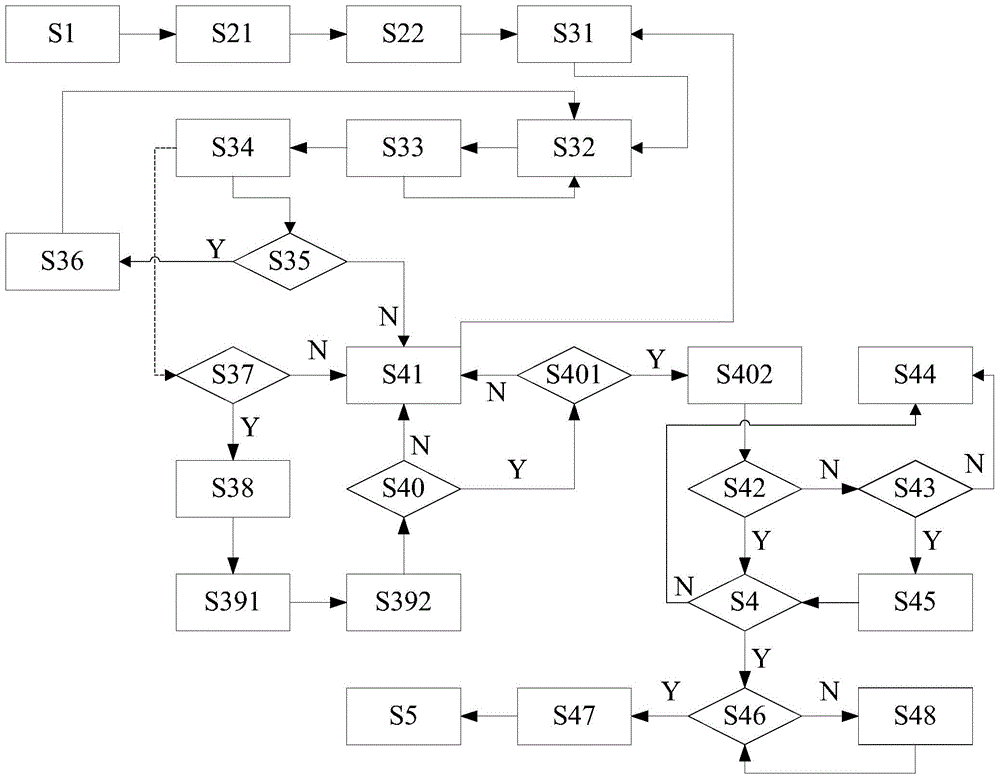
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
307 results about "Complex algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An algorithm is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. A complex algorithm is defined as an algorithm that embodies mathematical or logical methods and requires at least one thousand (1000) lines of the C/C tt programming language to implement.
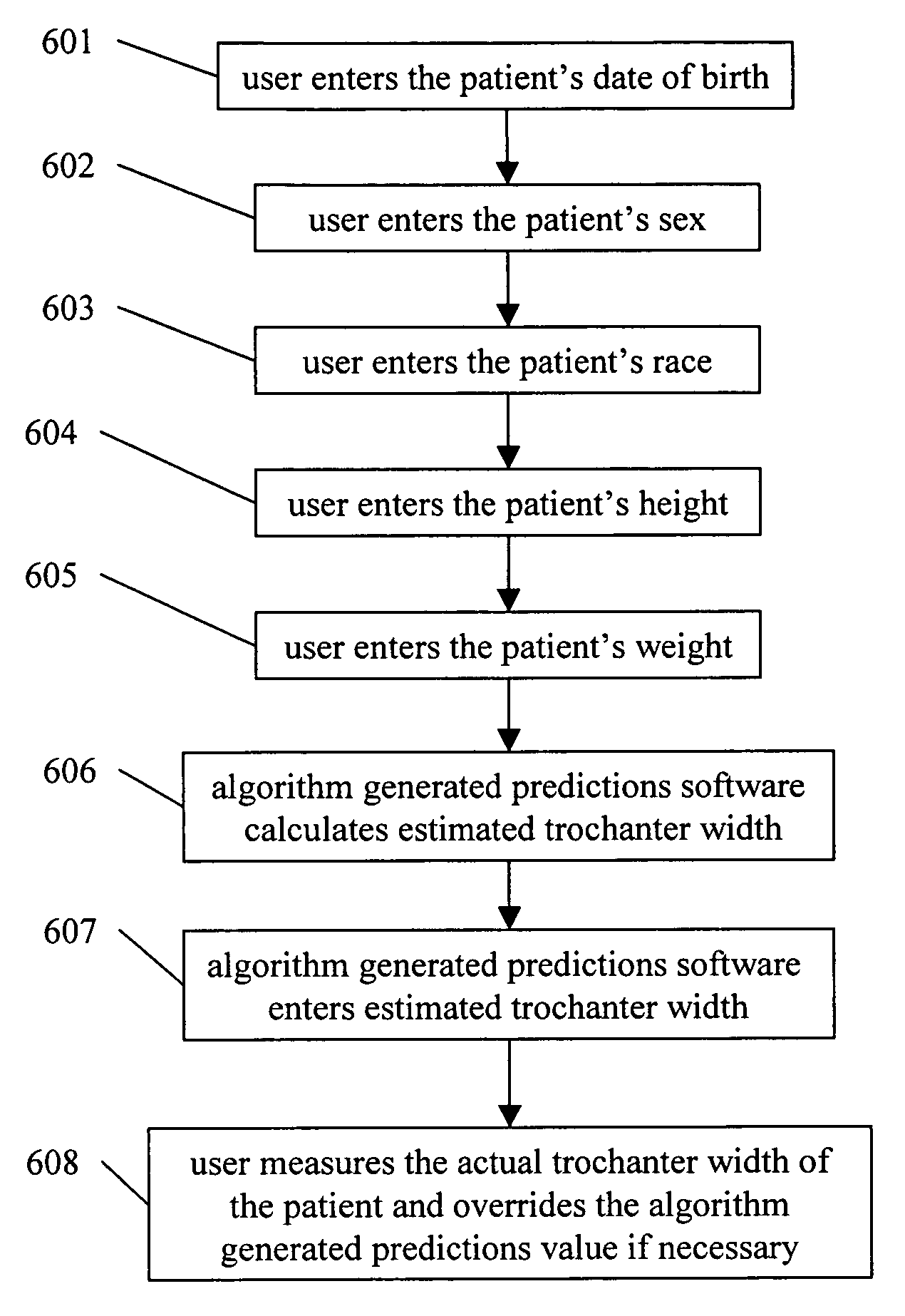
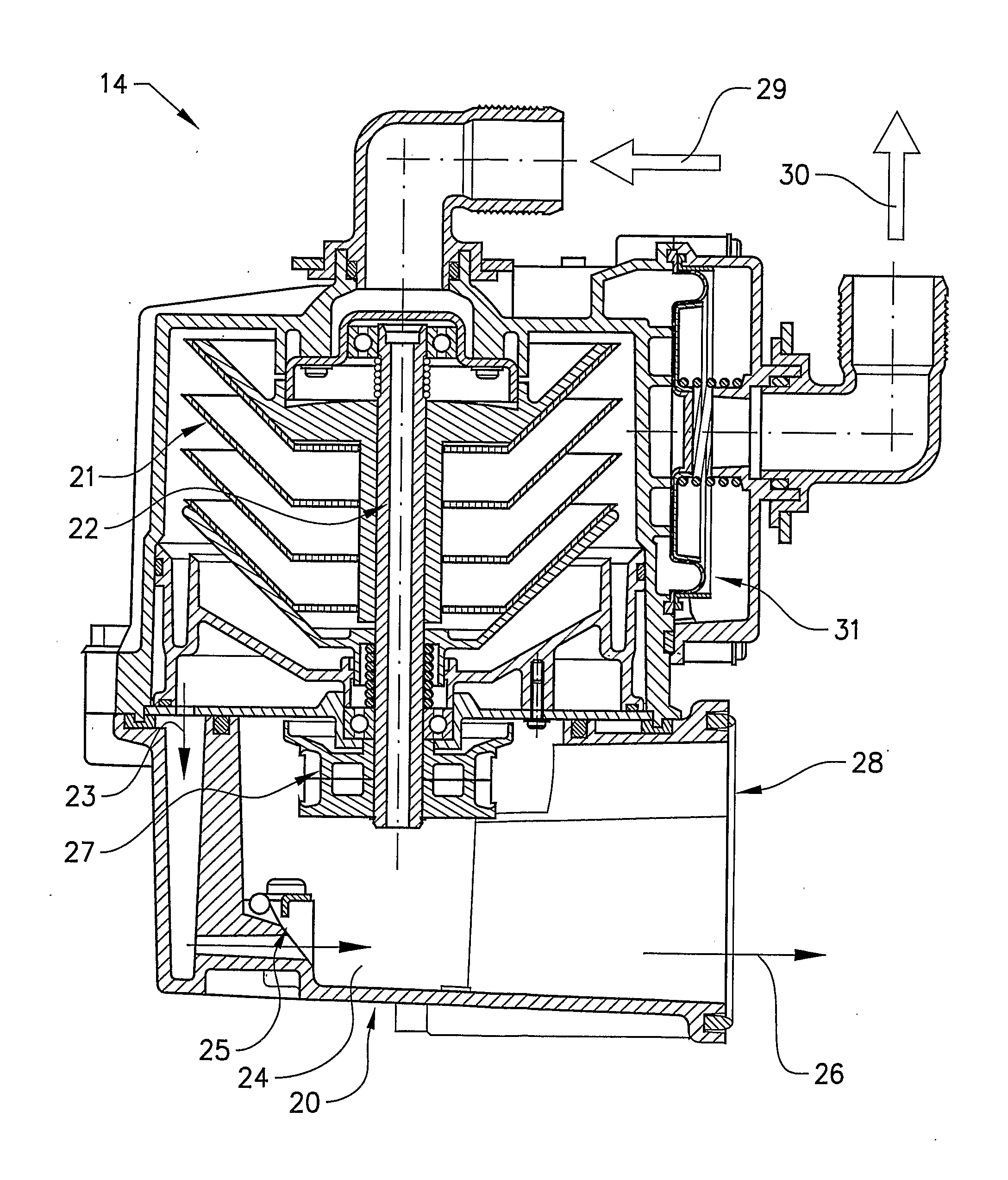
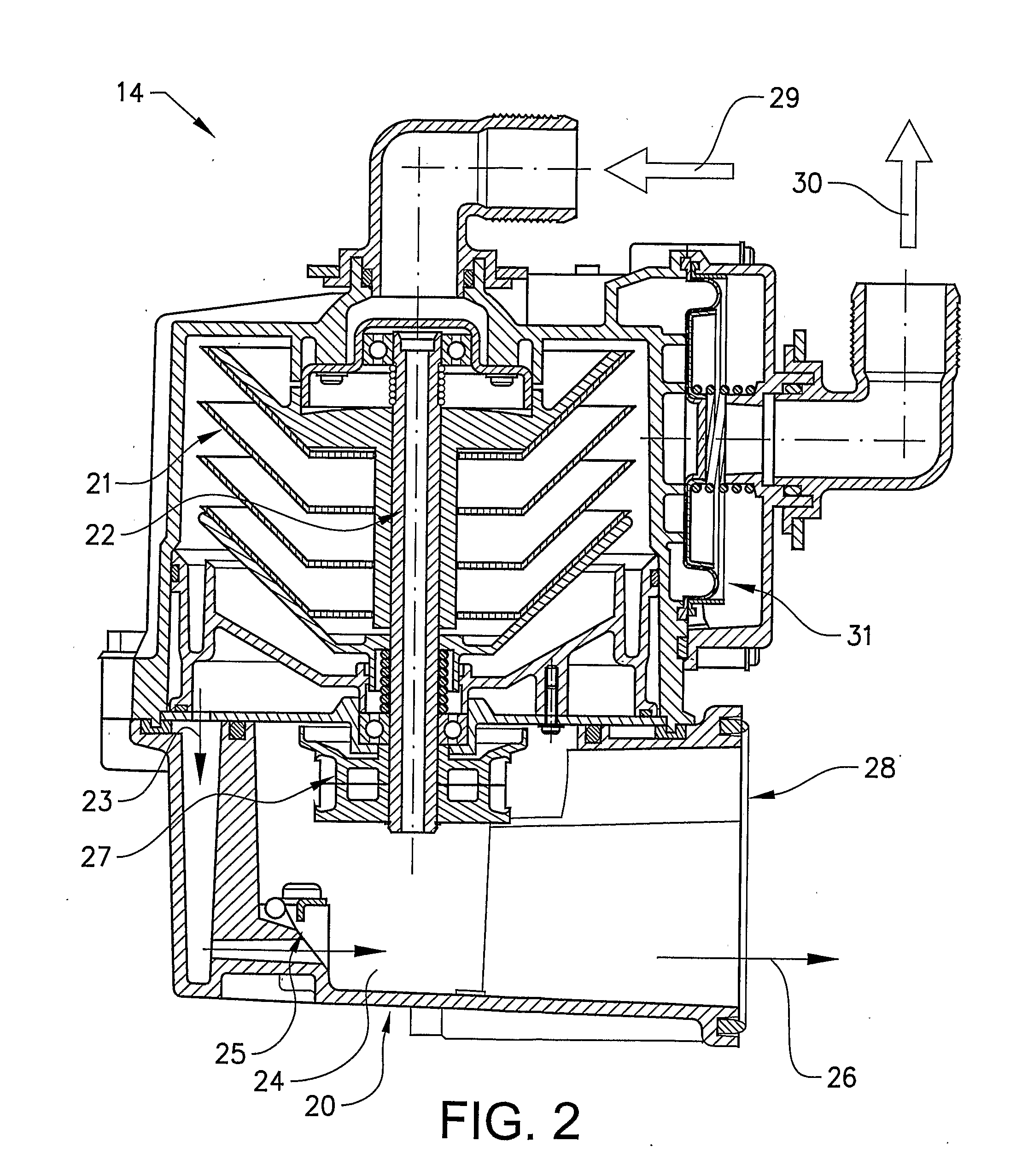
Method a designing, engineering modeling and manufacturing orthotics and prosthetics integrating algorithm generated predictions
InactiveUS20060100832A1More accurateMore scientificComputation using non-denominational number representationProsthesisComputer Aided DesignPhysical model
The present invention represents an advancement on the current processes involved in designing, engineering, modeling and manufacturing of orthotic and prosthetic devices. Orthotic and prosthetic computer aided design software has the option to apply measurements to a template to create a patient specific model. The use of algorithm generated predictions (also referred to as “AGP”) software takes this functionality and makes it more scientific. Algorithm generated predictions is the process of predicting the appropriate size and shape data through the use of complex algorithms. Certain key pieces of data are entered into the software that then calculates the appropriate dimensions and the appropriate computer aided design template. The dimensions are then applied to the computer aided design template. The computer aided design software modifies the templates by reducing and enlarging areas as necessary and a custom computer aided design model is created that can then be transformed into a physical model for the manufacture of the device.
Owner:BOWMAN GERALD DAVID
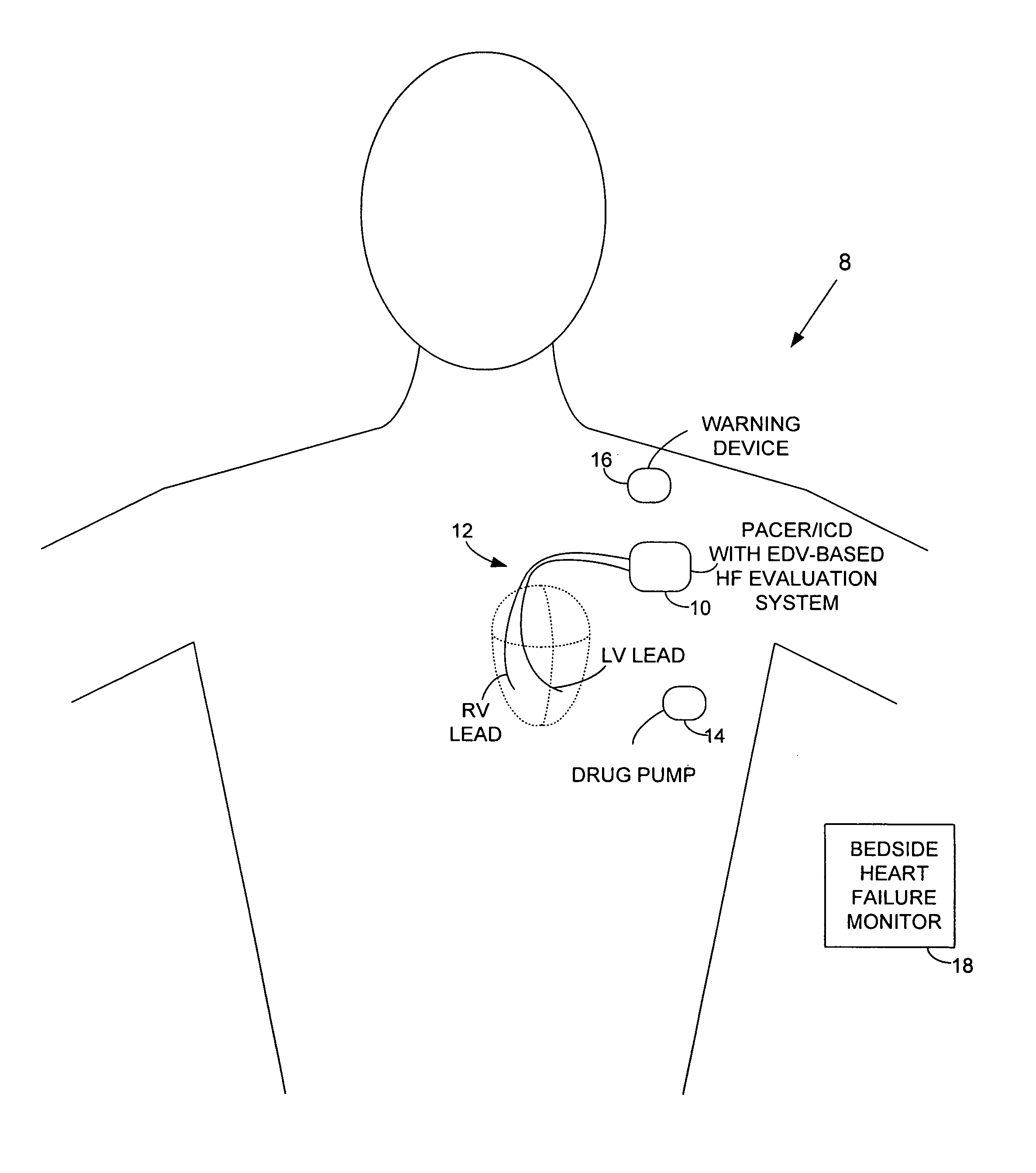
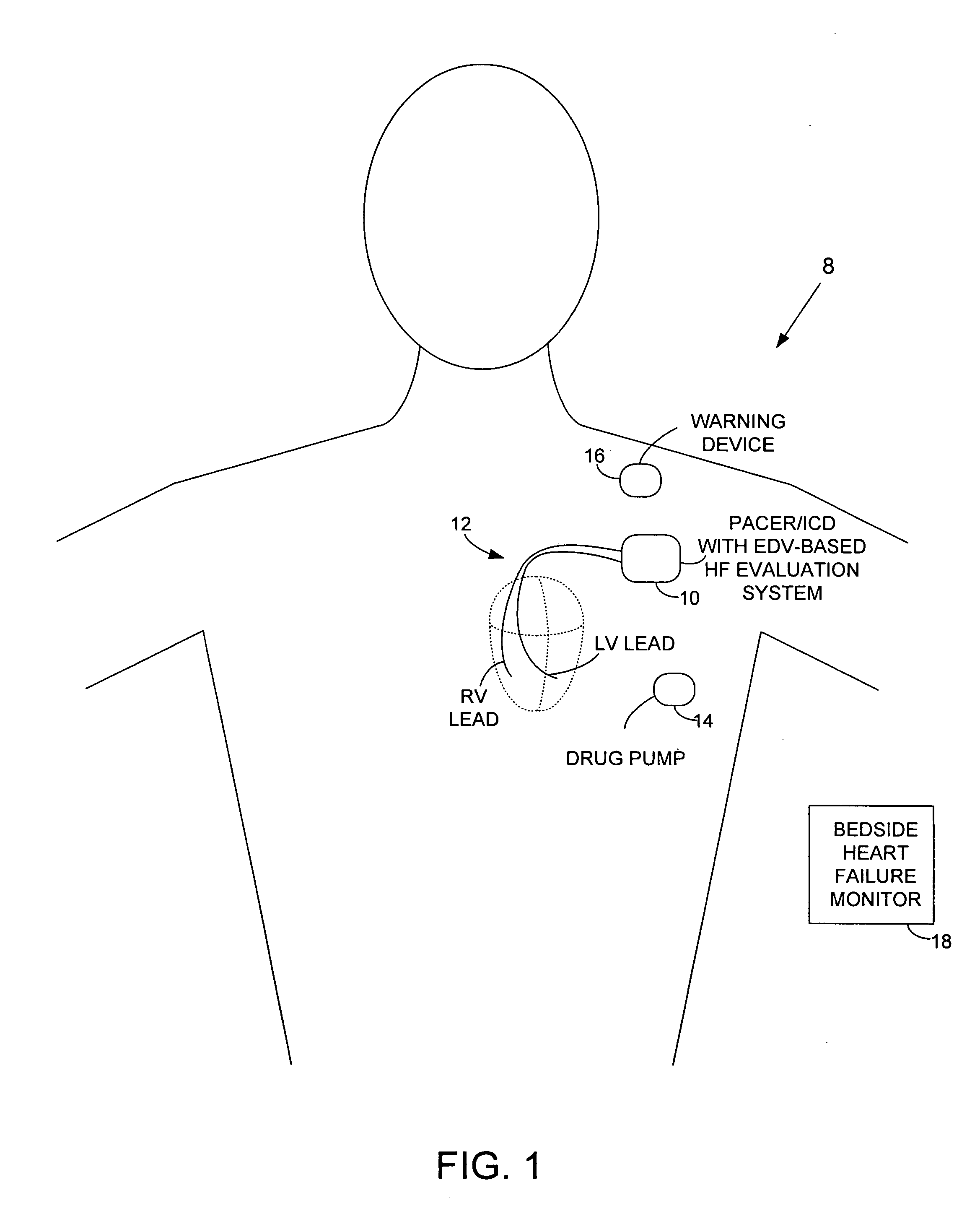
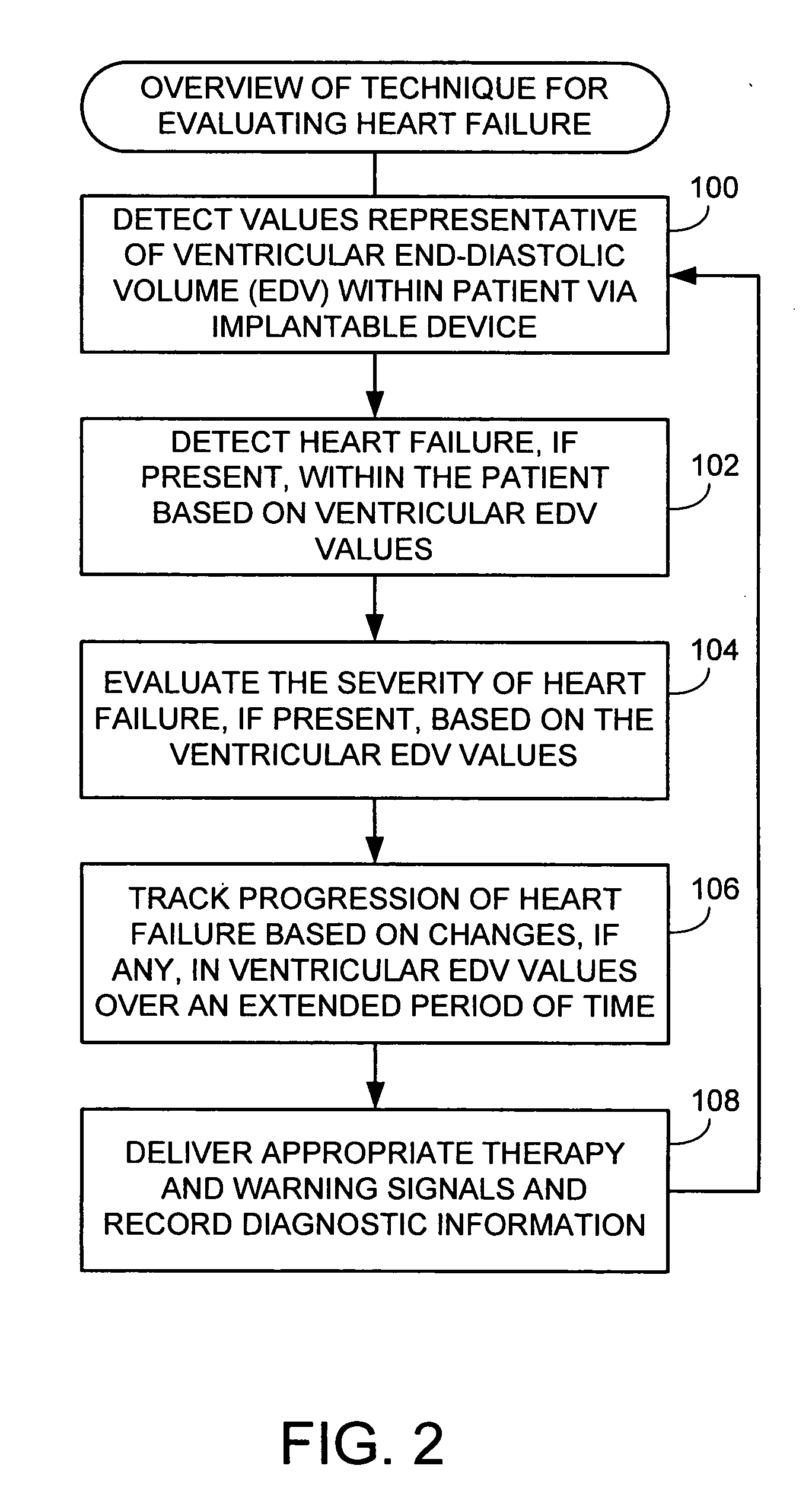
System and method for evaluating heart failure based on ventricular end-diastolic volume using an implantable medical device
Techniques are provided for evaluating heart failure within a patient based on ventricular impedance measurements. Briefly, values representative of ventricular end-diastolic volume (EDV) are detected using ventricular electrodes and then heart failure, if occurring within the patient, is evaluated based on ventricular EDV. In this manner, ventricular EDV is used as a proxy for ventricular end-diastolic pressure. By using ventricular EDV instead of ventricular end-diastolic pressure, heart failure is detected and evaluated without requiring sophisticated sensors or complex algorithms. Instead, ventricular EDV is easily and reliably measured using impedance signals sensed by implanted ventricular pacing / sensing electrodes. The severity of heart failure is also evaluated based on ventricular EDV values and heart failure progression is tracked based on changes, if any, in ventricular EDV values over time.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
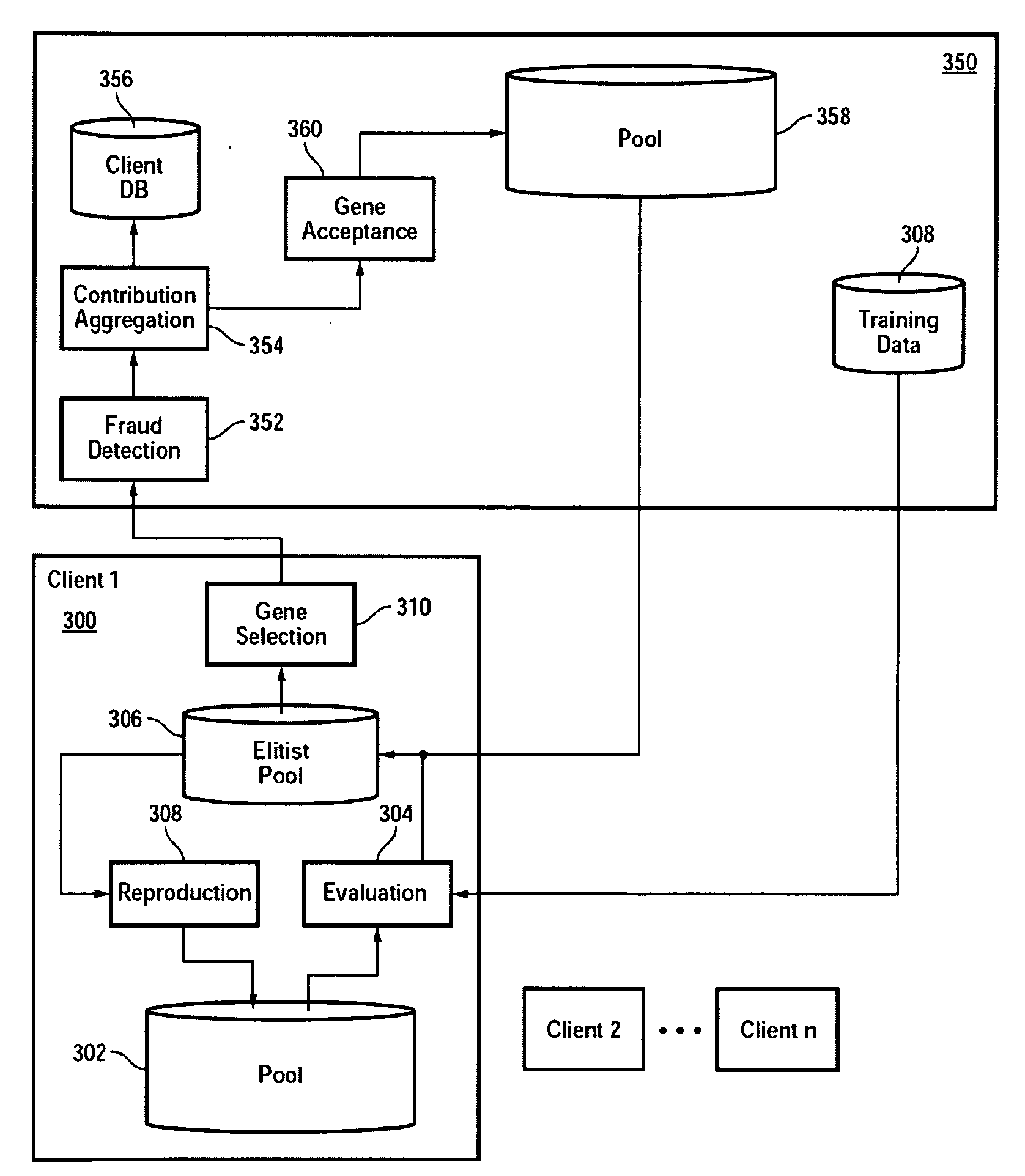
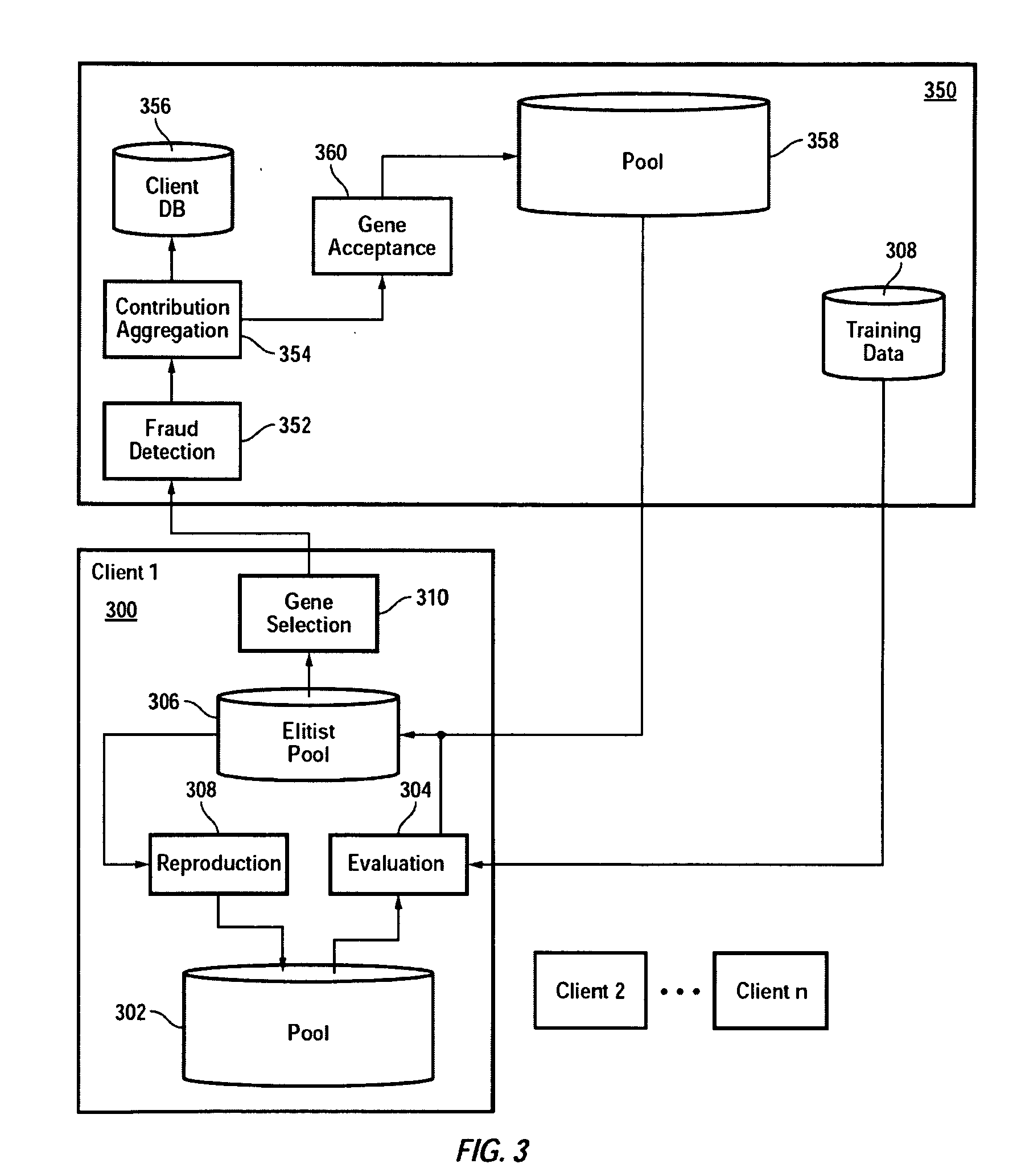
Distributed network for performing complex algorithms
InactiveUS20090125370A1Improve scalabilityLow costEnergy efficient ICTFinanceParallel computingSoftware
The cost of performing sophisticated software-based financial trend and pattern analysis is significantly reduced by distributing the processing power required to carry out the analysis and computational task across a large number of networked individual or cluster of computing nodes. To achieve this, the computational task is divided into a number of sub tasks. Each sub task is then executed on one of a number of processing devices to generate a multitude of solutions. The solutions are subsequently combined to generate a result for the computational task. The individuals controlling the processing devices are compensated for use of their associated processing devices. The algorithms are optionally enabled to evolve over time. Thereafter, one or more of the evolved algorithms is selected in accordance with a predefined condition.
Owner:COGNIZANT TECH SOLUTIONS U S CORP
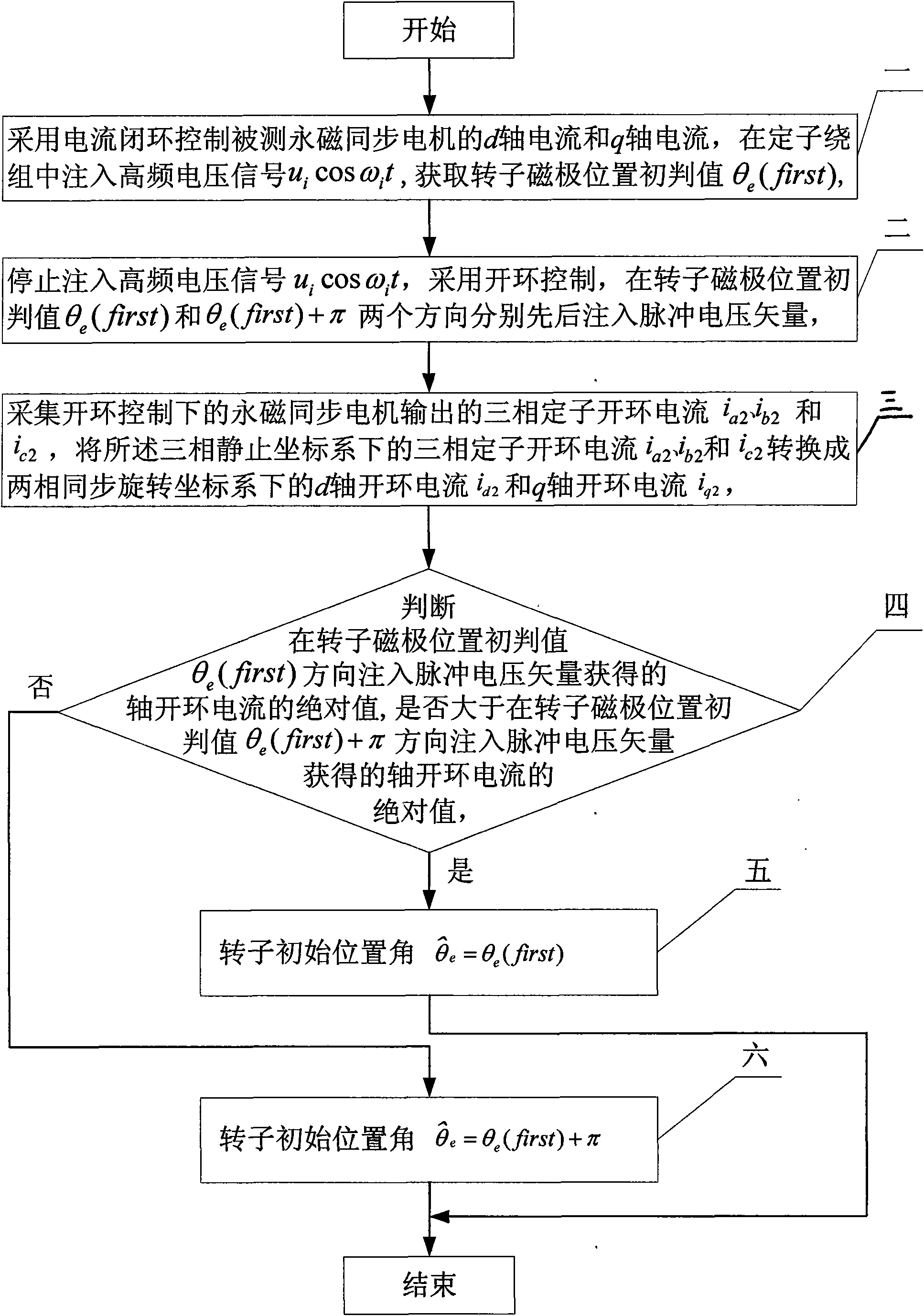
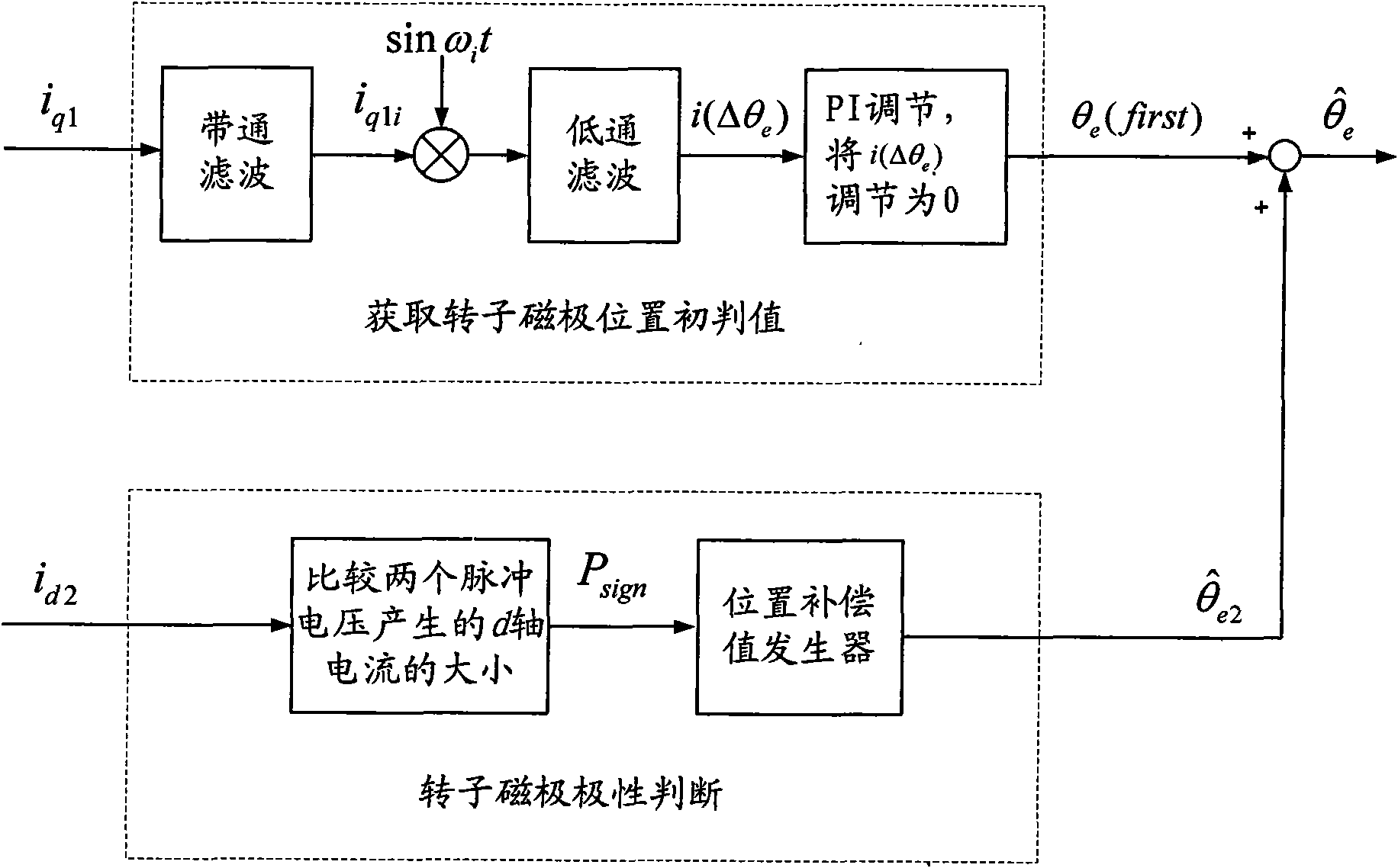
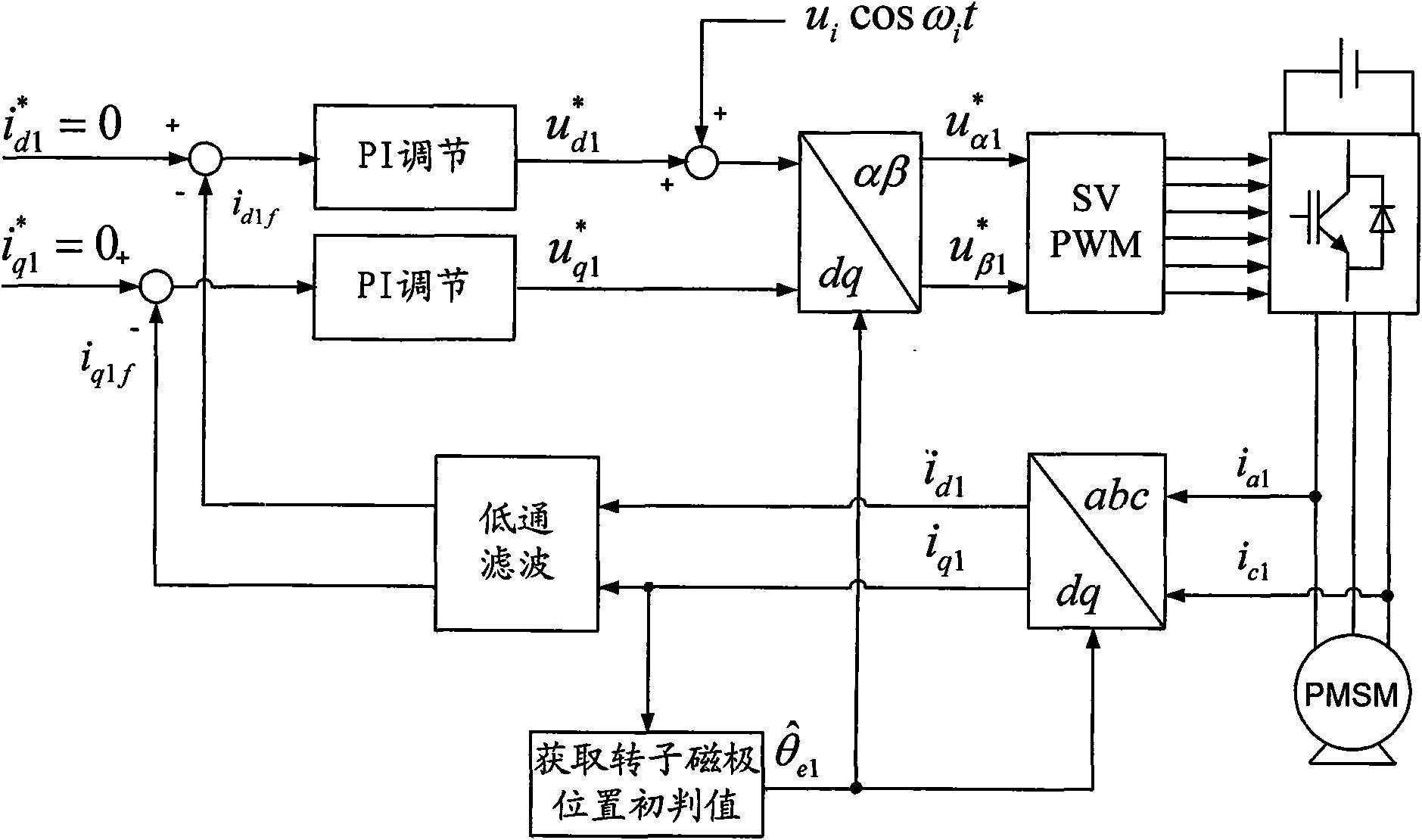
Method for identifying initial position of rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor of non-position sensor
InactiveCN101630938AEfficient identificationSatisfied with the initial position identification accuracyAC motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorPosition angle
A method for identifying an initial position of a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor of a non-position sensor belongs to the motor control field, and aims at solving the problems of the traditional method for identifying the initial position of magnetic poles of the rotor such as position change of the rotor, low identification precision or complex algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: maintaining the rotor under a static state during the identification process of the initial position of the rotor, injecting a high-frequency voltage signal to a stator winding, carrying out rotational coordinate conversion on three-phase stator current, and acquiring position information of the magnetic poles of the rotor by current components at q axis to obtain an initial judgment value of the magnetic pole position of the rotor; and then injecting two impulse voltage vectors in opposite directions to the stator winding, judging the polarity of the magnetic poles by comparing size of current components at d axis, and correcting the initial judgment value of the magnetic pole position obtained formerly by the judged polarity information of the magnetic poles to finally obtain an initial position angle of the rotor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
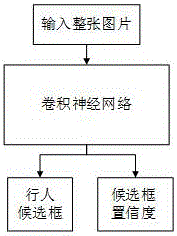
Pedestrian detection method based on end-to-end convolutional neural network
InactiveCN106022237AEasy to train and testImprove recallCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmConfidence measures
The invention discloses a pedestrian detection method based on an end-to-end convolutional neural network in order to solve the problem that the existing pedestrian detection algorithm has the disadvantages of low detection precision, complex algorithm and difficult multi-module fusion. A novel end-to-end convolutional neural network is adopted, a training sample set with marks is constructed, and end-to-end training is performed to get a convolutional neural network model capable of predicting a pedestrian candidate box and the confidence of the corresponding box. During test, a test picture is input into a trained model, and a corresponding pedestrian detection box and the confidence thereof can be obtained. Finally, non-maximum suppression and threshold screening are performed to get an optimal pedestrian area. The invention has two advantages compared with previous inventions. First, through end-to-end training and testing, the whole model is very easy to train and test. Second, pedestrian scale and proportion problems are solved by constructing a candidate box regression network, the pyramid technology adopted in previous inventions is not needed, and a lot of computing resources are saved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Mixed intrusion detection method of wireless sensor network
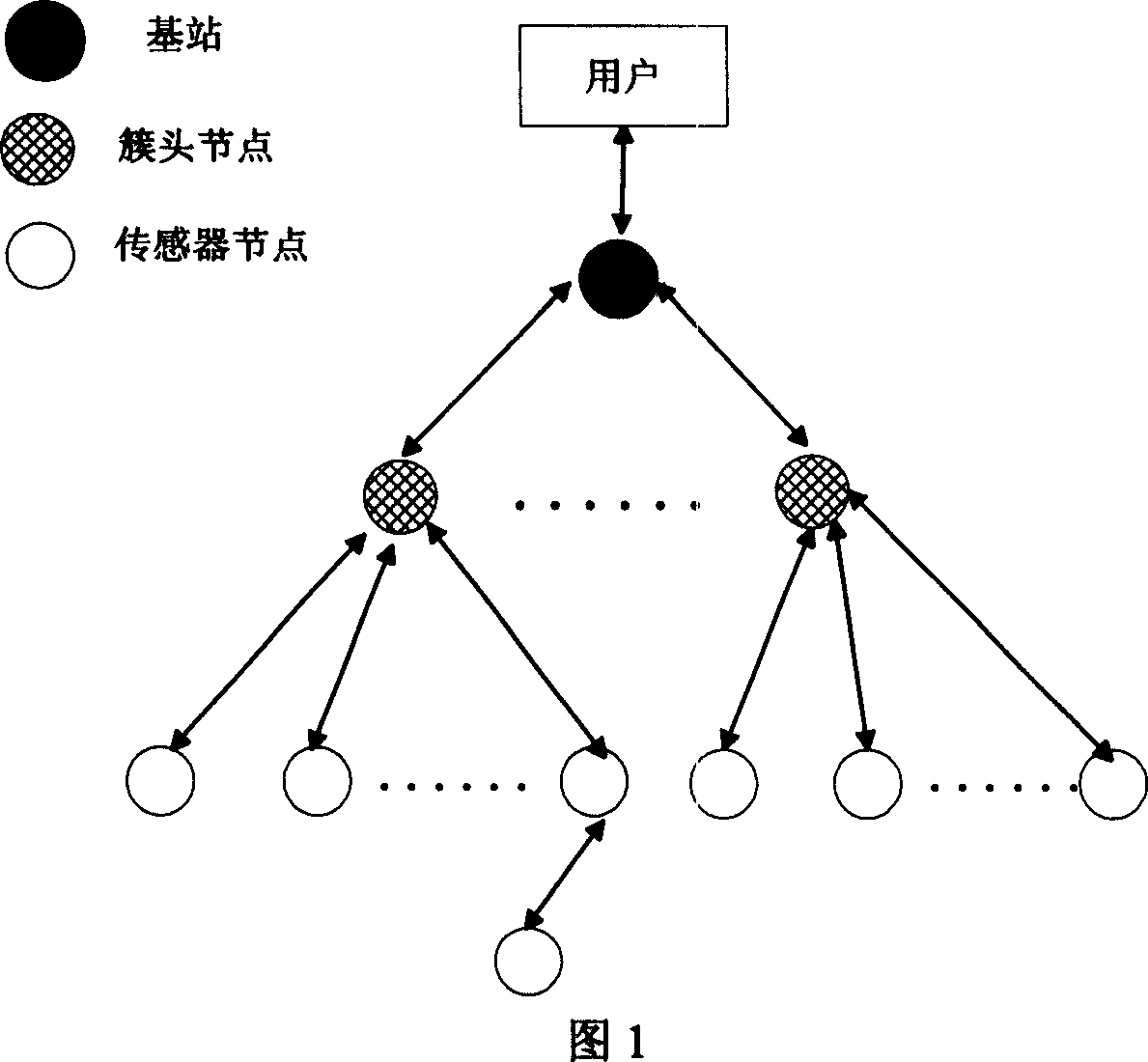
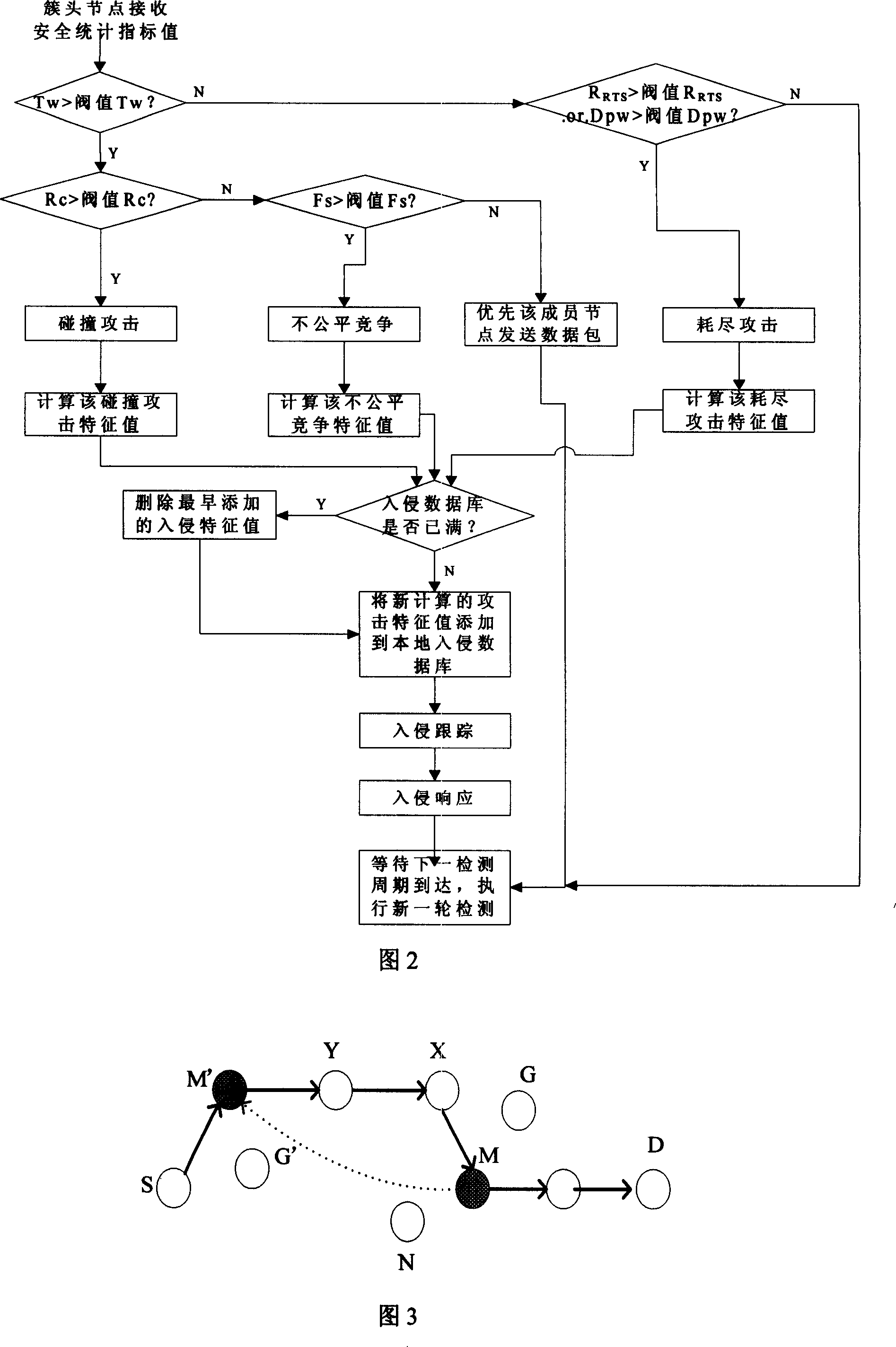
InactiveCN101013976AInspections are accelerated and simplifiedEffective detection and suppression of different attacksData switching by path configurationWireless sensor networkingSensor node
The invention relates to one wireless sensor network mixture intruding test method, which comprises the following steps: integrating multiple test method based on host machine, network, integration and abnormal mode, wherein, according to wireless sensor network property and outer and inner attack and distributing the test task onto sensor points, cluster point and base station point combined with host machine and network.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and system for carrying out searching on data
InactiveCN102915380AQuick searchReduce waiting timeSpecial data processing applicationsData matchingData mining
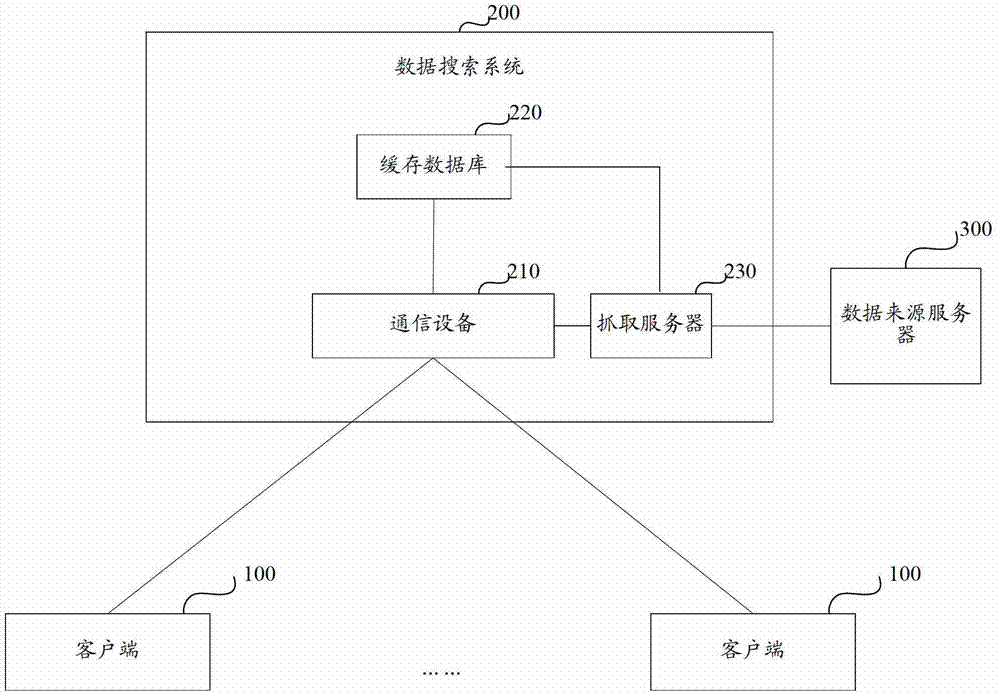
The invention discloses a method and system for carrying out searching on data. The system comprises a communication device, a cache database, a fetching server and a search server, wherein when the number of keywords matched with a search term and searched in the cache database according to a preset matching rule and the number of search results corresponding to the keywords are less than preset numbers, the obtained search results of the search server are sent to a client, and the search results of the search server are used as the supplement of the search results of the cache database. According to the method and system for carrying out searching on data, disclosed by the invention, the problem that in the prior art, when an information database and an index database are simultaneously set, a data matching process can be completed by using a complex algorithm so that the waiting time of users is too long is solved; and a beneficial effect of quickly finding matched data according to a preset cache database and a preset matching rule can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
Detecting and error-correcting method capable of rapidly and accurately obtaining element center and deflection angle
ActiveCN104981105AFind out exactlyOvercoming complex shortcomingsPrinted circuit assemblingCircuit board tools positioningCurve fittingEdge extraction
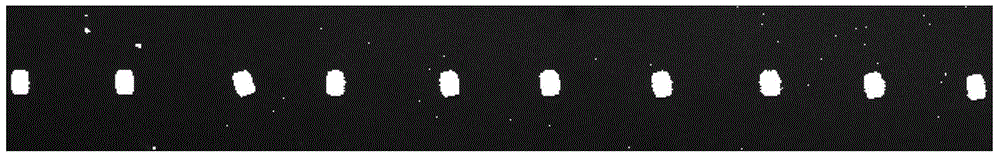
A detecting and error-correcting method capable of rapidly and accurately obtaining an element center and a deflection angle is disclosed. Interested edge area can be rapidly and accurately found out through an automatic edge area extraction method based on combination of binary morphology and image reduction, and subsequent edge extraction image scope is minimized as possible. Pixel level edge is roughly positioned at first, and accordingly a sub-pixel edge is rapidly extracted by one-dimensional curve fitting method. The method overcomes the defect of complex algorithm of a conventional sub-pixel edge extraction algorithm based on two-dimensional images, and the time of extracting accurate sub-pixel edge can be shortened. Weighted least square rectangular edge fitting algorithm based on linear hazen paradigm can detect straight lines on any positions of an image, and effectively minimizes influence of outlier on fitting precision due to uneven edges. The central positions of a plurality of elements and deflect angles can be rapidly and accurately detected at once, and the efficiency of visual detection is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
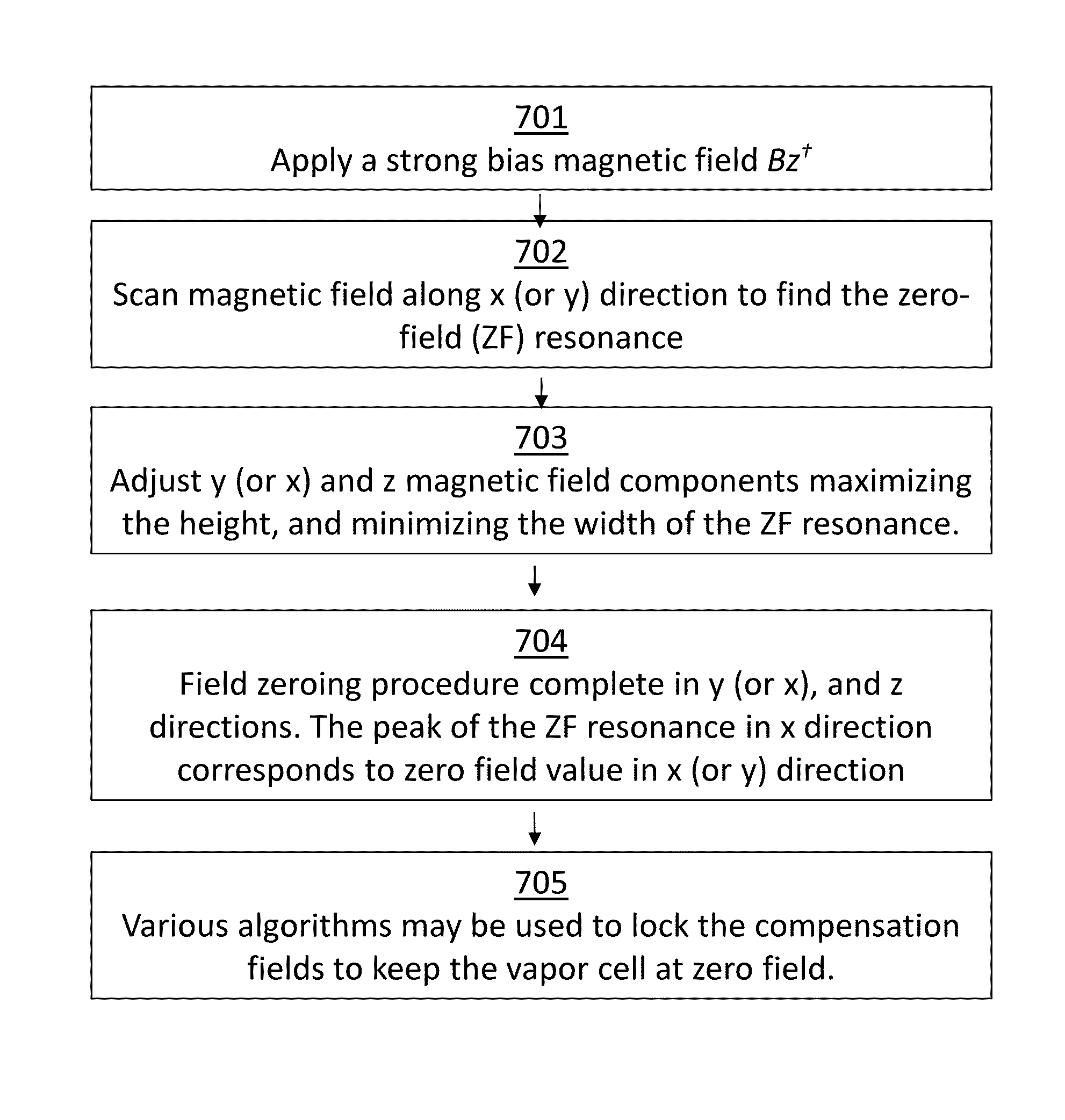
System for detecting zero-field resonance
ActiveUS20160223627A1Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
Data search method and data search system
InactiveCN102930054AReduce waiting timeSpeed up searchSpecial data processing applicationsSearch wordsData matching
The invention discloses a data search method and a data search system. The data search method comprises the following steps: pre-extracting a key word list, obtaining query results corresponding to key words in the key word list through visiting an external data source server, and associatively storing the key words and the query results corresponding to the key words in a cache database; obtaining a search request with a search word sent by a client, distributing the search request to the cache database, searching the key word matched with the search word and the query result corresponding to the key word according to a preset matching rule in the cache database; and sending the query result corresponding to the key word to the client. According to the data search method and the data search system, the problem of excessively long waiting time of a user caused by application of a complex algorithm to completion of a data matching process when an information database and an index database are configured at the same time in the prior art can be solved, and the benefit of quickly searching matched data according to the preset cache database and the matching rule can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
System and method for stochastic aircraft flight-path modeling
ActiveUS20060089760A1Eliminate disadvantagesDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsAirspeedLogistic distribution
Stochastic models of aircraft flight paths and a method for deriving such models from recorded air traffic data. Each stochastic model involves identifying the flight plan for one or more aircraft; identifying important parameters from each flight plan, such as aircraft type, cruise altitude, and airspeed; optionally identifying flight plan amendments for each flight; representing each route of flight as a series of navigational fixes; representing at least one aircraft flight parameter probabilistically; modeling realistic differences in at least one dimension between each planned route of flight and the flight path as it might actually be flown; and communicating the modeled deviations or simulated flight paths to the user. At least one aircraft flight parameter is represented as a random variable with a particular statistical distribution, such as a normal (Gaussian), Laplacian, or logistic distribution; or with a more complex algorithm containing one or more random elements. The modeled flight parameters may be any of lateral position, longitudinal position, climb altitude, descent altitude, climb airspeed, descent airspeed, cruise airspeed, cruise altitude transition, or response time to a flight plan amendment.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
Method for detecting zero-field resonance
ActiveUS9116201B2Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
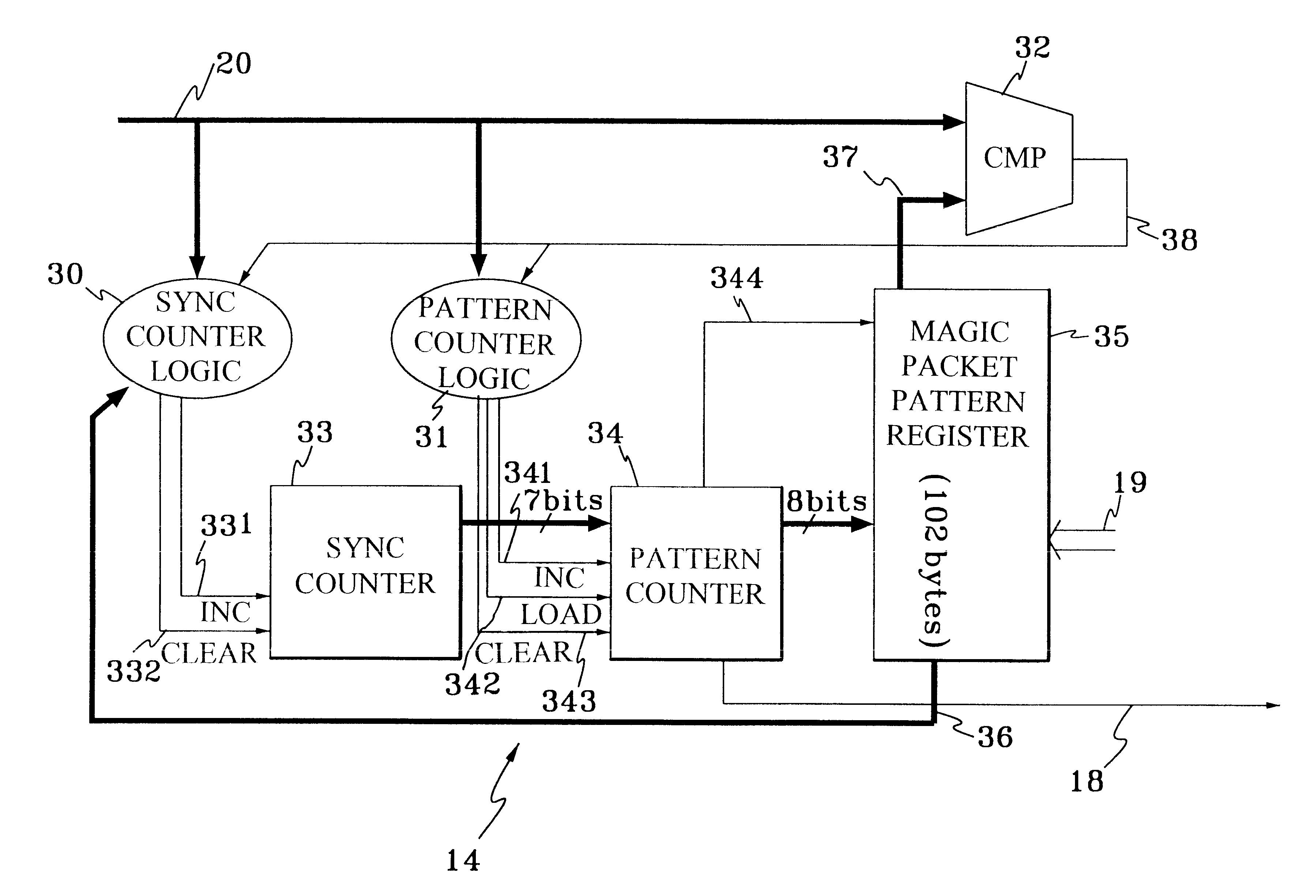
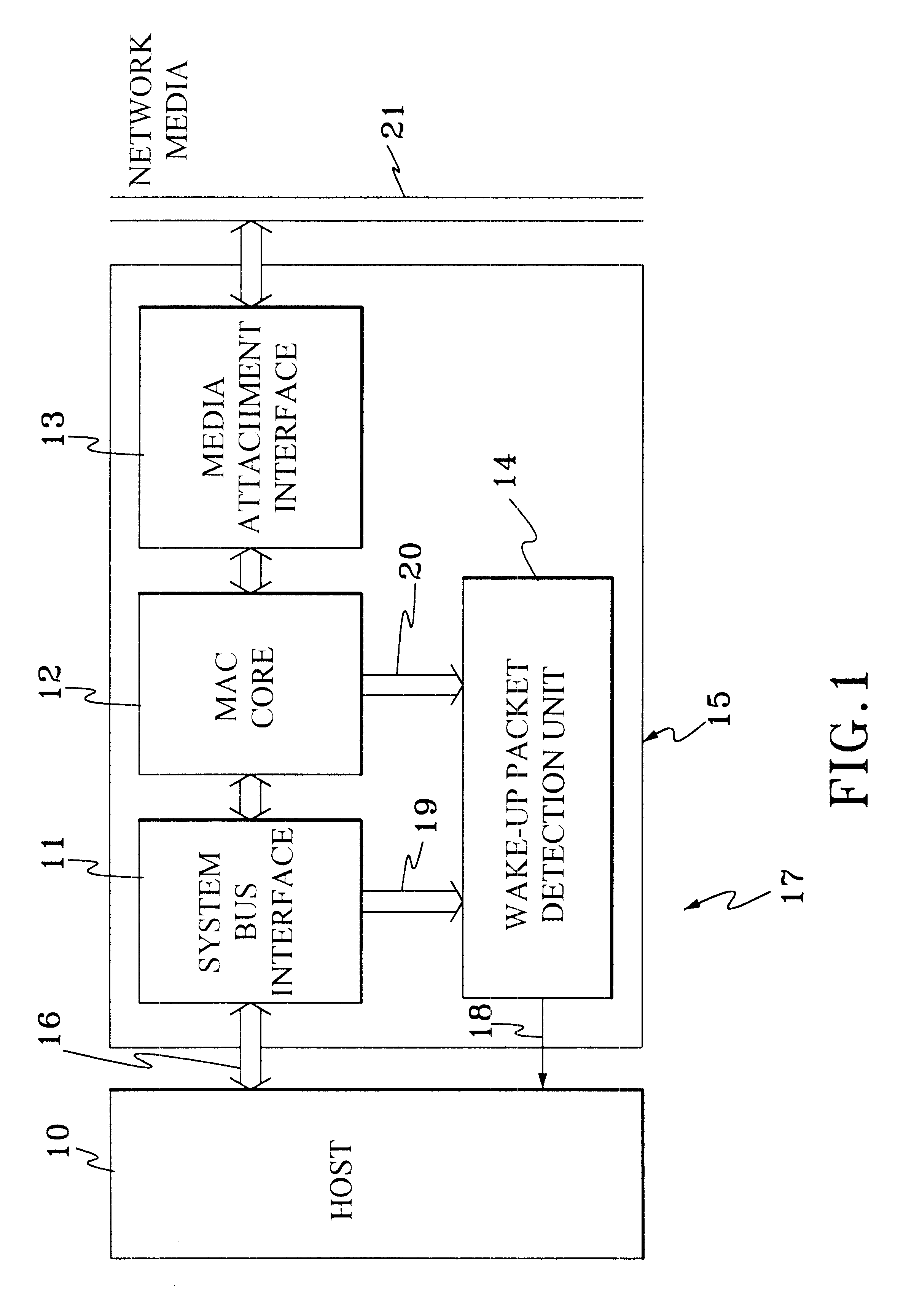
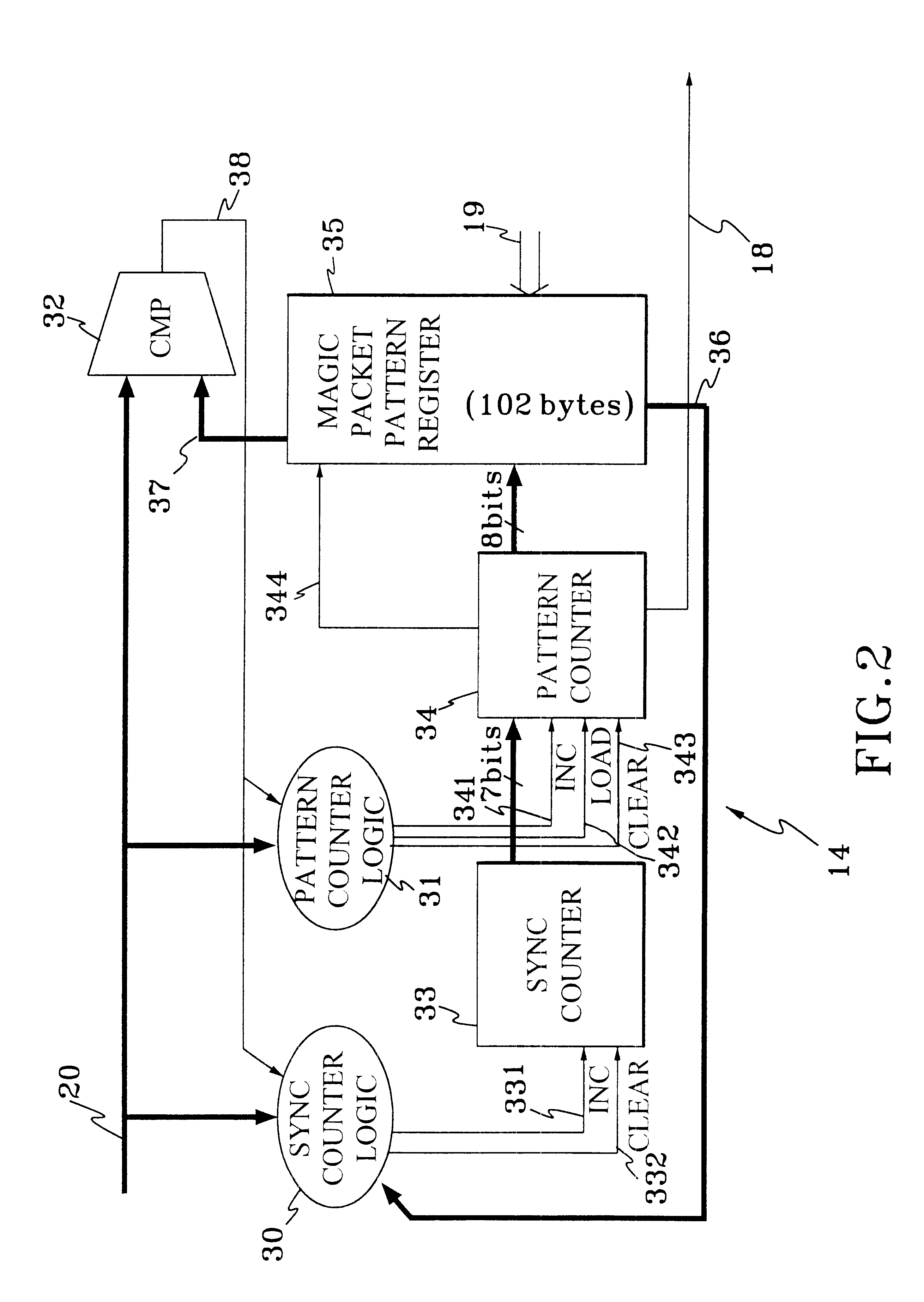
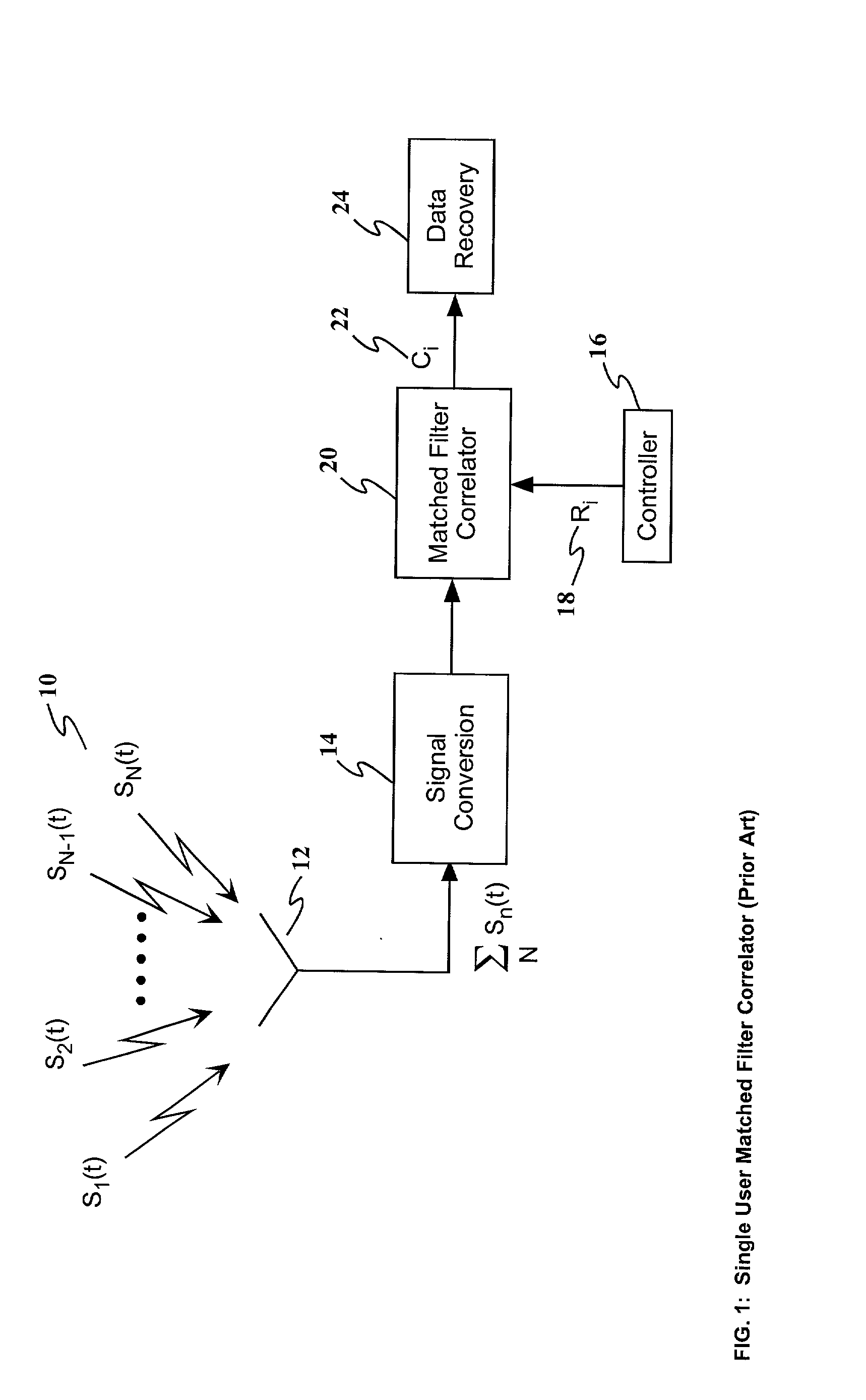
Method and apparatus for detecting data streams with specific pattern
Magic Packet technique is developed to remotely awake a computer host in a sleeping mode on a node through computer network. Instead of utilizing a large amount of memory or a complex algorithm, an algorithm and system, which only utilize two sets of counters and control logics to perfectly detect the Magic Packet according to the characteristics of magic packet are disclosed. According to the present invention, if a LAN controller on a node of the network is in magic packet mode, it will detect all input frames addressed in the node to search a specific data sequence indicative of the Magic Packet frame. Once the controller detects the data sequence, it will notice the power management circuitry of the computer host on the sleeping node to awake the system.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Distributed network for performing complex algorithms
InactiveUS20120239517A1Improve scalabilityLow costEnergy efficient ICTFinanceNODALParallel computing
The cost of performing sophisticated software-based financial trend and pattern analysis is significantly reduced by distributing the processing power required to carry out the analysis and computational task across a large number of networked individual or cluster of computing nodes. To achieve this, the computational task is divided into a number of sub tasks. Each sub task is then executed on one of a number of processing devices to generate a multitude of solutions. The solutions are subsequently combined to generate a result for the computational task. The individuals controlling the processing devices are compensated for use of their associated processing devices. The algorithms are optionally enabled to evolve over time. Thereafter, one or more of the evolved algorithms is selected in accordance with a predefined condition.
Owner:COGNIZANT TECH SOLUTIONS U S CORP
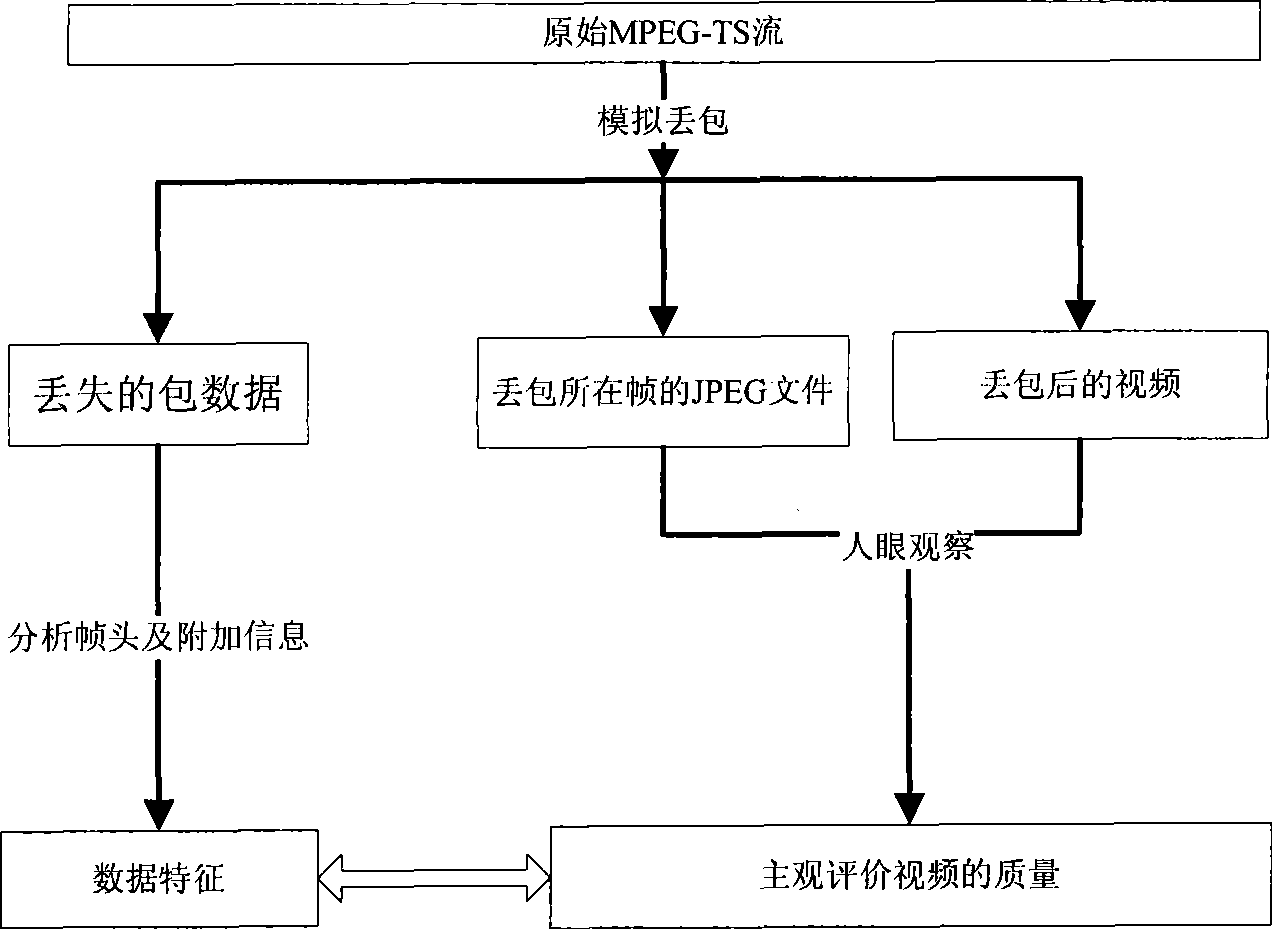
Method for evaluating quality of streaming video without reference
The invention discloses a method for evaluating quality of streaming video without reference. The method is realized in a simulation environment of simulating network loss on MPEG-TS stream; network damage is simulated through man-made loss, simultaneously loss data is recorded, attribute of the data is analyzed, an image of the loss is stored, and impact to visual effect after the data loss is observed by eye, thereby establishing a one-to-one correspondence. In practical application, a QOE evaluation value which is in accord with subjective feeling of a user can be acquired through sampling and analyzing a transmission media and analyzing the network damage. In the method, video flowing is directly analyzed without source file information, analysis process is simple and complex algorithm is not needed, quality of user experience is reflected in real time and an accurate evaluation value is given, and an objective evaluation method and a subjective evaluation method are combined to ensure the evaluation value is closer to the real feeling of the user.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Handheld thermal infrared imager and method for same to carry out quick locking and ranging on small target
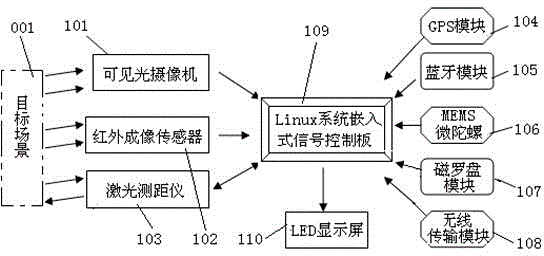
ActiveCN104155006APrecise positioningEasy to observeRadiation pyrometryClosed circuit television systemsGyroscopeMultiple sensor
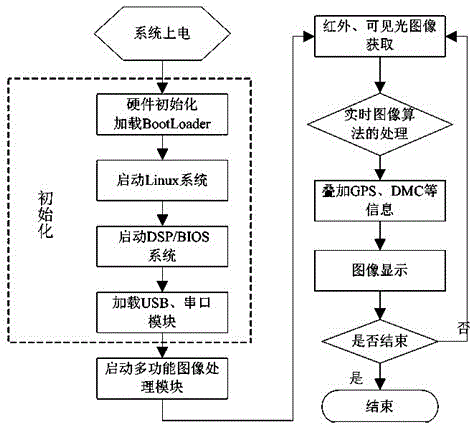
The invention relates to a handheld thermal infrared imager. The handheld thermal infrared image comprises infrared imaging sensors, a visible light camera, a laser range finder, a Bluetooth module, a magnetic compass module, an MEMS micro gyroscope, a GPS module, a wireless transmission module, a Linux system embedded signal control panel and an LED display screen. Data of the multiple sensors can be integrated, resources can be reasonably allocated, complex algorithms can be achieved, the performance of handheld equipment can be improved, and the systematization of single machines can be improved. The invention further discloses a Linux-system-based algorithm for the handheld thermal infrared to carry out quick locking and ranging on a small target. According the principle of the MEMS micro gyroscope and the image processing algorithm, the target can be quickly and accurately locked and traced through digital images of infrared light and visible light, and the quick locking and ranging functions are effectively achieved through the laser range finder. The handheld thermal infrared can eliminate video jitters in real time, improve the video quality, lock the target quickly, recognize and detect the target distance automatically and improve the functionality of the handheld equipment.
Owner:HUBEI JIUZHIYANG INFRARED SYST CO LTD
Intersection multiline public traffic vehicle priority request conflict coordination control method
ActiveCN104485005ARaise priorityImprove service qualityRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer scienceTraffic system
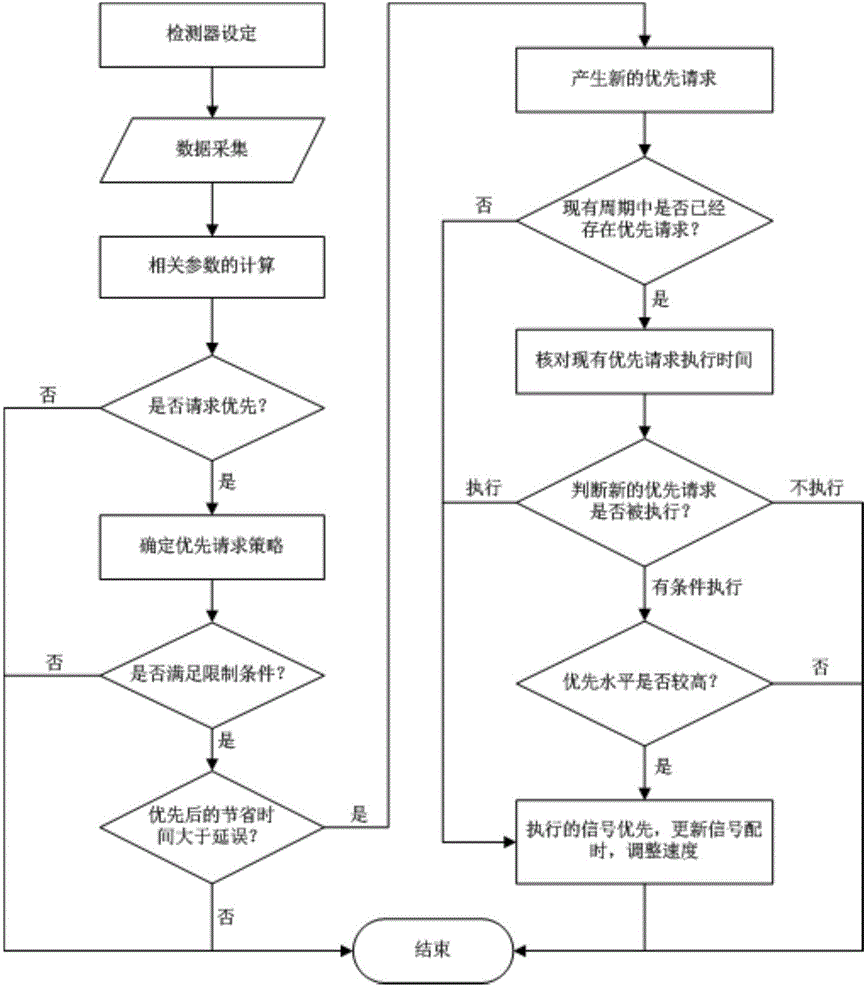
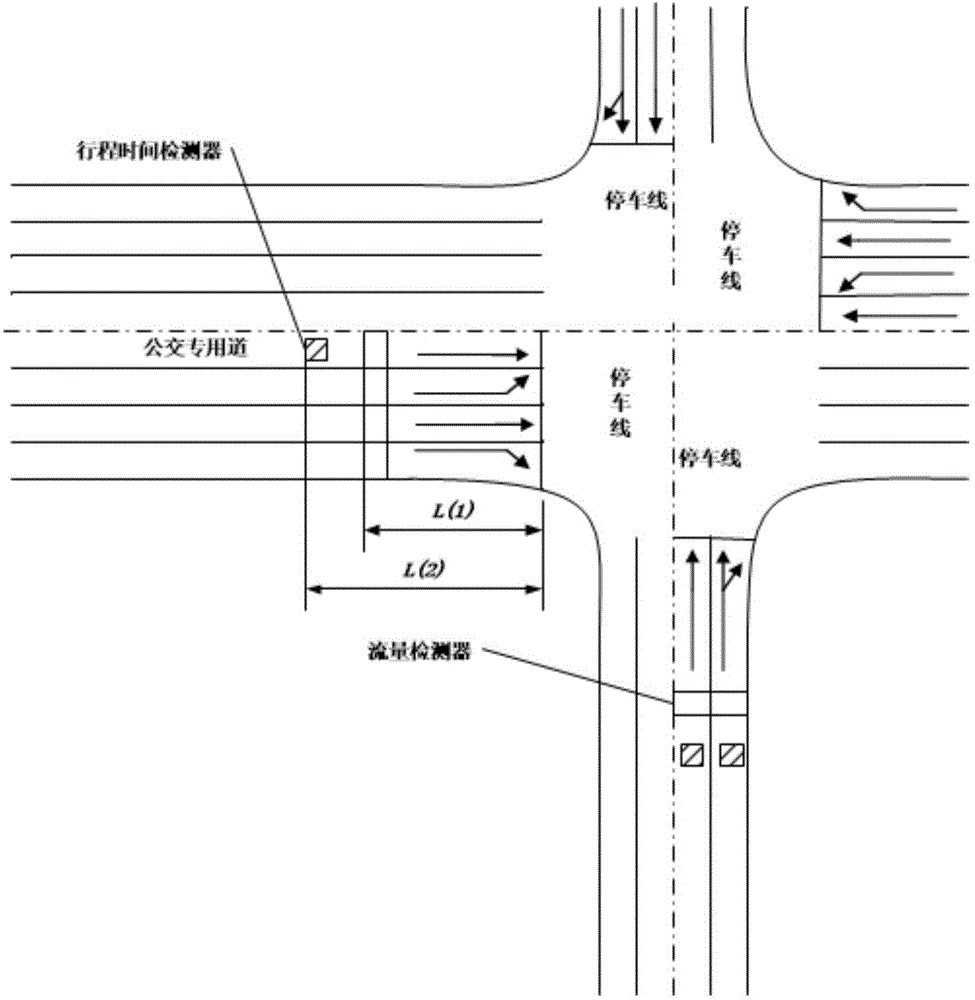
The invention discloses an intersection multiline public traffic vehicle priority request conflict coordination control method. By aiming at an intersection with the multiline public traffic vehicle priority request conflict and comprehensively considering factors such as travel time delay of vehicles, priority strategies and the road grade, a real-time multiline priority request conflict coordination control strategy is established. Only when travel time delay of one public traffic vehicle exceeds a certain threshold value, a priority request meets the limiting condition and the benefit brought by priority is higher than delay caused by the priority, the public traffic vehicle sends a priority request signal; when a multiline priority request is generated, a priority level evaluation model is utilized to sort conflicted priority requests, and the priority of passing is given to a line with the highest priority level. On one hand, the problem of unfairness of an original multiline priority request conflict solution is solved; on the other hand, parameters which the method relates to are fewer and are very easy to obtain, a complex algorithm, an optimizing process and the like are not required, practicality is high, and operating efficiency of an urban public traffic system can be greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
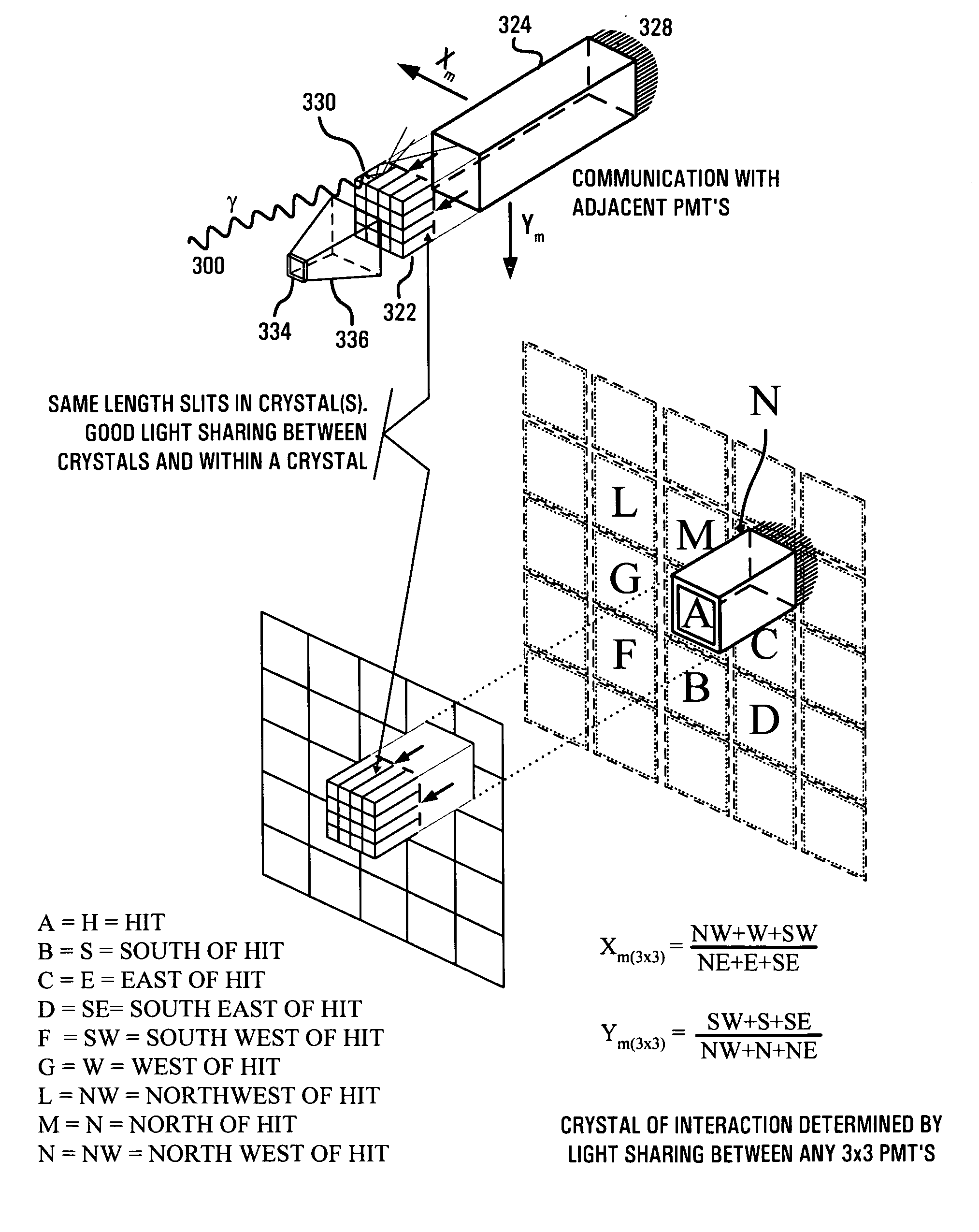
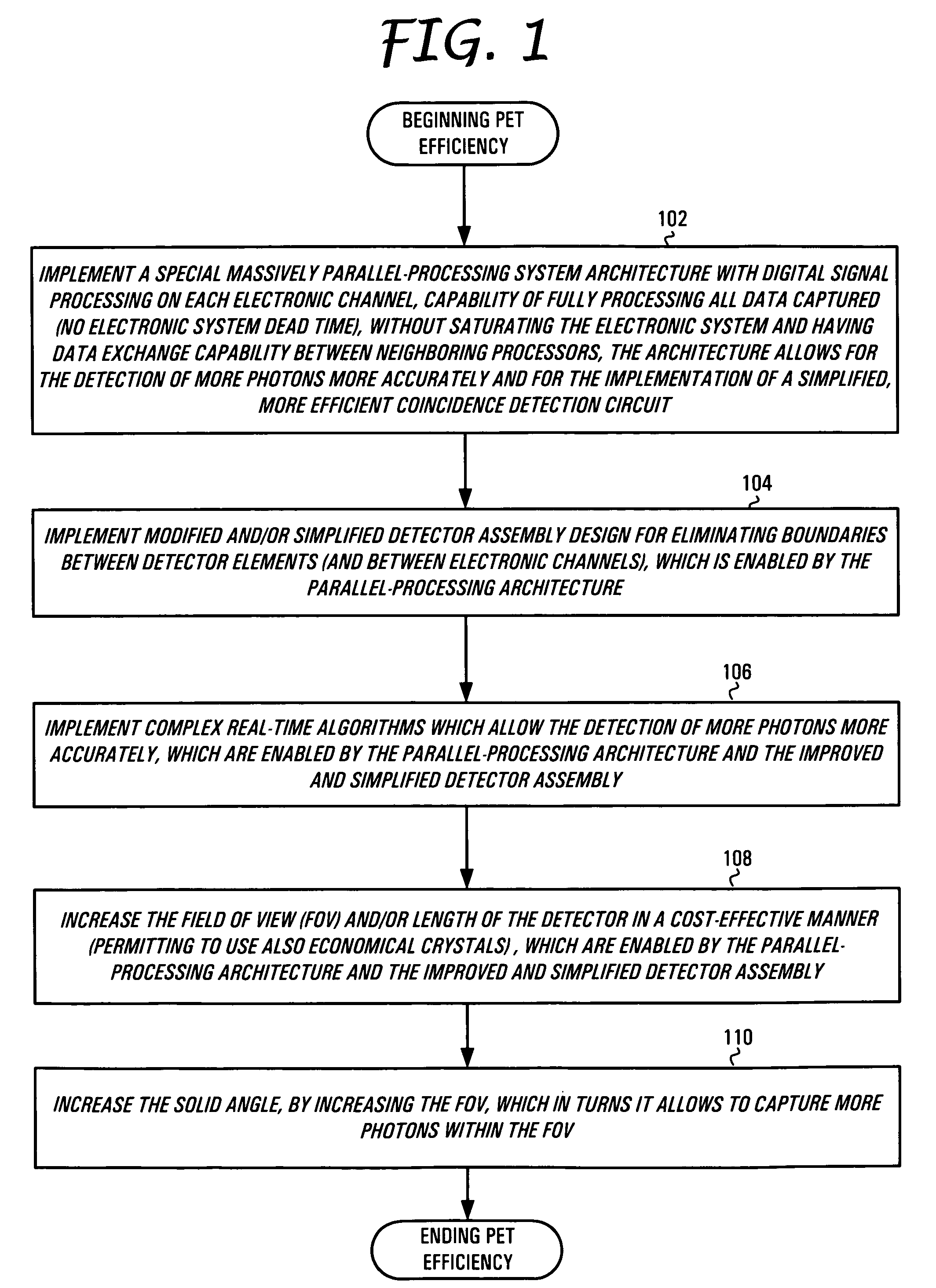
Method and apparatus for improving PET detectors
ActiveUS7132664B1Highly programmable computing capabilityHighly accurate spatial resolution informationMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyWhole bodyParallel computing
The present invention is directed to a system, method and software program product for implementing 3-D Complete-Body-Screening medical imaging which combines the benefits of the functional imaging capability of PET with those of the anatomical imaging capability of CT. The present invention enables execution of more complex algorithms measuring more accurately the information obtained from the collision of a photon with a detector. The present invention overcomes input and coincidence bottlenecks inherent in the prior art by implementing a massively parallel, layered architecture with separate processor stacks for handling each channel. The prior art coincidence bottleneck is overcome by limiting coincidence comparisons to those with a time stamp occurring within a predefined time window. The increased efficiency provides the bandwidth necessary for increasing the throughput even more by extending the FOV to over one meter in length and the execution of even more complex algorithms.
Owner:CROSETTO DARIO B
System and method for stochastic aircraft flight-path modeling
Stochastic models of aircraft flight paths and a method for deriving such models from recorded air traffic data. Each stochastic model involves identifying the flight plan for one or more aircraft; identifying important parameters from each flight plan, such as aircraft type, cruise altitude, and airspeed; optionally identifying flight plan amendments for each flight; representing each route of flight as a series of navigational fixes; representing at least one aircraft flight parameter probabilistically; modeling realistic differences in at least one dimension between each planned route of flight and the flight path as it might actually be flown; and communicating the modeled deviations or simulated flight paths to the user. At least one aircraft flight parameter is represented as a random variable with a particular statistical distribution, such as a normal (Gaussian), Laplacian, or logistic distribution; or with a more complex algorithm containing one or more random elements. The modeled flight parameters may be any of lateral position, longitudinal position, climb altitude, descent altitude, climb airspeed, descent airspeed, cruise airspeed, cruise altitude transition, or response time to a flight plan amendment.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
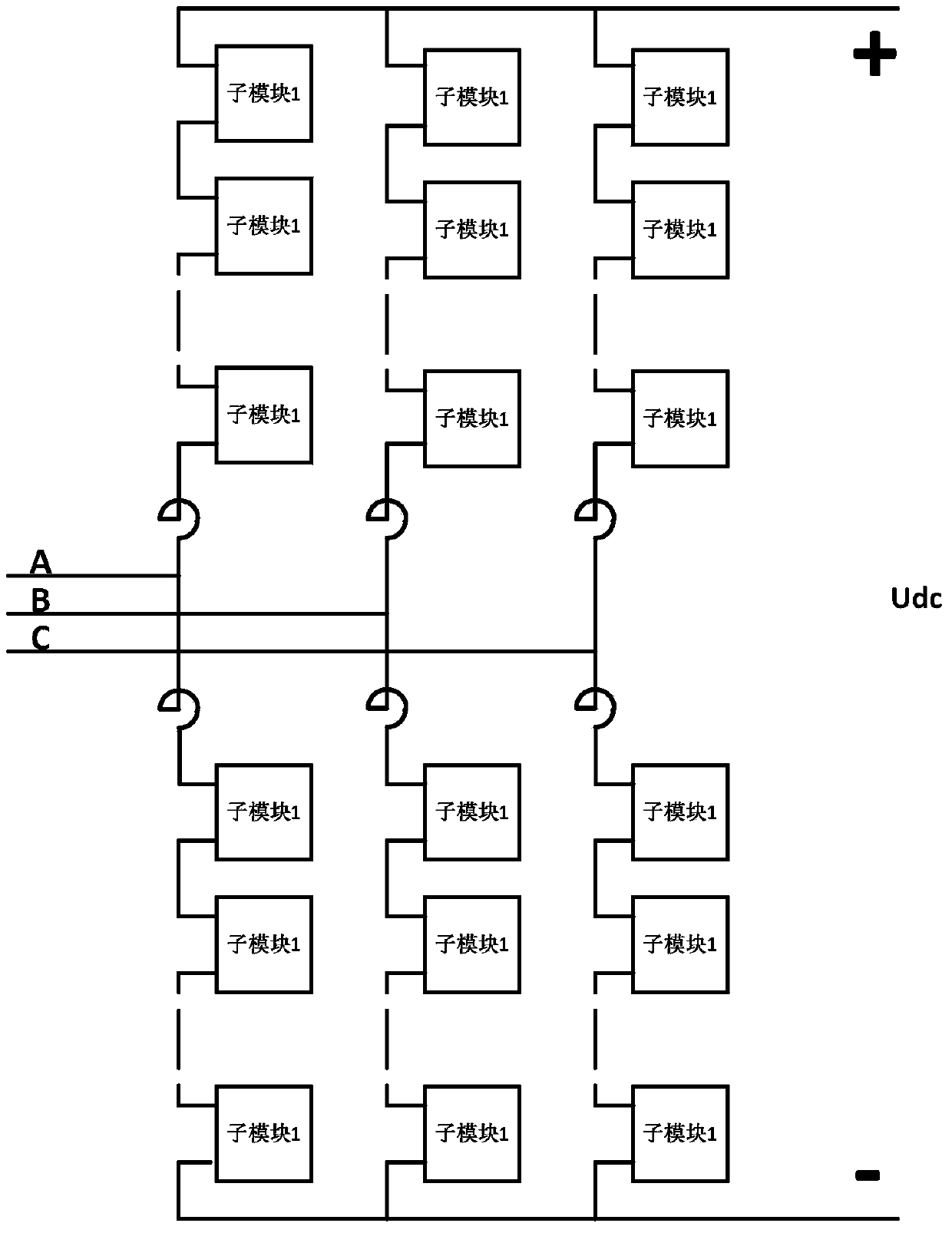
Sub module capacitance and voltage balancing and optimizing method for modularized multi-level converter
InactiveCN103633870AGuaranteed real-timeGuaranteed reliabilityAc-dc conversionControl systemControl objective
The invention relates to a sub module capacitance and voltage balancing and optimizing method for a modularized multi-level converter. The system used in the method is a modularized multi-level conversion system, and a flexible direct current power transmission system valve base control system framework taking a distributed parallel processing mode as a framework is established. The method comprises the following steps of (1) determining a control target of the balancing control for the sub module capacitance and voltage; (2) establishing a sub module state decision optimizing model; (3) performing balancing and equalizing on the sub module capacitance and voltage; (4) verifying the balancing and equalizing on the sub module capacitance and voltage. The distributed computation framework is adopted, the processing capability is greatly improved, and the aim of the application of a complex algorithm and a complex strategy in a high-voltage large-capacity flexible direct current power transmission system is ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
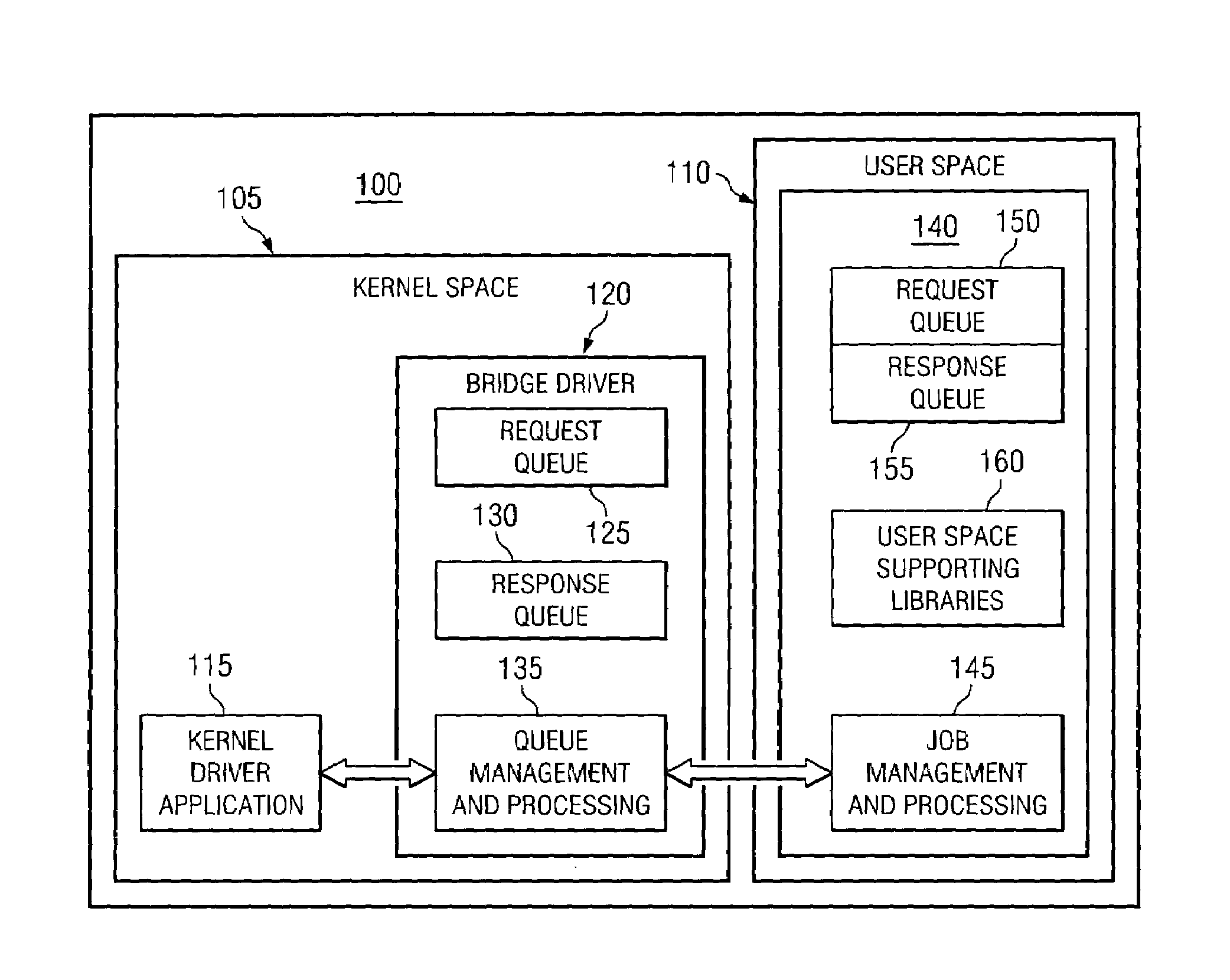
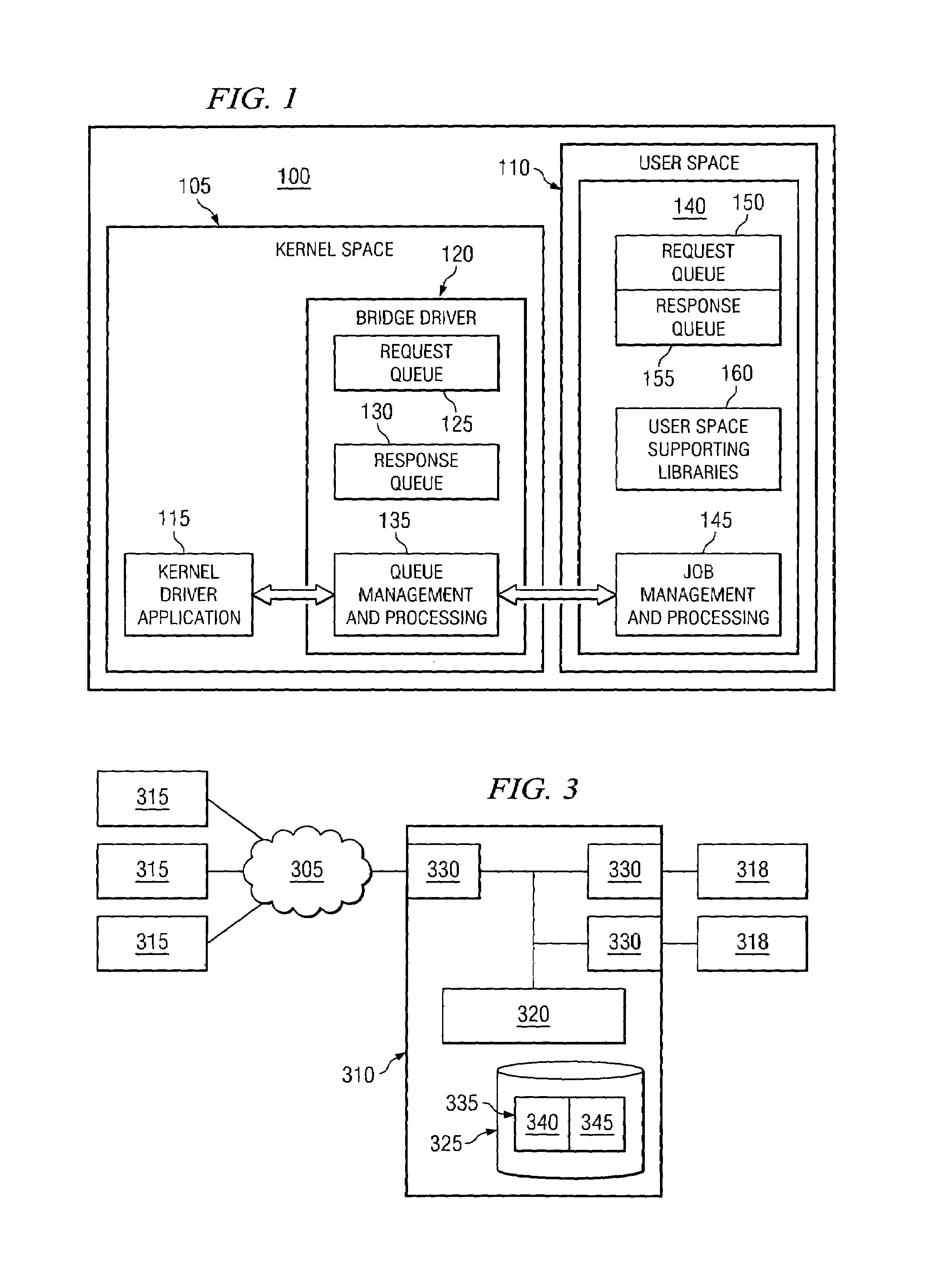
System and method of supporting kernel functionality
InactiveUS7448049B1Improve system efficiencySpace can be allowedInterprogram communicationComputer security arrangementsSoftware architectureComplex calculation
Embodiments of the present invention provide an advantage over prior art software architectures by allowing a kernel to send requests to and receive corresponding results from user space applications. Because the kernel can utilize user space applications, the kernel can use the results of complex calculations without requiring a significantly larger kernel. This provides advantages because programming and debugging of complex algorithms can occur at the user space level rather than the kernel space level.
Owner:KIP CR P1 +1
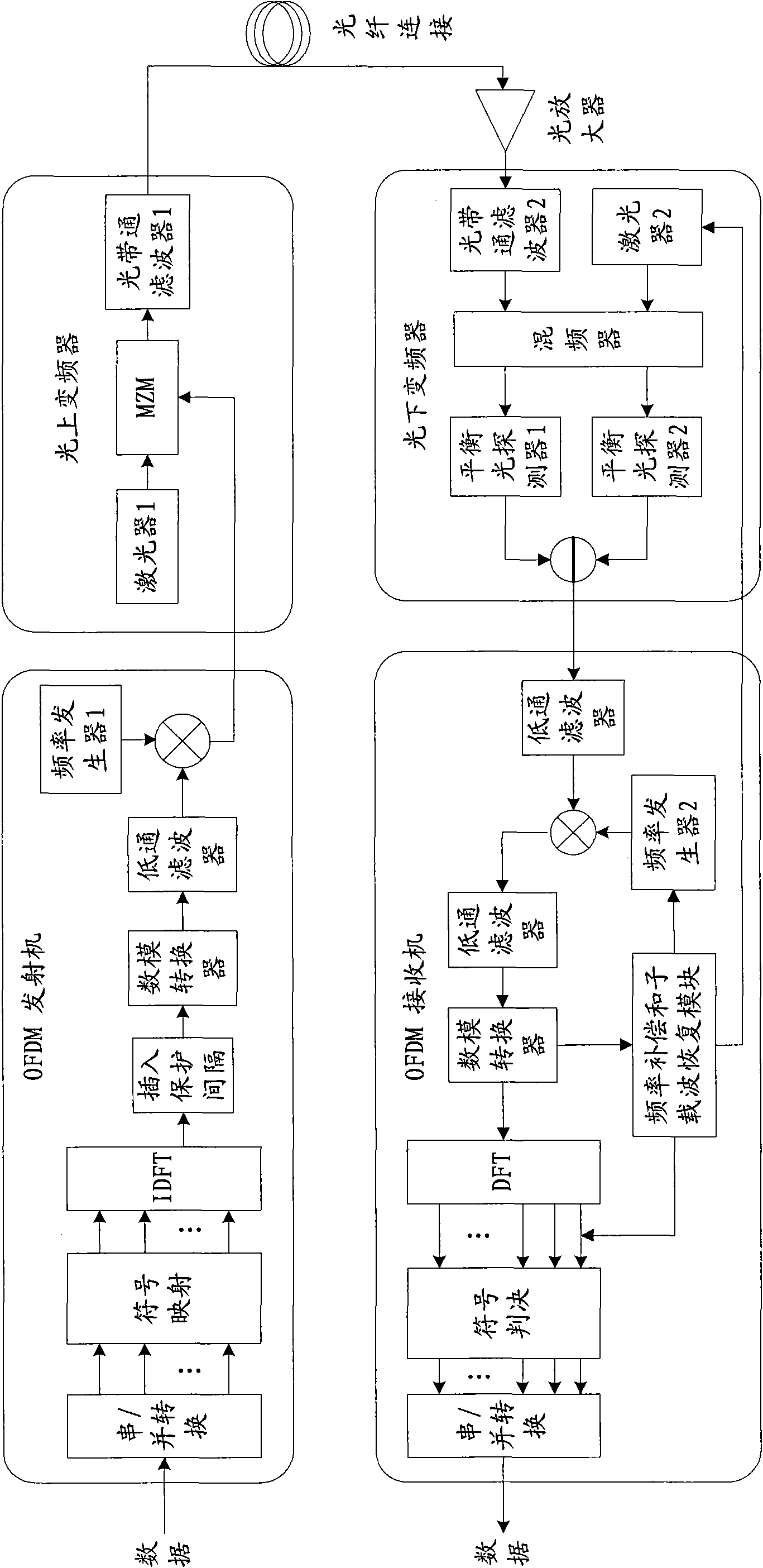
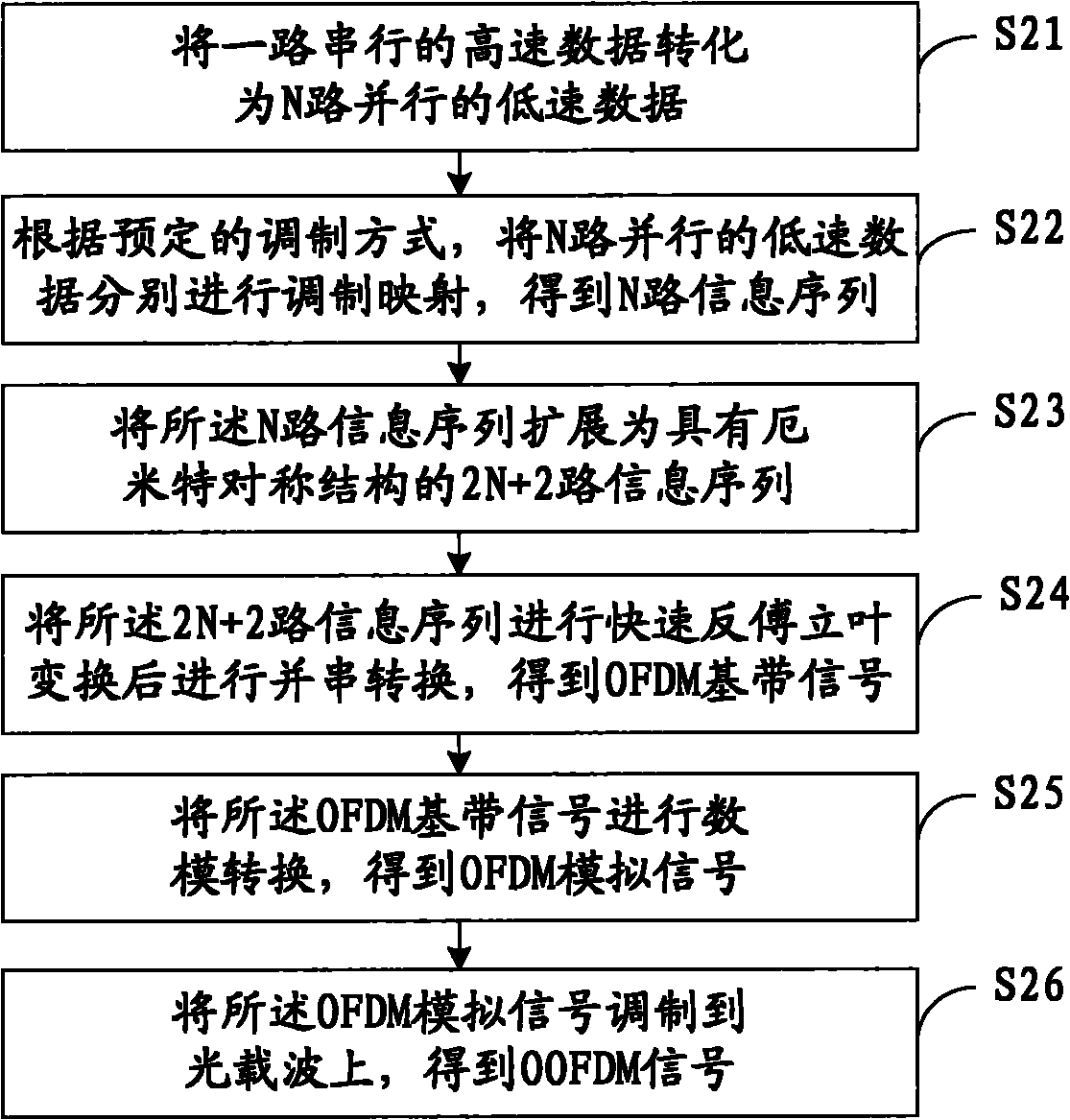
Method and device for generating and receiving OOFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) signal and wavelength division multiplexing system
ActiveCN101924722AReduce difficultyReduced Line Width RequirementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMulti-frequency code systemsLow speedCarrier signal
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for generating and receiving an OOFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) signal and a wavelength division multiplexing system, belonging to the communication field, wherein the method for generating the OOFDM signal comprises the steps of: converting one path of serial high-speed data into N paths of parallel low-speed data; respectively modulating and mapping the N paths of parallel low-speed data to obtain N paths of information sequences; expanding the N paths of information sequences into 2N+2 paths of information sequences with Hermitian symmetrical structures; carrying out rapid inverse Fourier conversion on the 2N+2 paths of information sequences to obtain an OFDM baseband signal; carrying out digital-to-analogue conversion on the OFDM baseband signal to obtain an OFDM analog signal; and modulating the OFDM analog signal to an optical carrier wave to obtain the OOFDM signal. The OOFDM signal generated in the embodiment of the invention is received without tracking and compensating phase and frequency with a complex algorithm, therefore, the cost of realizing the system is lowered.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Method and device for QR (quick response) two-dimension code position detection
ActiveCN104951726ASimple and fast operationHigh precisionSensing by electromagnetic radiationGraphicsRight triangle
The invention discloses a method and a device for QR (quick response) two-dimension code position detection. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, obtaining a first image containing a target and a background of a QR two-dimension code; S2, performing binarization processing on the first image so as to obtain a second image only containing black pixel points and white pixel points; S3, scanning the second image to acquire a position detection graph; S4, judging the position relation of center points of the position detection graph and forming an isosceles right triangle; S5, positioning the QR two-dimension code. According to the method and the device, the operation is simple and convenient, the precision is high, a large quantity of judgment operations caused by interference of a non-target graph are reduced, the efficiency is improved, and complicated algorithms are avoided.
Owner:FUJIAN LANDI COMML EQUIP CO LTD
Database function-based rule implementation and application method and device
InactiveCN103186579AReduce development difficultyLower requirementSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageUser input
The embodiment of the invention discloses a database function-based rule implementation and application method and a database function-based rule implementation and application device. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a business rule model comprising one or more rule key elements according to rule application requirements; establishing a plurality of rules which conform to the business rule model; converting the rules into rule description language and saving in a rule base; implementing the rules in the rule base as corresponding database functions; configuring incidence relation of source data and the applied rule according to application requirements; and acquiring values of the key elements in the configured rule input by a user, executing the rule by calling the database function associated with the rule, and returning an execution result. By using the method or the device provided by the embodiment of the invention, the implementation of a complex algorithm is realized by means of a simple database function based on the implementation result of a rule engine implemented by the database function, the development difficulty of the rule engine is reduced, the cost is saved, and the rule processing efficiency is increased.
Owner:BEIJING BOCO COMM TECH
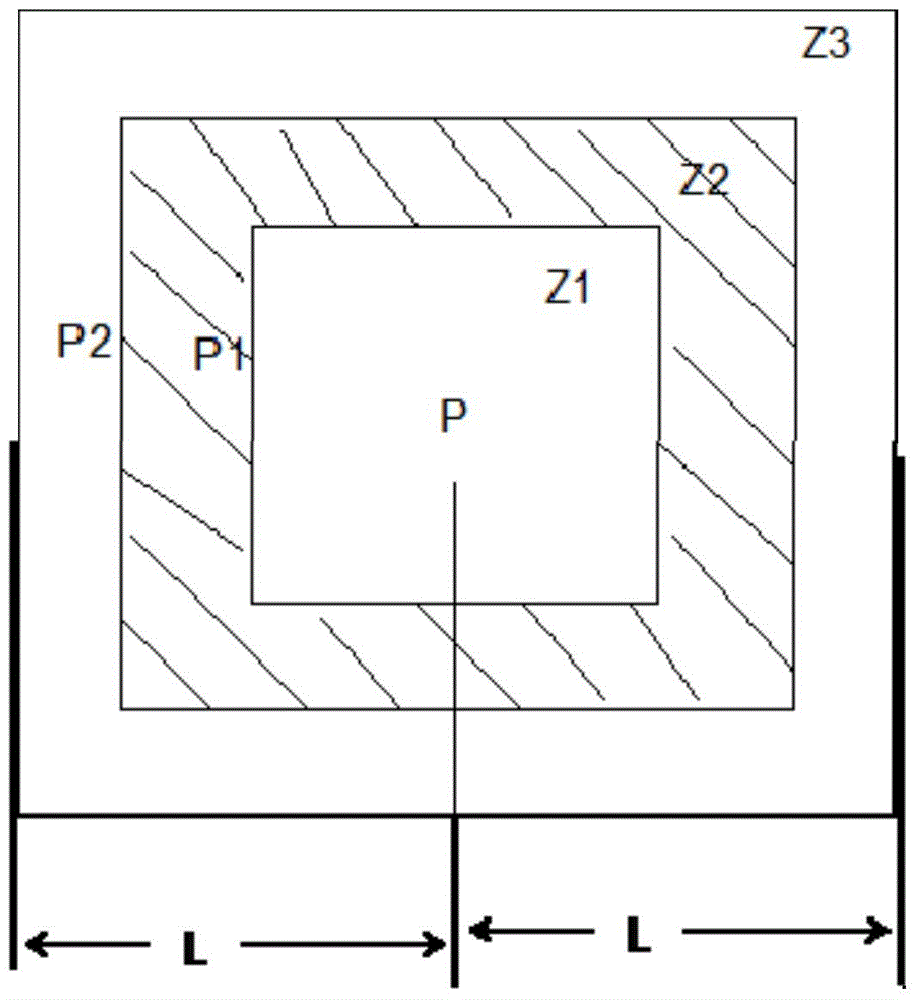
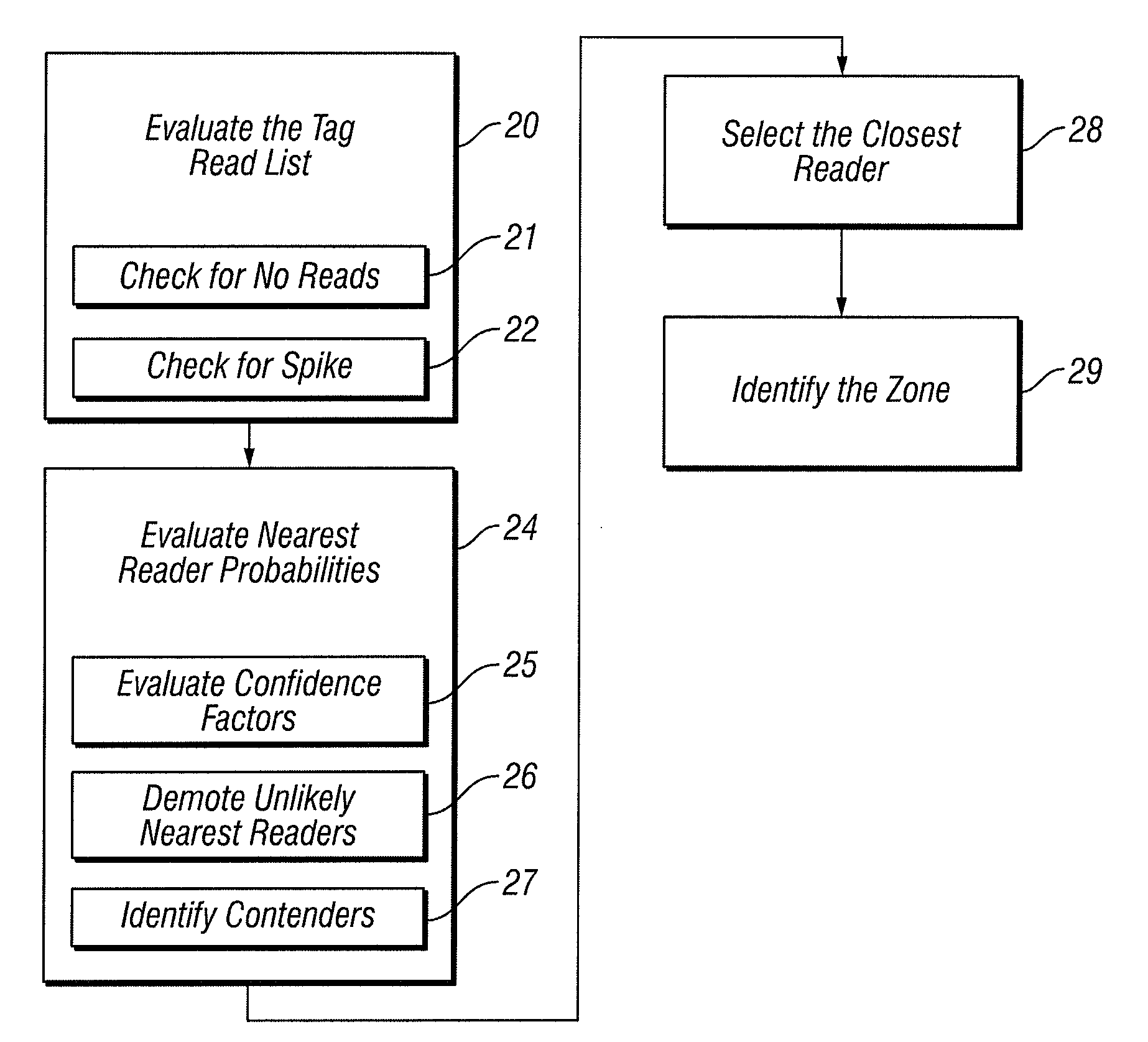
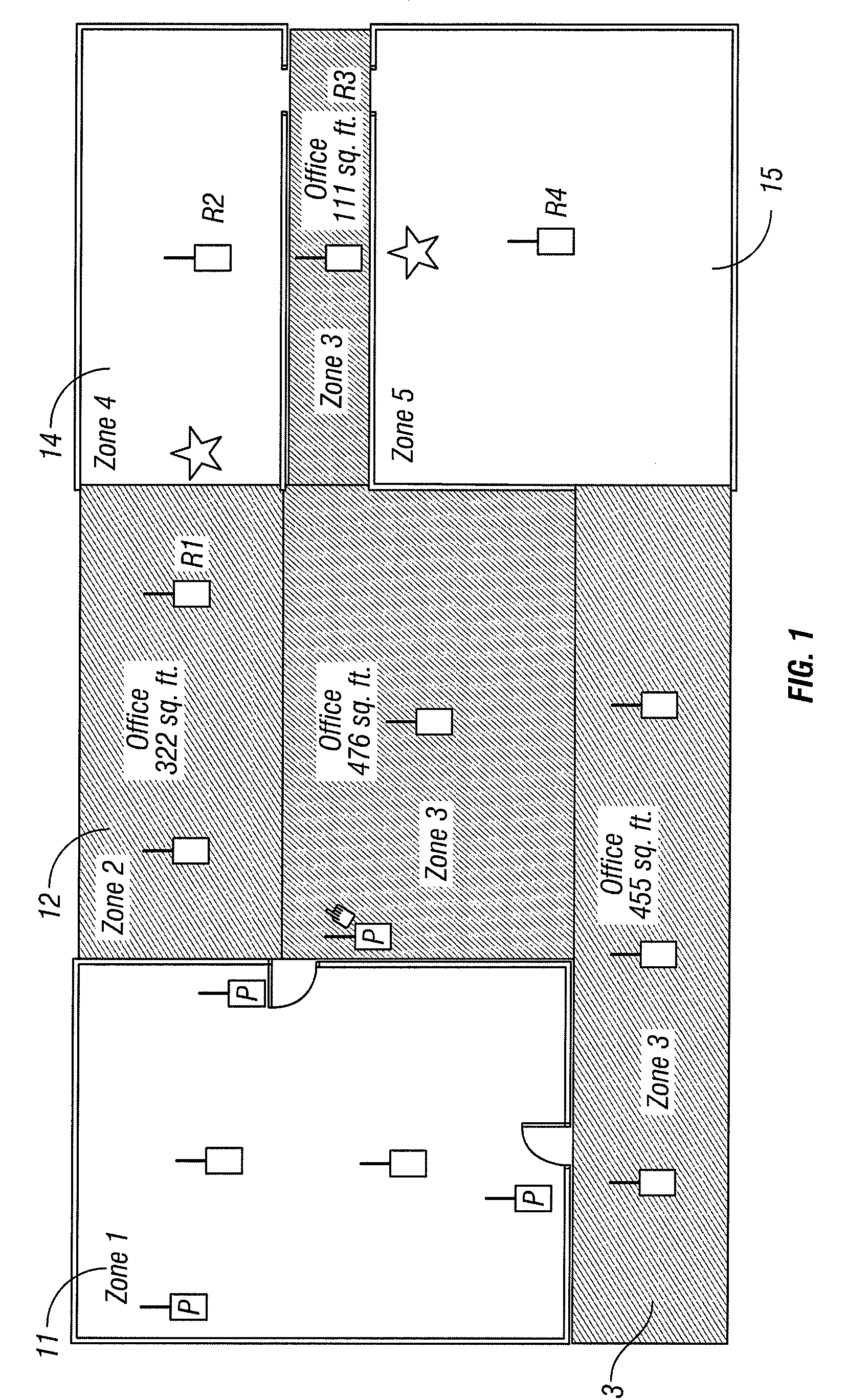
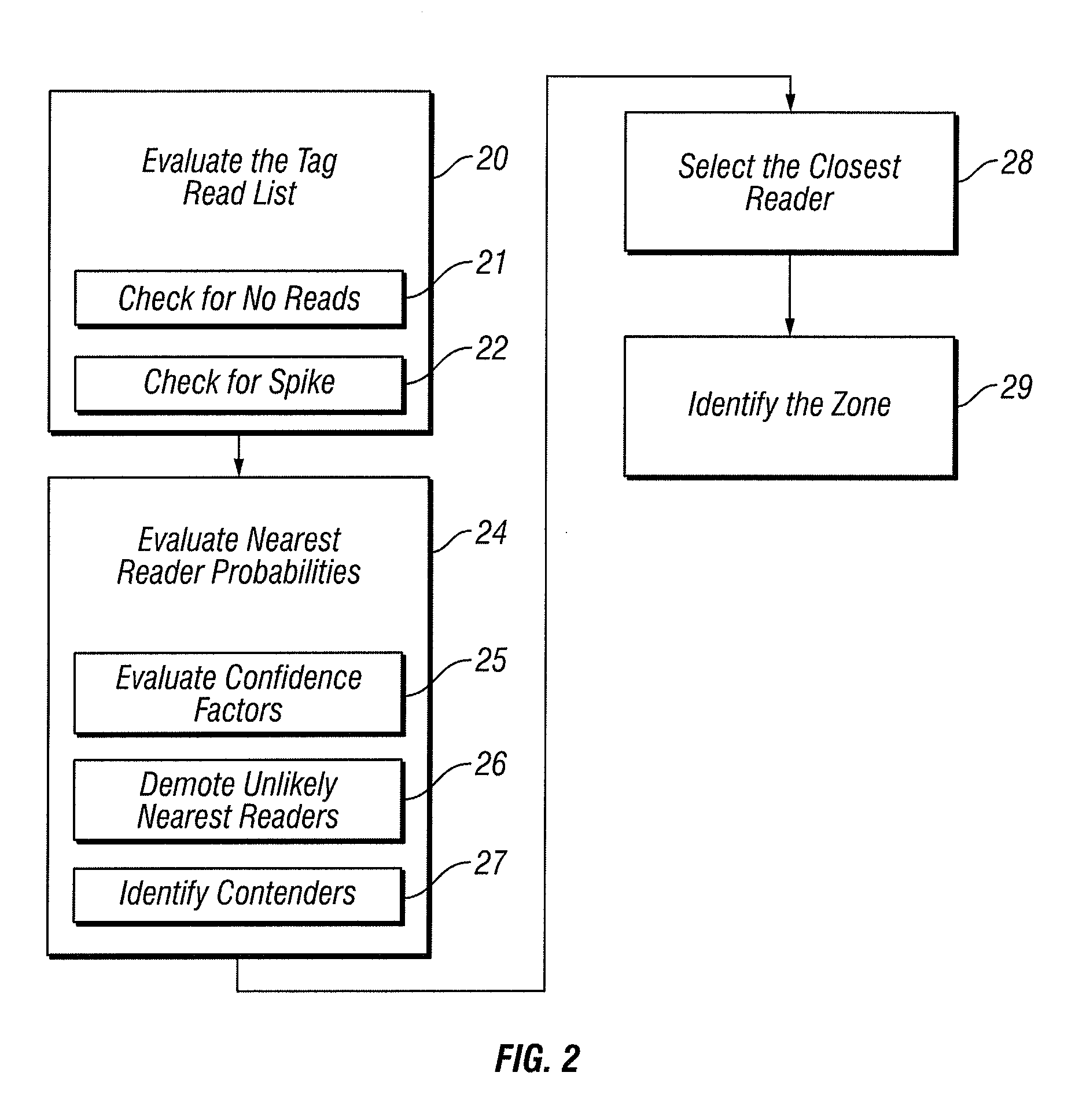
Zone Determination by Combining Signal Strength with Topological Factors
InactiveUS20100156599A1Accurately determineMultiplex system selection arrangementsDirection finders using radio wavesPhysical realityMedicine
Active RFID technologies are used to tag assets and people within buildings or open areas, such as parking lots or military bases; and to identify, preferably within a few meters, the real-time location (RTL) of the tag, i.e. to create a real-time location system, known as an RTLS. A novel and complex algorithm is provided that combines signal strength computations with factors that incorporate physical realities, such as walls and floors, to determine a tag's real-time location more accurately.
Owner:AL QEMMAH LETECHA AL MALOUMAT CO SIMTIX +1
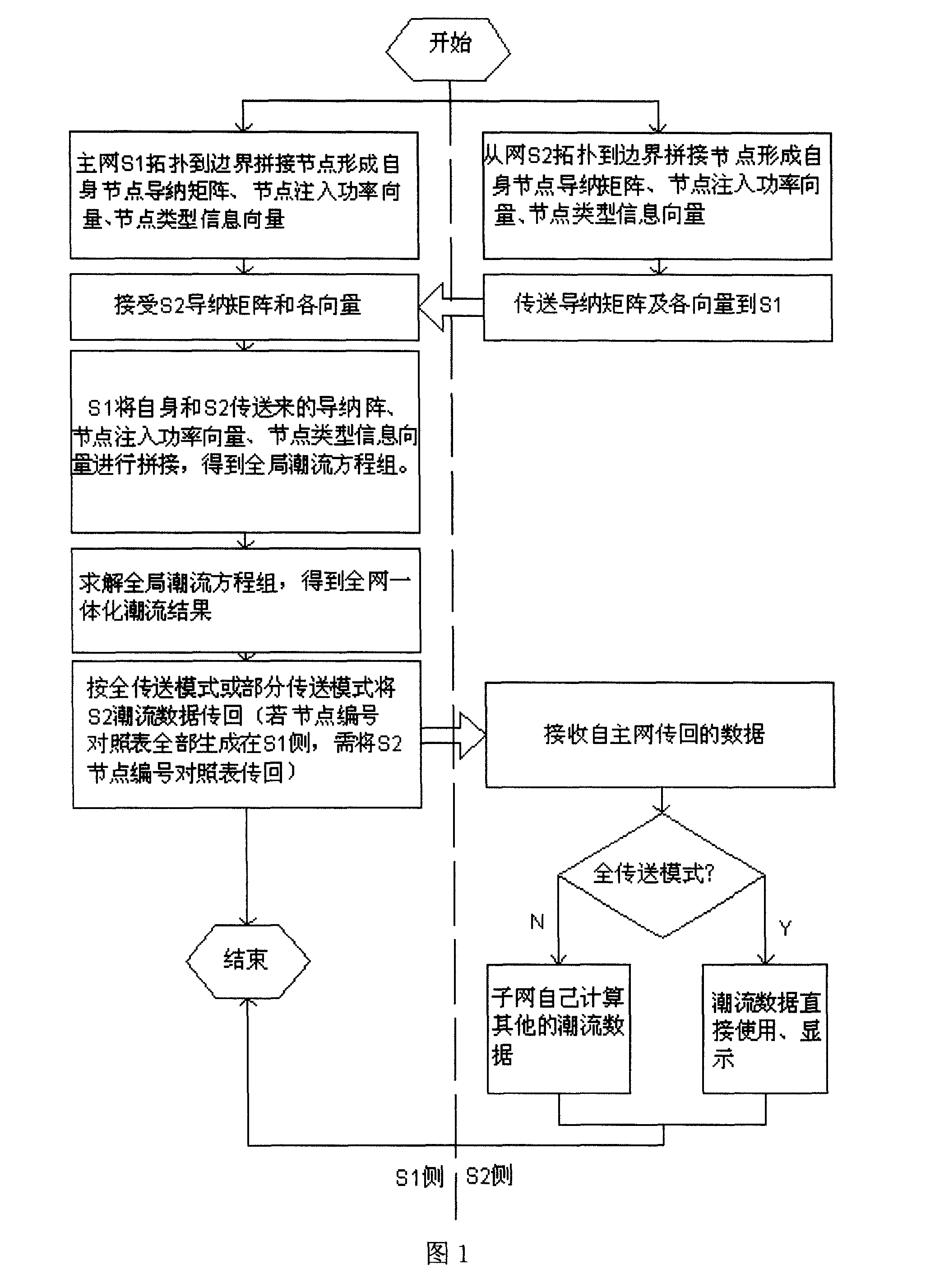
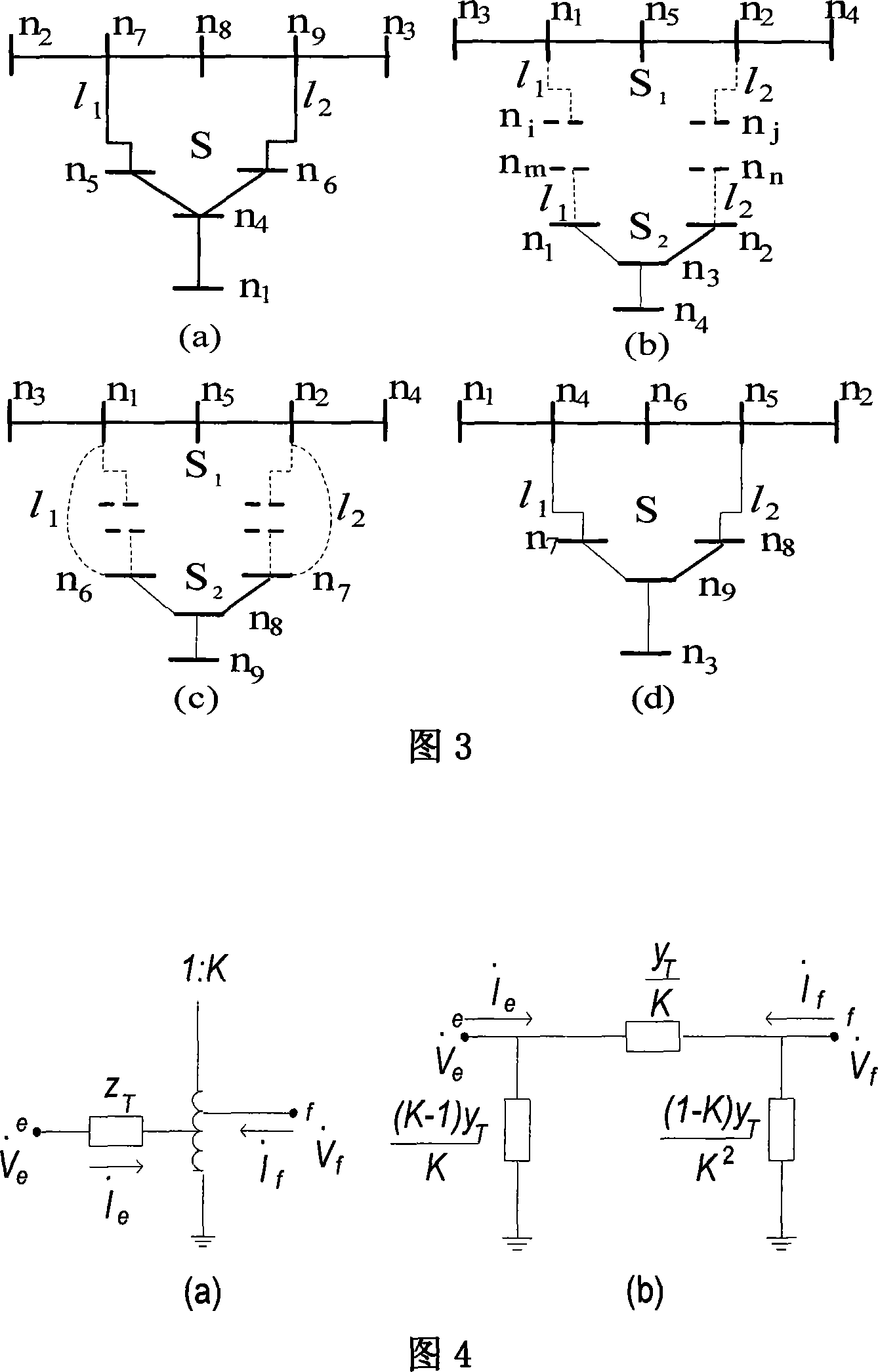
Interconnection system distributed tidal current computing method based on computation model split joint
ActiveCN101221599AAvoid stitchingAvoid normal workSpecial data processing applicationsComputational modelInterconnection
The invention relates to an interacted system distribution type tide computing method based on computational model marriage, which comprises the following steps: defining the handshaking branch and boundary node aggregate between subnets; respectively forming subnet information amount; selecting a main network and a slave network; merging the information amount of the main network and the slave network to obtain overall information amount and consequently obtain an overall tide computation equation set; generating a node number check list at the main network side or generating respective node number check lists of the subnets; unitedly selecting a voltage iteration initial value; solving at the main network side to obtain an overall integral tide result; returning the tide data of the slave network from the main network to the slave network in a complete transmission mode or a partial transmission mode to complete the distribution type tide computation. The invention avoids a large amount of model marriage and subsequent maintenance brought about by full network integral modeling or actual model merging, avoids complex algorithm organization patterns and simultaneously obtains a computing result in full accordance with that of centralized modeling.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
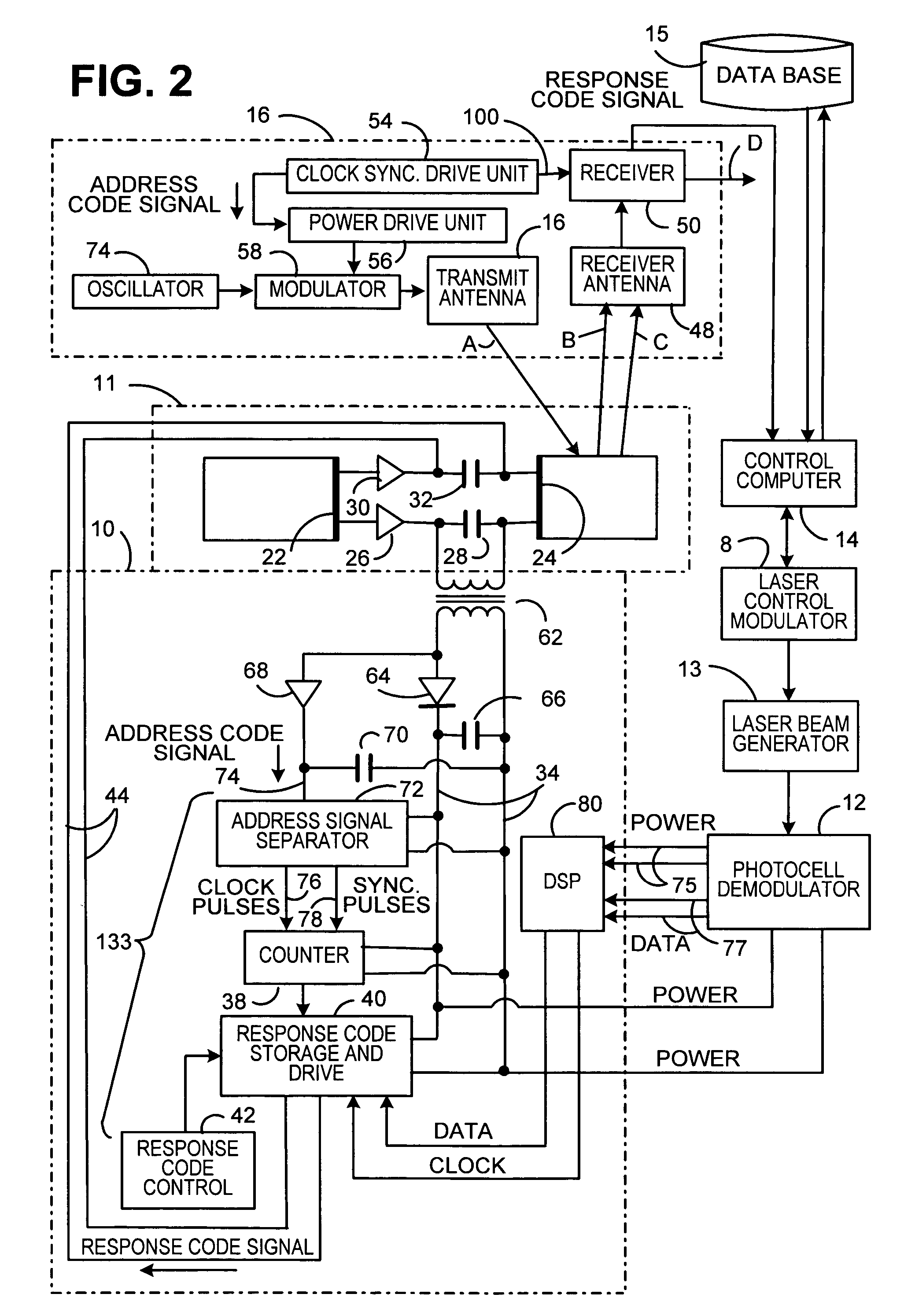
Utilizing a laser to securely communicate with radio frequency identification tags
InactiveUS20060127097A1Improve personal protectionIncrease power levelSensing record carriersElectromagnetic transmissionSecure communicationLaser beams
A method for providing a secure communications channel for the transmission of large amounts of information between a RFID tag and a RFID reader. A laser beam is utilized to carry information and power from the RFID reader to the RFID tag. Thus, the laser beam has a dual use as an information carrier and a source of power for the RFID tag. Thus, only individuals and / or equipment that can both see the laser transmission and hear the RFID transmission can eavesdrop on the RFID tag RFID reader transmissions. This invention allows the use of complex algorithms to protect data being communicated because they can use the increased level of power available to the RDIF tag.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
Method for functional diagnosis of a separator
ActiveUS20110011380A1Low costEmissions dangerous to the environment are more efficiently controlledDispersed particle separationCombustion enginesOperating pointCombustion
A method for functional diagnosis of a separator for separating oil present in a blow-by has from a crankcase in a combustion engine is provided. The crankcase includes a crankcase pressure sensor, and is in fluid communication with the separator. The method includes the steps of detecting a first output signal of the crankcase pressure sensor at a first operational point or interval, and comparing the first output signal of the crankcase pressure sensor with at least one reference value or signal, wherein the comparison between said first output signal of the crankcase pressure sensor and the at least one reference value or signal provides the functional diagnosis of the separator. A method can perform a functional diagnosis without the use of additional sensors or complex algorithms and as a consequence manufacturing costs can be held at a minimum.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
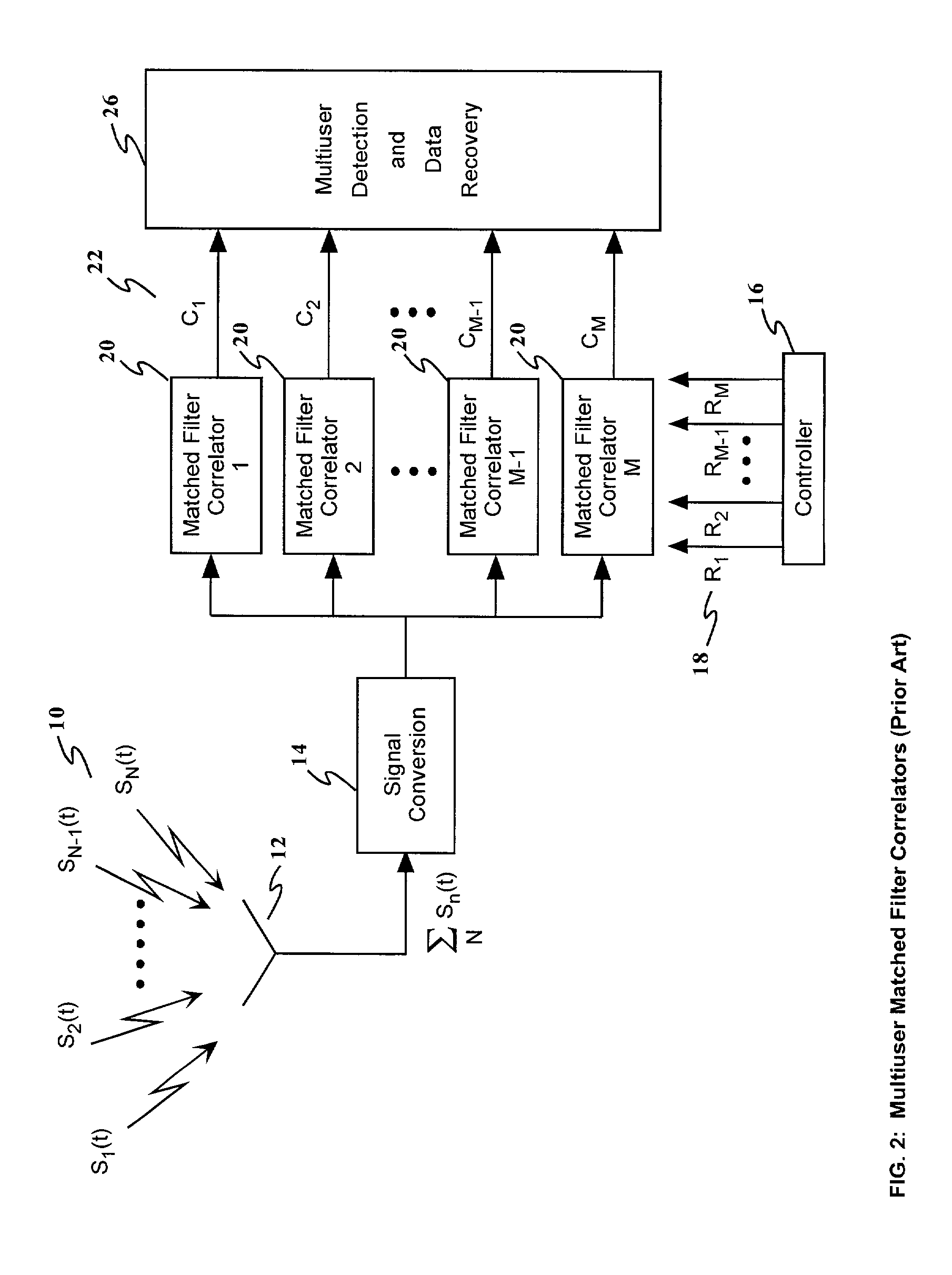
Optical processor enhanced receiver architecture (opera)
InactiveUS20020126644A1Improve performanceIncrease capacityMirrorsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime delaysReceiver function
A method and apparatus for enhancing the receiving and information identification functions of multiple access communications systems by employing one or more optical processors configured as a bank of 1-D correlators. The present invention is particularly useful in a DS / SS CDMA communications system, resulting in a multiuser CDMA system that approaches carrier to noise performance (C / N) as opposed to being limited by multiple access interference (MAI). The correlators are arranged in parallel to detect and / or demodulate the received signal, in conjunction with one or more complex algorithms to perform near-optimum multiuser detection, perform multipath combining and / or perform carrier Doppler compensation. An improved receiver in accordance with the present invention comprises means for receiving a plurality of signals transmitted through a communications channel; signal conversion means for converting the received signals into a form suitable for input to the multichannel correlator; a multichannel optical correlator for identifying the presence of particular waveforms and estimating the relative time delay or delays, carrier frequency offset from expected, RF amplitude and RF phase for each received spread spectrum waveform present in the received plurality of signals; a controller for determining and providing to the optical correlator the appropriate set of reference hypotheses; and one or more receiver algorithms depending on the exact receiver function to be performed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
General intelligent housing system
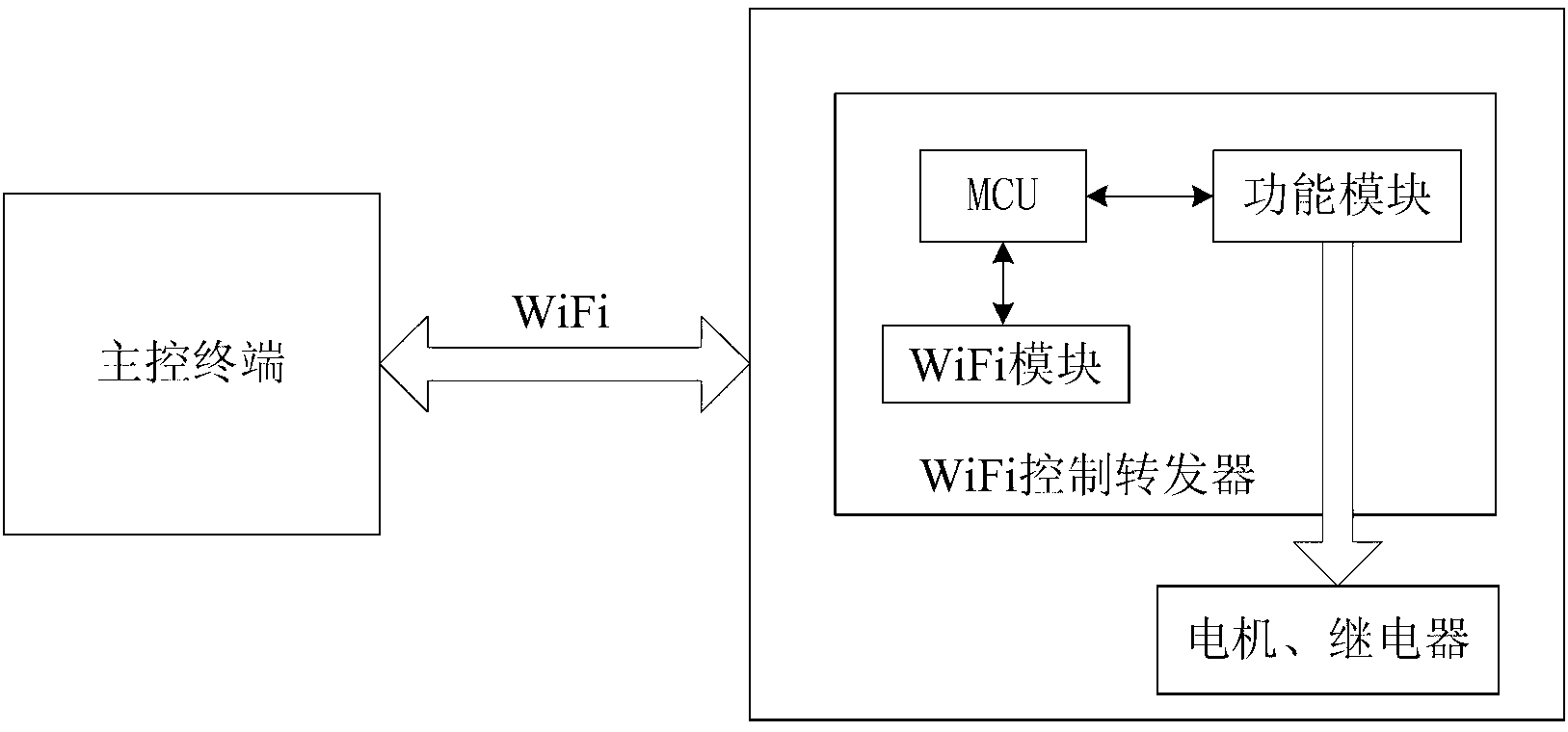
InactiveCN103217963AEasy to installEasy maintenanceTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlComputer moduleTerminal equipment
The invention relates to a general intelligent housing system which comprises a controlled terminal of an intelligent housing type and a main control terminal with a corresponding control program. A wireless fidelity (WiFi) controlled repeater is arranged in the controlled terminal of the intelligent housing type, and a microprogrammed control unit (MCU), a WiFi module connected with the MCU and a function module controlling function execution of the controlled terminal are arranged in the WiFi controlled repeater, wherein the function module is connected with the MCU through an I / O interface, and the controlled terminal is in wireless connection with the main control terminal through the WiFi module of the WiFi controlled repeater. The general intelligent housing system needs no complex on-site manual conduit wiring, the workload of equipment integration is low, applicability is good, and cost is greatly reduced. Processing of a complex algorithm is integrated in the main control terminal to complete, and the general intelligent housing system has generality in control over intelligent housing.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com