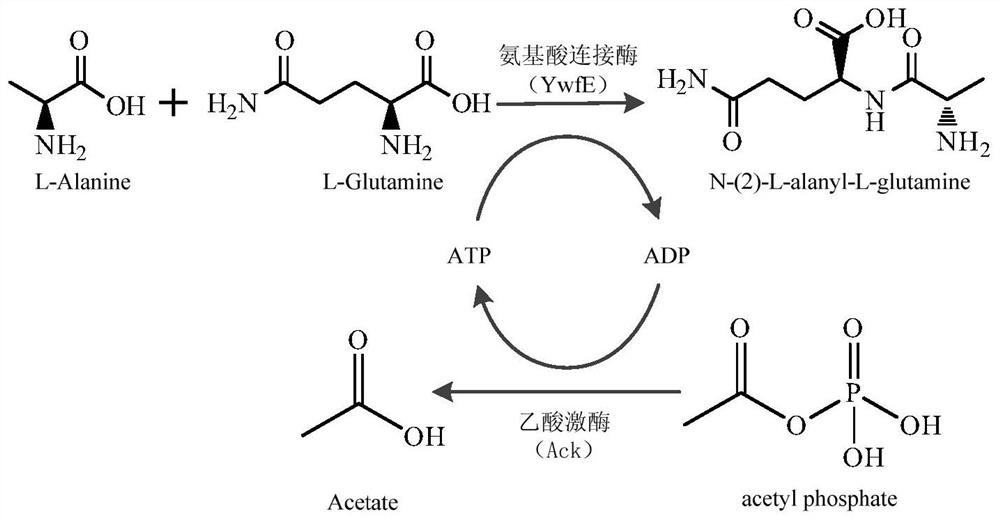
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Acetyl phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Jump to navigation Jump to search. In enzymology, a phosphate acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction. The substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA and phosphate, whereas its two products are CoA and acetyl phosphate.
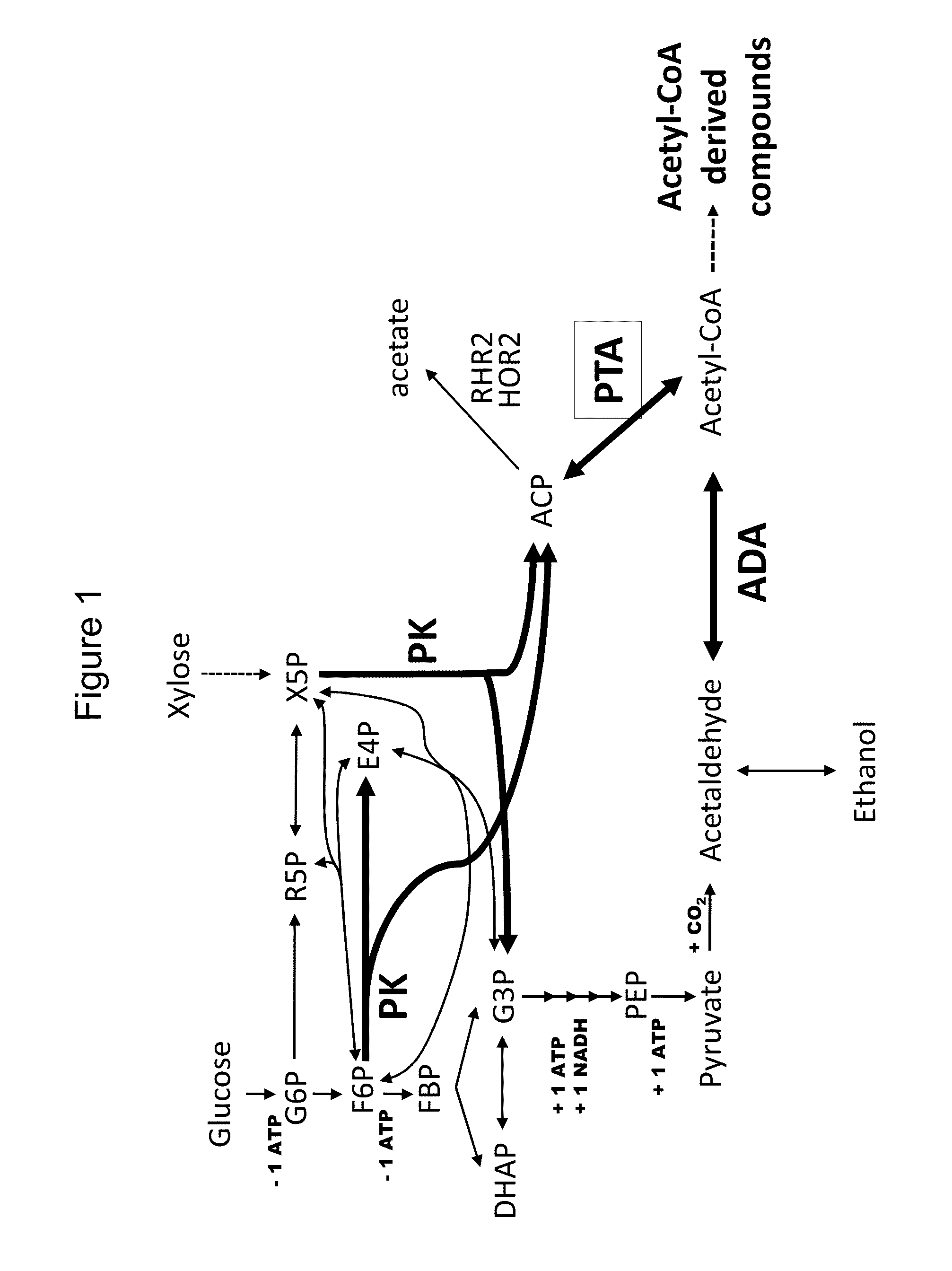
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
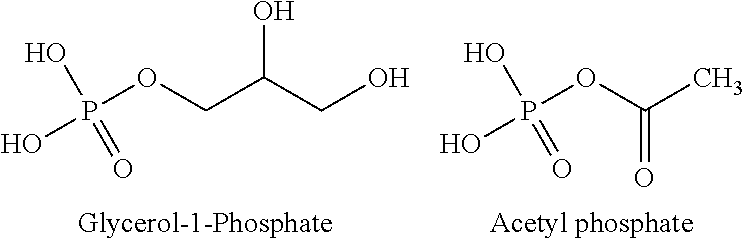
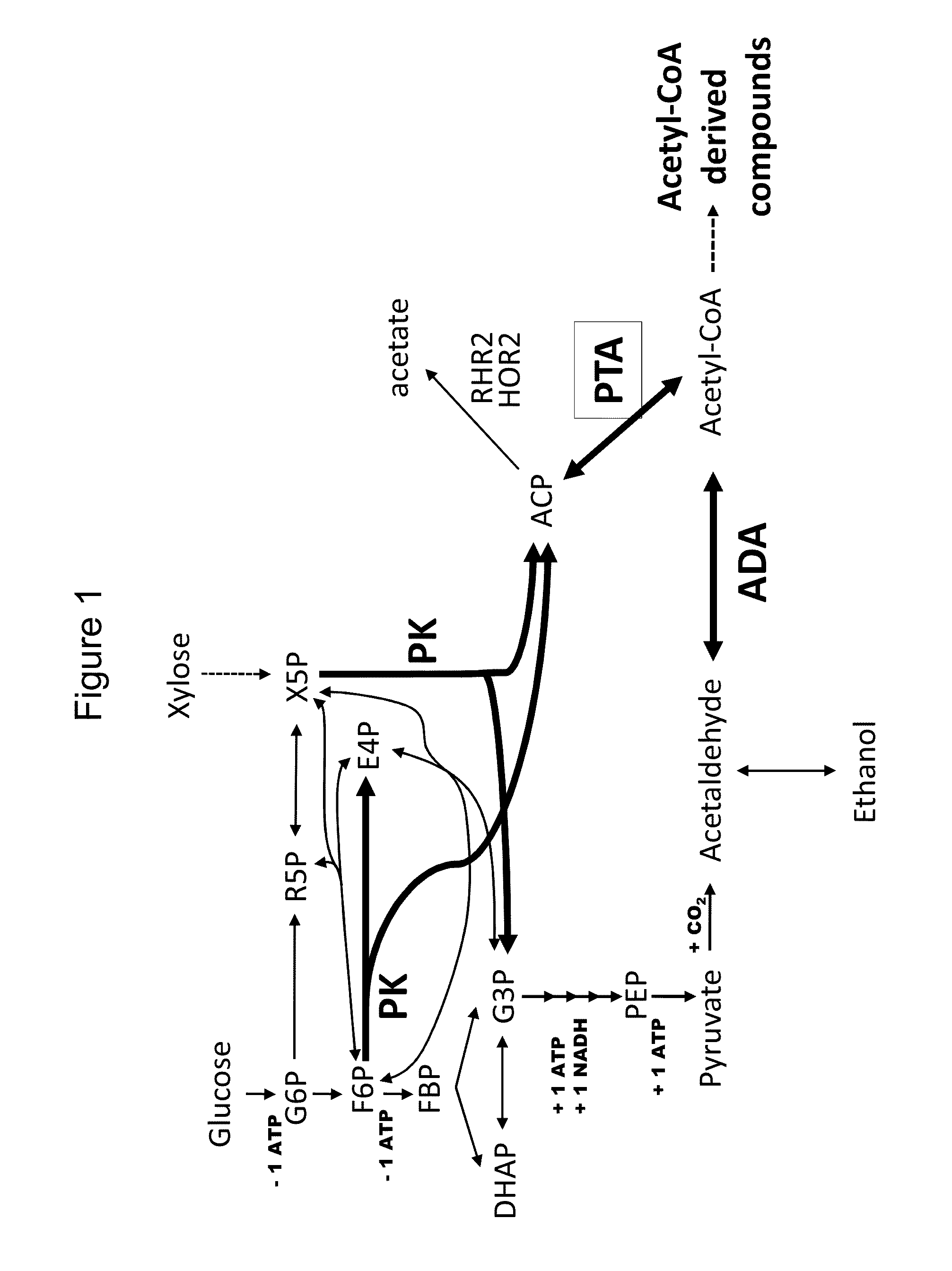
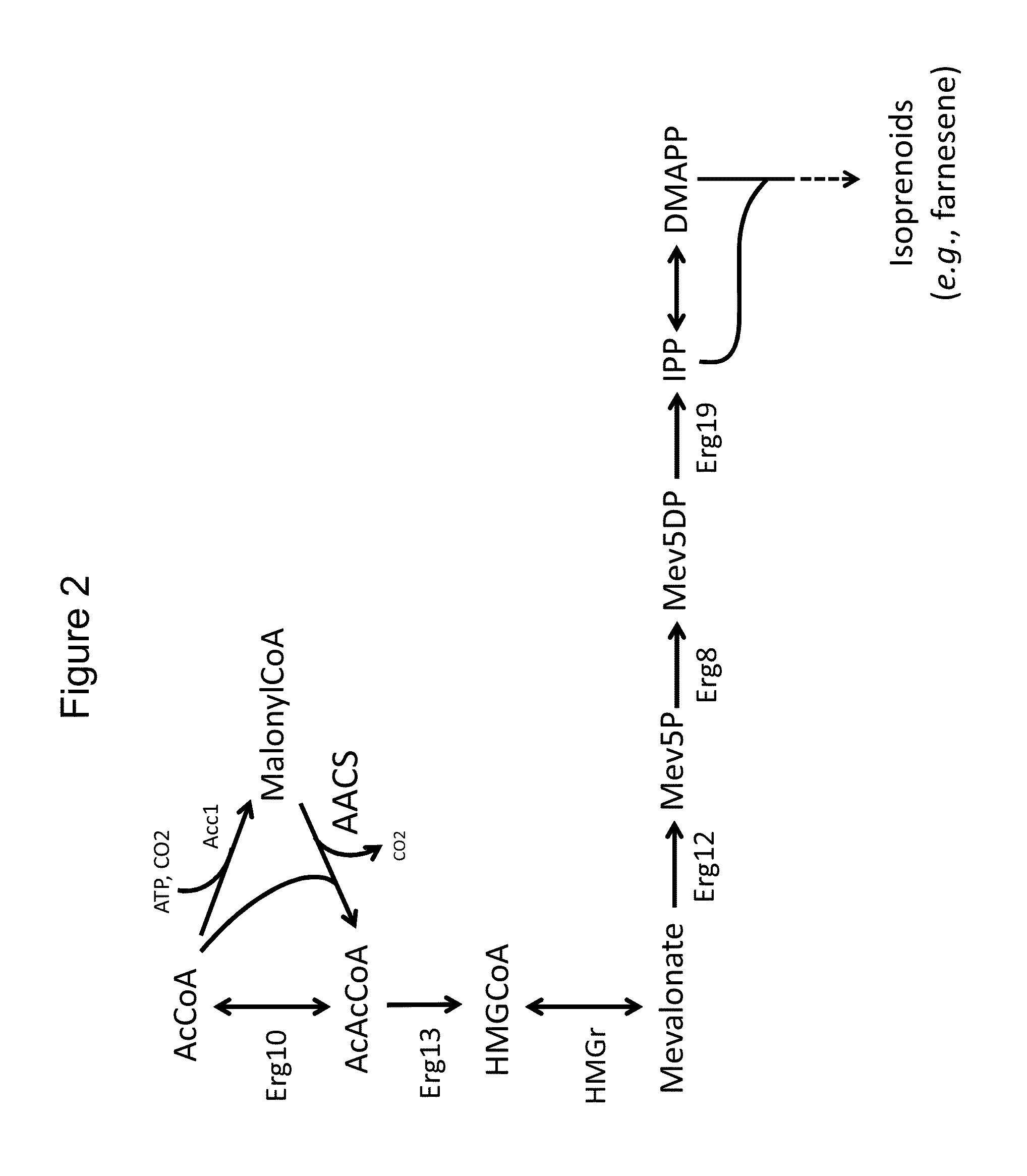
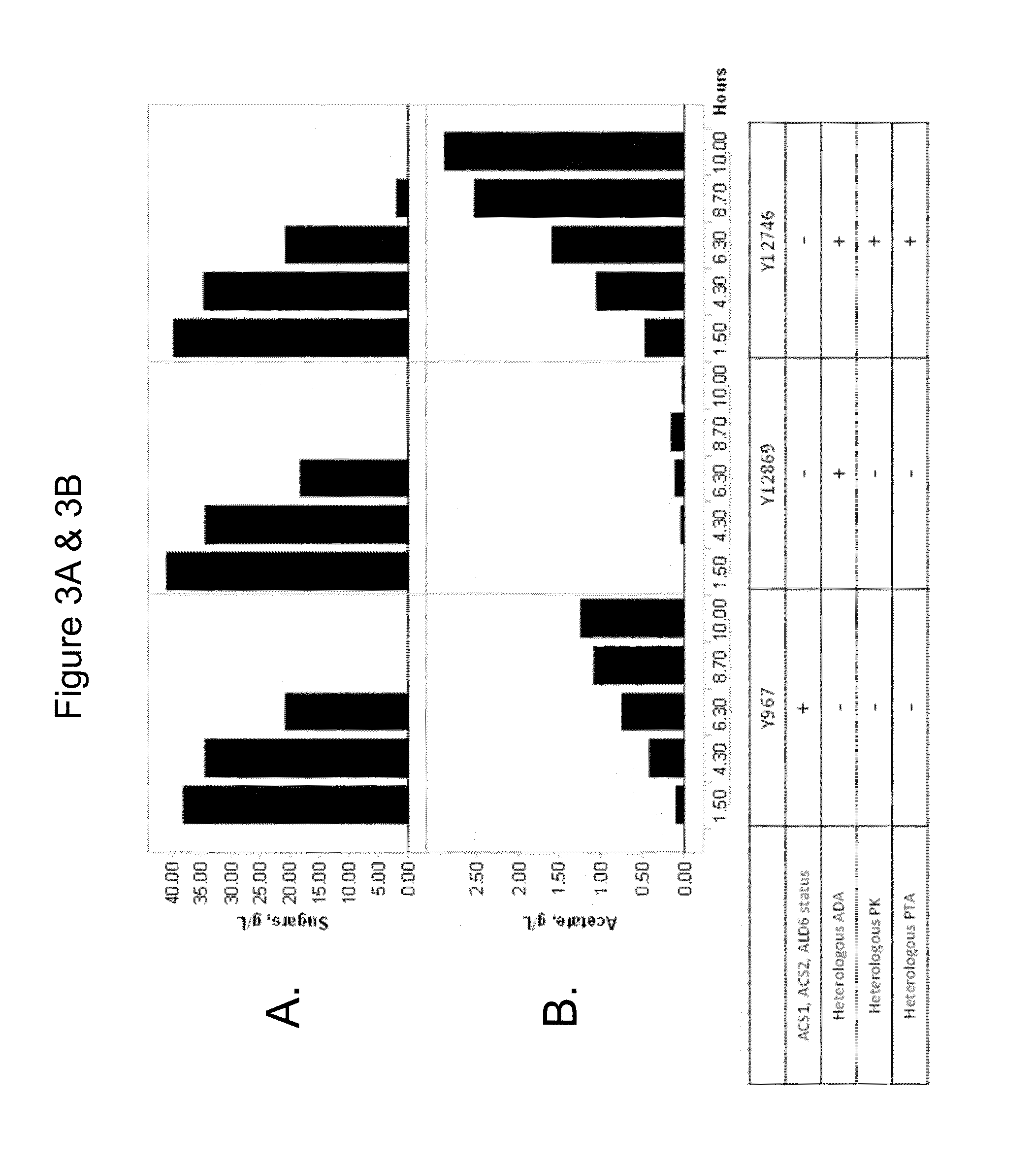
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
Enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and application thereof
ActiveCN106916794AEfficient aggregationNo inputFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesPhosphate acetyltransferasePhosphoric acid
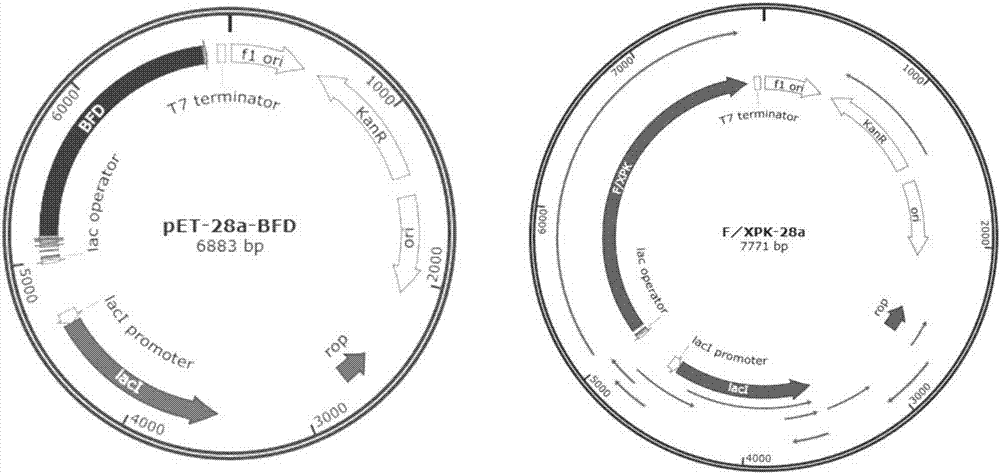
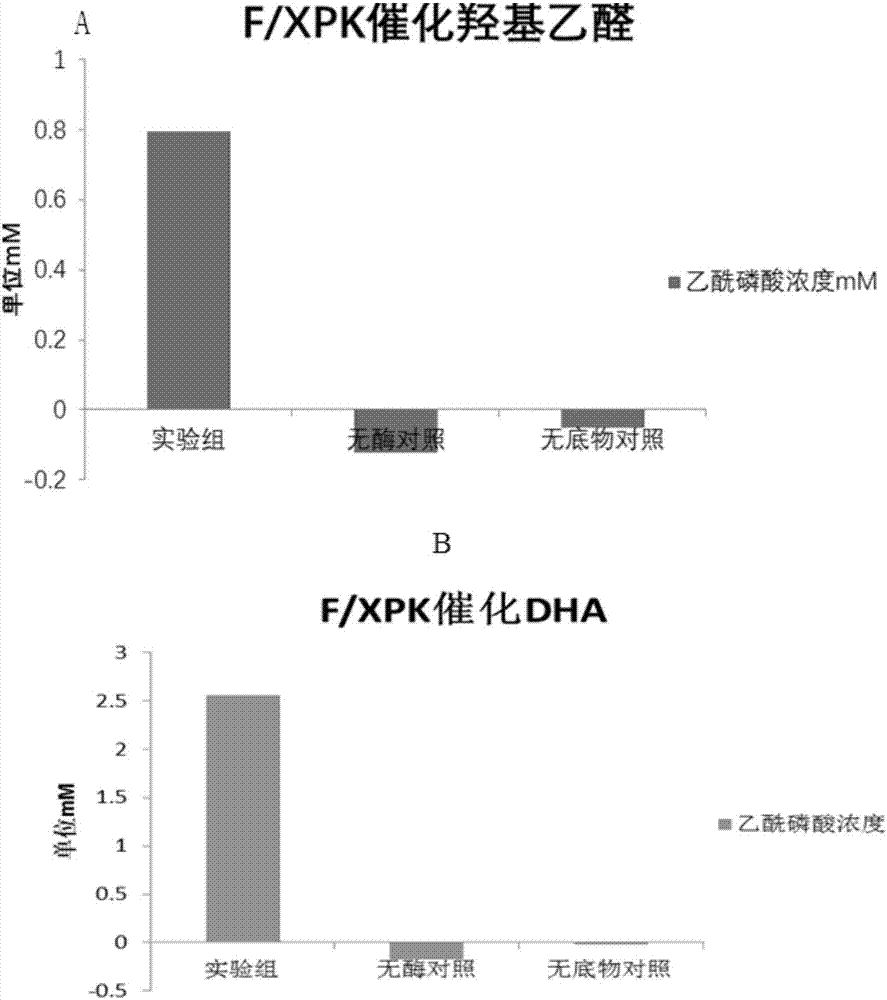
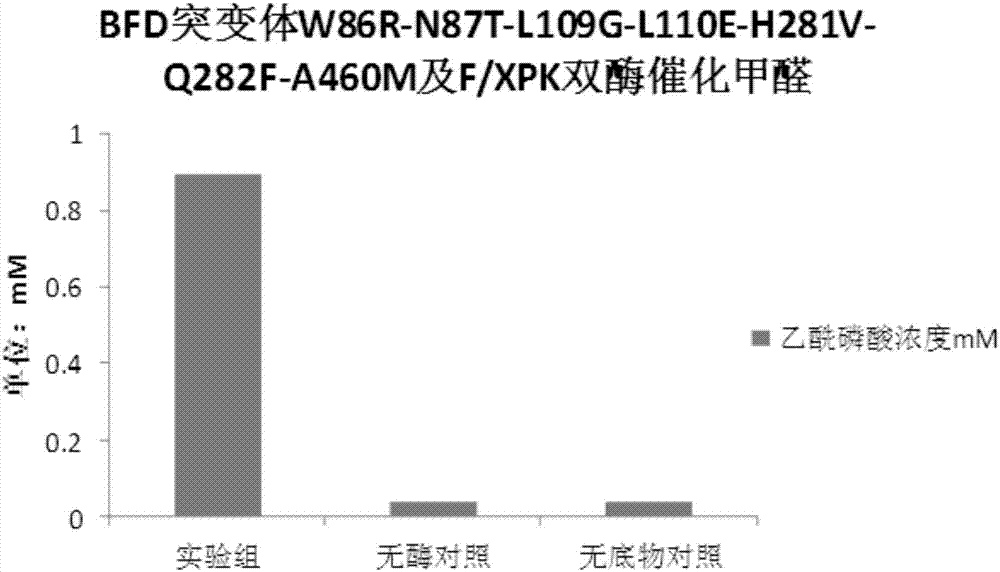
The invention discloses an enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and an application thereof. In the invention, through site-directed mutation of BFD, a mutant of the enzyme is found; and by means of the mutant of the enzyme, high-effect polymerization of the formaldehyde is achieved; meanwhile, through F / XPK, generation of acetyl phosphoric acid from the hydroxyl acetaldehyde or 1,3-dihydroxyacetone is achieved; with combination of phosphotransacetylase (Pta), a route from the formaldehyde to acetyl coenzyme A is achieved in three steps with the enzyme, thereby creating a new formaldehyde assimilation route, namely, synthesizing the acetyl coenzyme A from the formaldehyde in three steps. The route is short and is free of carbon loss and ATP input.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
In-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system and application thereof
The present invention discloses an in-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system. The system comprises cell extract, carbohydrate and a phosphate compound, wherein the carbohydrate is maltodextrin, lactose, or a combination of the maltodextrin and glucose, or a combination of the lactose and the glucose, or a combination of the maltodextrin, the lactose and the glucose. ATP is provided for an in-vitro reaction by low-cost substances such as the glucose, the maltodextrin and the lactose instead of energy sources such as phosphoenolpyruvic acid, phosphocreatine and acetyl phosphate, so that whilethe cost is reduced, a mode of providing energy by slow release prolongs the reaction time and increases the yield of target protein.
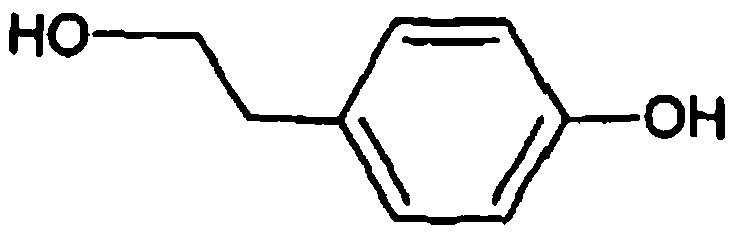
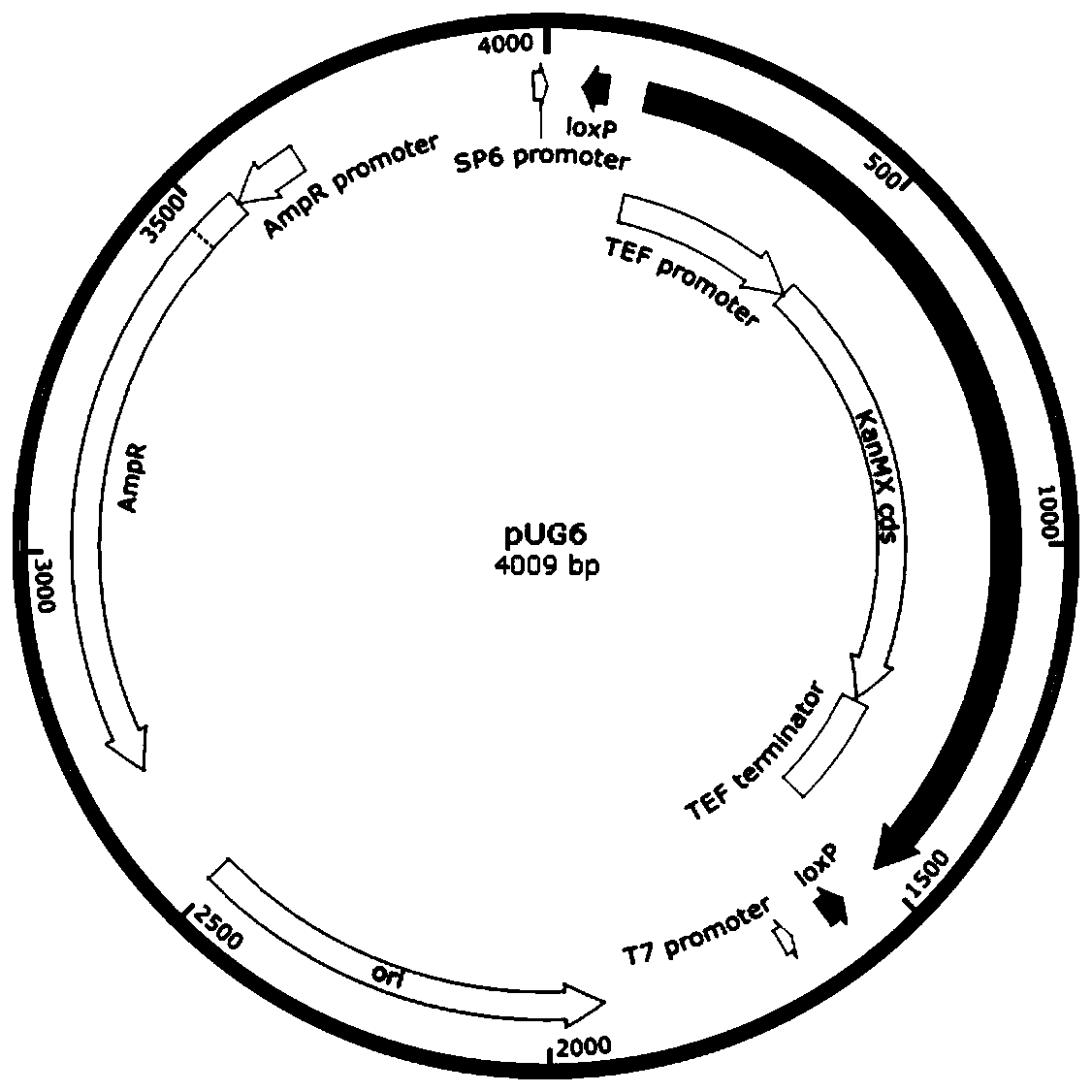
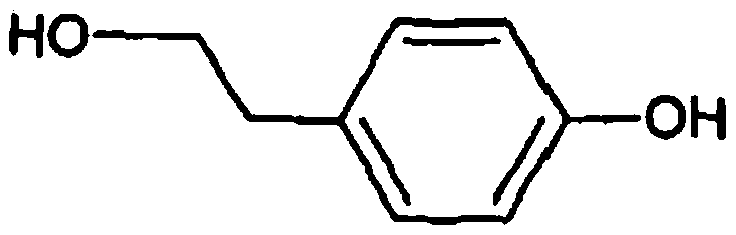
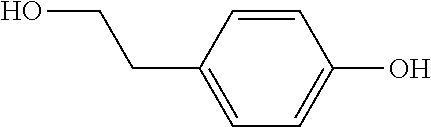
Recombinant yeast, construction method thereof and application thereof for producing tyrosol and derivative
InactiveCN109929883AAltered carbon flux distributionOptimizing Metabolic PathwaysFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
Owner:YANTAI HUAKANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for synthesizing glutathione by enzymatic catalysis
ActiveCN106086126AHigh synthesis efficiencyShort synthesis timePeptidesFermentationATP regenerationGlutamic acid
The present invention discloses a method for synthesizing glutathione by enzymatic catalysis, comprising the following steps: S1, mixing Upsilon-glutamylcysteine synthetase liquid and glutathione synthetase liquid to obtain mixed liquid A, mixing the mixed liquid A with acetate kinase to obtain mixed liquid B; S2, adding an immobilized carrier in the mixed liquid B, stirring for immobilizing, and filtering to obtain an immobilized enzyme; S3, blending glutamic acid, L-cysteine, glycine, magnesium sulfate, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and acetyl phosphate into a reaction liquid, adding the immobilized enzyme, and stirring for reacting; S4, after reacting, filtering the reaction liquid, and extracting and refining filtrate to obtain the glutathione. The method of the invention has high synthetic efficiency, the production content of the reaction liquid is higher than 10 g / L, and substrate conversion rate reaches higher than 90%; by introducing acetate kinase to construct an ATP regeneration and coupling system, ATP charge is greatly reduced and production cost is significantly reduced; the immobilized enzyme is reusable and highly stable.
Owner:KAIPING GENUINE BIOCHEM PHARMA
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme A derived compounds
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
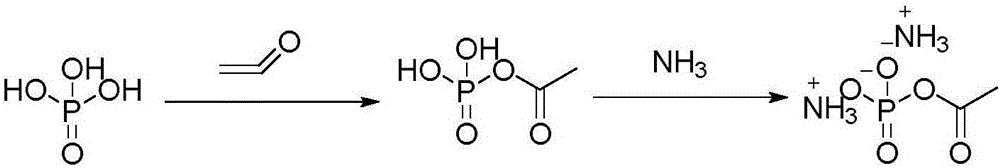
Preparation method of acetyl diammonium phosphate
InactiveCN104860984AHigh yieldHigh purityPhosphorus organic compoundsAcetic anhydrideDiammonium phosphate
The invention relates to an improved preparation method of acetyl diammonium phosphate. According to the improved preparation method, phosphoric acid is reacted with acetic anhydride firstly so as to obtain acetyl phosphate, and then ammonium hydroxide is added so as to obtain acetyl diammonium phosphate. The improved preparation method is simple in operation, high in yield, and low in cost, and is especially suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Method for preparing acetyl phosphate on basis of biological enzymes
The invention discloses a method for preparing acetyl phosphate on the basis of biological enzymes. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzyme catalysis reaction on lactic acid and / or lactate and phosphoric acid and / or phosphate and / or biphosphate by using an immobilized oxidase lactate-immobilized pyruvate oxidase composite enzyme as a catalyst; and after the reaction finishes, filtering and precipitating to obtain the high-purity acetyl phosphate. The method is simple to operate, has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, high raw material conversion rate, low cost and environmental protection, and satisfies the industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN FLAG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Enzymatic synthesis method and application of 3',5'-adenosine diphosphate (PAP)
PendingCN110982864ABig cost advantageEasy to store and transportTransferasesFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPhosphoric acid
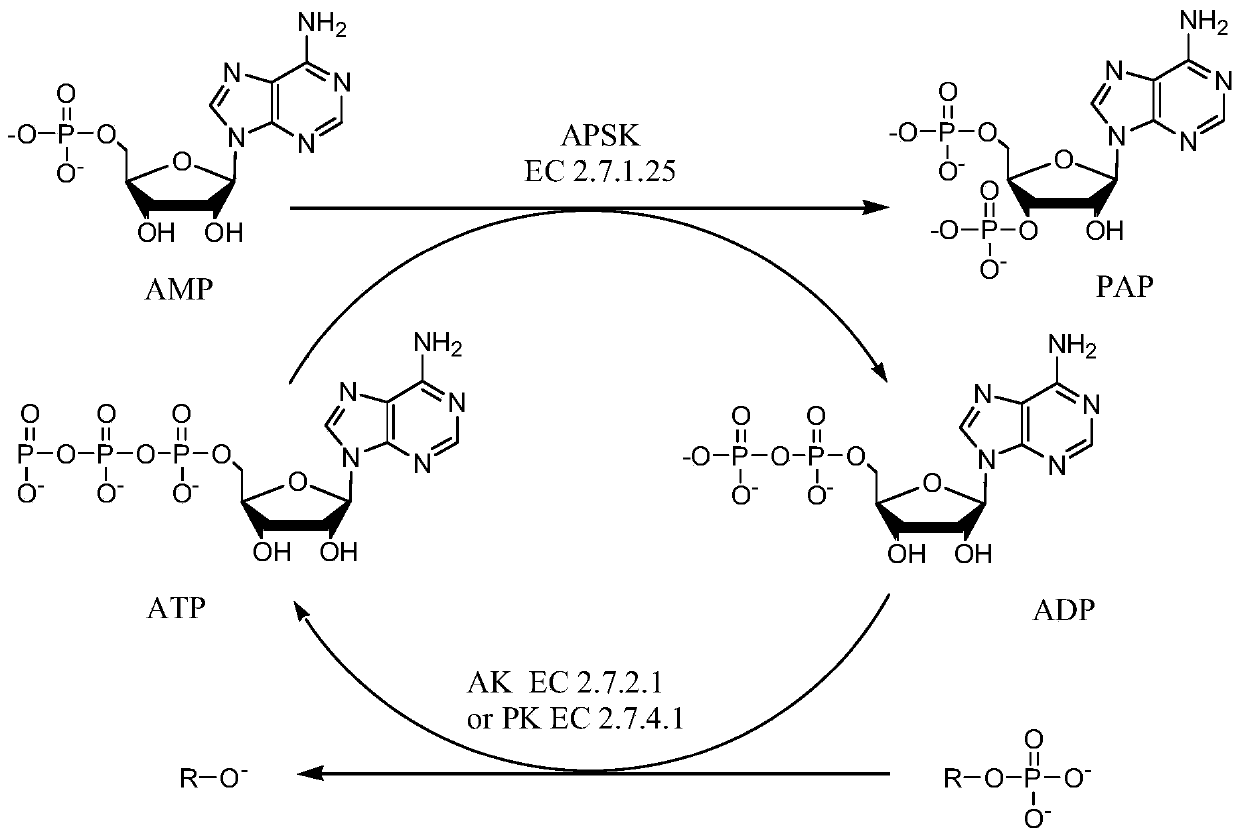
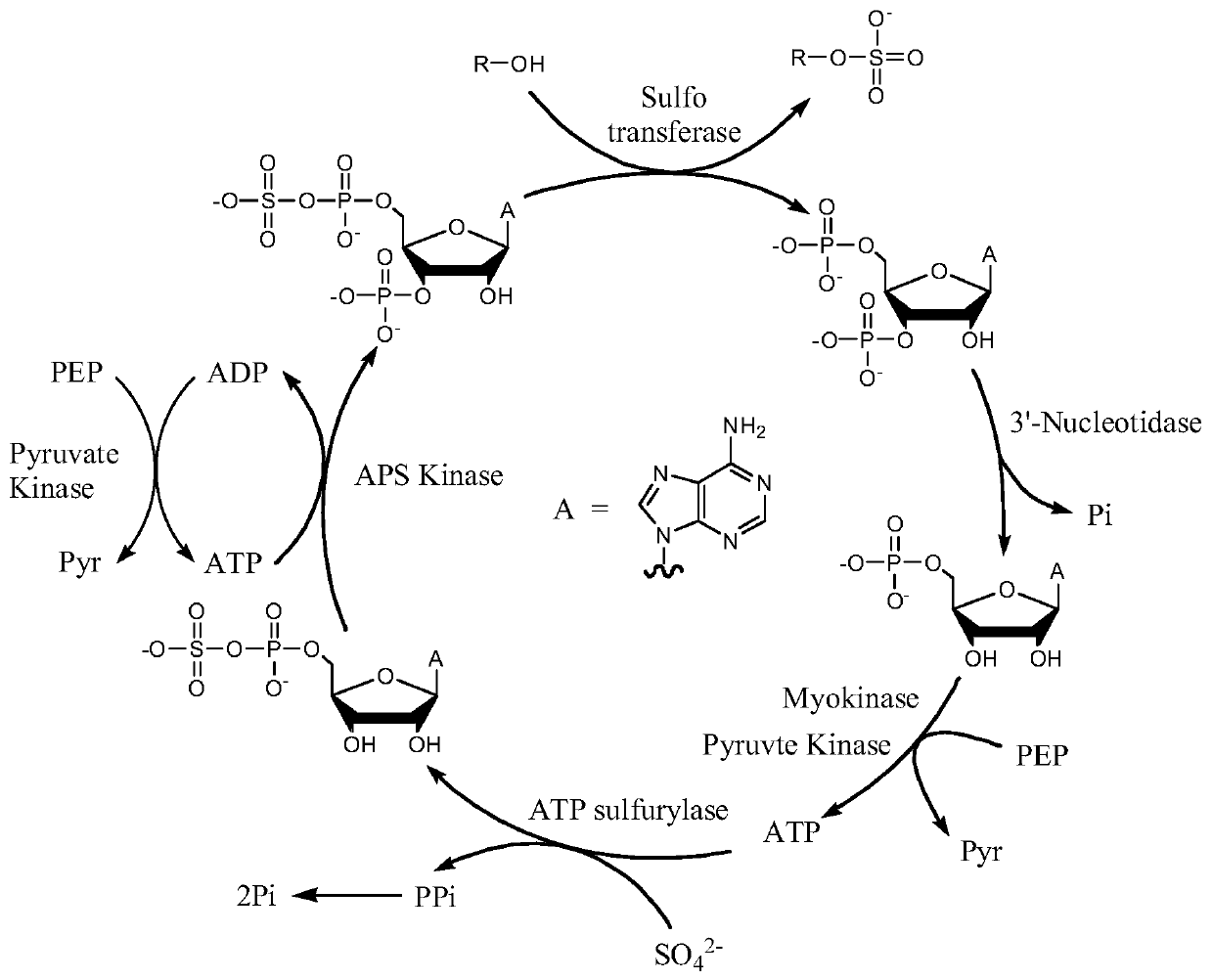
The invention provides an enzymatic synthesis method of PAP. The enzymatic synthesis method comprises the following steps: generating PAP with 5'-adenosine monophosphate (AMP) as a substrate, 5'-phosphosulfated kinase (APSK) as a catalyst and 5'-adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or 5'-adenosine diphosphate (ADP) as a coenzyme; and synthesizing ATP with acetylphosphoric acid or polyphosphoric acid as aphosphate group donor and acetokinase (AK) or polyphosphoric kinase (PK) as a catalyst, thereby realizing ATP circulation (as shown in Figure 1). The method has the advantages that the PAP is synthesized in one step by taking AMP as a substrate, and that the theoretical utilization rate of phosphorus reaches 100%.
Owner:孙军亭 +2
Recombinant yeast, construction method thereof and application of recombinant yeast in preparing tyrosol and derivatives
ActiveCN111139194AAltered carbon flux distributionOptimizing Metabolic PathwaysFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
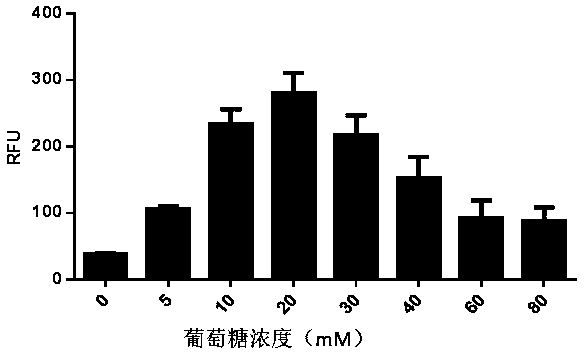
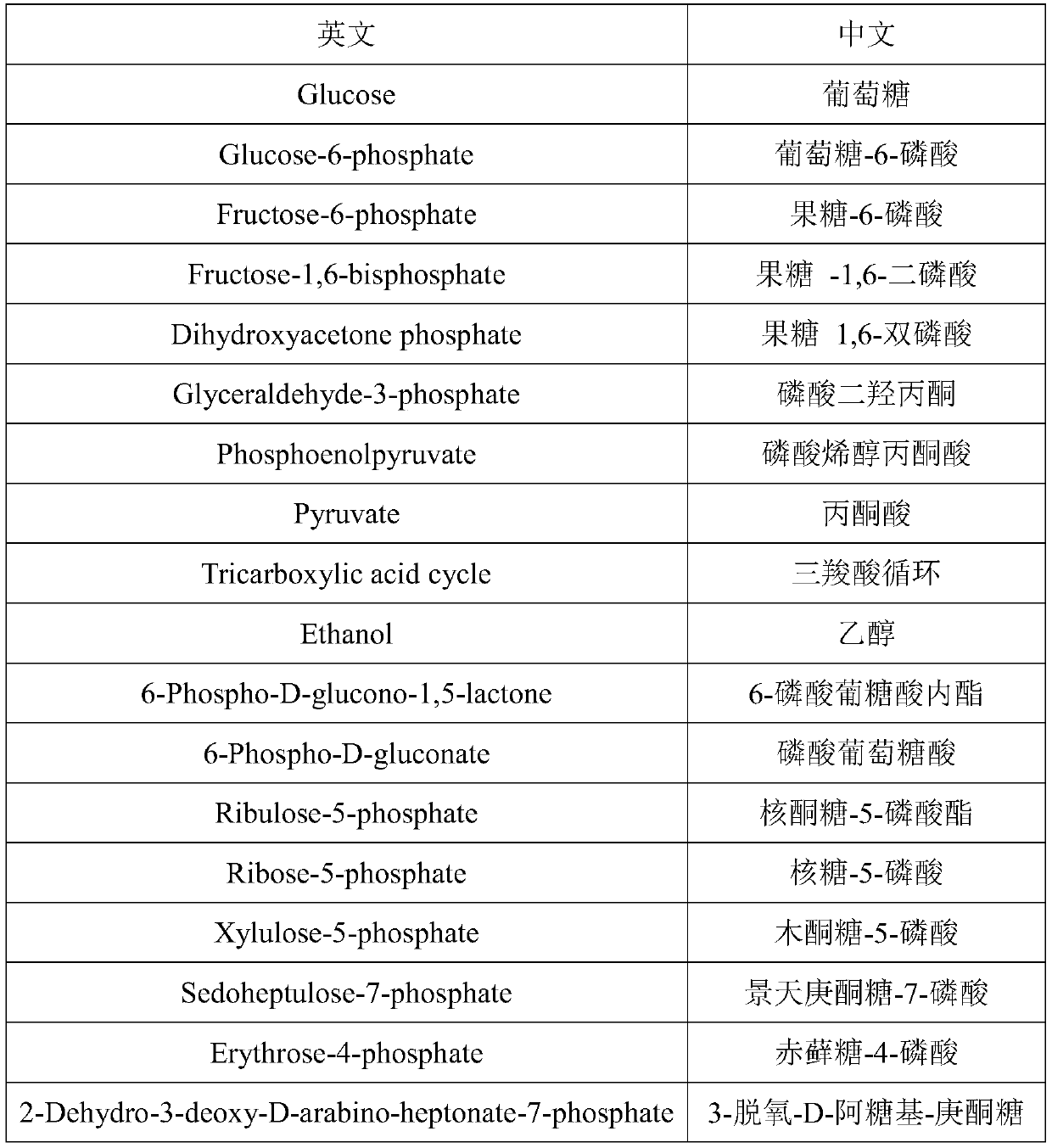
The invention relates to a recombinant yeast, a construction method thereof and an application of the recombinant yeast in preparing tyrosol and derivatives. The recombinant yeast is obtained by introducing an exogenous fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase expression gene into a modified yeast cell, and the modified yeast cell is a yeast cell with a metabolic pathway of synthesizing tyrosol through 4-erythrose phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvic acid. The invention first discloses the fact that in a process of expressing fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase in yeast, fructose-6-phosphoric acid iscatalyzed into erythrose-4-phosphoric acid and acetyl phosphoric acid while 1,6-fructose diphosphate is synthesized, and xylulose-5-phosphoric acid is catalyzed into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphoric acidand acetyl phosphoric acid, so that distribution of the carbon metabolism flow in yeast is changed, synthesis of an important intermediate substance erythrose-4-phosphoric acid in tyrosol biosynthesisis enhanced, the metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol is optimized, and the yield of tyrosol and derivatives such as hydroxytyrosol and the like is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG HENGLU BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for constructing the recombinant yeasts for preparation of tyrosol and derivatives and its application
PendingUS20220213512A1Increase synthesisIncrease productionFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
A recombinant yeast is constructed by introducing an expressed gene of exogenous Fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase into a modified yeast cell, and the modified yeast cell is a yeast cell with a metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol via Erythrose-4-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate. The present invention discloses for the first time that in the process of expressing Fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase in a yeast, Fructose-6-phosphate is synthesized into beta-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and also catalyzed into Erythrose-4-phosphate and Acetyl-phosphate, and Xylulose-5-phosphate is catalyzed into Glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate and Acetyl-phosphate, which change the metabolic flux distribution of carbon in the yeast, enhance the synthesis of Erythrose-4-phosphate as an important intermediate for the biosynthesis of tyrosol, optimize the metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol, and increase the yields of tyrosol and its derivatives such as hydroxytyrosol.
Owner:SHANDONG HENGLU BIOTECH CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of glutamic acid dipeptide
ActiveCN106834394BAchieve recyclingWide variety of sourcesTransferasesPeptidesDipeptidePhosphorylation
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ammonia ion diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and ammonia ion concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464346AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzymatic ColorimetryPyrophosphate
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring ammonia (ions) by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of ammonia (ions), and belongs to the technical field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, glutamic acid, adenyl pyrophosphate, acetyl phosphate, glutamine synthetase, acetokinase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the concentration of ammonia (ions).
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
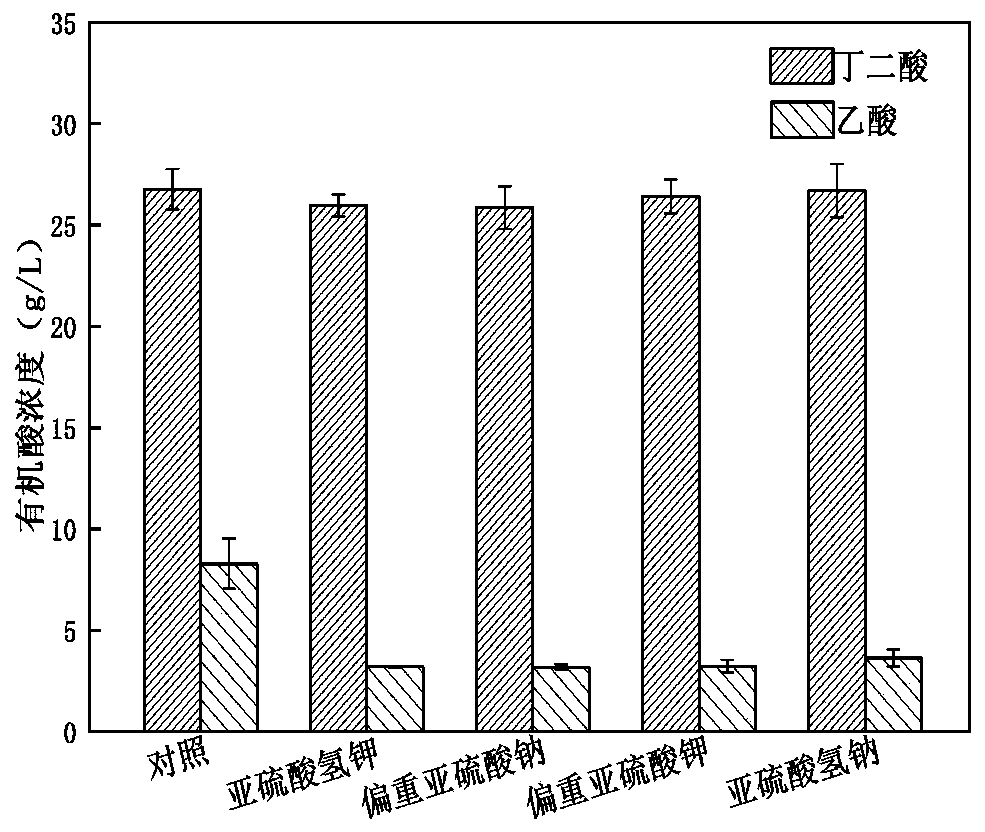
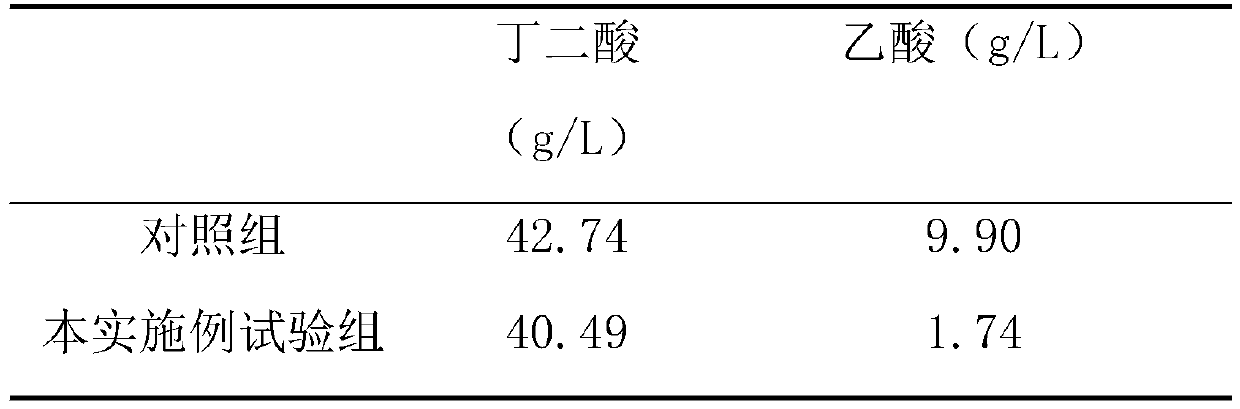
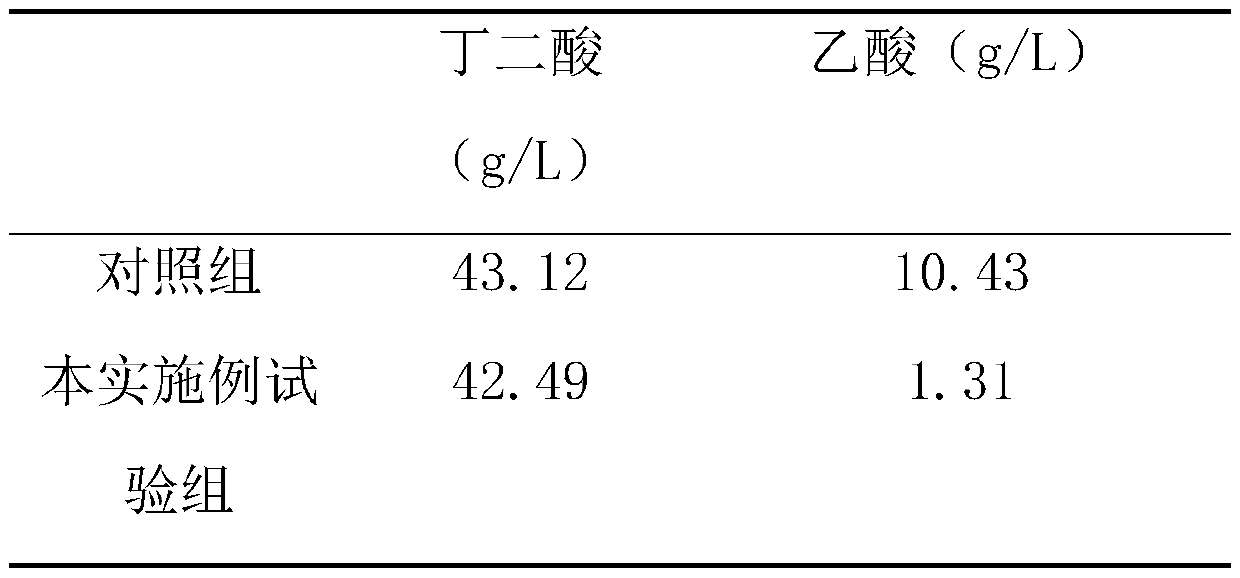
Method for reducing proportion of succinic acid fermentation by-products of actinobacillus succinogenes
ActiveCN110964754AReduce contentReduce accumulation concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetic acidButanedioic acid
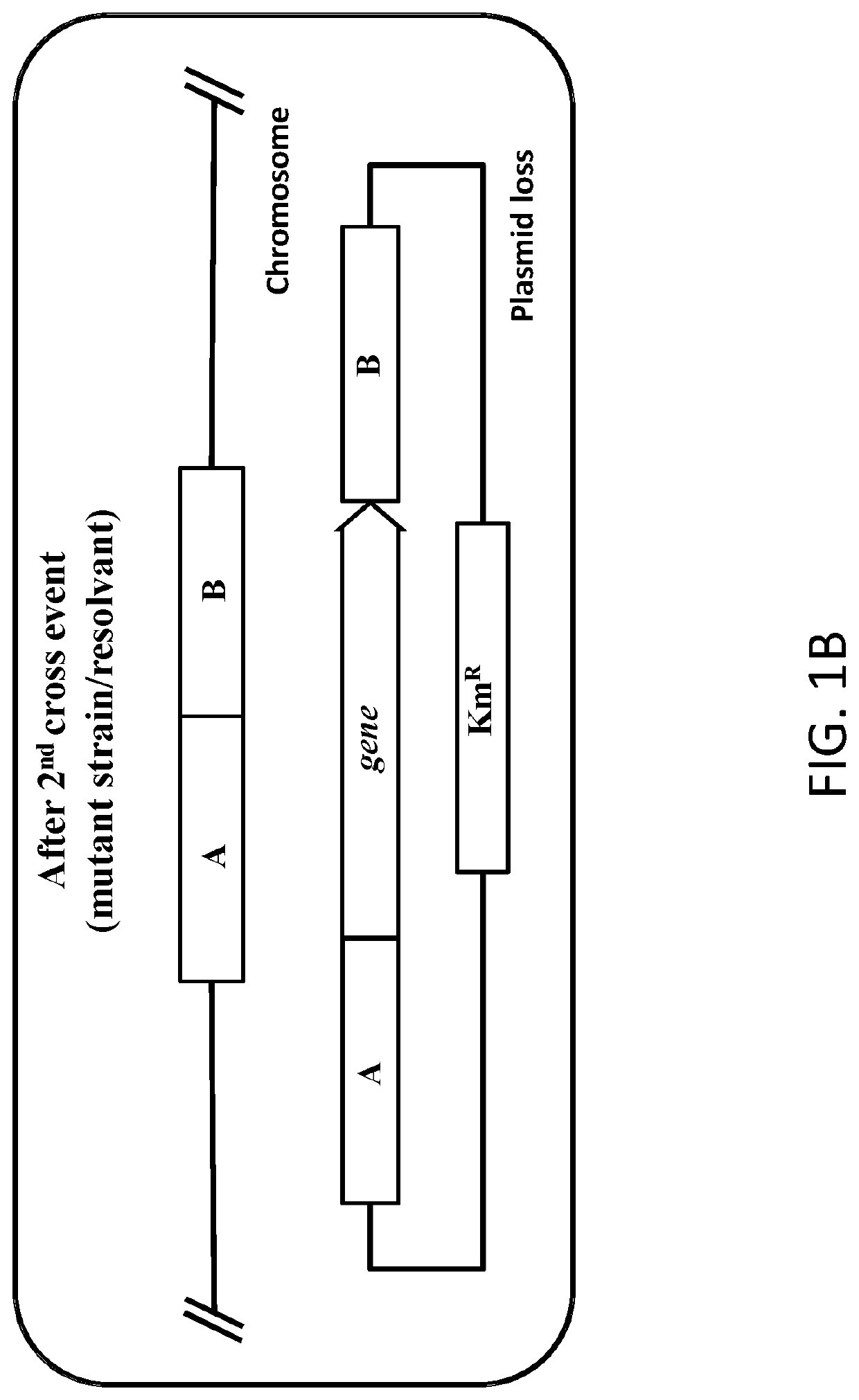
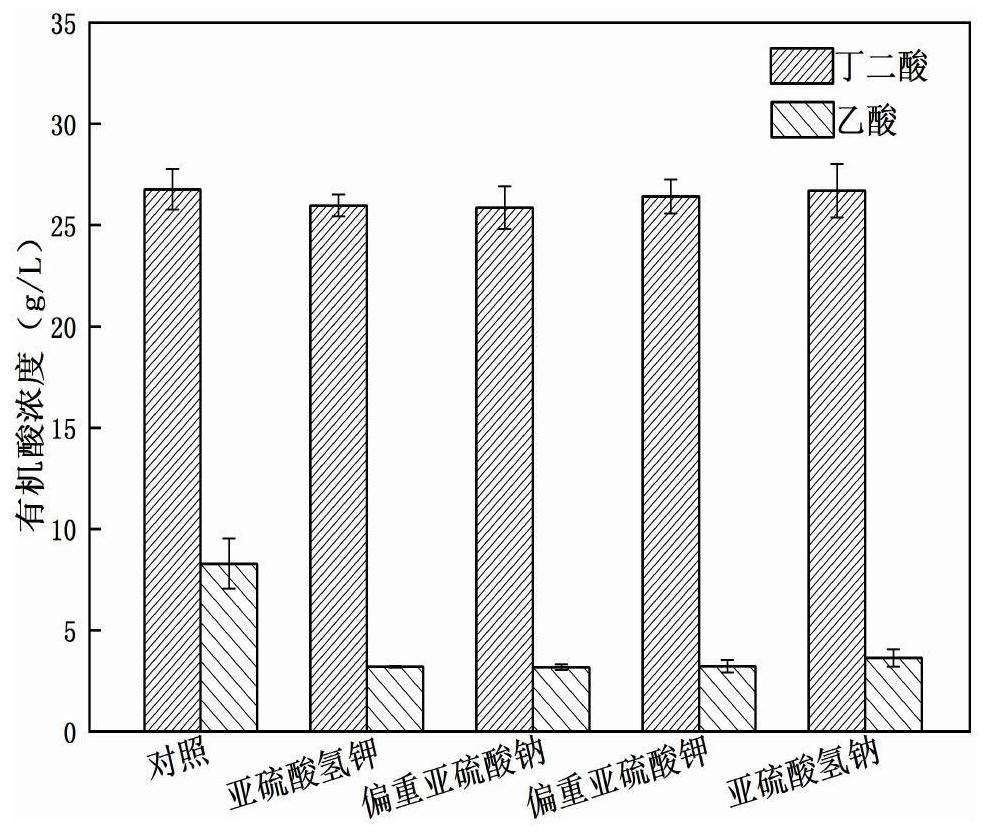
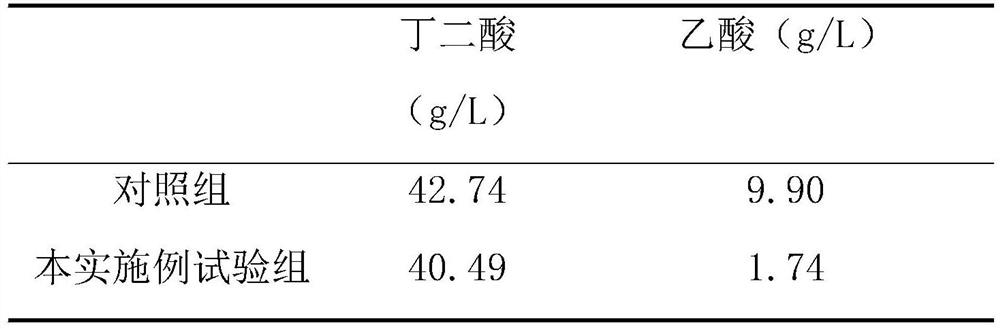
The invention discloses a method for reducing the proportion of succinic acid fermentation by-products of actinobacillus succinogenes, comprising the following steps: carrying out fermentation cultureon strains subjected to strain activation and propagation, with the inoculum size of 5-15% by volume; and adding 1-20 g / L of hydrosulphite or metabisulfite into the fermentation medium. According tothe invention, hydrosulphite or metabisulfite is added in the process of producing succinic acid by fermentation of actinobacillus succinogenes, and is subjected to addition reaction with an intermediate product acetyl phosphate generated in cells to hinder further conversion into acetic acid, so that the content of acetic acid by-products can be greatly reduced under the condition of not influencing the yield of succinic acid. The process is simple in operation process and low in cost, and has industrial application value.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Amino acid diagnosis/measurement reagent (kit) and amino acid concentration measurement method
InactiveCN101750289AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSodium bicarbonatePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to an amino acid diagnosis / measurement reagent (kit) utilizing an enzyme-colorimetry method and an enzyme immunoassay technology, and relates to a method for measuring the concentration of amino acid as well as the composition and the components of the reagent, belonging to the technical field of medical / food / environmental detection and measurement. The reagent (kit) mainly comprises the components of buffer solution, NADH, sodium bicarbonate (carbon dioxide), acetyl phosphate, taurine, amino acid oxidase, pyruvic oxidase, taurine dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The concentration of amino acid is measured by the steps of mixing a sample with the reagent in a certain volume radio to carry out a series of enzymatic reaction, placing the reactants under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and detecting the reducing degree of absorbance at the main wavelength of 340 nm.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit and method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration
InactiveCN101620087AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSodium bicarbonatePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of medical test and determination. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, coenzyme, amines, sodium bicarbonate (carbon dioxide), acetyl phosphate, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphoric acid, pyruvate oxidase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the ascending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the activity concentration of the monoamine oxidase.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A genetically engineered bacterium that weakens the accumulation of acetic acid in the fermentation process to enhance the production of l-tryptophan and its construction method
ActiveCN104651289BLower specific vitalityReduce accumulationBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyPhosphate acetyltransferase
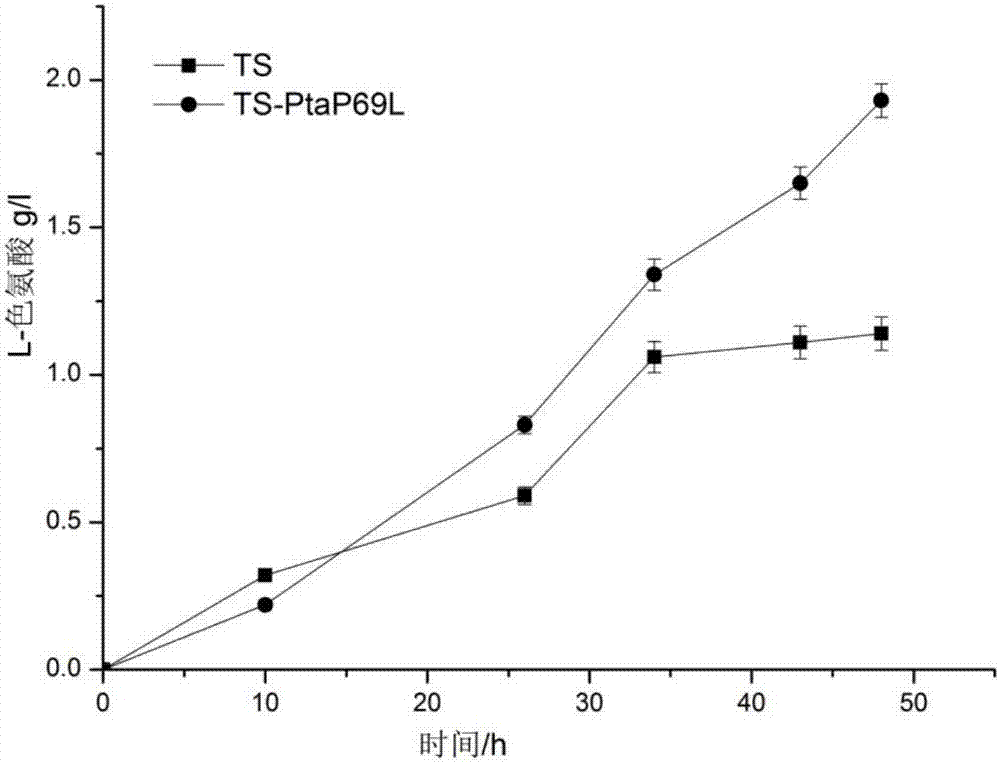
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium that weakens the accumulation of acetic acid in the fermentation process to enhance the production of L-tryptophan and a construction method thereof, belonging to the fields of metabolic engineering and genetic engineering. The present invention takes L-tryptophan production strain (recombinant Escherichia coli) FB-04 (referred to as TS) phosphate acetyltransferase (Pta) as the parent, and uses molecular biology techniques to perform site-directed mutation on it. Under this modification, the specific activity of Pta was 60.4% of that before the mutation. Using Red recombination technology, the pta gene on the TS genome was mutated by a two-step traceless gene replacement method to construct an engineering bacterium TS‑PtaP69L. This strategy significantly reduces the specific activity of Pta, and the engineering bacteria TS-PtaP69L is compared with TS in the fermentation process: 1) The content of tryptophan in shake flask fermentation increases by 80%, and the content of acetic acid decreases by 15.5%; 2) Tryptophan in 3L fermenter fermentation The acid content increased by 12.6%, and the acetic acid content decreased by 73%. The tryptophan mutant strain has better industrial fermentation performance. This genomic site-directed mutagenesis strategy can also be used to improve the fermentation performance of E. coli producing other amino acids.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
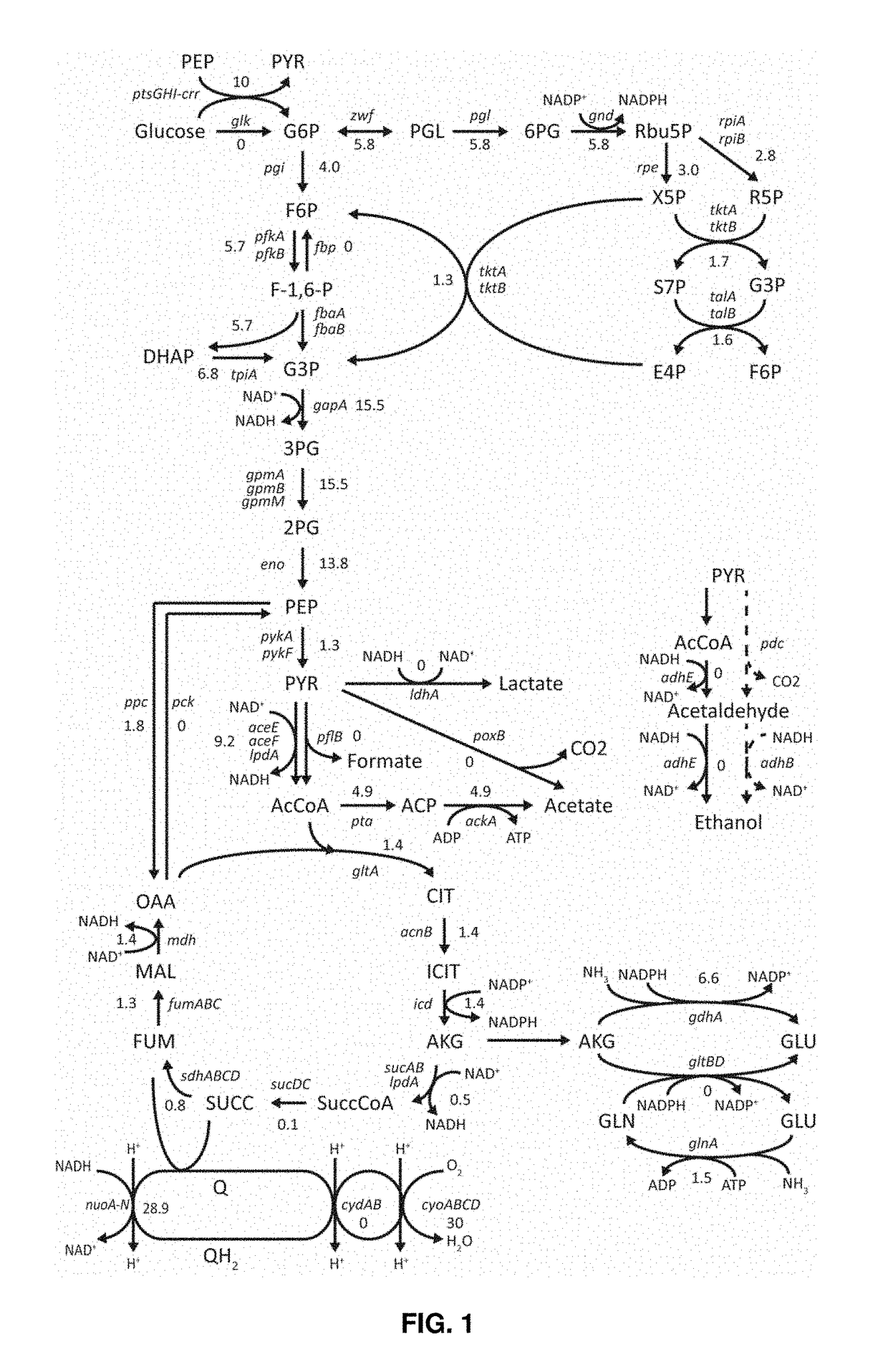
Microorganisms and methods for producing pyruvate, ethanol, and other compounds
Microorganisms comprising modifications for producing pyruvate, ethanol, and other compounds. The microorganisms comprise modifications that reduce or ablate activity of one or more of pyruvate dehydrogenase, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, phosphate acetyltransferase, acetate kinase, pyruvate oxidase, lactate dehydrogenase, cytochrome terminal oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, glutamate dehydrogenase, pyruvate formate lyase, pyruvate formate lyase activating enzyme, and isocitrate lyase. The microorganisms optionally comprise modifications that enhance expression or activity of pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase. The microorganisms are optionally evolved in defined media to enhance specific production of one or more compounds. Methods of producing compounds with the microorganisms are provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis/determination kit and method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration
InactiveCN101620110AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoric acidEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to an inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis / determination kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of test and determination of medical science, food, and environment. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, coenzyme, adenoside bisphosphate, oxaloacetic acid, acetyl phosphate, hydrogen peroxide, coenzyme A, pyruvate carboxylase, pyruvate oxidase, pyruvate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the ascending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit and method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration
InactiveCN101620085AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSodium bicarbonateLactate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of medical test and determination. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, amines, sodium bicarbonate (carbon dioxide), acetyl phosphate, pyruvate oxidase, lactate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the descending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the activity concentration of the monoamine oxidase.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Microorganisms and methods for producing pyruvate, ethanol, and other compounds
Microorganisms comprising modifications for producing pyruvate, ethanol, and other compounds. The microorganisms comprise modifications that reduce or ablate activity of one or more of pyruvate dehydrogenase, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, phosphate acetyltransferase, acetate kinase, pyruvate oxidase, lactate dehydrogenase, cytochrome terminal oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, glutamate dehydrogenase, pyruvate formate lyase, pyruvate formate lyase activating enzyme, and isocitrate lyase. The microorganisms optionally comprise modifications that enhance expression or activity of pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase. The microorganisms are optionally evolved in defined media to enhance specific production of one or more compounds. Methods of producing compounds with the microorganisms are provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit and method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration
InactiveCN101620082AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSodium bicarbonateEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of medical test and determination. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, amines, sodium bicarbonate (carbon dioxide), acetyl phosphate, pyruvic oxidase, alanine dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the descending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the activity concentration of the monoamine oxidase.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Monoamine oxidase diagnostic reagent (kit) and monoamine oxidase active concentration measuring method
InactiveCN101793725AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSodium bicarbonatePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a monoamine oxidase diagnostic / measuring reagent (kit) which utilizes enzyme colorimetry and enzyme-linked method technologies, and meanwhile, the invention also relates to a method for measuring monoamine oxidase active concentration and compositions and components of the reagent, which belong to the technical field of medical inspection and measurement. The main components of the reagent (kit) of the invention comprise a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, an amine compound, sodium bicarbonate (carbon dioxide), acetyl phosphate, taurine, pyruvate oxidase, tauropine dehydrogenase and a stabilizer; and the method comprises the following steps of: enabling a sample and the reagent to generate a series of enzymatic reactions through mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio, then placing the reactants under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer and detecting the descending speed of the absorbance at a position with the dominant wavelength of 340nm to measure and calculate the active concentration magnitude of monoamine oxidase.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
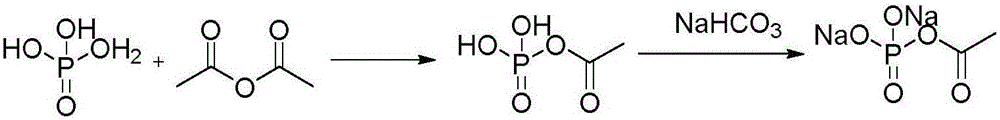
Method for continuous production of acetyl phosphate with microchannel reaction device
ActiveCN105906662AExcellent selectivityExcellent yieldPhosphorus organic compoundsAcetic anhydridePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for continuous production of acetyl phosphate with a microchannel reaction device. The method includes the steps of: (1) pumping a phosphoric acid solution and an acetic anhydride solution respectively into a microstructure mixer I at the same time, mixing the substances evenly, then pumping the mixture into a microchannel reactor I and carrying out reaction to obtain an acetyl phosphate solution; (2) pumping the acetyl phosphate solution and an alkali solution respectively into a microstructure mixer II at the same time, and then pumping the mixture into a microchannel reactor II to carry out reaction to obtain an acetyl phosphate solution; and (3) conducting standing, crystallization, filtering and drying on the acetyl phosphate solution to obtain acetyl phosphate. The method provided by the invention can achieve a phosphoric acid conversion rate of 100%, and a acetyl phosphate yield of more than 93%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
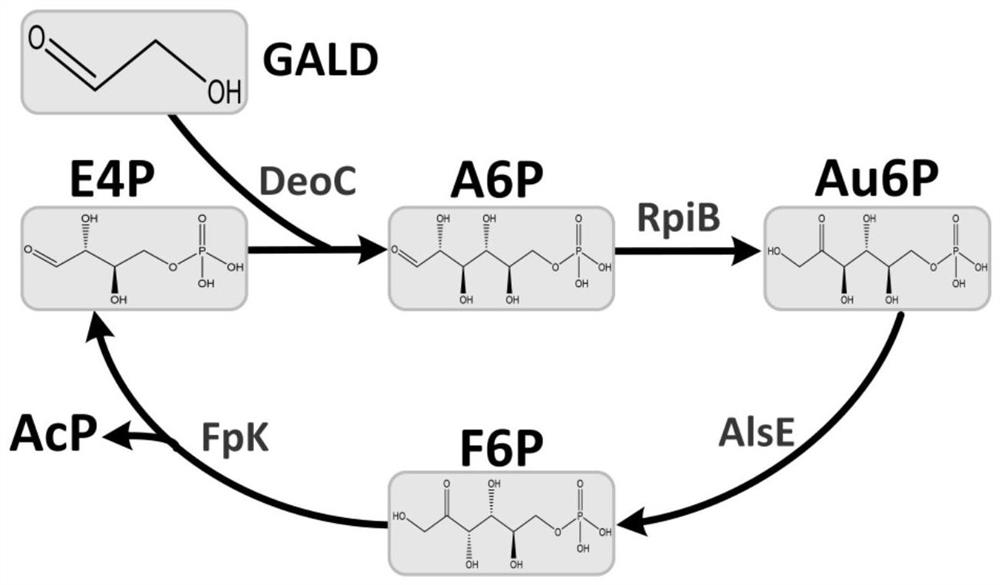
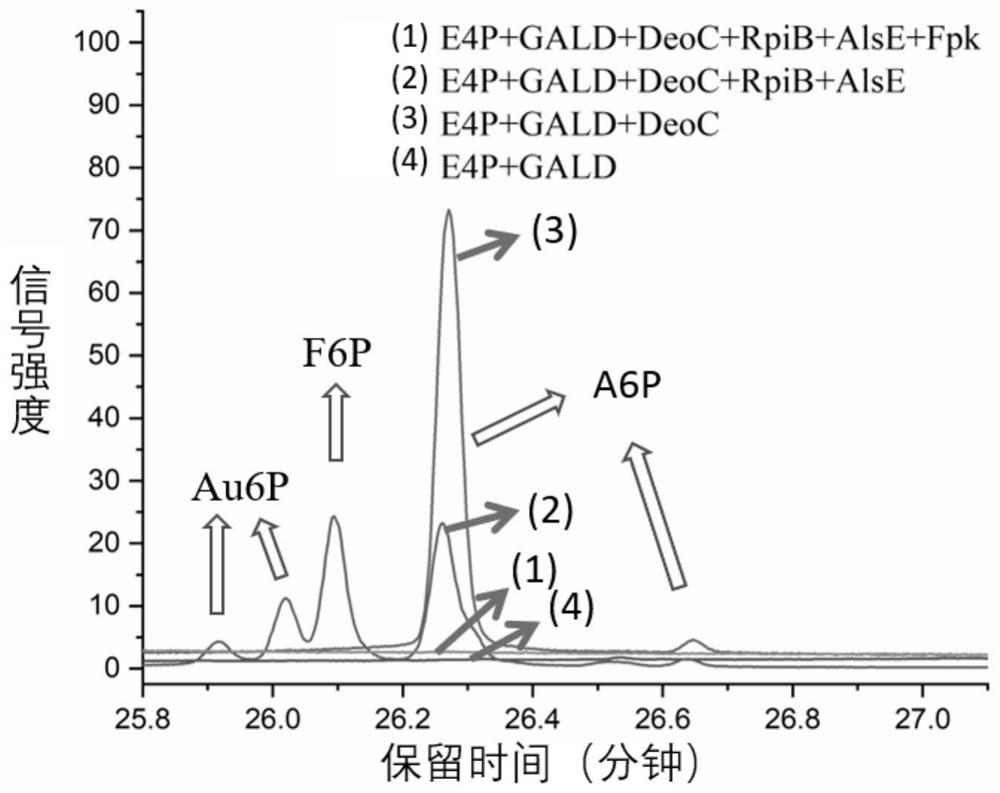
Preparation method of allose 6-phosphate, acetyl phosphate and acetyl coenzyme A
PendingCN114369633ALarge space for optimizationHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBatch fermentationCatalytic rate
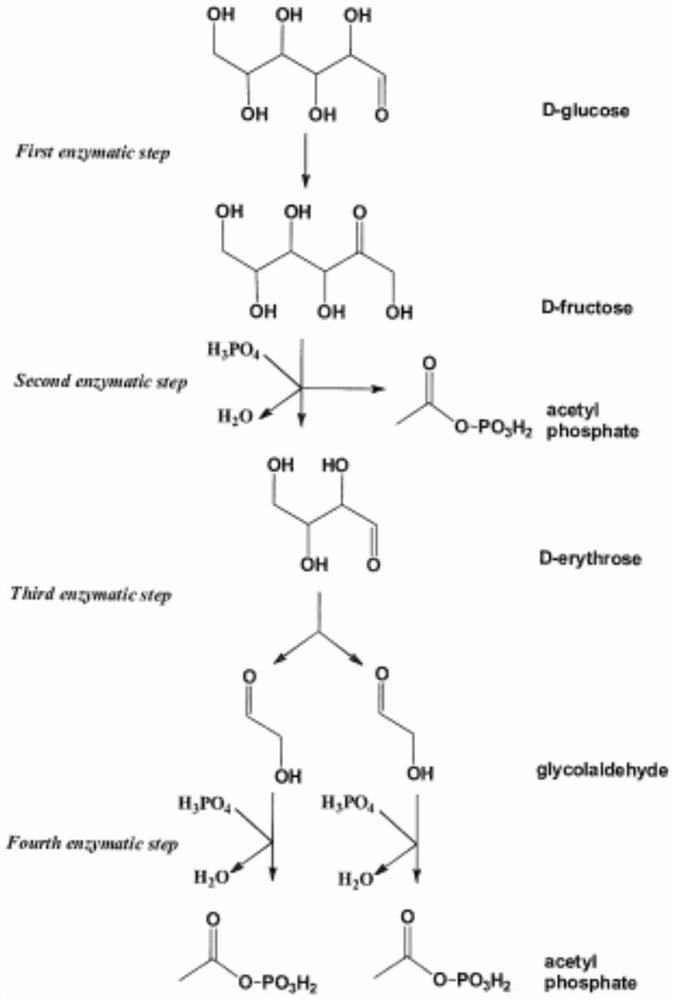
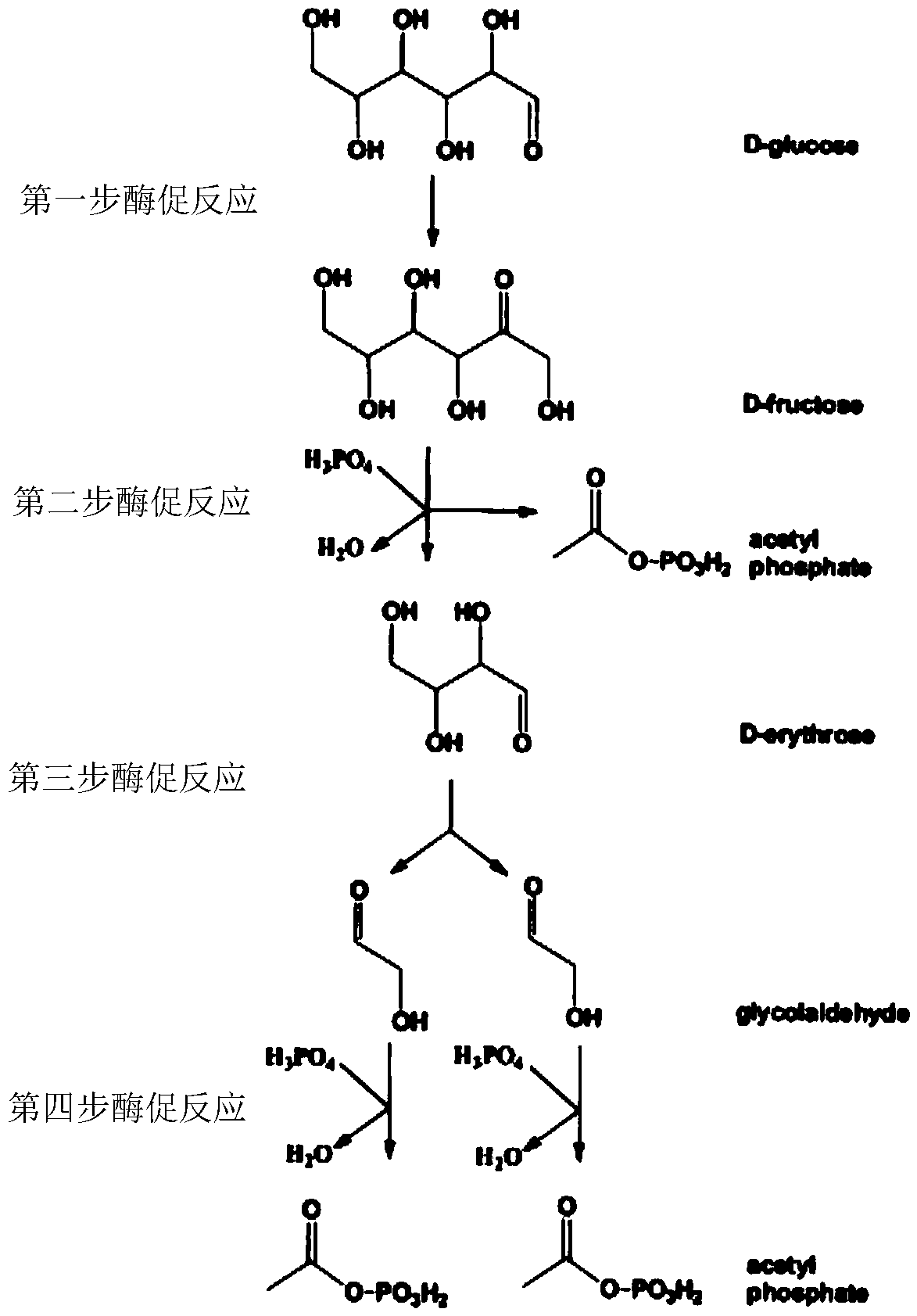
The invention discloses a method for further synthesizing acetyl coenzyme A by reacting glycolaldehyde with 4-erythrose phosphate under the catalysis of aldolase to generate 6-allose phosphate. The method disclosed by the invention is high in catalytic rate, the theoretical carbon yield of a reaction route is 100%, carbon loss is avoided, the 4-erythritol phosphate, the enzyme and the coenzyme can be recycled, and the reaction efficiency is relatively high. The method disclosed by the invention can play more obvious advantages in the production processes of in-vitro continuous multi-enzyme catalysis, fed-batch fermentation, continuous fermentation and the like capable of controlling the substrate level.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A new pathway for the synthesis of acetyl-CoA and its derivatives from glycolaldehyde
Disclosed is a new approach for synthesizing an acetyl coenzyme A and a derivative product thereof (5-phosphoarabinose, acetyl phosphoric acid, acetyl phosphate, and an acetyl coenzyme A derivative compound) using glycolaldehyde. The approach comprises a reaction of glycolaldehyde and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde under the catalysis of an enzyme to generate 5-phosphoarabinose, wherein the enzyme is selected from an aldolase, a transaldolase, an isoenzyme and a mutant enzyme thereof.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant Microorganism for Producing 2,3-Butanediol and a Method of Production of 2,3-Butanediol
A recombinant microorganism for producing 2,3-butanediol consisting of selecting at least three groups from uridine diphosphate glucose phosphate uroglycan transferase gene (galU), acetyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene (acoA), acetyl phosphate transferase gene (pta), adenosine glucosylphosphate transferase gene (glgC), lactose dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), and phosphodiesterase gene (pdeC) which were modified.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION
Inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnostic and measuring kit and method for measuring inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration
InactiveCN101609003AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to an inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnostic and measuring kit utilizing technologies of an enzymatic recycling method, an enzymatic-colorimetric method and an enzyme-link method, also relates to a method and a principle of measuring inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration and compositions and components of reagents, and belongs to the technical field of testing and measuring of medical science, food and environment. The kit mainly comprises the following components: buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, oxaloacetic acid, acetyl phosphate, hydrogen peroxide, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC), pyruvic oxidase, malate dehydrogenase and stabilizer; samples are mixed with the reagents in certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymatic reactions; then reactants are placed under a UV / visible analyzer; and the descending speed of absorbance is tested at the position where dominant wave length is 340nm so as to measure and calculate the inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A method for reducing the ratio of by-products of Actinobacillus succinogenes succinic acid fermentation
ActiveCN110964754BReduce contentReduce accumulation concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesButanedioic acidPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for reducing the proportion of by-products of succinic acid fermentation of Actinobacillus succinates, comprising fermenting and culturing the bacteria after activation and propagation of the bacteria, and the inoculation amount is 5-15% by volume. The medium is supplemented with bisulfite or partial sulfite, and the addition amount is 1g / L~20g / L. In the present invention, bisulfite or partial sulfite is added in the process of producing succinic acid by fermentation of Actinomyces succinic acid bacteria, and through addition reaction with the intermediate product acetylphosphoric acid generated in the cell, it is prevented from being further converted into acetic acid, The content of acetic acid by-product can be greatly reduced without affecting the production of succinic acid. The process is simple in operation, low in cost, and has industrial application value.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit and method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration
InactiveCN101620083AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSodium bicarbonateEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a monoamine oxidase diagnosis kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining monoamine oxidase activity concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of medical test and determination. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, coenzyme, amines, sodium bicarbonate (carbon dioxide), acetyl phosphate, coenzyme A, pyruvate oxidase, pyruvate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the ascending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the activity concentration of the monoamine oxidase.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com