In-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system and application thereof
A cell-free protein and synthesis system technology, applied in the field of cell-free protein synthesis system, can solve the problems of high cost and insufficient reaction efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
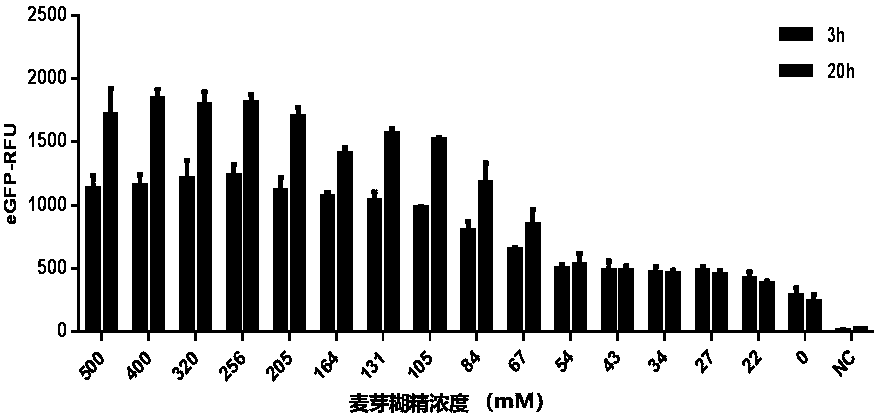
[0077] Example 1 In vitro cell-free protein synthesis system containing glucose + maltodextrin
[0078] In vitro protein synthesis reaction system: final concentration of 22 mM 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid (Hepes-KOH) at pH 7.4, 120 mM potassium acetate, 5.0 mM magnesium acetate, 1.5 mM nucleoside triphosphate mixture (adenoside Purine nucleoside triphosphate, guanosine triphosphate, cytidine triphosphate, and uridine triphosphate), 0.1 mM amino acid mixture (glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine amino acid, phenylalanine, proline, tryptophan, serine, tyrosine, cysteine, methionine, asparagine, glutamine, threonine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, lysine, arginine and histidine), 1.7 mM dithiothreitol, 20 mM glucose, 20 mM tripotassium phosphate, 0-500 mM maltodextrin (measured as glucose monomer), 0.002 mg / mL of α-amylase, 0.03 mg / mL T7 RNA polymerase, 2% polyethylene glycol, and finally 50% by volume of yeast cell extract.
[0079]In vitro protein syn...
Embodiment 2
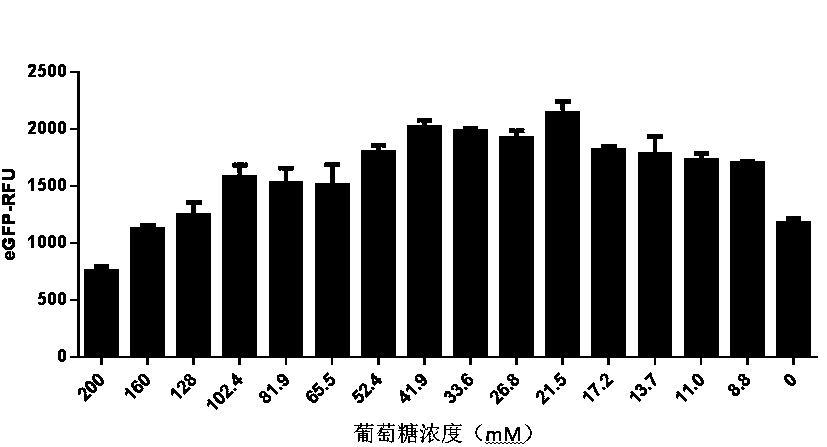
[0089] Example 2 In vitro cell-free protein synthesis system containing maltodextrin
[0090] In vitro protein synthesis reaction system: final concentration of 22 mM 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid (Hepes-KOH) at pH 7.4, 120 mM potassium acetate, 5.0 mM magnesium acetate, 1.5 mM nucleoside triphosphate mixture, 0.1 mM amino acid mix, 1.7 mM dithiothreitol, 0-500 mM maltodextrin, 20 mM tripotassium phosphate, 0.002 mg / mL alpha amylase, 0.03 mg / mL T7 RNA polymerase, 2% polyethylene glycol Alcohol, and finally add 50% volume of yeast cell extract.
[0091] In vitro protein synthesis reaction: add 15 ng / µL enhanced green fluorescent protein DNA to the above system, mix well and place it in an environment of 20-30 ℃ for reaction.
[0092] Fluorescent protein activity assay: Immediately after the reaction, place in Envision 2120 multi-functional microplate reader (Perkin Elmer) to detect the intensity of fluorescent signal, and use Relative Fluorescence Unit (RFU) as t...
Embodiment 3
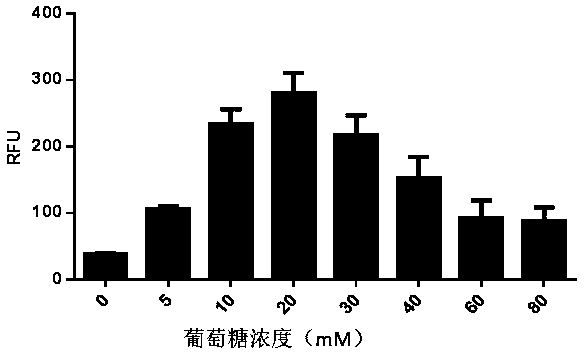
[0094] Example 3 In vitro cell-free protein synthesis system containing lactose
[0095] In vitro protein synthesis reaction system: final concentration of 22 mM 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid (Hepes-KOH) at pH 7.4, 120 mM potassium acetate, 5.0 mM magnesium acetate, 1.5 mM nucleoside triphosphate mixture, 0.1 mM amino acid mixture, 1.7mM dithiothreitol, 0-200 mM lactose, 20mM tripotassium phosphate, 0.03 mg / mL T7 RNA polymerase, 2% polyethylene glycol, and finally add 50% volume of yeast cells Extract.
[0096] In vitro protein synthesis reaction: add 15 ng / µL enhanced green fluorescent protein DNA to the above system, mix well and place it in an environment of 20-30 ℃ for reaction.
[0097] Fluorescent protein activity assay: Immediately after the reaction, place in Envision 2120 multi-functional microplate reader (Perkin Elmer) to detect the intensity of fluorescent signal, and use Relative Fluorescence Unit (RFU) as the activity unit.
[0098] Figure 5 It ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com