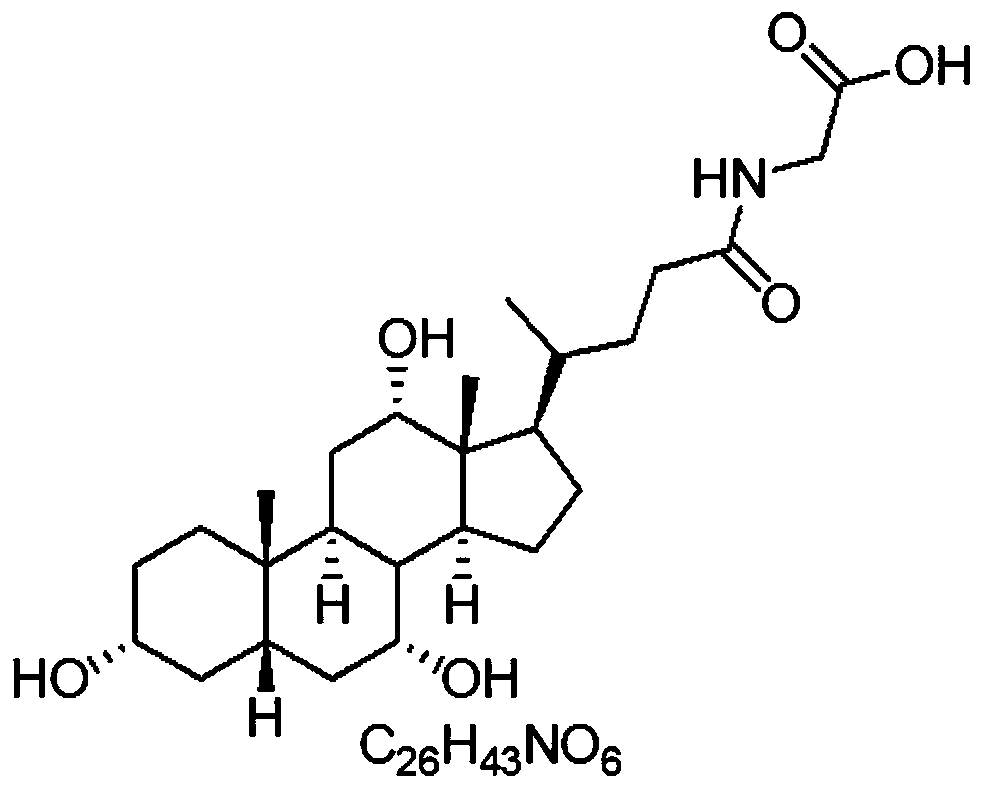
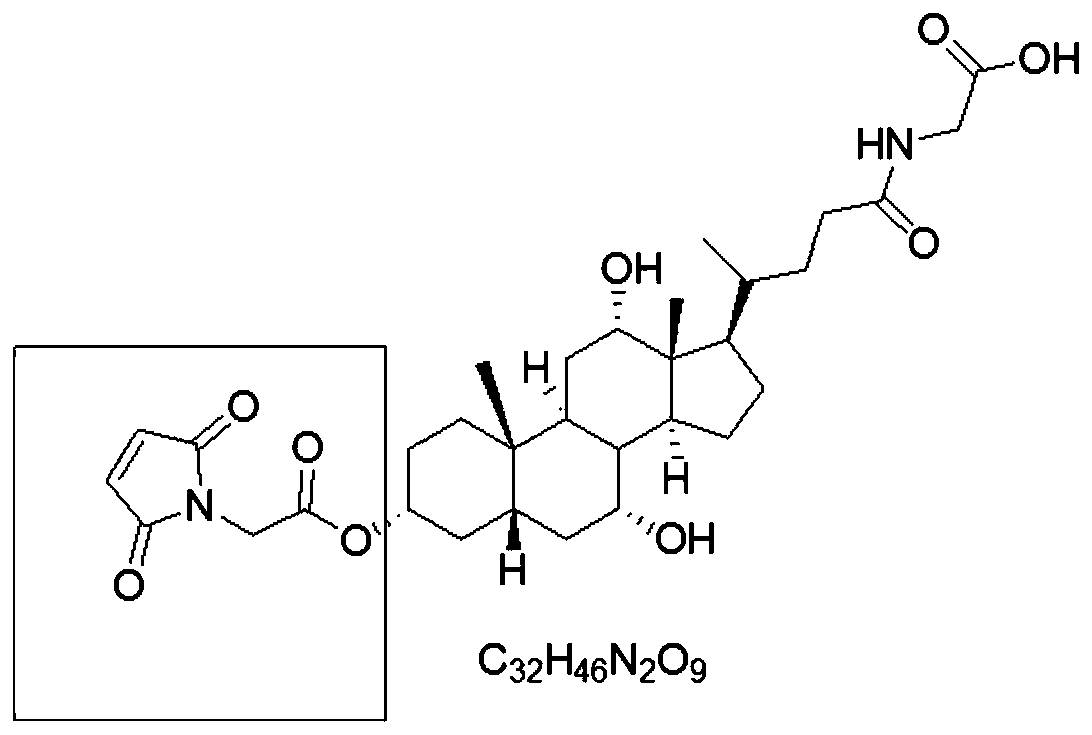
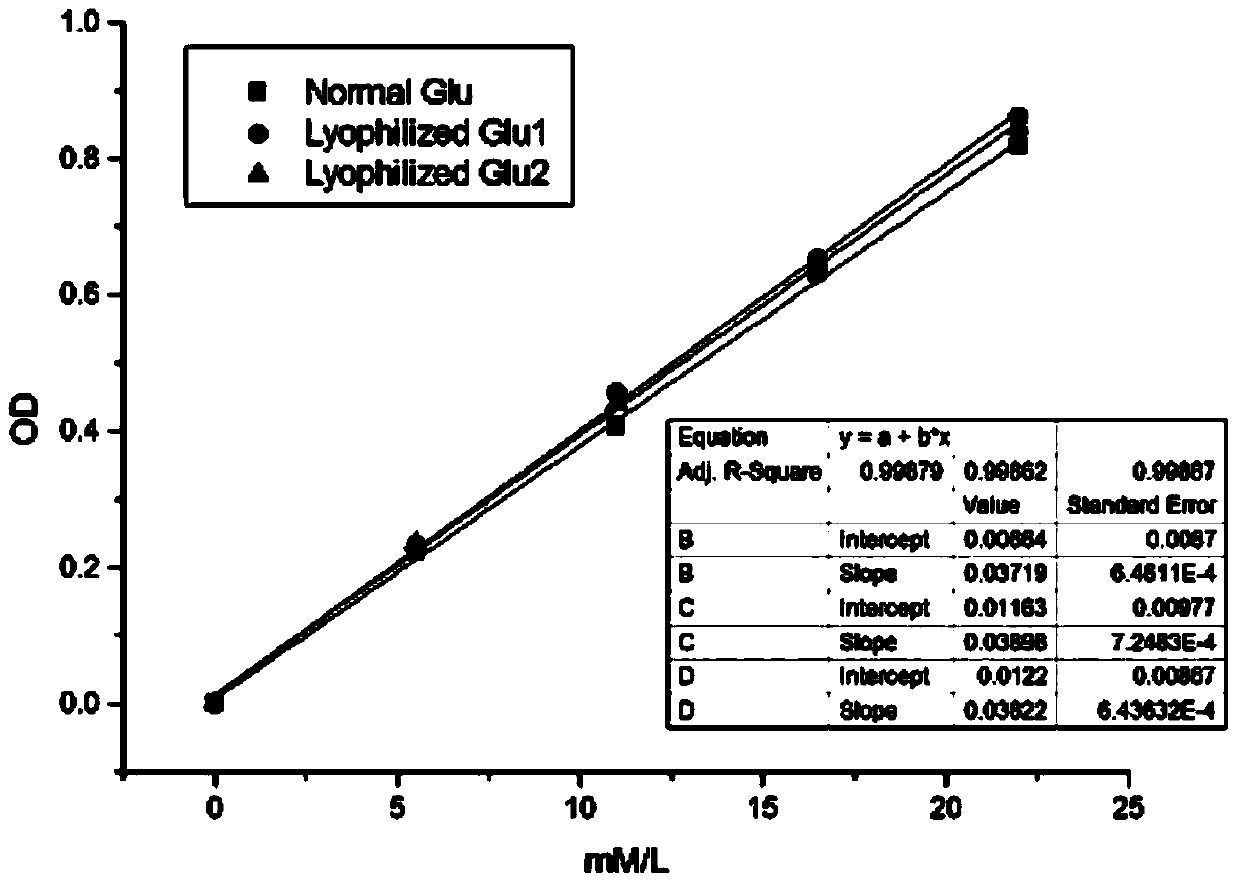
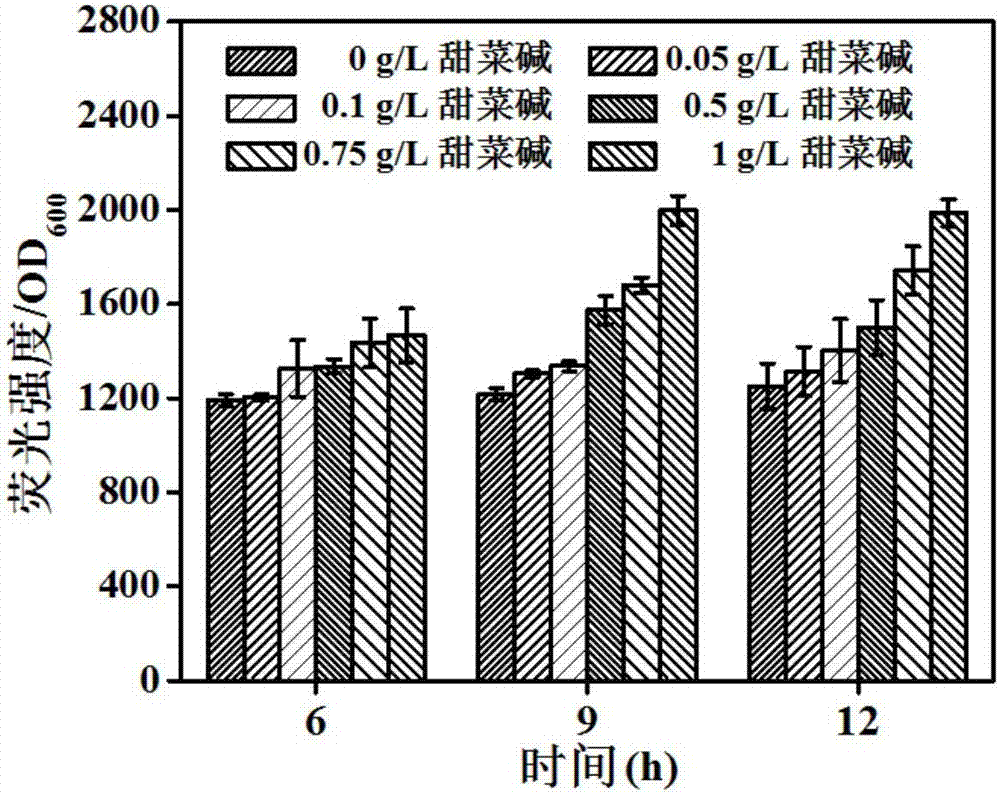
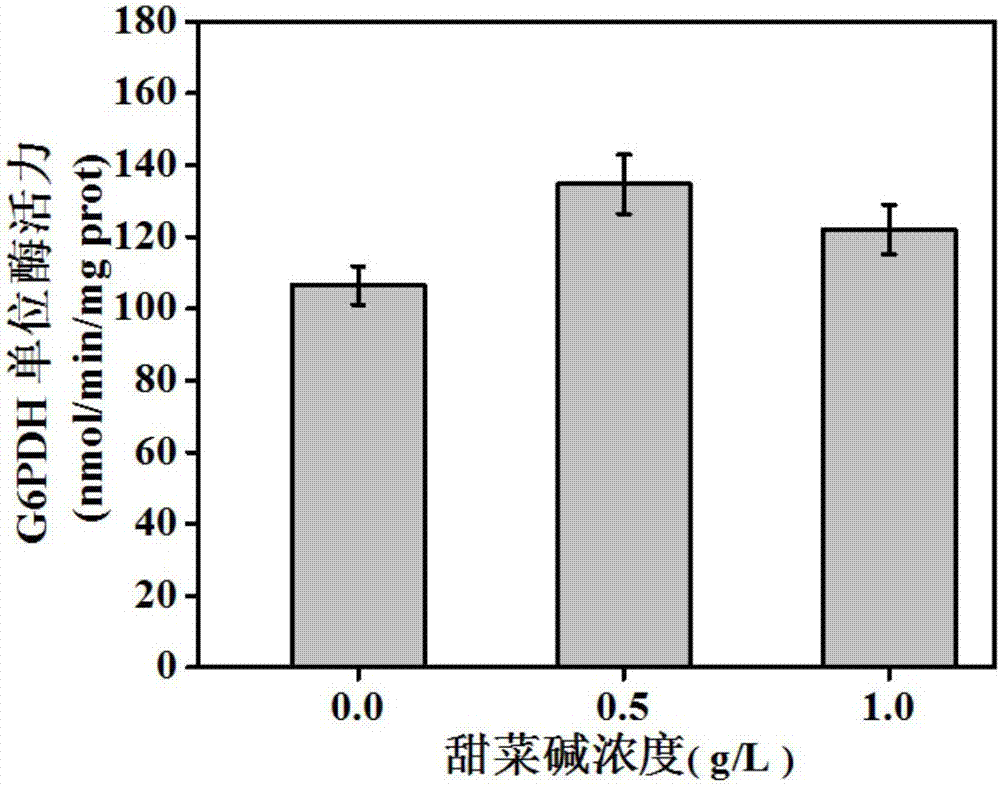
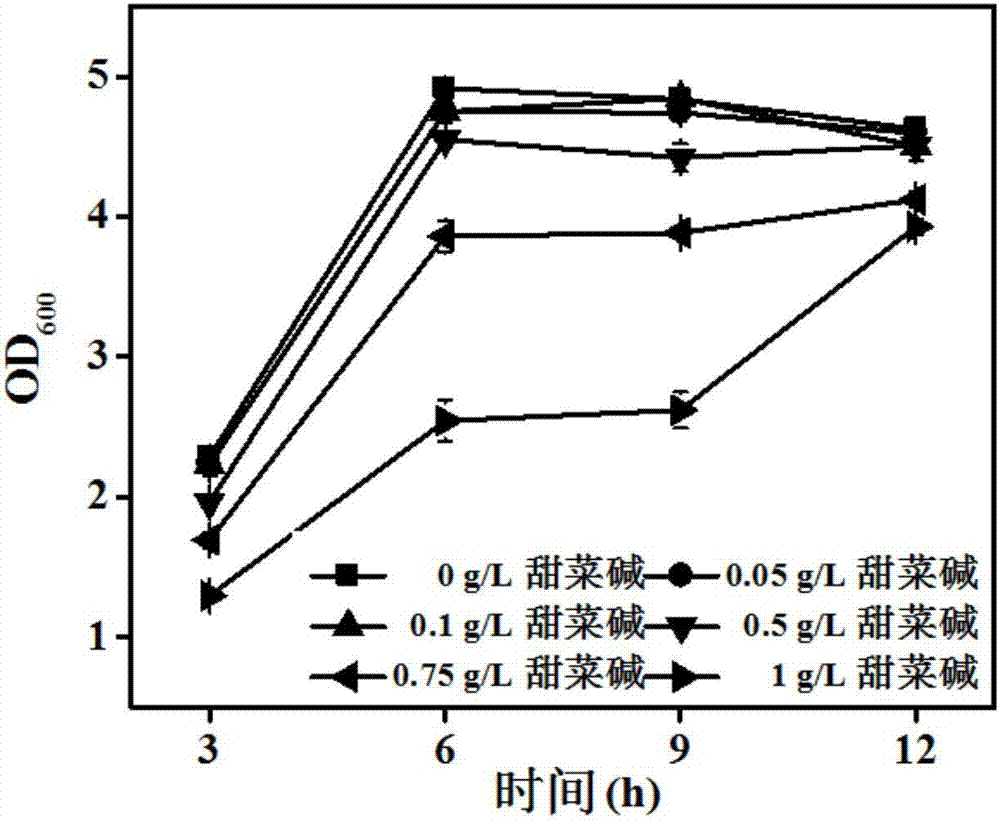
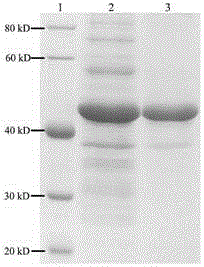
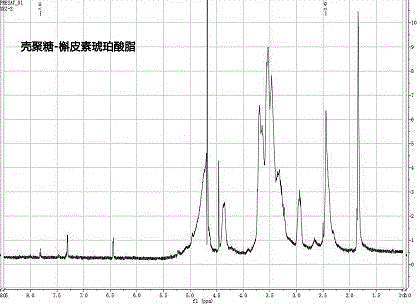
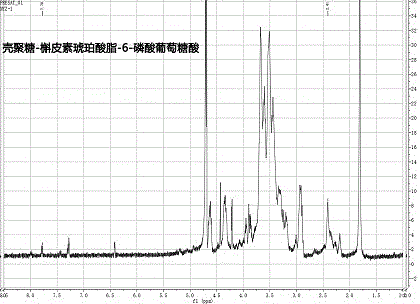
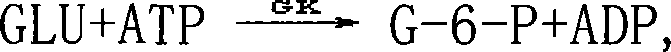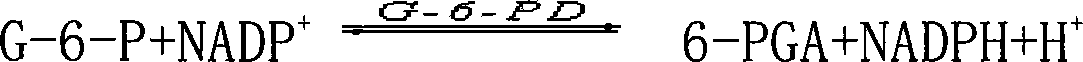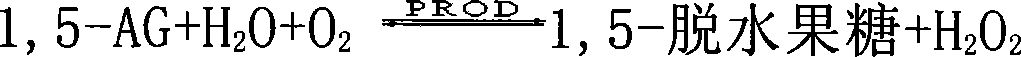Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
154 results about "Glucose phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
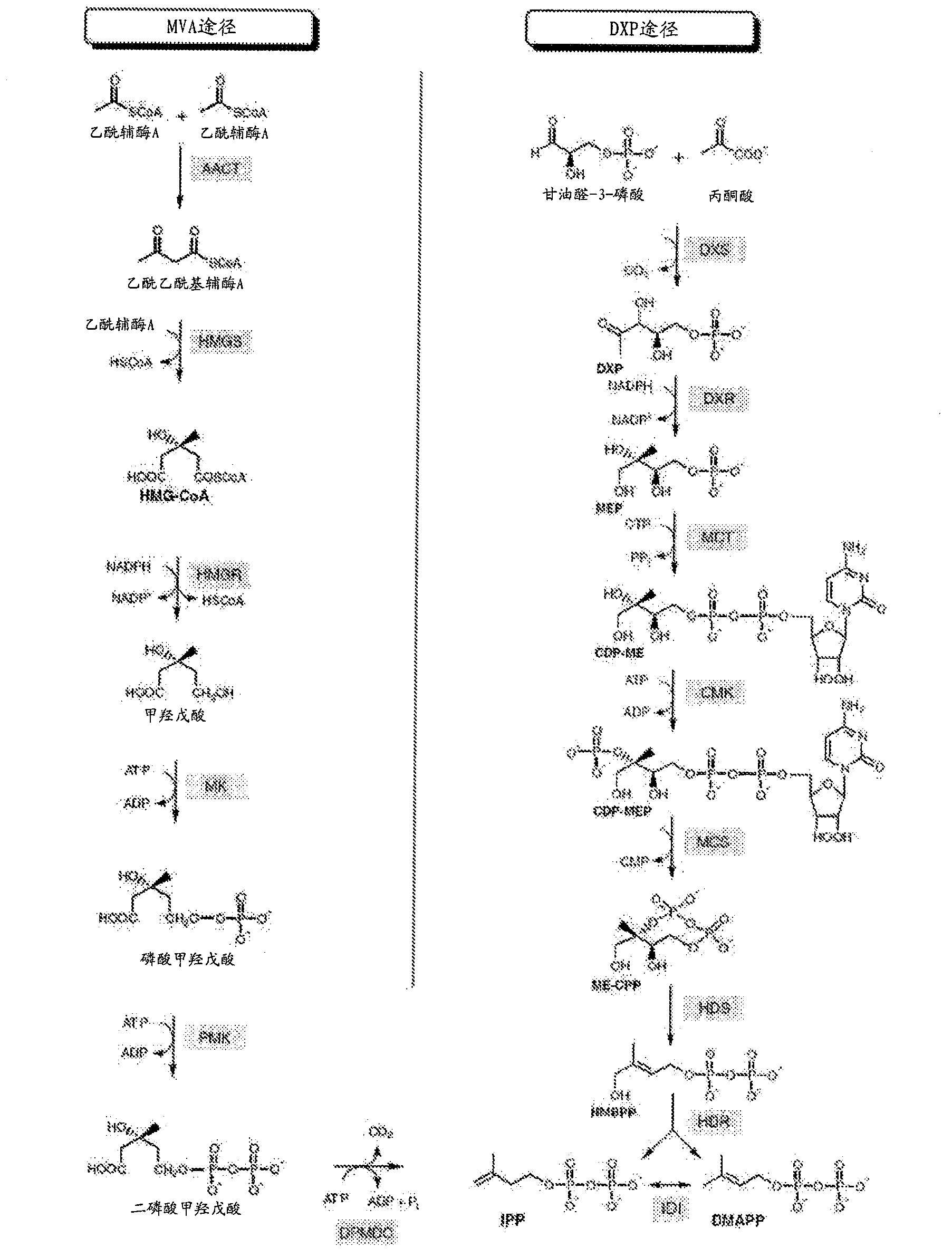
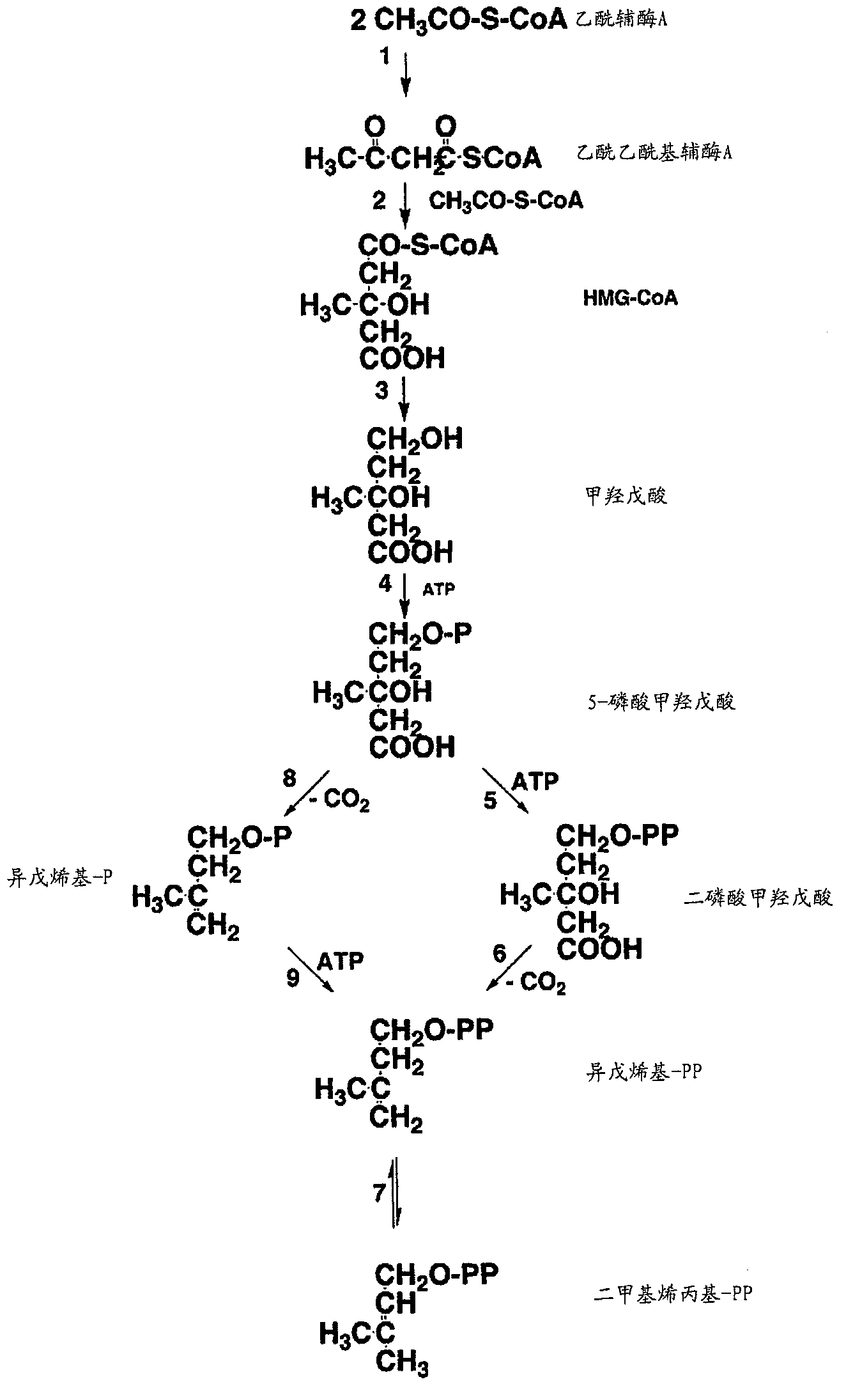
Intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism.
Relevant enzymes for preparing mannitol by performing anabolism on Chinese caterpillar fungus and hirsutella sinensis, gene and application thereof
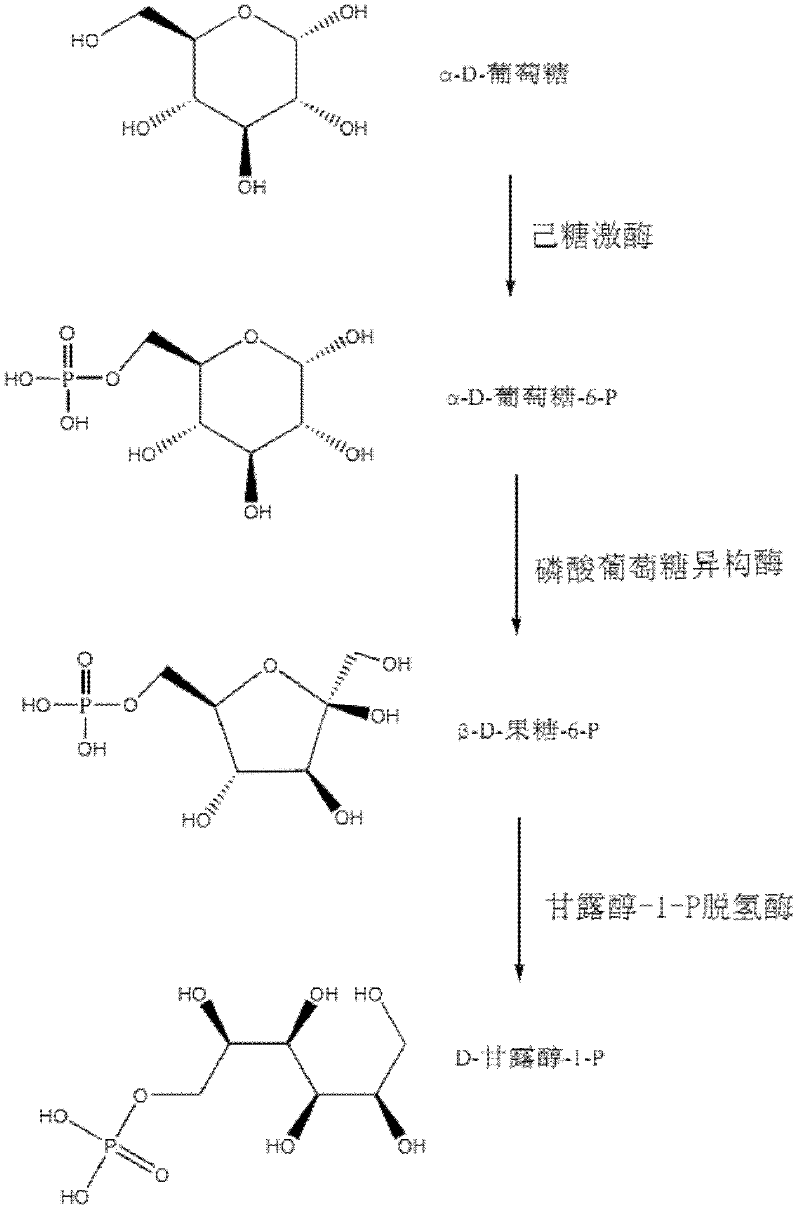
The invention provides a group of relevant enzymes for preparing mannitol by performing anabolism on Chinese caterpillar fungus serving as a multifunctional production fungus and hirsutella sinensis based on glucose, a gene for encoding these enzymes and application thereof. The relevant enzymes include (1) hexokinase: manA1-A6 proteins of which the sequences are SEQ ID No.1-6, (2) phosphoglucoisomerase: manB1-B3 proteins of which the sequences are SEQ ID No.7-9, and (3) mannitol-1-P dehydrogenase: manC protein of which the sequence is SEQ ID No.10. In the invention, detailed researches are performed on the metabolic pathway of mannitol synthesized by using Chinese caterpillar fungus serving as a multifunctional production fungus, hirsutella sinensis and glucose on the aspect of principle, cloned DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) comprising a nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred into engineering bacteria with transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer methods, and host mannitol is endowed with high expression by regulating the expression of a biosynthetic gene of the mannitol.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for producing L-amino acid using methylotroph
InactiveUS20040142435A1High activityHigh expressionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismMethylotroph
The present invention describes a method for producing an L-amino acid comprising culturing a microorganism having an ability to produce an L-amino acid in a medium, whereby the L-amino acid accumulates in the medium, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium, whereby said microorganism comprises a methanol-utilizing bacterium having the Entner-Doudoroff pathway in which 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase activity and / or 2-keto-3-dexoy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase activity is enhanced.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
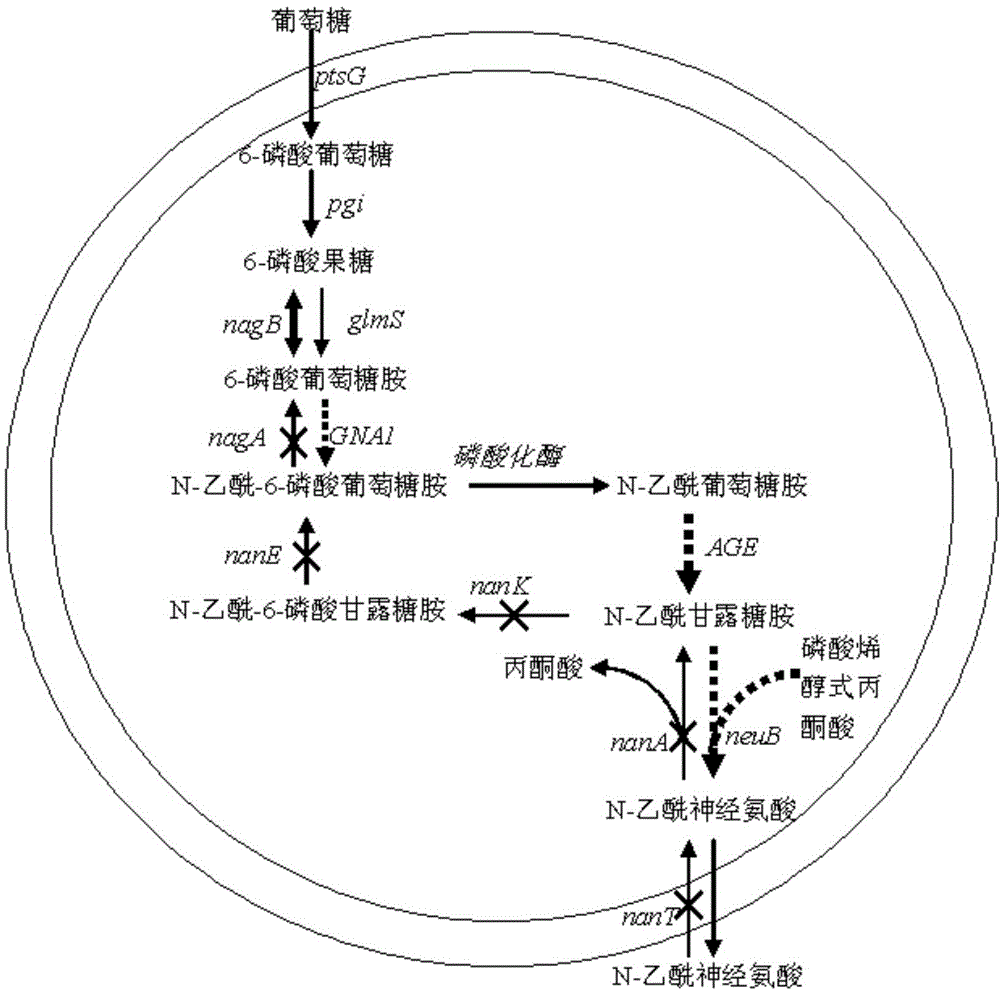
Novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103602627AEnhanced rate-limiting enzyme gene expressionPrevent backflowBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphate
The invention discloses novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as a construction method and application thereof. The engineering bacterial is constructed by introducing an encoded 6-glucosamine phosphate acetylase gene, an N-acetyl glucosamine-2-isomerase gene and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene into escherichia coli to express, carrying out strengthened expression on 6-glucosamine phosphate deaminase gene contained in the escherichia coli per se and knocking off genes, for decomposing and utilizing enzyme in metabolic pathways, of the N-acetylneuraminic acid in the engineering bacteria. The engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention can be used for fermentation culture to synthesize the N-acetylneuraminic acid by using glucose or glycerinum as a substrate.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
6-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof in preparing detection reagent
InactiveCN110174363AColor/spectral properties measurementsBulk chemical productionHigh fluxWild type
The application relates to a 6-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutant and an application thereof in preparing detection reagent. Specifically, the 6-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutant comprises one of the following mutants or combination thereof: D306C, D375C, and G426C in comparison with the wild type 6-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. The detection kit prepared from the 6-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutant has the advantages of being strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, convenient to operate, short in detection time, accurate in quantification, and suitable for high-flux detection.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Method for producing lacto-n-biose i and galacto-n-biose
ActiveUS20100120096A1Easily and conveniently carry-outGood value for moneyImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphorylation
A method for producing lacto-N-biose I and galacto-N-biose inexpensively and conveniently is provided. The method for producing lacto-N-biose I or galacto-N-biose, characterized in that the method comprises causing: (i) a combination of a carbohydrate raw material with an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorolysis of the carbohydrate raw material to give a-glucose-1-phosphate; and (ii) a combination of an enzyme that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate to UDP-glucose and an enzyme that converts UDP-galactose to galactose-1-phosphate with their cofactors, and / or a combination of an enzyme (UDP-Gly synthase) that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose and α-galactose-1-phosphate, respectively, with its cofactor(s) to act in the presence of N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine, phosphoric acid, lacto-N-biose phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.211), and UDP-glucose-4-epimerase (EC 5.1.3.2).
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG
L-histidine production method and special recombinant bacteria
ActiveCN104845923AIncrease productionPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Freeze-drying concentrated glucose detection reagent microsphere and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a freeze-drying concentrated glucose detection reagent microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The freeze-drying microsphere comprises a triethanolamine buffer solution, ATP, NADP, hexokinase, 6-glucose dehydrogenase phosphate, a preservative, trehalose, polyethylene glycol 8000, polyethylene glycol 20000, TrionX-100 and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a solution, and performing filtration and degassing; (2) preparing droplets by using a precise quantification liquid separation system, dropwise adding the droplets into liquid nitrogen, and preparing a freezing microsphere; and (3) transferring the freezing microsphere into a freeze dryer, and performing freeze-drying on the freezing microsphere to obtain a freeze-drying detection reagent microsphere. A glucose detection reagent provided by the invention is a spherical granular freeze-drying reagent and can be pre-packaged into a detection chip. Compared with an existing liquid detection reagent, the glucose detection reagent has the advantages that the storage, transportation and the like at the stable room temperature can be realized. Compared with a freeze-drying powder reagent, the glucose detection reagent has the advantages of accuracy in quantification, convenience in packaging treatment and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-yield acetyl-glucosamine recombinant bacillus subtilis and construction method thereof
ActiveCN106148260AIncrease productionEnhanced synthetic pathwaysBacteriaStable introduction of DNABacillus subtilisGlucose phosphate
The invention relates to a high-yield acetyl-glucosamine recombinant bacillus subtilis and a construction method thereof. Bacillus subtilis BSGN6 serves as an original strain, glucokinase encoding gene glck expression and glucose phosphate isomerase encoding gene pgi expression in the bacillus subtilis are regulated by xylose inducible promoters PxylA, moderate expression of glck and pgi genes is controlled, the yield of acetyl-glucosamine in the recombinant bacillus subtilis is greatly improved, and a foundation is laid for further producing glucosamine by modifying the bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering. The construction method is simple and easy to operate, the yield of acetyl-glucosamine can be greatly improved by the constructed recombinant bacillus subtilis, and the recombinant bacillus subtilis has a good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and method for producing L-threonine by using escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106867952AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to an escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and a method for producing L-threonine by using the escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium. The gene engineering bacterium is characterized in that a promoter P<ppc> of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) of an initial strain is replaced into a promoter P<zwf> of 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (zwf), so that the goal of regulating the L-threonine production capacity by glycine betaine is achieved. In the fermentation process, the glycine betaine is added, so that the L-threonine yield through shaking flask fermentation can reach 50 to 55g / L; the 5L fermentation tank yield reaches 120 to 150g / L; the saccharic acid conversion rate reaches 59 to 61 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bacillus licheniformis engineered bacterium capable of high production of poly-Gamma-glutamic acid
ActiveCN106497857AIncrease synthesis levelIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisGlucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
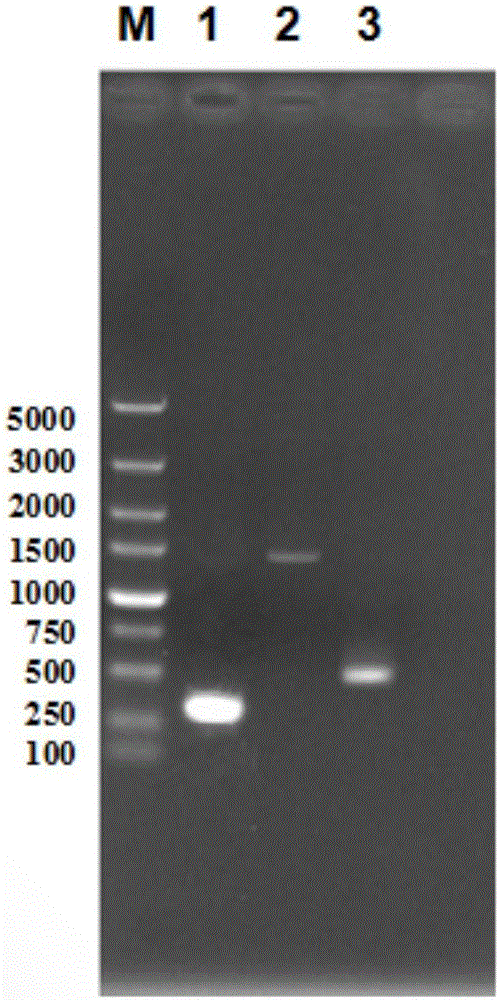
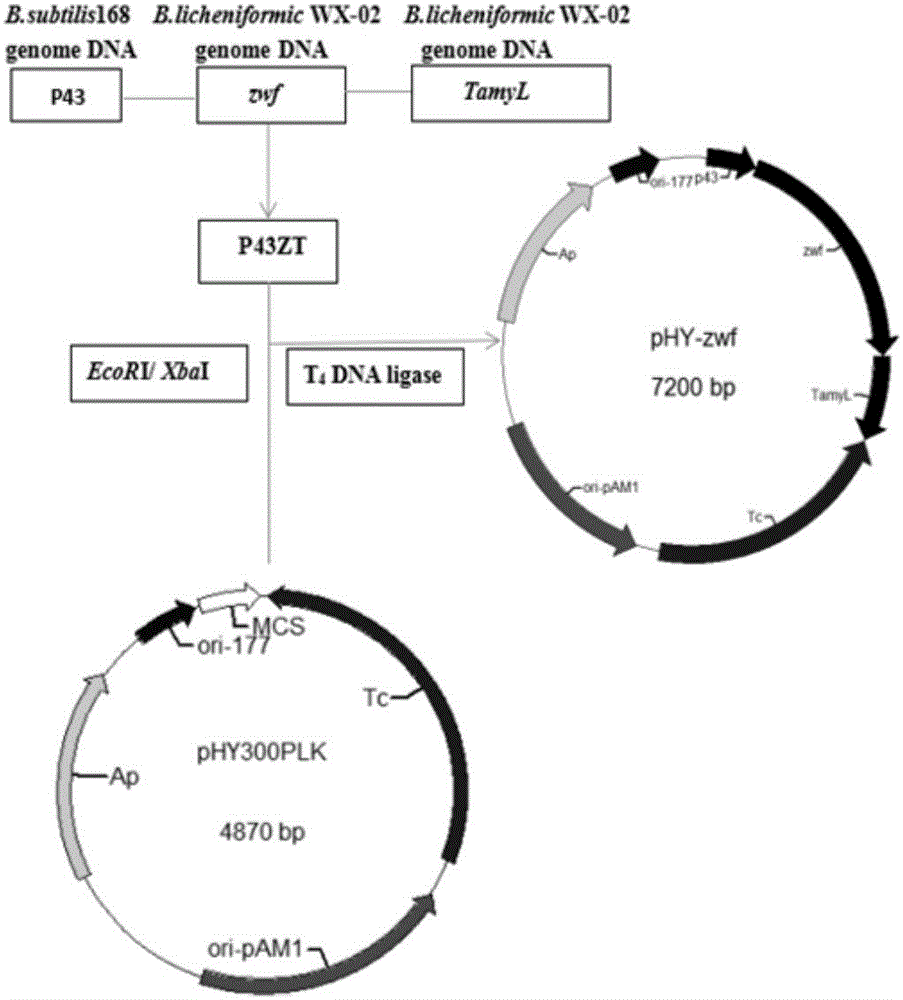
The invention provides a Bacillus licheniformis engineered bacterium capable of high production of poly-Gamma-glutamic acid, collected under CCTCC No: M2016439 and named as Bacillus licheniformis (WX-02) / pHY-zwf, and further provides a construction method of the Bacillus licheniformis (WX-02) / pHY-zwf and a method for high production of poly-Gamma-glutamic acid. The synthetic level of intracellular NADPH is increased through genetic engineering modification, and the yield of Gamma-PGA. By constructing glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase overexpression support pHY-zwf and converting to Gamma-PGA-producing Bacillus licheniformis WX-02 pre-stored in a lab, the Bacillus licheniformis (WX-02) / pHY-zwf capable of producing Gamma-PGA is re-constructed. The bacterium may provide significantly synthesis of Gamma-PGA under optimized media and culture conditions. The yield of Gamma-PGA is up to 51.13 g / L which is 49% significantly higher than the Gamma-PGA yield of an original bacterium.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Method for producing amino acids using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20090137010A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesDNA fragmentationA-DNA
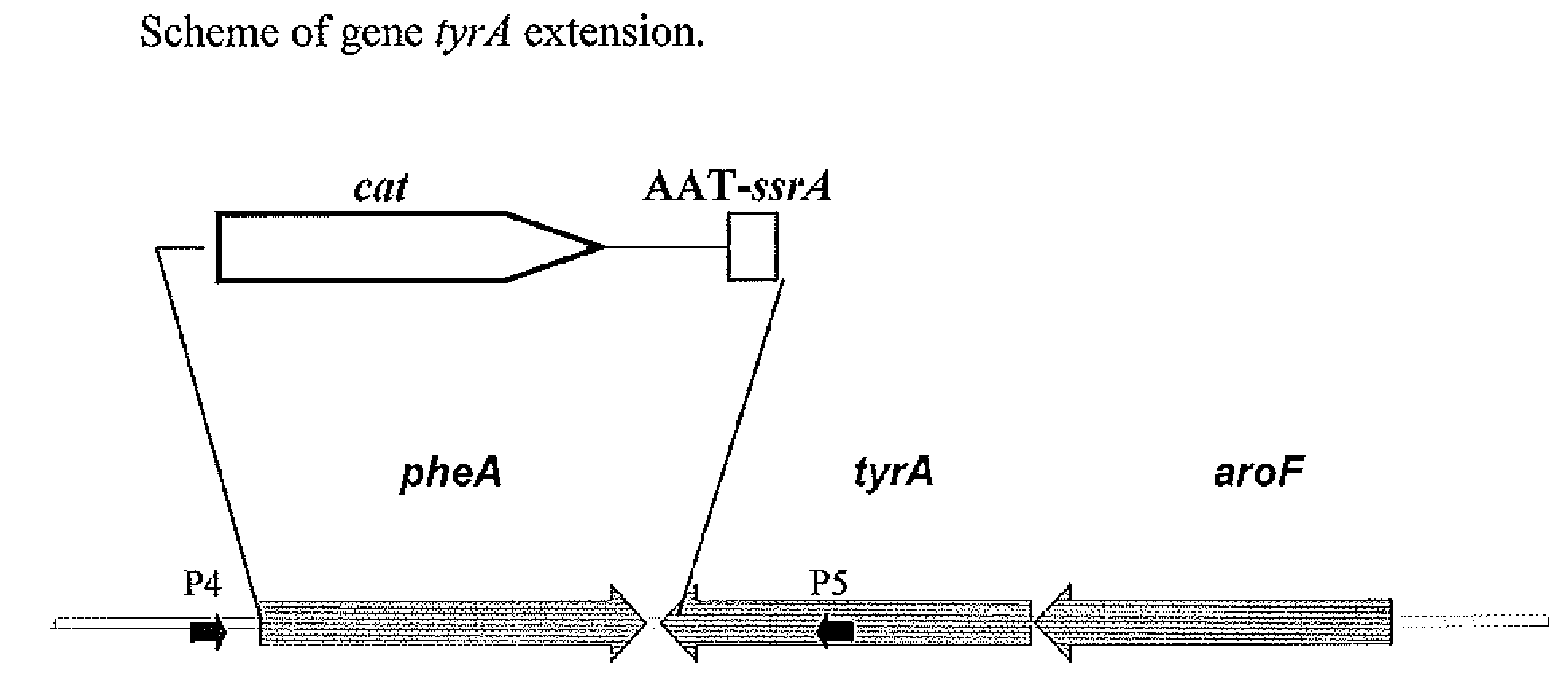
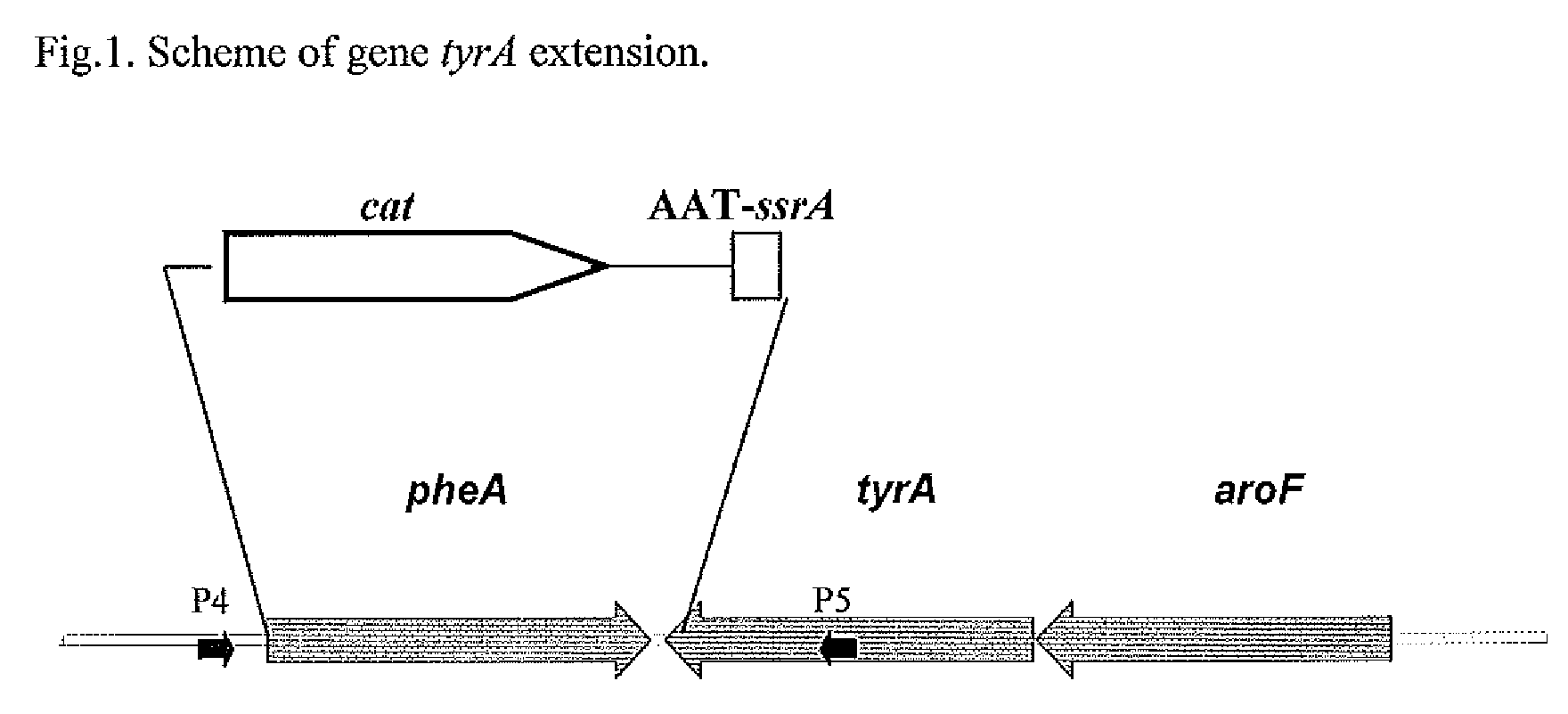
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example, L-phenylalanine and L-histidine, by fermentation using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified by attaching a DNA fragment able to be transcribed encoding the peptide represented in SEQ ID NO: 2, or a variant thereof, particularly a portion of the ssrA gene, to the 3′-end of gene encoding for the bacterial enzyme, which influences on the L-amino acid biosynthesis, such as chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydrogenase or phosphoglucose isomerase.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for improving transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase
The invention relates to a method for improving the transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase, belonging to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides the method for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol by recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 and 2-hydroxyacetophenone catalyzed by the recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 in multiple batches. In the invention, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and the Candida parapsilosis (S)-carbonyl reductase gene are simultaneously integrated into the Pichia pastoris genome, under the participation of 5% (w / v) glucose, the whole cells are reused for 10 batches, and the optical purity and yield of the (S)-phenyl glycol prepared by asymmetric transformation are maintained at 100% and higher than 85% all the time. The recombinant strain improves the batch stability of full cell transformation of the (S)-phenyl glycol by polygene coexpression, which well relieves the limit of coenzyme regenerative cycle in a biological transformation reaction; and simultaneously an efficient approach for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol industrially in multiple batches at low cost is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A novel glycosyltransferase derived from dolwoe and use thereof
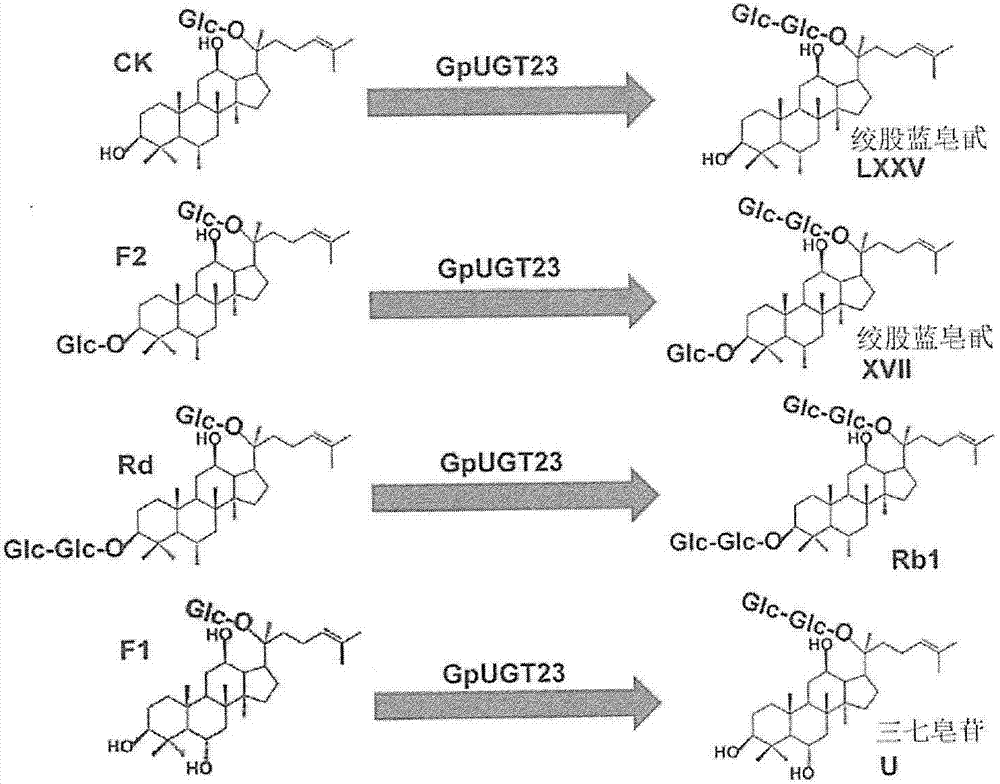
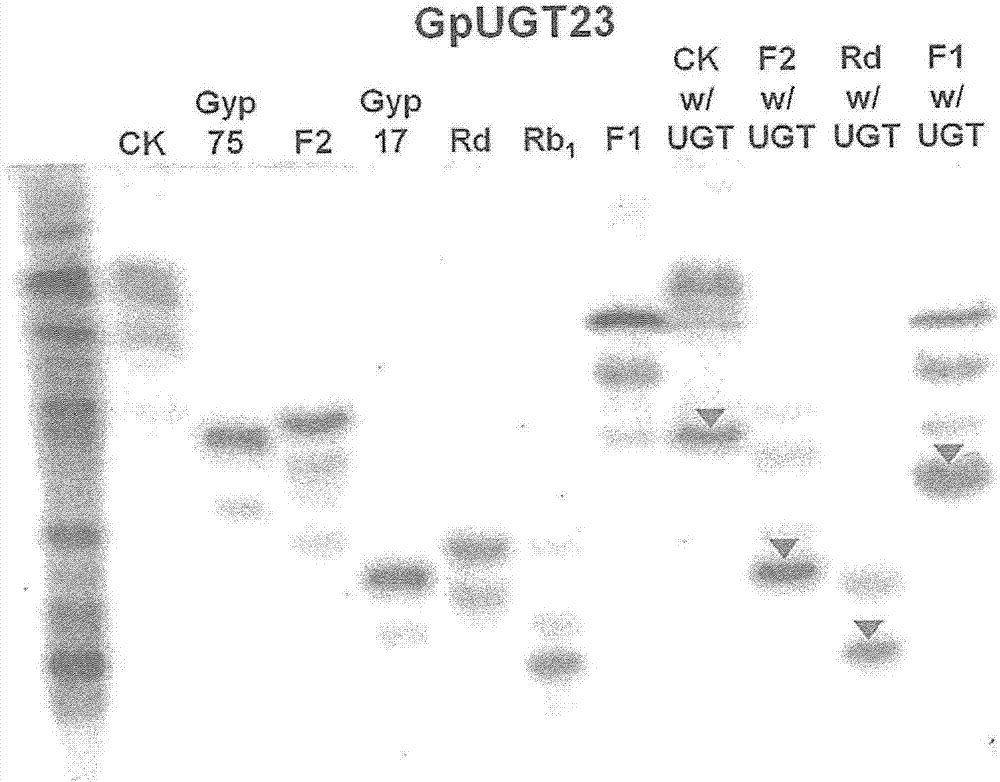
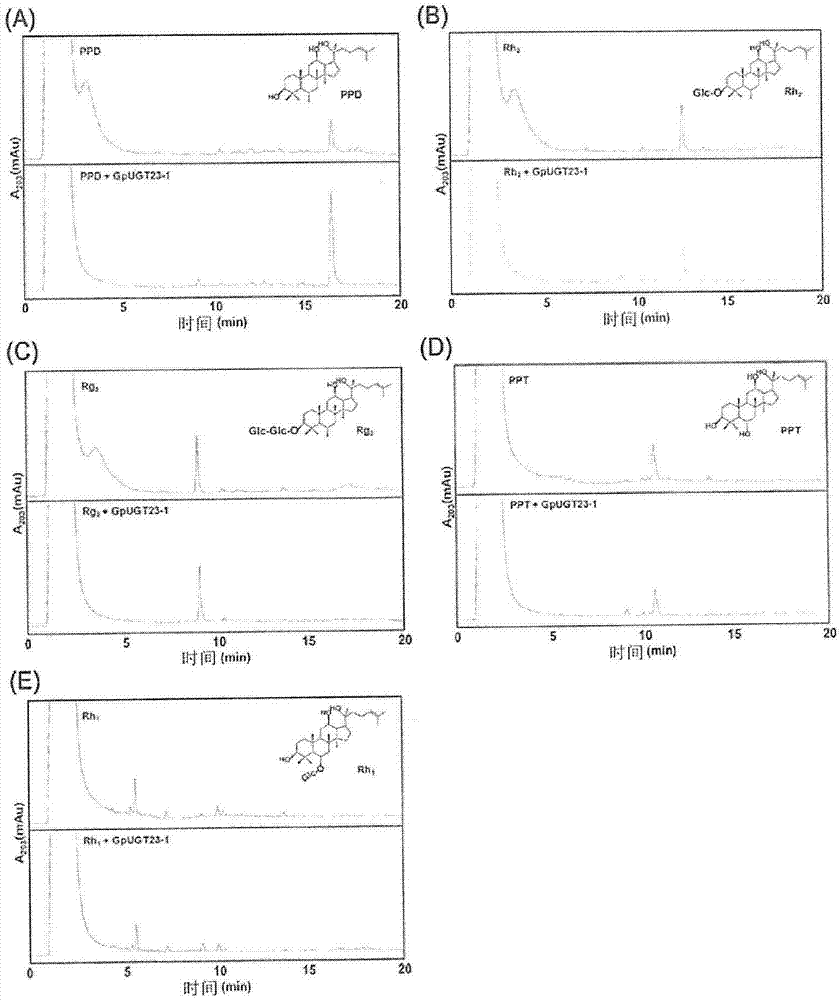
Provided are a novel UDP-glycosyltransferase (uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase) protein from Dolwoe (Gynostemma pentaphyllum) having glycosyltransfer activity for glucose linked by a glycosidic bond at the C-20 position of PPD (protopanaxadiol)-type or PPT (protopanaxatriol)-type ginsenoside, and use thereof.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
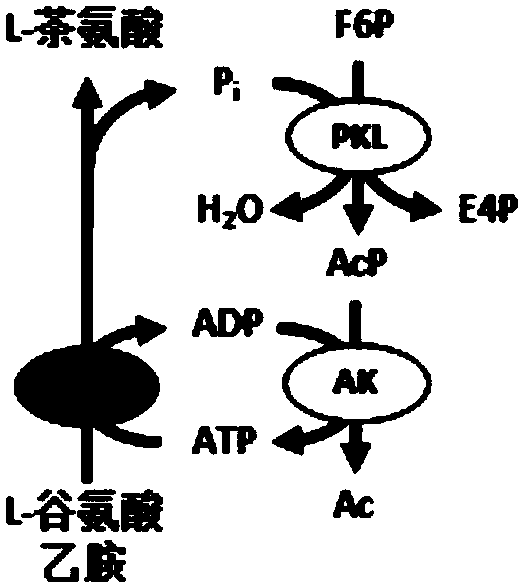
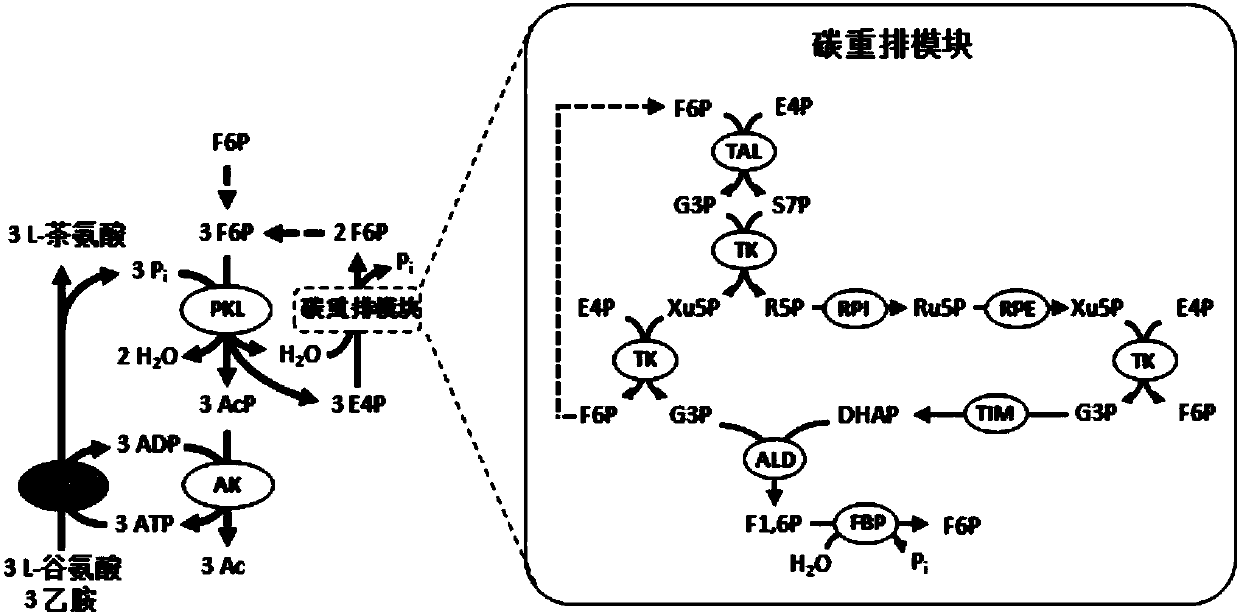
Chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application
The invention provides a chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application. The chassis system for ATP regeneration comprises the following five enzymes: alpha-glucan phosphorylase, glucophosphomutase, phosphoglucose Isomerase, phosphoketolase and acetokinase. In addition, the chassis system can further comprise the following seven enzymes: transaldolase, transketolase,ribose-5-phosphate isomerase, ribulose-3 epimerase, triosephosphate isomerase, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The chassis system can be coupled to an enzymic catalyticreaction needing ATP, utilizes starch or maltodextrin as energy, is not added with any coenzyme, can efficiently regenerate the ATP at low cost through a one-pot reaction and is an economical, highlyefficient, stable and sustainable ATP regeneration system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
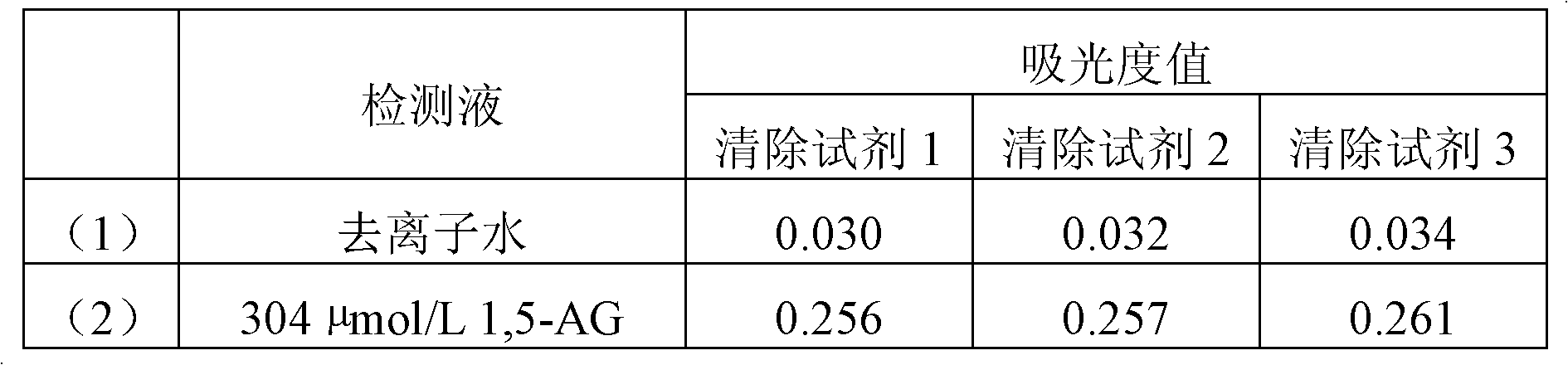
Method for determining glucose and 1,5-anhydroglucitol in identicial colorimetric cell
InactiveCN101071105AReduce testing costsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorylationPhosphate
This invention discloses a method to measure the same comparing color pool of glucose and 1,5-glucose alcohol dehydration. First, the buffer solution composed by 3-hydroxymethyl-methane and hydrochloric acid is used to deal with serum. Through the GK and glucose -6 -- phosphate dehydrogenase coupling system glucose can be completely converted in serum into the 6 - phosphorylation gluconic acid lactone which not responds to PROD, to remove the interference of endogenous glucose, and determine the absorption of light to detect glucose content. Then the concentration of 200 mmol / L N-2-hydroxyethyl piperazine N'-2 - ethane sulfonic acid solution is added, and the tested 1,5-dehydrated alcohol is oxide into 1,5 - dehydration fructose and H2O2. The new zoology oxygen that H2O2 releases will react with HRP, 4-AAP HTIB response system and after Trinders role color reaction (from colorless to red), colorimetric determinate of 1,5 - dehydration glucose alcohol content is detected. This invention measure in the same comparing color pool of glucose and 1,5 - alcohol dehydration glucose, is sensitive, accurate, stable, specific characteristics and can reduce the cost of testing, and provide a new method for the detection and treatment of diabetes monitoring.
Owner:冯景
Bacillus subtilis genetically-engineered bacteria for producing tagatose and method for preparing tagatose
ActiveCN112342179AEasy to manufactureGood for catalytic applicationsBacteriaHydrolasesTagatoseEngineered genetic
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis genetically-engineered bacteria for producing tagatose and a method for preparing the tagatose. The genetically-engineered bacteria are used for constructingheat-resistant alpha-glucan phosphorylase, heat-resistant phosphoglucomutase, heat-resistant glucose phosphate isomerase, heat-resistant 6-tagatose phosphate epimerase and heat-resistant 6-tagatose phosphate phosphatase which are independently expressed or co-expressed. By utilizing the genetically-engineered bacteria, starch can be effectively converted into the tagatose. Compared with the existing method for producing the tagatose, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of suitability for whole-cell recycling, high safety, high yield, simple production process, low cost, easiness in large-scale preparation and the like.
Owner:天工生物科技(天津)有限公司
Compositions and methods for the increased production of isoprene and other products with 6 - phosphogluconolactonase (PGL)
Provided herein are improved compositions and methods for the increased production of isoprene. Also provided herein are improved compositions and methods for the increased production of heterologous polypeptides capable of biological activity.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Method for preparing inositol through enzymic catalysis and inositol
InactiveCN105925643AImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processFermentationGlucose polymersD-Glucose
The invention relates to a method for preparing inositol through enzymic catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: performing enzyme-catalyzed conversion on a polysaccharide or an oligosaccharide which takes glucose as a unit to obtain glucose-1-phosphate; performing enzyme-catalyzed conversion on the glucose-1-phosphate to obtain glucose-6-phosphate; performing enzyme-catalyzed conversion on the glucose-6-phosphate to obtain inositol-1-phosphate; performing enzyme-catalyzed conversion on the inositol-1-phosphate to obtain inositol. The invention also provides an inositol product which is prepared according to the method. According to the method, the conversion efficiency of the inositol is effectively improved; moreover, a production process is simple, pollution-free, and low in production cost.
Owner:浙江欣诺医药有限公司
Preparation method of nano-micelles with mucous layer permeation and P-gp inhibition dual effects
ActiveCN106038485AChange particle sizeImprove permeabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryGluconic acid6-phosphogluconic acid
The invention discloses a preparation technology of nano-micelles for conveying anti-tumor medicines through oral administration, namely a preparation method of nano-micelles with mucous layer permeation and P-gp inhibition dual effects. Chitosan, quercetin and 6-phosphogluconic acid are used as raw materials to prepare an amphiphilic chitosan-quercetin succinate-6-phosphogluconic acid copolymer through a condensation and esterification method and a target product is synthesized through a self-assembling technology; the nano-micelles have a good mucous layer permeation capability and also has the P-gp inhibition effect; the oral administration conveying efficiency of the anti-tumor medicines can be effectively improved. The nano-micelles can be used for medical biological materials and medicine carriers and have good research and development application prospects.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Serum-free immune cell culture medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107574150AIncrease the proportion of positive phenotypesHigh positive rateBlood/immune system cellsCell phenotypeSalidroside
The invention discloses a serum-free immune cell culture medium. The serum-free immune cell culture medium is prepared mainly from amino acids, vitamins, minerals, D-glucose, 4-hydroxyethyl piperazinyl ethanesulfonic acid, insulin, phenol red, sodium pyruvate and transferrin. The invention discloses another serum-free immune cell culture medium which further comprises cofactors including salidroside, luteolin and resveratrol. The invention discloses another serum-free immune cell culture medium which further comprises activators including an acetyl coenzyme A, a coenzyme Q10, glucose 6-phosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. A part of embodiments of the invention can increase the positive ratio of cell phenotypes.
Owner:万向东方生物科技有限公司
High-concentration glucose removal method and kit for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on pyranose oxidase method
The invention discloses a high-concentration glucose removal method for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on a pyranose oxidase method, which comprises the following steps: preparing a 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid (MES) buffer solution having a pH value of 6.0-9.0, wherein the MES buffer solution contains a certain amount of glucokinase (GK), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), pyruvate kinase (PK), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP); and adding into a serum sample containing glucose (Glu), and reacting at 20-50 DEG C for 3-5 minutes, wherein the GK converts the Glu into glucose-6-phosphoric acid (G6P) in the presence of the ATP, and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is generated at the same time; the G6P is further converted into glucose-6-phosphate lactone (G6PL) by the G6PD in the presence of the NADP+; and the ADP generated in the reaction is converted into ATP again under the action of thePK in the presence of the PEP. The glucose removal agent prepared by the method can be stably stored at 2-8 DEG C for 14 months, and can be used for a clinical biochemical autoanalyzer extensively used at present.
Owner:浙江夸克生物科技有限公司
Recombinant vector over-expressing glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, and its application
InactiveCN104131025AReduce sizeEasy to cloneUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHomologous Sequences
The invention discloses a recombinant vector over-expressing a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, and its application. The recombinant vector comprises a screening labeled gene expression cassette and a target gene expression cassette; the screening labeled gene expression cassette comprises a resistance screening gene, the upstream of the resistance screening gene is fused with an Escherichia coli P1 promoter, and the downstream of the resistance screening gene is fused with an Escherichia coli ccdB terminator; and the target gene expression cassette comprises a Phaeodactylum tricornutum fcpC gene promoter, the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, a Phaeodactylum tricornutum fcpA gene terminator and an Omega leader sequence, and the Omega leader sequence is in the downstream of the Phaeodactylum tricornutum fcpC gene promoter. The recombinant vector is small, is suitable for converting, is easy to operate, is a homologous sequence of the Phaeodactylum tricornutum, and benefits for expression. The over-expression of the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene can substantially improve the content of lipids in micro-algal cells, and lays the foundation for the researches of biological energy.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
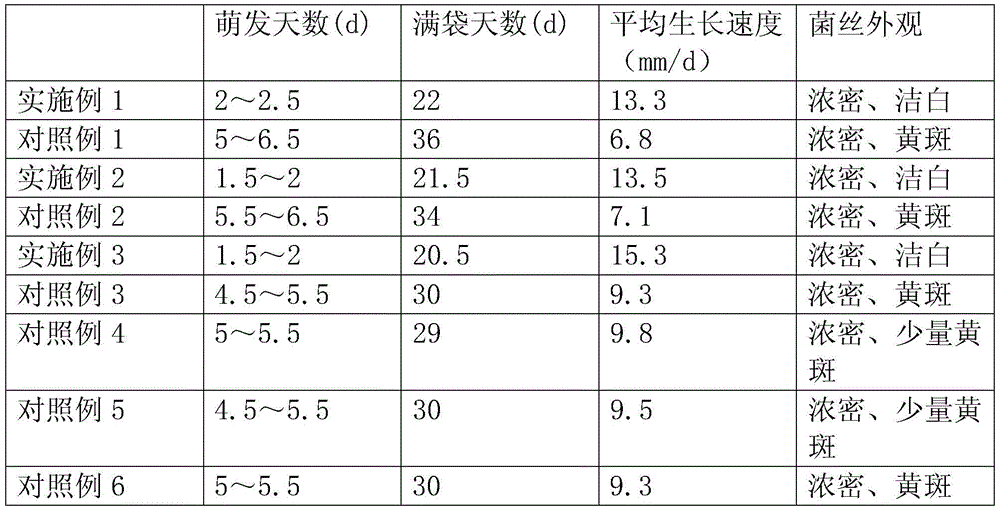
Lucid ganoderma cultivation method for promoting mycelial growth
InactiveCN105646067AHigh activityIncrease contentCultivating equipmentsOrganic fertilisersCulture fungusCulture mediums
The invention provides a lucid ganoderma cultivation method for promoting mycelial growth. The lucid ganoderma cultivation method comprises strain culture, culture medium preparation, mycelium culture and ganoderma lucidum growth management, wherein the culture medium preparation comprises mixing, smashing, bagging and sterilizing the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 to 35 parts of weed tree sawdust, 10 to 20 parts of corncobs, 5 to 10 parts of rice bran, 1 to 3 parts of burdock, 2 to 4 parts of grifola frondosa and 0.5 to 1.5 parts of milk sugar. According to the lucid ganoderma cultivation method, the grifola frondosa, burdock and milk sugar are added into a conventional culture medium, the activity of alpha-glucophosphomutase can be improved, and branch migration of lucid ganoderma cell metabolism to ganoderan synthesis preferably is promoted, so that the content of ganoderma exopolysaccharides is greatly increased; meanwhile, the growth of lucid ganoderma can be promoted, and the hypha bagful time is greatly shortened.
Owner:GUILIN DA YE LING YVU BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for measuring 1,5-anhydroglucitol by oxidase
InactiveCN103725749AEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphoric acidGlucose polymers
The invention relates to a method for measuring 1,5-anhydroglucitol by oxidase, which can be widely applied in the field of medical and biochemical technologies. The method comprises the following steps of: converting glucose (Glu) in a sample into fructose-6-phosphate (Fru-6-P) by glucokinase (GK) and phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI), and establishing an ATP regeneration system by pyruvate kanise (PK) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in the system so as to ensure that Glu is converted into Fru-6-P. In the sample, 1,5-AG reacts in the presence of pyranose oxidase (PROD) to produce 1,5-fructosan (1,5-AF) and H2O2, and then H2O2 is colored and quantified via a Trinder's system..
Owner:WENZHOU PEOPLES HOSPITAL
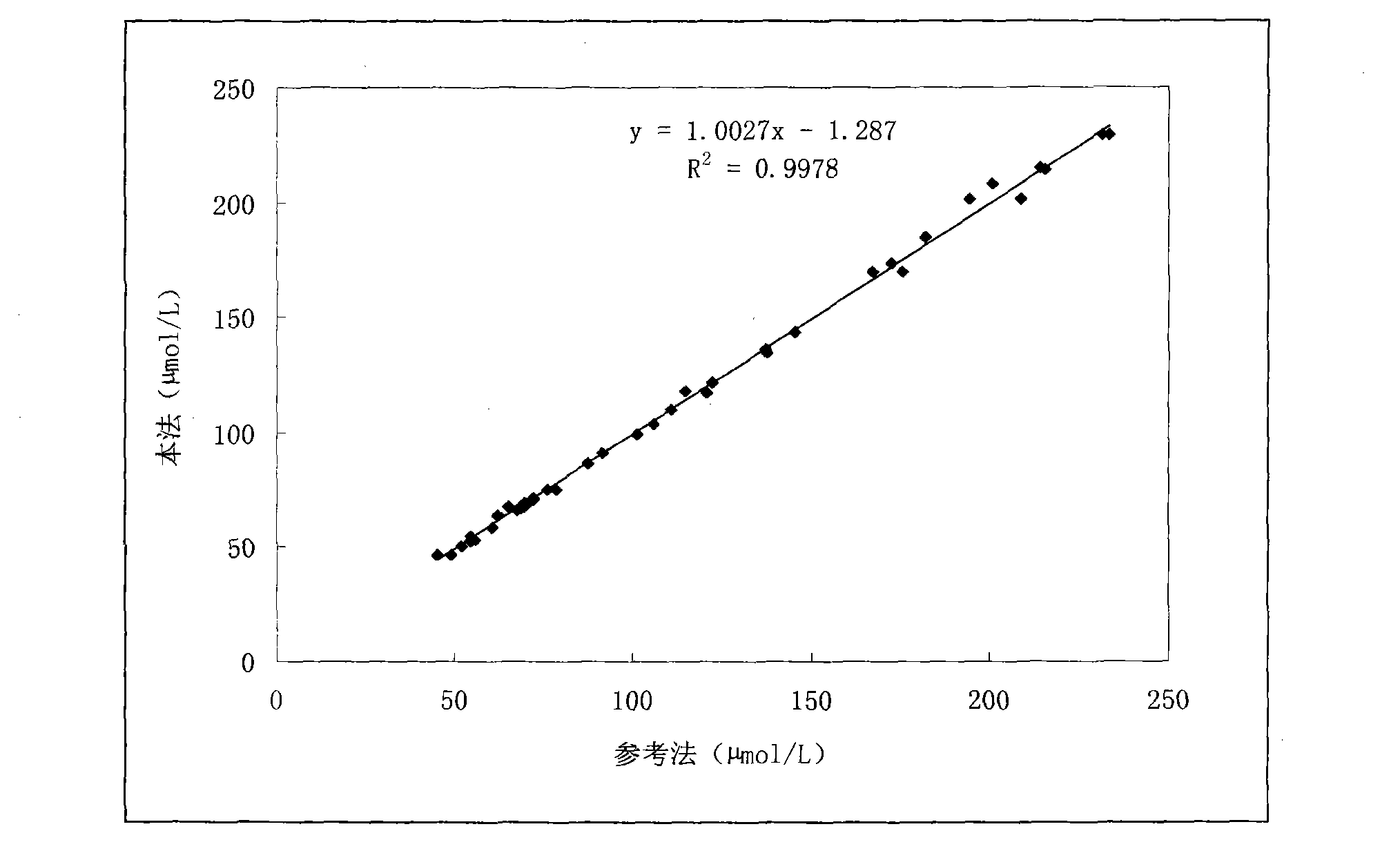
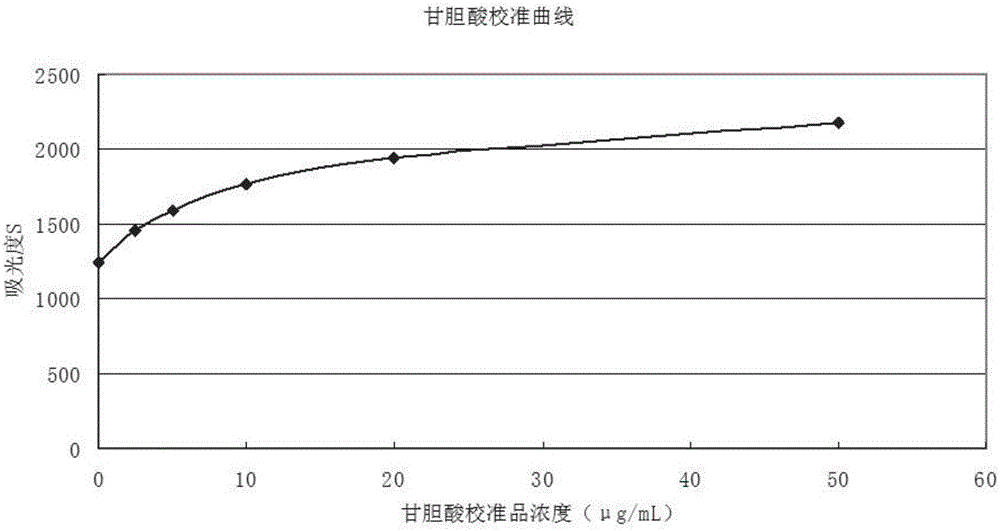
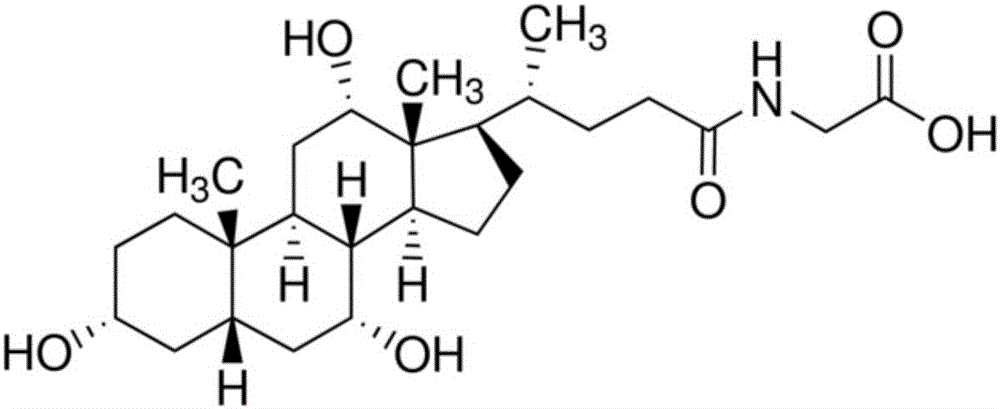
Preparation method for homogeneous enzyme immunodiagnosis reagent used for glycocholic acid
InactiveCN106405069AEasy to operateReliable responseColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological activationGlucose phosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method for a homogeneous enzyme immunodiagnosis reagent used for glycocholic acid, belonging to the technical field of biological medicine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparation of a glycocholic acid antibody solution; preparation of a glycocholic acid-enzyme conjugate solution; and preparation of a glycocholic acid calibrating substance. The glycocholic acid-enzyme conjugate solution is prepared by adding glycocholic acid into a MES buffer solution, adding a carboxyl activator for carboxyl activation, then adding 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase for a condensation reaction so as to obtain a crude glycocholic acid-enzyme conjugate product, carrying out dialysis and purification, adding the treated crude glycocholic acid-enzyme conjugate product into a Tris-HCl buffer solution, adding an auxiliary reagent and carrying out uniform mixing so as to obtain the glycocholic acid-enzyme conjugate solution. The homogeneous enzyme immunodiagnosis reagent for glycocholic acid prepared by using the method is safe, rapid, highly efficient and sensitive and can accurately detect the content of glycocholic acid in a to-be-detected sample.
Owner:李松羊
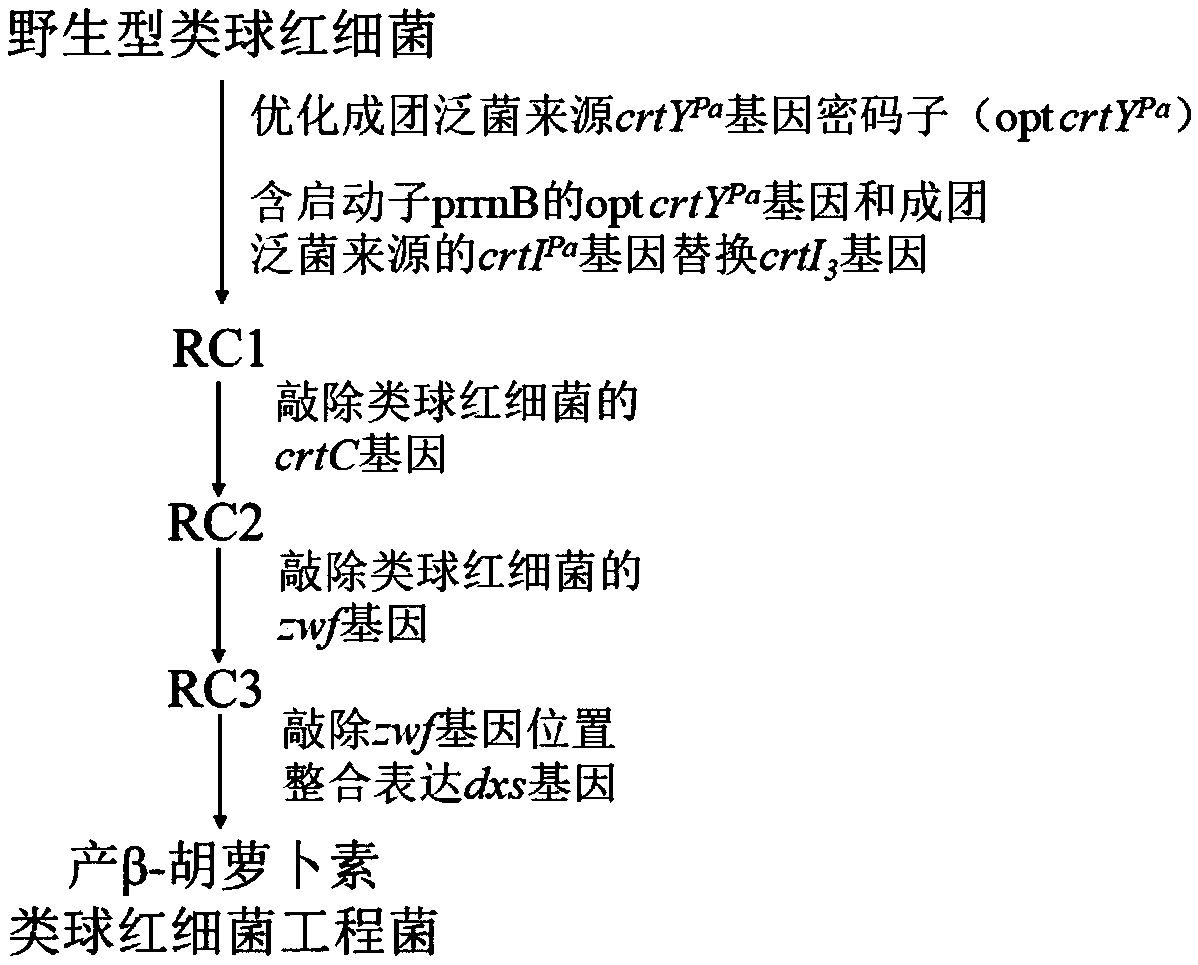
Rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and a construction method thereof. The method includes first optimizing a codon of a lycopene cyclase gene crtYPa derived from pantoea agglomerans to obtain an opt crtYPa gene, then replacing an endogenous phytoene three-step dehydrogenase gene crtI3 of rhodobacter sphaeroides with the opt crtYPa genecontaining a promoter prrnB and a phytoene four-step dehydrogenase gene crtIPa gene derived from the pantoea agglomerans in a traceless mode, then knocking out an endogenous neurosporene hydroxylase gene crtC of the rhodobacter sphaeroides and a 6-phosphoglucose dehydrogenase gene zwf and finally knocking out an endogenous 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene dxs of the rhodobacter sphaeroides with integration expression at zwf position to obtain the rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing the beta-carotene. The strain is cultured by fermentation, and the content of the beta-carotene can reach 30mg / g DCW.
Owner:SHAANXI HEALTHFUL BIOLOGICAL ENG
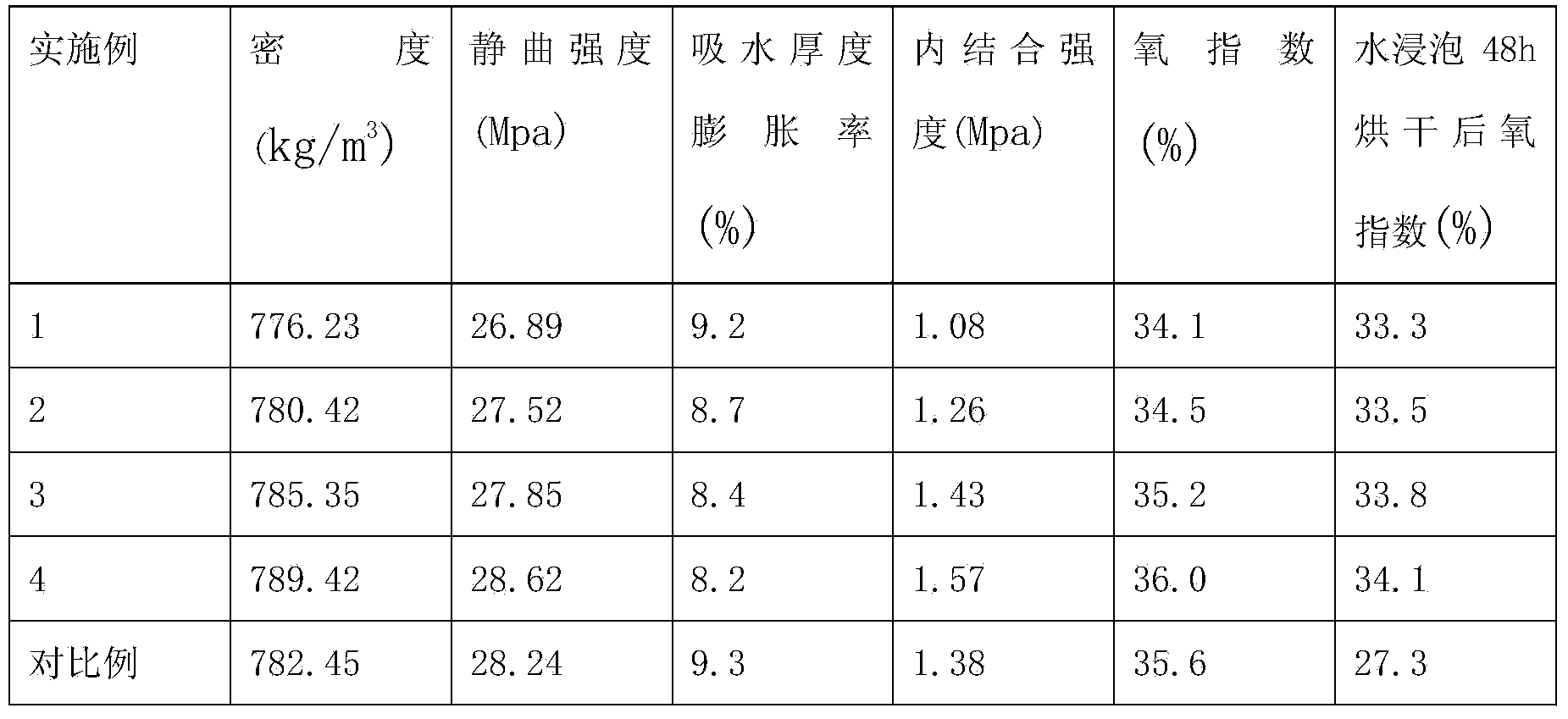
Flame-retardant wood adhesive as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103772640ANo pollution in the processImprove flame retardant performanceAdhesiveComposite lumber
The invention discloses a flame-retardant wood adhesive as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The flame-retardant wood adhesive is characterized by being prepared by the steps of adding 85-100 parts of water to a reactor, heating to 85-95 DEG C, adding 16-20 parts of polyvinyl alcohol while stirring so as to dissolve the polyvinyl alcohol, slowly adding 12-18 parts of a phosphogluconate melamine mixed salt flame retardant, and cooling to room temperature to obtain the flame-retardant wood adhesive, wherein diphenylmethane diisocyanate or polymethylene polyphenylene isocyanate is taken as a curing agent, and the adhesive and the curing agent are respectively packaged in storage. When the adhesive is used, 35-45 parts of the isocyanate curing agent is added to 100 parts of the adhesive. And an application method of the flame-retardant wood adhesive comprises the steps of mixing 18-25 parts of the flame-retardant wood adhesive and 6.3-11.25 parts of the isocyanate curing agent in a stirrer, adding 75-84 parts of wood meal, continuing to uniformly stir, injecting materials to a mold, placing the mold into a hot press, and hot-pressing for 20-25 minutes at 75-100 DEG C under 10-15MPa, thus obtaining flame-retardant composite wood.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Tagatose-producing bacillus subtilis genetic engineering bacteria and method for preparing tagatose
ActiveCN112342179BEasy to manufactureGood for catalytic applicationsBacteriaHydrolasesTagatoseEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a tagatose-producing Bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium and a method for preparing tagatose. The genetically engineered bacterium comprises constructing a single-expression or co-expression thermostable α-glucan phosphorylase, thermostable glucose phosphate Mutase, thermostable glucose phosphate isomerase, thermostable 6‑phosphate tagatose epimerase, and thermostable 6‑phosphate tagatose phosphatase. Starch can be effectively converted into tagatose by using the genetically engineered bacteria. Compared with the existing methods for producing tagatose, the method of the present invention has the advantages of being suitable for whole cell recycling, high safety performance, high yield, simple production process, low cost and easy large-scale preparation.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
Coenzyme II NADP+ or NADPH content testing kit and its method
InactiveCN107782684AEfficient determinationEffective contentColor/spectral properties measurementsHydrogenDistilled water
The invention discloses a coenzyme II NADP+ or NADPH content testing kit and its method. The kit comprises acid extractive fluid, alkali extractive fluid, mixed solution of HEPES and EDTA, glucose 6-phosphate, PMS, MTT, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase solution, NaCl solution and mixed solution of ethanol and double distilled water. The method includes steps of extracting NADP+ and NADPH in a sample by acid and alkali extracting fluids on the basis of a spectrophotometric method; performing PMS hydrogen delivering action on NADPH, and reducing MTT to be formazan; detecting light absorption value under 570 nm, and testing the NADPH content; reducing the NADP+ to be NADPH by glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, thereby detecting the NADP+ content. The kit and its testing method can effectively test the content of the coenzyme II NADP+ or NADPH, and are featured by high specifity, wide application range, high stability, and others.
Owner:SUZHOU COMIN BIOTECH
Gracilaria chouae uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGPase) gene
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering technology, and particularly relates to a gracilaria chouae uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGPase) gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene and the amino acid sequence of the coding protein are SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 respectively. According to the invention, the gene sequence is cloned through the gene cloning technology, and a prokaryotic expression vector is established; and enzyme activity detection on recombinant protein proves that the gene has the function of catalyzing UDP-glucose and pyrophosphoric acid to form glucose-1-phosphoric acid and UTP and belongs to a key enzyme coding gene of the synthesis path of agar-agar, starch, cellulose, trehalose, sucrose and the like. The gene has an important application value in increasing the content of economic components including algae agar-agar, starch, cellulose, trehalose, sucrose and the like.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com