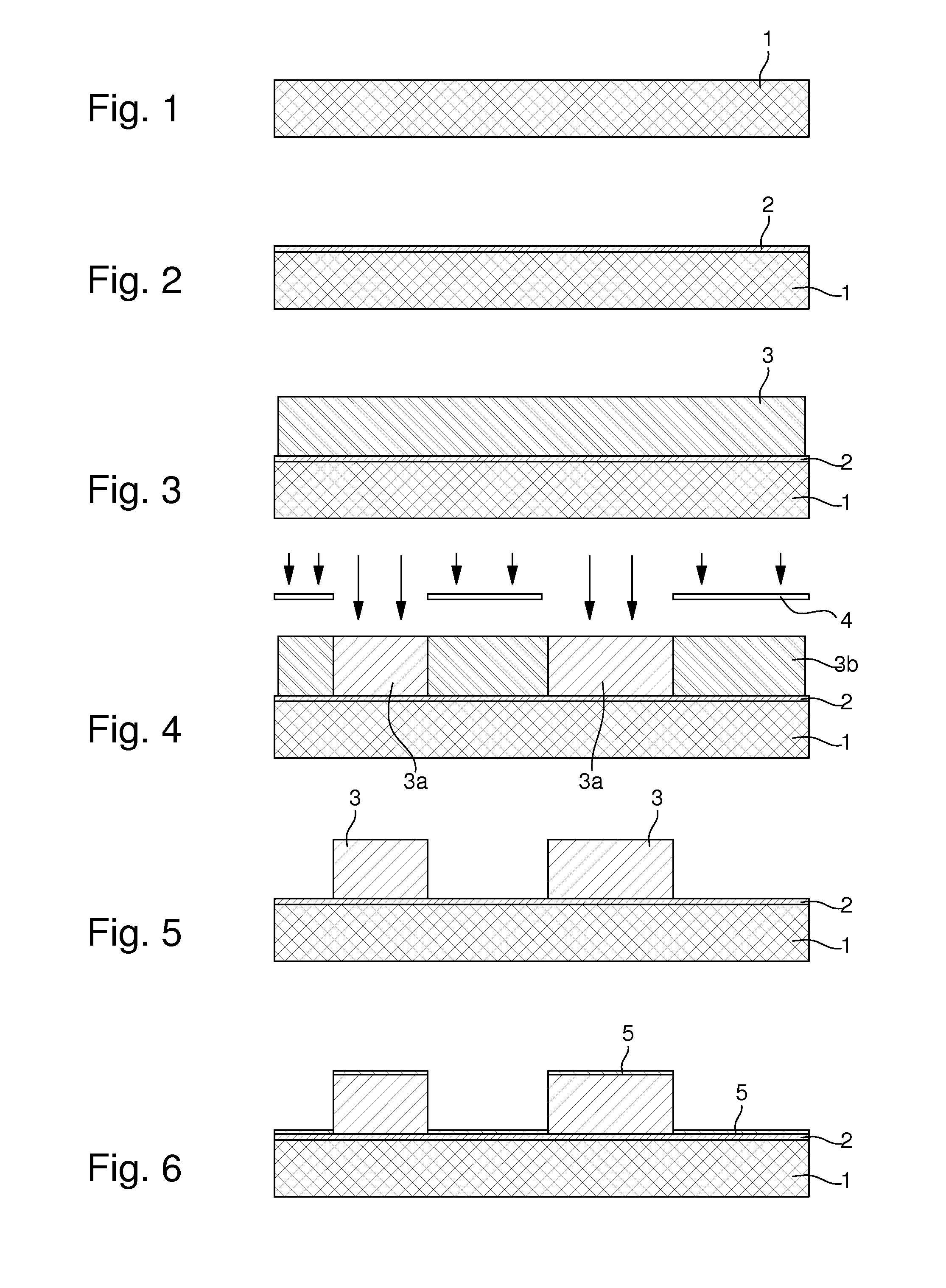
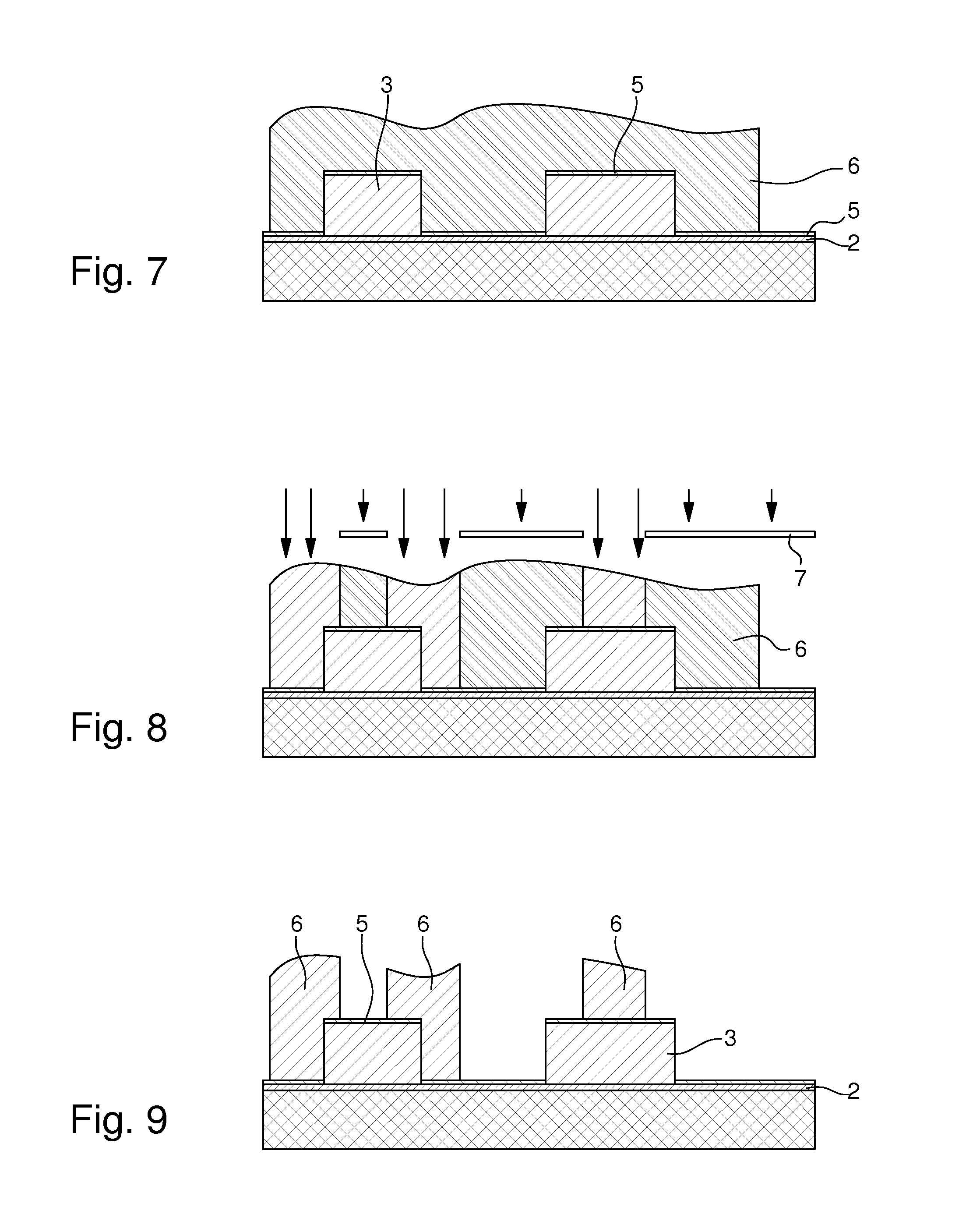
The method of fabricating metal microstructures includes the following steps:a) taking a substrate (1, 2) that has a conductive strike surface (2);b) to d) forming a first resin mould (3b) by UV photolithography, the apertures in the first resin mould revealing the conductive strike surface (2) of the substrate;e) electroforming the first element (5) by galvanic deposition of a first metal material in the apertures of the first resin mould (3b),f) removing the first mould (3b) around the first element (5) to expose the conductive strike surface (2) of the substrate;g) to i) forming a new resin mould (7b) by UV photolithography, the apertures in the new resin mould revealing the first element (5), and the conductive strike surface (2) of the substrate;j) electroforming the second element (10) by galvanic deposition of a second metal material in the apertures of the new resin mould (7b) to form said metal microstructure;k) separating said metal microstructure from the substrate (1) and from said new mould (7b).
Owner:NIVAROX FAR
Anomalous plane hollow microneedle based on surface micro processing process and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an anomalous plane hollow microneedle based on a surface micro processing process and a preparation method of the anomalous plane hollow microneedle. The method adopts a wet method etching process, an ultraviolet-lithographie -galanoformungand abformung (UV-LIGA) process and a casting process, the wet method etching is used for forming a needle point structure of the microneedle, the UV-LIGA is used for realizing the needle body part of the microneedle, and then, the microneedle structure with the hollow interior is formed by casting, so the anomalous plane hollow microneedle is realized. The anomalous plane hollow microneedle is formed through casting by a purpose-made mold, the expensive processing technology is not needed, the fast reproduction and the high-speed mass production can be realized, in addition, the wet method etching and the casting operation are relatively simple, and the whole set of technical process is simple and is easy to implement.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
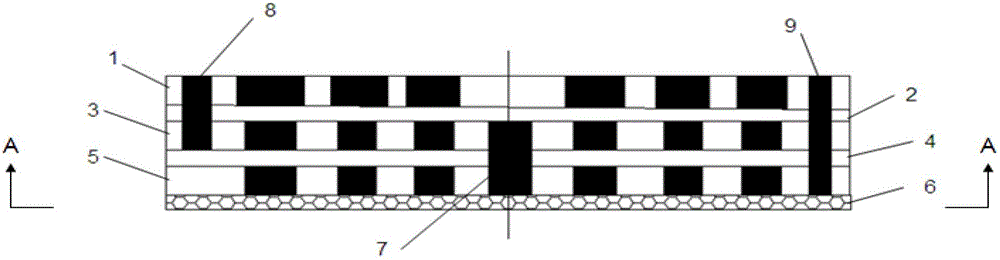
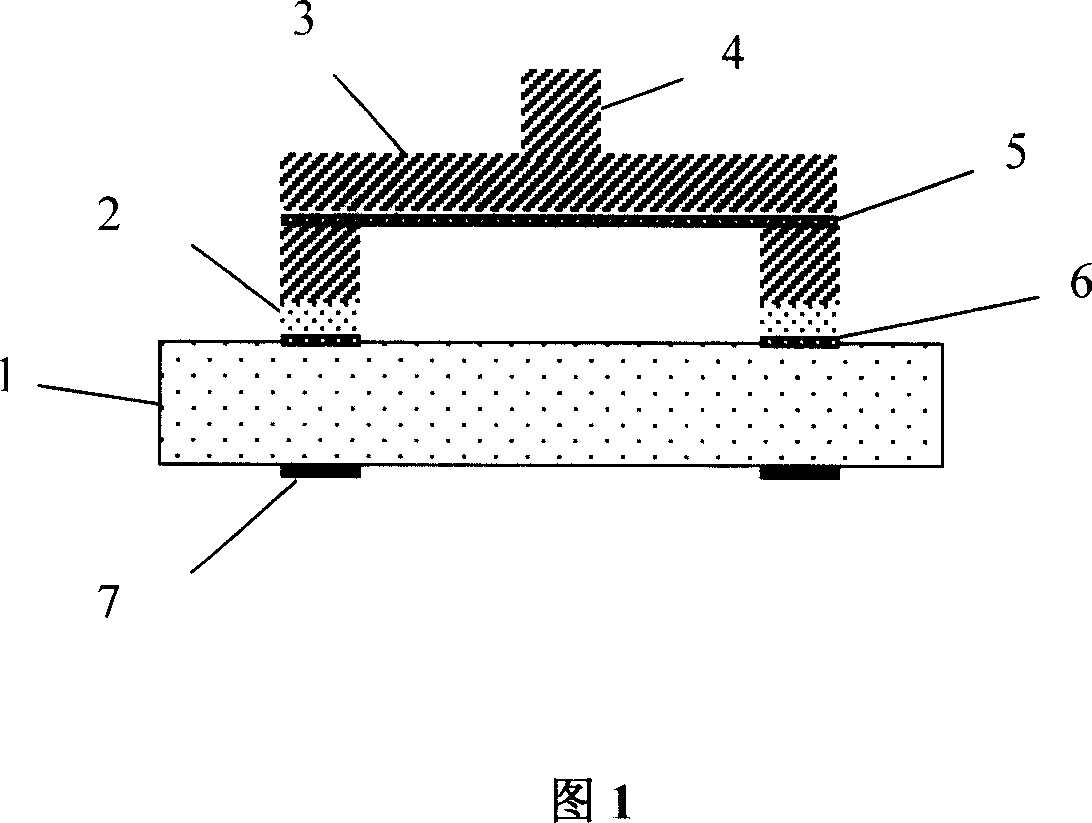
Flexible three-dimensional force sensor and decoupling method and manufacturing method thereof
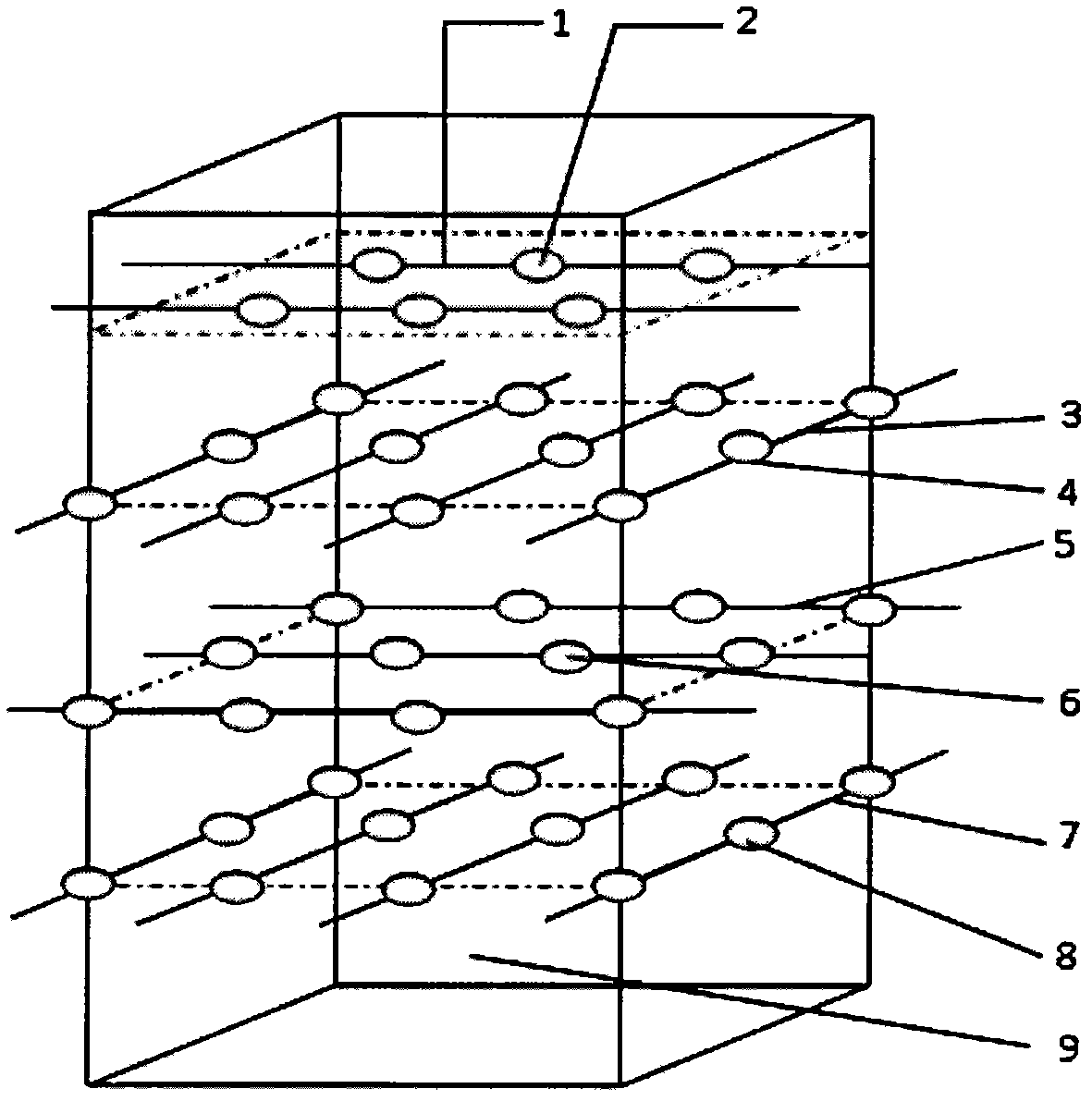
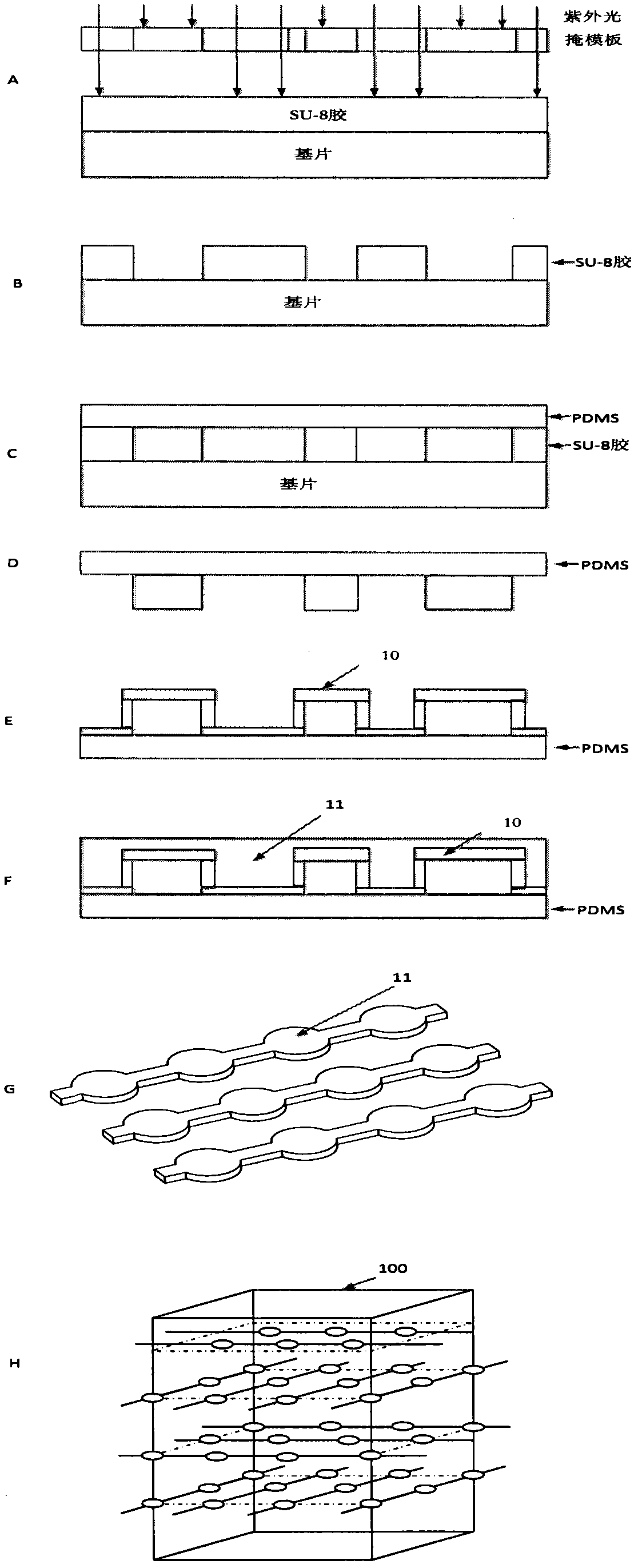
InactiveCN102435376AHigh densityPrevent frequent breakageForce measurementMeasurement of force componentsElectrical resistance and conductanceSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a flexible three-dimensional force sensor based on flexible conductive rubber and a manufacturing method thereof. The base body of the flexible three-dimensional force sensor is flexible conductive rubber; the middle of the flexible three-dimensional force sensor consists of four layers of micro electrodes and a lead array; the lead of each layer is externally connected with a signal processing circuit; and the magnitude of the three-dimensional force is measured by detecting the change of the resistance value. The key to the flexible three-dimensional force sensor is the manufacturing of the micro electrodes and the lead array. In the patent, the micro electrodes and the lead array are manufactured by the UV-LIGA technology based on SU-8+PDMS; then the manufactured micro electrodes and lead array are put into a die cavity of the sensor, and liquid flexible conductive rubber is injected into the die cavity; and finally, the flexible three-dimensional force sensor can be manufactured after a certain time of cooling and curing. Due to a small space between the micro electrodes, the sensitivity and accuracy of the sensor are greatly improved, and the sensor can be produced by batch.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
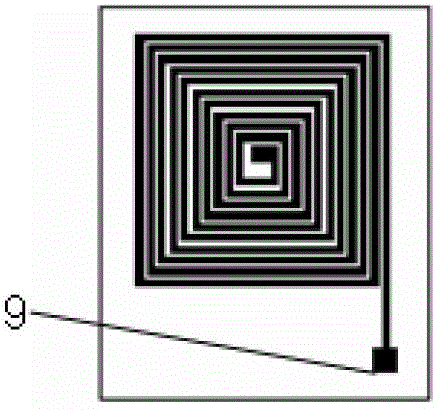
Eddy current sensor for detecting metal gap and defect under high-temperature and narrow-slit condition
InactiveCN101929833ASubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansLithographic artistMetallic materials
The invention relates to an eddy current sensor used under a high-temperature and narrow-slit condition, which belongs to the field of detection technology. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) manufacturing a micro scale planar coil 1 by using ultraviolet-lithography and galvanoplasty (UV-LIGA) technology; (2) manufacturing a nickel-iron alloy iron core 3 by a galvanoplasty manufacturing process; and (3) providing a two-layer eddy current sensor structure formed by laminating the micro planar coil and a magnetic core. The sensor has the advantages of simple structure, flexible application and capability of detecting a gap and a defect of a metal material under the narrow-slit and high-temperature condition.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
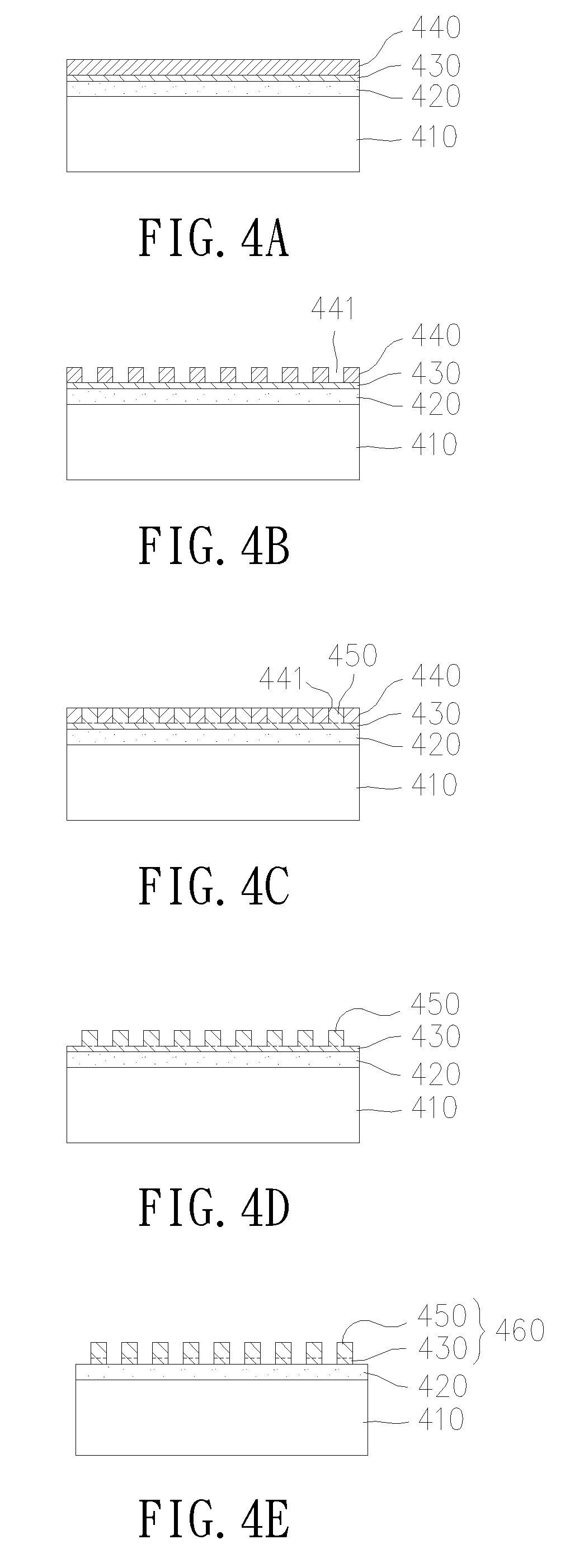
Method for fabricating metallic structure
InactiveUS20050208435A1High resolutionPhotosensitive material processingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentMetallurgyLIGA
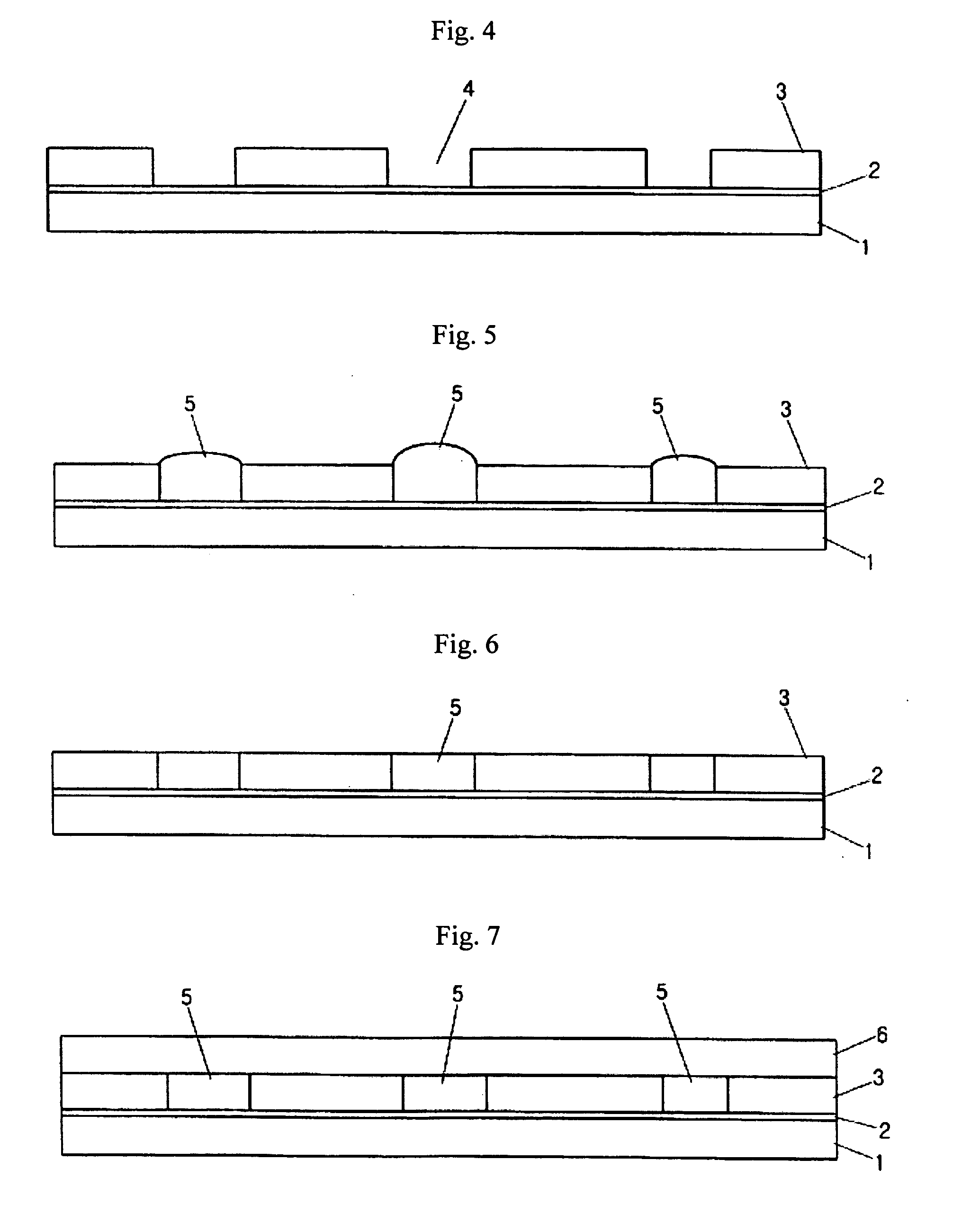
First, a substrate is provided and a photoresist layer is coated thereon. Then, a film having a pattern is used as a mask to perform an exposing and developing process for patterning the photoresist layer. Following that, LIGA technology is employed to form a thin film having a pattern corresponding to the pattern of the film.
Owner:U TECH MEDIA
Micro-tensile testing system
InactiveUS6983658B2Advantageously minimizing deflectionAdvantageously minimizing bendingForce measurement by measuring optical property variationStrength propertiesObservational errorCyclic test
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Miniature eddy current sensor with structure consisting of silicon substrate and multilayer coils
InactiveCN102721738AEasy to operateBreaking through macro limitationsMaterial magnetic variablesMultiple layerMonolayer
The invention relates to a miniature eddy current sensor with a structure consisting of a silicon substrate and multilayer coils, and belongs to the field of miniature sensors. The miniature eddy current sensor is used for detecting micro-cracks on surfaces of metal components, is based on the three-inch silicon substrate with the thickness of 200 micrometers and comprises a single-layer excitation coil, multiple layers of detection coils, conducting layers and insulating layers, each two layers of detection coils are serially connected and communicated by a central lead in a reverse spiral surrounding manner, flow directions of induced currents of the detection coils are consistent assuredly, and detection signals are intensified; and each silica insulating layer is filled between the corresponding detection coil and the excitation coil. The size of the section of each detection coil can be 10 micrometers X 10 micrometers, 20 micrometers X 15 micrometers and 30 micrometers X 15 micrometers, each coil includes 10 turns, the corresponding size of the section of the excitation coil can be 140 micrometers X 20 micrometers, 290 micrometers X 20 micrometers and 430 micrometers X 20 micrometers, and the excitation coil includes a single turn. The inductance coils are squarely or circularly spiral in a planar manner, and are distributed in a matrix manner according to the shapes and the sizes of the inductance coils, so that detection area is increased, and detection efficiency is improved. By the aid of via UV-LIGA (ultraviolet-lithography) which is precision processing technology on the basis of a micro-electro-mechanical system MEMS, the miniature eddy current sensor has the advantages of slim structure, miniaturization and high sensitivity and efficiency, and is applicable to nondestructive detection of microdefects on surfaces of metal workpieces.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Simple-beam type microelectronic mechanical system detection card and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1936593AImprove adaptabilityControl shape and sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingLithographic artistLIGA
This invention relates to a simple beam MEMS explore cards preparation methods, using UV-LIGA many lithography, preparation of flexible probe in the metal films with electroplating process, using the simple structure probe instead of the cantilever beam to bear the stress and greater oxide film holes, and regulate the probe displacement through the design of thickness of simple beams. Chip cards in accordance with the present invention, are obtained by the joint distribution and arrangement of the functions of the simple beam array, simply supported beam probe in the middle, and ensure the location of the needle position consistent with the corresponding pin chip. The bottom end of SR beam is the plating metal wire, which external from the bottom end around to the probe extension spot welding to connect to the corresponding printed circuit board, thus testing machine connected to the signal from the probe circuit. The invention process is simple, high productivity, control probe shape and size very well, high accuracy, suitable for mass production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Static suspension rotor micro inertia sensor and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1580701ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costRotary gyroscopesLIGAElectrostatic levitation
This is a static suspension rotator mini inertial sensor and its productive method. It comprises lower lining layer, the middle metal constructive layer and upper lining layer. The middle metal constructive layer comprises metal rotator and arouncd it there are a rotator cavity and radial electric poles, the lower and upper lining layer are bonded with the radial electric poles separately to form the rotator cavity. The wheel type metal rotator locates at the center of the rotator cavity. Between the lower and upper axial electric poles, which on the lower and upper lining layer, and between the rounded radial electric poles there are axial electric pole gap and radial electric pole gap. This mini inertial sensor's productive method contains: The working order of lower lining layer, and middle metal constructive layer, and upper lining layer, and the working order of bonded together, or include the working order of lower lining layer, upper lining layer, radial electric pole, metal rotator working order and mini assemble working order and bonded working order, to give out the productive method which base to UV-LIGA technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for manufacturing magnetosensitive device with giant magnetic impedance effect based on microelectrochenical system
InactiveCN1694276AHigh sensitivityImprove response speedMagnetic measurementsDecorative surface effectsHigh volume manufacturingEtching
This invention relates to a manufacturing method for a huge magnet impedance effect magnet-sensitive device based on micro-electromechanical system (MEMS), which applies MEMS technology to process a double-face oxidized silicon chip to get an aligned symbol carved in double faces so as to increase the aligned accuracy when exposing, applies a quasi-LIGA photo etching technology and micro plating to prepare a zigzag sandwich structure FeNi / Cu / FeNi soft magnet multiplayer membrane material, applies physical etching to remove the substrate to avoid the erosion brought with wet etching and offsets the huge magnet impedance effective curves by selecting suitable magnets to make the magnet-sensitive device to work in the linear zone.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
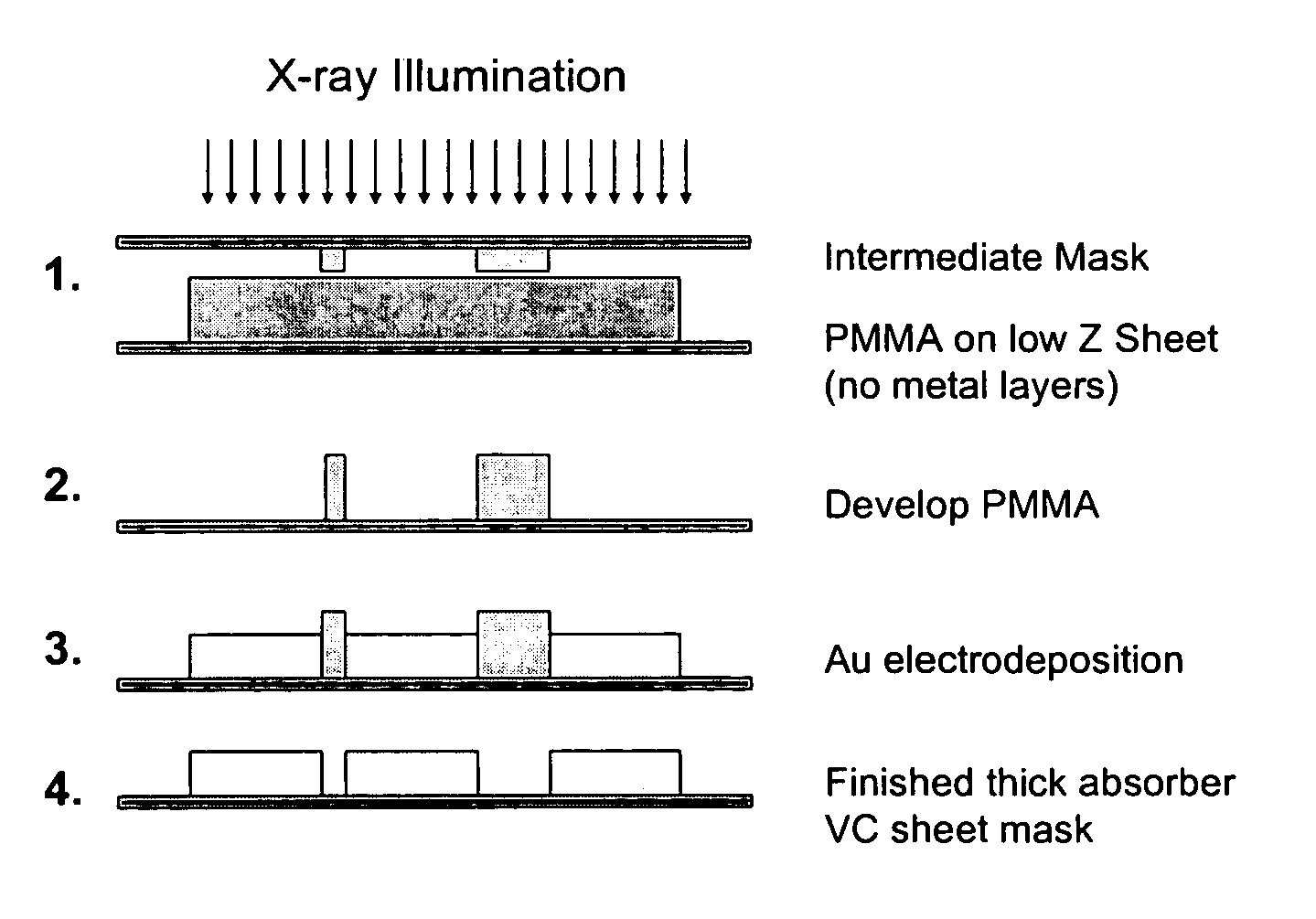
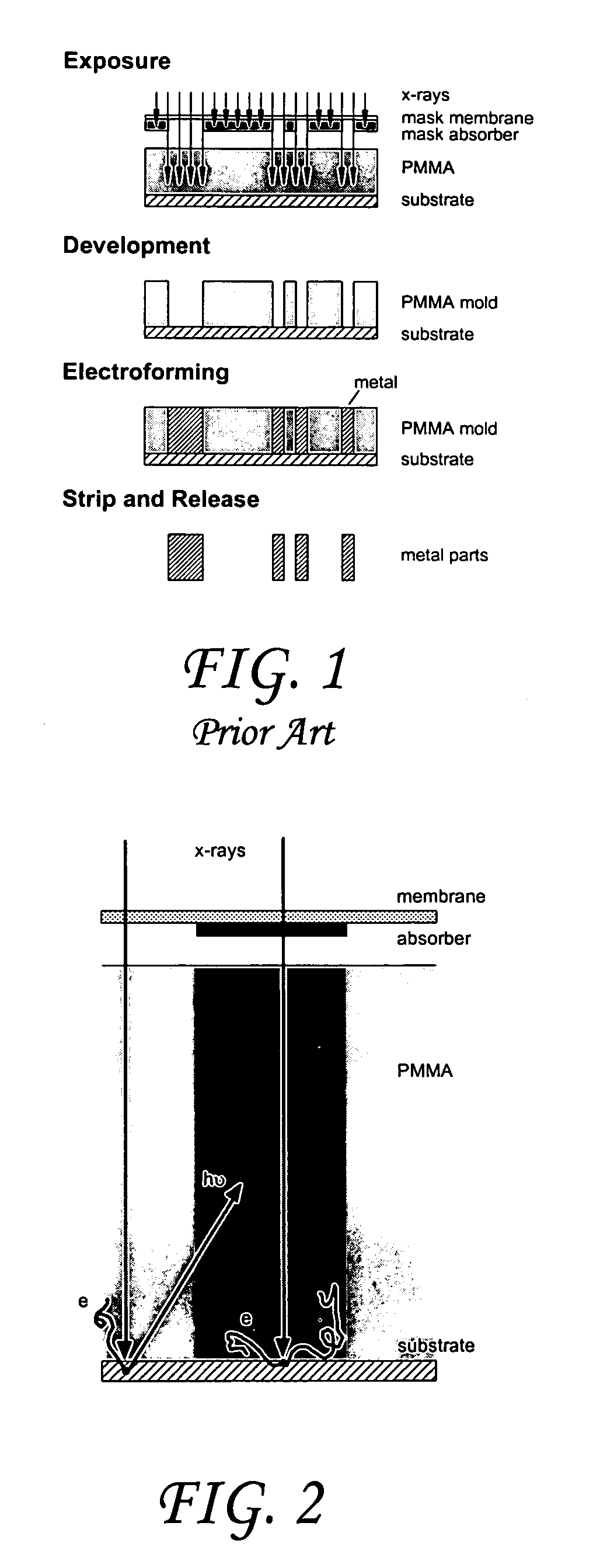
Vitreous carbon mask substrate for X-ray lithography
InactiveUS7608367B1Improve imaging resolutionIncrease contrastOriginals for photomechanical treatmentIrradiation devicesResistX-ray
The present invention is directed to the use of vitreous carbon as a substrate material for providing masks for X-ray lithography. The new substrate also enables a small thickness of the mask absorber used to pattern the resist, and this enables improved mask accuracy. An alternative embodiment comprised the use of vitreous carbon as a LIGA substrate wherein the VC wafer blank is etched in a reactive ion plasma after which an X-ray resist is bonded. This surface treatment provides a surface enabling good adhesion of the X-ray photoresist and subsequent nucleation and adhesion of the electrodeposited metal for LIGA mold-making while the VC substrate practically eliminates secondary radiation effects that lead to delamination of the X-ray resist form the substrate, the loss of isolated resist features, and the formation of a resist layer adjacent to the substrate that is insoluble in the developer.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Micro-tensile testing system
InactiveUS20040200293A1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationStrength propertiesObservational errorCyclic test
A micro-tensile testing system providing a stand-alone test platform for testing and reporting physical or engineering properties of test samples of materials having thicknesses of approximately between 0.002 inch and 0.030 inch, including, for example, LiGA engineered materials. The testing system is able to perform a variety of static, dynamic, and cyclic tests. The testing system includes a rigid frame and adjustable gripping supports to minimize measurement errors due to deflection or bending under load; serrated grips for securing the extremely small test sample; high-speed laser scan micrometers for obtaining accurate results; and test software for controlling the testing procedure and reporting results.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Methods of making extrusion dies
Methods for making extrusion dies using a LIGA process, a German acronym for lithography (Lithographie), electroplating (Galvanoformung), and molding (Abformung), are described. The resulting extrusion dies can be used, for example, for extrusion of cellular ceramic substrates, precision extrusion of optical fiber or optical fiber precursors, or other applications where profile extrusion requires high dimensional precision and / or has otherwise intricate patterns.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for preparing and duplicating three-dimensional micro-nano structure stamps in batches
InactiveCN101613076AFast processingExtended service lifeSemi-permeable membranesNanostructure manufactureMicro nanoEtching
The invention discloses a method for preparing and duplicating three-dimensional micro-nano structure stamps in batches based on an UV-LIGA process and FIB etching technology. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly preparing a nano stamp by the UV-LIGA process; then carrying out etching on the nano stamp to prepare a micro-nano pattern by FIB equipment; making the ion beam capacity between 1 and 60 kV, the etching current between 1 and 100 pA, and the point etching time between 0.01 and 1ms; and carrying out nano embossing on polymer of the obtained three-dimensional micro-nano structure stamps by a hot embossing or soft etching method. The heating temperature in the hot embossing method is higher than the glass transition temperature of the polymer by 10 to 100 DEG C, the added pressure is between 100 and 30 kN, and the ratio of polydimethylsiloxane prepolymer in the soft etching method to a curing agent is between 9 to 1 and 11 to 1. The method can rapidly process the pattern with nano-dimension, and can continuously process the nano-pattern in the pattern so as to prepare the three-dimensional complex micro-nano pattern with different lengths, widths and heights on the same stamp according to the requirements. The method can prepare pressure-withstanding metal stamps in batches and prolongs the service life of the stamps.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
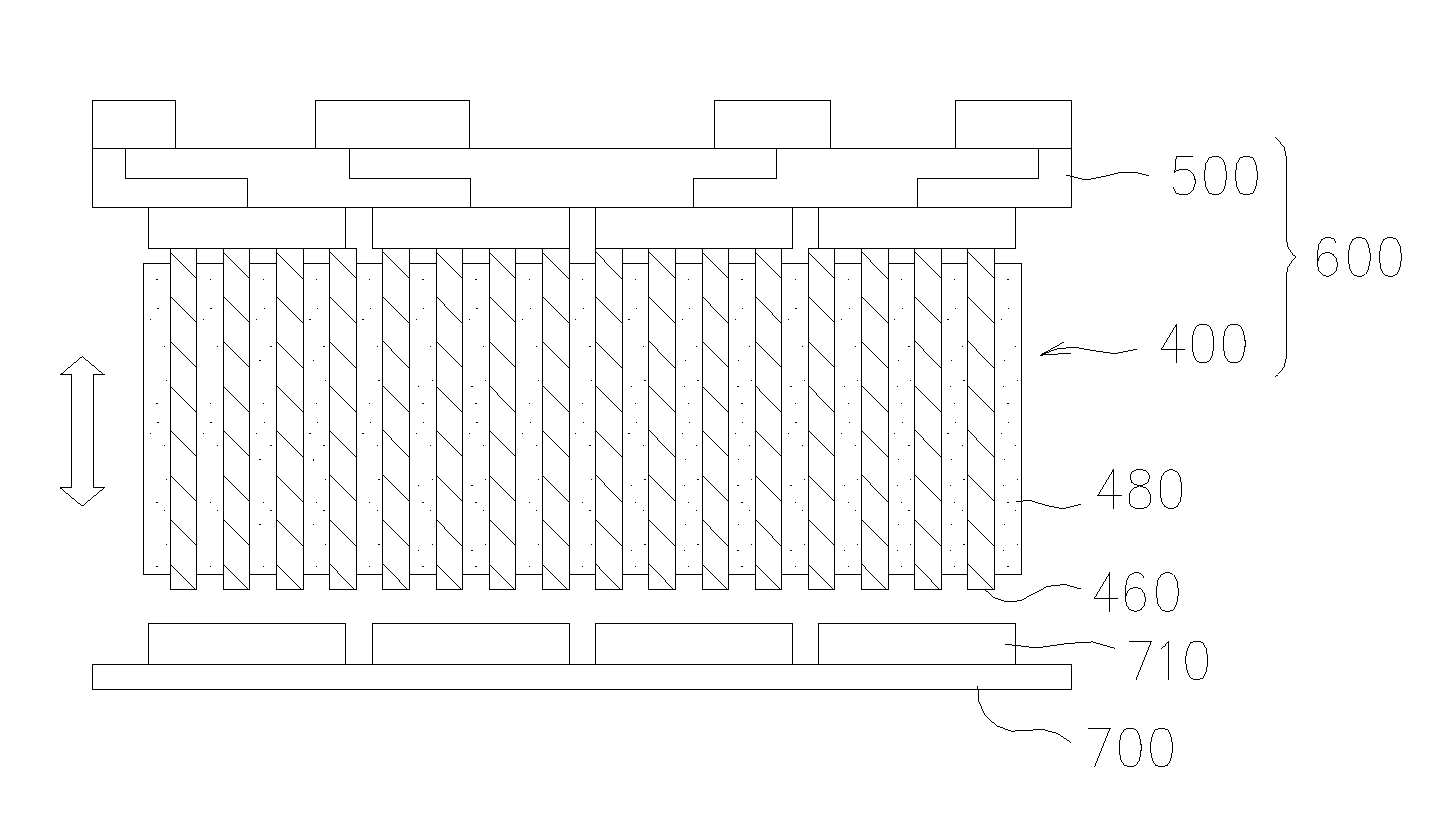
Mass production method for three-dimensional micro structure having high aspect ratio
InactiveUS20050100828A1High aspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing3-dimensional image productionLIGAMetal microstructure
The present invention relates to mass production method for three-dimensional micro structure and especially to the mass production method for three-dimensional metal micro structure having high aspect ratio. According to the present invention, the manufacturing of the three-dimensional micro structure having high aspect ratio is possible, which was impossible with the prior art of MEMS or LIGA. Especially, micro structure with complex shape can be obtained through dividing into layers and depositing the layers. Micro structure with any shape can be obtained with the method according to the present invention.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Composite method for processing metallic mold with partial three-dimensional microstructure
The present invention relates to a combined machining method of a metal mould with a partial three-dimensional microstructure, which belongs to the field of micromachining techniques. Combined with the quasi-LIGA micromachining technique and the tiny electric spark micromachining technique, the combined machining method resolves the problem on how to machine the metal mould with a complex microstructure, part of which is three-dimensional and the rest part of which is two-dimensional. In the technical scheme, based on the LIGA technique, a planar two-dimensional microstructure is produced on a metal baseplate; according to the tiny electric spark machining mode, tool electrodes are produced; at a specified position on the two-dimensional microstructure, the shape of the two-dimensional microstructure is modified by tiny electric sparks until a three-dimensional microstructure is formed. The combined machining method has the following advantages: the machining precision and the surface quality of the two-dimensional microstructure on the metal mould are high; the shape of the two-dimensional microstructure can be modified at a specified area in order to obtain an inclined or stepped three-dimensional microstructure or a three-dimensional microstructure with any curved surface; since the material of the mould is metal, the strength of the mould is high, and the life span is long.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus and method for electroforming high aspect ratio micro-parts
InactiveUS7608174B1Uniform depositionQuickly and easily establishing electrical contactCellsCurrent insulating devicesElectrical connectionLIGA
A fixture is disclosed to more easily affix a workpiece in the proper orientation and spacing with sealed electrical interconnection within an electrochemical plating bath. The workpiece can be any planar metallic or non-metallic substrate such as a silicon wafer commonly used in LIGA or microsystem fabrication. The fixture described allows the workpiece to be submerged deep within an electrolytic cell, facing upwards, and allows easy transfer from one cell to another. The edges, backside, and electrical connections are sealed and protected from the electrolyte.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
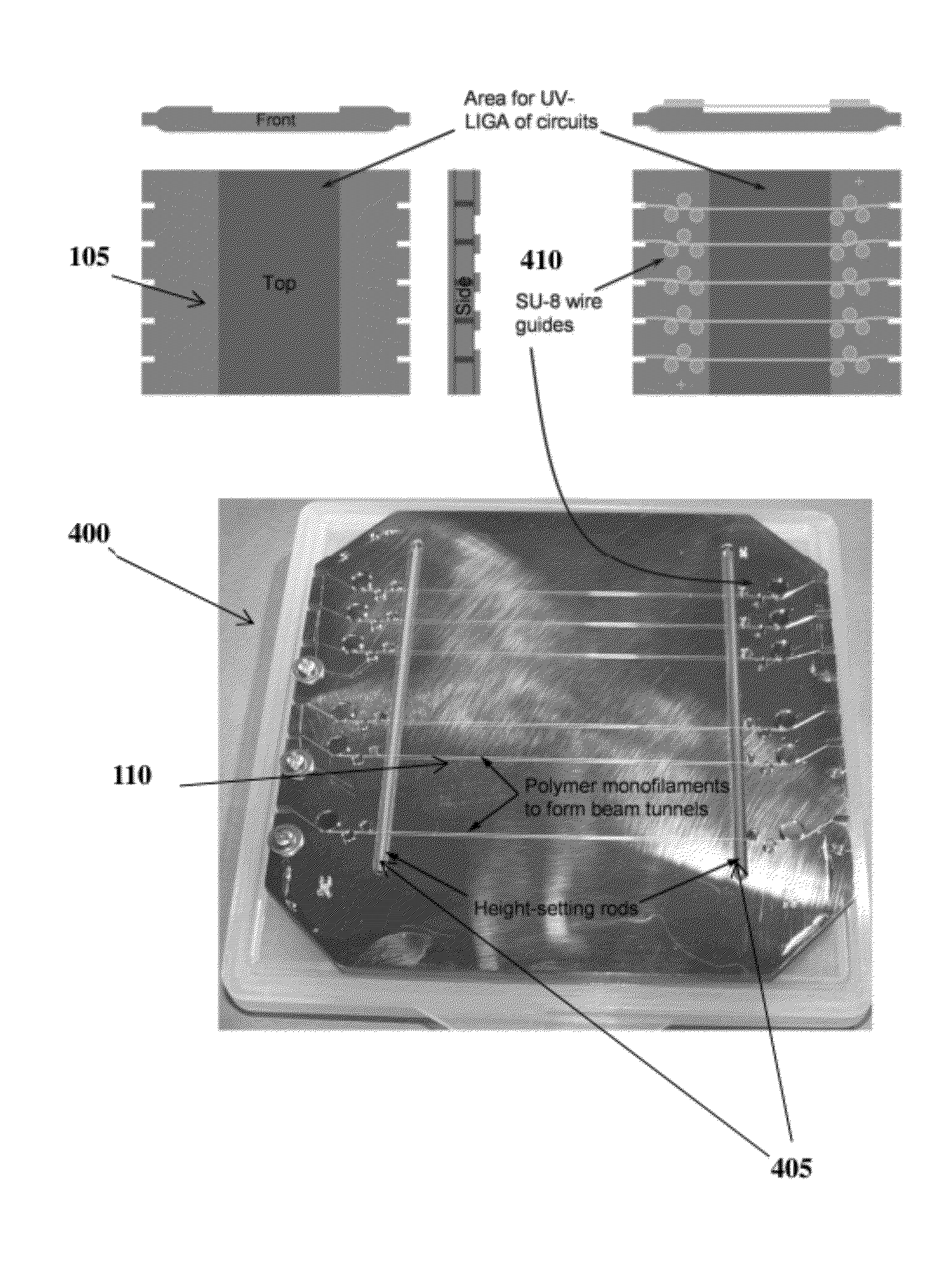
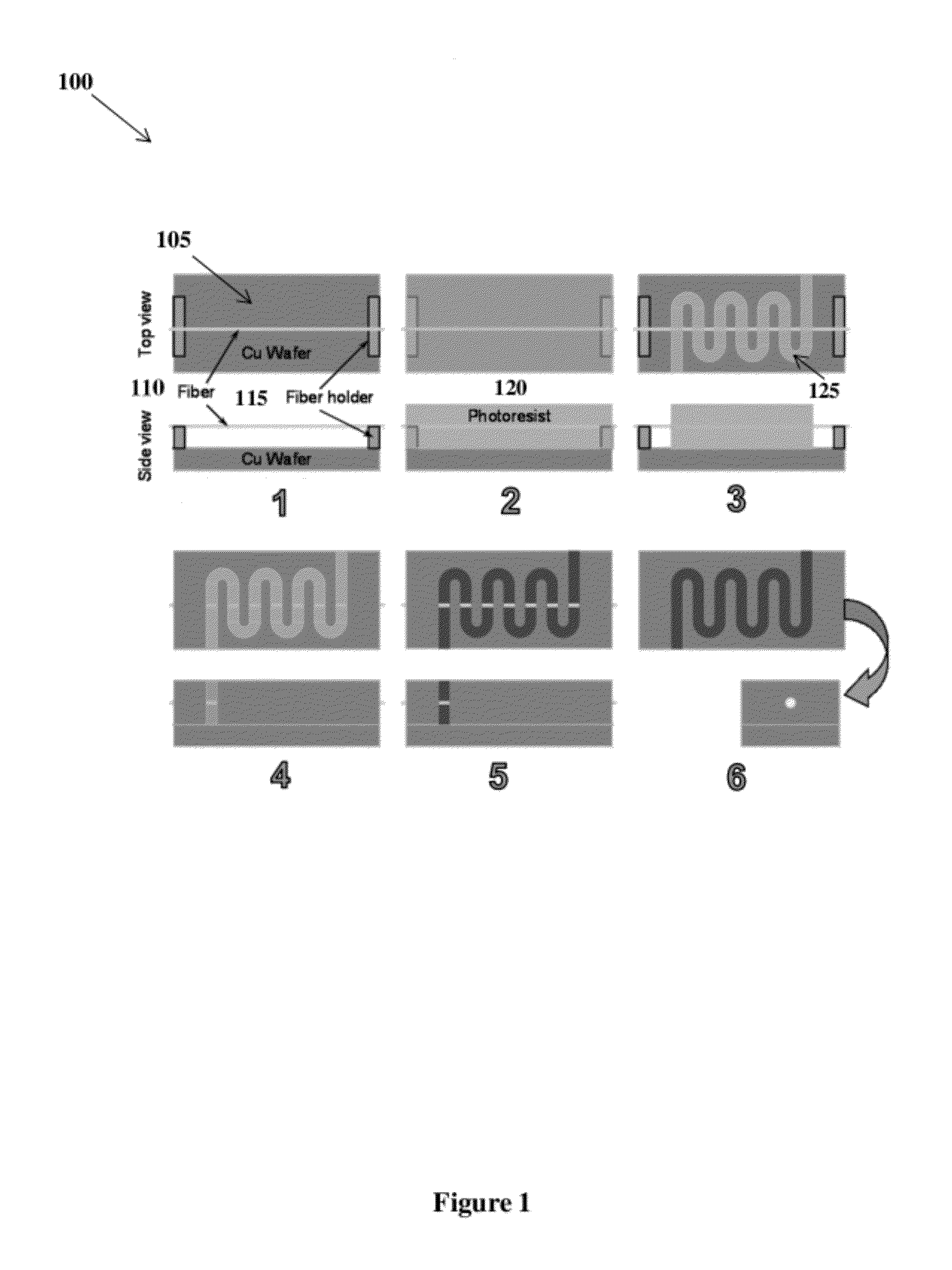
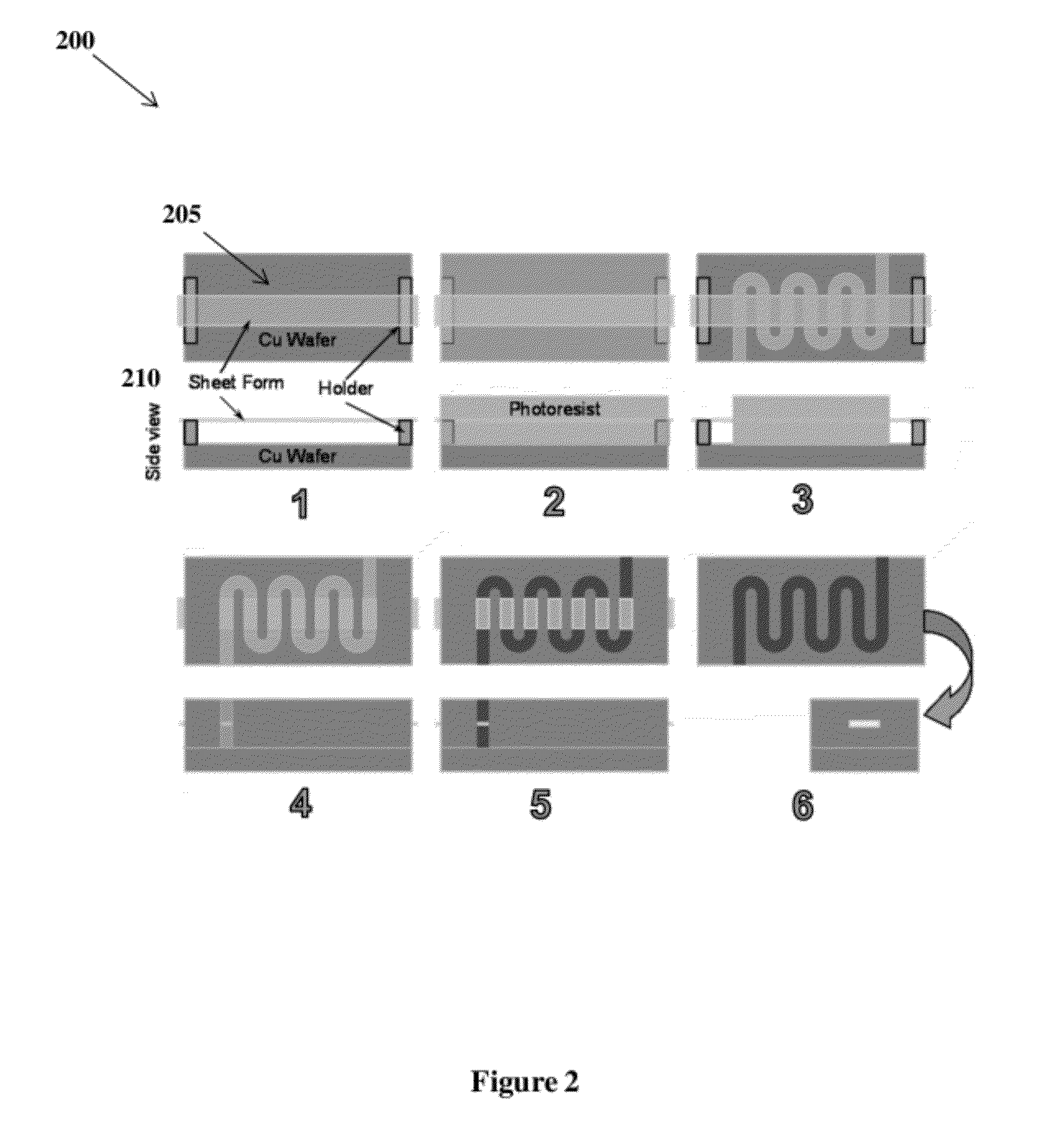
Microfabrication of Tunnels
A system and method to form beam tunnels in interaction circuits. Forms, such as fibers or sheets can be located and secured above a substrate at a desired size and desired shape to form the final shape of the beam tunnels. Fiber holders can be utilized to position the forms above the substrate. A photoresist can then be applied over the substrate embedding the forms. A single exposure LIGA process can be performed on the photoresist, including the steps of ultraviolet photolithography, molding, and electroforming. After the process, the forms can be removed to leave the beam tunnels in the interaction circuits.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Micro-tensile testing system
InactiveUS7258022B2Advantageously minimizing deflectionAdvantageously minimizing bendingForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesObservational errorCyclic test
A micro-tensile testing system providing a stand-alone test platform for testing and reporting physical or engineering properties of test samples of materials having thicknesses of approximately between 0.002 inch and 0.030 inch, including, for example, LiGA engineered materials. The testing system is able to perform a variety of static, dynamic, and cyclic tests. The testing system includes a rigid frame and adjustable gripping supports to minimize measurement errors due to deflection or bending under load; serrated grips for securing the extremely small test sample; high-speed laser scan micrometers for obtaining accurate results; and test software for controlling the testing procedure and reporting results.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Waveguide device and method for making same
ActiveUS7256667B1Improve welfarePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical frequenciesWave shape
A monolithic micromachined waveguide device or devices with low-loss, high-power handling, and near-optical frequency ranges is set forth. The waveguide and integrated devices are capable of transmitting near-optical frequencies due to optical-quality sidewall roughness. The device or devices are fabricated in parallel, may be mass produced using a LIGA manufacturing process, and may include a passive component such as a diplexer and / or an active capping layer capable of particularized signal processing of the waveforms propagated by the waveguide.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Preparation method of composite structure of photoresist film and substrate for LIGA (Lithographie, Galvanoformung and Abformung) technology
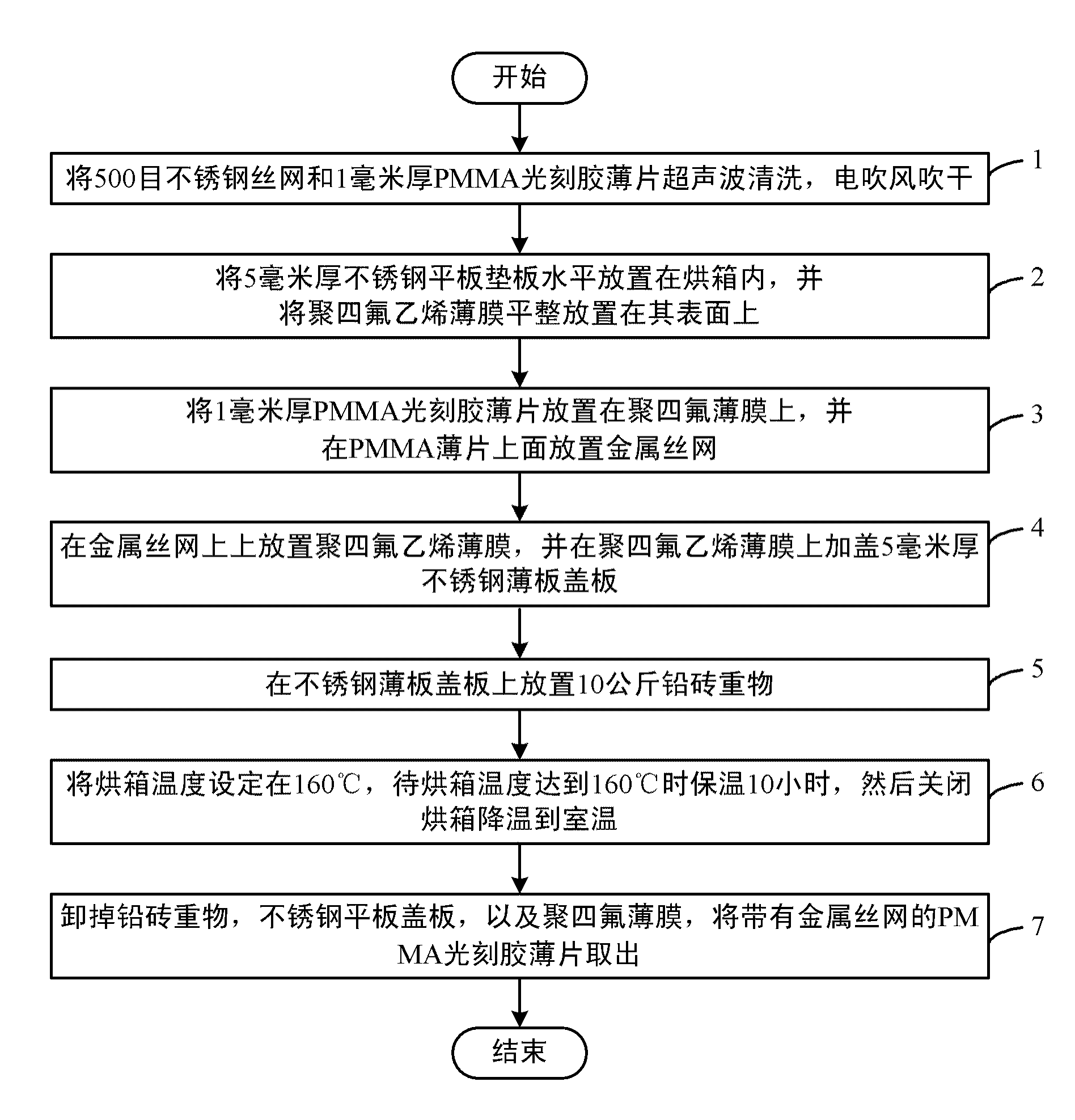
ActiveCN103488051AStrong adhesionImprove bindingDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical coating apparatusPolymethyl methacrylatePhotoresist
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite structure of a photoresist film and a substrate for an LIGA (Lithographie, Galvanoformung and Abformung) technology. According to the method, a wire mesh is used as the substrate; a PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) photoresist sheet is adhered to the wire mesh through a hot pressing method. By using the preparation method, the full wrapping and fusion of the PMMA photoresist and the wire mesh can be effectively realized by using the wire mesh structure, so that a PMMA photoresist pillar structure after synchronous radiation lithography is firmly combined with the wire mesh without collapse or fall, and an extremely large depth-width ratio of the PMMA photoresist pillar structure is guaranteed, so that the research level of the LIGA technology is improved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Manufacturing method of precision metal reflection grating
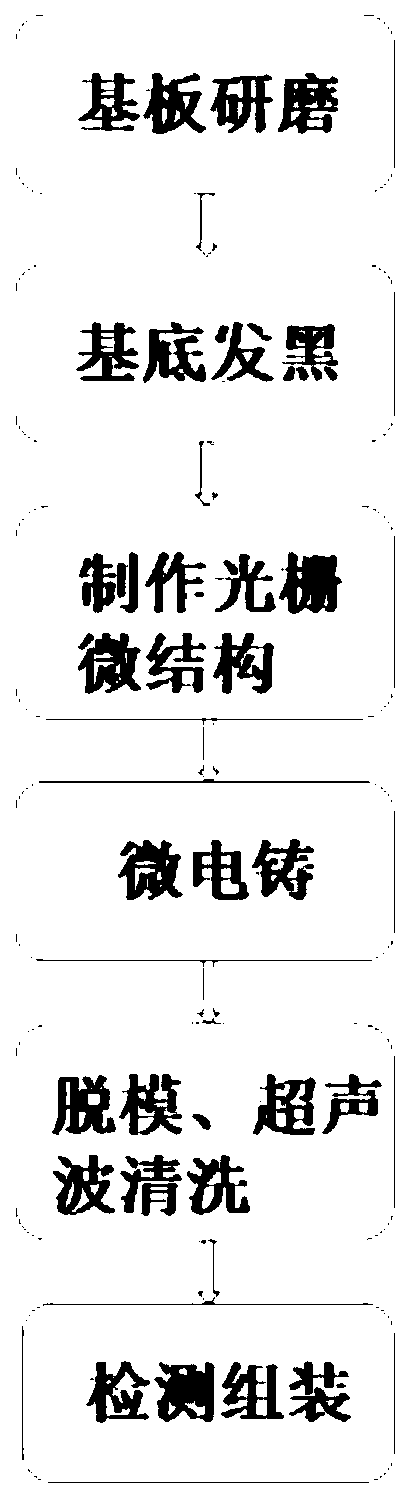
The invention relates to the field of manufacturing of reflection gratings, and discloses a manufacturing method of a precision metal reflection grating. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: grinding a substrate; blackening the substrate; manufacturing a grating microstructure; carrying out micro electroforming; carrying out demolding and ultrasonic cleaning; and carrying out detection and assembly. According to the manufacturing method, the technologies such as micro electroforming, UV-LIGA technology, electrolytic polishing and electroplating blackening are fused, so thatthe precision metal reflection grating with good reflection effect, high surface smoothness, high reflection line precision, batch production and relatively low cost can be manufactured.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
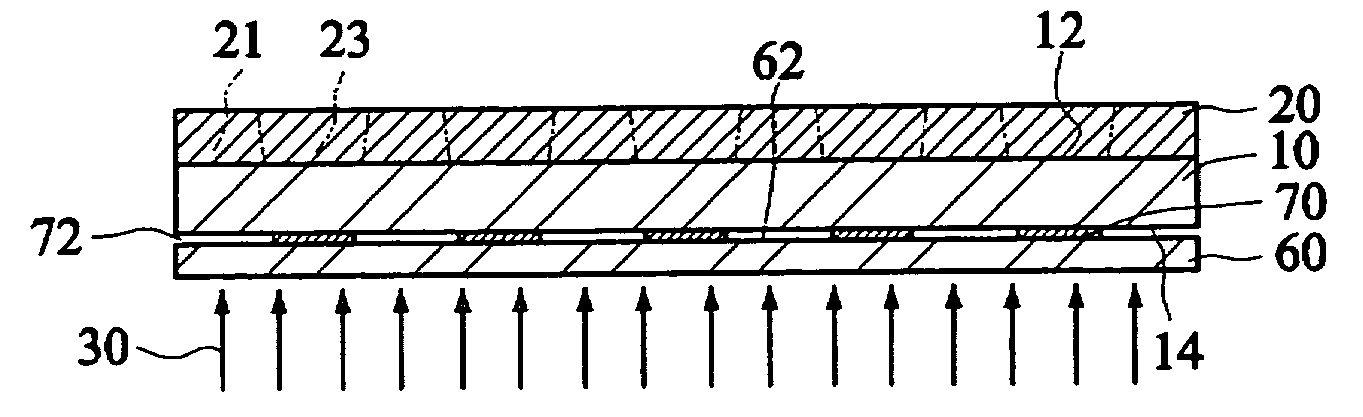
Method of fabricating multi-level metallic parts by the liga-uv technique
ActiveUS20110146070A1Simple processHot-dipping/immersion processesPhotosensitive material processingLIGAOptoelectronics
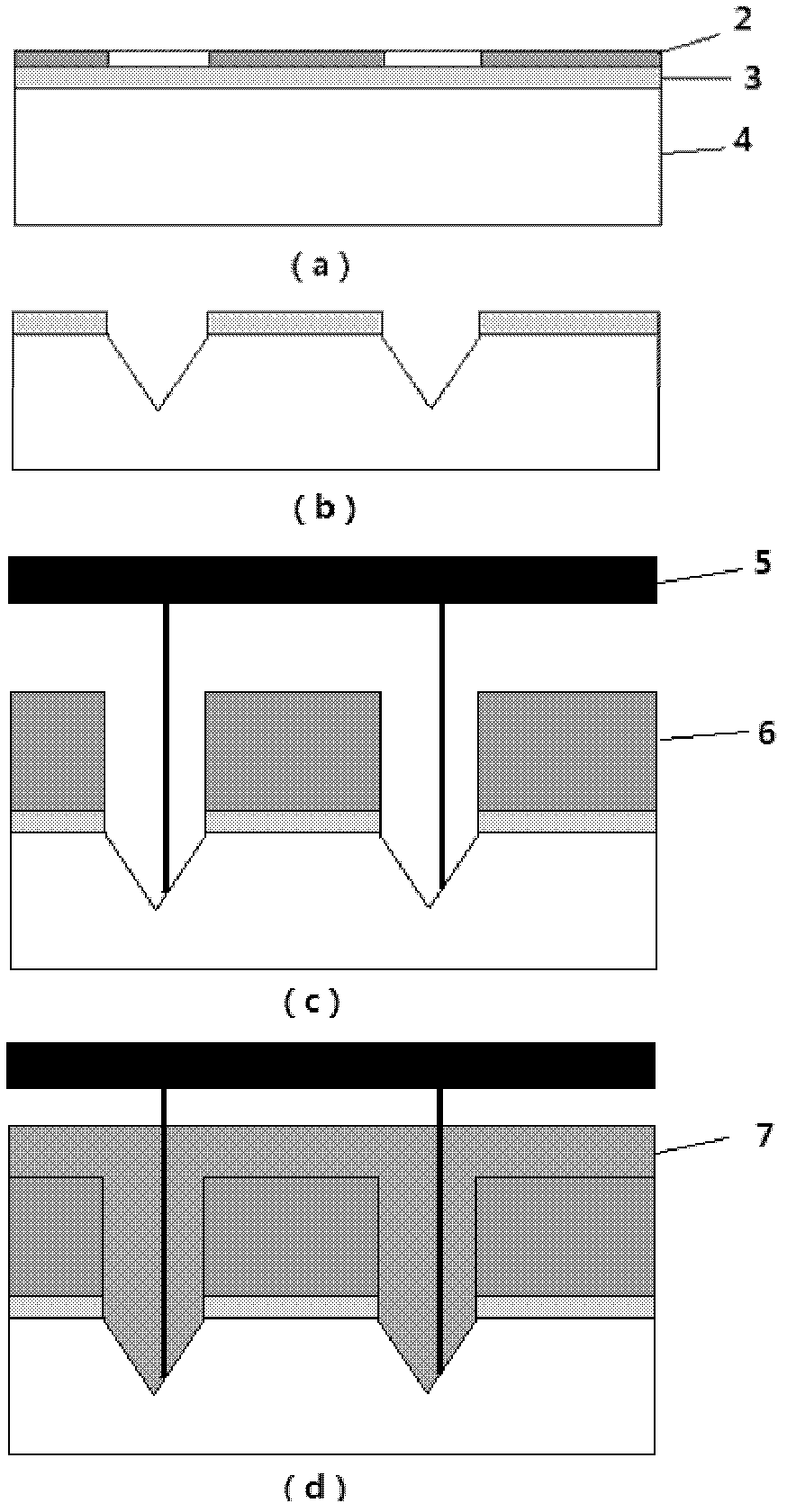
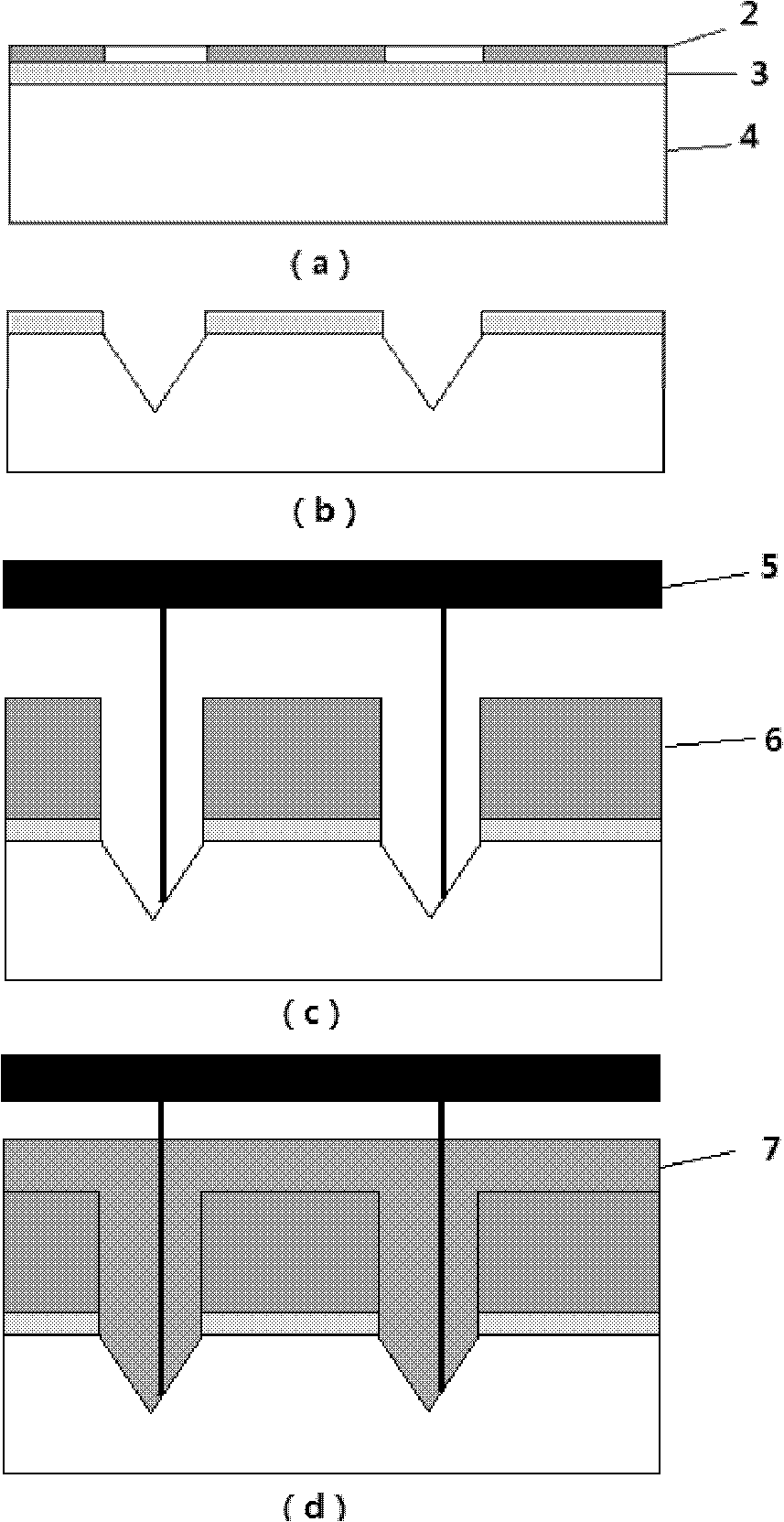
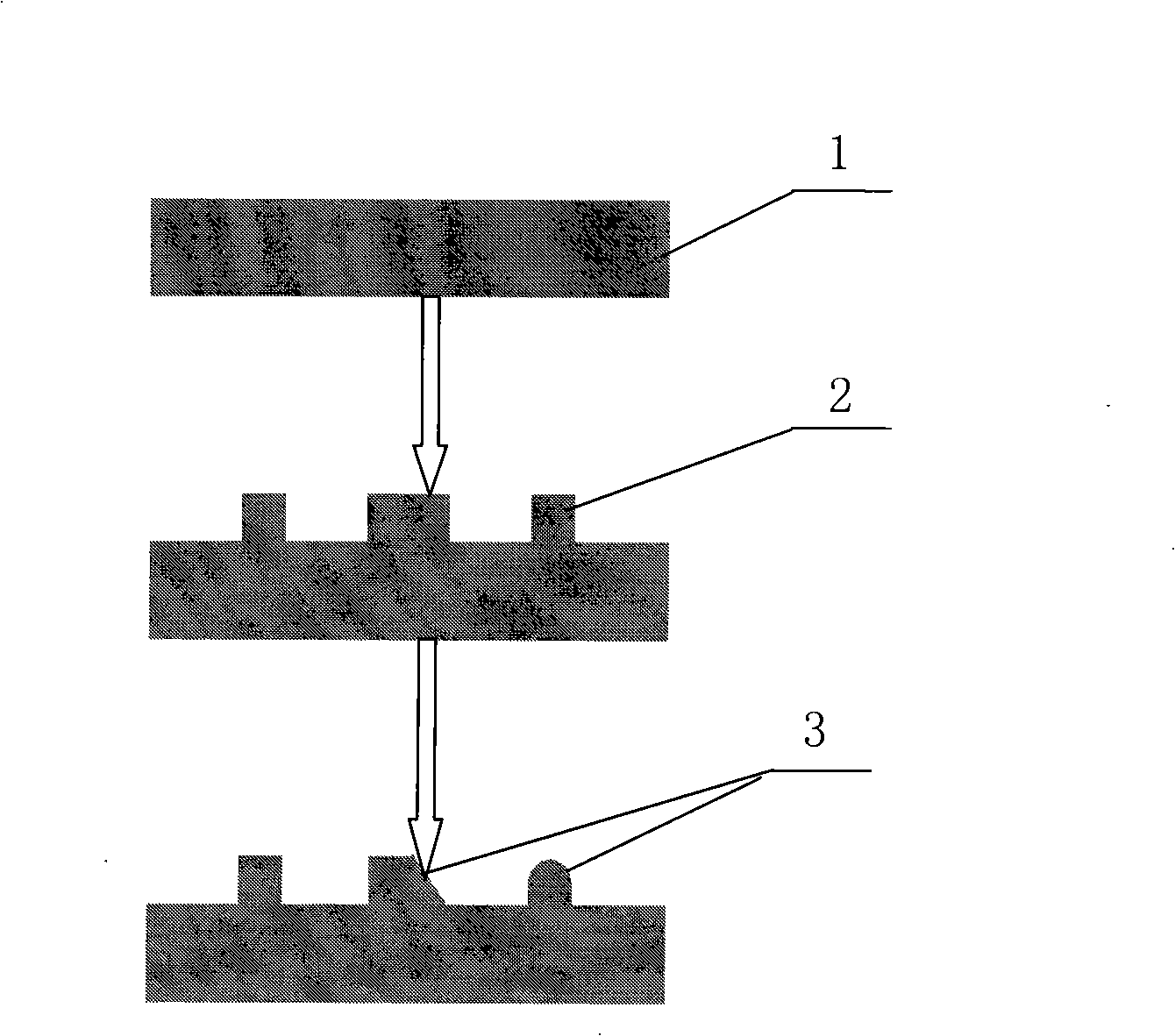
The method of fabricating a multi-level, metallic microstructure includes the steps consisting in:a) taking a substrate (1) that has a conductive surface (2);b) covering the conductive surface (2) with a first layer of photosensitive resin (3);c) irradiating the first layer of photosensitive resin (3) through a mask (4) that matches the desired pattern cavity;d) developing the first layer of photosensitive resin (3) so as to hollow out apertures therein and thus obtain a first level of a resin mould, the aperture in the first resin layer revealing the conductive surface (2) of the substrate;e) depositing a new layer of photosensitive resin (6) over the developed resin layer (3), so as to cover the latter and, preferably, to fill the apertures therein;f) irradiating the new photosensitive resin layer (6) through a mask (7) that matches the desired pattern cavity;g) developing the new photosensitive resin layer (6) so as to hollow out apertures therein and to obtain a multi-level resin mould, the apertures in the multi-level mould revealing the conductive surface (2) of the substrate;h) galvanically depositing a metal or alloy in the apertures of the multi-level resin mould;i) separating the substrate, then removing the resin layers so as to reveal a multi-layer metallic structure (8) formed by said metal or alloy deposited in the apertures.
Owner:NIVAROX FAR
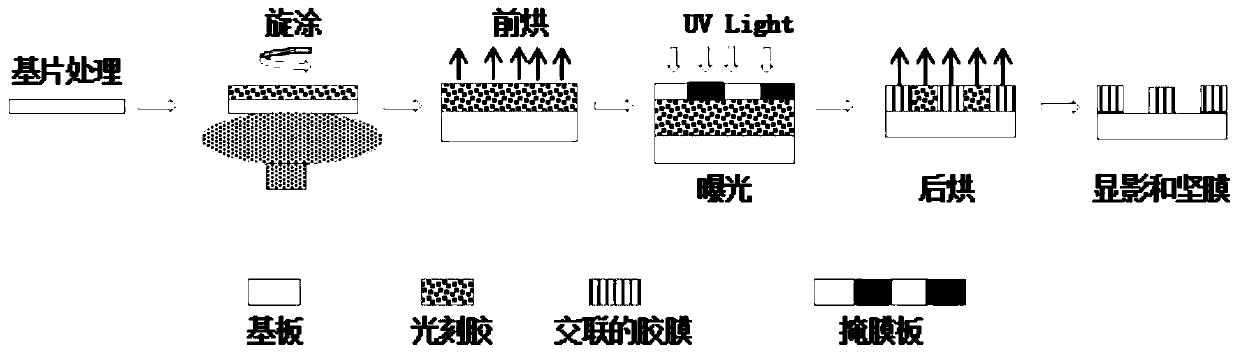
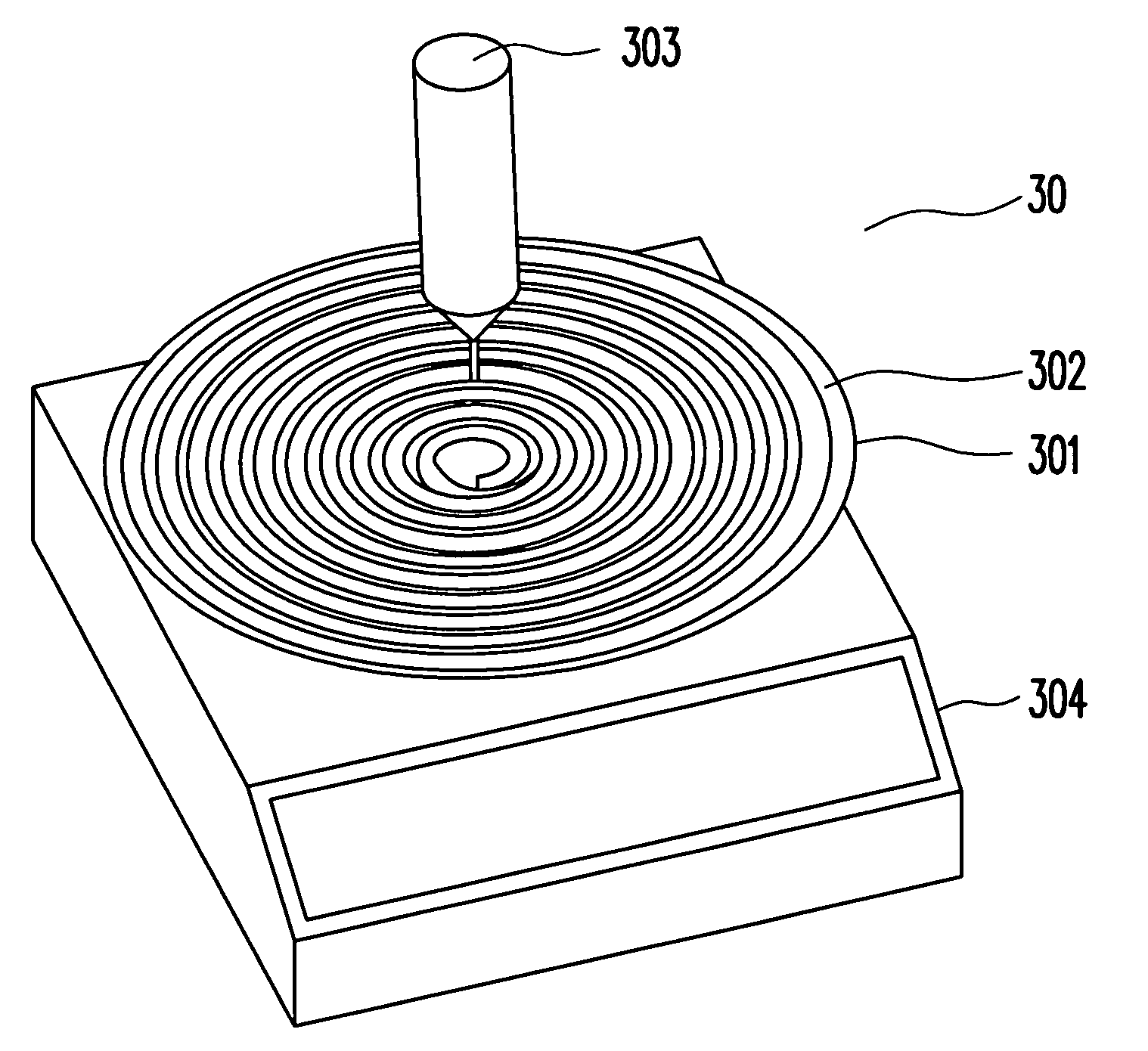
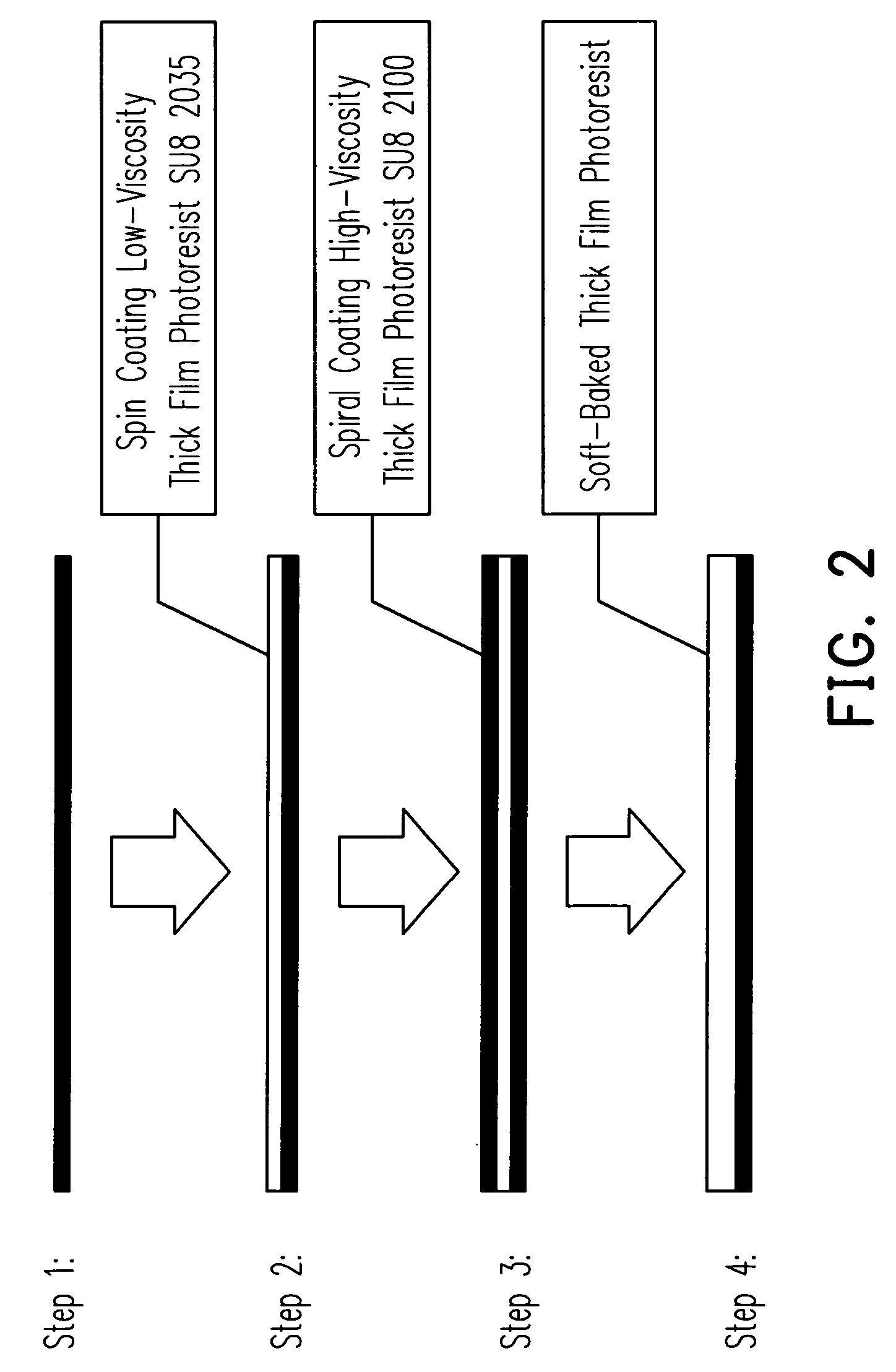
Method for improving high-viscosity thick film photoresist coating in UV LIGA process
InactiveUS20060263520A1Control flatnessControl thicknessPhotomechanical apparatusPretreated surfacesVitrificationResist
A method for improving high-viscosity thick film photoresist coating in UV LIGA process is provided. Two photoresists of identical material but different solvent amount are coated on a silicon wafer in different ways to improve film thickness and flatness. The thick film photoresist SU8-2035 and SU8-2100 from MicroChem Corp. have a viscosity of 7000 (cSt) and 45000 (cSt), respectively. First, SU8-2035 is coated on the wafer at a constant speed, then SU8-2100 is coated from an edge to a center of the wafer in a spiral way, while the mass is measured to control the thickness of photoresist. In the soft baking step, the photoresist and wafer are heated on a hot plate. When the temperature rises over the glass transition temperature of the photoresist, the photoresist spreads on the wafer uniformly due to lower viscosity, cohesion and surface tension, while the wafer is rotated to improve the flatness of the photoresist.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Method of manufacturing a LIGA mold by backside exposure
InactiveUS7384729B2Low costPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLIGAEngineering
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com