Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Transcatheter aortic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
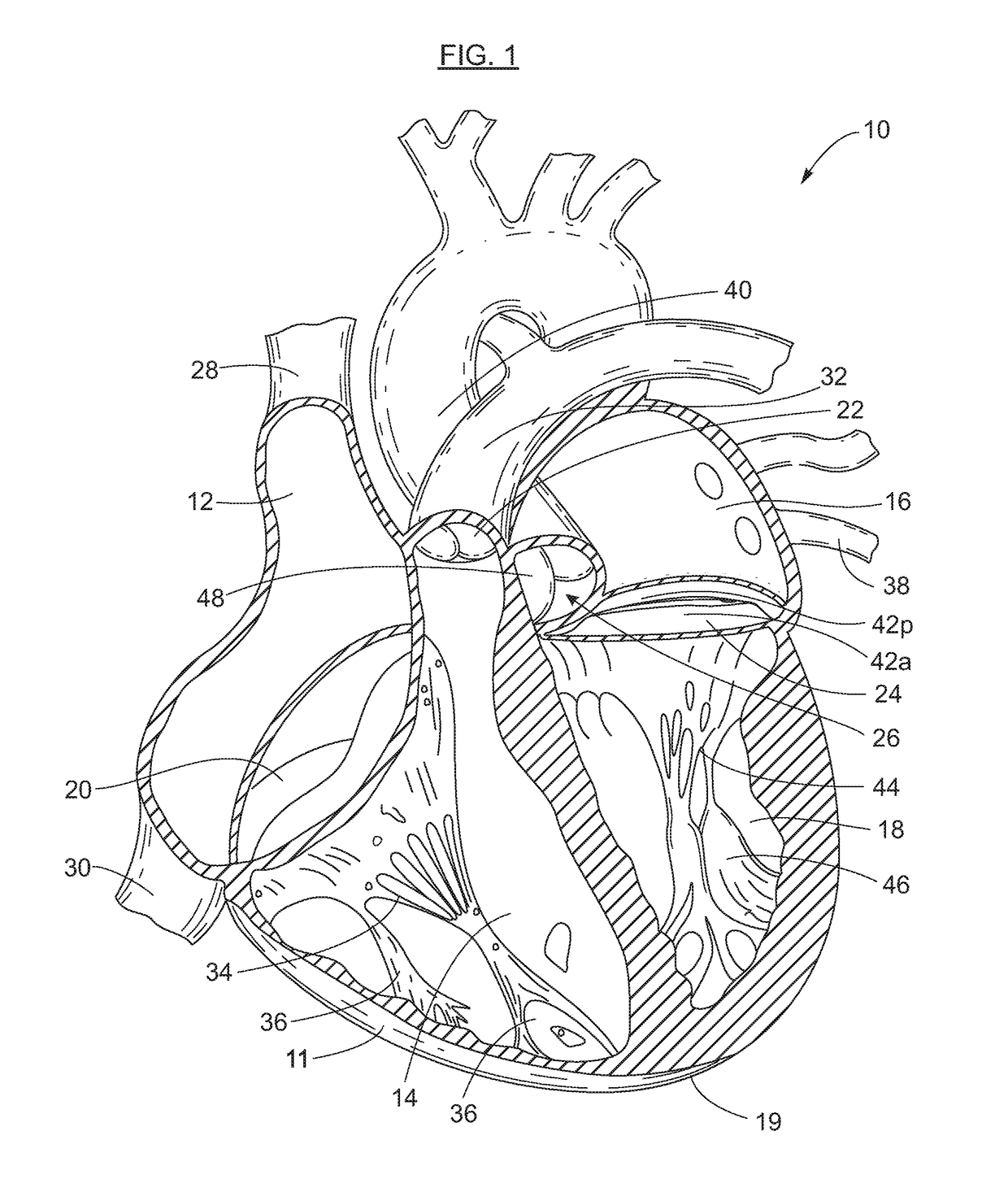
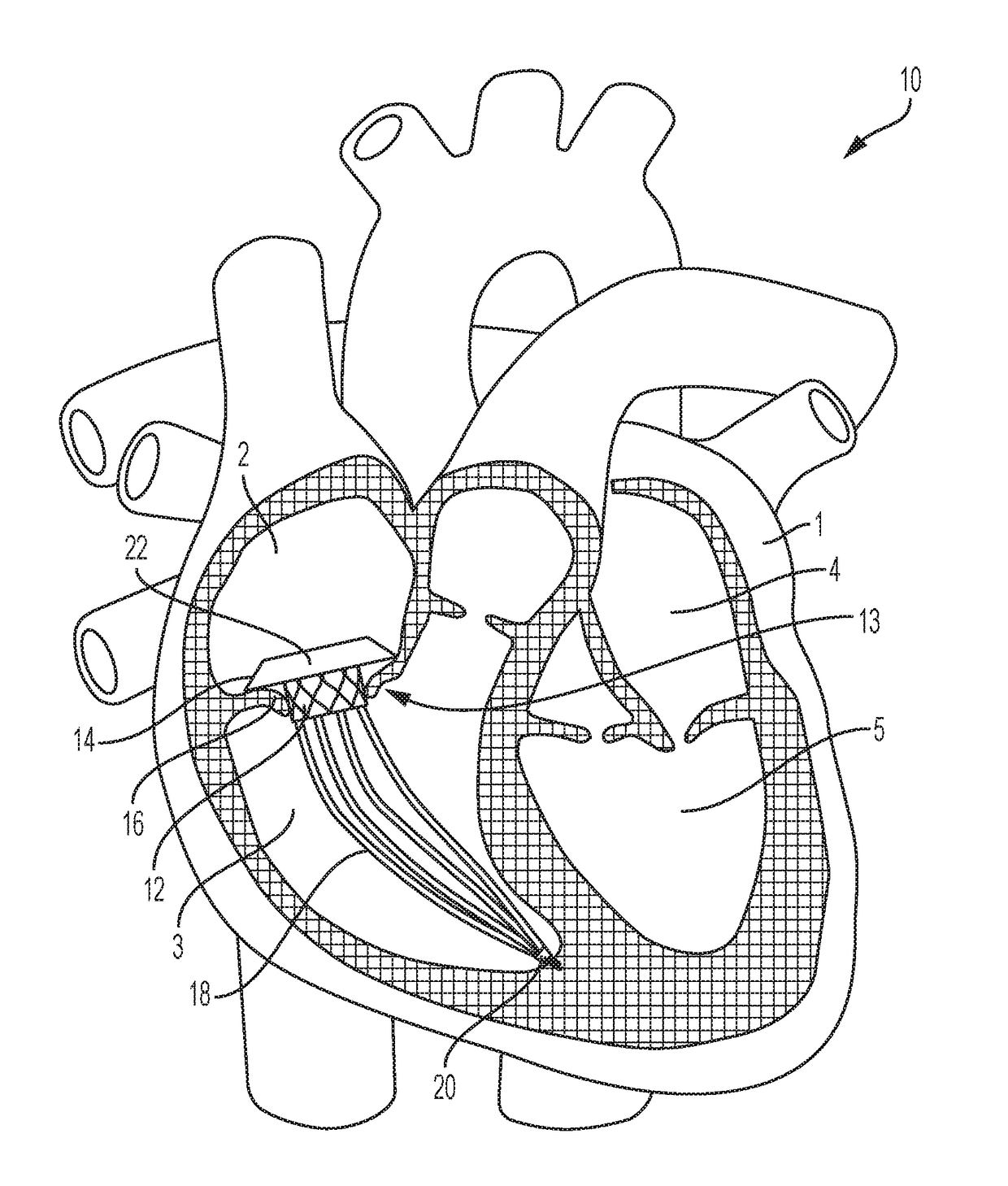
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR - also known as TAVI or transcatheter aortic valve implantation) is a new technology for use in treating aortic stenosis. A bioprosthetic valve is inserted percutaneously using a catheter and implanted in the orifice of the native aortic valve.
"inflatable medical devices"
Inflatable medical devices and methods for making and using the same are disclosed. The devices can be medical invasive balloons, such as those used for transcutaneous heart valve implantation, such as balloons used for transcatheter aortic-valve implantation. The balloons can have high strength, fiber-reinforced walls.
Owner:LOMA VISTA MEDICAL
Method and Apparatus Useful for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
InactiveUS20140018912A1Reduce contactReduce riskBalloon catheterHeart valvesAscending aortaGuide tube
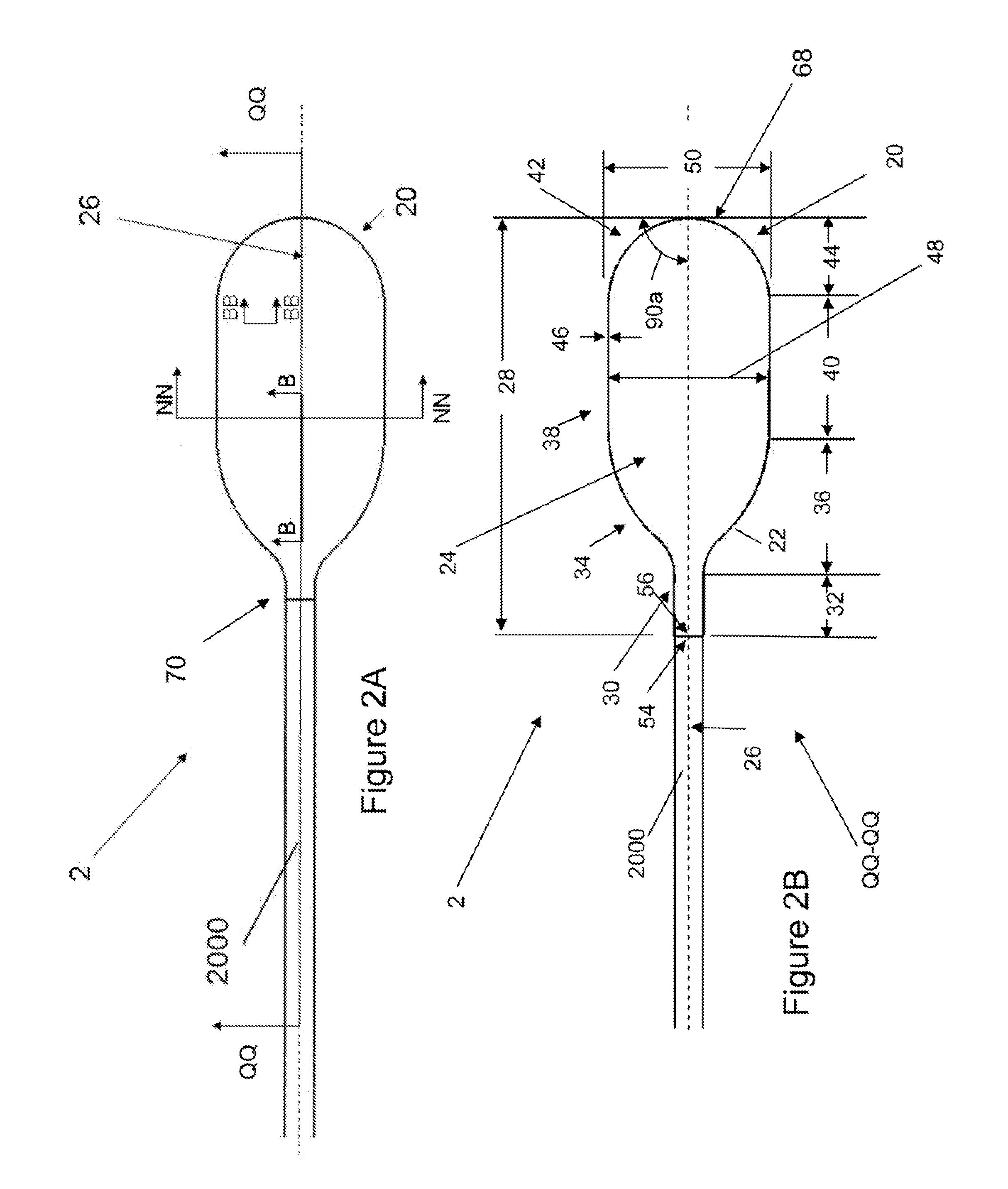
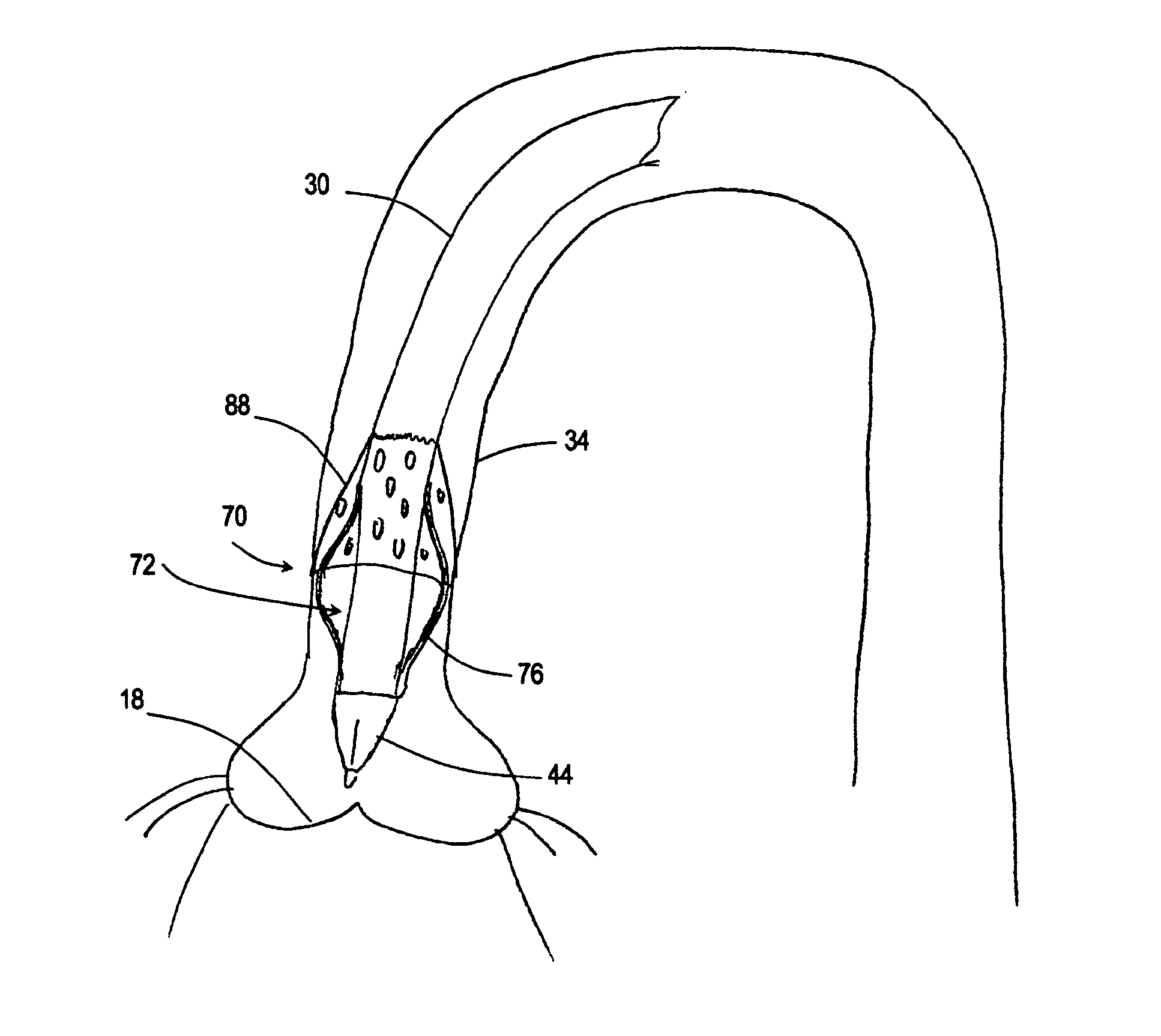
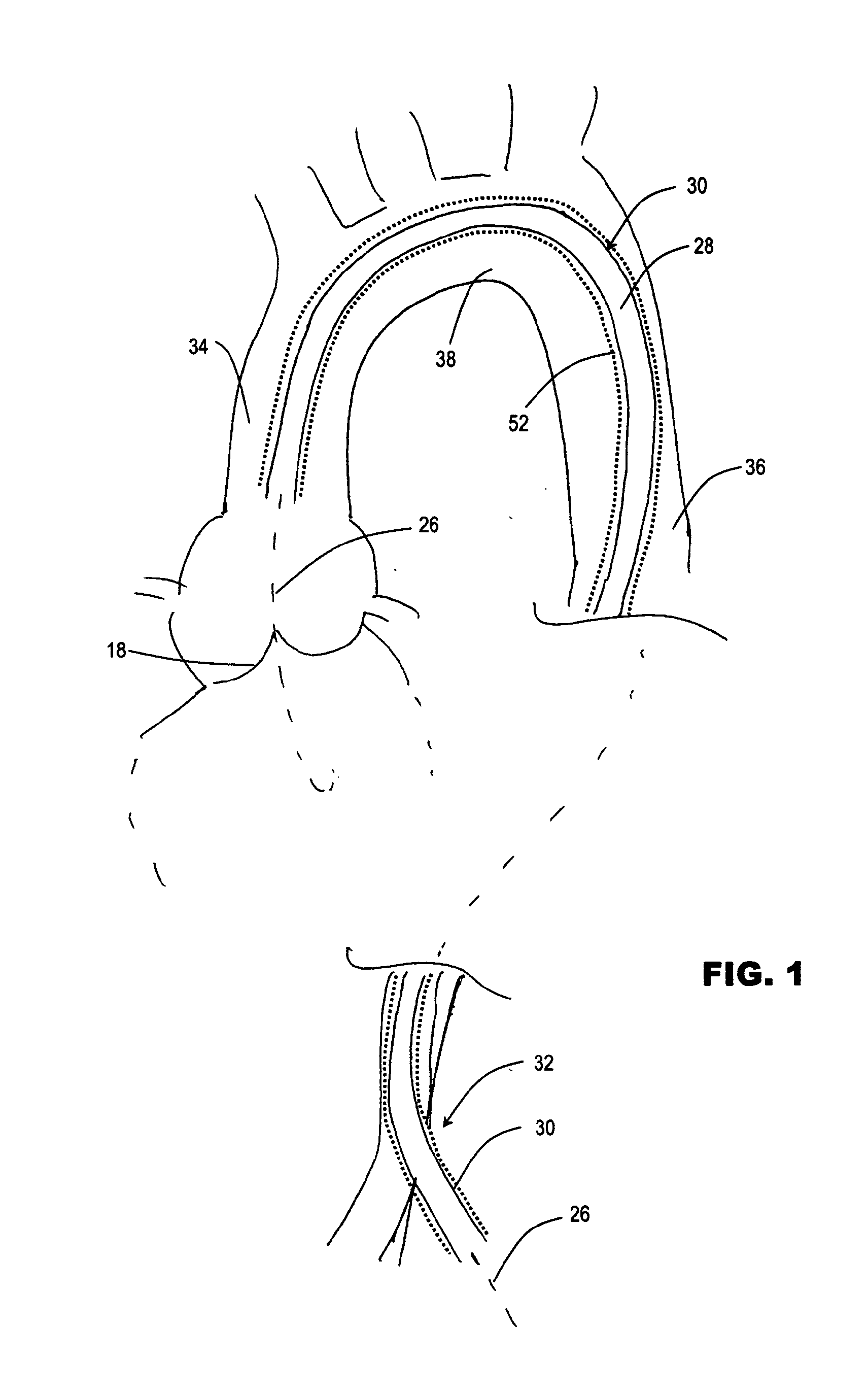
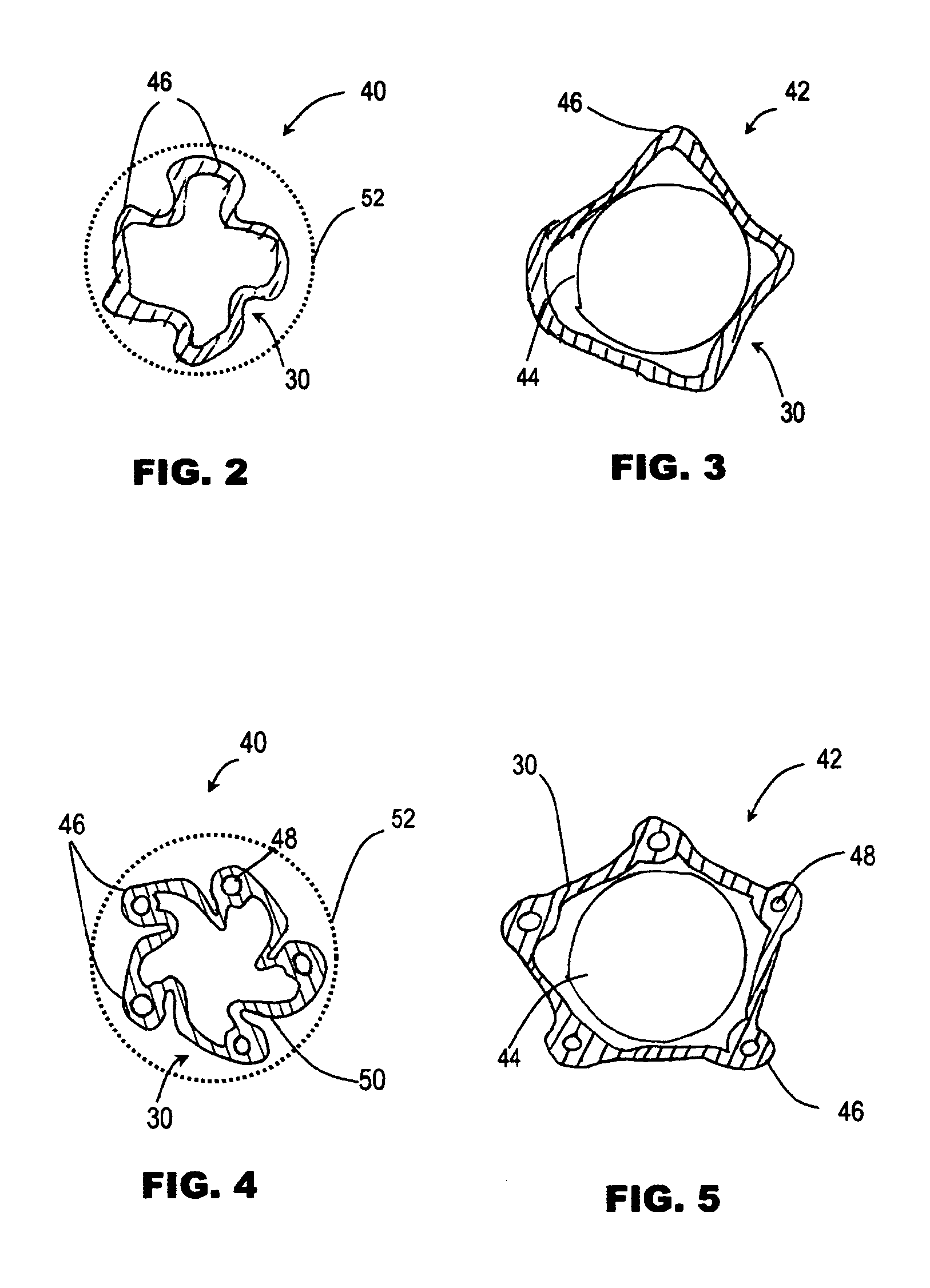
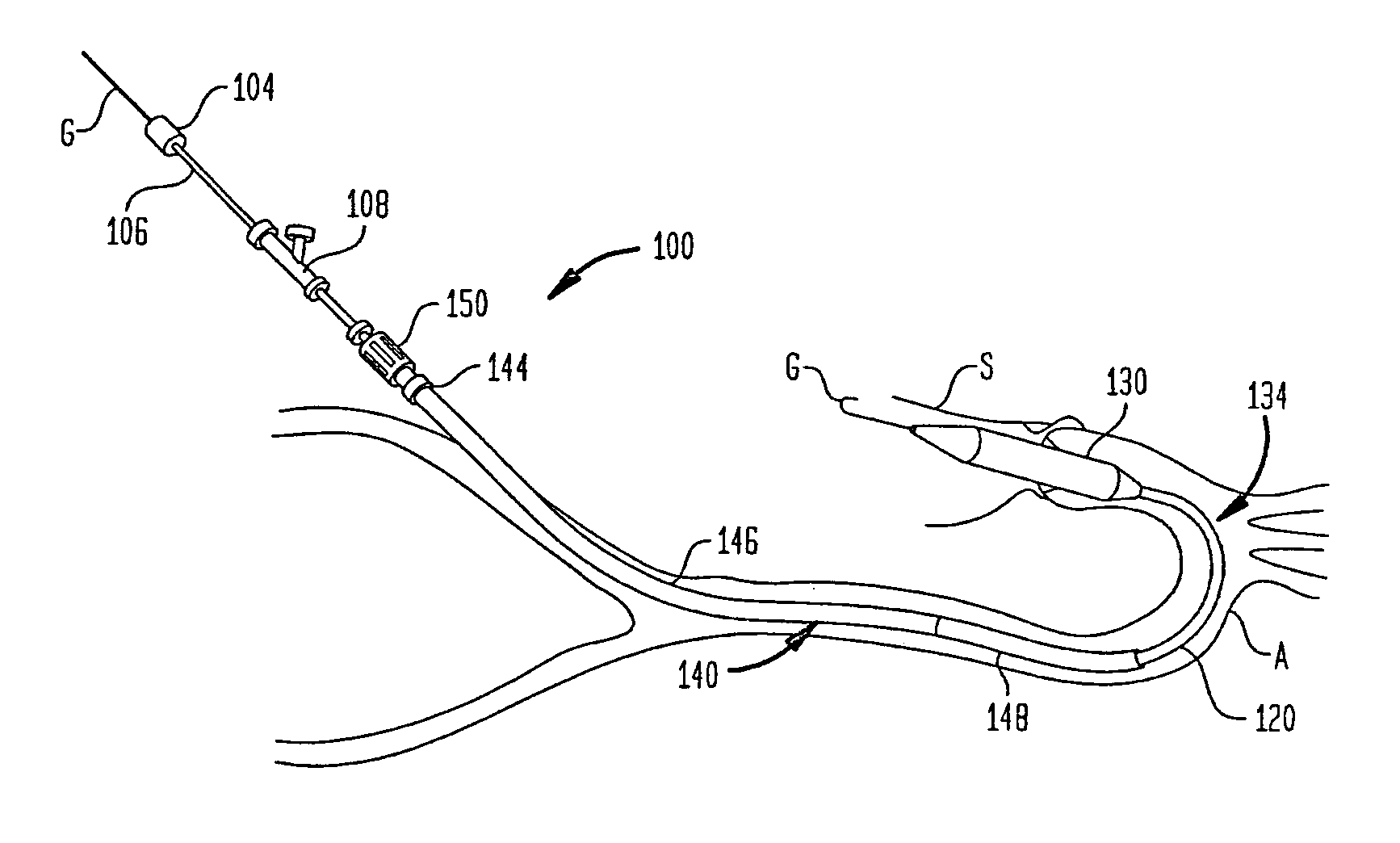
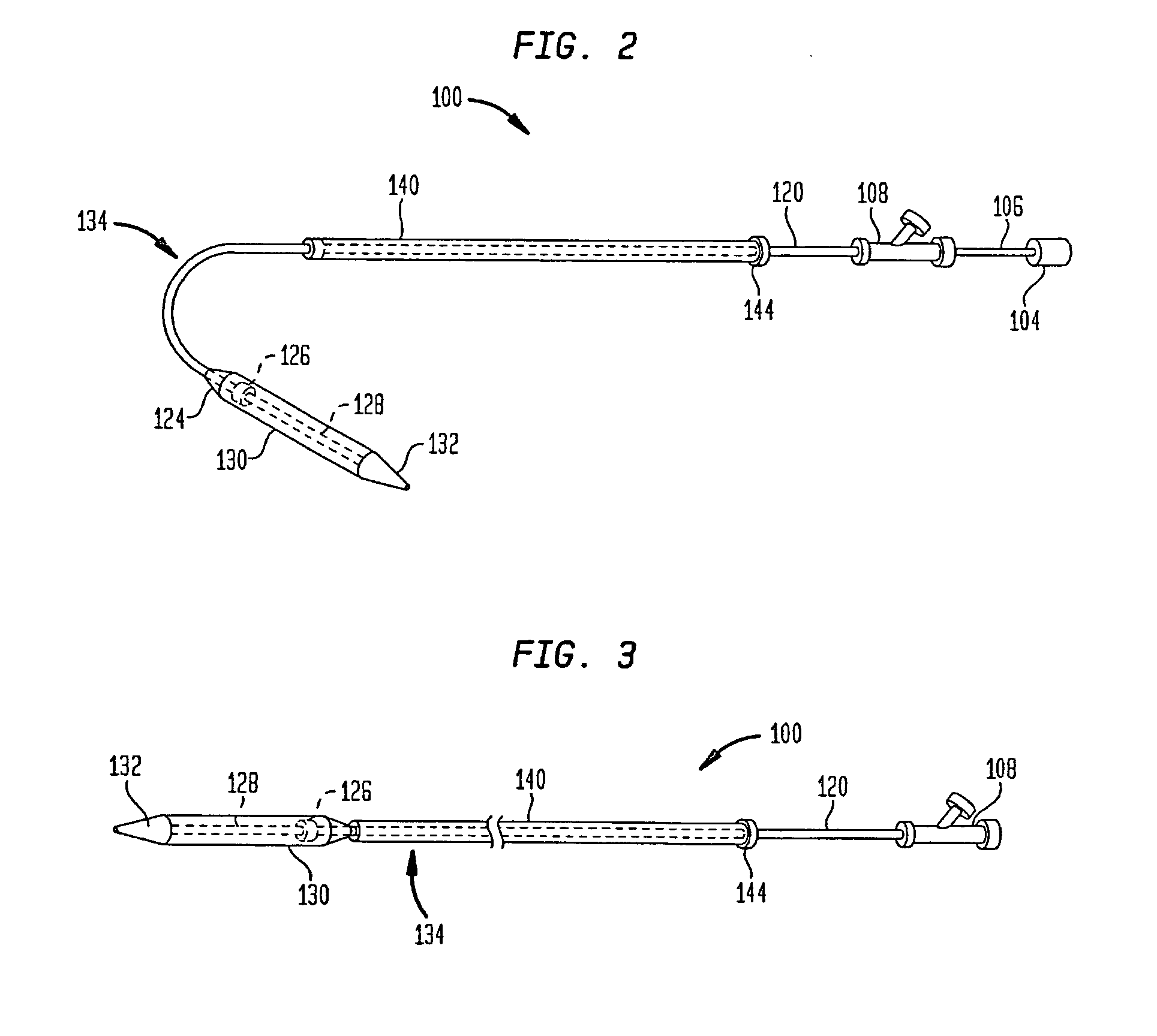
A guide catheter (30) is described for introduction into a patient's vasculature, to provide a substantially continuous guide lumen (28) within the vasculature to the ascending aorta (34), through which one or more other functional catheters (44) may be introduced and removed during the procedure. The guide catheter includes an aligner (70) at its distal region for aligning the position and / or inclination of the distal region of the guide catheter with respect to the ascending aorta. The aligner includes an embolic protection filter (88). The guide catheter is made of material collapsible / distensible in cross section to adopt a small shape when no catheter is present inside, and to distend to a large shape to accommodate passage of functional catheter therethrough. The cross-section shape collapses / distends by folding / unfolding of material without elastic stretching of the material.
Owner:SYMETIS
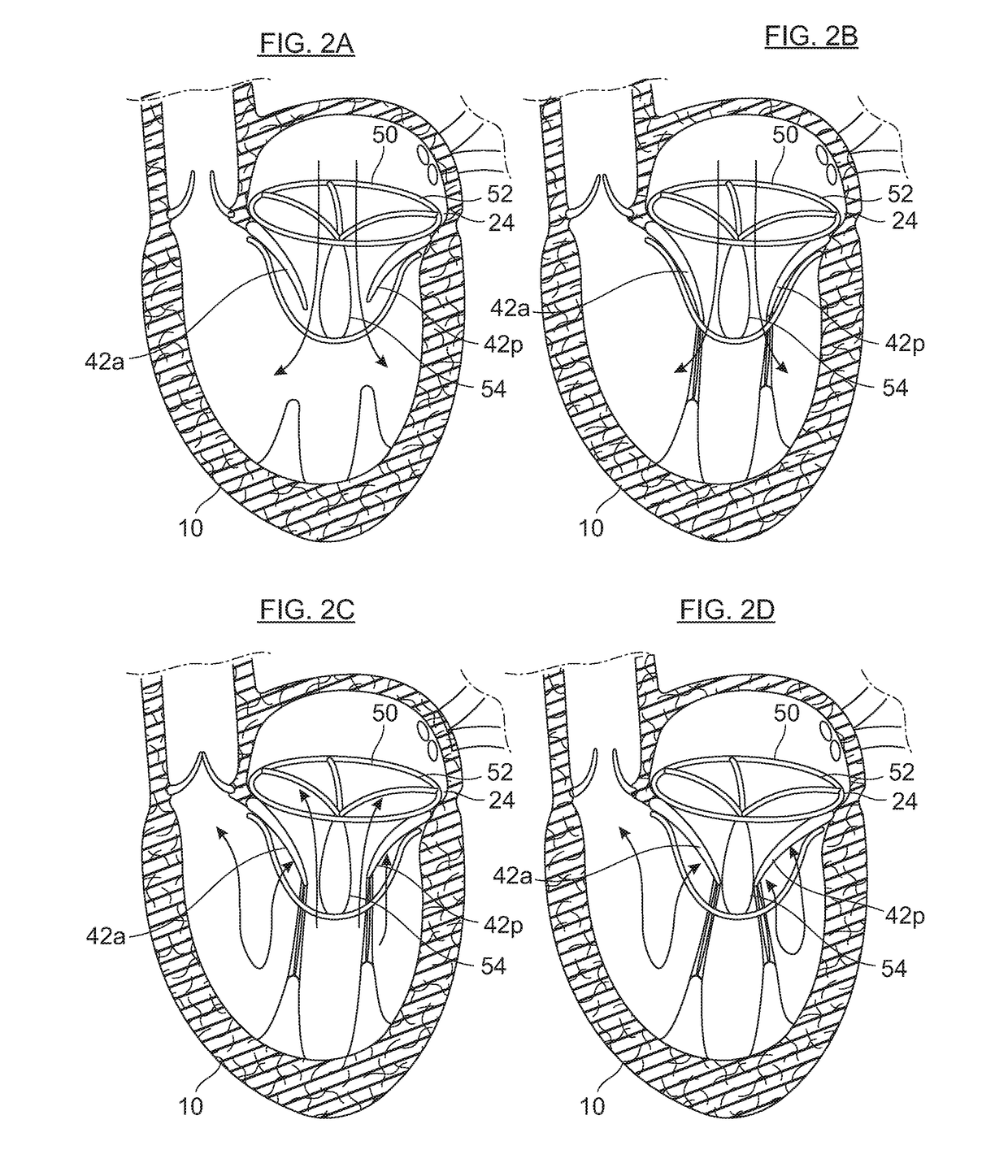
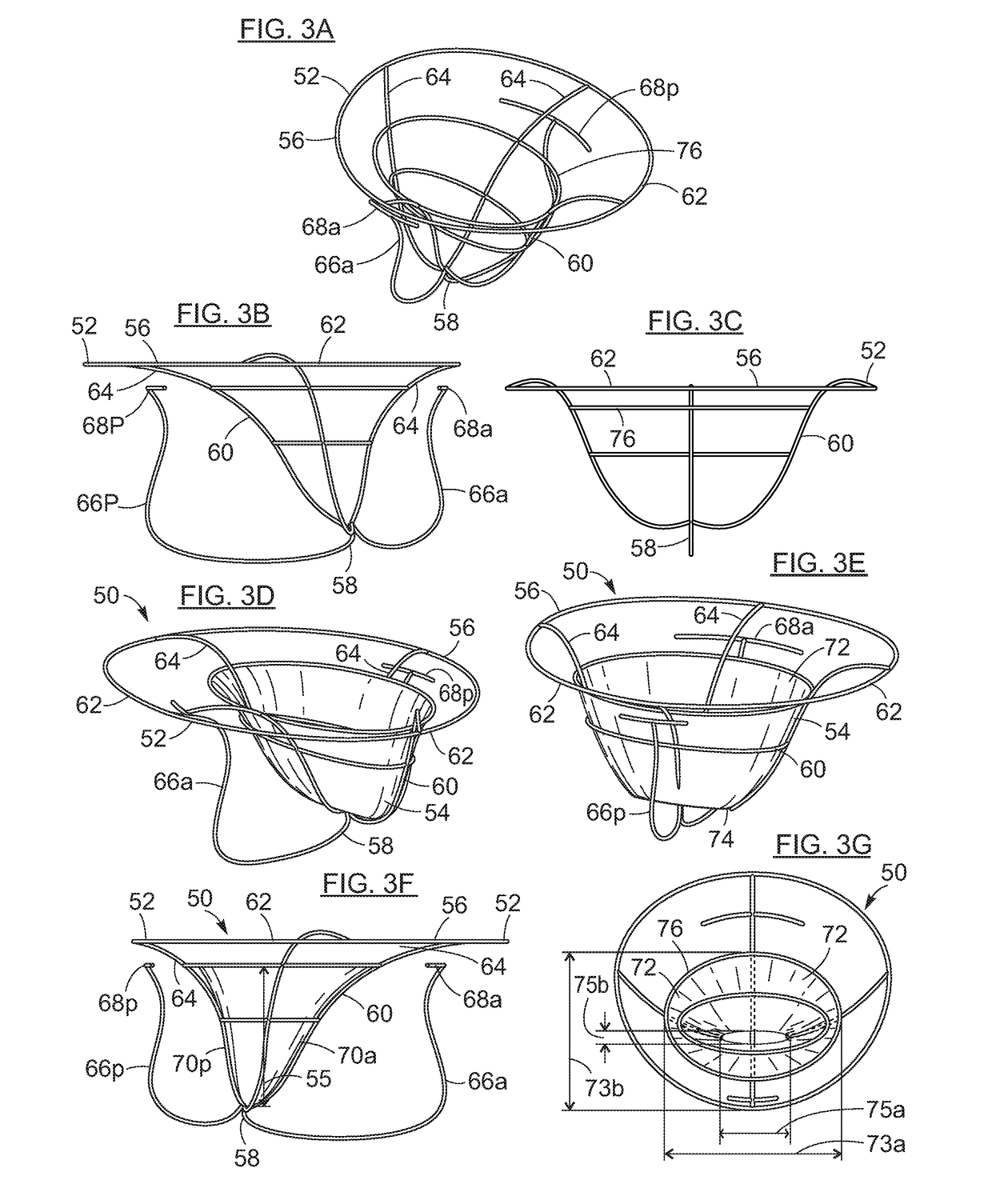
Transcatheter device for treating mitral regurgitation
ActiveUS20190060072A1Improve valve functionReduce and eliminate valve regurgitationAnnuloplasty ringsMitral valve functionHeart chamber
The invention is a prosthetic device for improving function of a mitral valve. The device includes a sealing member configured for positioning between mitral valve leaflets. The device also includes an expandable anchor frame configured to be positioned within one or more heart chambers, for maintaining the sealing member at a desired position between valve leaflets. The sealing member reduces mitral regurgitation be filling the gap that can occur between opposing leaflets of a damaged mitral valve, thus restoring proper mitral valve closure.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
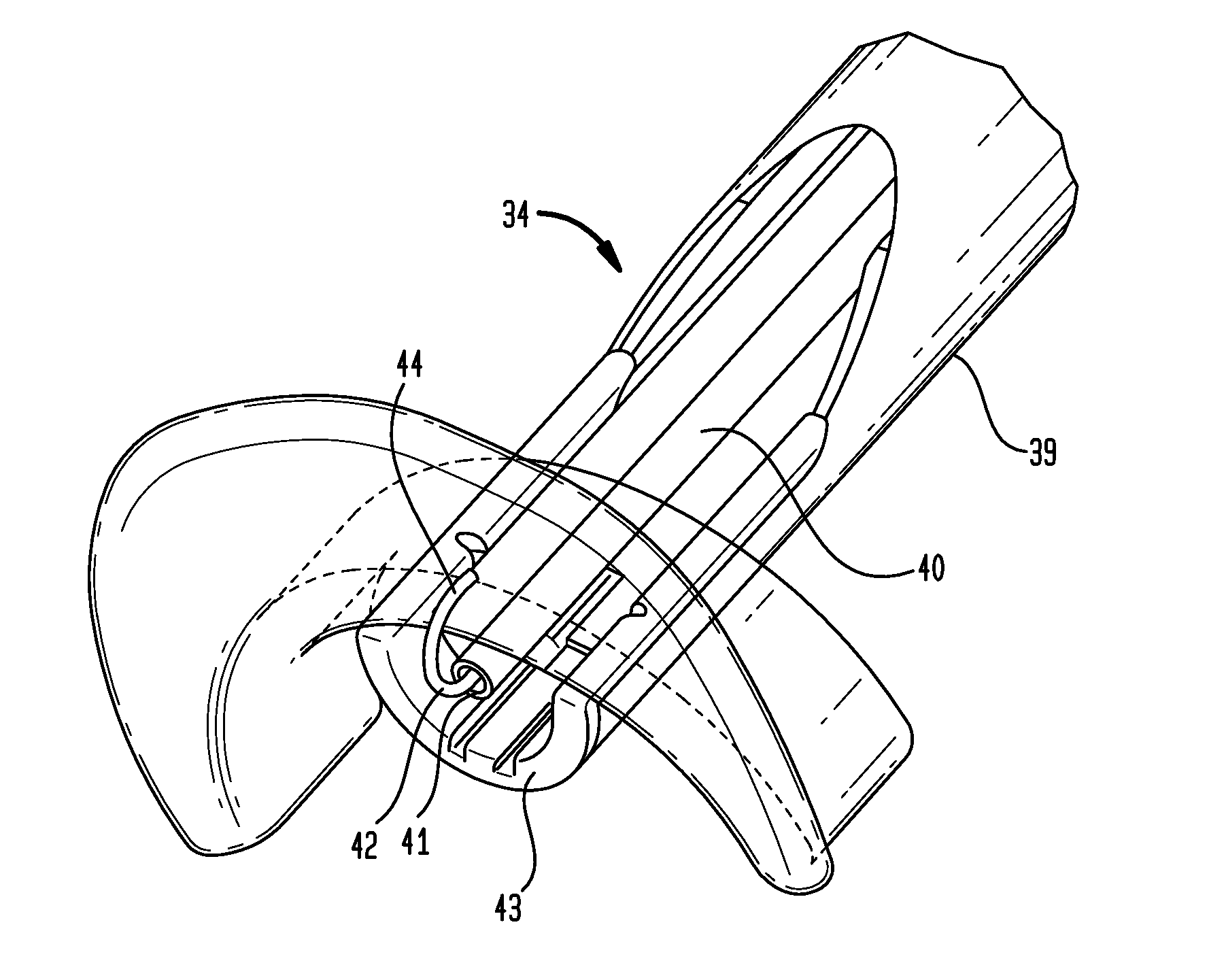
Mitral valve leaflet clip
A clip used to repair the tissue of a heart valve leaflet may include a shaft having a barb and a plurality of legs connected to the shaft. The plurality of legs may extend away from the barb in a first condition, and may extend towards the barb in a use condition. The clips may be delivered to the heart valve leaflet and applied to the same in a minimally invasive procedure using a transcatheter device. The device may be used to apply a single clip to the leaflet tissue or multiple clips.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
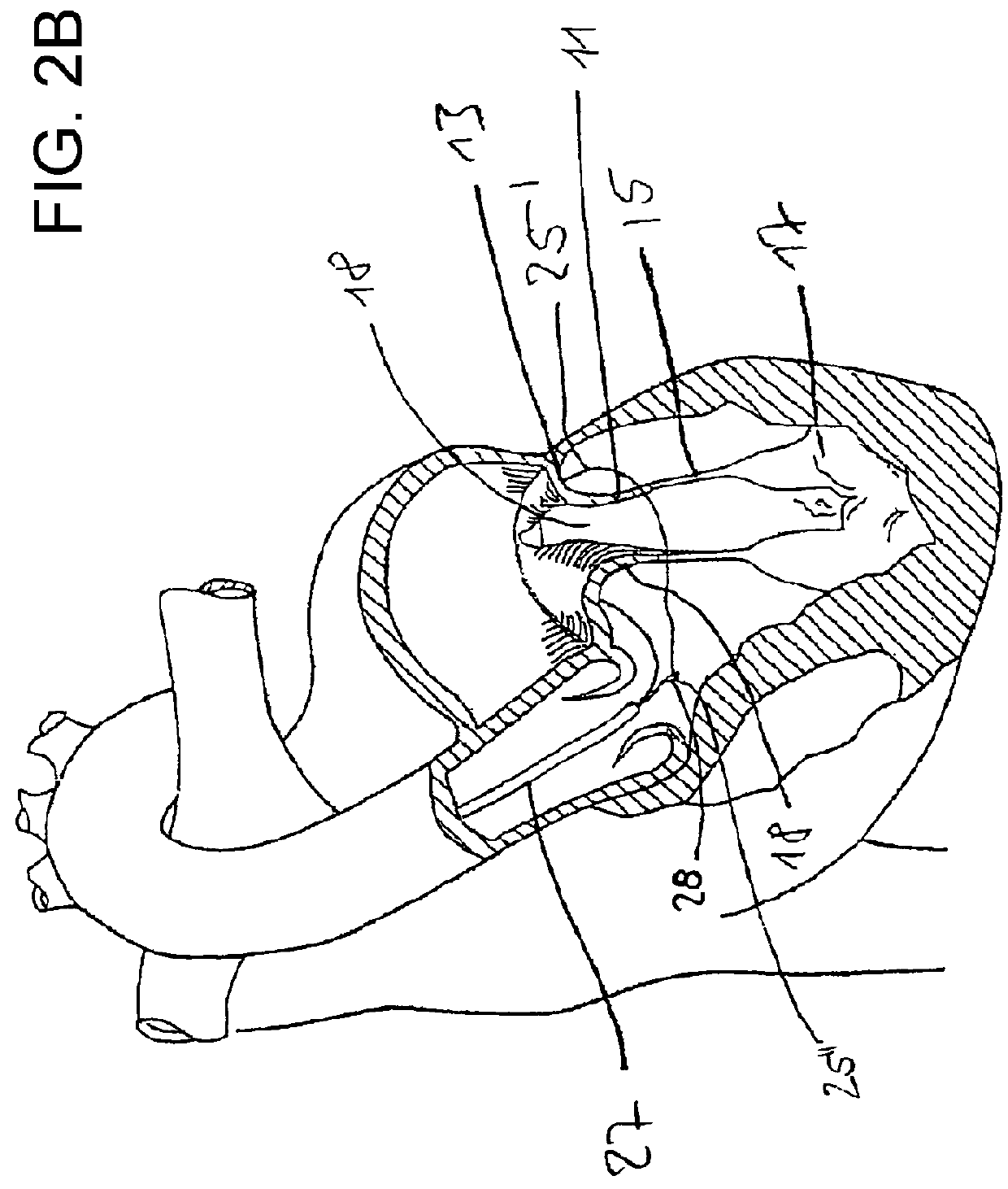
Transcatheter atrio-ventricular valve prosthesis
A transcatheter atria-ventricular valve prosthesis for functional replacement of an atrio-ventricular valve in a connection channel, having a circumferential connection channel wall structure, between atrial and ventricular chambers of a heart, including an inner device to be disposed in the interior of the connection channel, the inner device having a circumferential support structure which is radially expandable and having a valve attached to the circumferential support structure, and an outer device to be disposed on the exterior of the connection channel, wherein the outer device at least partly extends around the inner device at a radial distance to the inner device, wherein the inner and outer devices form a securing mechanism for securing the circumferential connection channel wall structure therebetween.
Owner:HIGHLIFE
Transcatheter atrial sealing skirt and related method
Owner:OPUS MEDICAL THERAPIES LLC
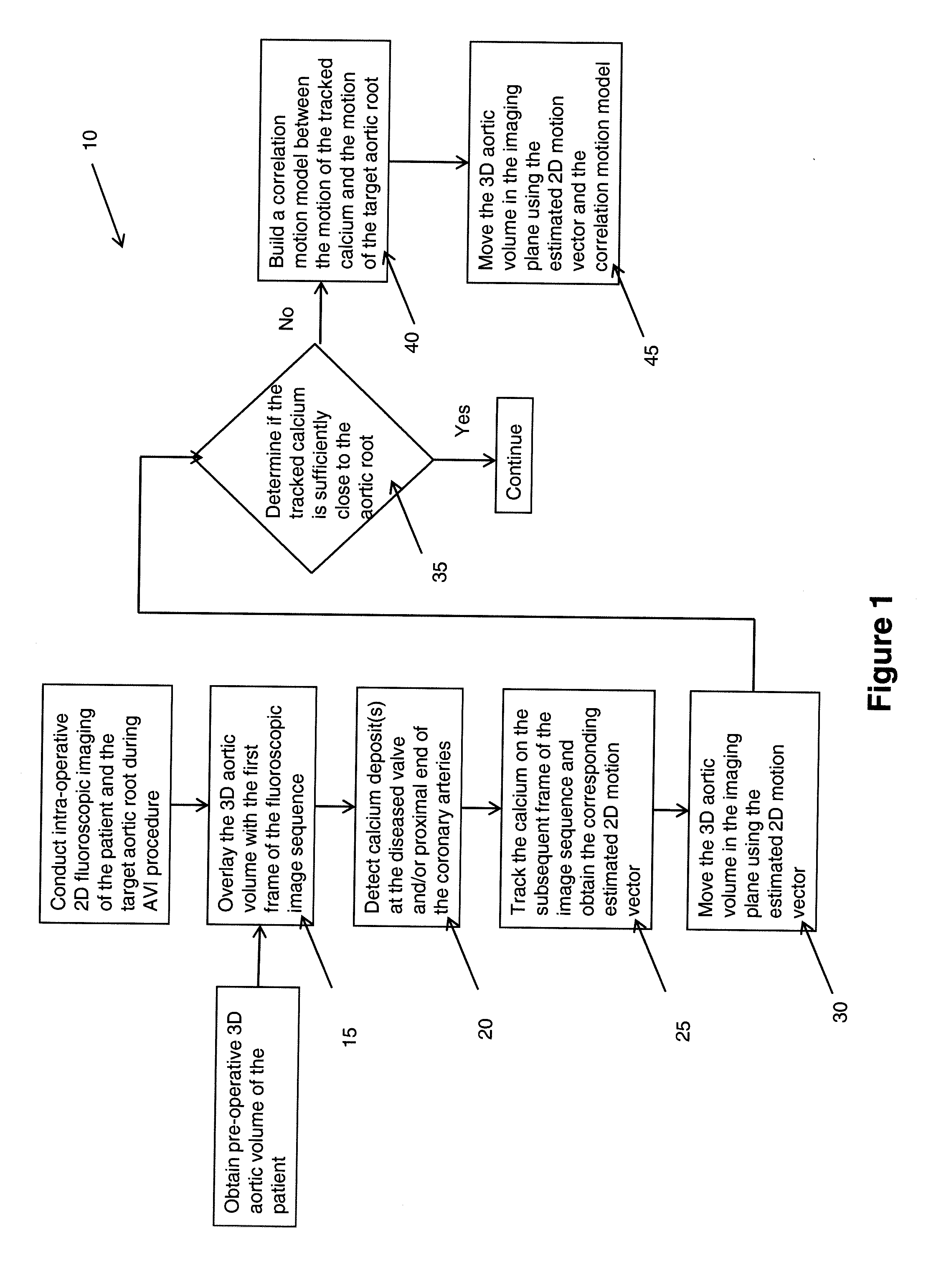
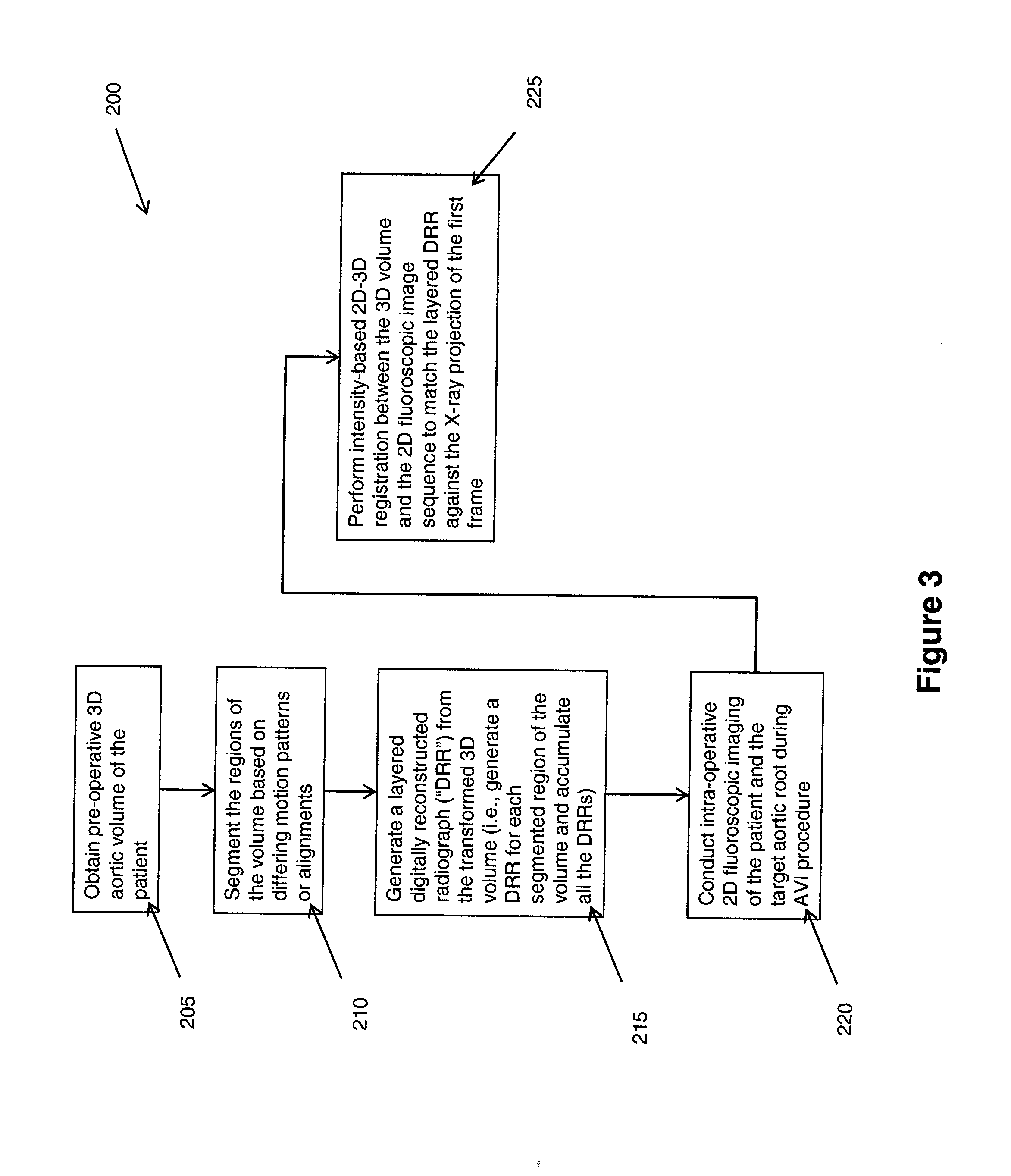
Method of motion compensation for trans-catheter aortic valve implantation
ActiveUS20110164035A1Not utilizeMotion compensationImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCardiac imaging
A method (10) to compensate for cardiac and respiratory motion in cardiac imaging during minimal invasive (e.g., trans-catheter) AVI procedures by image-based tracking (20, 25) on fluoroscopic images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Inflatable medical devices
Inflatable medical devices and methods for making and using the same are disclosed. The devices can be medical invasive balloons, such as those used for transcutaneous heart valve implantation, such as balloons used for transcatheter aortic-valve implantation. The balloons can have high strength, fiber-reinforced walls.
Owner:LOMA VISTA MEDICAL
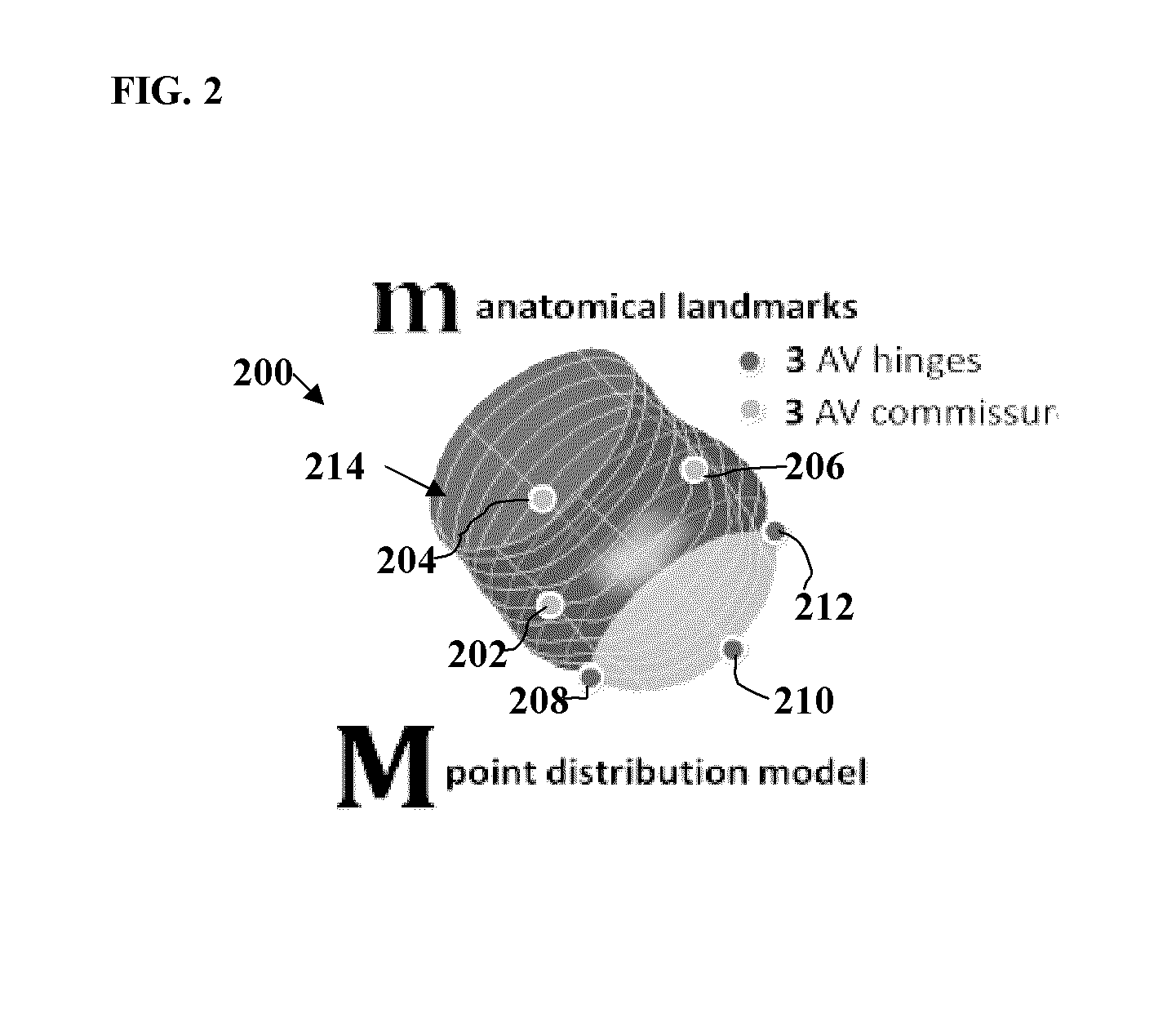
Method and System for Advanced Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Planning
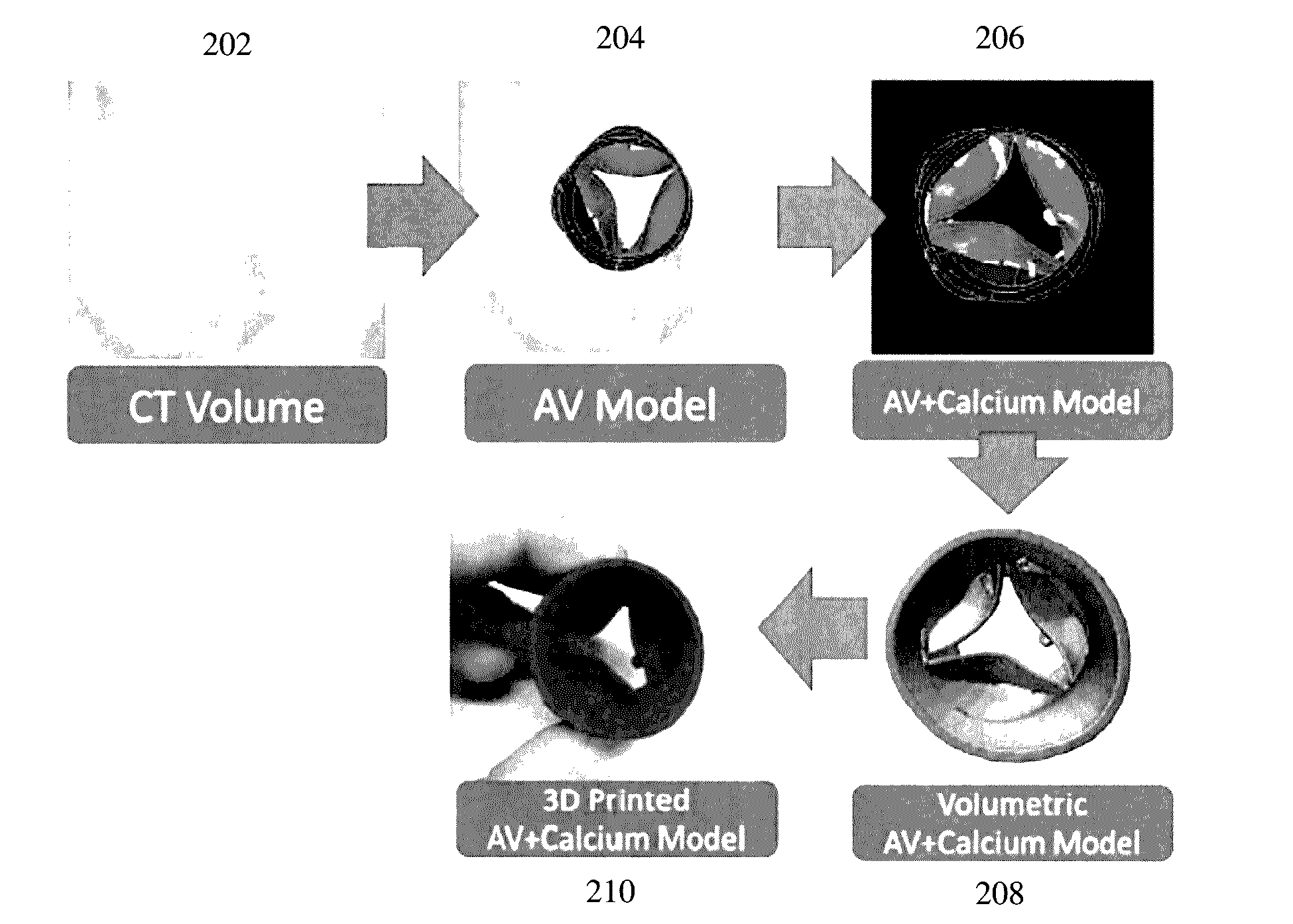
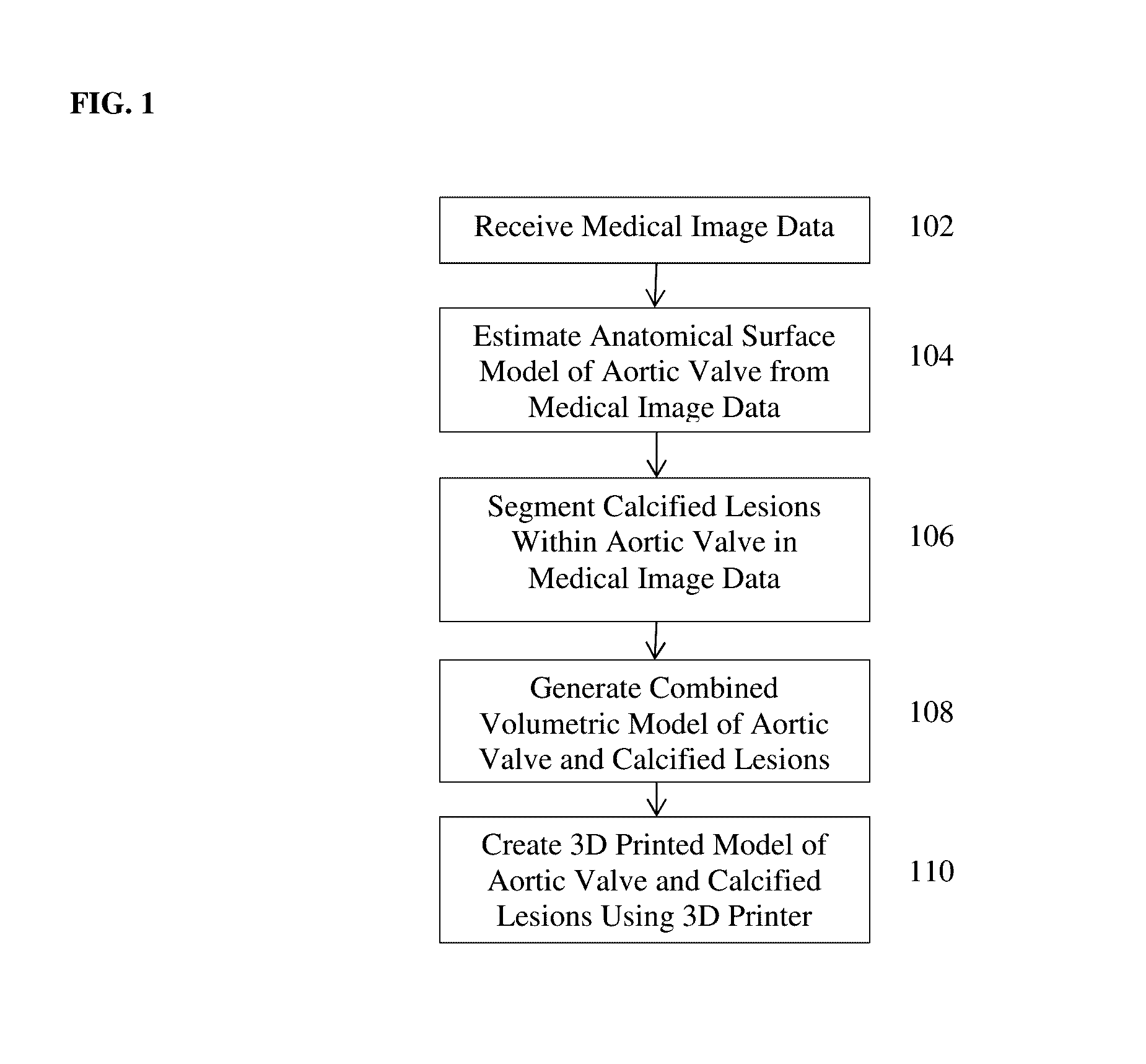
A method and system for transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) planning is disclosed. An anatomical surface model of the aortic valve is estimated from medical image data of a patient. Calcified lesions within the aortic valve are segmented in the medical image data. A combined volumetric model of the aortic valve and calcified lesions is generated. A 3D printed model of the heart valve and calcified lesions is created using a 3D printer. Different implant device types and sizes can be placed into the 3D printed model of the aortic valve and calcified lesions to select an implant device type and size for the patient for a TAVI procedure. The method can be similarly applied to other heart valves for any type of heart valve intervention planning.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Transcatheter atrial sealing skirt, anchor, and tether and methods of implantation
A medical assembly and methods for endovascularly implanting a valve in the heart having a valve and an anchor assembly for positioning and restraining the valve. An anchor delivery system introduces and implants the anchor into the implantation site and a valve delivery system introduces and seals the valve at the deployment site. The present invention also relates to methods of implantation of the medical assembly and the valve.
Owner:OPUS MEDICAL THERAPIES LLC
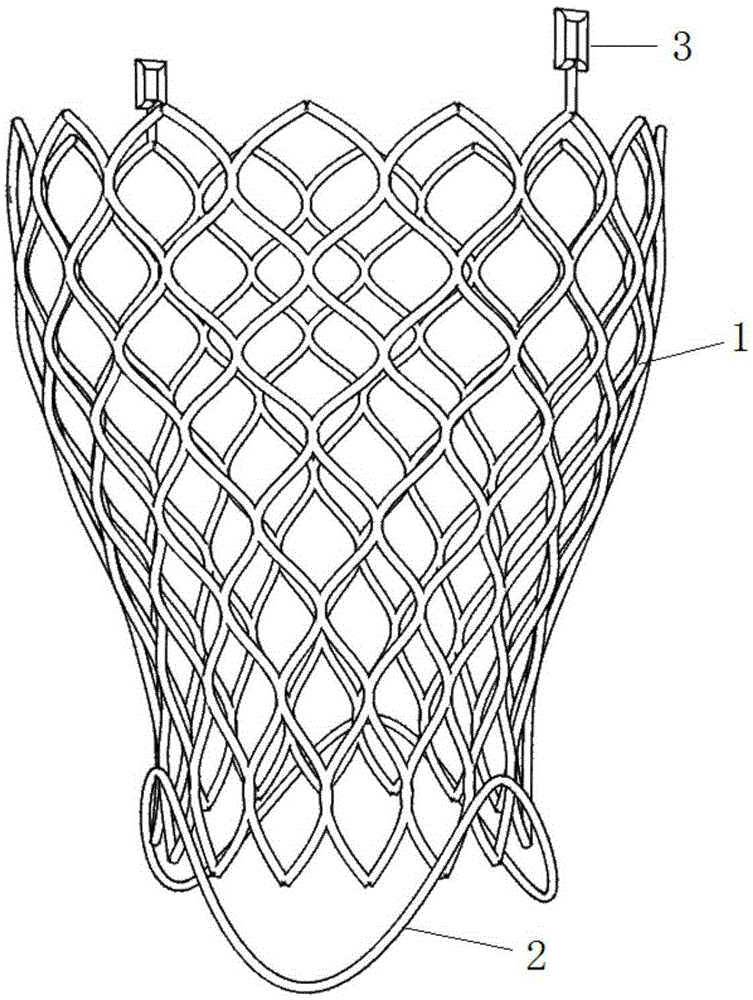
Transcatheter aortic valve and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109124829AAvoid problems with increased risk of being blockedReduced risk of cloggingHeart valvesCatheterAorta
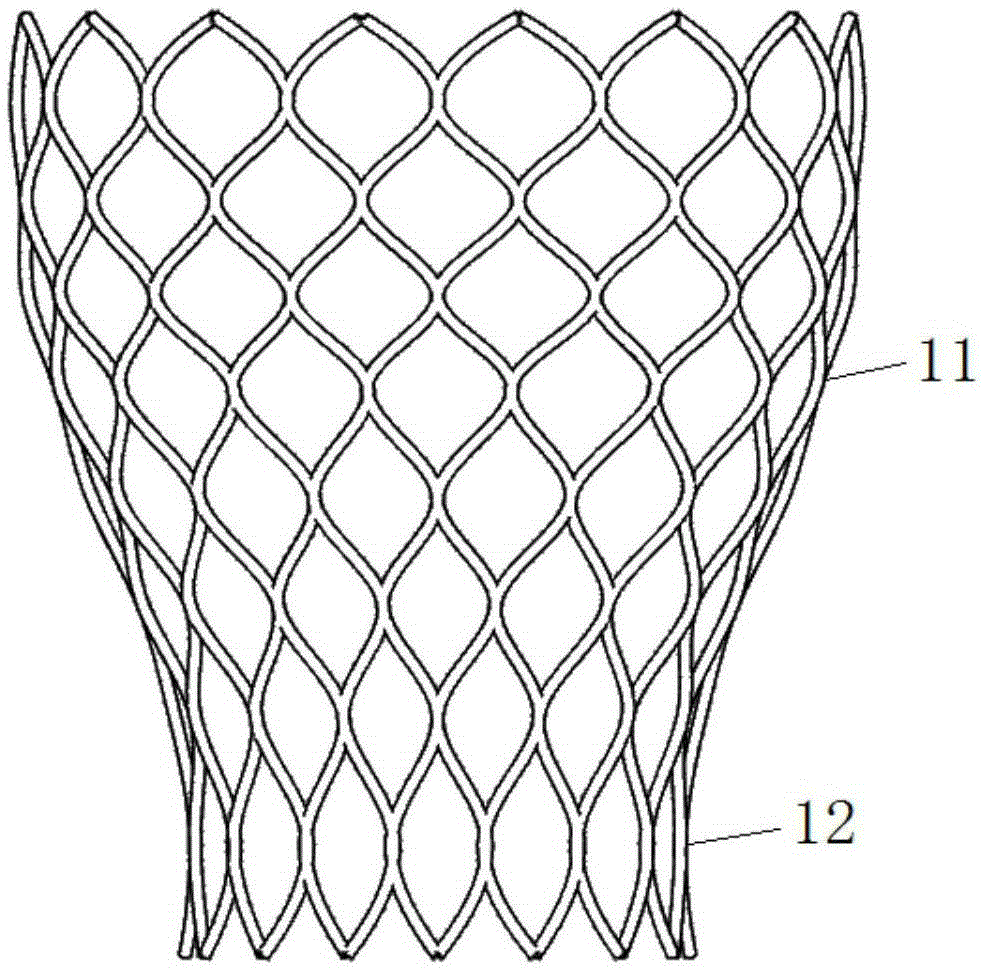
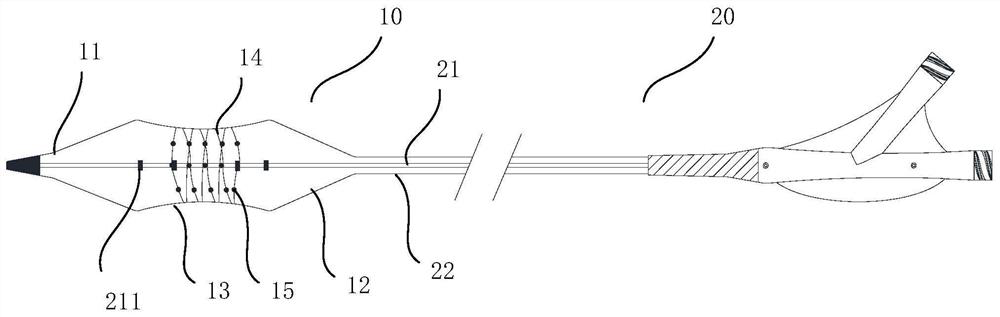
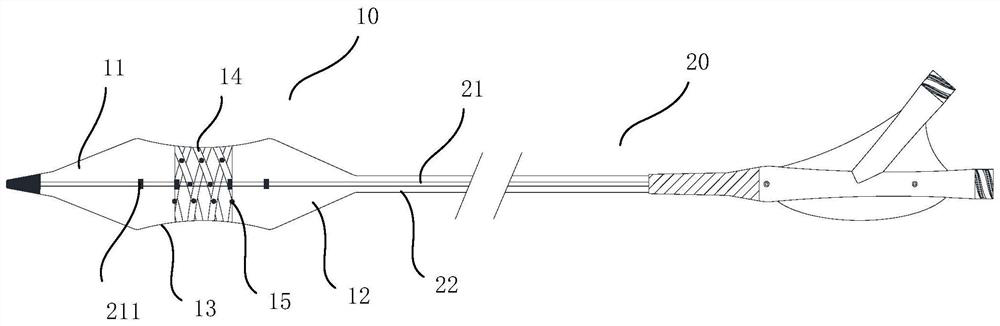
The invention provides a transcatheter aortic valve and preparation method thereof. The transcatheter aortic valve comprises a radially telescopic reticular valve frame, pedal skirts and multiple lobes, wherein the petal skirts are arranged on the inner side of the petal holder, the lobes are located in the lumen of the valve carrier, wherein the petal skirt is divided into a first region and a second region, the first region faces an inflow end of the aortic valve, the second region faces the outflow end of the aortic valve and the second region is provided with a mesh hole capable of communicating the inside and outside of the valve frame. The transcatheter aortic valve provided by the invention solves the problems that the coronary orifice is easy to be blocked after the aortic valve isimplanted in the prior art and the aortic valve is suitable for a patient.
Owner:KINGSTRONBIOCHANGSHU CO LTD
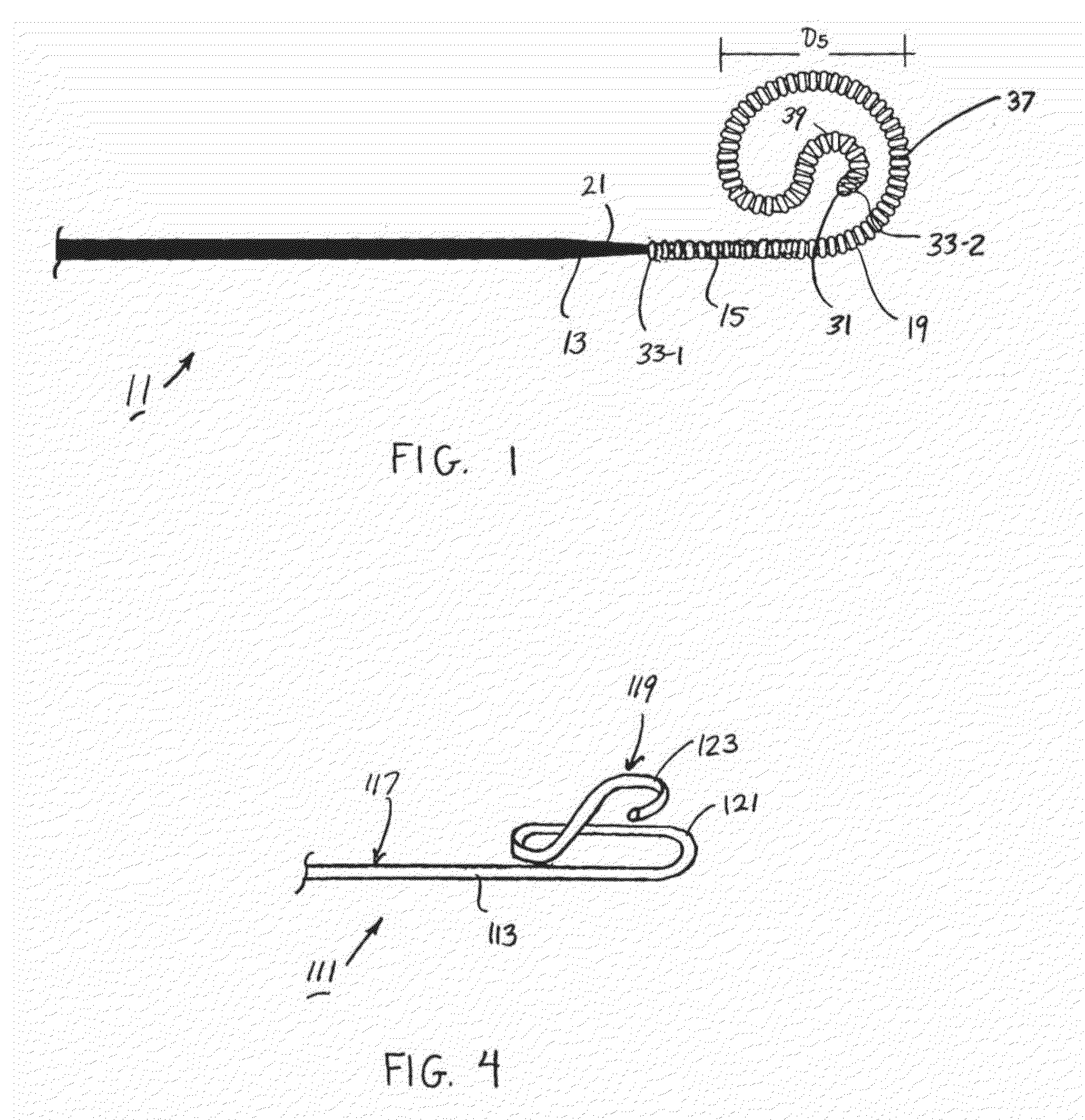
Preformed guidewire
ActiveUS20150290432A1Risk minimizationReduce manufacturing costGuide wiresProsthesisProximateDistal segment
A preformed guidewire particularly well-suited for use in percutaneous medical procedures, such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement, includes an inner corewire of discontinuous, tapered stiffness that is surrounded along a portion of its length by a flexible, outer casing of uniform cross-section, such as a tightly wound, stainless steel, spring coil wire. The inner corewire is constructed of a shape-memory material, such as a nickel-titanium alloy, that is preformed into an encircled S-shaped configuration in its atraumatic distal region. Specifically, the distal region includes an enlarged, stiffened, proximate segment that encircles a smaller, more flexible, distal segment. As a feature of the invention, the distal and proximal segments project along fixed-radial arcuate paths that extend in opposite directions from one another. As a result, the distal region is optimally configured to limit the risk of trauma to the immediate site of treatment when inserted through a straightened guide catheter.
Owner:CONCERT MEDICAL
Transcatheter atrio-ventricular valve prosthesis
A transcatheter atria-ventricular valve prosthesis for functional replacement of an atrio-ventricular valve in a connection channel, having a circumferential connection channel wall structure, between atrial and ventricular chambers of a heart, including an inner device to be disposed in the interior of the connection channel, the inner device having a circumferential support structure which is radially expandable and having a valve attached to the circumferential support structure, and an outer device to be disposed on the exterior of the connection channel, wherein the outer device at least partly extends around the inner device at a radial distance to the inner device, wherein the inner and outer devices form a securing mechanism for securing the circumferential connection channel wall structure therebetween.
Owner:HIGHLIFE
TAVR Ventricular Catheter
InactiveUS20140155994A1Minimally invasiveControl flowHeart valvesGuide wiresVentricular cathetersAortic Valve Annulus
A catheter for positioning a valve during a transcatheter aortic valve replacement is formed from a resilient hollow body conformable to a guide wire when a guide wire is passed in through an upper opening in the hollow body and through the hollow body. When the guide wire is retracted, the catheter deploys to form a substantially straight upper shaft portion that extends downwardly from the upper opening and a distal ring perpendicular to the upper shaft portion. The distal ring approximates the size and shape of the patient's aortic valve annulus. A lower loop connects the upper shaft portion of the catheter to the distal ring. An outer surface of the distal ring is radiopaque, and the distal ring comprises openings for dispersing radio opaque medium used in imaging of the patient's aortic valve annulus. The deployed catheter is retracted until it snugly contacts the aortic valve annulus. The distal ring will be viewed as a straight line when the x-ray C-arm is properly aligned with the aortic valve annulus.
Owner:MCDONALD MICHAEL B
Transcatheter device and system for the delivery of intracorporeal devices
ActiveUS20180099078A1Improve fluid flowImprove control of fluid flowIntravenous devicesBlood pumpGuide tubeMedical device
An intracorporeal device for delivery into a patient is provided. The intracorporeal device includes a proximal end and a distal end. The distal end is detachably coupled from the transcatheter delivery device. The device relates to a transcatheter system and corresponding devices and methods of treatment, and is particularly useful for the delivery and implantation into the body of a patient of medical devices, such as mechanical circulatory support devices, but also has a wider variety of applications.
Owner:NUHEART
Method and System for Intervention Planning for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation from 3D Computed Tomography Data
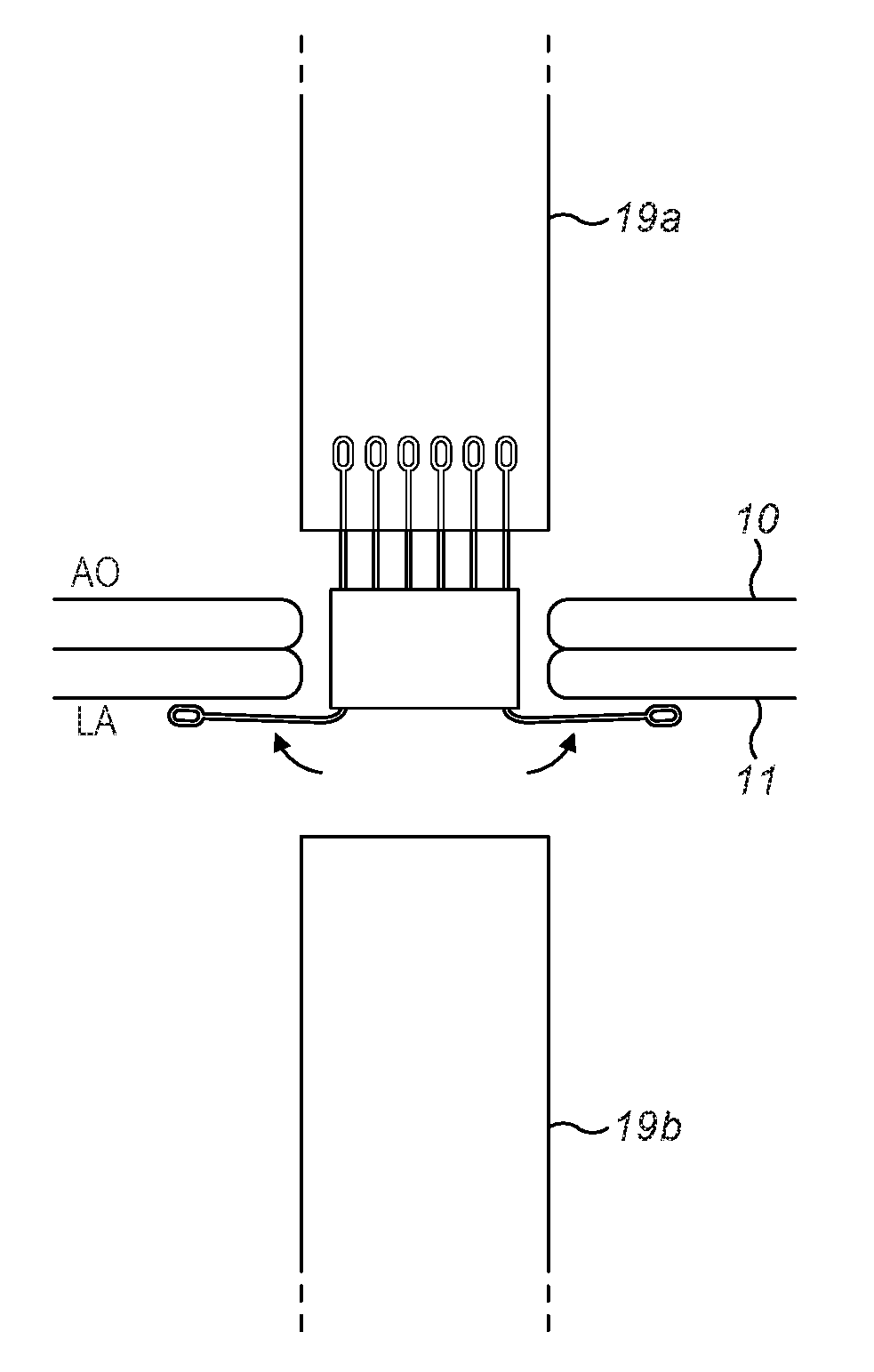
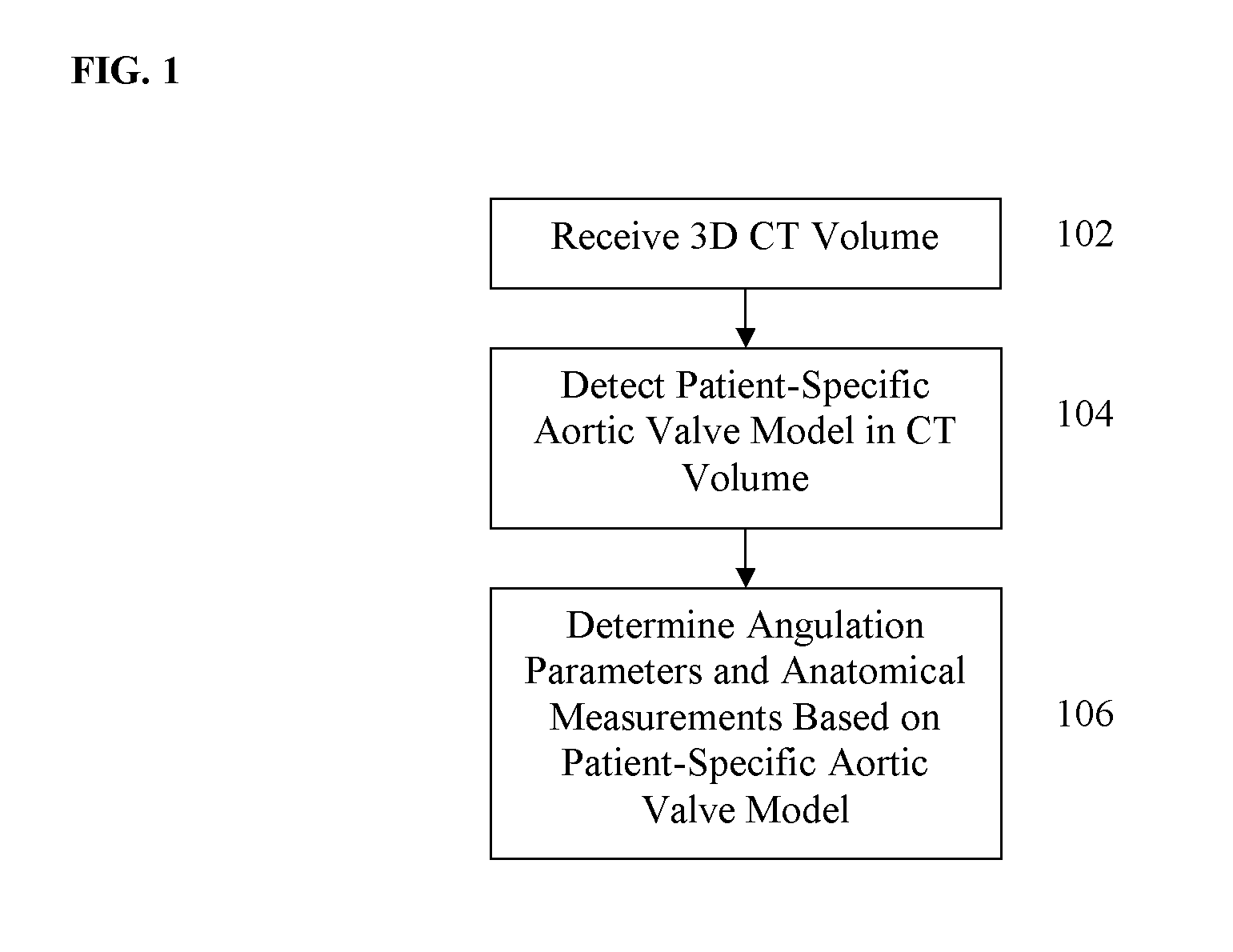
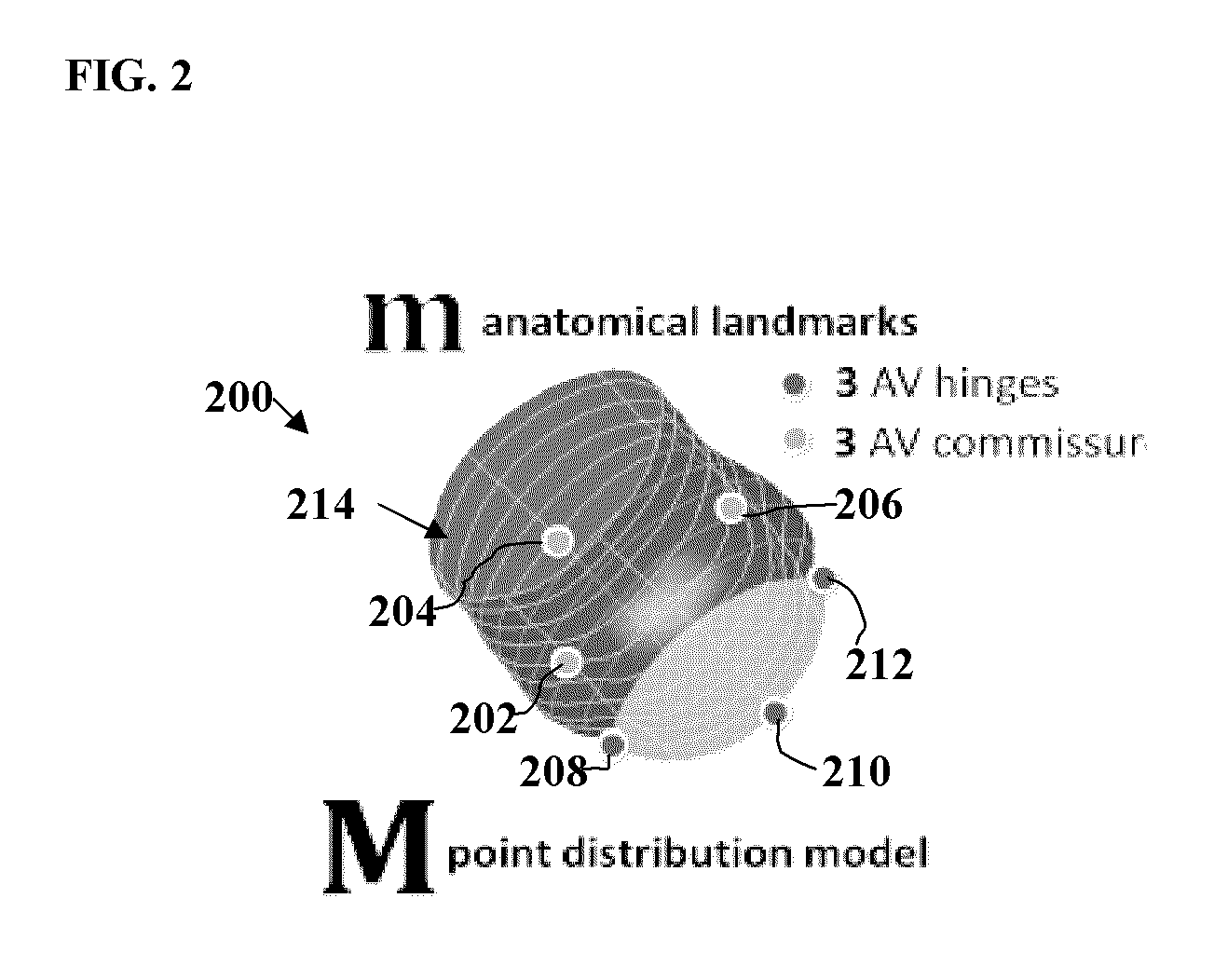
A method and system for automated intervention planning for transcatheter aortic valve implantations using computed tomography (CT) data is disclosed. A patient-specific aortic valve model is detected in a CT volume of a patient. The patient-specific aortic valve model is detected by detecting a global location of the patient-specific aortic valve model in the CT volume, detecting aortic valve landmarks based on the detected global location, and fitting an aortic root surface model. Angulation parameters of a C-arm imaging device for acquiring intra-operative fluoroscopic images and anatomical measurements of the aortic valve are automatically determined based on the patient-specific aortic valve model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation pressure wires and uses thereof
Described herein is a guide wire that includes one, two or multiple pressure transducers for use in TAVI. The guide wire may include an aortic pressure sensor spaced from a left ventricular pressure sensor with sufficient length to allow the aortic pressure sensor to be located in the aorta while the ventricular pressure sensor is simultaneously located in the left ventricle. The pressure readings between the left ventricle and aorta may be subtracted to determine an improved indication of the prognosis of a patient with intermediate post-TAVR aortic regurgitation after assessment with transesophageal echocardiography.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation pressure wires and uses thereof
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Systems for transcatheter ablation of adventitial or perivascular tissue while preserving medial and intimal vascular integrity through convergence of energy from one or more sources, and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20130325000A1Reduce riskEasy to participateSurgical instruments for heatingTunica intimaPerivascular space
Under one aspect of the present invention, a system for performing renal denervation in a patient having an aorta and a renal artery and a branchpoint therebetween includes a flexible catheter comprising a main section, first and second arms, and a bifurcation between the first and second arms, the main section having a proximal end and a distal end, the distal end configured to be disposed in the aorta, the first arm being coupled to the distal end of the main section and configured to be disposed in the renal artery, the second arm being coupled to the distal end of the main section and configured to be disposed in the aorta, the bifurcation between the first and second arms being configured to engage the branchpoint between the aorta and the renal artery.
Owner:BATES MARK C
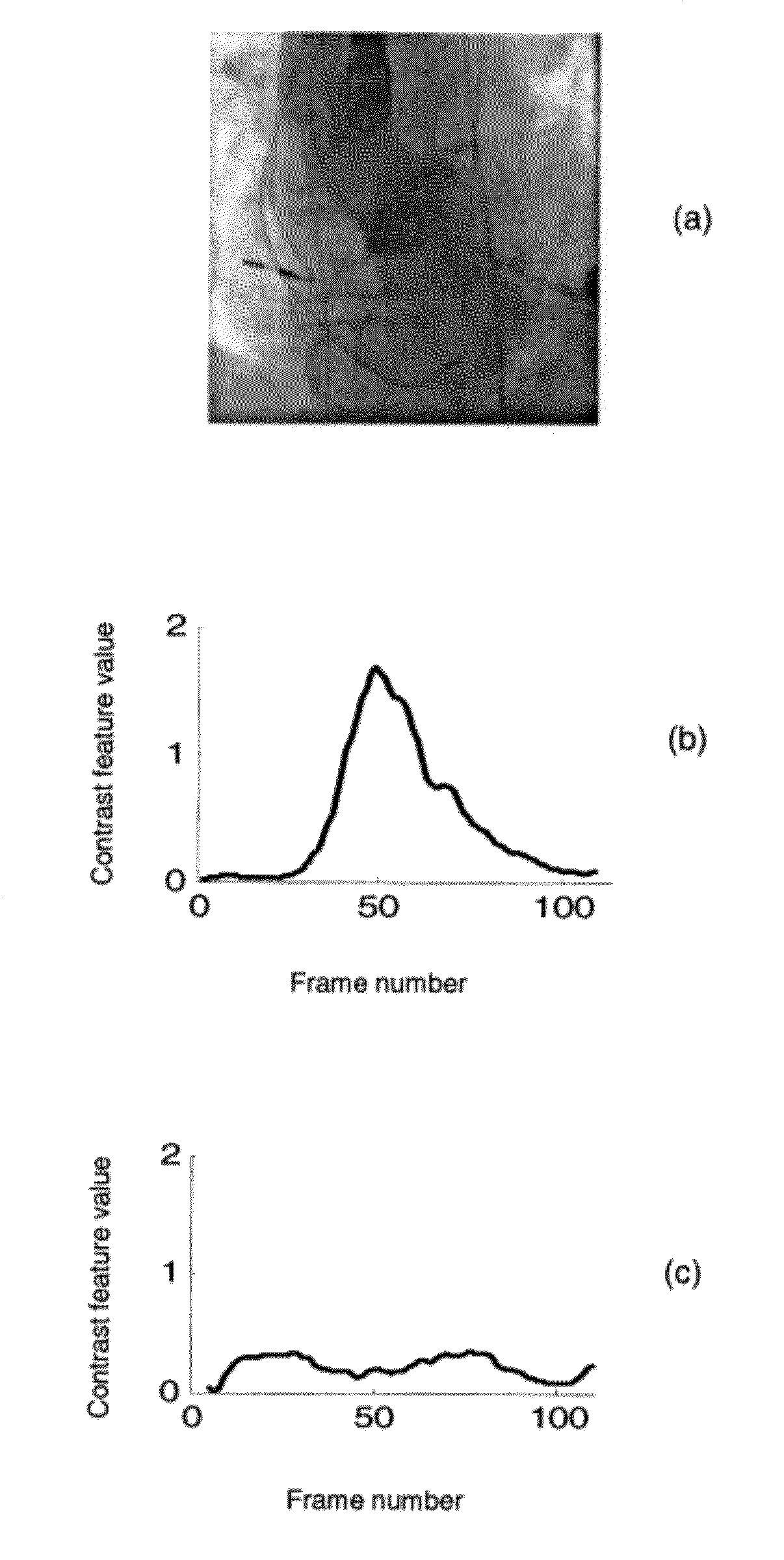
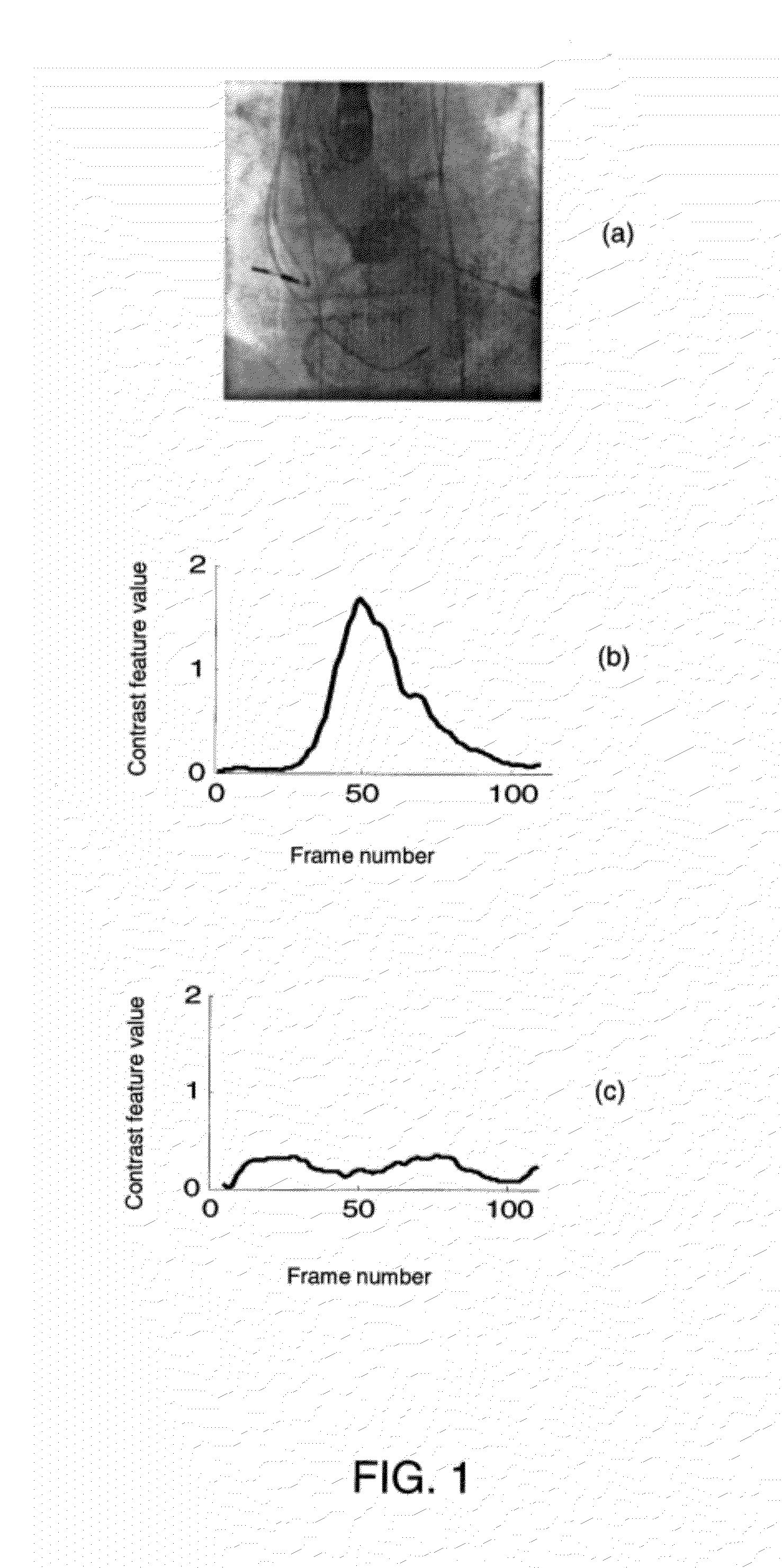
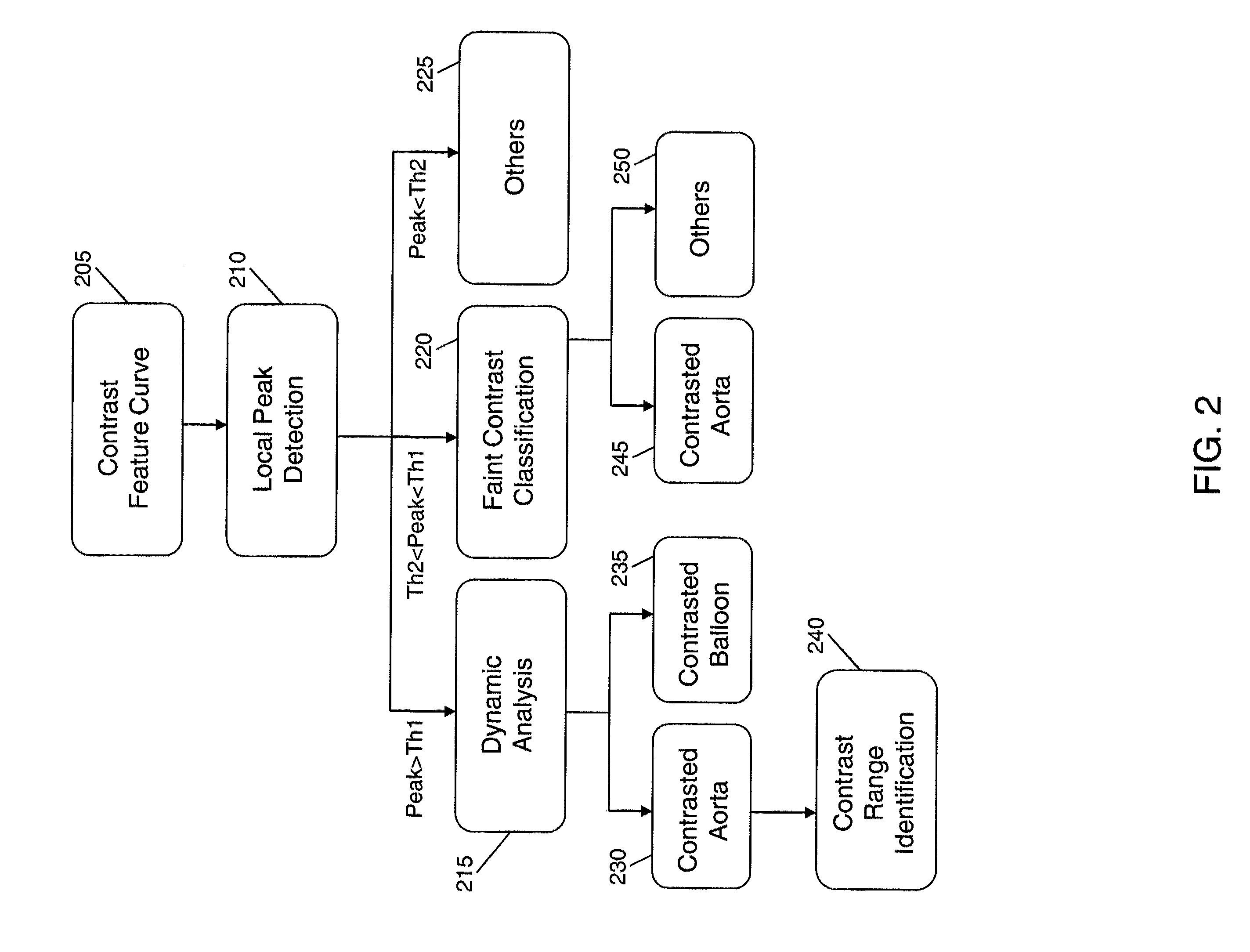
Spatio-Temporal Analysis for Automatic Contrast Injection Detection on Angiography During Trans-Catheter Aortic Valve Implantation
A method that includes generating a contrast feature curve for a medical image sequence including a plurality of frames, where the contrast feature curve represents contrast feature values of the frames. The method further includes detecting a peak in the contrast feature curve, and determining whether the peak corresponds to at least one of contrast injection in an aortic root, contrast injection in a balloon, and a non-contrast injected region.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and apparatus comprising a multisensor guidewire for use in interventional cardiology
InactiveUS20160128583A1Reduce disadvantagesAvoiding tissue trauma or perforationHeart valvesCatheterControl systemMultiple sensor
A system and apparatus comprising a multisensor guidewire for use in interventional cardiology, e.g. for Transcatheter Valve Therapies (TVT), comprises a plurality of optical sensors for direct measurement of cardiovascular parameters, e.g. transvalvular blood pressure gradients and flow. A conventional outer coil contains a shaped core wire having a cross-section defining helical grooves extending along its length, which accommodate optical fibers and optical sensors within a diameter Dcore of the core wire. Advantageously, the diameter and material of the core wire provides the guidewire with sufficient stiffness for use as a support guidewire for valve replacement, e.g. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI), while accommodating multiple sensors and optical fibers within a guidewire of outside diameter ≦0.89 mm. An optical connector couples the guidewire to a control system. Optionally, the guidewire includes a contact force sensor; a pre-formed tip; and / or a separable micro-connector for proximal mounting of over-the-guidewire components.
Owner:THREE RIVERS CARDIOVASCULAR SYST
Transcatheter device for the ablation of calcified tissue at the flaps of an aortic valve
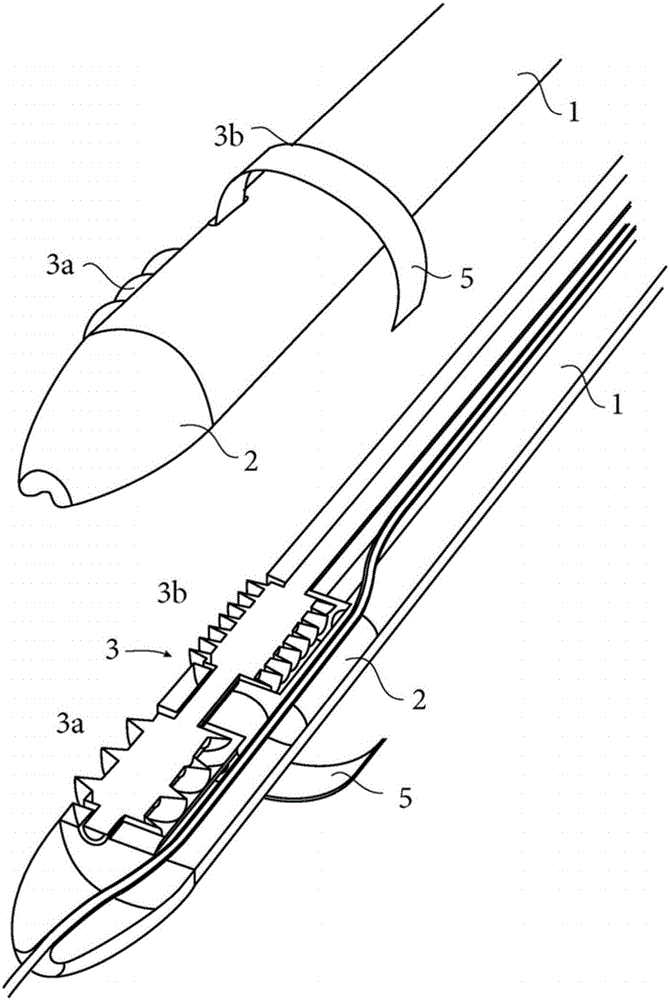
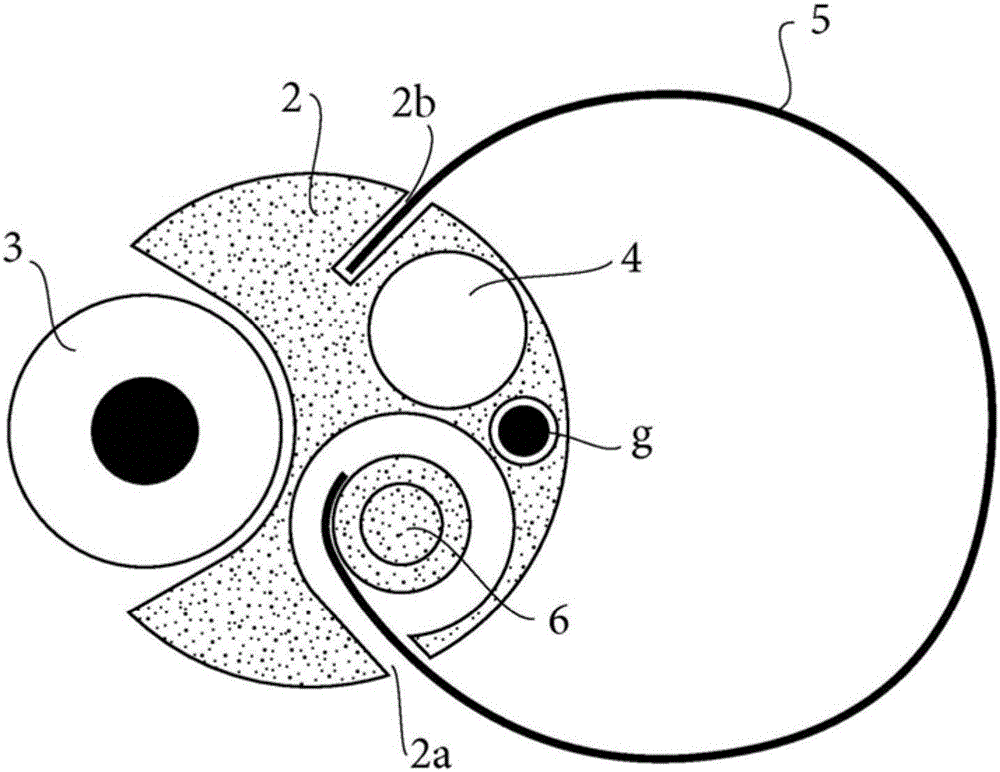
This transcatheter device for the ablation of calcified tissue at the flaps of an aortic valve, is characterised in that it comprises a flexible body (1) acting as a catheter and having a soft and flexible end piece (2) that engages with a previously inserted wire guide (g) suitable for passing through the flaps of the valve above the part where the calcified tissue needs to be removed, said end piece (2) having at least one cutting system (3) comprising two motorised rotating cutting heads (3a) and (3b) disposed coaxially one above the other, the head (3a) located at the end of the end piece and acting first to remove the calcified tissue, has arrangements suitable for making a rough cut by grinding, while the other head (3b) has arrangements suitable for making a fine cut by grinding, said cutting system being mounted in combination with a vacuum suction means (4), said end piece (2) being provided with an adjustable guide means (5) suitable for engaging with the calcified tissue over the course of the ablation operation performed by the cutting system (3) in combination with a spiral path effect applied to the end piece.
Owner:奥蒂科勒勃(股份)责任有限公司 +1
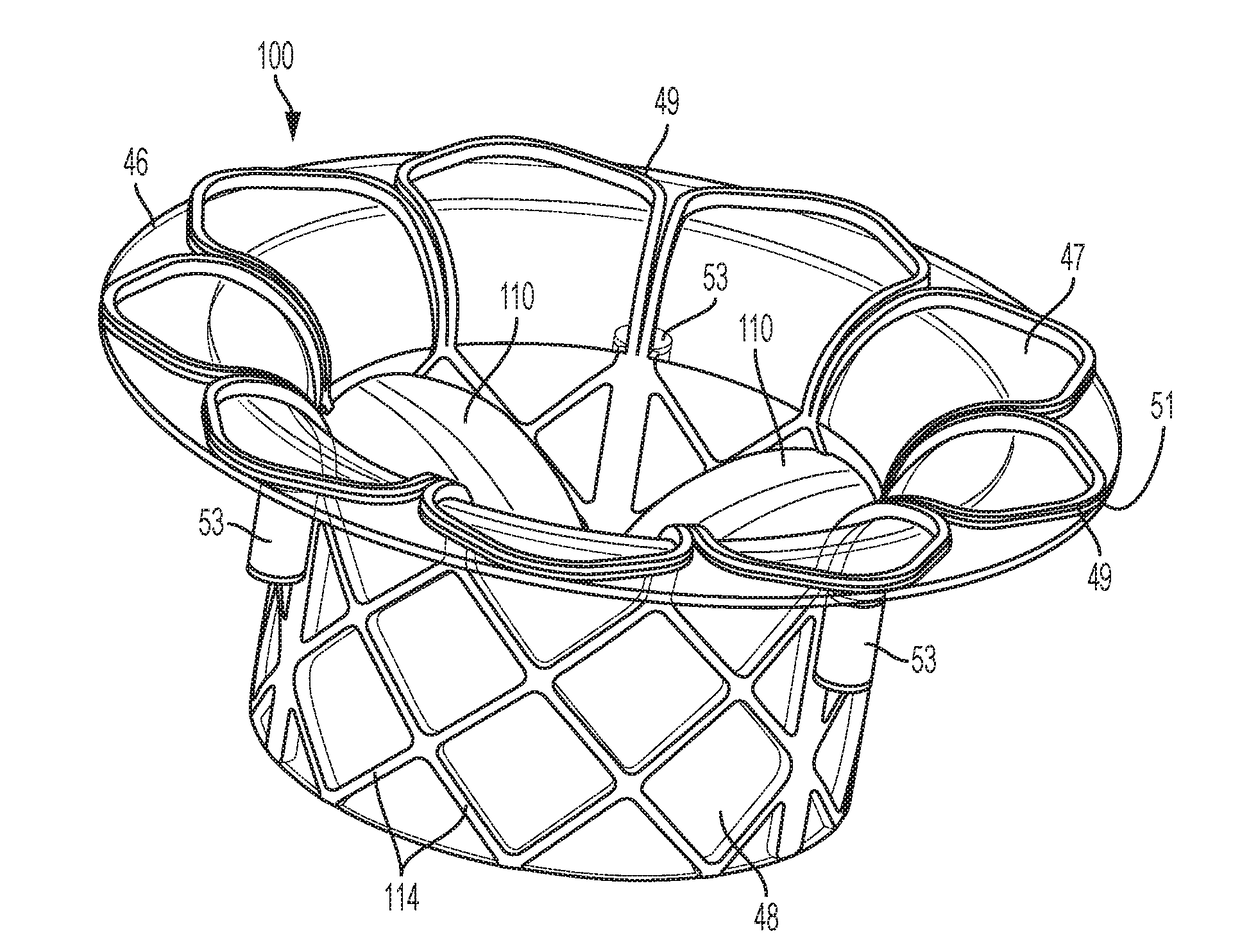
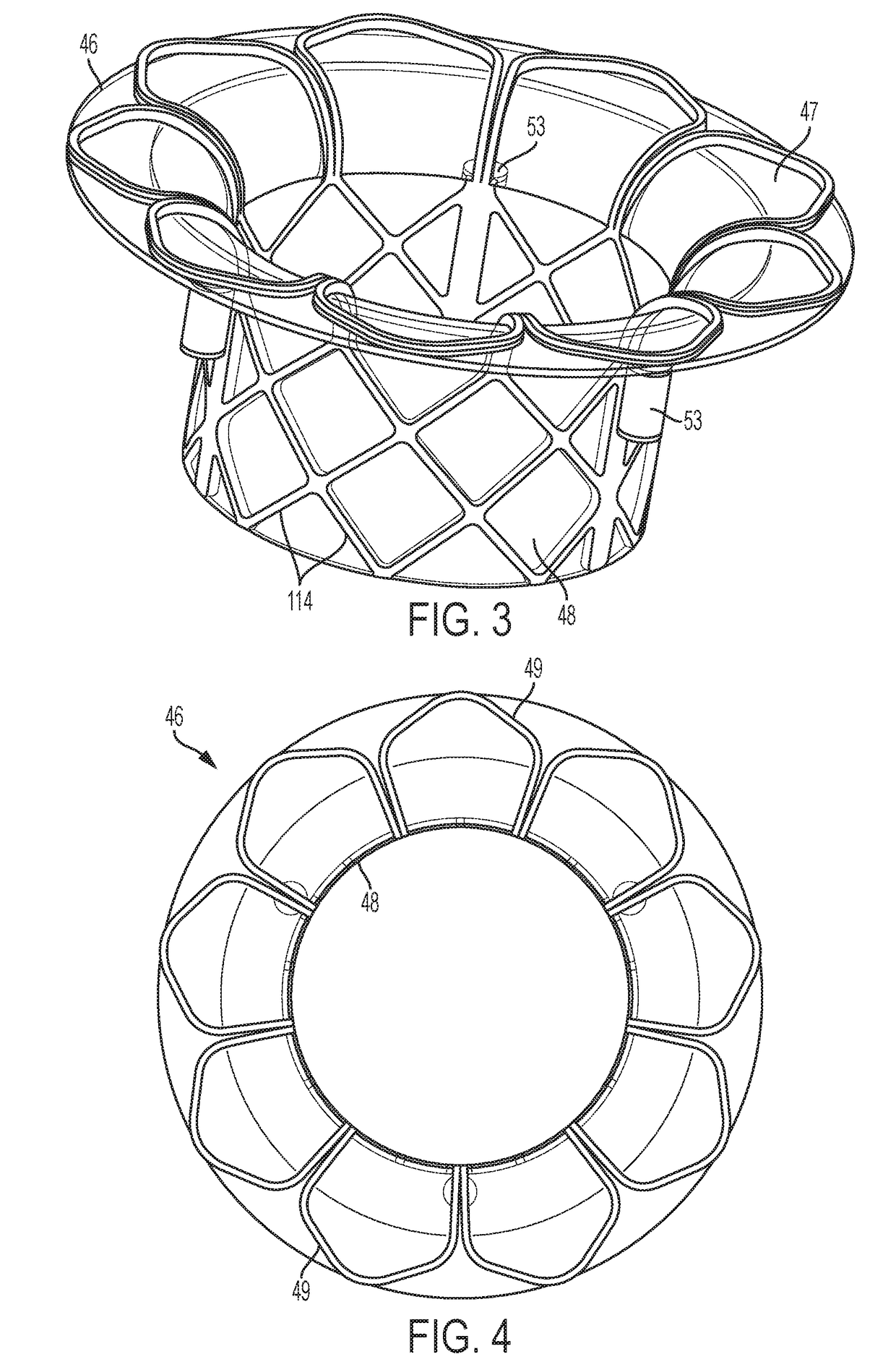
Expandable radiopaque marker for transcatheter aortic valve implantation
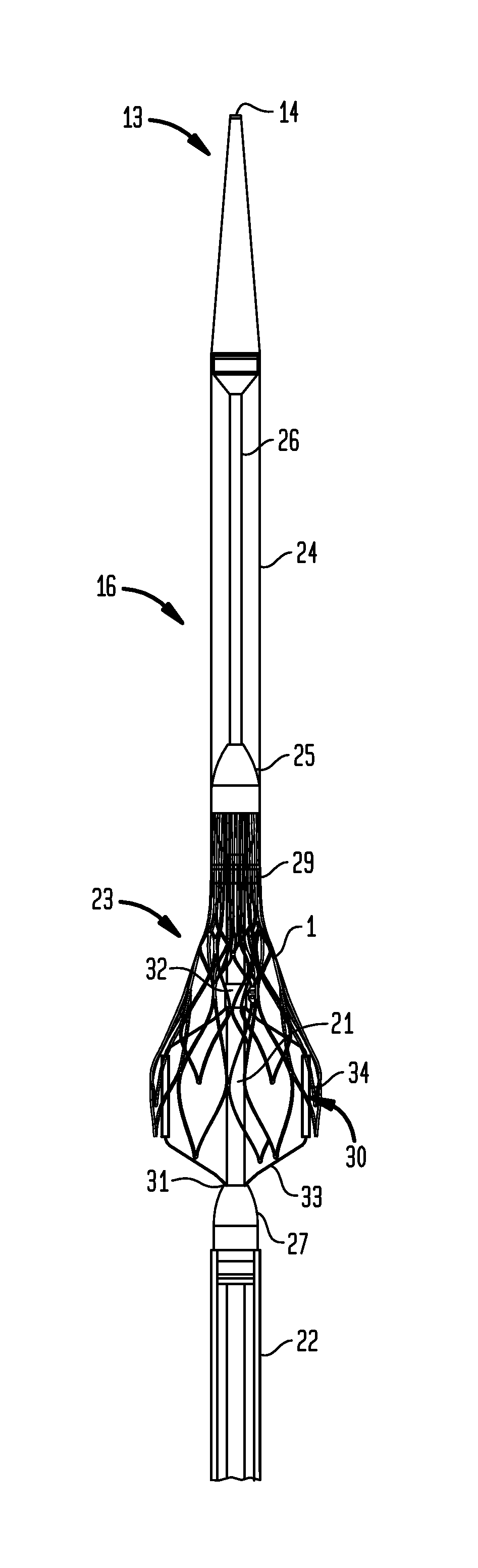
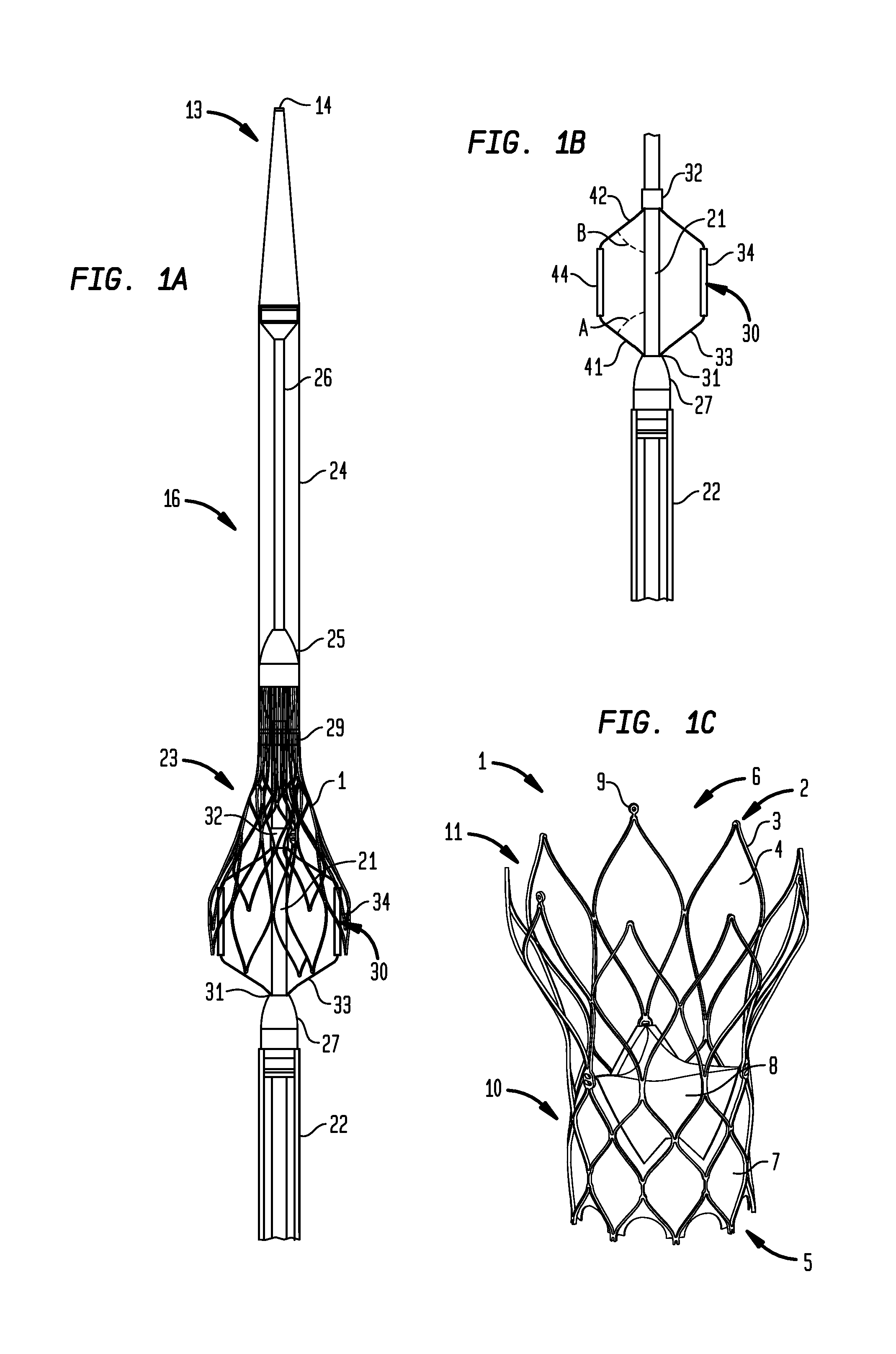
A delivery device for a collapsible prosthetic heart valve includes a support shaft around which a compartment for the valve is defined, a distal sheath adapted to selectively cover and uncover the compartment and the valve, and a marker cage having a collapsed condition when the distal sheath covers the compartment and an expanded condition when the compartment is uncovered. The marker cage includes at least one rib having a radiopaque marker for determining the positioning of the valve as it is deployed. The valve may be assembled around the marker cage so that the marker cage does not interfere with the radial expansion of the valve during deployment.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LLC
Method and system for intervention planning for transcatheter aortic valve implantation from 3D computed tomography data
A method and system for automated intervention planning for transcatheter aortic valve implantations using computed tomography (CT) data is disclosed. A patient-specific aortic valve model is detected in a CT volume of a patient. The patient-specific aortic valve model is detected by detecting a global location of the patient-specific aortic valve model in the CT volume, detecting aortic valve landmarks based on the detected global location, and fitting an aortic root surface model. Angulation parameters of a C-arm imaging device for acquiring intra-operative fluoroscopic images and anatomical measurements of the aortic valve are automatically determined based on the patient-specific aortic valve model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Delivery device having a curved shaft and a straightening member for transcatheter aortic valve implantation
A delivery device (100) includes a support member (128), a distal sheath (130), an outer shaft (120) and a strengthening member (140). The support member is adapted to hold a prosthetic heart valve. The distal sheath is slidable relative to the support member between a first position in which the distal sheath is adapted to maintain the prosthetic heart valve in a collapsed condition, and a second position in which the distal sheath is adapted to expose the prosthetic heart valve. The outer shaft is connected to the distal sheath and has a curved portion (134). The straightening member is slidable on the outer shaft between a proximal position in which the straightening member does not cover the curved portion of the outer shaft, and a distal position in which the straightening member covers and substantially straightens at least a portion of the curved portion of the outer shaft.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
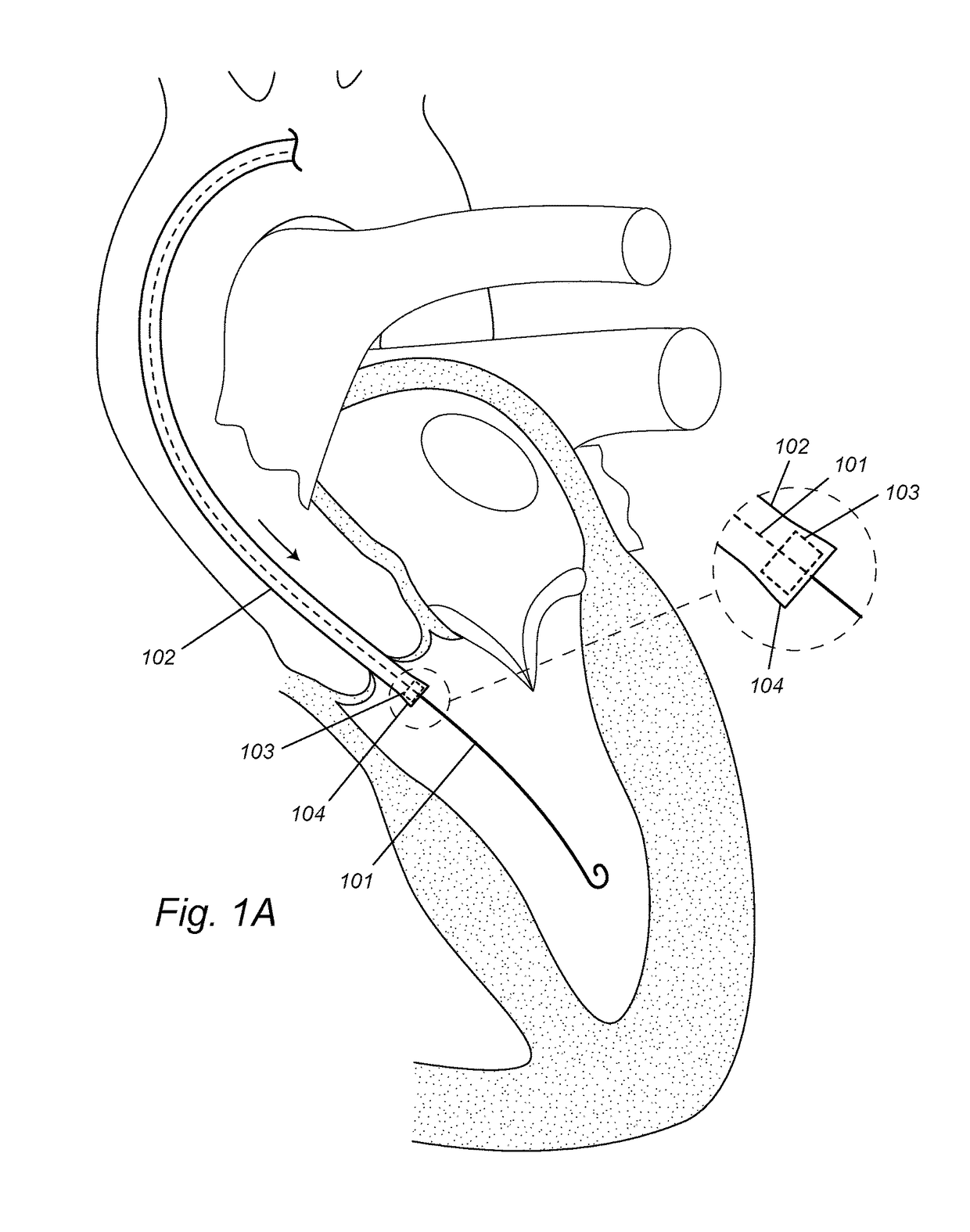
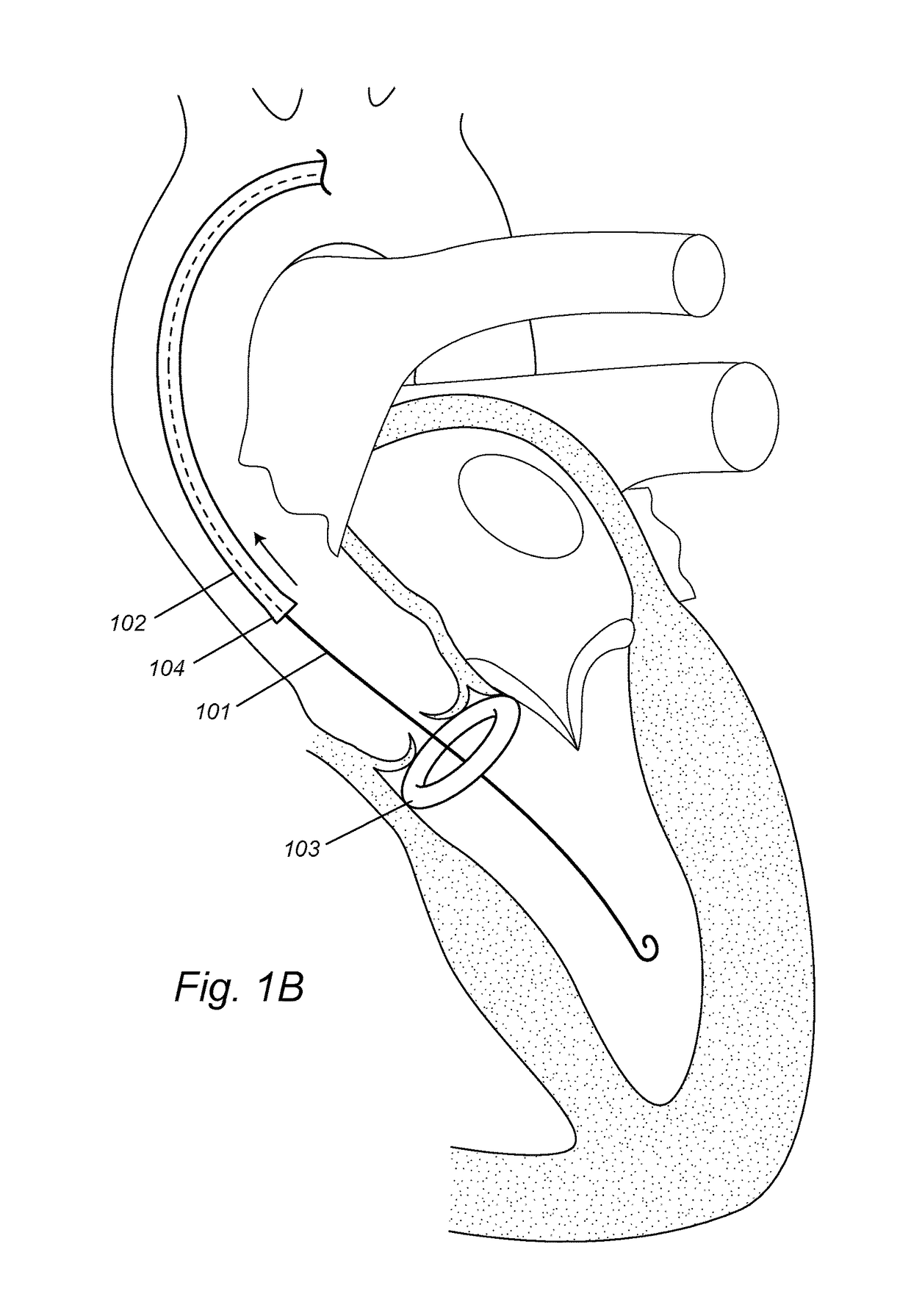
Transcatheter device for interatrial anastomosis
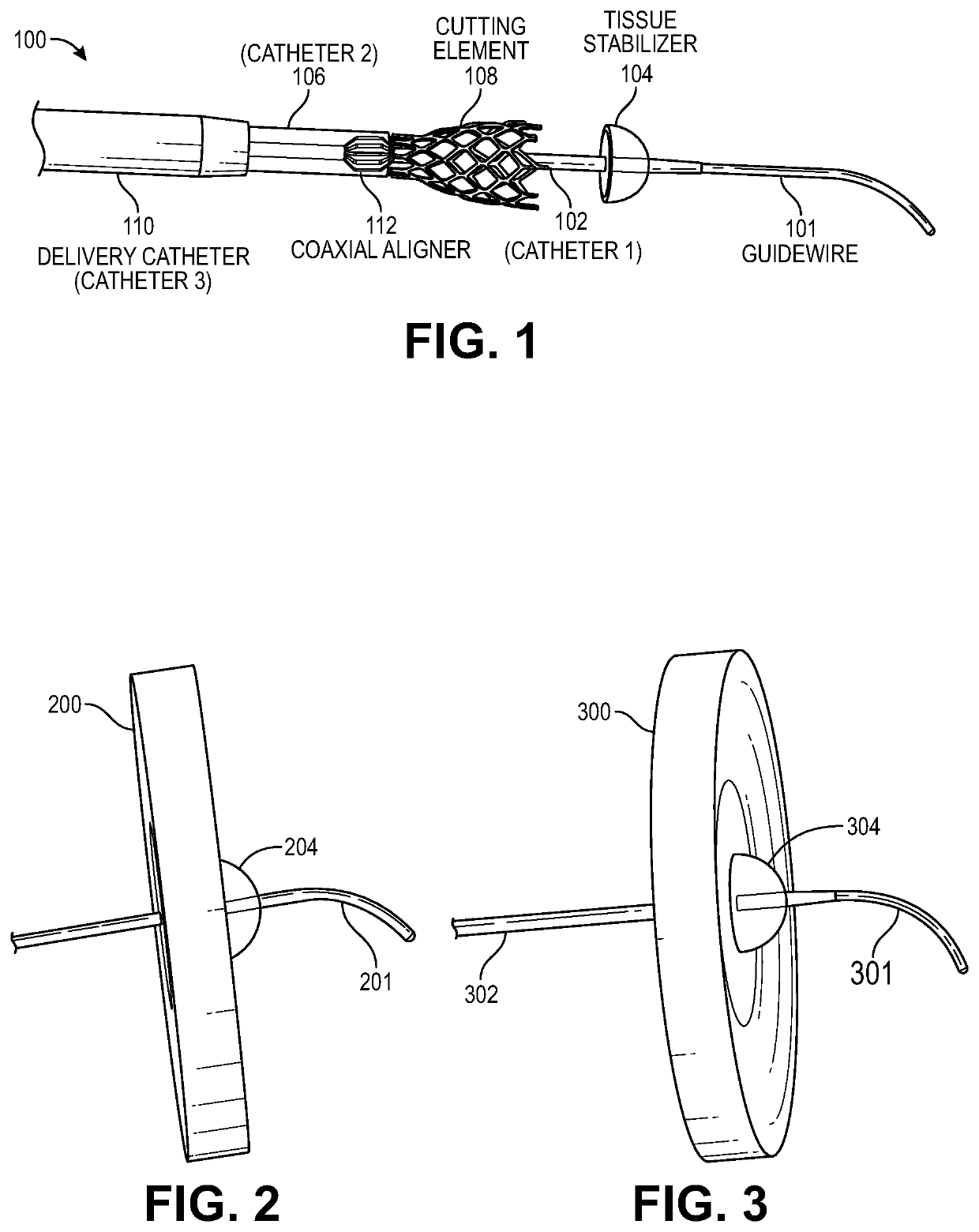
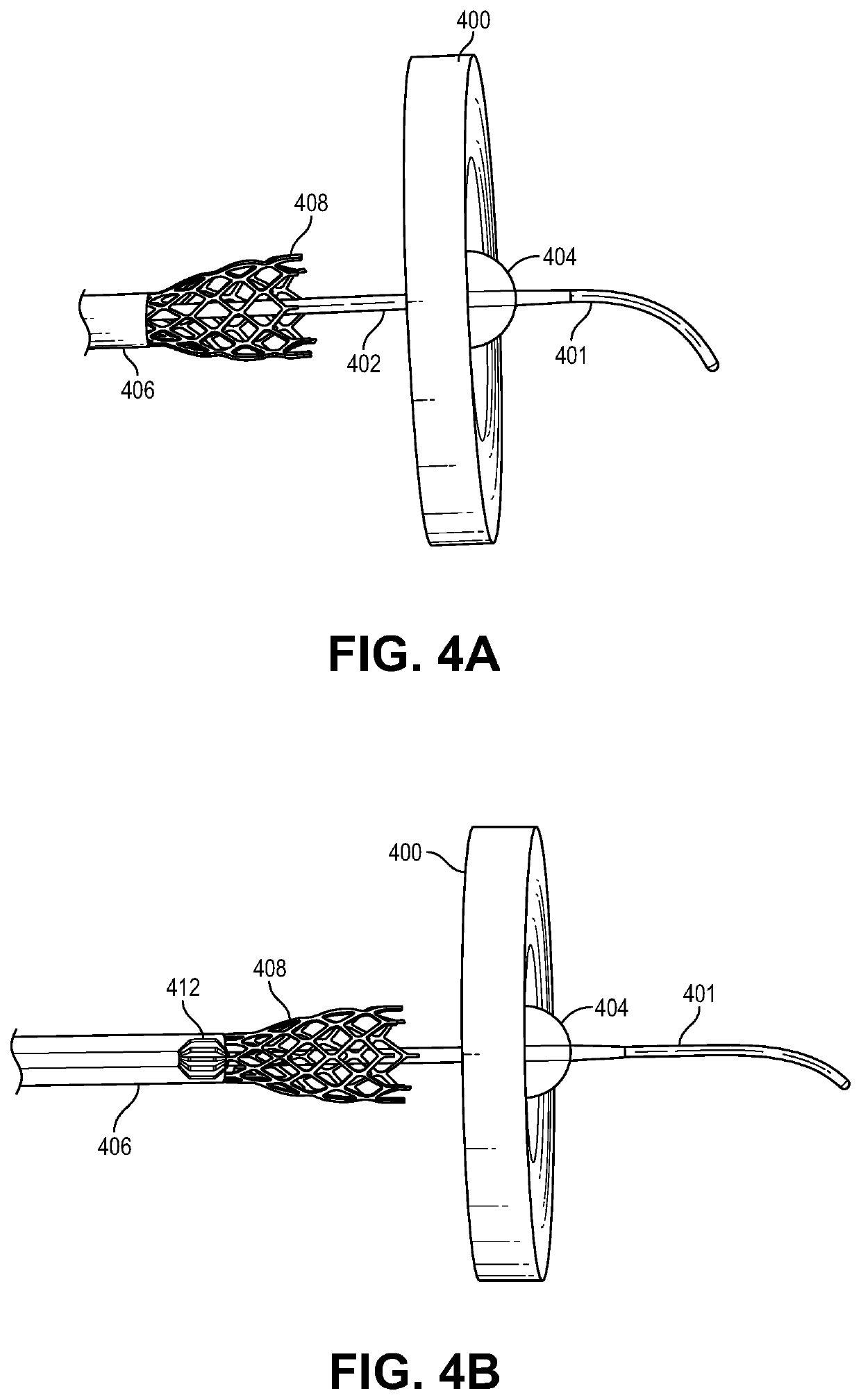
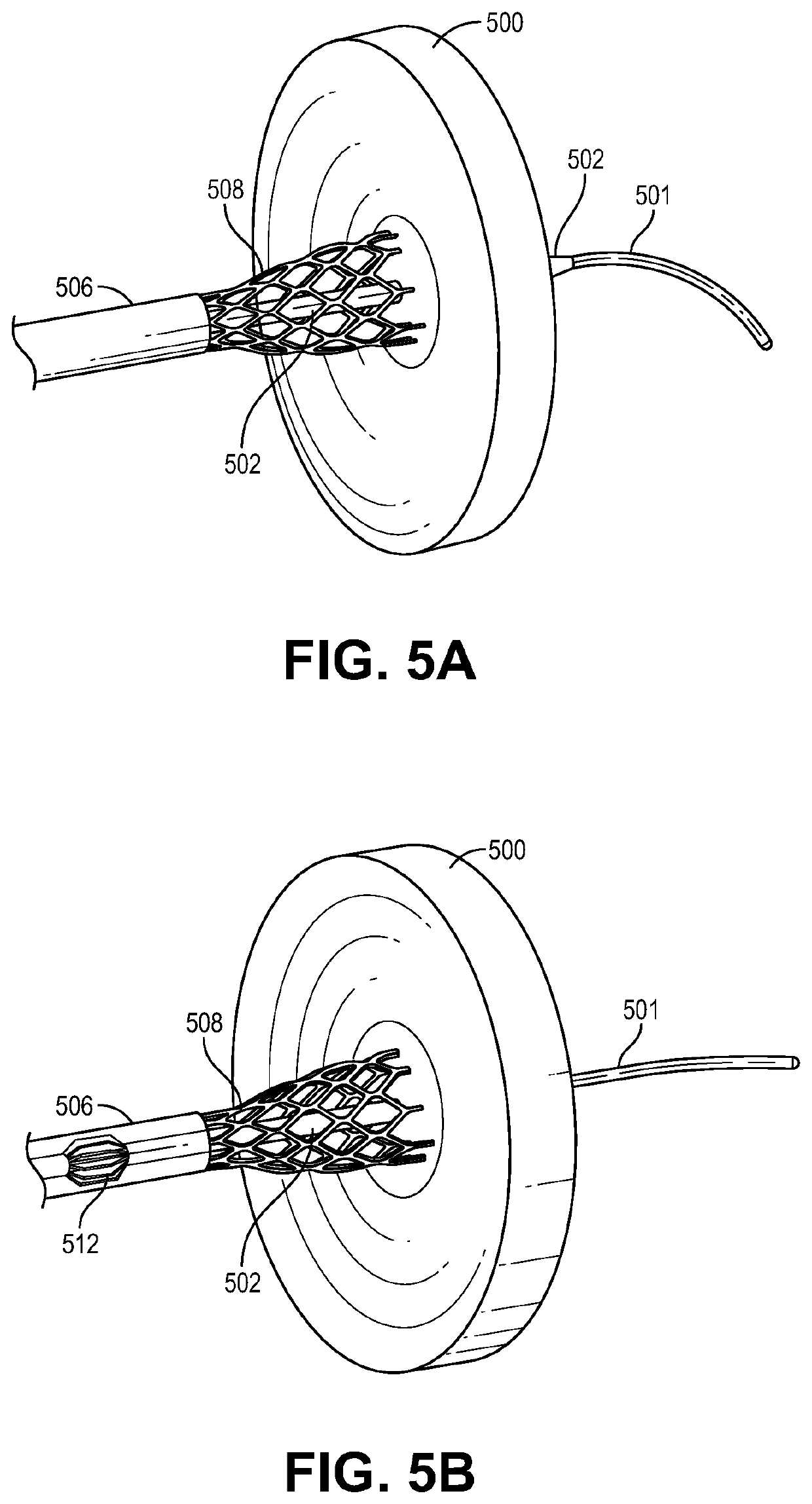
PendingUS20190374254A1Small sizeGuide needlesIncision instrumentsLeft atrial pressureAppliance component
The present disclosure relates to a device assembly and a method for treating heart failure by normalizing elevated blood pressure in the left atrium of a heart of a mammal. Disclosed herein is a transcatheter interatrial septum excision device assembly configured to create a sized interatrial aperture between the right and left atria of a heart for the relief of elevated left atrial pressure. The device assembly comprises a delivery catheter, a tissue stabilizer attached to a first catheter having a central lumen and a penetrating tip that permits passage of a guidewire, and a cutter attached to a second catheter having a central lumen that permits passage of the first catheter. Alternative configurations comprise a (third) catheter having a central lumen that permits passage of the aforementioned components to and from the right atrium, a tissue retention mechanism and an optional coaxial alignment mechanism.
Owner:TEXAS MEDICAL CENT
Artificial aortic valve ring system implanted through peripheral arterial approach
ActiveCN105287051AWill not cause blockingDoes not affect cardiac conduction systemHeart valvesCalcificationAortic root
The invention discloses an artificial aortic valve ring system, which is used for taking effects of supporting and fixing in trans-catheter aortic valve replacement on patients of aortic valve regurgitation without calcification. The system comprises a valve ring scaffold at distal end and anchoring legs at proximal end, wherein the valve ring scaffold is fixedly connected to the anchoring legs; the valve ring scaffold is of a tubular structure and has a gridding structure; the anchoring legs are arranged along the periphery of the valve ring scaffold and are embedded in a cavity structure on ascending aortic root so as to fix the system; and the system is capable of transforming between a first form of radial expansion and a second form of radial shrinkage. With the implantation of the system, the trans-catheter aortic valve replacement on patients of aortic valve regurgitation without calcification becomes possible.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement auxiliary device
PendingCN114081675AImprove stress resistanceIncrease frictionBalloon catheterHeart valvesCatheterBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a transcatheter aortic valve replacement auxiliary device which comprises a balloon body capable of contracting in the radial direction, the balloon body comprises a far-end part, a near-end part and a middle part located between the far-end part and the near-end part, and the far-end part is converged at the far end; the periphery of the middle part is provided with a plurality of fiber belts and a salient point array; the fiber bands intersect with each other, and the fiber bands and the salient point array area are at least partially overlapped; the near-end part converges at the near end. The fiber belt and the salient point array are arranged in the middle of the balloon of the transcatheter aortic valve replacement auxiliary device, so that the friction force on the surface of the balloon can be increased, and the balloon is prevented from sliding relative to the aortic valve in the pre-expansion process. Due to the fact that the surface of the balloon is covered with the fiber band, the overall compression resistance of the balloon is improved, the balloon can bear larger pressure in the pre-expansion link, and the diseased position of a valve of a patient can be fully expanded conveniently.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Transcatheter device and minimally invasive method for constricting and adjusting blood flow through a blood vessel
ActiveUS20170215885A1Impact treatment approachAvoid complicationsStentsDilatorsRadiologyThree vessels
A pulmonary artery flow restrictor system includes a funnel shaped membrane with a proximal base and a restrictive distal opening which is stretchable to larger sizes. A self-expanding frame is attached to the proximal base of the membrane for securing the membrane within the pulmonary artery.
Owner:VIVONICS
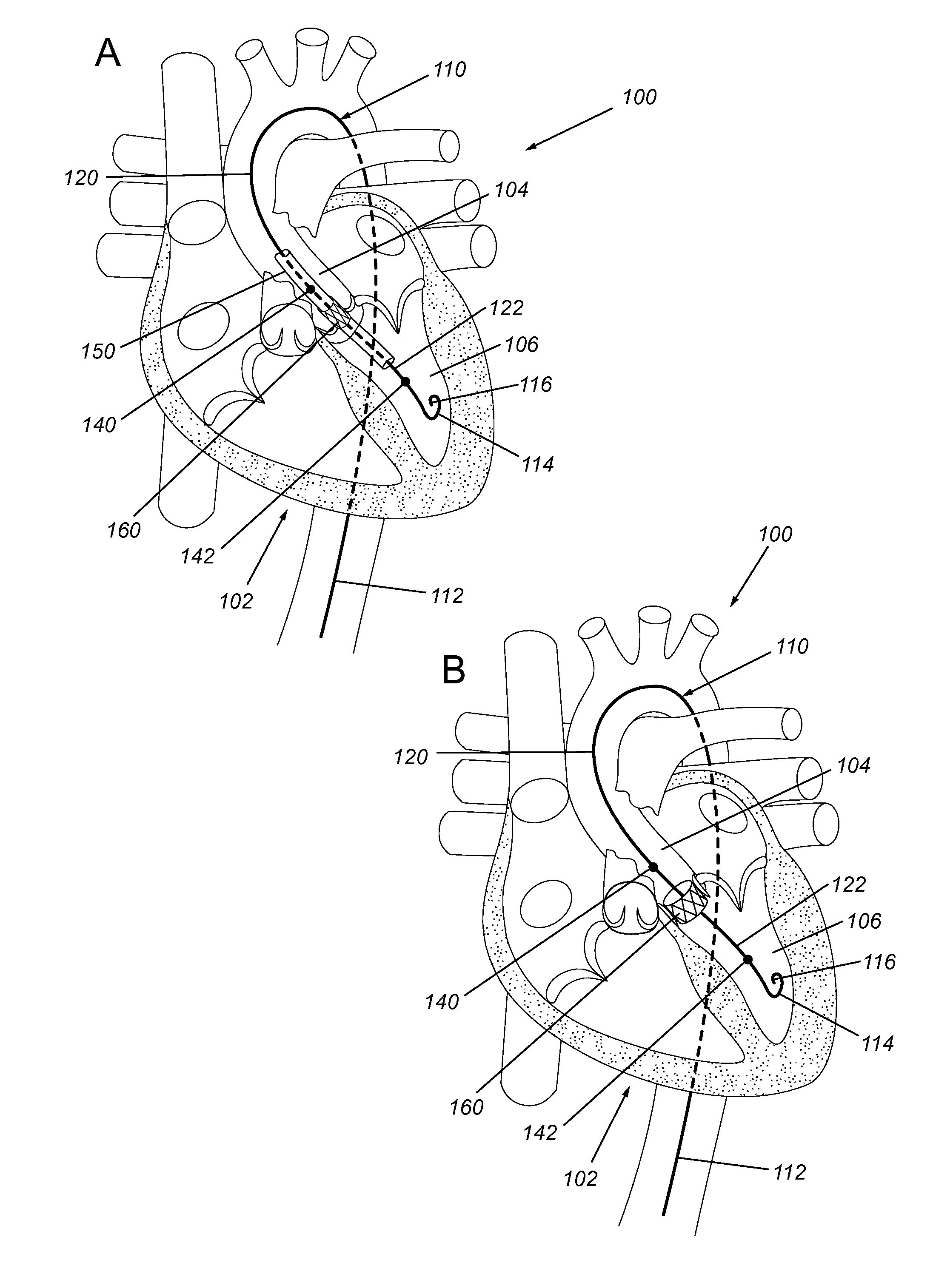
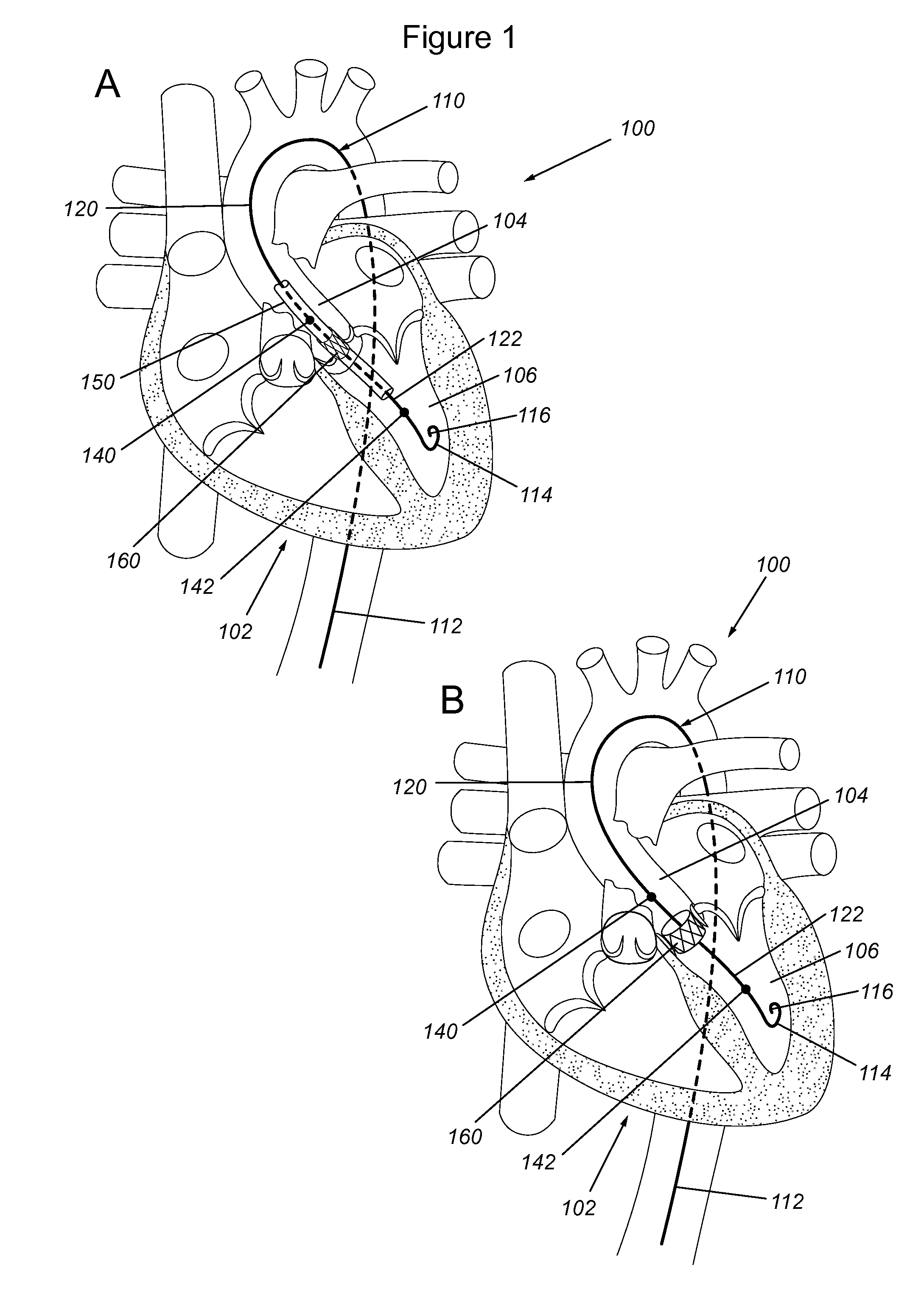
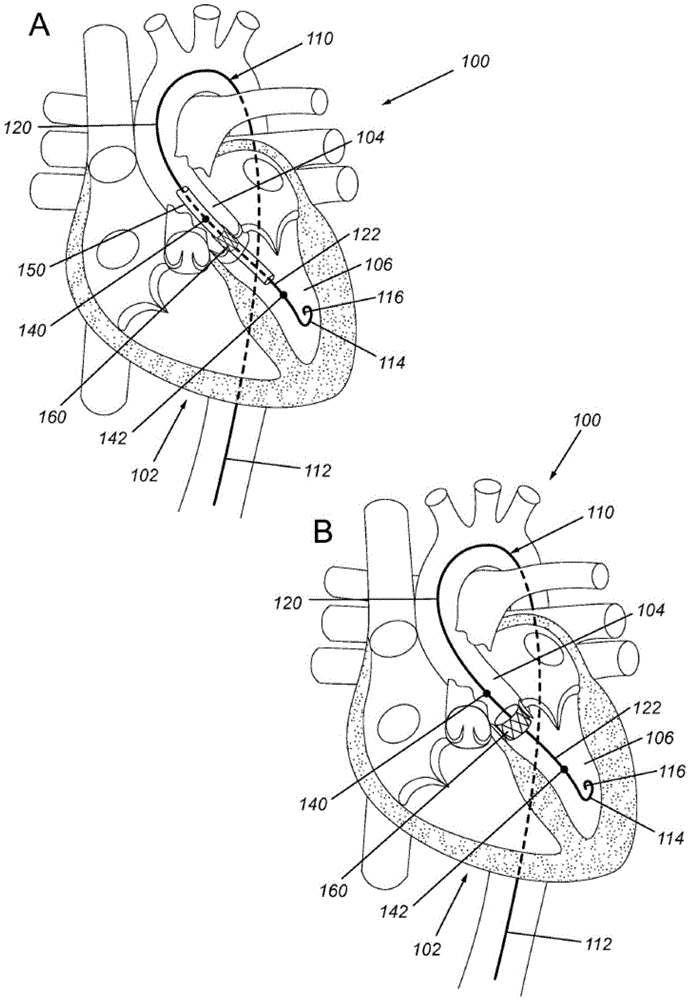
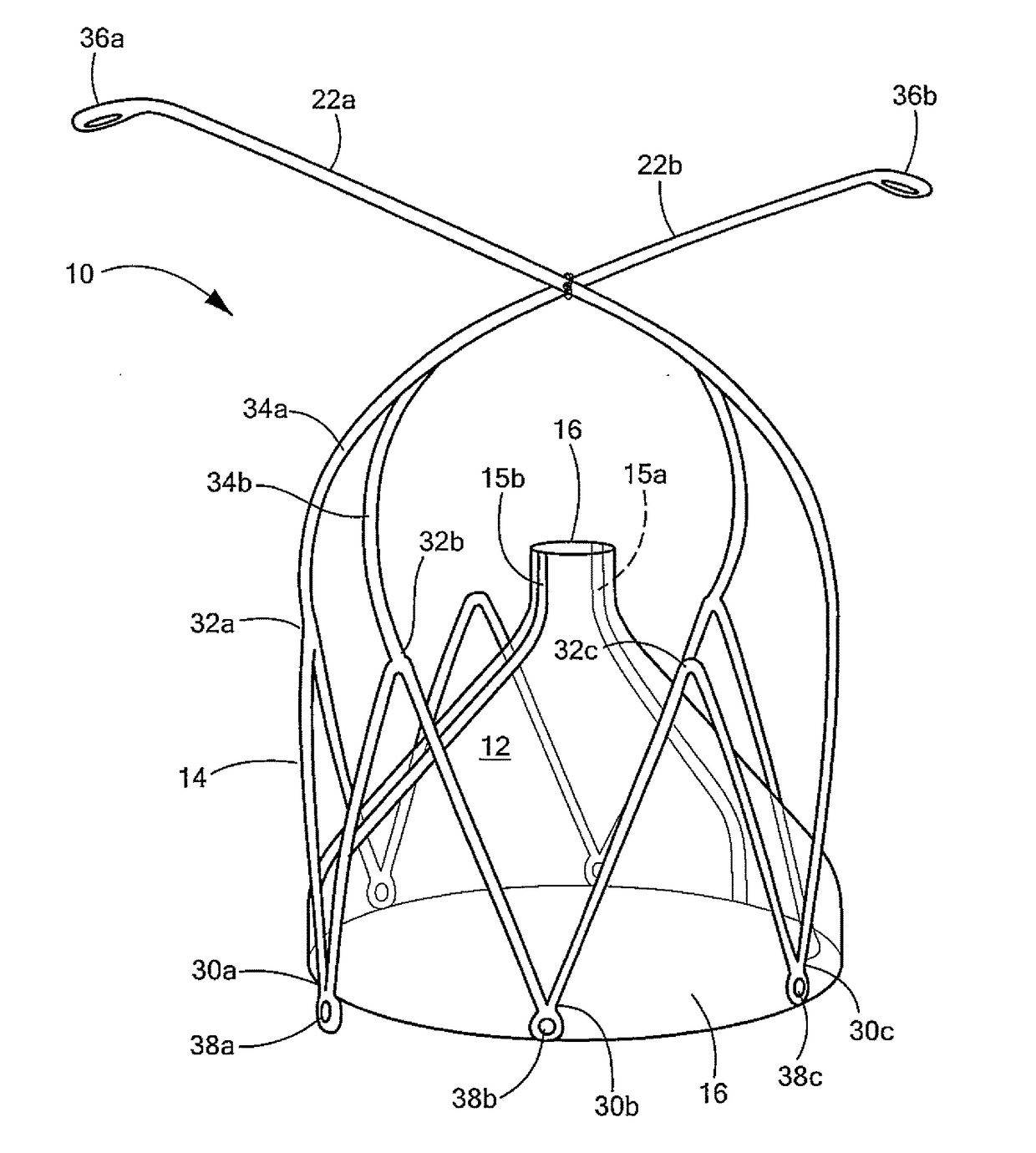
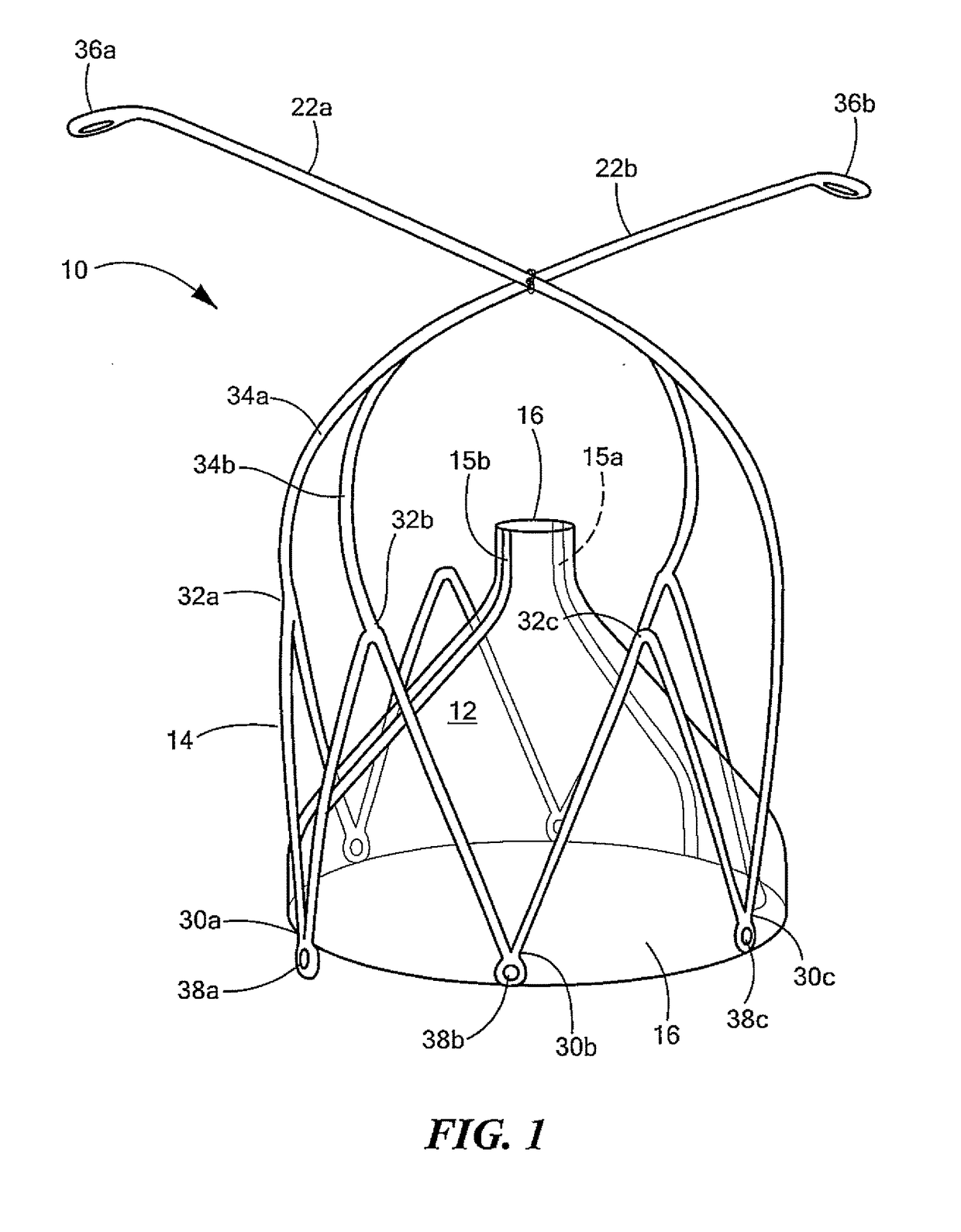
Devices, systems, and methods to optimize annular orientation of transcatheter valves
In various embodiments, provided herein are methods, devices and systems to optimize annular orientation of transcatheter valves and thereby facilitate transcatheter aortic valve replacement in the setting of challenging cardiovascular anatomy. These methods, devices and systems are used to treat patients with valvular diseases. To solve these problems, described herein is a Device to Optimize aNnUlar orientation of Transcathether valves (DONUT). DONUT can correct large differences between a native valve's anatomical dimensions and the external dimensions of a transcatheter valve stent frame.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com