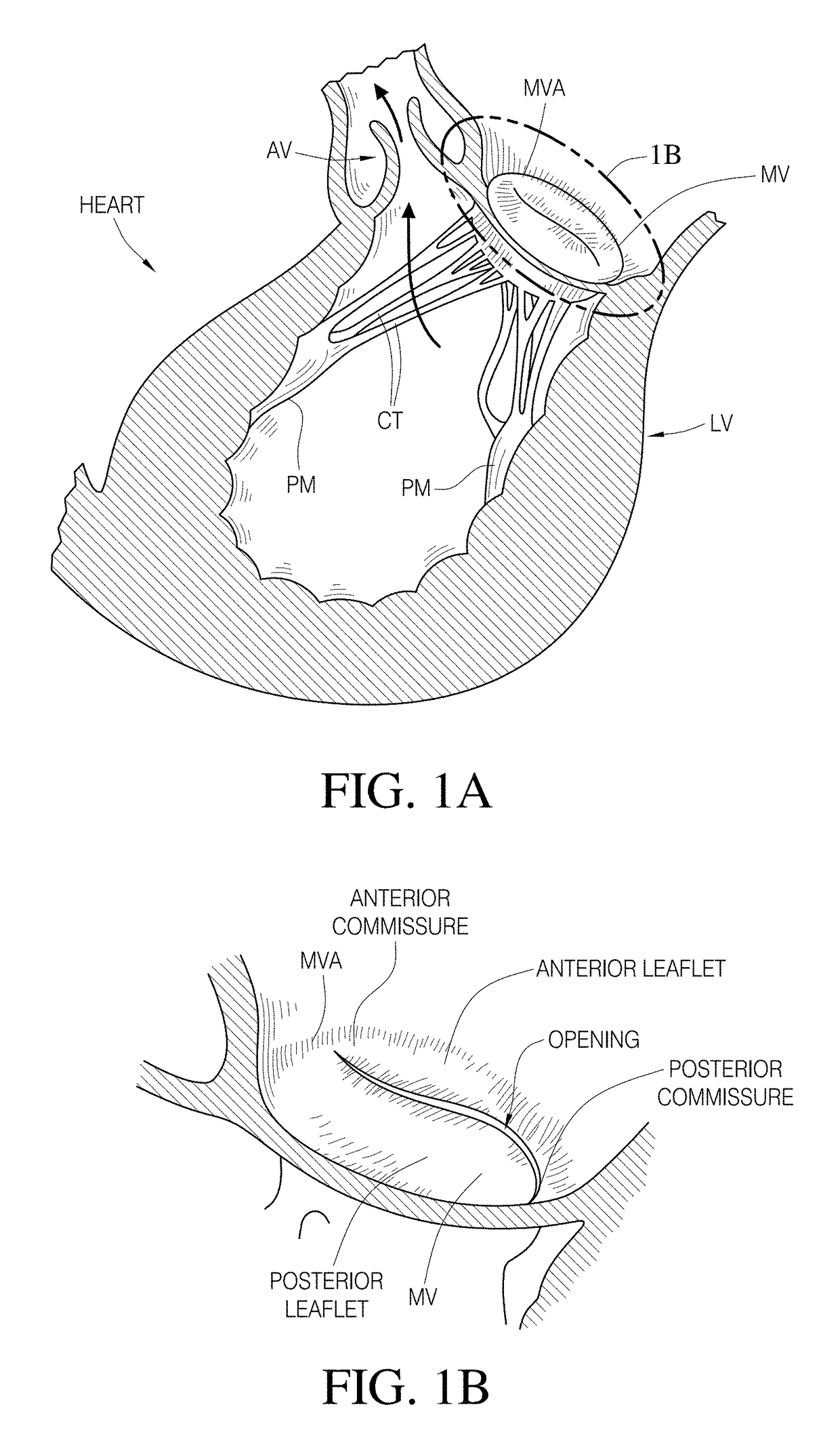
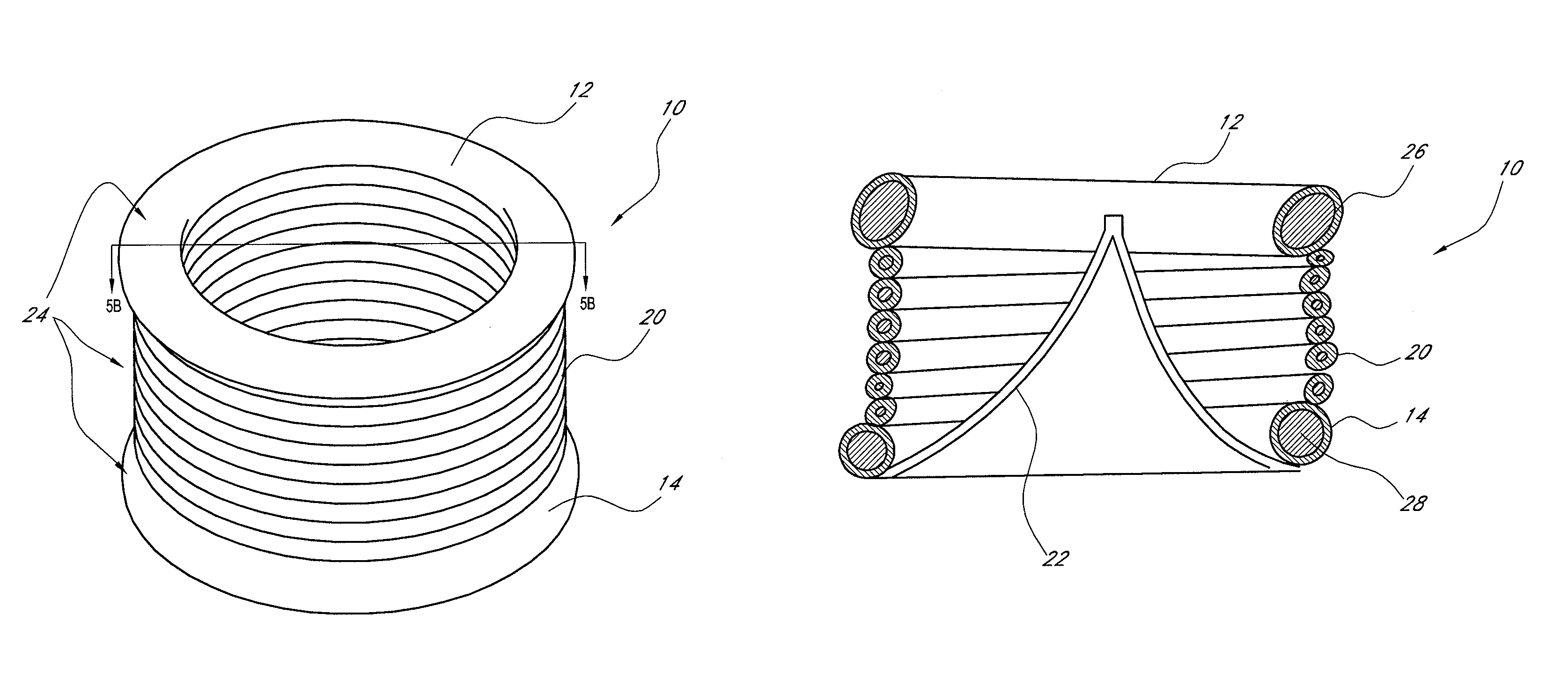
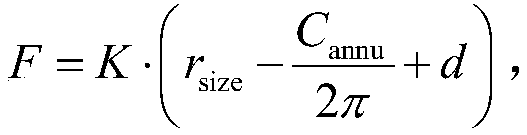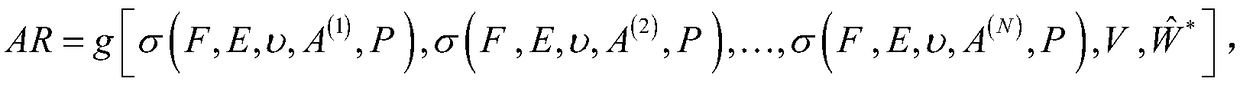Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Aortic valve replacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
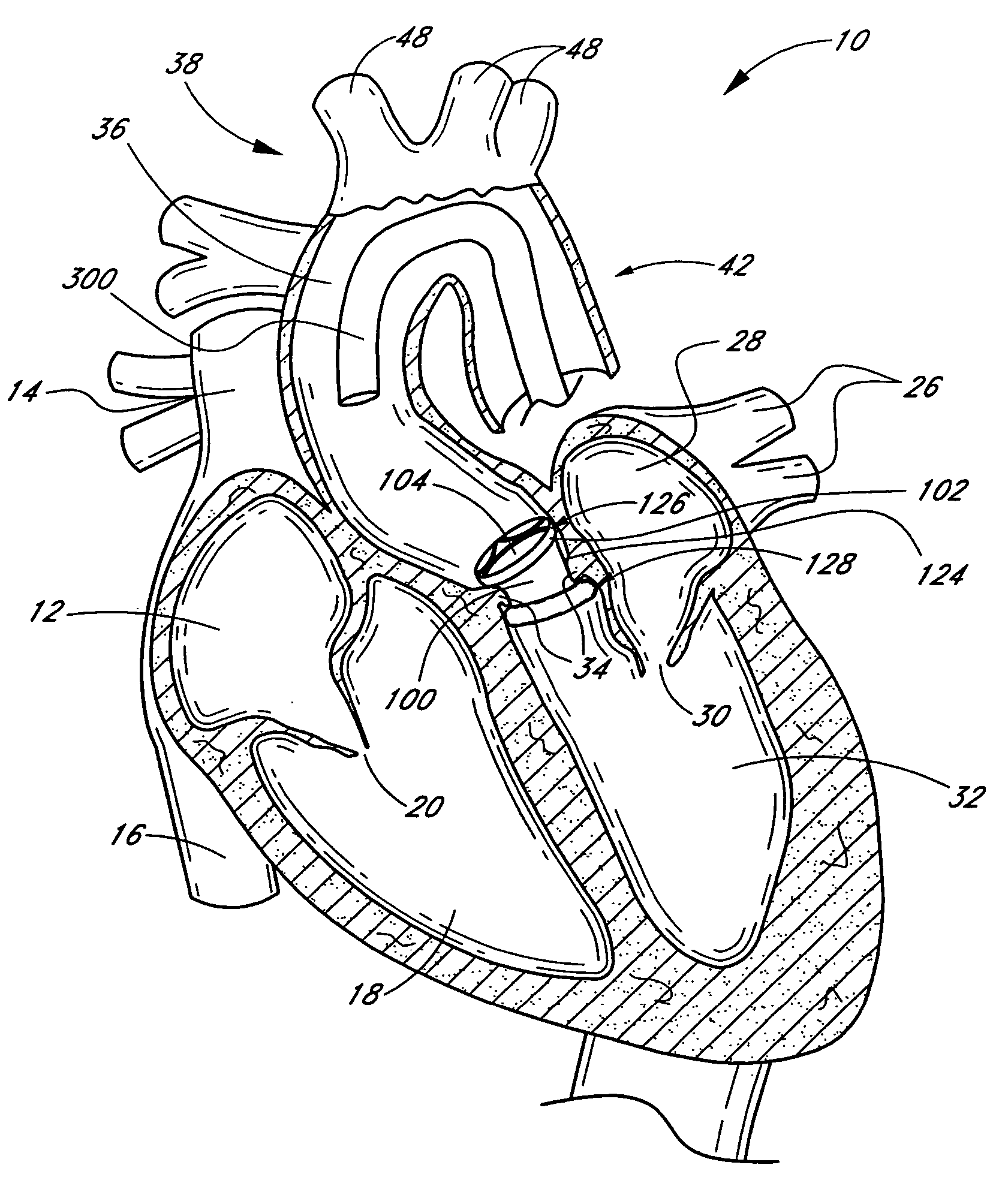
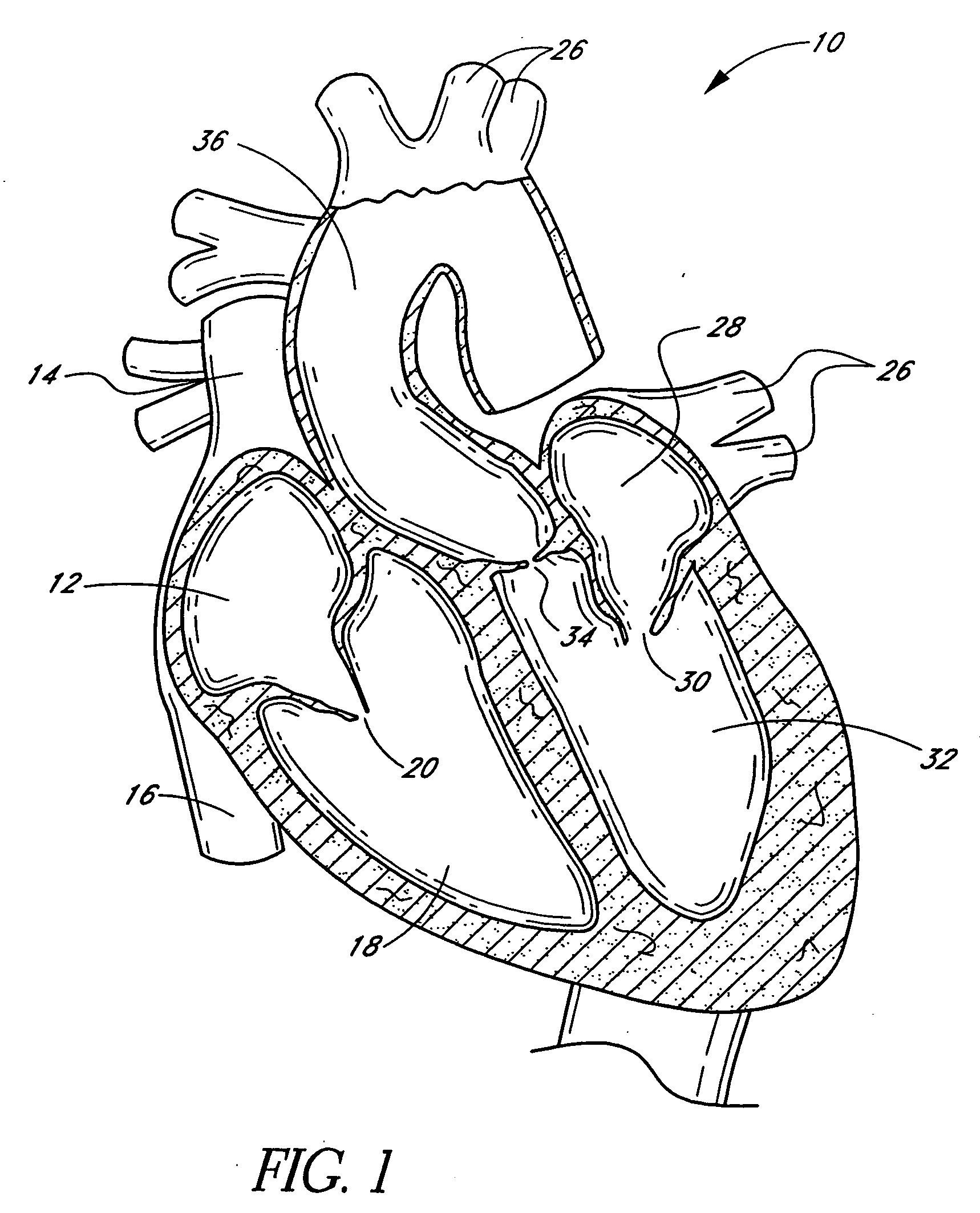
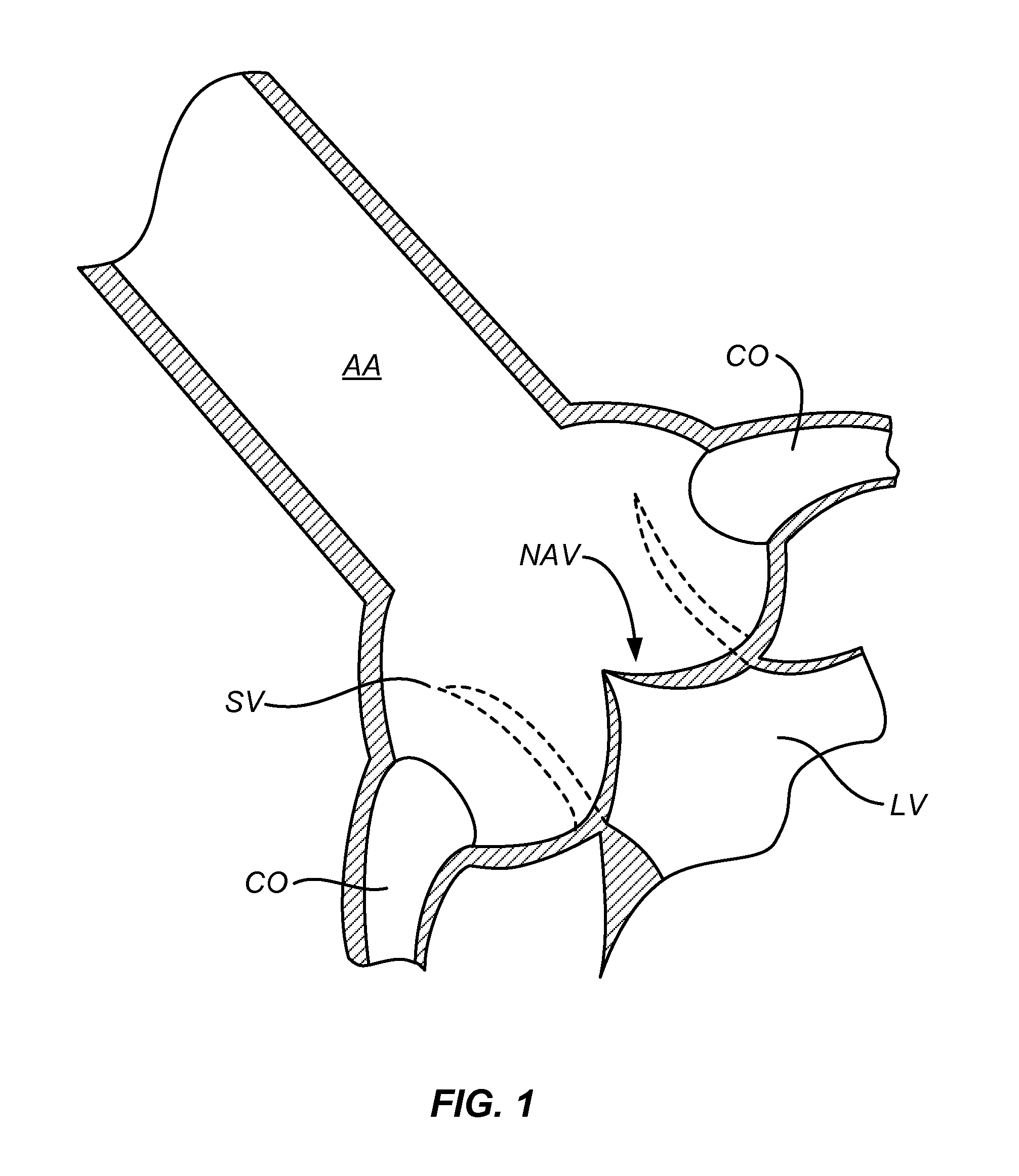
Aortic valve replacement is a procedure whereby the failing aortic valve of a patient's heart is replaced with an artificial heart valve. Current methods for aortic valve replacement include open heart surgery, minimally invasive cardiac surgery (MICS) and transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
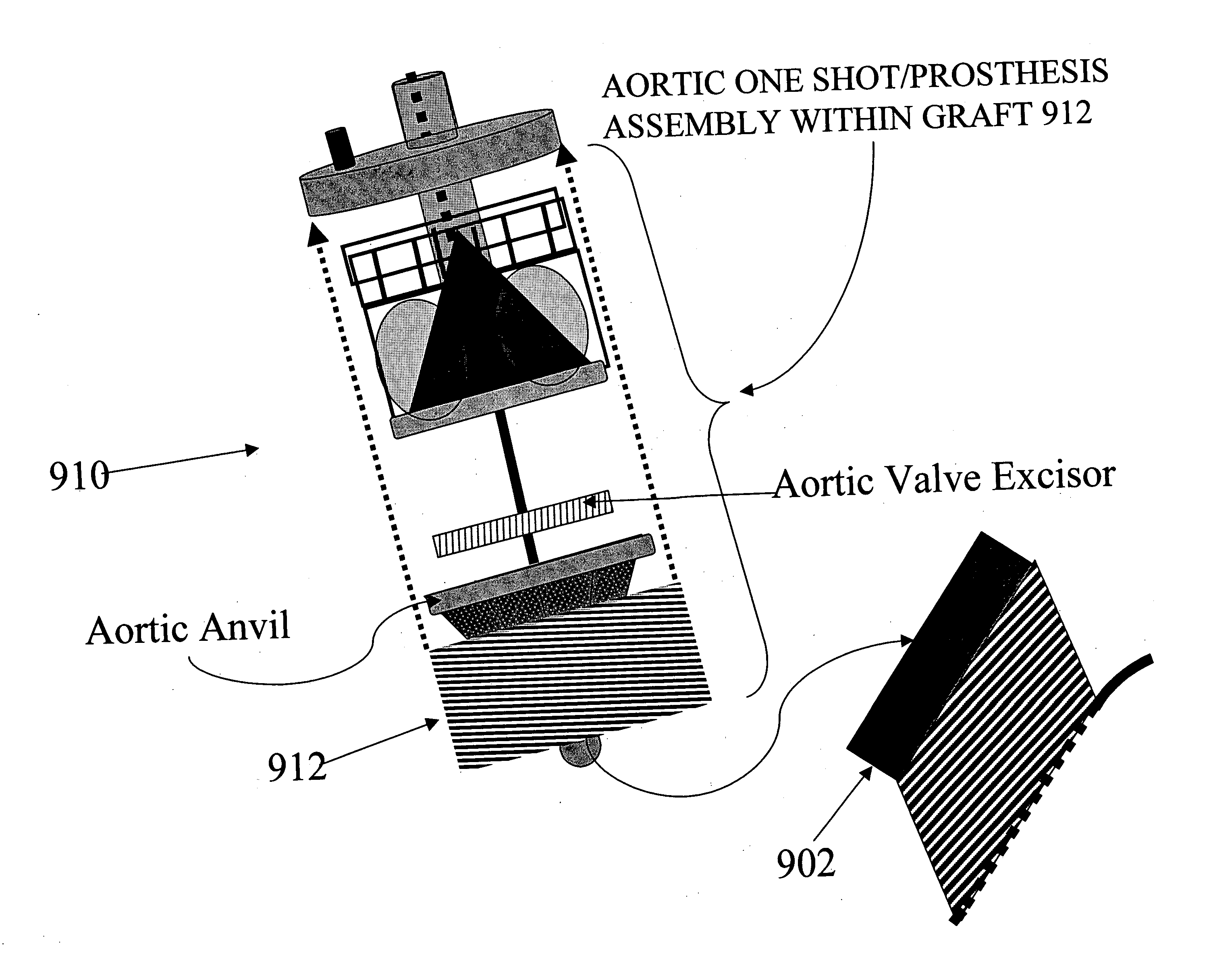
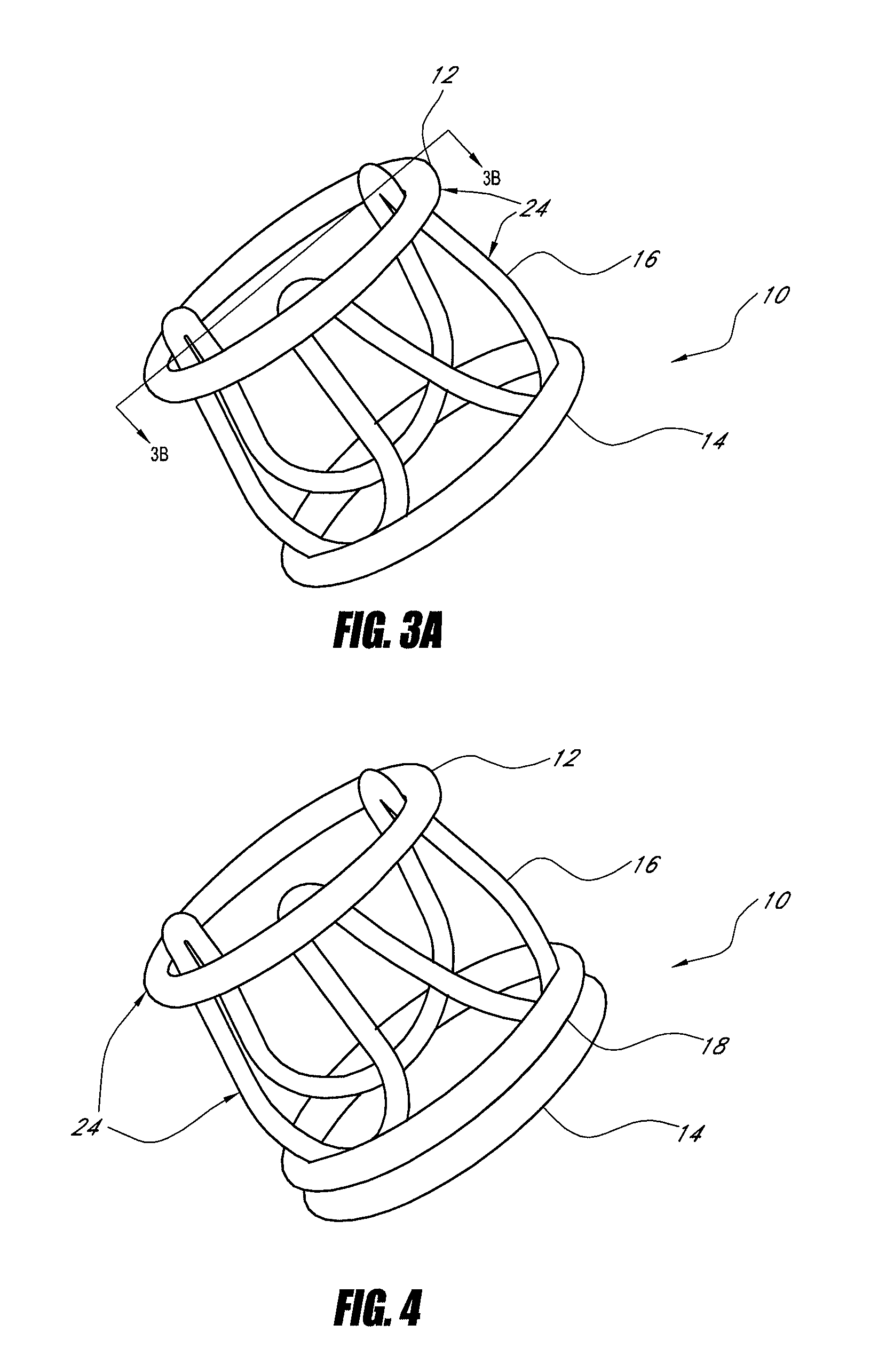
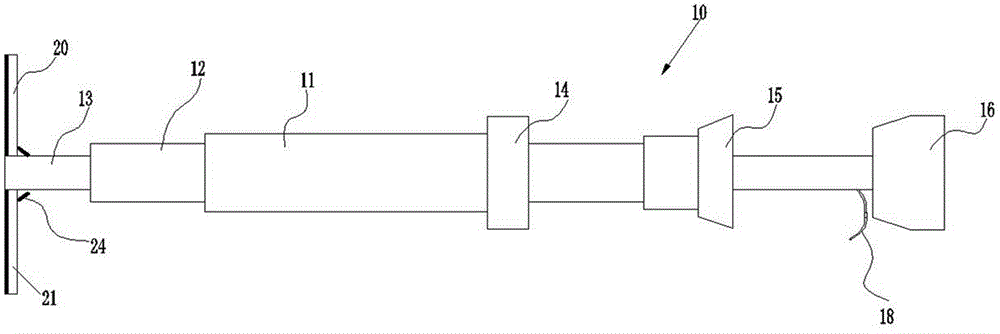
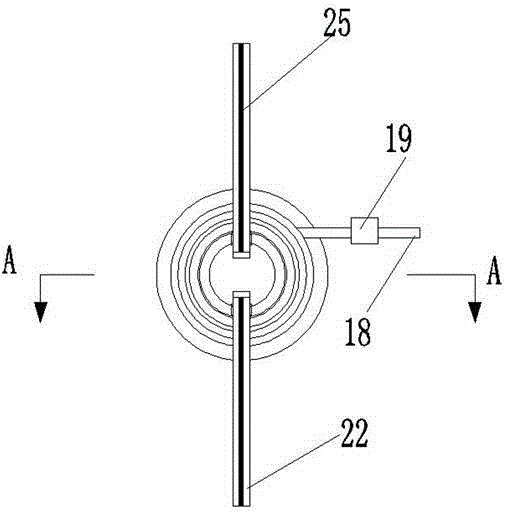
Methods and apparatus for off pump aortic valve replacement with a valve prosthesis
InactiveUS20050203549A1Promote recoveryPromote resultsHeart valvesExcision instrumentsMedicineProsthesis
Methods and apparatus are provided for valve repair or replacement. In one embodiment, the method comprises providing an apparatus having a valve prosthesis, a valve leaflet support and a valve excisor, the apparatus having a first configuration and a second configuration; accessing the aortic root without placing the patient on a heart-lung machine; advancing the apparatus in the first configuration where the valve leaflet support is advanced through a valve, wherein the support is positioned below a valve annulus; expanding the apparatus into a second configuration so that the support will engage the valve; and moving the valve leaflet support and valve excisor together to remove leaflets of the valve. Penetrating members may be advanced into the tissue wherein the penetrating members may act as fasteners to hold the prosthesis in place.
Owner:REALYVASQUEZ FIDEL
Stapling apparatus and method for heart valve replacement
A surgical stapler for securing a prosthetic heart valve within a patient generally includes a first cylindrical portion for carrying at least one staple assembly on a distal end thereof; a second cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the first cylindrical portion and having a camming arm on a distal end thereof, the camming arm configured to cam the at least one staple assembly radially outward and drive the at least one staple assembly distally such that a first leg of the at least one staple assembly penetrates a cuff of the prosthetic heart valve and a second leg of the at least one staple assembly pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, as the second cylindrical portion is moved distally relative to the first cylindrical portion; and a third cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the second cylindrical portion and having an anvil flange on a distal end thereof, the anvil flange configured to crimp the second leg of the at least one staple assembly toward the first leg of the at least one staple assembly to secure the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue as the third cylindrical portion is moved relative to the second cylindrical portion. A method of installing a heart valve within a patient which includes the steps of accessing a site within a heart from which a natural heart valve has been removed; lowering a prosthetic heart valve into position within the site in the heart; positioning a surgical stapler having at least one staple assembly removably held on a distal end thereof adjacent the prosthetic heart valve within the site in the heart; driving a first leg of the at least one staple assembly through a peripheral cuff of the prosthetic heart valve; and crimping a second leg of the at least one staple assembly in a direction toward the first leg such that the second leg pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, thereby securing the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
Methods of cardiac valve replacement using nonstented prosthetic valve
InactiveUS20060020334A1Minimally invasive procedurePrevent disengagementSuture equipmentsHeart valvesProximateProsthesis
A method of implanting a prosthetic valve within a heart comprises translumenally advancing a prosthetic valve comprising an inflatable structure to a position proximate a native valve of the heart. A portion of the inflatable structure that is distal to the native valve is inflated. A portion of the inflatable structure that is proximal to the native annular valve is inflated.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
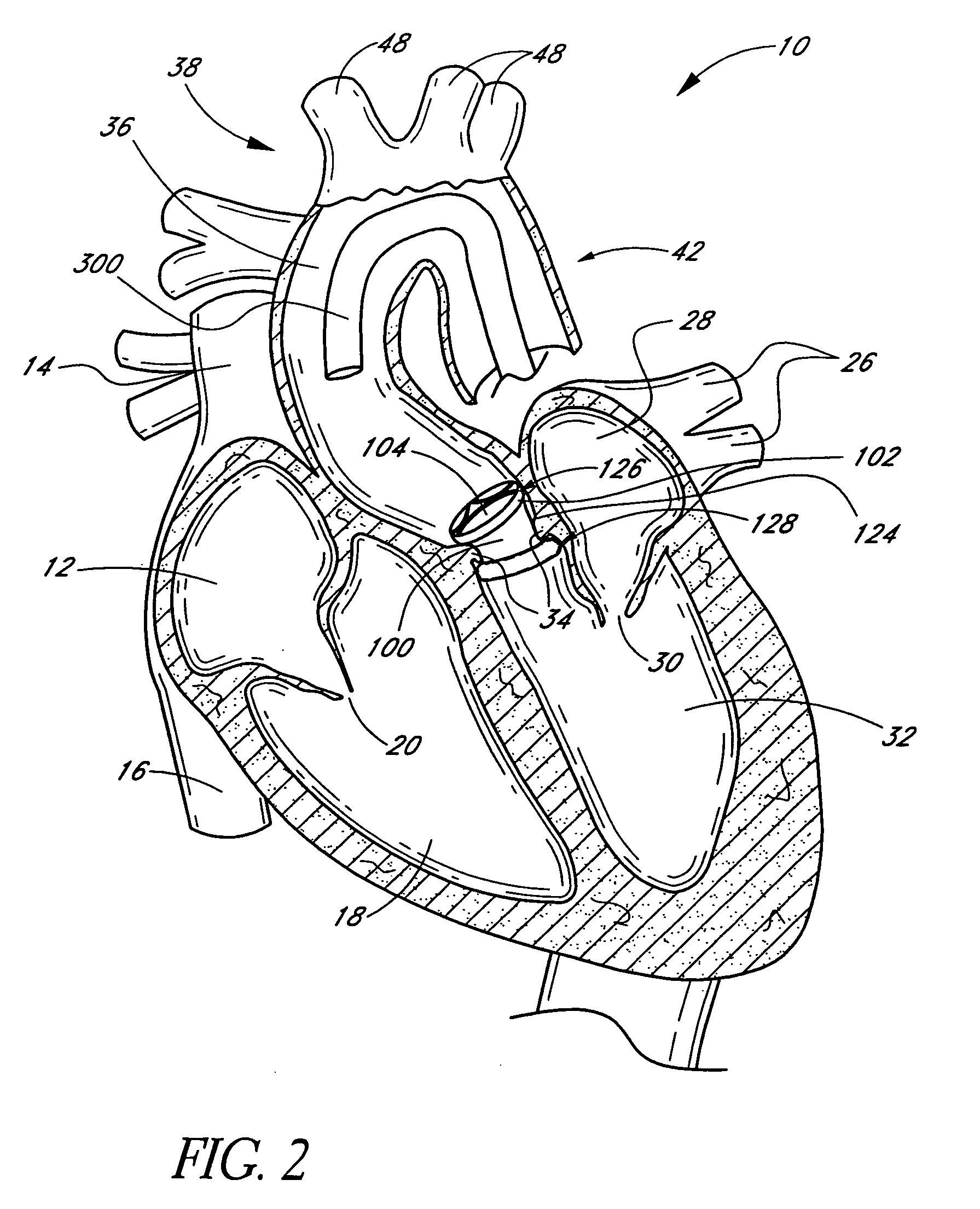
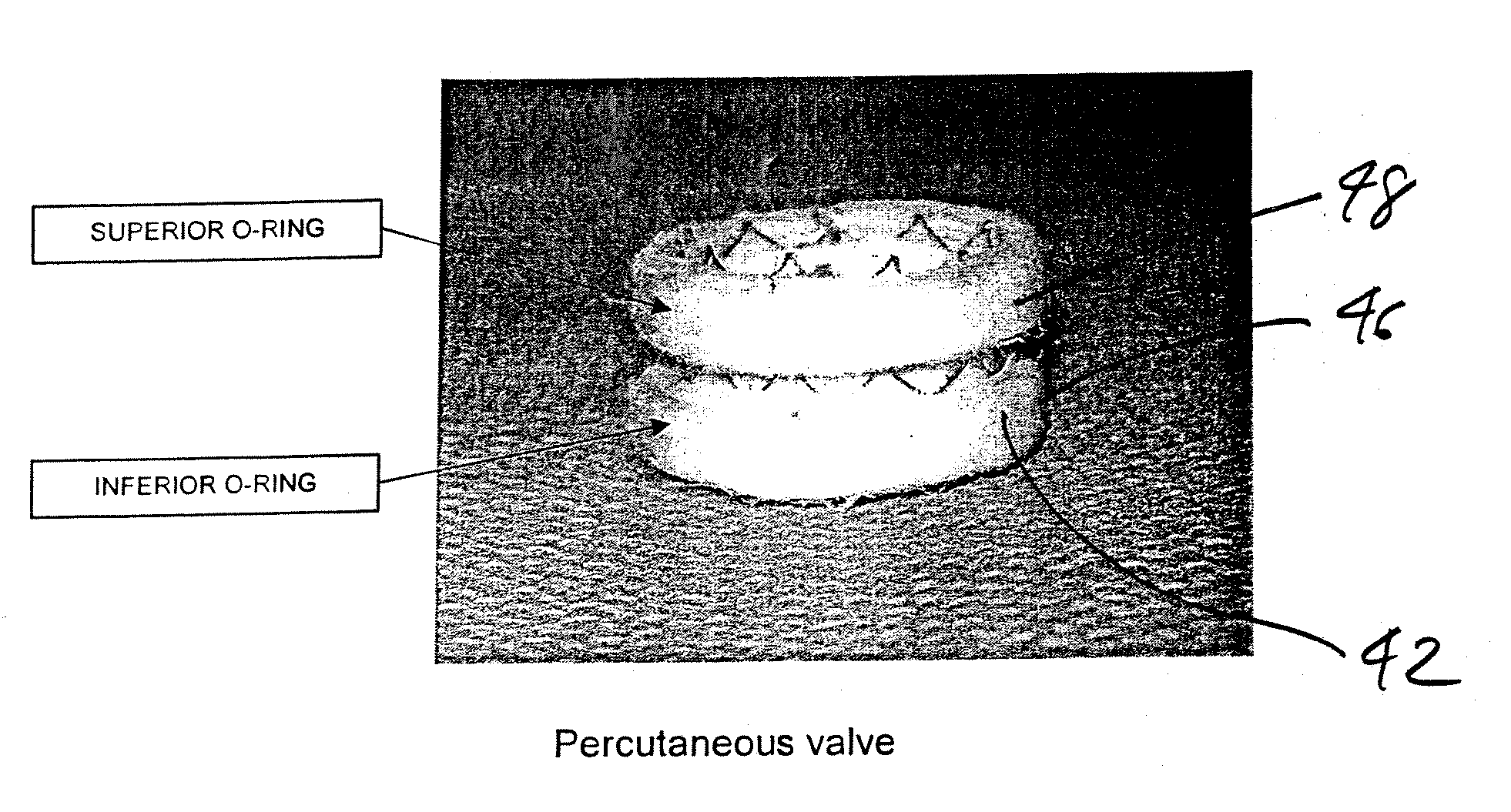
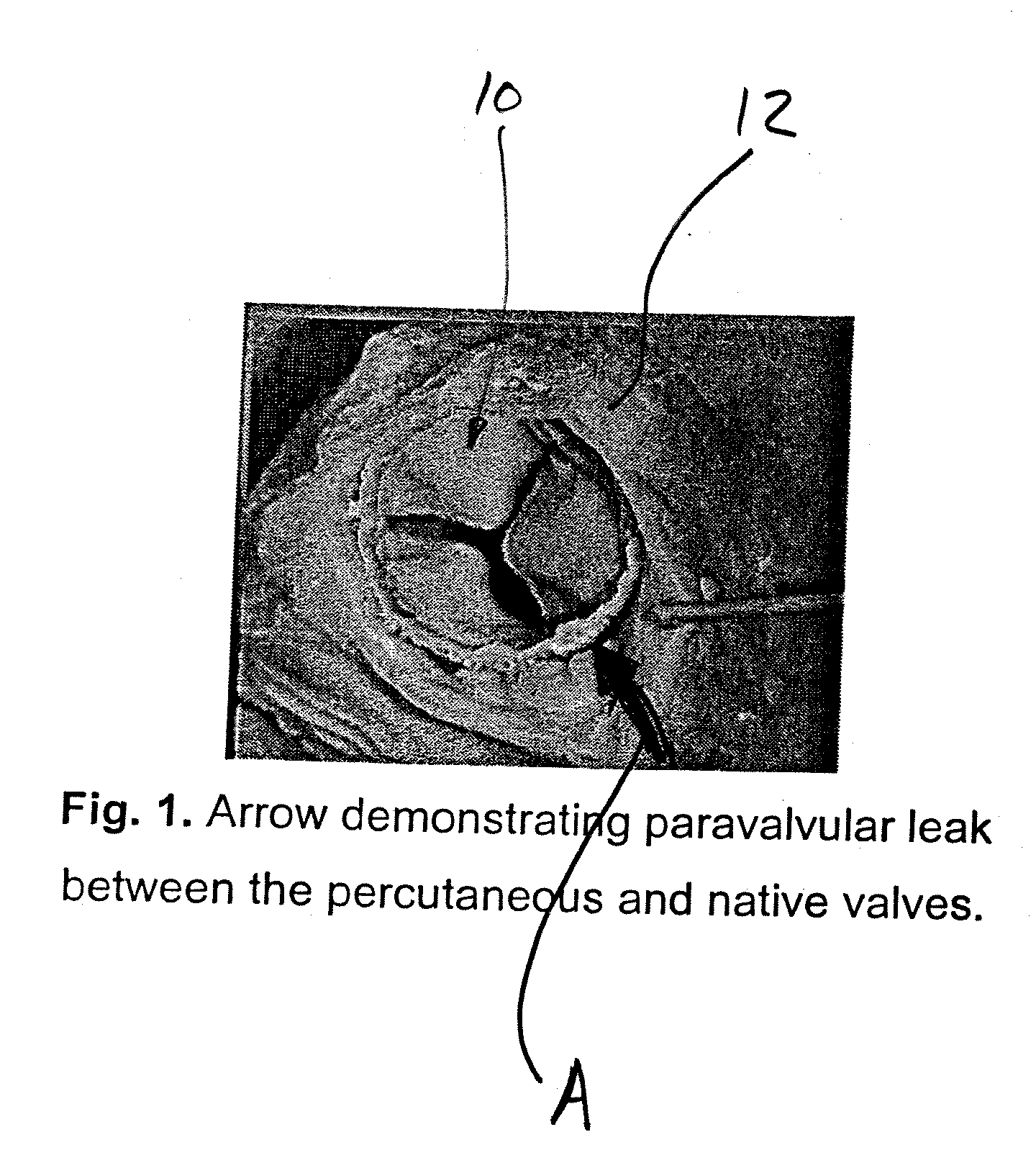
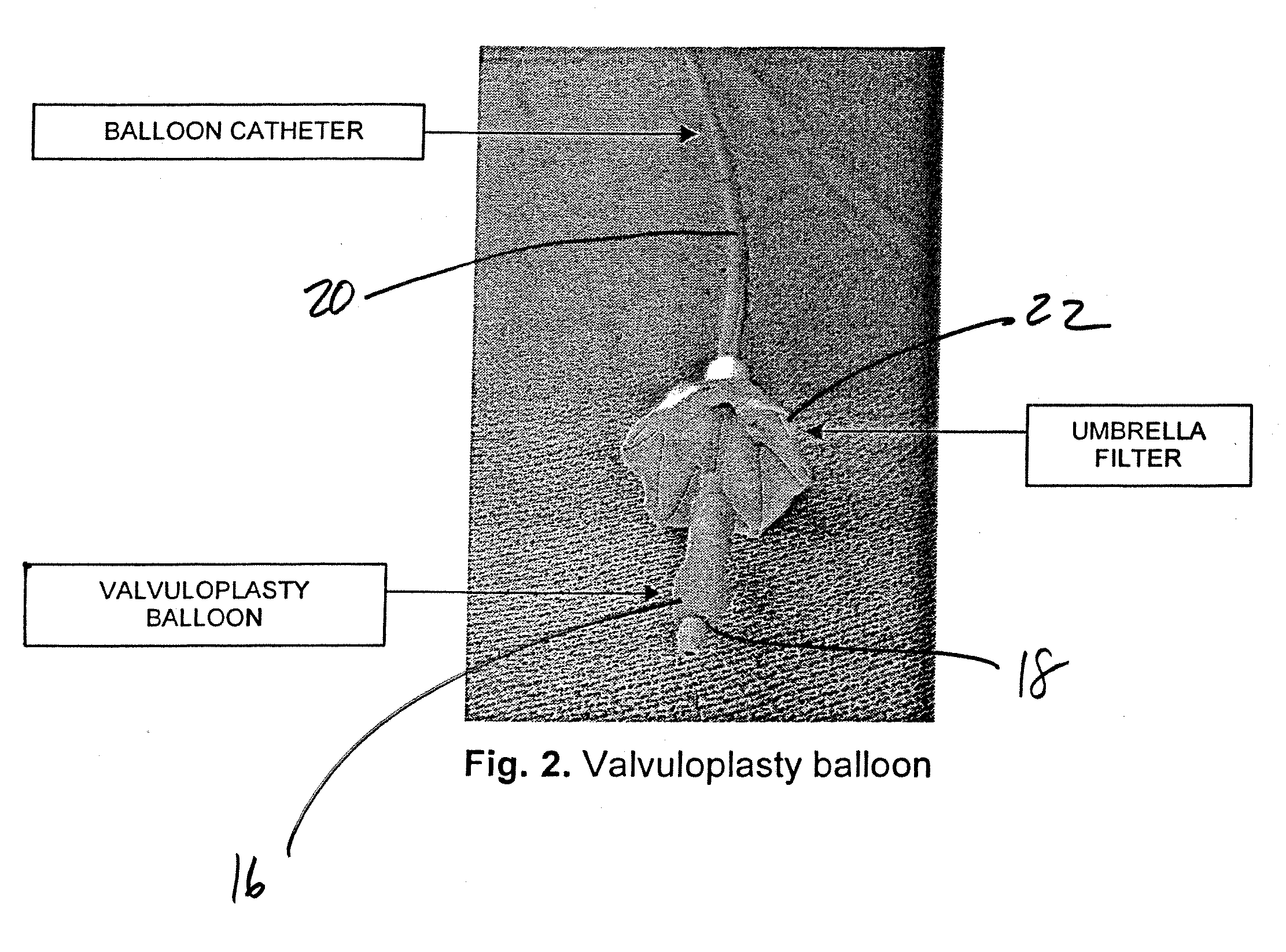
Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Replacement
A replacement cardiac valve for placement adjacent the native annulus comprises a valve body having a multi-leaflet valve, a supporting stent surrounding and operatively coupled to the valve body, a superior O-ring and an inferior O-ring spaced from one another to span the native annulus, the O-rings surrounding the valve body and operatively coupled the valve body or the supporting stent, the valve body, the supporting stent, and the O-rings adapted for transcatheter placement using a deployment catheter.
Owner:TEHRANI HASSAN
Systems and methods for enabling heart valve replacement
ActiveUS20090157174A1Increase heightEasy to optimizeStentsHeart valvesProsthesisHeart valve replacement
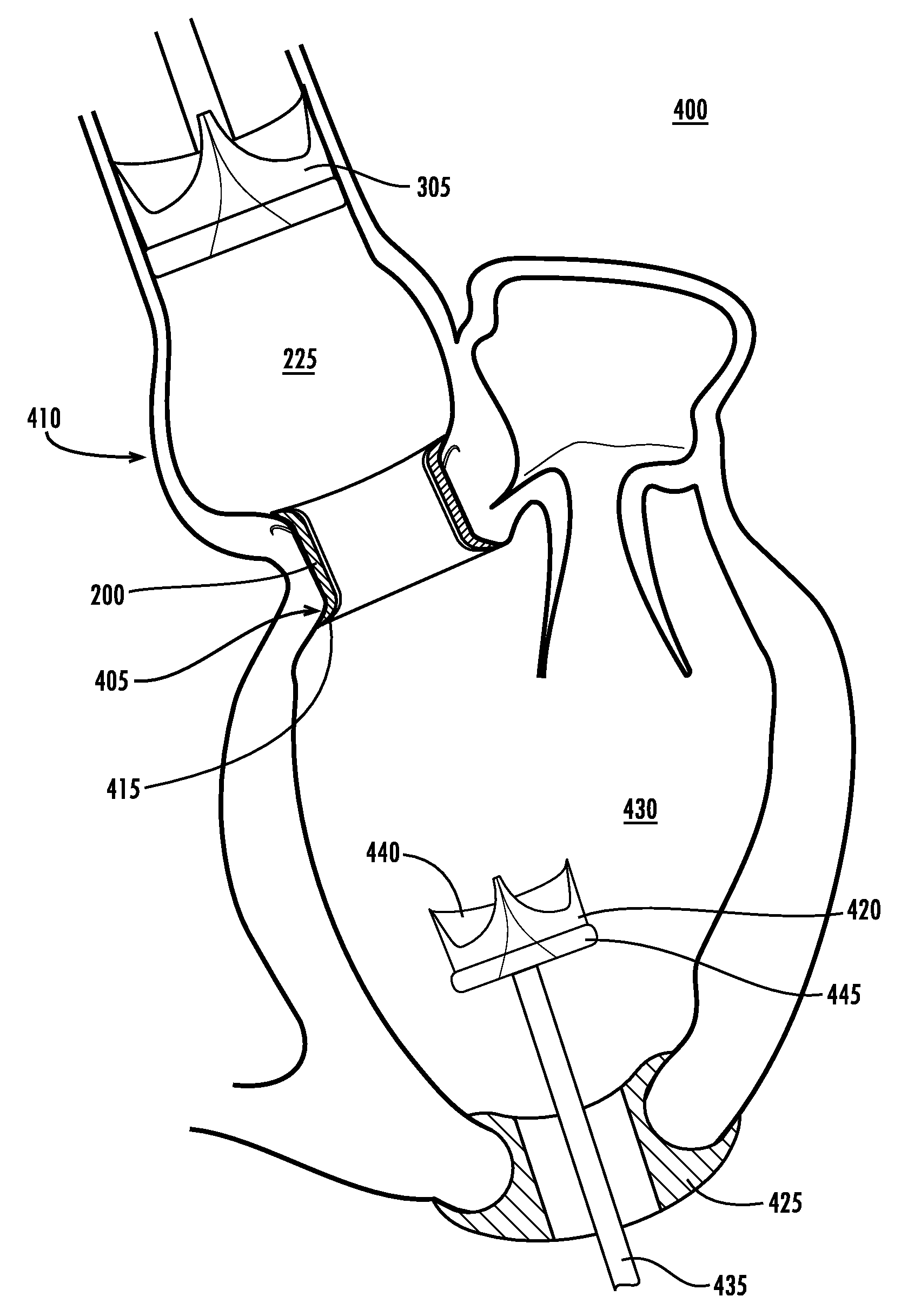
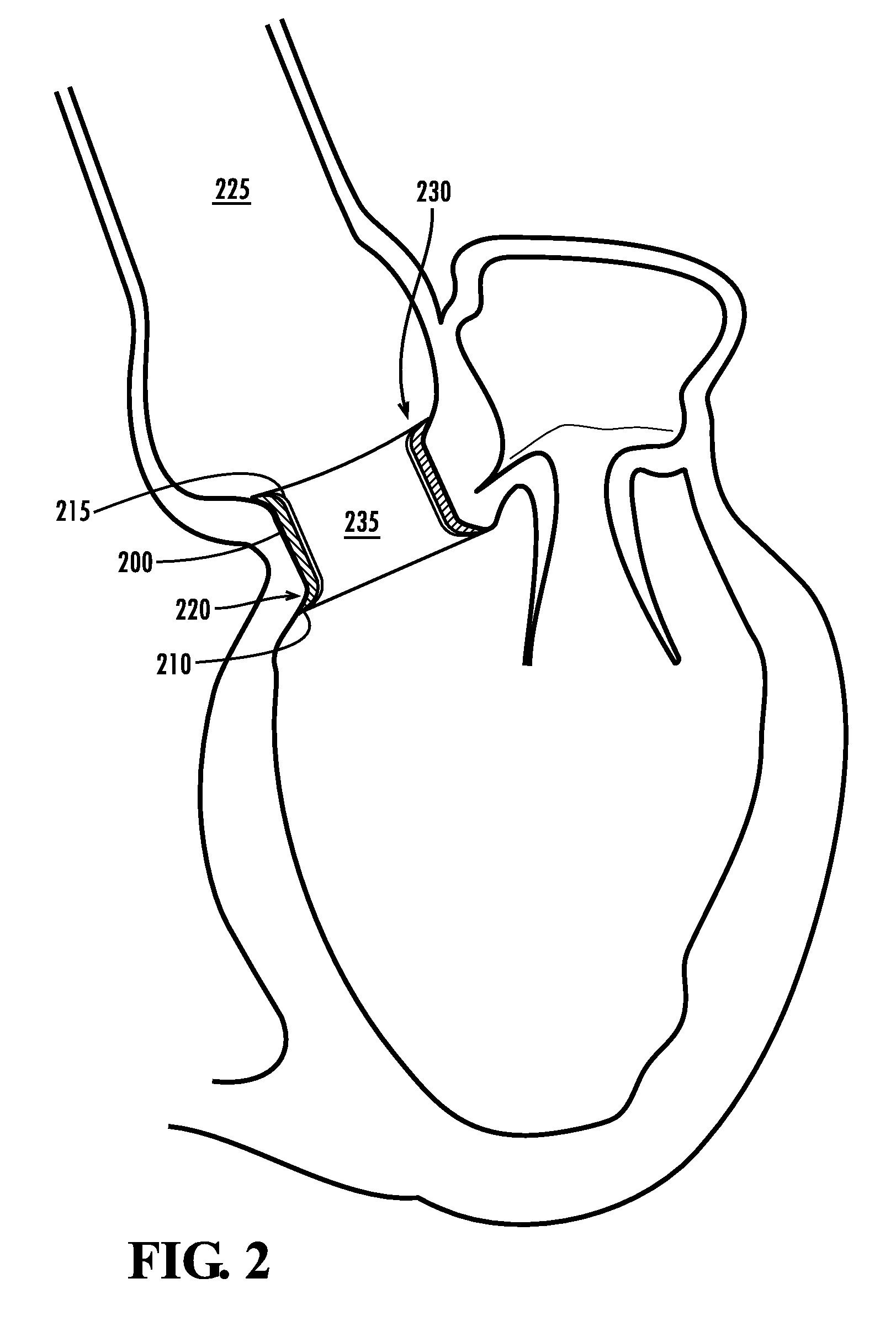
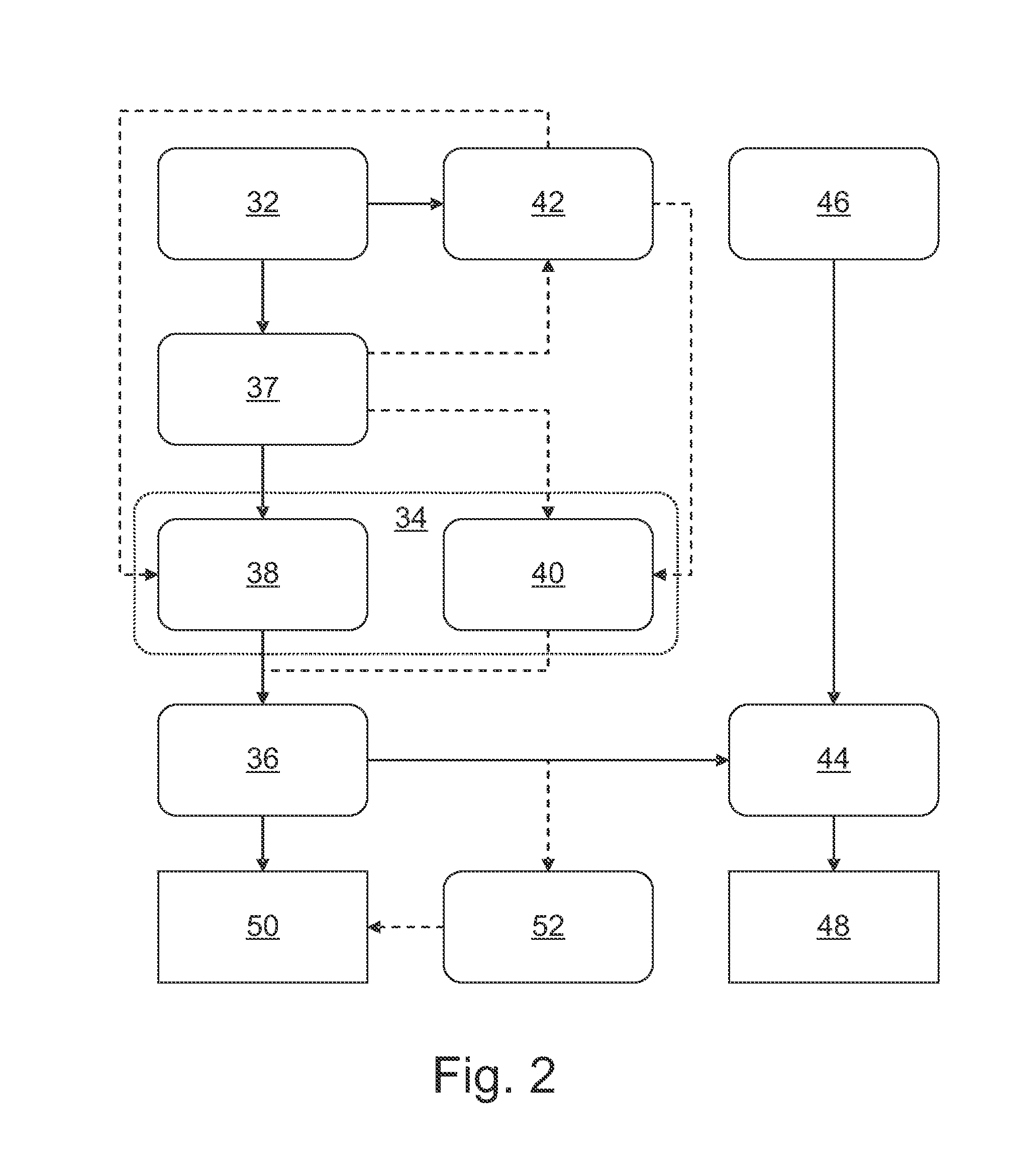
The present invention describes a cardiac prosthetic system (400) comprising: an anchoring conduit (200) having a harbour (415), the harbour including a first releasably engaging component (515); a temporary valve (305) and a heart valve prosthesis (420) having a second releasably engaging component (445) enabled to be securely coupled and uncoupled from the first releasably engaging component (515) of the harbour (415).
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Valve replacement using rotational anchors
ActiveUS9848983B2Inhibiting perivalvular leaksReduce the angleBalloon catheterAnnuloplasty ringsImplanted deviceMitral valve replacement
Features for a heart valve device are described. The device may include a frame with anchors configured to secure the device to tissue. The frame may include a flared end or skirt for additional securement of the implanted device. The device may include a seal such as a barrier and / or cuff for preventing leakage. The device may contract for endovascular delivery of the device to the heart and expand for securement within the heart, such as the within the native mitral valve annulus. The device may include a replacement valve. The valve may have leaflets configured to re-direct blood flow along a primary flow axis.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
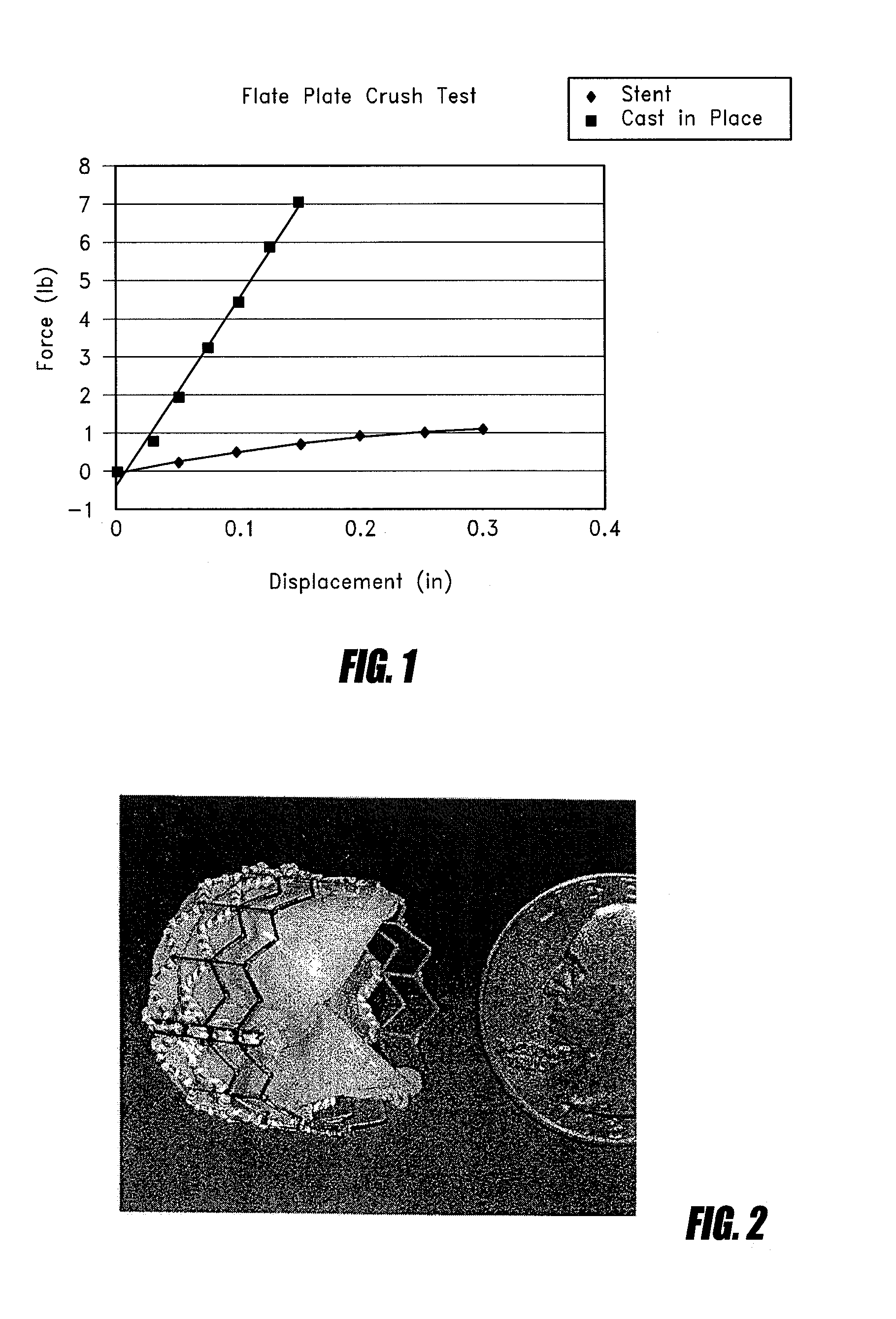
Stentless aortic valve replacement with high radial strength
InactiveUS8568477B2Improve radial strengthMinimally invasiveHeart valvesInsertion stentUltimate tensile strength
Disclosed is a stentless transluminally implantable heart valve, having a formed in place support. The formed in place support exhibits superior crush resistance when compared to conventional balloon expandable or self expandable stent based valves.
Owner:SPEYSIDE MEDICAL LLC
Method and system for balloon counterpulsation during aortic valve replacement
Methods and systems for regulating aortic regurgitation during aortic valve replacement or repair procedures utilize a temporary aortic valve (TAV) catheter and a controller. The temporary aortic valve catheter has an expandable occlusion device which can partially occlude the aortic lumen during ventricular diastole with a lesser occlusion during ventricular systole. Exemplary balloon structures include multiple, independently inflatable balloons which are inflated in synchrony with the cardiac cycle by the controller. By controlling aortic regurgitation, the repair or replacement protocols can be conducted with less interference from blood flow.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement
A minimally invasive method of implanting a prosthetic aortic valve includes forming a surgical site within a patient's chest that includes a first access port, a second access port, a viewing port and a delivery port. A camera is inserted into the viewing port. The native aortic valve leaflets may each be grasped and removed via tools inserted through the first and second access ports. The prosthetic aortic valve may be delivered through the delivery port to the valve annulus using a delivery device. The prosthetic aortic valve is implanted at the valve annulus and the delivery device is withdrawn. A surgeon may perform the remotely operated steps while viewing images provided by the camera.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method and system for balloon counterpulsation during aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS9308086B2Reduce occlusionPercentage of aortic luminal occlusion can be maximizedBalloon catheterHeart valvesSystoleCardiac cycle
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
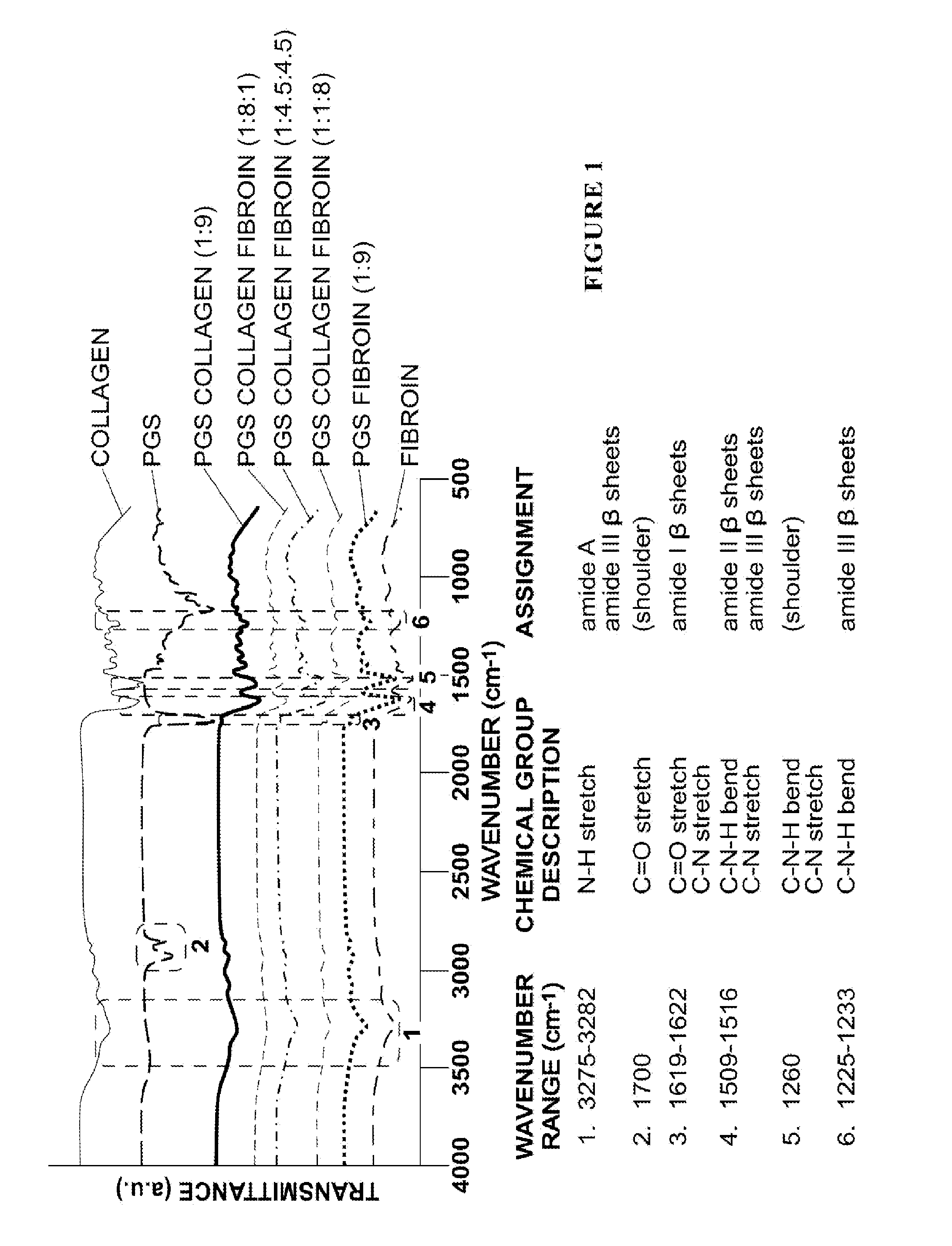
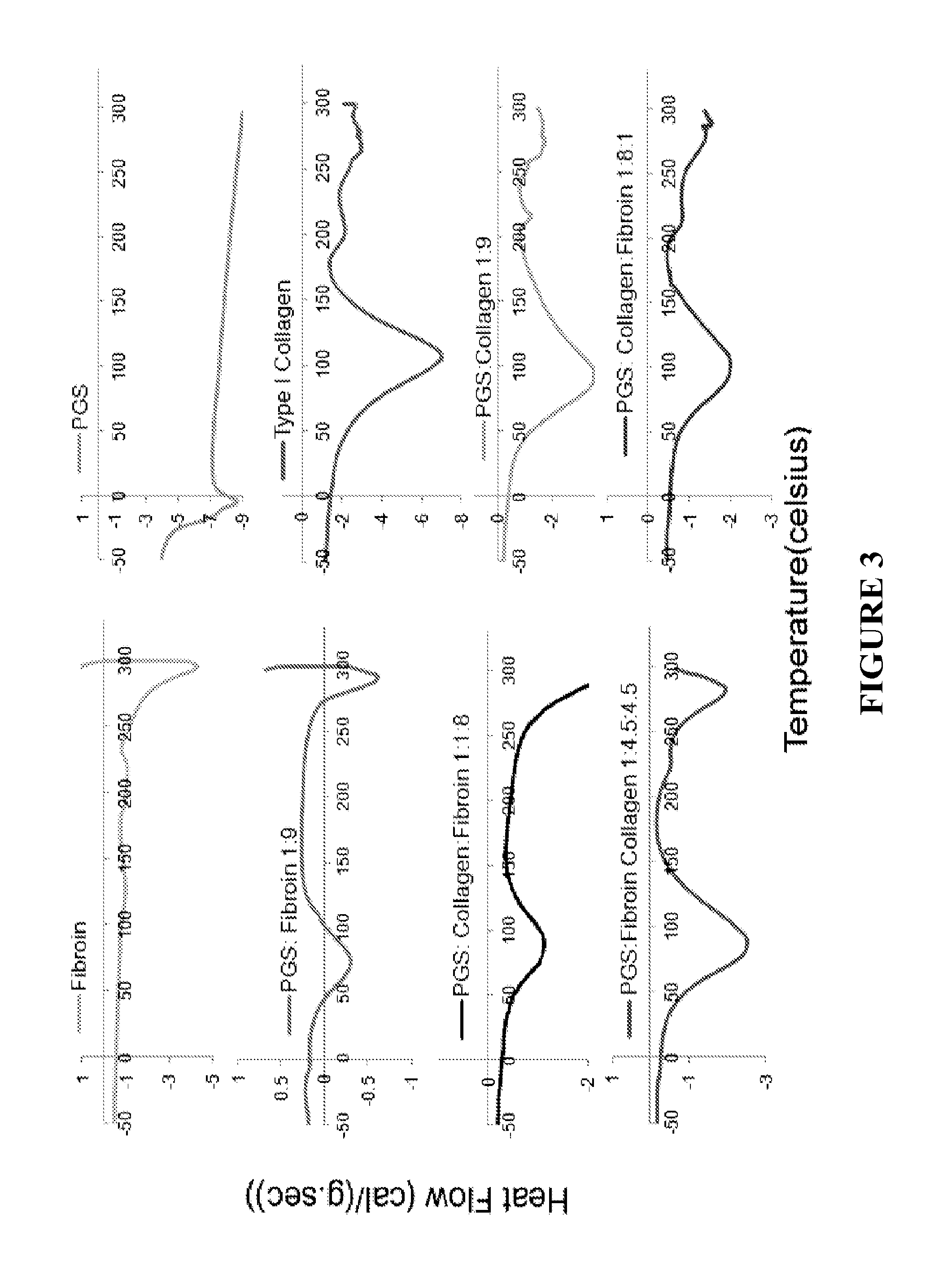
Nanofiber-based graft for heart valve replacement and methods of using the same
InactiveUS10219895B2OptimizationImprove mechanical propertiesStentsHeart valvesNanofiberHeart valve replacement
Nanofiber-based biomaterials containing fibroin for wound repair and tissue replacement and, more particularly, heart valve replacement.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
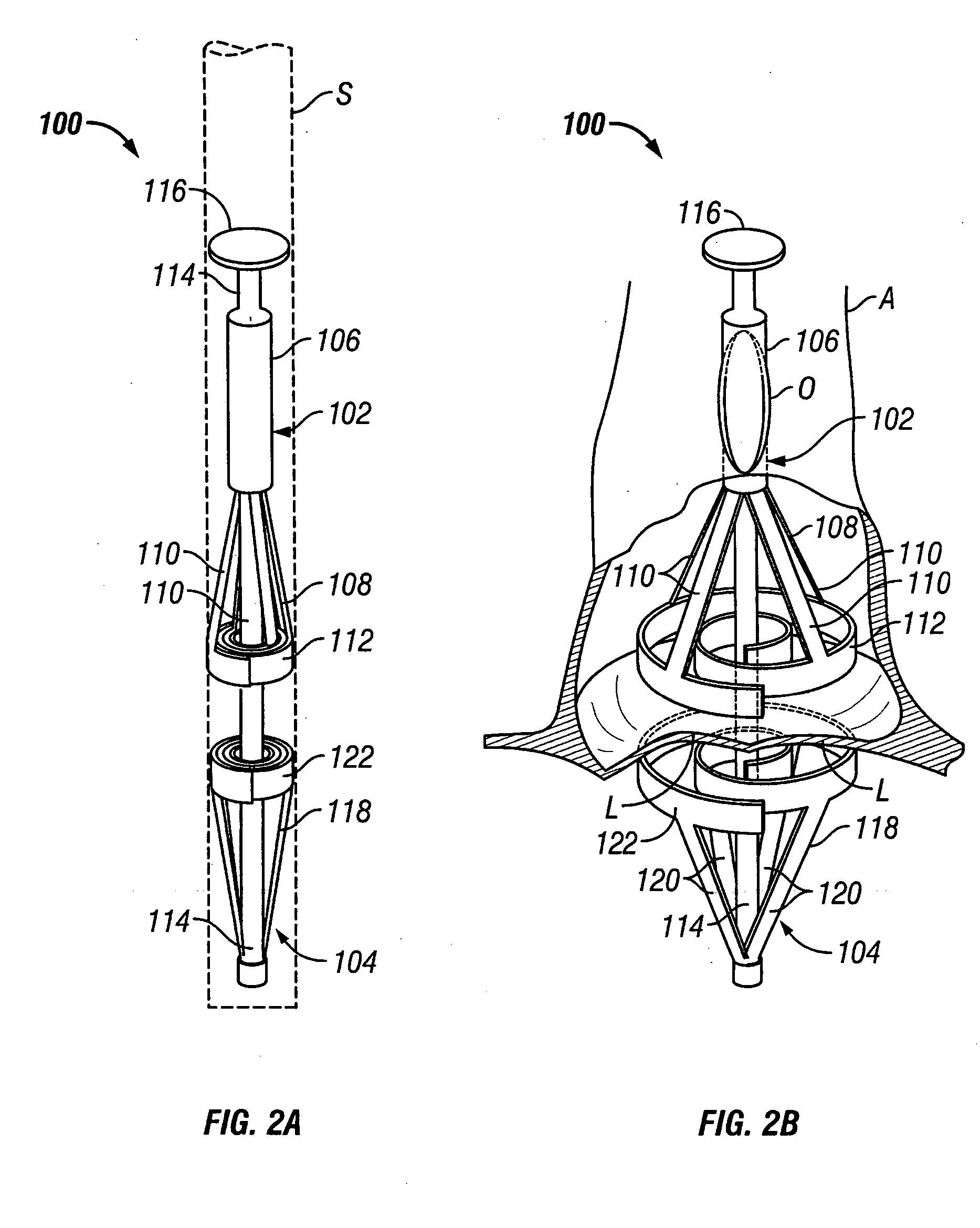
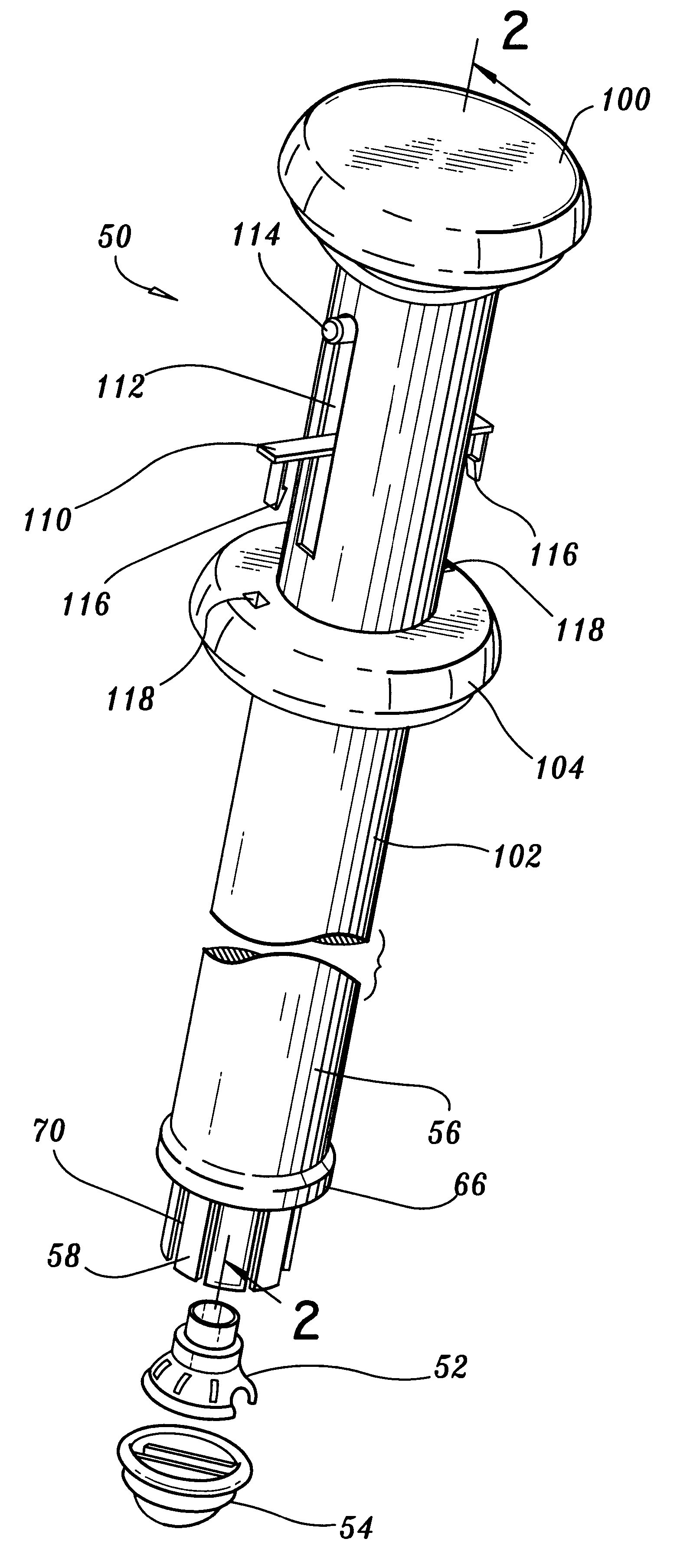
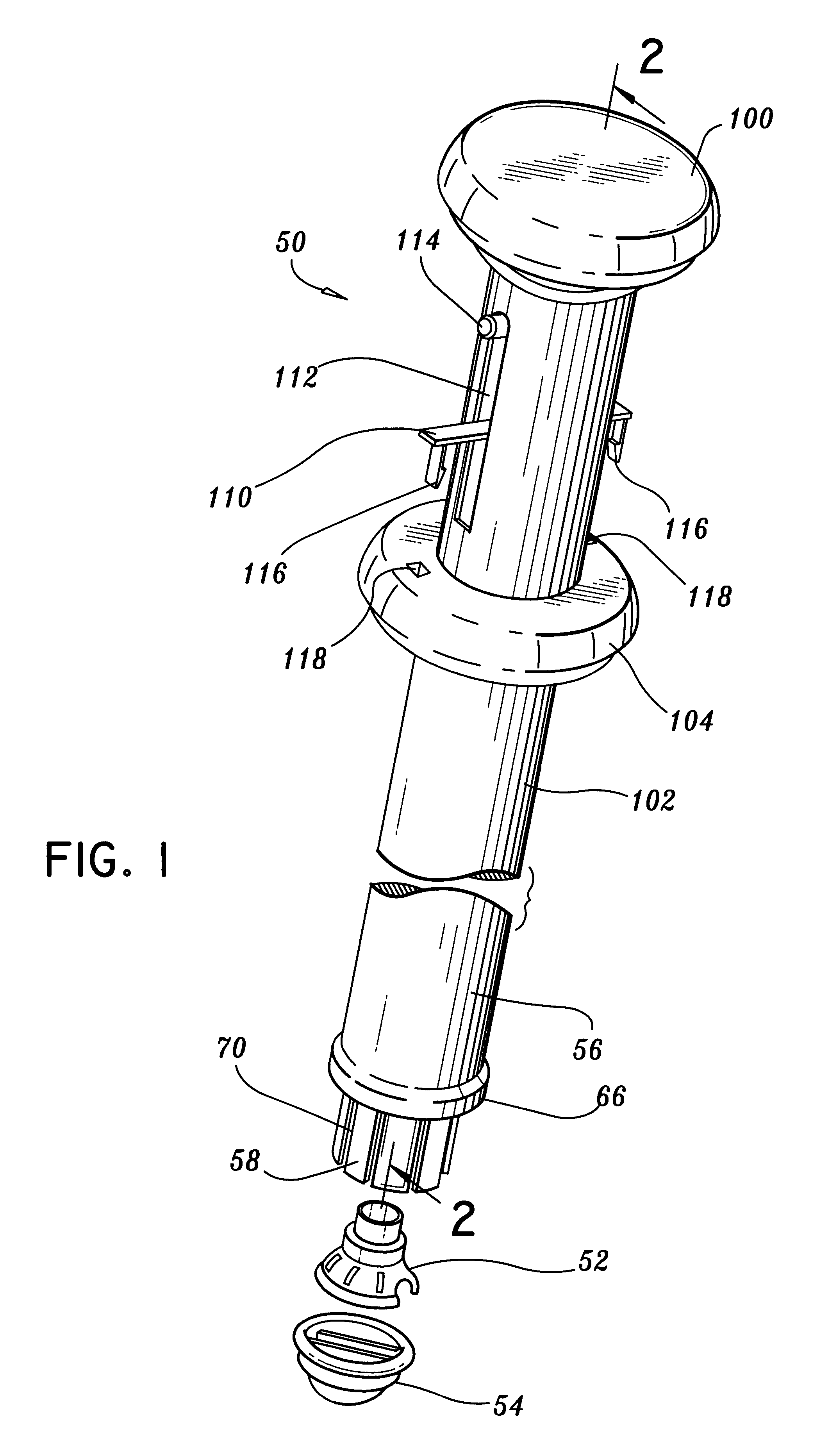
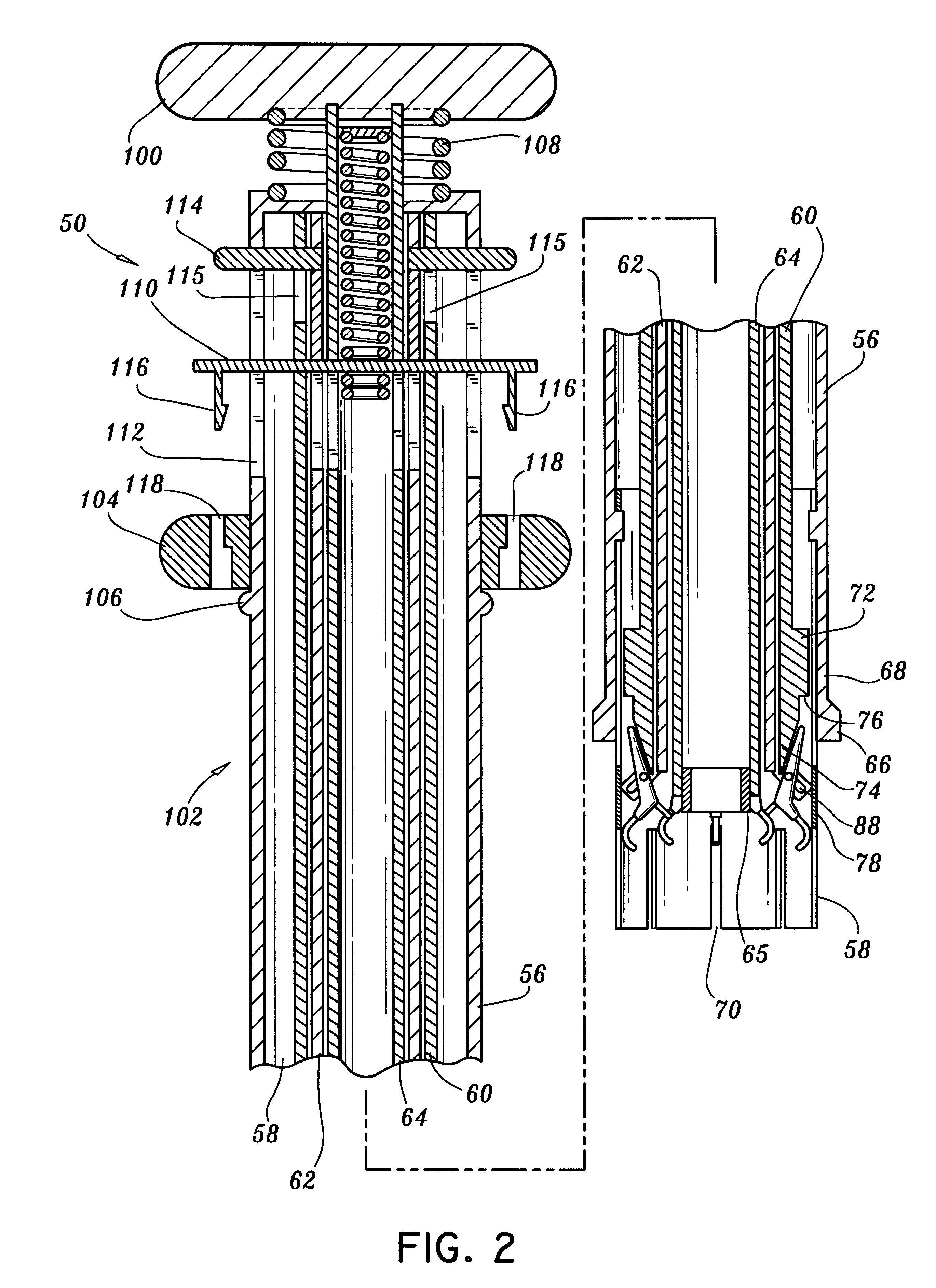
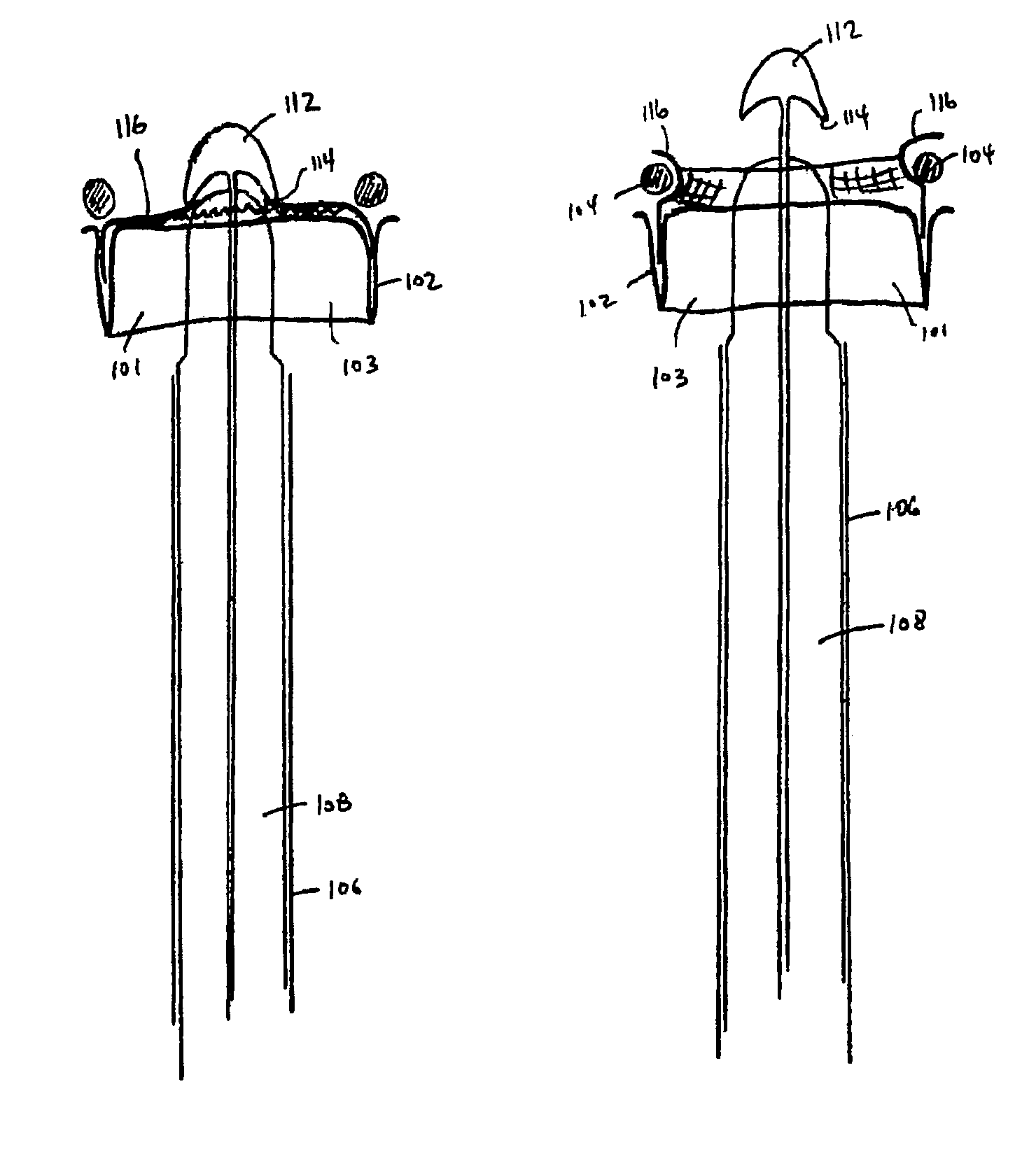
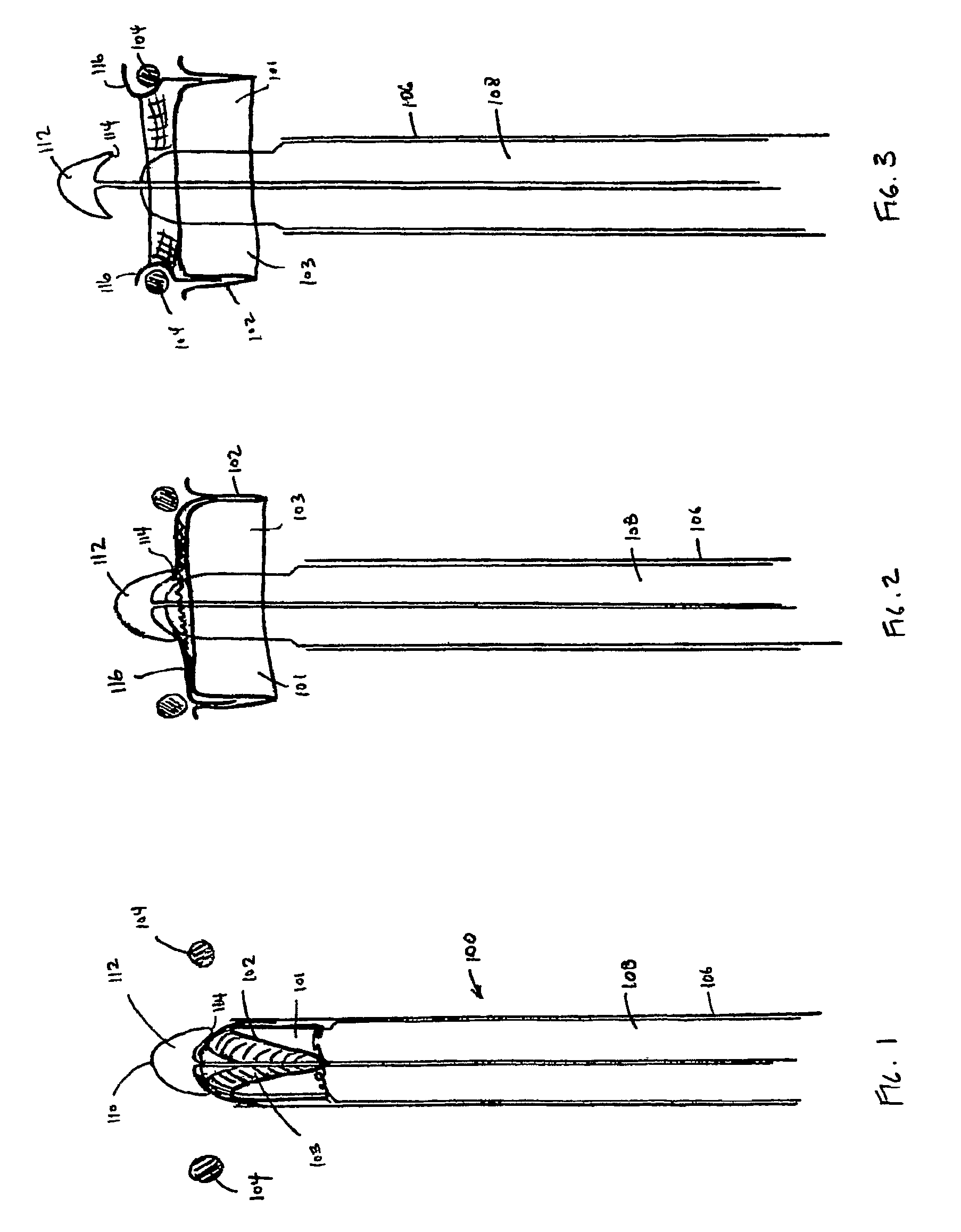
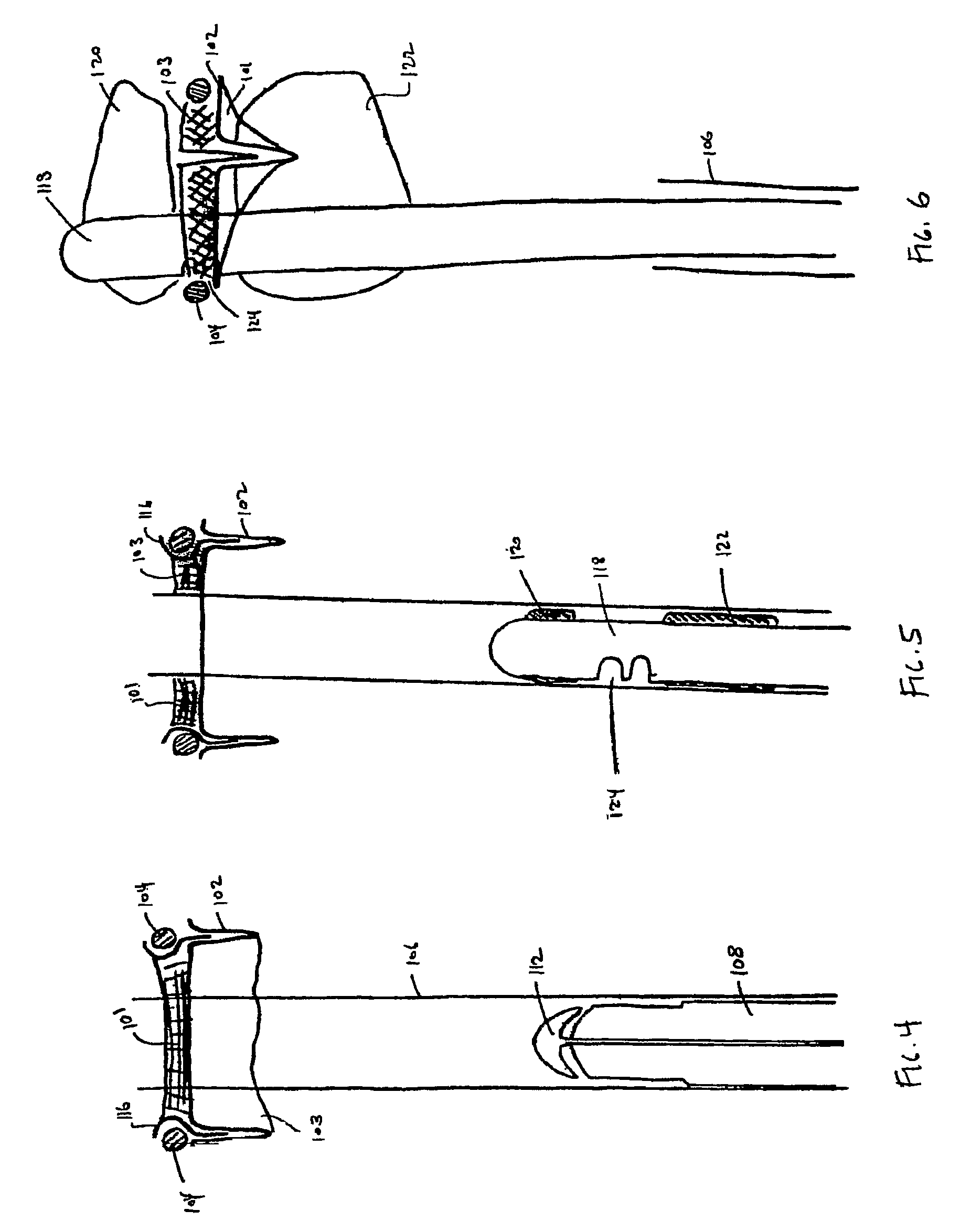
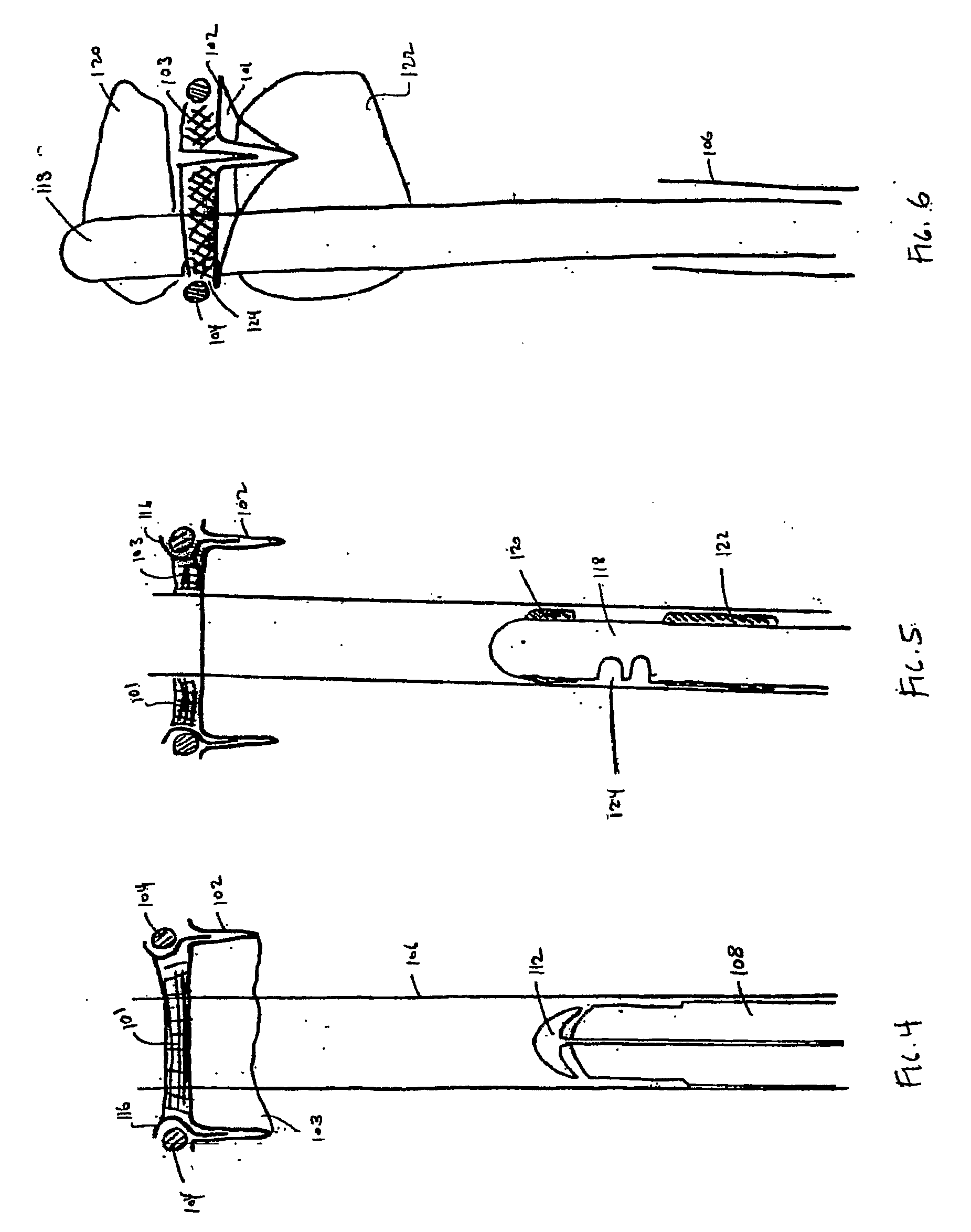
Aortic valve replacement
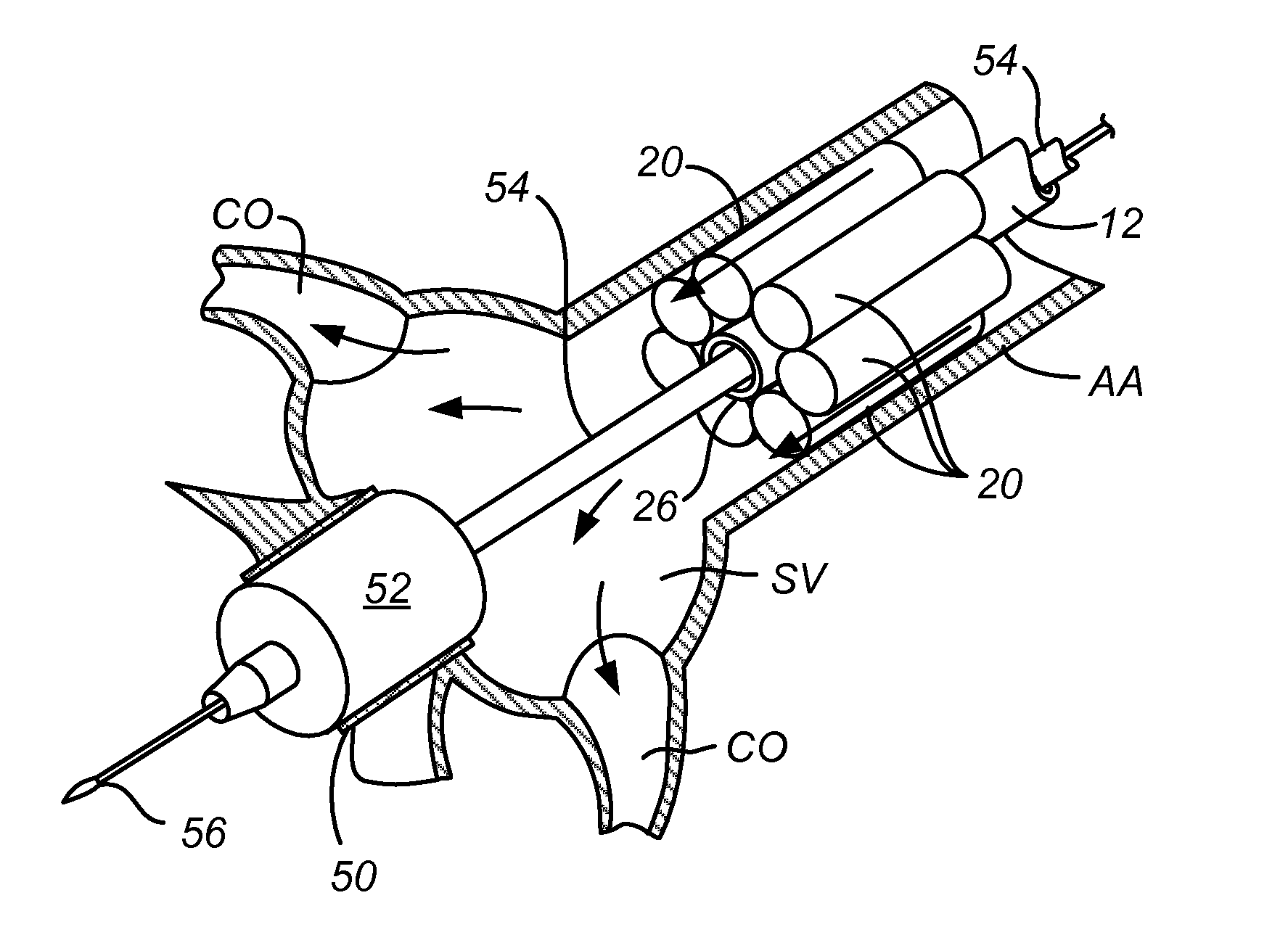
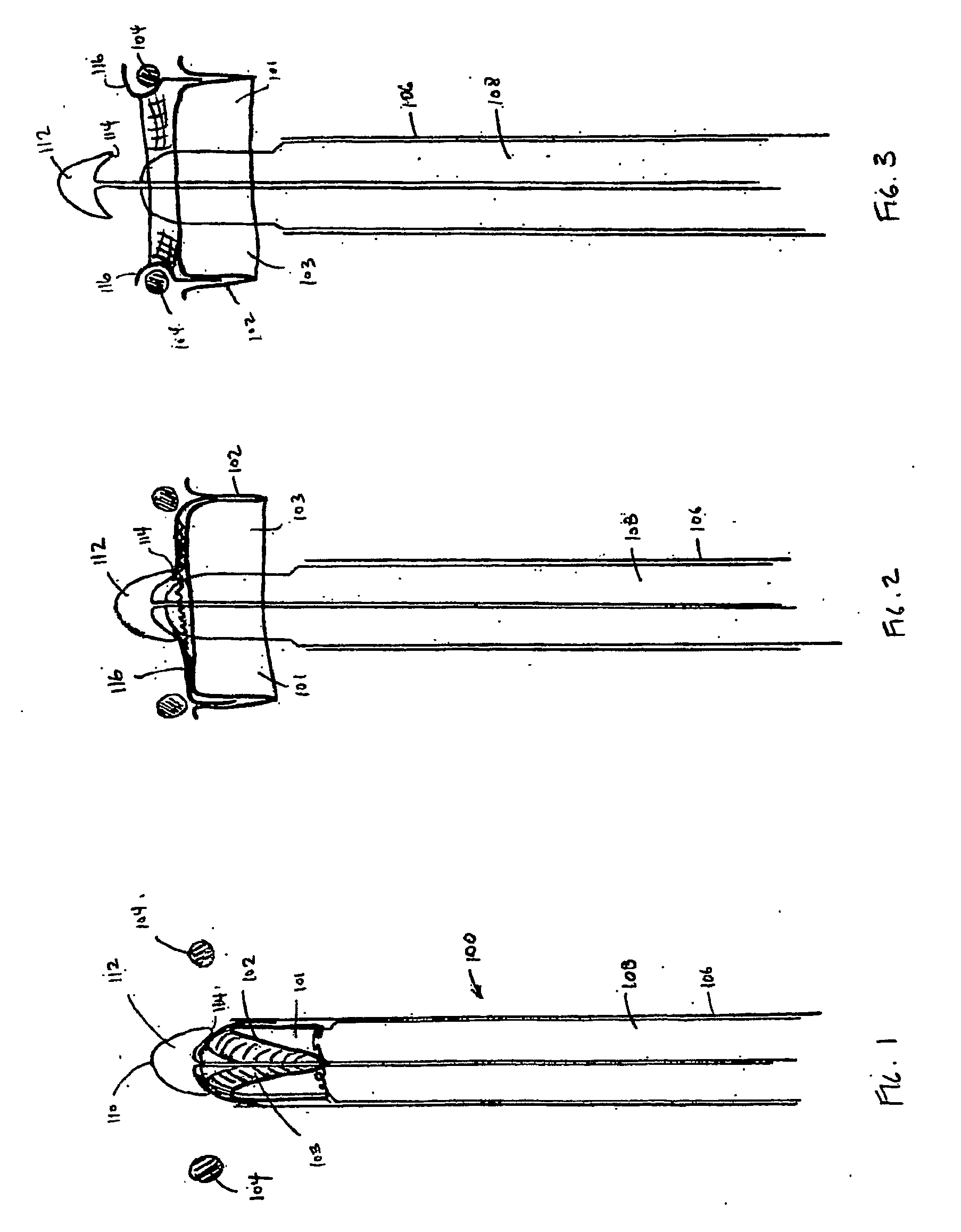
A device for replacement of a bioprosthetic valve having an annulus (104) and one or more leaflets (105), the device having an outer housing (106) and an inner shaft (108) with a distal end (110). The outer housing (106) is slideable relative to the inner shaft (108) such that a portion of the inner shaft (108) may be revealed. A cap (112) is associated with the distal end (110) of the inner shaft (108), the cap (112) movable between a first position adjacent the inner shaft (108) and a second position displaced from the inner shaft (108). The cap (112) is adapted to trap a skirted valve frame (102) between said cap (112) and the inner shaft (108) when in the first position. The skirted valve frame (102) may be released by the cap (112) upon sliding of the outer housing (106) relative to the inner shaft (108) to reveal the inner shaft (108) and upon movement of the cap (112) to the second position. Also disclosed are associated methods.
Owner:EDRICH HEALTH TECH
Automatic road mapping for heart valve replacement
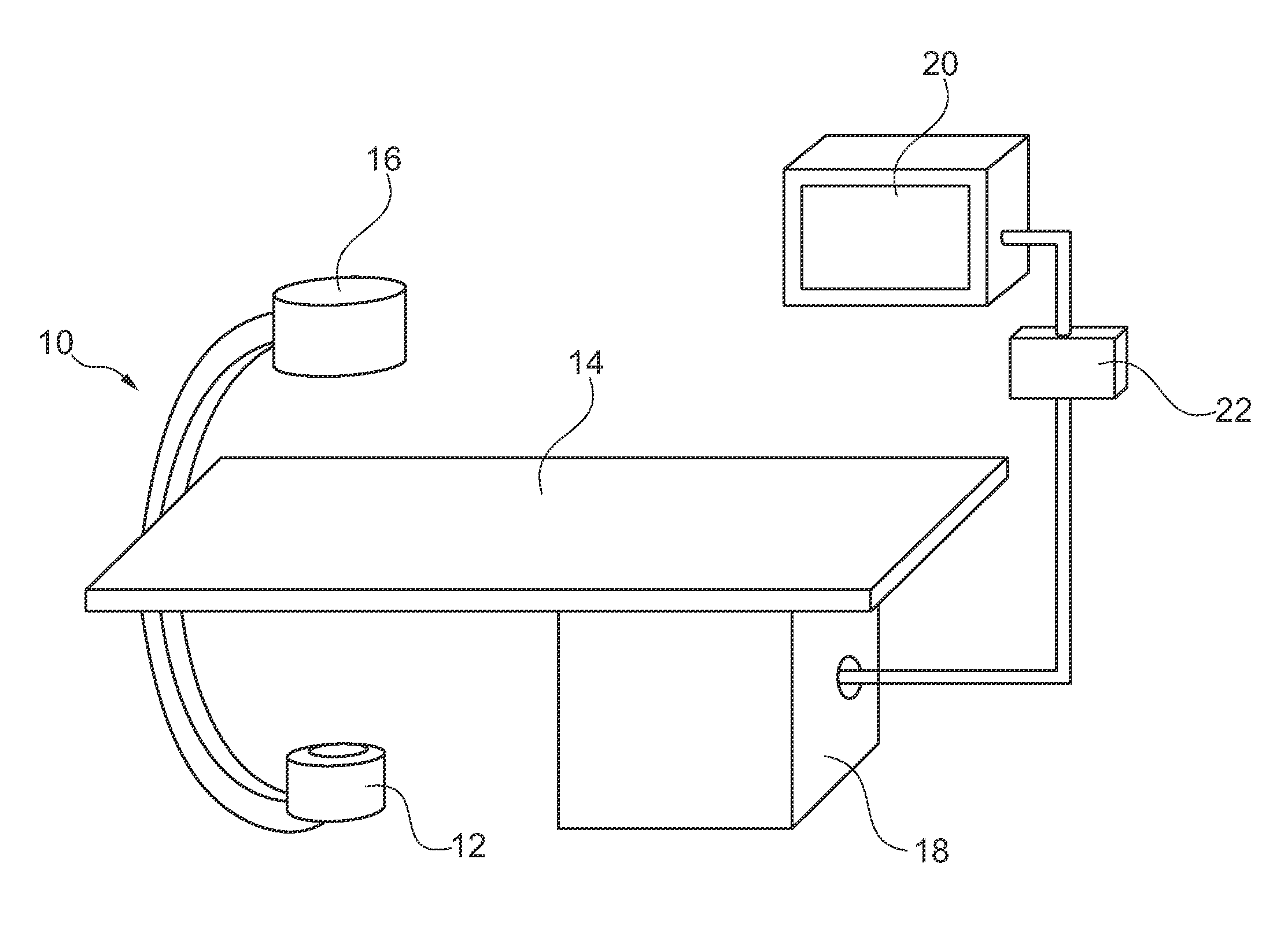
ActiveUS20110249794A1Good informationEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisData modelingX-ray
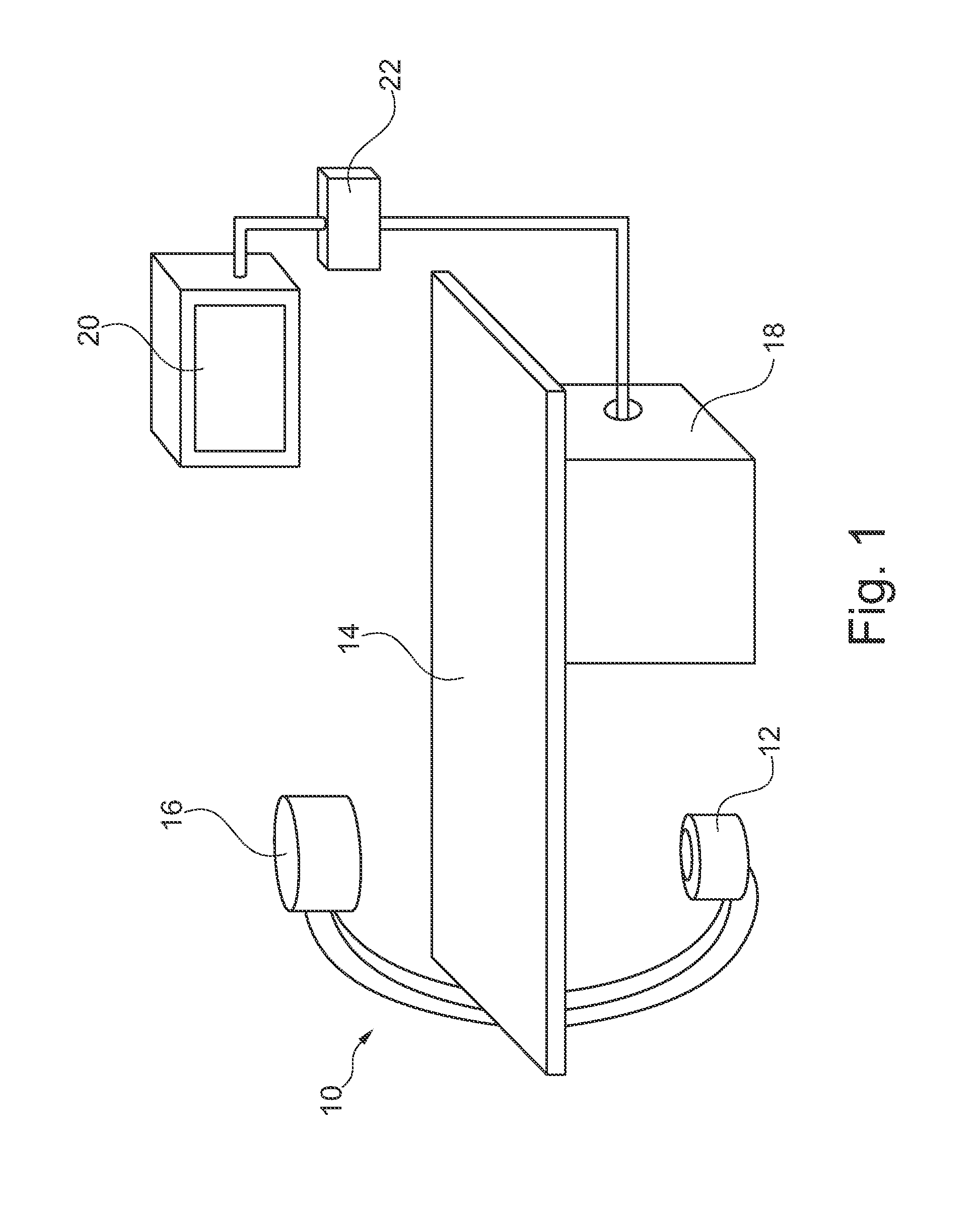
The present invention relates to a method for automatic road mapping for heart valve replacement and an examination apparatus for automatic road mapping for heart valve replacement. In order to provide the cardiologist or surgeon with better information during PHV implantation, an examination apparatus for automatic roadmapping for heart valve replacement is provided, that comprises at least one X-ray image acquisition device (10), a calculation unit (18) and a display device (20). The image acquisition device is adapted to acquire (32) at least one X-ray image of a vessel root region of a heart with injected contrast agent and to acquire (46) at least one current fluoroscopy image of the vessel root region with a replacement valve inserted into the vessel. The calculation unit is adapted to identify (34) vessel information data within the at least one acquired image, to model (36) vessel root representation using the vessel information data and to generate (44) a composite image by a combination of the model of the vessel root representation with the at least one fluoroscopy image. The display unit is adapted to display (48) the composite image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Aortic valve replacement
A device for replacement of a bioprosthetic valve having an annulus (104) and one or more leaflets (105), the device having an outer housing (106) and an inner shaft (108) with a distal end (110). The outer housing (106) is slideable relative to the inner shaft (108) such that a portion of the inner shaft (108) may be revealed. A cap (112) is associated with the distal end (110) of the inner shaft (108), the cap (112) movable between a first position adjacent the inner shaft (108) and a second position displaced from the inner shaft (108). The cap (112) is adapted to trap a skirted valve frame (102) between said cap (112) and the inner shaft (108) when in the first position. The skirted valve frame (102) may be released by the cap (112) upon sliding of the outer housing (106) relative to the inner shaft (108) to reveal the inner shaft (108) and upon movement of the cap (112) to the second position. Also disclosed are associated methods.
Owner:EDRICH HEALTH TECH
Novel nanofiber-based graft for heart valve replacement and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20150272729A1OptimizationImprove mechanical propertiesStentsSurgical adhesivesNanofiberHeart valve replacement
Nanofiber-based biomaterials containing fibroin for wound repair and tissue replacement and, more particularly, heart valve replacement.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Artificial aortic valve ring system implanted through peripheral arterial approach
ActiveCN105287051AWill not cause blockingDoes not affect cardiac conduction systemHeart valvesCalcificationAortic root
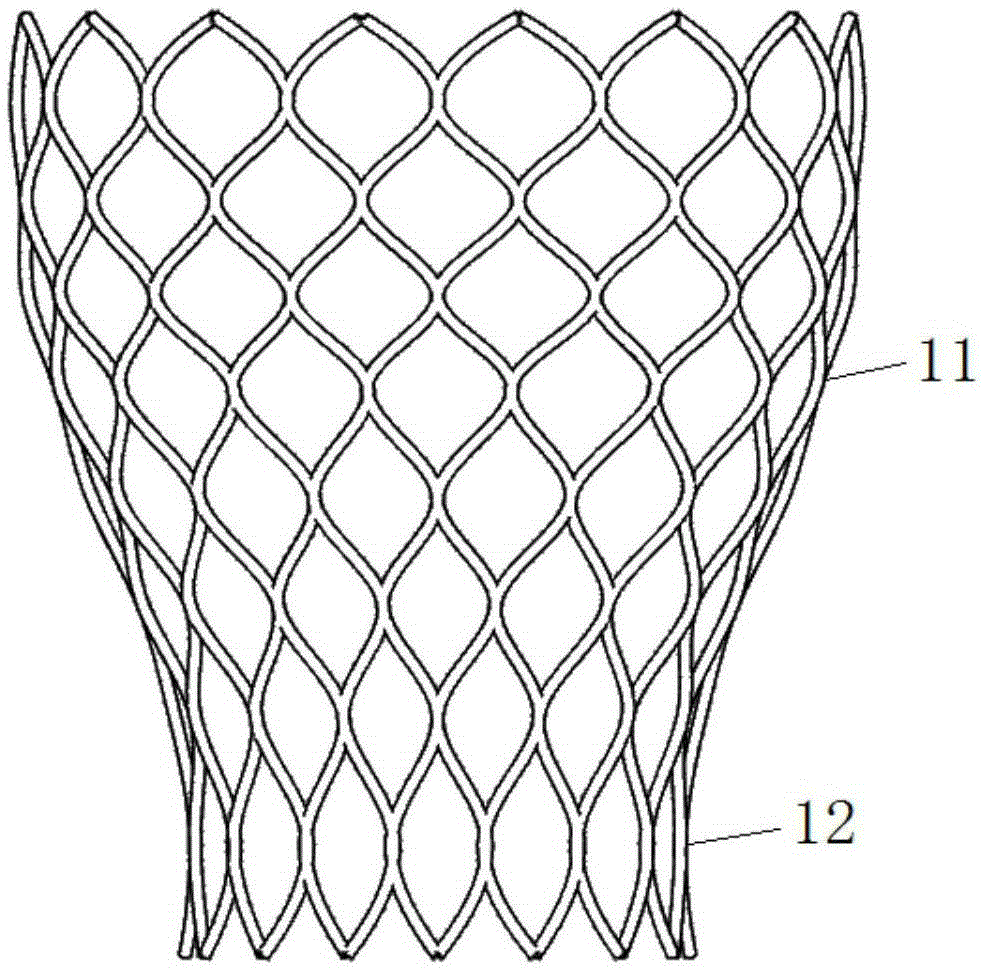
The invention discloses an artificial aortic valve ring system, which is used for taking effects of supporting and fixing in trans-catheter aortic valve replacement on patients of aortic valve regurgitation without calcification. The system comprises a valve ring scaffold at distal end and anchoring legs at proximal end, wherein the valve ring scaffold is fixedly connected to the anchoring legs; the valve ring scaffold is of a tubular structure and has a gridding structure; the anchoring legs are arranged along the periphery of the valve ring scaffold and are embedded in a cavity structure on ascending aortic root so as to fix the system; and the system is capable of transforming between a first form of radial expansion and a second form of radial shrinkage. With the implantation of the system, the trans-catheter aortic valve replacement on patients of aortic valve regurgitation without calcification becomes possible.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Implantable mechanical heart valve assembly
InactiveUS8167936B2Reduce complicationsThickness minimizationHeart valvesSuturing guideHeart valve replacement
A mechanical heart valve implantable as heart valve replacement comprising of an annular valve body with a central orifice and an exterior surface incorporating a suture ring having a plurality of suture tunnels, and a valve implantation flap assembly disposed on the valve body surface and wrapping around the suture ring. The inside lumen carries the occluder mechanism. The valve holder comprises of at least two parts, both parts having suture guiding grooves on the outer surface corresponding to and matching with the tunnels on the suture ring, such as to form a continuous path for the sewing material. The parts of the valve holder can be detached separately from the valve after taking all the sutures, the part on the ventricular side before lowering the valve into the heart and the other part after lowering and positioning the heart valve in the; desired position inside the heart.
Owner:KURIAN VALIKAPATHALIL MATHEW
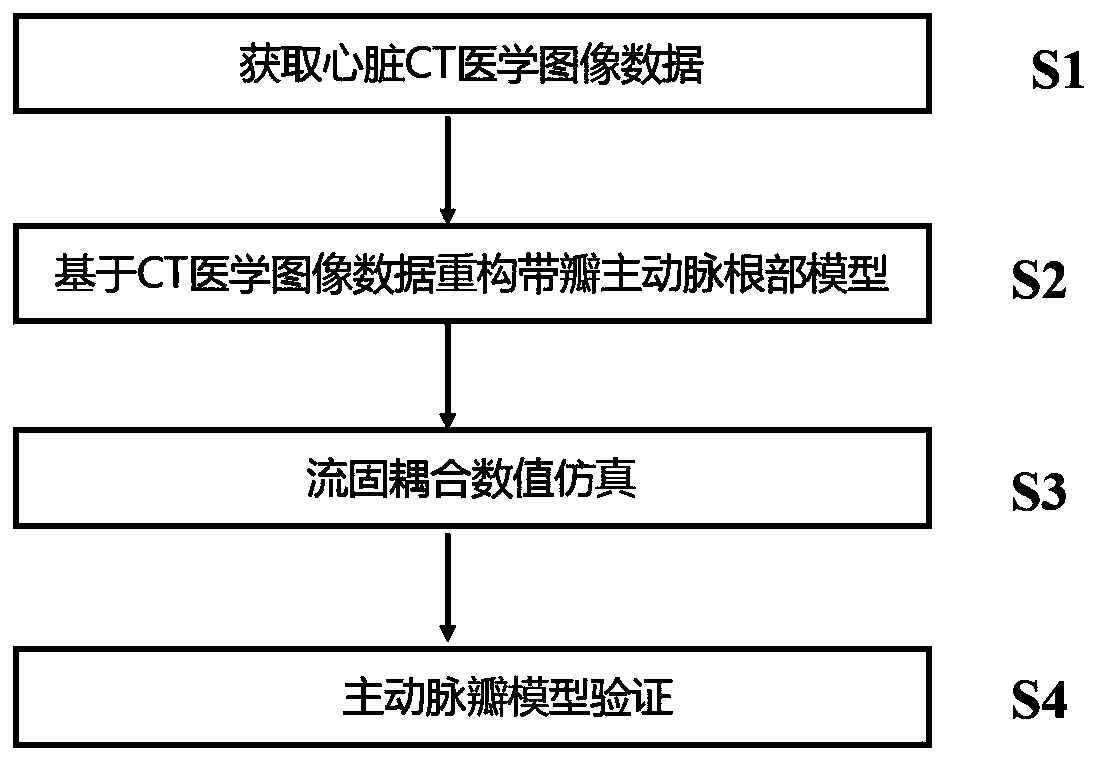
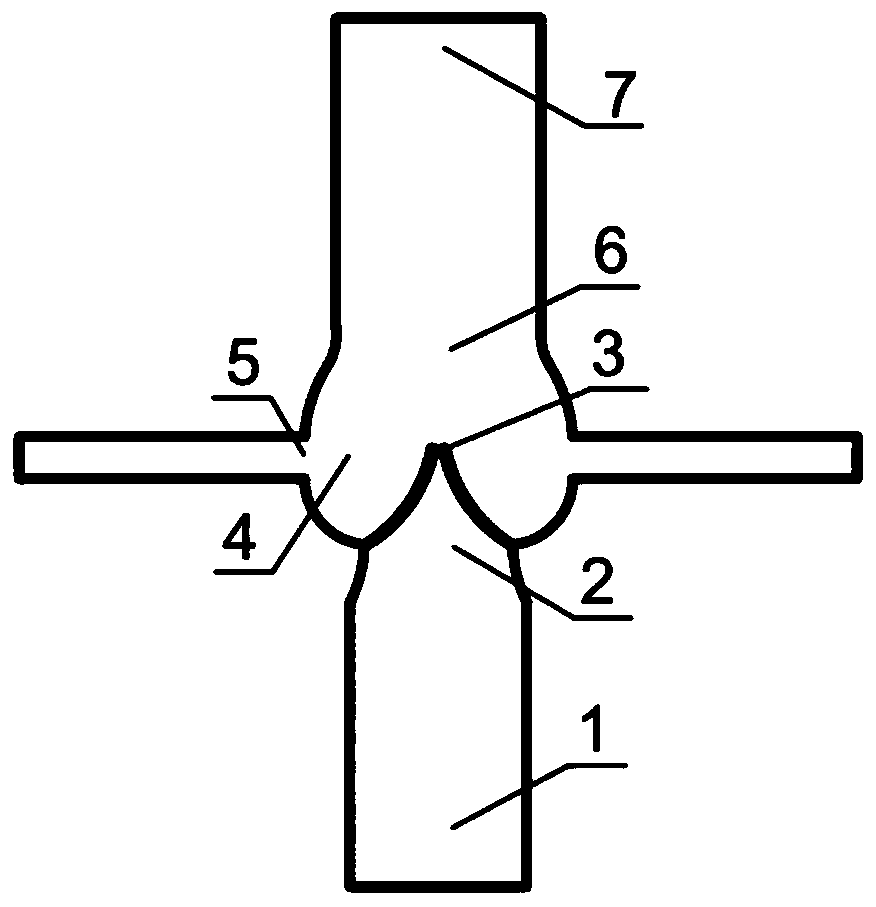
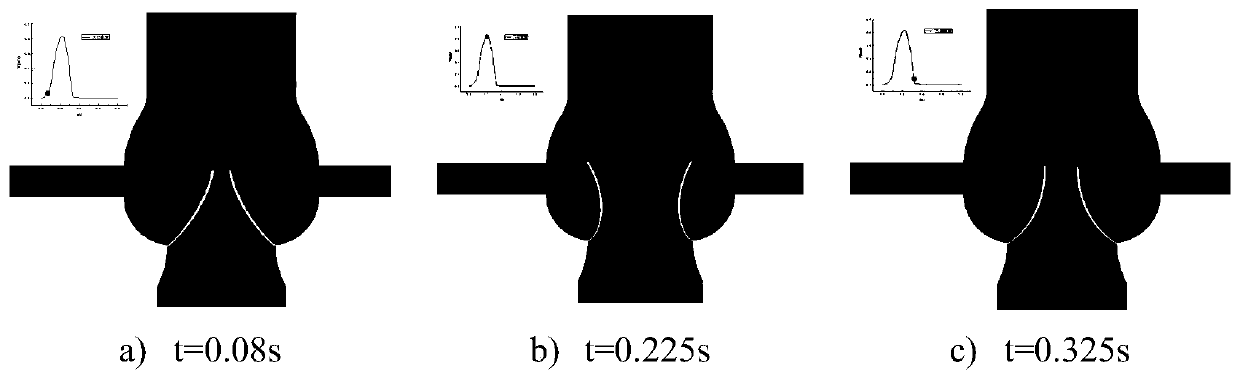
Aortic valve fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method based on CT medical image data
The invention discloses an aortic valve fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation method based on CT medical image data, and belongs to the field of aortic valve and fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring heart CT medical image data; reconstructing a valved aorta root model based on the CT medical image data; carrying out fluid-solid couplingnumerical simulation; and verifying the aortic valve model. According to the invention, the aortic valve model is reconstructed through CT medical image data, aortic root fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation is carried out based on Comsol software, and the complex deformation problem of the aortic valve in the complete cardiac cycle is solved. The method truly reflects the hemodynamics of the root of the aorta, and the result has more guiding significance for reality. The aortic valve fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation developed by the invention can provide reference for artificial valve design and aortic valve replacement.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Seamless aortic valve replacement device
The invention provides a seamless aortic valve replacement device implanted under surgical orthophoria. The seamless aortic valve replacement device is characterized by comprising a metal support, a terylene ring, a joint tab and an artificial valve, wherein the metal support comprises a support inflow end, an oar-shaped support part and a support outflow end, wherein the oar-shaped support part is connected with the support inflow end and the support outflow end respectively; the terylene ring is fixed at the support inflow end; the joint tab is fixed at the oar-shaped support part; and a near end of the artificial valve is fixed on the inner side of the terylene ring, and a far end of the artificial valve is fixed on the inner side of the joint tab. According to the seamless aortic valve replacement device, the whole height of the device can be effectively reduced; and at the same time, large-area circular terylene is seamed at the support inflow end, fixation of the whole device in a left ventricle outflow tract is enhanced, and integrated expansion is facilitated, so that the inflow end and the outflow end of the metal support can be well anchored an aorta wall, and the occurrence rate of complication of valve displacement, perivalvular leakage, atrioventricular block and the like is decreased.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
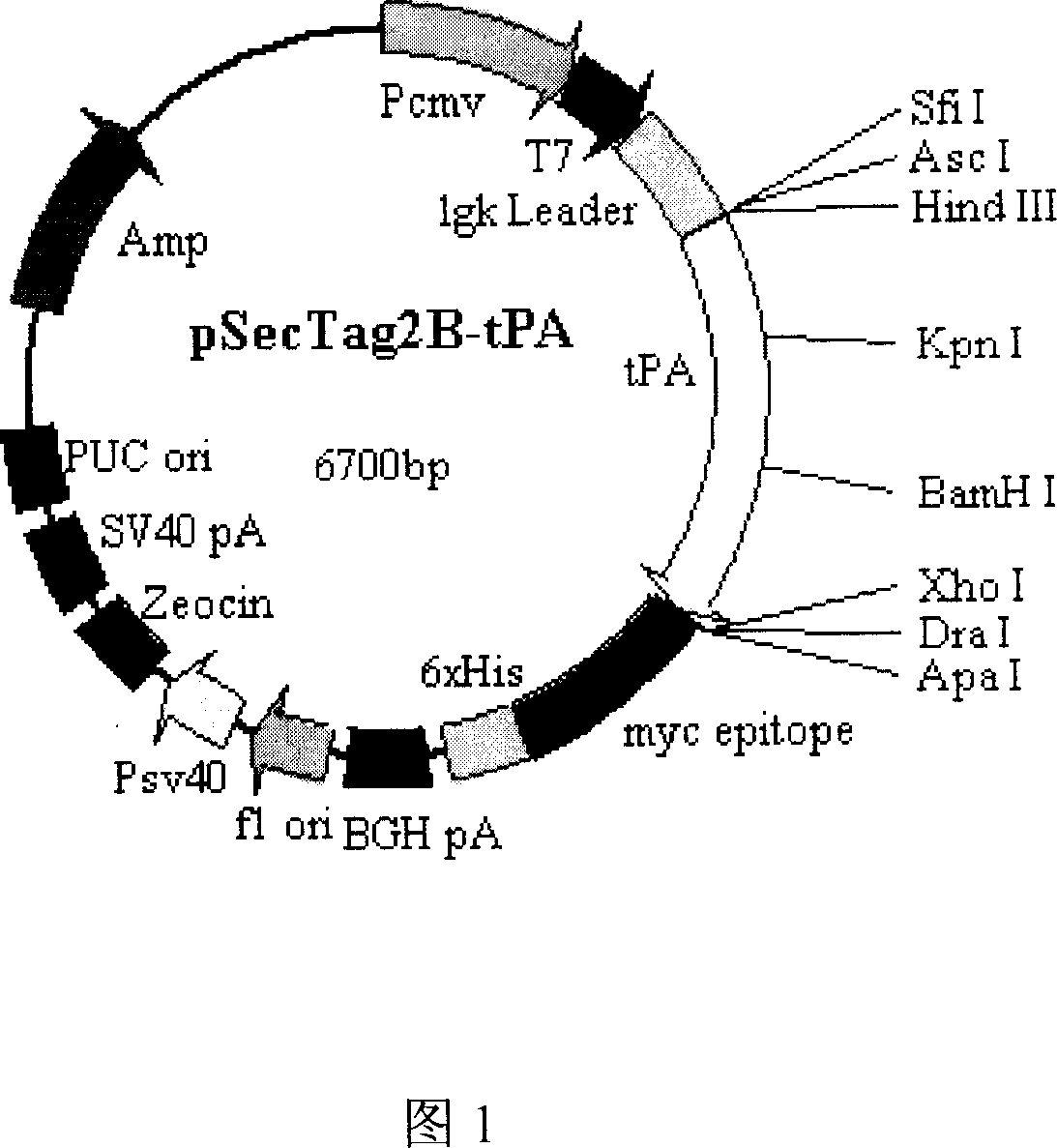
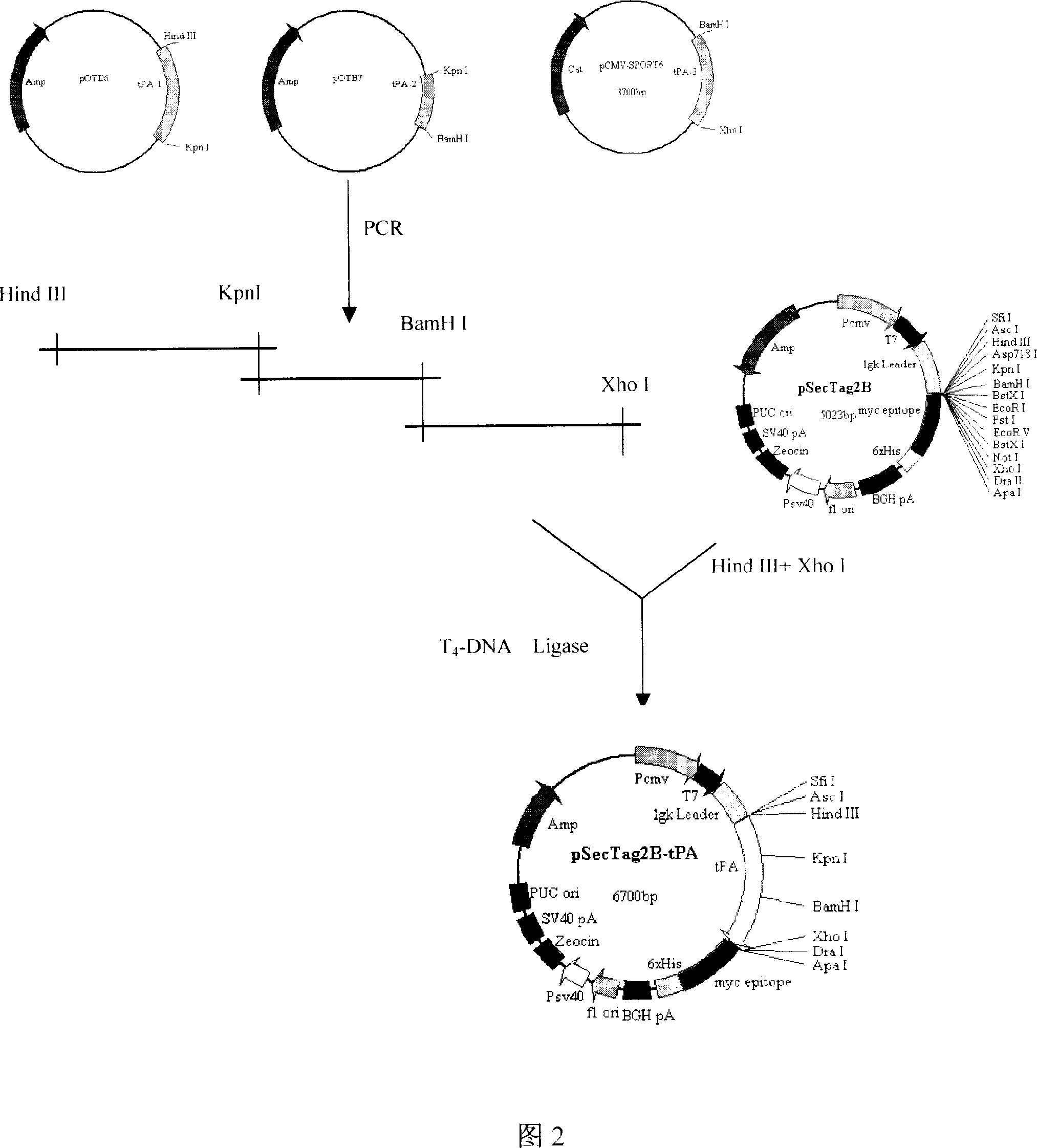
TPA gene thread and its preparation method
InactiveCN101007181AIncrease fibrinolytic activityProlong survival timeSuture equipmentsFermentationCardiac muscleThrombus
The invention relates to a kind of tPA gene suture as well as preparing method, the characteristic of the invention is that the eukaryotic expression vector pSecTag2B-t-PA of modified gene tPA is attached to the suture. The preparing procedure includes the following steps: labeling the pSecTag2B-t-PA recombinant plasmid with basic ion bangosome; soaking the suture into bangosome / plasmid DNA compound solution repeatedly to get the tPA gene suture. The invention can be used in the saturation of cardiac muscle in cardiac valve replacement; it can remove or prevent the sludged blood so that it can prevent the form of thrombus around the valvula which can impact the valvula function after cardiac valve replacement.
Owner:姬尚义
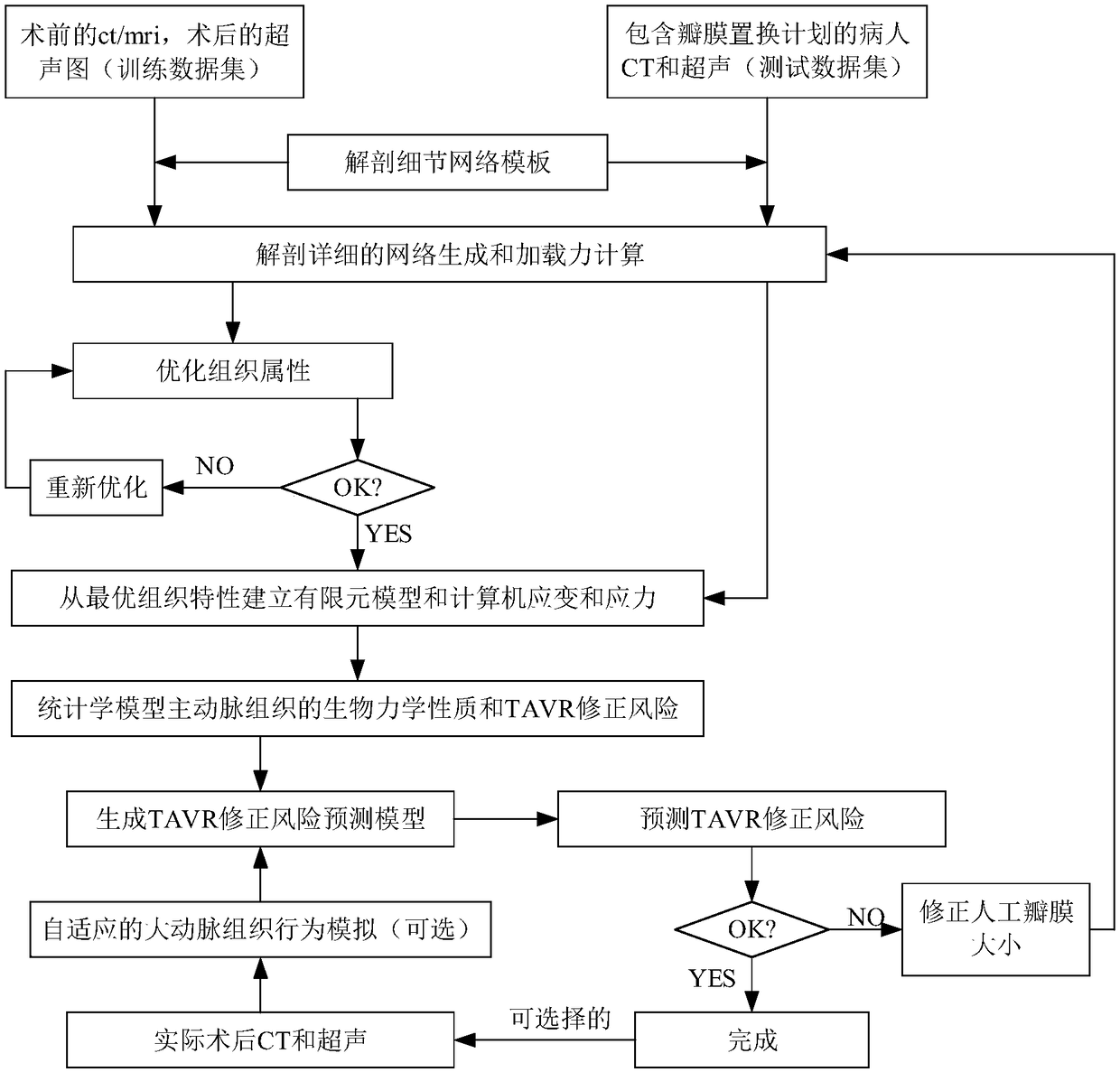
A method and system for optimizing cardiac valve replacement
ActiveCN109360273AReduce clinical riskImage enhancementImage analysisProsthetic valveAortic Valve Insufficiency
The invention relates to a method and a system for optimizing cardiac valve replacement. The method comprises the following steps: (1) calculating load forces of different patients after transcatheteraortic valve replacement; (2) simulating the behavior of aortic root and valve tissue, and extracting biomechanical characteristics by finite element method; (3) establishing an aortic valve insufficiency risk prediction model; (4) using the risk prediction model to predict the risk of heart valve and optimize the prosthetic valve, repeating the steps (1)-(3) until the risk prediction results aresafe. As compare with that prior art, the method and system of the present invention can guide doctors to use different optimize valves for different patients to minimize clinical risks.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Bicuspid percutaneous aortic valve incision device
ActiveCN104352265AAvoid the risk of infectionAddress the risk of surgical failureIncision instrumentsMedical devicesHead injury sequelaeTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a bicuspid percutaneous aortic valve incision device, which comprises a conveying device and a cutting device; the conveying device comprises an outer sheathing canal, a middle sheathing canal and a hollow inner sheathing canal; the inner sheathing canal is movably sheathed in the middle sheathing canal; the middle sheathing canal is movably sheathed in the outer sheathing canal; the cutting device comprises two fixed mounts and blades respectively arranged on the fixed mounts; the length of each fixed mount is greater than the external diameter of the outer sheathing canal; the fixed mounts are rotatably arranged on the excircle surface of the far end of the inner sheathing canal; when the inner sheathing canal shrinks into the middle sheathing canal, the fixed mounts and the inner sheathing canal are axially contained in the middle sheathing canal in parallel; when the inner sheathing canal extends out of the outer sheathing canal, the two fixed mounts are fixedly arranged on the excircle surface of the inner sheathing canal in a straight line. The invention provides the bicuspid percutaneous aortic valve incision device which is simple in structure, does not need to implant outside matter and has a good treatment effect, so that the defects that surgery sequelae are numerous and the recovery degree is low due to the fact that the fixed mounts need to be implanted by adopting the existing novel aortic valve replacement are solved.
Owner:陈良龙
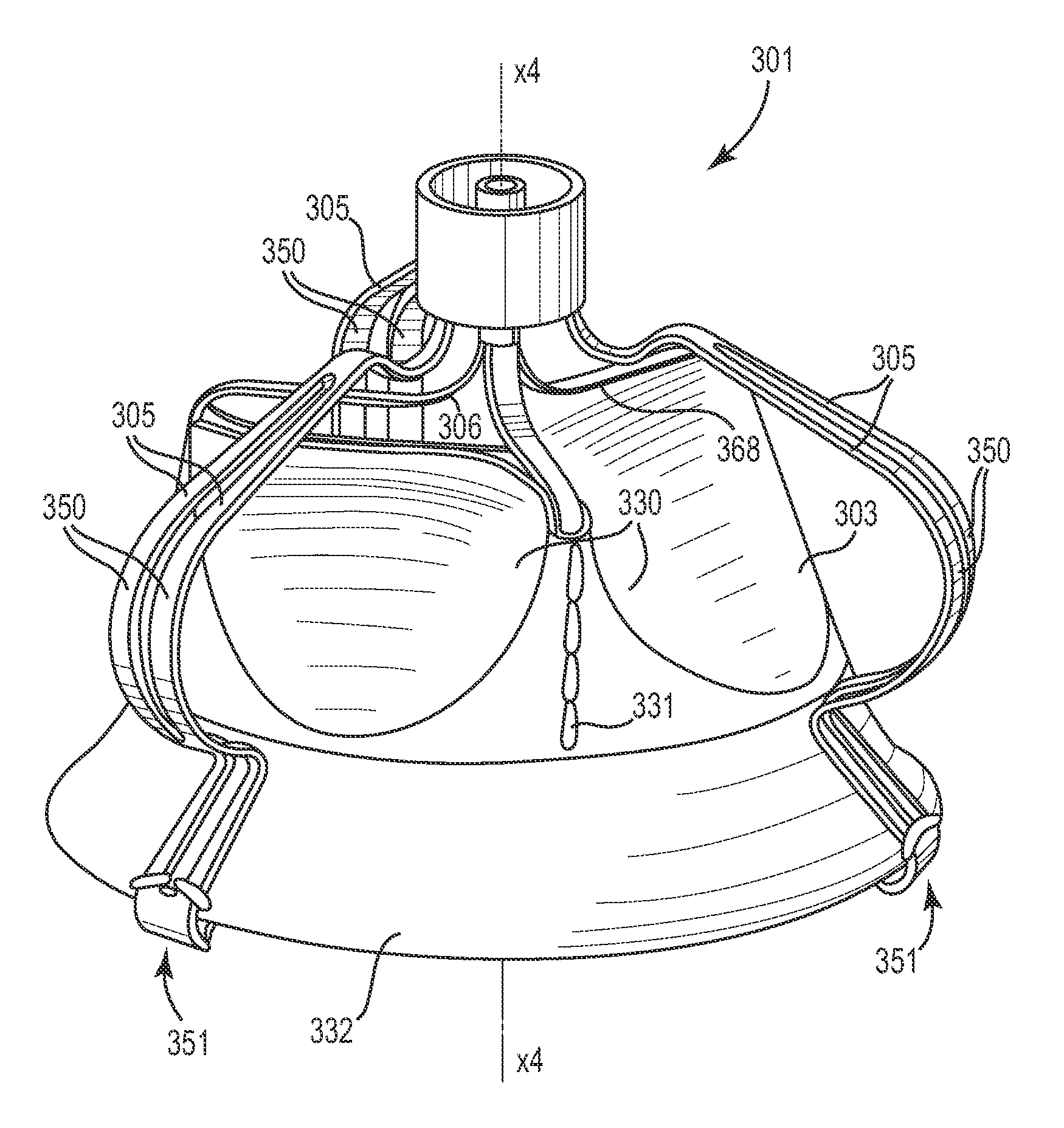
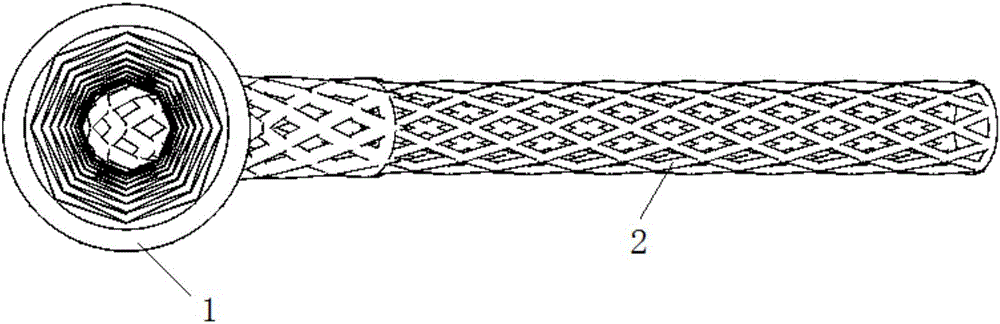
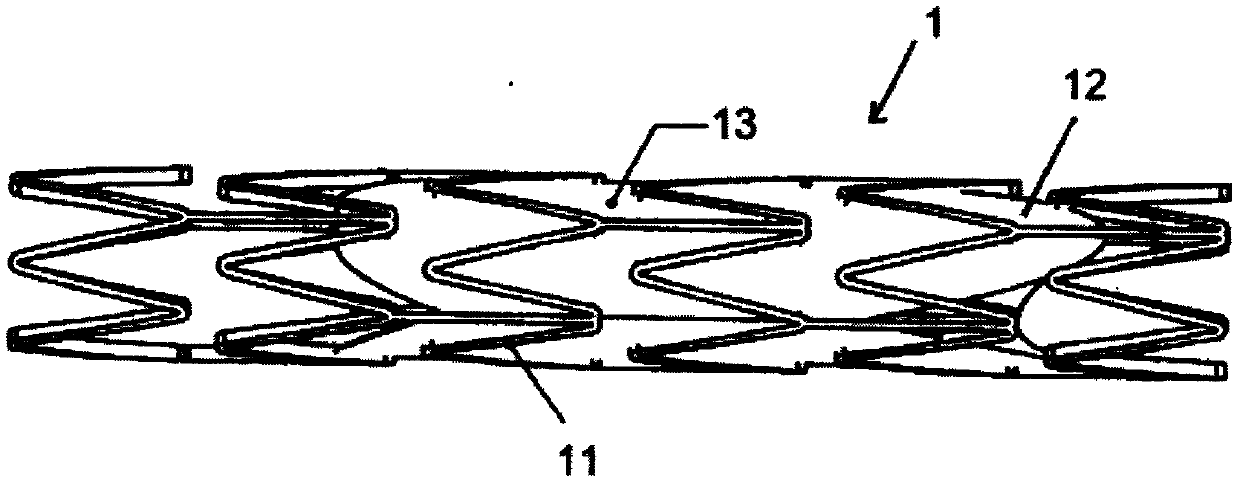
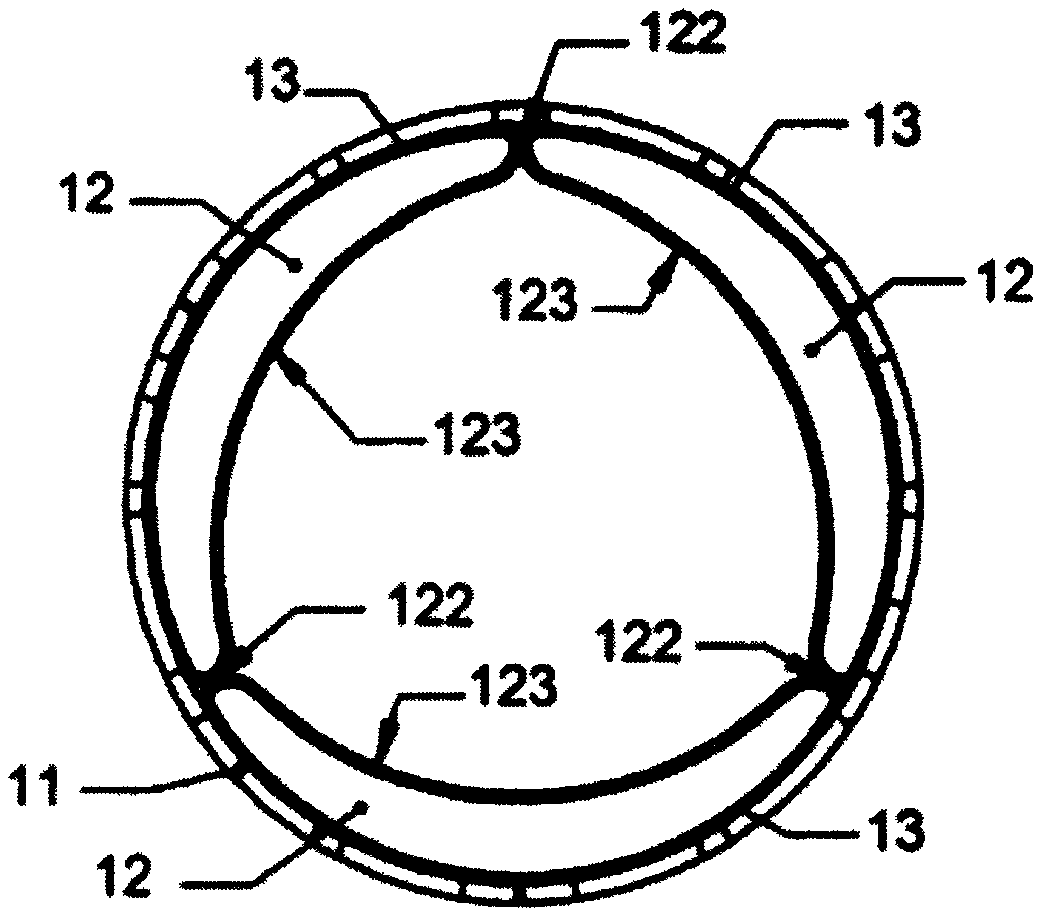
Tubular supporting prosthesis with a heart valve, in particular for aortic valve replacement
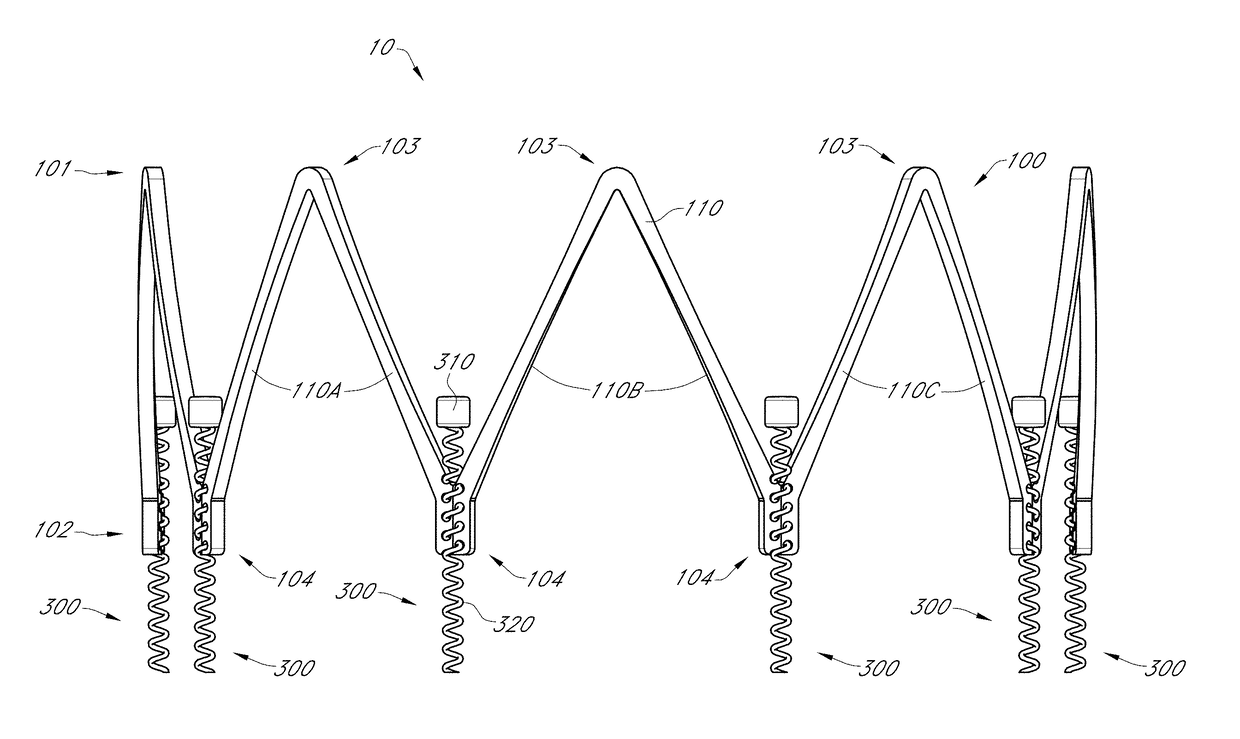
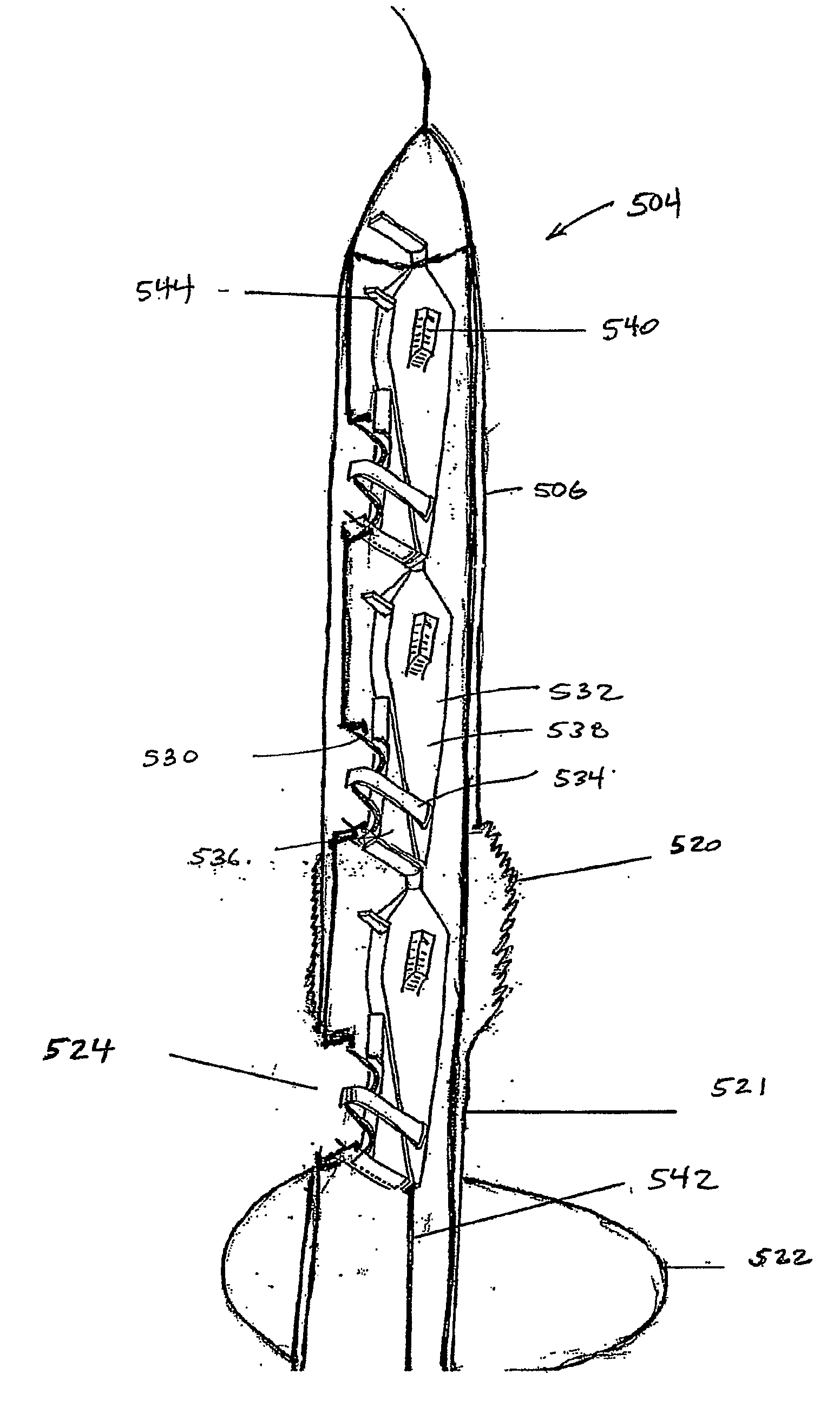
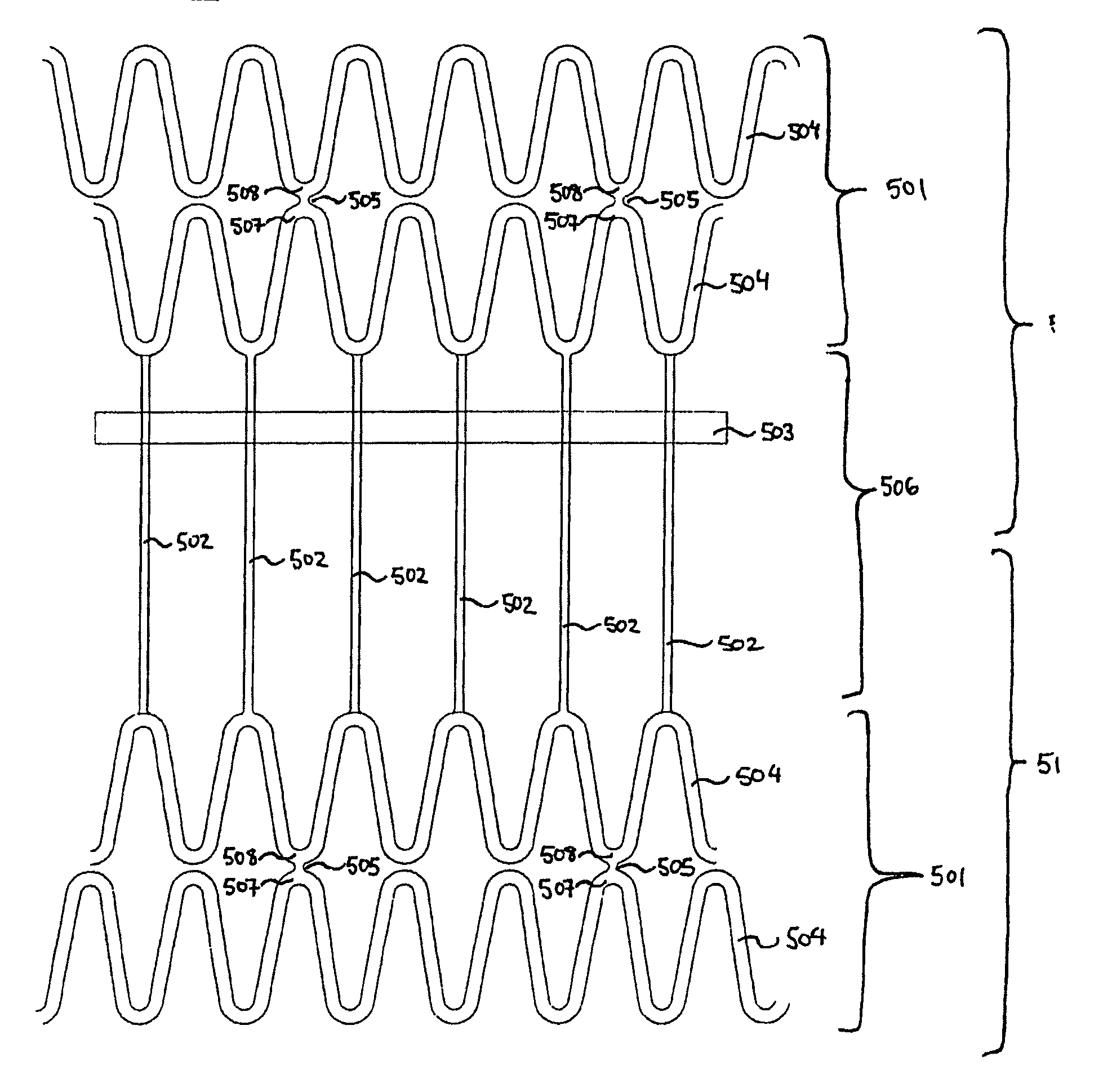
The invention relates to a tubular supporting prosthesis, comprising two terminal regions relative to the longitudinal supporting prosthesis axis and a center region disposed between the two terminal regions, wherein every terminal region is provided with a mesh structure made of at least two structural rings, which are connected to each other via connecting members and are disposed point-symmetrically about the longitudinal supporting prosthesis axis. The center region is formed by elongated connecting members, which are connected to the structural rings respectively disposed adjacent to the center of the longitudinal supporting prosthesis axis. An aortic valve, which is produced by means of tissue engineering, is fastened and / or integrated in the center region.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
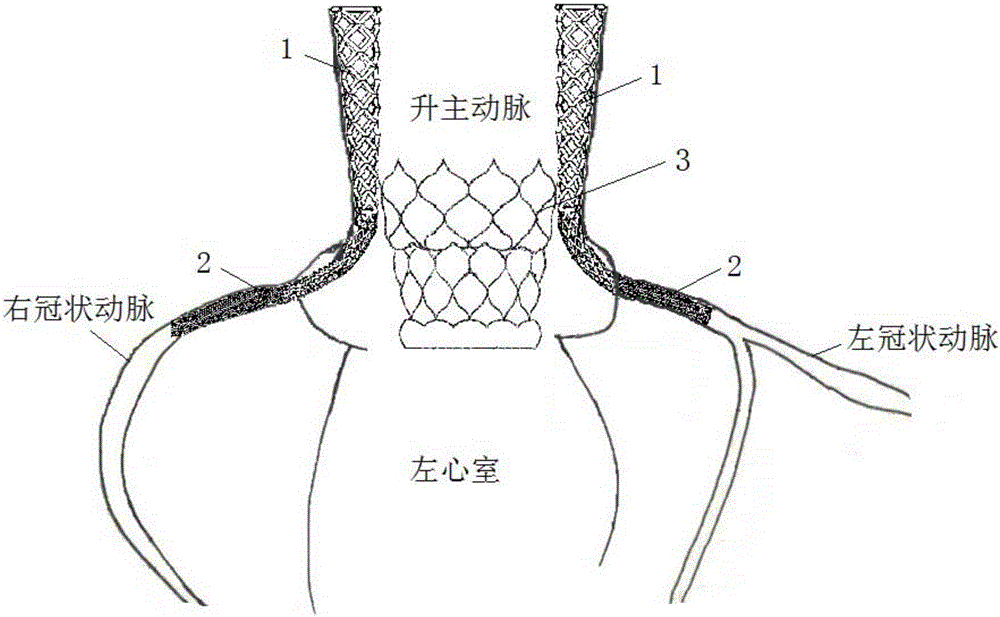
Coronary artery protecting device
InactiveCN105662654ADoes not affect functionalityDoes not affect fixationHeart valvesAnatomical structuresCoronary arteries
The invention discloses a coronary artery protecting device which comprises an isolating part and a fixing part. The isolating part is used for isolating a potential obstacle from a coronary artery opening, and the fixing part is used for fixing the position of the isolating part. The device is provided with a grid structure, the grid structure is implanted into the joint portion of the ascending aorta and coronary artery through the peripheral arterial path, the grid structure is implanted before transcatheter aortic valve replacement, smoothness of blood flow in the coronary artery during the transcatheter aortic valve replacement operation and after the operation can be guaranteed, coronary occlusion complications is avoided, and therefore transcatheter aortic valve replacement can be achieved for an aortic valve disease patient whose ascending aorta root anatomical structure does not meet the current standard.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
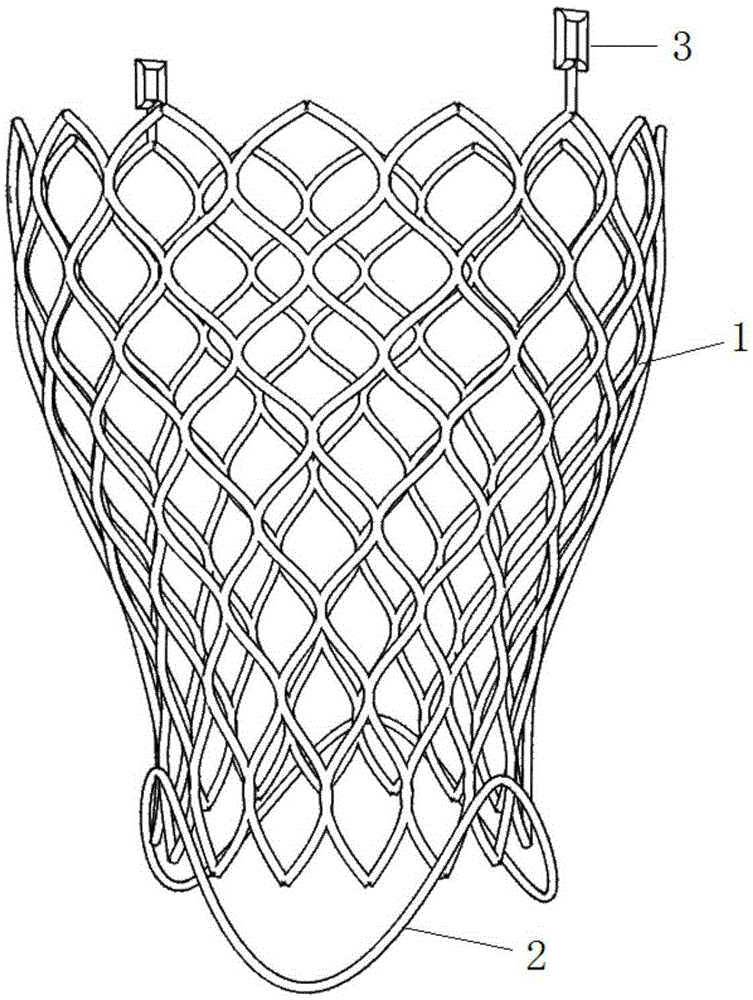
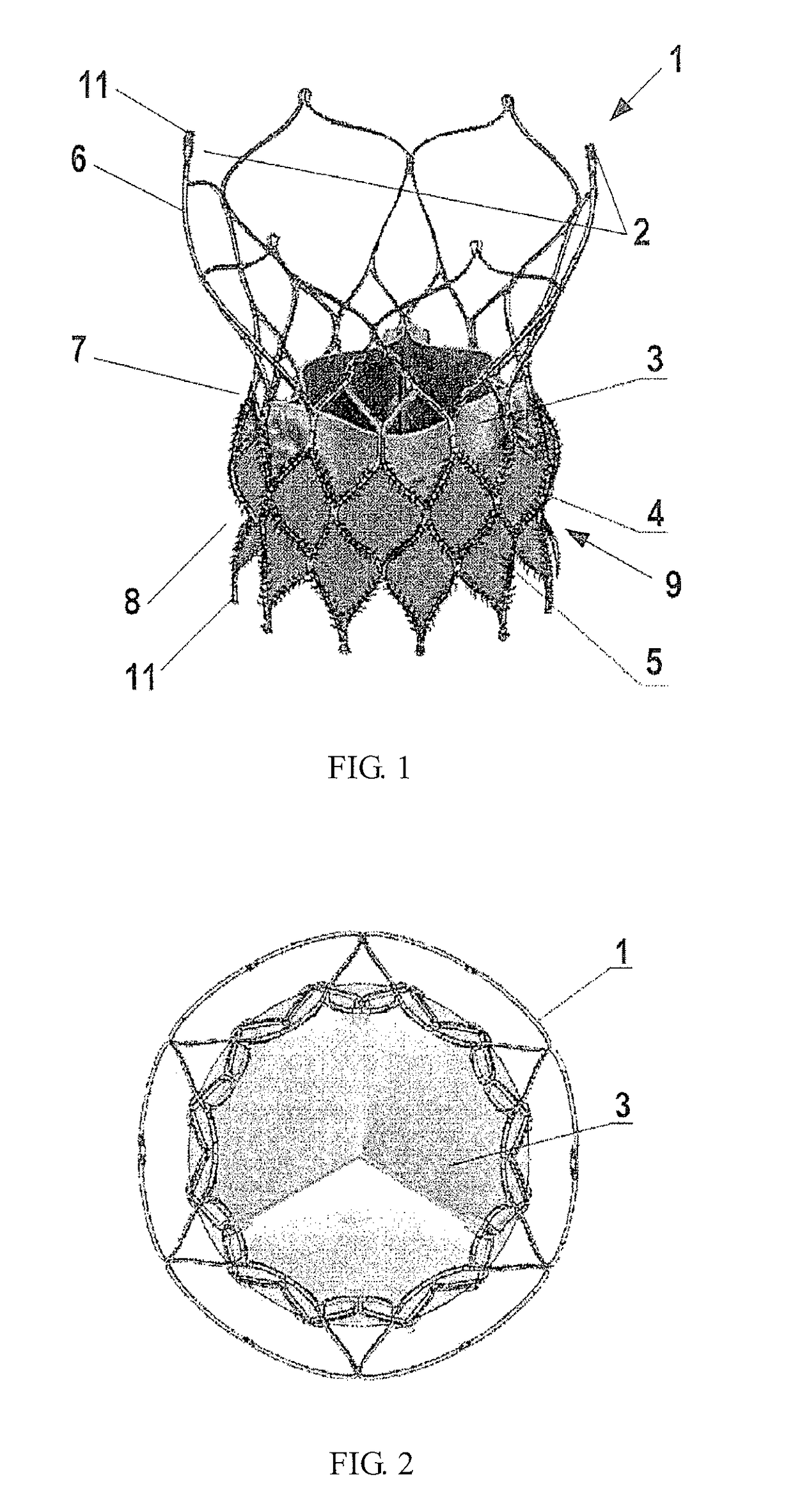
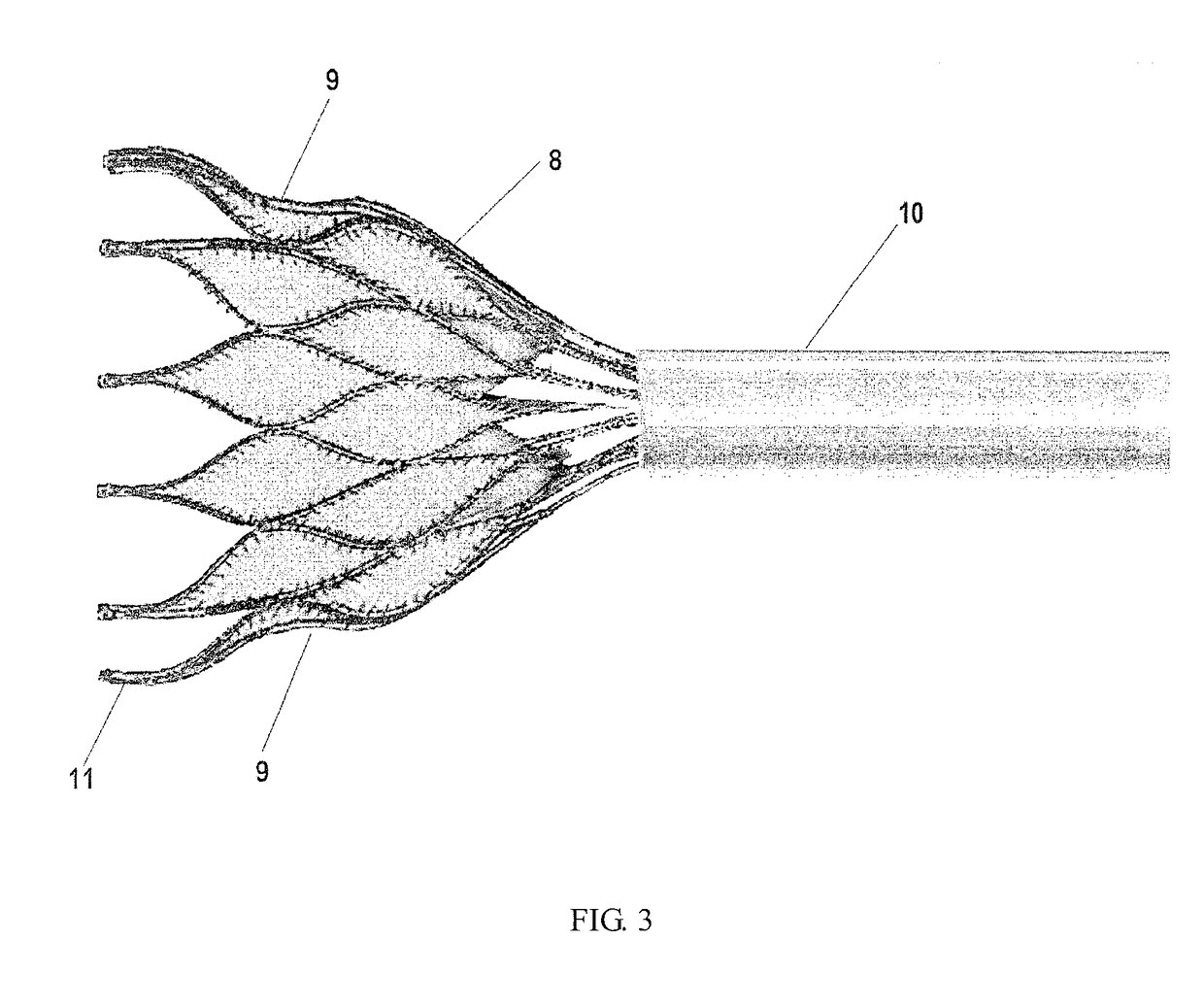
Heart valve prosthesis
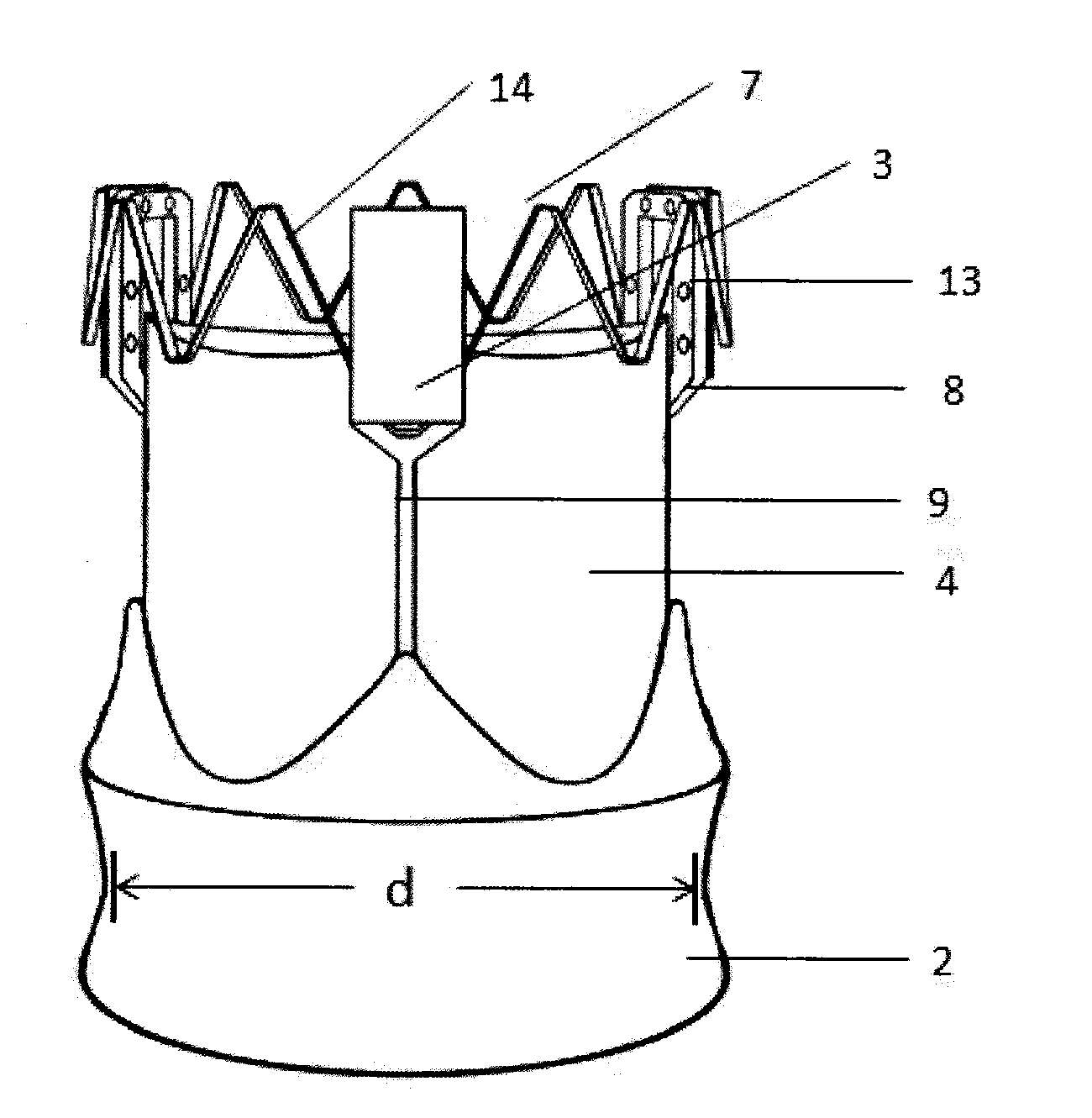
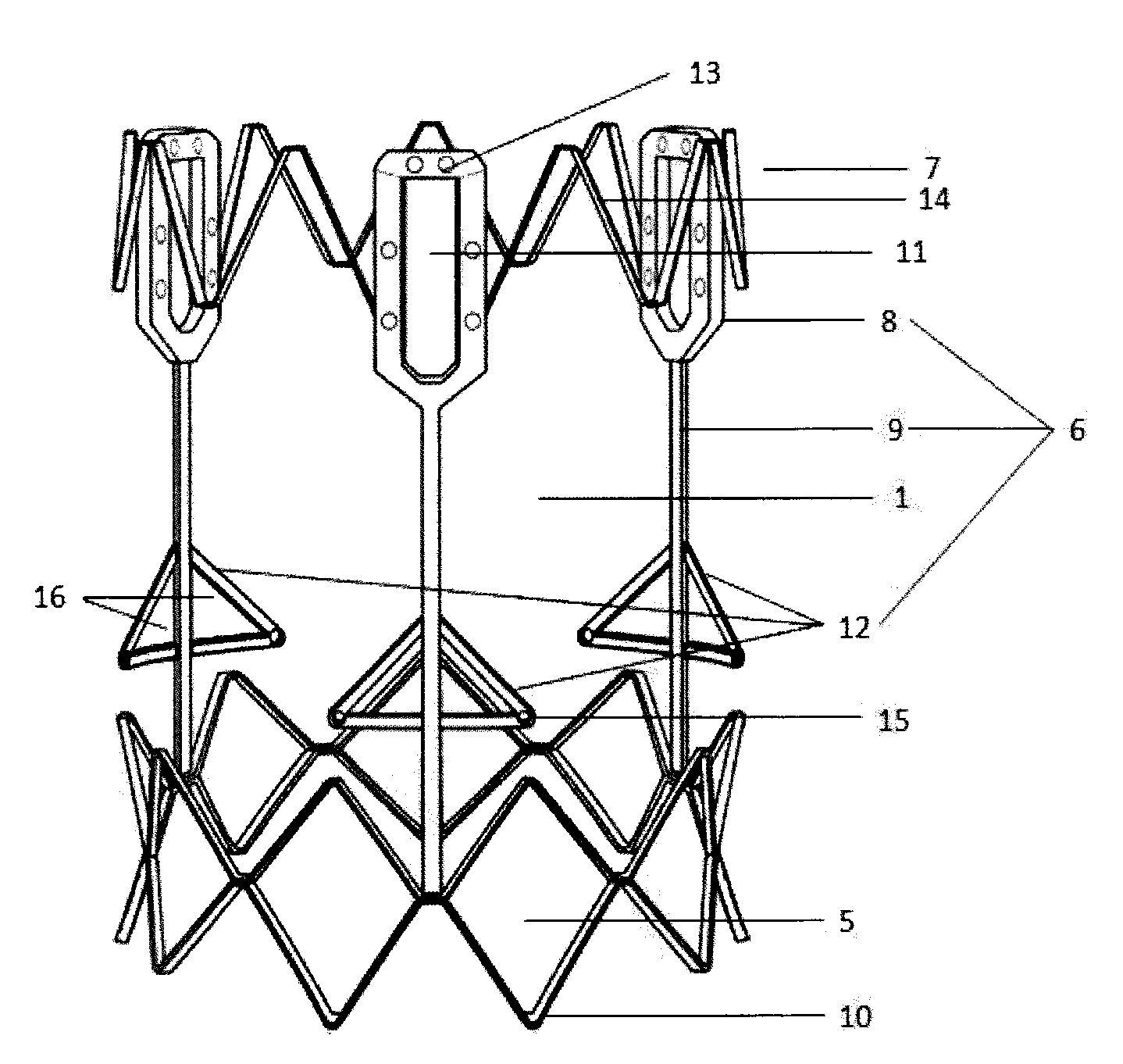
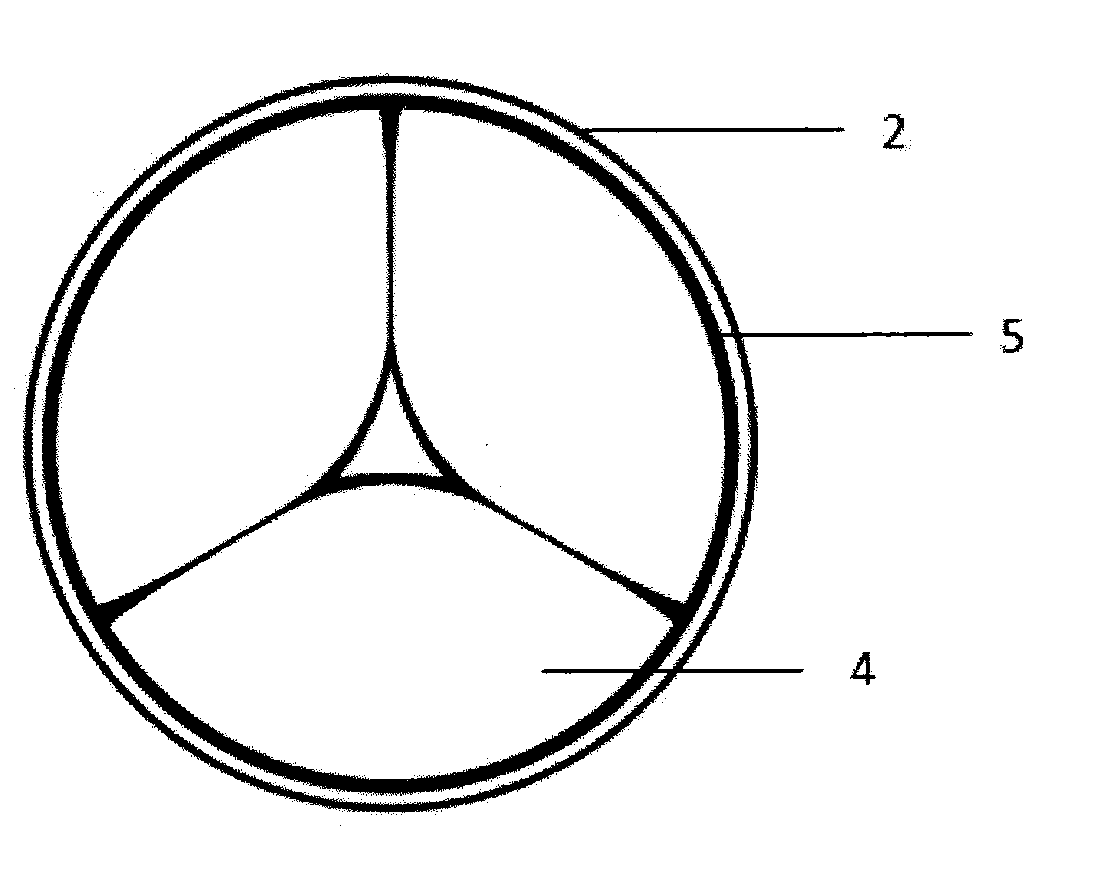
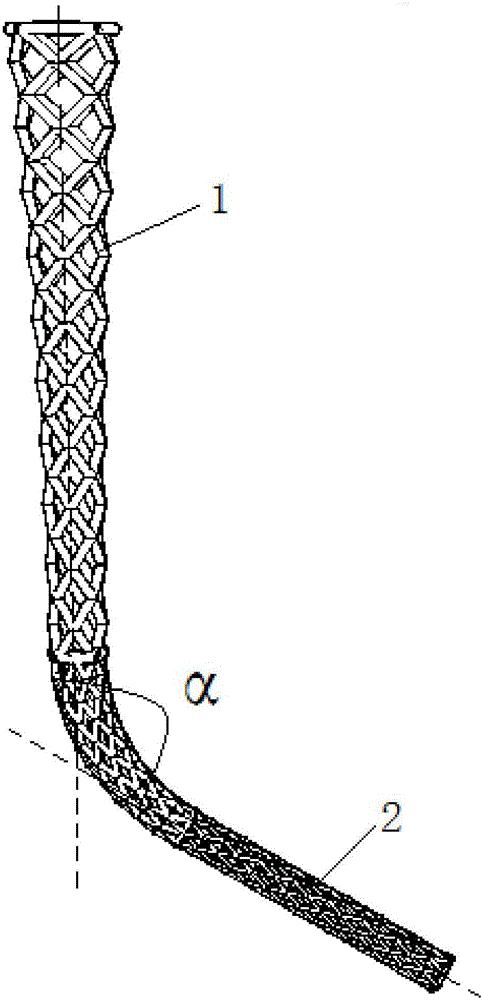
A stent (1) used for a heart valve prosthesis and the heart valve prosthesis that includes the stent (1) and is used for heart valve replacement. The stent is configured to support a heart valve (3) and includes, along a longitudinal axis, an inflow section (8), an outflow section (6) and a transition section (7) between the inflow section (8) and the outflow section (6). The stent (1) has a contracted delivery configuration and an expanded deployed configuration. In the expanded deployed configuration, the inflow section (8) defines a concave contour that is complementary to a structure of a native valve annulus. The concave contour enables self-deployment and close adherence of the stent (1), thereby preventing its displacement and perivalvular leakage after implantation.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT CARDIOFLOW MEDTECH CO LTD
Docking Device for Aortic Valve Replacement
A docking device for aortic valve replacements is a self-expanding nitinol structure including a lattice forming a tubular (e.g., cylindrical) upper framework or cage, and three struts forming a lower structure. The struts are formed by elongated loops that are attached to the lattice or that are an integral part of the upper framework. The struts extend down beneath the lattice, eventually forming “feet” to anchor at the base of the aortic cusps. The docking device can be positioned near a sinotubular junction of a patient. An aortic valve replacement is locked inside the docking device.
Owner:MCDONALD MICHAEL B
Clinical auxiliary device for cardiac aortic valve replacement surgery
The invention provides a clinical auxiliary device for cardiac aortic valve replacement surgery. The problem that time and labor are wasted during preoperative disinfection is effectively solved. The device comprises a rectangular cylinder, wherein kidney-shaped annular grooves are formed in the left side wall and the right side wall in the rectangular cylinder respectively, toothed belt wheels are rotationally connected to the left side wall and the right side wall in the rectangular cylinder respectively; the two toothed belt wheels on the same side wall are opposite to each other up and down and are connected through a toothed belt; a plurality of connecting blocks which are uniformly distributed along the outer surface of the toothed belt are arranged on the toothed belt; inserting columns which are axially inserted into the annular grooves in the corresponding sides are arranged on the connecting blocks left and right; a U-shaped plate is arranged between every two inserting columns which are opposite to each other left and right; clamping boxes are detachably connected in the U-shaped plates; wiping cotton is detachably connected in the clamping boxes; a liquid storage box located on the inner side of the toothed belt is arranged in the rectangular cylinder; a fixing cylinder which is axially arranged up and down is rotationally connected in the rectangular cylinder; a conveying pipe is coaxially arranged in the fixing cylinder; hinge grooves are formed in the left side and the right side of the conveying pipe respectively; and fixing rods are hinged in the hinge grooves. The device is simple in structure, novel in conception, convenient to use and high in usability.
Owner:NANYANG CITY CENT HOSPITAL
Invasive prosthetic heart valve
InactiveCN109549757AReduce frictionPrevent ingrownHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic heart
The present invention provides an interventional prosthetic heart valve. The interventional prosthetic heart valve includes a tubular frame that can be radially deformed, at least one movable or switchable valve leaf is attached to the inside of the tubular frame, and the inner and / or outer side of the tubular frame is covered with a coating film. An implant device includes a delivery tube, a locking wire, a stay wire, a guide wire, a wire fixing bolt and a locking wire fixing bolt. The implant and recovery device includes a sheath tube, an open sheath tube, a recovery tube, and a recovery hook. The interventional prosthetic heart valve of the invention and the implantation and recovery device thereof are mainly used for human heart valve replacement, include replacement of the artificialbiological valve which is surgically implanted, thoracotomy is not required during a heart valve replacement surgery, extracorporeal circulation is not required, valve displacement is carried out on beating heart without general anesthesia, moreover, the patient does not need long-term anticoagulation, and the inserted valve can be removed by percutaneous intervention for valve replacement.
Owner:启铭医疗器械(上海)有限公司
A bioprosthetic heart valve with reproducible valve leaflet replacement through minimally invasive surgery
ActiveCN103536377BAvoid safety hazardsAvoid bleedingHeart valvesLess invasive surgeryBioprosthetic valve
Owner:李莉
Drape used in cardiac surgery
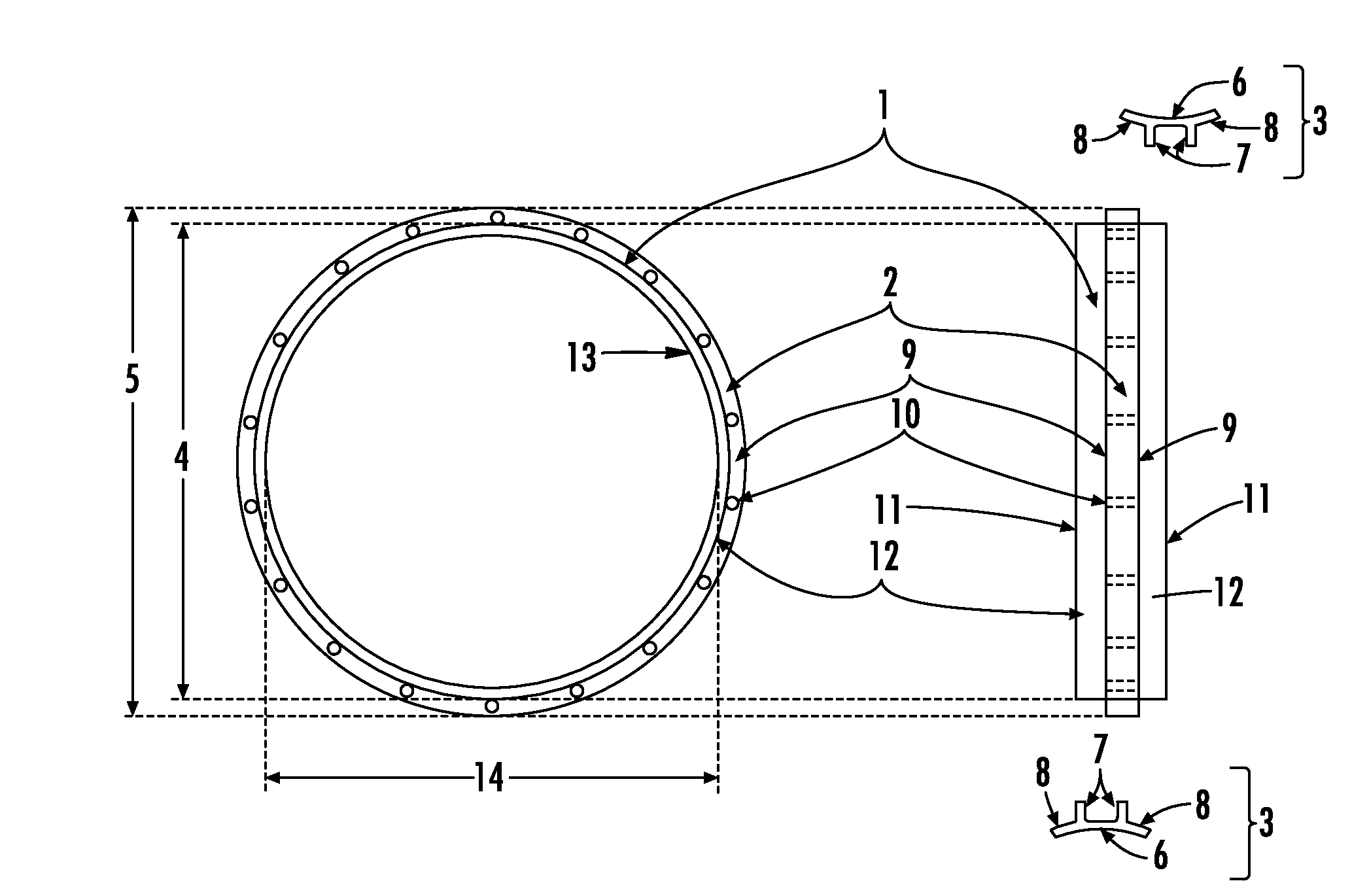
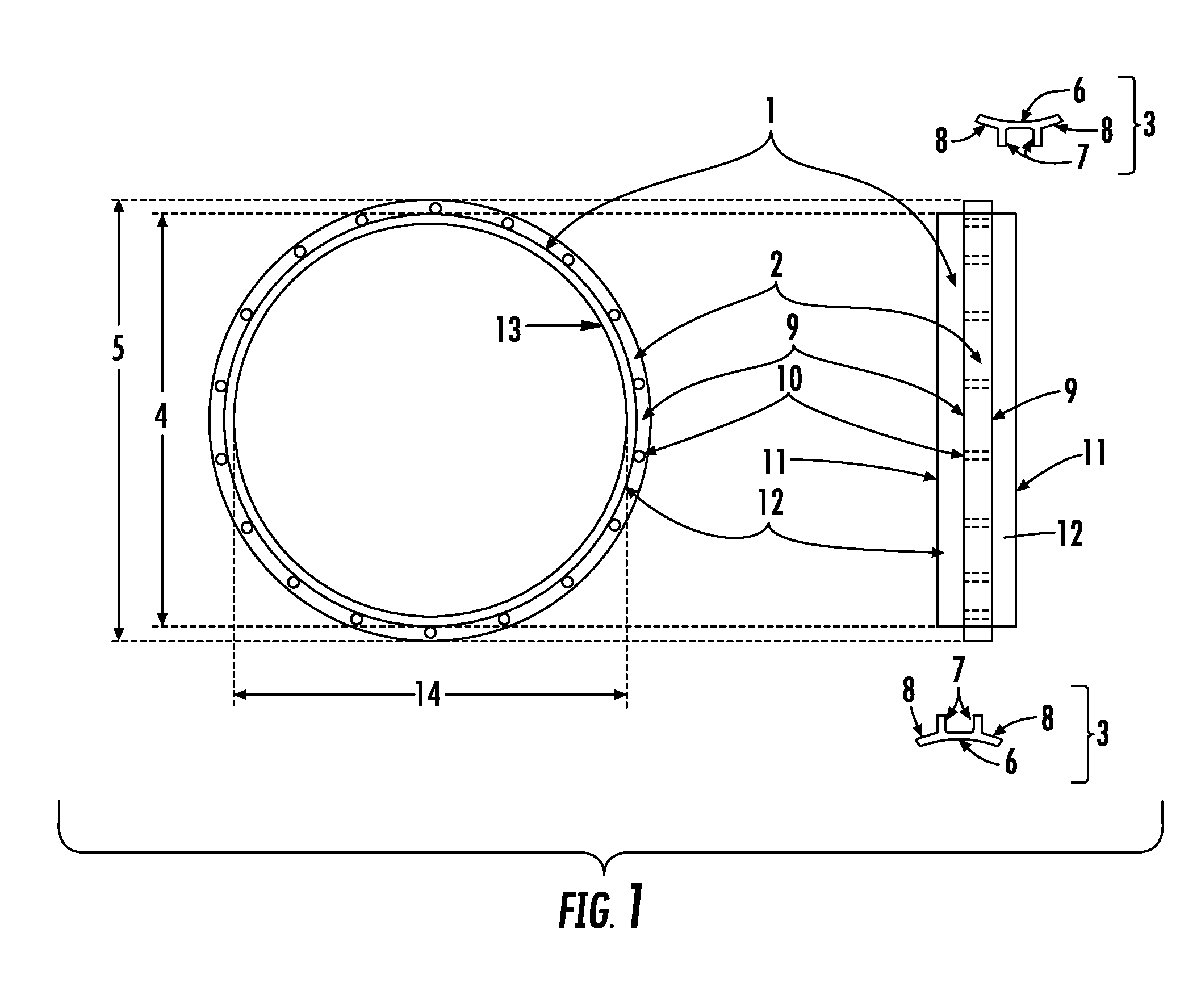
InactiveCN104382658AReduce usage timeGuarantee the safety of lifeSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsProsthetic valveBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
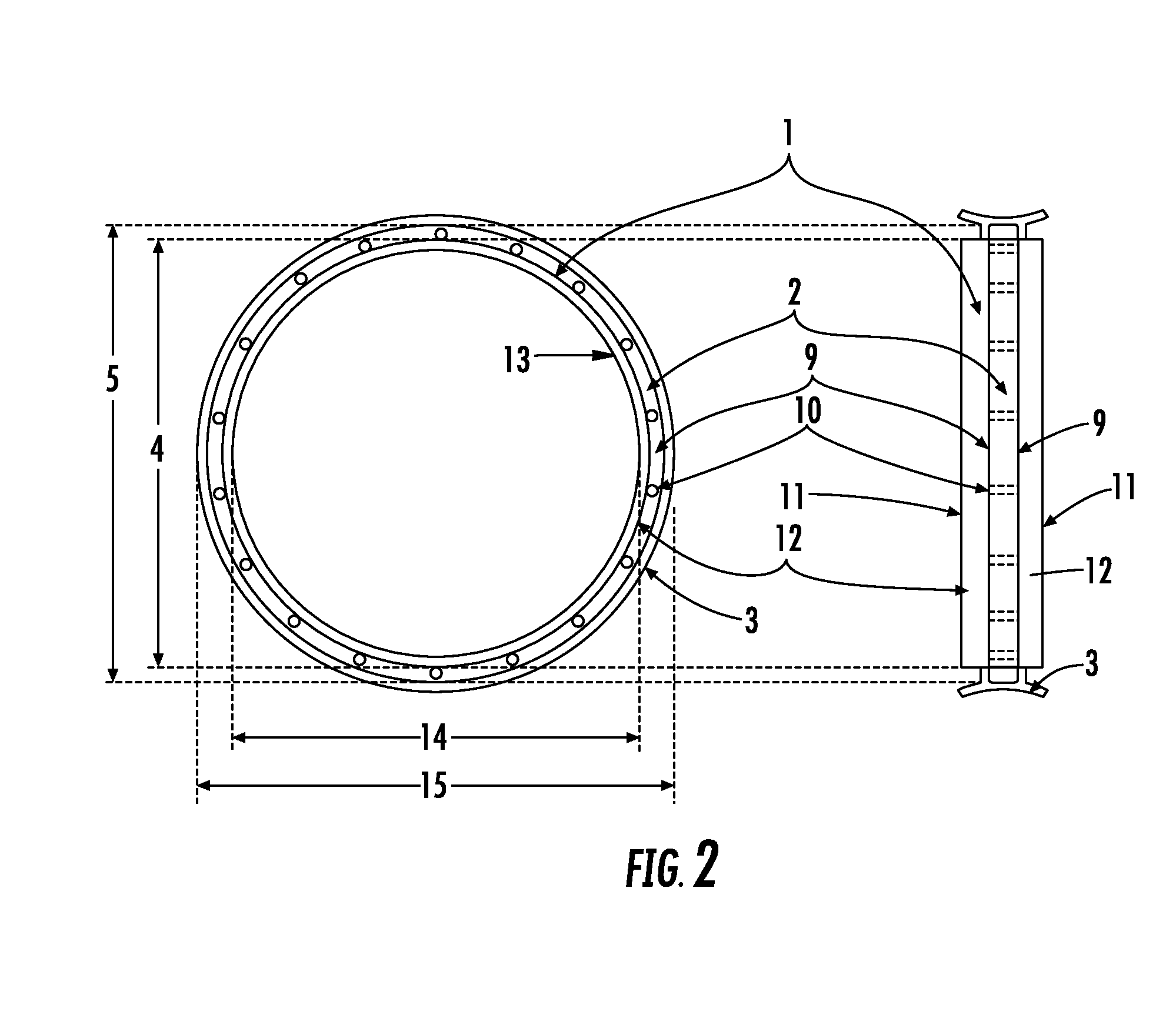
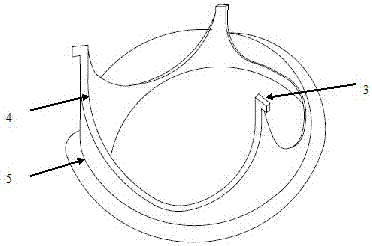
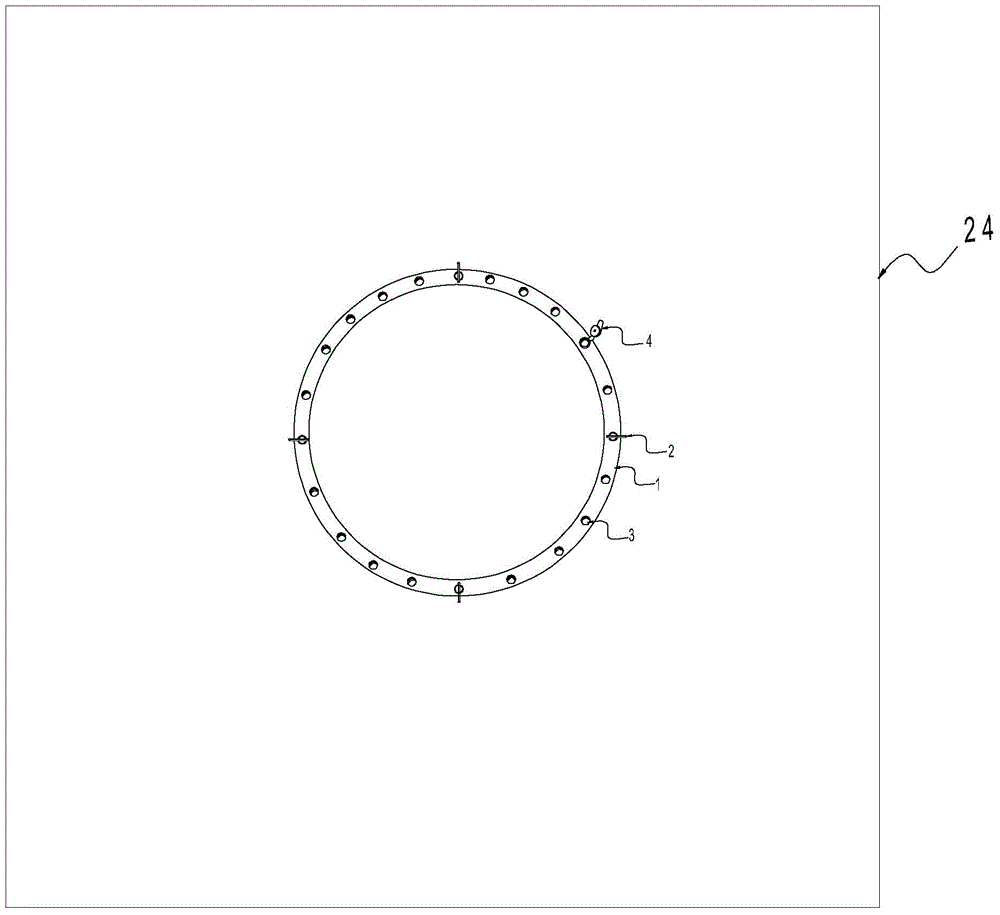
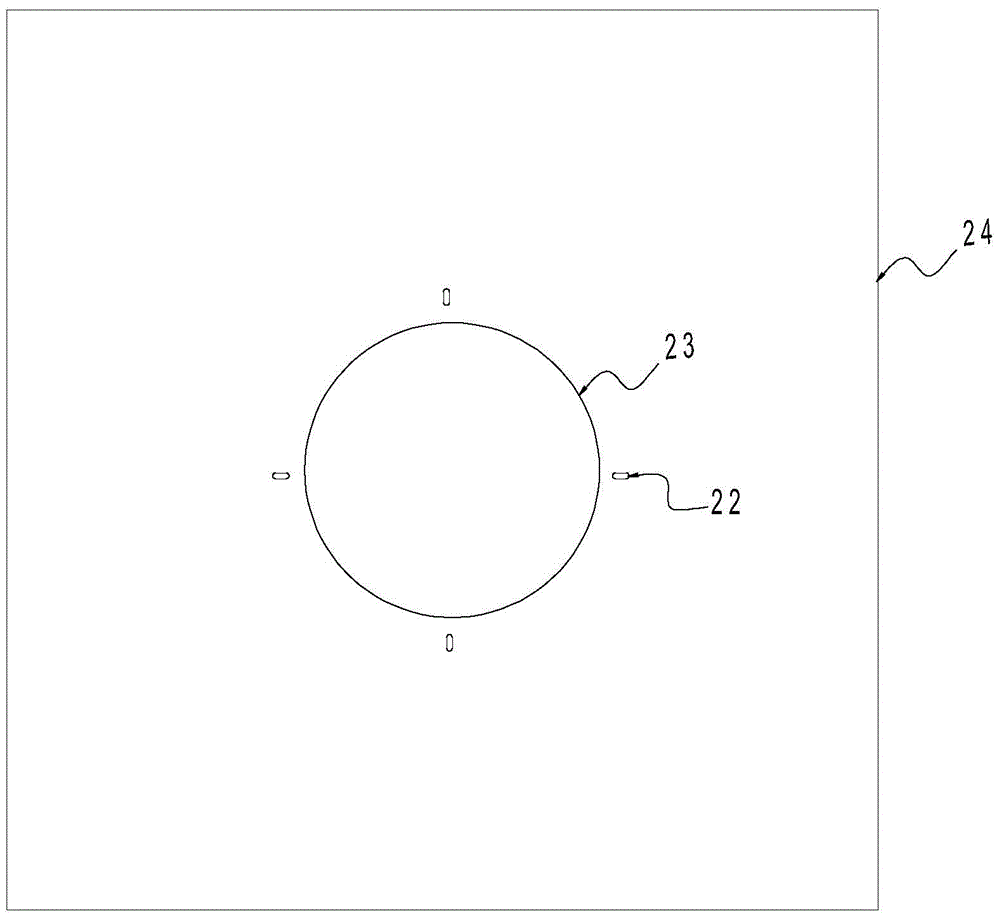
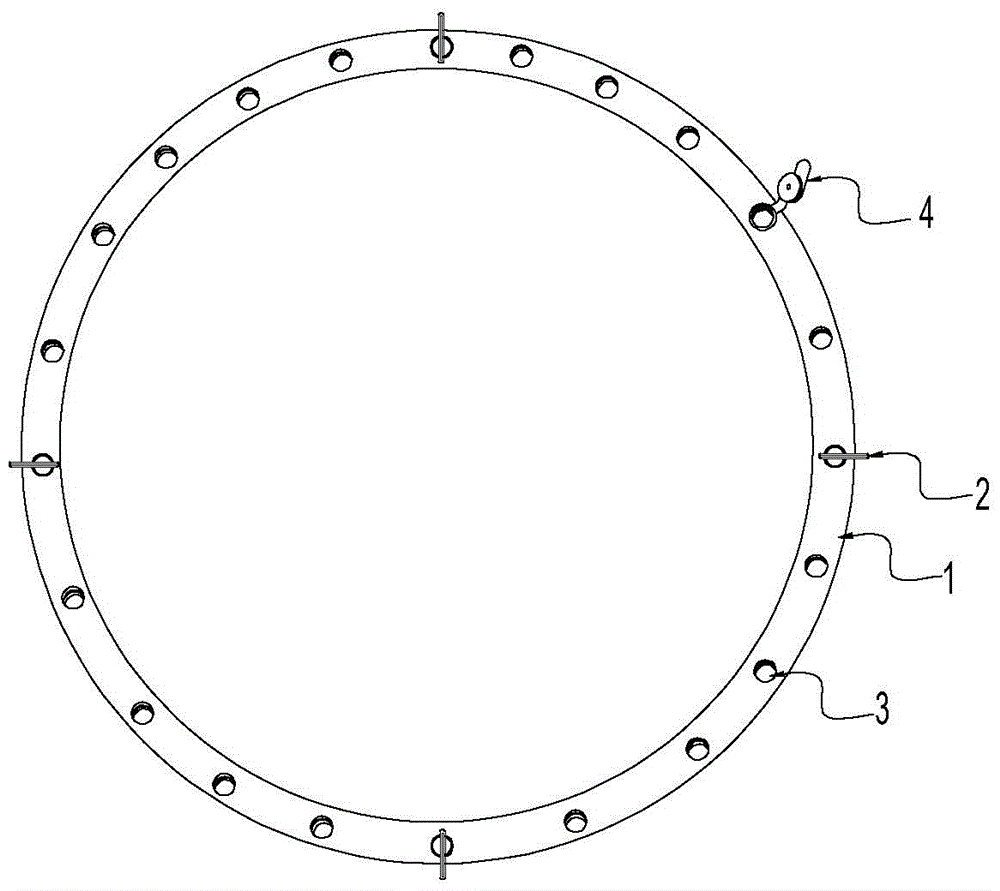
The invention mainly aims to provide a surgery aid which is applied to aortic valve replacement and mitral valve replacement and convenient for suturing artificial valves with the heart valve ring in an equal stitch length and uniform distribution manner, and relates to a drape used in cardiac surgery. The drape is characterized by comprising a heart drape body (24), and a round opening (23) is formed in the center of the heart drape body (24). The drape is characterized by further comprising a multifunctional ring (1) fixed outside the round opening (23), at least two mark points on the multifunctional ring can be used for quadrant partition, and the multifunctional ring has a surgery wire clamping function. By application of the mark type heart drape, occurrence of complications of perivalvular leakage and the like can be lowered greatly, the surgery time is shortened, the use time of all monitoring devices is shortened as well, and the medical cost of patients is lowered correspondingly.
Owner:李艳荣
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com