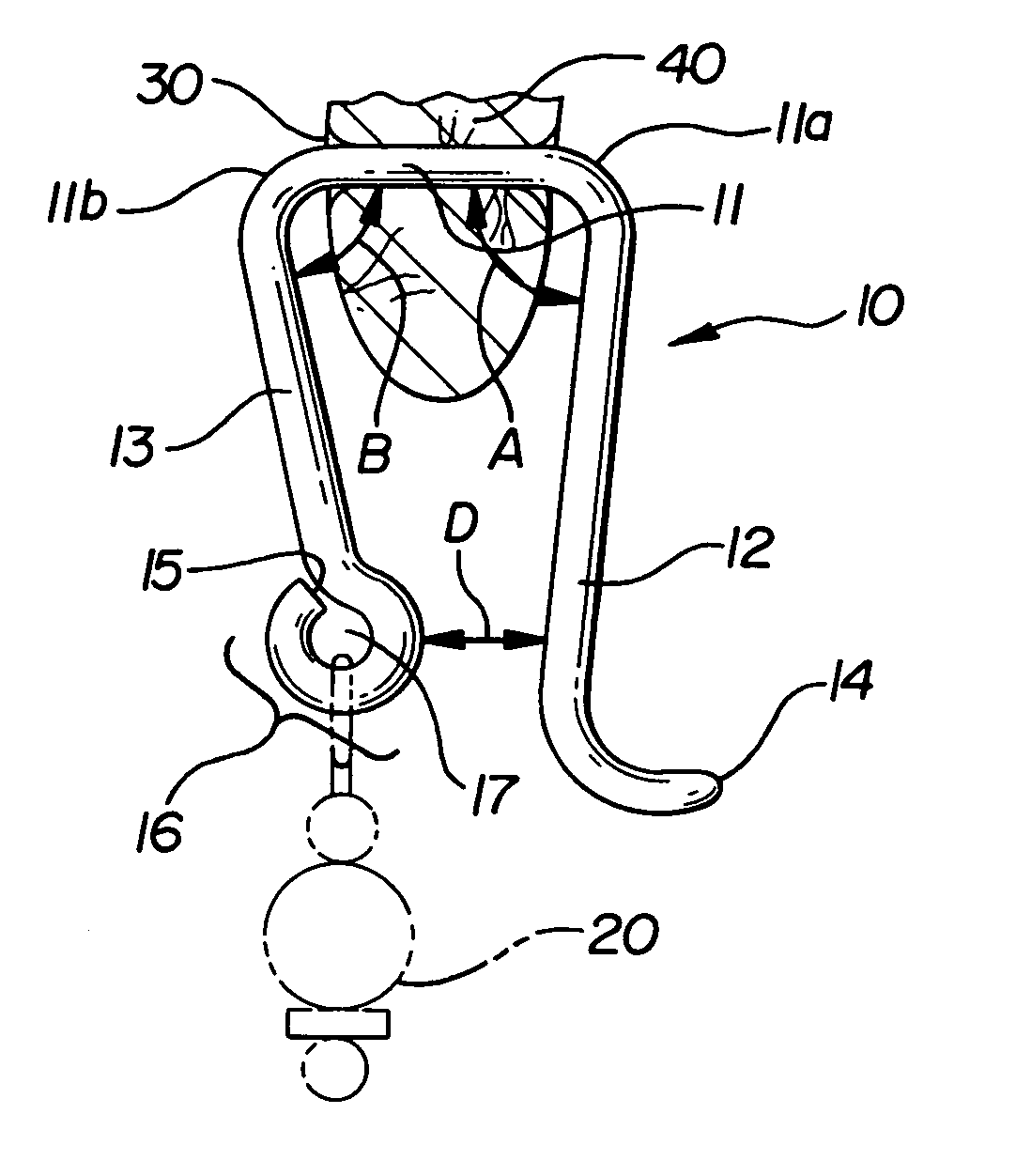
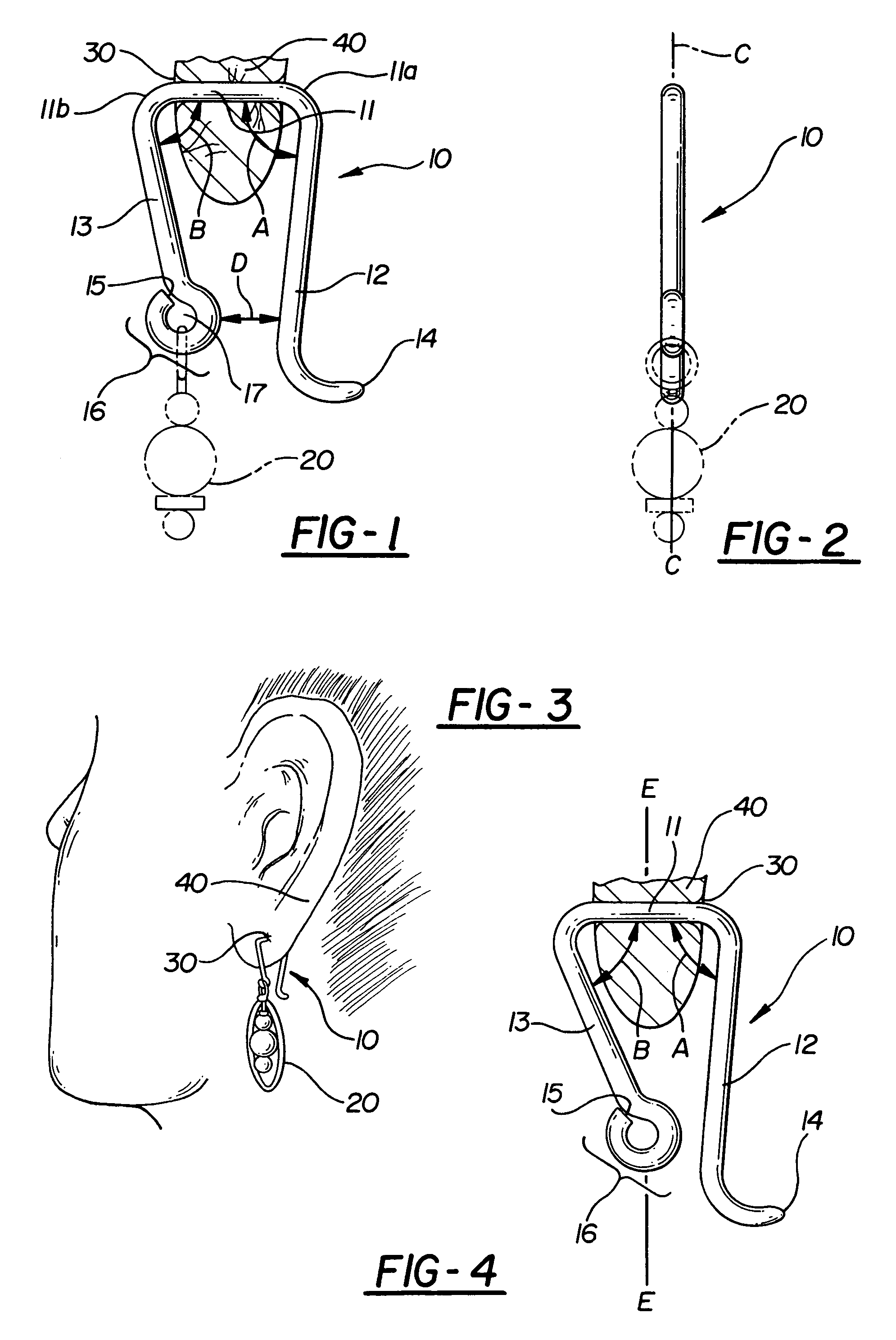
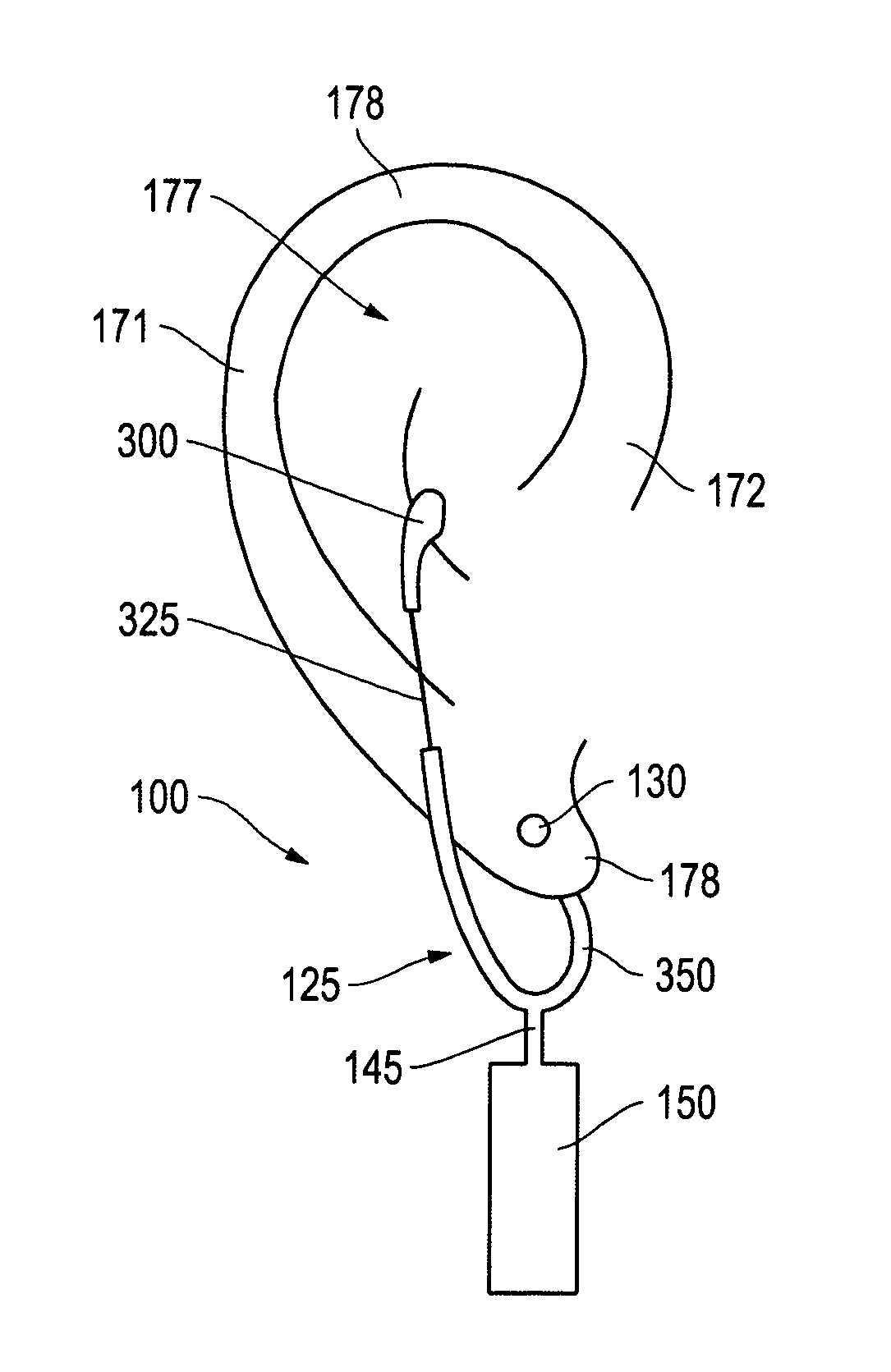
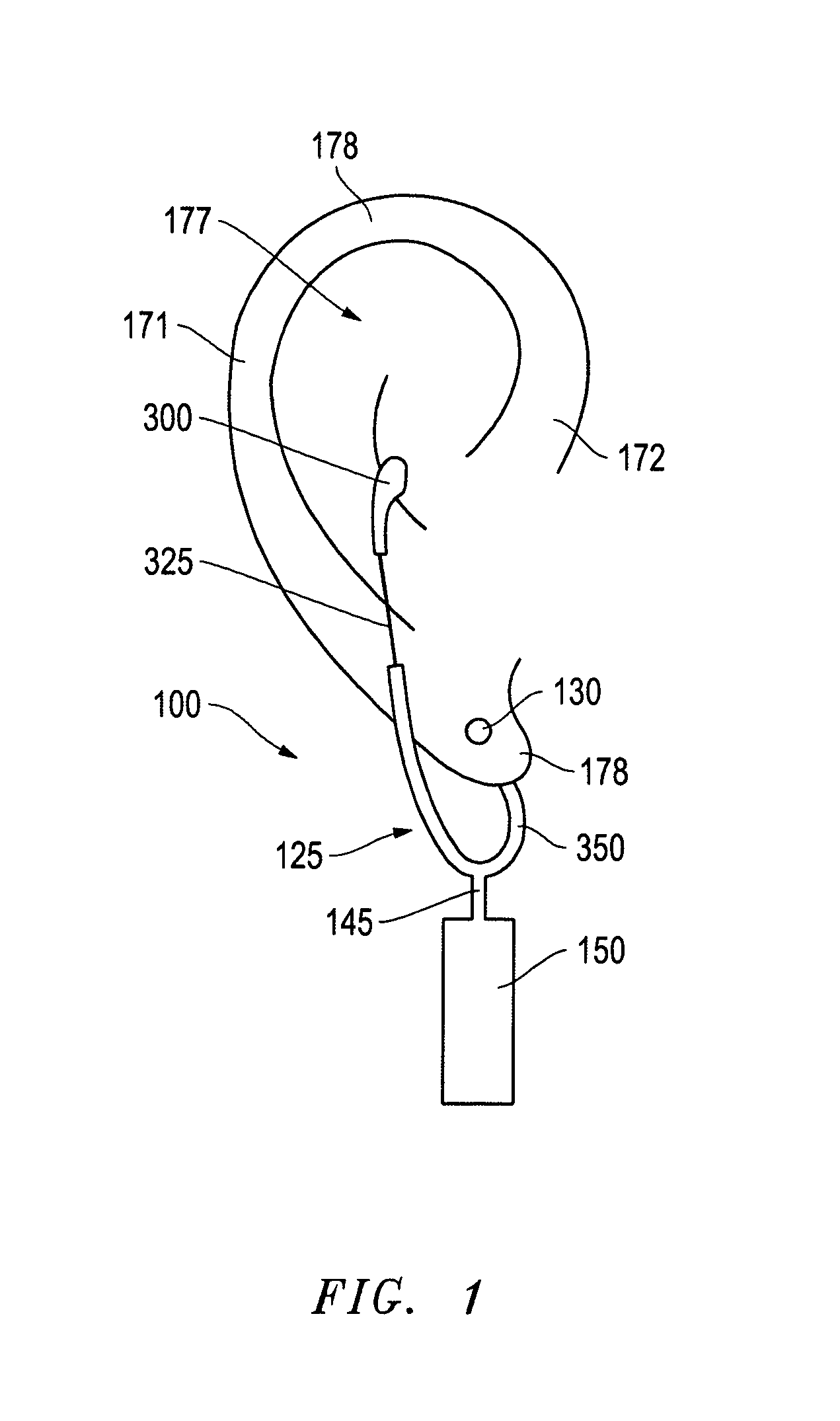
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
174 results about "Earlobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
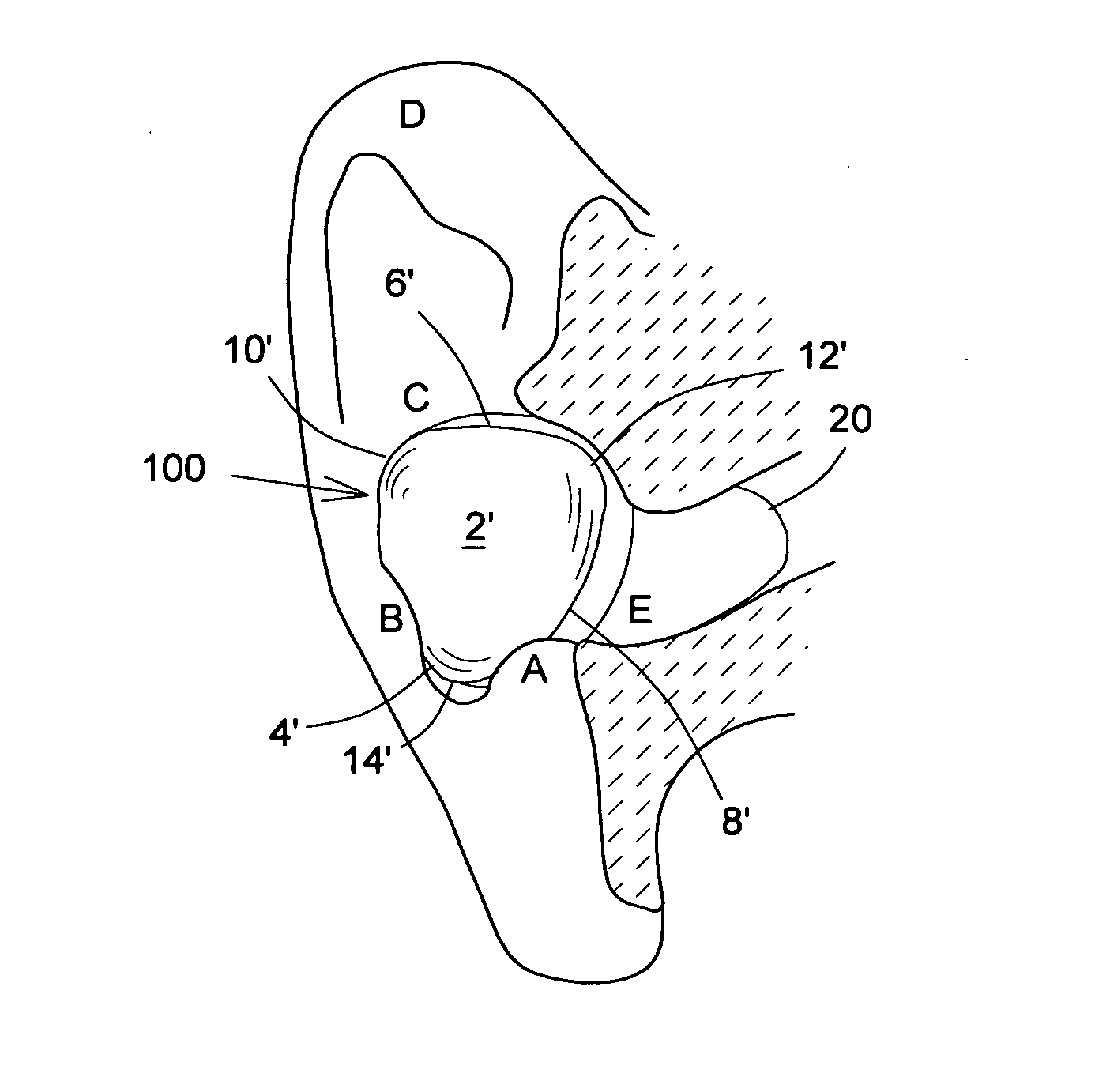
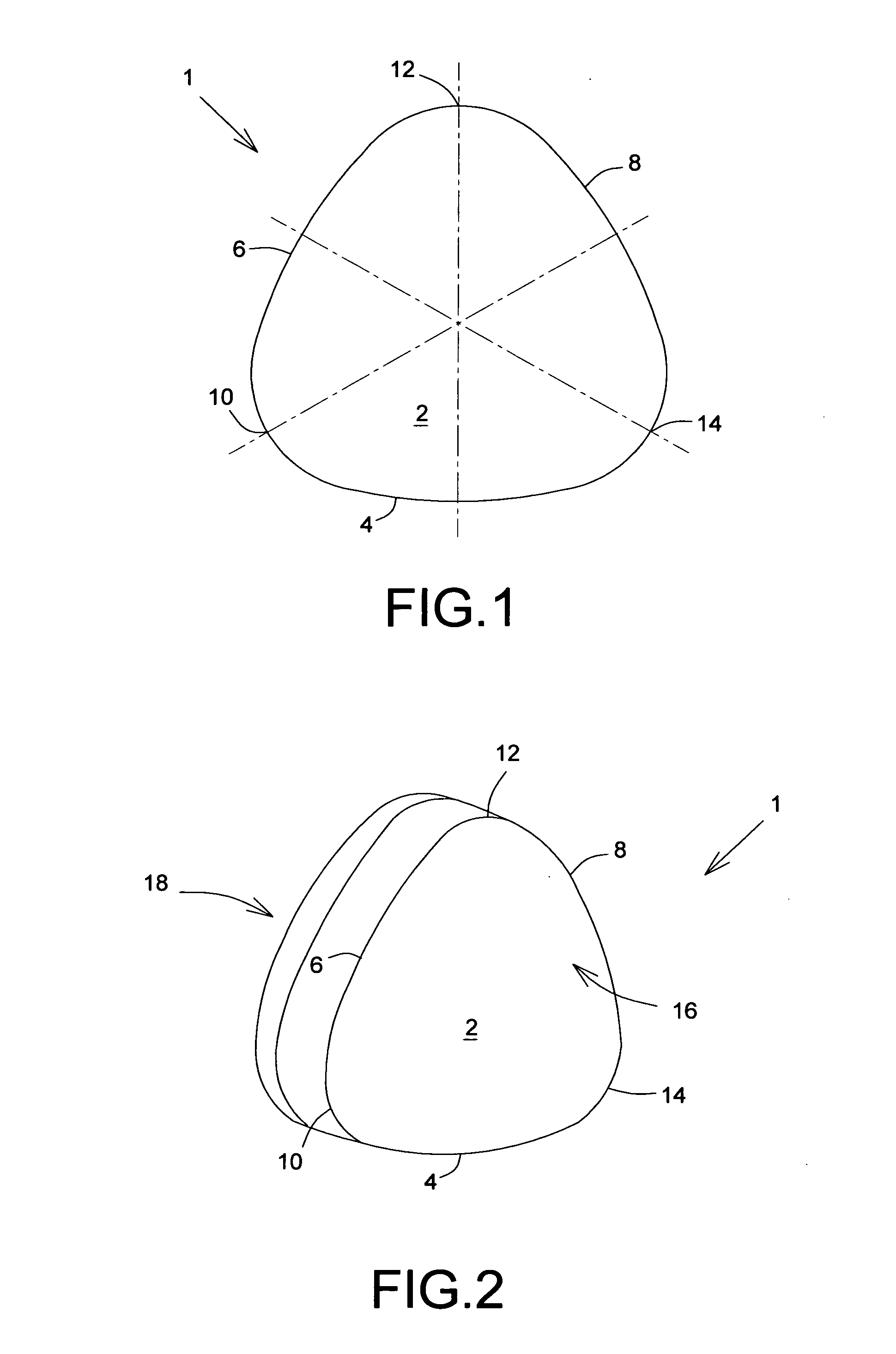
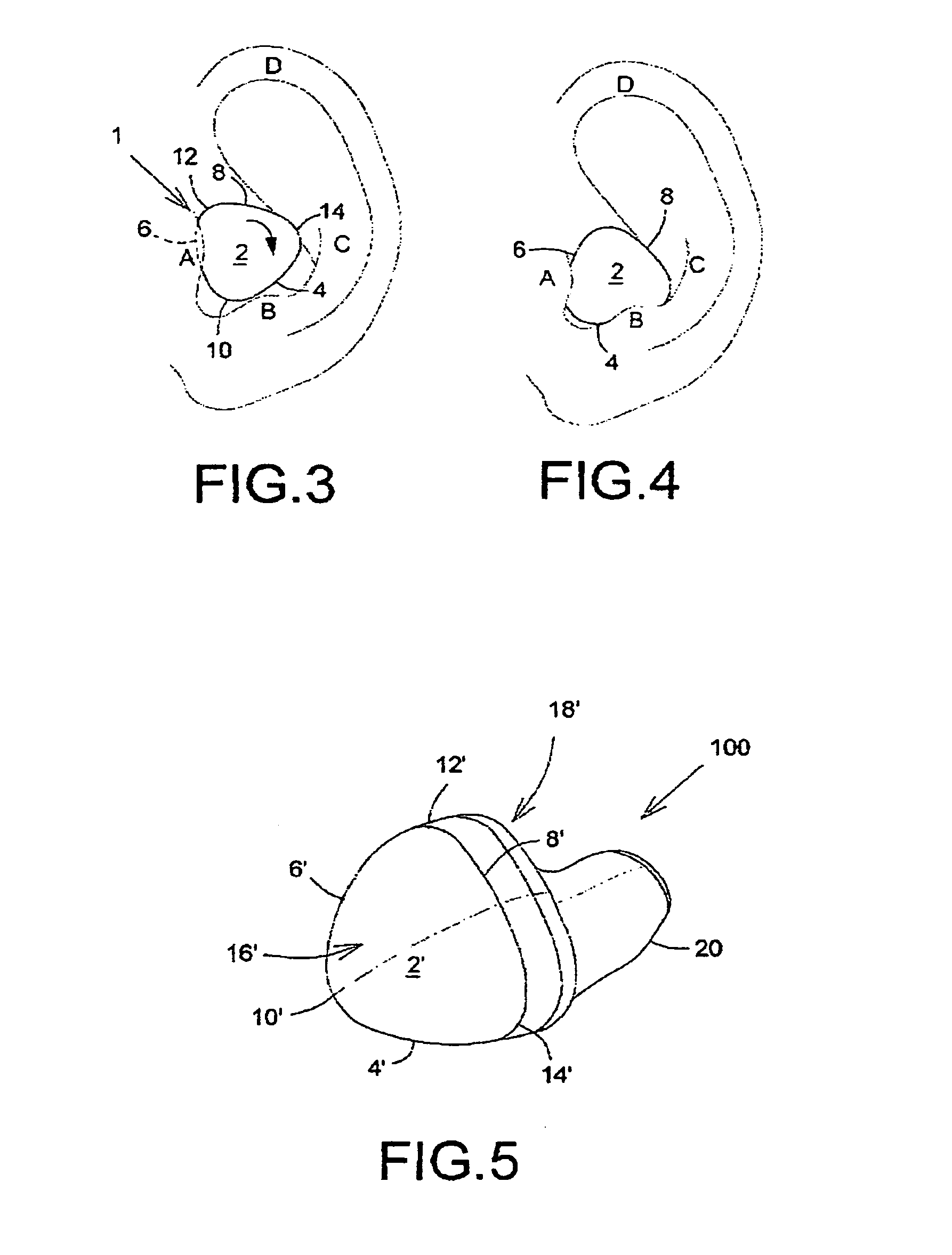
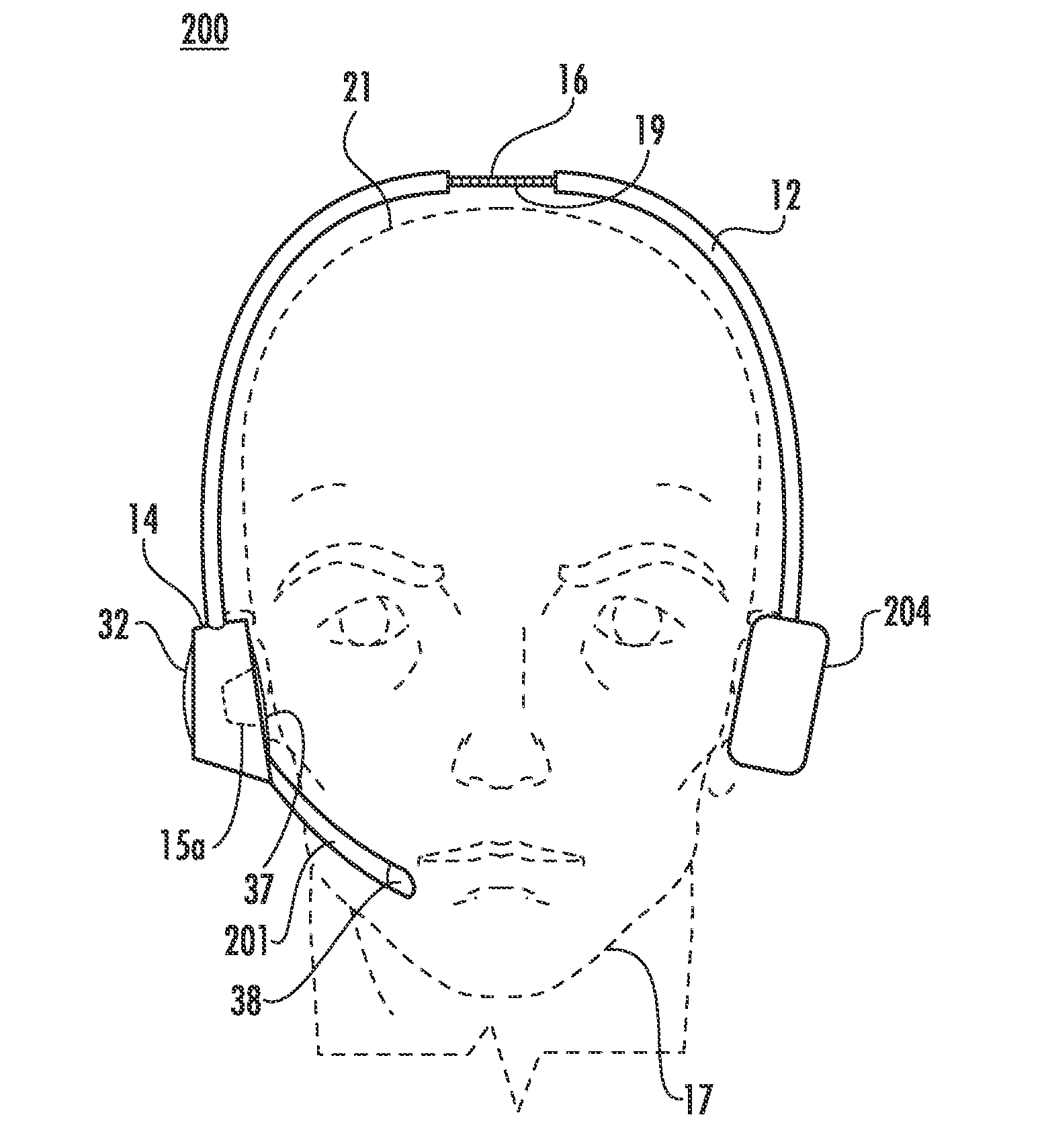
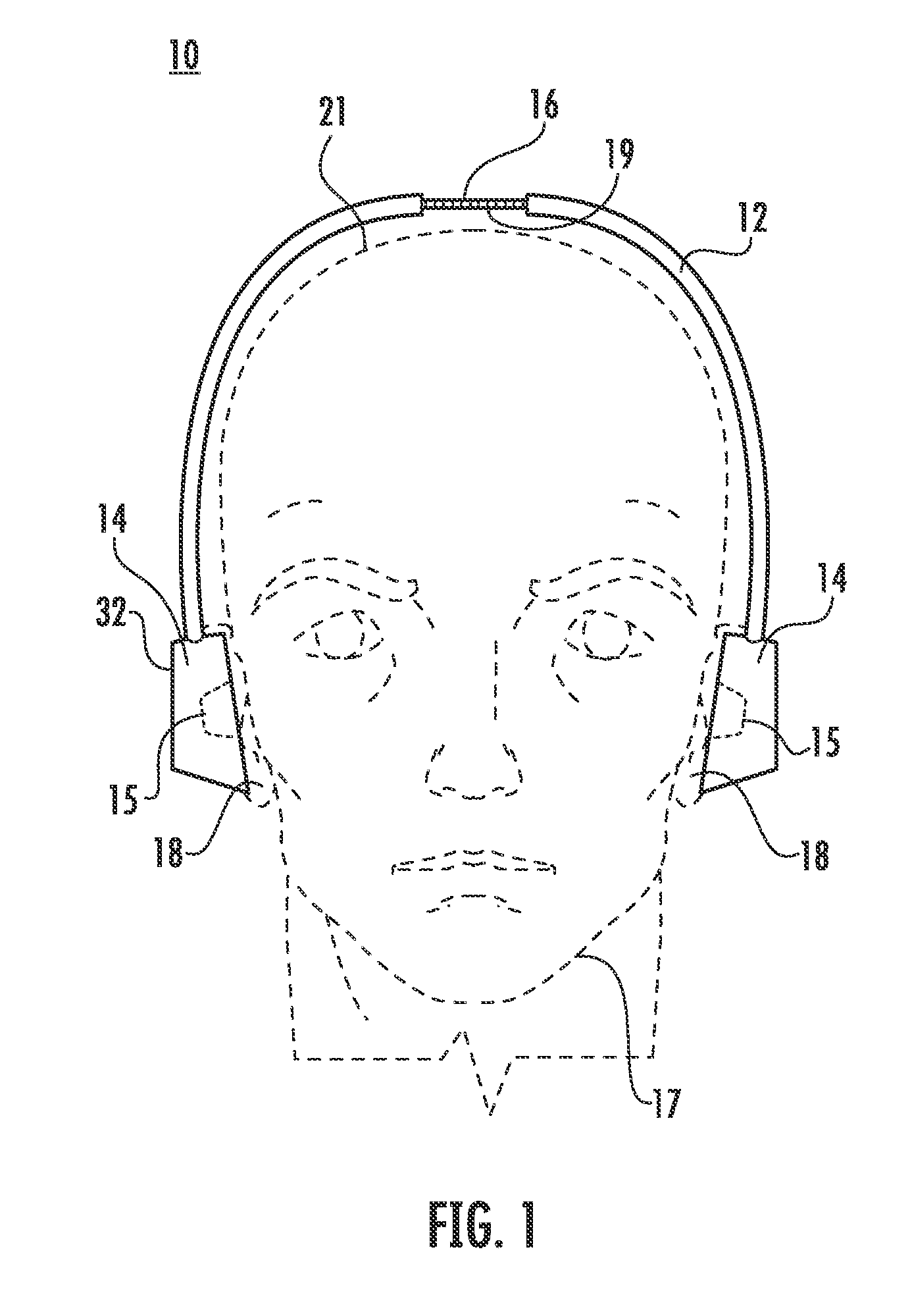
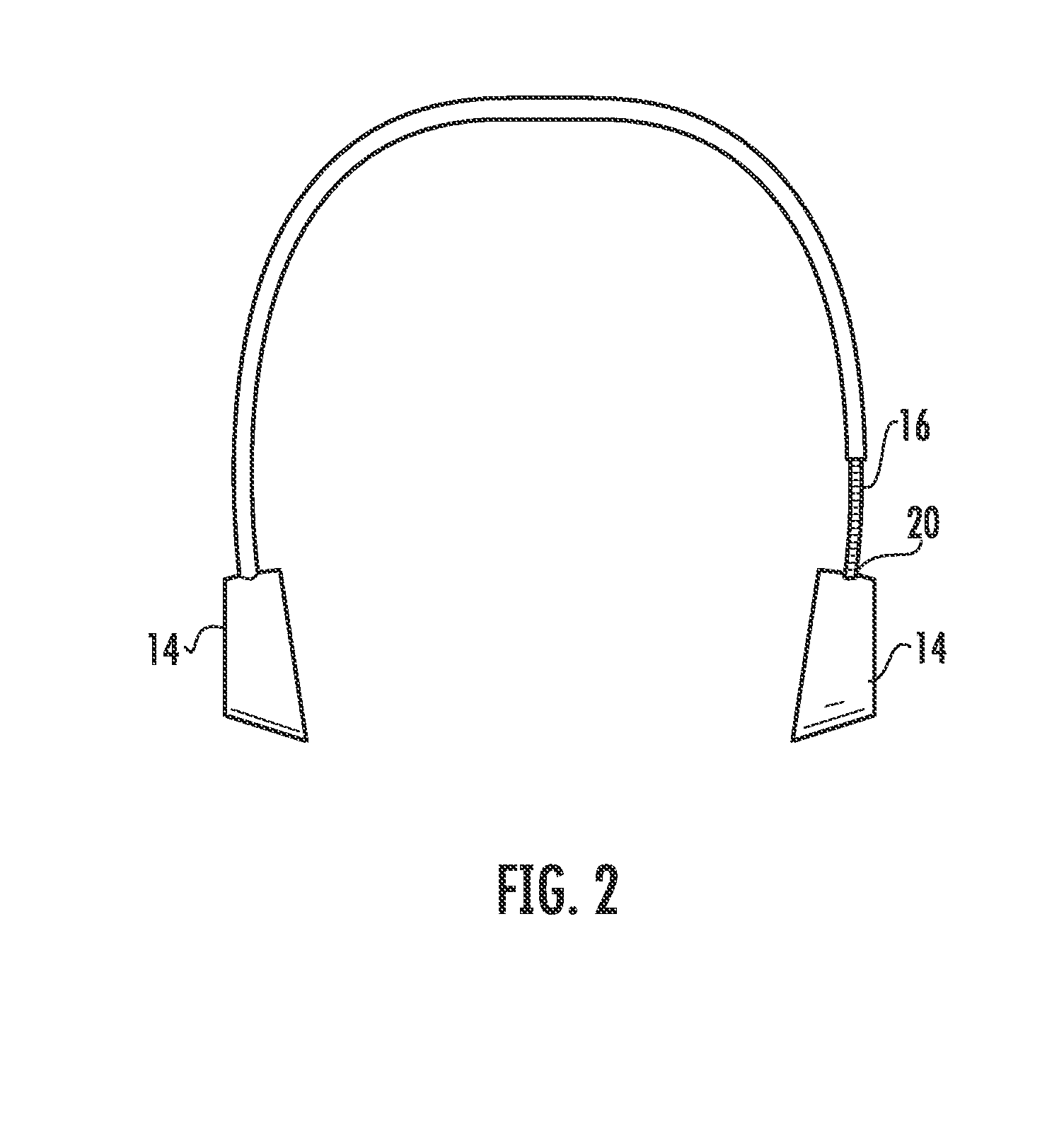
The human earlobe (lobulus auriculae) is composed of tough areolar and adipose connective tissues, lacking the firmness and elasticity of the rest of the auricle (the external structure of the ear). In some cases the lower lobe is connected to the side of the face. Since the earlobe does not contain cartilage it has a large blood supply and may help to warm the ears and maintain balance. However, earlobes are not generally considered to have any major biological function. The earlobe contains many nerve endings, and for some people is an erogenous zone.
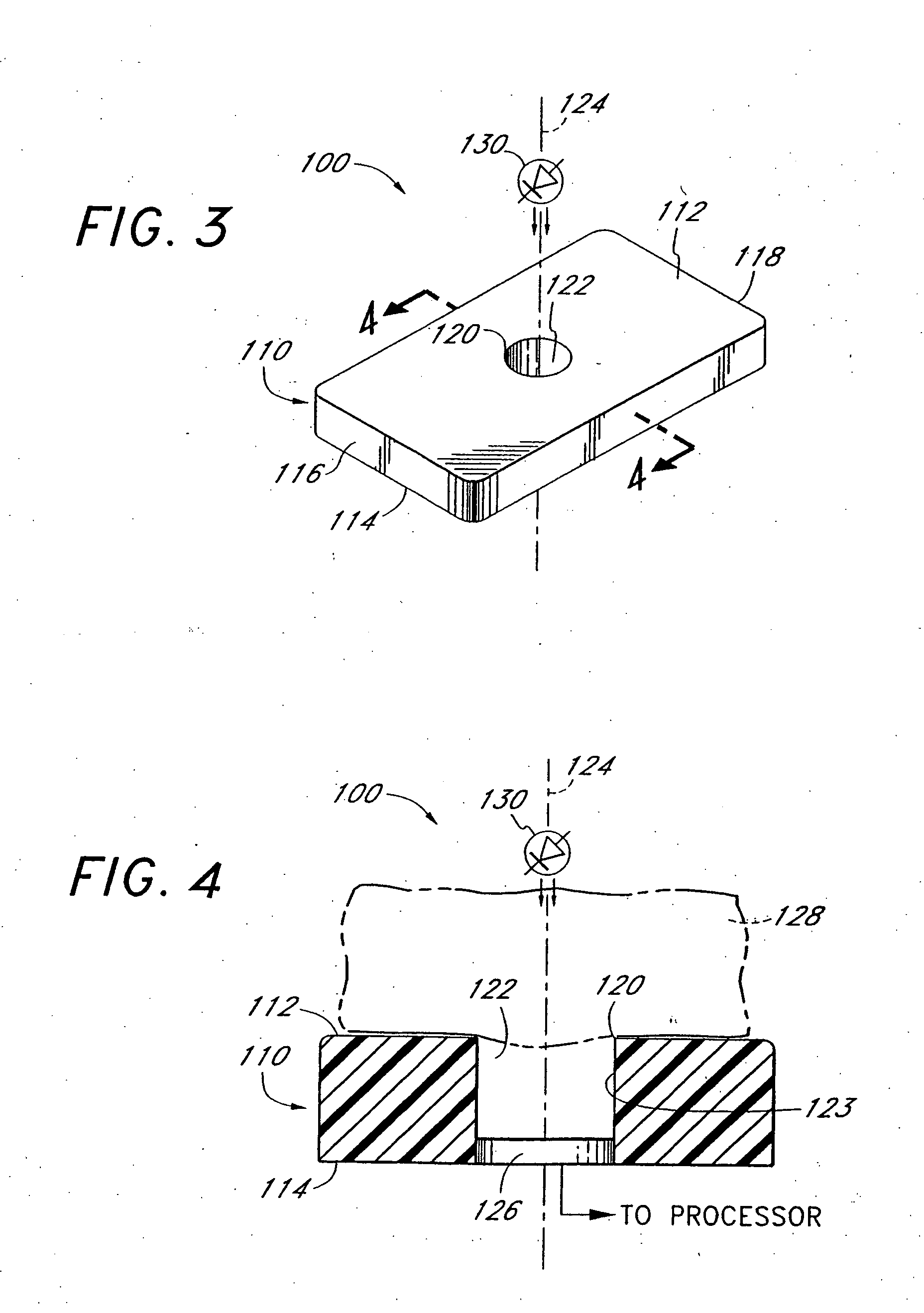
Low-noise optical probes for reducing ambient noise
InactiveUS7483730B2Minimize light pipingReduce optical decouplingEvaluation of blood vesselsTransmissivity measurementsLow noiseCompressible material
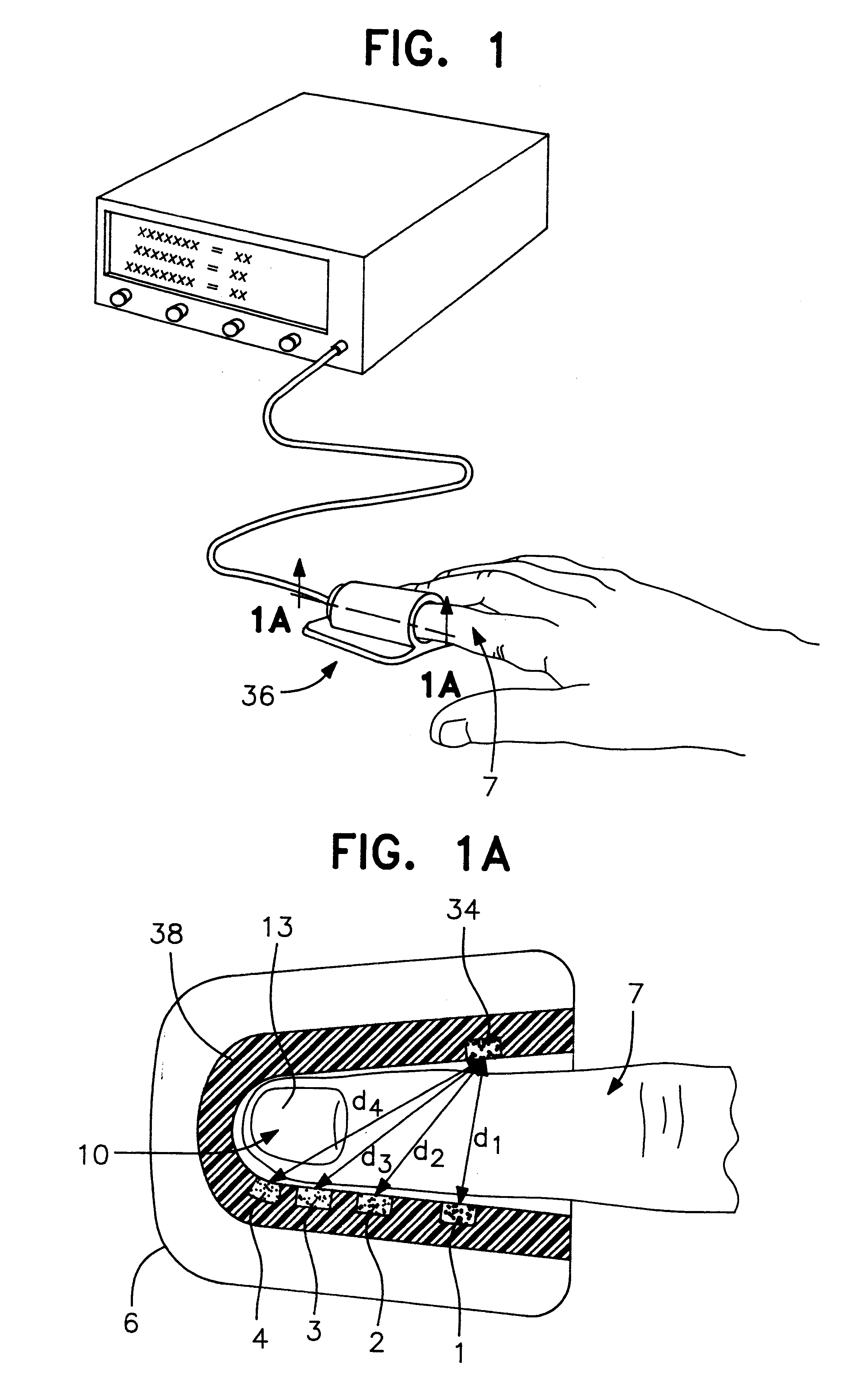
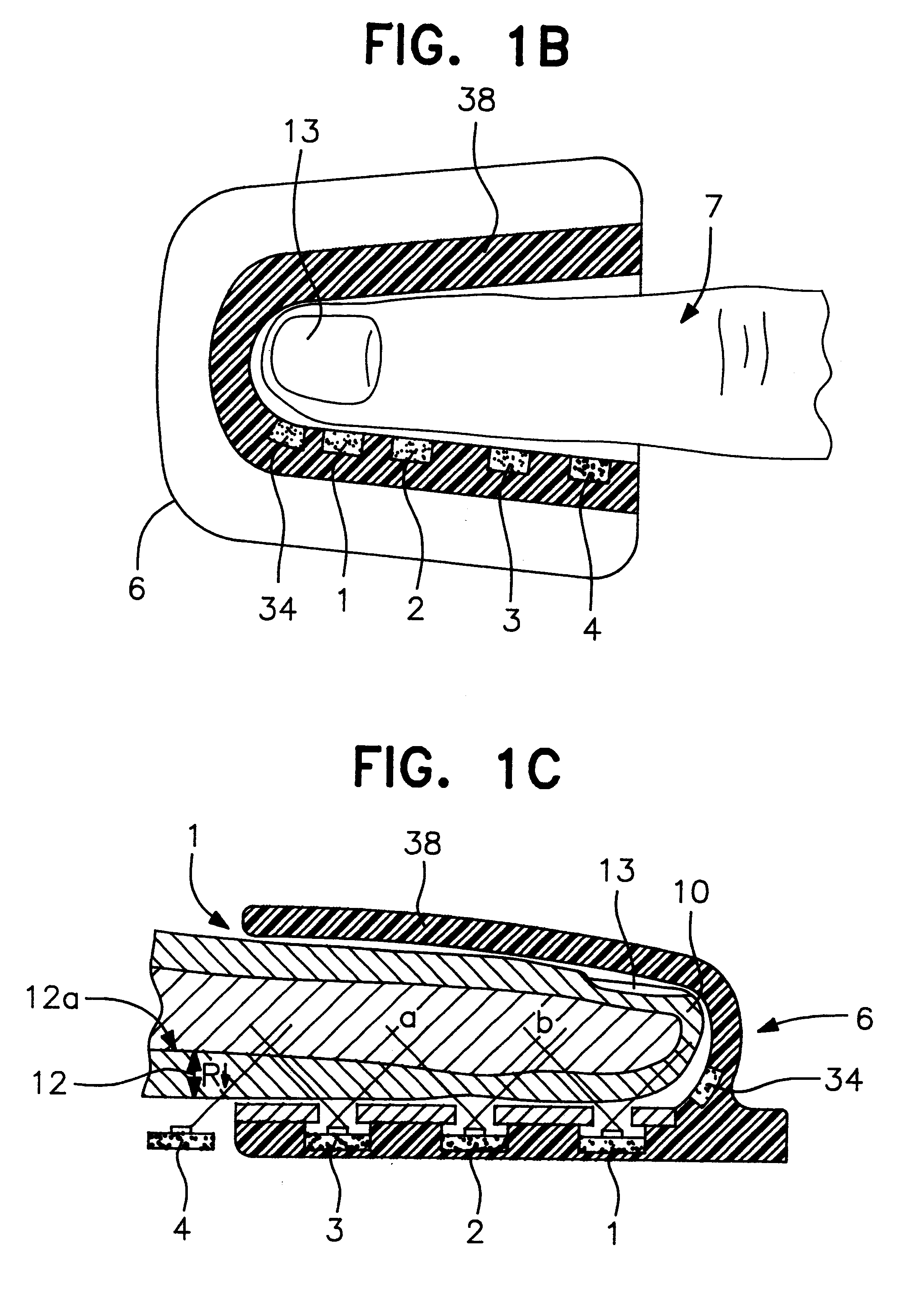
An optical probe, which is particularly suited to reduce noise in measurements taken on an easily compressible material, such as a finger, a toe, a forehead, an earlobe, or a lip, measures characteristics of the material. A neonatal and adult disposable embodiment of the probe include adhesive coated surfaces to securely affix the probe onto the patient. In addition, the surface of the probe is specially constructed to reduce the effect of ambient noise.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
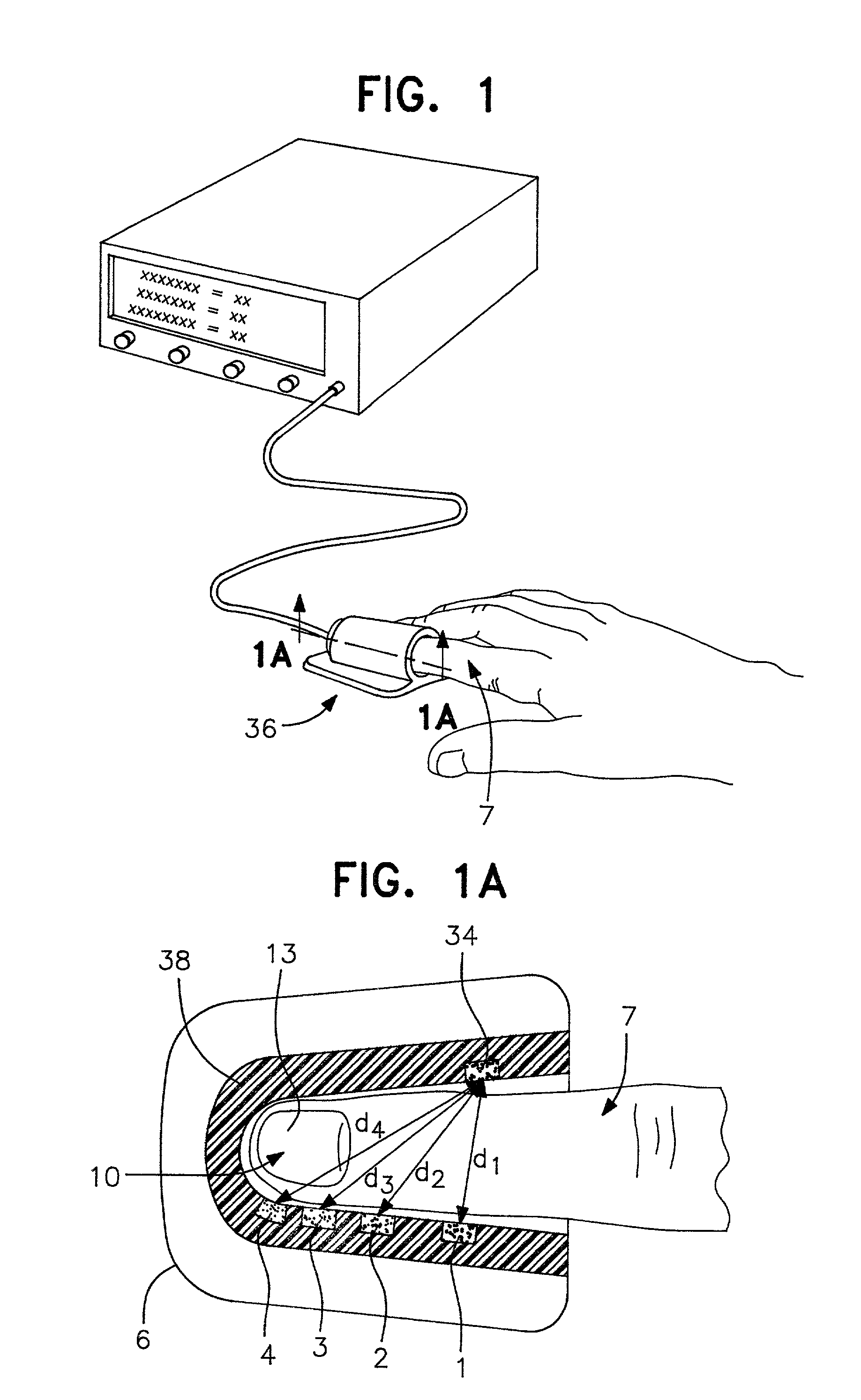
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
InactiveUS6181958B1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveHemoglobin G Szuhu
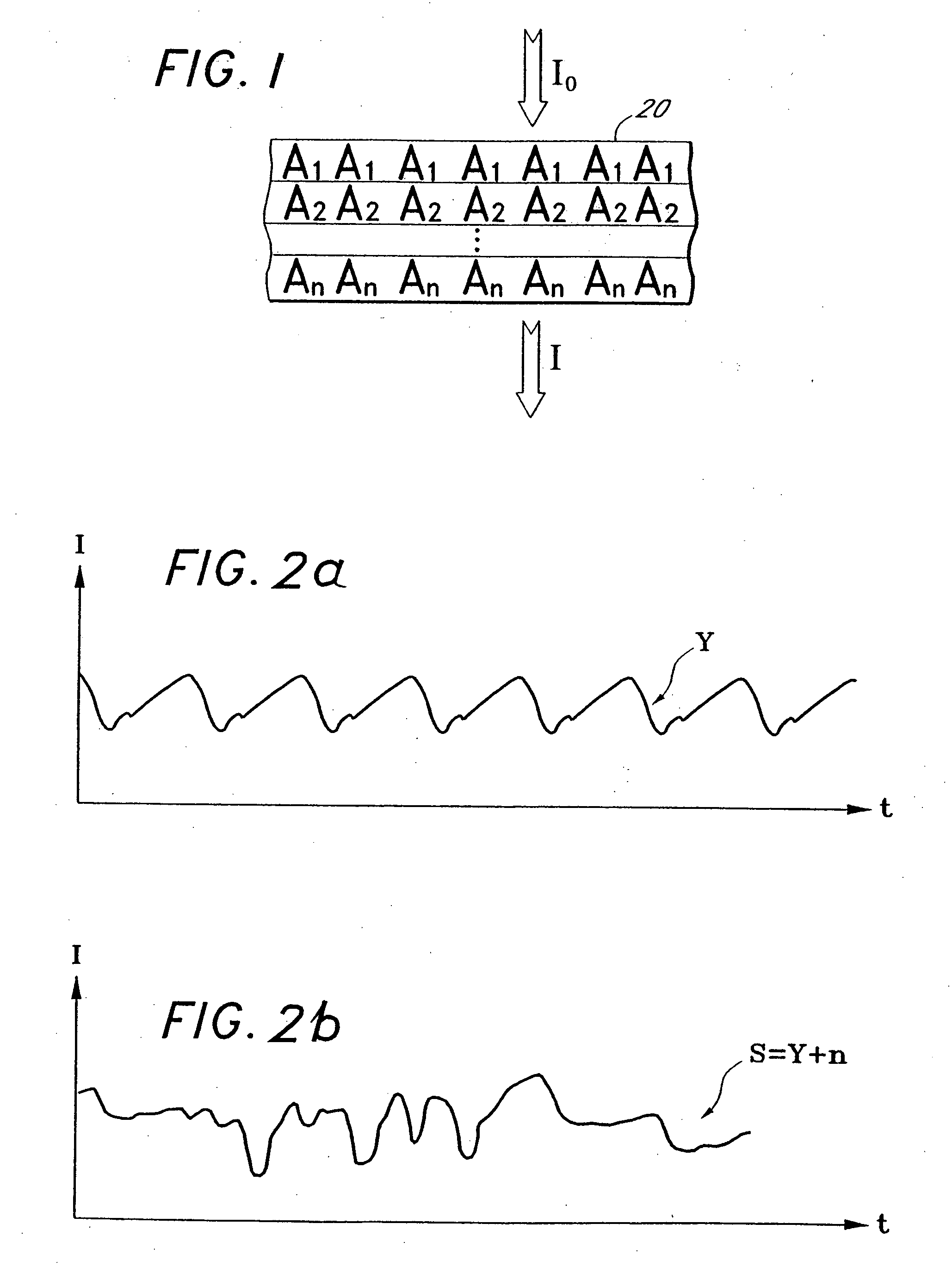
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
Low-noise optical probes for reducing ambient noise
InactiveUS20050043600A1Easy to useMinimize light pipingEvaluation of blood vesselsTransmissivity measurementsCompressible materialLow noise
An optical probe, which is particularly suited to reduce noise in measurements taken on an easily compressible material, such as a finger, a toe, a forehead, an earlobe, or a lip, measures characteristics of the material. A neonatal and adult disposable embodiment of the probe include adhesive coated surfaces to securely affix the probe onto the patient. In addition, the surface of the probe is specially constructed to reduce the effect of ambient noise.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
InactiveUS20010039376A1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveTwo step
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
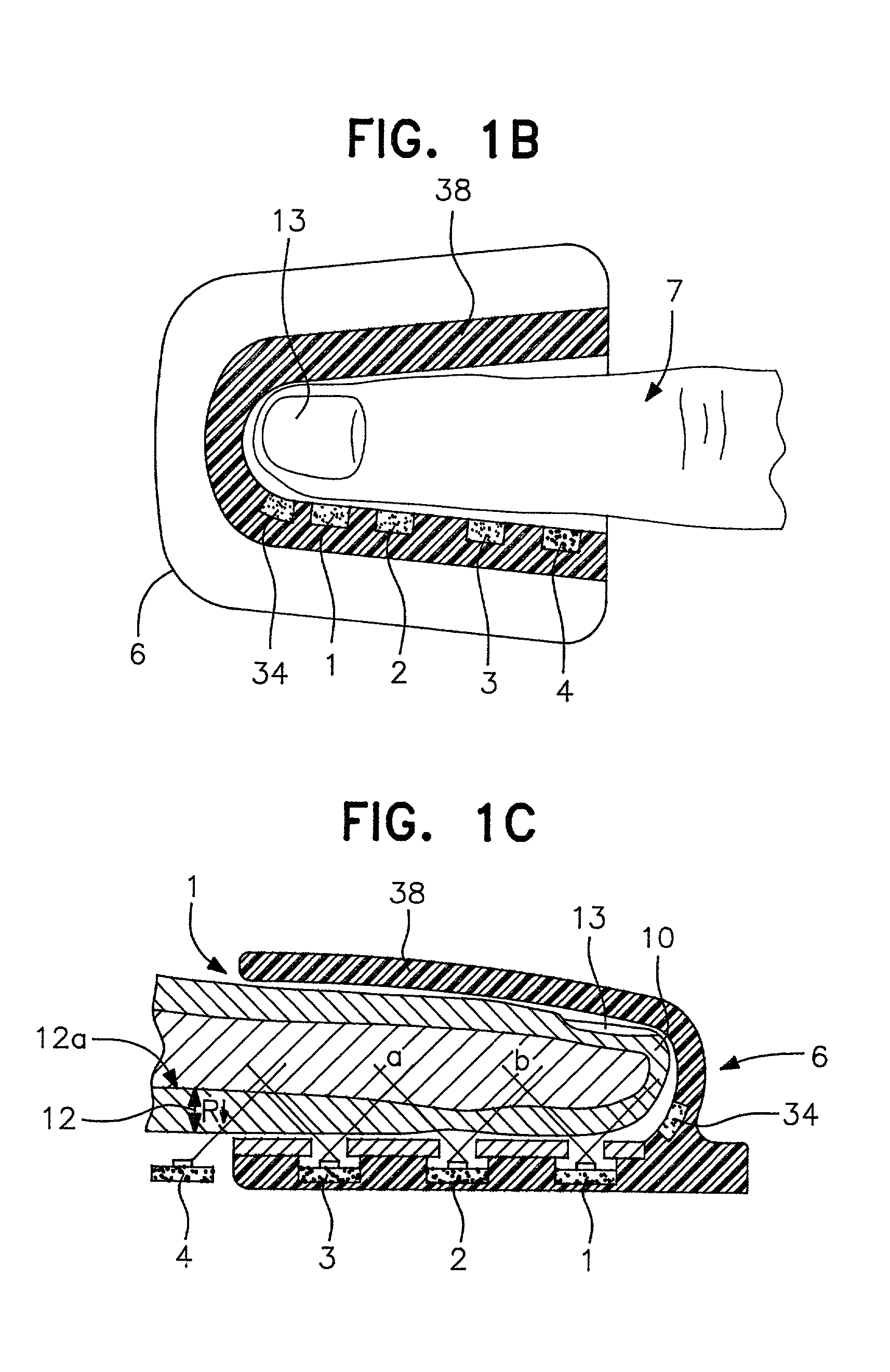
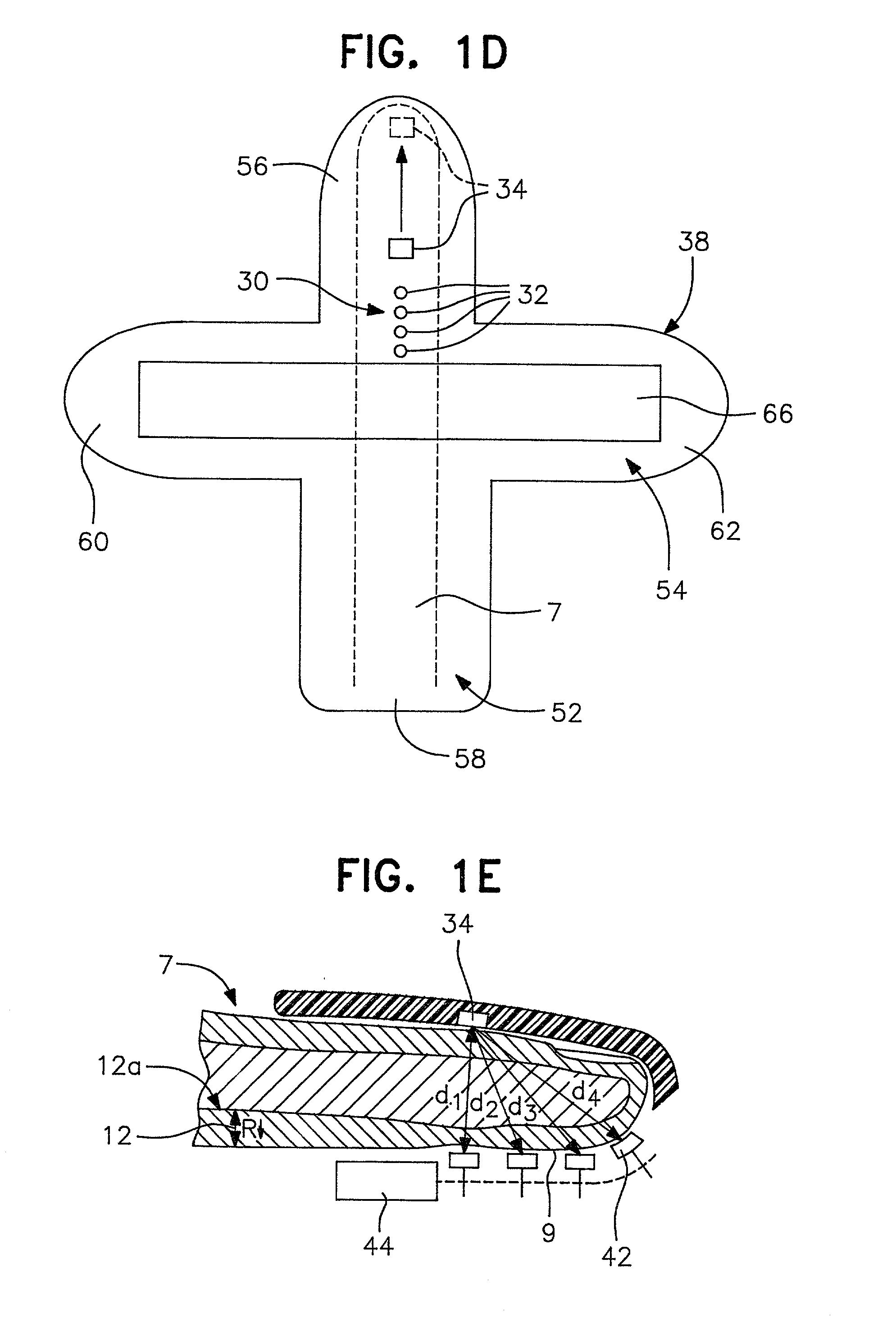
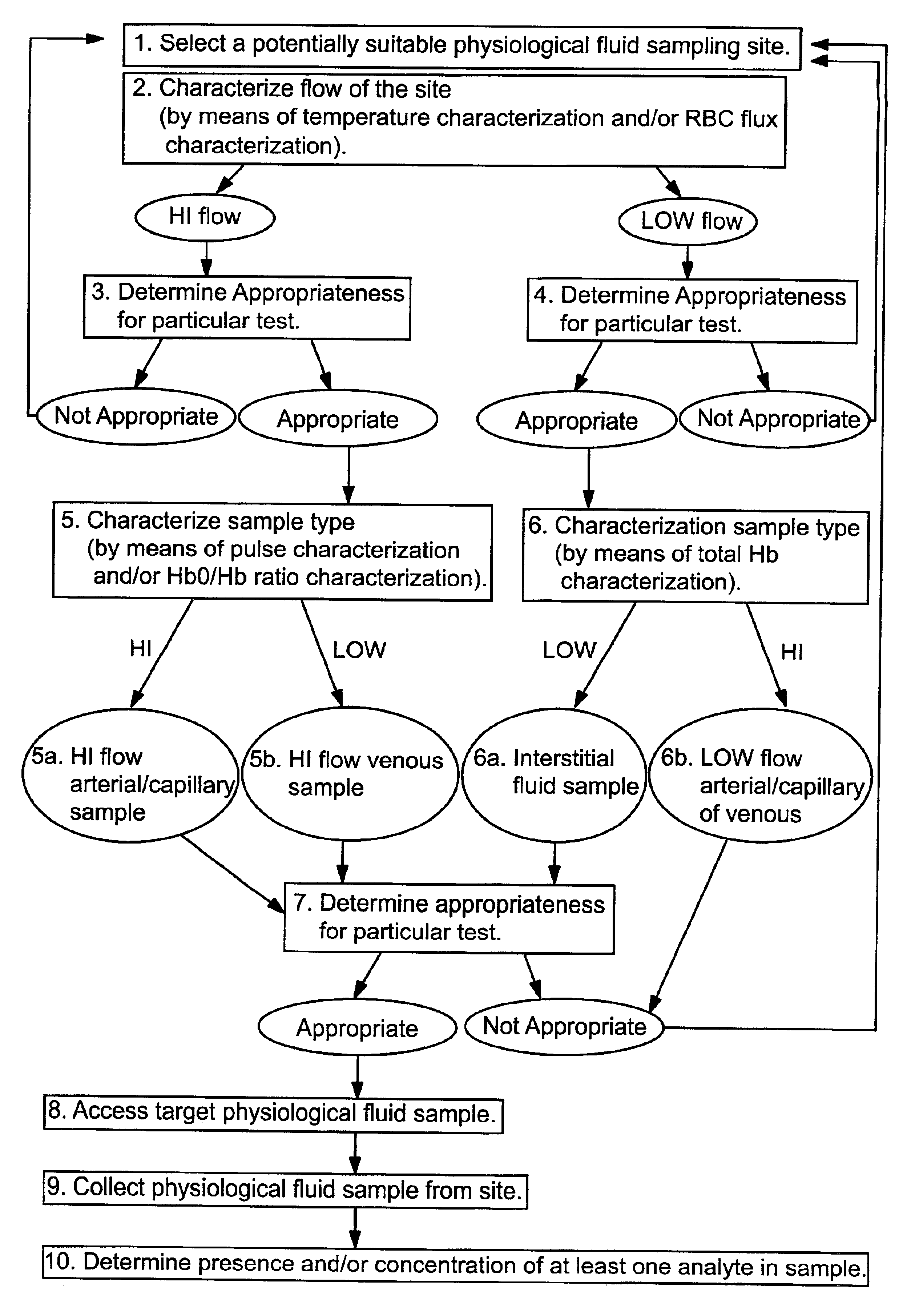
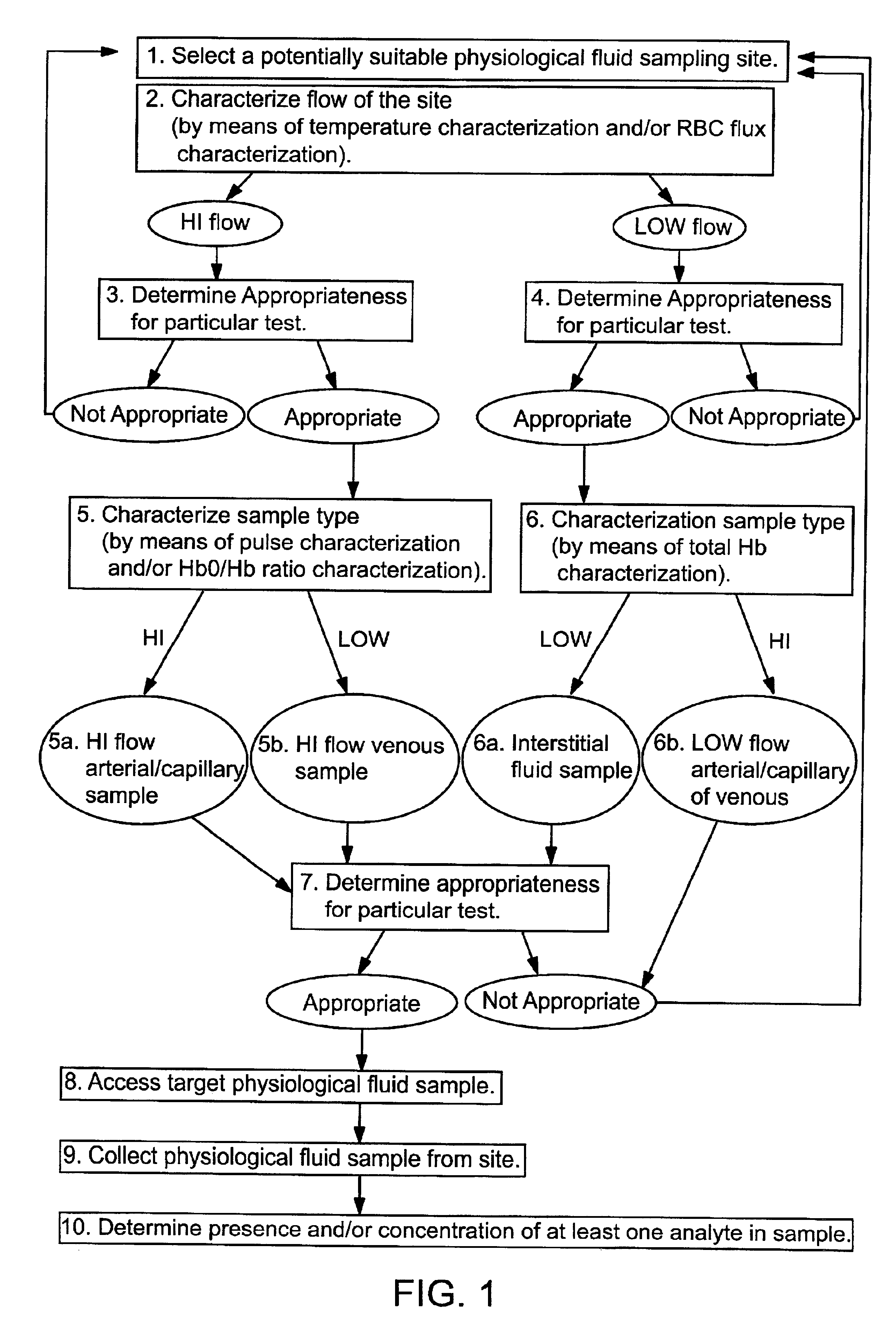
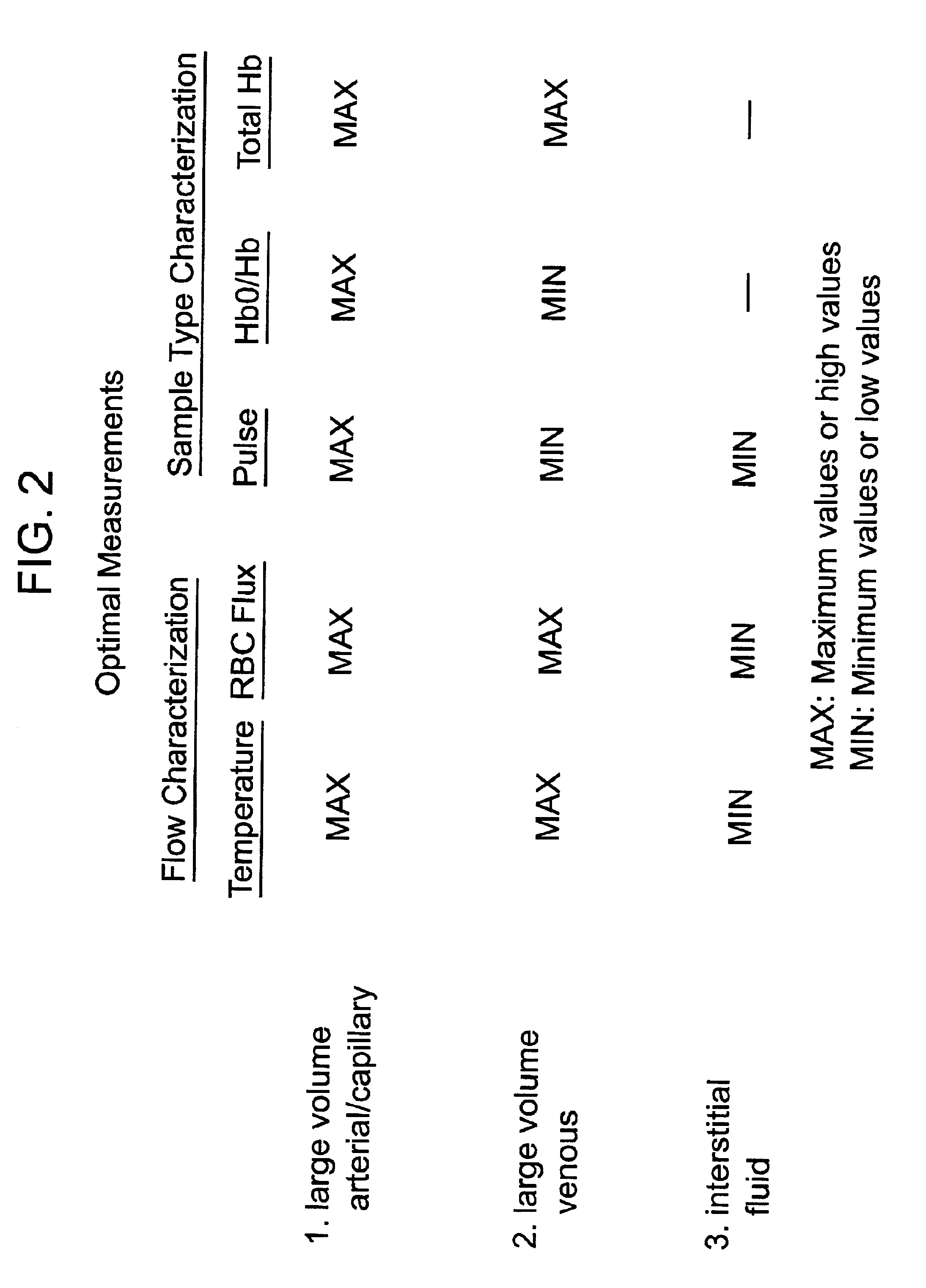
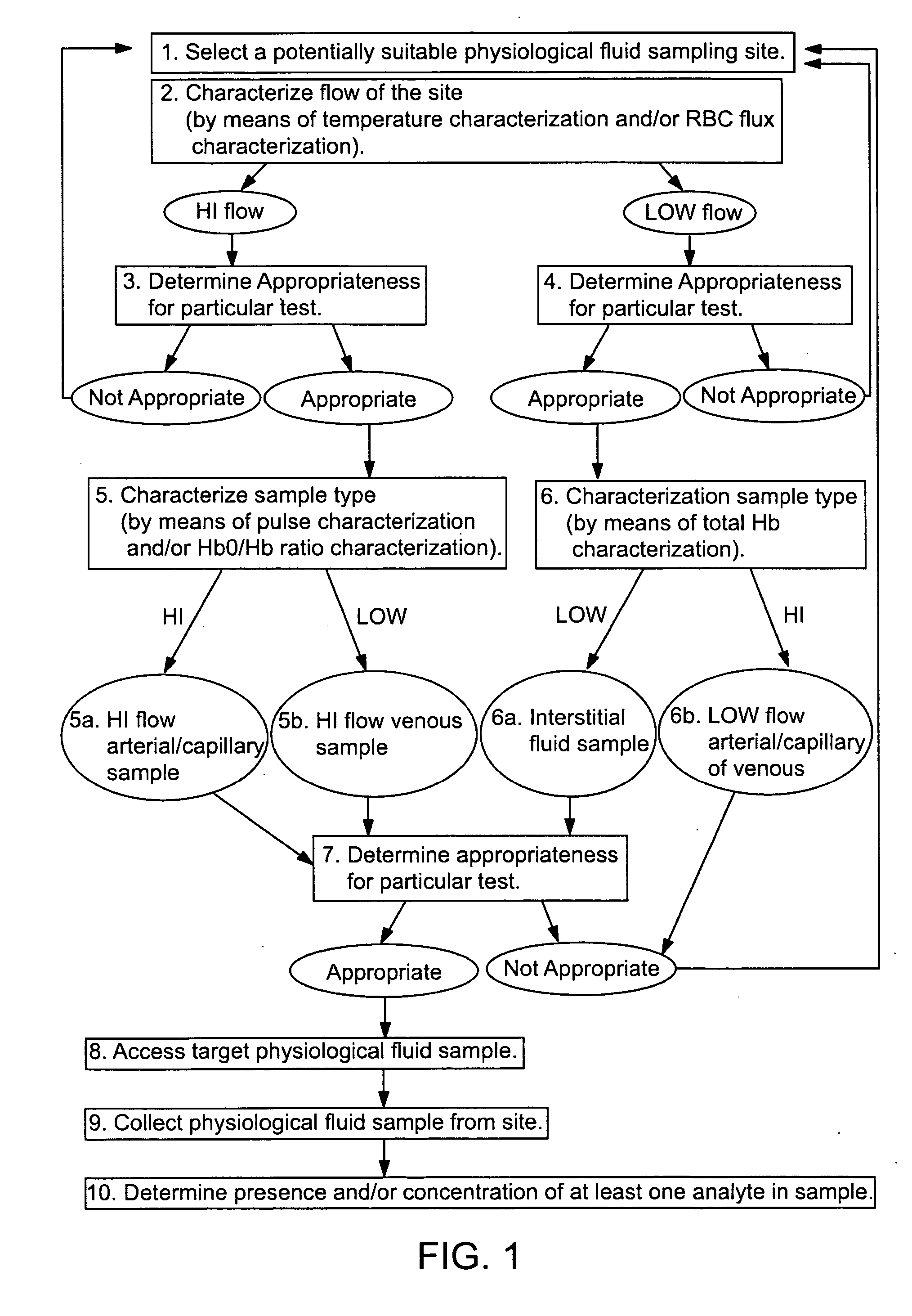
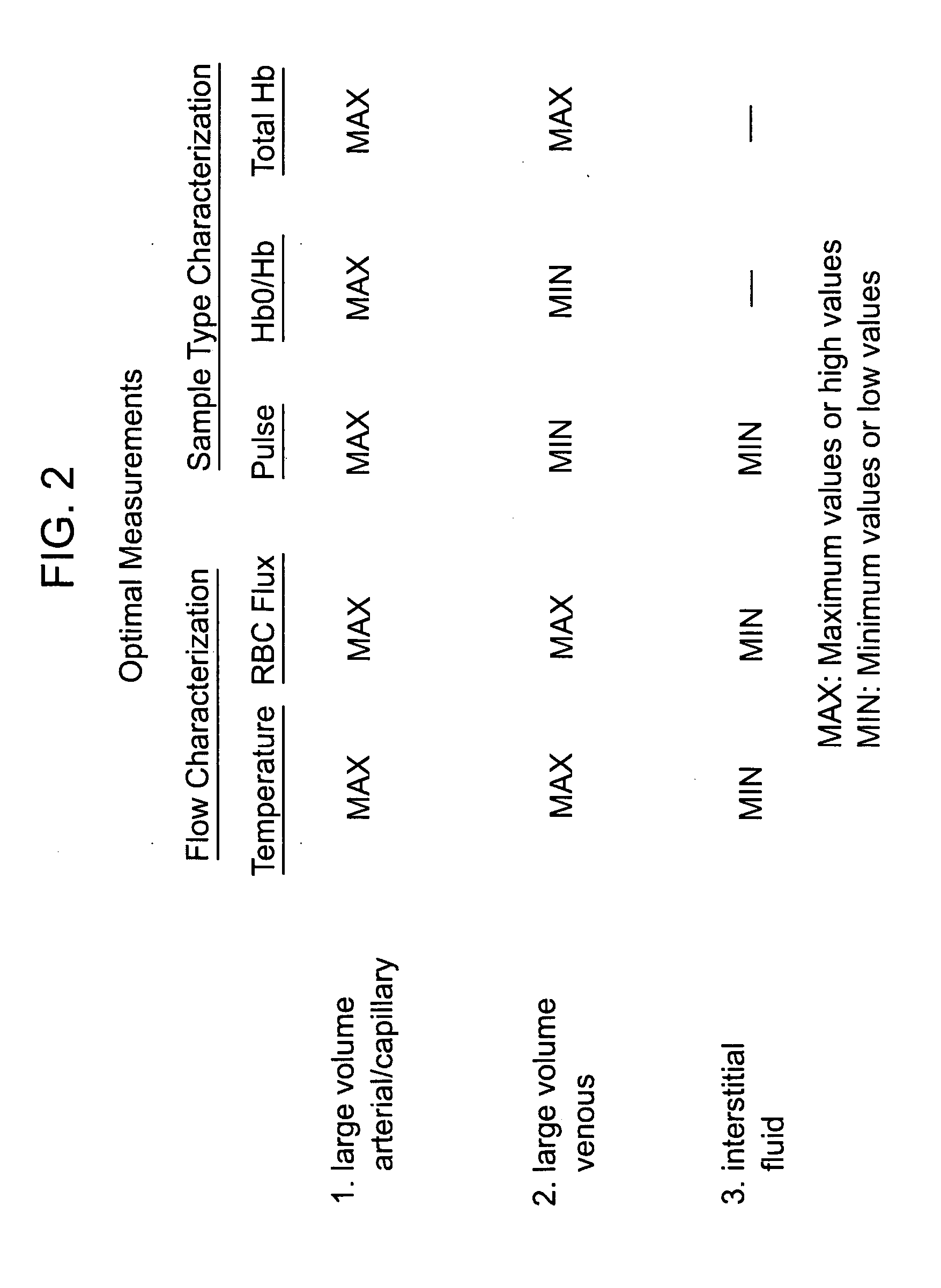
Devices for physiological fluid sampling and methods of using the same
Methods and devices are provided for determining a suitable site for sampling physiological fluid. In the subject methods, a potentially suitable physiological sampling site is selected, the fluid flow of the site is characterized and the site is then determined to be suitable based on the whether the site has high or low flow. Suitability may also be determined based on the type of sample obtainable from the site, where the order of the above-described steps may be altered. The subject devices include at least one site flow characterization element for determining the flow characteristics of a potential physiological sampling site and / or at least one sample type characterization element for determining whether the vasculature is arterial, venous or neither, i.e., an interstitial fluid sampling site. The subject methods and devices are particularly suited for use in the detection of physiological sampling sites in the fingers, arms, legs, earlobes, heels, feet, nose and toes. Also provided are kits that include the subject devices for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
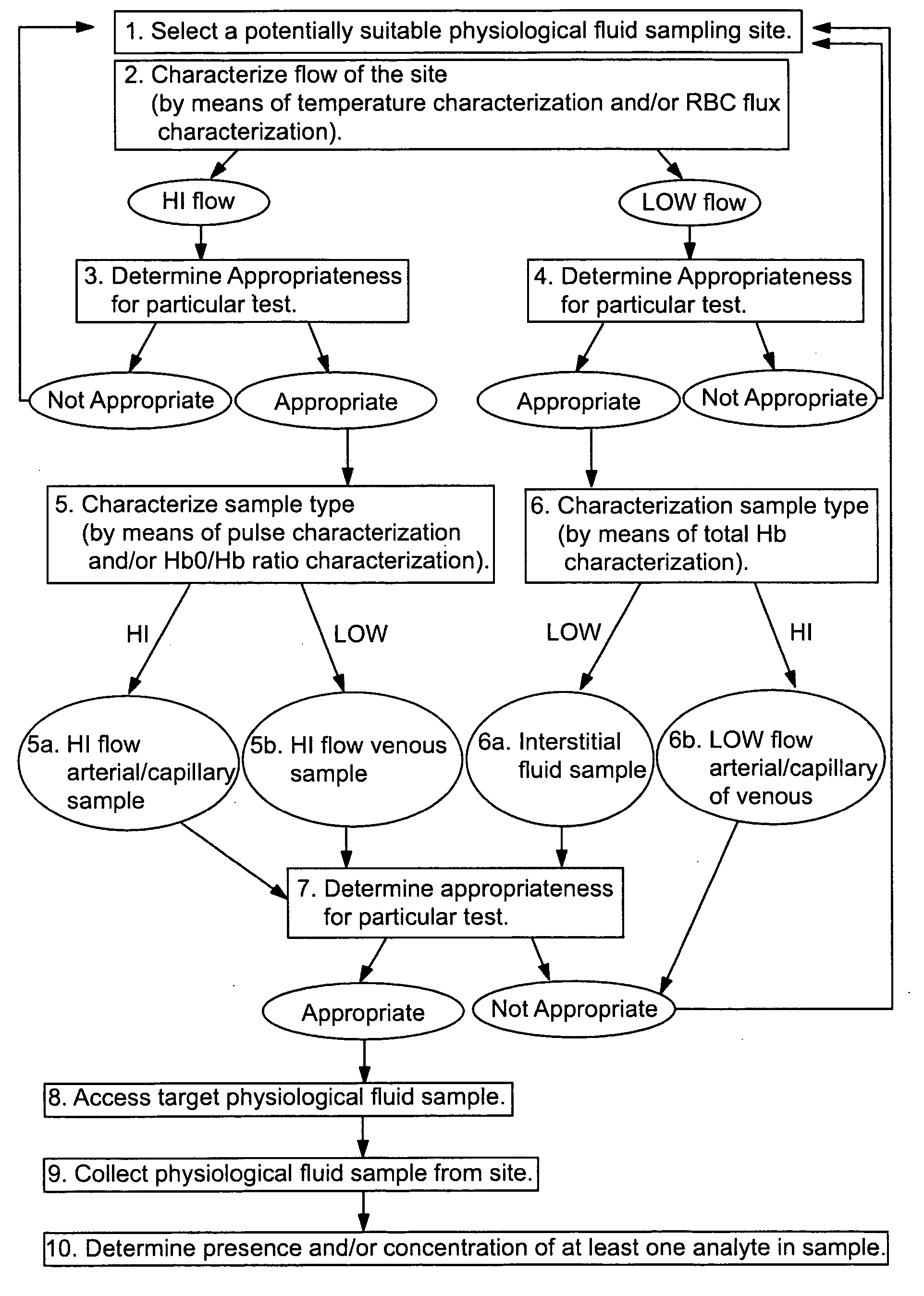
Devices for physiological fluid sampling and methds of using the same
Methods and devices are provided for determining a suitable site for sampling physiological fluid. In the subject methods, a potentially suitable physiological sampling site is selected, the fluid flow of the site is characterized and the site is then determined to be suitable based on the whether the site has high or low flow. Suitability may also be determined based on the type of sample obtainable from the site, where the order of the above-described steps may be altered. The subject devices include at least one site flow characterization element for determining the flow characteristics of a potential physiological sampling site and / or at least one sample type characterization element for determining whether the vasculature is arterial, venous or neither, i.e., an interstitial fluid sampling site. The subject methods and devices are particularly suited for use in the detection of physiological sampling sites in the fingers, arms, legs, earlobes, heels, feet, nose and toes. Also provided are kits that include the subject devices for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
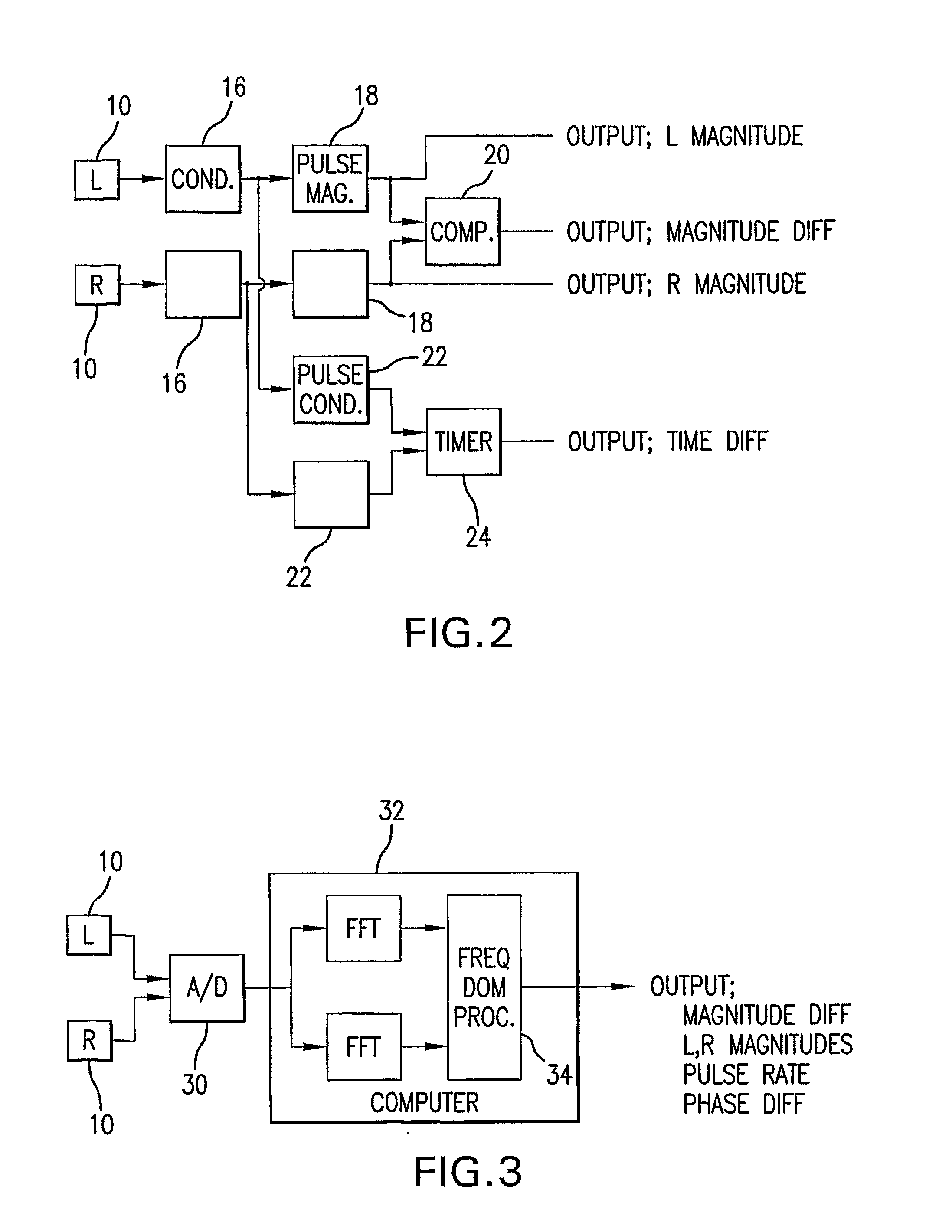
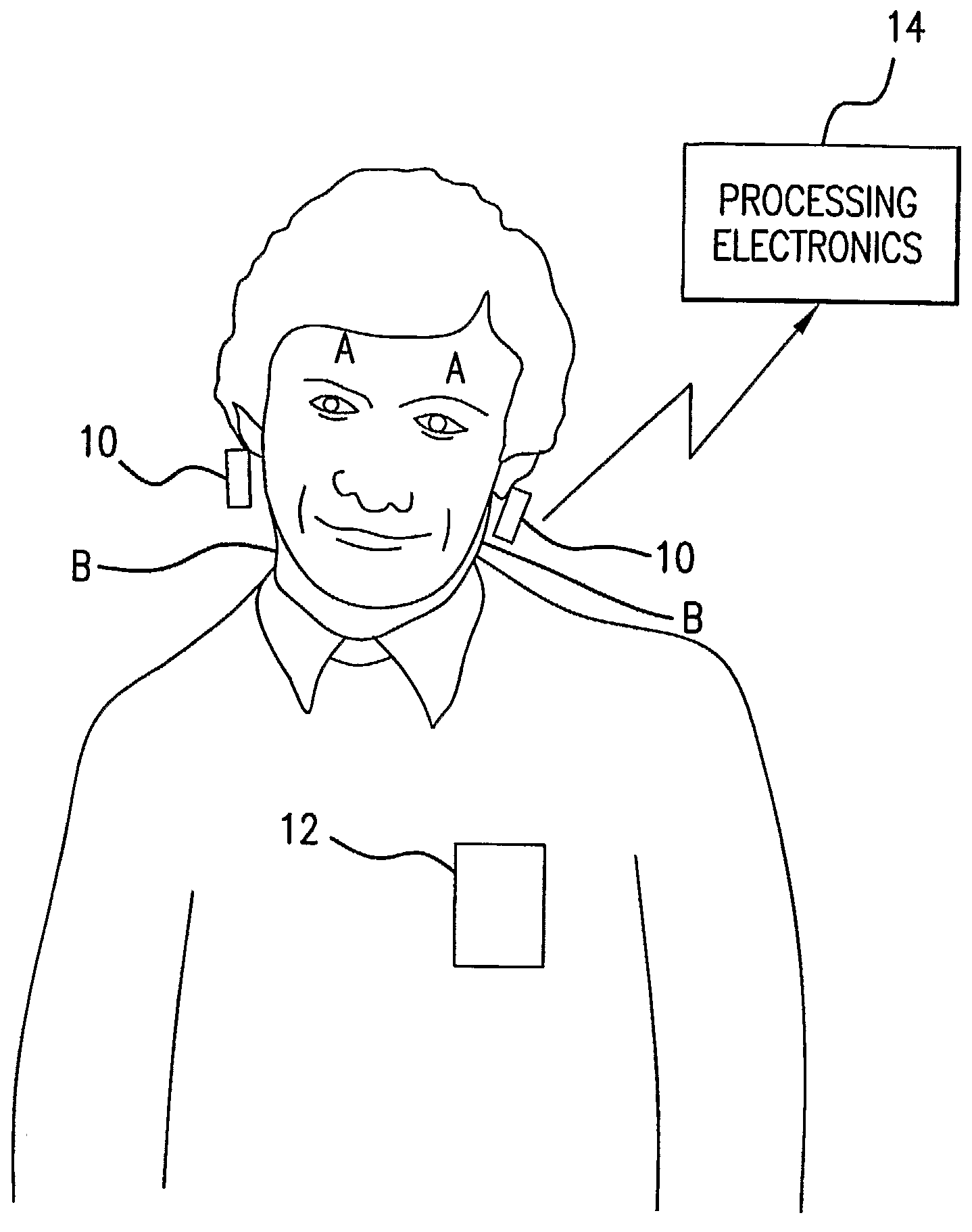
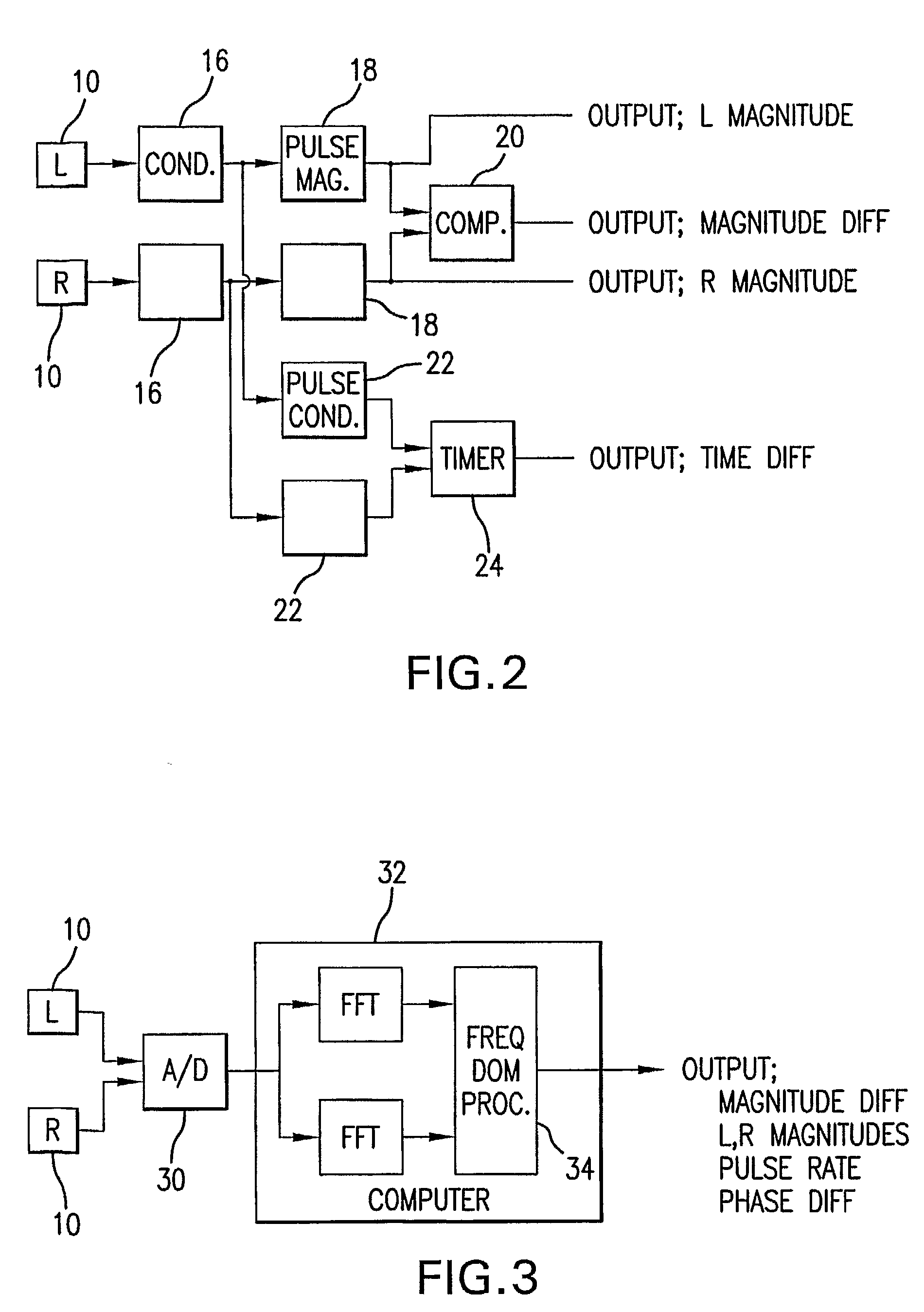
Bilateral Differential Pulse Method For Measuring Brain Activity
InactiveUS20080021332A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterPhase differencePulse characteristics
A method of measuring human brain activity includes the steps of simultaneously measuring pulses at two locations on a human subject that each receives blood from a different carotid artery that feeds a respective one of left and right hemispheres of the brain of the human subject, determining pulse characteristics from the measured pulses, and evaluating relative left and right hemisphere activity of the brain of the human subject based on the determined pulse characteristics. The method may use dual photoplethysmograhic blood pulse sensors that measure left and right hemisphere activity by determining pulse amplitude difference and time or phase differences between the earlobes while the subject carries out various mental functions. The data from the sensors are processed to provide a measure of brain function and the mental activity of the subject.
Owner:ATLANTIS PARTNERSHIP
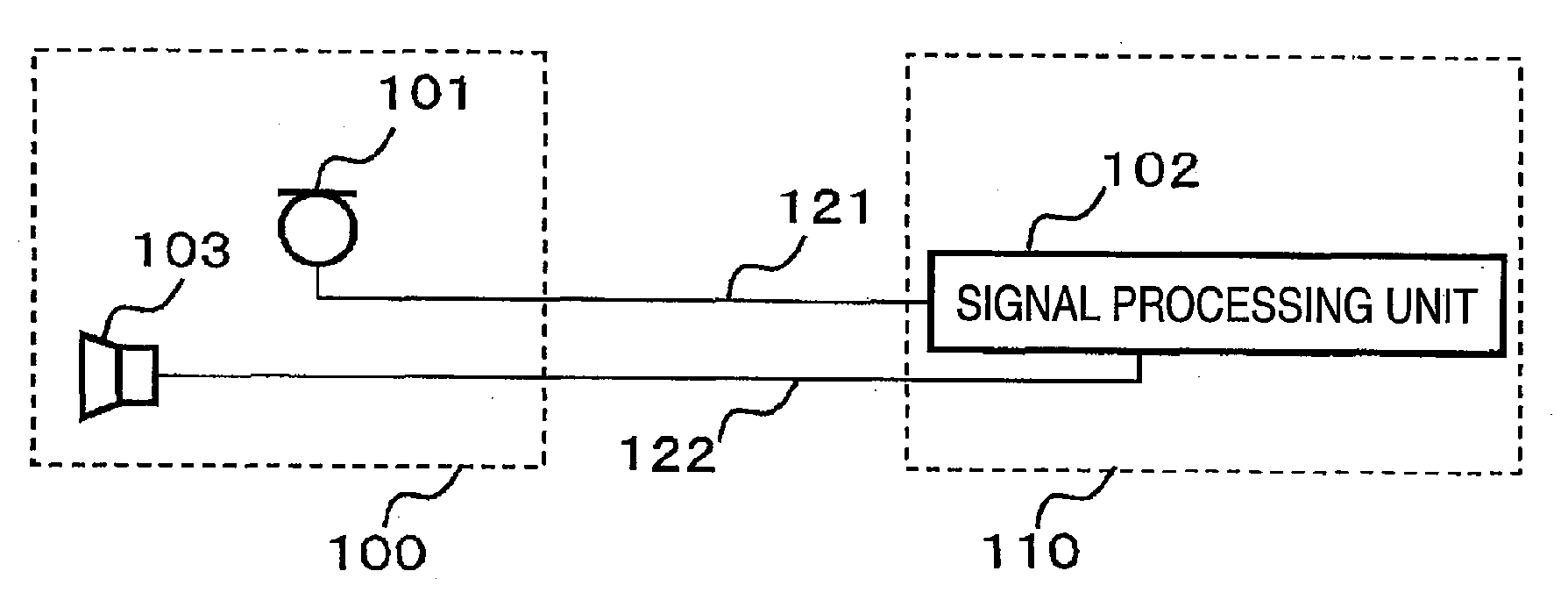
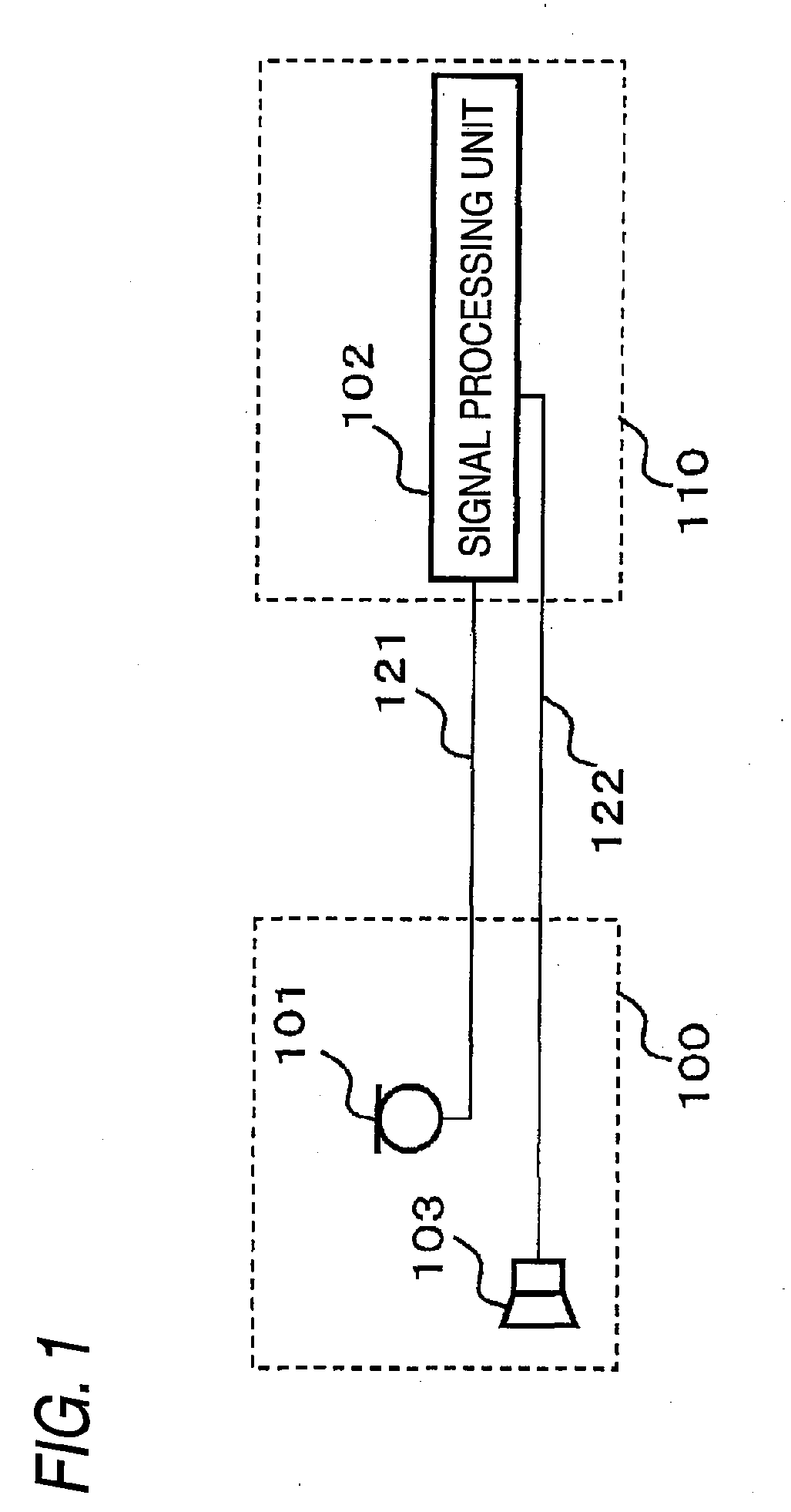
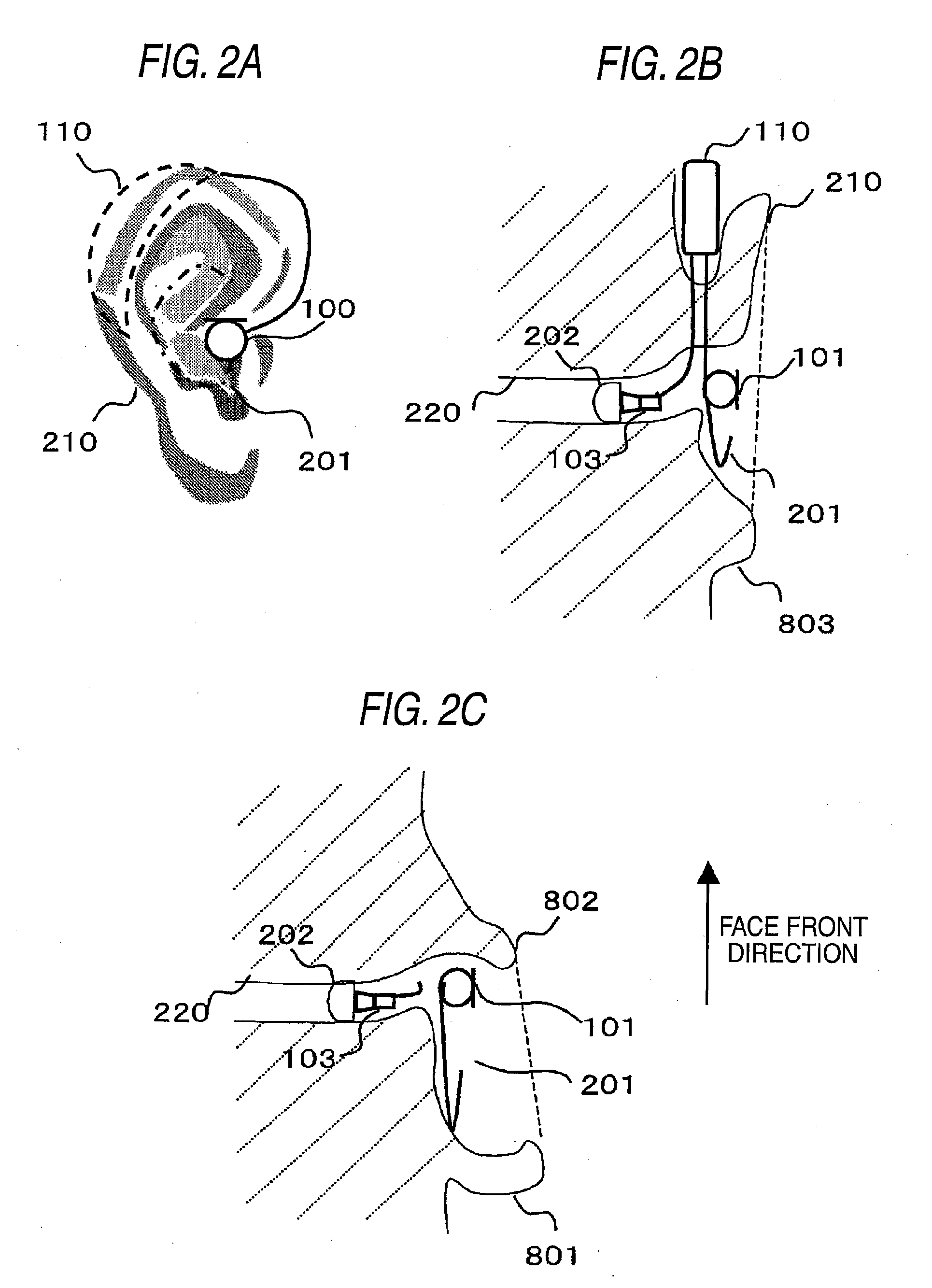
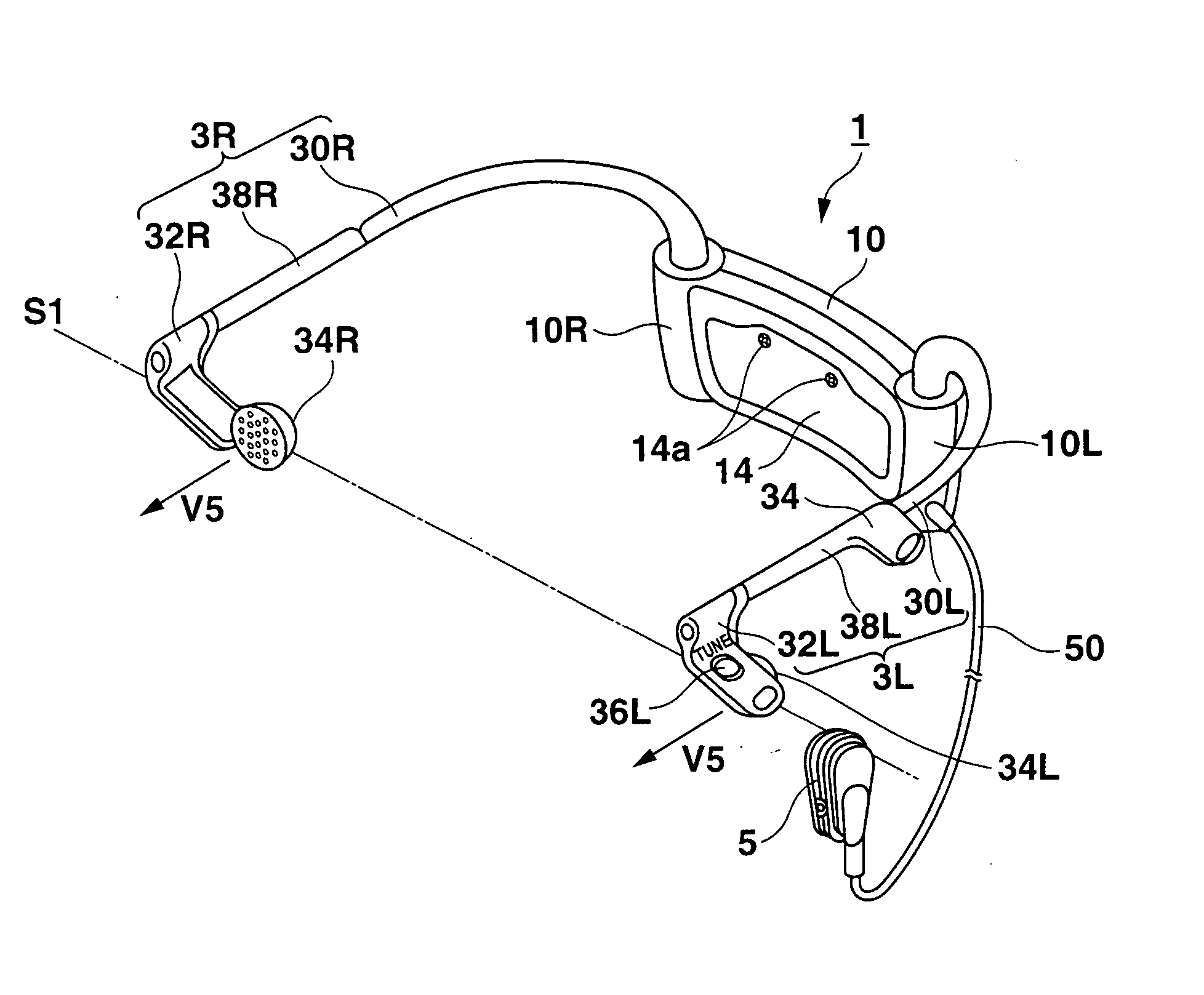
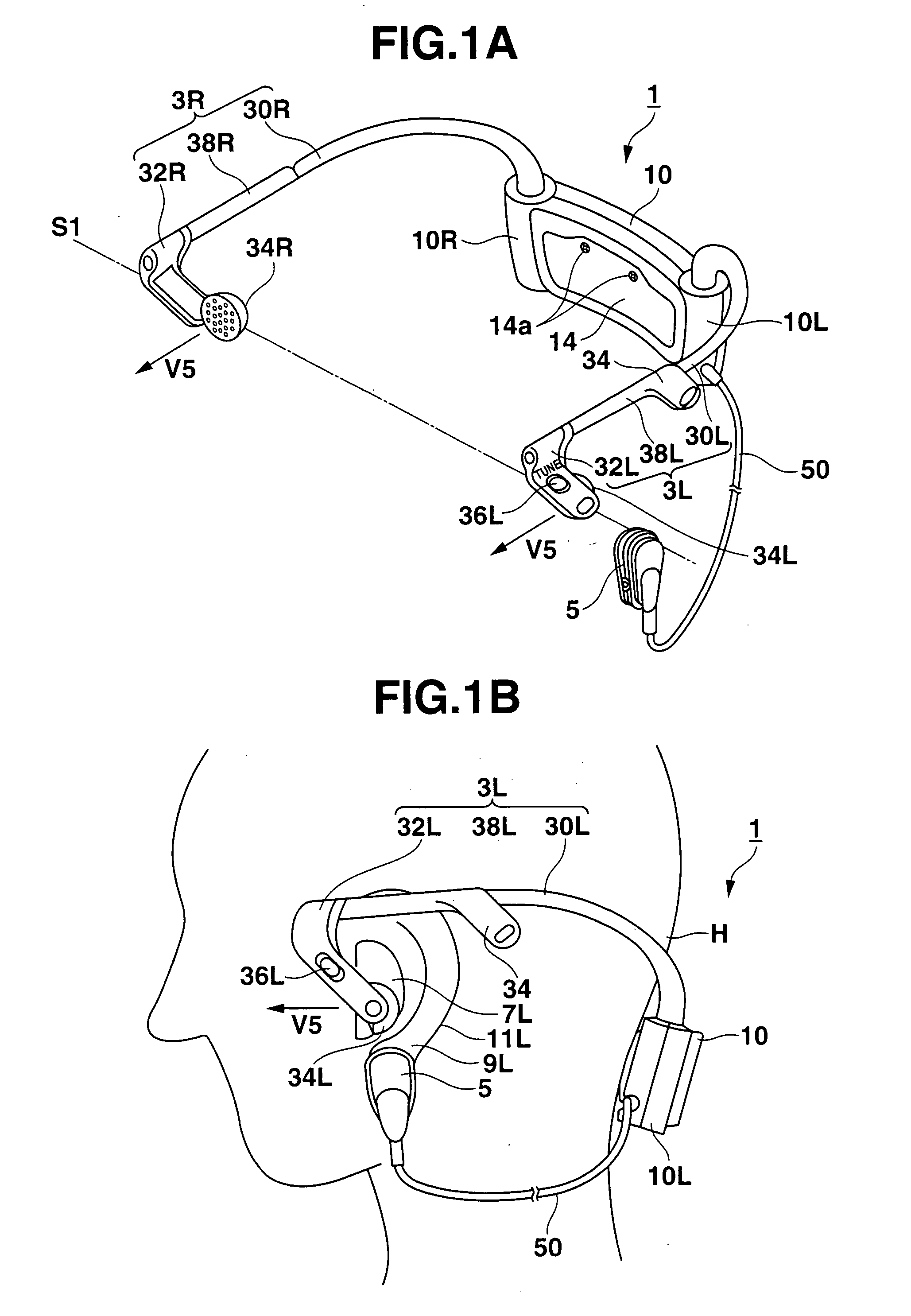
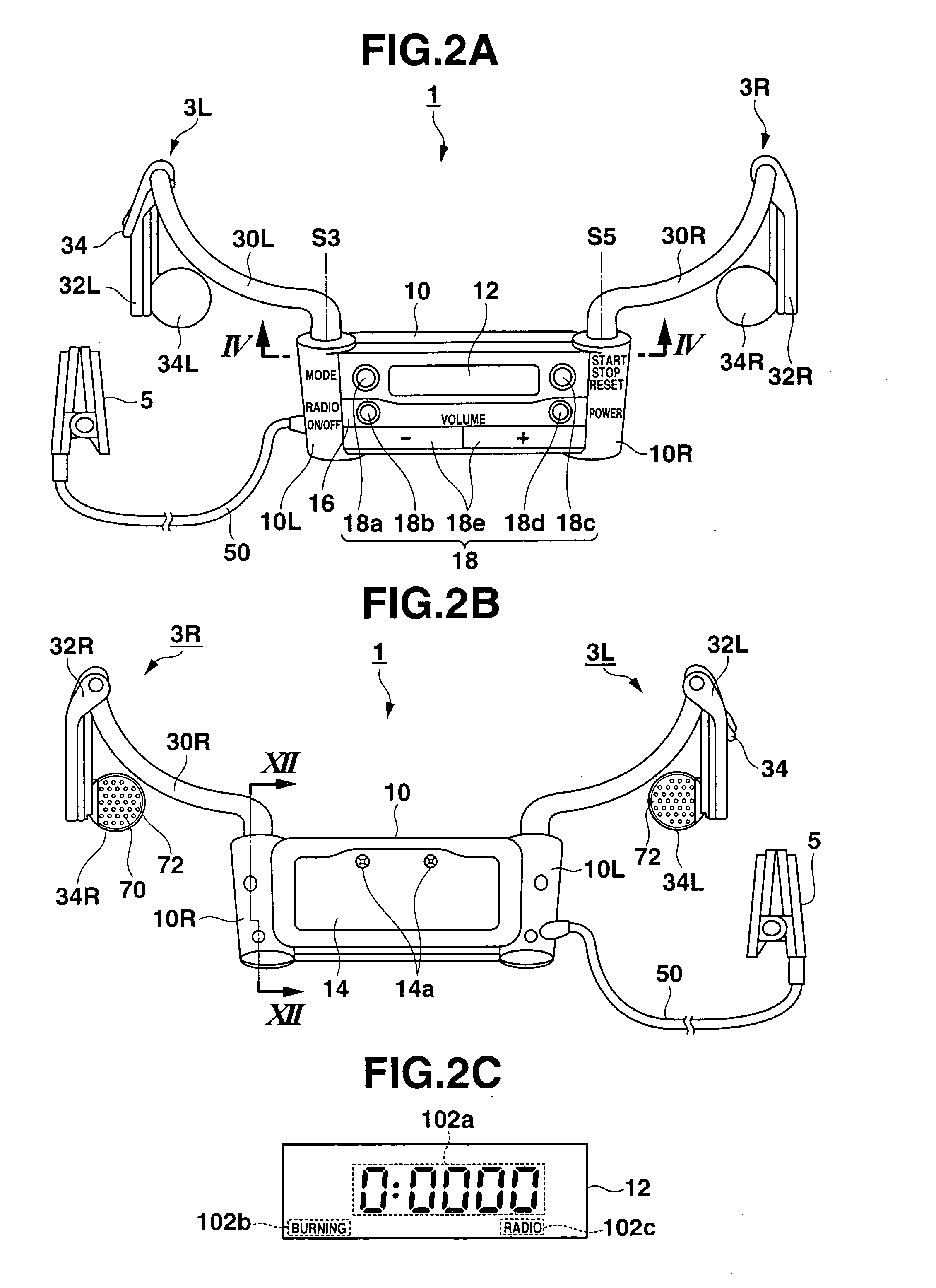
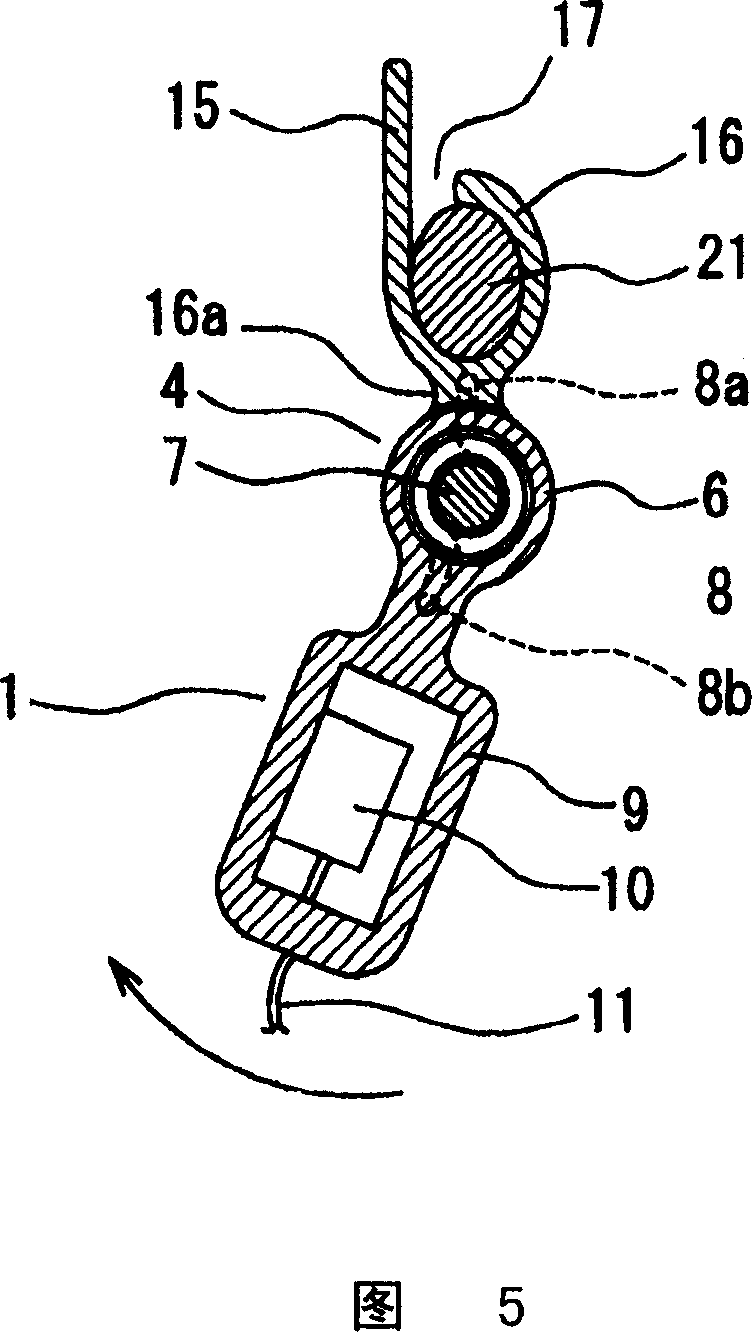
Behind-the-ear hearing aid whose microphone is set in an entrance of ear canal
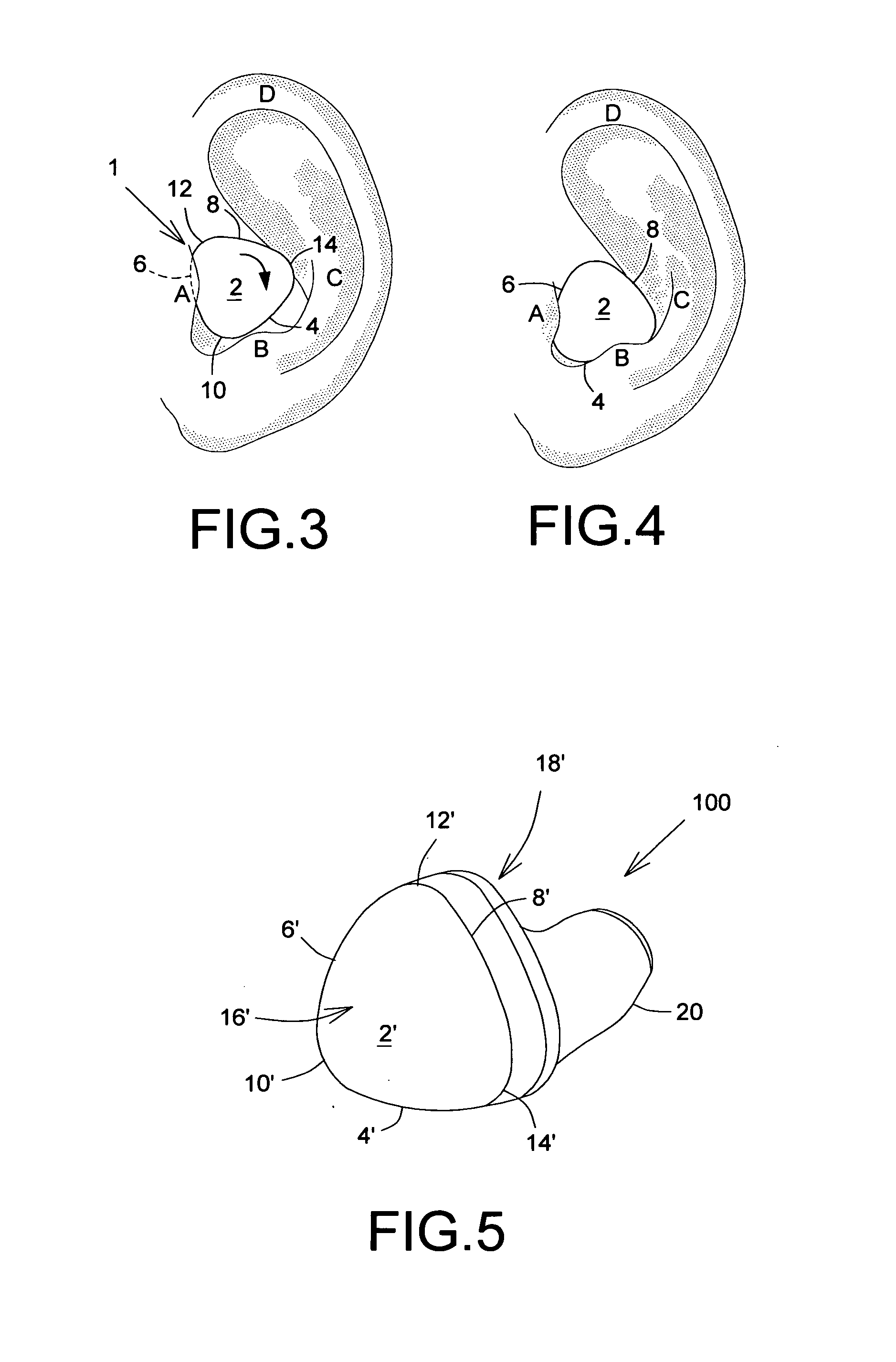
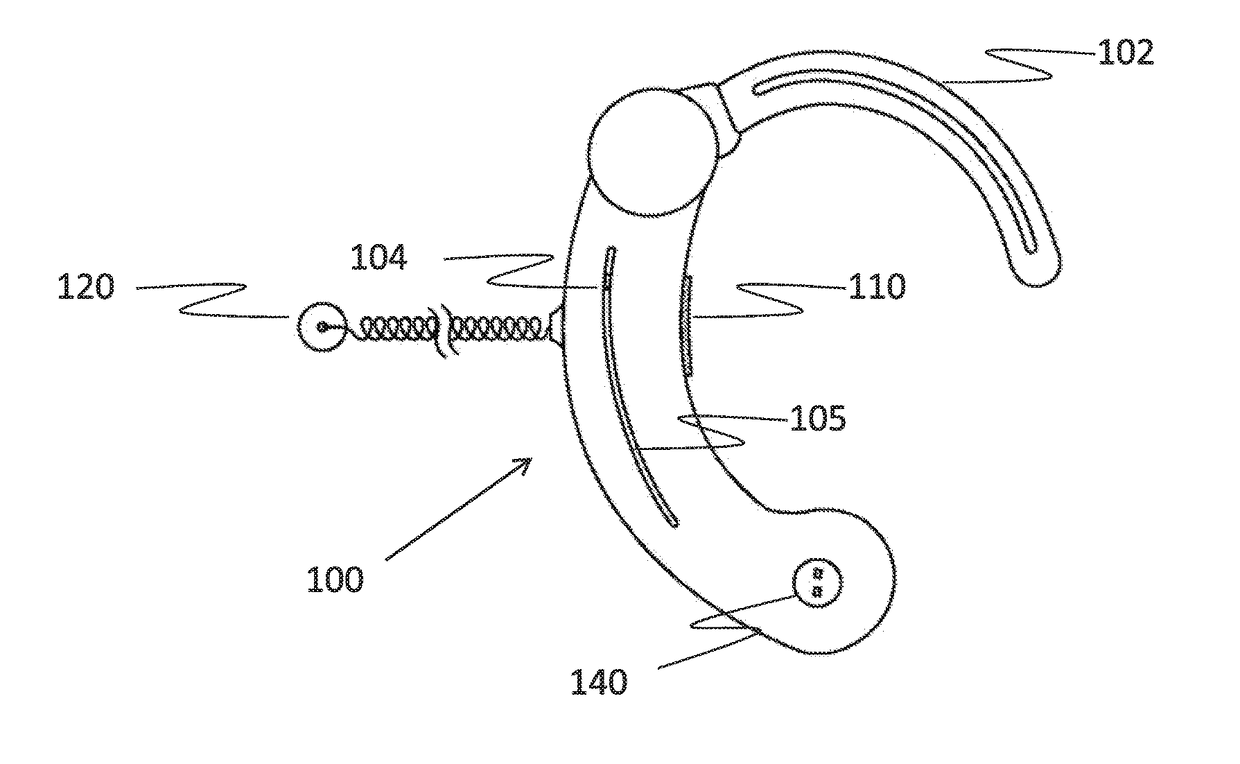
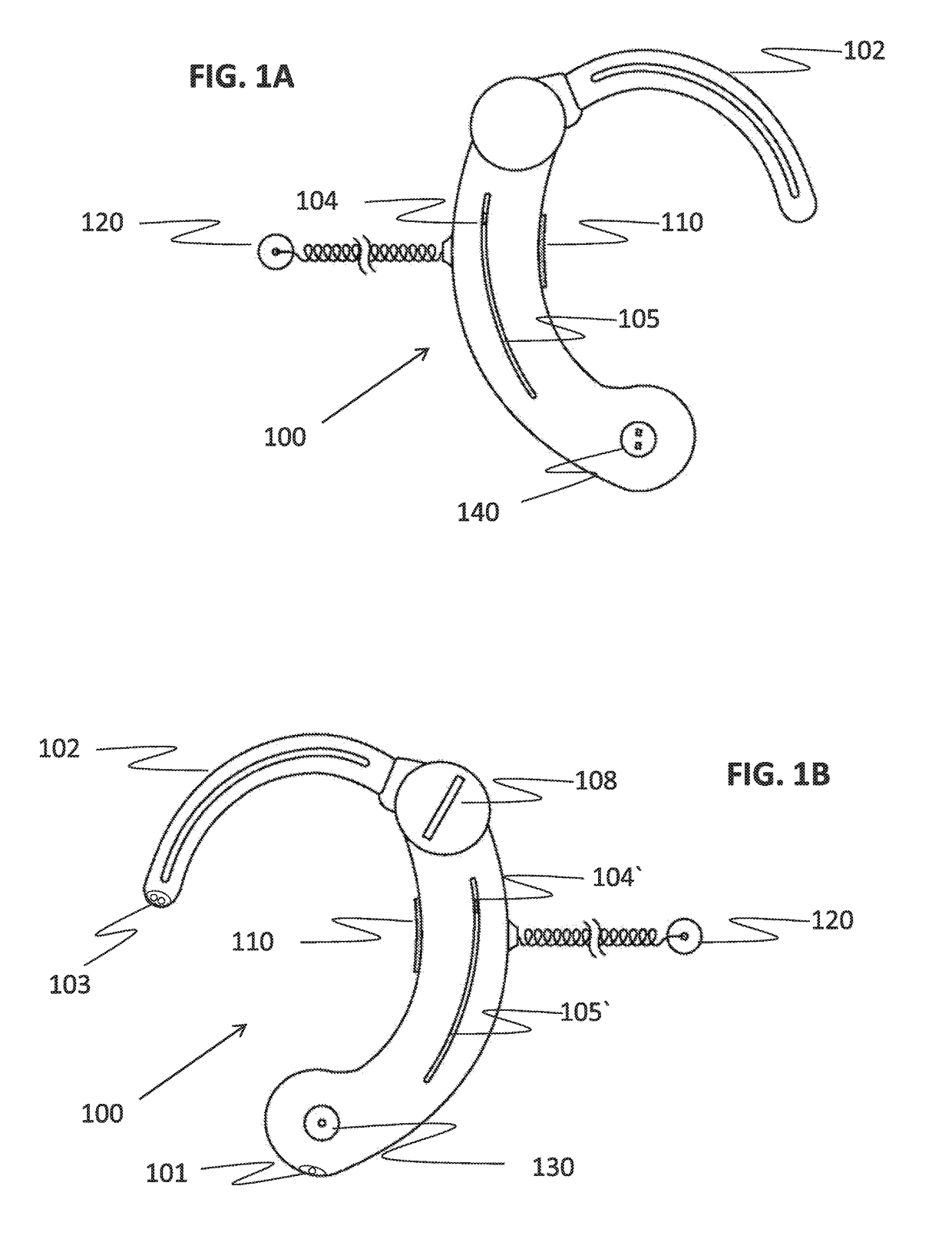
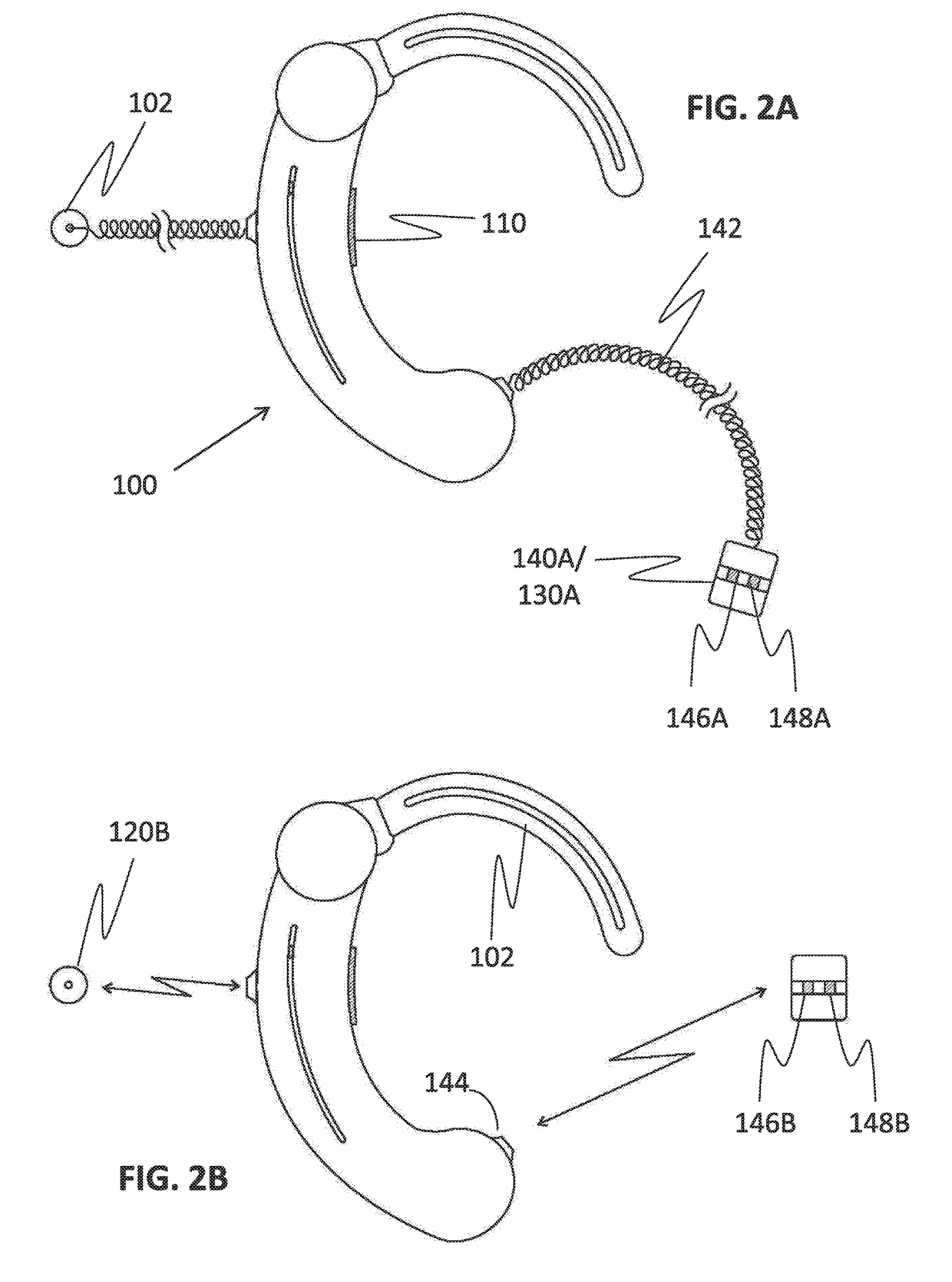
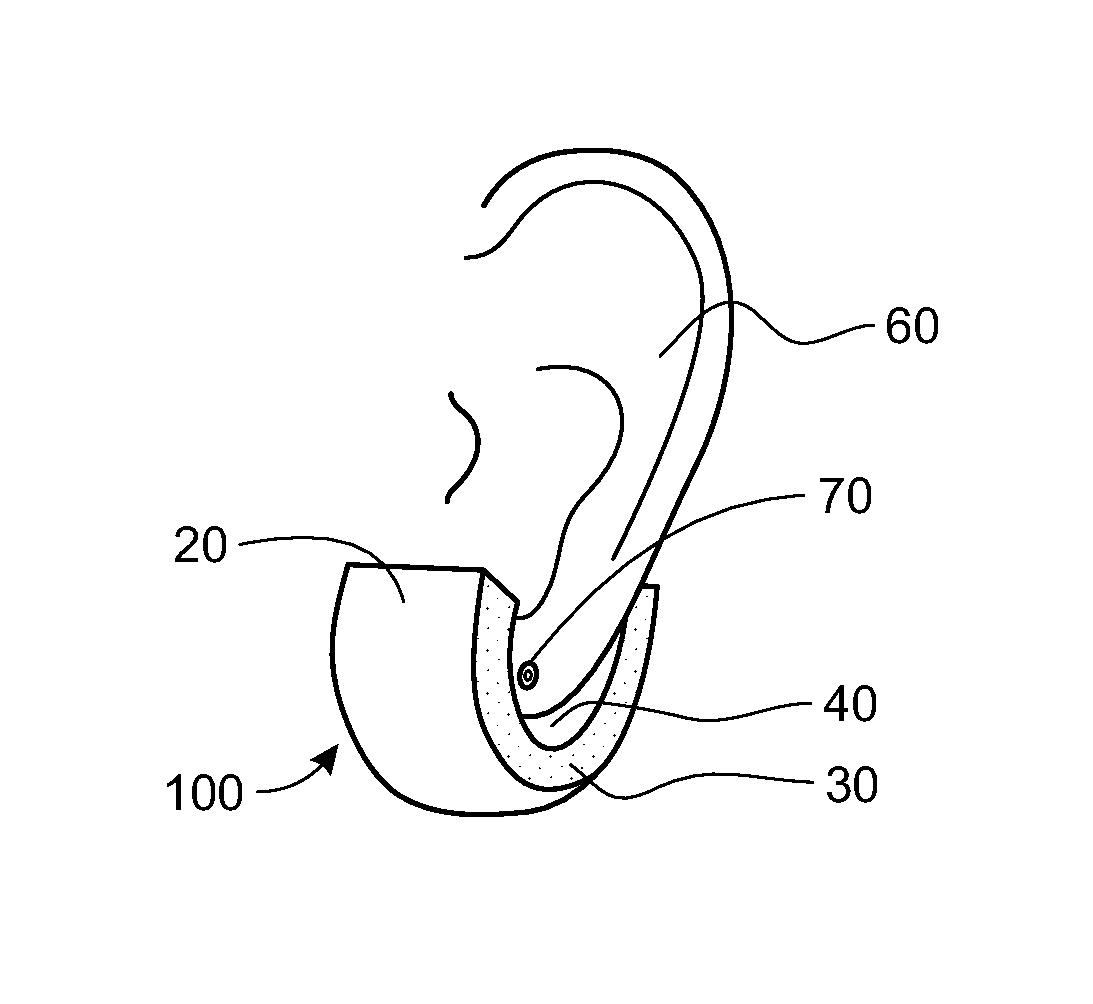
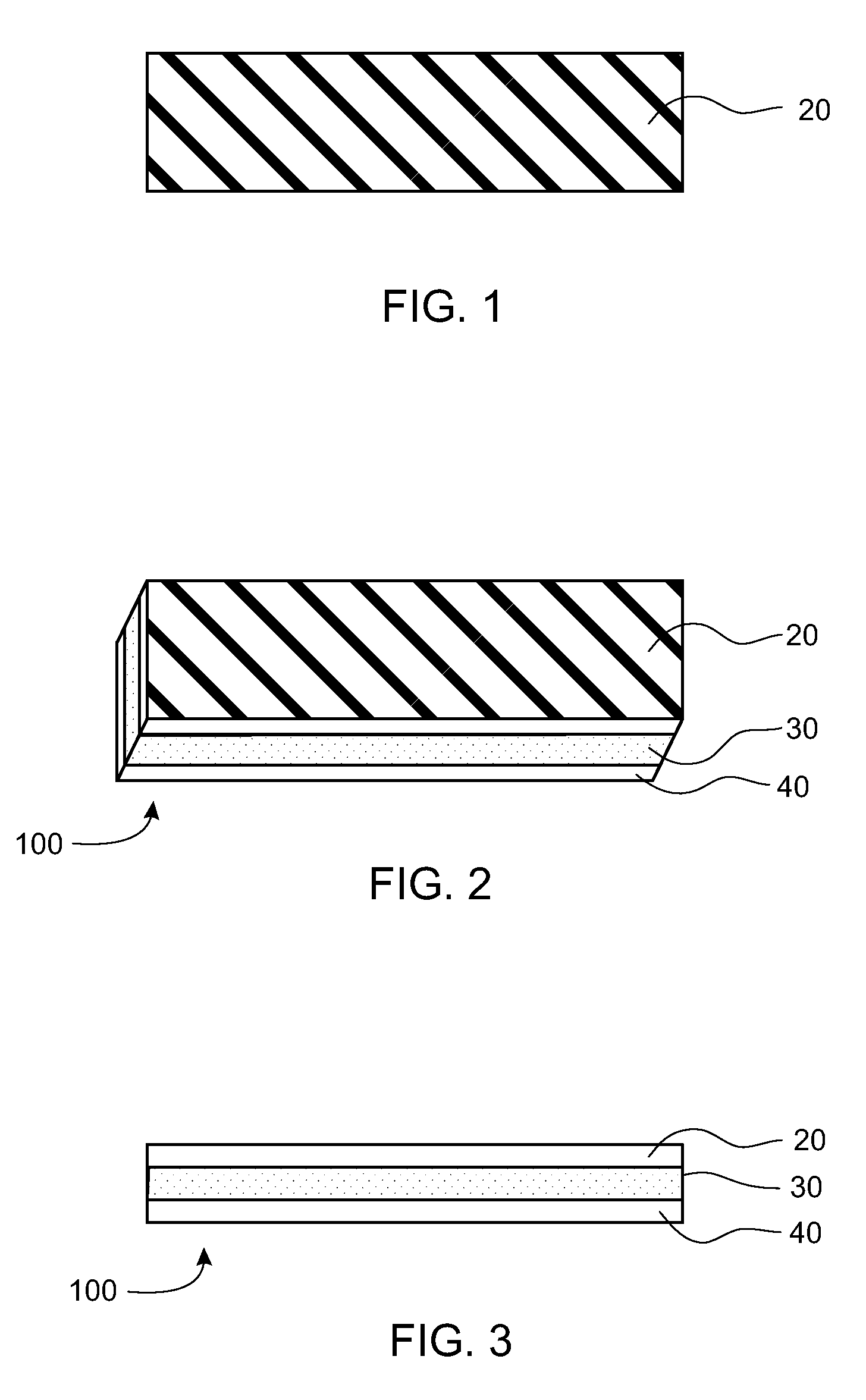
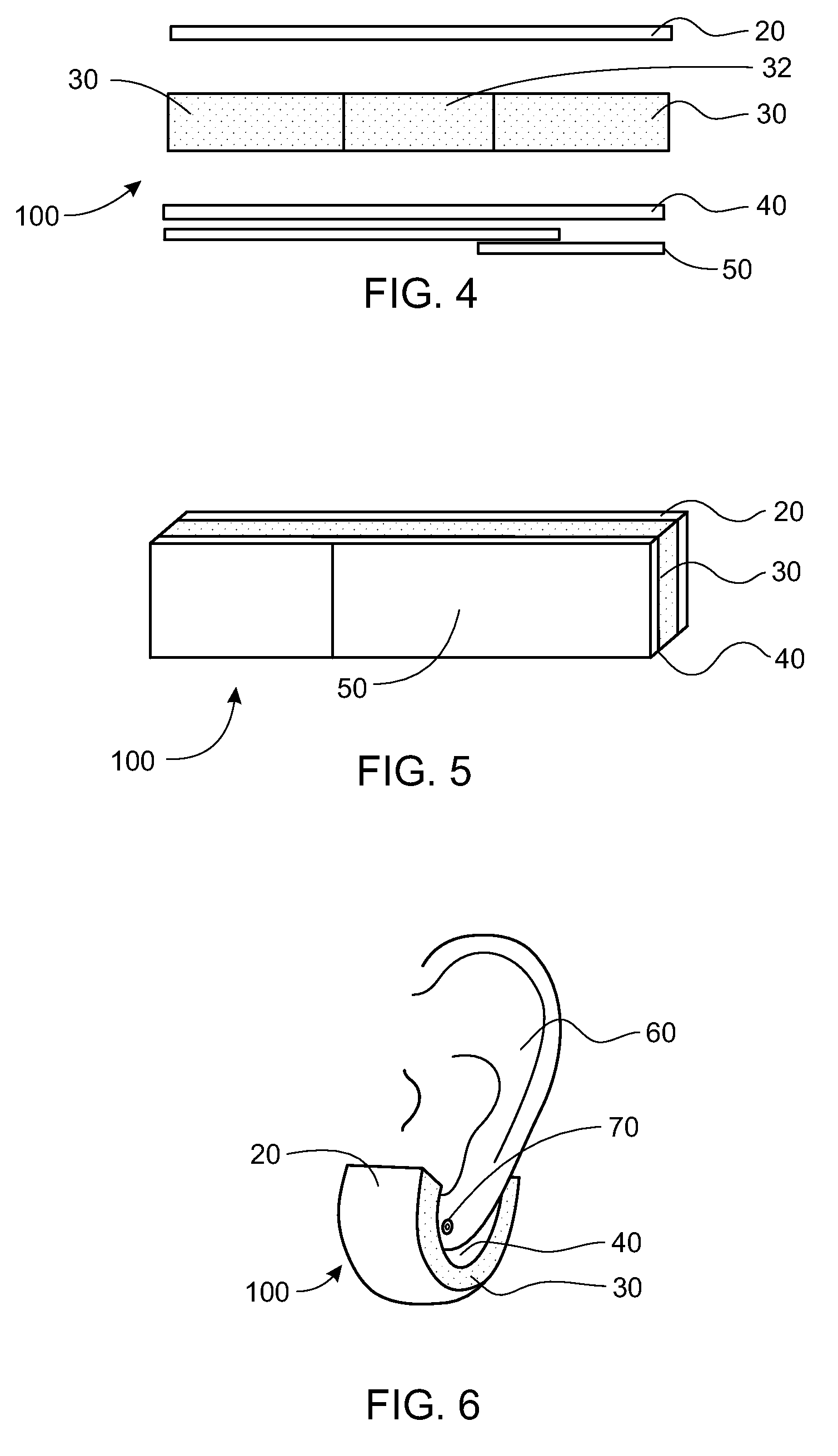
There is provided a behind-the-ear hearing aid that makes it easy for a hearing aid wearer to estimate a position of a sound source with respect to a front-back direction and that enables an increase in aesthetic property when the hearing aid is worn. A behind-the-ear hearing aid of the present invention is used while fitted to an ear of a human body, and includes at least a microphone 101 which collects ambient sound, thereby generating an input signal and signal processing unit 102 that generates an output signal from the input signal. The hearing aid also has a behind-the-ear portion 110 that can be fitted to the ear and a receiver 103 that reproduces output sound from the output signal. When the behind-the-ear portion 110 is fitted to the ear, the microphone 101 is arranged in an entrance of an ear canal that lies in the extension of an ear canal 220 and that is disposed closer to an eardrum than to a plane that is defined by a helix 901, a tragus 902, and an earlobe 903.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Quasi-triangular in-ear device
InactiveUS8776801B2Comfortably fit a wide variety of wearersEar supported setsHearing aid design aspectsConvex sideEngineering
The in-ear device is shaped to fit a wearer's ear morphology. The device includes a main body having at least three generally convex sides, an innermost face and an outermost face. A first side is shaped to fit the tragus of a wearer's ear, and a second side is shaped to fit an antitragus of a wearer's ear. At least three tips, generally rounded, join respective two adjacent sides. The main body is within an outer ear plane substantially perpendicular to an entrance of an ear canal of a wearer's ear.
Owner:SONOMAX TECH INC
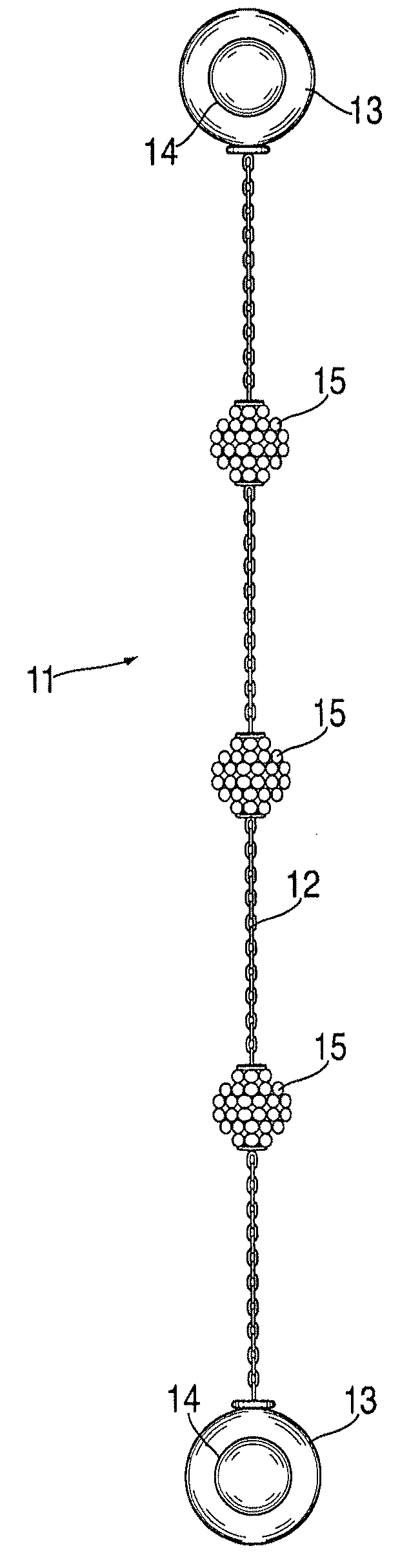
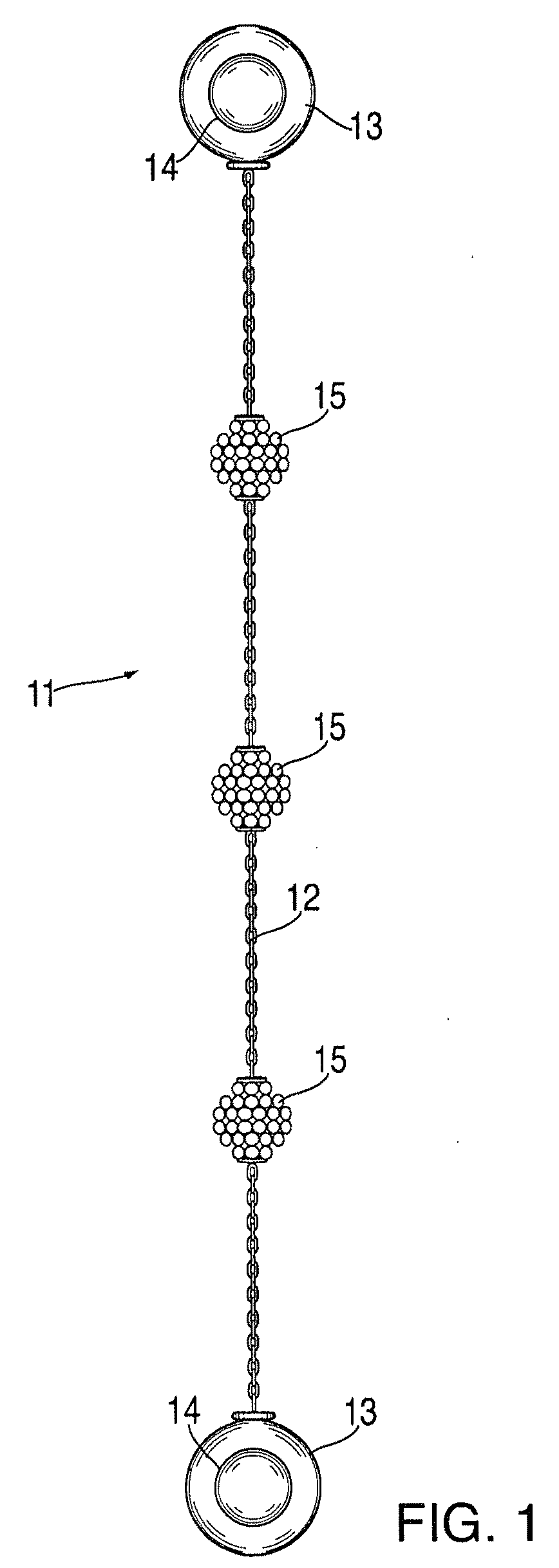
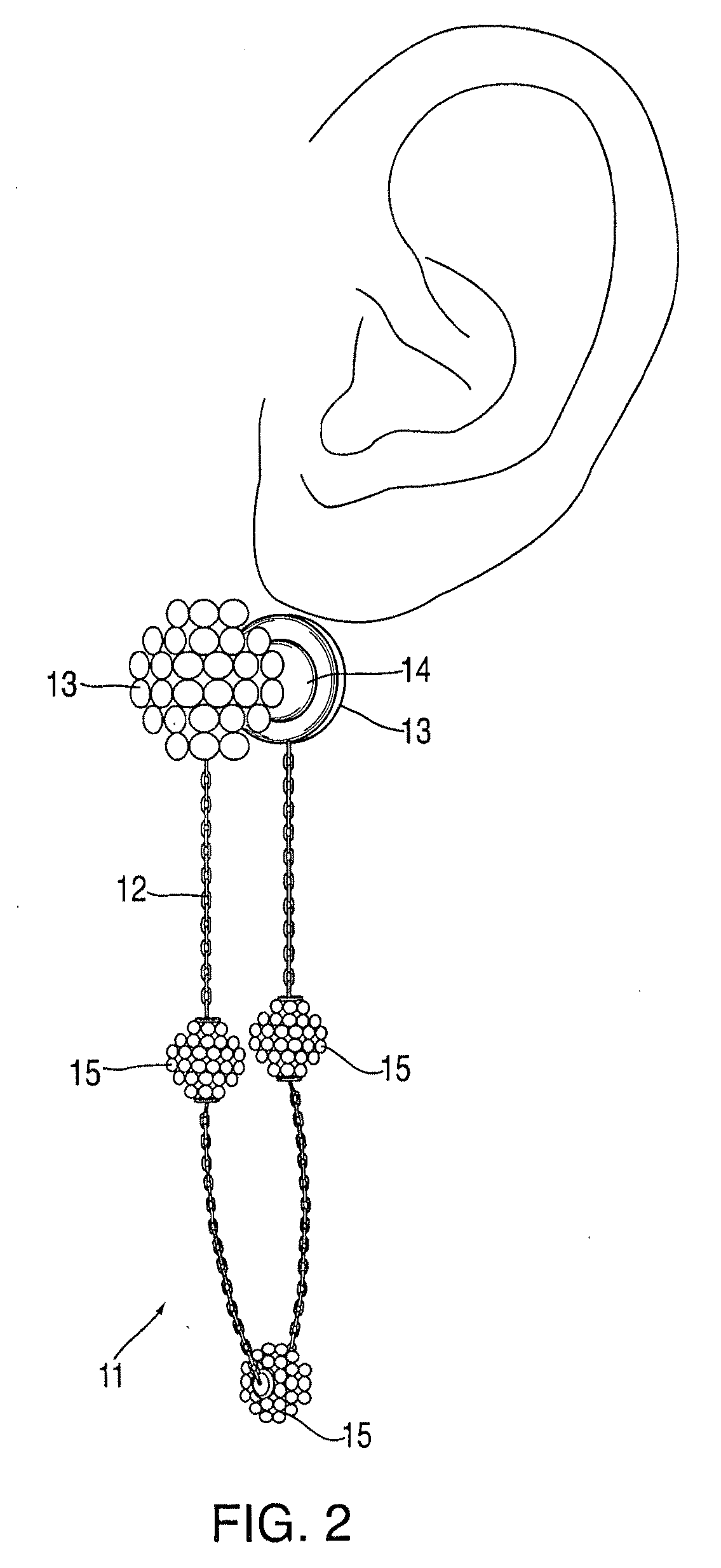
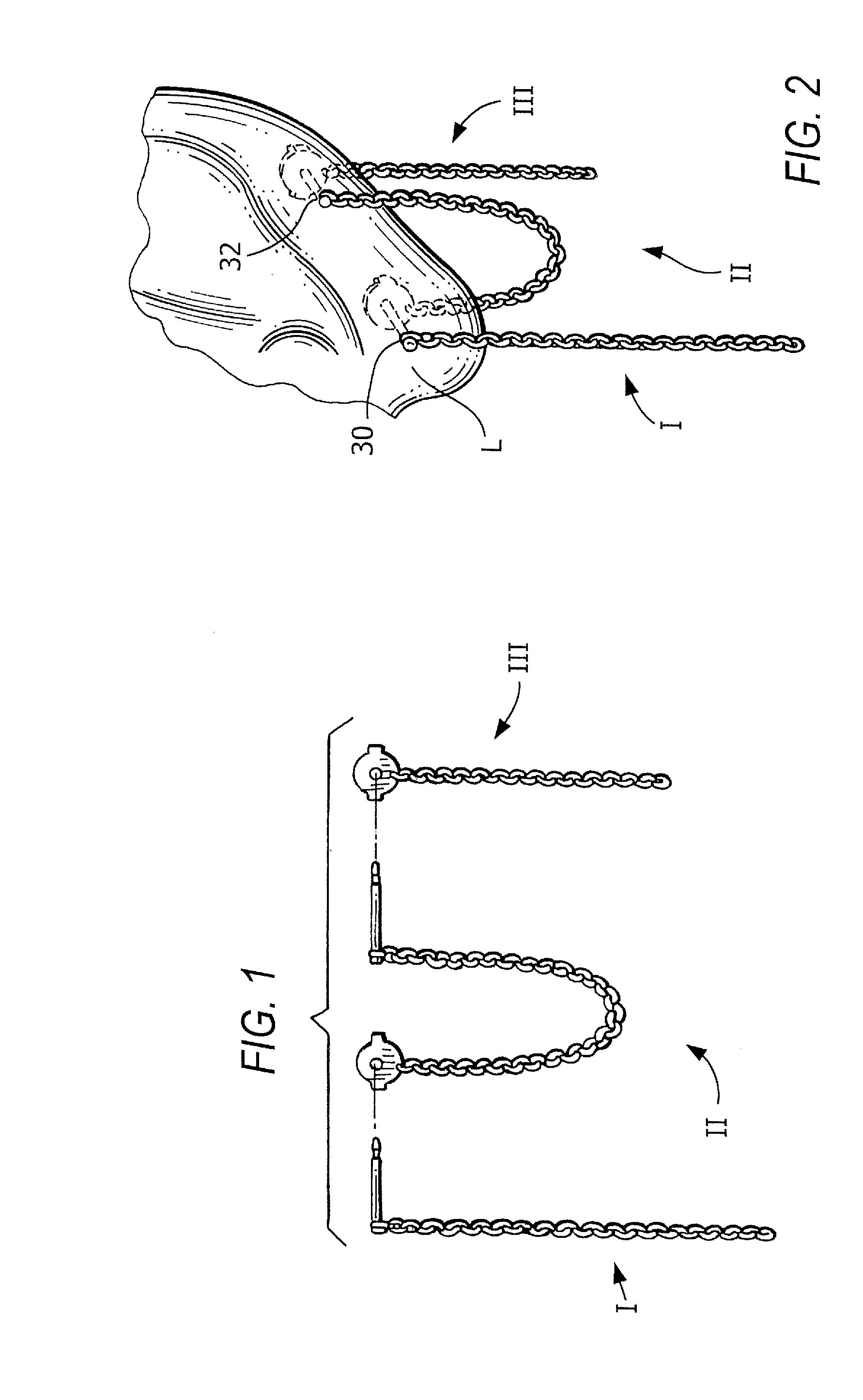
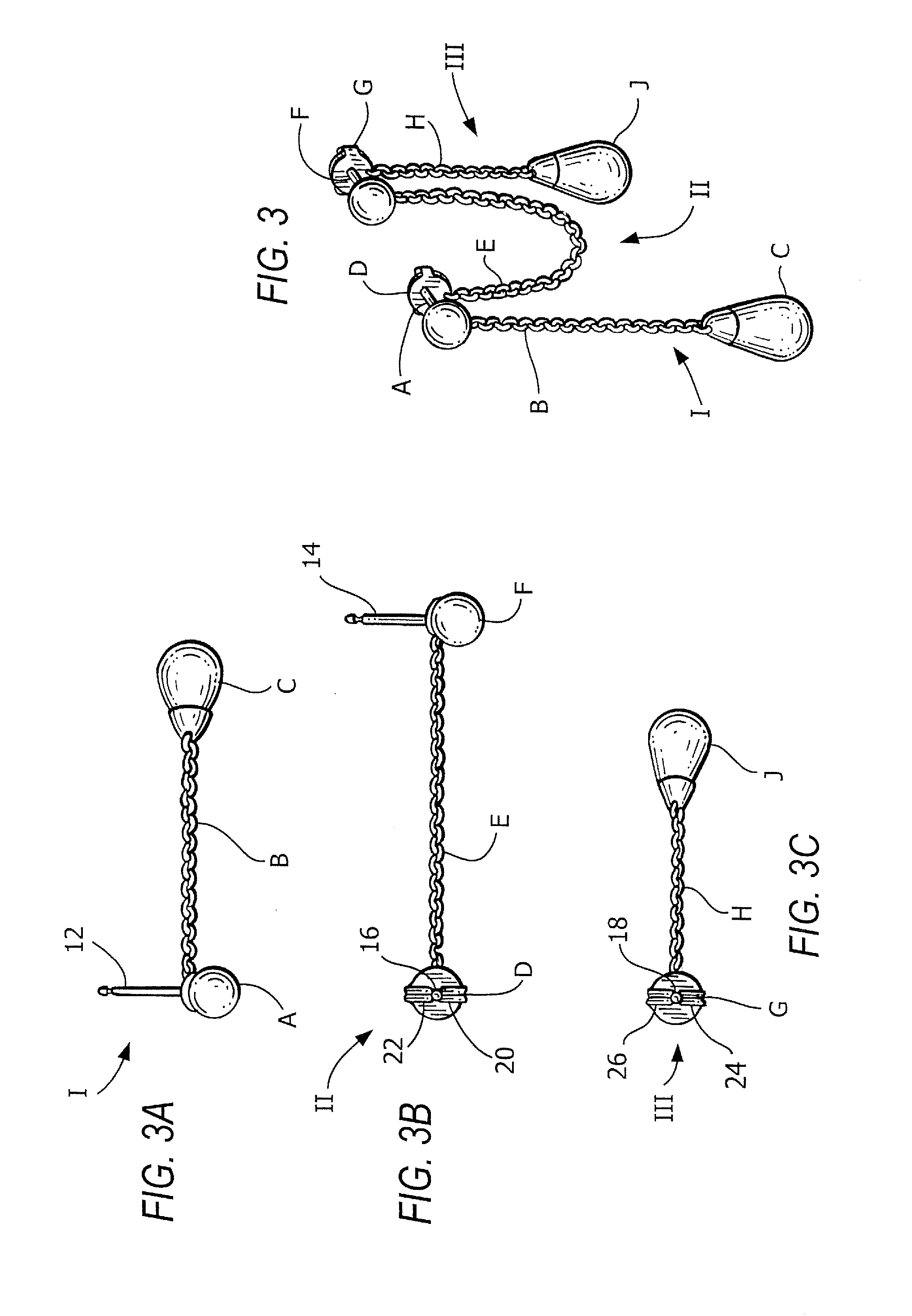
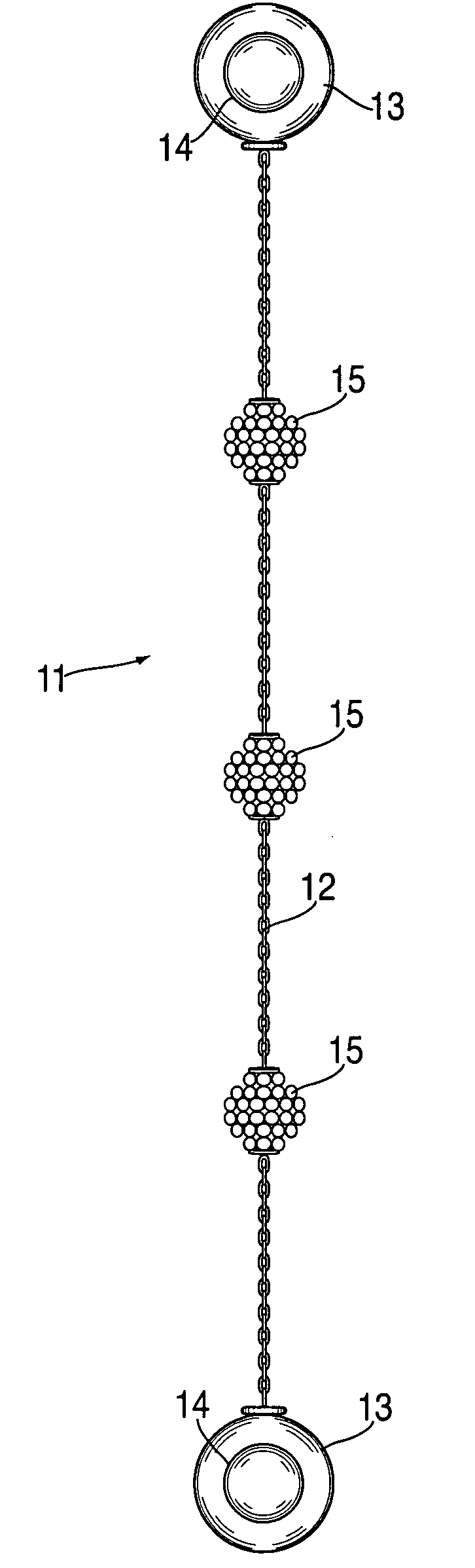
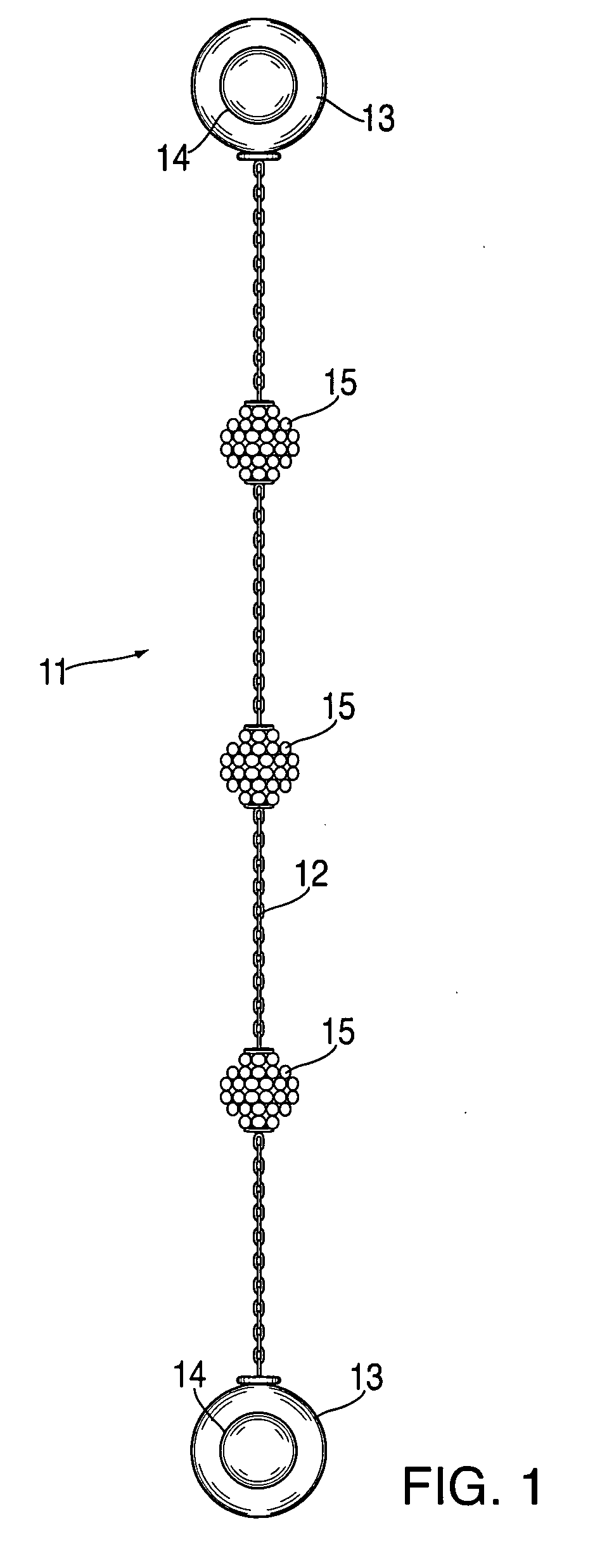
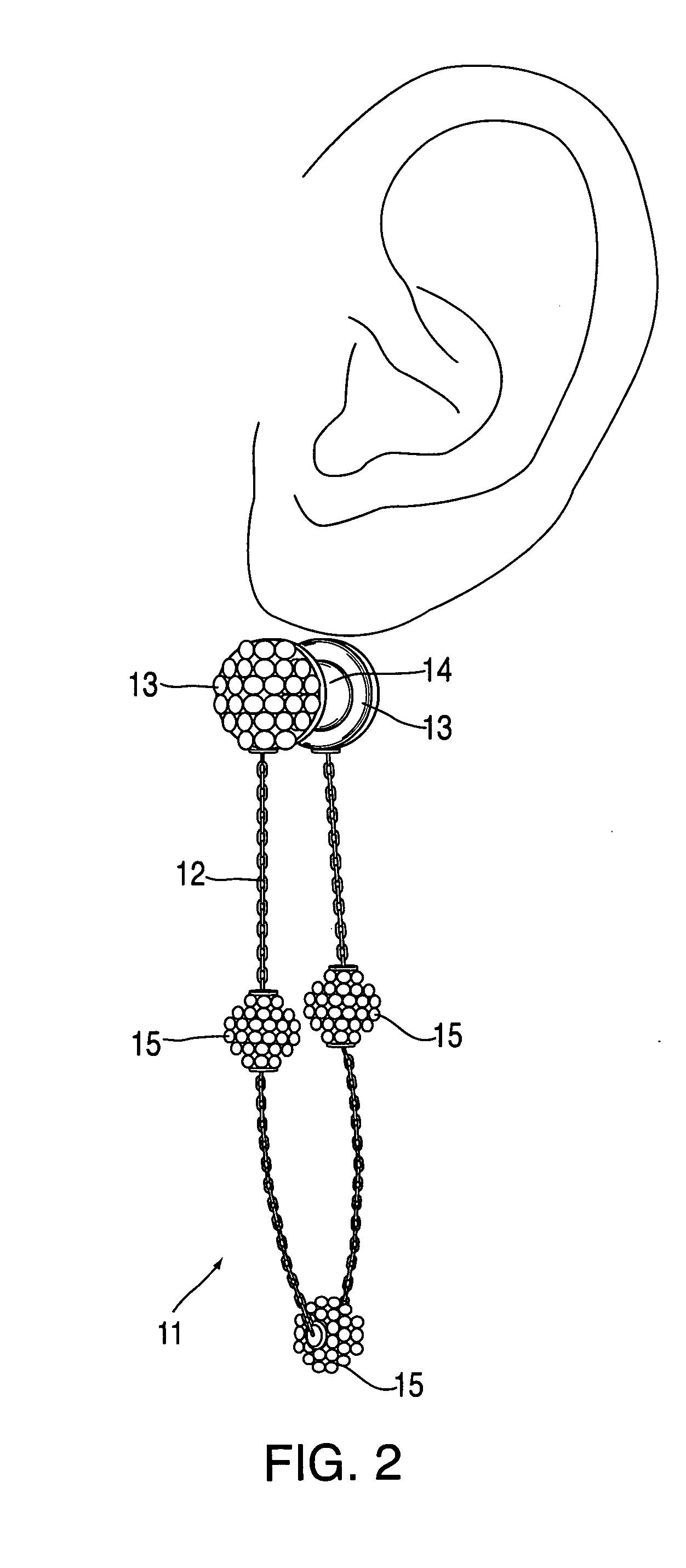
Interchangeable jewelry item
An earring that is convertible to a bracelet and vice versa is provided. The design comprises a chain of any type with magnetic clasps affixed at either end. Each earring may be attached to a person's ear lobe by using the magnetic elements in each clasp—the magnet elements attract one another when each clasp is fixed on either side of the earlobe. Alternatively, the two earrings can be coupled together in order to form a bracelet. Corresponding clasps from each of the earrings are mated together (via their internal magnets) in order to form a pair of decorative globes.
Owner:AYA INT
Quasi-triangular in-ear device
InactiveUS20110155147A1Comfortably fit a wide variety of wearersHearing aid design aspectsNon-occlusive ear tipsConvex sideEngineering
The in-ear device is shaped to fit a wearer's ear morphology. The device includes a main body having at least three generally convex sides, an innermost face and an outermost face. A first side is shaped to fit the tragus of a wearer's ear, and a second side is shaped to fit an antitragus of a wearer's ear. At least three tips, generally rounded, join respective two adjacent sides. The main body is within an outer ear plane substantially perpendicular to an entrance of an ear canal of a wearer's ear.
Owner:SONOMAX TECH INC
Ear-attaching type electronic device and biological information measuring method in ear-attaching type electronic device
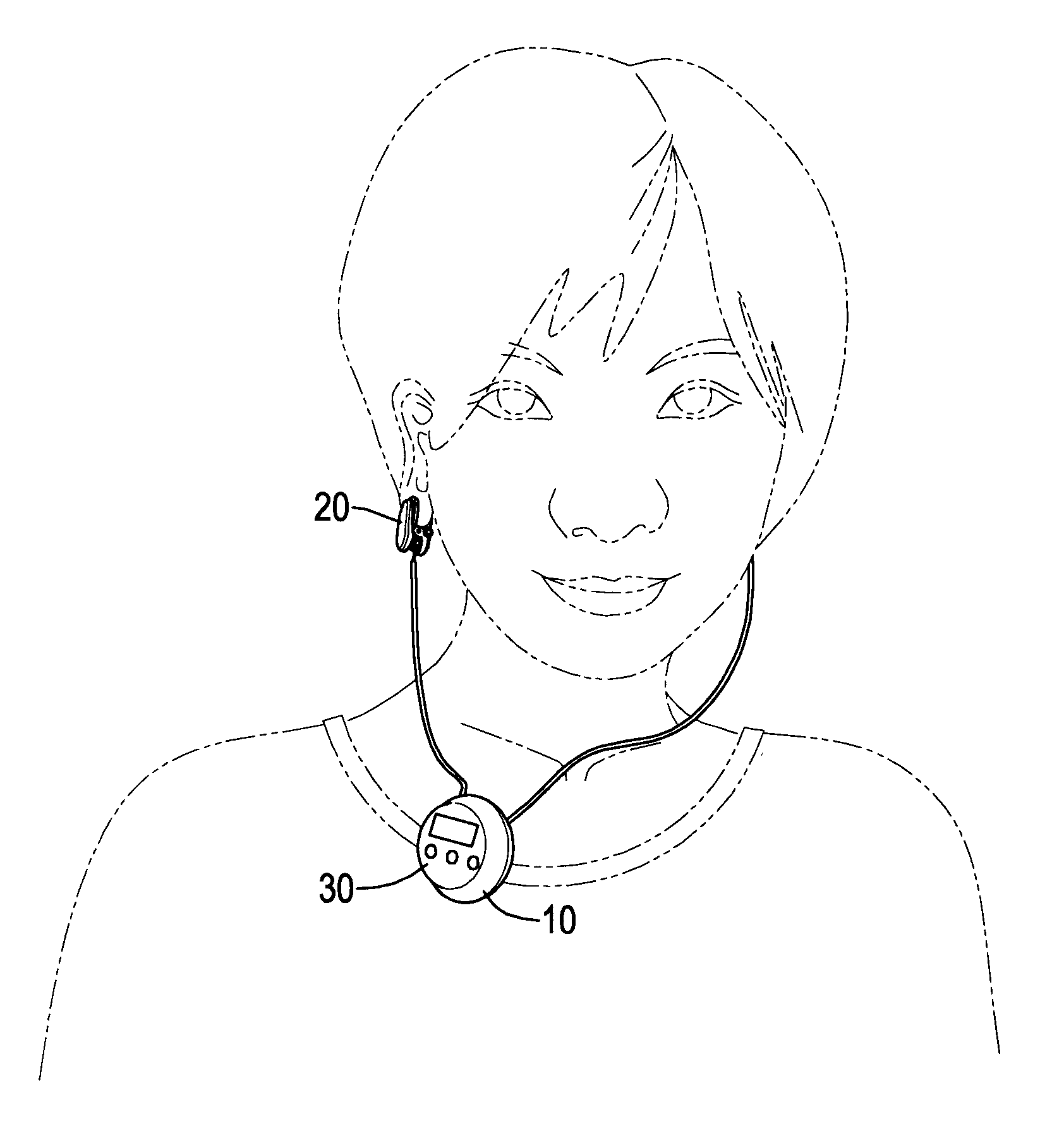
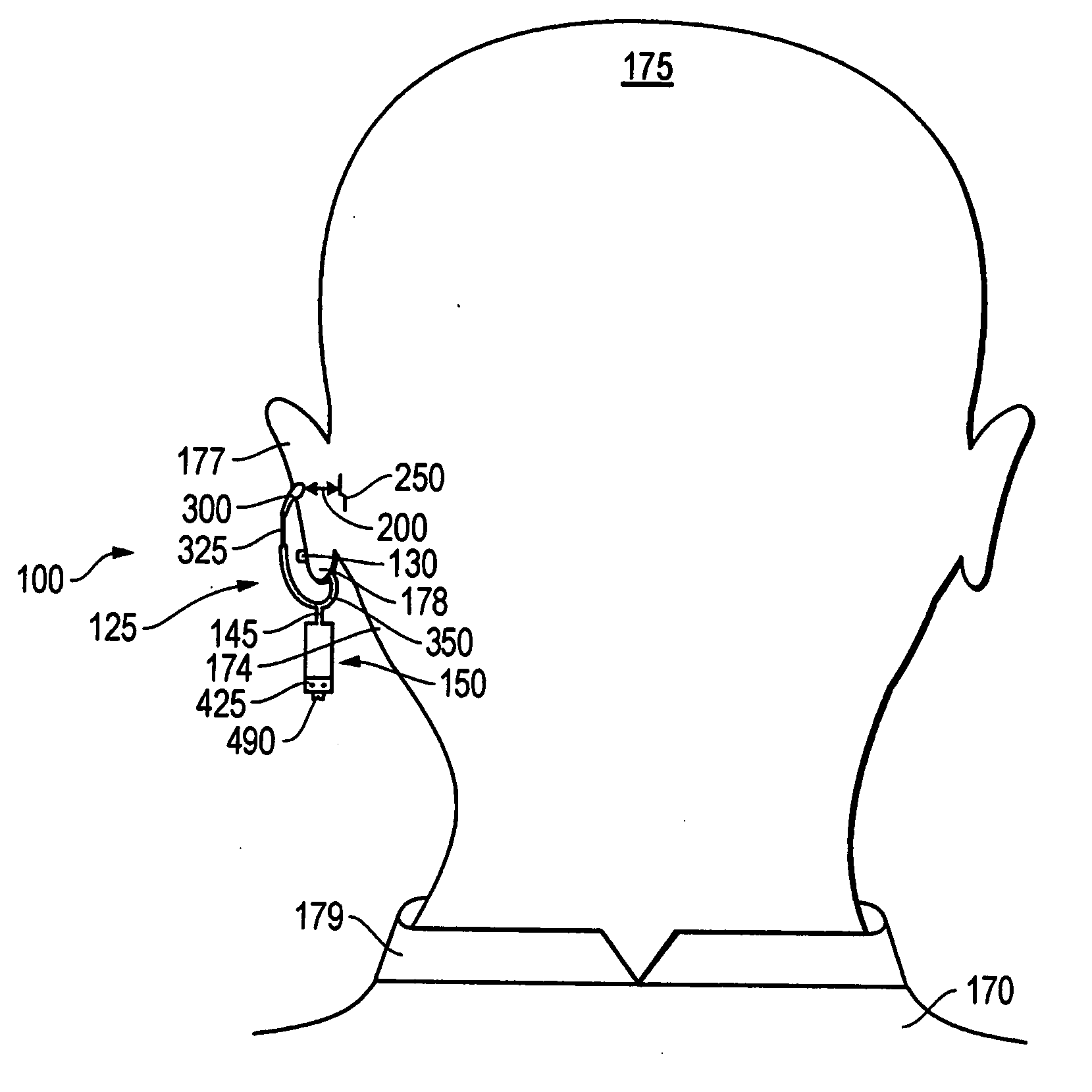
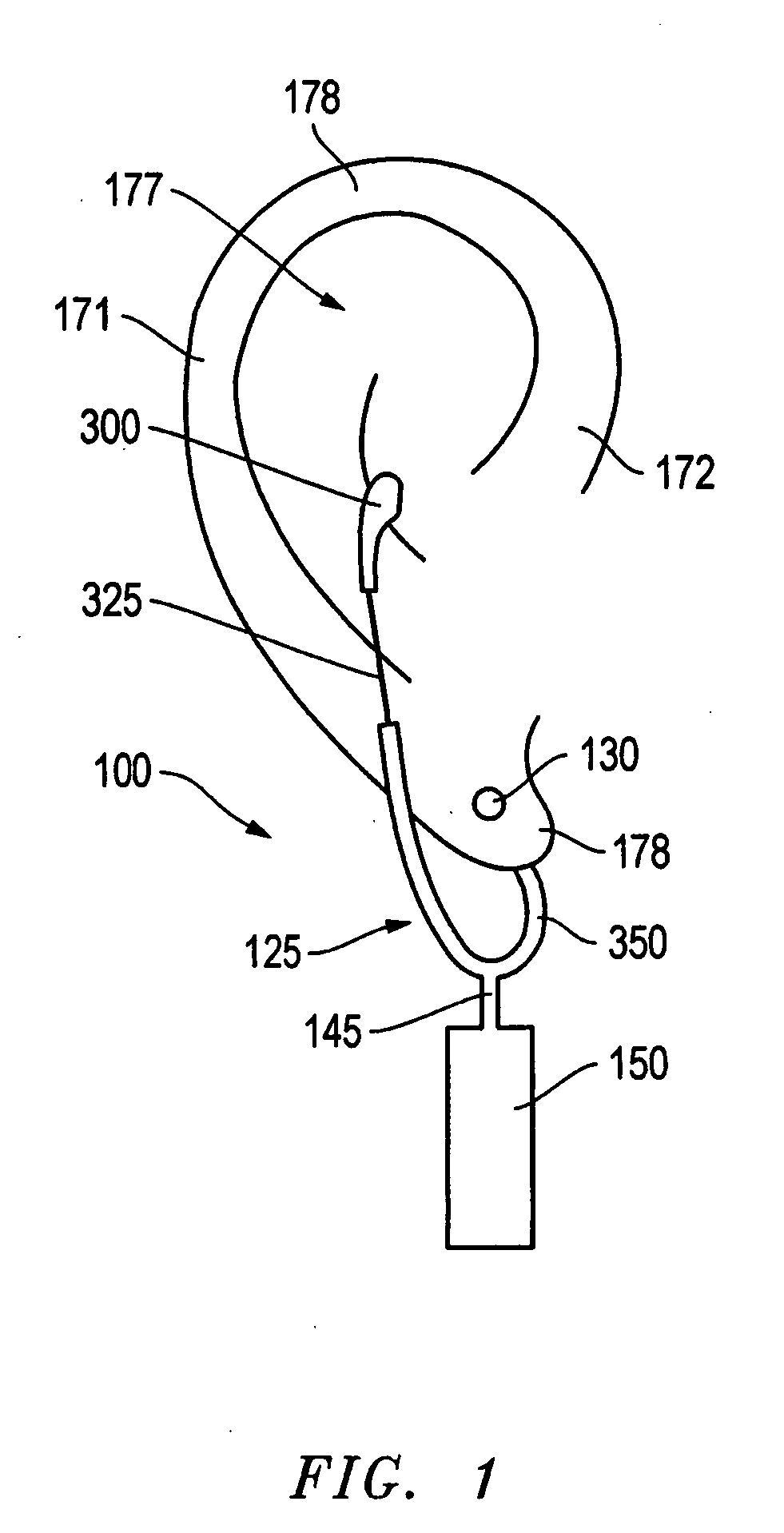
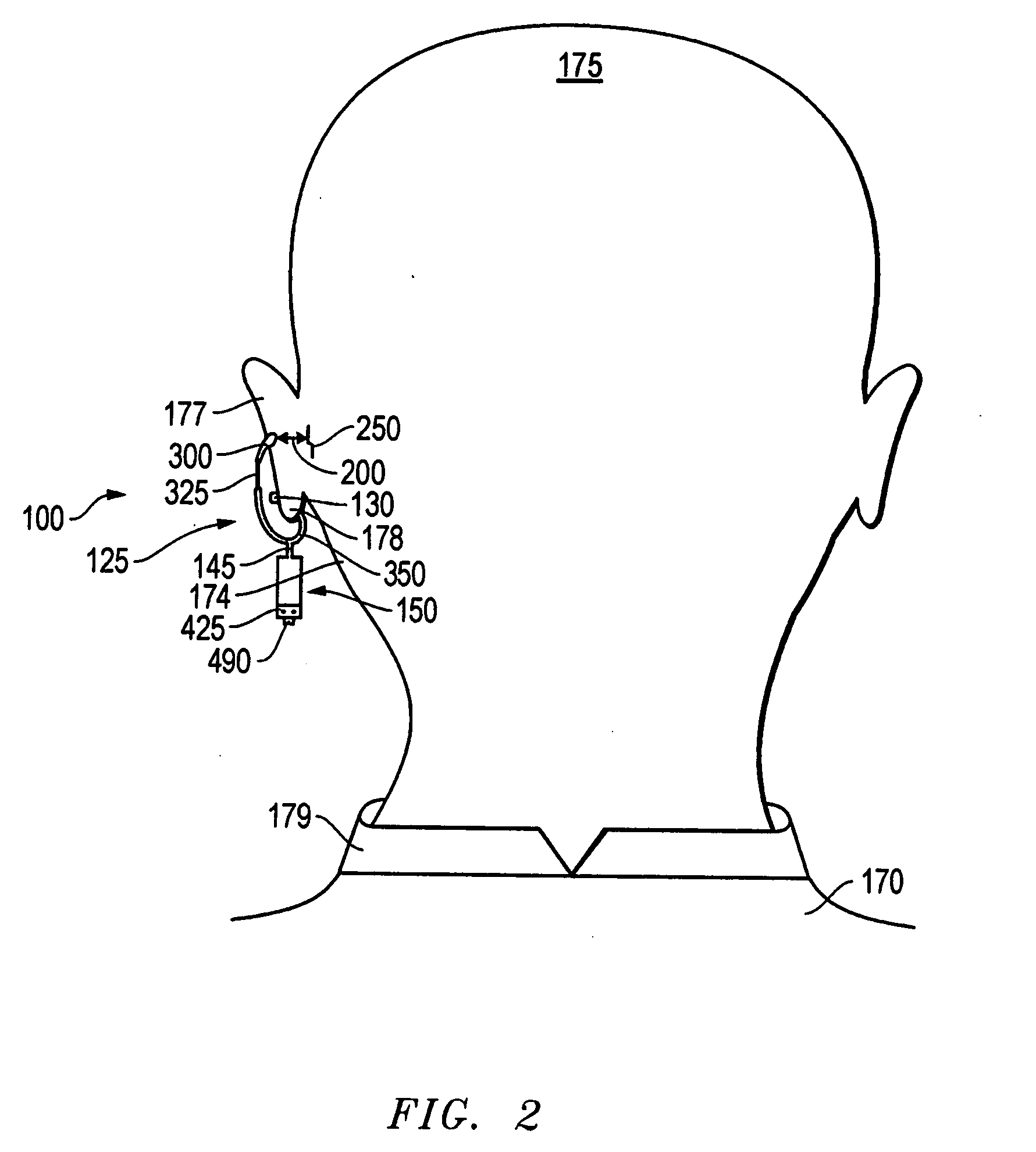
An ear-attaching type electronic device includes: a body part supported in a vicinity of a lower part of an occipital part when the device is attached; a pair of arm parts extending from the body part, to which a connecting member is placed therein; and a pulse sensor section for detecting pulse by being attached to an earlobe, wherein advice is outputted according to a comparison between a detected pulse rate and a previously-set pulse rate range.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
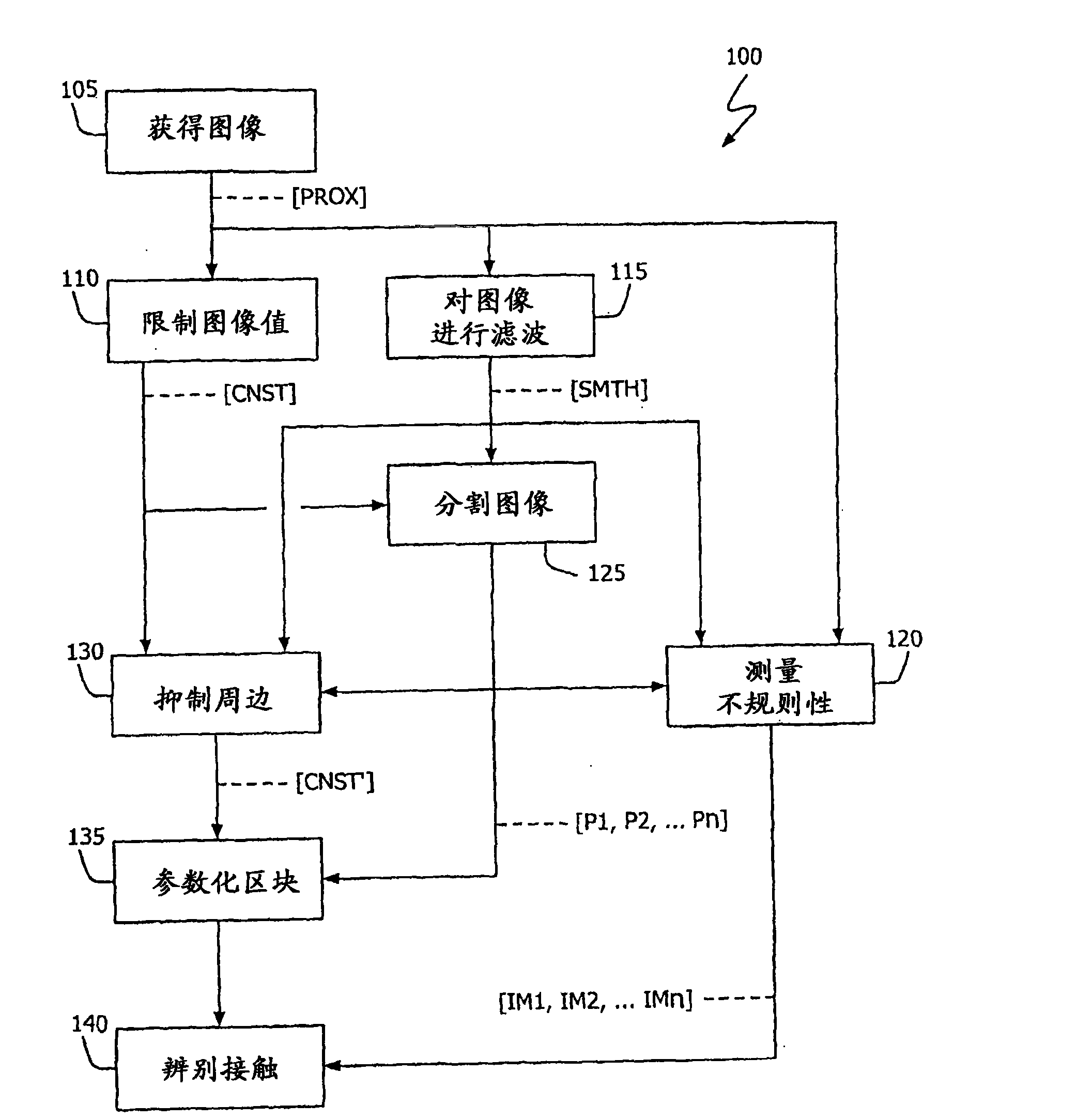
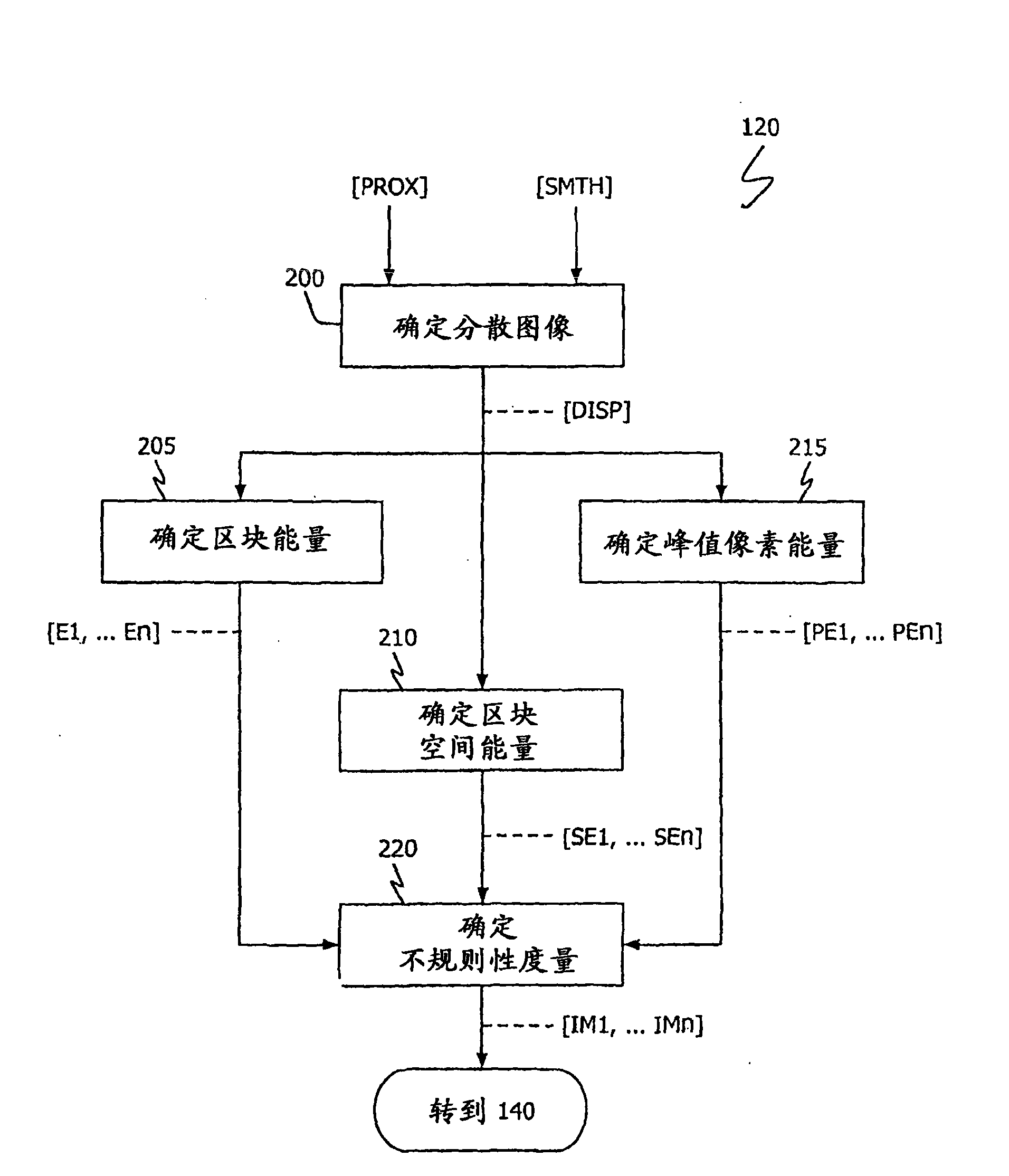
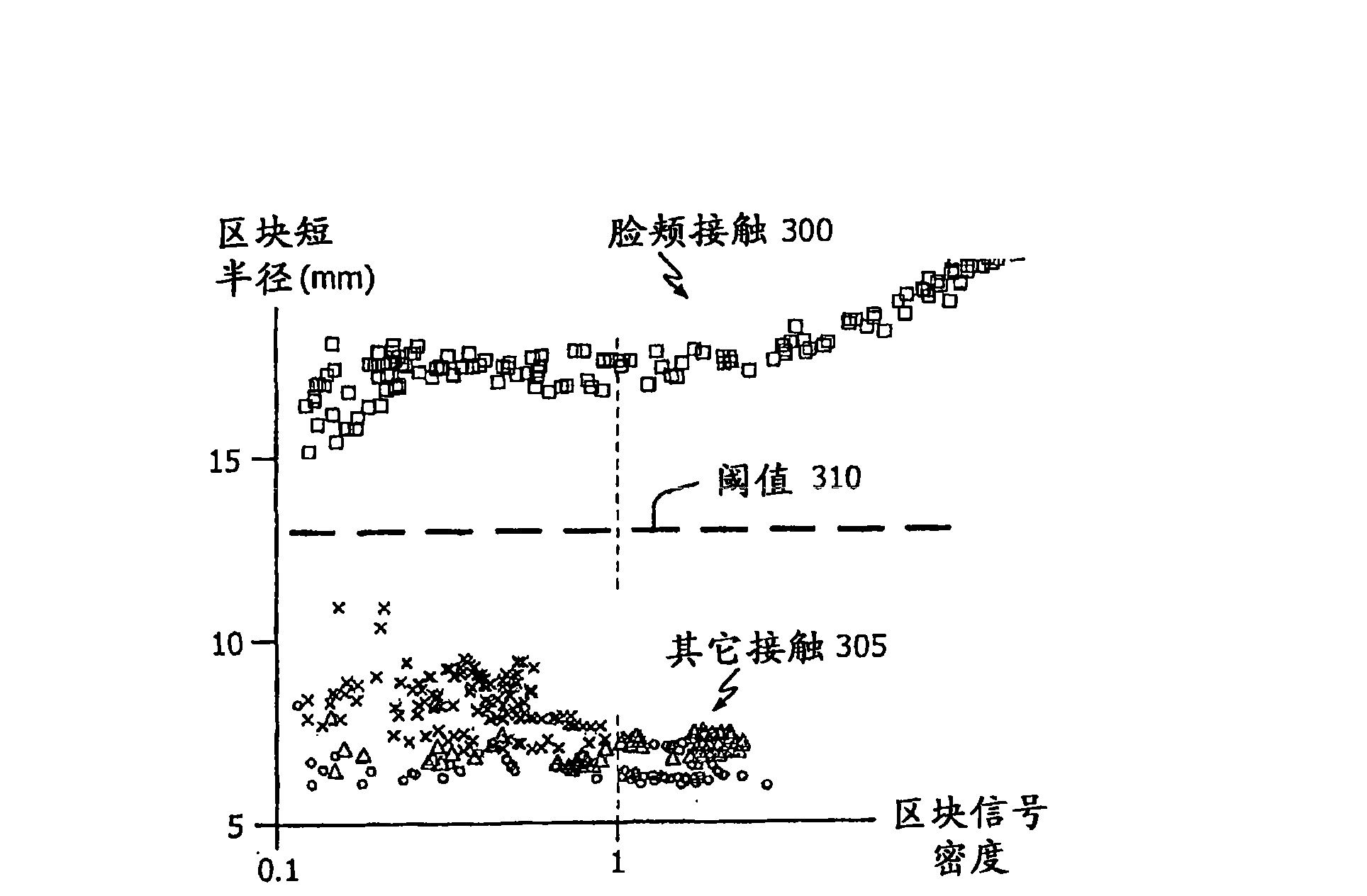
Multi-touch input discrimination
ActiveCN101583924ACharacter and pattern recognitionInput/output processes for data processingThighShortest distance
Techniques for identifying and discriminating between different input patterns to a multi-touch touch-screen device are described. By way of example, large objects hovering a short distance from the touch-surface (e.g., a cheek, thigh or chest) may be identified and distinguished from physical contacts to the surface. In addition, rough contacts due to, for example, ears and earlobes, may be similarly identified and distinguished from contacts due to fingers, thumbs, palms and finger clasps.
Owner:APPLE INC
Single earring set for double pierced ears
An earring assembly for doubled pierced ear is provided. The assembly includes a first element comprising a first linkage, a middle element comprising a second linkage and third element comprising a third linkage. The first linkage of the first element has first and second ends. Similarly, the second linkage of the middle element has first and second ends and the third linkage of the third element has first and second ends. Corresponding ends of the linkages are attached utilizing post and back mating connections in order to attach the earring assembly to a wearer's earlobe.
Owner:CICCONE GERALD A
Supporting earring along root of ear
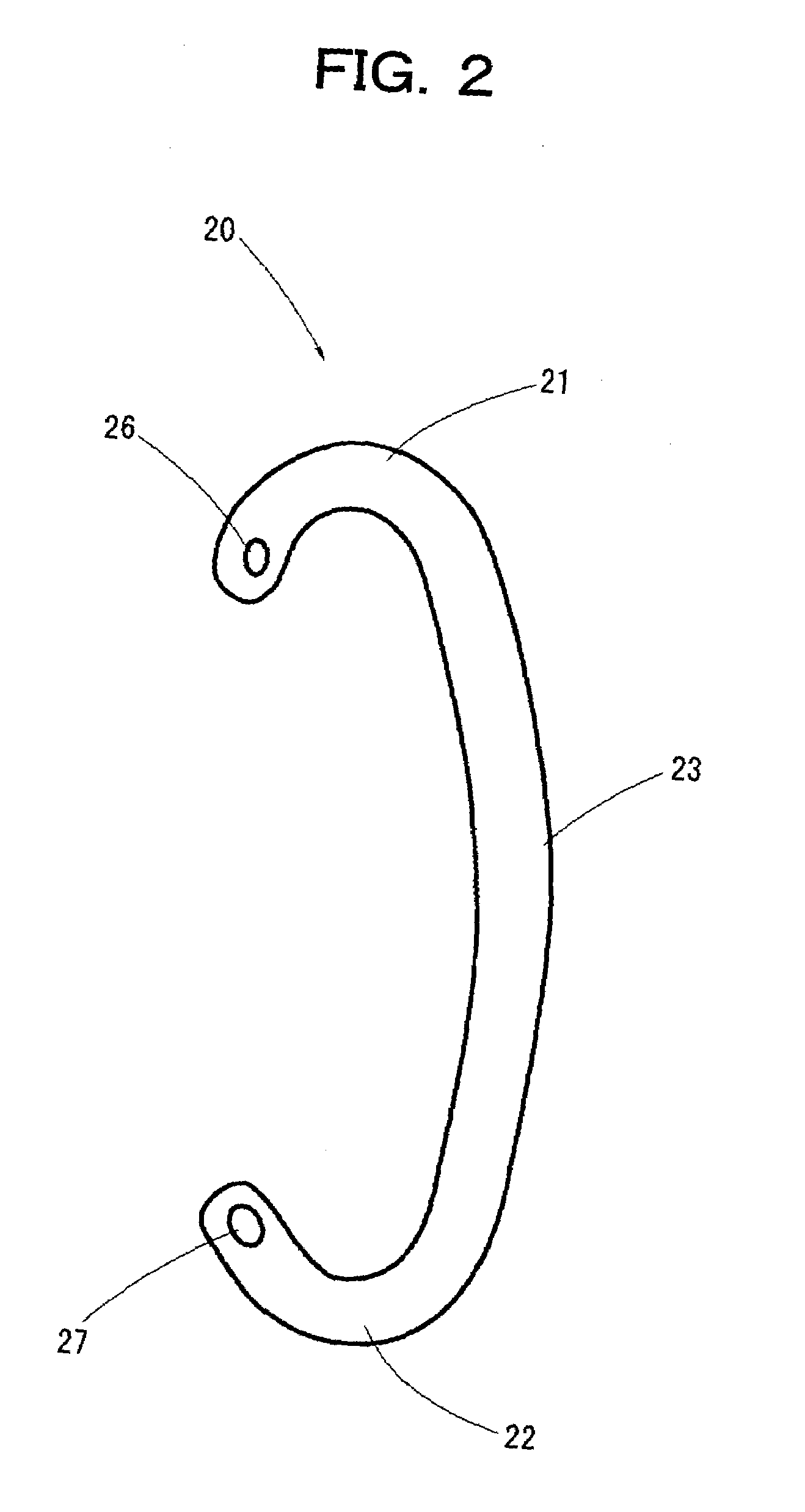
An earring that can be easily put on an ear without coming off during a use thereof and causes no pains in the earlobe of the ear is provided. Moreover, the earring can give a gorgeous decorative feeling. The earring includes a supporting portion formed in a shape of a letter C to be put along a root of a human ear and a decorative body provided at an end of the supporting portion, wherein one end of the supporting portion is caught by an upper end of the ear, and a central part of the supporting portion abuts against a reverse side of the root of the ear. The decorative body is exchangeable.
Owner:NAMIKI TOSIKI
Interchangeable jewelry item
An earring that is convertible to a bracelet and vice versa is provided. The design comprises a chain of any type with magnetic clasps affixed at either end. Each earring may be attached to a person's ear lobe by using the magnetic elements in each clasp—the magnet elements attract one another when each clasp is fixed on either side of the earlobe. Alternatively, the two earrings can be coupled together in order to form a bracelet. Corresponding clasps from each of the earrings are mated together (via their internal magnets) in order to form a pair of decorative globes.
Owner:AYA INT
Wireless earring assembly
A wireless or “Bluetooth” earpiece assembly configured to physically contact a user substantially exclusively at an outer ear location of a user's ear when in use. For example, the outer ear location may be an ear lobe providing the assembly with an appearance of an earring. The assembly is configured to distribute a significant portion of its bulk away from the isolated location of a user's ear for long term user comfort without sacrifice of audio or communicational integrity. The wireless earpiece assembly simultaneously eliminates extraneous wiring in order to optimize the un-encumbering user-friendly advantages afforded by wireless technology.
Owner:RYANN WILLIAM FREDERICK
Device for providing tactile feedback for robotic apparatus using actuation
InactiveUS20140214206A1Avoid stackingEasy to replaceInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme controlEngineeringActuator
A haptic feedback system includes a transducer that presses an actuator against an operator's skin with a force corresponding to a sensed parameter. Embodiments provide a simulated sense of touch corresponding to actual interactions between a robotic system and an environment. In other embodiments, the sensed parameter is heat, magnetic field, radioactivity, or electromagnetic field strength. A sensing system generates a signal that is proportional to the sensed parameter, and a controller proportionately manipulates a mechanical linkage or a fluid pressure supplied to the transducer. The transducer can be attached by a band, wrap, or other mechanism anywhere on the operator's body, such as a wrist, ankle, or frontal or occipital bone. An actuator movement range can be adjustable without opening the device. In embodiments, the pressure transducer includes a pair of elements that press an ear lobe or other skin of the operator there between.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE SURGICAL INSTR
Bone conduction receiver
InactiveCN1984505AComfortable to useImprove versatilityBone conduction transducer hearing devicesContact microphone transducersMedicineCoil spring
The subject of the invention is to provide a bone conduction receiver employing a bone conduction speaker which can be used without causing strange feeling even for a person wearing spectacles and when in use, can be fixed to an existing temple or end cover regardless of its shape. The bone conduction receiver comprises a bone conduction speaker (1), and a fixing means for fixing the bone conduction speaker (1) removably to the temple of spectacles, wherein the bone conduction speaker (1) is urged to abut constantly against a portion a little ahead of the earlobe when the spectacles are worn. The fixing means is a tube member (2) for receiving the temple of spectacles, and the bone conduction speaker (1) is urged when it is fixed to the shaft portion (4) secured to the vicinity of the temple insertion end of the tube member (2) through a helical torsion spring.
Owner:TEMCO JAPAN
Hearing aid with exchangeable shell parts and wireless communication
Hearing aid or audio device having a behind the ear part adapted to rest behind an earlobe of a user and a speaker unit comprising a speaker, whereby the speaker unit is adapted for insertion into the ear of a user, and whereby electric leads are provided between the speaker unit and the behind the ear part, said leads having a connection part opposite the speaker unit for connection with a corresponding socket in the behind the ear part, wherein the exterior and visible parts of the behind the ear part are defined by a generally U-shaped shell element, a battery drawer and a microphone cover plate characterized in that all further inside parts of the behind the ear part are interconnected to form a single sub-assembly and in that said sub-assembly is releasably coupled to the U-shaped shell element between two upright walls thereof by latch-locks provided to interact between the microphone cover plate and the upright wall elements
Owner:OTICON
Earring support device
InactiveUS6925838B1Minimize discomfortEasy to placeBraceletsWrist-watch strapsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An earring support device, or finding, which is inserted through a substantially horizontal piercing in the user's earlobe and from which an earring ornament is suspended. A horizontal straight center section of the support is provided to correspond with the piercing of the earlobe and minimize discomfort from the weight of the ornament. The device has two downward portions curvedly attached to, and, suspended, from each end of the horizontal section. One downward portion has a loop at its end to suspend an ornament. The other downward portion is inclined inwardly to hold the support in place.
Owner:CARMACK JACQUELINE M
Wireless earring assembly
A wireless earpiece assembly configured to physically contact a user substantially exclusively at an outer ear location of a user's ear when in use. For example, the outer ear location may be an ear lobe providing the assembly with an appearance of an earring. The assembly is configured to distribute a significant portion of its bulk away from the isolated location of a user's ear for long term user comfort without sacrifice of audio or communicational integrity. The wireless earpiece assembly simultaneously eliminates extraneous wiring in order to optimize the un-encumbering user-friendly advantages afforded by wireless technology.
Owner:RYANN WILLIAM FREDERICK
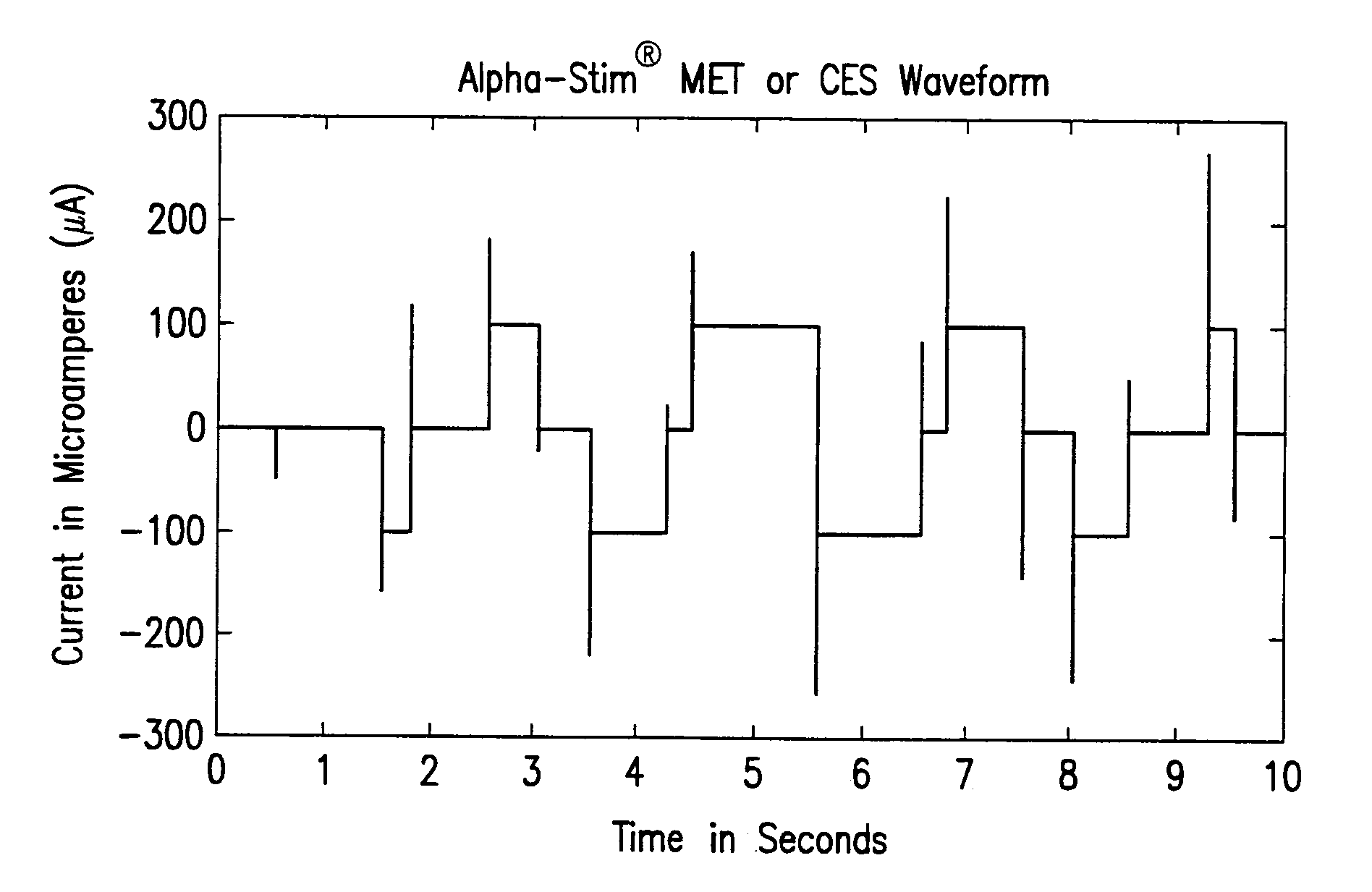
Microcurrent and cranial electrotherapy stimulator for control of anxiety, insomnia, depression and pain
ActiveUS8612008B2Improve performanceAssures electrical safetyElectrotherapyStress-related disordersClinical psychology
Owner:ELECTROMEDICAL PRODS INT
Electroencephalogram-based wearable anti-fatigue intelligent monitoring and pre-warning system for driver
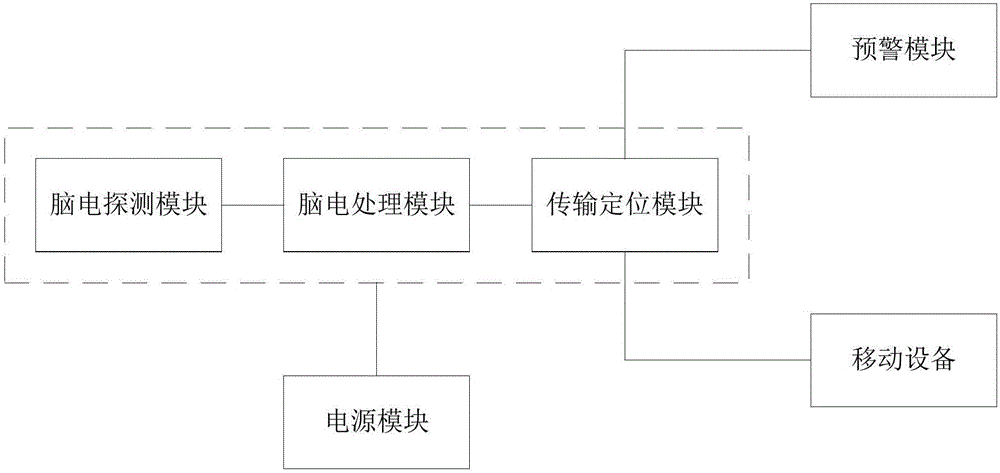
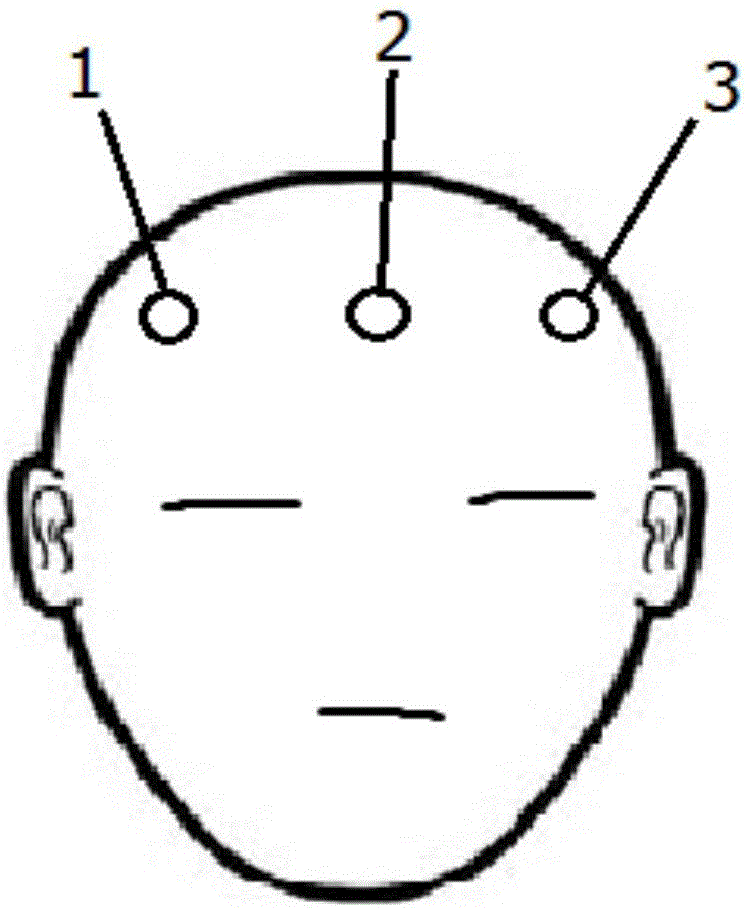
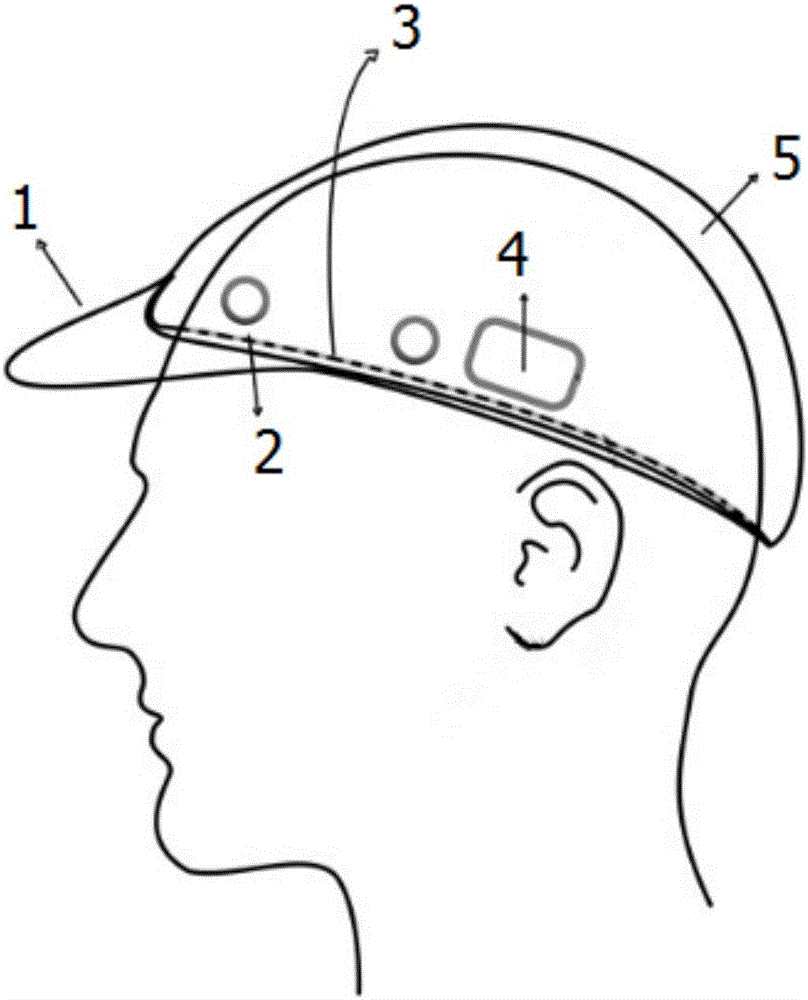
ActiveCN106691443ADoes not affect daily driving operationReduce volumeSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringElectroencephalogram featureTraffic accident
The invention discloses an electroencephalogram-based wearable anti-fatigue intelligent monitoring and pre-warning system for a driver. The electroencephalogram-based wearable anti-fatigue intelligent monitoring and pre-warning system is characterized in that when a driver drives, self-developed wearable electroencephalogram detecting equipment is used to detect the electroencephalogram features of the driver, a specific fatigue algorithm is provided, whether the driver is in a fatigue state or not or has a fatigue trend or not is monitored precisely in real time, timely pre-warning can be performed, and traffic accidents caused by fatigue driving can be prevented effectively. The system has the advantages that the system is high in precision, good in timeliness, capable of effectively preventing the traffic accidents caused by the fatigue driving, high in practicality and promising in prospect; the used wearable cap structure is small in size, easy to wear and free of influence on the daily driving operation of the driver; the used electrode structure does not need to use the earlobe as the reference voltage, the driver does not need to wear an ear clip on the ear, and discomfort is avoided; false alarm and alarm failure are reduced effectively by the specific fatigue algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bilateral differential pulse method for measuring brain activity
InactiveUS7547284B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterPhase differencePulse characteristics
A method of measuring human brain activity includes the steps of simultaneously measuring pulses at two locations on a human subject that each receives blood from a different carotid artery that feeds a respective one of left and right hemispheres of the brain of the human subject, determining pulse characteristics from the measured pulses, and evaluating relative left and right hemisphere activity of the brain of the human subject based on the determined pulse characteristics. The method may use dual photoplethysmograhic blood pulse sensors that measure left and right hemisphere activity by determining pulse amplitude difference and time or phase differences between the earlobes while the subject carries out various mental functions. The data from the sensors are processed to provide a measure of brain function and the mental activity of the subject.
Owner:ATLANTIS PARTNERSHIP
Systems and methods for vital signs monitoring with ear piece
A vital signs monitoring system, the system including: (a) an ear device including: a curved body adapted to a shape of an ear, an upper end, a lower end, two opposite facing sides, a first side adapted to be proximal a skull and a second side adapted to be proximal an earlobe, the ear device including: (i) a temperature sensor adapted to sense a body temperature from a depression between a lower jawbone and skull; and (b) a control system, including a processor and a memory, configured and operable to control operation of the ear device, to collect signals received from at least one sensor including the temperature sensor, to process the signals to provide medically significant results.
Owner:G MEDICAL INNOVATIONS HLDG LTD
Devices and methods for collecting and stabilizing biological samples
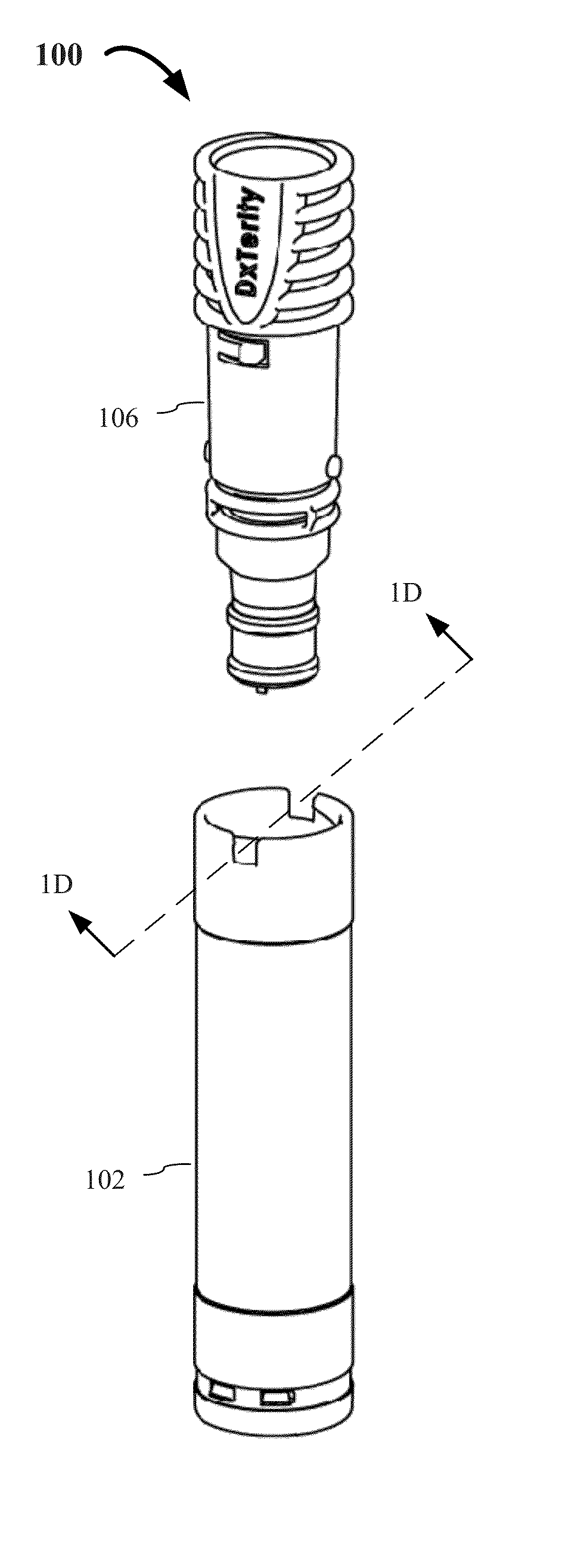
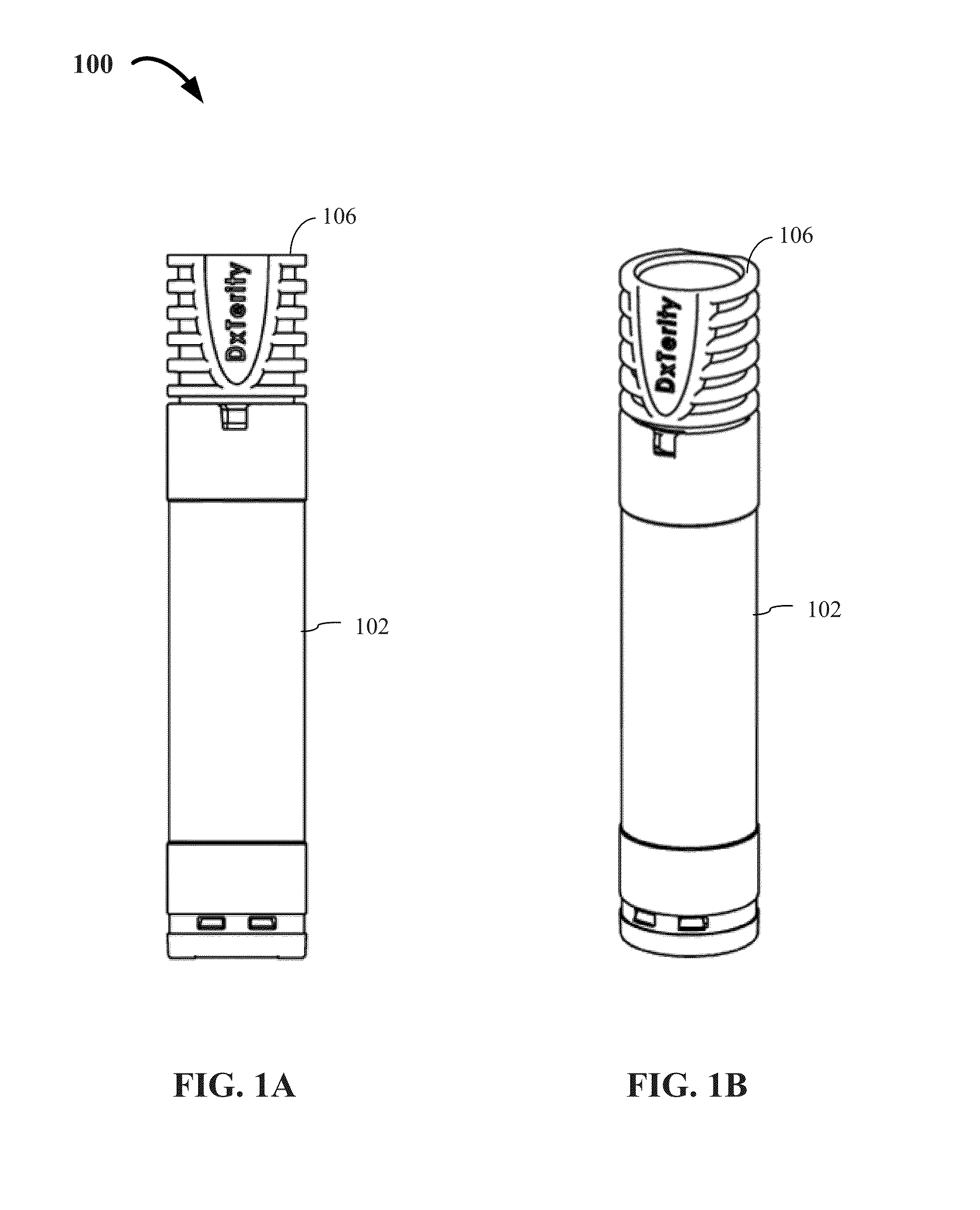
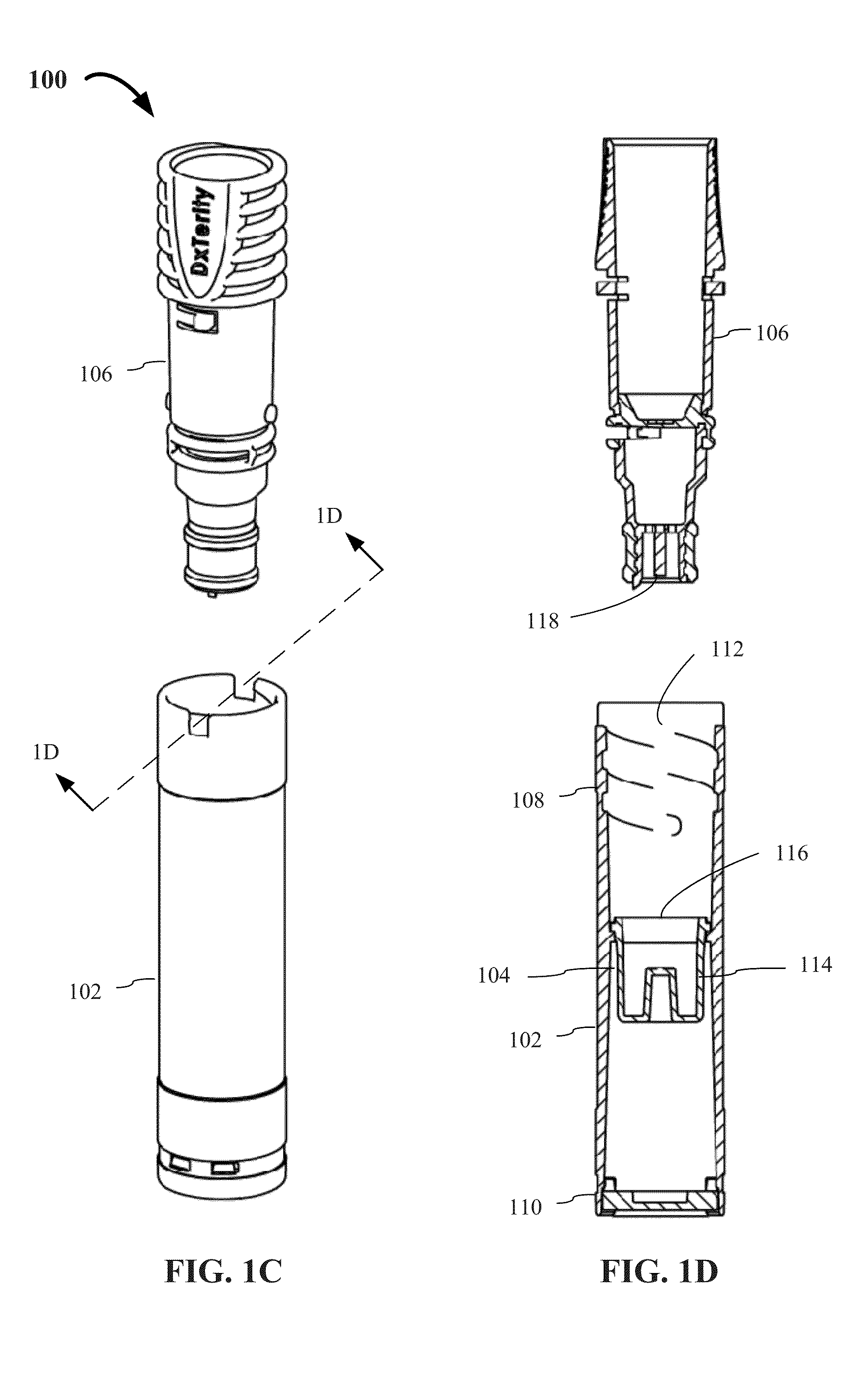
ActiveUS20160045187A1Simplify the collection processWell mixedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBody fluid
The present invention generally relates to devices and methods for collecting and stabilizing biological samples, and more particularly, for collecting and stabilizing blood or other bodily fluids from a user's fingertip, earlobe, heel or other locations. The present invention also relates to sample collection devices that simplify the process for mixing the biological samples with an additive or additives, provide for efficient storage and safe transport of the samples, and provide for easy access to the samples for subsequent processing.
Owner:DXTERITY DIAGNOSTICS
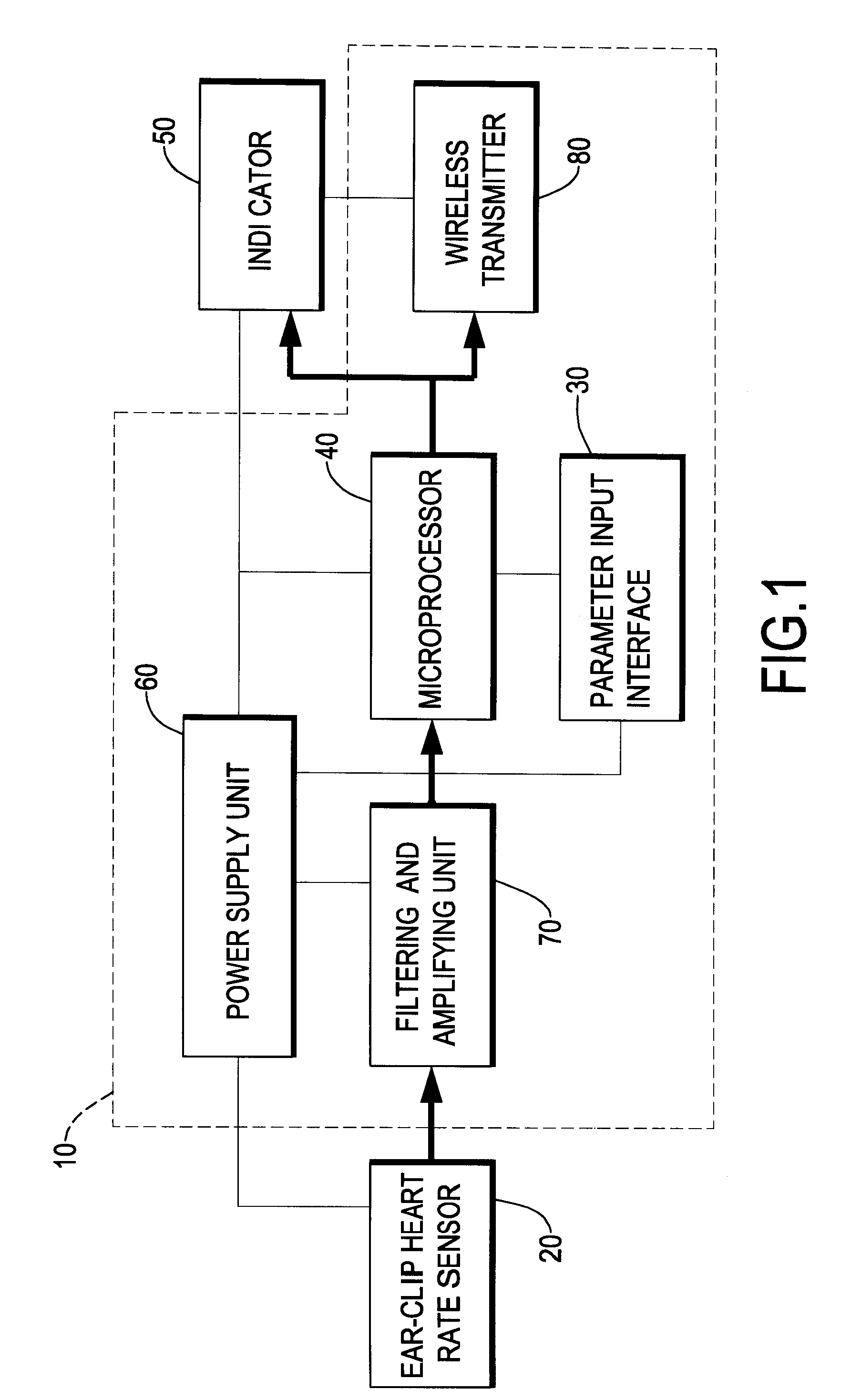
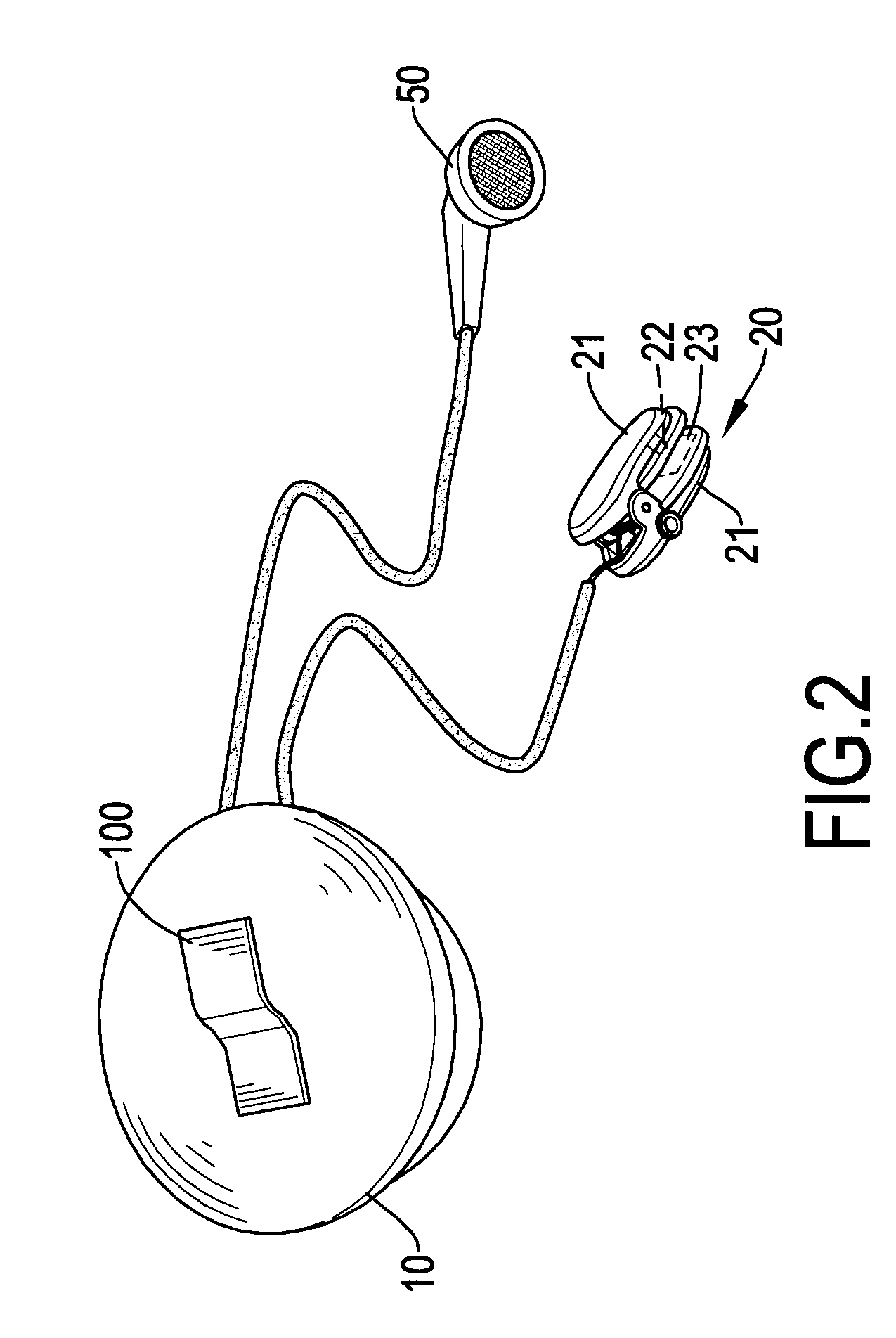
Exercise auxiliary device
The exercise auxiliary device comprises a body, a fastener, an ear-clip heart rate sensor, a microprocessor and an indicator. The fastener is mounted on the body for attaching the body to a garment on a user. The ear-clip heart rate sensor is adapted to clip an earlobe of the user, senses blood pulse from the earlobe and accordingly generates a voltage signal. The microprocessor is mounted in the body, electrically connected to the ear-clip heart rate sensor, computes an instantaneous heart rate according to the voltage signal. The indicator is connected to the microprocessor, controlled by the microprocessor to generate a reminding signal. The exercise auxiliary device can be easily worn by attaching the body to a garment of a user with the fastener and clipping an earlobe with the ear-clip heart rate sensor.
Owner:V TAC TECH
Device to enhance an ear bud
ActiveUS20110044463A1Enhance ear budSufficient pressureEar treatmentSubstation equipmentExternal Auditory CanalsBud
The present invention relates to a device to enhance an ear bud including a headband coupled to one or more ear pads. The ear pad being formed of a material for providing dampening of ambient sound and physiologic compression. For example, the pad can be formed of a visco-elastic foam having a thickness to provide noise reduction and sufficient comfort by avoiding excessive compression on any one part of the ear. The headband and the ear pad provide a force for compressing the tragus and antitragus to partially isolate the ear bud in the external auditory canal.
Owner:DIRUSSO GREGORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com