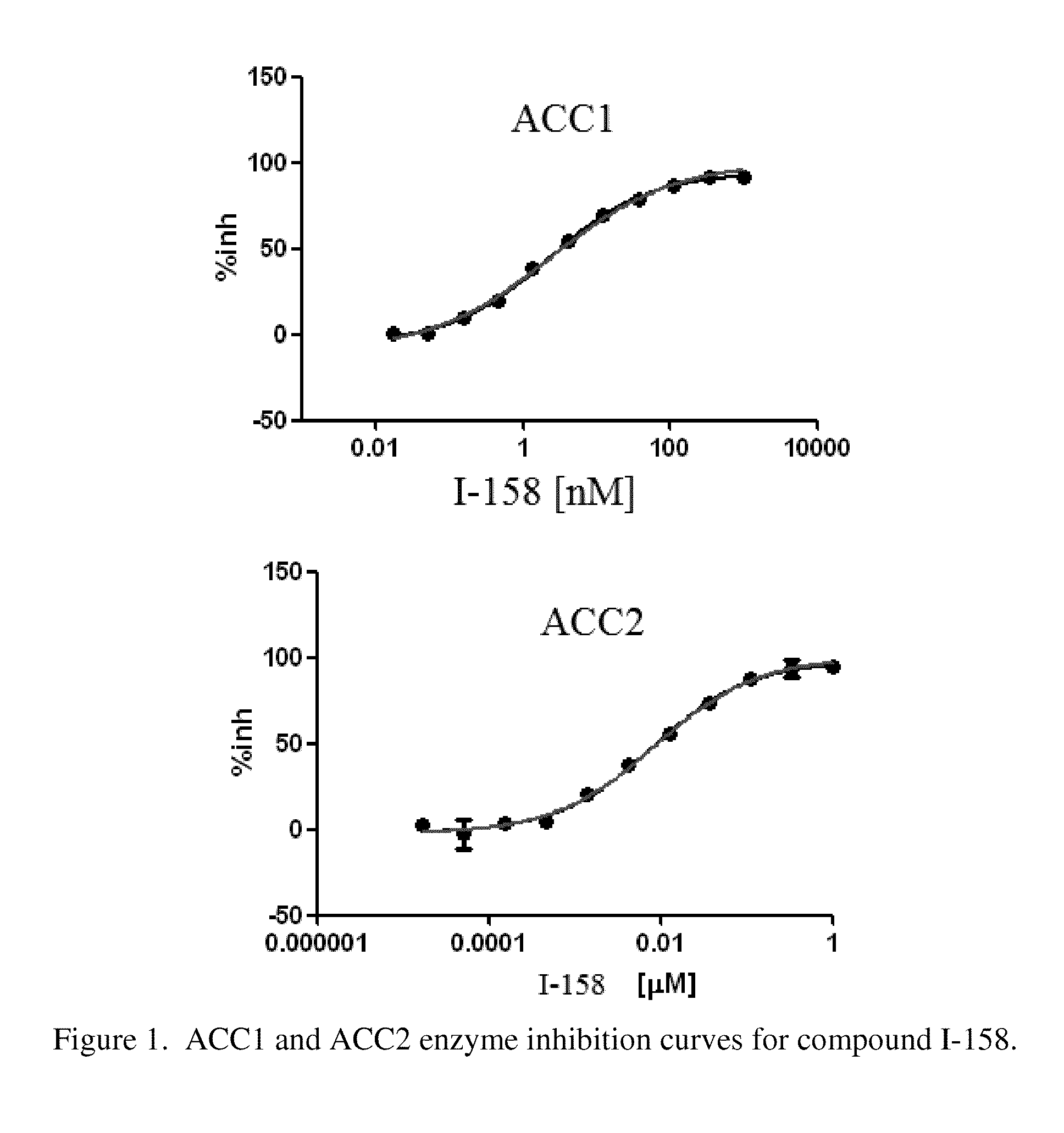
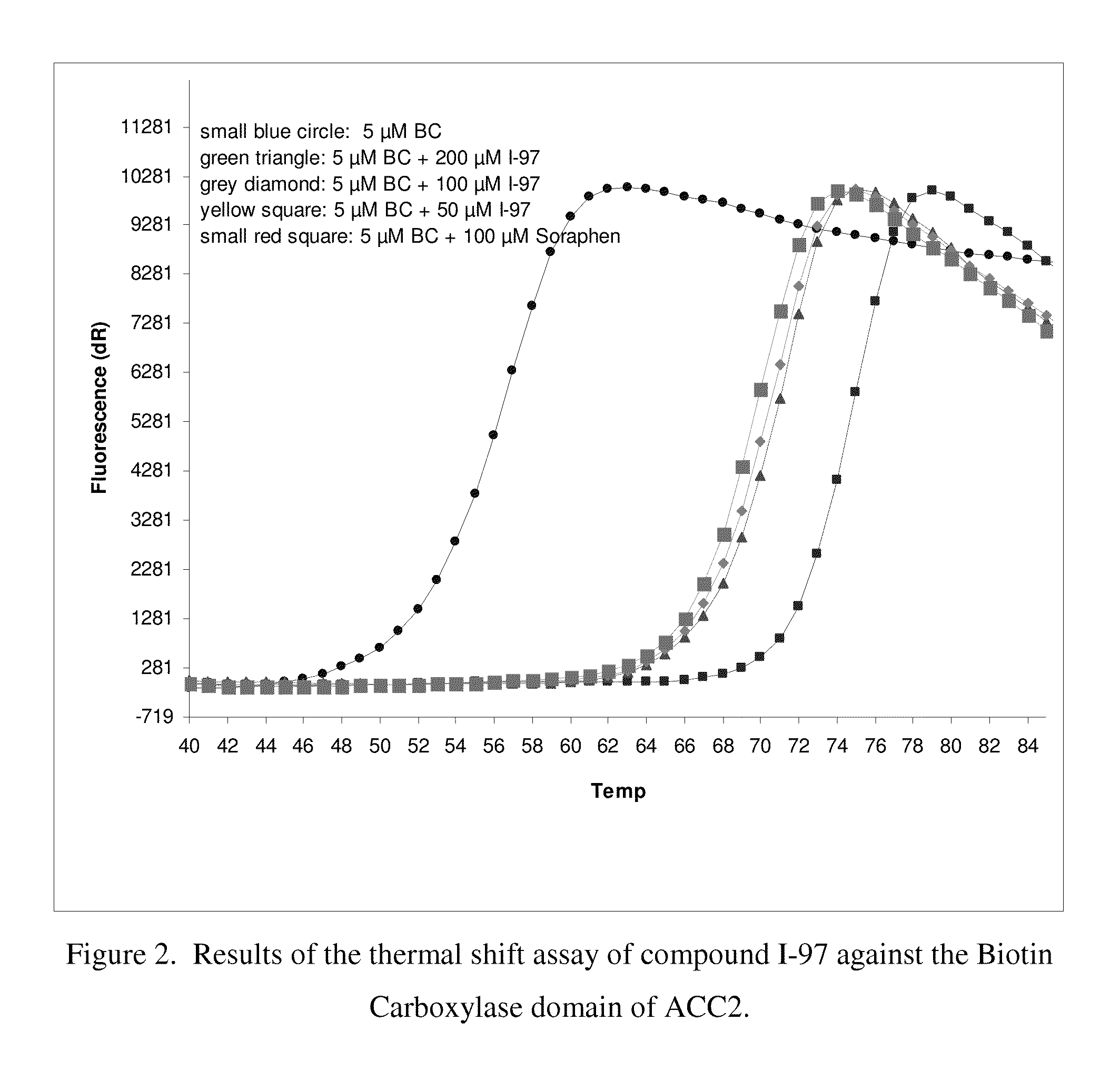
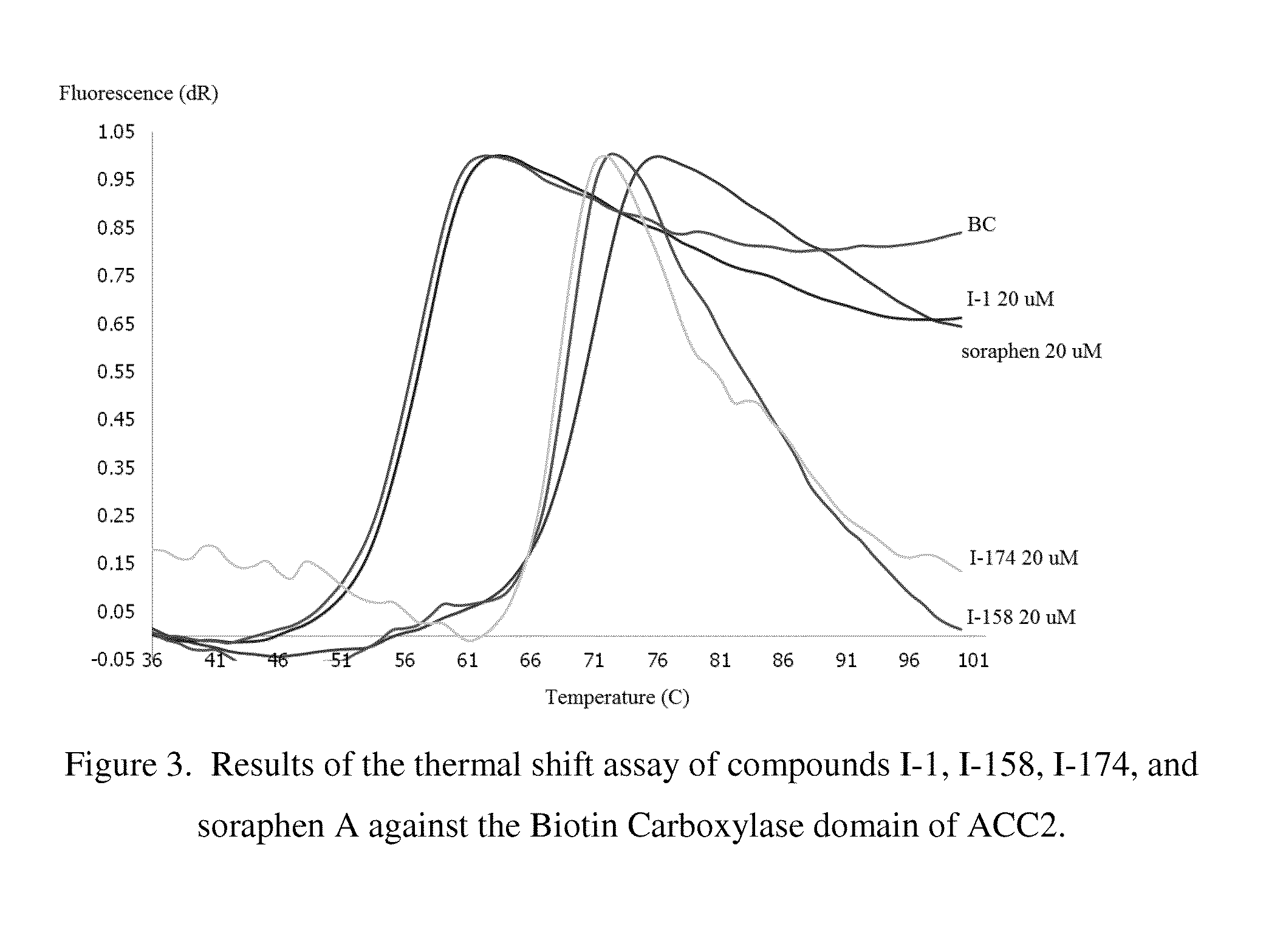
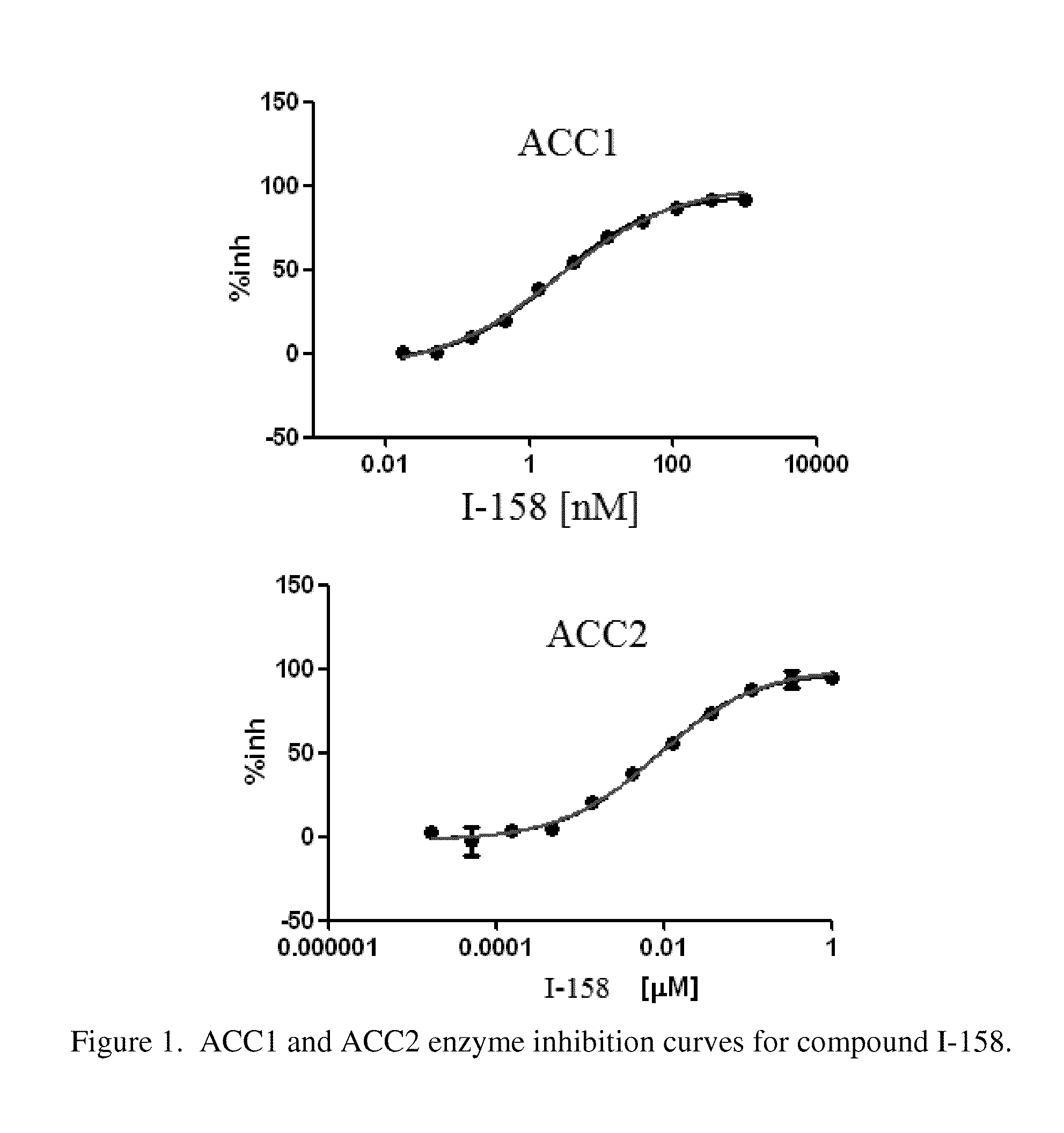
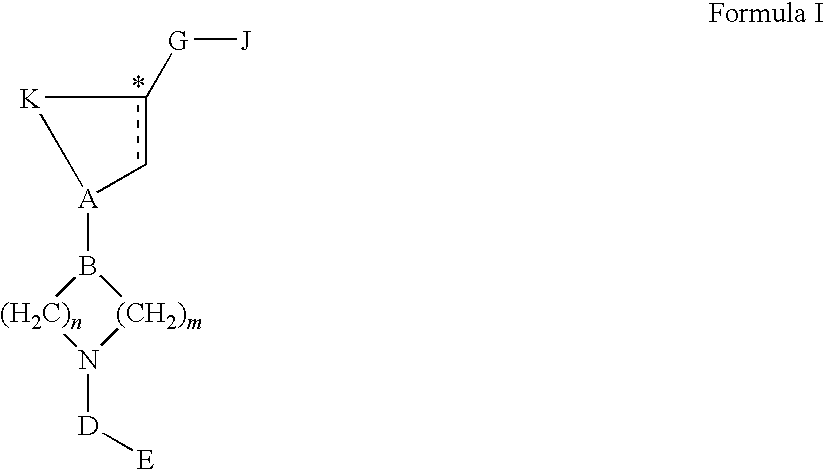Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Acyl-CoA carboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
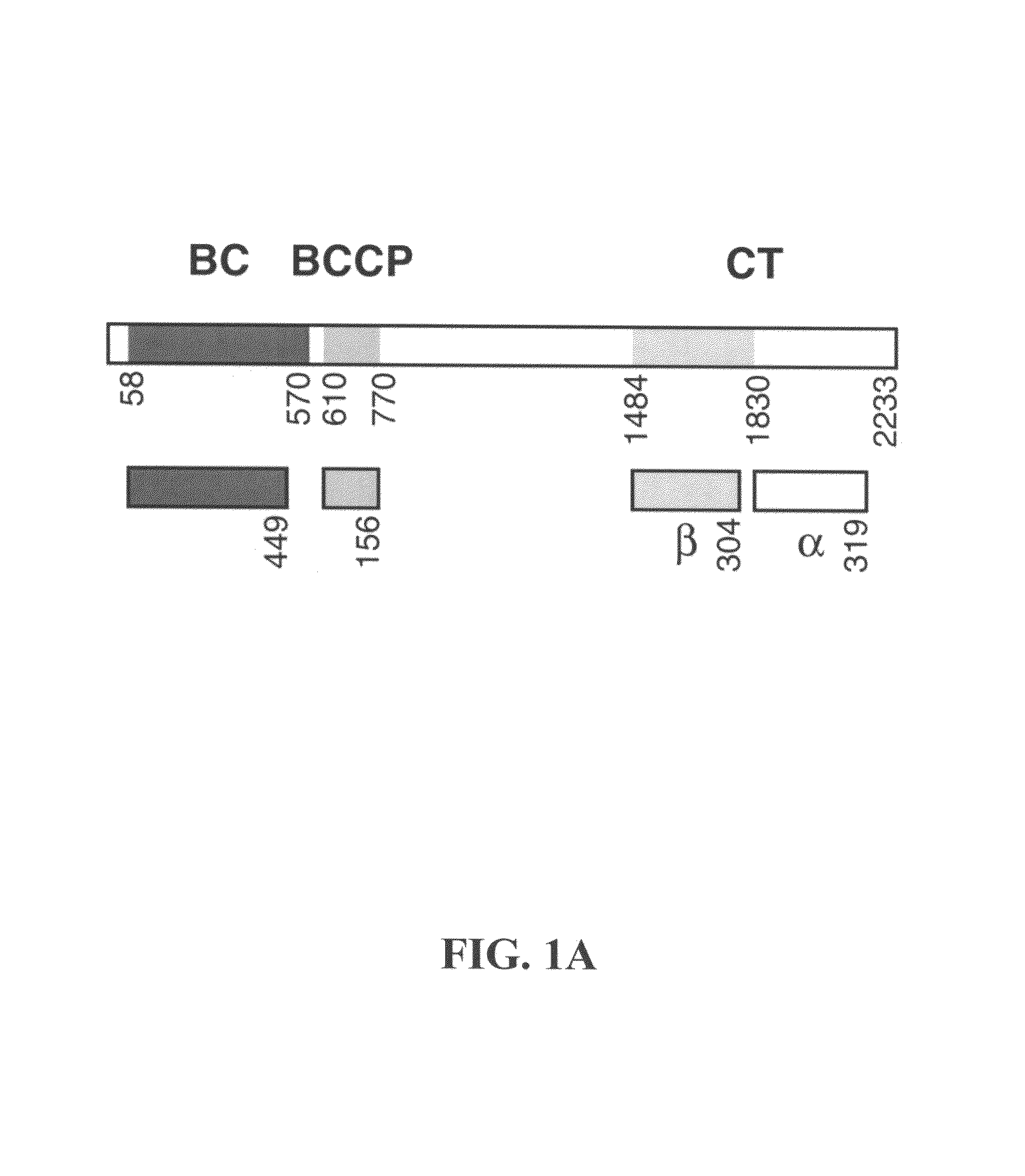
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to produce malonyl-CoA through its two catalytic activities, biotin carboxylase (BC) and carboxyltransferase (CT).
ACC inhibitors and uses thereof
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC +1
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC +1
ACETYL CoA CARBOXYLASE (ACCase) GENE FROM JATROPHA CURAS
InactiveUS20090205079A1High oil contentFacilitates detection and selectionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesJatrophaGene
The present invention provides methods for increasing oil content in Jatropha Curcas L. plants. The invention further provides the cDNA and protein sequences of Jatropha acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase) and methods for cloning and expressing the Jatropha ACCase gene to produce transgenic plants with increased oil content.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
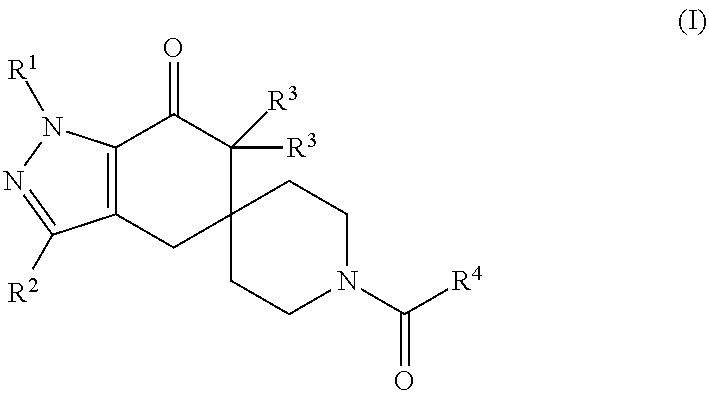
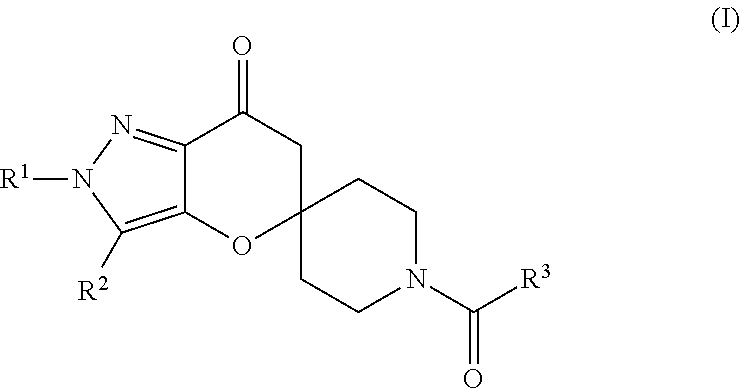
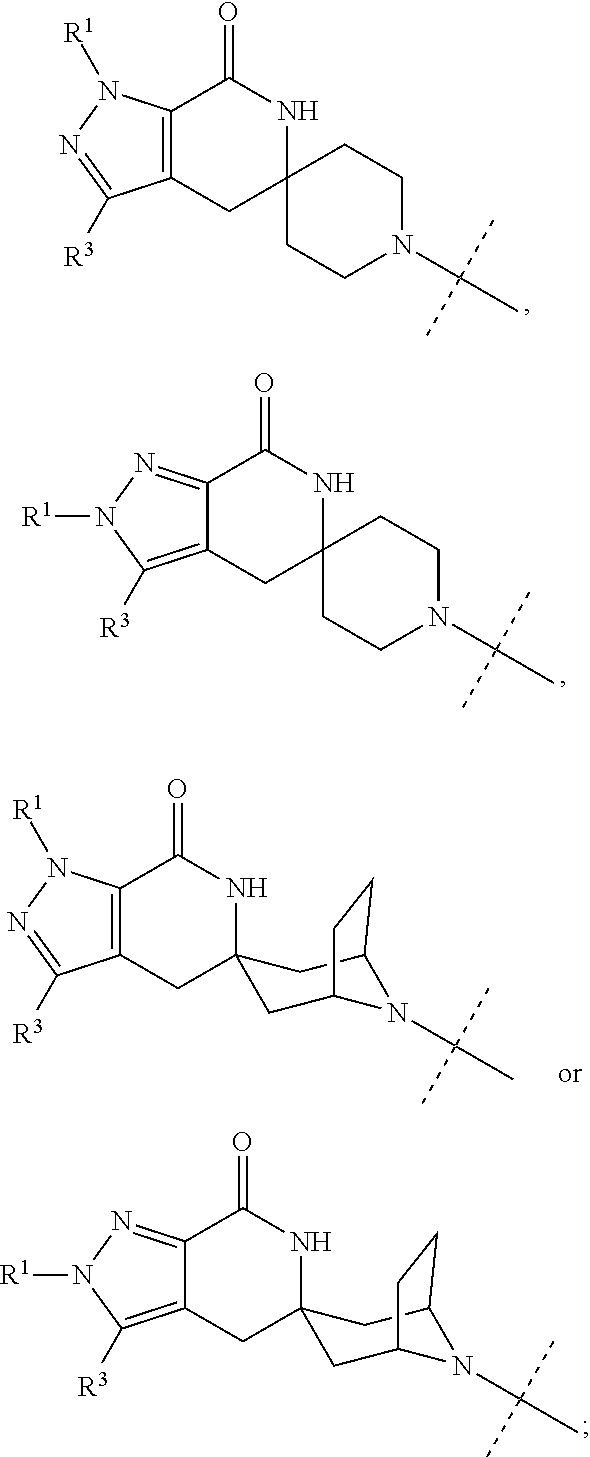
N1-Pyrazolospiroketone Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibitors
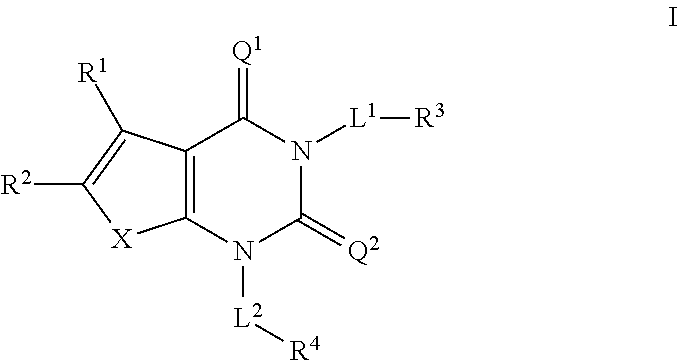
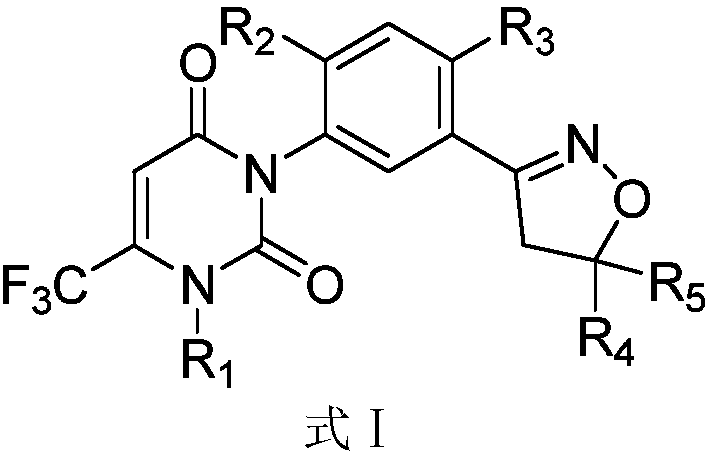
The invention provides a compound of Formula (I)or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the compound, wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating diseases, conditions or disorders modulated by the inhibition of an acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme(s) in an animal.
Owner:PFIZER INC
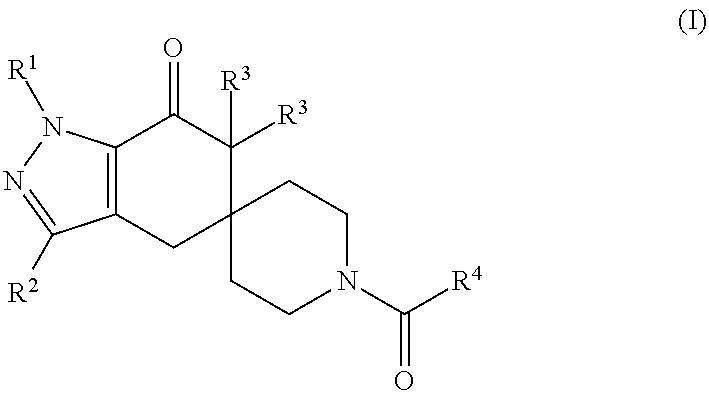
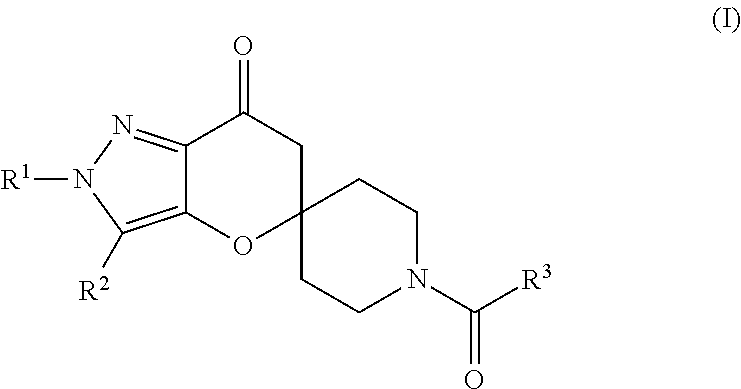
N1-pyrazolospiroketone acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors
The invention provides a compound of Formula (I)or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the compound, wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating diseases, conditions or disorders modulated by the inhibition of an acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme(s) in an animal.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Pyrazolospiroketone Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibitors
The invention provides compounds of Formula (1) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of said compound, wherein R1, R2, and R3 are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating diseases, conditions or disorders modulated by the inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme(s) in an animal.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:GILEAD APOLLO LLC
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC
Pyrrolidine derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Herbicide composition and application method thereof
ActiveCN109864068ASynergistic effect is obviousReduce dosageBiocideAnimal repellantsActive componentGlyphosate
The invention relates to a herbicide composition and an application method thereof. The composition comprises an active component A and an active component B, wherein the component A is selected froma compound represented by a following general formula, and the component B is one selected from acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) inhibitor type herbicides. The herbicide composition disclosed by the invention is particularly suitable for preventing and removing weeds with tolerance or resistance to organophosphorus herbicides, especially glyphosate.
Owner:SHENYANG SINOCHEM AGROCHEMICALS R&D CO LTD
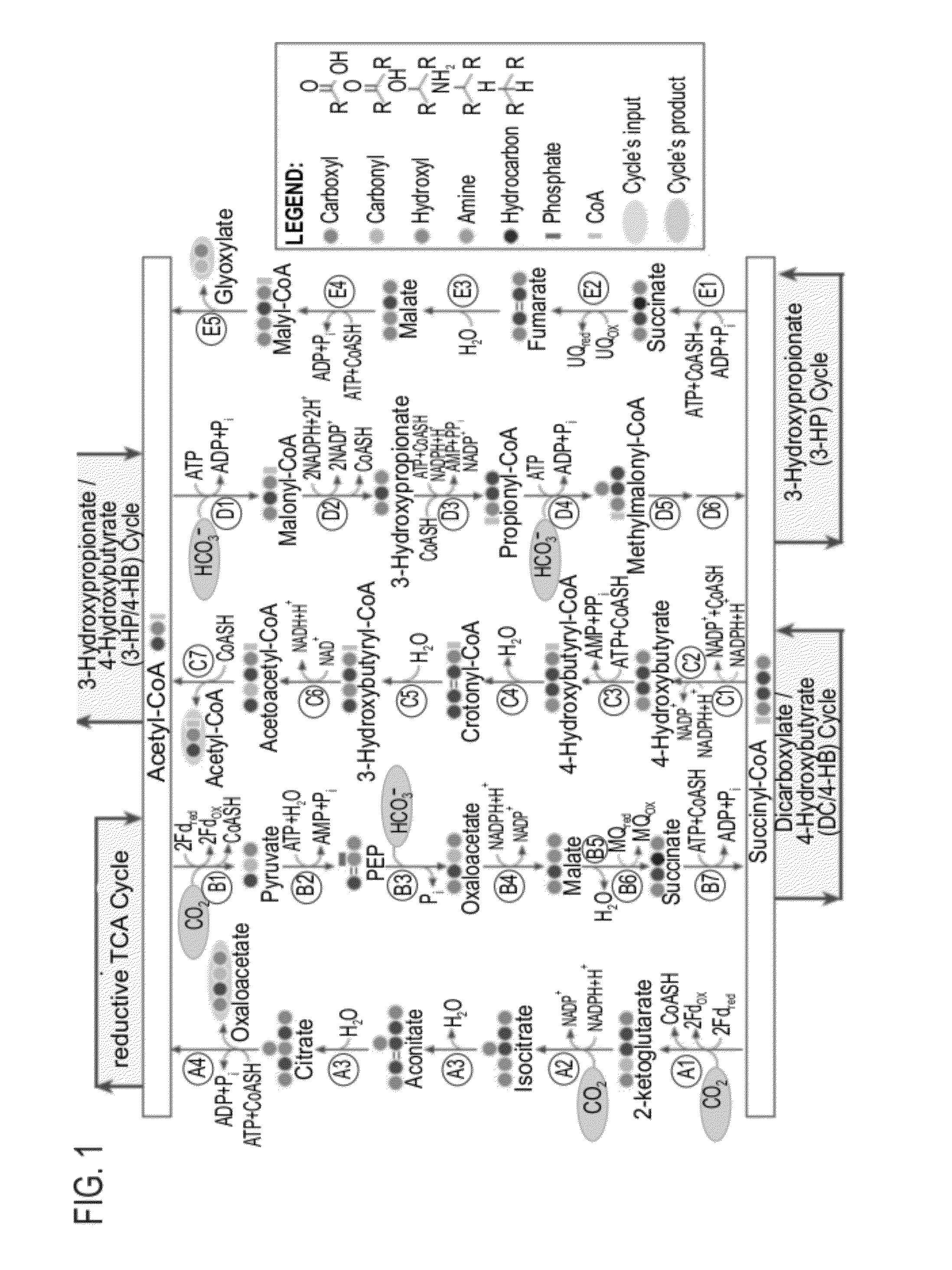
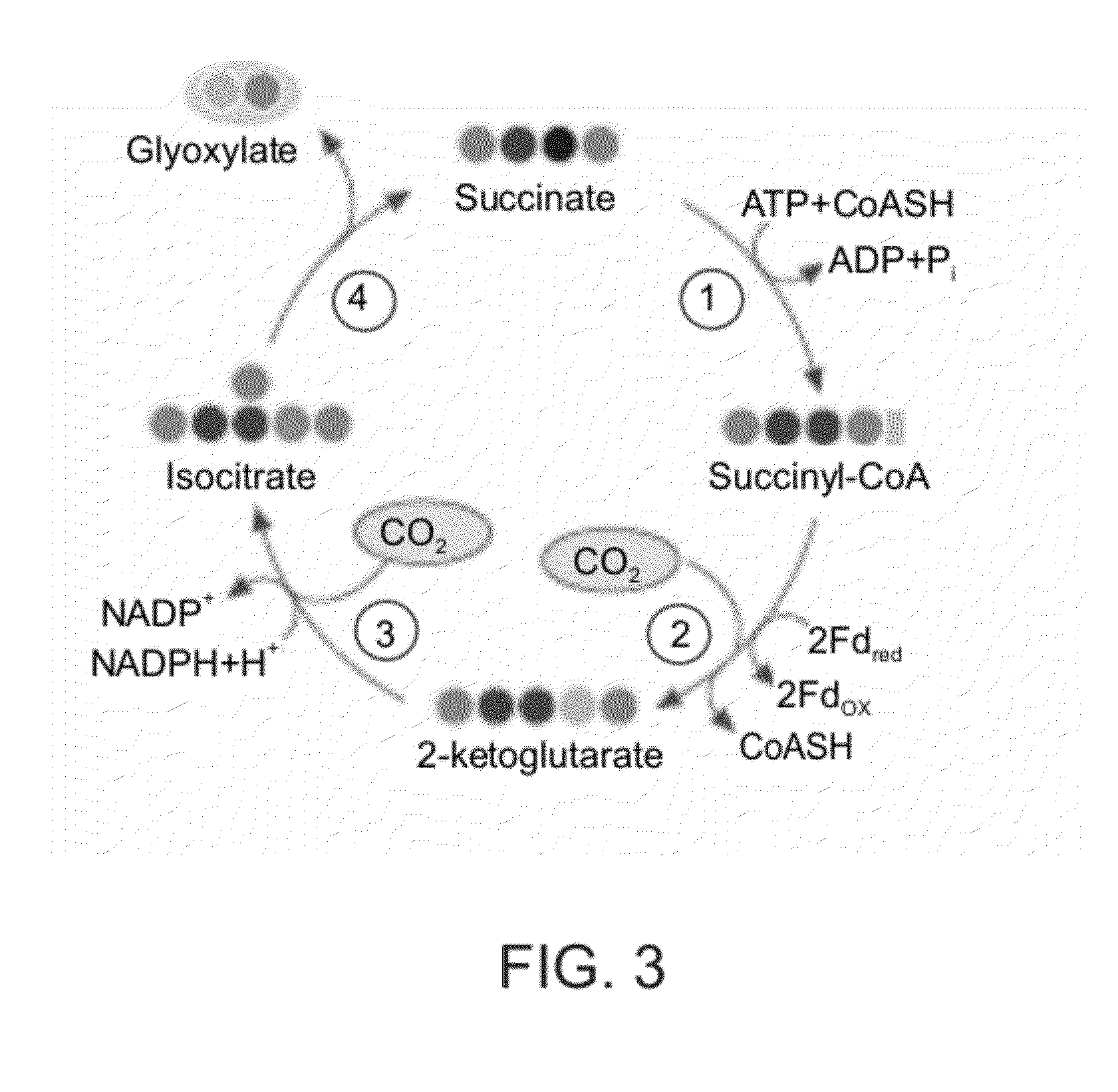
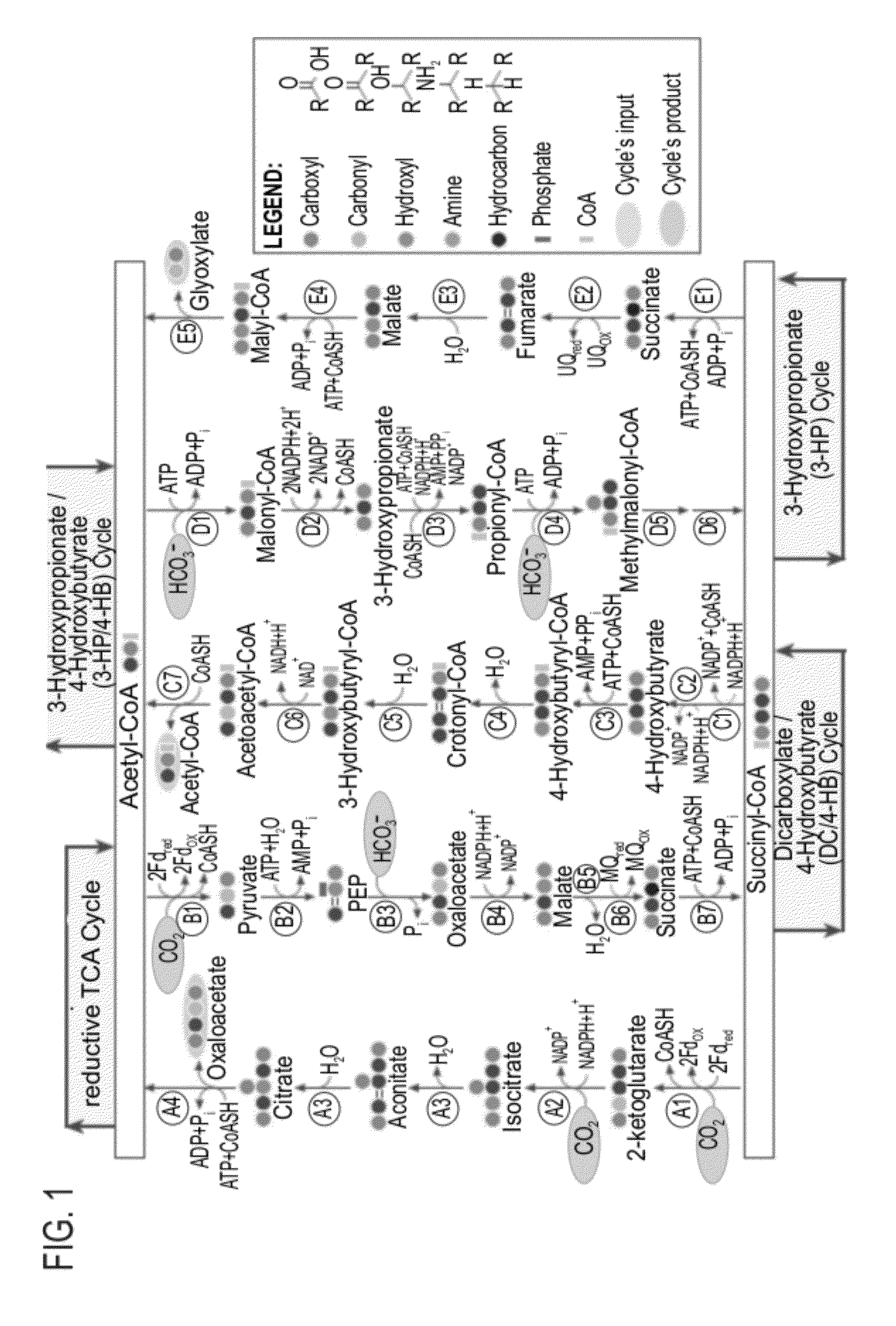
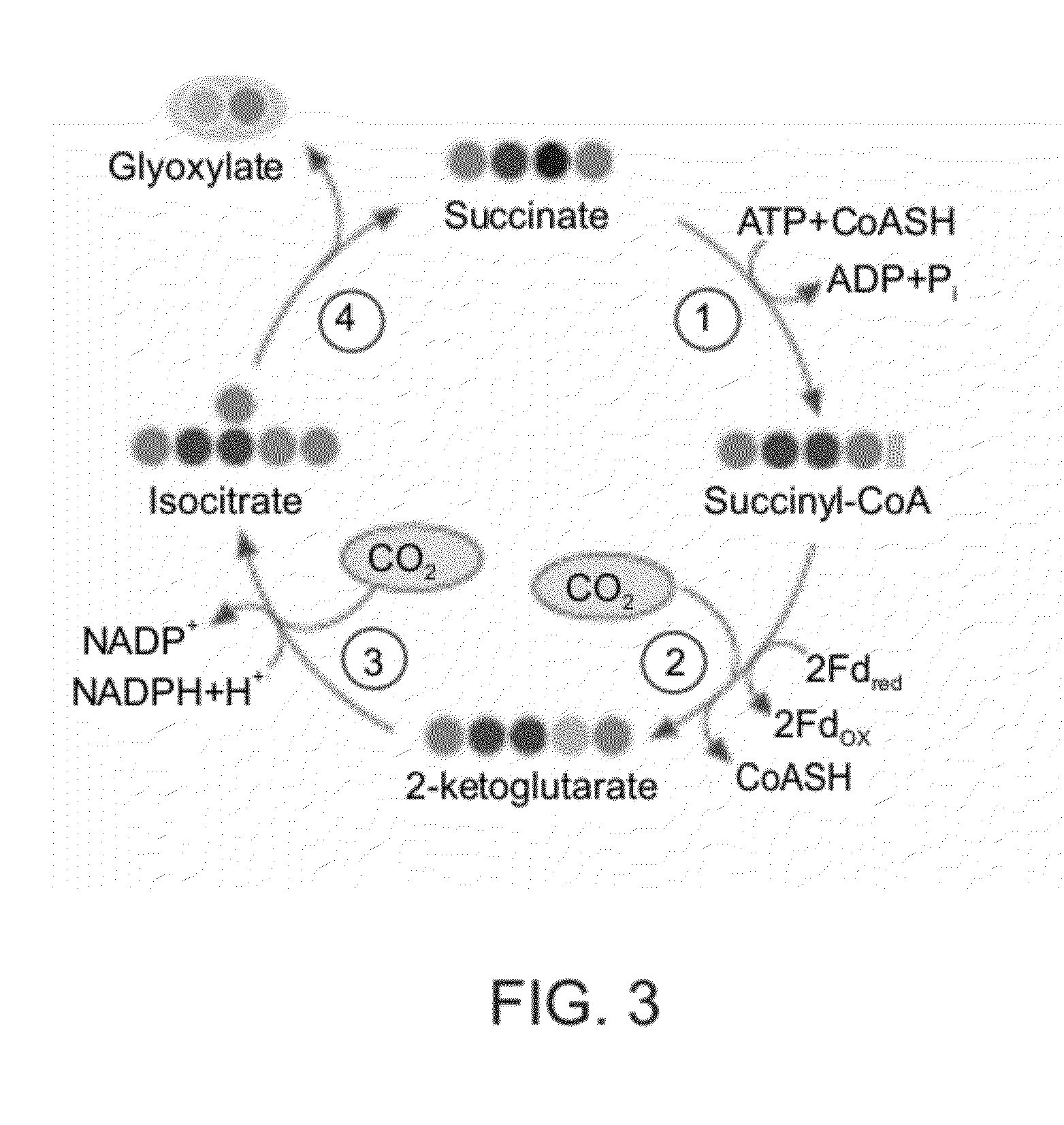
Enzymatic systems for carbon fixation and methods of generating same
A system for carbon fixation is provided. The system comprises enzymes which catalyze reactions of a carbon fixation pathway, wherein at least one of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway is a carboxylation reaction, wherein products of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway comprise oxaloacetate and malonyl-CoA, wherein an enzyme which performs the carboxylation reaction is selected from the group consisting of phophoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxlase, pyruvate carboxylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase and wherein an export product of the carbon fixation pathway is glyoxylate. Additional carbon fixation pathways are also provided and methods of generating same.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
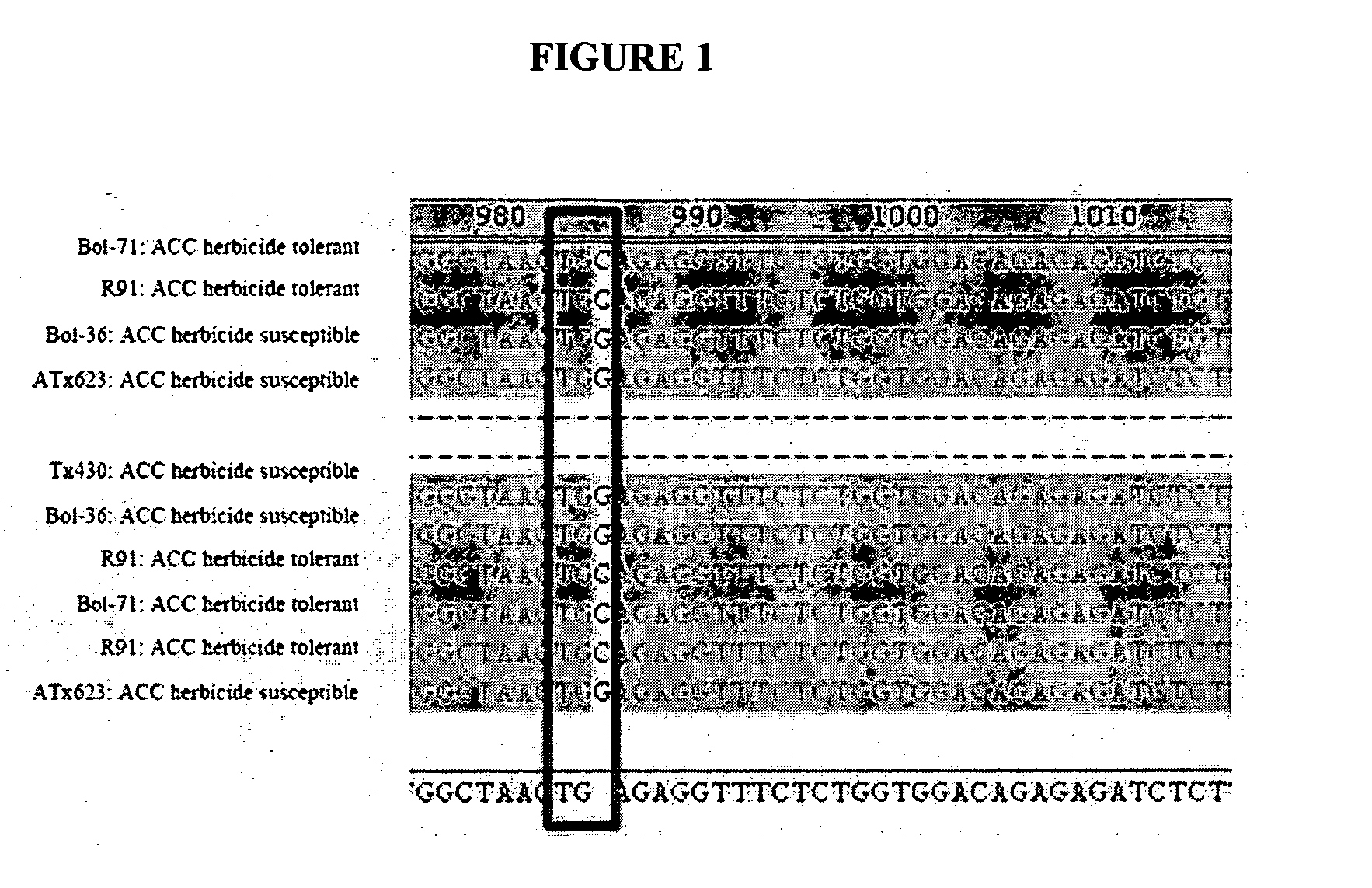
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Herbicide Resistant Sorghum
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for producing crop plants that are resistant to herbicides. In particular, the present invention provides for sorghum plants, plant tissues and plant seeds that contain altered acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) genes and proteins that are resistant to inhibition by herbicides that normally inhibit the activity of the ACC protein.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Ester acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides ester compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC +1
ACC inhibitors and uses thereof
Owner:GILEAD APOLLO LLC +1
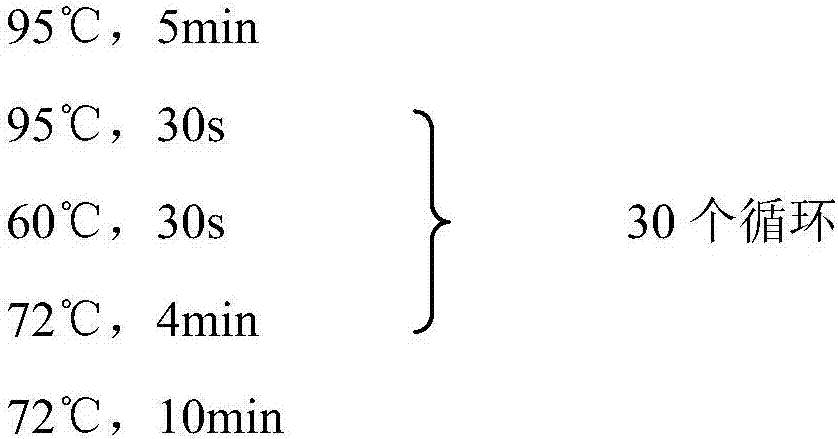
Method for improving fermentation level of salinomycin by increasing supply of precursors
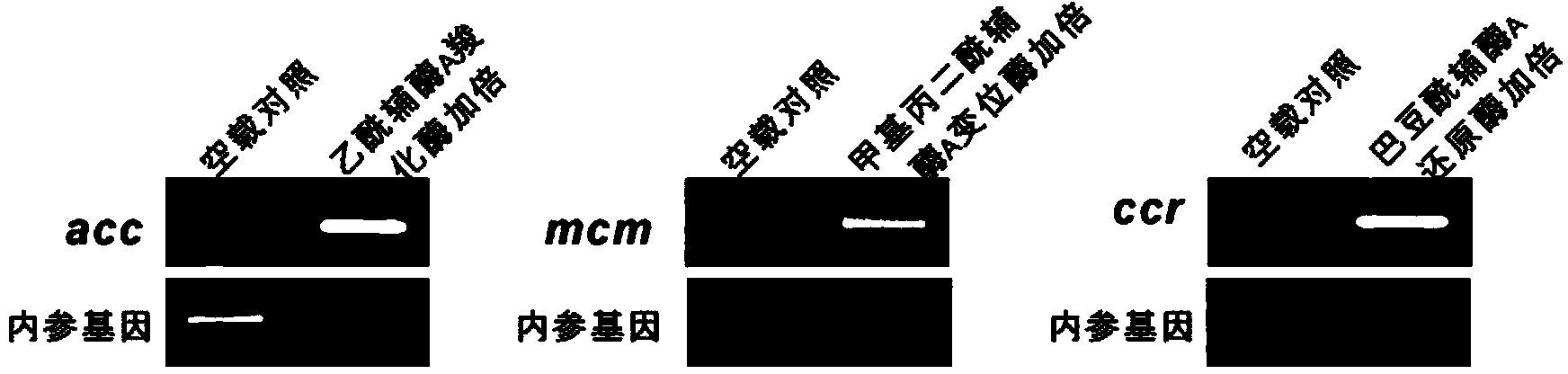
ActiveCN104357506AIncrease supplyImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcyl-CoA carboxylase
The invention discloses a method for improving the fermentation level of salinomycin by increasing supply of precursors. The method comprises the following steps: doubling acetyl coA carboxylase genes from streptomyces coelicolor, methyl malonyl coA mutase genes from streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 and crotonoyl coA reductase genes from the streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 on the chromosomes of the streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 through an integrating vector pSET152 respectively to increase supply of three precursors required for synthesizing salinomycin so as to increase the salinomycin yield. According to the method, the final fermentation yield of engineering strain salinomycin is increased by 260% and the shake flask level of a lab reaches 2 g / L.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Use of acetyl-coa carboxylase inhibitors for treating acne vulgaris
The present invention relates to methods of treating and / or preventing acne in patients comprising the step of administering to patients in need of such treatment a therapeutically effective amount of an ACC inhibitor or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Acetyl CoA carboxylase inhibitors
The present invention relates to acetyl coenzyme-A carboxylase (“ACC”) inhibiting compounds of the formulawherein the variables are as defined herein. In particular, the present invention relates to ACC1 and / or ACC2 inhibitors, compositions of matter, kits and articles of manufacture comprising these compounds, methods for inhibiting ACC1 and / or ACC2, and methods of making the inhibitors.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Triazole acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides triazole compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:GILEAD APOLLO LLC +1
Modified plants with increased oil content
InactiveUS20140230091A1High oil contentAvoid inhibitionLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionImmunoglobulinsAcyl carrier proteinCoenzyme A biosynthesis
Methods and means are provided to increase the oil content of plants, particularly oleaginous plants by preventing feedback inhibition by 18:1-Coenzyme A or 18:1-Acyl Carrier Protein of the acetyl CoA-carboxylase enzyme in cells of these plants in various manners.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Carboxyltransferase domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
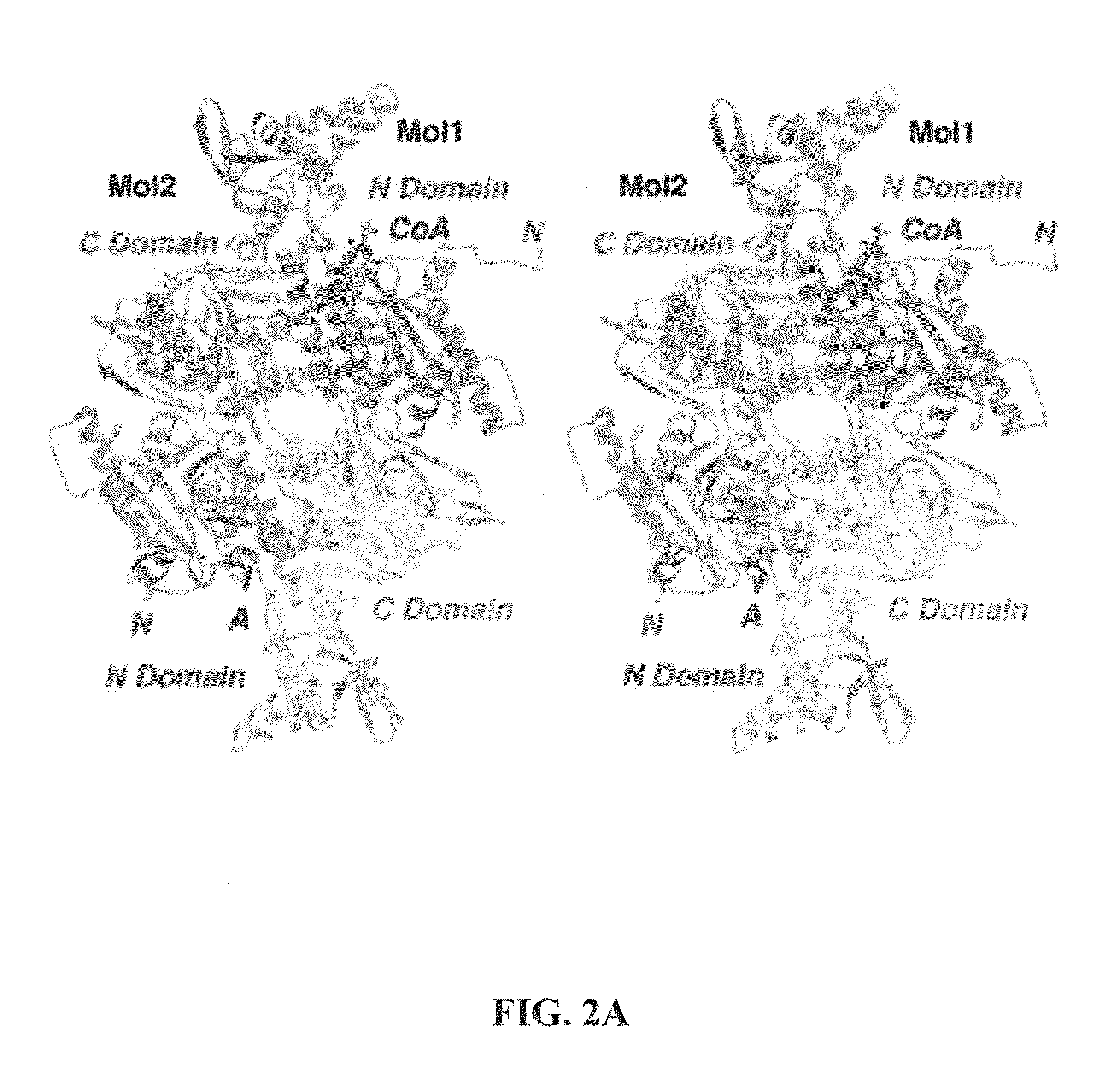
The present invention provides compositions and crystals of the carboxyltransferase (CT) domain (the C-terminal ˜90 kDa fragment) of various acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) proteins, including yeast, mouse and human ACCs. Further, the present invention provides methods for identifying and designing compounds that can modulate ACC activity. These methods are based, in part, on the X-ray crystallographic structures of the CT domain of yeast ACC, either alone or bound to acetyl-CoA or a CT inhibitor, such as haloxyfop or diclofop or CP-640186. Thus, the present invention relates to the crystal structures of the carboxyltransferase (“CT”) domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (“ACC”), and to the use of these structures in the design of anti-obesity compounds, anti-diabetes compounds, antibiotic compounds, herbicide compounds, and in the design of herbicide resistant plants.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
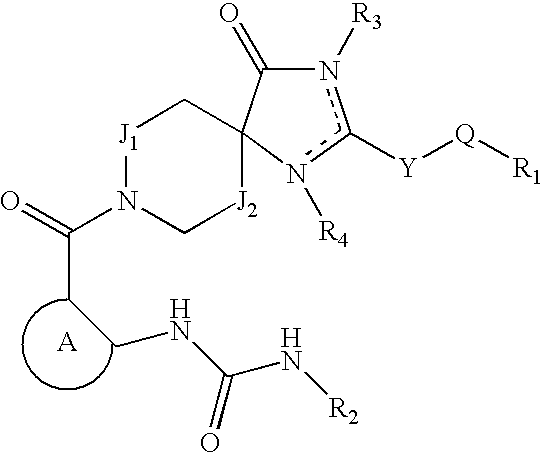
Compound used as ACC (Acetyl CoA Carboxylase) inhibitor and application thereof
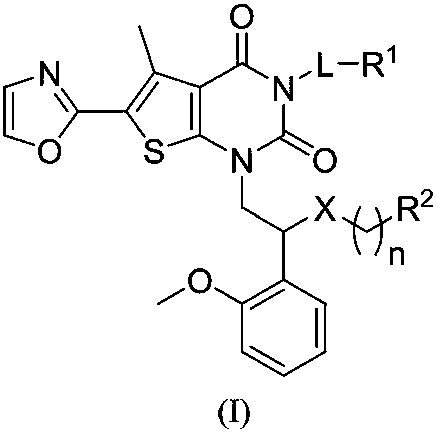
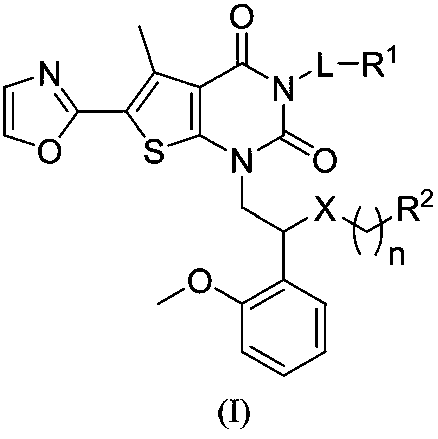
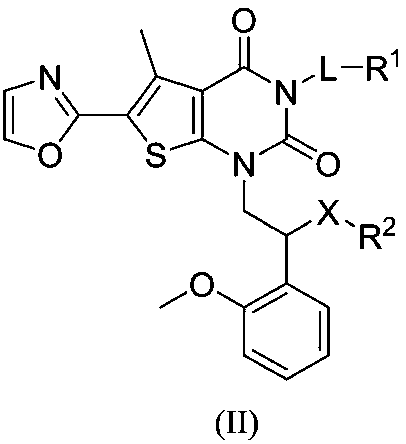
The invention belongs to the field of medical chemistry and relates to a compound used as an ACC (Acetyl CoA Carboxylase) inhibitor and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a compound shown as a formula I or isomers, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, crystals or prodrugs thereof, a preparation method of the compounds, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compounds and application of the compounds or the pharmaceutical composition to treatment and / or prevention ACC expression related diseases, such as fibrotic diseases, metabolic diseases, cancers or tissue proliferation diseases. The compound provided by the invention has very good inhibition activity on ACC and is very hopefully prepared into a treatment medicine for the fibrotic diseases, the metabolic diseases, the cancers or the tissue proliferation diseases. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:NANJING SANHOME PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Agent for promoting energy consumption
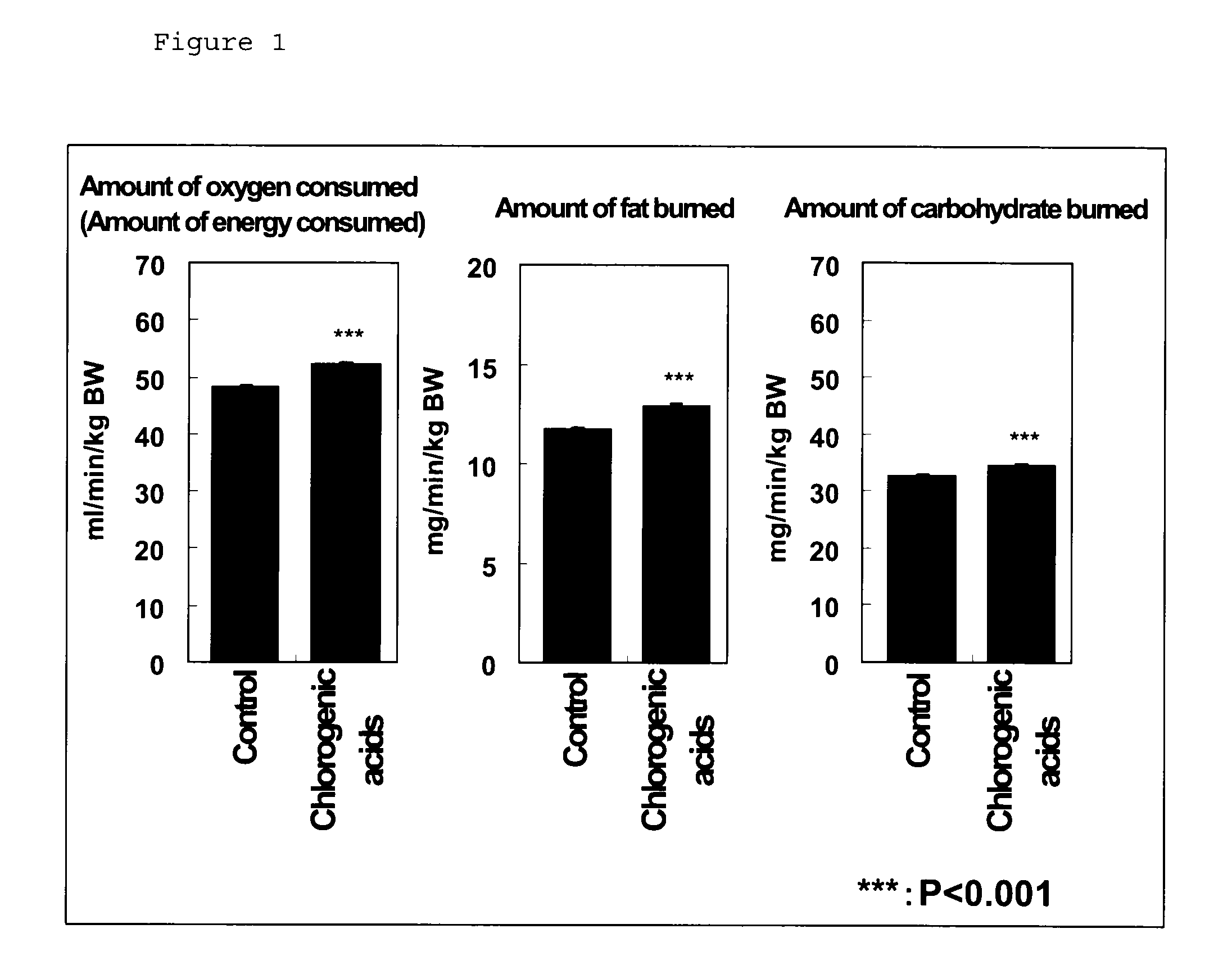
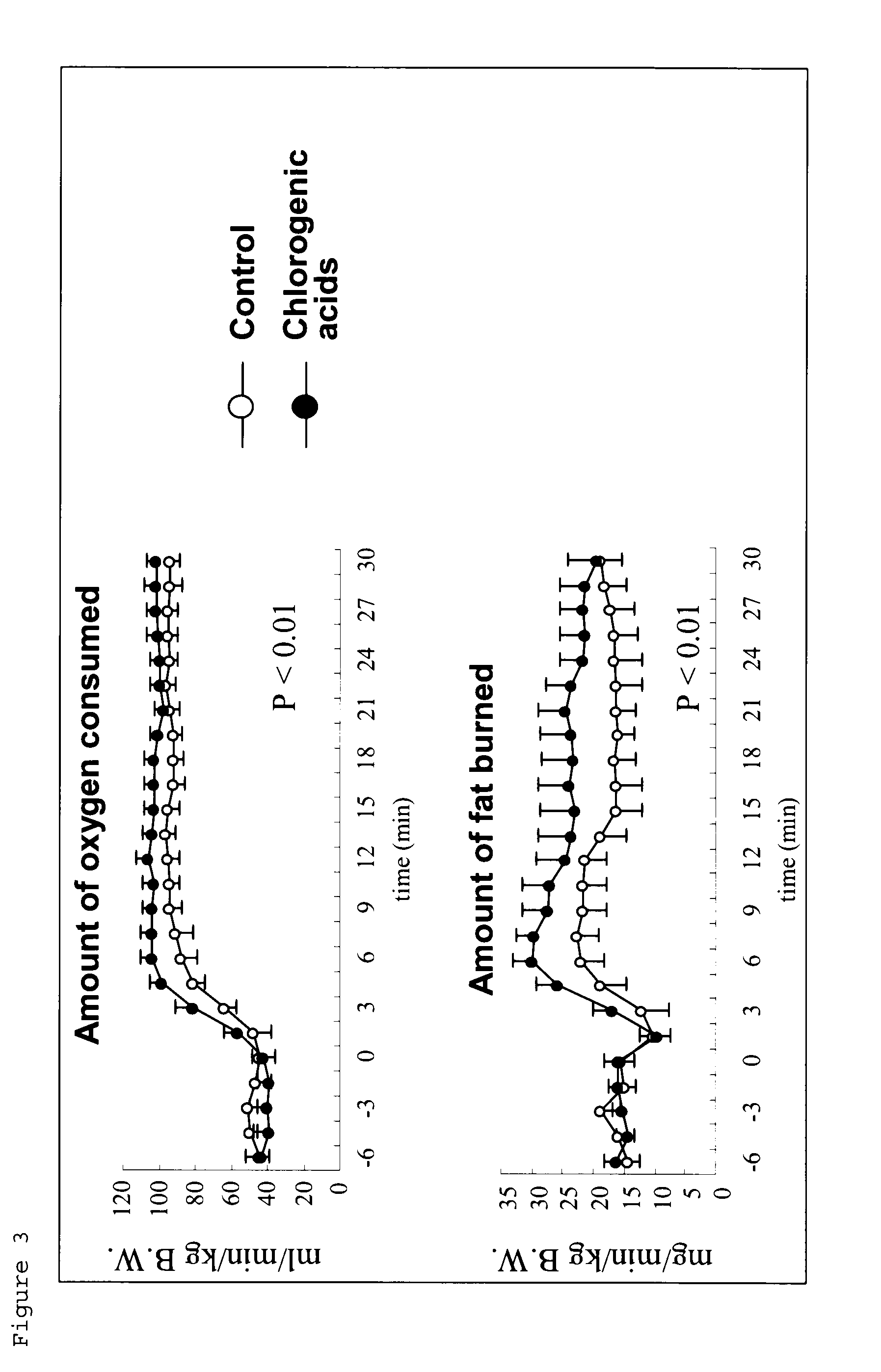
InactiveUS20120010285A1Improve athletic abilityHigh energyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideChlorogenic acidEnergy expenditure
Provision of a pharmaceutical product, a quasi-drug, a food, a beverage, a pet food, a feed, and others which are highly safe, have excellent action of promoting energy consumption, promoting fat burning, promoting carbohydrate burning, or improving an effect of exercise, and which are effective for the prevention or amelioration of obesity or metabolic syndrome or the improvement of motor functions.An agent for promoting energy consumption, an agent for promoting fat burning, an agent for promoting carbohydrate burning, an agent for improving an effect of exercise, an agent for improving motor functions, an agent for inhibiting acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2, and an agent for inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 containing chlorogenic acids or salts thereof as an active ingredient.
Owner:KAO CORP
ACC inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:GILEAD APOLLO LLC
Enzymatic systems for carbon fixation and methods of generating same
ActiveUS20120301947A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPyruvate synthesisAcetaldehyde
A system for carbon fixation is provided. The system comprises enzymes which catalyze reactions of a carbon fixation pathway, wherein at least one of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway is a carboxylation reaction, wherein products of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway comprise oxaloacetate and malonyl-CoA, wherein an enzyme which performs the carboxylation reaction is selected from the group consisting of phophoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxlase, pyruvate carboxylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase and wherein an export product of the carbon fixation pathway is glyoxylate. Additional carbon fixation pathways are also provided and methods of generating same.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Recombinant bacteria for synthesizing succinic acid from fixed amount of carbon dioxide, as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacteria
ActiveCN106967662AAvoid excessive dependenceIncrease profitBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPropionyl-CoA carboxylase
The invention provides recombinant bacteria for synthesizing succinic acid from a fixed amount of carbon dioxide, as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A recombinant bacteria host is escherichia coli, which can express a gene accADBC of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, a gene mcr of malonyl CoA reductase, a gene pcs of propionyl CoA synthase, a gene pcc of propionyl CoA carboxylase, a gene mcE of methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, a gene mcM of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and a gene sucCD of succinyl-coenzyme A synthase. According to the construction method, recombinant carriers pACYCDuet-accADBC-pcs and pETDuet-mcr-pcc-sucCD-mcEM are transformed into a host cell. The recombinant bacteria constructed through the construction method can adopt glucose serving as a unique carbon source to synthesize the succinic acid, and fermentation is performed for 48 hours, thus obtaining the succinic acid with the concentration of 6.06 g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
RECOMBINANT BIOTIN CARBOXYLASE DOMAINS FOR IDENTIFICATION OF ACETYL CoA CARBOXYLASE INHIBITORS
A peptide comprising an Acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase) having a deleted biotin binding domain, having a deleted carboxy transferase domain, and having a functional biotin carboxylase (BC) domain is described. A nucleic acid that encodes the peptide described above and a recombinant host cell that contains the nucleic acid and expresses the encoded peptide is also described. A method of identifying Acetyl CoA carboxylase inhibitors, fungicides, herbicides and pharmaceuticals is also described herein.
Owner:CROPSOLUTION
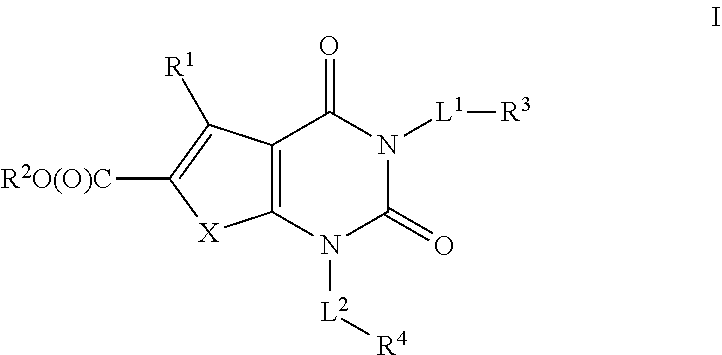
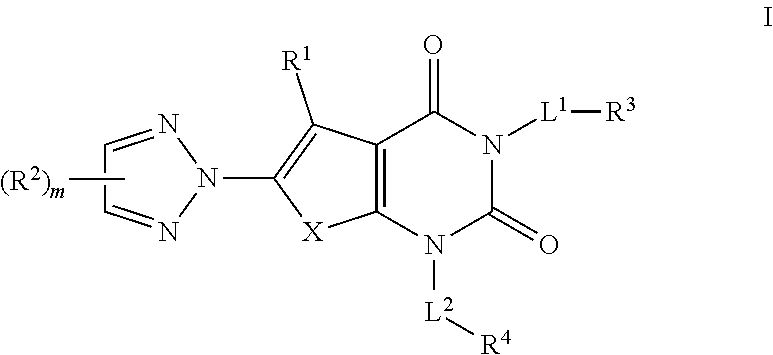
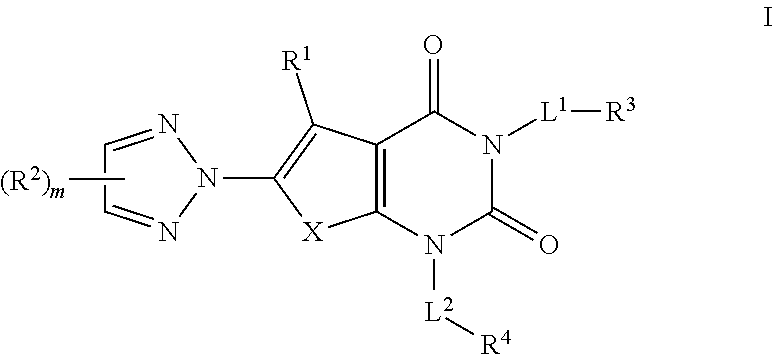
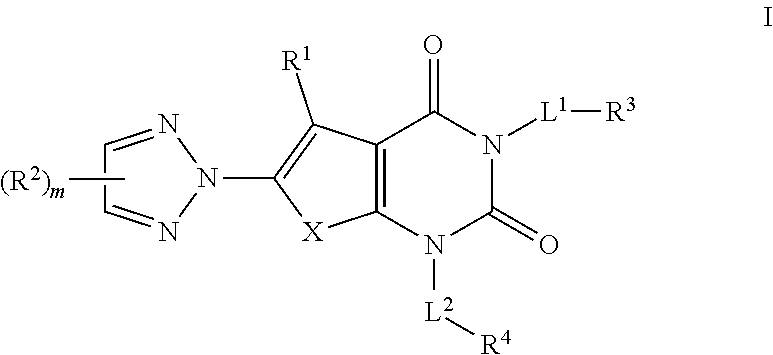
N1/N2-lactam acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors
The invention provides a compound of Formula (I)or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; whereinG isR1, R2 and R3 are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating diseases, conditions or disorders modulated by the inhibition of an acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme(s) in an animal.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Inhibitors of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase for Treatment of Neuronal Hypometabolism
InactiveUS20110003767A1Lower metabolismLoss of cognitive functionBiocideNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaMild cognitive impairment (MCI)
This invention relates to methods of using inhibitors of the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) for the treatment, prevention, inhibition or alleviation of diseases associated with neuronal hypometabolism and / or loss of cognitive function caused by reduced neuronal metabolism such as, for example, Age Associated Memory Impairment (AAMI), Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Friedreich's Ataxia (FRDA), GLUT1-deficient Epilepsy, Leprechaunism and Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome, Coronary Arterial Bypass Graft (CABG) dementia, anesthesia induced memory loss, Huntington's disease and many others.
Owner:CERECIN INC +1
Use of acetyl-coa carboxylase inhibitors for treating acne vulgaris
InactiveCN105530940AOrganic active ingredientsDermatological disorderAcyl-CoA carboxylasePharmacology
Owner:PFIZER INC
Method for using nanoparticles as nucleation agents for the crystallization of proteins
ActiveUS20170101436A1Increase opportunitiesHigh success ratePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein structureBovine serum albumin
The present invention relates to a method for the crystallization of protein using nanoparticles as nucleation agents. Precisely, the inventors performed the crystallization of such proteins as Bacillus subtilis YesR, chicken egg white lysozyme, bovine serum albumin, Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and Listeria monocytogenes hypothetical protein which have his-tag at amino terminal by using gold nanoparticles in diverse sizes and shapes in the presence of Ni2+ ions. As a result, it was confirmed that the chance of successful crystallization was higher with the gold nanoparticles than without the gold nanoparticles and the various crystallization conditions were successfully screened. Therefore, the method for inducing nucleation of the invention can be advantageously used for the disclosure of protein structure by increasing the chance of successful crystallization of protein.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com