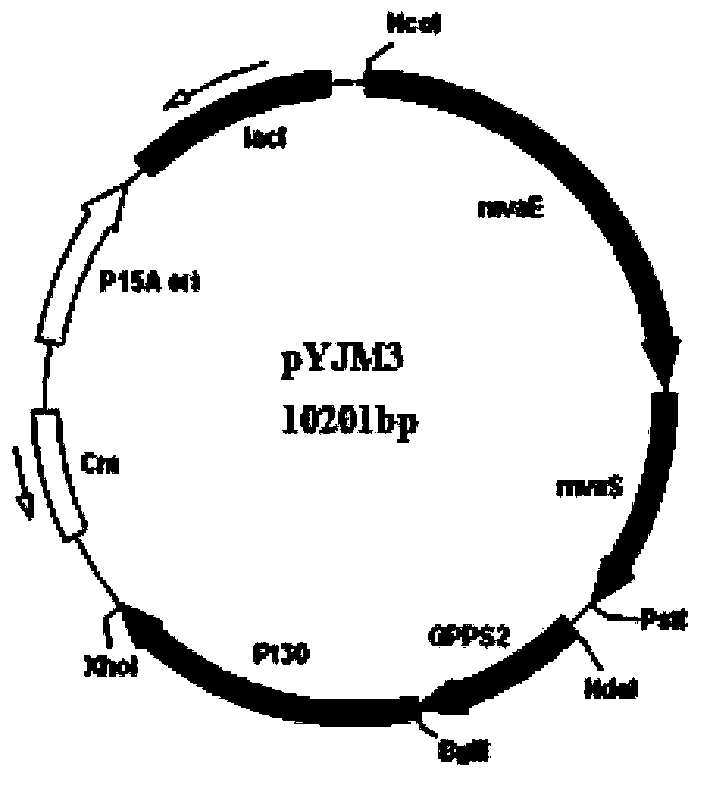
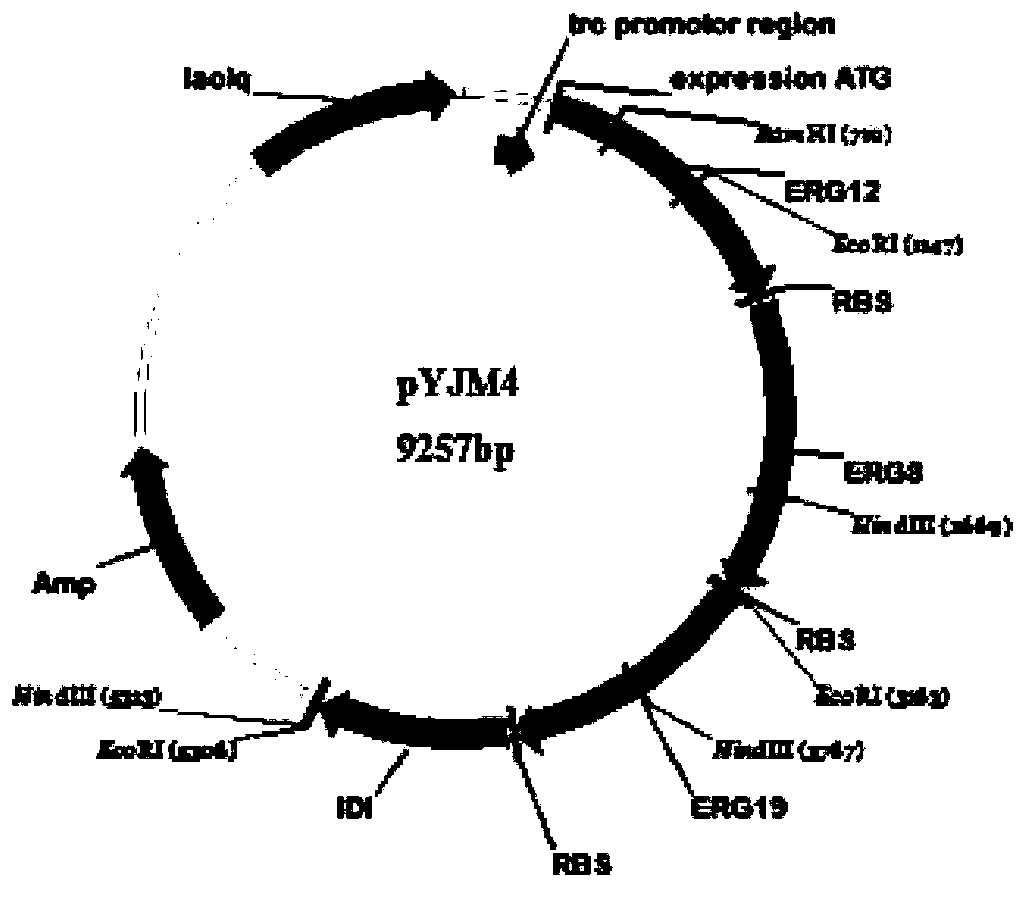
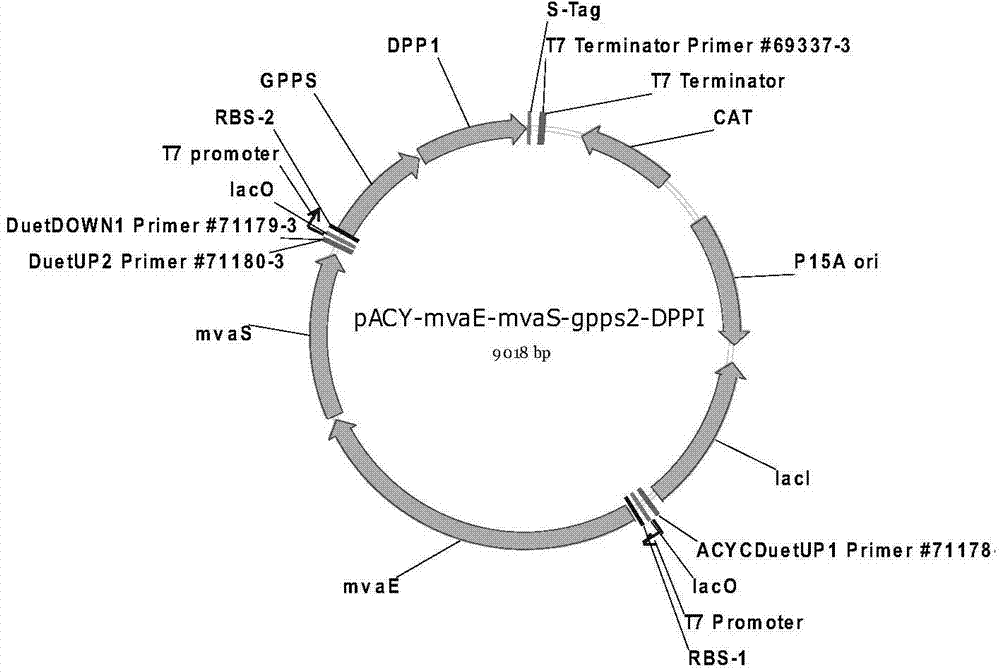
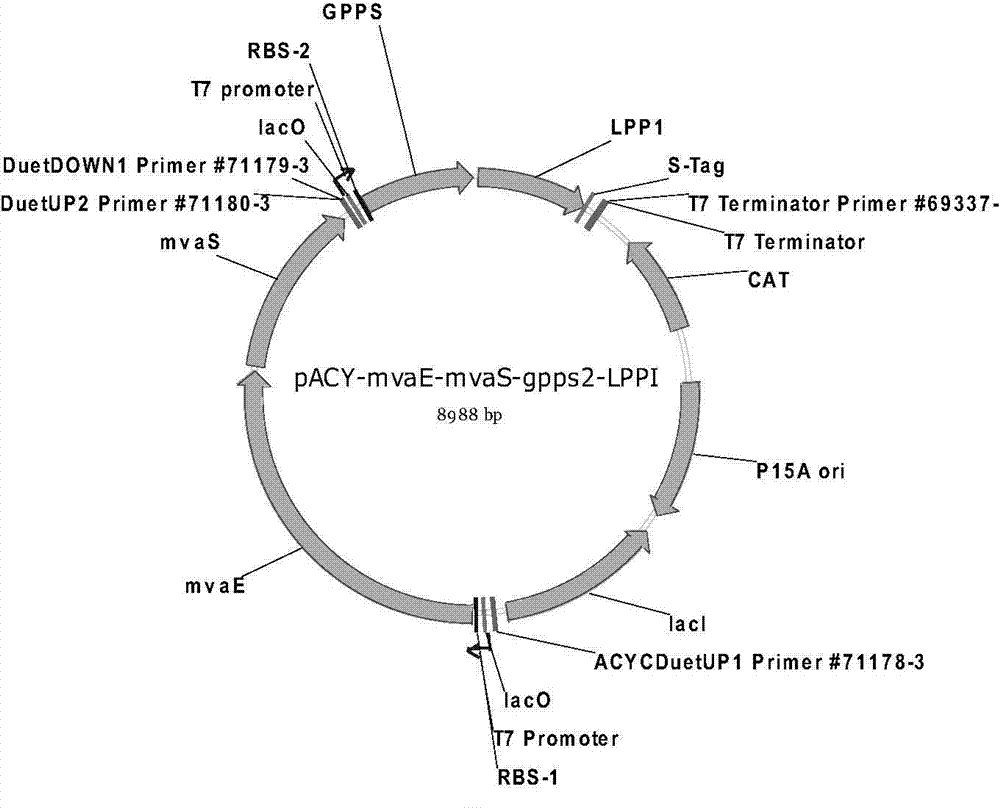
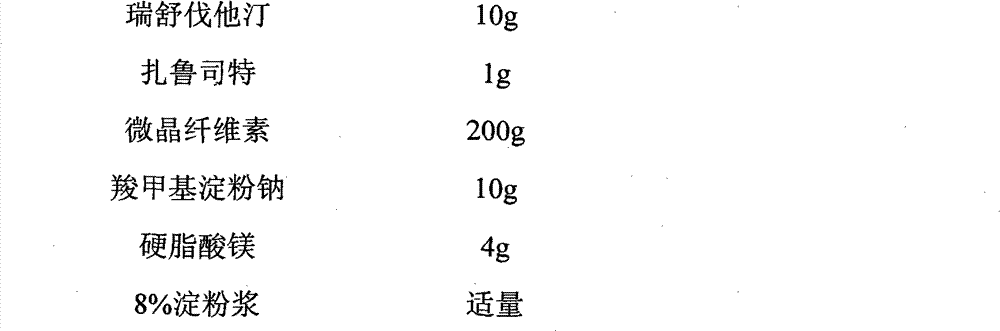
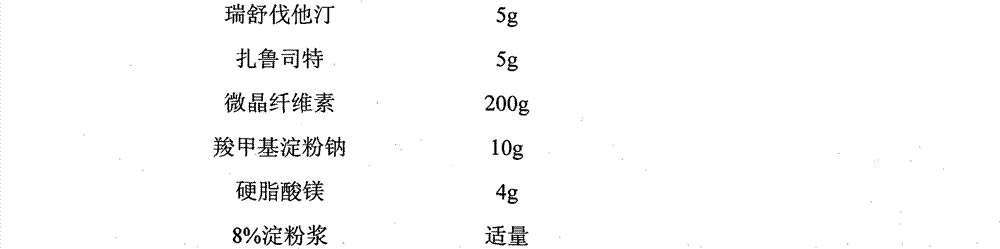
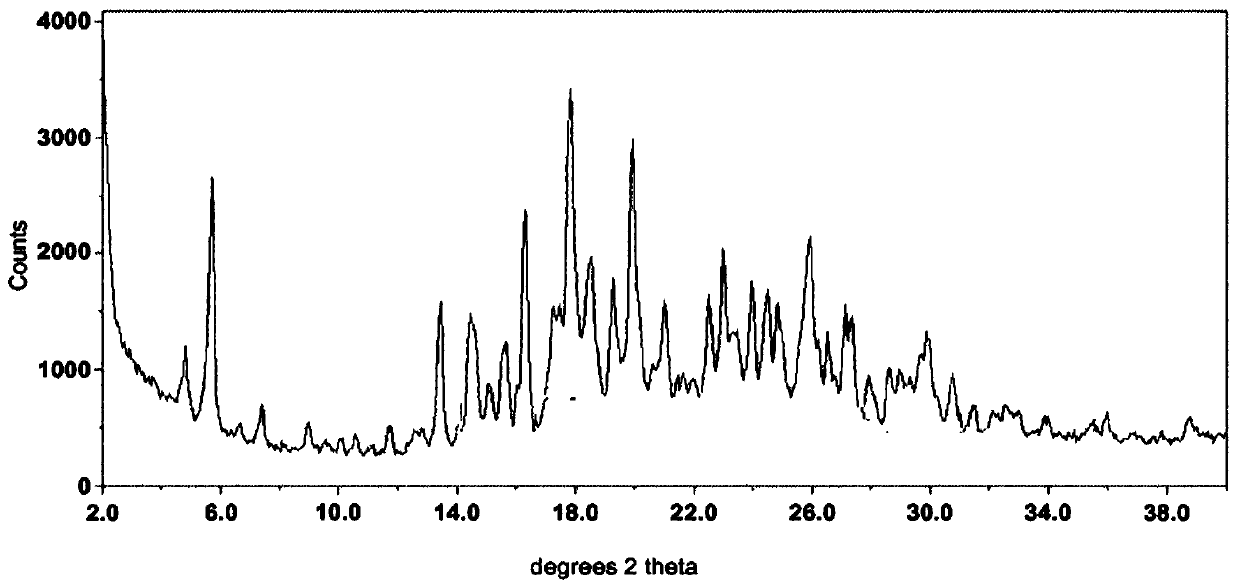
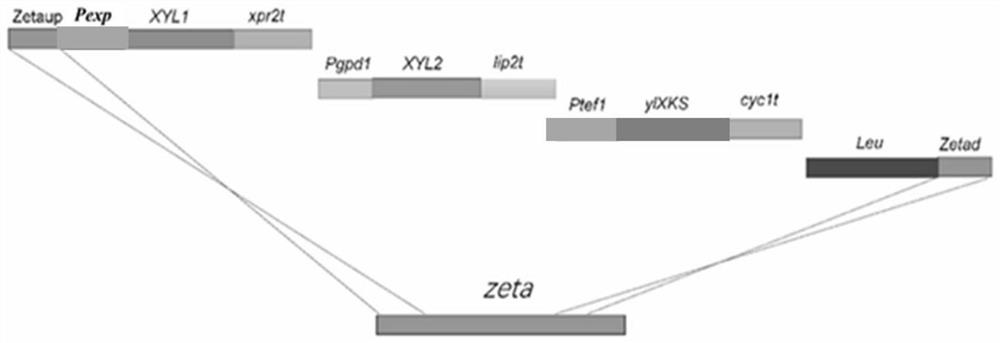
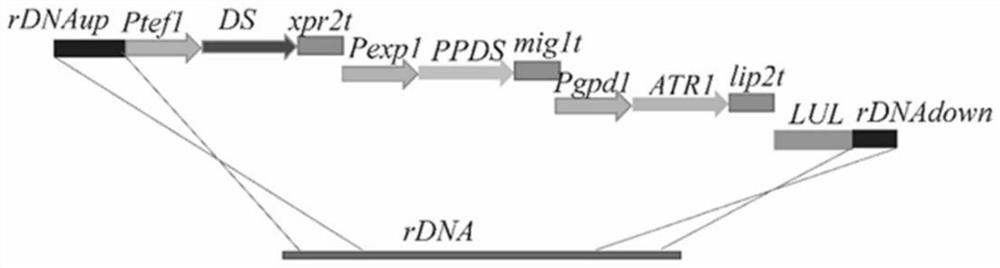
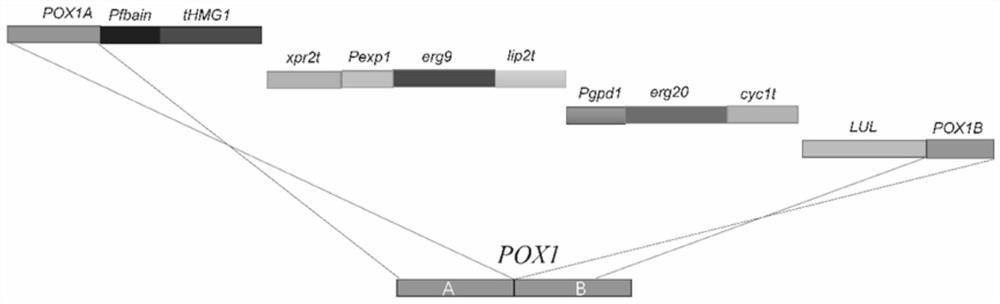
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Glutaryl-coenzyme A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glutaryl-coenzyme A is an intermediate in the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan. See also. Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase; References This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it ...
Statin and omega-3 fatty acids for lipid therapy
InactiveUS20070191467A1Lower triglyceride levelsBiocideMetabolism disorderLipid formationLow-density lipoprotein
A method of lipid therapy, comprising providing a subject group having a baseline triglyceride level of 200 to 499 mg / dl and being at or near its low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level goal, and reducing the triglyceride level and the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) level of the subject group as compared to treatment with a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) inhibitor alone, by administering to the subject group an effective amount of an HMG CoA inhibitor and a composition comprising omega-3 fatty acids.
Owner:RELIANT PHARMACEUTICALS INC +1
Prophylactic/ameliorating or therapeutic agent for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
InactiveUS20110082119A1Slow downGood treatment effectBiocideAntipyreticNonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs/NSAIDsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A highly safe and effective prophylactic / ameliorating or therapeutic agent for NACH and the method for using the same are provided.A prophylactic / ameliorating or therapeutic agent for NASH containing a combination of at least one first ingredient selected from the group consisting of an ω3PUFA and pharmaceutically acceptable salts and esters thereof and at least one second ingredient selected from the group consisting of (a) a biguanide hypoglycemic agent, (b) a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, (c) a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, and (d) an angiotensin II receptor blocker as the active ingredients; and its method of use.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Statin and Omega-3 Fatty Acids For Lipid Therapy
InactiveUS20090239927A1Lower triglyceride levelsBiocideMetabolism disorderLipid formationTG - Triglyceride
A method of lipid therapy, comprising providing a subject group having a baseline triglyceride level of 200 to 499 mg / dl and being at or near its low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level goal, and reducing the triglyceride level and the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) level of the subject group as compared to treatment with a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) inhibitor alone, by administering to the subject group an effective amount of an HMG CoA inhibitor and a composition comprising omega-3 fatty acids.
Owner:BOBOTAS GEORGE +3
Methods and compositions for inhibiting inflammation associated with pulmonary disease
The present invention provides an aerosol formulation of a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor. The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor can be, for example, a statin such as lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, cerivastatin, fluvastatin, atorvastatin or mevastatin. The invention also provides a method of treating a pulmonary disease with an aerosol formulation of a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting biological process
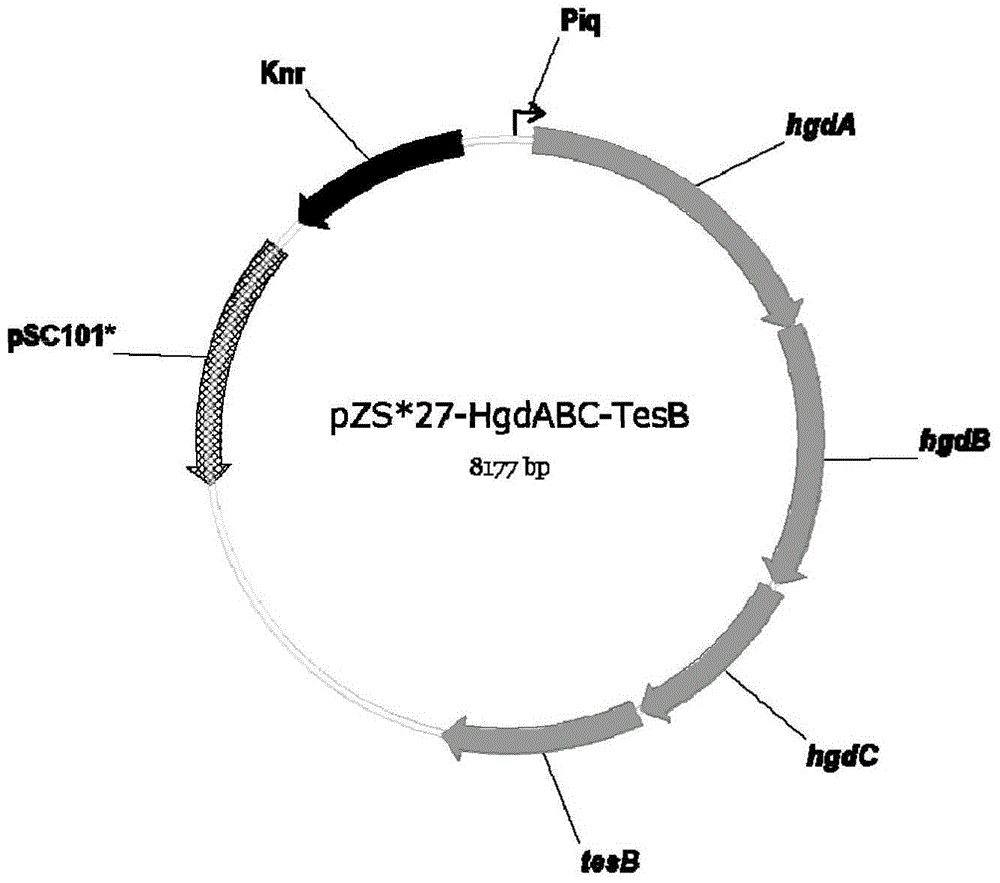
InactiveCN104120148AFast growthShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxy methyl glutarylGlutaryl-coenzyme A
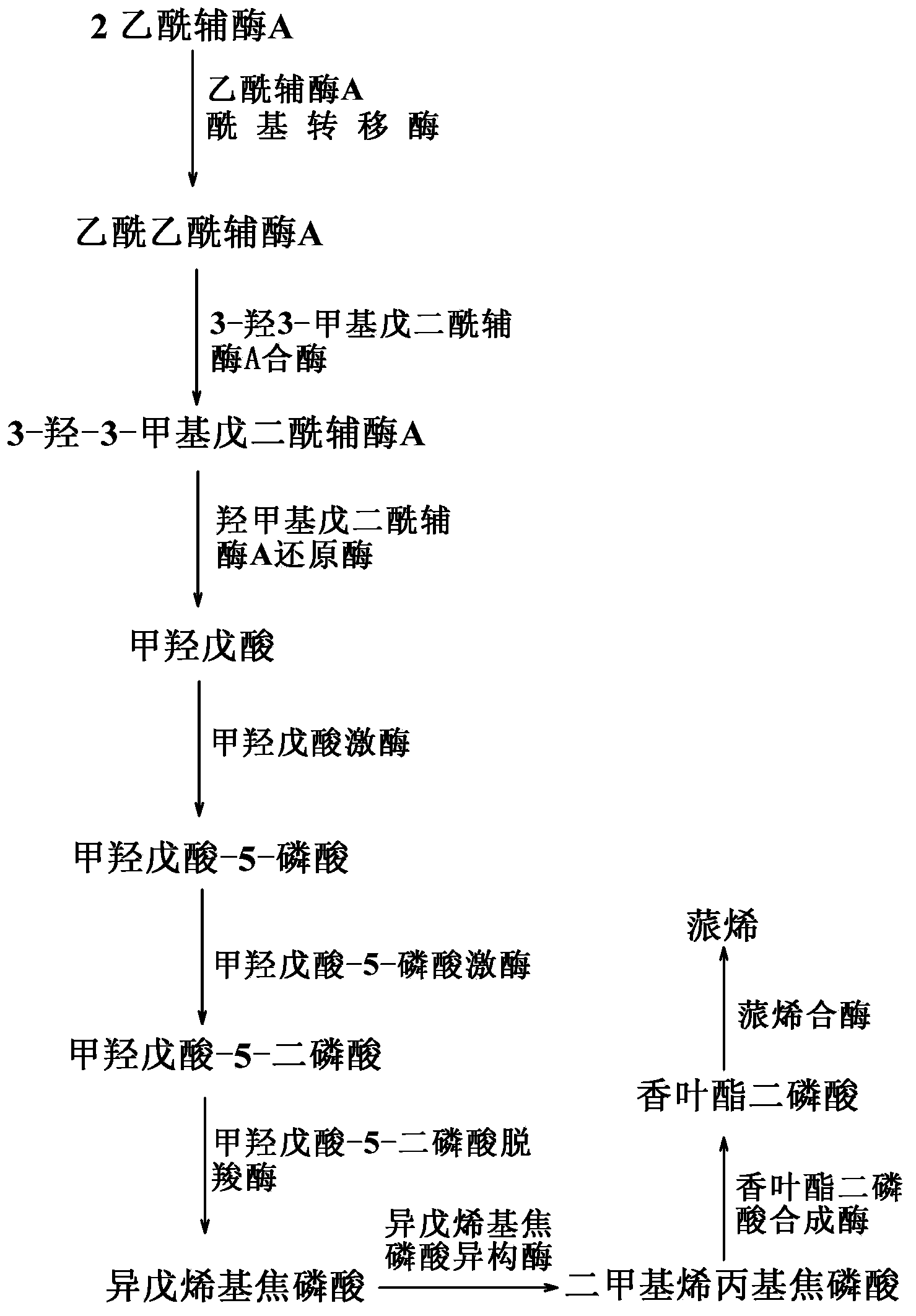
The invention provides a biological method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene from acetyl coenzyme A and a reconstitution cell capable of synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene, wherein the acetyl coenzyme A is obtained from a simple starting material like glucose. The method for synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting a biological process comprises the following steps: transferring acetyl coenzyme A acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthase, hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, mevalonic acid kinase, mevalonic acid-5-phosphokinase, mevalonic acid-5-diphosphonic acid decarboxylase, isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase, geranyldiphosphate synthetase and pinene synthase into an appropriate host cell by adopting metabolic engineering technology, and culturing the obtained reconstitution cell, so that the target product, namely alpha-pinene or beta-pinene can be obtained.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacterium co-generating geraniol and nerol and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103898037AFast growthShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGenetically engineered
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium co-generating geraniol and nerol and a construction method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of generic field. According to the genetically engineered bacterium disclosed by the invention, acetyl coenzyme A acyltransferase / hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, 3-hydroxyl-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthase, mevalonic acid kinase, mevalonic acid-5-phosphokinase, mevalonic acid-5-diphosphonic acid decarboxylase, isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase, geranyl diphosphonic acid synthetase and geraniol synthetase or phosphatase are expressed. The metabolic pathways of geraniol and nerol synthesized in escherichia coli are successfully constructed by genetic engineering means, and glucose is biologically converted into geraniol and nerol.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof
ActiveCN104031872AAvoid the influence of own metabolismShort reaction timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering technology. According to the invention, a recombinant bacterium is obtained by transforming a gene containing acetyl-CoA acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase, terminal alkene formed fatty acid decarboxylase and oleic acid hydratase into a host bacterium, and is used for fermentation production of isoprene. Such a method substantially shortens reaction process for synthesis of isoprene through an exogenous MVA approach, only five reaction steps are needed for synthesis of isoprene of acetyl-CoA, so influence of excess exogenous gene expression on metabolism of cells is avoided. Through optimization of fermentation conditions, the yield of the fermentation product isoprene can reach 39.49 mu g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Limonene-producing yarrowia lipolytica and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN108587934AExtensive living environmentBack mutationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and relates to limonene-producing yarrowia lipolytica genetic engineering bacterium and the application thereof. The genetic engineering bacterium is obtained by introducing a D-limonene synthase gene or an L-limonene synthase gene into a yarrowia lipolytica host and overexpressing a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase(HMGR) gene. After shake flask fermentation in an YPD culture medium, limonene can be heterologously synthesized, the yield of D-limonene heterologously synthesized by a D-limonene-producing engineering strain is 0.6305mg / L and the yield of L-limonene heterologously synthesized by an L-limonene-producing engineering strain is 0.3672mg / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
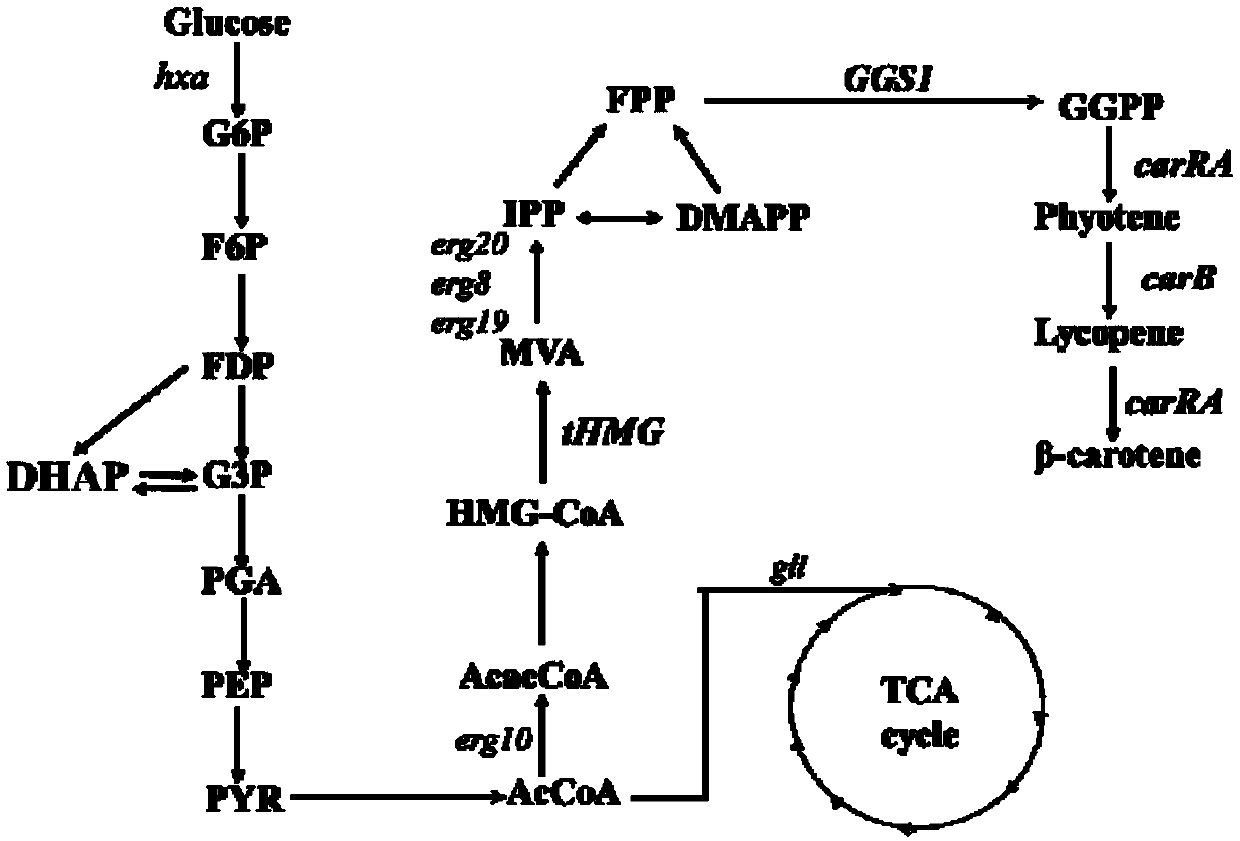
Recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and construction method utilizing Crispr-Cas9 technology
PendingCN109666596AIncrease the efficiency of homologous recombinationImprove stabilityFungiStable introduction of DNABeta-CaroteneKu70
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and a construction method utilizing a Crispr-Cas9 technology. A Ku70 gene is subjected to knockout from yarrowia lipolytica, and then phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA), phytoene desaturase (carB), geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene take snfas a target point and are integrated in a yarrowia lipolytica gene set after knockout of the ku70 gene, wherein the phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA) and phytoene desaturase (carB) are from blakeslea trispora, and the geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and the 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene are from the yarrowia lipolytica; the Crispr-Cas9 technology isutilized for regulating the copy number of the carRA, the carRA, the GGS1 and the tHMG, and the recombinant bacteria capable of producing the high-yield beta-carotene is constructed. After the recombinant bacteria is fermented, cultured, extracted and separated, the content of the beta-carotene can reach the dry cell weight of 35 mg / g, and the bacterial strain stability is high.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
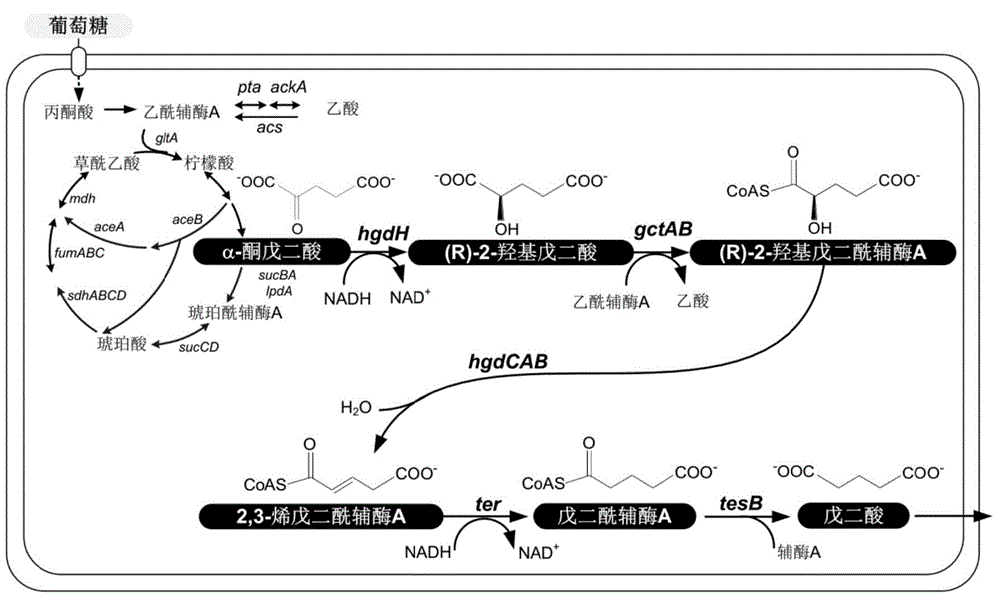
Biological improvement synthesis method of glutaric acid
The invention relates to a biological improvement synthesis method of glutaric acid. According to the present invention, the method is achieved by expressing 2-hydroxyglutaric acid dehydrogenase, glutaryl-coenzyme A transferase, 2-hydroxyglutaryl coenzyme A dehydratase, trans-CoA reductase and thioesterase in a recombinant host Escherichia coli, the recombinant Escherichia coli expressing the genes is subjected to fermentation production, and the generation of the target product glutaric acid and the by-products such as glutaconic acid and 2-hydroxyglutaric acid is successfully detected in the fermentation broth; and the constructed biological synthesis approach provides the new method for the utilization of the renewable resources to synthesize the glutaric acid.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Nanjing bass 3-hydroxyl-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase protein encoding sequence
InactiveCN1769436AIncrease contentPromote healthy growthOxidoreductasesFermentationMetaboliteNucleotide
The invention provides a Nanjing Linden tm-Hmgr protein encoding sequence, wherein the separated DNA molecules comprise, nucleic acid sequence encoding polypeptides having Nanjing Linden tm-Hmgr protein activity, the nucleic acid sequence has at least 70% homology with position No:131-1888 nucleic acid sequence in the SEQ ID No:3 in the sequence table, the nucleic acid sequence can be hybridized with position No:131-1888 nucleic acid sequence in the SEQ ID No:3 at 40-55 deg C.
Owner:蒋继宏
Yarrowia lipolytica capable of producing bisabolene and constructing method for yarrowia lipolytica and use of yarrowia lipolytica
InactiveCN111088175ARealize the needs of industrializationIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBisaboleneMicrobiology
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria of yarrowia lipolytica capable of producing bisabolene and use of the genetically engineered bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The genetically engineered bacteria are obtained by introducing an alpha-bisabolene synthase gene, a beta-bisabolene synthase gene or a gamma-bisabolene synthase gene into a host of the yarrowia lipolytica and by overexpression of a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene (HMGR gene). After the genetically engineered bacterium undergo shake-flask fermentation in respective yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD) mediums, the yield of the bisabolene produced by genetically engineered bacteria Po1g Delta ku70 alpha-HR is 100.22 mg / L, the yield of the bisabolene produced by genetically engineered bacteria Po1g Delta ku70 beta-HR is 5.66 mg / L, and the yield of the bisabolene produced by genetically engineered bacteria Po1g Delta ku70 gamma-HR is 3.55 mg / L. After themediums are optimized, the yield of the bisabolene produced by the genetically engineered bacteria Po1g Delta ku70 alpha-HR is 162.24 mg / L, the yield of the bisabolene produced by genetically engineered bacteria Po1g Delta ku70 beta-HR is 20.811 mg / L, and the yield of the bisabolene produced by genetically engineered bacteria Po1g Delta ku70 gamma-HR is 6.25 mg / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Medicine composition containing lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 inhibitors and application thereof
ActiveCN104840963APharmaceutical active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderLipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2Triglyceride metabolism
The invention relates to a medicine composition containing lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 inhibitors and application of the medicine composition, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The medicine composition consists of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 inhibitors and one or several kinds of the following ingredients including HMG-CoA (3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl CoA) reductase inhibitors, cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism influence medicine, cholesterol absorption influence medicine, polysaccharide lipid-lowering medicine, gastrointestinal lipase inhibitors or butylphenyl phthaleine. The medicine composition provided by the invention has the surprising curative effect in the aspect of treating atherosclerotic diseases, and the surprising curative effect cannot be achieved by previous lipid-lowering medicine.
Owner:HEBEI DONGKANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Escherichia coli expression strain for high yield of geraniol glucoside and application thereof
ActiveCN110317765AEasy to synthesizeEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGeranyl pyrophosphate
The invention provides an Escherichia coli expression strain for high yield of geraniol glucoside, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The Escherichia coli expression strain jointly expresses an acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase gene, a methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthetase gene, a HMG-CoA reductase gene, a mevalonate kinase gene, phosphomevalonate kinase gene, a pyrophosphate mevalonate decarboxylase gene, an isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase gene, a geranyl pyrophosphate GPP synthetase ispA*, a geraniol synthetase gene, a geranyl pyrophosphate GPP synthetase ERG20* and a glycosyltransferase gene. The yield of geraniol glucoside produced from the Escherichia coli expression strain is high, reliable in mass and good in application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Medicament composition for treating diabetes and application of medicament composition
ActiveCN102526739AGood effectSignificant progressOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTHydroxymethyl
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to a medicament composition for treating diabetes and application of the medicament composition, in particular to application of the medicament composition in treatment of diabetic nephropathy and diabetic merged hyperlipidemia. For better treating the diabetes and complications thereof, the invention provides the medicament composition. The medicament composition contains hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, glycosaminoglycan and insulin sensitizer serving as active ingredients, and particularly contains low molecular weight heparin, pioglitazone and rosuvastatin.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Composition with lipase inhibitor and hydroxymethyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor
The invention provides a composition with a lipase inhibitor and a hydroxymethyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, and a pharmaceutical preparation with the composition. Preferentially, the lipase inhibitor is one of orlistat and cetilistat, and the hydroxymethyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor is one of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin and pitavastatin or pharmaceutically-acceptable salt thereof. The composition can have the synergistic antibacterial effect and the synergistic histamine releasing inhibition effect, and therefore thetreatment effect and economic characteristics of bacterial infection-caused allergic disease patients can be improved.
Owner:黄泳华
Medicinal composition containing zafirlukast and statins
InactiveCN102824638AReduce dosageGood synergyOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderActive componentStatine
Owner:HAIMEN THE YELLOW SEA ENTREPRENEURSHIP PARK SERVICE CO LTD
Silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP capable of reducing blood fat, and application of silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP
ActiveCN110734470AReduce expressionReduce synthesisMetabolism disorderTripeptide ingredientsA lipoproteinMethyl palmoxirate
The invention provides a silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP capable of reducing blood fat, and application of the silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP, and belongs to the biotechnology field. The amino acid sequence of the silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP capable of reducing the blood fat is His-Pro-Pro. The invention also discloses the application of the silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP for preparing a drug capable of reducing the blood fat. Blood fat reduction is realized through reduction of the synthetic amount of cholesterol and / or removal of a low density lipoprotein. An experiment indicates that the silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP has the functions of down-regulating the expression level of HMGCCR and SQS genes and / or proteins and / or up-regulating the expression level of LDLR genes and / or proteins. An enzyme activity inhibition experiment indicates that the silkworm pupa protein peptide HPP also can inhibit the activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Eutectic compound formed by lipase inhibitor and hydroxy methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor
The invention provides a eutectic compound formed by a lipase inhibitor and a hydroxy methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor and composition containing the eutectic compound. The eutectic compound is characterized in that the lipase inhibitor is selected from one of orlistat and cetilistat; the hydroxy methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor is selected from one of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin and pitavastatin or pharmacologically acceptable salts thereof. The eutectic compound can simultaneously have synergistic antibacterial action and synergistic histamine release inhibition function, so that the treatment effect on patients with allergic diseases caused by bacterial infection and the economic characteristics can be improved.
Owner:黄泳华
Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain for producing protopanoxadiol by utilizing xylose and construction method and application of recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain
PendingCN111690549ATo achieve effective applicationBig advantageFungiTransferasesCytochrome P450 reductasePyrophosphate
The invention discloses a recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain for producing protopanoxadiol by utilizing xylose and a construction method and application of the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain. Yarrowia lipolytica ATCC 201249 is used as an original strain, optimized xylose reductase XYL1, xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 and an overexpressed endogenous xylulokinase XKS expression cassette areintroduced, and a recombinant strain 1 is obtained; a dammarendiol synthase gene DS, a protopanoxadiol synthase gene PPDS and a cytochrome P450 reductase gene ATR1 are introduced into the recombinantstrain 1 to obtain a recombinant strain 2; a gene tHMG1 for encoding nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, a gene erg9 for squalene synthase and an erg20 for encoding farnesene pyrophosphate synthase in a truncated mevalonic acid pathway are introduced into the recombinant strain 2 to obtain a recombinant strain 3; and the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica isused for producing the protopanoxadiol by using the xylose, and the shake flask yield reaches 80.88 mg / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Dipeptide QE with dual functions of lowering blood pressure and lowering blood fat and application thereof
ActiveCN103739666AHas HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activityInhibitory activityDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorder3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric AcidDipeptide
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnologies, particularly relates to a dipeptide which can be combined with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), can inhibit the activity of ACE and can inhibit the activity of 3-hydroxyl-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, and specifically discloses a dipeptide QE with dual functions of lowering blood pressure and lowering blood fat. The amino acid sequence of the dipeptide QE is Gln-Glu. The invention further simultaneously discloses application of the dipeptide QE in the preparation of ACE inhibition peptides and / or HMG-CoA reductase inhibition peptides.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUREN UNIV
Poly-substituted pyrimidine statin fluorine-containing derivative and uses thereof
ActiveCN105175399AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical drugPerylene derivatives
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and provides a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, which is a poly-substituted pyrimidine statin fluorine-containing modifier of 1-fluoro-3-hydroxy pentanoic acid and a salt or an ester thereof formed by carrying out ring opening on 3-fluoro-caprolactone-containing fragment and a lactone thereof, wherein the structure formula is represented in the specification. According to the present invention, the test results show that the compounds have the HMG-CoA reductase activity inhibition effect, and can be used as the new generation of the potential HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
Owner:SHANGHAI ECUST BIOMEDICINE CO LTD
Application of atorvastatin or medical salt thereof in preparation of medicines for treating uterine fibroid
InactiveCN108078981AGrowth inhibitionPrevent proliferationAntineoplastic agentsSexual disorderMitogen-activated proteinCancer research
The invention discloses application of atorvastatin in preparation of medicines for treating uterine fibroid. The medicine is used for inhibiting the growth of immortalized uterine fibroid cells and primary uterine fibroid cells, including inhibiting of cell proliferation, and promoting of cell apoptosis. The atorvastatin is used for inhibiting the growth of uterine fibroid cells by down-regulating the expression of proliferation protein PCNA and anti-apoptosis protein Bc1-2, up-regulating the expression of apoptosis protein cleaved-caspase 3 and Bim, inhibiting a signal channel of MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase), down-regulating the activity of p-ERK1 / 2 (phospho-extracellular regulated protein kinases 1 / 2), inhibiting the activity of HMG-CoA (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A), and inhibiting the mevalonate pathway. The application of the blood fat-decreasing medicine, namely the atorvastatin, in the treatment of the uterine fibroid is proofed by the experiment, and the effect of inhibiting the growth of the uterine fibroid is obtained.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Statin and omega-3 fatty acids for lipid therapy
A method of lipid therapy, comprising providing a subject group having a baseline triglyceride level of 200 to 499 mg / dl and being at or near its low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level goal, and reducing the triglyceride level and the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) level of the subject group as compared to treatment with a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) inhibitor alone, by administering to the subject group an effective amount of an HMG CoA inhibitor and a composition comprising omega-3 fatty acids.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Lechang michelia 3-hydroxy-3-methy glutaryl CoA reductase protein coding sequence
InactiveCN1888067AIncrease contentPromote healthy growthPlant peptidesFermentationMetaboliteCholesterol
The Lechang michelia Mc-Hmgr protein coding sequence belongs to the field of gene engineering. The separated DNA includes nucleotide sequence coding polypeptide with Lechang michelia Mc-Hmgr protein activity, and the nucleotide sequence has at least 70 % homolog with the nucleotide sequence of sites 56-1726 in SEQ ID No. 3 or can hybridize with the nucleotide sequence of sites 56-1726 in SEQ ID No. 3 at 40-55 deg.c. The present invention is one kind of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase capable of raising the content of secondry metabolite or its precursor in Lechang michelia. The secondry metabolite has the functions of regulating blood pressure of human body in bi-direction, lowering cholesterol content, preventing cardiac and cerebral angioscerosis, etc.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of eutectic compound composed of proton pump inhibitor and hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor in preparation of antitumor drug
The invention provides an application of a eutectic compound composed of a proton pump inhibitor and a hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor in preparation of an antitumor drug. The compound is characterized in that: the proton pump inhibitor is selected from one of omeprazole, esmeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole and lansoprazole; and the hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor is selected from one of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin and pitavastatin or pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin and pitavastatin. The antitumor drug can be used for treating one of liver cancer, lung cancer, stomach cancer, ovarian cancer, colon cancer, cervical cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma and leukemia.
Owner:黄泳华
Dipeptide SD with dual functions of lowering blood pressure and blood fat and application thereof
ActiveCN103772484BInhibitory activityHas HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activityDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorder3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric AcidDipeptide
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a dipeptide which can be bonded with angiotensin converting enzyme, inhibit the activity thereof, and also can inhibit the activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Specifically, the invention discloses a dipeptide SD with dual functions of lowering blood pressure and blood fat. The amino acid sequence of the dipeptide SD is as follows: Ser-Asp. The invention also provides an application of the dipeptide SD in preparation of ACE (ASCII-compatible encoding) inhibitory peptide and / or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory peptide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Lechang michelia 3-hydroxy-3-methy glutaryl CoA reductase protein coding sequence
InactiveCN100406559CIncrease contentPromote healthy growthOxidoreductasesPlant peptidesMetaboliteNucleotide
The Lechang michelia Mc-Hmgr protein coding sequence belongs to the field of gene engineering. The separated DNA includes nucleotide sequence coding polypeptide with Lechang michelia Mc-Hmgr protein activity, and the nucleotide sequence has at least 70 % homolog with the nucleotide sequence of sites 56-1726 in SEQ ID No. 3 or can hybridize with the nucleotide sequence of sites 56-1726 in SEQ ID No. 3 at 40-55 deg.c. The present invention is one kind of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase capable of raising the content of secondry metabolite or its precursor in Lechang michelia. The secondry metabolite has the functions of regulating blood pressure of human body in bi-direction, lowering cholesterol content, preventing cardiac and cerebral angioscerosis, etc.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Dipeptide SD with dual functions of lowering blood pressure and blood fat and application thereof
ActiveCN103772484AInhibitory activityHas HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activityDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorder3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric AcidDipeptide
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a dipeptide which can be bonded with angiotensin converting enzyme, inhibit the activity thereof, and also can inhibit the activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Specifically, the invention discloses a dipeptide SD with dual functions of lowering blood pressure and blood fat. The amino acid sequence of the dipeptide SD is as follows: Ser-Asp. The invention also provides an application of the dipeptide SD in preparation of ACE (ASCII-compatible encoding) inhibitory peptide and / or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory peptide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Statin and Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Lipid Therapy
A method and composition for lipid therapy. In some embodiments, the method comprises providing a subject group having a baseline triglyceride level of 200 to 499 mg / dl and being at or near its low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level goal, and reducing the triglyceride level and the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) level of the subject group as compared to treatment with a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) inhibitor alone, by administering to the subject group an effective amount of an HMG CoA inhibitor and a composition comprising omega-3 fatty acids.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com