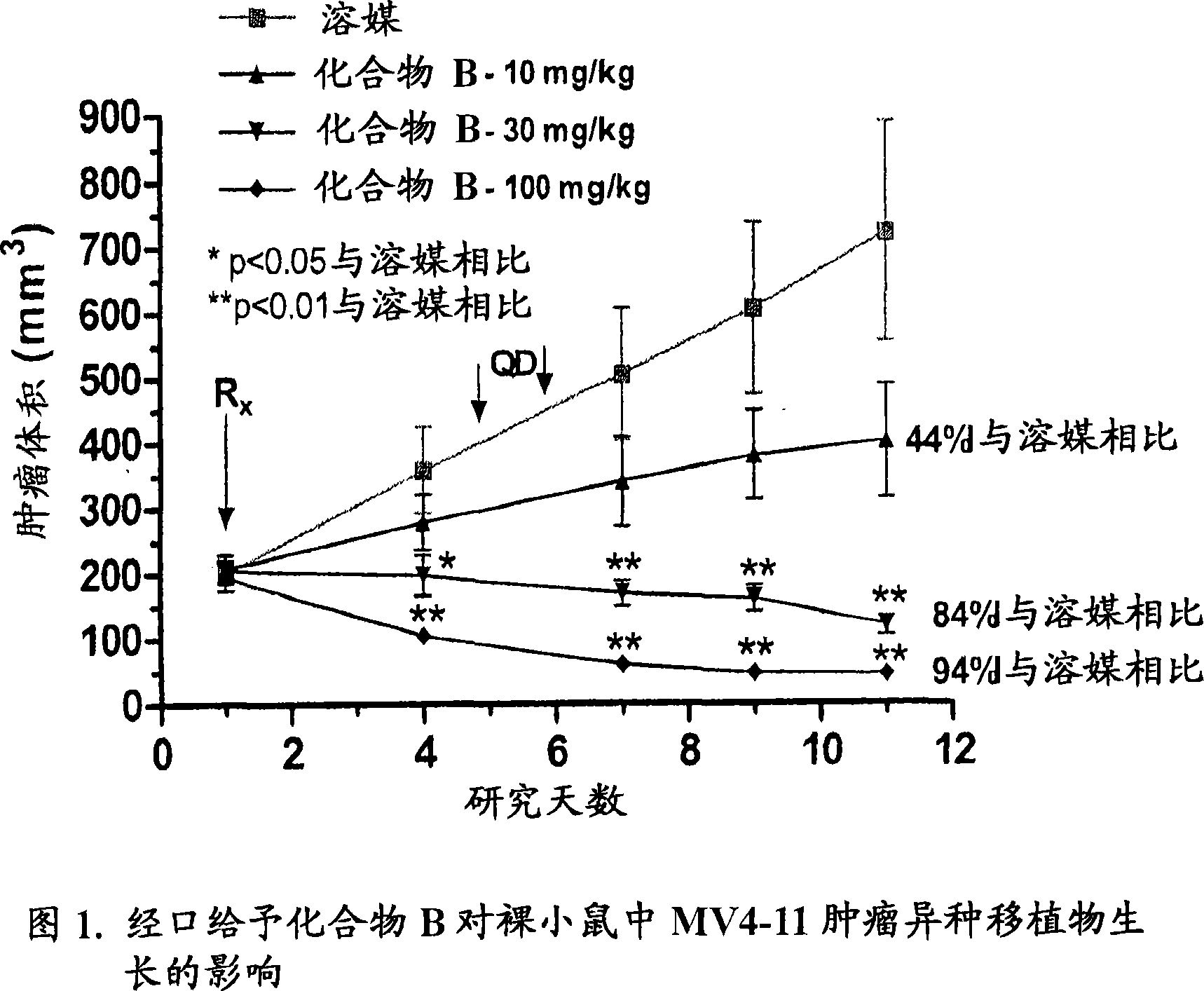
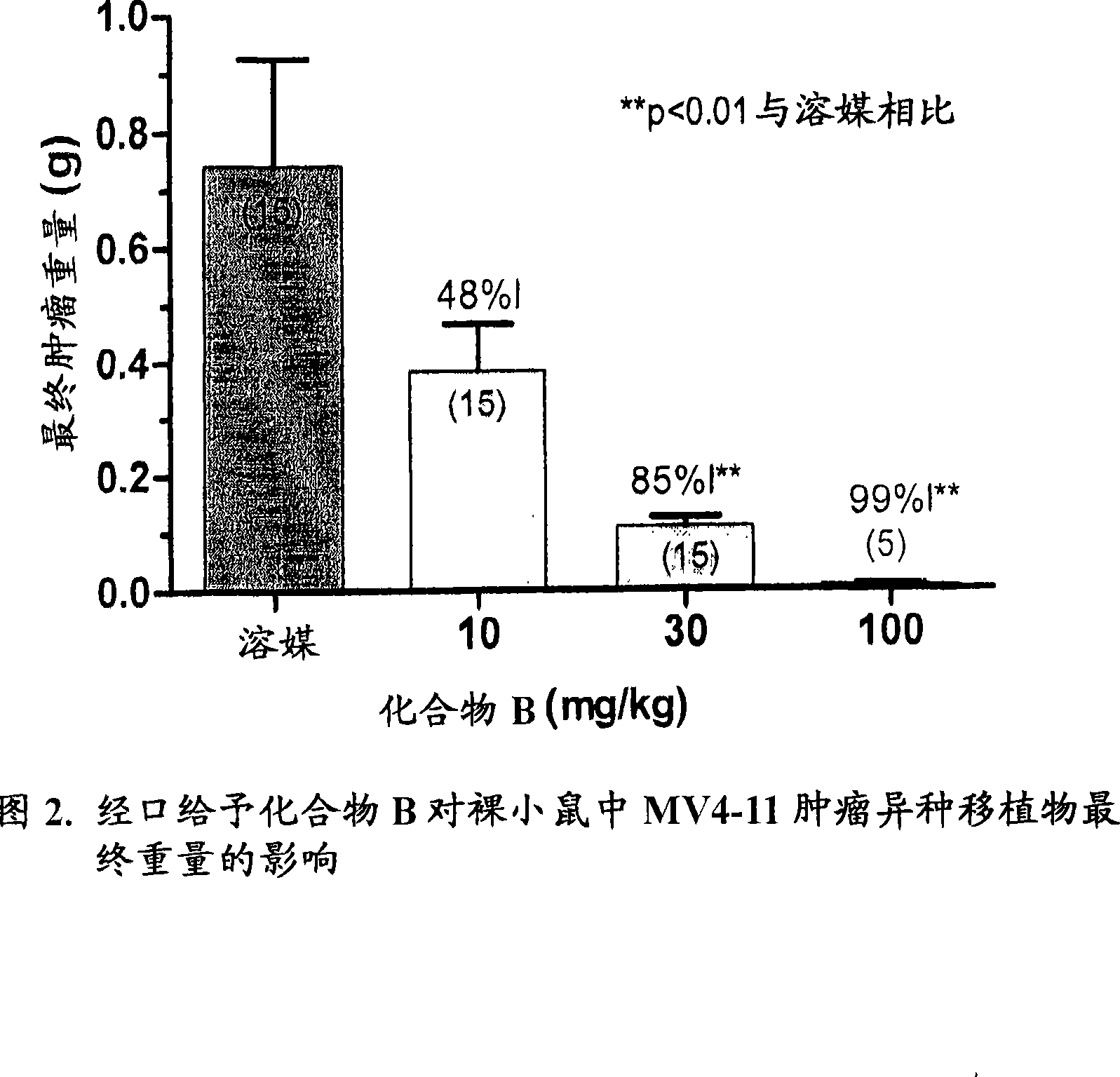
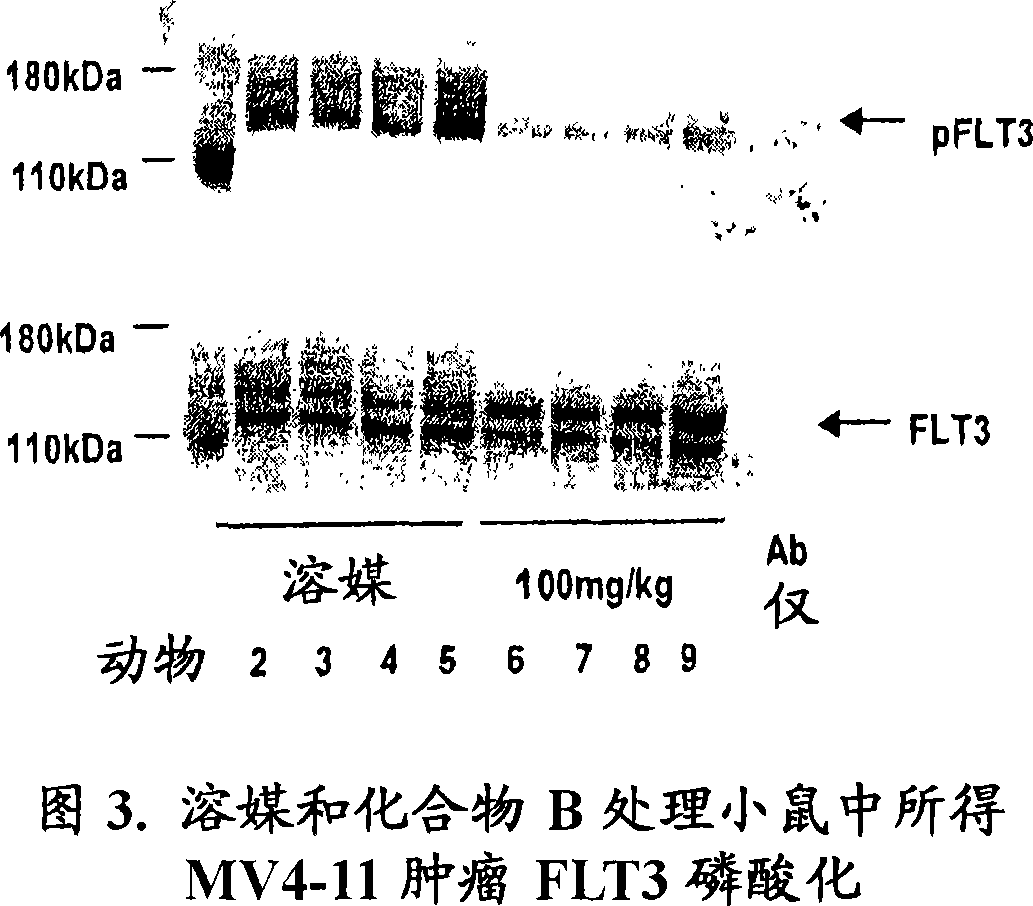
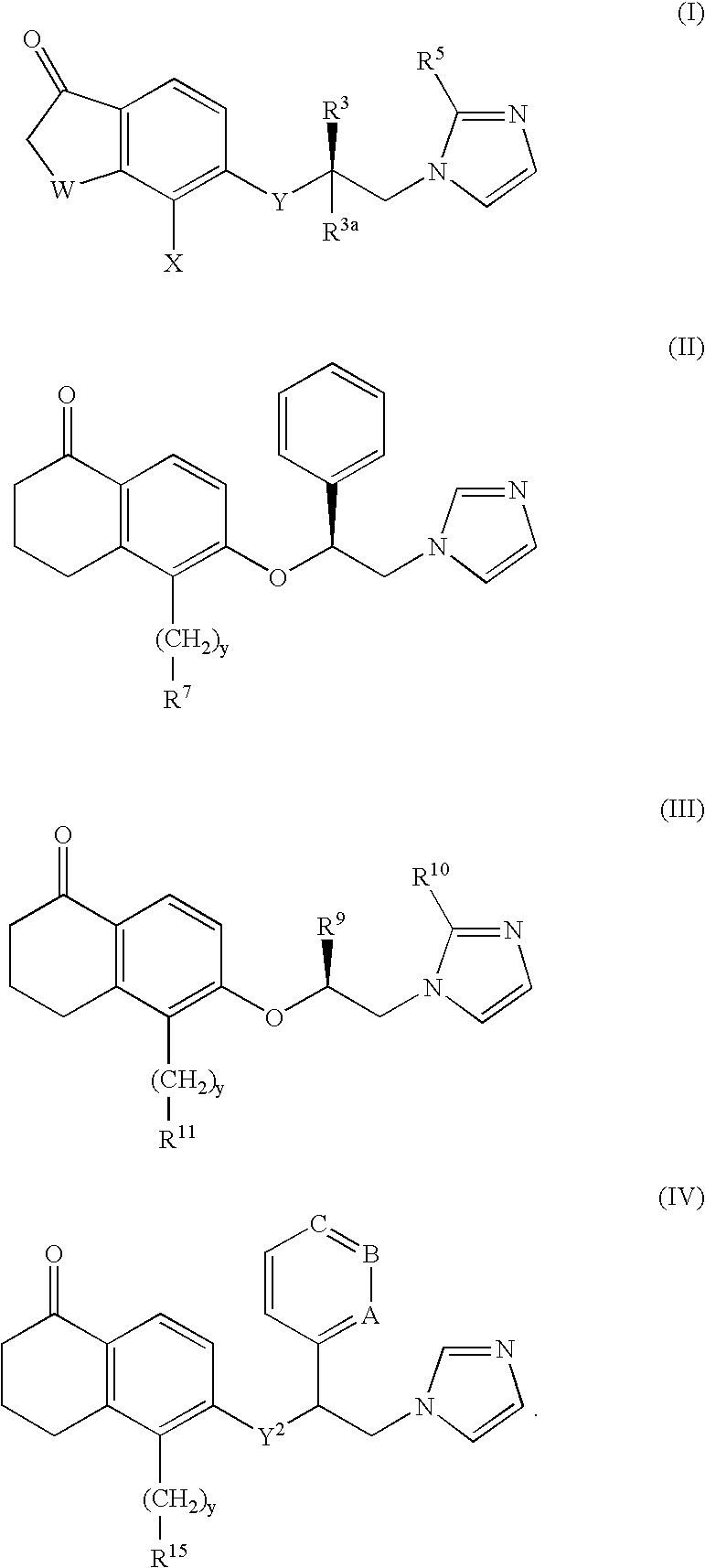
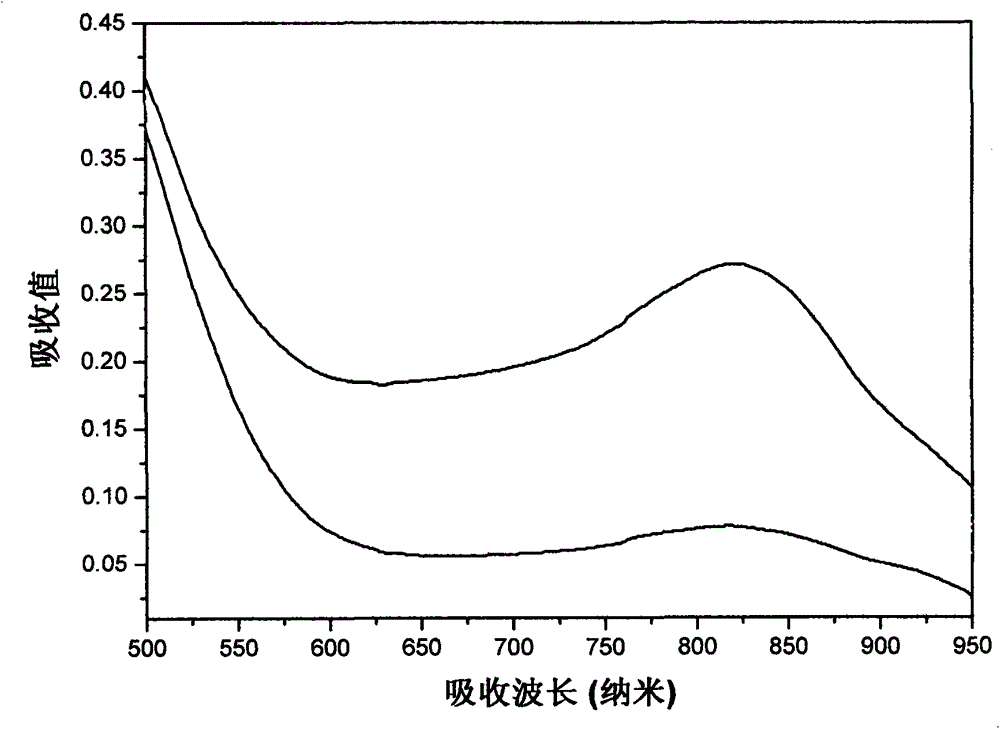
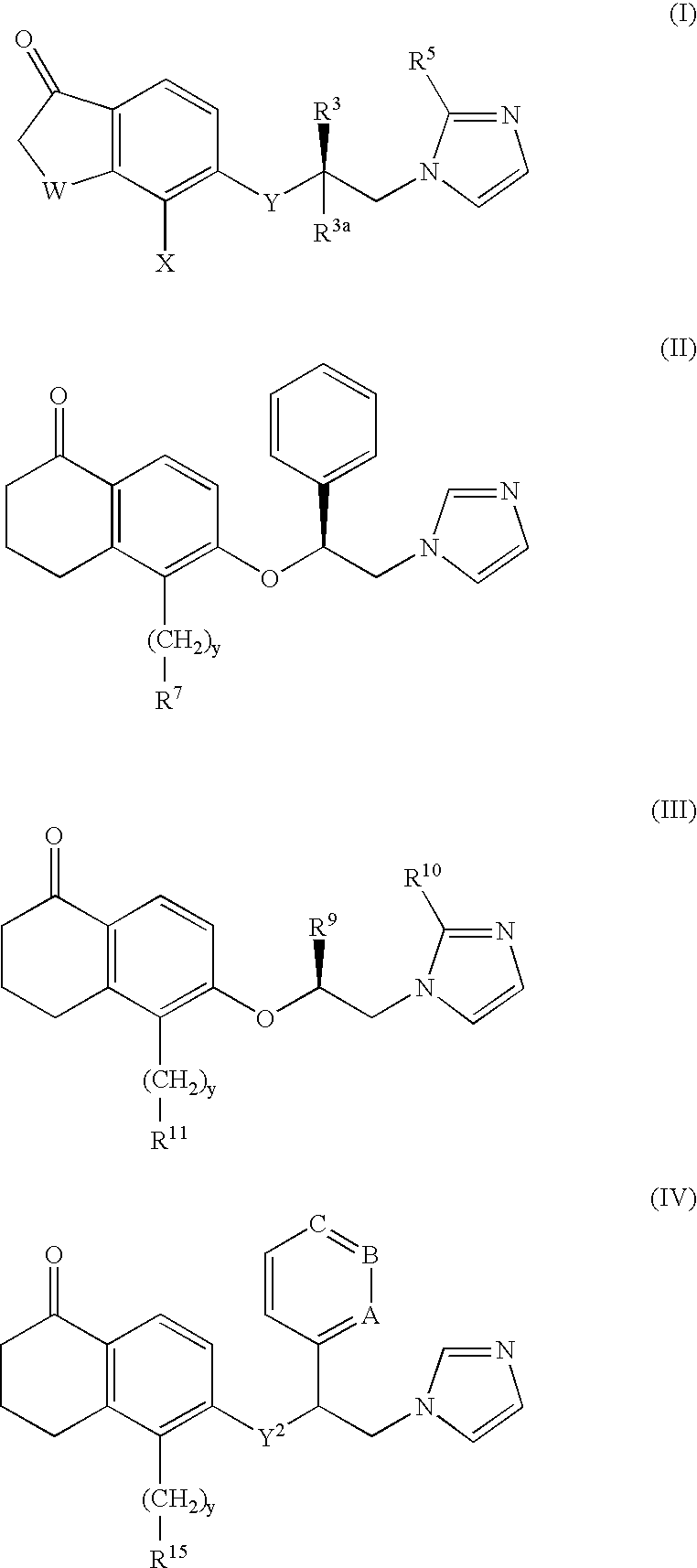
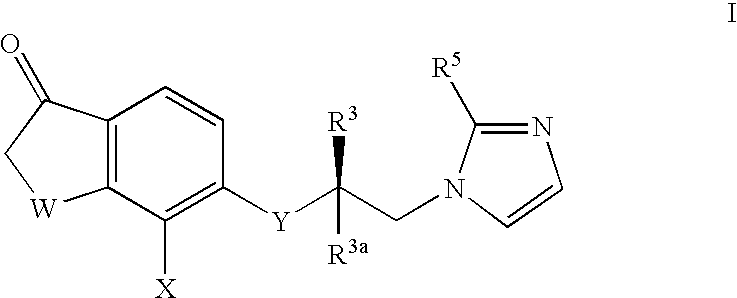
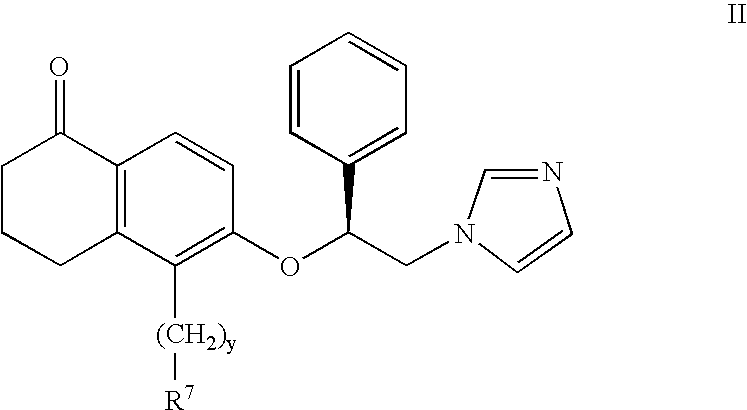
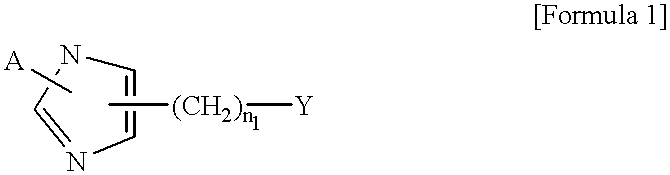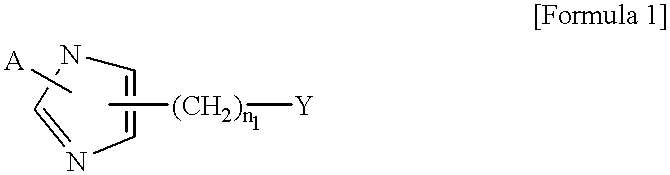Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Farnesyl Transferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
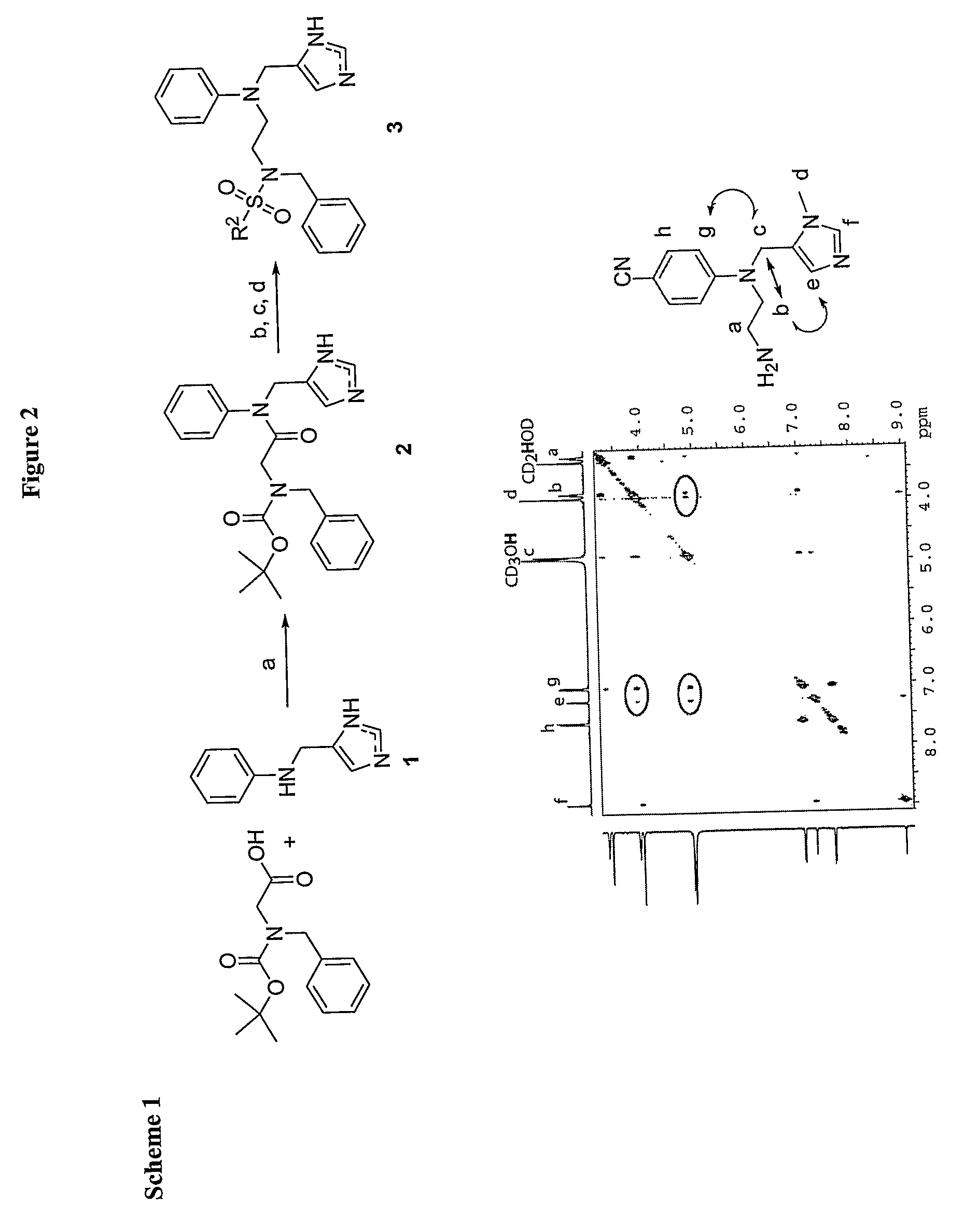
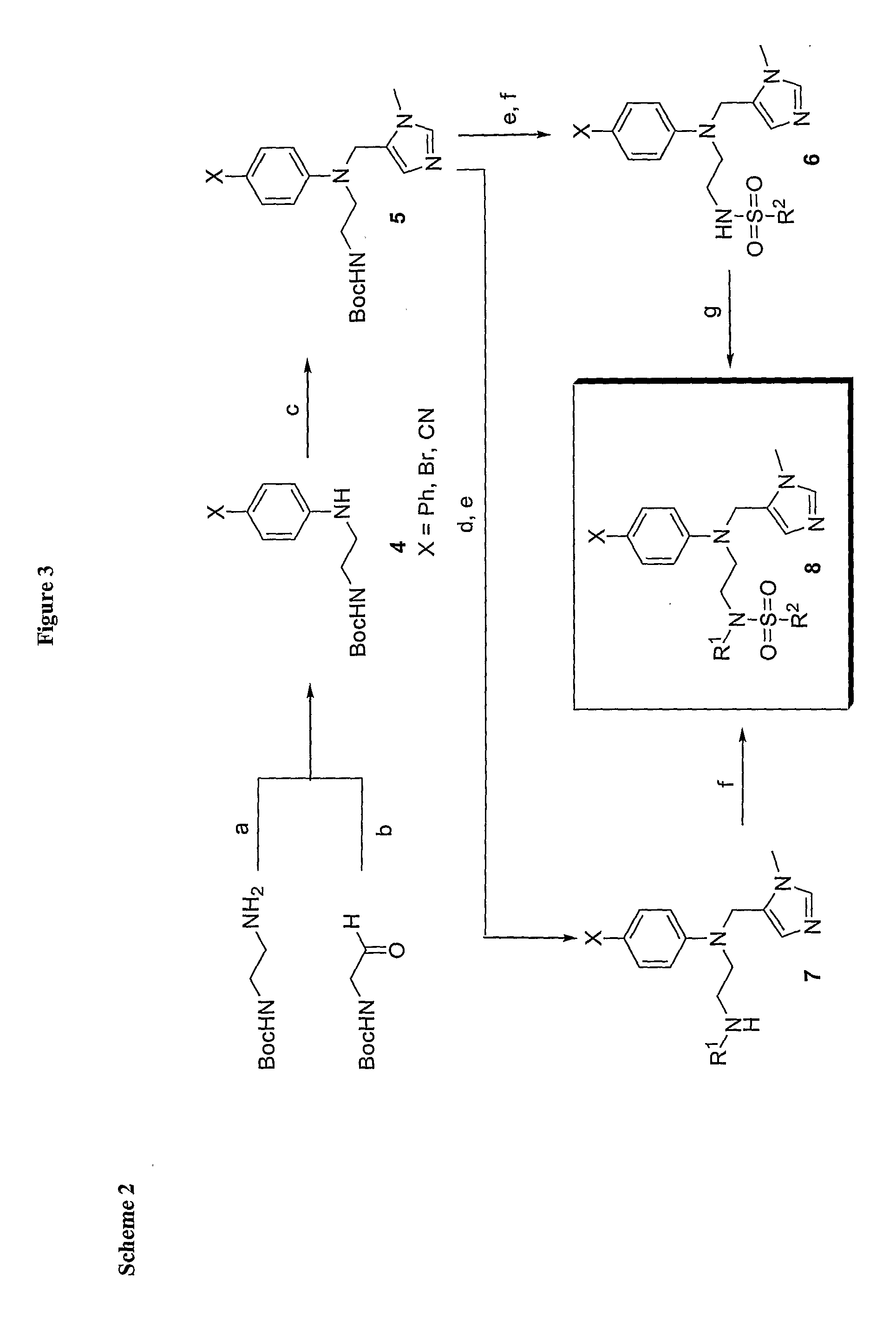
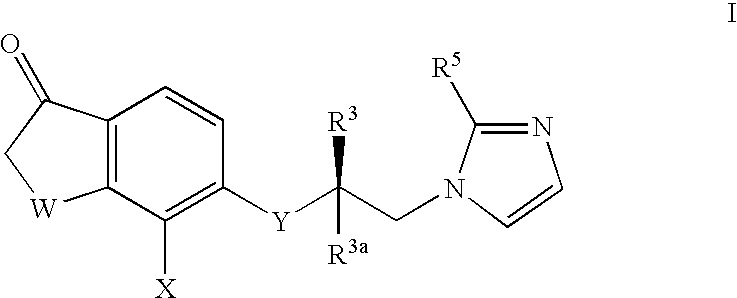
Imidazole derivatives having an inhibitory activity for farnesyl transferase and process for preparation thereof
InactiveUS6268363B1Inhibition is effectiveInhibitory activityOrganic chemistryUrinary disorderFarnesyl Protein TransferaseBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a novel imidazole derivative represented by formula (1) which shows an inhibitory activity against farnesyl transferase or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or isomers thereof, in which A, n1 and Y are defined in the specification; to a process for preparation of the compound of formula (1); to intermediates which are used in the preparation of the compound of formula (1); and to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound of formula (1) as an active ingredient.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
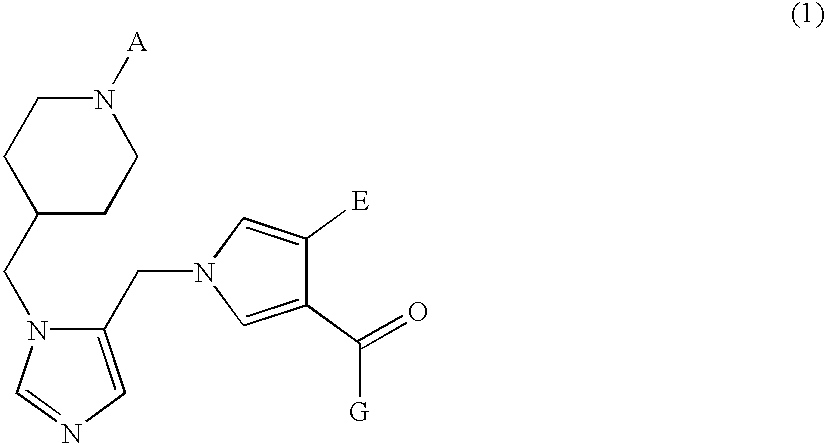
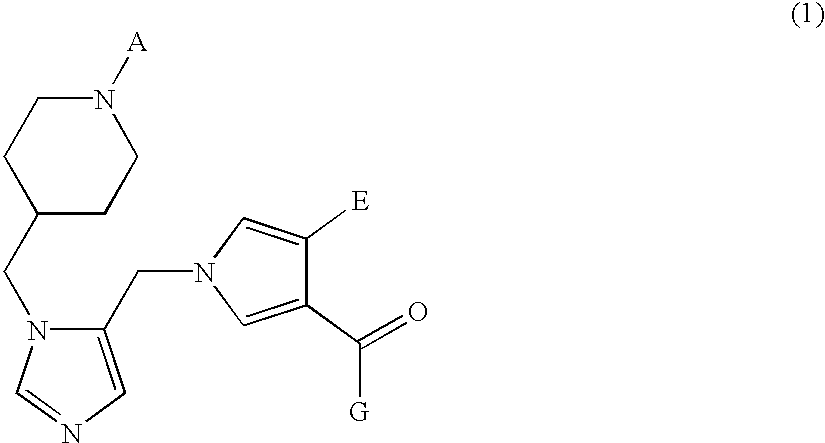
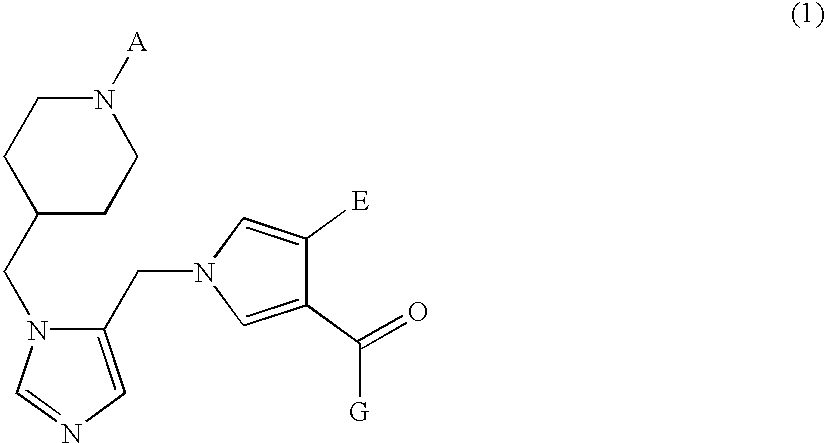
Farnesyl transferase inhibitors having a piperidine structure and process for preparation thereof
InactiveUS6436960B1Inhibition is effectiveInhibitory activityBiocideOrganic chemistryFarnesyl TransferaseFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
The present invention relates to a novel piperidine derivative represented by formula (1) which shows an inhibitory activity against farnesyl transferase or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, in which A, E and G are defined in the specification; to a process for preparation of the compound of formula (1); to an intermediate which is used in the preparation of the compound of formula (1); and to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound of formula (1) as an active ingredient.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Isolated nucleic acids encoding farnesyl transferase alpha
Owner:PERFORMANCE PLANTS INC
Hydantoin compounds and methods related thereto
InactiveUS6384061B1Easy to useEffective activityBiocideOrganic chemistryAnticarcinogenCombinatorial chemistry
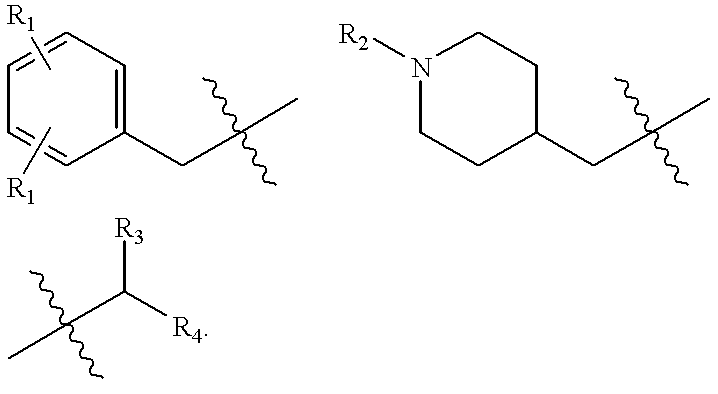
The present invention relates to novel hydantoin compounds represented by formula (I) which shows an inhibitory activity against farnesyl transferase, and thus can be used as an anti-cancer agent, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, in which R1, R2, R3 and R4 are as defined in the present application. The present invention also relates to a process for preparation of the compound of formula (I), and to an anti-cancer composition comprising the compound of formula (I) as an active ingredient.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Stress tolerance and delayed senescence in plants
InactiveUS20060021092A1Improve drought toleranceImprove stress toleranceHydrolasesClimate change adaptationTolerabilityAdemetionine
The novel constructs and methods of this invention improve tolerance in plants to environmental stresses and senescence. Nucleic acids encoding a plant farnesyl transferase are described, as are transgenic plants and seeds incorporating these nucleic acids and proteins. Also provided are inhibitors of naturally-occurring farnesyl transferase which, when expressed, will enhance drought tolerance in the plants, improve resistance to senescence and modify growth habit.
Owner:MCCOURT PETER +3
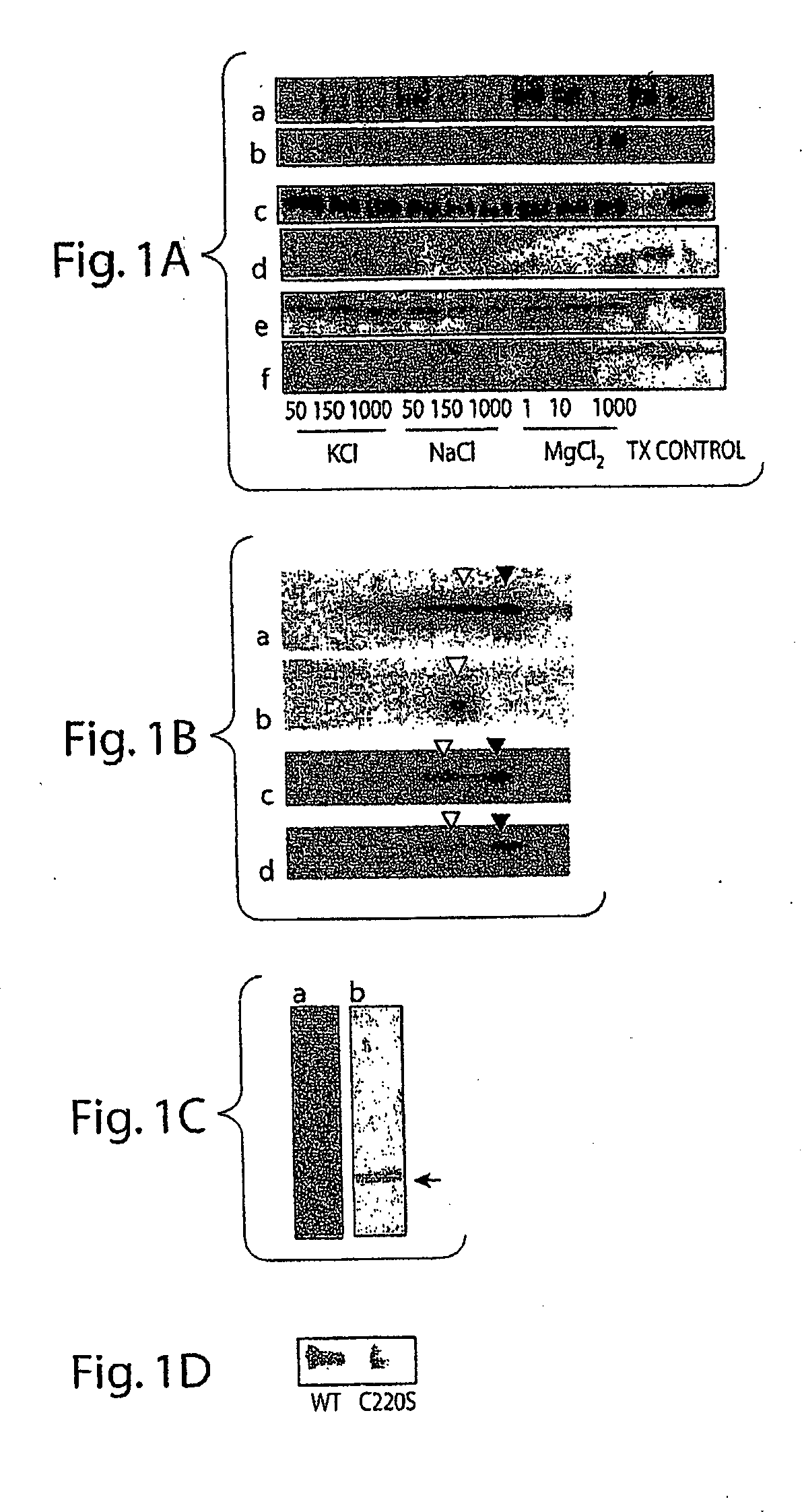
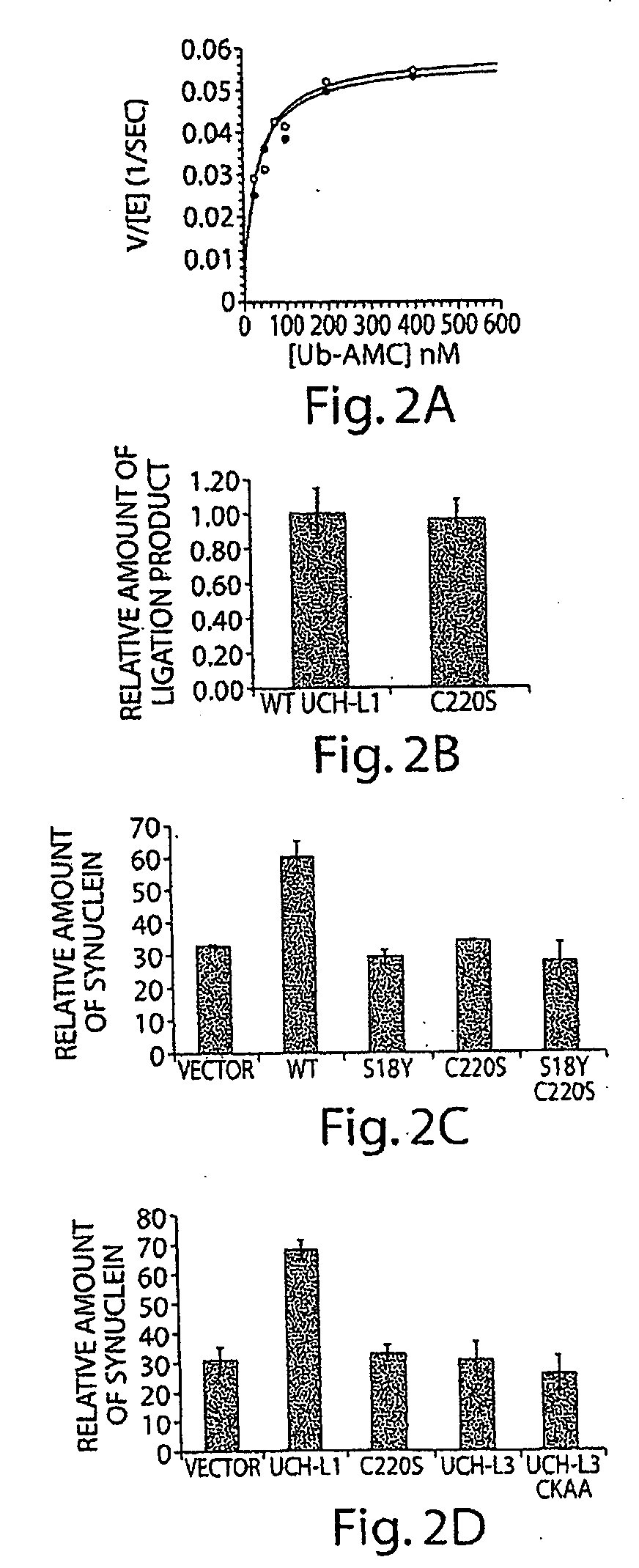
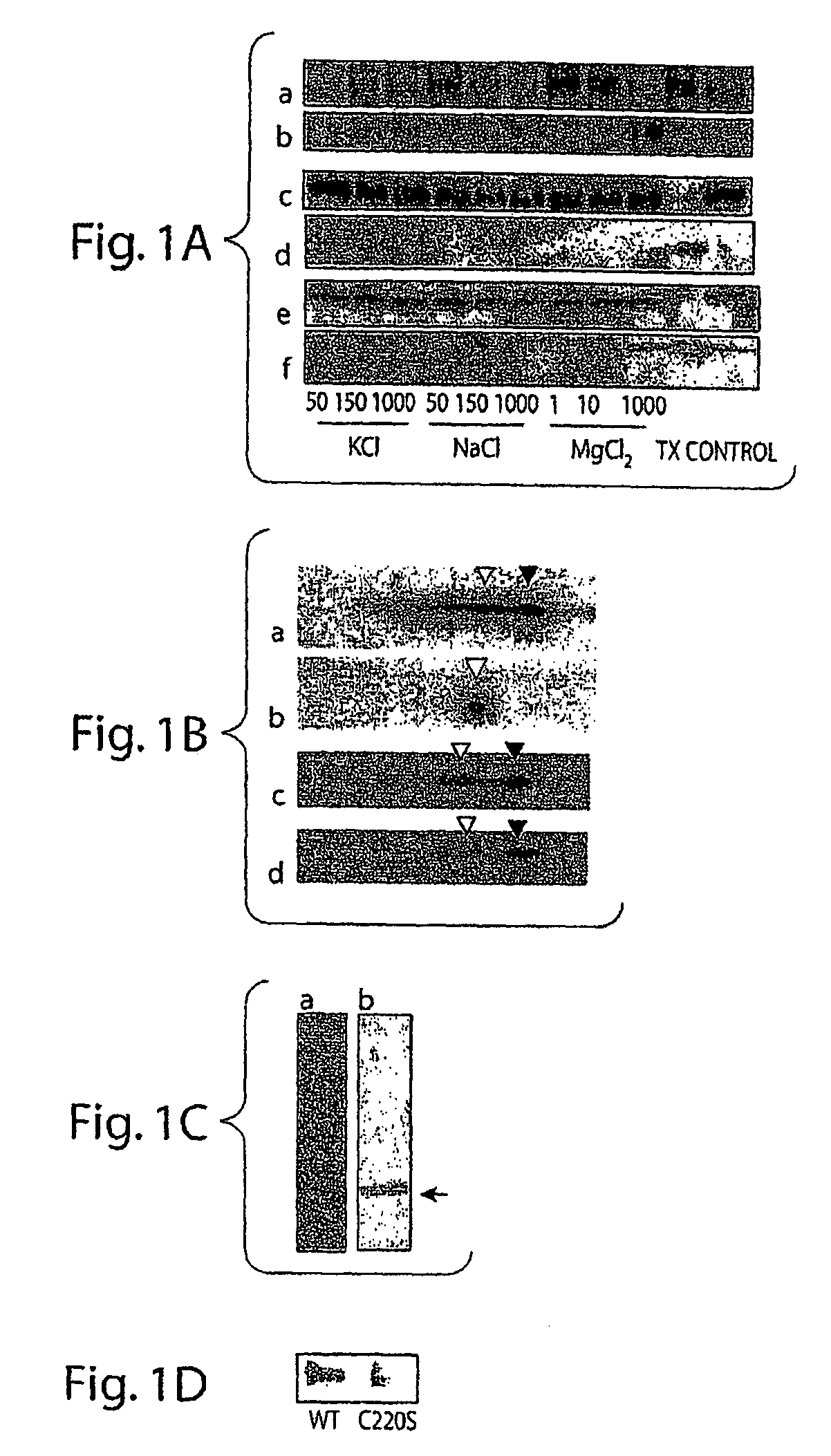
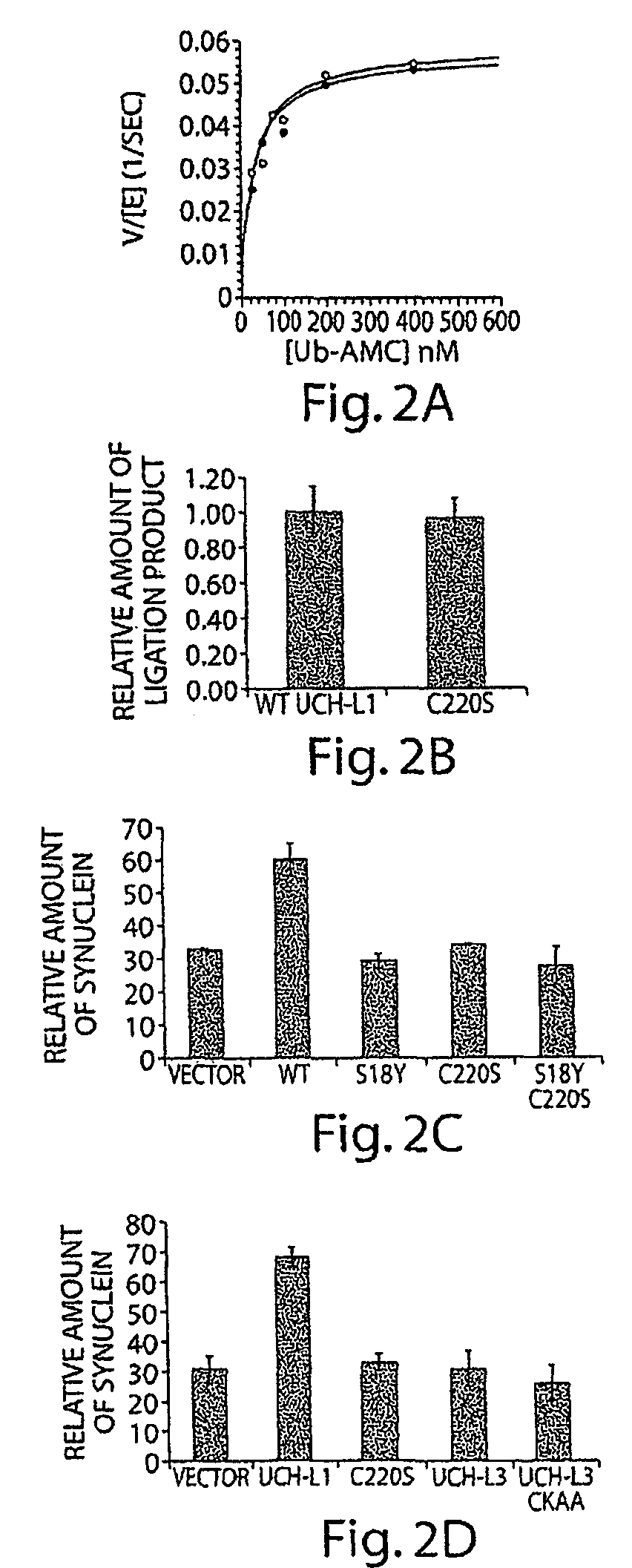
UCH-L1 expression and cancer therapy
InactiveUS20050272068A1Reduce anti-proliferative effect of UCH-LImprove the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTransferase inhibitorCancer therapy
Methods are provided of treating cancer with one or more farnesyl transferase inhibitors. Methods are provided for identifying cancers that are particularly susceptible to treatment with one or more farneseyl transferase inhibitors by identifying cancers that express low levels of UCH-L1.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Compound and Methods For the Treatment of Cancer and Malaria
Formula (I): Where R1 is an optionally substituted C3-C12 hydrocarbyl group (preferably a cyclic alkyl group), an optionally substituted heterocyclic group, an optionally substituted aromatic group or an optionally substituted heteroaromatic group; R is a C(O)yR′ group (preferably forming an optionally substituted C2-C5 acyl group), or a S(O)xR′ group, where y is 0 or 1 and x is 0, 1 or 2 and R′ is H or an optionally substituted C1-C12 alkyl group, or R′ is an optionally substituted C5-C12 cycloalkyl group, an optionally substituted heterocyclic group, an optionally substituted aromatic group or an optionally substituted heteroaromatic group; R5, R6, R7, R8, R9 and R10 are each independently selected from H, an optionally substituted C1-C12 hydrocarbyl group, including a C5-C12 cycloalkyl group, an optionally substituted heterocyclic group, an optionally substituted aromatic group or an optionally substituted heteroaromatic group, or R5 and R6, R7 and R8 or R9 and R10 together form a keto (C═O) group; RN is H, an optionally substituted C1-C12 hydrocarbyl group, an optionally substituted heterocyclic group, an optionally substituted aromatic group, or an optionally substituted heteroaromatic group; A is Formula (II): a Formula (III): group, or a Formula (IV) or Formula (V) group, where Z is N, O or S; Ra is H, a C1-C12 optionally substituted hydrocarbyl group or an optionally substituted aromatic group; n is from 0 to 3; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Compounds according to the invention are useful in one or more aspects to inhibit farnesyl transferase, or to treat malaria, neoplasia, a hyperproliferative disease state or arthritis, including rheumaroid arthritis or osteoarthritis.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF SOUTH +2
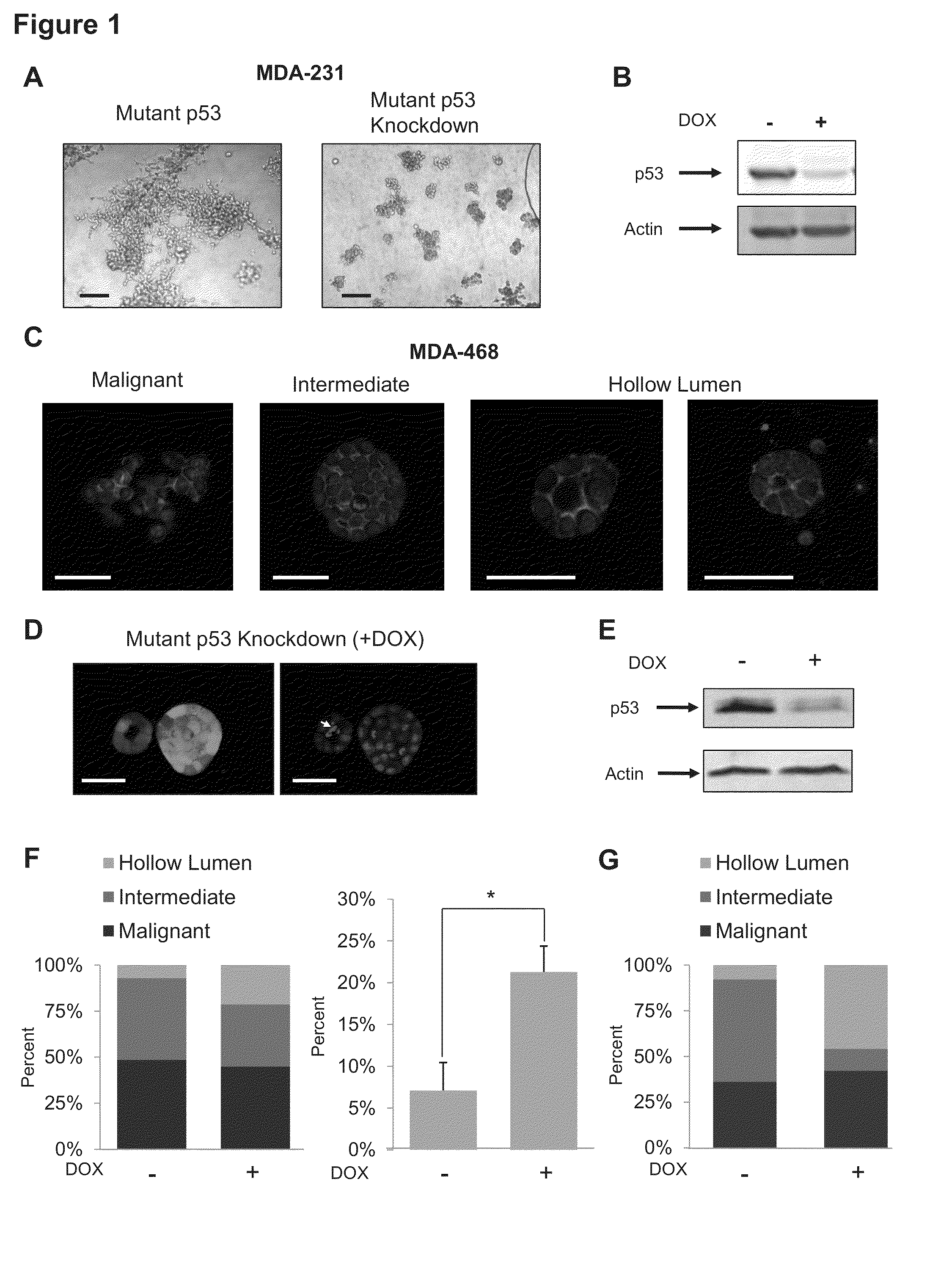
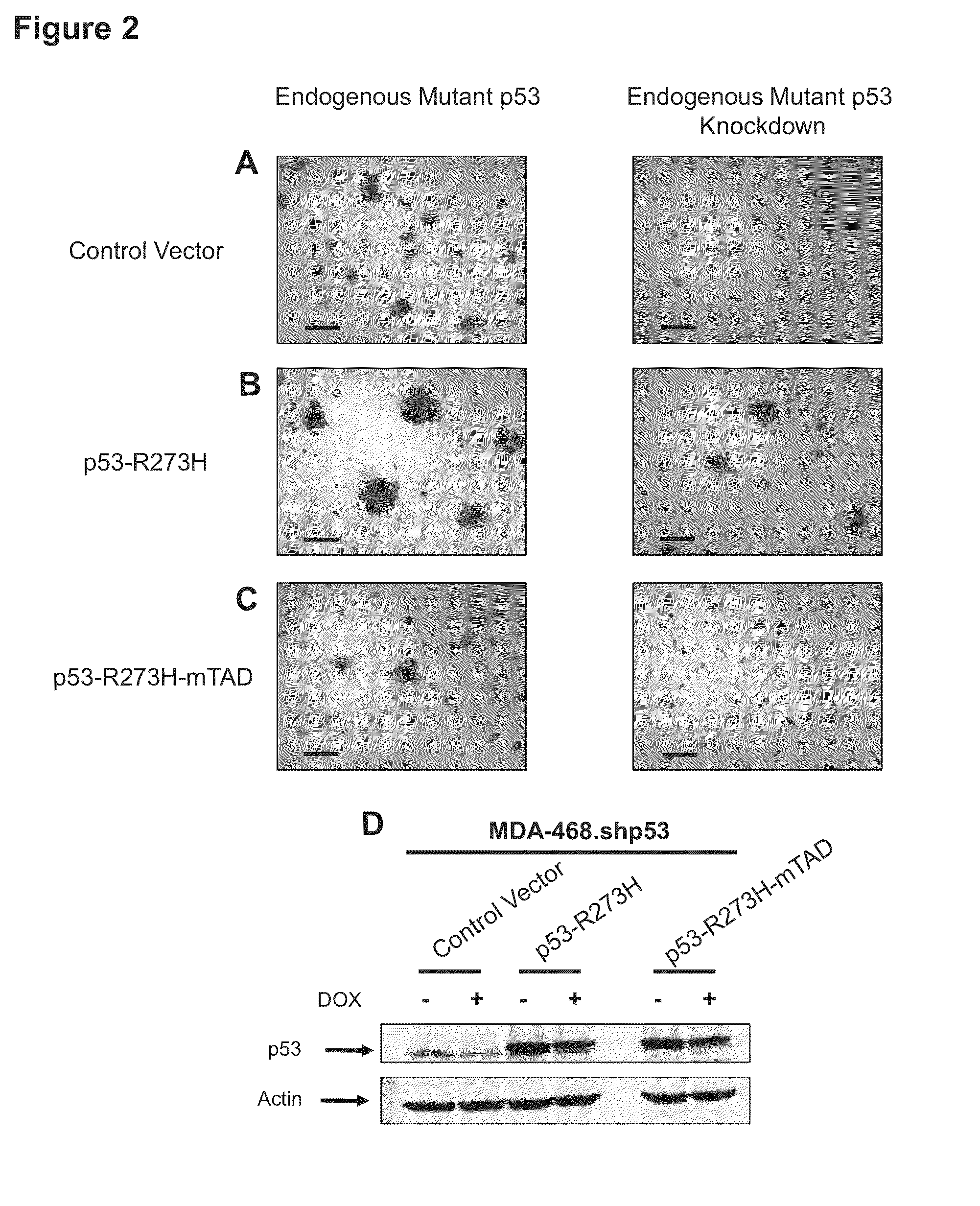
Method for Treating Cancer Harboring a p53 Mutation
InactiveUS20130281493A1Preventing or delaying the onset (or reoccurrence)Reduce the possibilityBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellFhit gene
A method for determining if a subject with cancer or precancerous lesions or a benign tumor, will respond to treatment with an inhibitor selected from the group comprising an inhibitor of one or more enzymes in the mevalonate pathway, an inhibitor of geranylgeranyl transferase, an inhibitor of farnesyl transferase or an inhibitor of squalene synthase, by (i) obtaining a sample of the cancer cells, precancerous cells or benign tumor cells from the subject, (ii) assaying the cells in the sample for the presence of a mutated p53 gene or a mutant form of p53 protein or a biologically active fragment thereof, and (iii) if the cells have the mutated p53 gene or mutant form of the p53 protein, then determining that the subject will respond to treatment with the inhibitor or combinations thereof. Some embodiments are directed to treatment with the inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Stress tolerance and delayed senescence in plants
InactiveUS20060031966A1Improve toleranceImprove drought toleranceHydrolasesClimate change adaptationTolerabilityAdemetionine
The novel constructs and methods of this invention improve tolerance in plants to environmental stresses and senescence. Nucleic acids encoding a plant farnesyl transferase are described, as are transgenic plants and seeds incorporating these nucleic acids and proteins. Also provided are inhibitors of naturally-occurring farnesyl transferase which, when expressed, will enhance drought tolerance in the plants, improve resistance to senescence and modify growth habit.
Owner:MCCOURT PETER +3
Methods of treating cancer patients with farnesyl transferase inhibitors
ActiveCN107787373AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferase inhibitorGenotyping
The present invention relates to the field of molecular biology and cancer biology. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods of treating a subject with a farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) that include determining whether the subject is likely to be responsive to the FTI treatment based on genotyping and expression profiling of certain immunological genes and RAS mutation status inthe subject.
Owner:KURA ONCOLOGY
Quinolinone farnesyl transferase inhibitors for the treatment of synucleinopathies and other indications
InactiveUS20090253655A1Low toxicityReduce accumulationBiocideTissue cultureSynucleinopathiesFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
Novel quinolinone farnesyl transferase inhibitors are provided. These new compounds are useful in the treatment or prevention of synucleinopathies, such as Parkinson's Disease, Diffuse Lewy Body Disease, multiple system atrophy, and disorders of brain iron concentration including pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (e.g., PANK1), or other neurodegenerative / neurological diseases. Provided compounds are also useful in the treatment of proliferative diseases such as cancer, and in the treatment of neurological diseases, such as cognitive impairment, depression, and anxiety.The treatment including administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of an inventive farnesyl transferase inhibitor compound.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Methods for assessing patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Methods for treating cancer, and preferably hematological malignancy, patients include analyzing gene expression profiles and / or molecular markers of a patient to determine status and / or prognosis of the patient. The invention also provides methods of analyzing whether a non-relapsed or non-refractory patient is likely to respond to treatment with farnesyl transferase inhibitors (FTIs) and, optionally, other therapeutics. The methods are also useful for monitoring patient therapy and for selecting a course of therapy. Genes modulated in response to FTI treatment are provided and are used in formulating the profiles.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Methods for assessing patients with acute myeloid leukemia
InactiveCN1704478ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTransferase inhibitorRegimen
Methods for treating cancer, and preferably hematological malignancy, patients include analyzing gene expression profiles and / or molecular markers of a patient to determine status and / or prognosis of the patient. The invention also provides methods of analyzing whether a non-relapsed or non-refractory patient is likely to respond to treatment with farnesyl transferase inhibitors (FTIs) and, optionally, other therapeutics. The methods are also useful for monitoring patient therapy and for selecting a course of therapy. Genes modulated in response to FTI treatment are provided and are used in formulating the profiles.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
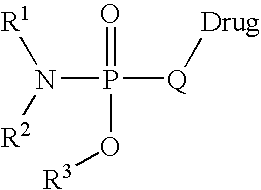
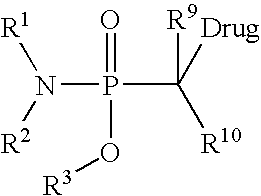
Prodrugs and conjugates of prenylation inhibitors
Described herein are neutral prodrugs of phosphorus-containing inhibitors of farnesyl transferase that include one or more phosphate fragments or analogs of phosphate fragments. Analogs of phosphate fragments include various linkers other than oxygen connecting the phosphate fragment to the remaining portion of the drug, such as but not limited to linkers forming phosphoramidates, phosphonates, difluorophosphonates, phosphordiamidates, and the like.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Methods for assessing and treating cancer
InactiveCN1721553AMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansRegimenFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
Methods for treating cancer, and preferably hematological malignancy, patients include analyzing gene expression profiles and / or molecular markers of a patient to determine whether the patient is likely to respond to treatment with farnesyl transferase inhibitors (FTIs) and, optionally, other therapeutics. The methods are also useful for monitoring patient therapy and for selecting a course of therapy. Genes modulated in response to FTI treatment are provided and are used in formulating the profiles.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
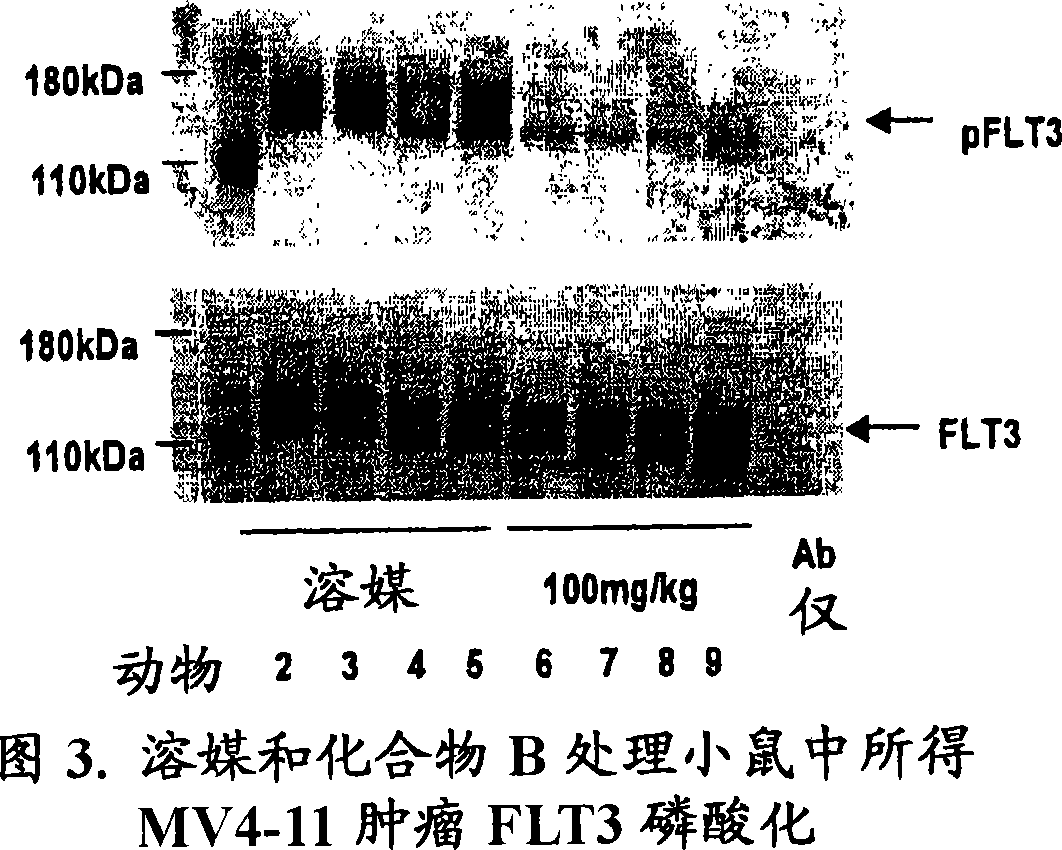
Synergistic modulation of FLT3 kinase using aminoquinoline and aminoquinazoline kinase modulators
InactiveCN101242838AOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsKinase activityFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting FLT3 tyrosine kinase activity or expression, or reducing FLT3 kinase activity or expression in cells or patients, the method comprising administering a farnesyltransferase inhibitor and a FLT3 kinase inhibitor, wherein the FLT3 kinase inhibitor is selected from Aminoquinoline and aminoquinazoline compounds of formula (I'): wherein R1, R2, R3, B, Z, Q, p, q and X are as defined herein. The present invention includes prophylactic and therapeutic methods of treating patients at risk of (or susceptible to) developing a cell proliferative disorder or a disorder associated with FLT3.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Quinolinone farnesyl transferase inhibitors for the treatment of synucleinopathies and other indications
InactiveUS8232402B2Low toxicityReduce accumulationBiocideNitro compound active ingredientsNervous systemFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
Novel quinolinone farnesyl transferase inhibitors are provided. These new compounds are useful in the treatment or prevention of synucleinopathies, such as Parkinson's Disease, Diffuse Lewy Body Disease, multiple system atrophy, and disorders of brain iron concentration including pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (e.g., PANK1), or other neurodegenerative / neurological diseases. Provided compounds are also useful in the treatment of proliferative diseases such as cancer, and in the treatment of neurological diseases, such as cognitive impairment, depression, and anxiety. The treatment including administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of an inventive farnesyl transferase inhibitor compound.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Synergistic modulation of FLT3 kinase using aminopyrimidines kinase modulators and a farnesyl transferase inhibitor
The present invention relates to a method for inhibiting the activity or expression of FLT3 tyrosine kinase in cells or patients, or reducing the activity or expression of FLT3 kinase, the method comprising administering a farnesyltransferase inhibitor and a FLT3 kinase inhibitor, the FLT3 kinase inhibitor being selected from Aminopyrimidine compounds of formula I'; wherein R3, B, Z, r and R1 are as defined herein. The invention also includes prophylactic and therapeutic methods of treating patients at risk of developing (or susceptible to) a cell proliferative disorder or a disorder associated with FLT3.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
5-substituted tetralones as inhibitors of ras farnesyl transferase
InactiveUS6943183B2Treating and preventing uncontrolled or abnormal proliferation of tissuesEasy to synthesizeBiocideSenses disorderTetralonePercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention provides novel 5-substituted tetralones of Formulas I, II, III, and IV and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, amides, and prodrugs thereof, which are useful for treating and preventing uncontrolled or abnormal proliferation of tissues, such as cancer, atherosclerosis, restenosis, and psoriasis. Specifically, the present invention relates to compounds that inhibit the farnesyl transferase enzyme
Owner:WARNER LAMBERT CO LLC
Imidazole derivatives having an inhibitory activity for farnesyl transferase and process for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20020137769A1Inhibition is effectiveInhibitory activityBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMedicinal chemistryEnzyme
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Effects of combined administration of farnesyl transferase inhibitors and signal transduction inhibitors
InactiveUS20050020516A1Reducing (totallyIncreased apoptosisBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsApoptosisFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
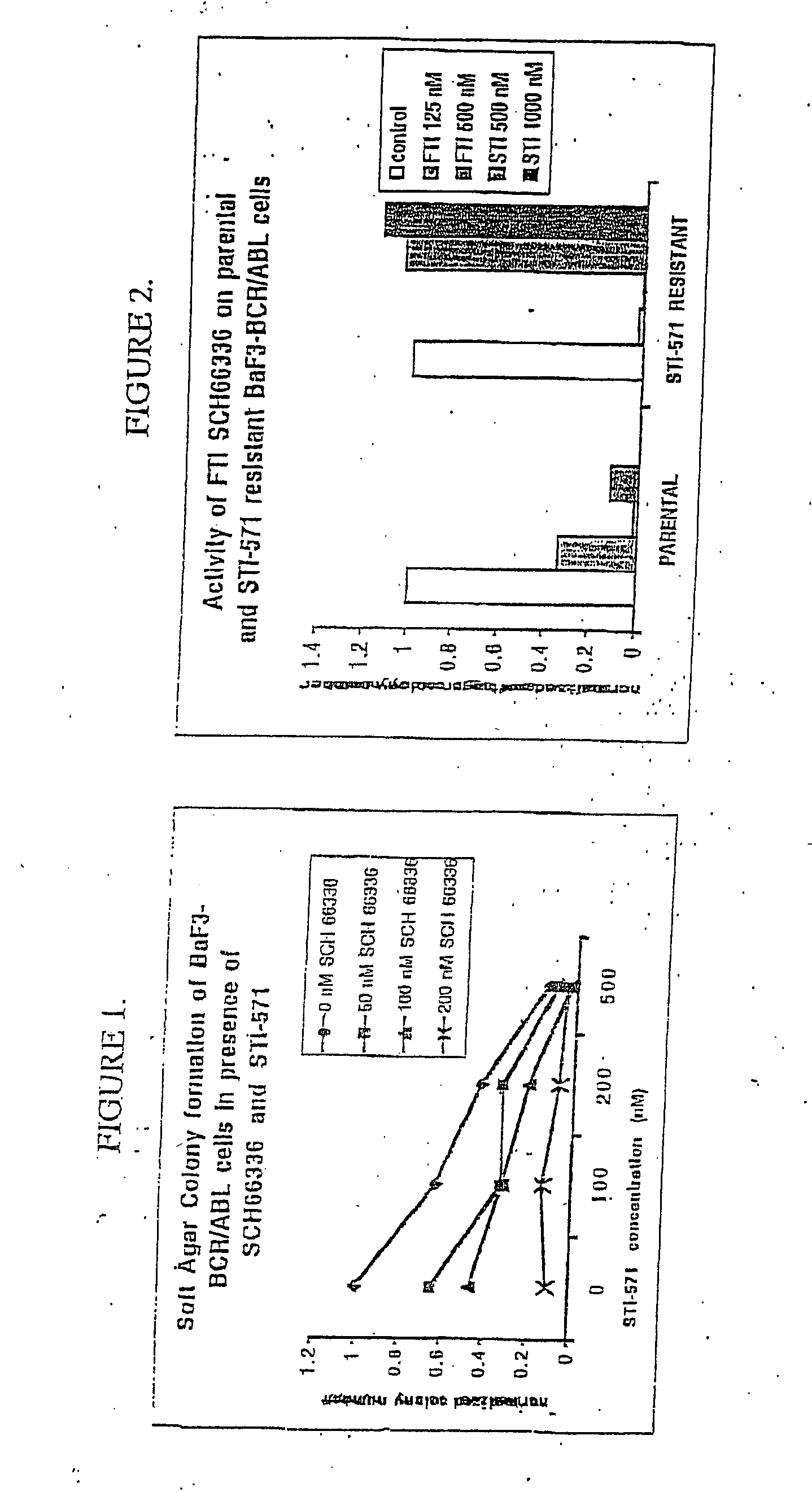
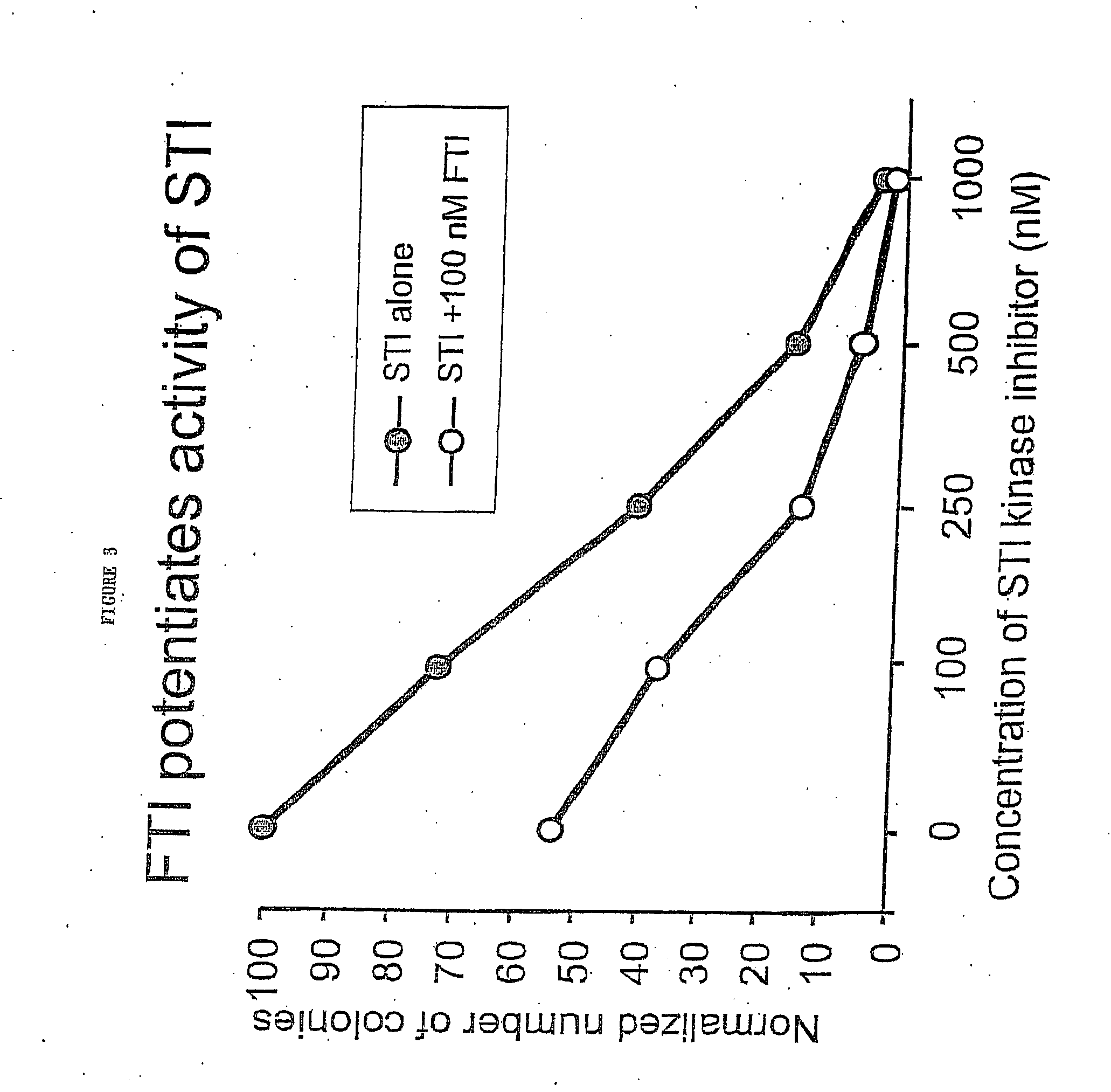
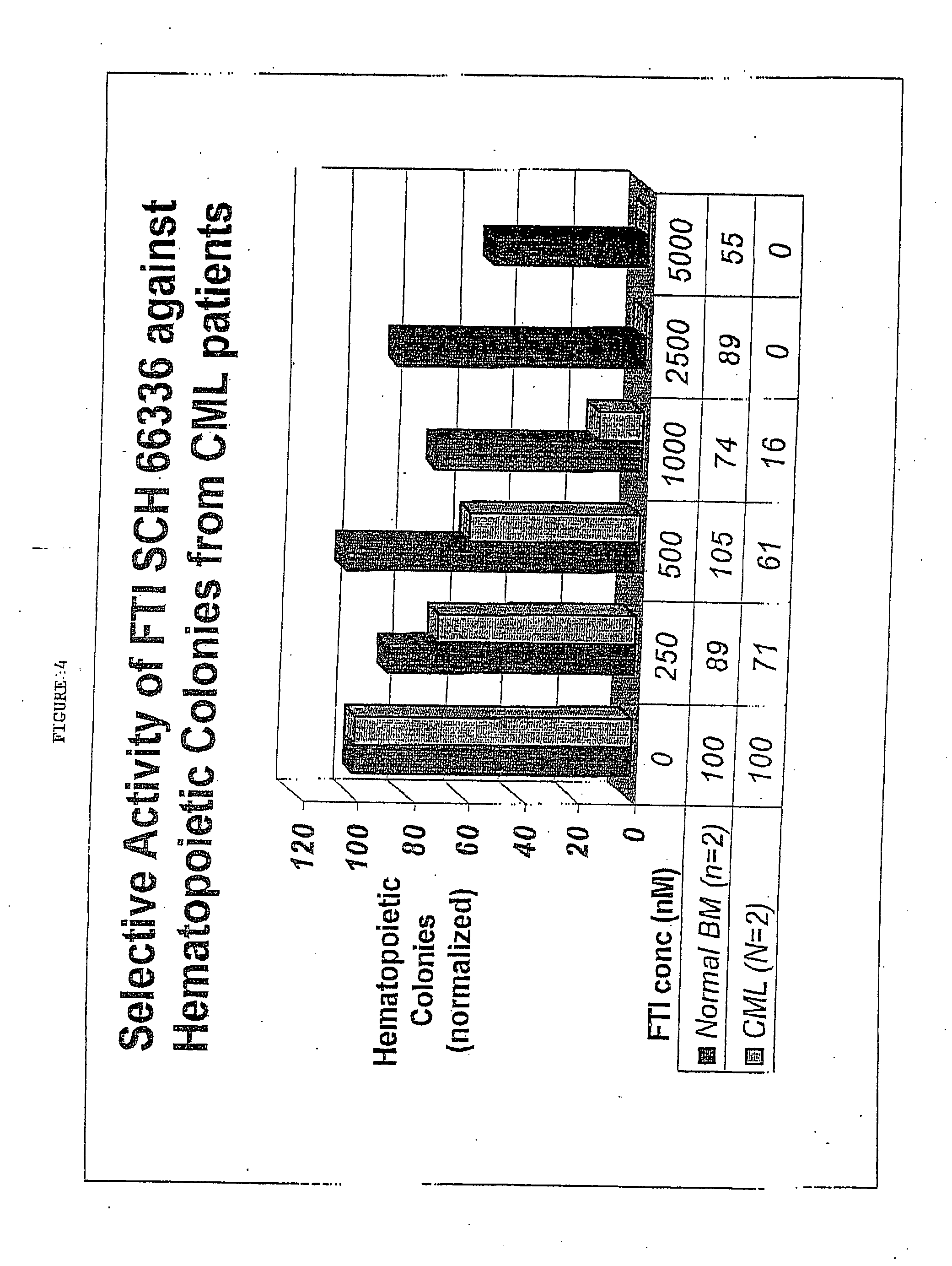
The present invention relates to methods of reducing proliferation of cells, enhancing apoptosis of cells or both in an individual in need thereof, comprising administering to the individual a combination of at least one farnesyl transferase inhibitor (FTI), such as an inhibitor of Ras function, and at least one signal transduction inhibitor (STI) in a therapeutically effective amount, wherein proliferation of cells is reduced and / or apoptosis of cells is enhanced in the individual. In one embodiment, the invention relates to a method of reducing proliferation of STI resistant cells, enhancing apoptosis of STI resistant cells, or both in an individual in need thereof, comprising administering to the individual a combination of at least one FTI and at least one STI in a therapeutically effective amount, wherein proliferation of STI resistant cells is reduced and / or apoptosis of STI resistant cells is enhanced in the individual. The present invention can be used to treat leukemia (e.g., CML) in an individual comprising administering to the individual a combination of at least one FTI and at least one STI in a therapeutically effective amount.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Methods of treating cancer patients with farnesyl transferase inhibitors
InactiveCN108371711AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferase inhibitorGenotyping
The present invention relates to the field of molecular biology and cancer biology. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods of treating a subject with a farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) that include determining whether the subject is likely to be responsive to the FTI treatment based on genotyping and expression profiling of certain immunological genes and RAS mutation status inthe subject.
Owner:KURA ONCOLOGY
Determination method for activity of enzymes like farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase
InactiveCN104101595AFriendly detection environmentSimple and fast operationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorGeranylgeranyl pyrophosphateFluorescence
So far, activity of enzymes can only be detected by using radio isotope or fluorophore labeling methods when substrates of the enzymes do not have ultraviolet-visible absorption. The detection methods have the disadvantages of high cost, unfriendliness to the environment and difficult operation. The invention provides a determination method for the activity of enzymes like farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. The method is characterized by using colourimetry to detect a produced product--pyrophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, then reacting pyrophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid with a specific reagent and carrying out reduction so as to obtain a colored compound. The determination method has the advantages of high efficiency, sensitivity, economic performance, etc. The determination method has broad spectrum activity, can be used for detecting the activity of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGPPS), squalene synthetase (SS), farnesyl transferase (FTase), geranylgeranyl transferase (GGTase), mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase (MDD), etc. except the activity of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, and is applicable to high flux screening of enzyme inhibitors and development of drugs.
Owner:张岩 +2
5- substituted tetralones as inhibitors of ras farnesyl trransferase
InactiveUS20040044057A1Treating and preventing uncontrolled or abnormal proliferation of tissuesEasy to synthesizeBiocideSenses disorderTetralonePercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention provides novel 5-substituted tetralones of Formulas (I), (II), (III) and (IV) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, amides, and prodrugs thereof, which are useful for treating and preventing uncontrolled or abnormal proliferation of tissues, such as cancer, atherosclerosis, restenosis, and psoriasis. Specifically, the present invention relates to compounds that inhibit the farnesyl transferase enzyme.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
Farnesyl transferase inhibitors and uses thereof
Disclosed herein are novel compounds and uses thereof. The present compounds may suppress the activity of farnesyl transferase and thus, may act as modulators of immune cells; therefor, they are useful for the development of a medicament for treating diseases that are associated with or caused by excessive levels of farnesyl transferase or immune response. Also disclosed herein are pharmaceutical compositions containing the present compounds.
Owner:MACKAY MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
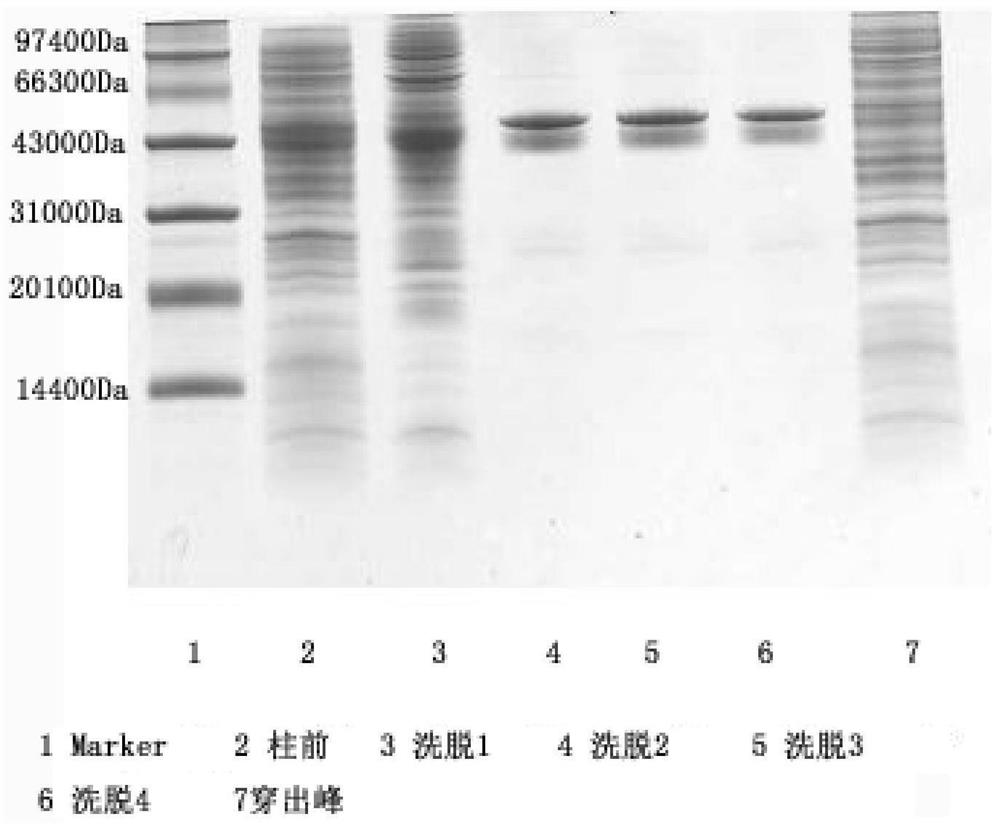
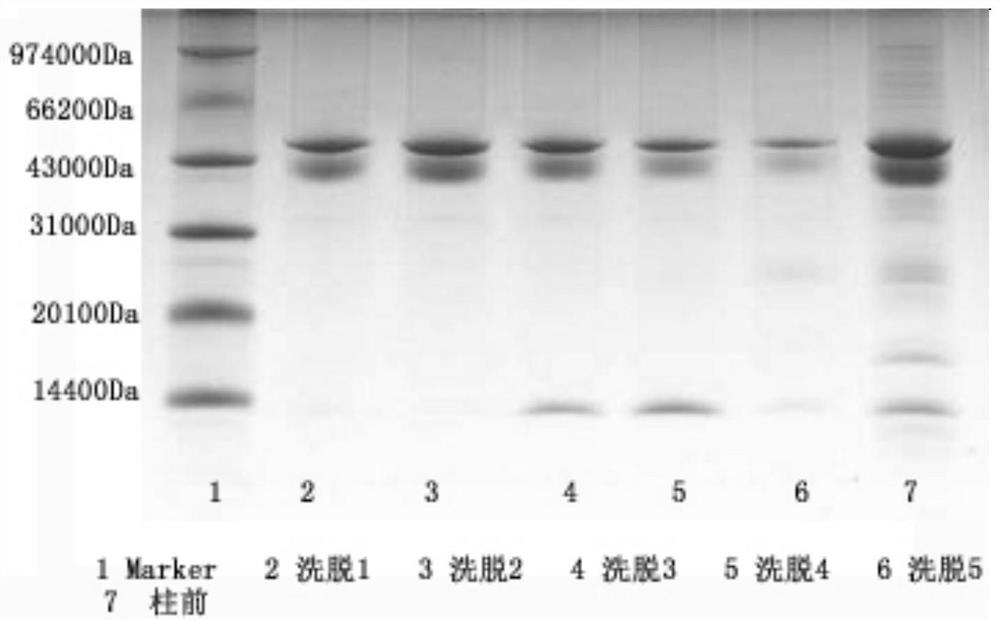
Farnesyl transferase variant and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113025591APurification work is simple and easyCorrect spatial structureTransferasesNucleic acid vectorEscherichia coliSpecific enzyme
The invention relates to a farnesyl transferase variant and a preparation method thereof, a farnesyl transferase protein sequence is screened out, genes of the farnesyl transferase protein sequence are subjected to high-density fermentation induced expression through an escherichia coli expression system after codon optimization, and the expression quantity is high; The invention further provides a soluble expression method without deformability and renaturation, and the purification step is simple and convenient. The specific enzyme activity detection shows that the prepared farnesyl transferase has very strong enzyme activity, and a tool enzyme capable of being industrially produced is provided for protein coupling.
Owner:江苏万邦医药科技有限公司 +1
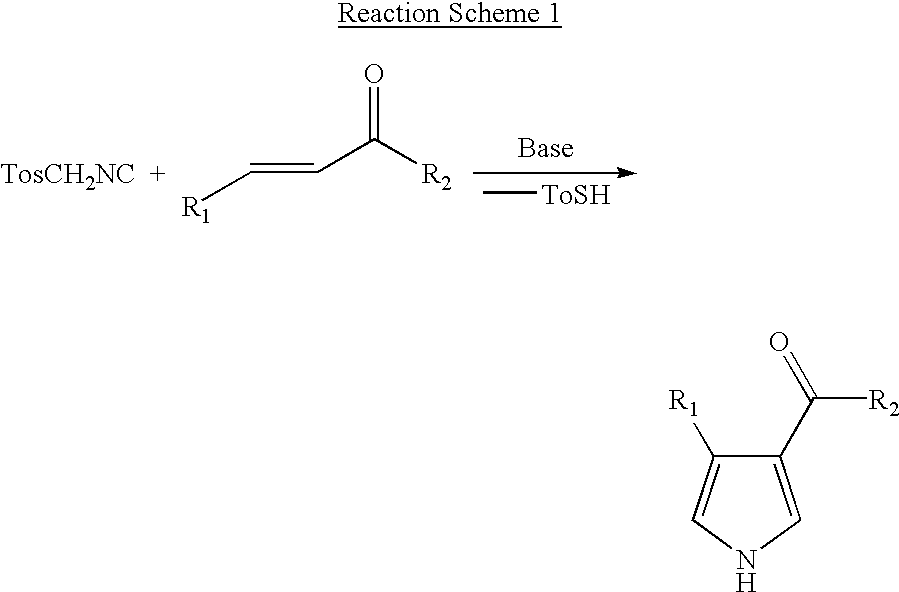
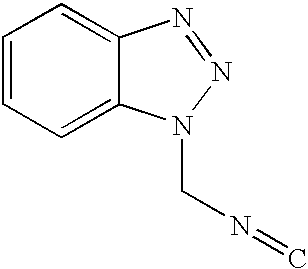
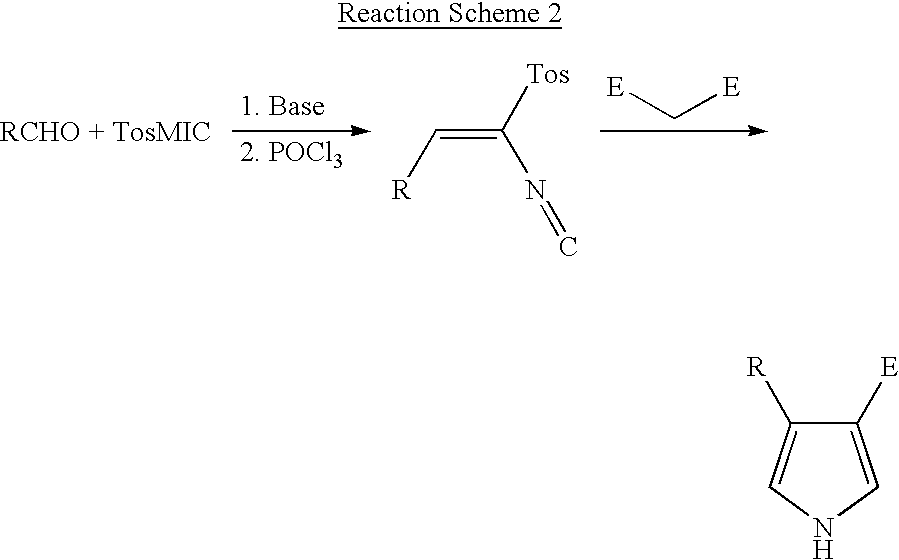
Novel process for preparing 4-substituted-1h-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid ester
InactiveUS20030069432A1Reduce decreaseImprove processing efficiencyOrganic chemistryAnticarcinogenAcyl group
The present invention relates to a novel process for preparing pyrrole ester compounds, which are key intermediates in the preparation of farnesyl transferase inhibitors, an anti-cancer agent. Horner-Emmons reaction of aldehyde compounds provides the corresponding alpha,beta-unsaturated esters, which without any separation and / or purification steps, are treated with toluenesulfonylmethylisocyanate in the presence of base to give pyrrole esters in one-pot fashion.
Owner:LG CHEM INVESTMENT LTD
Methods of treating cancer with farnesyl transferase inhibitors
InactiveCN109999037AOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer therapyFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
Owner:KURA ONCOLOGY
Methods for the Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20090181369A1Microbiological testing/measurementTherapeutic effectFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
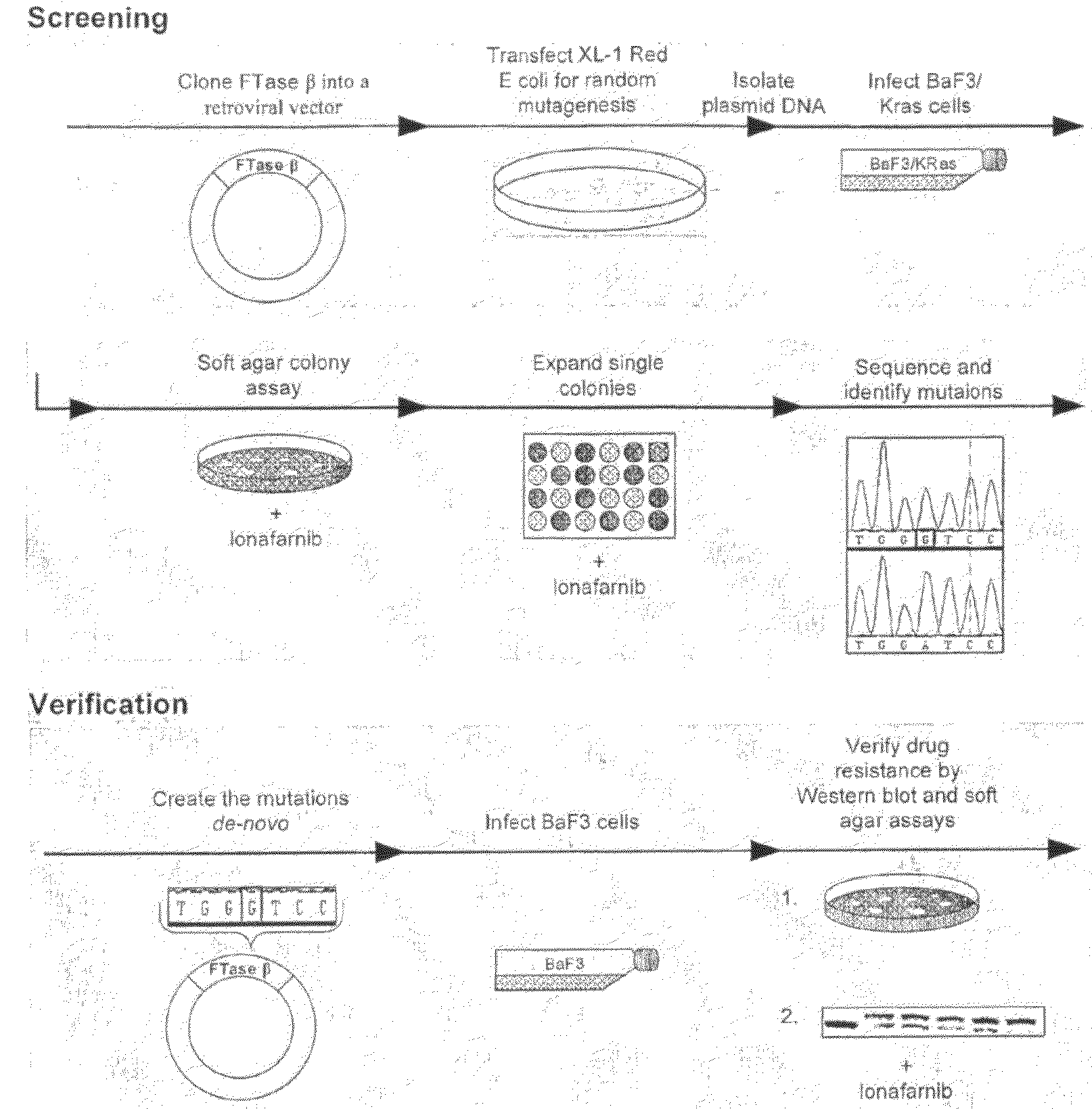
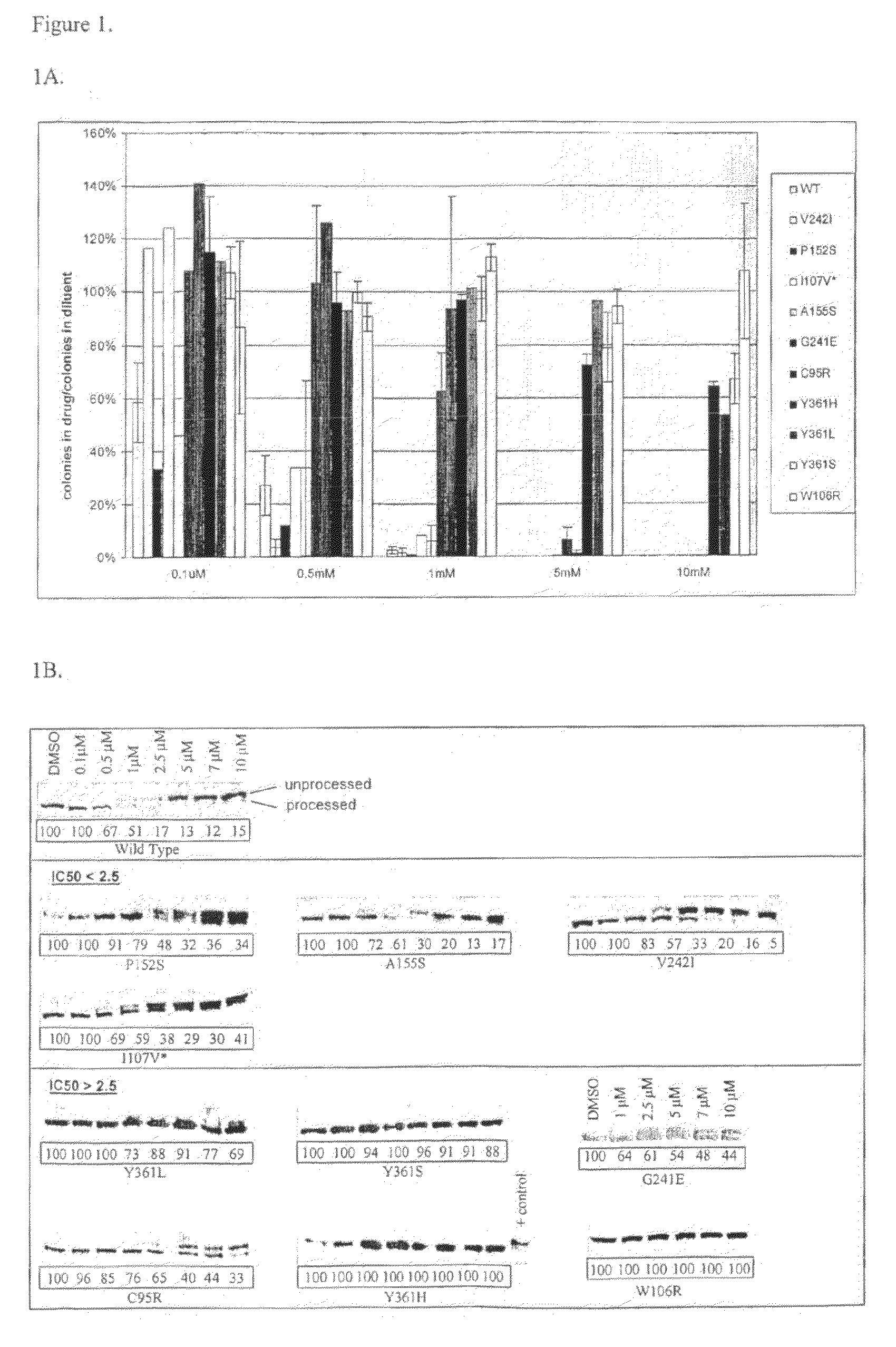
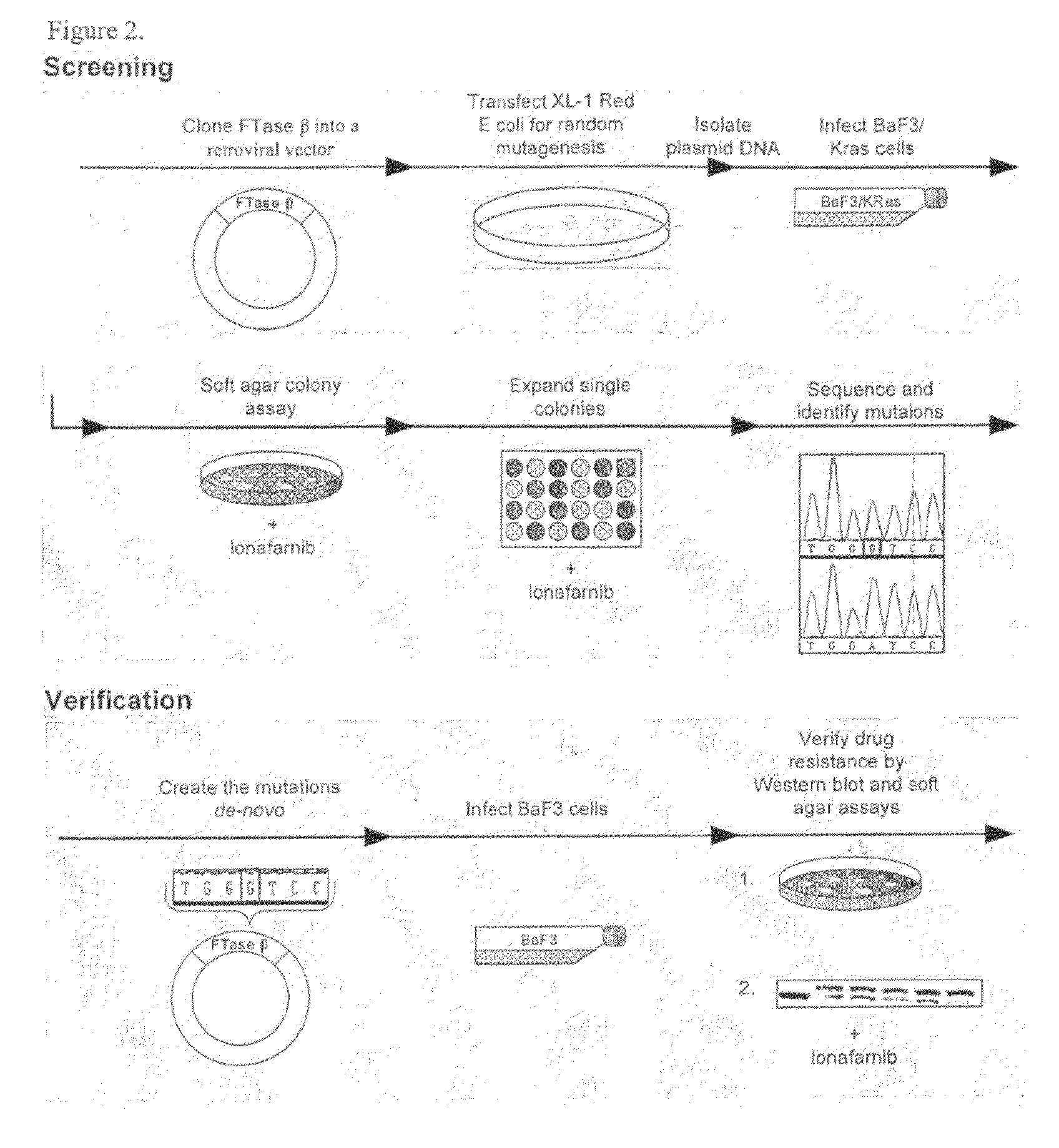
The present invention is directed to methods to determine the likelihood of therapeutic effectiveness of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor (FTI). The method comprises determining whether the gene encoding the farnesyl transferase beta subunit (FNTB) of said patient comprises at least one nucleic acid variance that causes an alteration in an amino acid residue. The change in the amino acid residue is associated with resistance to a FTI. The absence of at least one variance indicates that the FTI is likely to be effective.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Method for treating cancer having resistance to kinase inhibitors
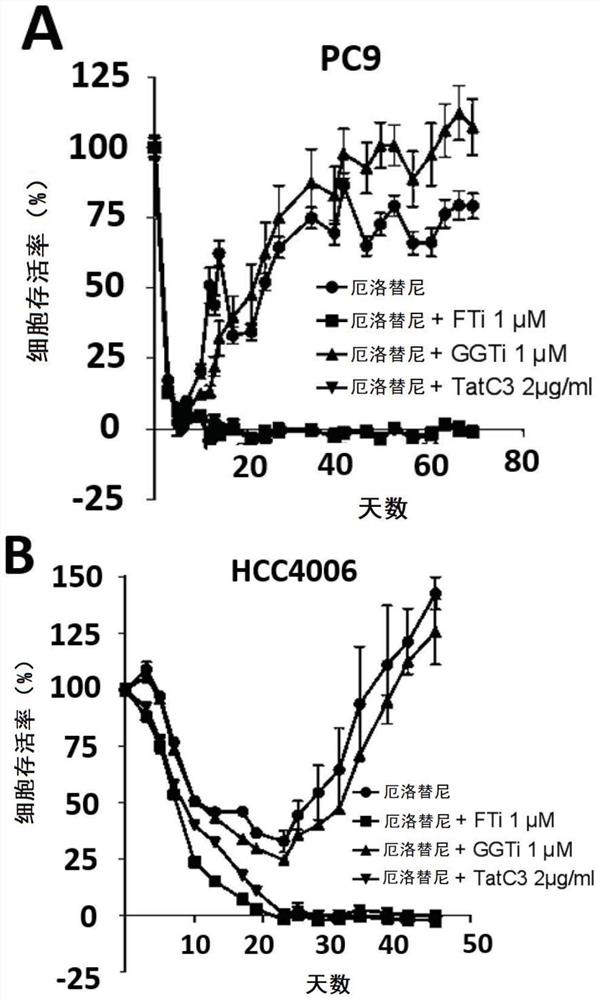
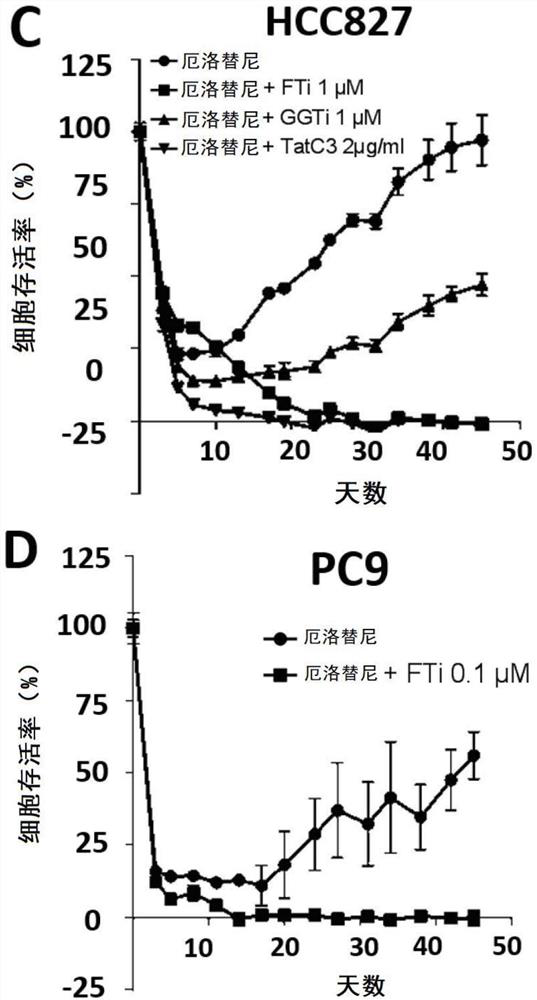
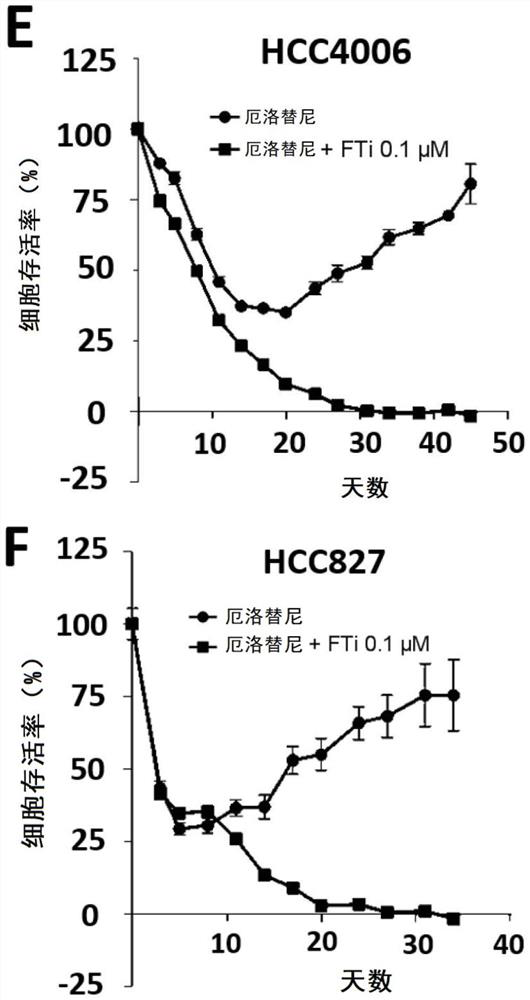
Resistance to kinase inhibitors is the biggest disorder of effective treatment for cancer patients. The recent research shows that the occurrence of the drug resistance may not only be generally considered by people to be explained by the existing drug-resistant subcloning drug selection, but also be caused by the generation of a small amount of drug-resistant cells (DTC) and entering a slow circulation state through the cells, so that the drug resistance has a resistance effect on treatment at the beginning. Therefore, a novel promising method should be adopted for the DTCs to prevent secondary drug resistance to kinase inhibitors. At present, the inventor has proved that inhibition of farnesyl transferase (but not geranyl geranyl transferase) can prevent the drug resistance in different carcinogenic environments. Particularly, the inventor determines the curative effect of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor (namely tipifarnib) and erlotinib which are jointly used in several EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) mutant cell lines in vitro. It is shown that the combination can effectively eliminate all drug-resistant cells and completely prevent the occurrence of drug-resistant cloning. It is interesting that similar results are also observed in other oncogenic models, such as ALK-translocated lung cancer cells or BRAF-mutated melanoma cells. Therefore, the present invention relates to the use of farnesyltransferase inhibitors in the treatment of kinase inhibitor resistant cancers.
Owner:INSERM法国国家健康医学研究院 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com