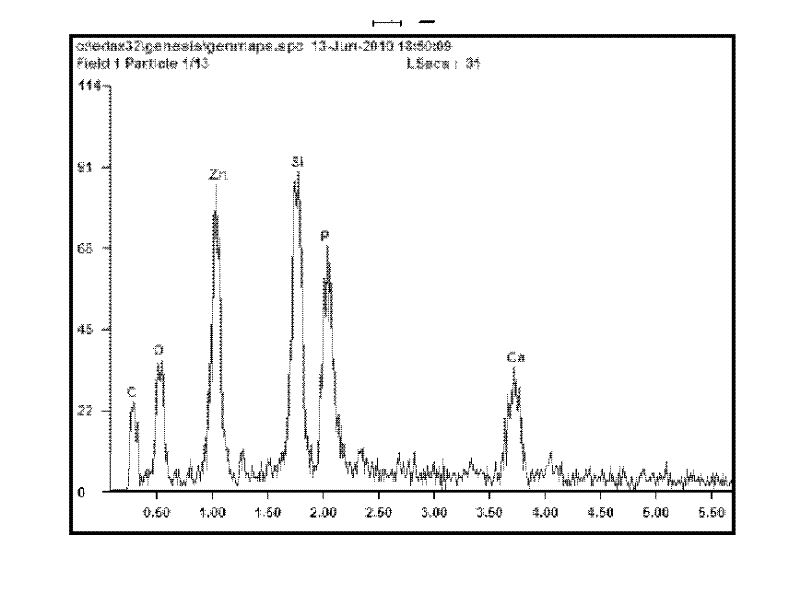
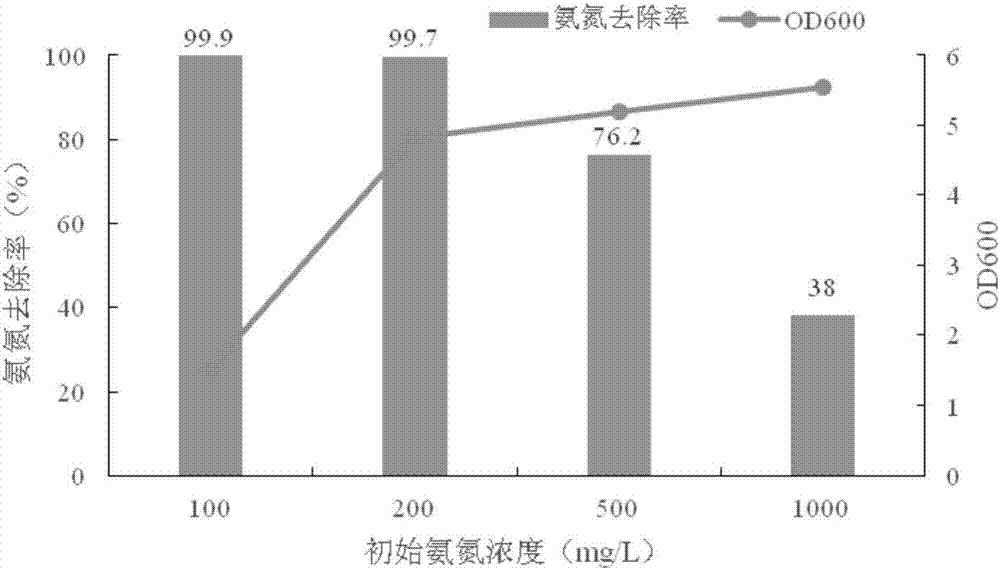
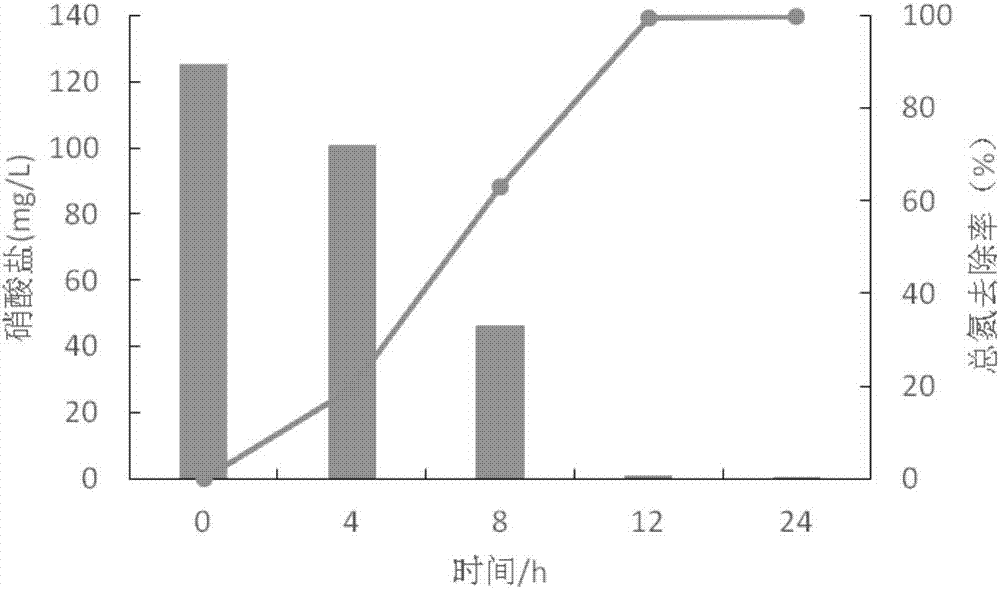
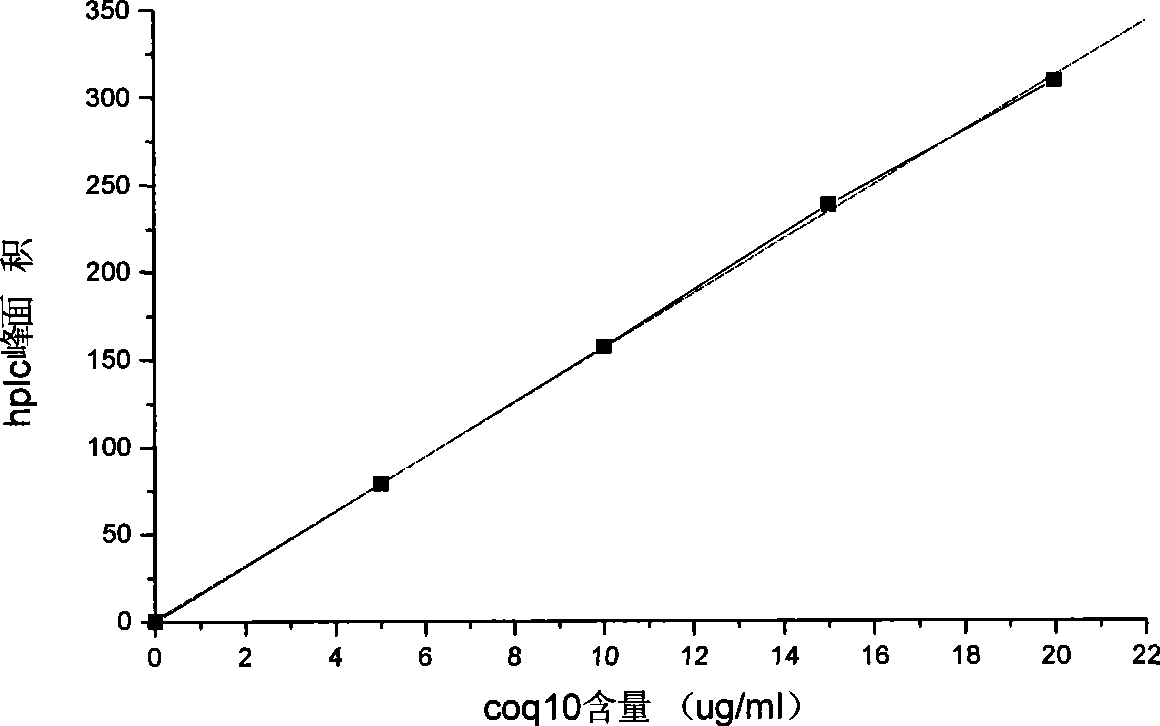
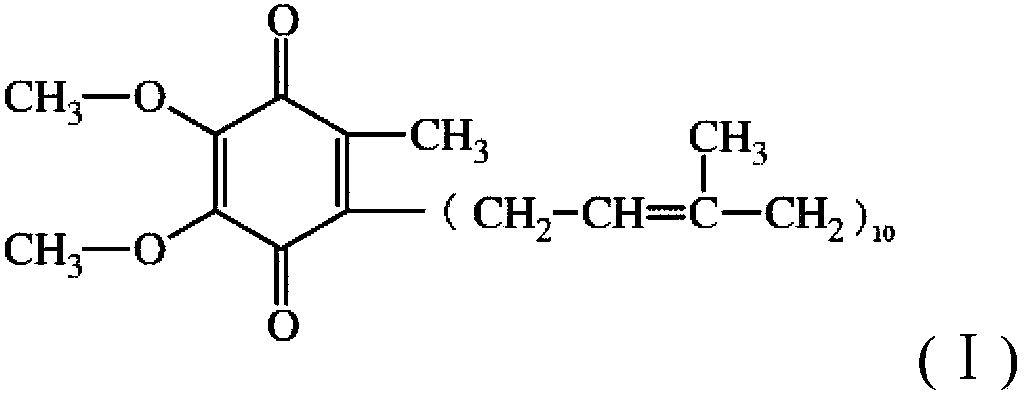
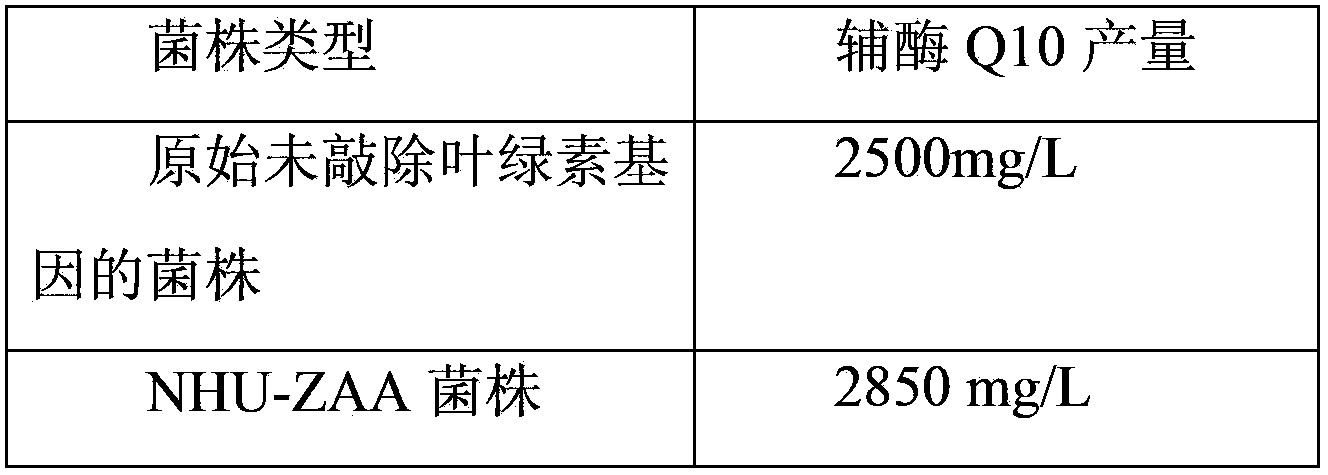
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
150 results about "Rhodobacter sphaeroides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhodobacter sphaeroides is a kind of purple bacterium; a group of bacteria that can obtain energy through photosynthesis. Its best growth conditions are anaerobic phototrophy (photoheterotrophic and photoautotrophic) and aerobic chemoheterotrophy in the absence of light. R. sphaeroides is also able to fix nitrogen. It is remarkably metabolically diverse, as it is able to grow heterotrophically via fermentation and aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Method for repairing microorganisms in heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN102240670AEasy to shapeReduce accumulationContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismRhodobacter
The invention provides a method for repairing microorganisms in heavy metal contaminated soil, specifically comprising the following steps of: step 1, separating rhodobacter sphaeroides; step 2, culturing the rhodobacter sphaeroides; and step 3, using the rhodobacter sphaeroides to repair the heavy metal contaminated soil. By means of the method for repairing the microorganisms in the heavy metalcontaminated soil provided by the invention, the existence shapes of heavy metals in the soil can be improved effectively; and the plant accumulations of the heavy metals are greatly reduced. The method for repairing the microorganisms in the heavy metal contaminated soil disclosed by the invention belongs to in-situ repairing and has the advantages of simple operation, low cost and good repairing effect. Furthermore, the soil fertility is not damaged; and the secondary contamination of the environment does not exist.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Composite microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106906170AReduce phosphorus concentrationGrowth inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite microbial agent includes a pseudomonas preparation, an acinetobacter preparation, a bacillus amyloliquefaciens preparation, a bacillus subtillis preparation, a bacillus licheniformis preparation, a pediococcus acidilactici preparation, a rhodobacter sphaeroides preparation, an alkali-lake dietzia preparation and a rhodopseudomonas palustris preparation. The preparation method includes the following steps that 1, composite microbial agent components are prepared; 2, the composite microbial agent components are mixed in proportion to obtain the composite microbial agent. The composite microbial agent can simultaneously decompose different organic matter, degrade amino nitrogen and nitro nitrogen in water, reduce phosphorus concentration in the water body and inhibit the growth of algae. The composite microbial agent is used for urban-rural sewage in-situ remediation, has the advantages of being high in efficiency, quick to take effect, free of no secondary pollution, simple in operation and the like, and large-scale application and popularization are facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNTIME ENVIRONMENTAL REMEDIATION
Method for extracting coenzyme Q10 from microorganism
ActiveCN101381747AEasy to operateEasy extractionOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for extracting coenzyme Q10 from microorganisms, wherein the ultrasonic disintegration is to mix microorganisms with the ability of producing the coenzyme Q10 and an organic solvent in which the coenzyme Q10 is well dissolved according to the mass volume ratio of 1-5 to 10-20, and to obtain the coenzyme Q10 after ultrasonication at a temperature of 0 DEG C, wherein the ultrasonic frequency is between 0.2 and 0.8 and the power is between 300 and 500 watts; and the alkaline splitting method is to extract the coenzyme Q10 from fermentation broth of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. The microorganisms are preferred to be microorganisms of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides. The method for extracting the coenzyme Q10 has the advantages of high efficiency, low pollution, low requirements on apparatuses and equipment, low cost and so on, and is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Construction method of engineering bacterium for producing coenzyme Q10, engineering bacterium and application of engineering bacterium
ActiveCN103509729AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention relates to the biotechnical field, and discloses a construction method of an engineering bacterium for producing coenzyme Q10, the engineering bacterium and an application of the engineering bacterium. The bacterium has a Latin scientific name of Rhodobacter sphaeroides, is named as an NHU-ZDD strain, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 13, 2012, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.5998. The invention provides a method for improving the output of the coenzyme Q10 by modifying EMP pathway related metabolism pathways. The method can improve the synthesis capability of the coenzyme Q10 by about 30%, and is suitable for the large-scale industrialized production of the coenzyme Q10.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
Biological agent capable of repairing heavy metal contaminated soil and soil remediation method
InactiveCN103114039AAdaptableChange metabolismBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEndurance capacityOperability
The invention discloses a biological agent capable of repairing heavy metal contaminated soil. The biological agent comprises rhodopseudomonas palustris ATCC17001 strain, N strain and NO.37 strain of rhodopseudomonas in photosynthetic bacteria and rhodobacter sphaeroides ATCC17023 strain, T2 strain and NO.55 strain of rhodobacter. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the biological agent capable of repairing the heavy metal contaminated soil, wherein the production process is a process for amplification culture of microorganisms step by step. The biological agent has the beneficial effects that the endurance capacity of functional microorganisms to heavy metals is high, and the functional microorganisms still maintain the activity and efficiently repair the heavy metal seriously contaminated soil; the biological agent not only can adsorb and accumulate the heavy metals and can convert the forms of the heavy metals, so that the heavy metals are changed into a stable state from a water soluble state which is big in environment hazards; and the biological agent is simple in preparation, wide in application range, low in treatment cost, short in treatment time, complete in treatment and strong in operability, and can be popularized and applied in a wide range.
Owner:广州天壤生物科技有限公司
Strain and method for preparing D-allulose by microbial transformation of D-levulose
ActiveCN101177672AImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial transformationFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a strain for producing D-piscose by using microorganism to transform D-fructose and a preparation method thereof, pertaining to food biotechnology field. The invention relates to a strain of spherical Rhodobacter sphaeroides SK011 screened from bottom mud of a fish-pond with the preservation number, CCTCC NO: M 207185, and the preparation method that the spherical Rhodobacter sphaeroides SK011 is used for transforming the D-fructose and producing the D-piscose through culture and fermentation. The invention adopts the SK011 as the strain and a fermentation culture medium which consists of carbon and nitrogen sources, inducer and inorganic salt; the obtained strain is further treated, so as to obtain cell biocatalyst; then by using the D-fructose as a substrate to do bio-transformation, the D-piscose is prepared. Under optimum conditions during the fermentation culture, fermenting solution or free cells or permeability cells or frozen dry powder or solidified cells thereof are used for transforming the D-fructose for 0.5 to 4.8 hours, and the content of the D-piscose in the transformation solution is 2 to 50g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
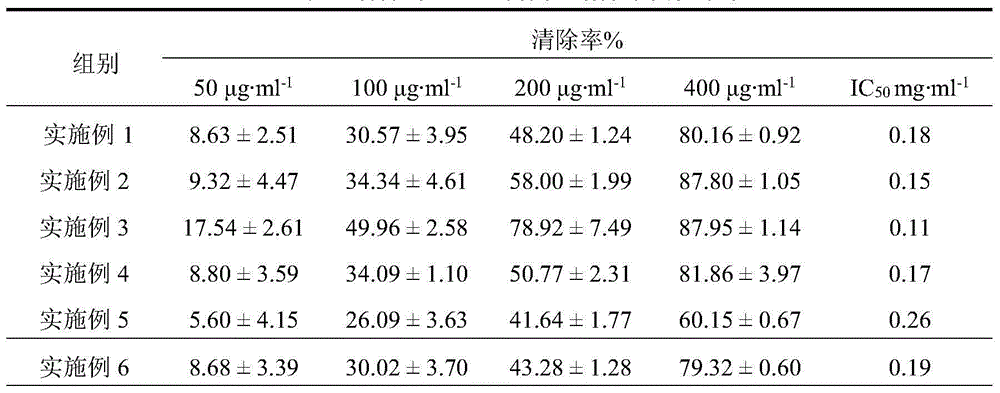
Method for quickly producing carotenoid by utilizing microaerobic fermentation of rhodobacter sphaeroides
ActiveCN104805168AIncrease production capacityShort fermentation timeMicroorganism based processesFermentationDPPHFermentation
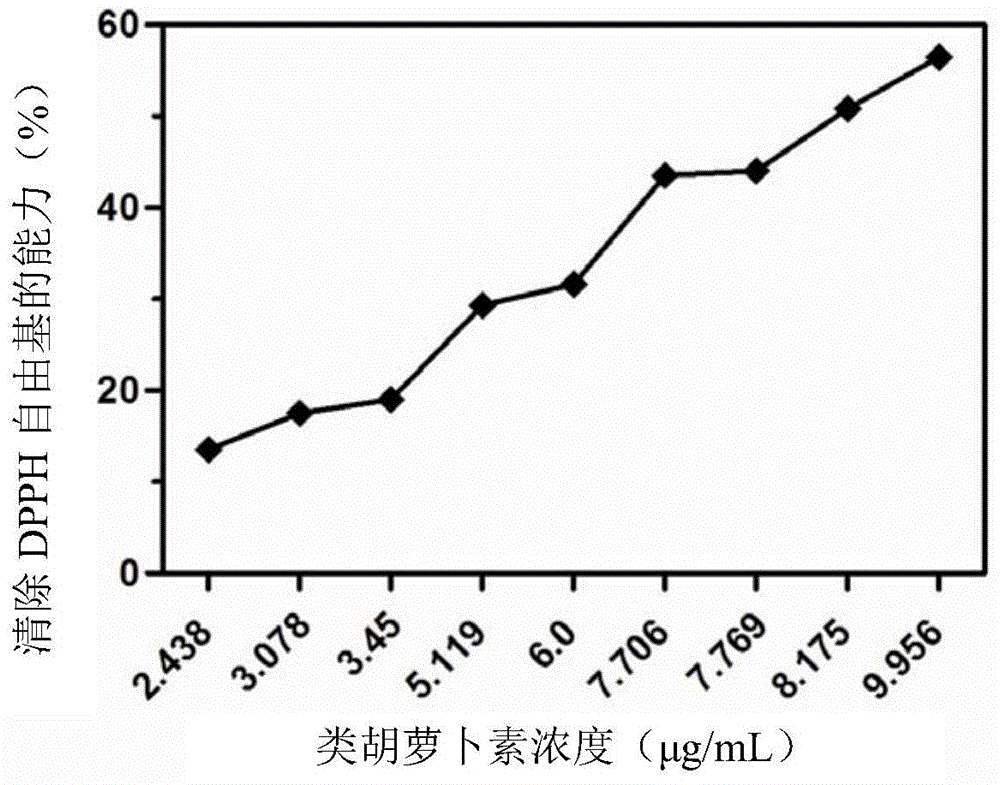
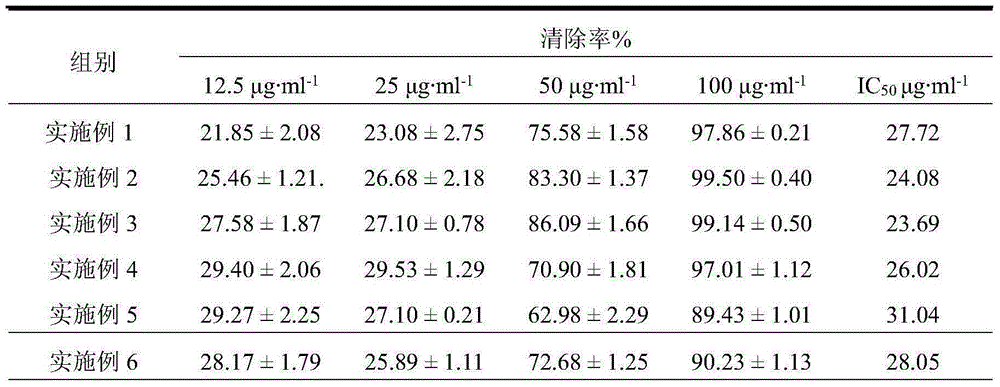
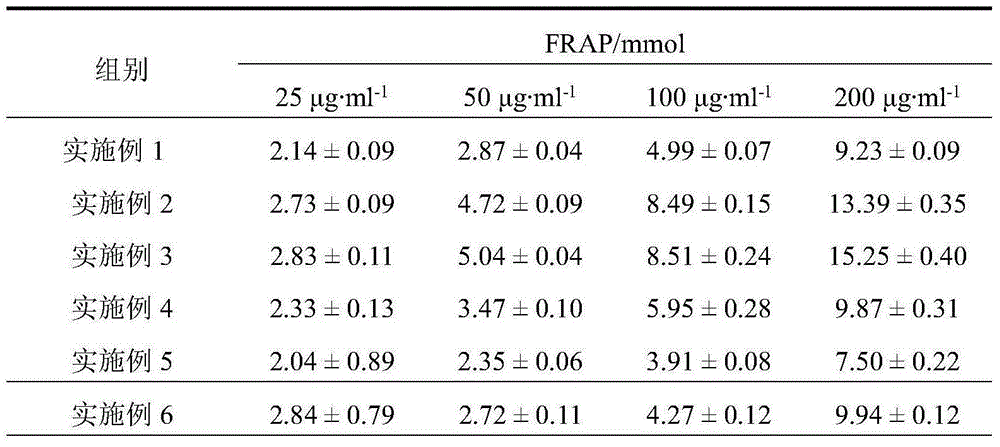
The invention discloses a method for quickly producing carotenoid by utilizing microaerobic fermentation of rhodobacter sphaeroides. The method comprises the following particular steps that the activated rhodobacter sphaeroides is inoculated to an MMS (methylmercuric sulfate) culture medium; aerobic culture is performed until OD600 (optical density 600) is 0.6-0.8; a culture condition is adjusted to be microaerobic; the carotenoid is induced to be quickly and greatly synthesized; and then extraction and purification are performed. The time for producing the carotenoid by the method is short and only 36h; the yield of thallus is up to 6g / L; the yield and the productivity of the carotenoid are 8.287mg / L and 1911mug / g respectively; the carotenoid has good capacity for removing DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl) radicals; and IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) is about 8mug / mL.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Production method of agricultural photosynthetic bacteria preparation
ActiveCN101597579AQuality assuranceGuaranteed quantityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsCulture fluidBottle
The invention relates to a production method of an agricultural photosynthetic bacteria preparation, adopting the following steps: 1. strain amplification culture: adjusting the pH value of a strain amplification medium from 6.0 to 8.5; placing the medium into a glass bottle and carrying out heat disinfection; inoculating a mixed culture of two photosynthetic bacteria including Rhodopeudomonas palustris and Rhodobacter sphaeroides based on 5-40% of the volume of a strain medium; anaerobically culturing the mixed culture for 3-4 days under the conditions that the temperature is 15-35 DEG C and the illumination intensity is 1000-3000lux, thus obtaining strain culture fluid; 2. fermentation production: placing a fermentation medium into a fermentation cylinder and carrying out heat disinfection; inoculating the strain culture fluid based on the inoculation amount, namely 5-40% of the volume of the fermentation production medium; the strain culture fluid is fermented for 6 days to obtain the agricultural photosynthetic bacteria preparation under the conditions that the temperature is 28-30 DEG C, the stirring rate is 150-300r / m, the cylinder pressure is kept between 0.02MPa and 0.05MPa and the illumination intensity is 2000-3000lux. Compared with the prior art, the preparation has the advantages of stable product quality and diversified functions.
Owner:SHUNDE HONGLONG BIOLOGY SCI & TECH
Method for producing rhodobacter sphaeroides microbial fertilizer from citric acid waste water
InactiveCN102180710AHigh cost savingsReduce manufacturing costClimate change adaptationSewage/sludge fertilisersBacteroidesSodium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for producing a rhodobacter sphaeroides microbial fertilizer from citric acid waste water, and belongs to the microorganism field. The method comprises the following steps: a. diluting citric acid waste water with clear water till the COD concentration is 12000-15000 mg / L, adjusting the pH to 6.5-7.5 with a sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, sterilizing the solution at 115-126 DEG C for 10-35 min; b. inoculating rhodobacter sphaeroides preserved by a slant into an erlenmeyer flask containing the citric acid waste water, performing shaking culture at 30-37 DEG C under 120-200 rpm for 24-48 hours to obtain liquid seeds; c. inoculating the liquid seeds into a fermentor containing the citric acid waste water with a volume ratio of 2%-20%, culturing the seeds in sterile air at 25-37 DEG C for 12-48 hours to obtain fermentation broth; d. determining the cultured fermentation broth by a spectrophotometer, packaging the broth when the OD660 value is 1.0-1.5 orthe bacterial count reaches 109-1010 CFU / ml so as to obtain a finished product. Compared with the prior art, the invention produces a microbial fertilizer from citric acid waste water, and has the characteristics of low production cost, energy saving and environmental protection, good product application effect, etc.
Owner:无锡中科活力生物技术有限公司
Coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and application thereof
ActiveCN103509816AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps that: a, total genomic DNA is extracted from Rhodobacter sphaeroides cacterial liquid; b, UbiG gene is obtained by amplification with a polymerase chain reaction; c, the amplified UbiG gene is connected with broad-host plasmid, such that recombinant vector is constructed; d, the recombinant vector is transferred to Escherichia coli S17-1; and e, the Escherichia coli S17-1 is subjected to conjugal transfer with the Rhodobacter sphaeroides, such that the engineered bacteria are obtained. According to the method provided by the invention for improving coenzyme Q10 yield through regulating Rhodobacter sphaeroides aromatic ring modification pathway, the operation is simple, and coenzyme Q10 synthesis capacity can be improved by higher than 30%. The method is suitable for coenzyme Q10 large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
Coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and application thereof
ActiveCN103509728ALarge amount of synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGenomic DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps that: a, total genomic DNA is extracted from Rhodobacter sphaeroides cacterial liquid; b, bchG homologous gene is obtained by amplification with a polymerase chain reaction; c, the amplified homologous gene is connected with broad-host plasmid, such that recombinant vector is constructed; d, the recombinant vector is transferred to Escherichia coli S17-1; and e, the Escherichia coli S17-1 is subjected to conjugal transfer with the Rhodobacter sphaeroides, such that the engineered bacteria with chlorophyll synthesis gene bchG knocked out are obtained. According to the method provided by the invention for improving coenzyme Q10 yield through knocking out Rhodobacter sphaeroides chlorophyll synthesis gene, coenzyme Q10 synthesis capacity can be improved by higher than approximately 15%. The method is suitable for coenzyme Q10 large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
Biological preparation for deodorization and chromium reduction and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102872475AReduce generationEliminate odorMedical waste disposalDeodrantsSodium BentoniteMicrobial agent
The invention discloses an environment-friendly composite microorganism preparation and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of environmental biology; the composite microorganism preparation of the invention comprises the following components: (1) a composite microbial agent accounting for 10% of the total weight and comprising sporobolomyces, bacillus sphaericus, lactobacillus plantarum and rhodobacter sphaeroides; (2) a microorganism carrier accounting for 90% of the total weight and comprising 20-50 parts of wheat bran or rice bran, 160-300 parts of organic bentonite, and 40-80 parts of water. The invention compounds bacteria and fungi, enlarges the application scope, and is applicable to not only deodorization treatment of municipal solid household garbage, production sewage, and the like, but also degradation of waste water polluted by heavy metal chromium.
Owner:TIANJIN BOMAN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Rhodobacter sphaeroides extracting solution with antioxidant activity and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a rhodobacter sphaeroides extracting solution with antioxidant activity and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of rhodobacter sphaeroides extracting solutions. The extracting solution contains carotenoids or a coenzyme Q10 or an SOD (superoxide dismutase). The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: activating strains, fermenting rhodobacter sphaeroides, performing centrifugal separation on the rhodobacter sphaeroides and preparing the rhodobacter sphaeroides extracting solution. The prepared rhodobacter sphaeroides extracting solution has the groundbreaking significance.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
Industrial preparing process, fermented liquid and use of spheroidal erythrocyte
InactiveCN1986774AShorten fermentation timeReduce manufacturing costBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismRhodobacter
The present invention discloses production process of multifunctional fermented liquid with bacterium, and is especially functional fermented liquid producing process with Rhodobacter sphaeroides. The Rhodobacter sphaeroides has preservation number of CGMCC No.1562. The production process includes separation from culture dish, strengthening of the bacterial seed in a shaking bottle, expanded culturing in the first seed tank (200L) and secondary seed tank (2000L) and large scale fermentation in large fermenting tank of 5000-20000 L.
Owner:无锡中科活力生物技术有限公司
Aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane and using method thereof
ActiveCN104150606ASimple structureReduce processing costsBiological water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention provides an aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane and a using method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of aquaculture and environmental protection. A functional element of the composite microbial membrane is a membrane component in which paenibacillus polymyxa, lactobacillus plantarum, rhodobacter sphaeroides, rhodococcus pyridinovorans, bacillus amyloliquefaciens and other beneficial microorganisms are immobilized. A preparation process of the aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane comprises selecting of a soft packing microorganism carrier, composite bacteria liquid preparation, microorganism immobilization and other steps; the composite microbial membrane is mounted in aquaculture water, beneficial microbes begin activation reproduction, long-term regulation of microbial ecology of the aquaculture water can be realized, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite and hydrogen sulfide and other toxic and harmful substances in pond can be controlled, metabolites can be licked by farmed fish, shrimp, and other aquatic organisms, so that the immunity is improved, the growth speed of the farmed species is increased, and the aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane is especially adapt to ponds for high density aquaculture of shrimp, crab, fish and the like.
Owner:无锡中科活力生物技术有限公司 +1
Compound microbial agent for anaerobic digestion treatment of sludge and production method of compound microbial agent
ActiveCN104152378AStable stateImprove the efficiency of anaerobic digestionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyStaphylococcus lactis
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent for anaerobic digestion treatment of sludge and a production method of the compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent is a liquid microbial agent which is prepared through fermentation culture and comprises the following bacteria: bacillus subtilis, streptomyces albus, streptomyces griseus, candida utilis, aspergillus sojae, lactobacillus bulgaricus, lactococcus lactis, rhodopseudomonas palustris, rhodopseudomonas capsulate and rhodobacter sphaeroides, and the number of total viable bacteria in 1ml of the compound microbial agent is not less than 2*10<8>. All the bacteria used by the compound microbial agent have metabiosis and symbiosis effects and form a biodegradation system with very high enzymatic activities. When the compound microbial agent disclosed by the invention is used for carrying out anaerobic digestion treatment on sludge, the degradation rate of organic matters can be effectively increased, the sludge hydrolytic process can be accelerated, the anaerobic digestion time of the sludge can be shortened, and the biological gas yield can be increased.
Owner:河北协同环境科技有限公司
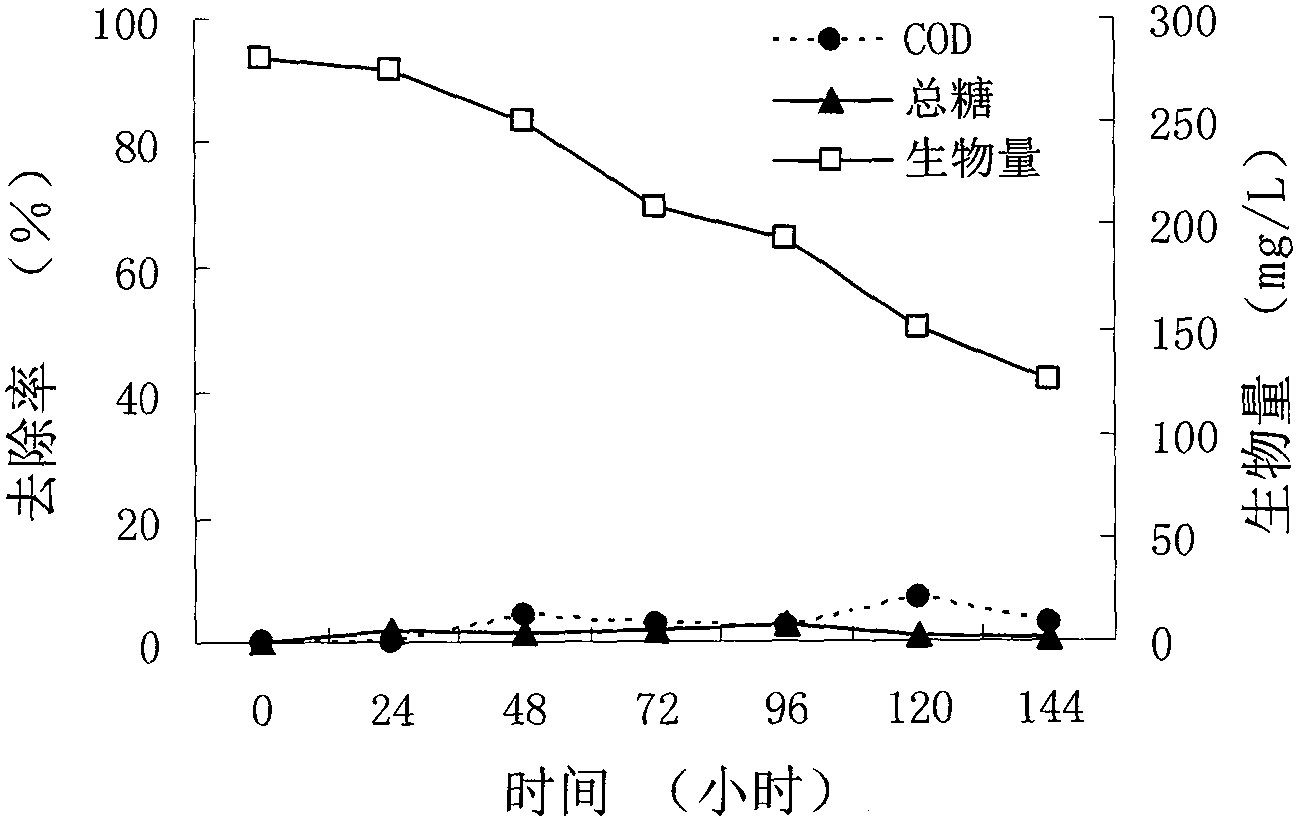
Method for processing starch waste water and realizing resourcezation of waste water by one photosynthetic bacterium strain
InactiveCN102701460AAvoid secondary pollutionDirect degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhodobacterSewage treatment
The invention relates to a method for processing starch waste water and realizing resourcezation of waste water by one photosynthetic bacterium strain, relating to the field of development of waste water treatment and resourcezation. The starch waste is used as the object, 200 mg / L-600mg / L malic acid is added in the starch waste water in order to adjust the pH value of the starch waste water into 7.0-9.0, and then 160 mg / L-500mg / L rhodobacter sphaeroides at the exponential phase is added. The starch waste water is processed under the illumination anaerobic condition, a filament lamp with illumination strength of 2000lux-3000lux is used as the light source, and the processing temperature is 25 DEG C to 30 DEG C. With the adoption of the method, the photosynthetic bacterium waste water treatment process is simplified, and meanwhile, the large amount of generated bacteria can be directly and comprehensively utilized, so that the purposes of disposing pollution and generating bacterium resources can be synchronously fulfilled.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Composite germ pulp, and production method and application thereof
ActiveCN102352316AFully recycleAvoid breedingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPaenibacillus polymyxaSlurry
The invention discloses composite germ pulp, and a production method and an application thereof, which belong to the field of microorganism application. The composite germ pulp is prepared in the following way that amino acid waste pulp is used as a fermentation substrate, paenibacillus polymyxa with the inoculation quantity being 6 percent and rhodobacter sphaeroides with the inoculation quantity being 4 percent are inoculated, the fermentation is carried out for 24h at the pH value being 6.5 to 7.0 and the temperature being 30 DEG C and 34 DEG C under the oxybiontic condition, and the composite germ pulp is obtained. The paenibacillus polymyxa content in the composite germ pulp is higher than or equal to 5*10<9> CFU / ml, the rhodobacter sphaeroides content is higher than or equal to 3*10<9> CFU / ml, and the composite germ pulp can be applied to culture water body purification or organic fertilizer preparation. Compared with the prior art, the composite germ pulp uses the amino acid waste pulp as the fermentation substrate, has the characteristics of low production cost, energy saving, environment protection and the like and can be widely applied to the culture water body purification and organic fertilizer production.
Owner:宜兴市天石饲料有限公司
Method for efficiently preparing salvianolic acid components from overground stems and leaves of salviae miltiorrhizae employing bioconversion technology
InactiveCN104611373AEfficiently obtainedImprove technical effectFermentationFood preparationSalvianolic acid BCaffeic acid
The invention discloses a method for efficiently preparing salvianolic acid components from overground stems and leaves of salviae miltiorrhizae. The method comprises the following steps: extracting overground stems and leaves of salviae miltiorrhizae, and carrying out bioconversion through photosynthetic bacteria including rhodopseudomonas palustris, green sulphur rhodop seudanonas palustris, rhodobacter sphaeroides, rhodobacter capsulatus and the like to prompte rise of salvianolic acid components in the stems and leaves, wherein the content of an active component salvianolic acid B is 3-4 times of that of the medicinal material, namely roots of the salviae miltiorrhizae, and the content of rosmarinic acid is dozens of times higher than that of the medicinal material salviae miltiorrhizae; and carrying out separation and purification through a macroporous resin column, so as to efficiently obtain the high-content extracts of phenolic acid components such as the salvianolic acid B, tanshinol, rosmarinic acid, ferulic acid and caffeic acid. The salvianolic acid components disclosed by the invention have good efficacies of resisting oxidation, protecting vascular endothelial cells, and promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis, and can be applied to preparation of medicines or functional health products for preventing and treating cardiovascnlar and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10
The present invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10. The genetically engineered bacteria comprises coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria and desired genes transferred into the coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria, and the desired genes are a demethylnaphthoquinone methyltransferase gene, a 2-octo isoprene-3-methyl-6-methoxy-1,4-hydroquinone hydroxylase gene and a 3-demethyl ubiquinone-93-methyl transferase gene. Rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF in a coenzyme Q10 synthetic route are transferred into rhodobacter sphaeroides, and by in-series over-expression of the three rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF, coenzyme Q10 synthesizing capability of the rate-limiting enzyme genes can be strengthened; and compared with the rhodobacter sphaeroides with no desired gene being transformed, by use of the genetically engineered bacteria for coenzyme Q10 producing, the yield of the coenzyme Q10 is increased by more than 20%.
Owner:SHANGYU NHU BIOCHEM IND
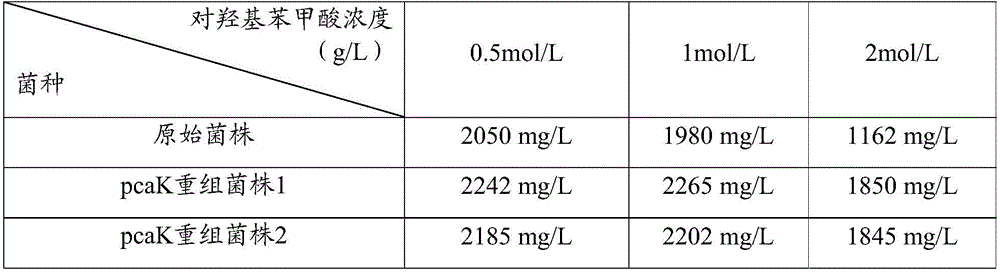
Rhodobacter sphaeroides strain and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106148263ASolve outputSolve the costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRhodobacter
The invention provides a rhodobacter sphaeroides strain and a preparation method and application thereof. P-hydroxybenzoic acid transportprotein pcaK gene from acinetobacter calcoaceticus is introduced into the rhodobacter sphaeroides strain, the ability of taking p-hydroxybenzoic acid from an extracellular medium of the rhodobacter sphaeroides strain is enhanced, and therefore, the yield of synthesizing coenzyme Q10 in the rhodobacter sphaeroides strain is improved. By the rhodobacter sphaeroides strain, the shortcomings that in production of coenzyme Q10 by microbiological fermentation, the yield is low, the production cost is high and the like are overcome, the yield of the intracellular coenzyme Q10 of rhodobacter sphaeroides can be improved remarkably, and the cost of industrialized production of the coenzyme Q10 is reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN FUKANG PHARMA
Use of Rhodobacter sphaeroides fermentation liquid in degrading pesticide residue
The invention discloses a applied technique for Rhodobacter sphaeroides fermentation liquid in degradation for pesticide residue. Compared with prior art, this invention has high degradation ratio, and has no toxic effect to human.
Owner:无锡中科活力生物技术有限公司
High-yield coenzyme Q10 rhodobacter sphaeroides and mutation breeding and application thereof
ActiveCN109762757AQuadruple resistantIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention provides high-yield coenzyme Q10 rhodobacter sphaeroides and mutation breeding and application thereof, and relates to the field of microbial mutation breeding. Strains screened by spacemutagenesis are used as starting bacteria and subjected to plasma mutagenesis at normal pressure and room temperature. The high-yield coenzyme Q10 rhodobacter sphaeroides are obtained after multi-resistance screening, high-throughput screening and step-by-step amplification verification, and are deposited in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the deposit number of CGMCCNo. 16625. The average titer of a mutant strain of the rhodobacter sphaeroides can reach 2694[mu] / mL according to 20m<3> fermentation production verification, and the yield of the coenzyme Q10 is significantly improved. In addition, the strain has quadruple resistance and broad application prospects.
Owner:SHENZHOU BIOLOGY & TECH CO LTD +1
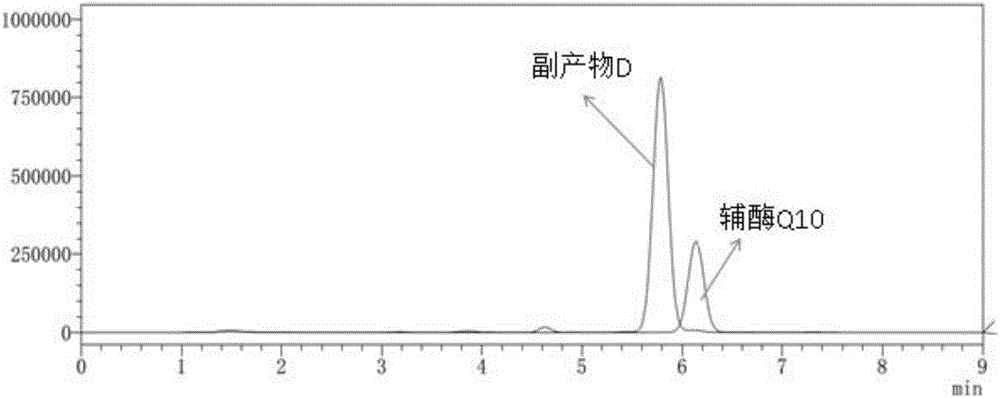
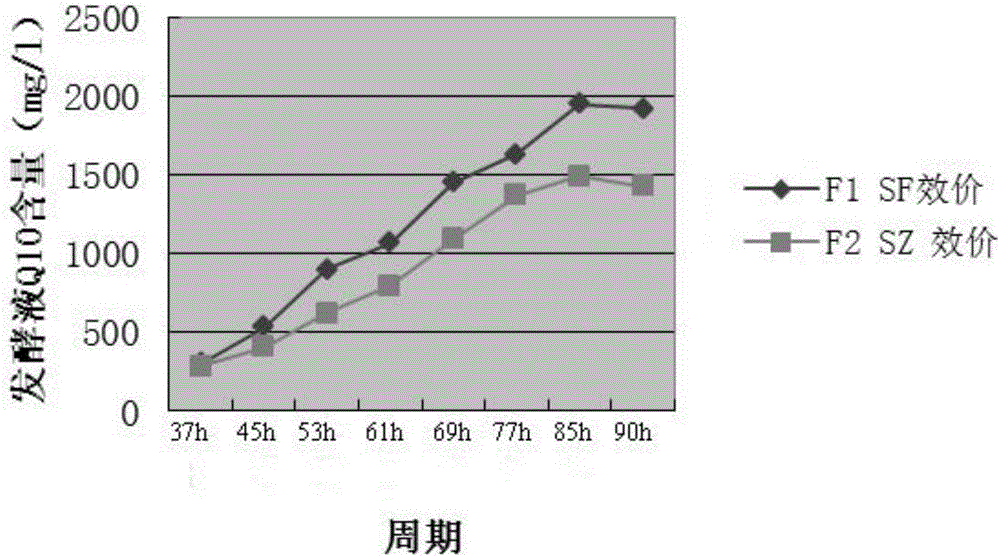
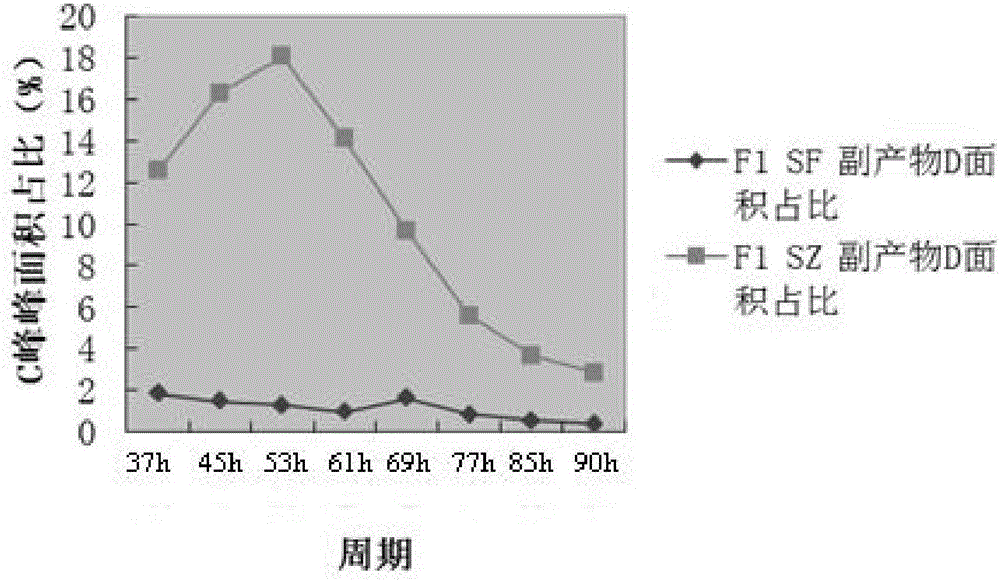
Method for reducing or eliminating by-product D in coenzyme Q10 producing strain SZ, coenzyme Q10 high-yield strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105925519AIncrease productionStable genetic traitsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRhodobacter
The invention discloses a method for reducing or eliminating a by-product D in a coenzyme Q10 producing strain SZ. According to the method, the gene of 5-demethoxy panthenol hydroxylase is expressed in the coenzyme Q10 producing strain SZ, so that the accumulation of the by-product D is reduced or eliminated, wherein the producing strain SZ is classified and named as rhodobacter sphaeroides, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 3, 2016, with preservation number of CGMCC NO. 12177. The invention also discloses a coenzyme Q10 high-yield strain SF and an application thereof, wherein the high-yield strain SF is classified and named as rhodobacter sphaeroides, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 3, 2016, with preservation number of CGMCC NO. 12178. The high-yield strain SF is obtained by expressing the gene of the 5-demethoxy panthenol hydroxylase in the producing strain SZ; and with the application of the high-yield strain SF, the yield of produced coenzyme Q10 reaches 2g / L or above; therefore, the high-yield strain SF has a broad application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU BIOSYNTHETICA CO LTD +1
Fodder premix and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105360609AGrowth inhibitionPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsPurslane extractCulture mediums
The invention discloses fodder premix and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that lactobacillus plantarum BW2013 strains, bacillus amyloliquefaciens A3 strains, bacillus substilis szx11 strains, rhodobacter sphaeroides WD-2 strains and baker's yeast are adopted as fermentation strains, a compound culture solution formed by compounding purslane extract, hairyvein agrimony extract, milkvetch root extract, humifuse euphorbia herb extract and licorice extract is adopted as a culture medium, fermentation is carried out, and the fodder premix with the effective viable count larger than or equal to 5*108 CFU / ml is prepared.
Owner:无锡中科活力生物技术有限公司
A construction method for producing coenzyme q10 engineering bacteria, engineering bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN103509729BHigh coenzyme Q10 synthesis abilityImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a construction method for producing coenzyme Q10 engineering bacteria, engineering bacteria and applications thereof. The bacteria is Rhodobacter sphaeroides with a Latin name Rhodobacter sphaeroides ; Named as NHU-ZDD strain; Deposit unit: General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee; Preservation time: April 13, 2012; Preservation number: CGMCC No.5998. The invention provides a method for improving the production of coenzyme Q10 by modifying the metabolic pathway related to the EMP pathway, which can increase the synthesis ability of coenzyme Q10 by about 30%, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production of coenzyme Q10.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
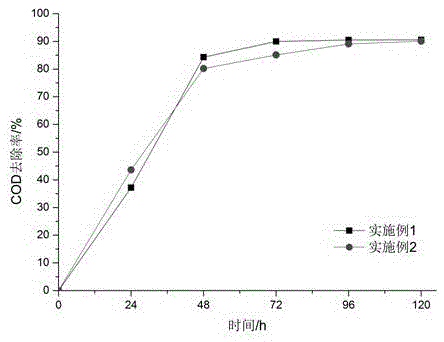
Method for processing and recycling soybean processing wastewater through photosynthetic bacteria
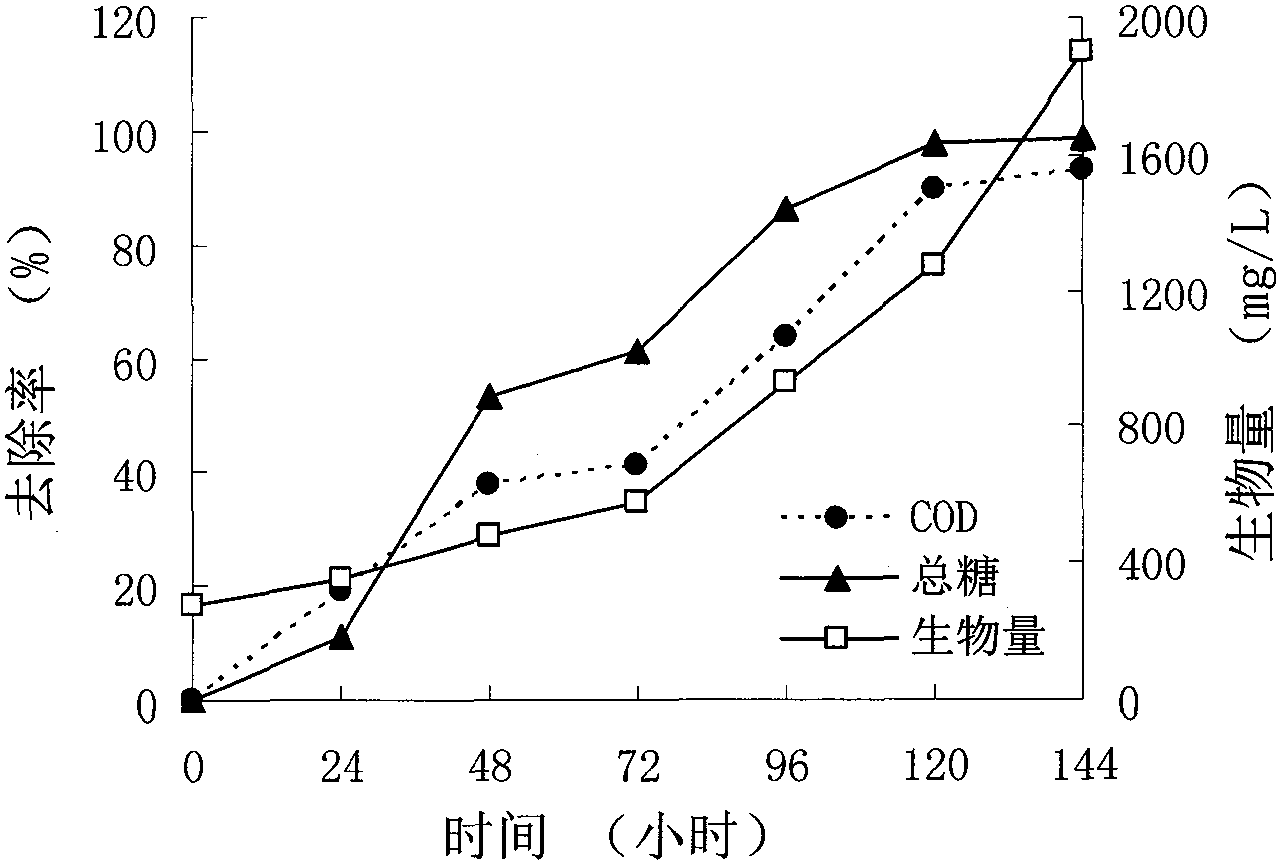
InactiveCN105461082AHigh activityOmit the preprocessing sectionWaste water treatment from food industryBiological water/sewage treatmentRhodobacterWater resources
The invention discloses a method for processing and recycling soybean processing wastewater through photosynthetic bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of sewage processing. Soybean processing wastewater is processed through Rhodobacter sphaeroides, and small-molecular carbon source substances are added to the soybean processing wastewater till the final concentration is 400-1200 mg / L; the pH value of the wastewater is then adjusted to be 7.0-9.0; Rhodobacter sphaeroides in the logarithmic phase is put in wastewater till the final concentration is 600-1900 mg / L; processing is conducted for 96-120 hours at a temperature of 25-30 DEG C; meanwhile, the external illumination intensity is controlled to be 4500-5000 lux by an incandescent light bulb, and the oxygen dissolution concentration in sewage is controlled to be 0.5-1.0 mg / L. The method is easy to operate, the technological procedure is simplified, the sewage recycling degree is improved, the problem of secondary pollution caused by a traditional sewage processing process is solved, and sewage recycling can be achieved.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and construction method thereof
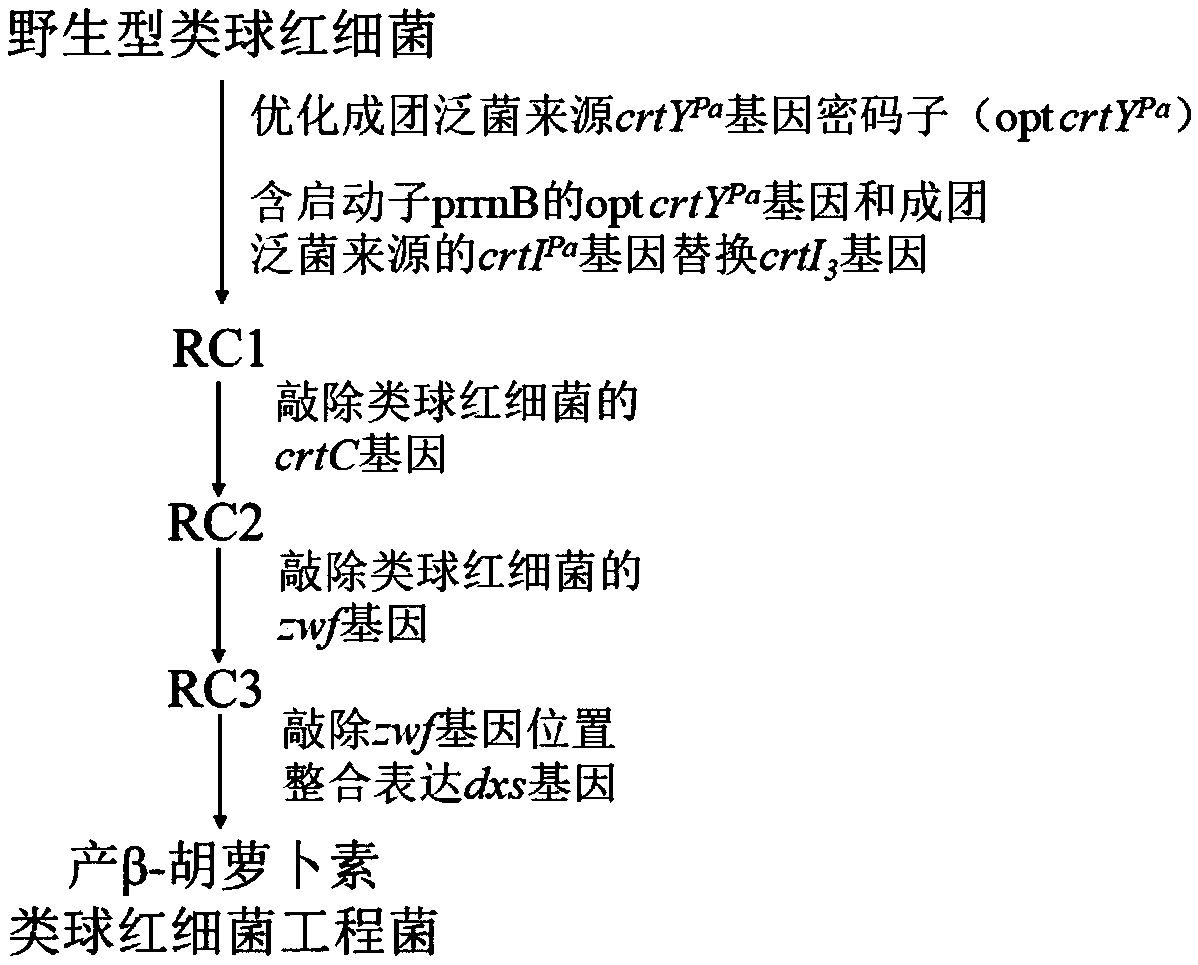
The invention discloses a rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and a construction method thereof. The method includes first optimizing a codon of a lycopene cyclase gene crtYPa derived from pantoea agglomerans to obtain an opt crtYPa gene, then replacing an endogenous phytoene three-step dehydrogenase gene crtI3 of rhodobacter sphaeroides with the opt crtYPa genecontaining a promoter prrnB and a phytoene four-step dehydrogenase gene crtIPa gene derived from the pantoea agglomerans in a traceless mode, then knocking out an endogenous neurosporene hydroxylase gene crtC of the rhodobacter sphaeroides and a 6-phosphoglucose dehydrogenase gene zwf and finally knocking out an endogenous 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene dxs of the rhodobacter sphaeroides with integration expression at zwf position to obtain the rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing the beta-carotene. The strain is cultured by fermentation, and the content of the beta-carotene can reach 30mg / g DCW.
Owner:SHAANXI HEALTHFUL BIOLOGICAL ENG
Rhodobacter sphaeroides mutant strain and uses thereof
InactiveCN101285048AIncrease productionReduce chromatography media costsBacteriaQuinone separation/purificationBacteroidesRhodobacter
The invention provides a Rhodobacter sphaeroides mutant strain, which can reduce the use of chromatography media during the production of coenzyme Q 10 by fermentation, and consequently reduce the production cost. The mutant strain can also improve the output of THE conezyme Q10.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY +1
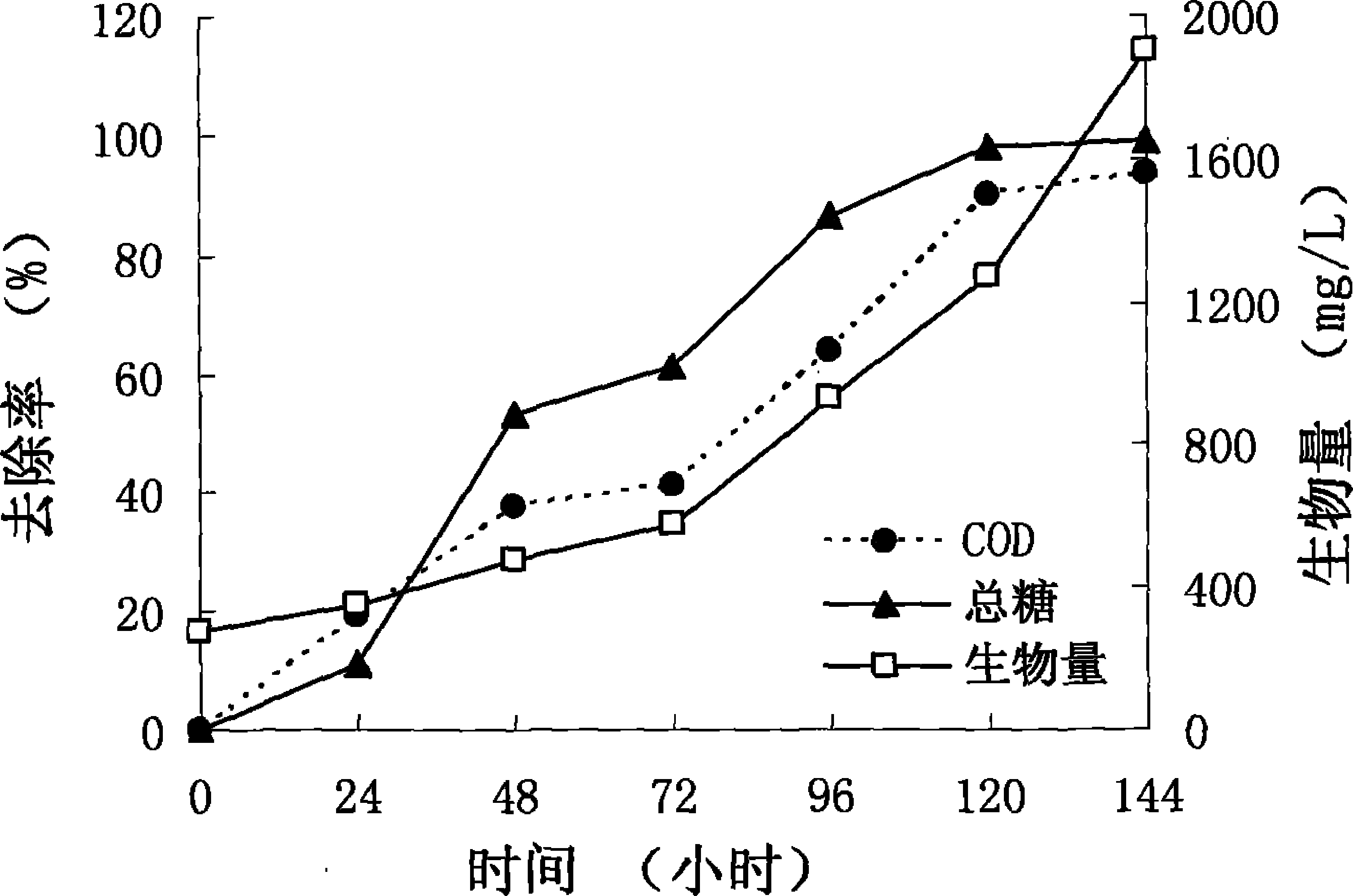
Method for treating soybean processing wastewater by utilizing photosynthetic bacteria and recycling wastewater
InactiveCN103043804ARealize resourcesImprove processing efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentRhodobacterMolecular nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for treating soybean processing wastewater by utilizing photosynthetic bacteria and recycling the wastewater, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises the steps as follows: adding small molecular carbon source substances with the final concentration of 400-1200 mg / L and small molecular nitrogen source substances with the final concentration of 200-2000 mg / L into the soybean processing wastewater at first; adjusting the pH value of the wastewater to be 7.0-9.0; adding rhodobacter sphaeroides with the final concentration of 400-1500 mg / L during logarithmic growth phase into the wastewater; treating for 96-120 h at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C; and micro-aerating in the wastewater and controlling the dissolved oxygen concentration in the soybean processing wastewater to be 0.5-1.0 mg / L during the treatment process. According to the method, the energy consumption is reduced, the process of treating sewage with the photosynthetic bacteria is simplified, a large amount of bacterial resources capable of being directly and comprehensively utilized are produced, and the problem of secondary pollution is avoided, so that the sewage recycling rate is increased.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com