Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
14148results about "Dynamo-electric gear control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
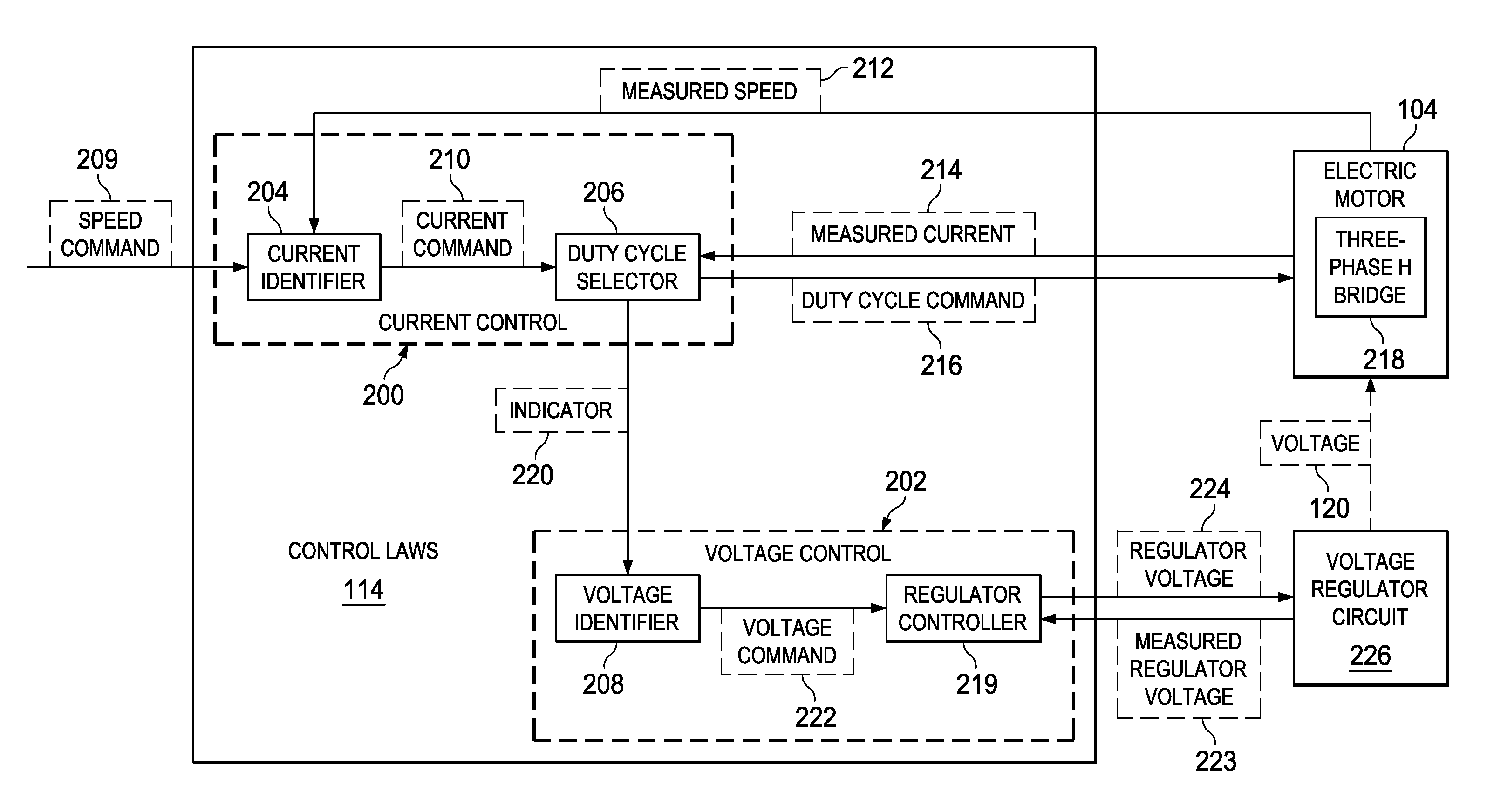
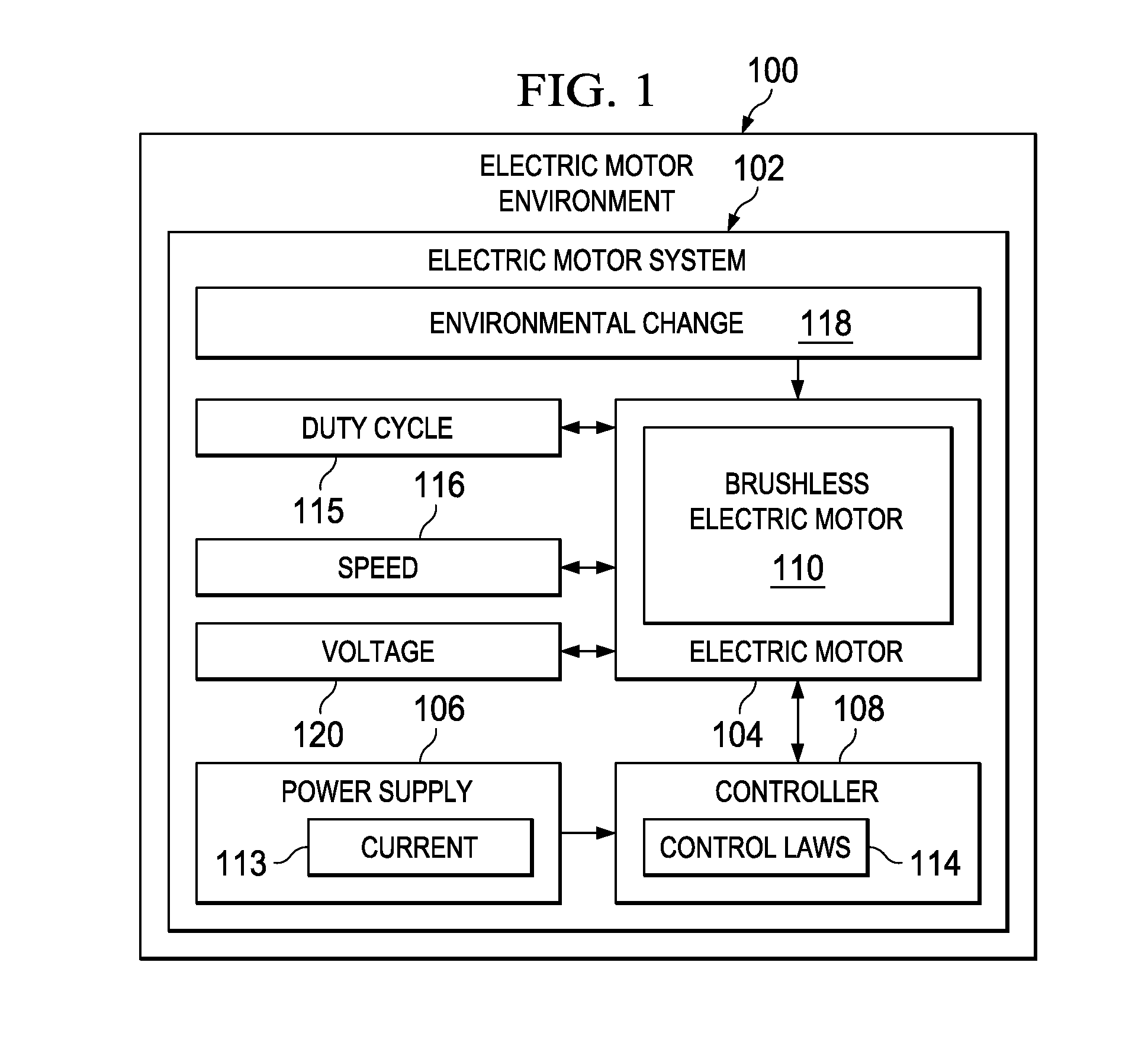
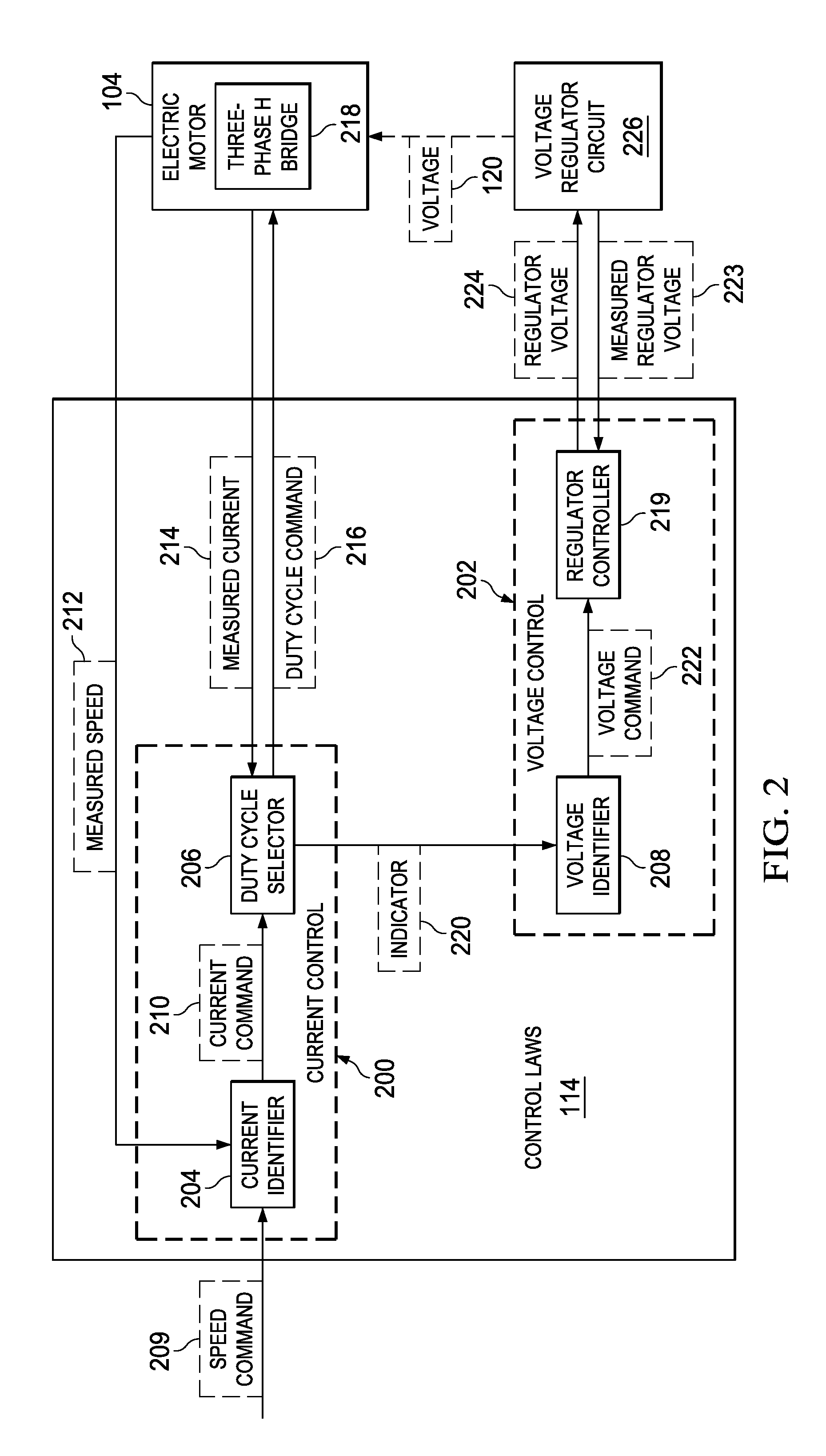
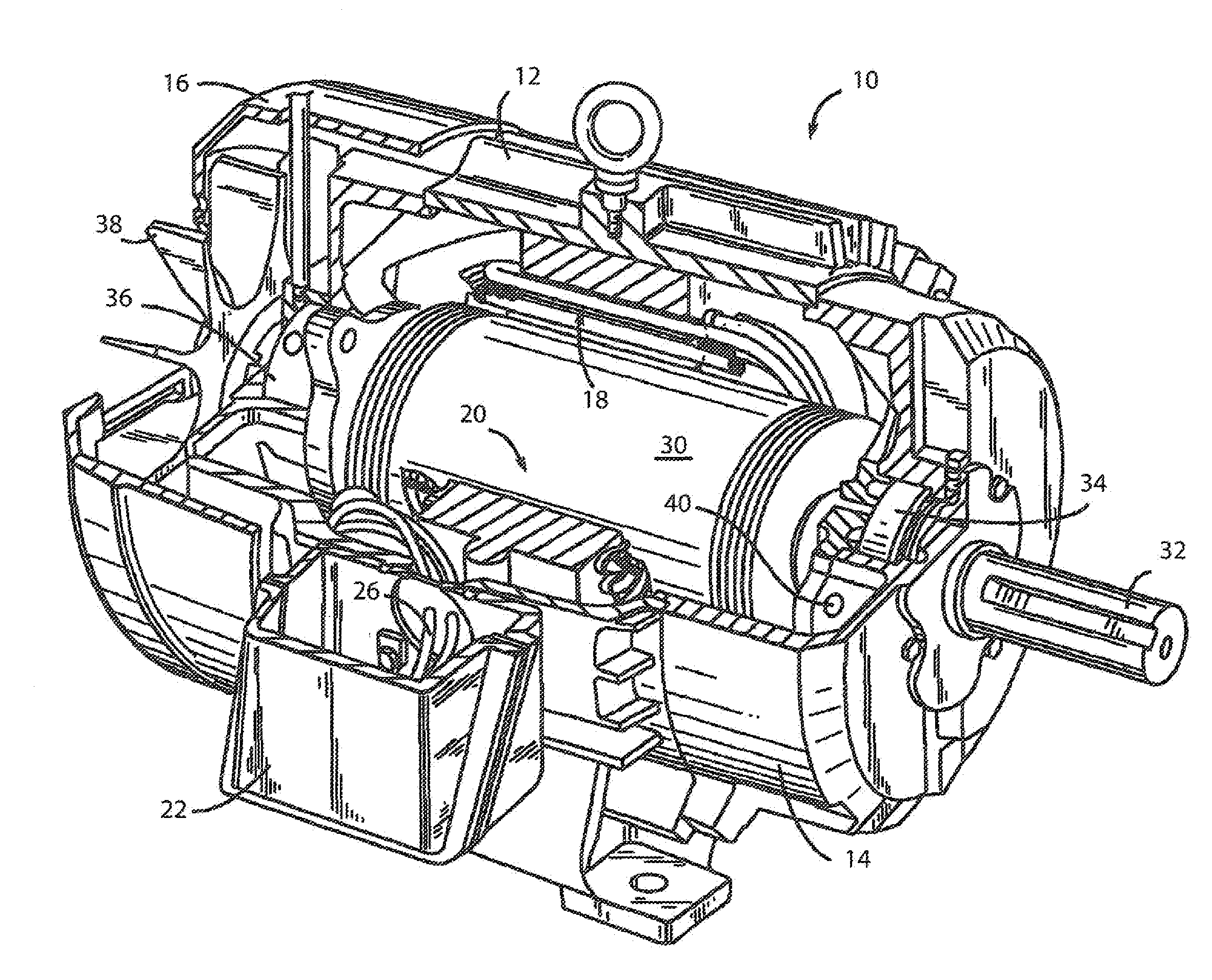
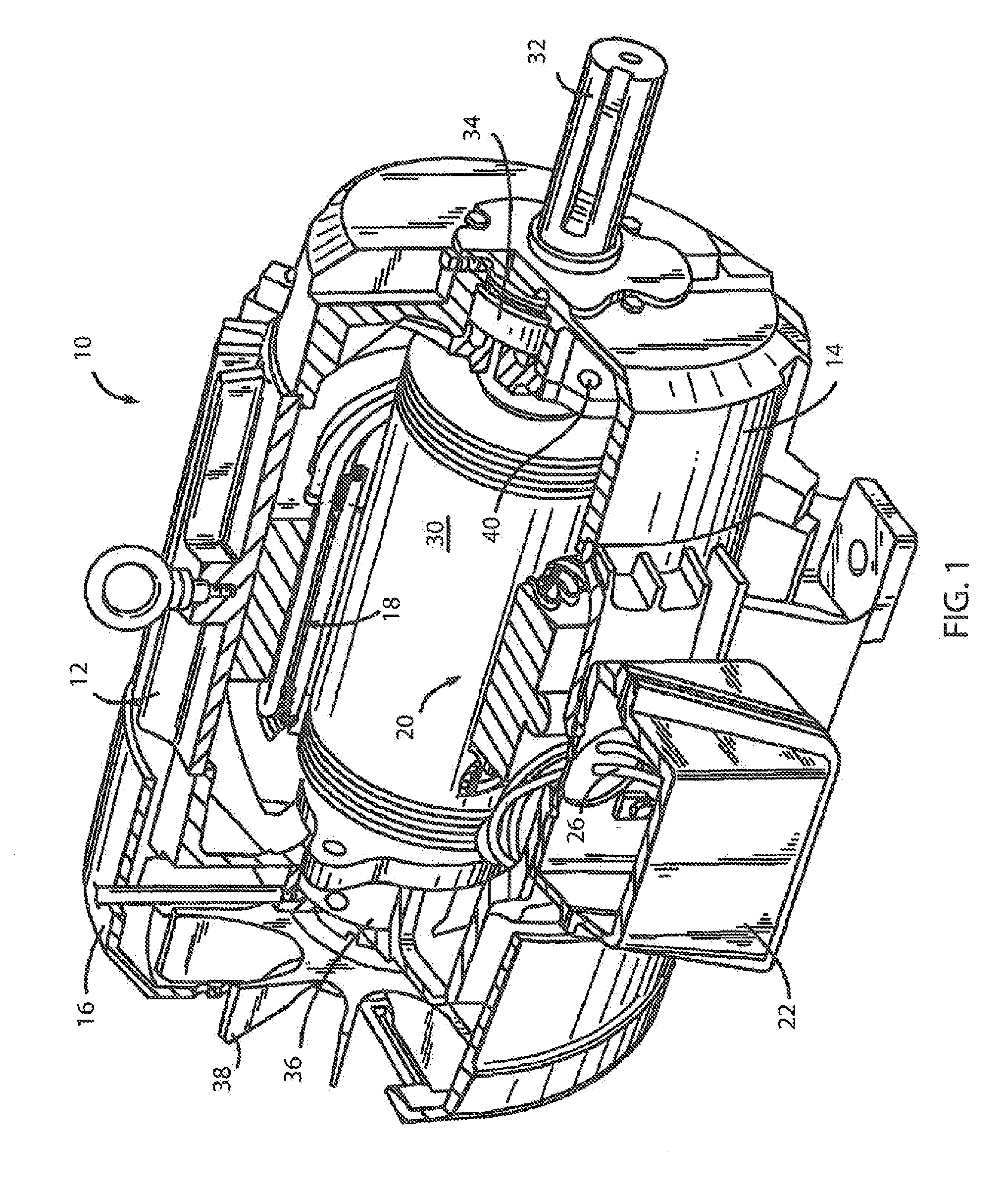
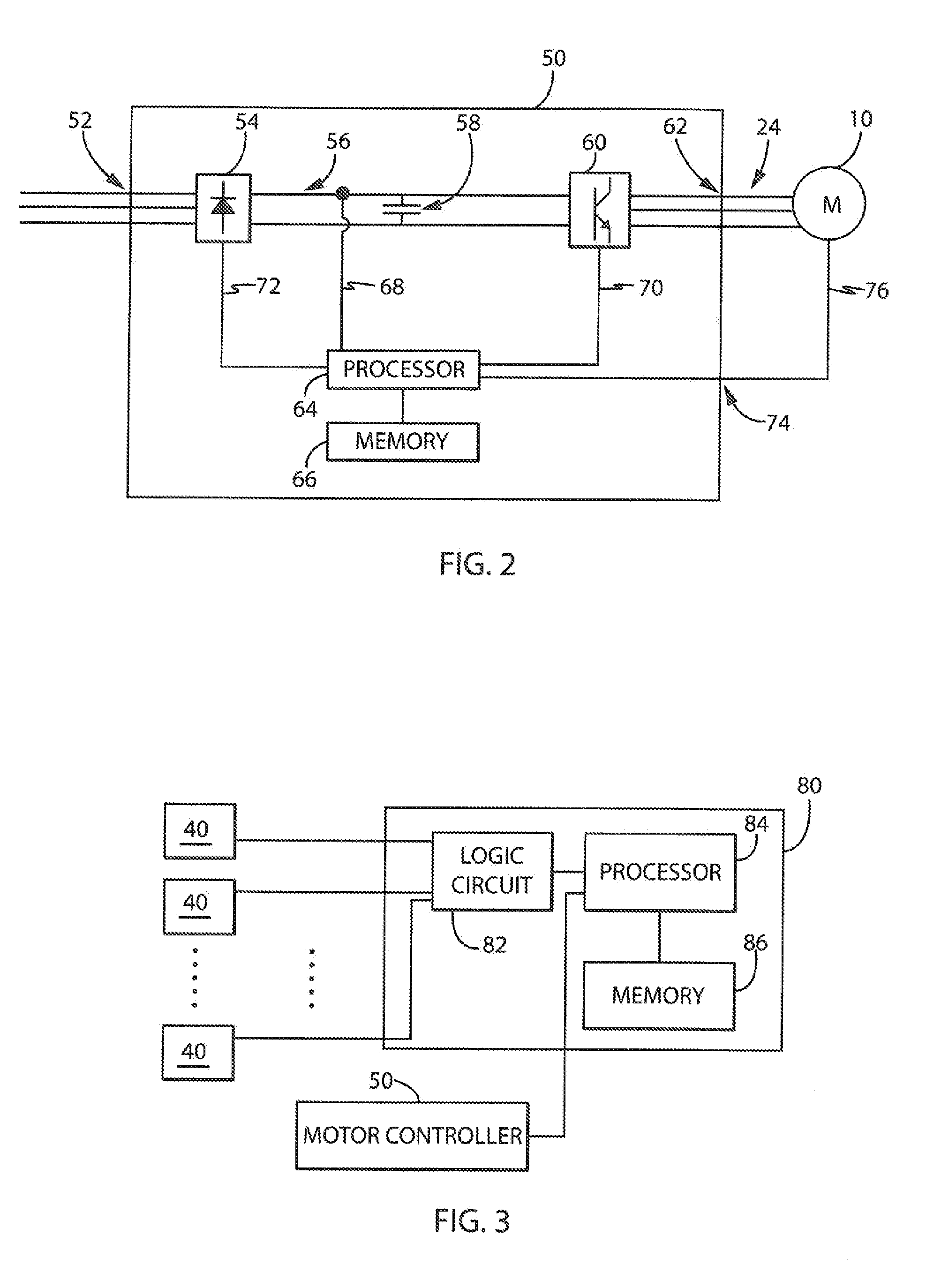
Active voltage controller for an electric motor
A method for controlling an electric motor. A desired speed is identified for the electric motor during operation of the electric motor. A voltage is identified to cause the electric motor to turn at the desired speed. The voltage is applied to the electric motor and actively controlled during operation of the electric motor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
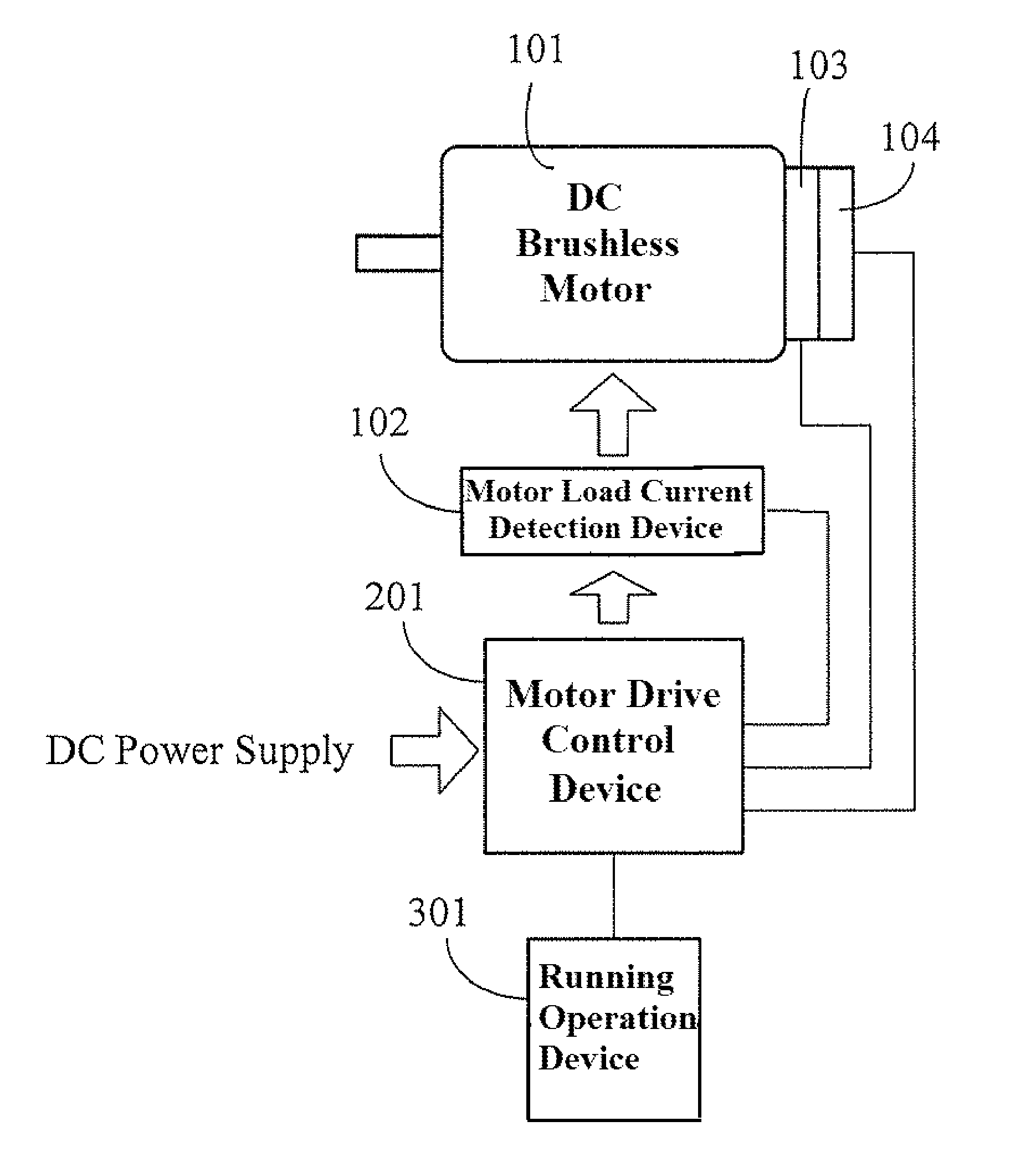
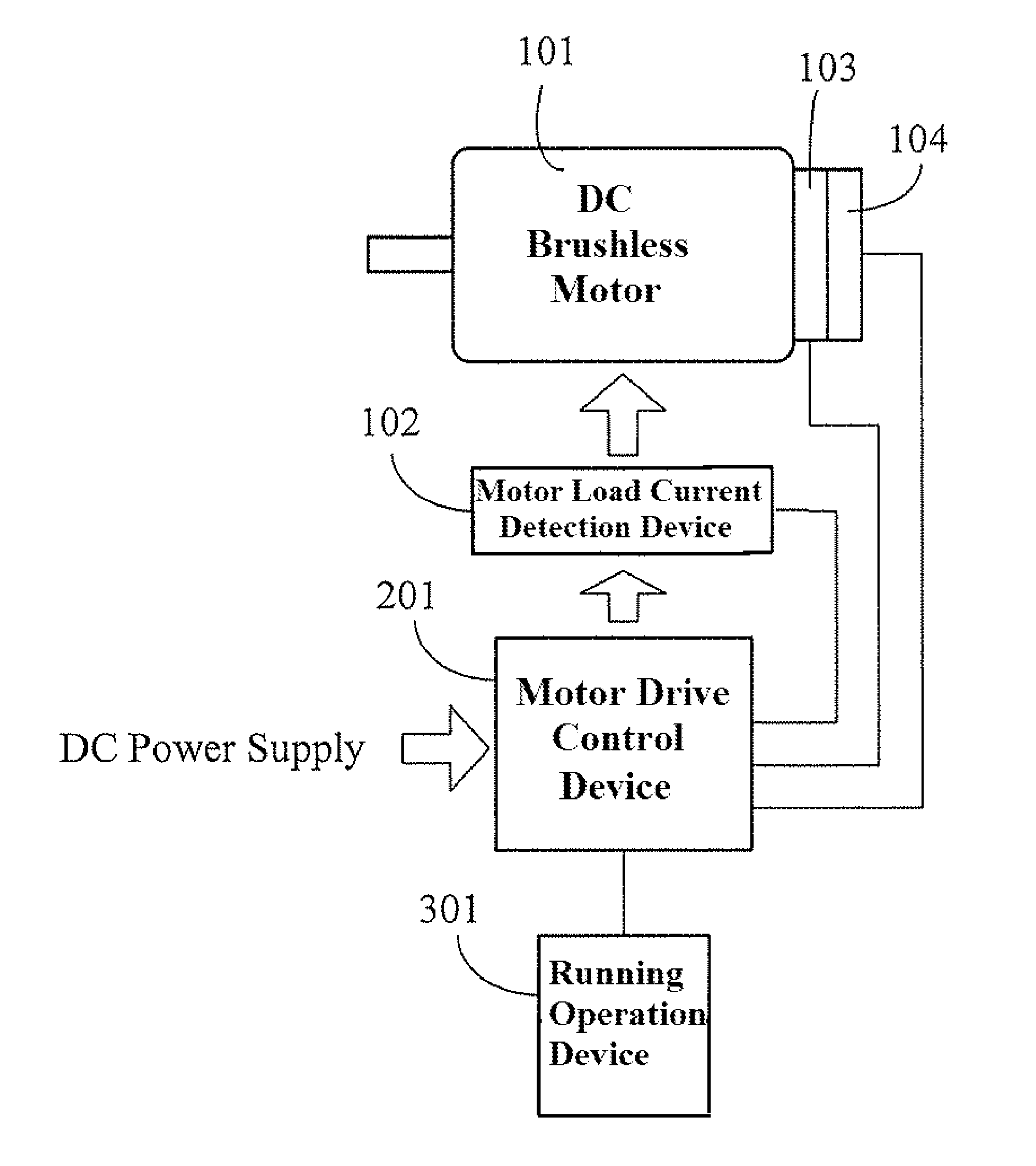
DC brushless motor drive circuit with speed variable-voltage
ActiveUS8288984B2Increase inputOvercome increased inductive impedanceTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersBrushless motorsMotor drive
For the present invention, under various running speeds statuses, the voltage supplied to the DC brushless motor is relatively increased or decreased on the basis of the internal setting of the motor drive control device according to the increased or decreased rotational output speed, so as to prevent the shortcoming of too much variation of the input impedance caused by the inductive reactance of the winding accordingly changed when the speed of the DC brushless motor is changed, specifically, to prevent the shortcoming of unable producing required torque resulting from the increased inductive reactance caused by increasing the rotational speed which makes the current value become too low when input by the original working voltage.
Owner:YANG TAI HER
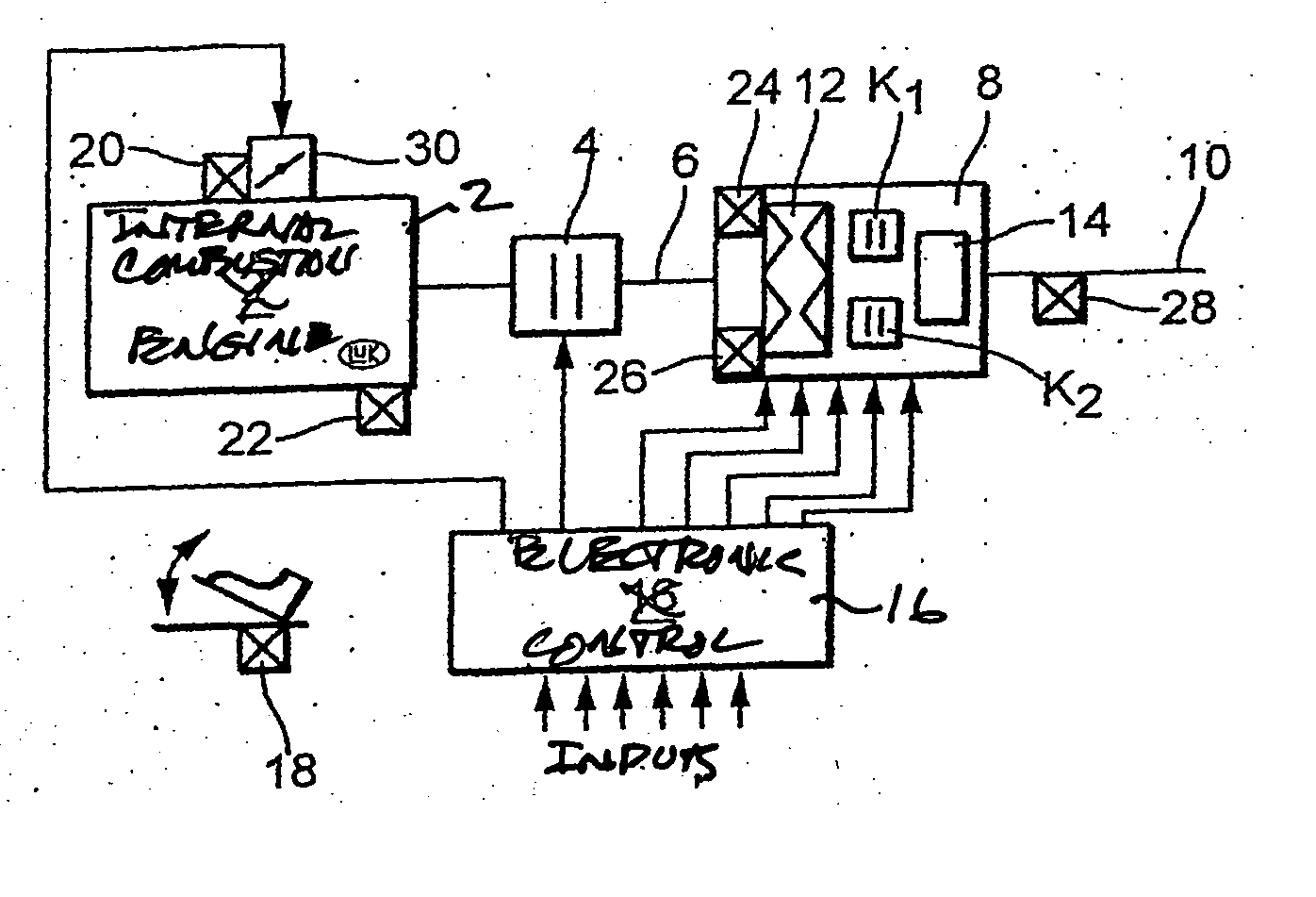
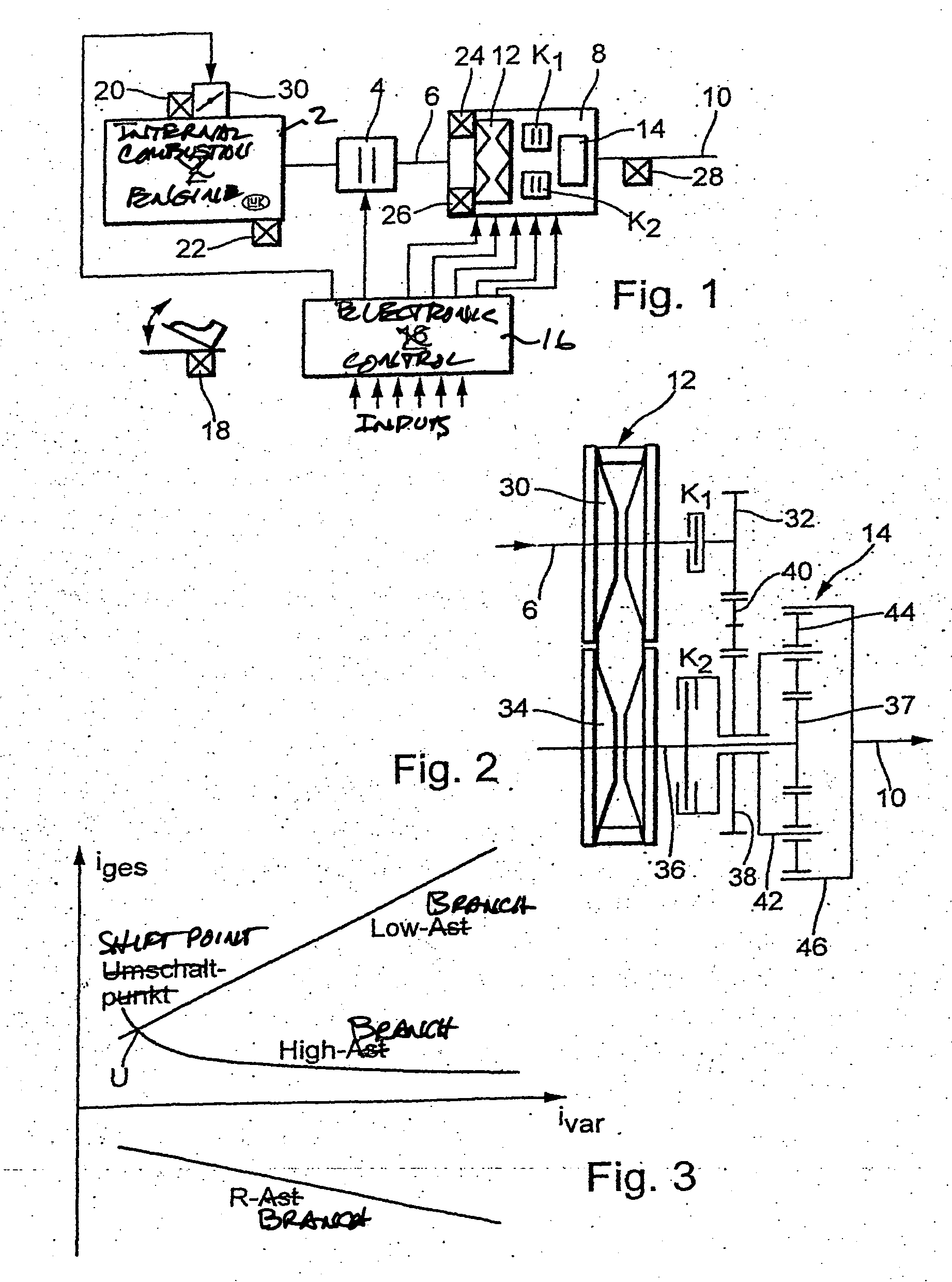
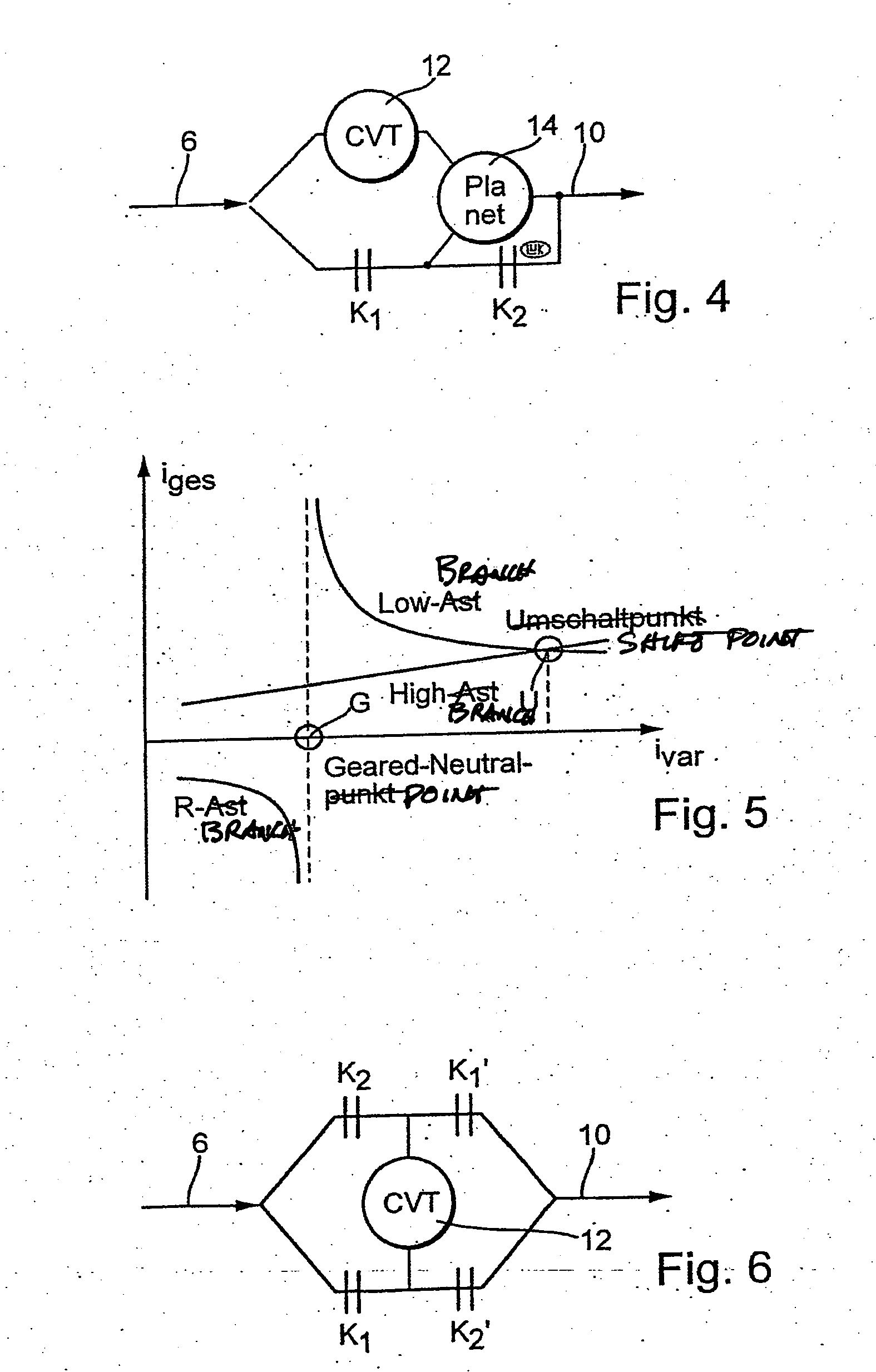
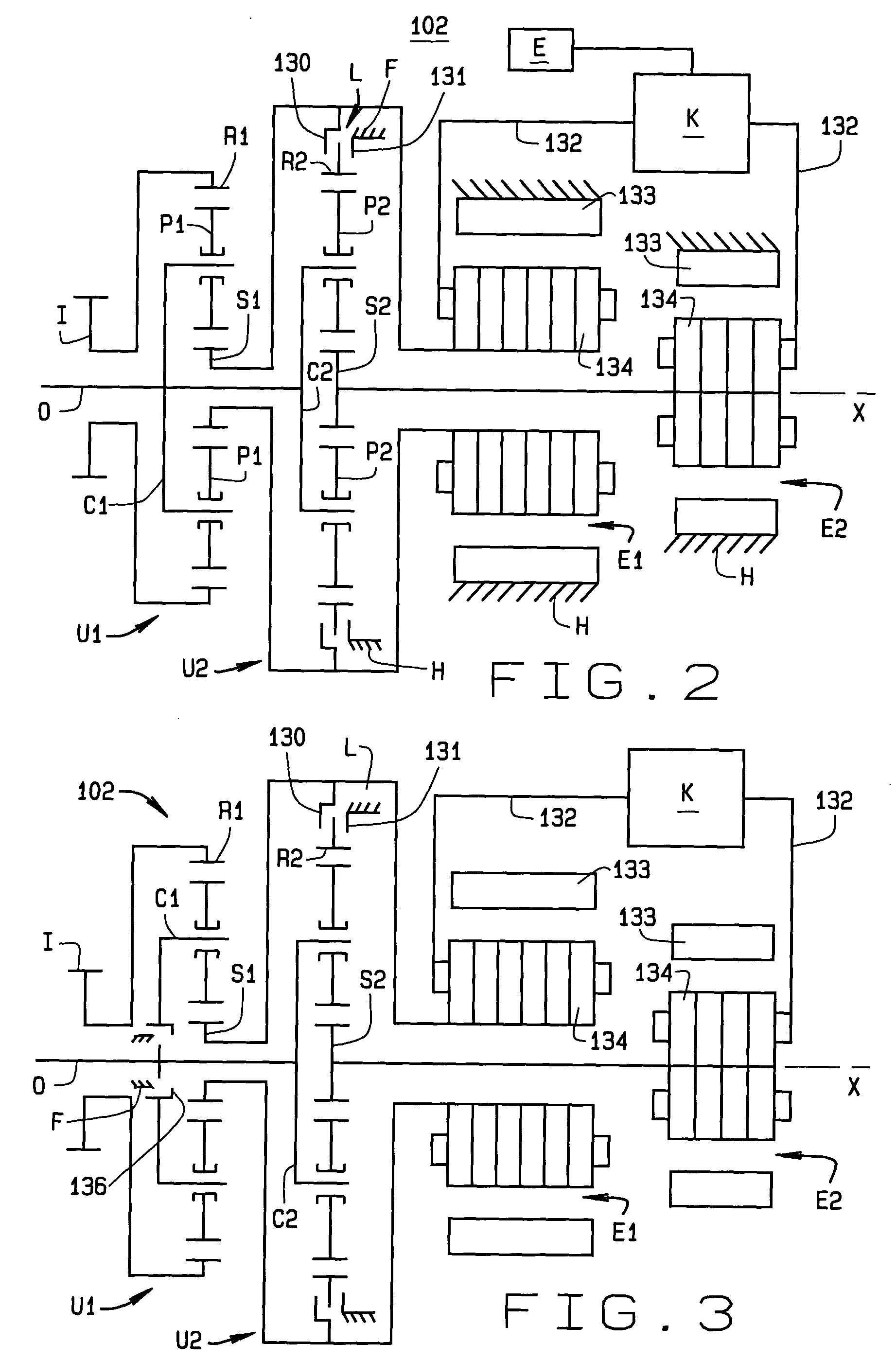
Methods for regulating the gear ratio of an automatic power-branched transmission, and automatic power-branched transmission
A method for regulating or controlling the transmission ratio of an automatic power-branched transmission. Power is transmitted through a shaft driven by an engine, a variable speed drive, a gear transmission, a driven shaft, and at least two control clutches. The variable speed drive and the gear transmission are connected to each other in such a way that the regulating range of the variable speed drive is traversed in one direction within a first range of transmission ratios, and is traversed in the opposite direction within a second range of transmission ratios during traversing of the entire range of transmission ratios. The shifting strategies result in reduced wear of the endless belt device and allow for comfortable changing between the transmission ratio ranges.
Owner:LUK LAMELLEN & KUPPLUNGSBAU BETEILIGUNGS KG
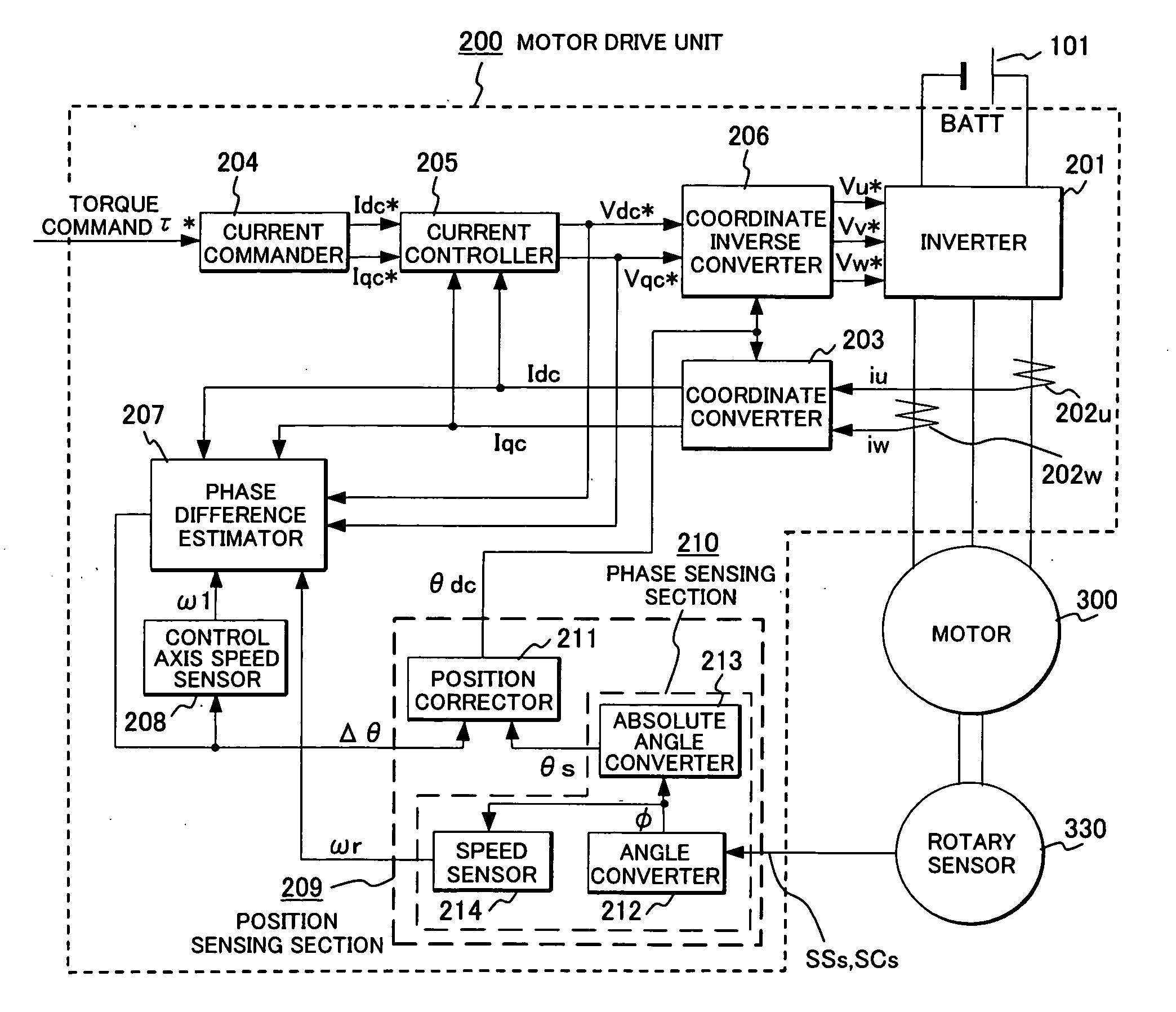
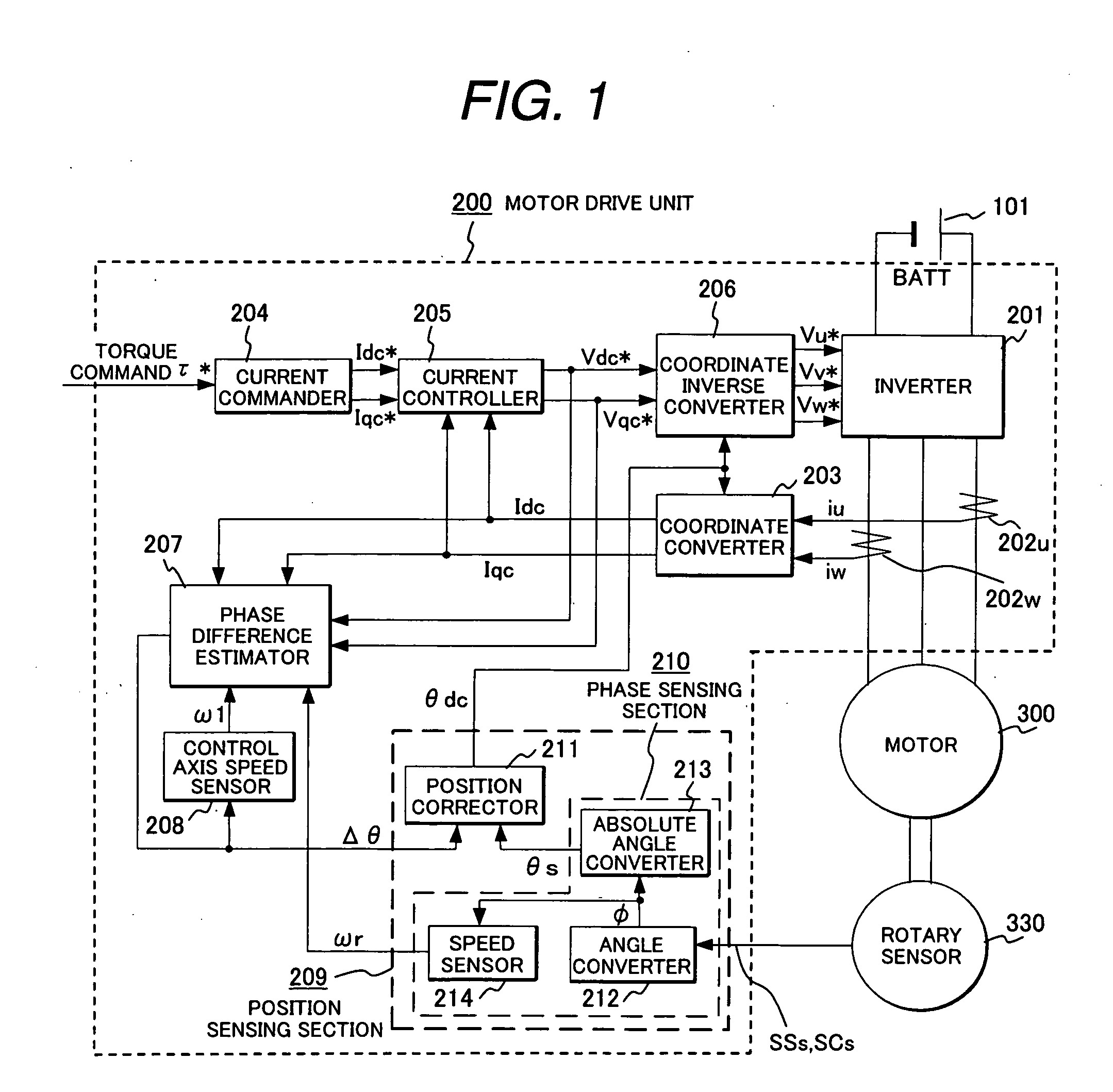
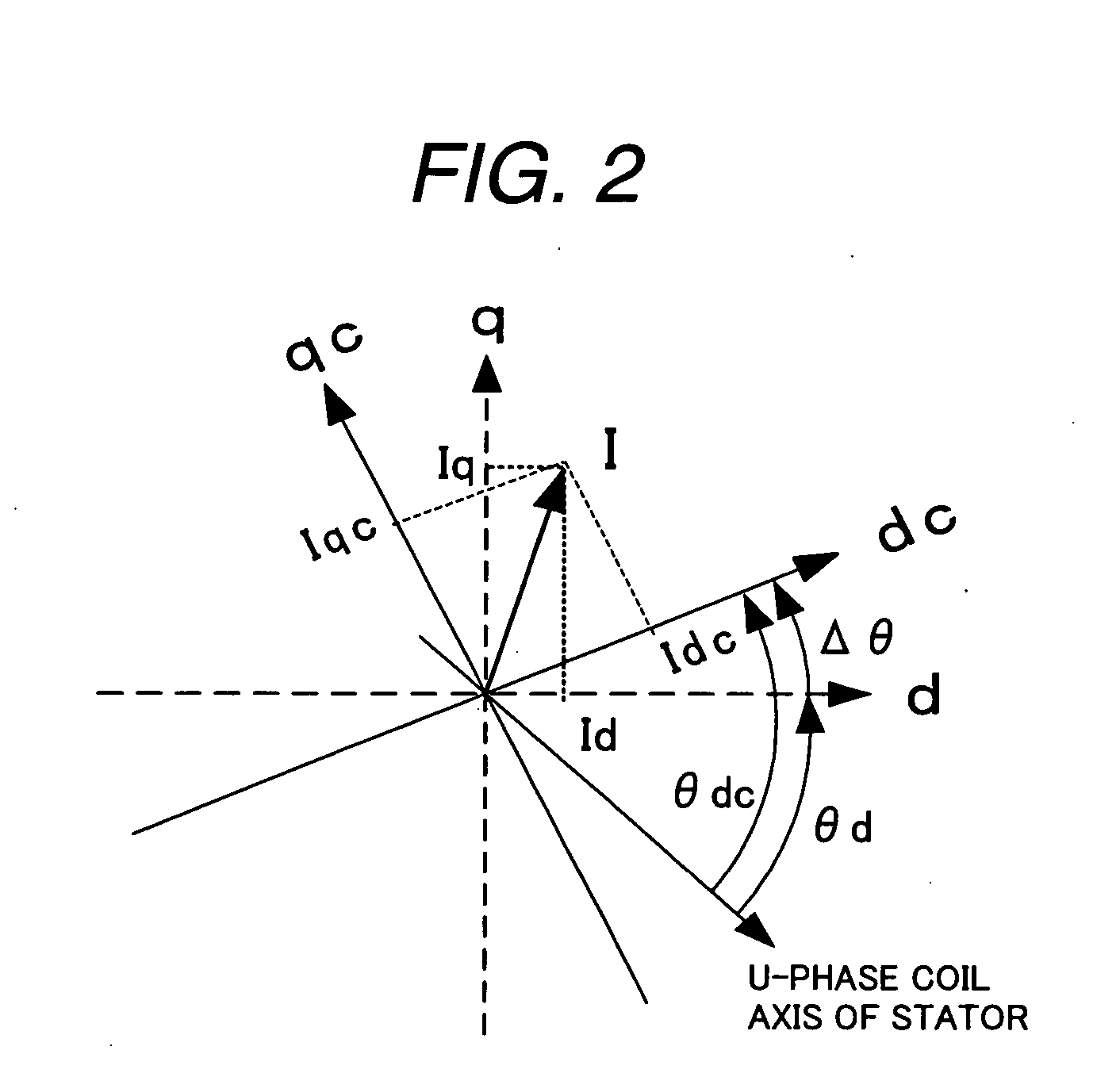
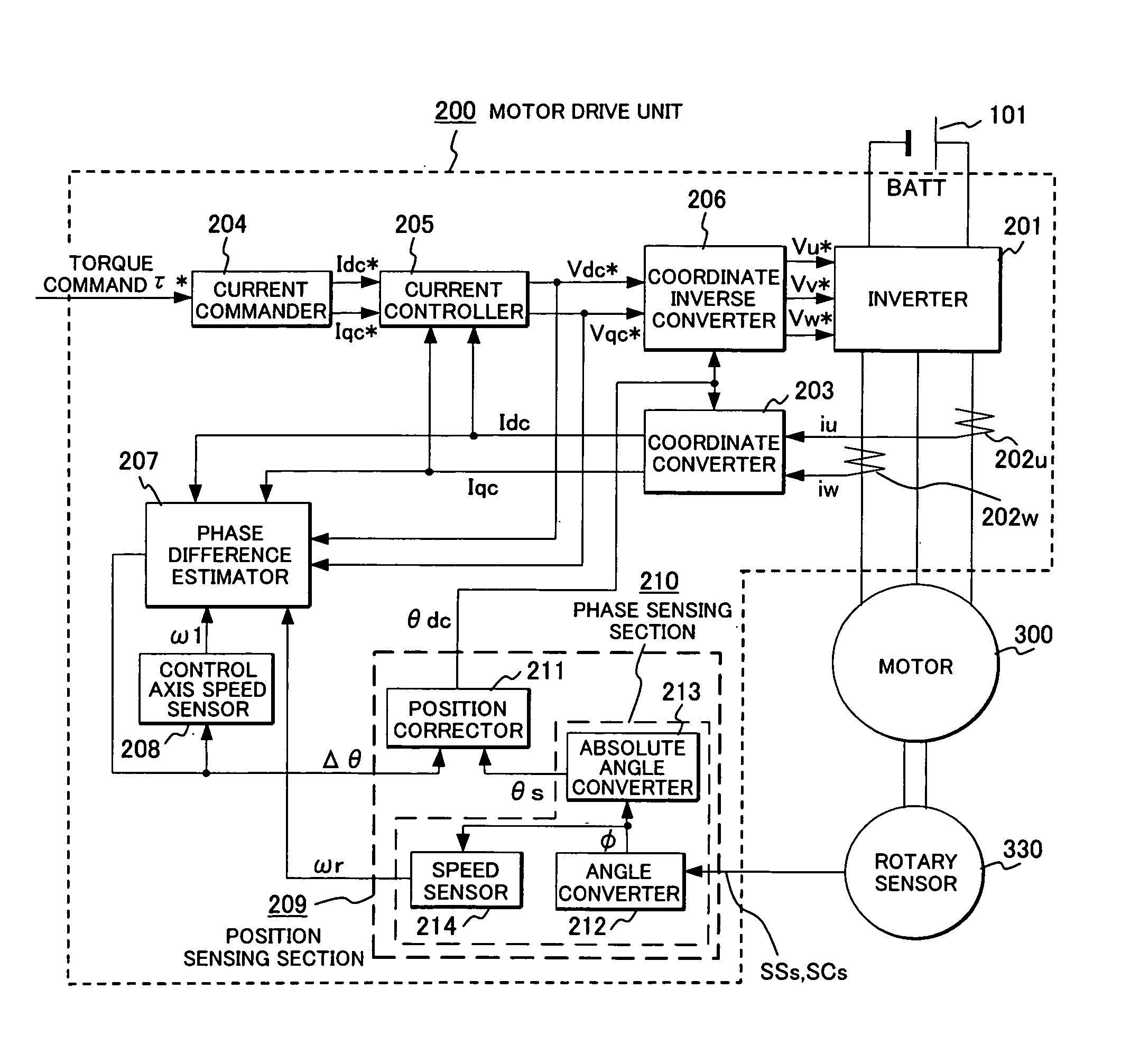
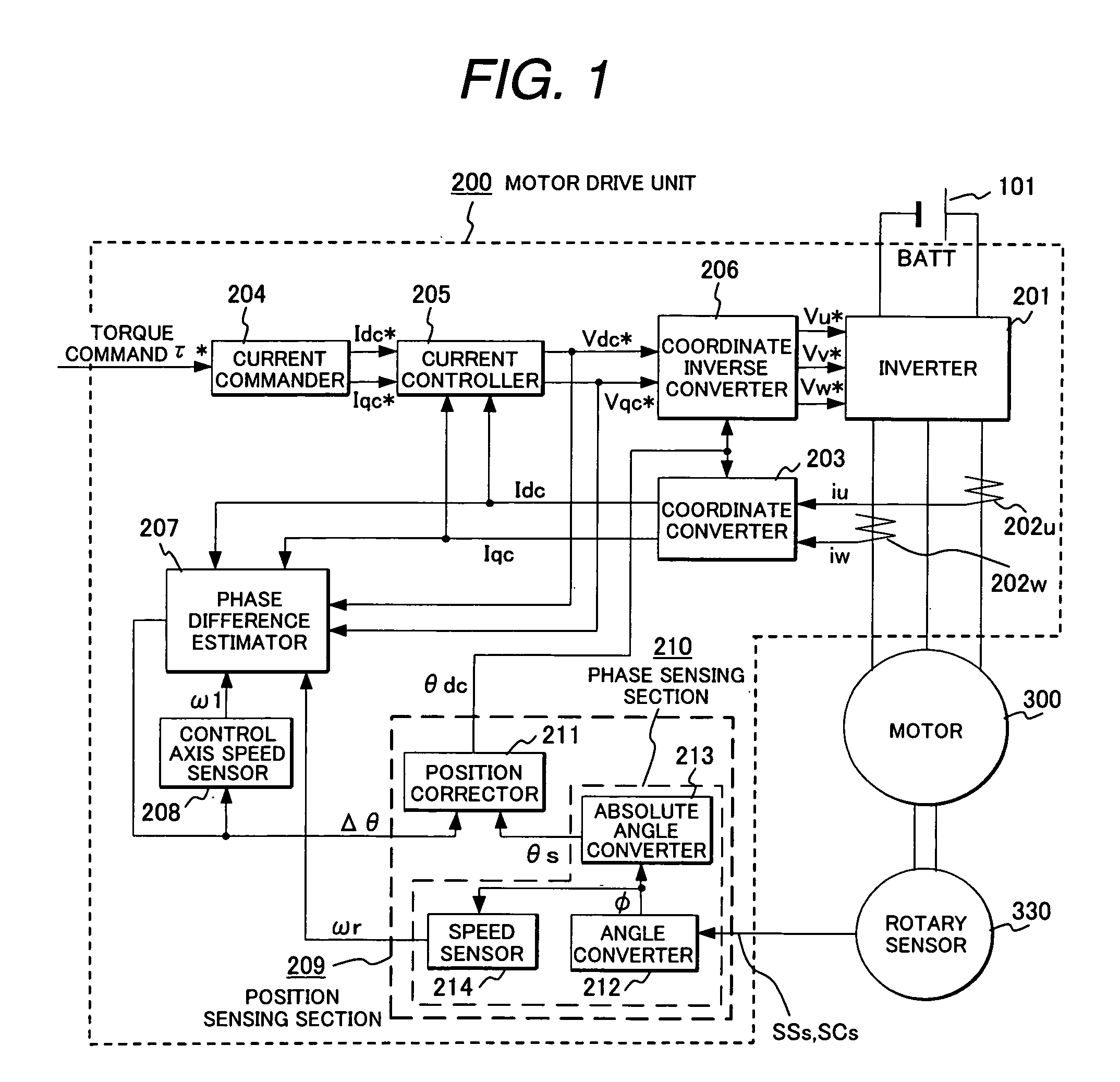
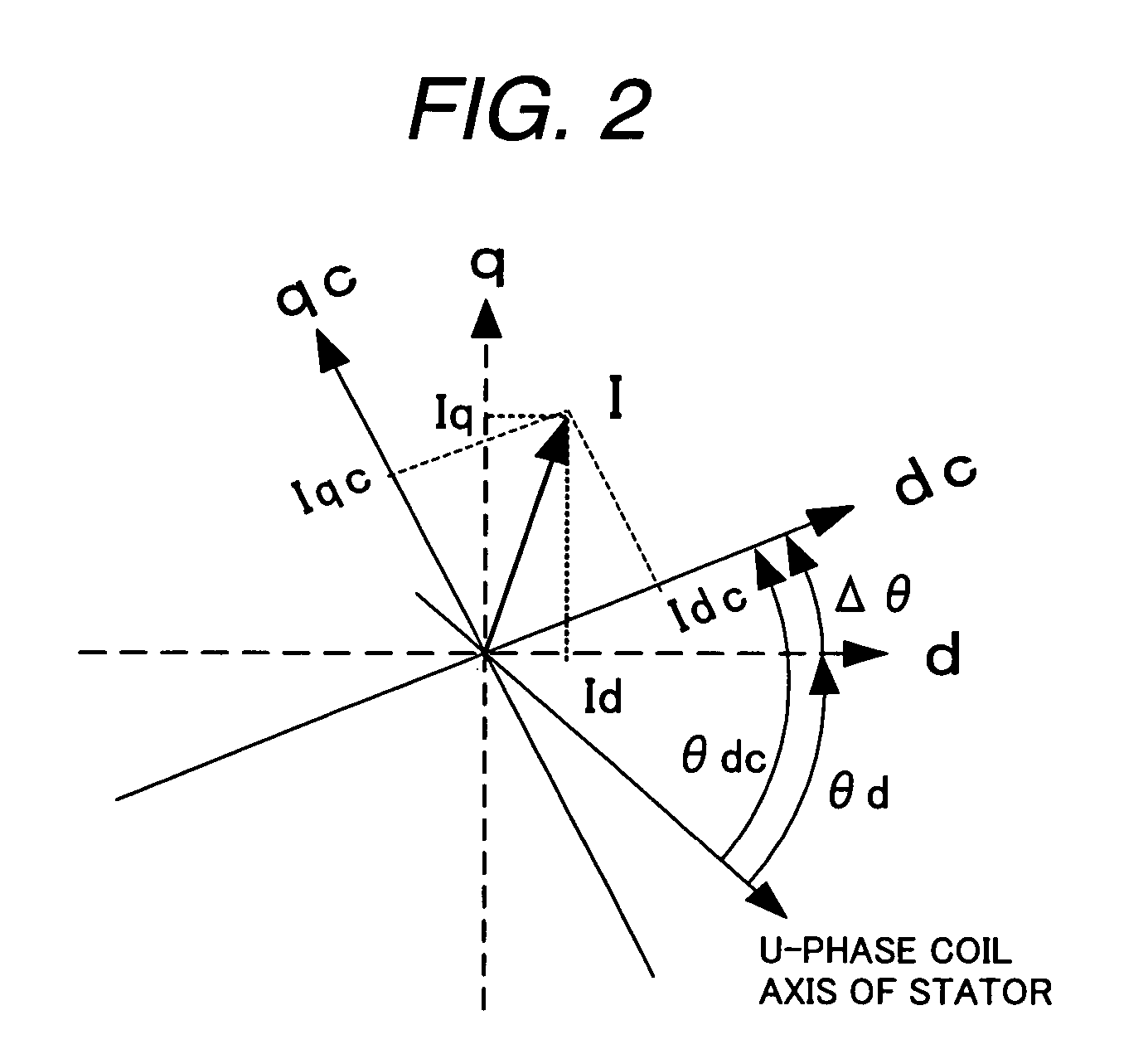
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060125439A1Efficient driveImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorPhase difference
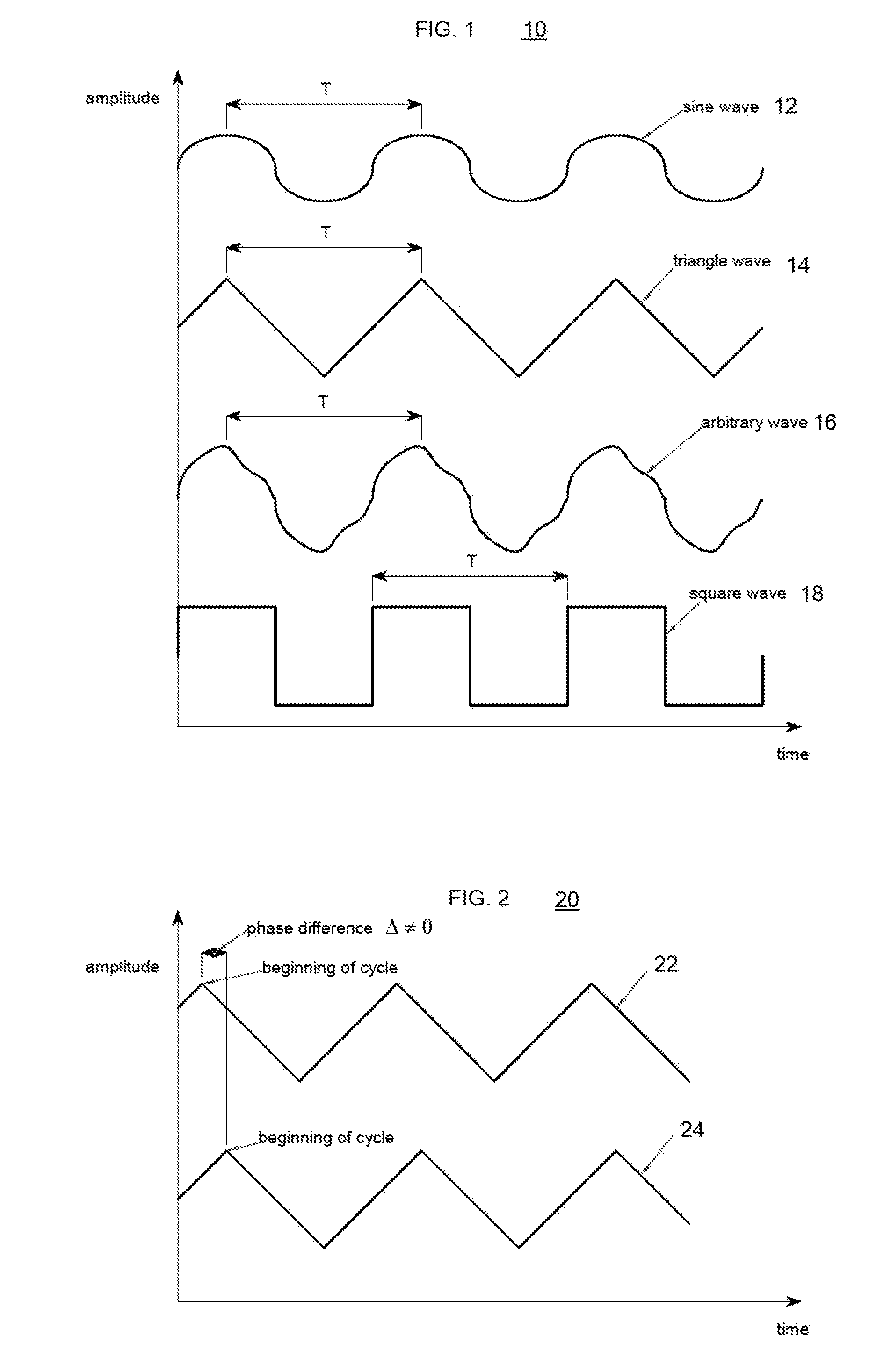
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position. A high-efficiency motor drive unit with improved maintainability of rotary sensor and improved accuracy of sensing the magnet pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor that accelerates and decelerates very quickly in a wide range of speed is realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
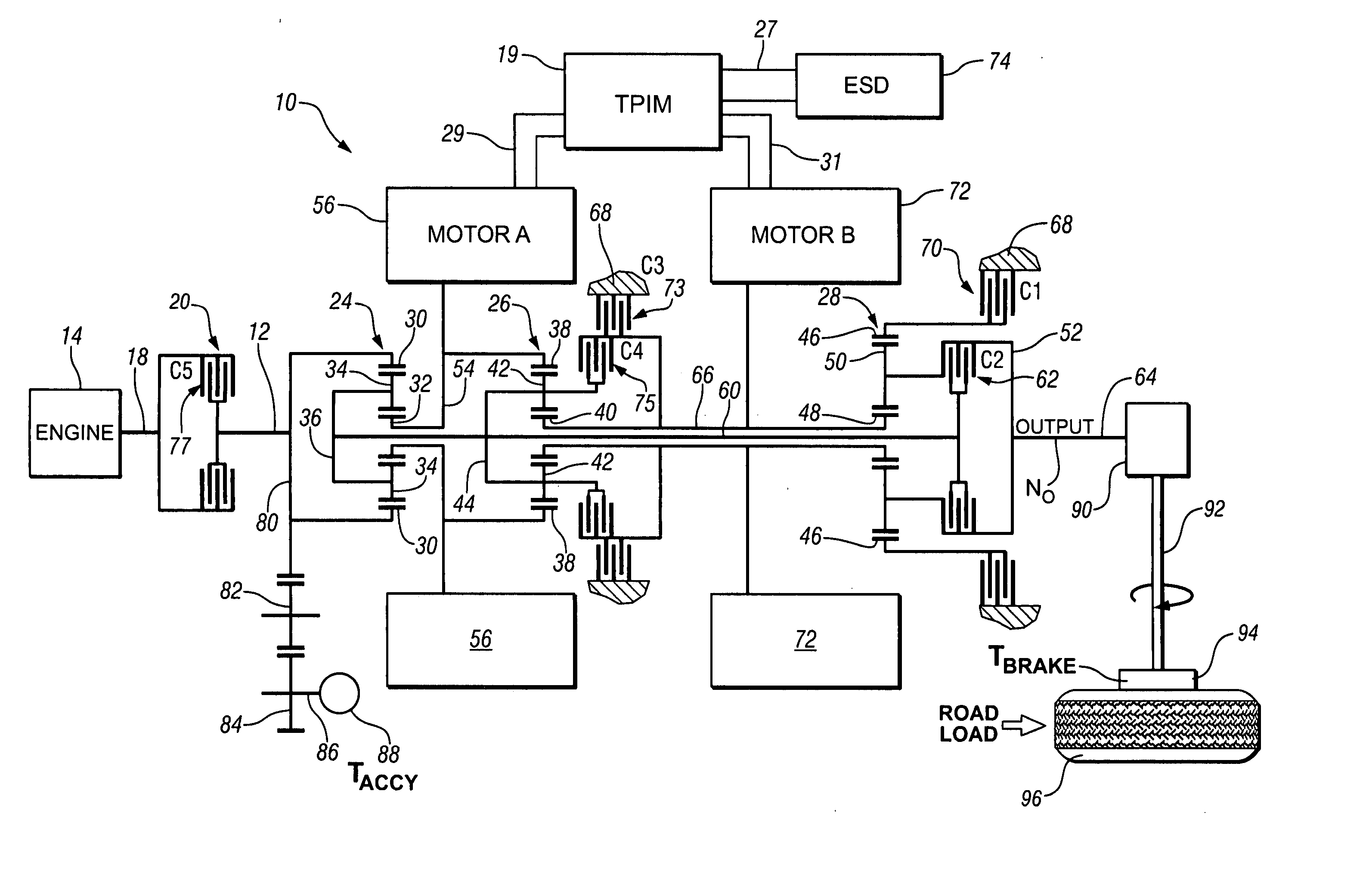
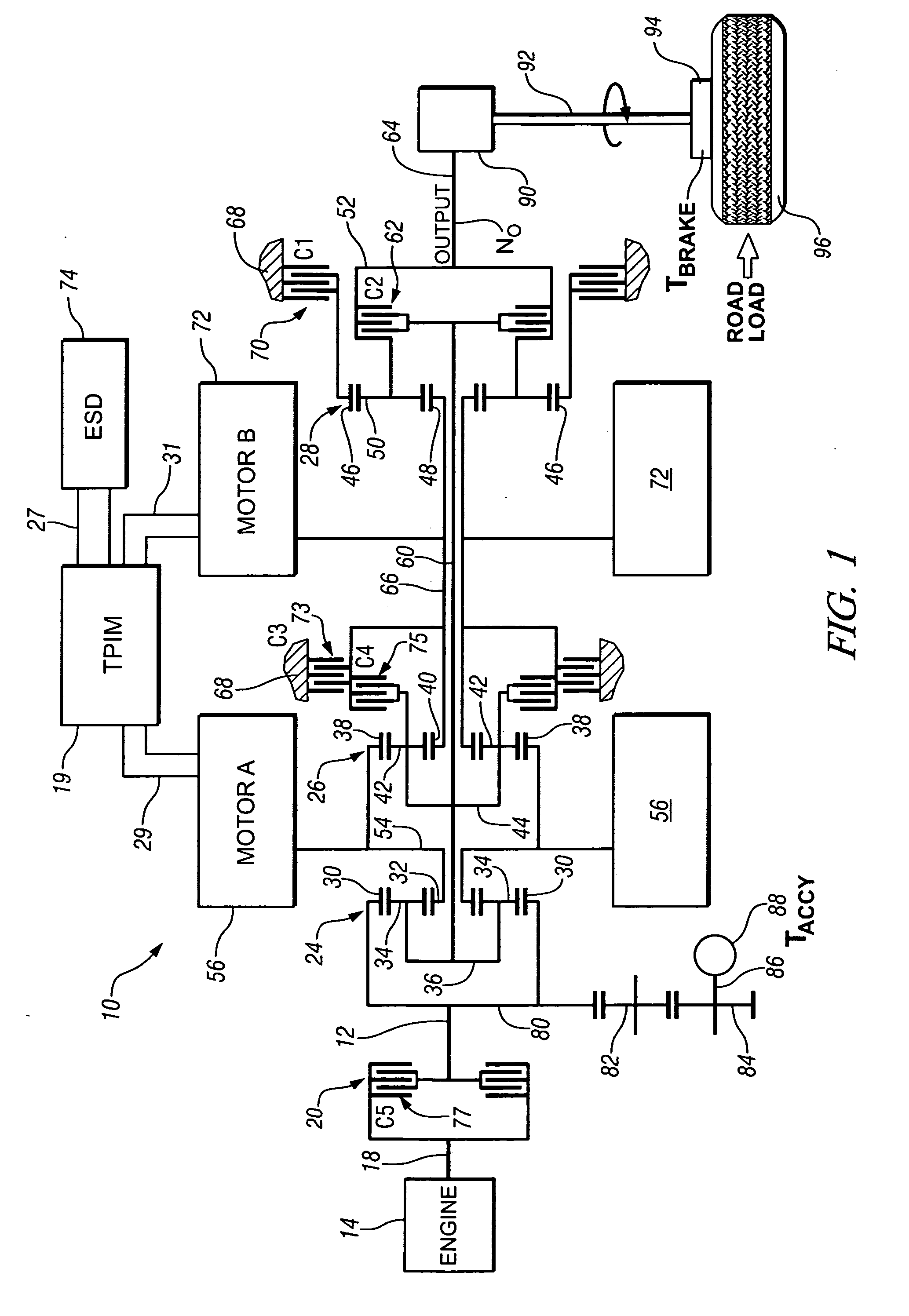
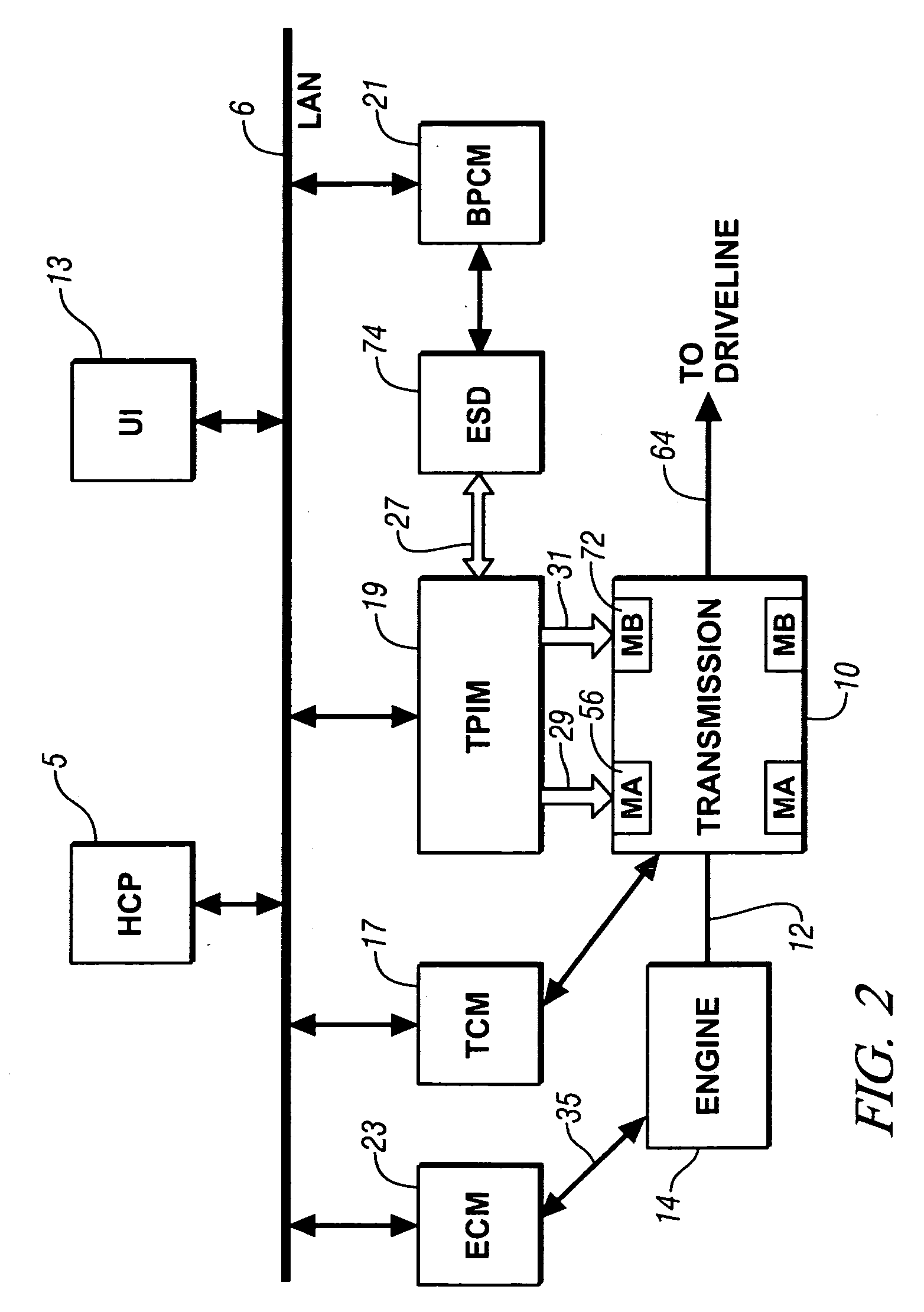
Method and apparatus to control operation of an electro-mechanical transmission
InactiveUS20080176706A1Hybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsTorque transmissionHydraulic circuit
A method and apparatus are provided to control operation of an electro-mechanical torque transmission device selectively operative in one of a plurality of fixed gear modes and two continuously variable modes, and operative to transmit torque input from a plurality of torque-generative devices. The transmission device includes a hydraulic circuit and is operative in one of a plurality of operating modes by selective actuation of a plurality of hydraulically-actuated torque-transfer clutches. The method comprises monitoring pressures in the hydraulic circuit, and restricting operation of the transmission when any one of the monitored hydraulic pressures does not correspond to an expected pressure thereat. Presence of a fault is verified during the restricted operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Control device for electric motor
ActiveUS7005828B2Improve artSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlDriving currentAcquired characteristic
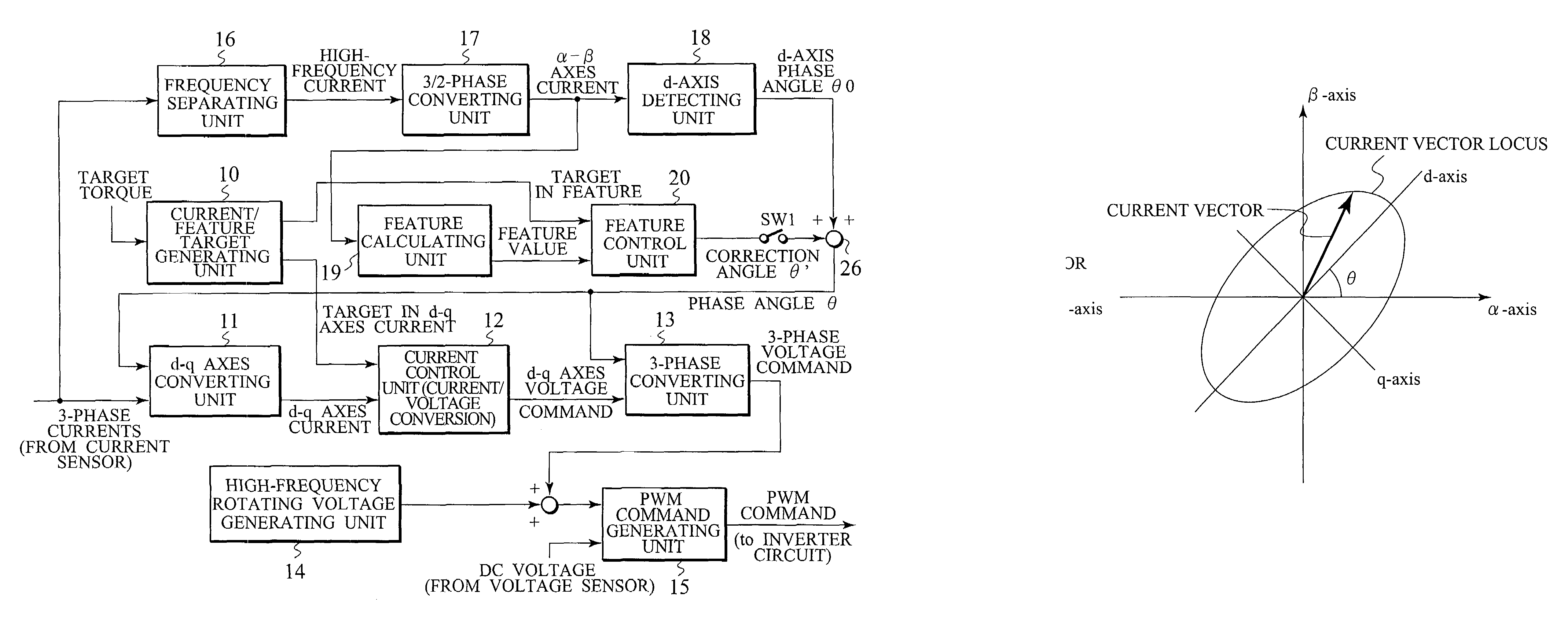
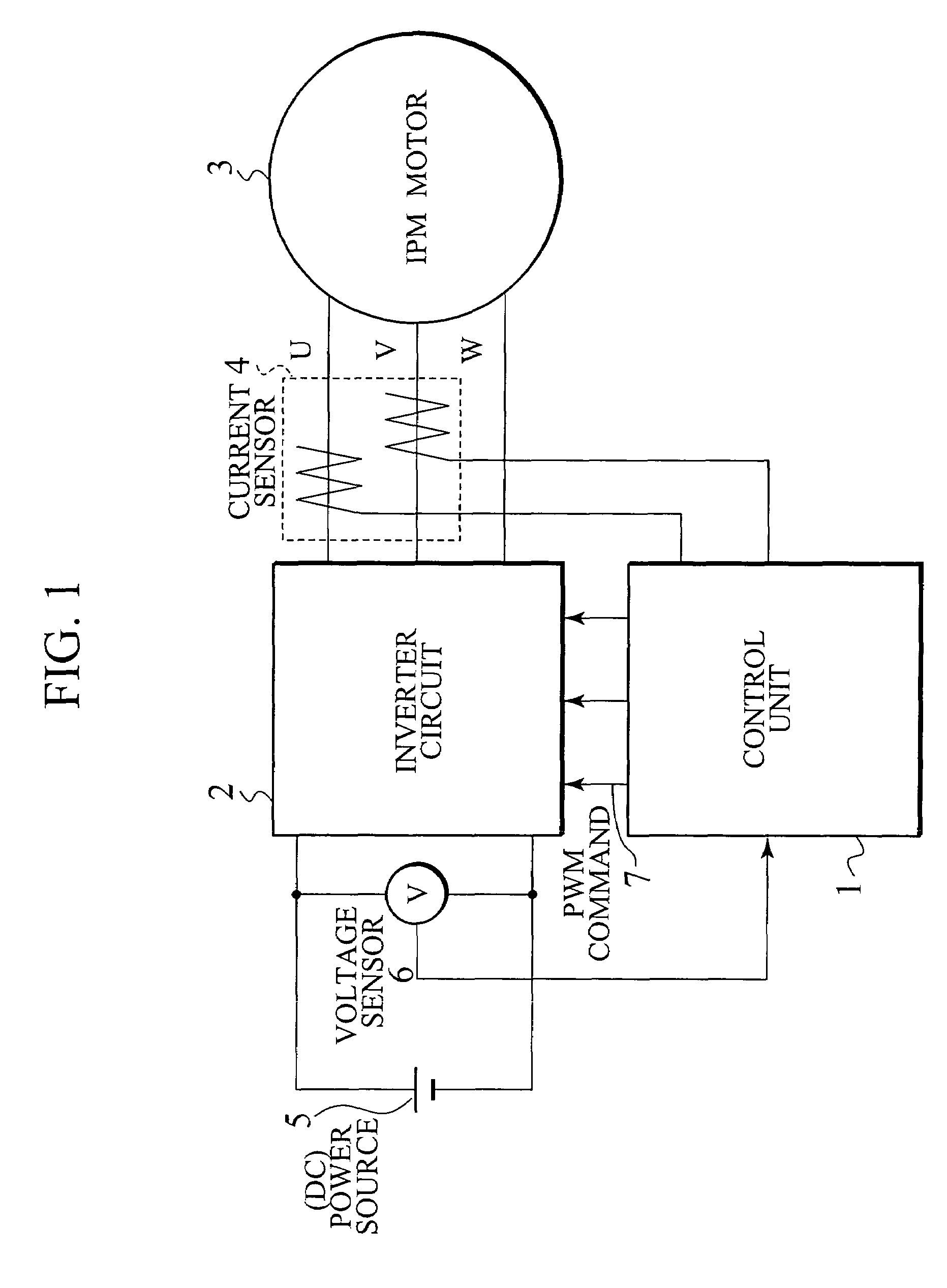
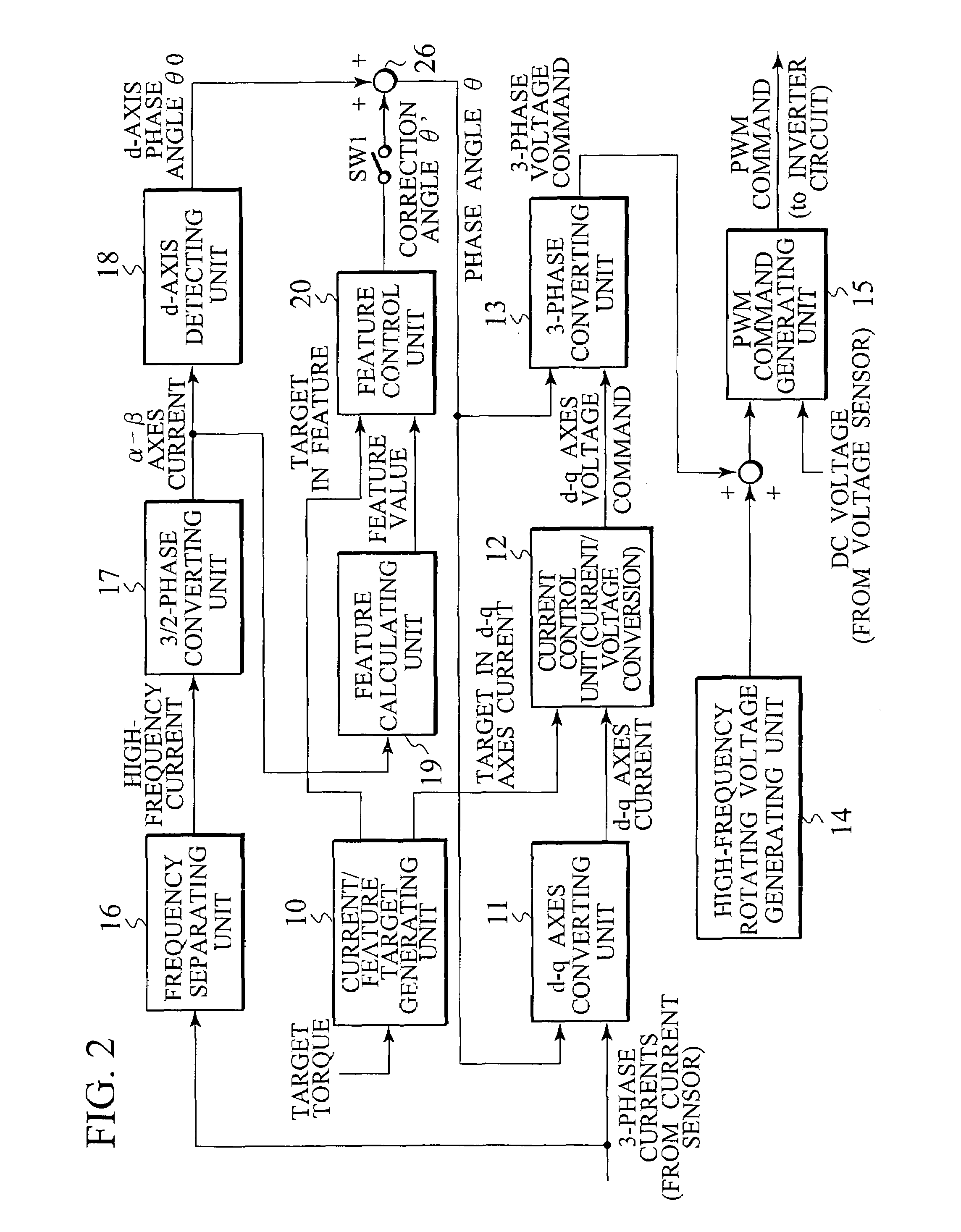
Corresponding to a target torque, the control device calculates a target value of a feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus and the length of the short axis and further superimposes a superimposed current on a drive current for the motor, the superimposed current having a frequency different from the frequency of the drive current. Further, the control device detects an actual value of the feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus of the superimposed current and the length of the short axis of the same and finally detects a phase angle of the motor based on the target value and the actual value for the feature. The manipulation of a detecting phase is performed by feedback of a feature obtained by the magnitude of the superimposed current. That is, when the actual feature is more than the target value, the detecting phase is advanced. Conversely, when the actual feature is less than the target value, the detecting phase is delayed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
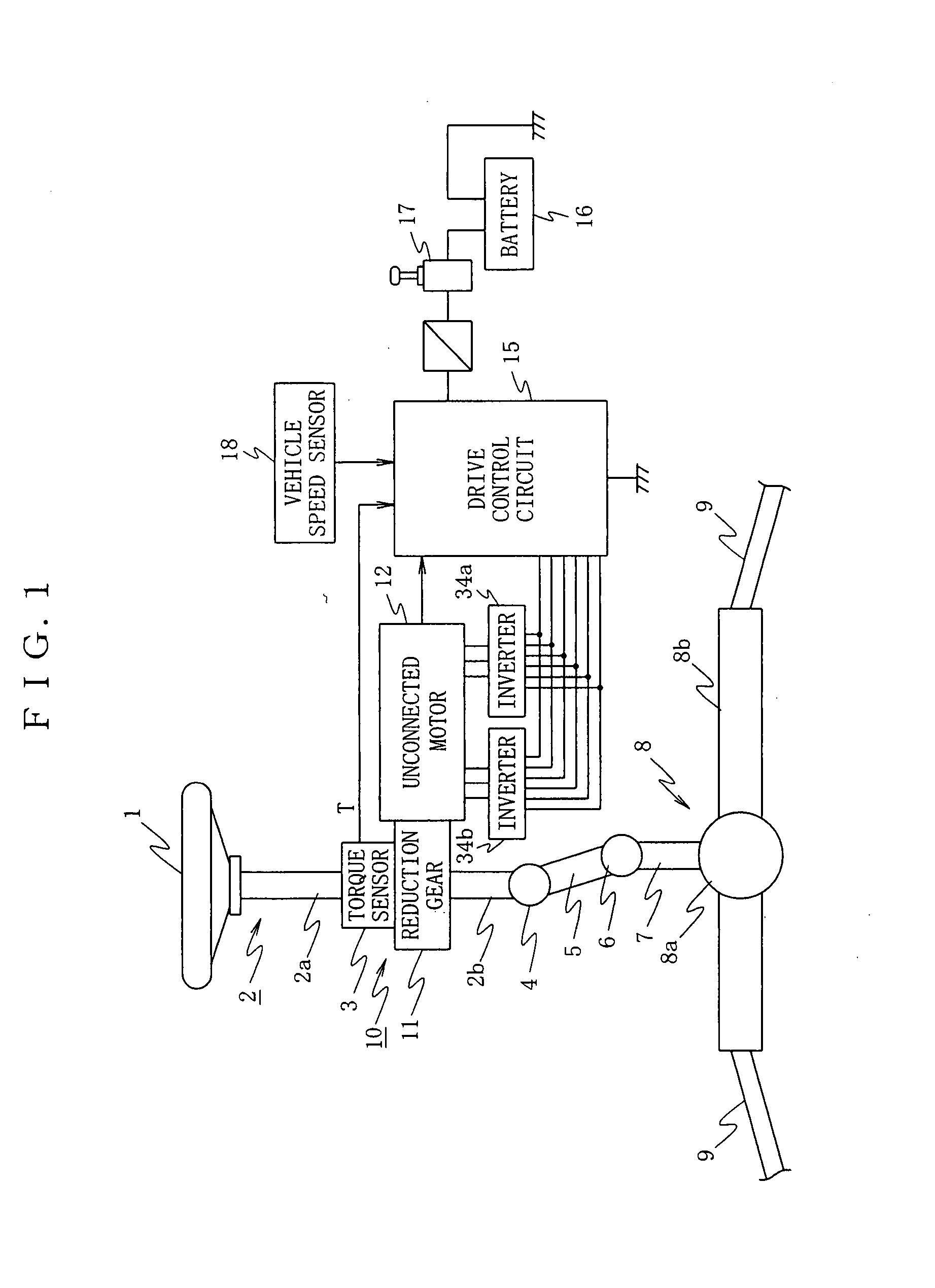
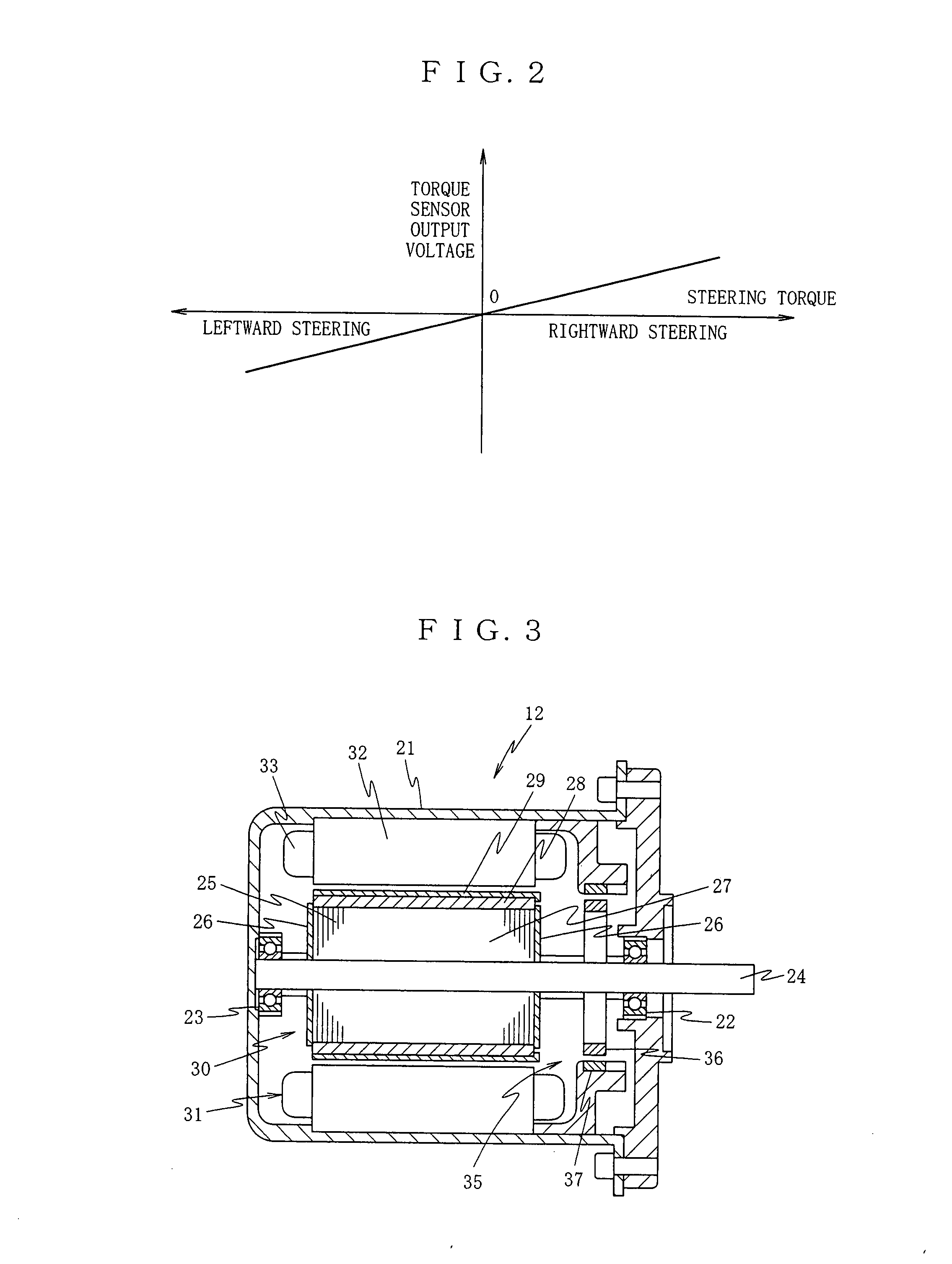
Unconnected Motor, Drive Control Device Thereof, And Electric Power Steering Device Using Drive Control Device Of Unconnected Motor
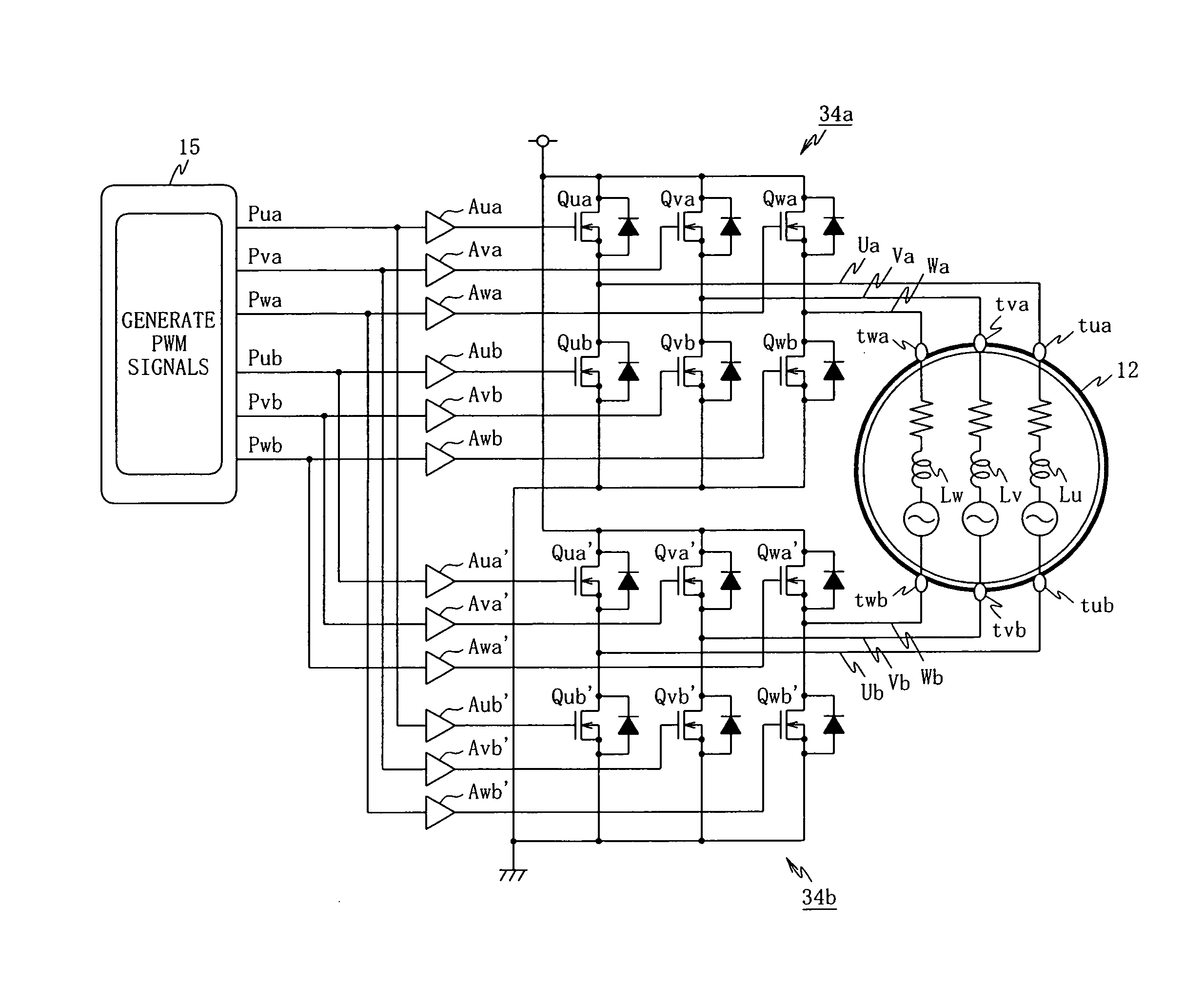
InactiveUS20080067960A1Constant gainIncreased current consumptionMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric power steeringControl signal
A drive control device of an unconnected motor capable of resolving power shortage and increasing motor output without using a boost circuit, and an electric power steering device using the unconnected motor. The drive control device comprises an unconnected motor (12) having a rotor in which permanent magnets are allocated and a stator opposing the rotor, in which armature winding Lu to Lw of a plurality (N number) of phases are independently arranged, a pair of inverter circuits (34a, 34b) individually connected to both ends of each armature winding, and a drive control circuit (15) which drives the pair of inverter circuits (34a, 34b) with a predetermined number (e.g. 2N) of PWM drive control signals.
Owner:NSK LTD
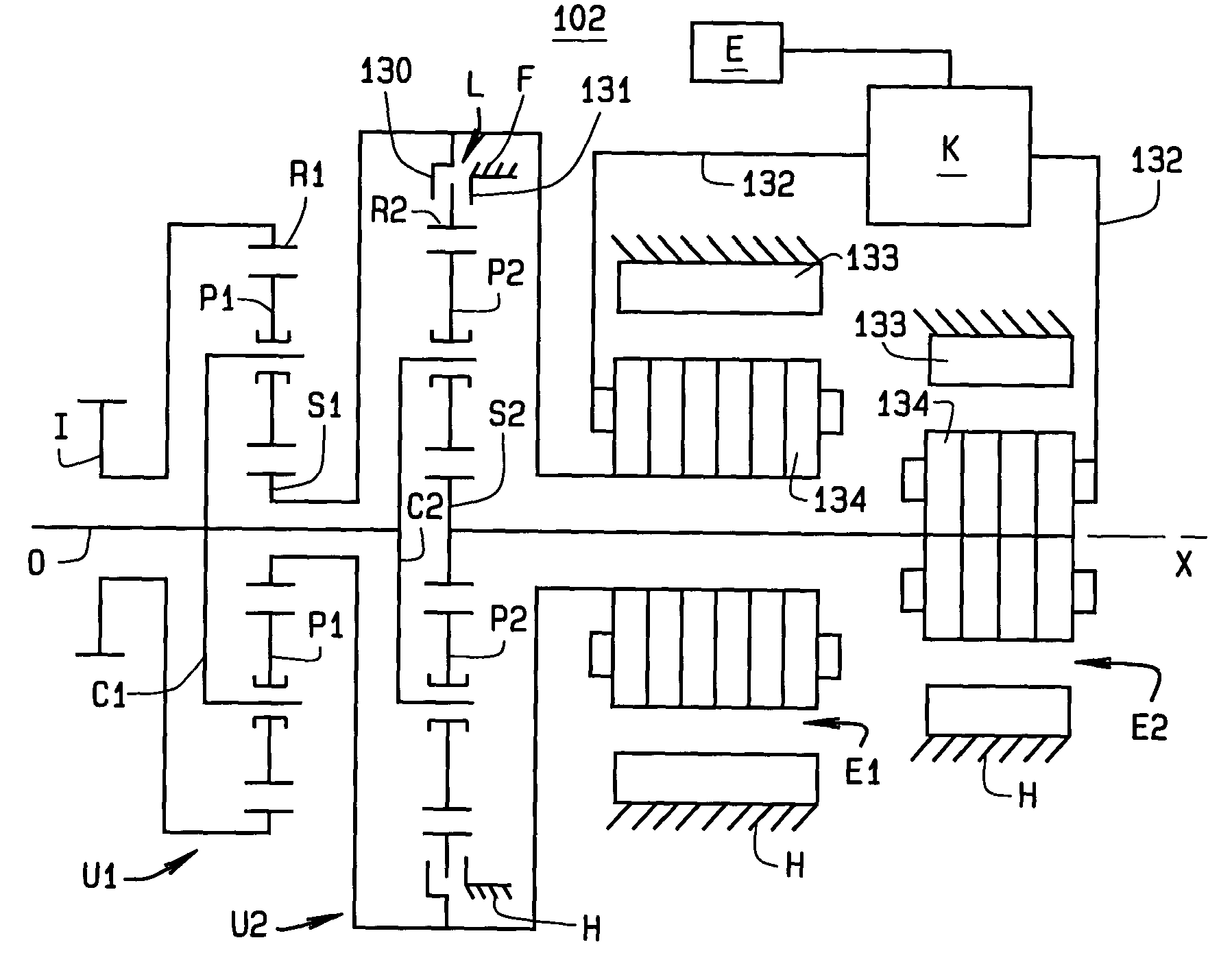
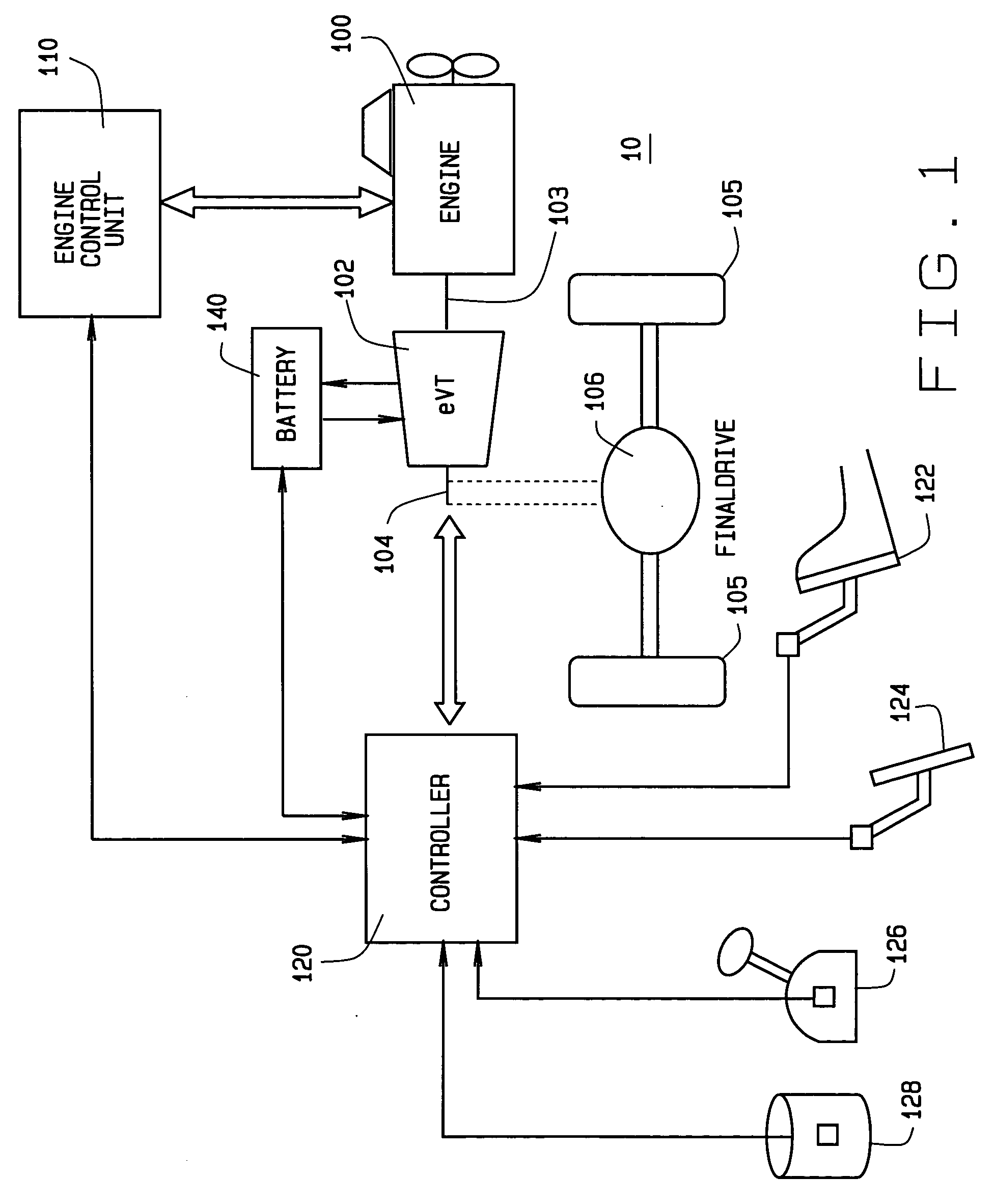
Method and apparatus for power flow management in electro-mechanical transmissions
A method for power management in an electro-mechanical power-split infinitely variable transmission (eVT) designed to operated within a designated speed ratio range for vehicular applications. The eVT is comprised of an input shaft coupled to the output shaft of a drive engine to receive power, a drive shaft, two electric machines, and a pair of planetary trains each having a sun member, a ring member, a set of planetary members, and a planet carrier. The eVT further contains one or more torque transfer devices to connect or disconnect members of the planetary trains for transferring torque. The drive shaft is coupled with a final drive of a vehicle for delivering or recapturing power to or from the vehicle drive wheels. The two electric machines are interconnected electronically via a power control unit and are coupled respectively with members of the planetary train. The method of power management in the eVT is selected based on the current speed and torque of the input and drive shafts, and upon the desired operating parameters.
Owner:THE TIMKEN CO
Synchronous shift execution for hybrid transmission
InactiveUS20070260381A1Reduce capacityReducing motive torqueHybrid vehiclesDC motor speed/torque controlControl systemClutch
An apparatus and method are provided to execute synchronous shifting in a powertrain system having multiple torque-generative devices each operable to independently supply motive torque to the transmission device. The exemplary transmission device comprises a two-mode, compound-split, hybrid electromechanical transmission. Operation includes operating in an initial fixed gear ratio, operating the transmission in a mode operation, and, operating the transmission in a final fixed gear ratio. The control system reduces reactive torque of a clutch activating the initial gear, and deactivates the first torque-transfer device when the reactive torque is less than a predetermined value. It determines that speed of an input shaft to the transmission is substantially synchronized with a rotational speed of the second torque-transfer device, and actuates the second torque-transfer device.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and Method for Detection of Motor Vibration
ActiveUS20150288257A1Reduce vibration detectedReduce and eliminate identified vibrationDC motor speed/torque controlVector control systemsMotor vibrationElectric machine
An improved system for monitoring vibration of an electric machine is disclosed. According to one embodiment, sensors are positioned in a plane orthogonal to the motor shaft and each sensor detects vibration along at least one axis of the motor. The sensors are oriented such that the polarity of each sensor is reversed. The pairs of sensors may be used to isolate specific vibrations within the motor. According to another embodiment, a sensor may be mounted directly to the motor shaft. The sensor on the motor shaft directly detects vibrations along the motor shaft. Optionally, a second sensor may be mounted to a fixed location within the motor housing, and the combination of the sensor on the motor shaft and the sensor at a fixed location may be used to isolate specific vibrations within the motor. A motor controller may adjust operation of the motor to reduce the isolated vibration.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Motor control device
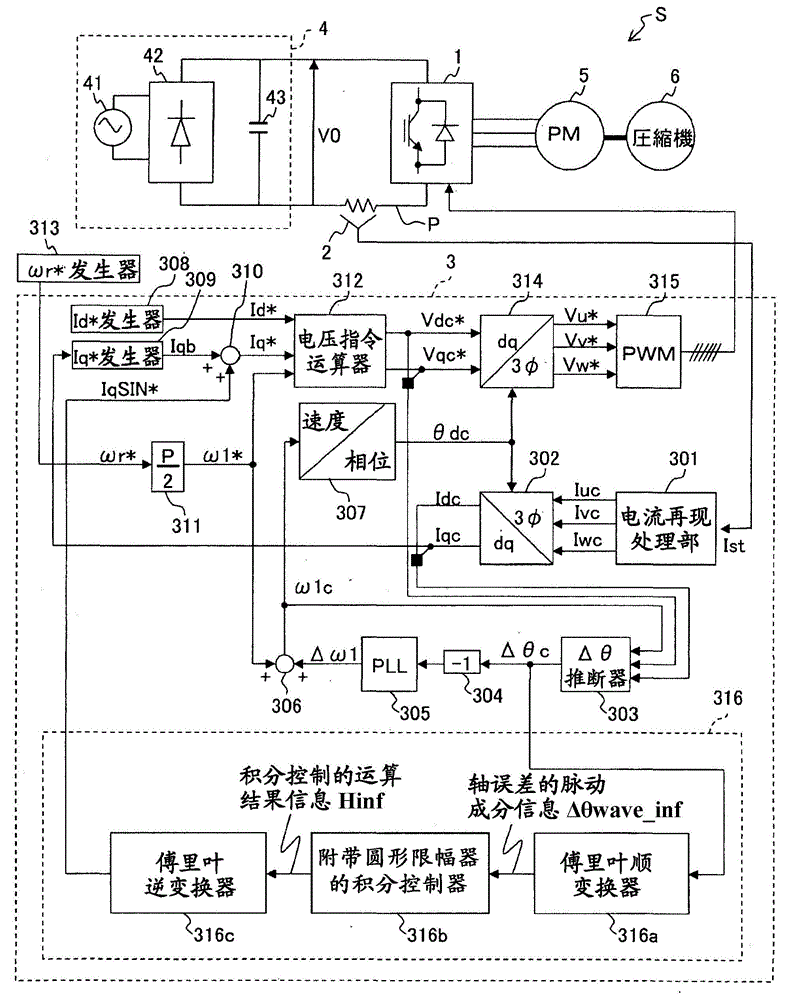
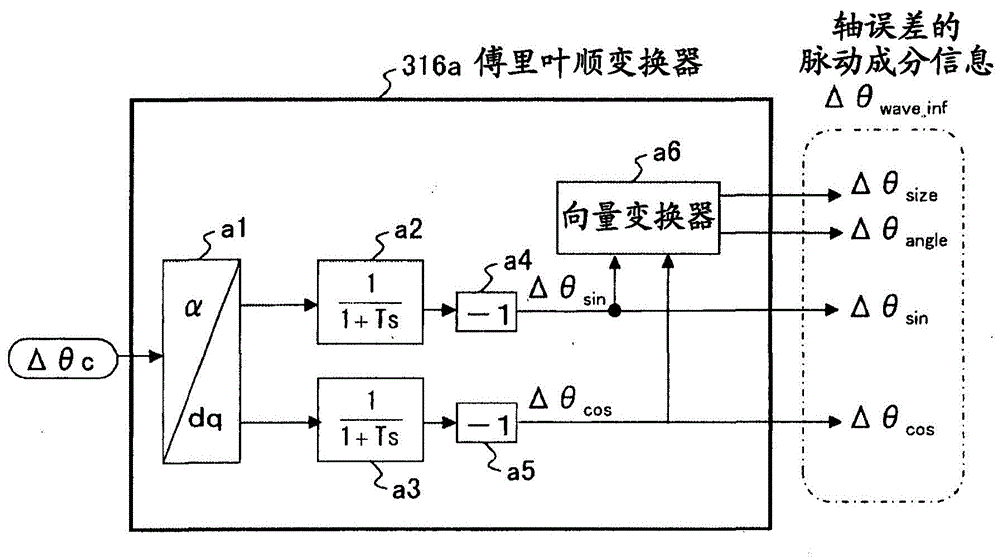
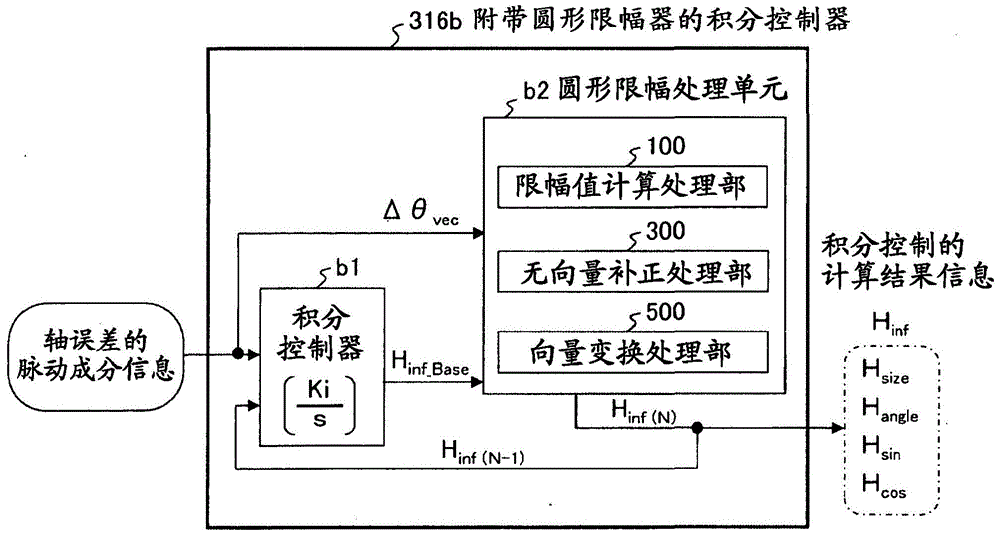
ActiveCN104038127ASuppression of pulsating torqueVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlCurrent sensorIntegral controller
A motor control device capable of suitably inhibiting the pulsating torque of an alternating-current motor is provided. The motor control device comprises an axis error inference machine (30) which infers an axis error based on a current value of an inverter, detected by a current sensor (2); a Fourier rectification machine (316a) which extracts an axis error vector from the time-base changes of the axis error; an integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with a circular amplitude limiter, which is used to calculate a correction current vector for offsetting the pulsating torque, wherein a circle with a set amplitude limiting value serving as the radius is used as the base for limiting the movement of the correction current vector, and the integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with the circular amplitude limiter performs the circular amplitude limiting for limiting the movement of the correction current vector so as to enable the deflection angle of the correction current vector to be close to the deflection angle of the axis error vector.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
System and method for controlling motor using parameter associated with magnetic flux
InactiveUS20080129243A1Reliably graspTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersDriving currentOperating point
A control method for a motor that rotates based on flux linkages to a winding member of the motor when the winding member is energized by a drive current is provided. The method includes storing magnetic-state information indicative of a relationship between each of a plurality of predetermined operating points of the drive current and a magnetic-state parameter associated with the flux linkages. The method includes obtaining at least one of command information associated with an operating state of the motor and detection information associated with the operating state of the motor. The method includes referencing the magnetic-state information with the use of the obtained at least one of the command information and detection information to obtain a value of the magnetic-state parameter based on a result of the reference. The method includes controlling an output of the motor based on the obtained value of the magnetic-state parameter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method for improving estimation accuracy of rotor position of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN106788071AEasy to implementReduce computing burdenElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlControl systemHarmonic
The invention discloses a method for improving the estimation accuracy of the rotor position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of realizing estimation of the rotor position of the permanent magnet synchronous motor by utilizing a pulse-shake high frequency voltage injection method, processing the extracted position estimation error function, eliminating a second harmonic component introduced due to asymmetric motor parameters, so as to obtain a processed position estimation error function, then establishing a phase-locked loop, and adjusting the phase-locked loop to be 0, thus obtaining estimated rotor speed and estimated rotor position. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively inhibit position estimation second harmonic error caused by the asymmetric motor parameters, and the performance of a control system without a position sensor can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
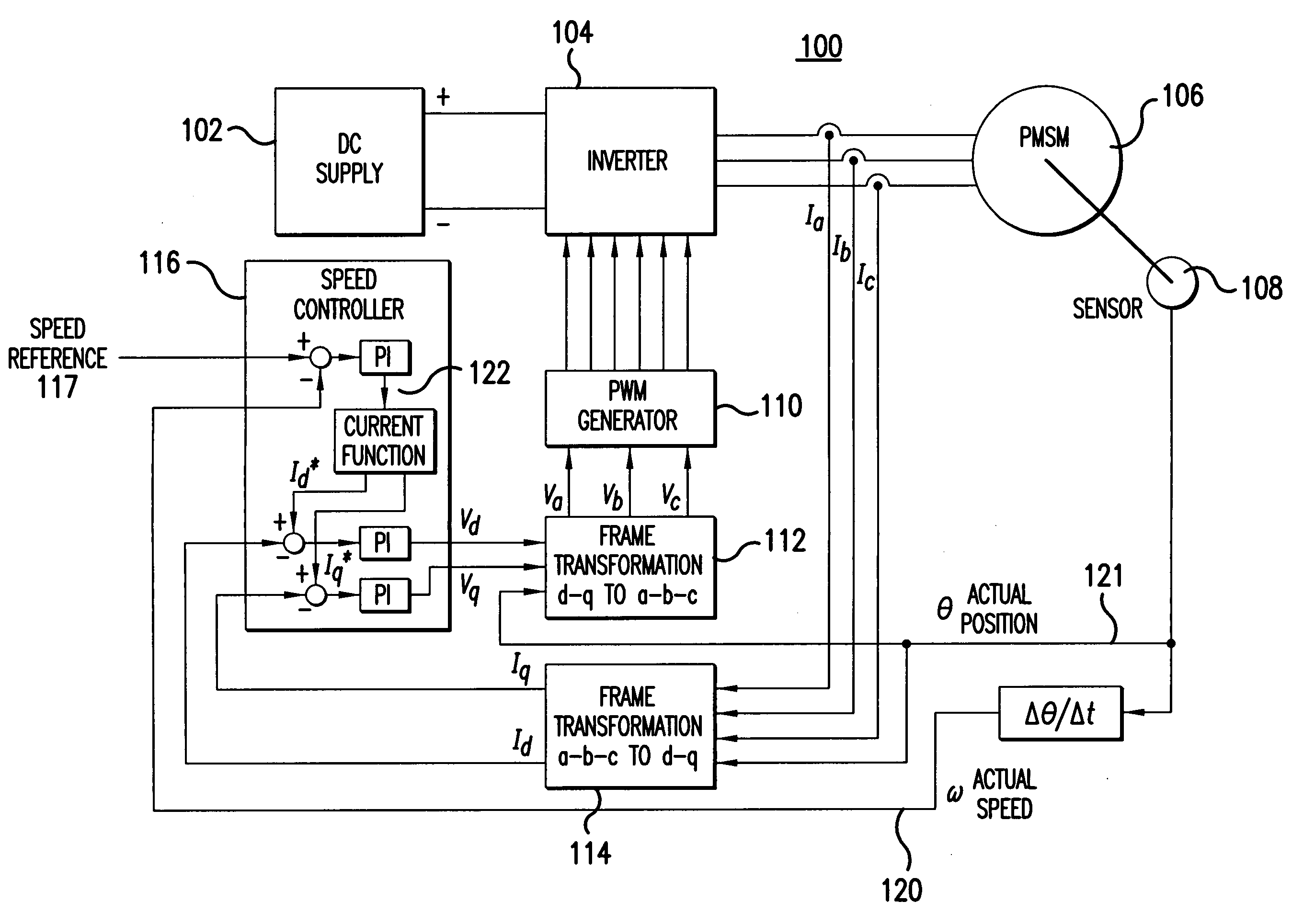
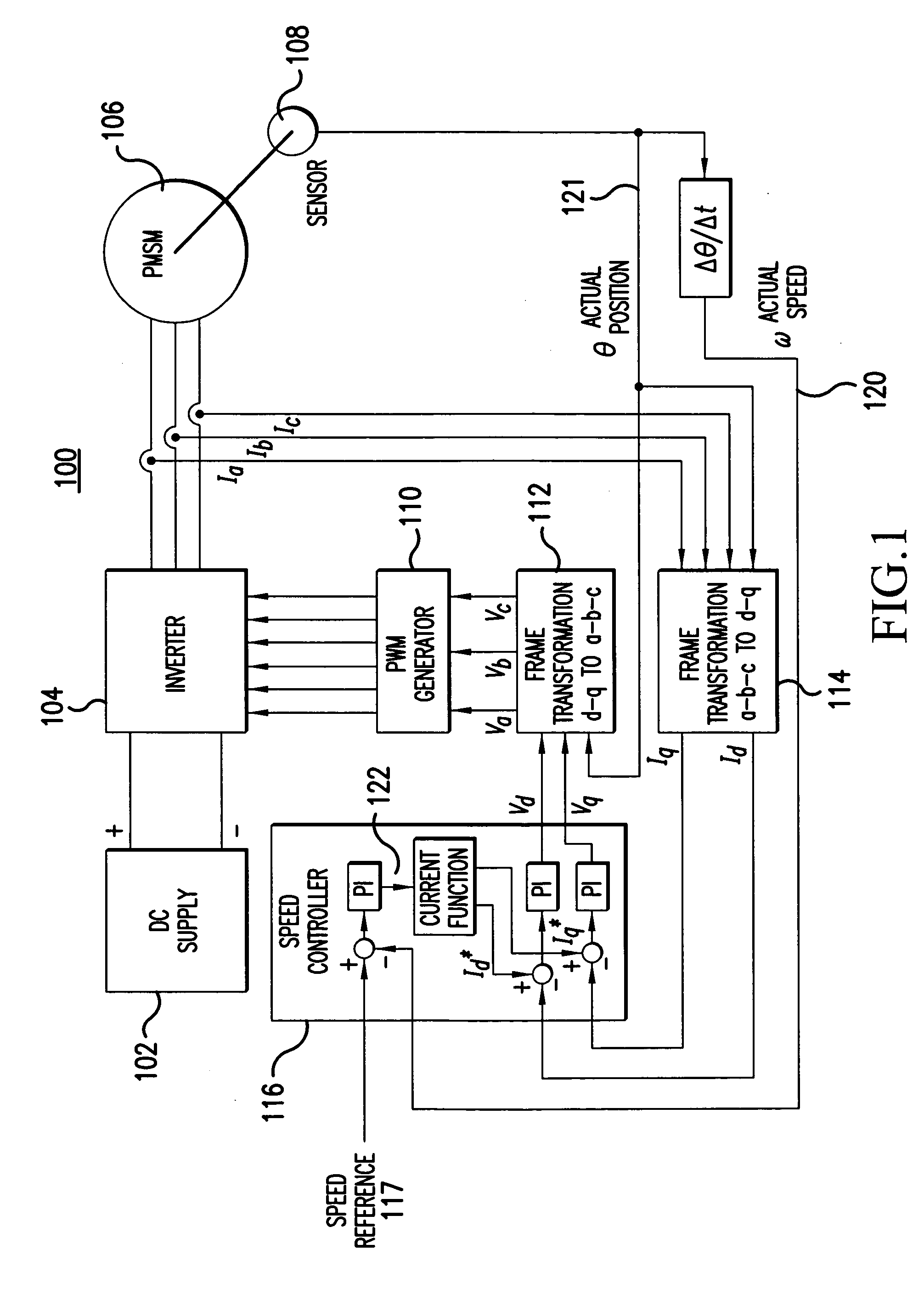
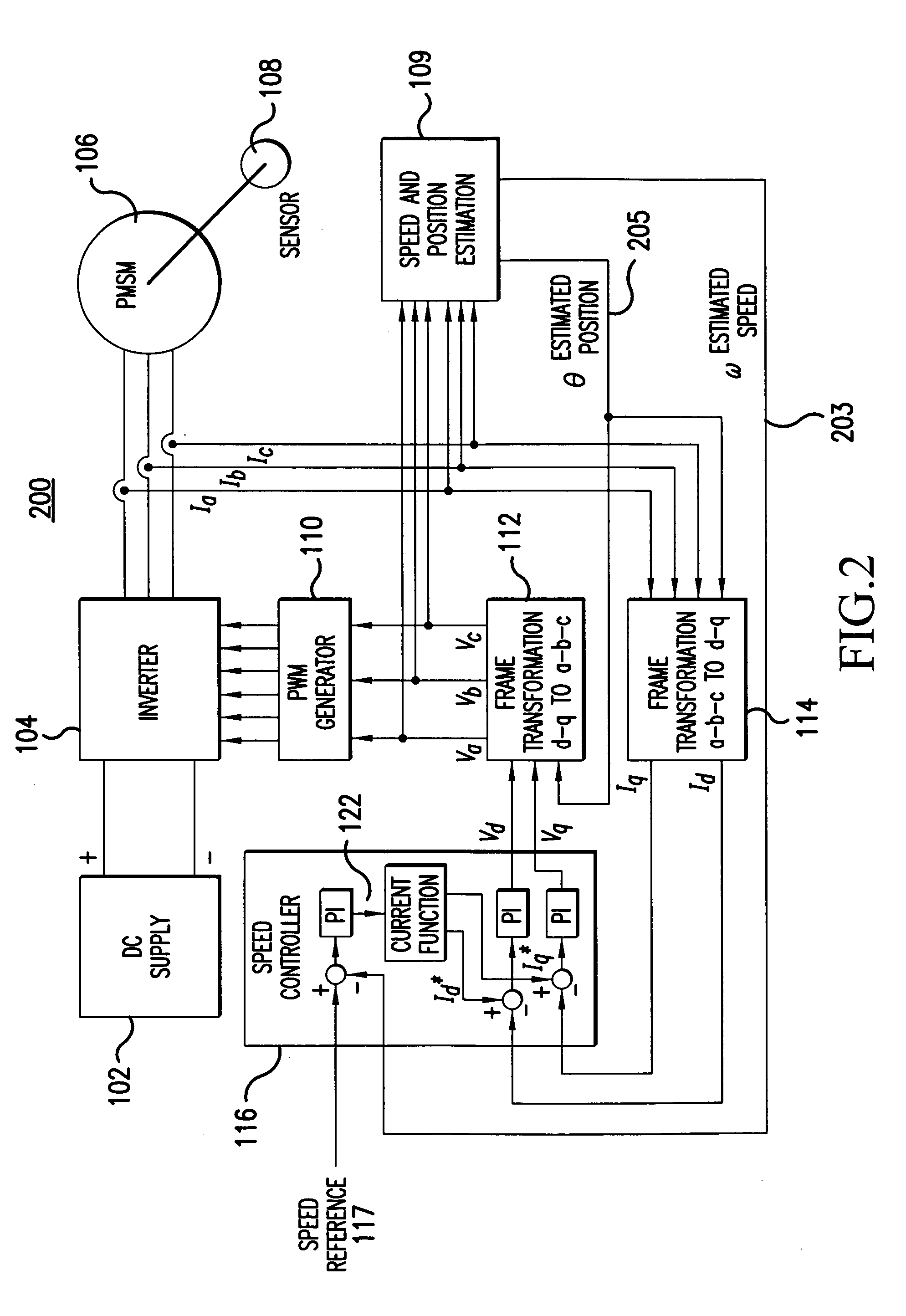
Sensorless control method and apparatus for a motor drive system
InactiveUS20050007044A1Quick calculationAccurate predictionDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlKaiman filterControl power
A method and apparatus provide a state observer control system 600 for a motor 106 that uses an extended Kalman filter 330 to predict initial rotor position and afterwards accurately predict rotor position and / or speed under variable types of loading conditions. A control system model 300 is generated that allows variable setting of an initial rotor position to generate estimated rotor position and speed as outputs. The control system model 300 includes an EKF (extended Kalman filter) estimator 330, speed controller 322, a current controller 324, and a variable load component 310. During operation, EKF estimator 330 estimates rotor speed 327 and position 333 based on reference voltages 402, 404 and currents 1325 generated by speed and current controllers 322, 324 and input from frame transformers 326, 328. Additionally, the reference currents and voltages 402, 404, 1325 are frame-transformed to be used as feedback signals 418, 346 in the system 600 and as drive signals to control power to be applied to a motor load 602.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
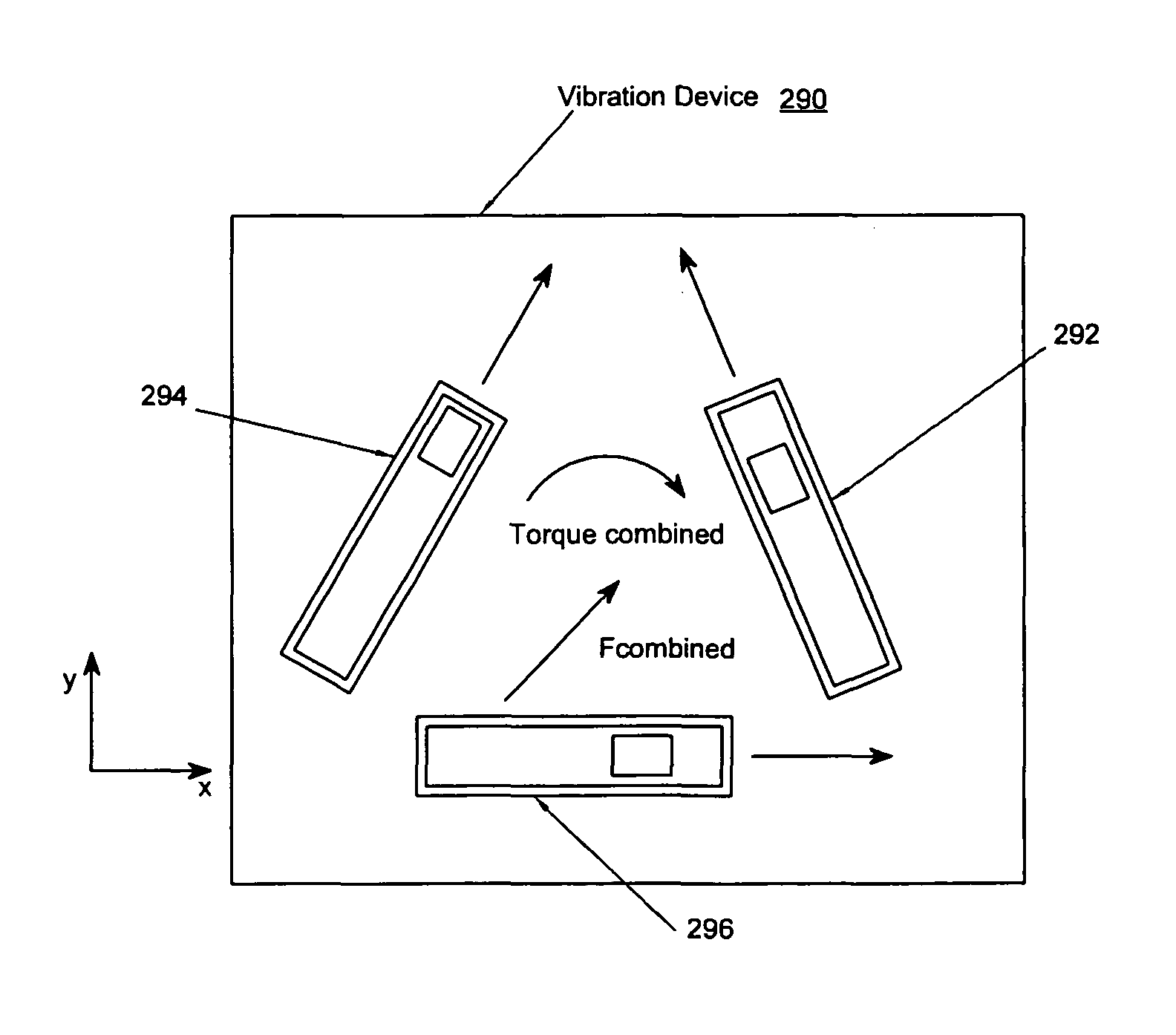
Synchronized vibration device for haptic feedback
ActiveUS7919945B2DC motor speed/torque controlAc-dc conversion without reversalDriver circuitVibration control
The present invention relates to synchronized vibration devices that can provide haptic feedback to a user. A wide variety of actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear actuators, rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller may send signals to one or more driver circuits for directing operation of the actuators. The controller may provide direction and amplitude control, vibration control, and frequency control to direct the haptic experience. Parameters such as frequency, phase, amplitude, duration, and direction can be programmed or input as different patterns suitable for use in gaming, virtual reality and real-world situations.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
Inverter system
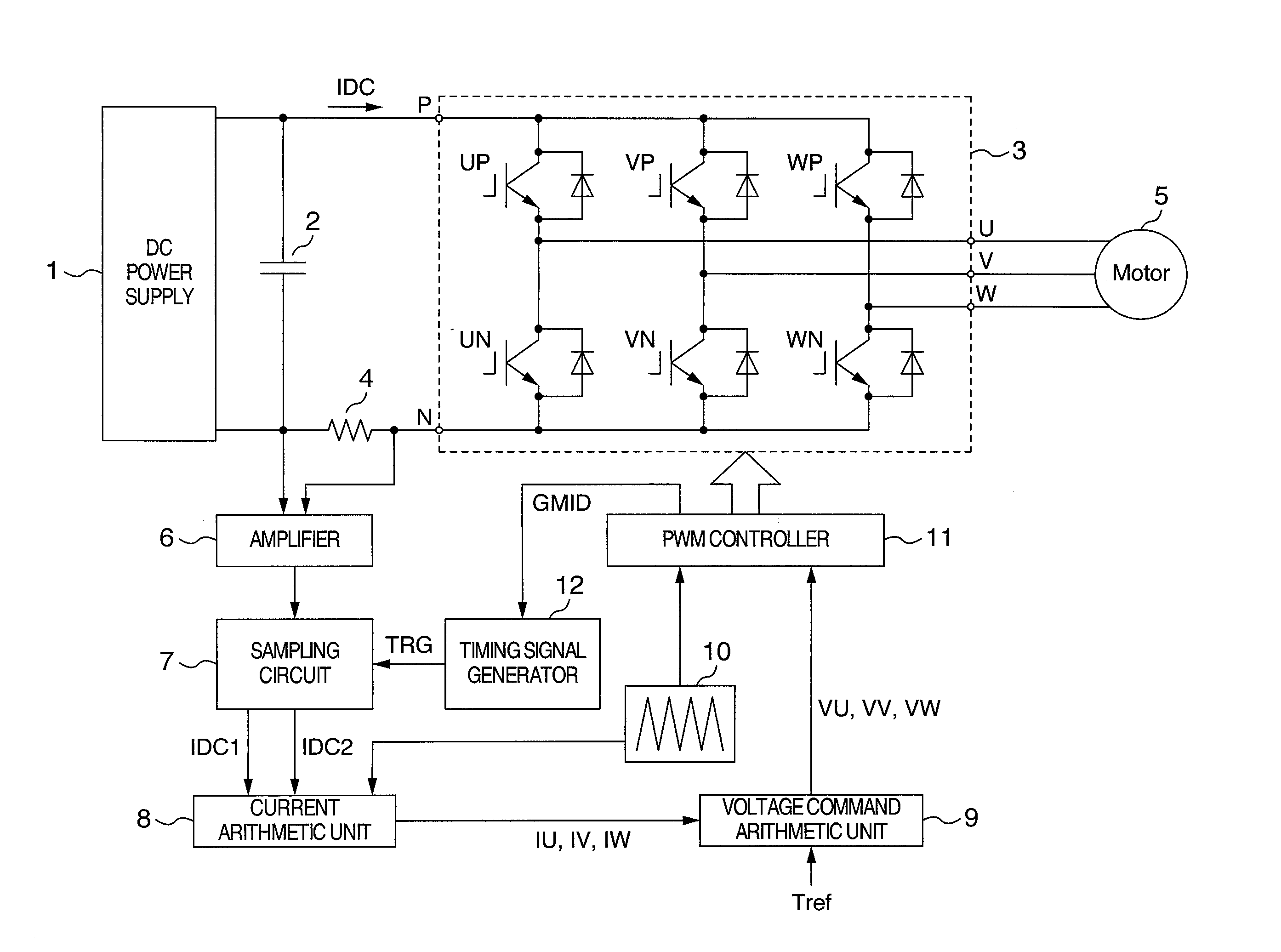
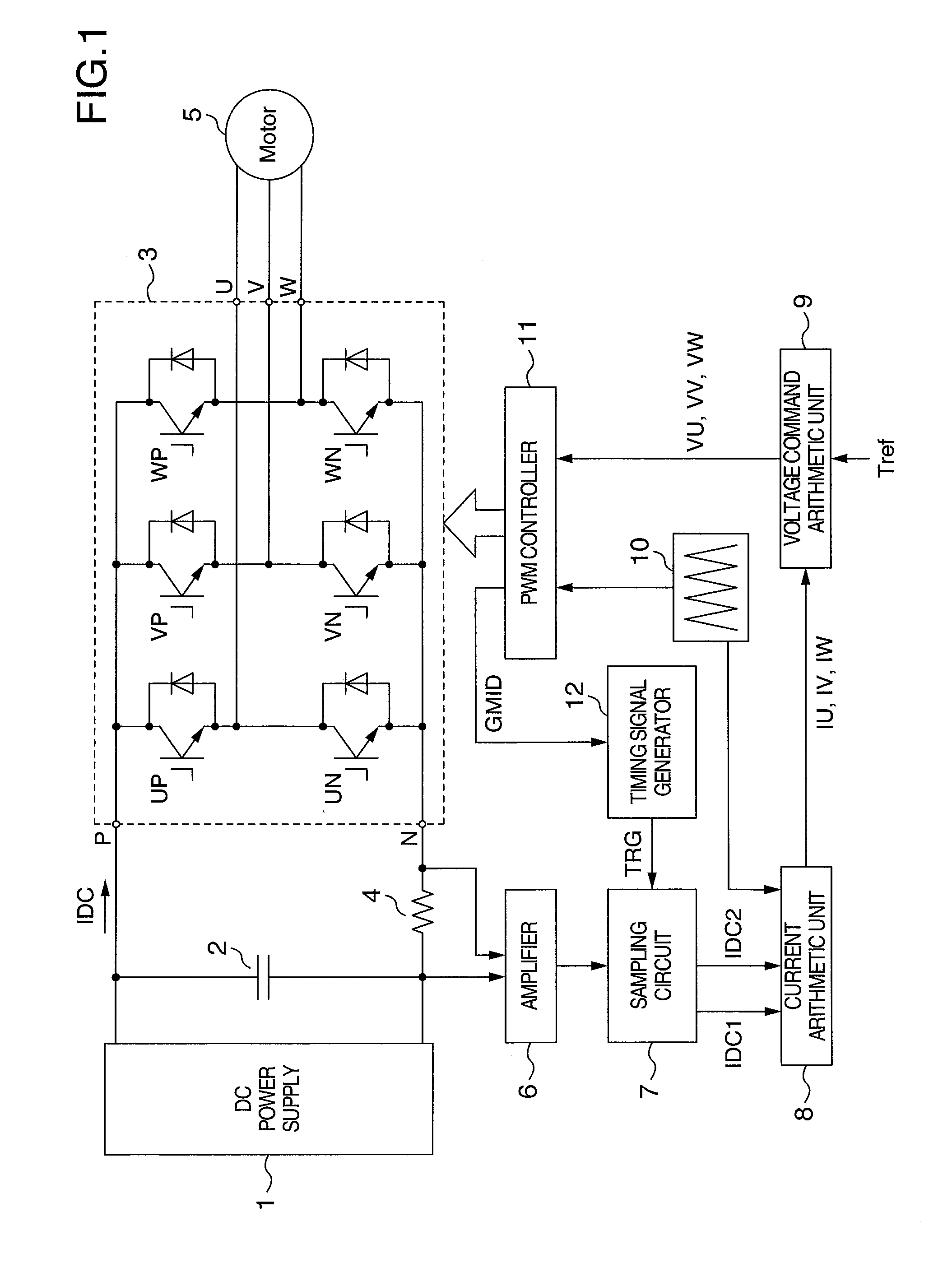
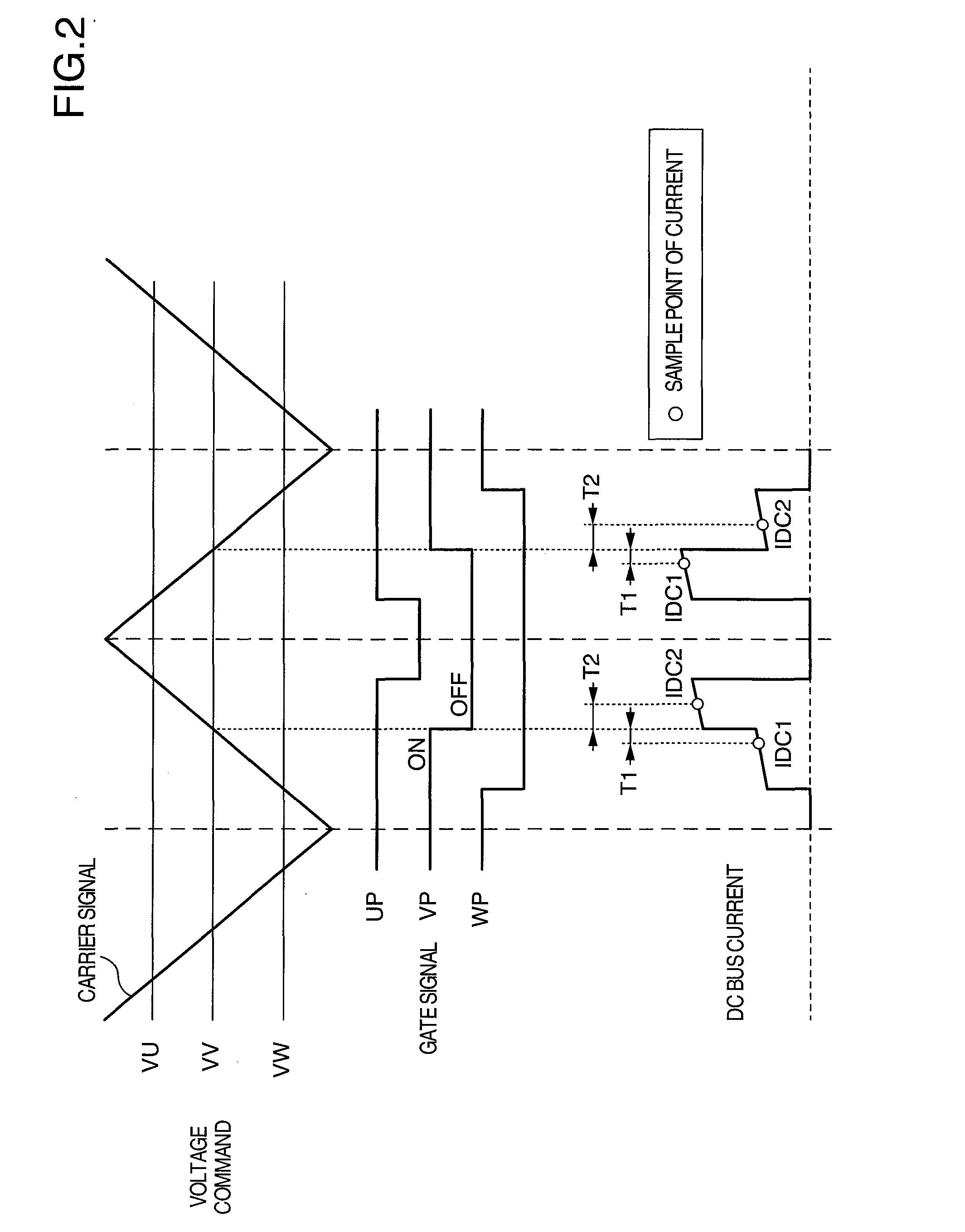
InactiveUS20070241720A1High precisionEfficient processElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlCurrent sampleCarrier signal
When finding a current on an AC side of an inverter by observing that on a DC side, a current that is not affected by pulsating components contained in the AC current must be detected. Timing of change of a gate signal for driving a switch element of a phase having an intermediate magnitude among three-phase voltage command signals to ON / OFF is used as a reference time point for DC bus current detection. DC bus currents sampled T1 before and T2 after the reference time point are designated as IDC1 and IDC2, respectively. A detected current value of a maximum voltage phase is computed by using IDC2 and IDC1 respectively in an increase period and a decrease period of a carrier signal alternately. A detected current value of a minimum voltage phase is computed by using IDC1 and IDC2 respectively in an increase period and a decrease period alternately.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP +1
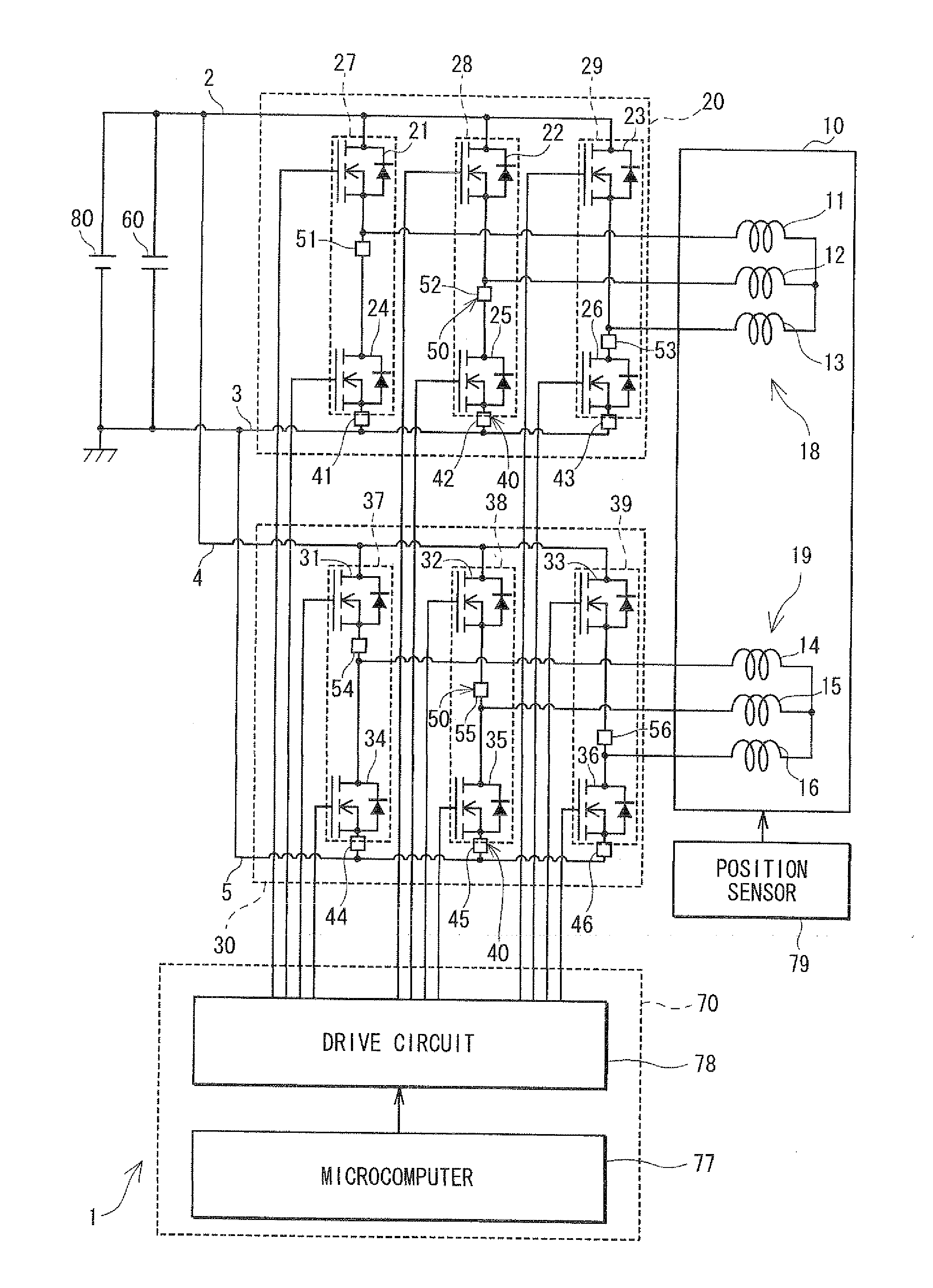
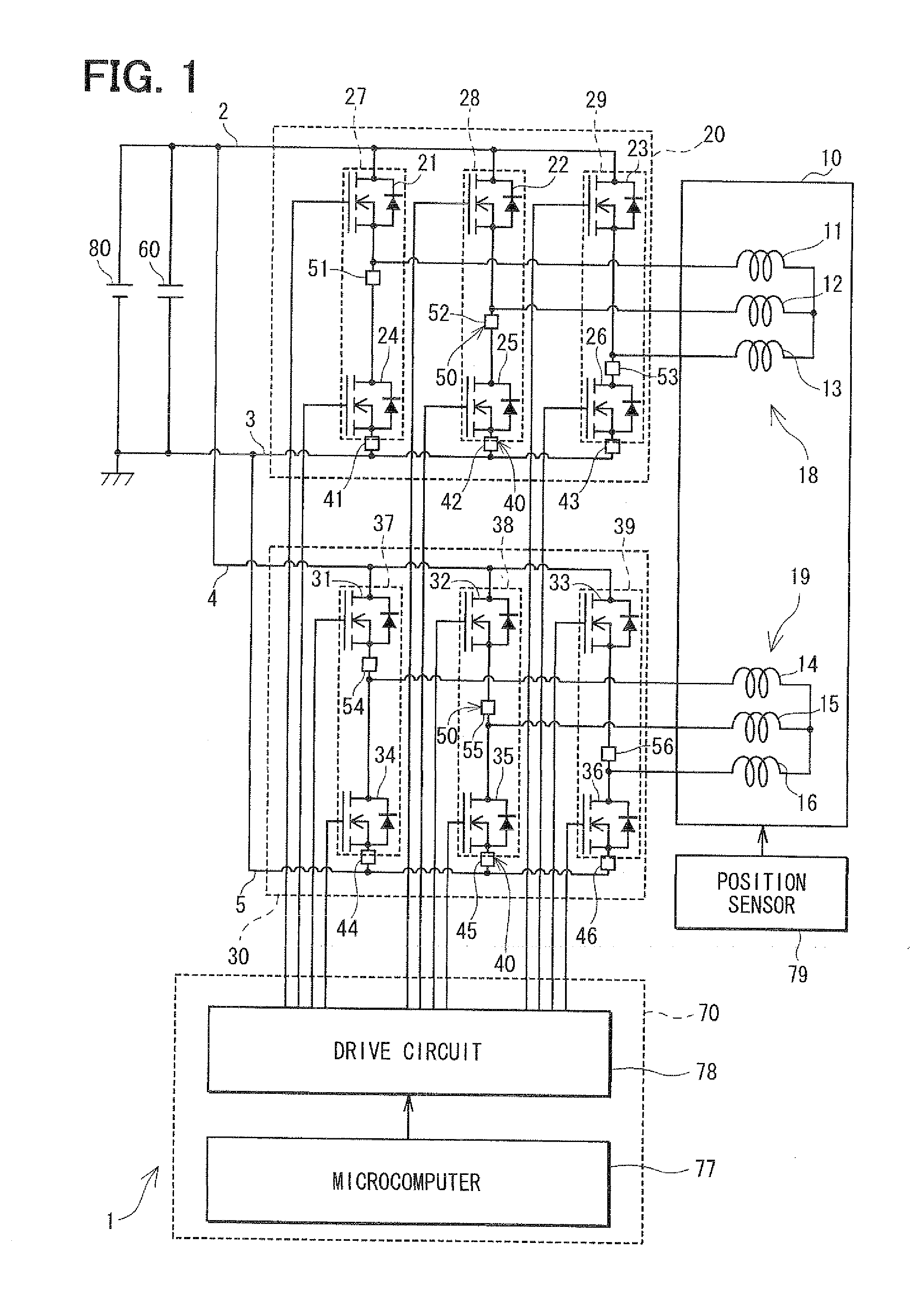
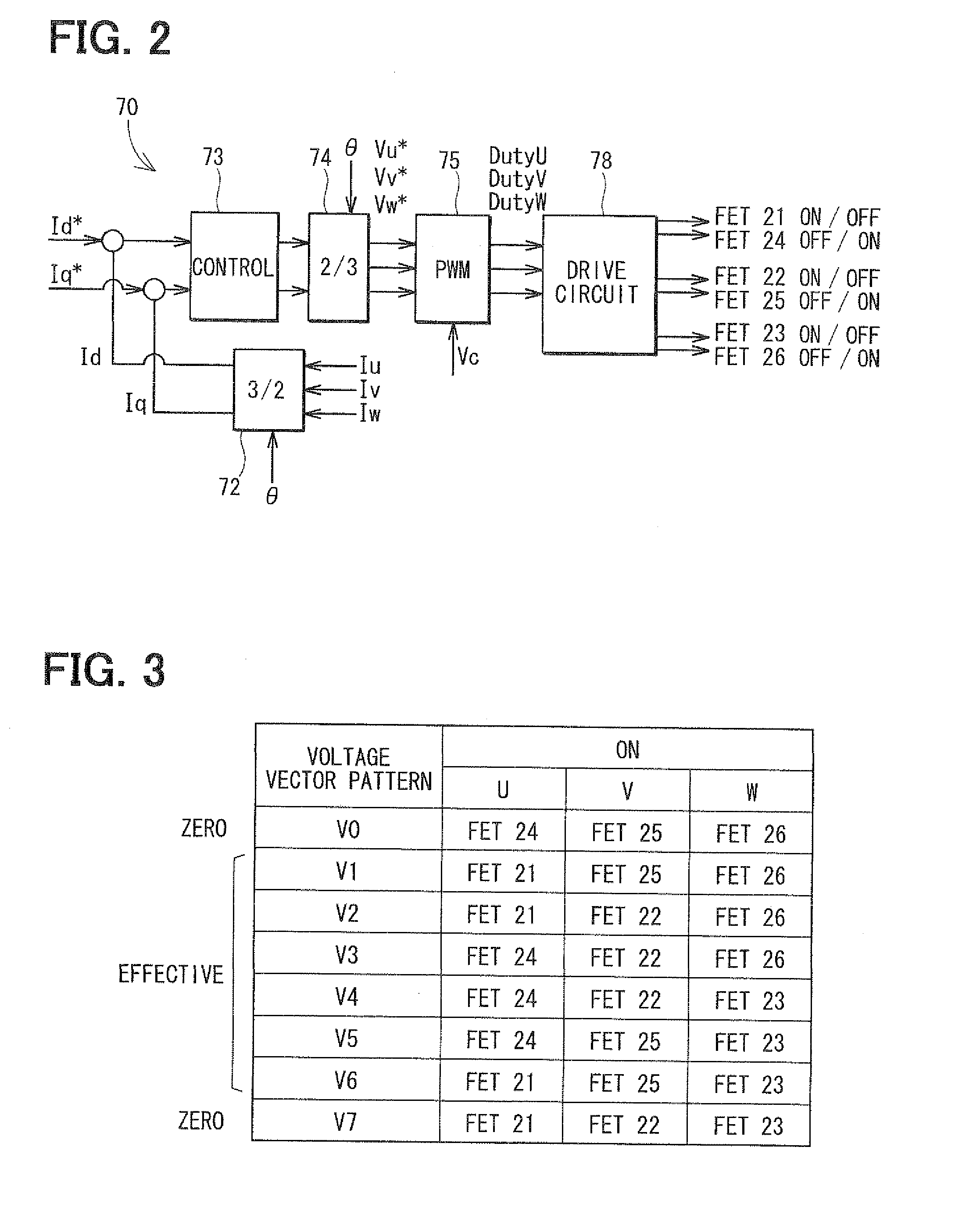
Control apparatus for multi-phase rotary machine and electric power steering system
ActiveUS20110074333A1Smooth rideInhibition effectCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlBrake torqueElectric power steering
A control apparatus for a multi-phase rotary machine includes a control unit and a plurality of power supply systems including respective inverter units. When a short-circuiting failure occurs in one of the systems due to an ON-failure in any one of FETs in an inverter unit of the failure system, the control unit stops driving of the rotary machine by bringing all the FETs in the failure system into the OFF state. The control unit controls FETs of the non-failure system such that a brake torque generated in the failure system is cancelled or the influence of the brake torque exerted on the driving of the motor is reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
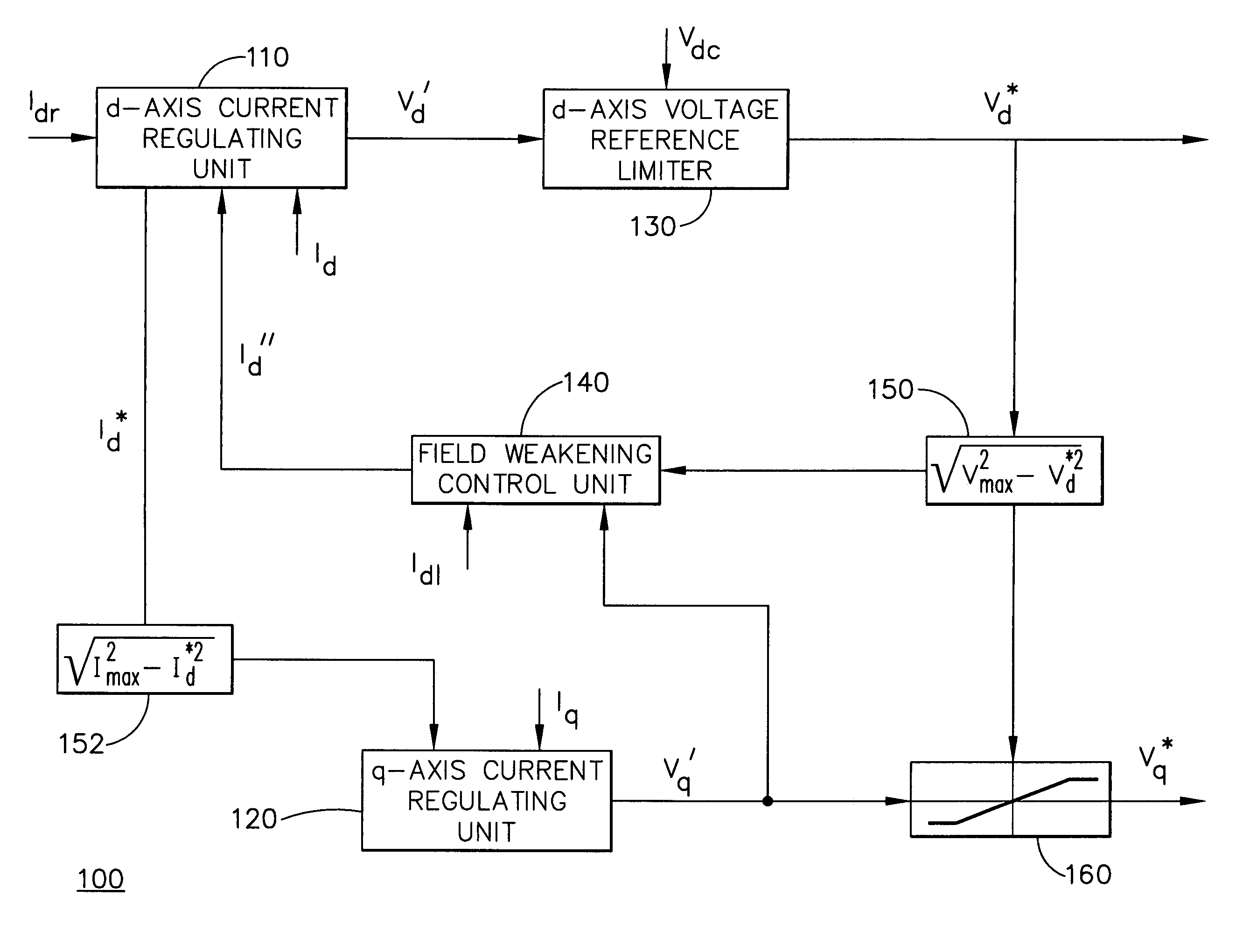
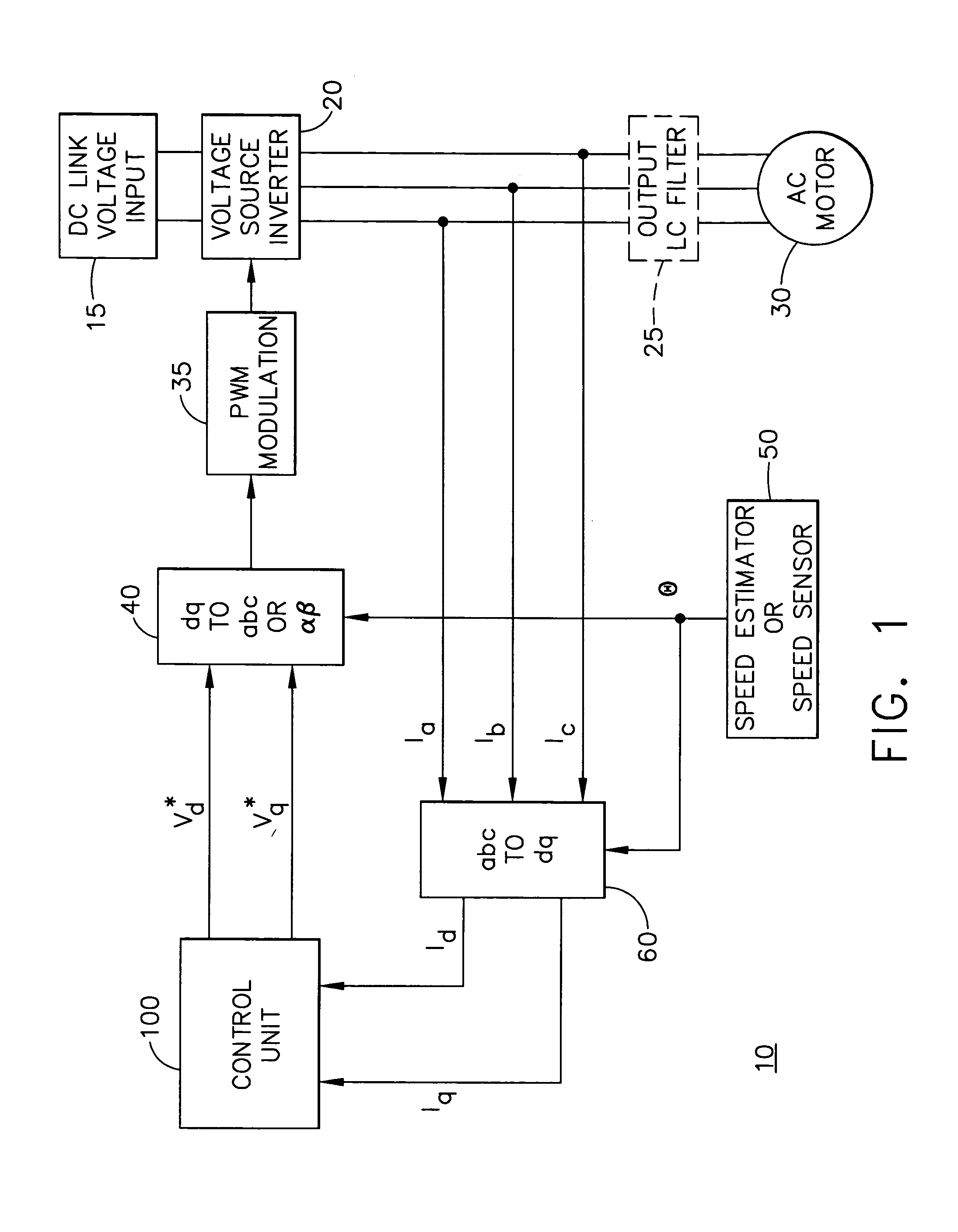
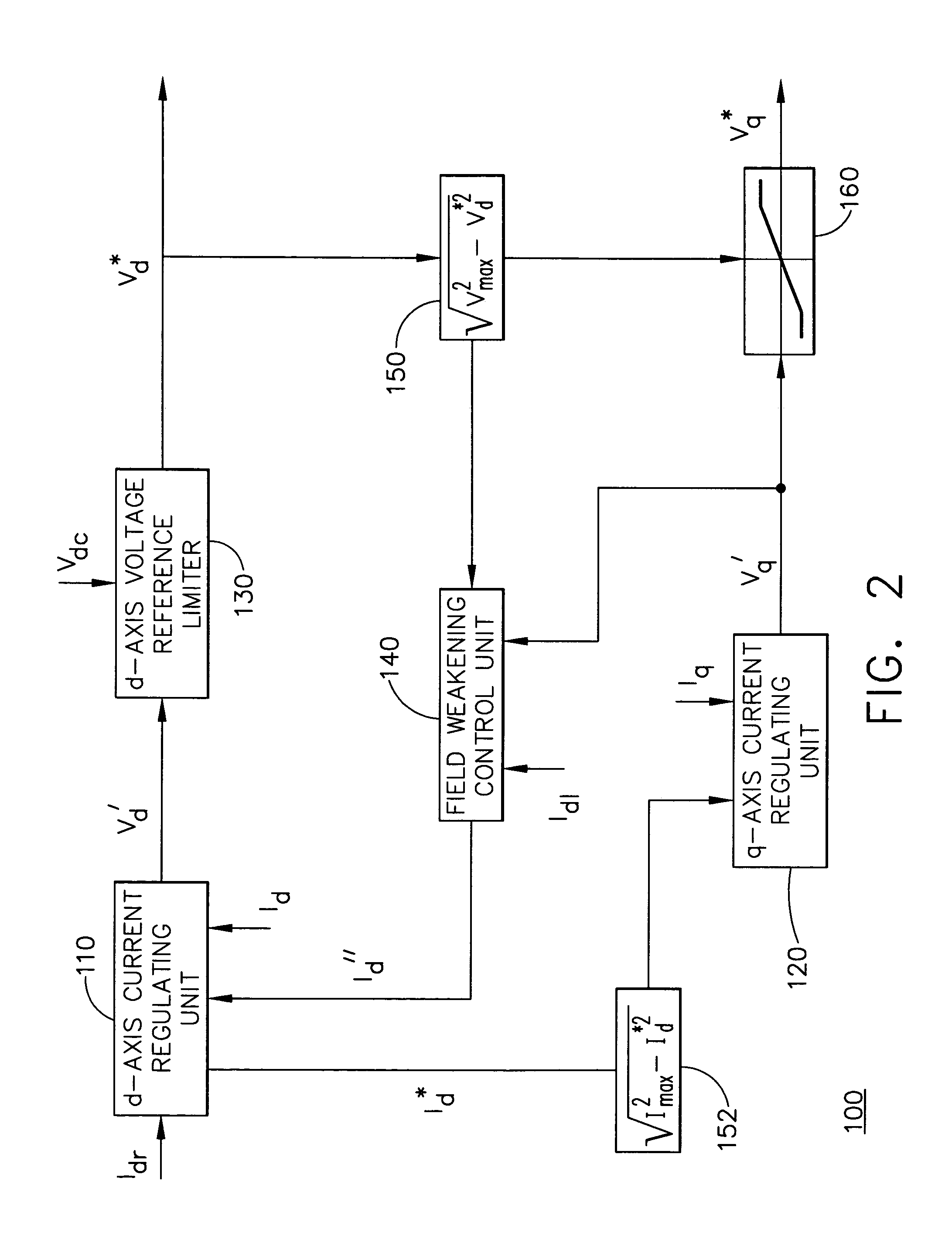
Method and apparatus for field weakening control in an AC motor drive system
InactiveUS6965212B1Reduce selection requirementsElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl signalExcitation current
A method and apparatus control a power converter (20) of an AC motor drive system (10). The method and apparatus: generate a field current regulating signal to control a field current component flowing from the power converter (20) to the AC motor (30), thereby achieving field current regulation; generate a torque current regulating signal to control a torque current component flowing from the power converter (20) to the AC motor (30), thereby achieving torque current regulation, the torque current regulation having lower priority than the field current regulation; and execute a close-loop field weakening control scheme, which generates a field weakening control command as a function of the difference between a torque current regulation voltage demand and voltage available for torque current regulation. The field current regulating signal is adjusted in accordance with the field weakening control signal to selectively reduce back EMF of the AC motor (30), thereby enabling the step of generating a toque current regulating signal to achieve a toque current component needed to drive the AC motor (30) at a desired speed despite a limitation on DC voltage available to the power converter (20).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
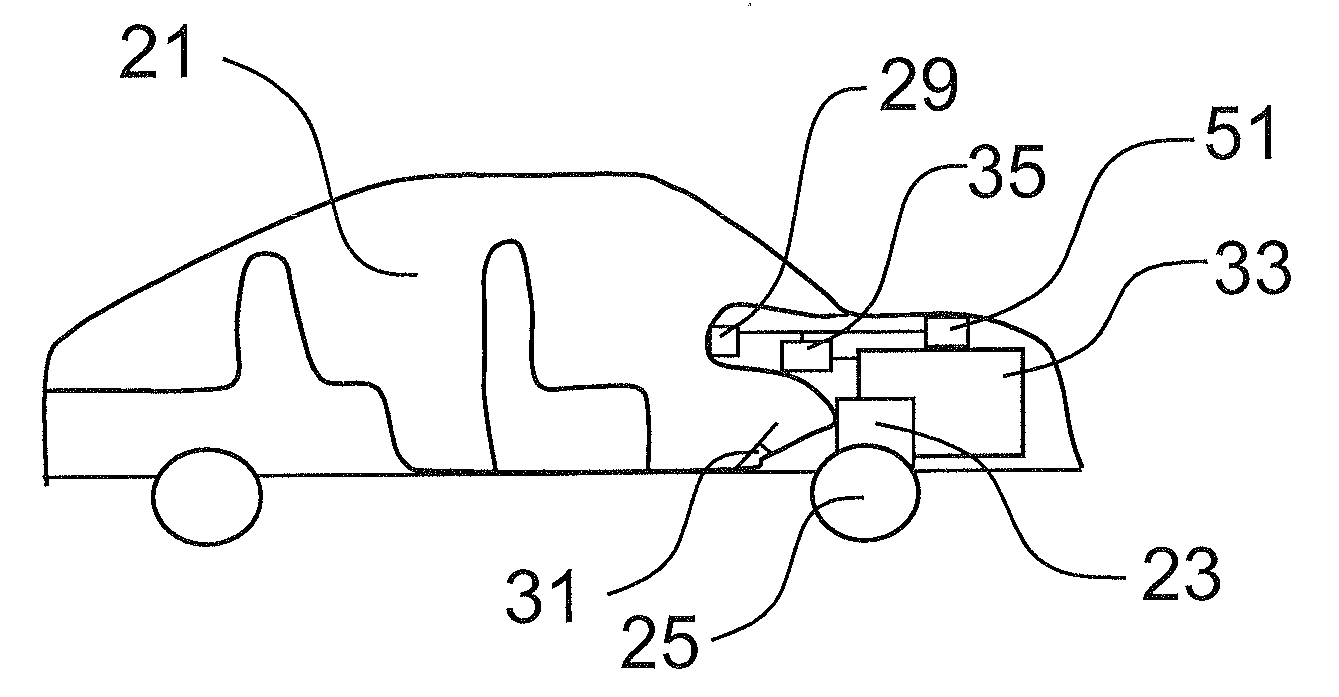
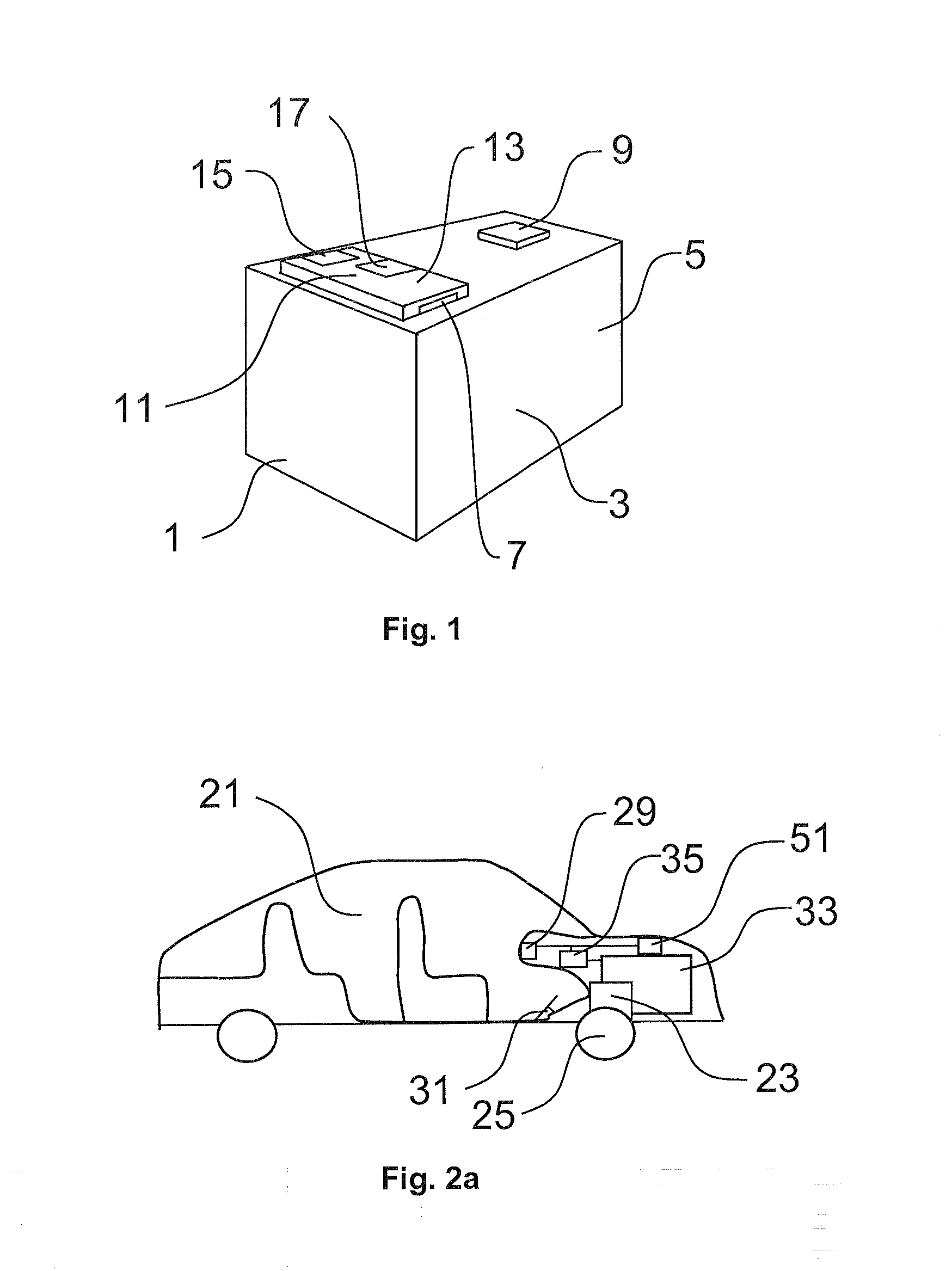
Battery pack with safety device, control device and control method
InactiveUS20120229056A1Reduce decreaseReduce riskVector control systemsPropulsion by batteries/cellsControl signalEngineering
A battery pack (33) includes at least one battery cell (39), and is designed to supply an output voltage for feeding electric energy to a load (23) so that the load may perform a function. A battery control device (35) arranged to generate control signals for controlling a battery pack, a device (21) including a battery pack, and a method for controlling a battery pack are also described.
Owner:HDD SERVO MOTORS
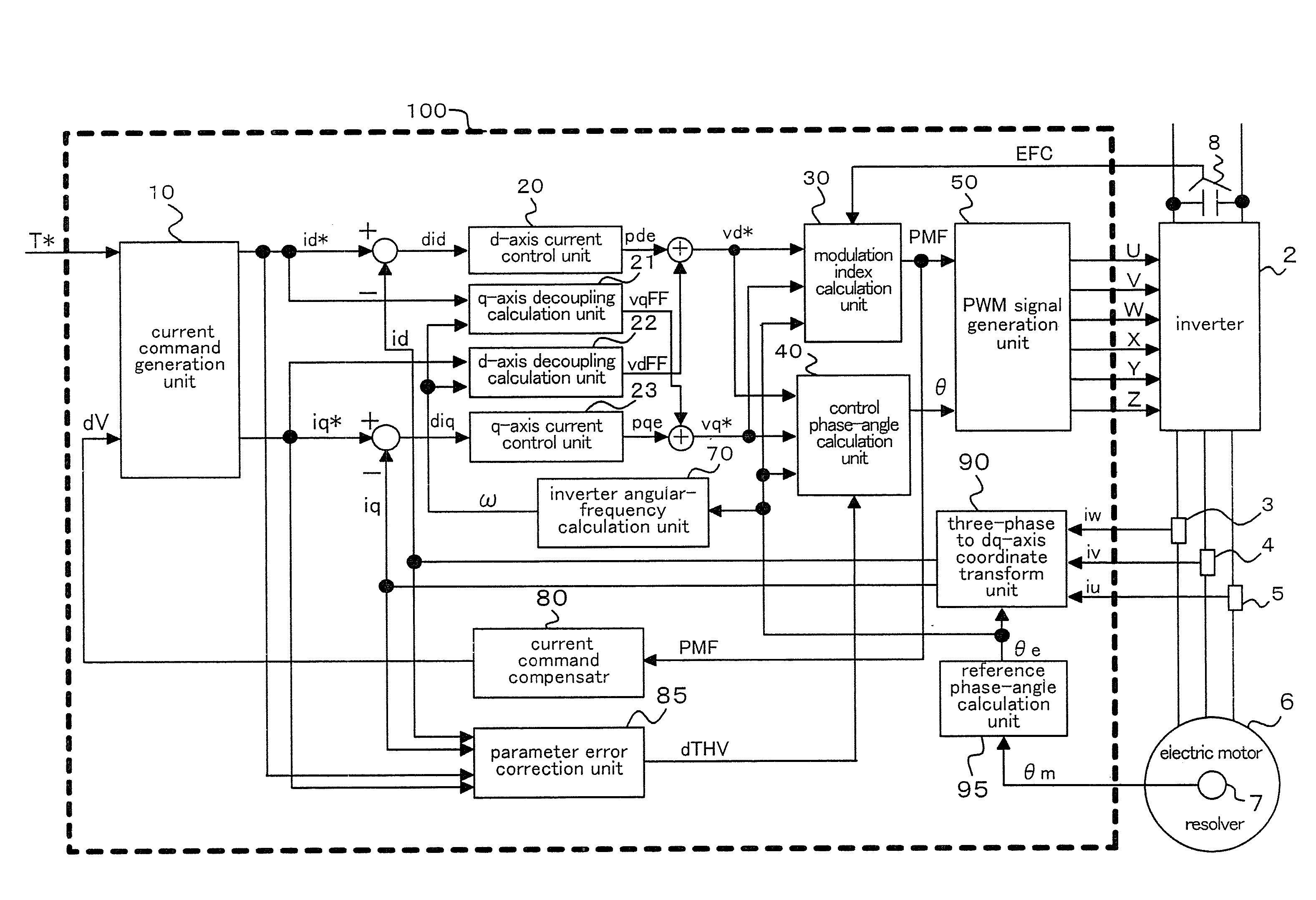
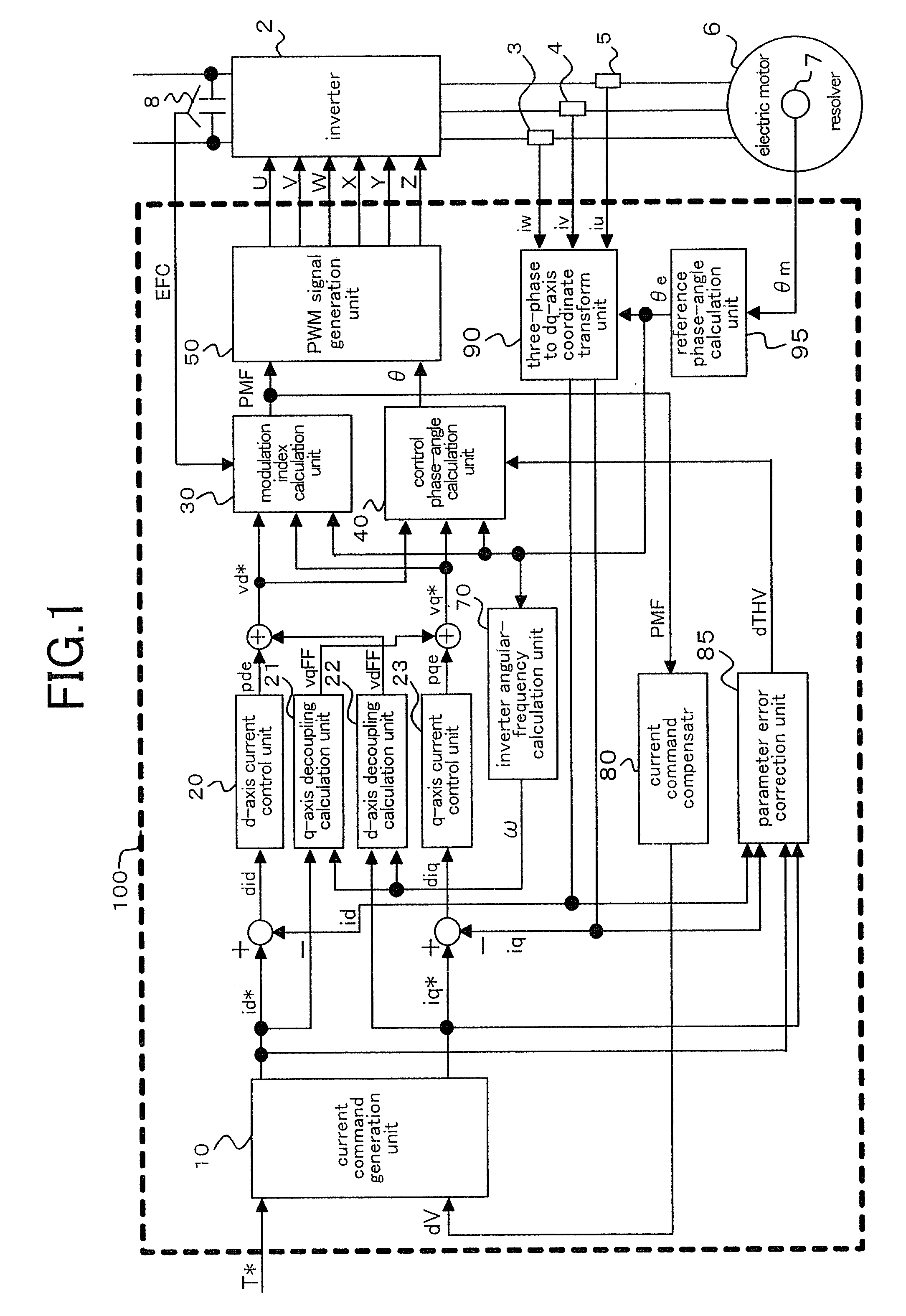
Vector controller for permanent-magnet synchronous electric motor
InactiveUS20100066283A1High speed rangeIncrease rangeDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPulsed mode
A method of controlling a current command by comparing voltage with a set value needs to vary the set value depending on voltage fluctuation, which involves taking a complicated control. A vector controller for a permanent-magnet synchronous electric motor, according to the present invention, can realize with a simplified configuration a field-weakening operation in a one-pulse mode in a high speed range by providing a current command compensator that corrects a current command by a corrected current command calculated based on a modulation index.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Unified power control method of double-ended inverter drive systems for hybrid vehicles
A method of providing a unified power control of a motor including providing a first inverter system, a second inverter system, and a motor coupled therebetween; coupling the first inverter system coupled to a first energy source; coupling the second inverter system coupled to a secondary energy source; generating a first pulse width modulated signal; and generating a second pulse width modulated signal. The first inverter system and the second inverter system are driven with the first pulse width modulated signal and the second pulse width modulated signal respectively in order to control a fundamental component of an output voltage of the first inverter system and the second inverter system to control the motor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Motor drive apparatus, electric actuator and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20060001392A1Increase driving speedHigh areaTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringHigher order harmonics
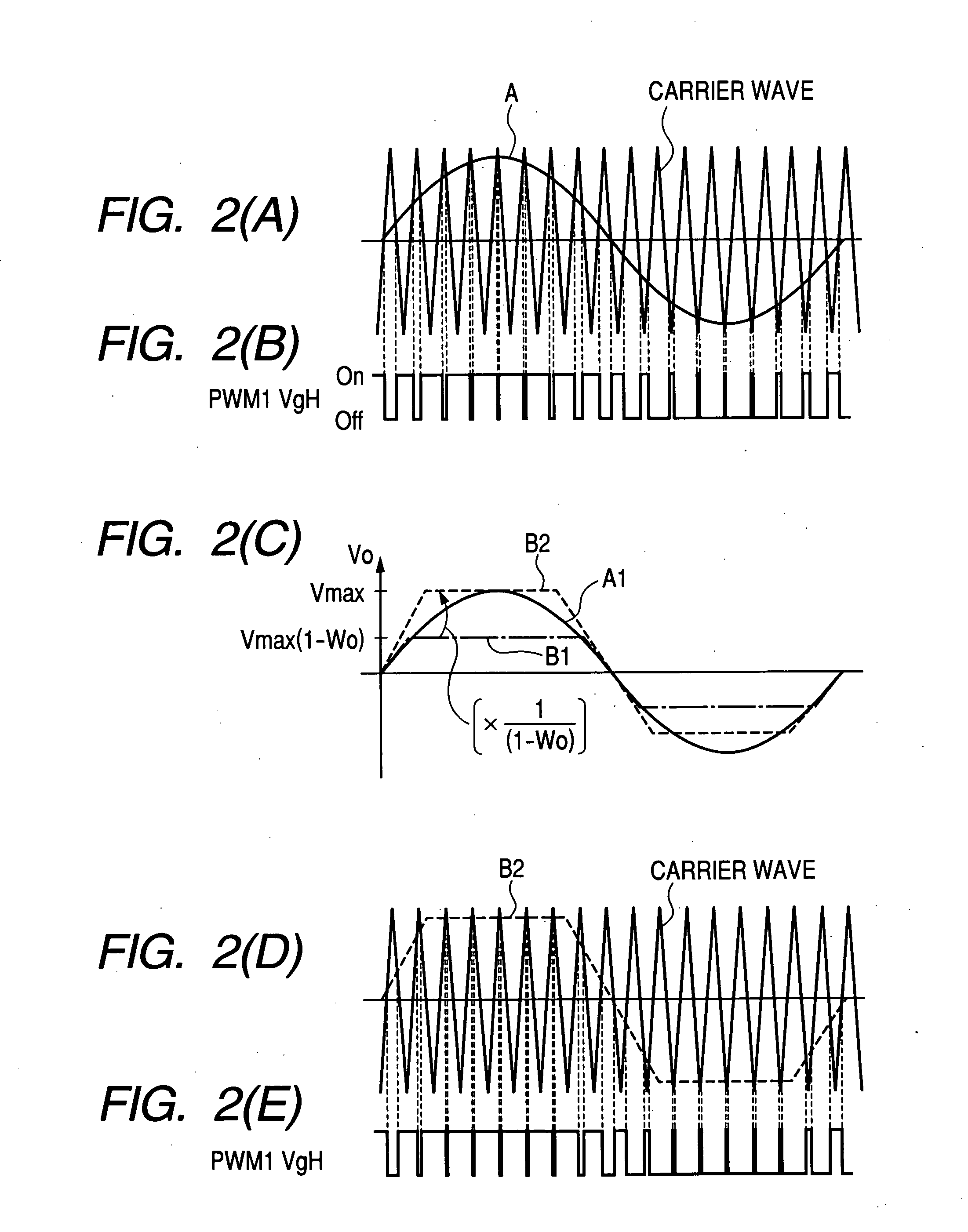
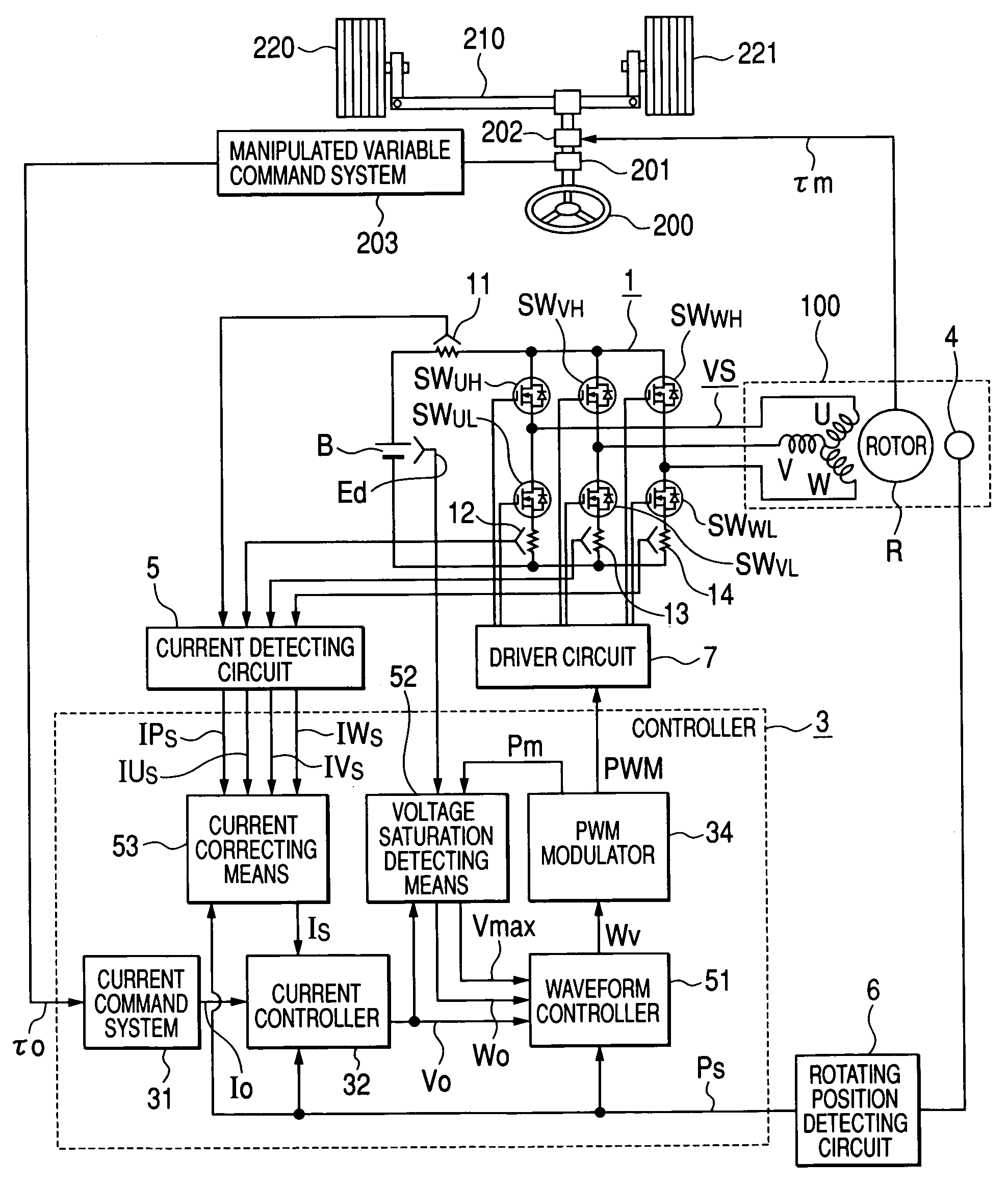
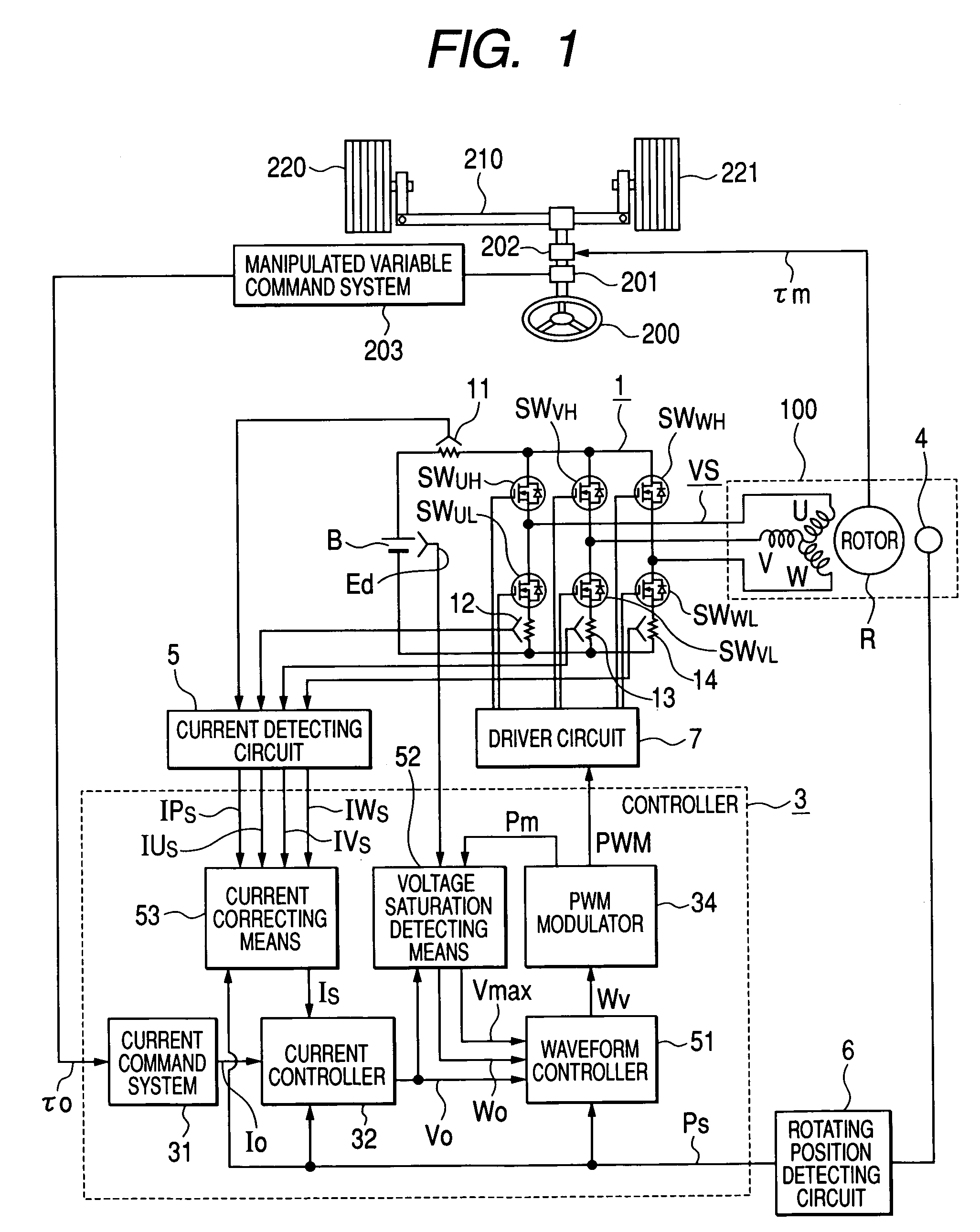
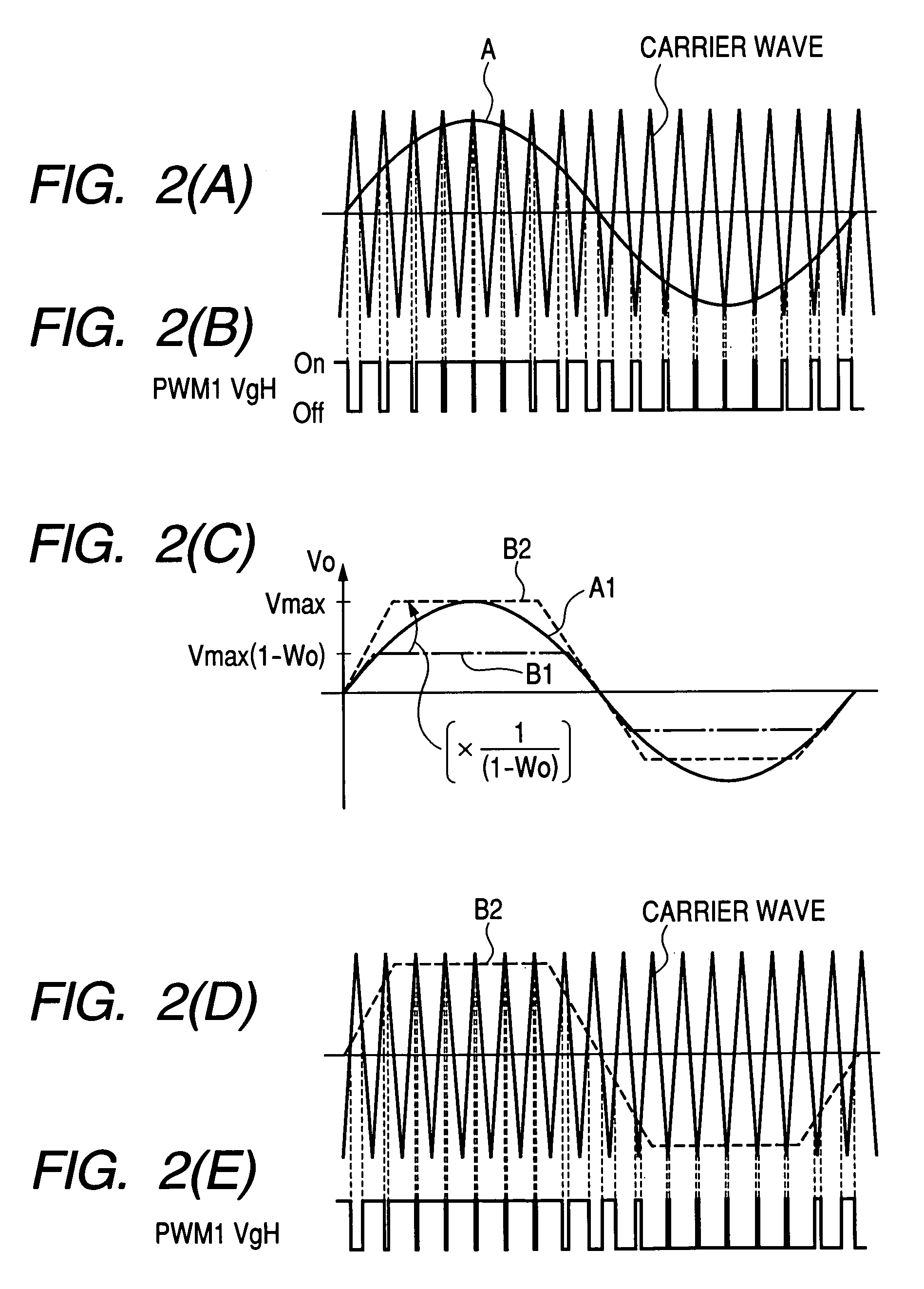
In an operation range of an actuator subjected to quick acceleration and deceleration, a motor drive apparatus, an electric actuator and an electric power steering apparatus capable of continuous torque control up to the high drive speed and high torque area. A controller comprises a voltage saturation detecting means for detecting the voltage saturation of the output voltage of an inverter circuit, based on the battery voltage, and a waveform controller that converts the drive waveform of the inverter circuit into the waveform created by superimposing harmonics of high odd-numbered order on a sinusoidal wave as a fundamental wave of the modulated wave modulated by a PWN carrier wave; and continuously changes the ratio of superimposing the high-order harmonics in response to the voltage saturation detected by a voltage saturation detecting means. This arrangement allows the controller to continuously change the drive waveform of the inverter circuit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Motor drive apparatus, electric actuator and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS7161323B2Increase torqueTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringMotor drive
The disclosure concerns a a motor drive apparatus, an electric actuator and an electric power steering apparatus capable of continuous torque control up to the high drive speed and high torque area, in order to enable quick acceleration and deceleration. A controller comprises a voltage saturation detecting apparatus for detecting the voltage saturation of the output voltage of an inverter circuit, based on the battery voltage, and a waveform controller that converts the drive waveform of the inverter circuit into the waveform created by superimposing harmonics of high odd-numbered order on a sinusoidal wave as a fundamental wave of the modulated wave modulated by a PWN carrier wave; and continuously changes the ratio of superimposing the high-order harmonics in response to the voltage saturation detected by a voltage saturation detecting means. This arrangement allows the controller to continuously change the drive waveform of the inverter circuit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
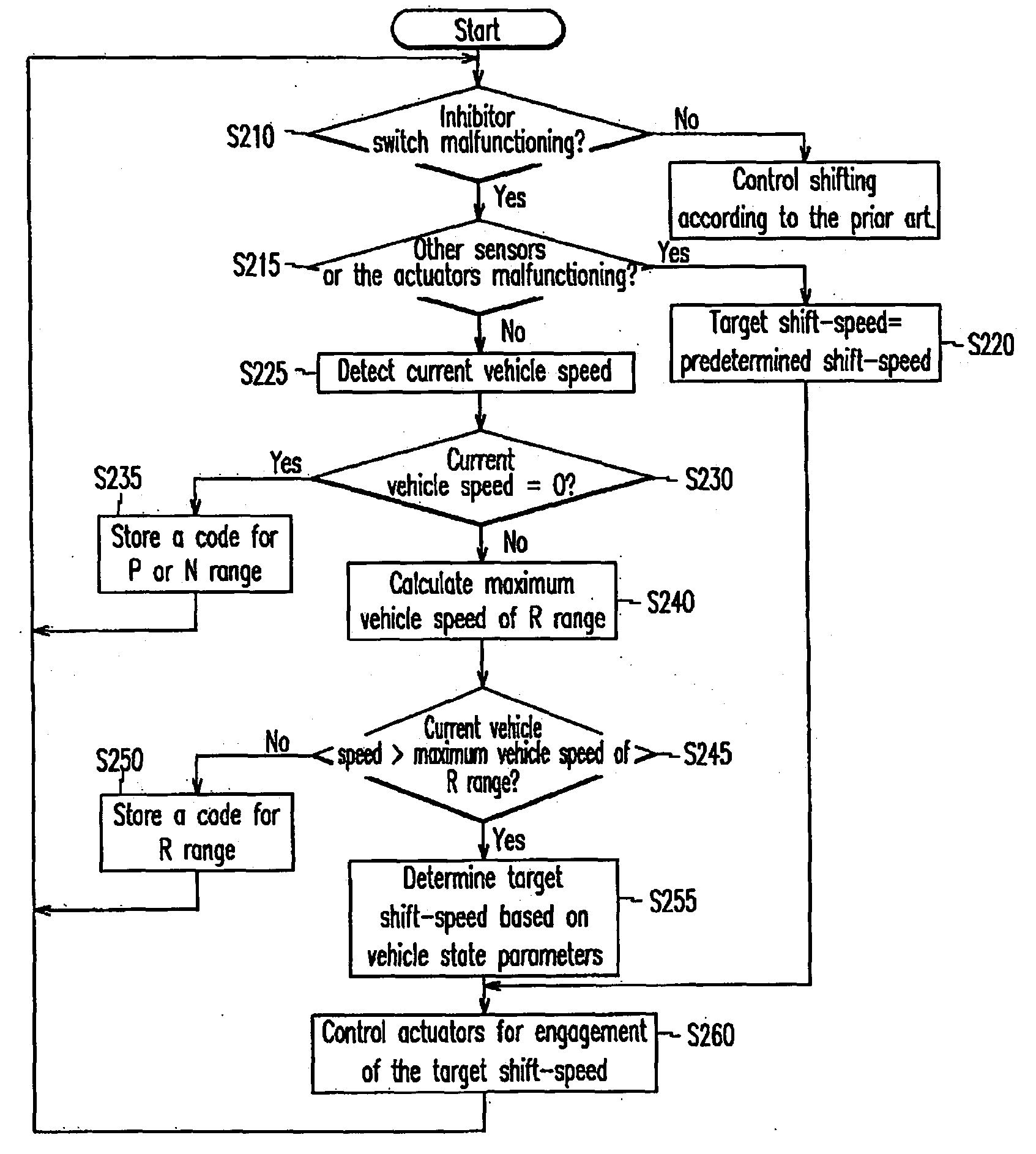
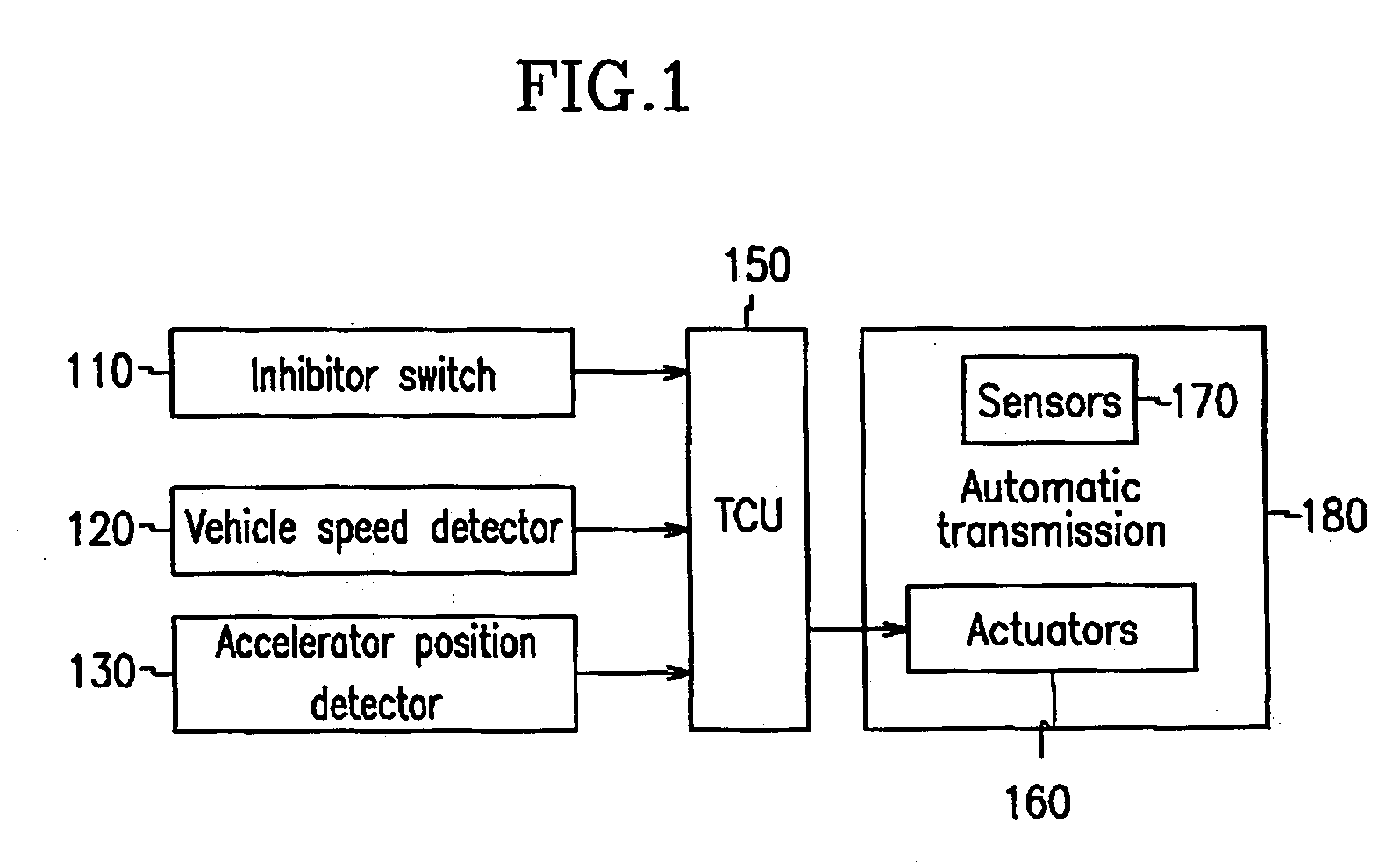
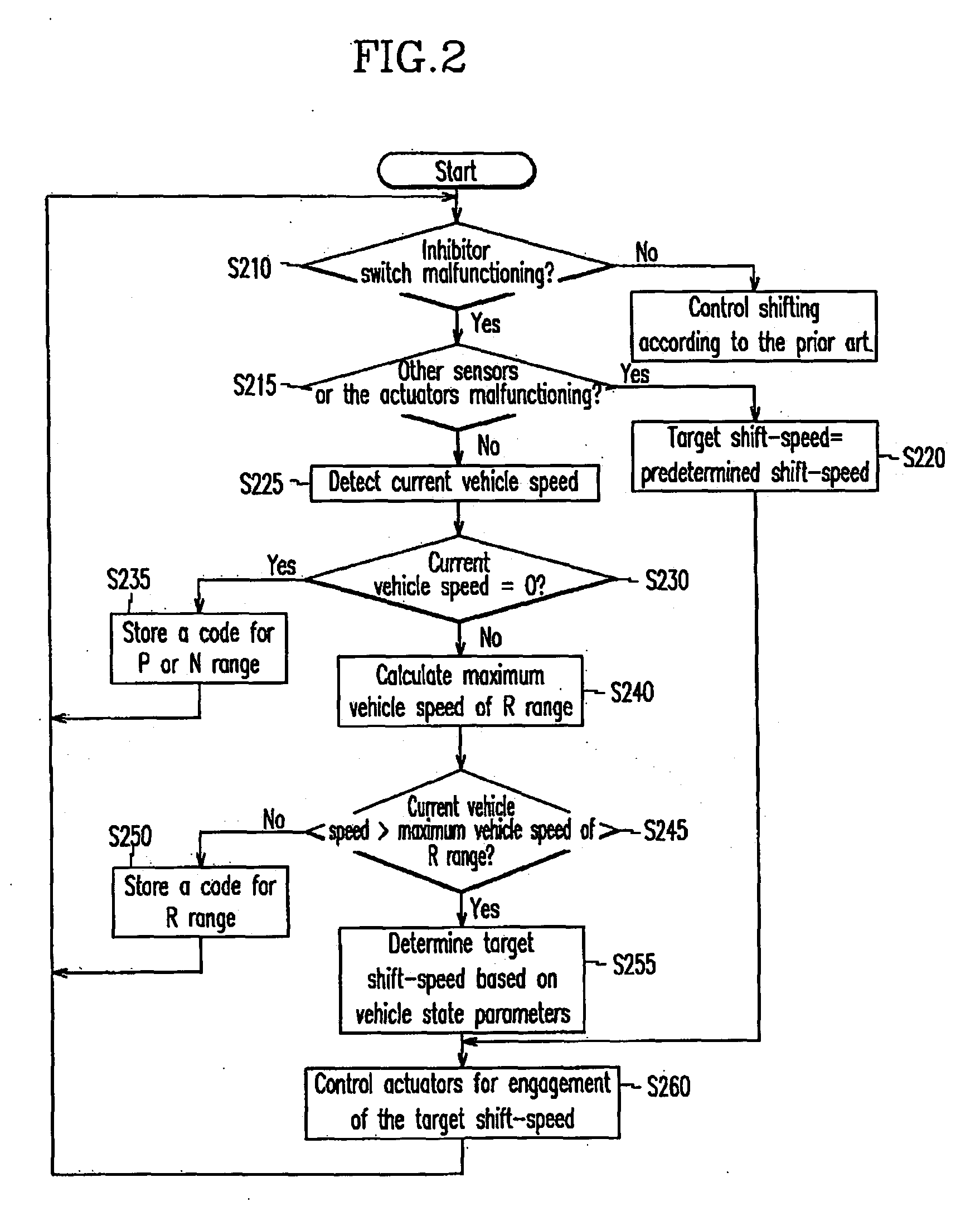
Shift control method and apparatus of an automatic transmission
InactiveUS20050075776A1Digital data processing detailsToothed gearingsAutomatic transmissionState parameter
In the case of malfunctioning of an inhibitor switch of an automatic transmission, a current vehicle speed is compared with a maximum vehicle speed of a reverse speed when the current vehicle speed is other than 0. The transmission is then controlled to a target shift-speed determined on the basis of vehicle driving state parameters, when the current vehicle speed is higher than the maximum vehicle speed of the reverse speed.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
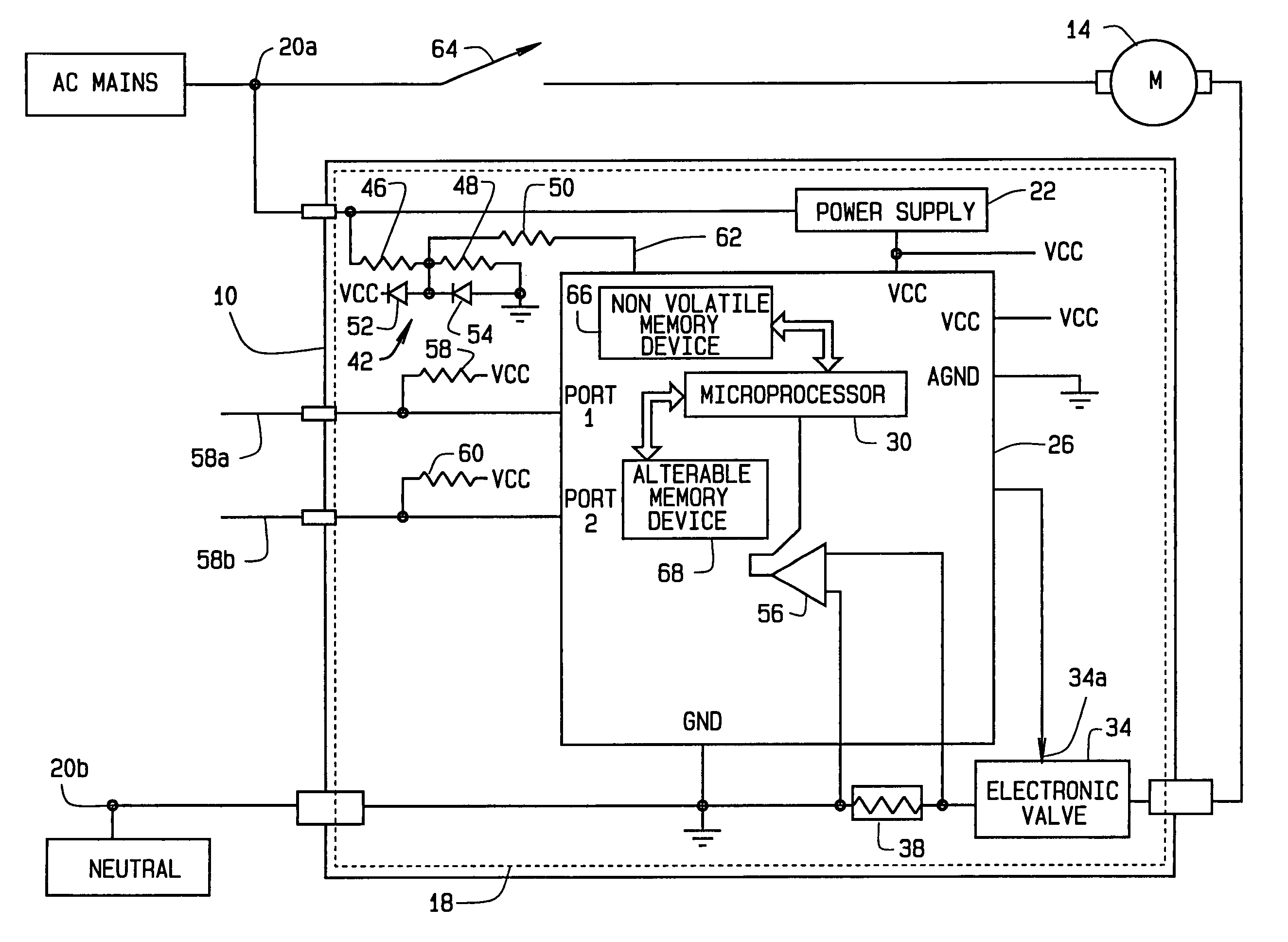
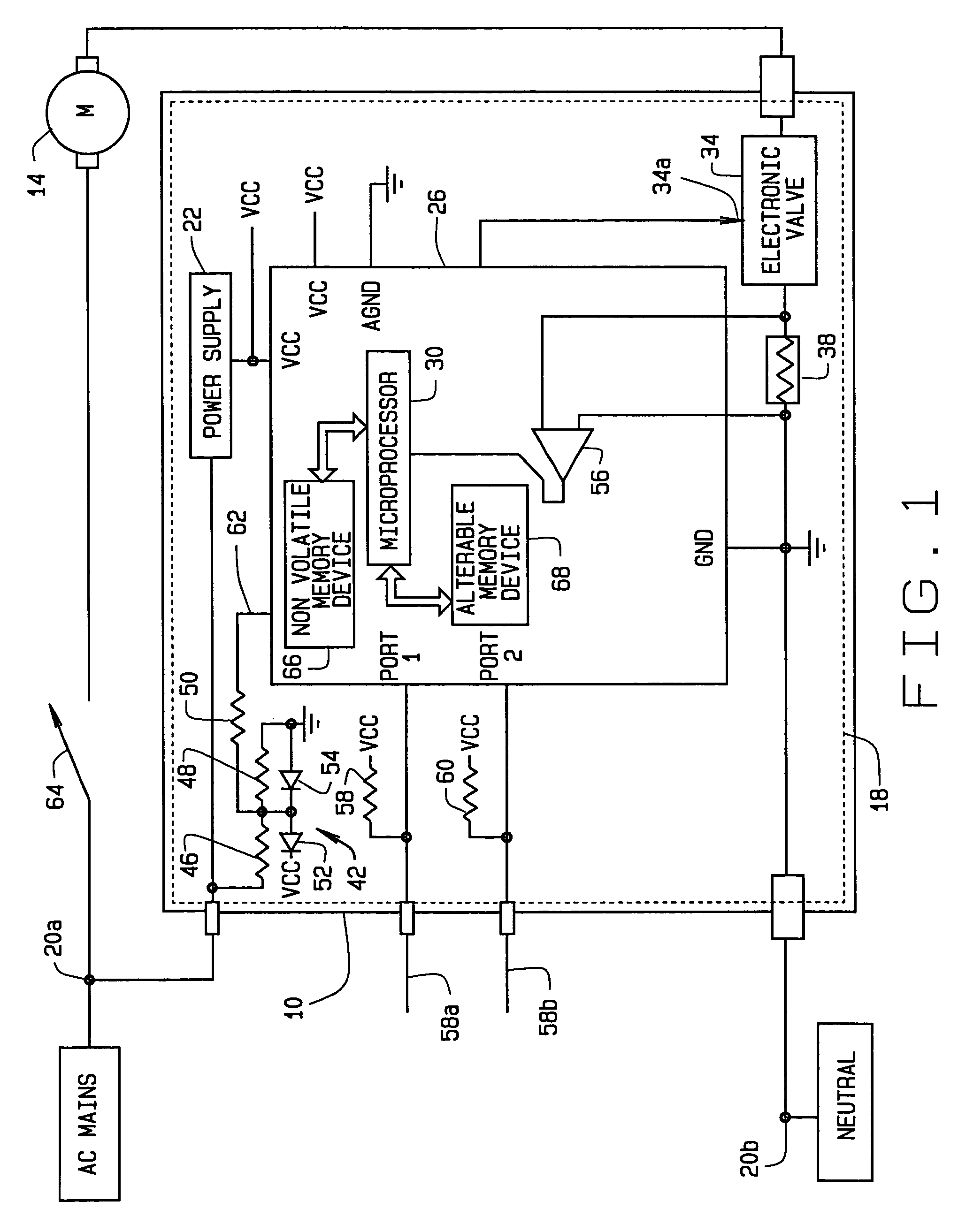
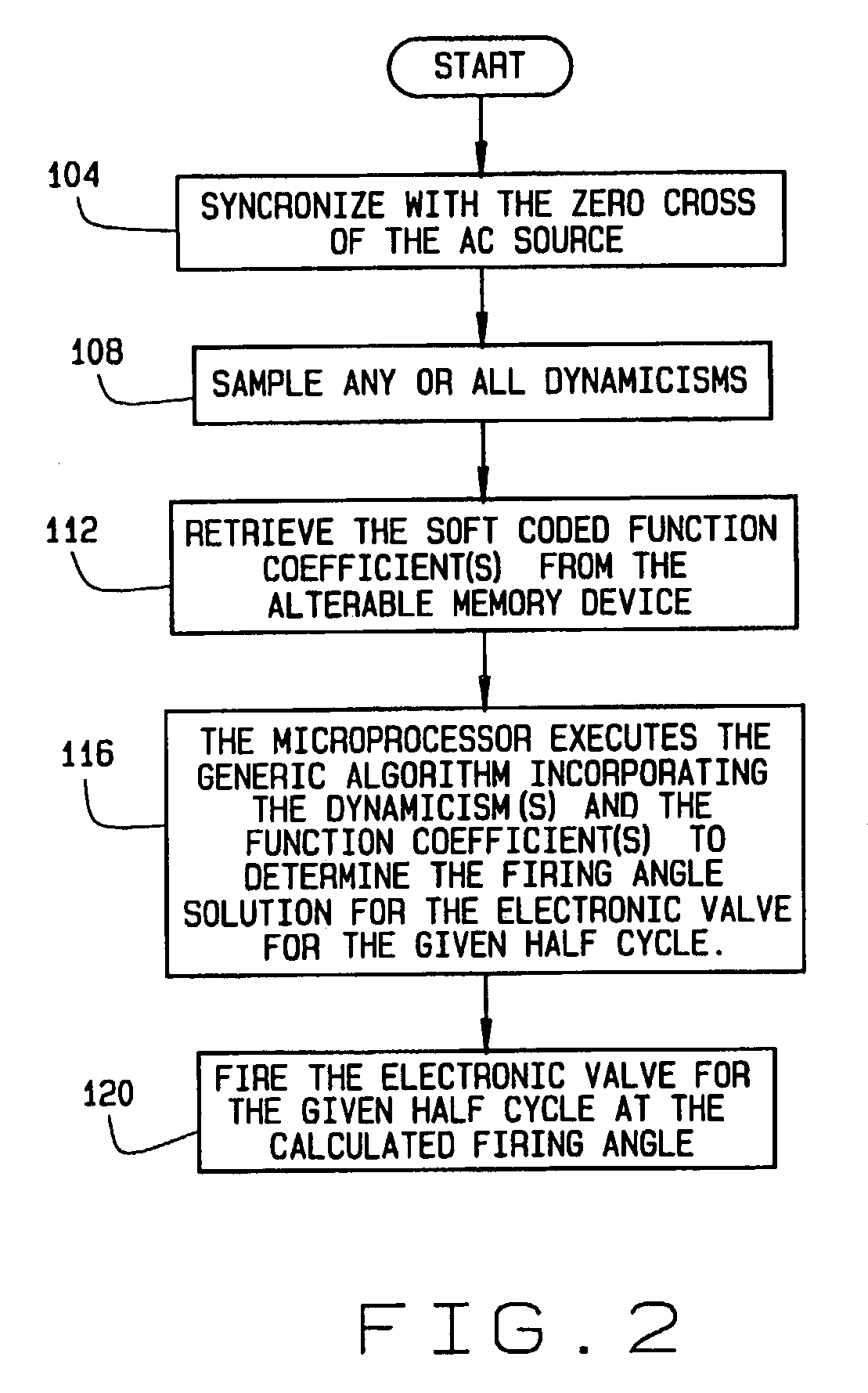
Generic motor control system and method
InactiveUS7102303B2Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor controlMotor function
A method for controlling the operation of a motor utilizing a universal motor control module. The method includes sampling at least one motor operating criterion during operation of the motor and executing a universal control algorithm at a predetermined periodic interval of an AC line signal. Execution of the algorithm provides a firing angle solution for an electronic valve for each periodic interval, thereby controlling the behavior of the motor. Additionally, the method includes firing the electronic valve at the calculated firing angle during each periodic interval such that the motor functions in accordance with desired operational parameters.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
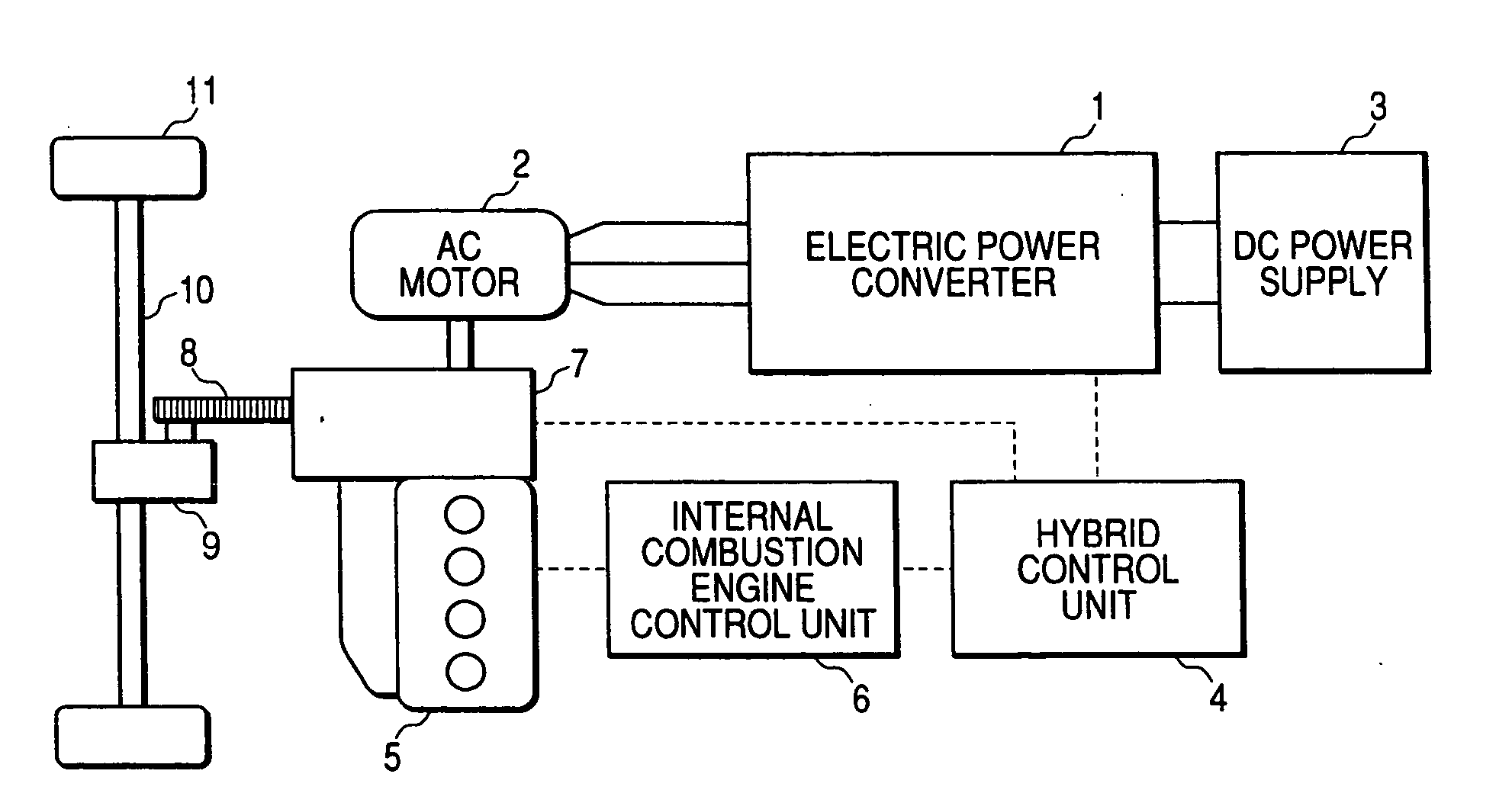
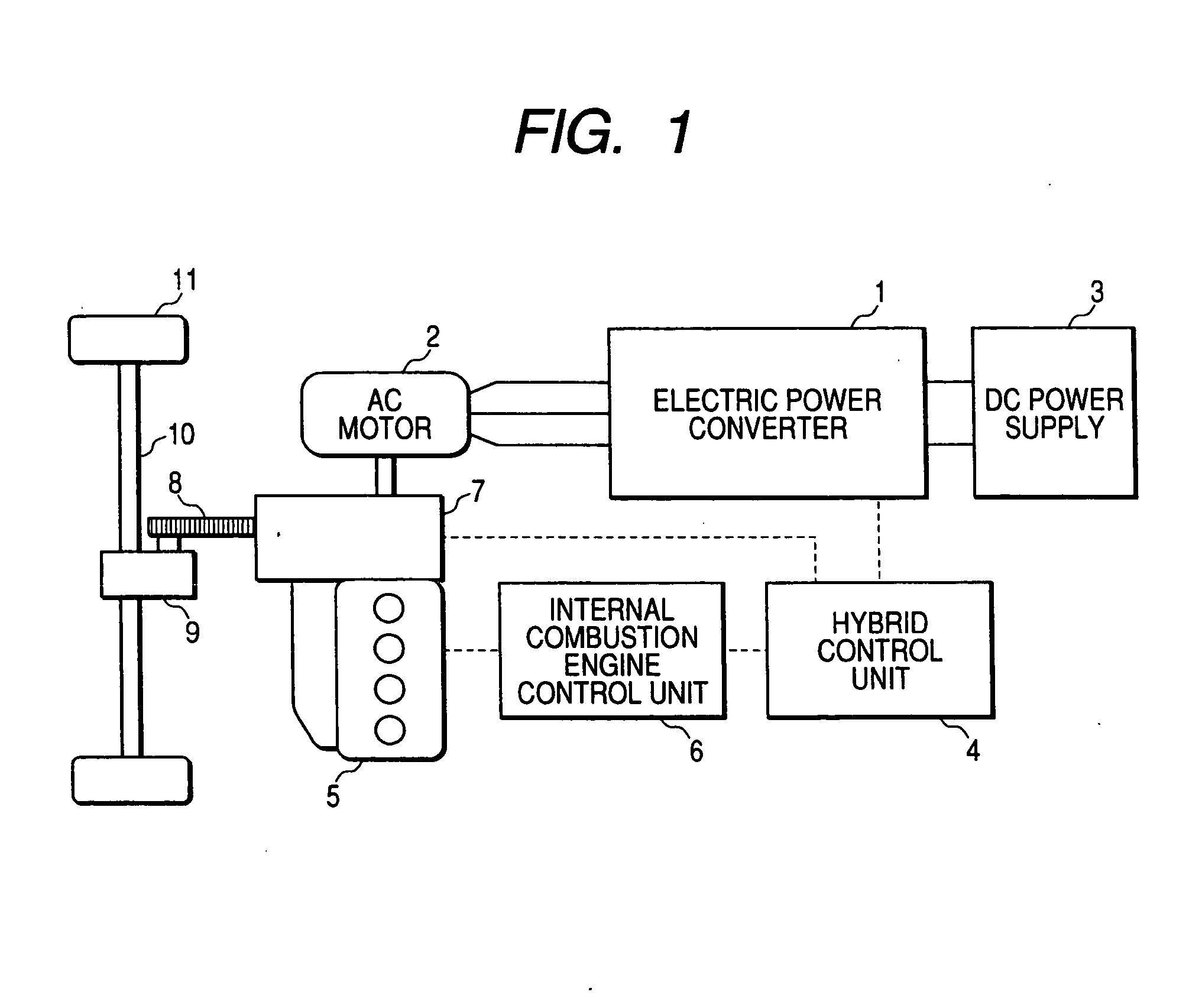
Vehicular power control apparatus
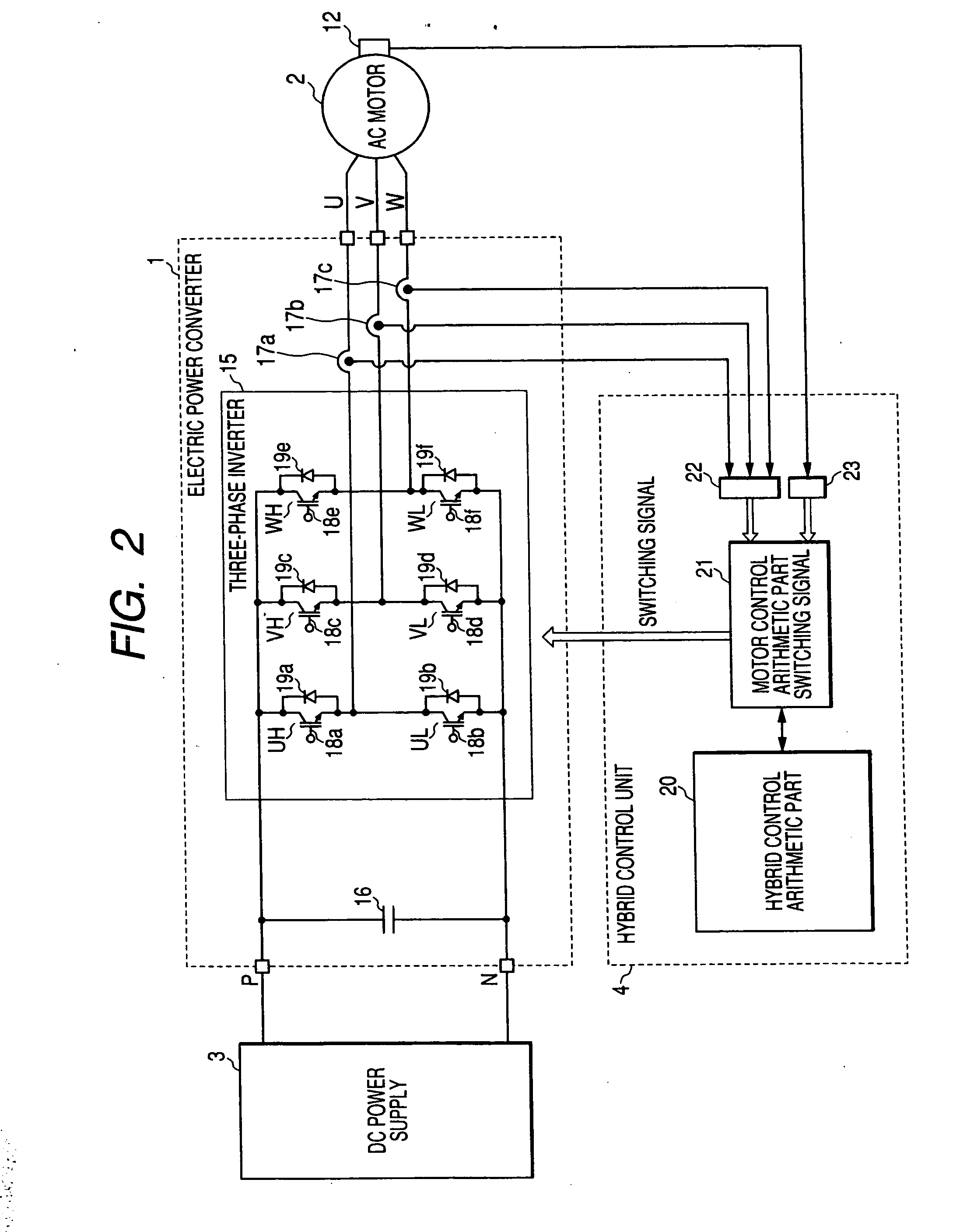
InactiveUS20070093359A1Not to damage safetyAvoid it happening againAC motor controlVector control systemsInstruction unitSwitching signal
A protection operation control part switches a gate signal interruption switch for protection of power elements to a gate signal interruption side, and invalidates a switching signal from a hybrid control unit to place transistors into a nonconducting operation. A motor current signal from a motor current detector is converted into a current value by a motor current calculation unit, and is inputted to a short-circuit abnormality detection unit through a motor control arithmetic part, and a short-circuit abnormality is detected. At a time of detecting the short-circuit abnormality, an internal combustion engine operation instruction unit gives an instruction to an internal combustion engine control unit so as to limit output of an internal combustion engine, and releases a conduction state of an abnormal motor current.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS7294988B2Improve sensing accuracyImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorEngineering
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for identifying initial position of rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor of non-position sensor
InactiveCN101630938AEfficient identificationSatisfied with the initial position identification accuracyAC motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorPosition angle
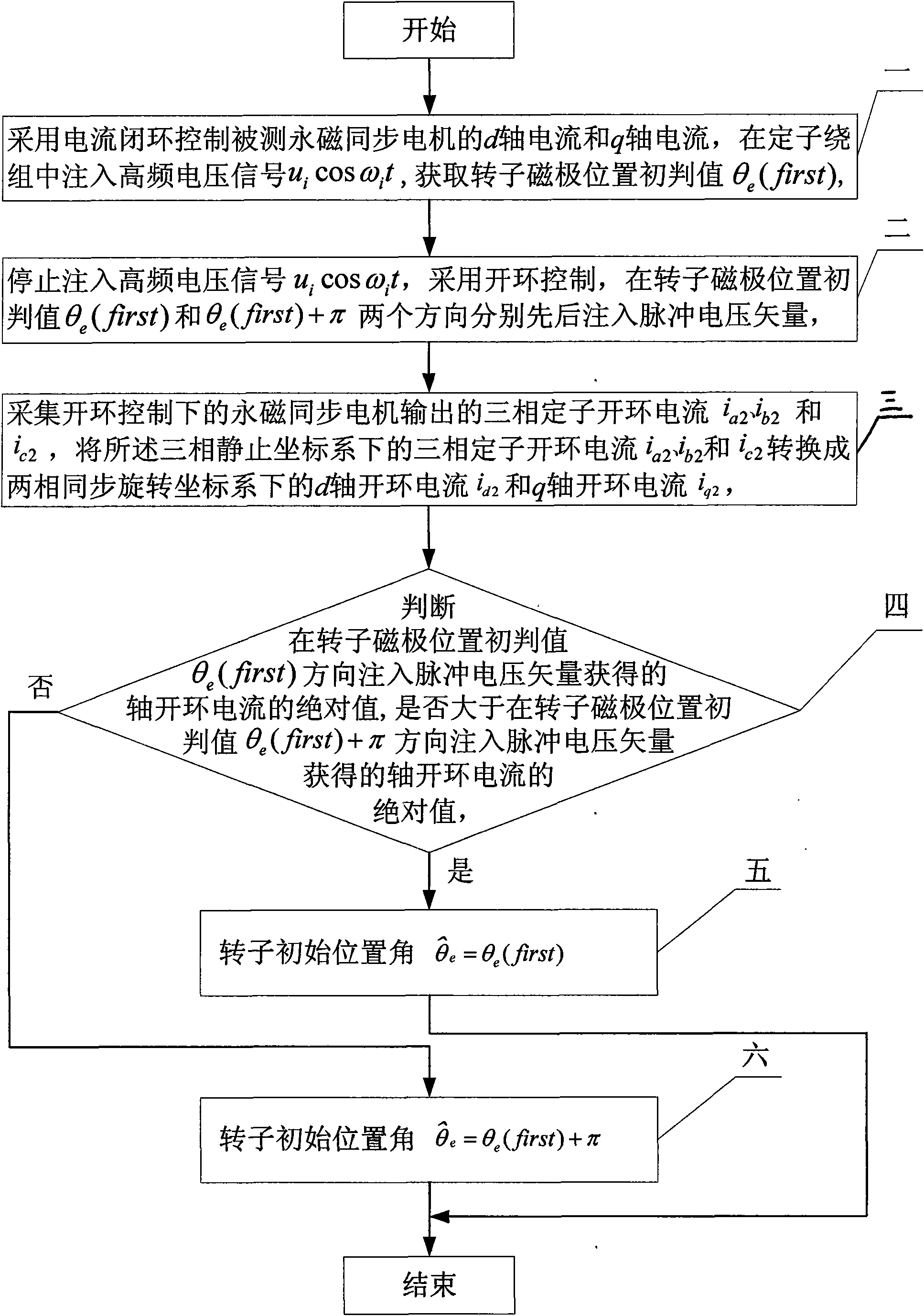
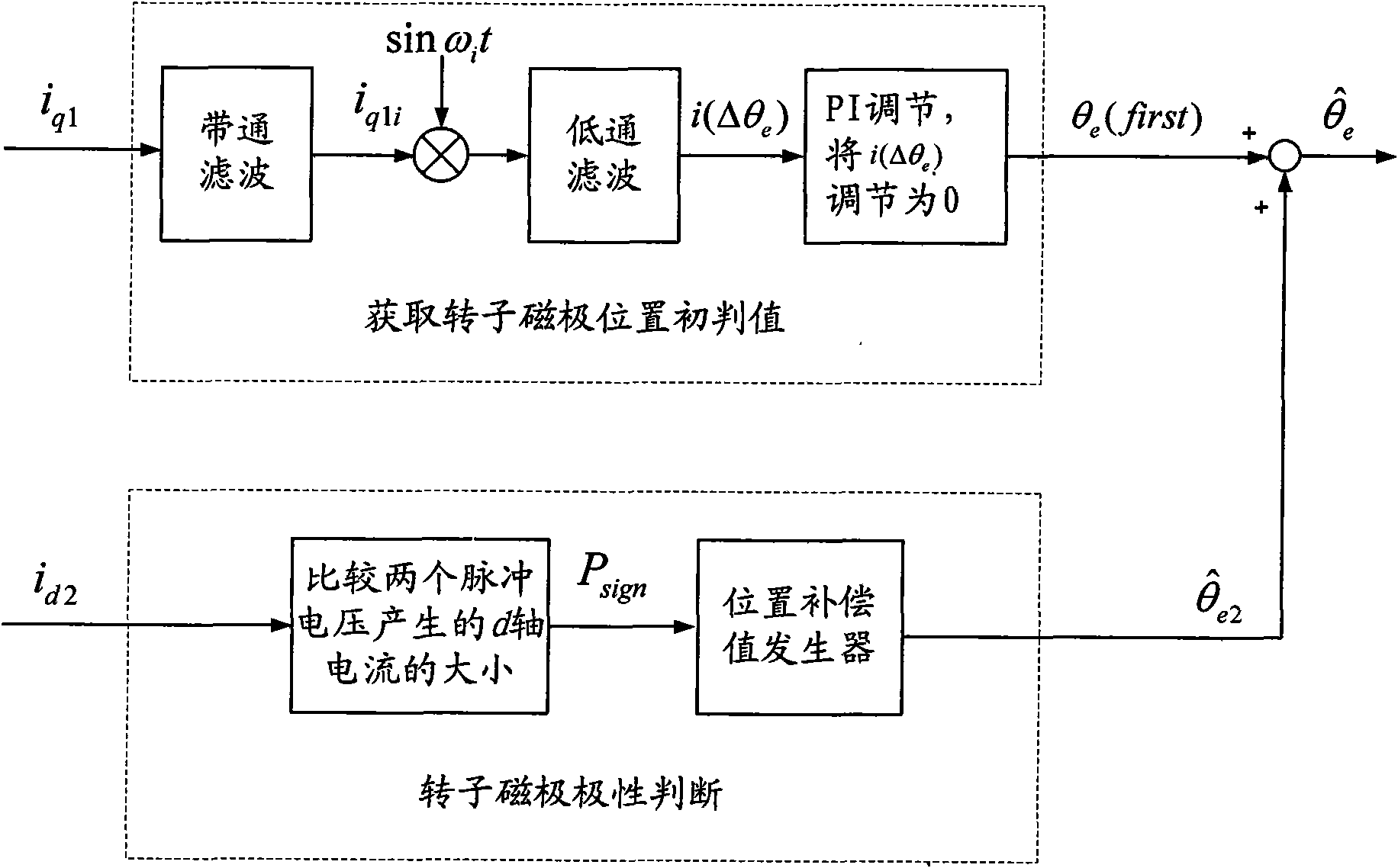
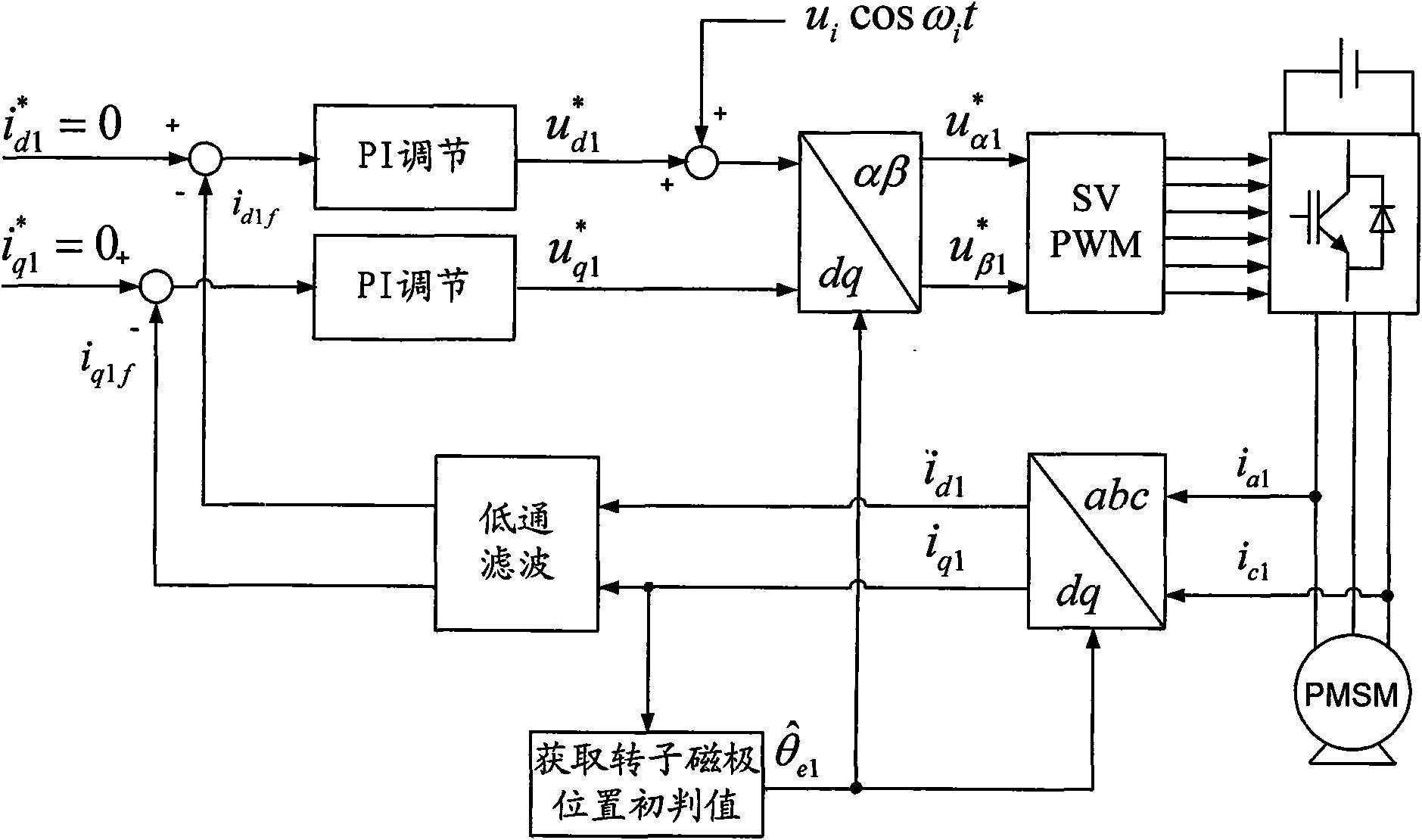
A method for identifying an initial position of a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor of a non-position sensor belongs to the motor control field, and aims at solving the problems of the traditional method for identifying the initial position of magnetic poles of the rotor such as position change of the rotor, low identification precision or complex algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: maintaining the rotor under a static state during the identification process of the initial position of the rotor, injecting a high-frequency voltage signal to a stator winding, carrying out rotational coordinate conversion on three-phase stator current, and acquiring position information of the magnetic poles of the rotor by current components at q axis to obtain an initial judgment value of the magnetic pole position of the rotor; and then injecting two impulse voltage vectors in opposite directions to the stator winding, judging the polarity of the magnetic poles by comparing size of current components at d axis, and correcting the initial judgment value of the magnetic pole position obtained formerly by the judged polarity information of the magnetic poles to finally obtain an initial position angle of the rotor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Motor driving apparatus
ActiveUS7176644B2Low costIncrease freedomSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsBrushless motorsMotor drive
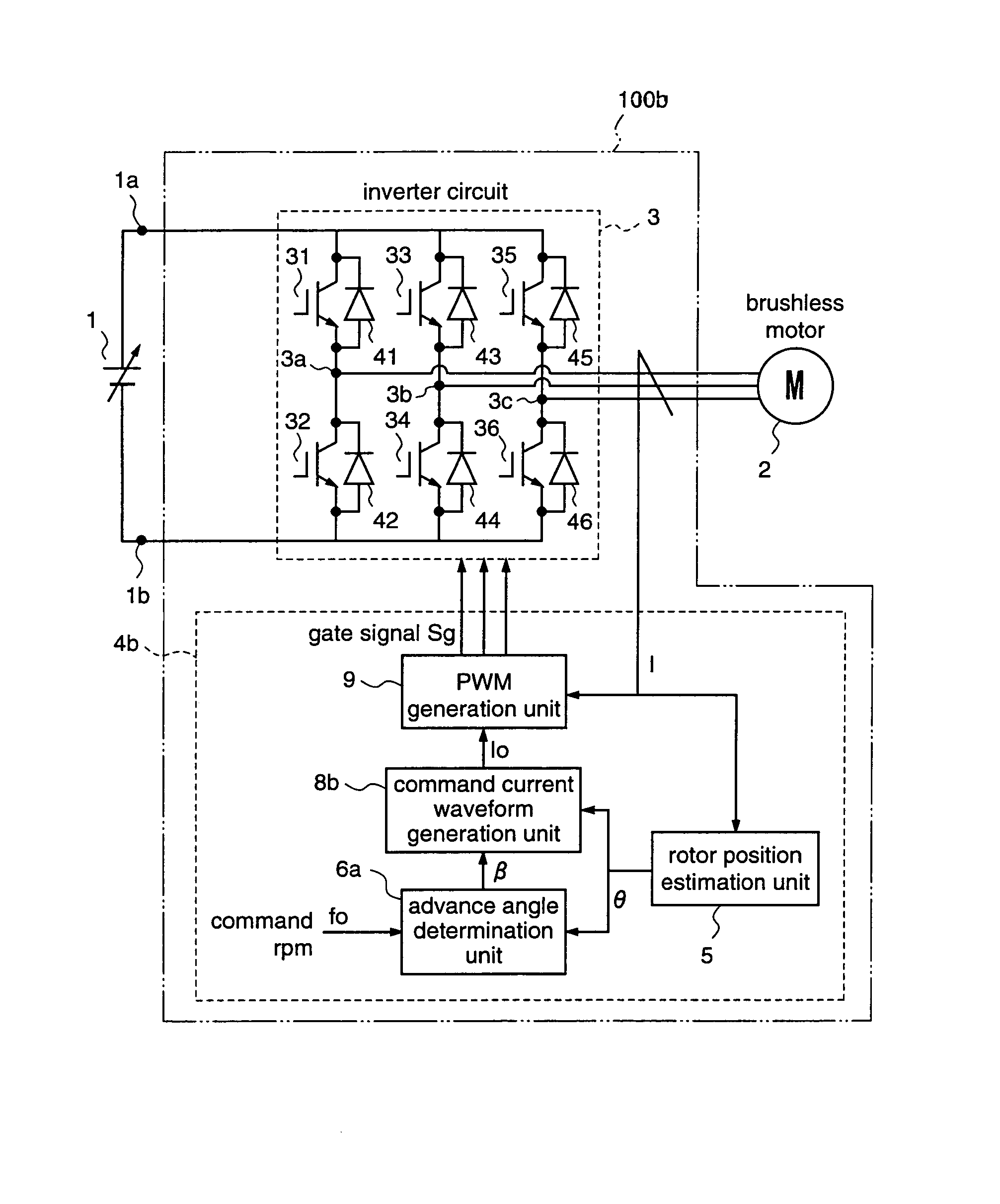
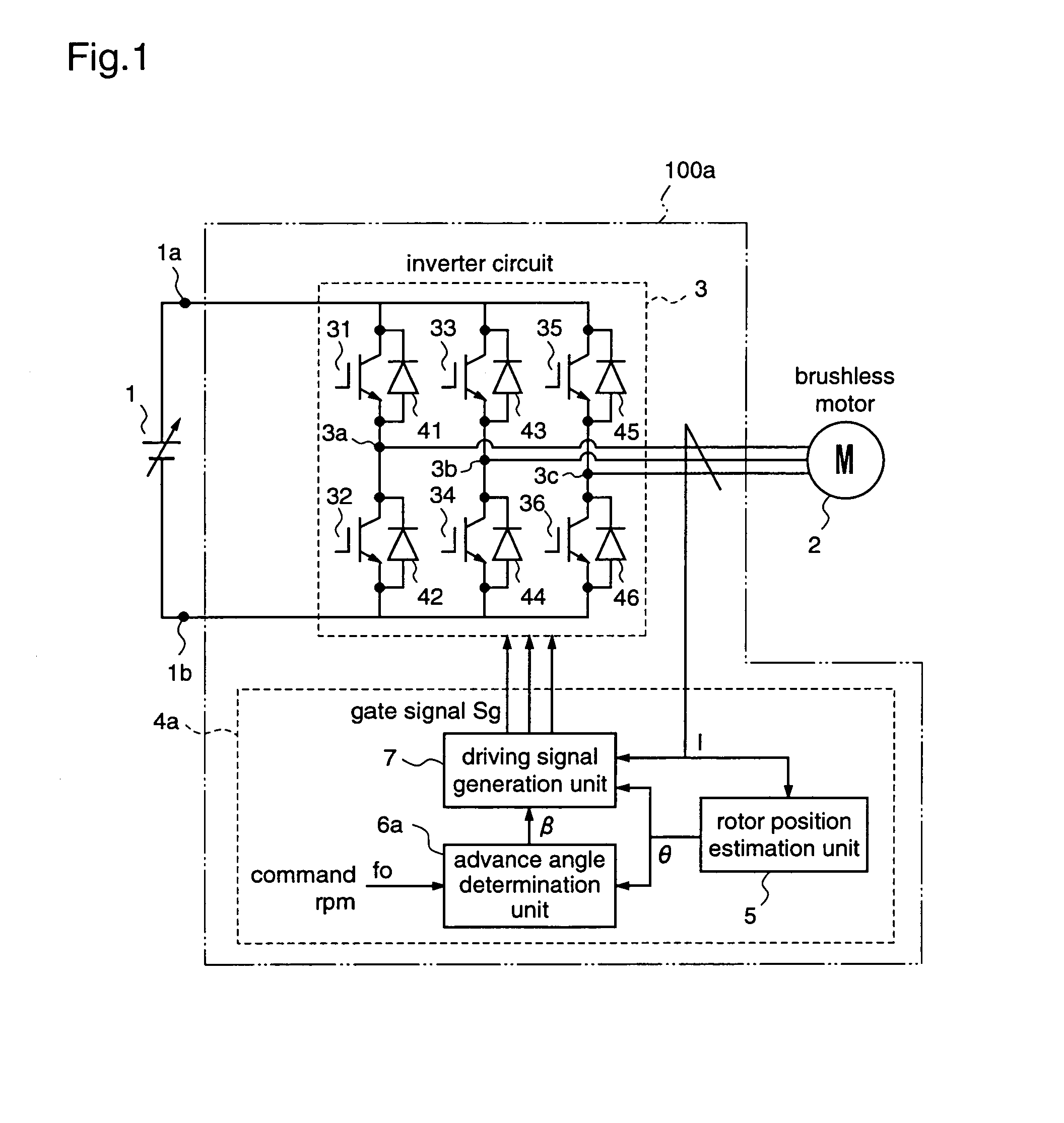
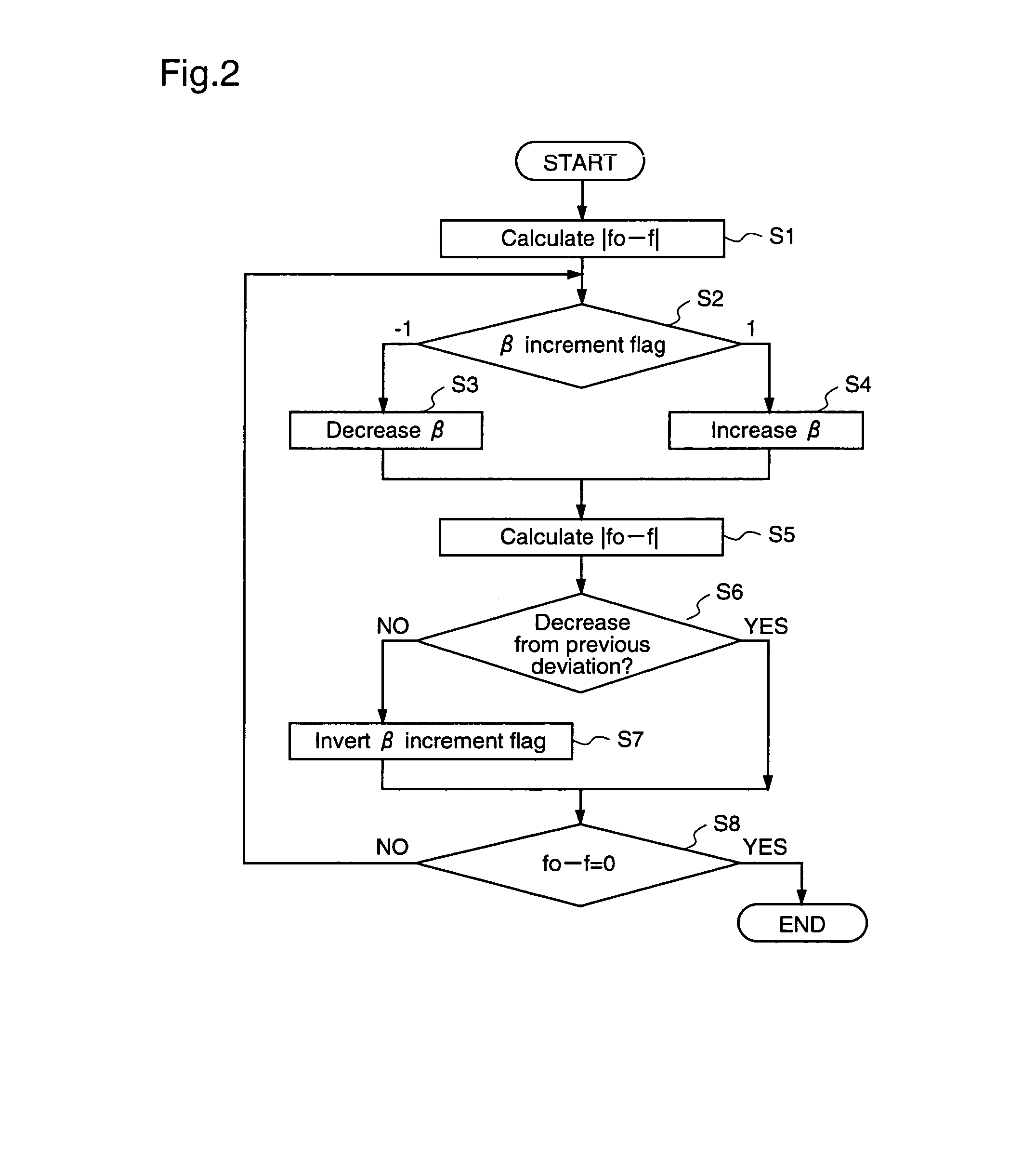
A motor driving apparatus includes an inverter circuit for converting an output voltage of a power supply into a three-phase AC and outputting the same to the brushless motor, a rotor position estimation unit for estimating a rotor position of the brushless motor, and an inverter control unit for controlling the inverter circuit so that the brushless motor is driven by a current based on the estimated rotor position. The inverter control unit determines an advance angle of the current supplied to the brushless motor with respect to the estimated rotor position so as to minimize a deviation between a command rpm and an actual rpm. Therefore, it is possible to perform stable weak field control for the brushless motor, independently from the input voltage of the inverter circuit, without using predetermined control variables such as table values.
Owner:III HLDG 7
Position sensorless drive for permanent magnet synchronous motors
ActiveUS20050151502A1AC motor controlSynchronous motors startersLow speedPermanent magnet synchronous motor
A sensorless motor control algorithm that single-handedly permits operation over the entire speed range from low speed to high speed. This “fusion” algorithm seamlessly fuses the position data generated respectively by high speed and low speed sensorless algorithms. The resulting sensorless drive permits effective position sensorless operation over the entire speed range of a PM motor.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com