Method for identifying initial position of rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor of non-position sensor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, rotor initial position technology, applied in the control of generator, motor generator control, AC motor control and other directions, can solve the problems of rotor position change, complex algorithm, low identification accuracy, etc., to achieve satisfactory initial position identification The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
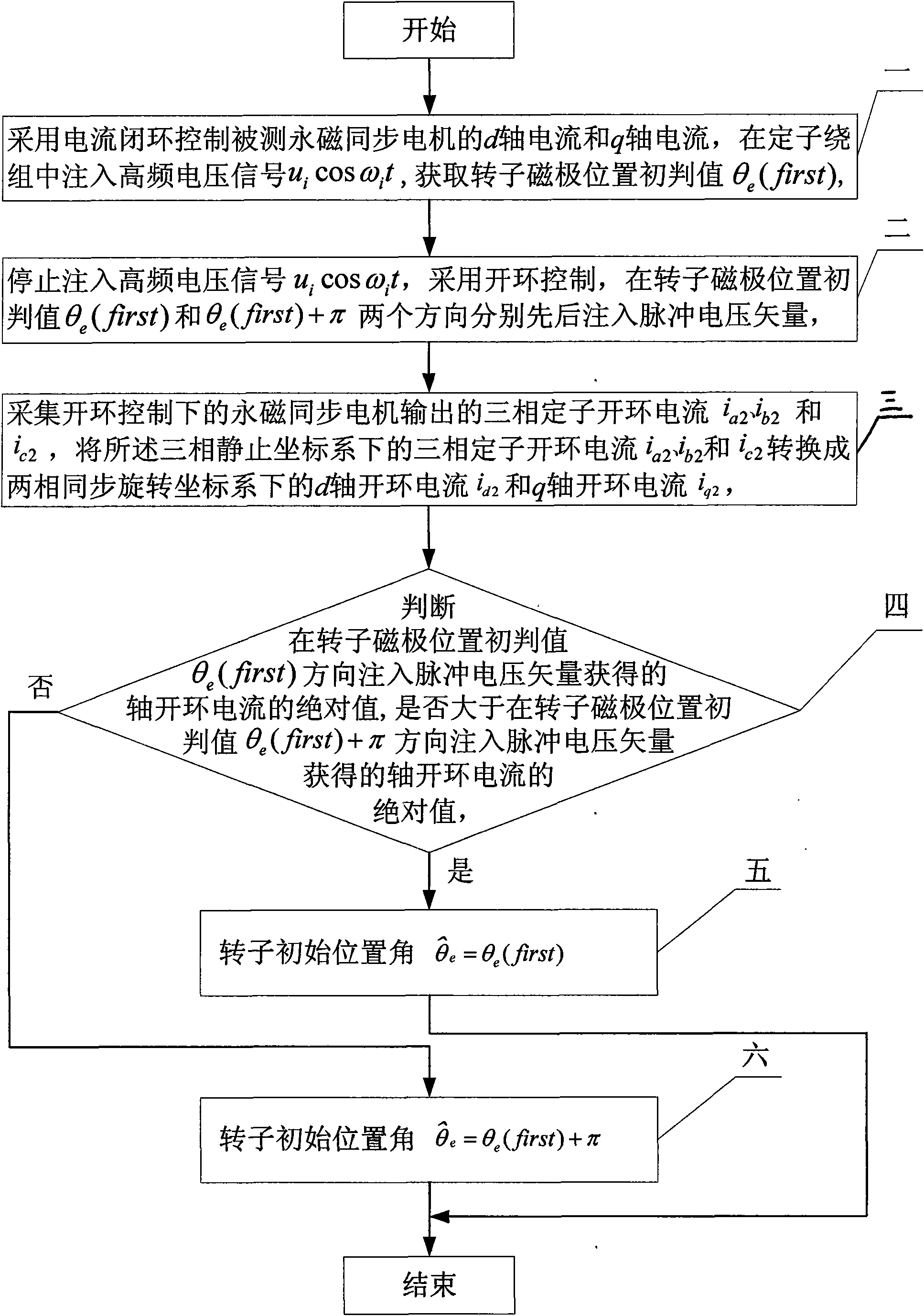
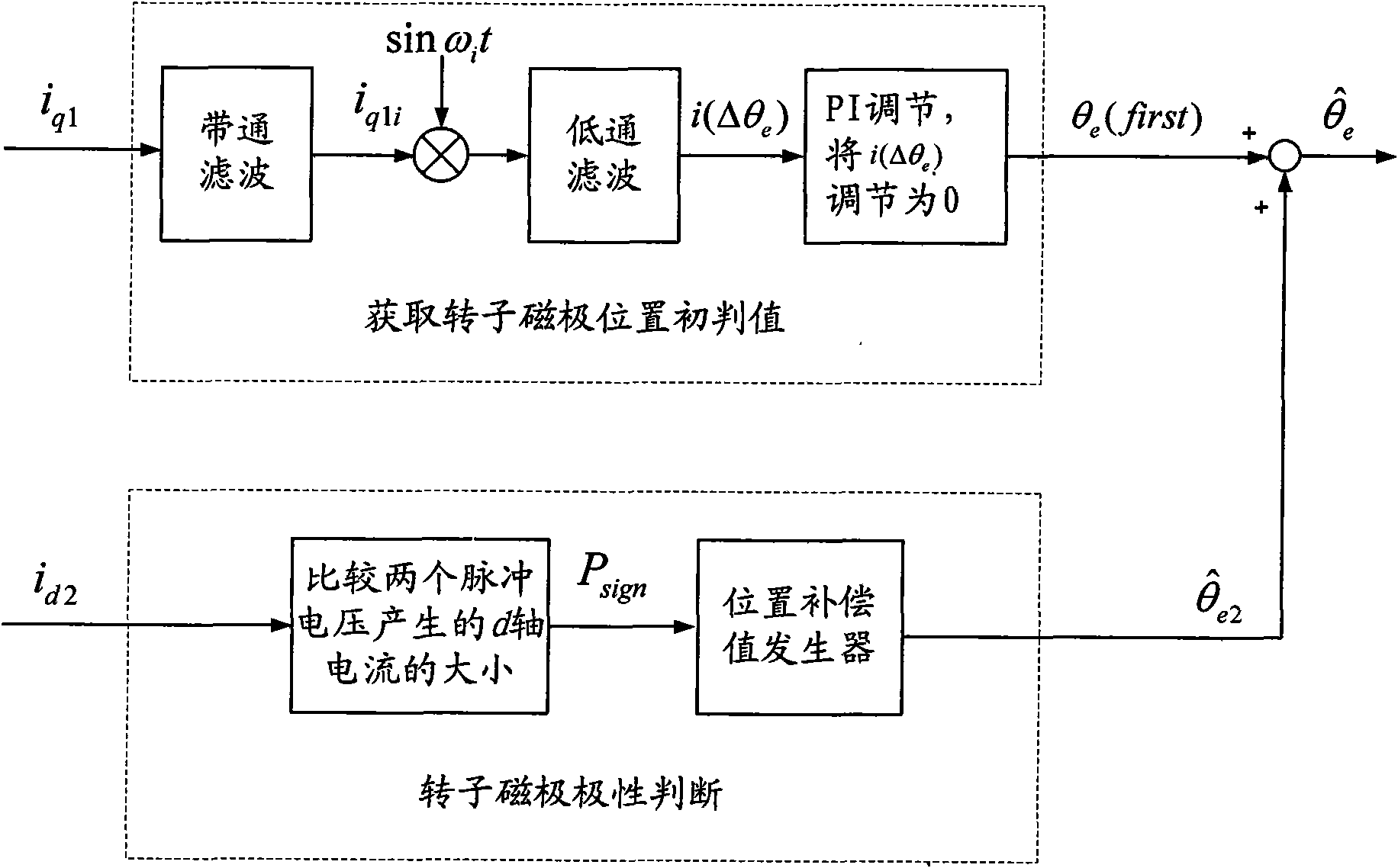
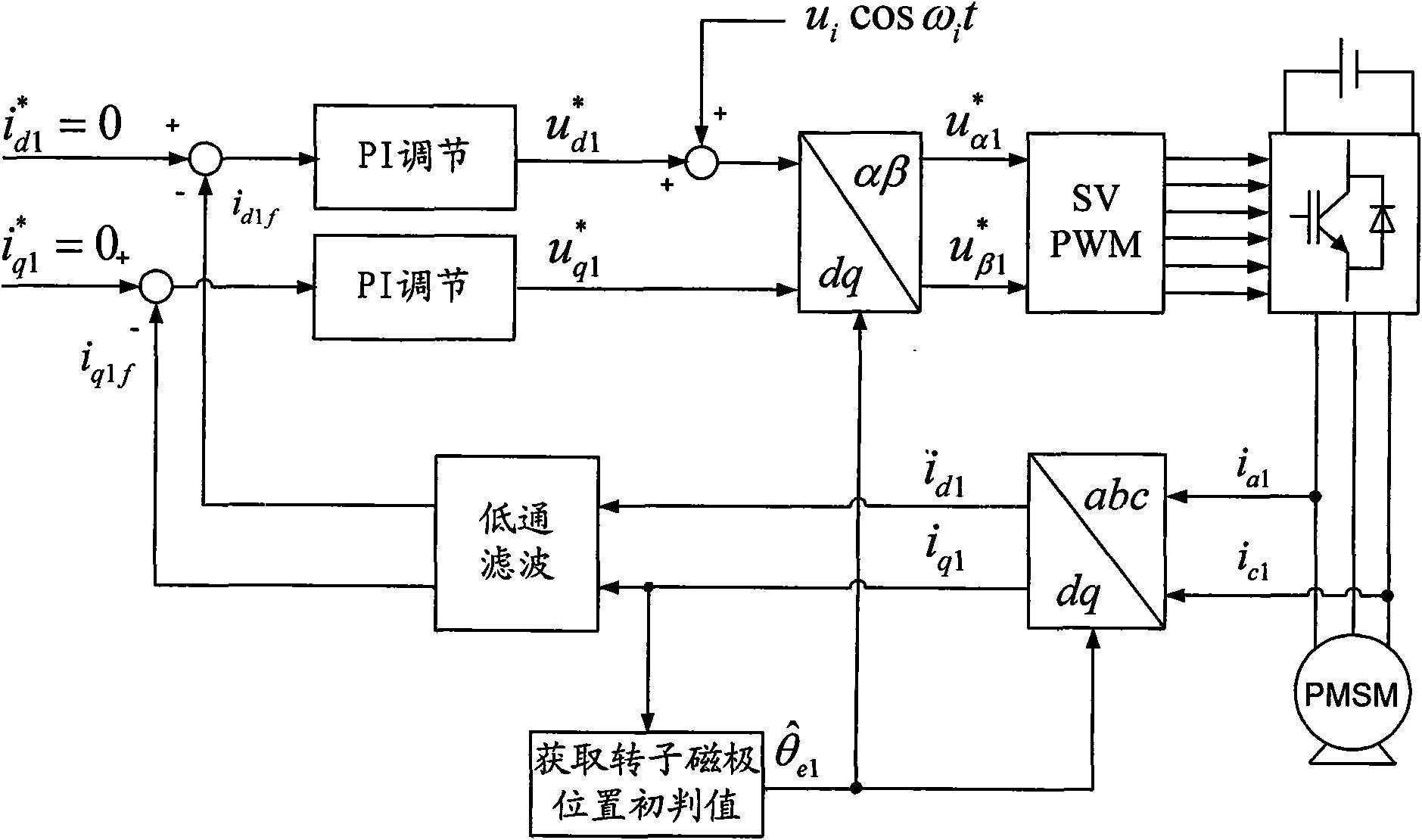
[0018] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 5 Describe this embodiment, the method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0019] Step 1. Use current closed-loop control of the d-axis current and q-axis current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to be tested, and inject a high-frequency voltage signal u into the stator winding i cos ω i t, to obtain the initial judgment value of the rotor pole position θ e (first), the specific method is:
[0020] Step a, initialize the following variable values:
[0021] The q-axis closed-loop given current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor stator i q 1 * = 0 , The d-axis closed-loop given current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor stator i d 1 * = ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0069] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the high-frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i The frequency of t is 500Hz ~ 2Hz, the high-frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i Amplitude u of t i It is 15%-30% of the rated voltage of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to be tested, and the other is the same as the first embodiment.
[0070] The injected high frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i The frequency of t is much higher than the rated operating frequency of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the rated operating frequency of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is generally 50Hz.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0071] Specific Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the high-frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i The frequency of t is 1kHz, the high frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i The frequency of t is 1kHz, the high frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i Amplitude u of t i It is 18% of the rated voltage of the measured permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the other is the same as the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com