Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3514results about How to "Achieve mass production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
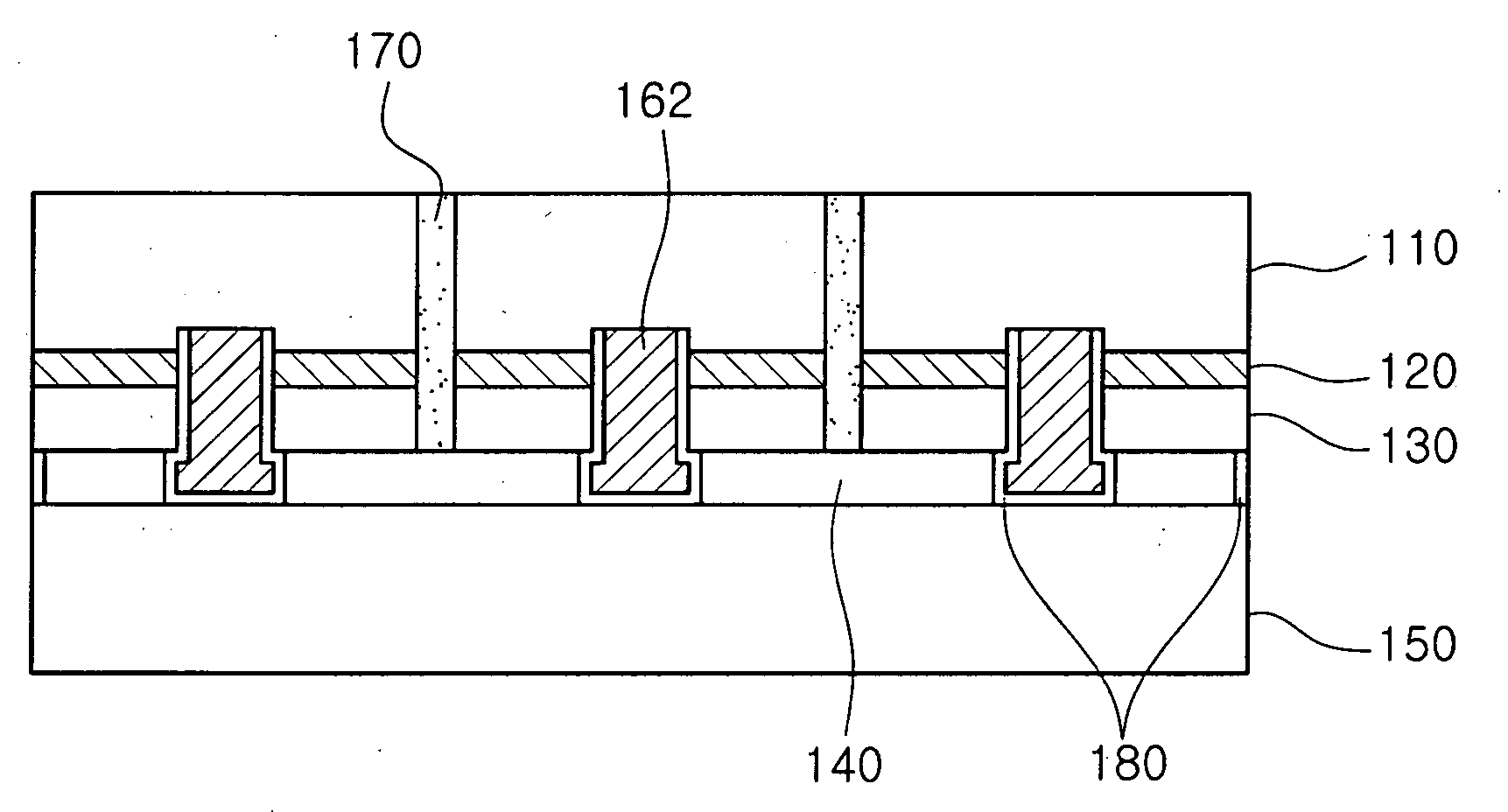
Light emitting device and package having the same
ActiveUS20080237622A1Minimize reflection and absorptionQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesActive layerLight emitting device
There is provided a light emitting device that can minimize reflection or absorption of emitted light, maximize luminous efficiency with the maximum light emitting area, enable uniform current spreading with a small area electrode, and enable mass production at low cost with high reliability and high quality. A light emitting device according to an aspect of the invention includes a light emitting lamination including a first conductivity type semiconductor layer, a second conductivity type semiconductor layer, and an active layer, and a conductive substrate at one surface thereof. Here, the light emitting device includes a barrier unit separating the light emitting lamination into a plurality of light emitting regions, a first electrode structure, and a second electrode structure. The first electrode structure includes a bonding unit, contact holes, and a wiring unit connecting the bonding unit to the contact holes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
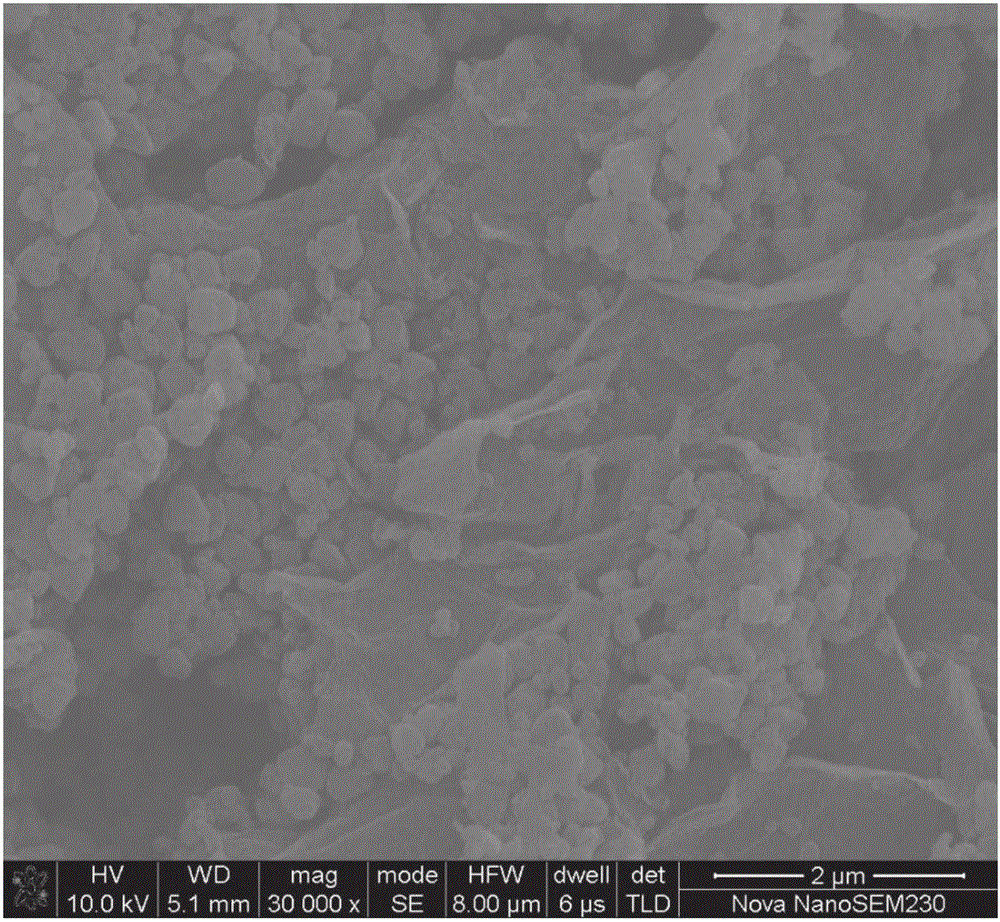
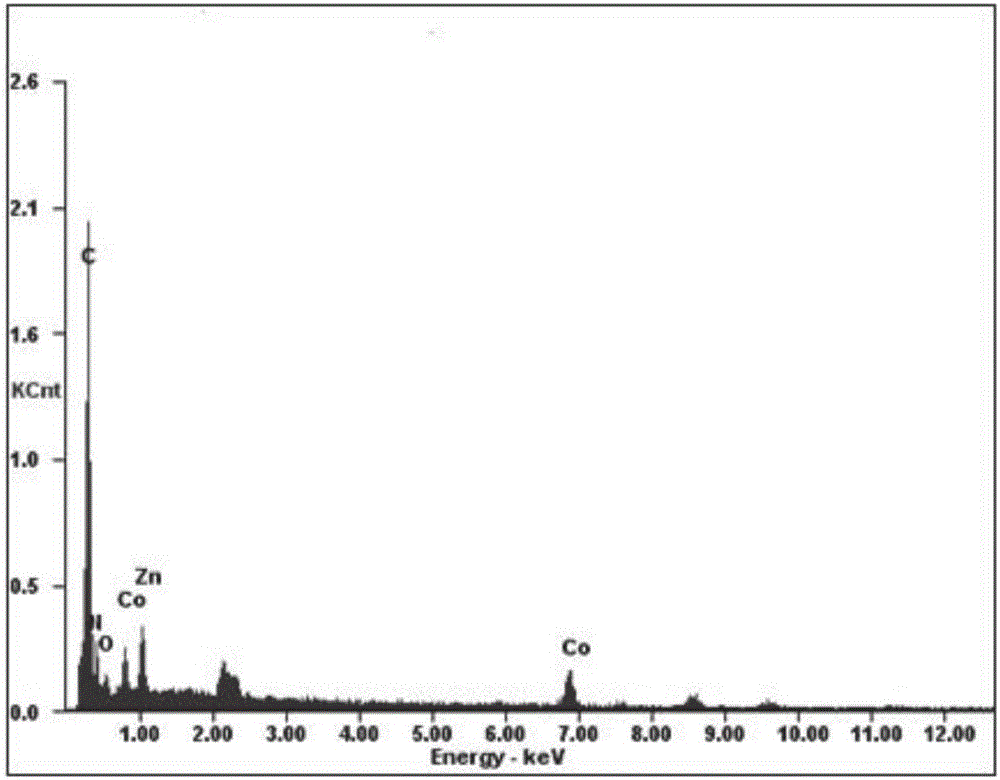
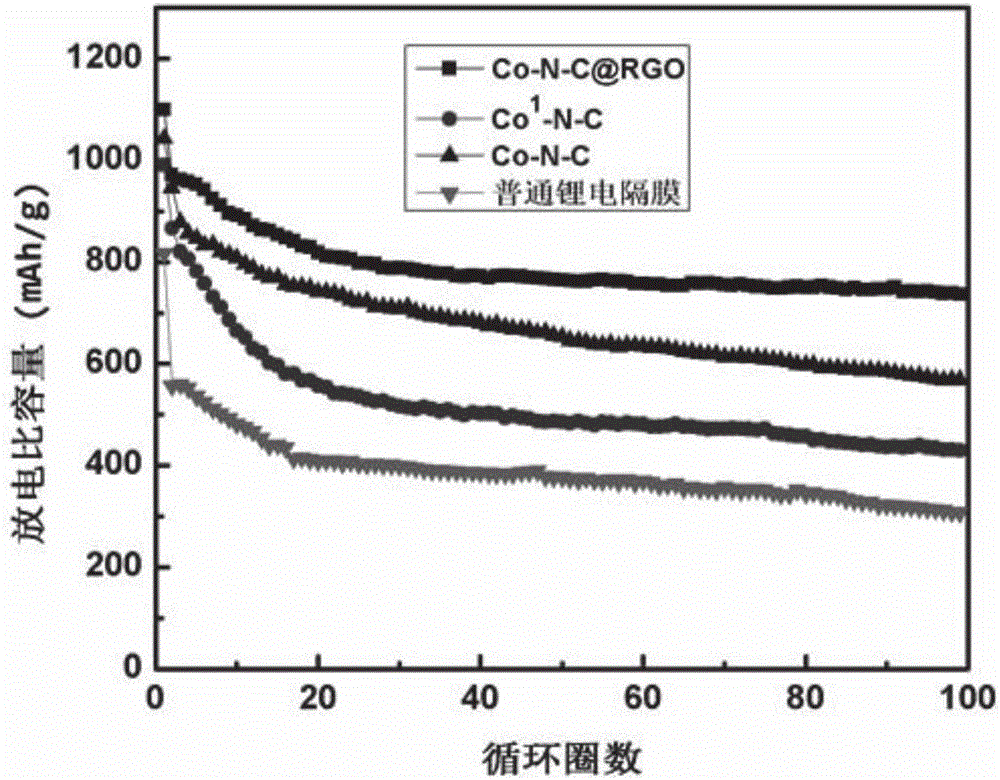
Co-N-C@RGO composite material, preparation method and application to modification of lithium-sulfur battery diaphragms
ActiveCN106784525AIncrease the areaHigh porosityLi-accumulatorsCell component detailsPorous carbonElectrical battery
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous carbon@graphene composite material by taking a bimetal organic framework material as a precursor and application to modification of lithium-sulfur battery diaphragms thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking zinc salt and cobalt salt in a certain ratio as the raw materials, synthesizing a zinc / cobalt-bimetal organic framework@graphene composite material through a room-temperature liquid phase method, taking the zinc / cobalt-bimetal organic framework@graphene composite material as the precursor, carrying out high-temperature reaction under inert atmosphere, pickling and drying to obtain a cobalt / nitrogen double-doped porous carbon@graphene (Co-N-C@RGO) composite material. Co-N-C@RGO has high conductivity; the specific surface area of Co-N-C@RGO reaches up to 750-1000m<2> / g; the content of Co is 2-4At%; the content of N is 10-20At%. When the material is applied to the modification of the lithium-sulfur battery diaphragms, the material has the function of obviously inhibiting polysulfide shuttle effect and is capable of greatly improving actual specific capacity and cyclic performance of the lithium-sulfur batteries; meanwhile, the raw materials needed for synthesizing the material are simple; the operation is convenient; the large-scale production can be achieved; the material has certain promoting effect on commercialization of lithium-sulfur battery systems.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method and apparatus for manufacturing group iii nitride crystals
InactiveUS20070215033A1Reduce defect densityAchieve mass productionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsAlkaline earth metalNitrogen
There is provided a group III nitride crystal growth method capable of obtaining a material which is a GaN substrate of low defect density capable of being used as a power semiconductor substrate and in which characteristics of n-type and p-type requested for formation of transistor or the like. A growth method of group III nitride crystals includes: forming a mixed melt containing at least group III element and a flux formed of at least one selected from the group consisting of-alkaline metal and alkaline earth metal, in a reaction vessel; and growing group III nitride crystals from the mixed melt and a substance containing at least nitrogen, wherein after immersing a plurality of seed crystal substrates placed in an upper part of the reaction vessel in which the mixed melt is formed, into the mixed melt to cause crystal growth, the plurality of seed crystal substrates are pulled up above the mixed melt.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Photosensitive resin combination and method of preparing quantum dot pattern from photosensitive resin combination
ActiveCN103728837ASimple preparation processFine graphicsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhotosensitive material processingPhotoresistQuantum dot
The invention discloses a photosensitive resin combination and a method of preparing a quantum dot pattern from the photosensitive resin combination. The photosensitive resin combination is prepared from quantum dots which are dispersed in the photosensitive resin combination and are respectively provided with a modified layer. The method of preparing the quantum dot pattern from the photosensitive resin combination comprises the steps: with the photosensitive resin combination as a photoresist, carrying out coating, exposure and development to obtain the quantum dot pattern. The method of preparing the quantum dot pattern from the photosensitive resin combination has the advantage of being simple, the fine graph, the boding stability of the combination and a substrate, the difficulty in abscission, the high resolution and the like can be achieved. In addition, with the adoption of the method, based on existing equipment, the mass production of the quantum dot pattern can be realized, and the application potential of the quantum dots is greatly improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Steel plate with low welding crack sensitivity and production method thereof
InactiveCN101096738AHigh strengthMeet the requirements of different site construction process conditionsRoll mill control devicesHeat treatment process controlChemical compositionSheet steel
The invention discloses a low-welding crack sensitivity steel board and manufacturing method, which comprises the following parts: not more than 0.07% C, 0.15-0.40% Si, 1.00-1.60% Mn, not more than 0.015% P, not more than 0.010% S, not more than 0.30% Cu, not more than 0.50% Ni, not more than 0.30% Cr, not more than 0.30% Mo, not more than 0.08% V, not more than 0.08% Nb, 0.010-0.020% Ti, not more than 0.003% B, Fe and inevitable impurity. The invention is characterized by the following: (1)displaying lower welding crack sensitivity component with Pcm not more than 0.20%; (2)mating the strength and flexibility reasonably with fitful yielding ratio; (3)making the price and property of the steel board superior to the congeneric import product; (4)making the maximum breadth of steel board to 4000mm; (5)simplifying the technique to ensure higher flatness without quenching water.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL
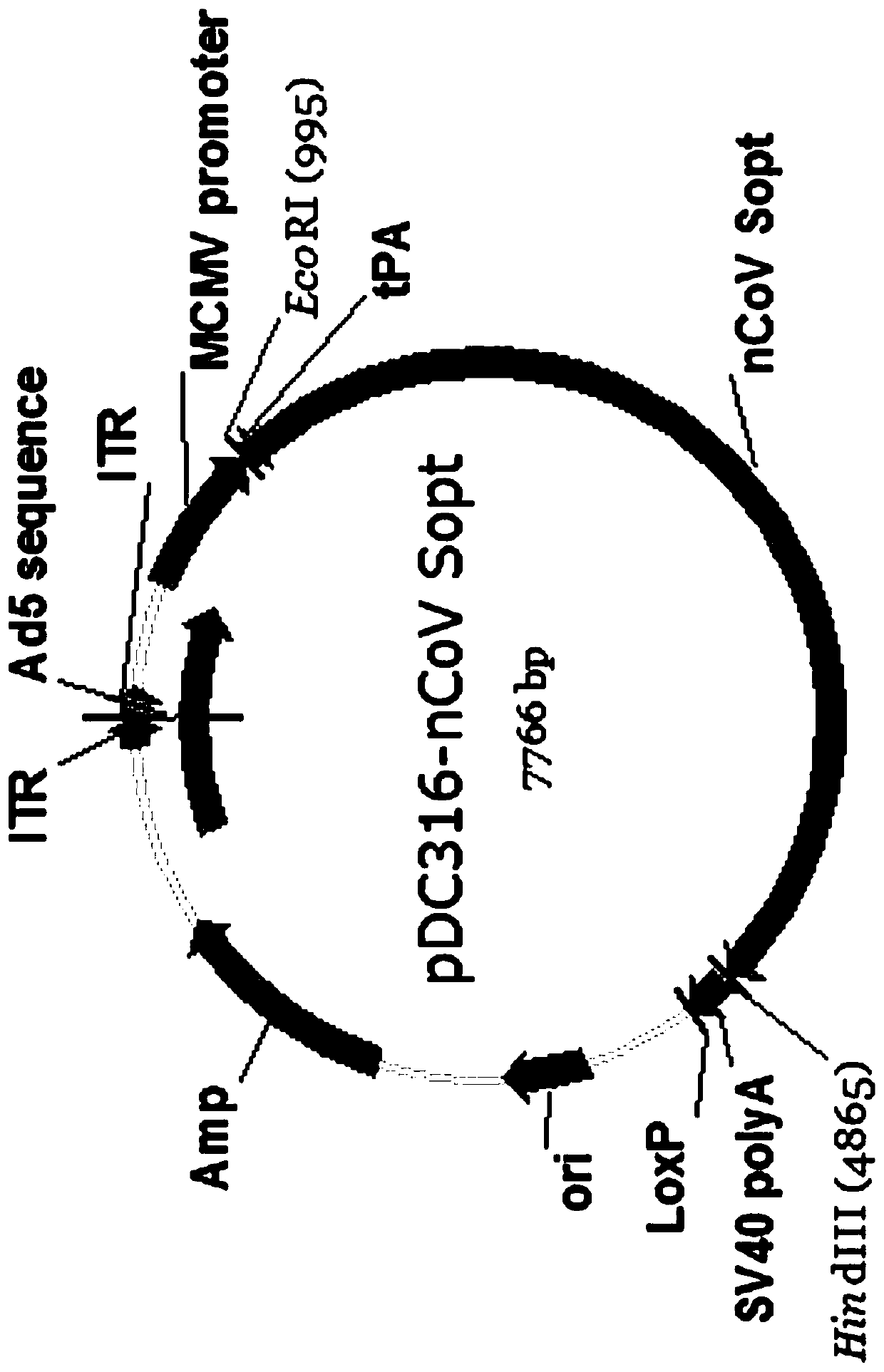
Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 vaccine using human replication-defective adenovirus as vector
ActiveCN111218459AReduce loadSimple manufacturing methodSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsProtective antigenCoronavirus vaccination
The invention provides a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine using human type-5 replication-defective adenovirus as a vector. The vaccine uses E1 and E3 to be combined with replication-defective human type-5 adenovirus as the vector and HEK293 cells integrating adenovirus E1 gene as a packaging cell line, and a protective antigen gene carried is the 2019 SARS-CoV-2 S protein gene (Ad5-nCoV) which is subjected to optimization design. After the S protein gene is optimized, the expression level in transfected cells is increased significantly. The vaccine has good immunogenicity in mouse and guinea pig models, andcan induce a body to produce a strong cellular and humoral immune response in a short time. Studies on the protective effect of hACE2 transgenic mice show that after 14 days of single immunization ofAd5-nCoV, the viral load in lung tissue can be significantly reduced, and it is indicated that the vaccine has a good immunoprotective effect on the 2019 SARS-CoV-2. In addition, the vaccine is quick, simple and convenient to prepare, and can be mass-produced in a short period of time to respond to sudden outbreaks.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI +1
Preparation method of hollow-structure metal or ceramic part
InactiveCN102351542AShort cycleShorten the production cycleCeramic shaping apparatusAdhesiveCo injection
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hollow-structure metal or ceramic part, which comprises the following steps: selecting metal or ceramic powder as the raw material, mixing, and granulating to obtain a feed material; selecting a core material; injecting the core material into a die by co-injection molding to obtain a core in hollow shape, and injecting the metal or ceramic feed material to be completely coated on the core, thereby obtaining a green body; and carrying out solvent extraction and heating on the green body to remove the adhesive and core, and sintering to obtain the hollow-structure product. The invention implements one-step molding of the hollow metal or ceramic part; from the raw material to the product, the production cycle is short, and the automation degree of equipment is high, thereby greatly enhancing the efficiency and forming a randomly complex and completely hollow die cavity; and thus, the invention can be used for preparing a completely hollow part with no joint, greatly lowers the cost of the product, and is especially suitable for preparing hollow metal and ceramic parts.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing graphene by using supercritical fluid
ActiveCN102115078AThe process is simpleLow costBulk chemical productionSingle layer grapheneCvd graphene
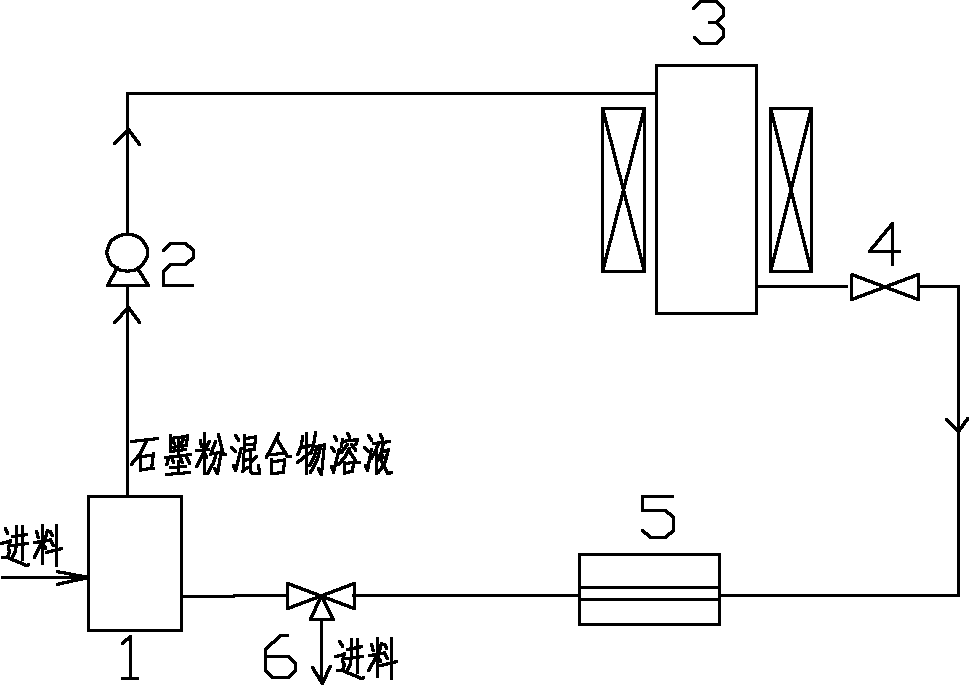
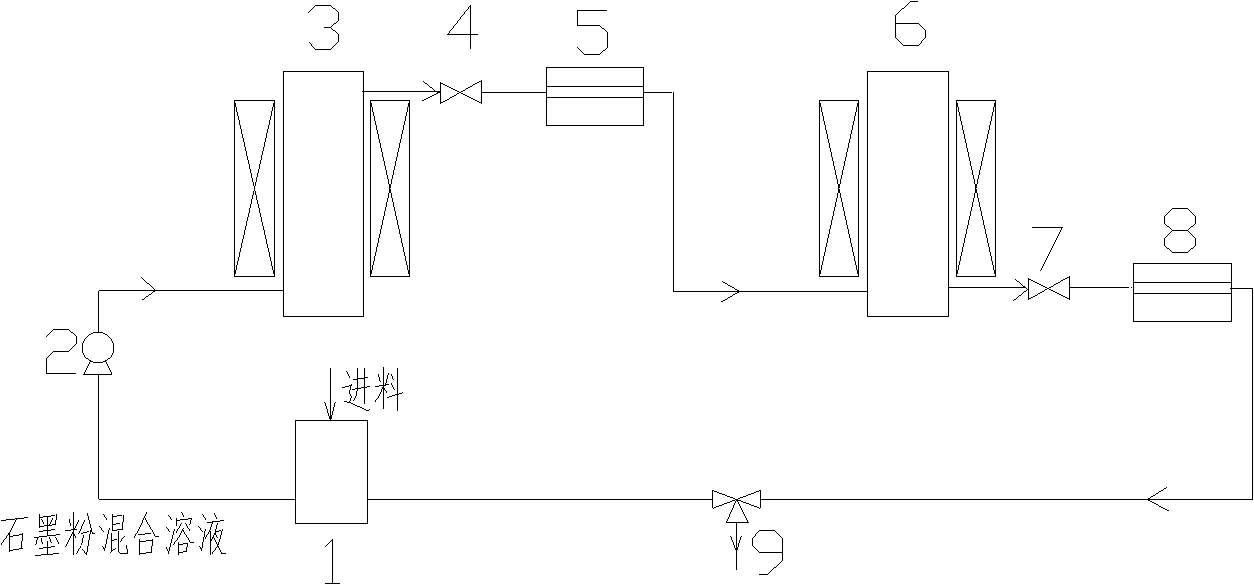
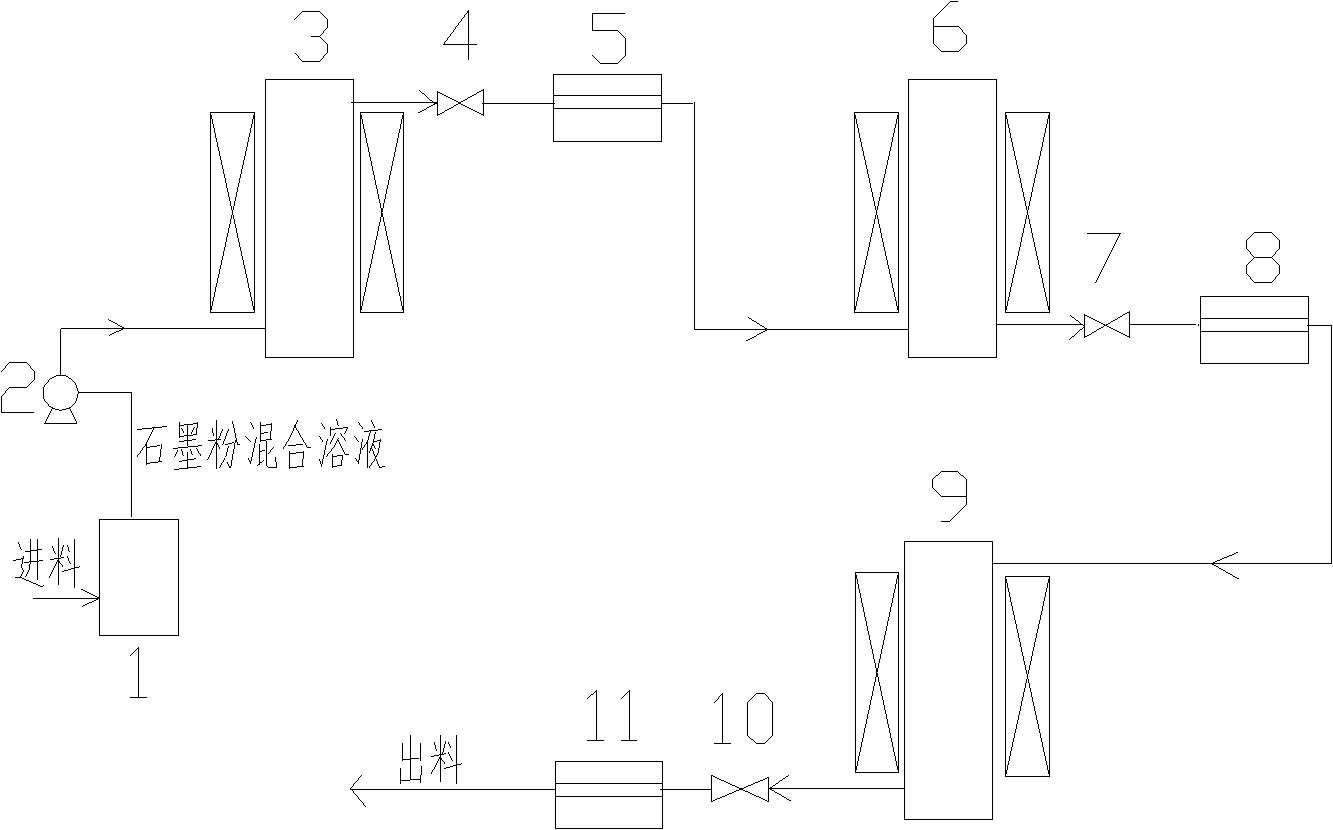
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene by using a supercritical fluid, which relates to the technical field of novel nano materials. The graphene is prepared by repeatedly and circularly treating and cooling graphite powder dispersion liquid. Graphene of less than eight layers, prepared by the method, accounts for 90-95 percent and single-layer graphene accounts for over 10 percent; meanwhile, continuous operation is performed, so that mass production can be realized, and the graphene has the advantages of simple process, nontoxicity and lower cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Biomass-based porous carbon material, preparation method thereof, and application thereof in supercapacitor
InactiveCN106587055AWide variety of sourcesLow priceCarbon compoundsHybrid capacitor electrodesPorous carbonBiological activation
The invention belongs to the field of material science and energy storage and discloses a biomass-based porous carbon material, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof in a supercapacitor. The method includes the steps of: 1) drying and crushing rice straws; 2) non-carbonizing or pre-carbonizing the crushed rice straws, uniformly mixing the rice straws with an activator water solution and drying the mixture, or non-carbonizing or pre-carbonizing the crushed rice straws and directly mixing the rice straws with a solid activator uniformly to produce a mixed product; and 3) placing the mixed product in a tube furnace to perform carbonizing activation in an inert gas atmosphere at high temperature; 4) washing the carbonized product in an acid solution and an alkali solution, and washing the carbonized product with deionized water to neutral, and drying the washed product to prepare the biomass-based porous carbon material. The porous carbon material has excellent supercapacitor performance and is simple in preparation method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
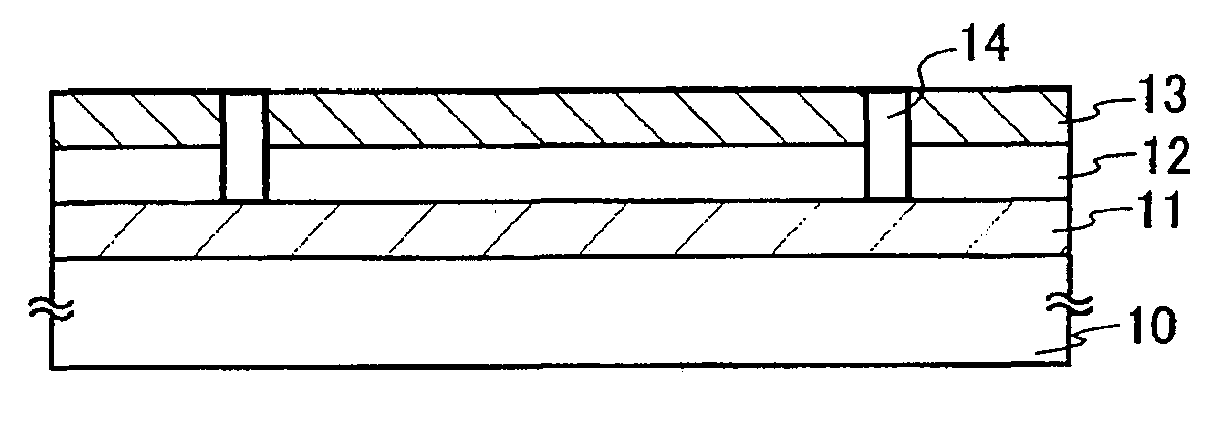
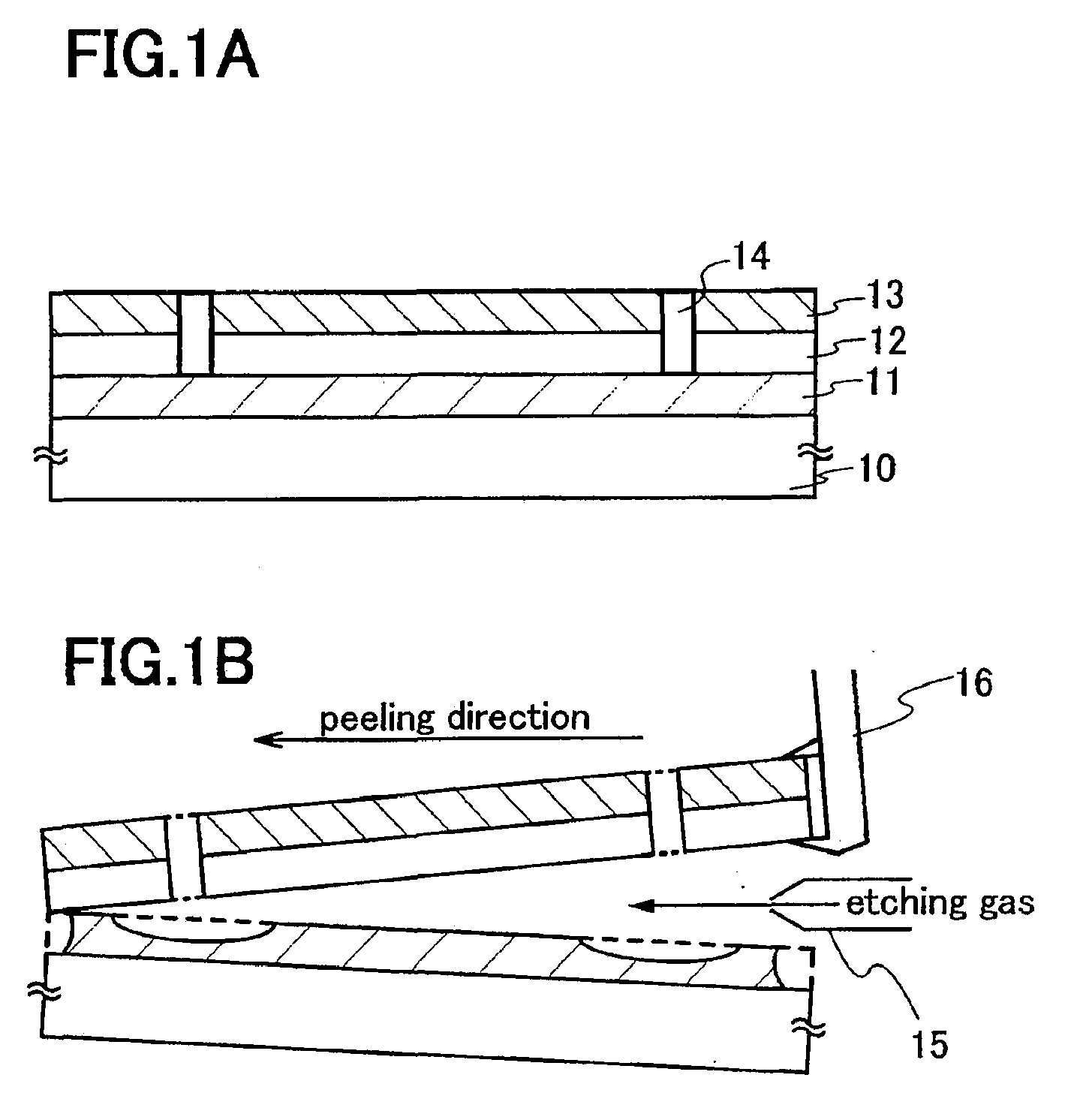
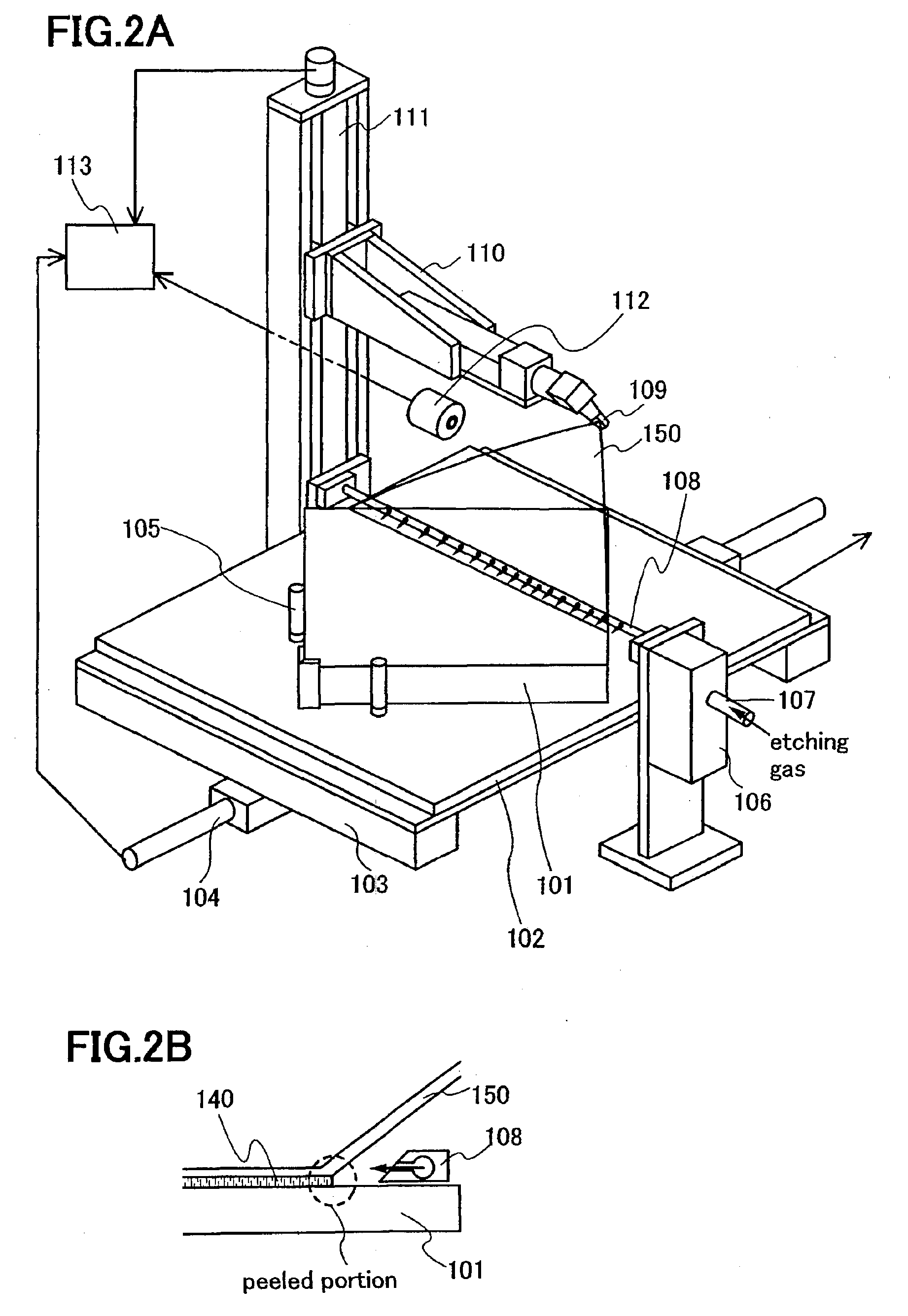
Manufacturing Method of Semiconductor Device
InactiveUS20060199382A1Reduce weightAchieve mass productionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
The present invention has an object to perform a peeling treatment in a short time. Peeling is performed while a peeling layer is exposed to an atmosphere of an etching gas. Alternatively, peeling is performed while an etching gas for a peeling layer is blown to the peeling layer in an atmosphere of an etching gas. Specifically, an etching gas is blown to a part to be peeled while a layer to be peeled is torn off from a substrate. Alternatively, peeling is performed in an etchant for a peeling layer while supplying an etchant to the peeling layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
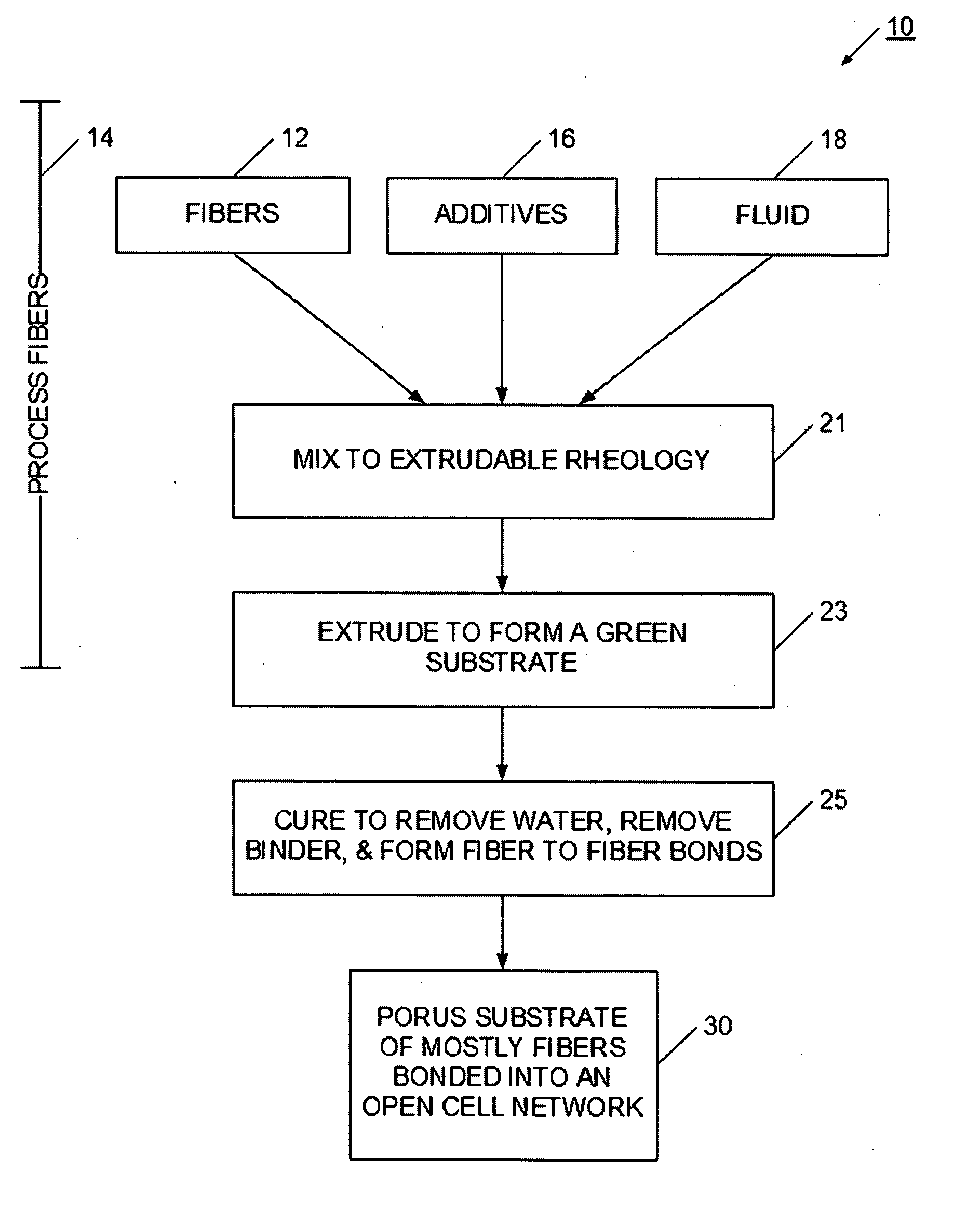
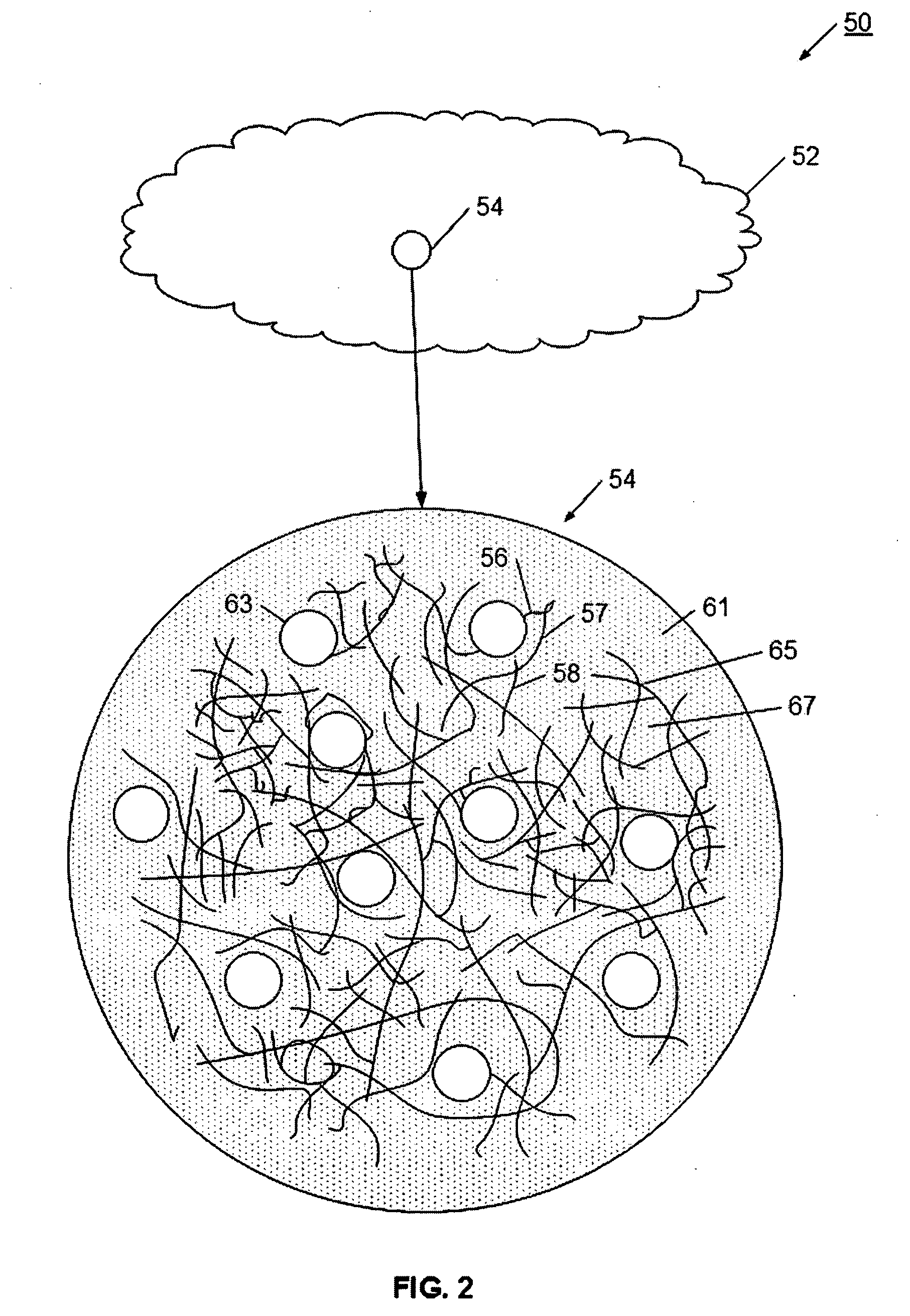
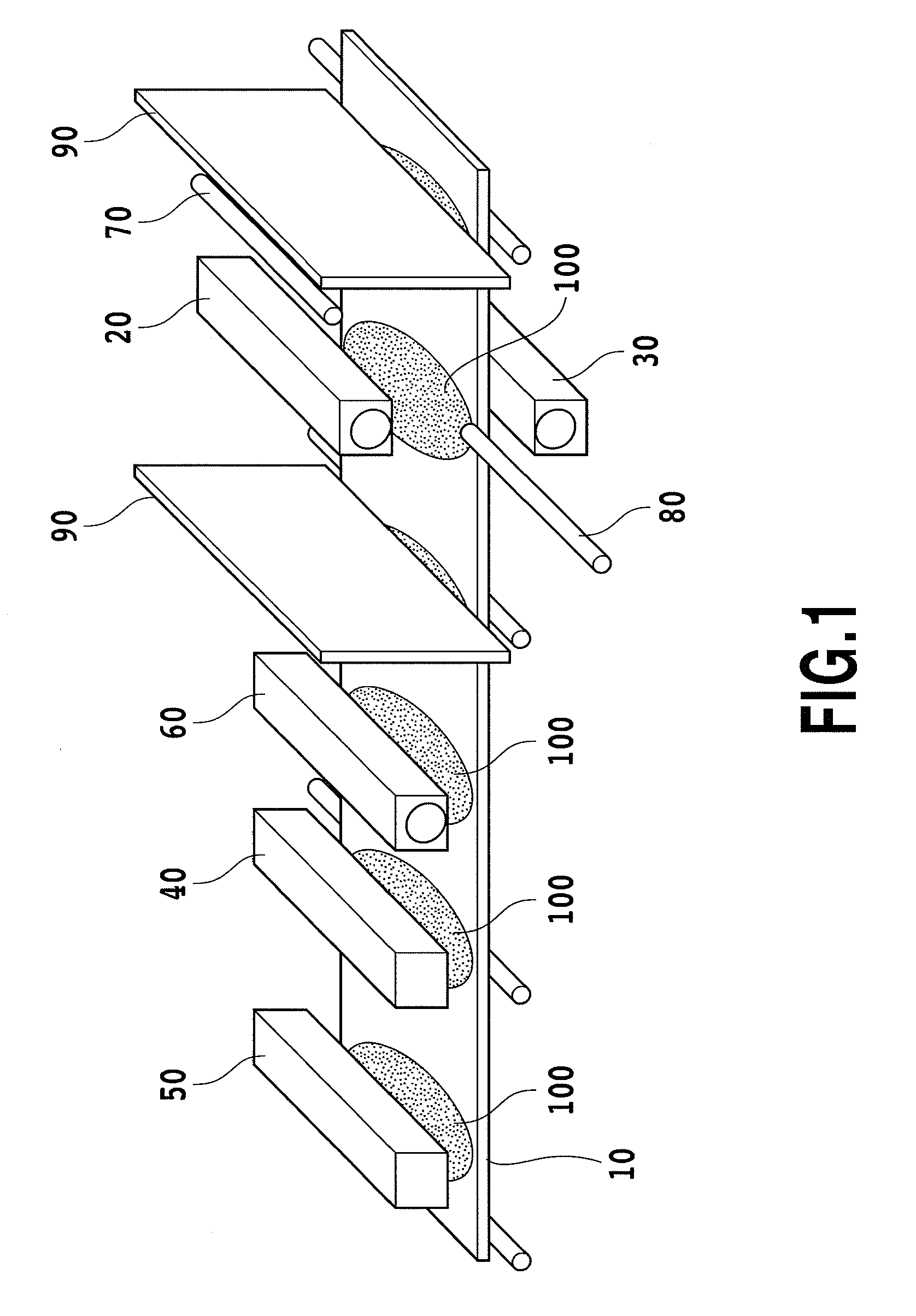
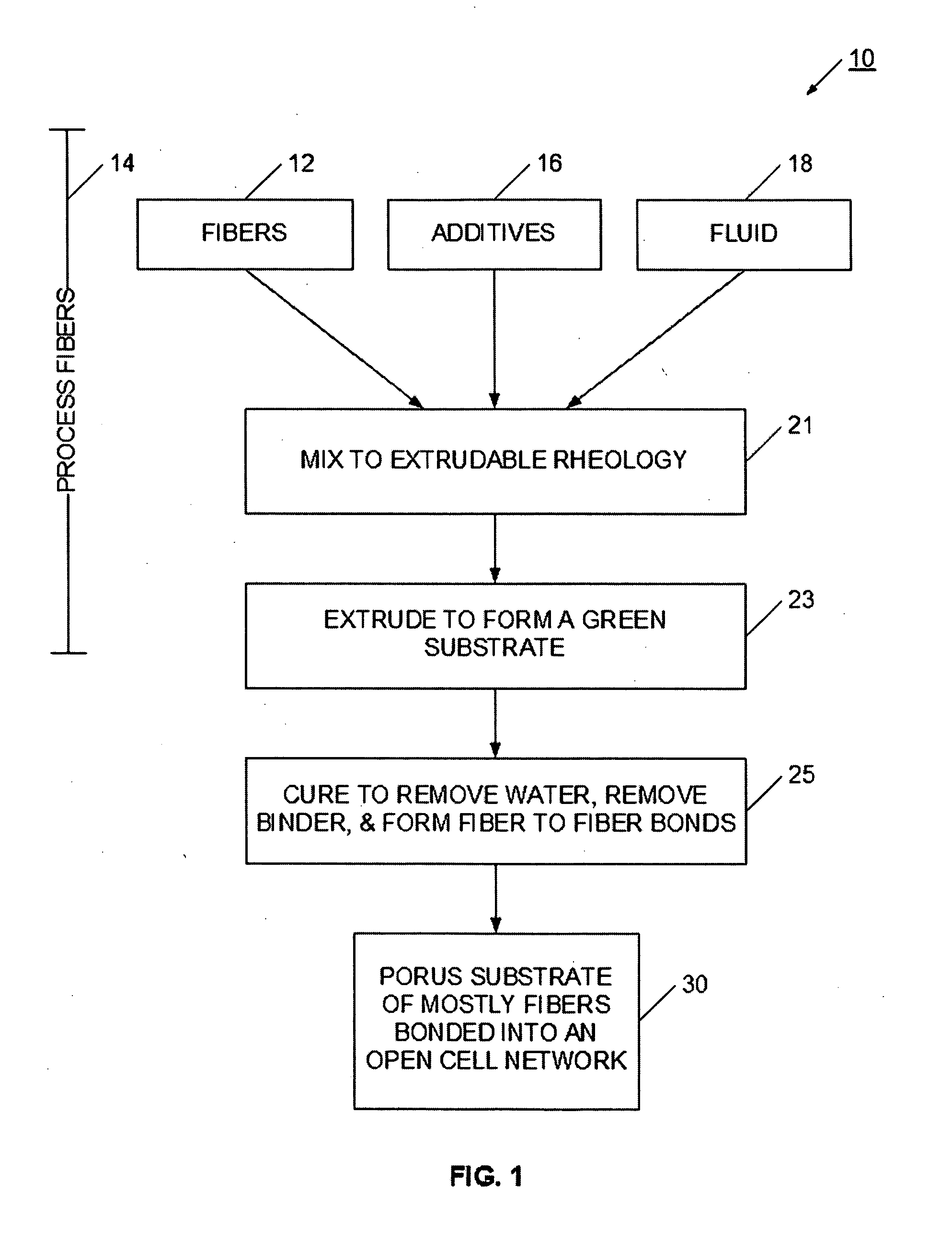
Extrudable mixture for forming a porous block
InactiveUS20070111878A1Highly porousHigh porosityDispersed particle filtrationExhaust apparatusAspect ratioOperating environment
An extrudable mixture is provided for producing a highly porous substrate using an extrusion process. More particularly, the present invention enables fibers, such as organic, inorganic, glass, ceramic or metal fibers, to be mixed into a mass that when extruded and cured, forms a highly porous substrate. Depending on the particular mixture, the present invention enables substrate porosities of about 60% to about 90%, and enables process advantages at other porosities, as well. The extrudable mixture may use a wide variety of fibers and additives, and is adaptable to a wide variety of operating environments and applications. Fibers, which have an aspect ratio greater than 1, are selected according to substrate requirements, and are mixed with binders, pore-formers, extrusion aids, and fluid to form a homogeneous extrudable mass. The homogeneous mass is extruded into a green substrate. The more volatile material is preferentially removed from the green substrate, which allows the fibers to interconnect and contact. As the curing process continues, fiber to fiber bonds are formed to produce a structure having a substantially open pore network. The resulting porous substrate is useful in many applications, for example, as a substrate for a filter or catalyst host, or catalytic converter.
Owner:GE02 TECH INC
Apparatus for manufacturing silicon oxide thin film and method for forming the silicon oxide thin film
InactiveUS20100140756A1Improve plasticityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon oxideSemiconductor
An object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor thin film device which employs a silicon oxide thin film having an equivalent level of high insulating performance to those currently used in electronic devices, through a low-temperature printing process on a plastic substrate having plasticity or other types of substrates at a temperature equal to or lower than the heat resistant temperature of the substrate, and to provide a method for forming the device. The semiconductor thin film device is formed as follows: a coating film of a silicon compound including a silazane structure or a siloxane structure is formed on a plastic substrate having plasticity; the coating film is converted into a silicon oxide thin film; and the thin film is utilized as part of an insulating layer or a sealing layer.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
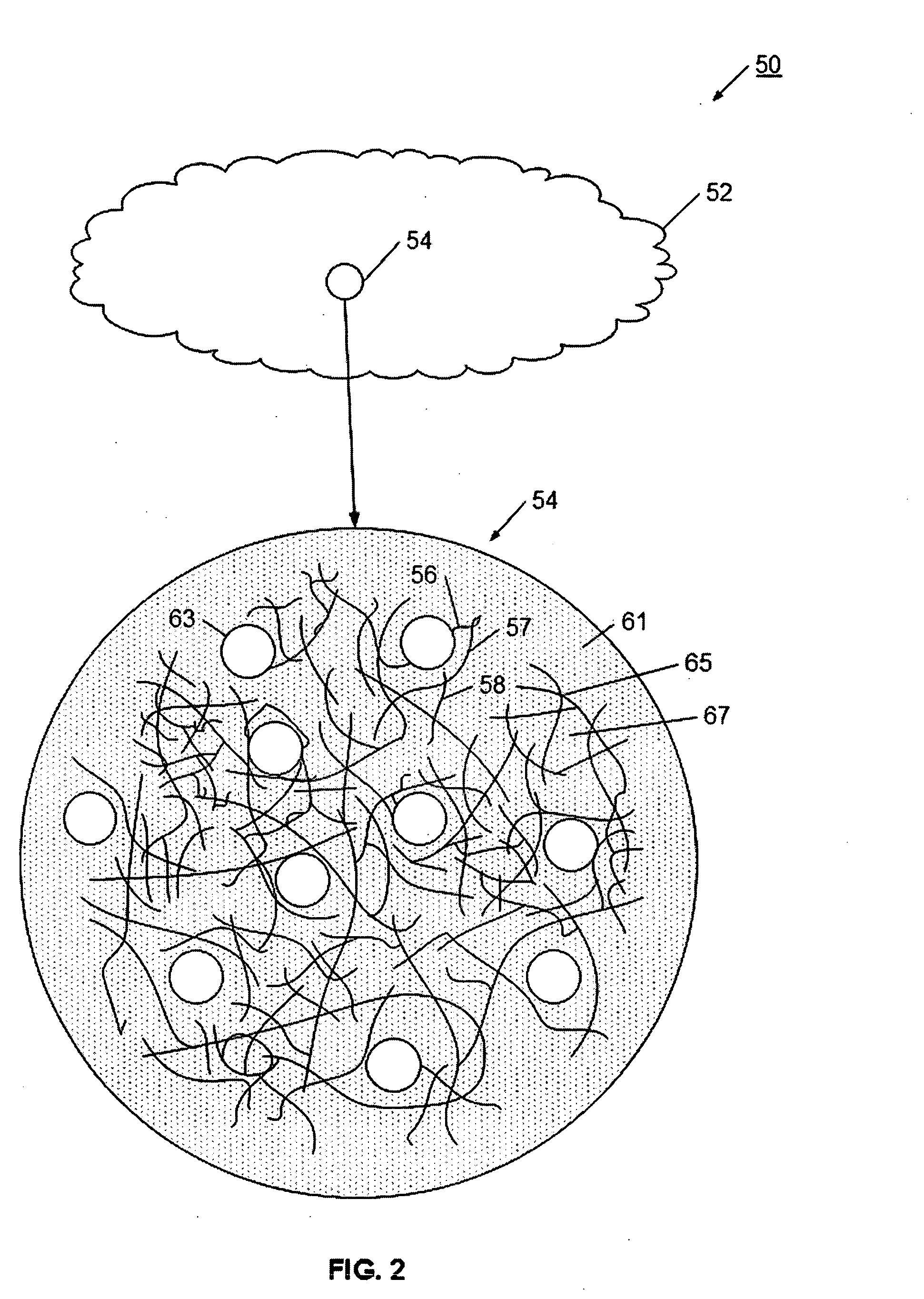
Extruded porous substrate and products using the same
InactiveUS20070107395A1Highly porousHigh porosityDispersed particle filtrationExhaust apparatusPorous substrateFiber
A highly porous substrate is provided using an extrusion system. More particularly, the present invention enables the production of a highly porous substrate. Depending on the particular mixture, the present invention enables substrate porosities of about 60% to about 90%, and enables advantages at other porosities, as well. The extrusion system enables the use of a wide variety of fibers and additives, and is adaptable to a wide variety of operating environments and applications. Fibers, which have an aspect ratio greater than 1, are selected according to substrate requirements, and are typically mixed with binders, pore-formers, extrusion aids, and fluid to form a homogeneous extrudable mass. The homogeneous mass is extruded into a green substrate. The more volatile material is preferentially removed from the green substrate, which allows the fibers to form interconnected networks. As the curing process continues, fiber to fiber bonds are formed to produce a structure having a substantially open pore network. The resulting porous substrate is useful in many applications, for example, as a substrate for a filter or catalyst host, or catalytic converter.
Owner:GE02 TECH INC
Polymeric thin film polarization method, polarizing film and electronic device
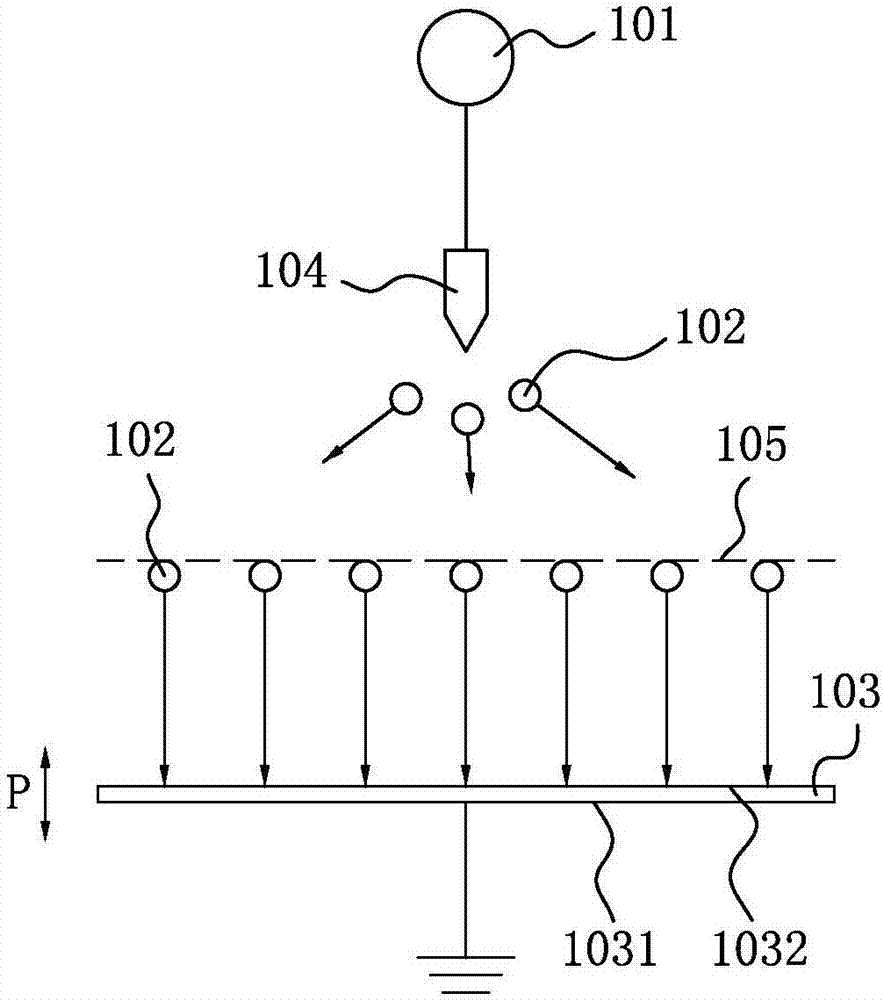
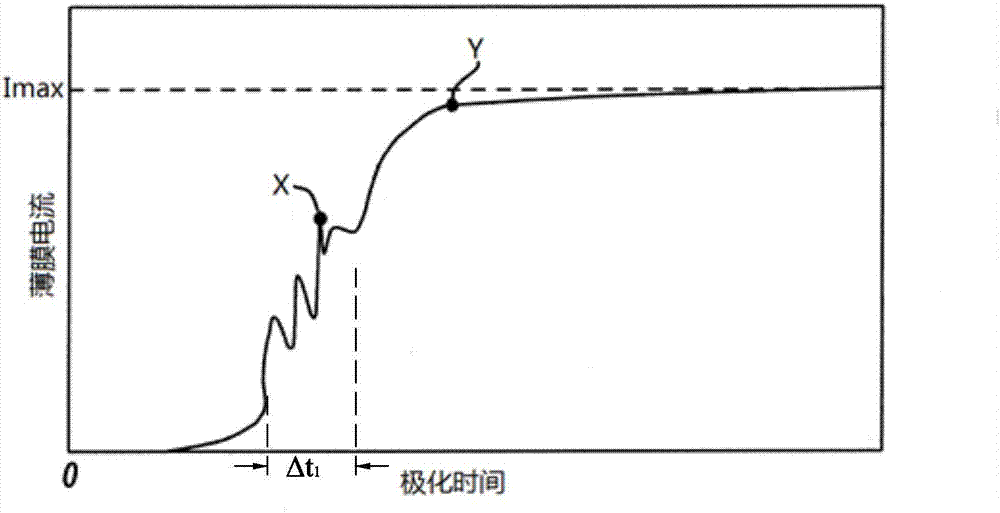
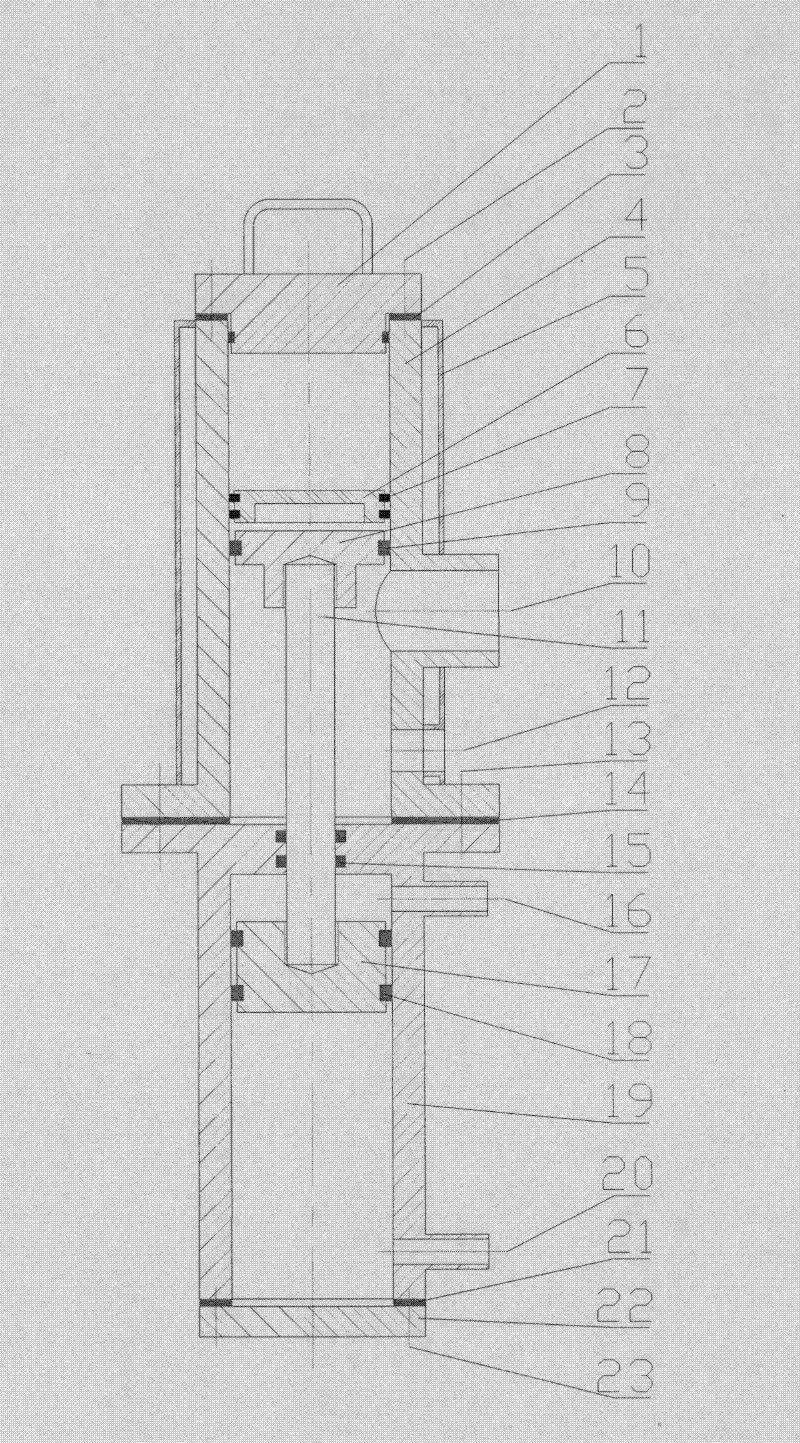
ActiveCN107104179APrevent breakdownImprove production pass ratePiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesProduction rateElectricity
A method for polarizing a polymer film is disclosed. An ambient gas above a polymer film under the action of a first electric field is ionized, the ambient gas accumulates on the second surface of the polymer film through the second electric field, an organic electric field in the film thickness direction is formed in the molecular thin film, and the polymer film is polarized. The polymer film polarization method can avoid the breakdown of the polymer film, effectively improve the production rate of the polarized film, can achieve large-scale production; and the resulting polarized film has a strong piezoelectric effect and longer Service life. The present invention also provides a polarizing film prepared by the above-described method of polymer film polarization, which has a strong piezoelectric effect and a long service life. The present invention also provides an electronic device comprising a substrate and a polarizing film as described above.
Owner:科锐昇微系统(苏州)有限公司
Preparation method for vanadyl sulfate electrolyte of all-vanadium flow battery
ActiveCN102683733AAchieve mass productionSimple processRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium compoundsAlkaline earth metalKerosene
The invention discloses a preparation method for vanadyl sulfate electrolyte of an all-vanadium flow battery. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: adjusting pH value of vanadyl sulfate solution obtained from leaching vanadium slag and stone coal, back extracting and resin-analyzing treatments by using oxide or hydroxide of alkali metal or alkaline earth; adding an inorganic reducing agent; performing multi-grade counter-current extraction by using P204 or P507: TBP: sulfonated kerosene extracting agent; after the two-phase separation, washing the vanadium-loaded organic phase; performing 2-5 grades of multi-grade counter-current back extraction on the vanadium-loaded organic phase by using sulfuric acid solution to obtain the back extracting liquid of vanadyl sulfate; adjusting the pH value of the back extracting liquid of vanadyl sulfate, adding the organic reducing agent to adjust the potential value of the solution; extracting the solution by using the extracting agent; after the two-phase separation, washing the vanadium-loaded organic phase by using the sulfuric acid solution; performing multi-grade counter-current back extraction by using the sulfuric acid solution to obtain the vanadyl sulfate solution; and distilling until the concentration required for all-vanadium flow battery. The method provided by the invention can improve the purity, simplify the preparation procedure and reduce the cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF RARE METALS
Method for preparing graphene
InactiveCN102491314AImprove permeabilityImprove diffusion abilityGrapheneBulk chemical productionCrystal structureHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene, characterized by carrying out explosion treatment for one or more times on carbonaceous materials by using fluids under supercritical state. By using the fluids under supercritical state to penetrate and dissolve the carbonaceous materials and having the aid of sudden release of high pressure hot steam, the shearing and peeling between layers of the carbonaceous materials are promoted to realize the preparation of graphene. Compared with using ball milling, mechanical peeling, high temperature and high pressure to prepare graphene in the prior art, the invention has the advantages of mild process conditions (low pressure), short process time, large area of prepared graphene, and complete preserved crystal structure. According to the invention, the content of graphene which comprises less than 5 layers is higher than 90 %, and the batch production of graphene powder products can be really realized.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of azilsartan
InactiveCN102766138AReduce usageEmission reductionOrganic chemistryEthyl chloroformateCarboxylic salt
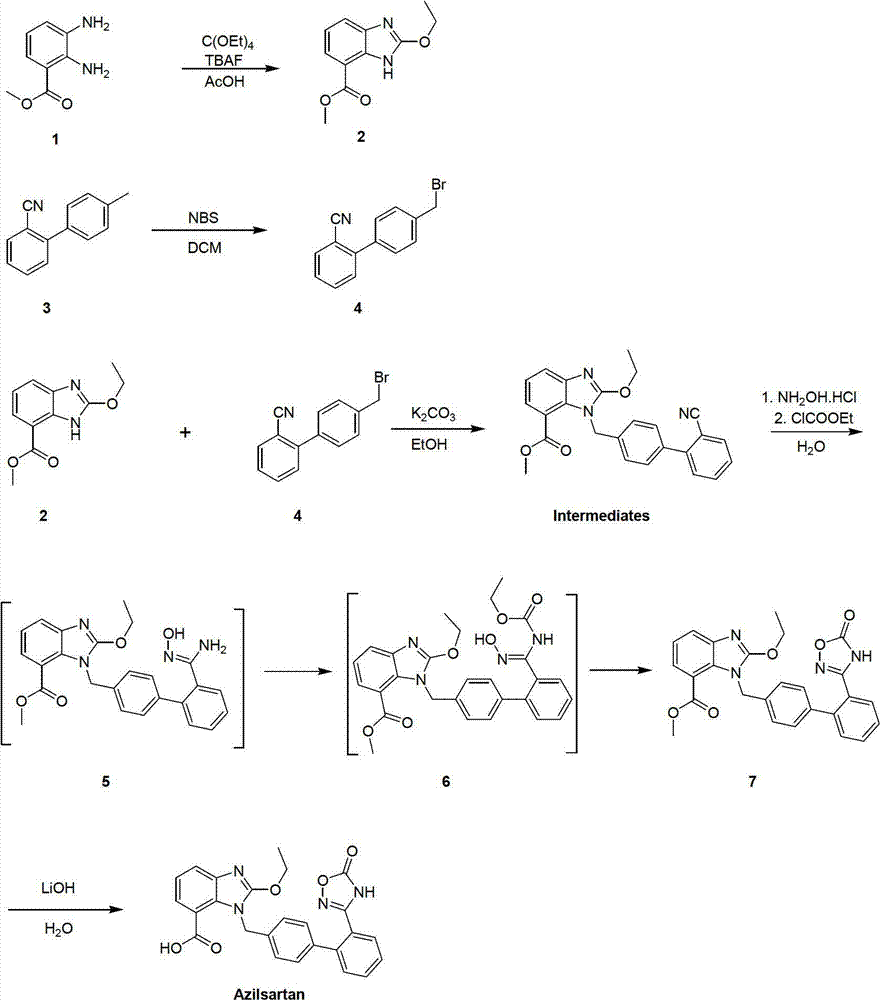
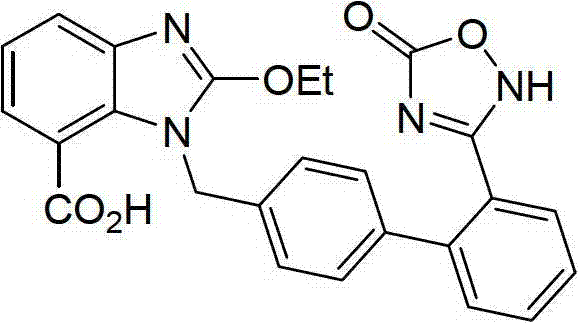
The invention relates to a preparation method of azilsartan, comprising the following steps of: (1) preparing ethoxybenzimidazole-7-methyl carboxylate; (2) preparing 2-cyan-4'-bromomethyl biphenyl; (3) dissolving the ethoxybenzimidazole-7-methyl carboxylate and the 2-cyan-4'-bromomethyl biphenyl into ethanol; adding potassium carbonate to react to obtain 1-[(2'-cyan diphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-2-ethoxybenzimidazole-7-methyl carboxylate; (4) suspending the 1-[(2'-cyan diphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-2-ethoxybenzimidazole-7-methyl carboxylate in water; adding hydroxylamine hydrochloride, sodium hydroxide and tetrabutylammonium fluoride; heating and reflowing, and then cooling; adding the sodium hydroxide and ethyl chloroformate, heating and reflowing to obtain azilsartan methyl ester; and (5) hydrolyzing the azilsartan methyl ester to obtain a product. The preparation method of the azilsartan, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of being short in process route, high in yield, and safe and reliable; and the purity of the azilsartan obtained by using the method is high.
Owner:WENZHOU PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Preparation method of titanium dioxide/active carbon composite nanofibrous membrane
InactiveCN102021676AAchieve mass productionImprove bindingWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesSpinningPhosphoric acid
The invention provides a preparation method of a titanium dioxide / active carbon composite nanofibrous membrane, characterized by comprising the following specific steps: dissolving polyacrylonitrile powder in N, N-dimethyl formamide; mixing titanium hydroxide gel with the polyacrylonitrile solution to obtain electrostatic spinning stock solution, and performing electrostatic spinning to get the composite nanofibrous membrane; placing the composite nanofibrous membrane in an electrically heated drying cabinet for being pre-oxidized; soaking the composite nanofibrous membrane in phosphoric acid or potassium hydroxide solution, washing the solution to be neutral by distilled water, and drying the composite nanofibrous membrane in the drying cabinet; and then, under nitrogen protection, heating up to 450-550 DEG C, and cooling to room temperature to get the titanium dioxide / active carbon composite nanofibrous membrane. The preparation method improves combination firmness between fibers and active ingredients of a photocatalyst, and also improves charge capacity of the fibers; the titanium dioxide / active carbon composite nanofibrous membrane is high in photo catalytic activity, good in absorption effect, reproducible and simple in a reproduction method, and can use sunlight, so that operations are easy and operation cost is low.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Multilayered gradient diamond like nano composite coating for aluminum alloy piston and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102092166AOvercome stressOvercome adhesionLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingDiamond-like carbonSurface layer
The invention discloses a multilayered gradient diamond like nano composite coating for an aluminum alloy piston and a preparation method thereof. The coating consists of a piston matrix, a bottom adhesive layer, a middle transition layer and a surface layer in turn, wherein the bottom is provided with a metal Ti or Cr adhesive layer; the middle transition layer is metal nitride and a Si layer; and the surface layer is a metal-doped diamond like carbon film. The wear life of the coating is improved by more than 40 times compared with that of a single-layer diamond like coating with the same thickness directly formed on the surface of aluminum alloy, and the friction coefficient under the oil lubricating condition is stabilized to be 0.05. The piston with the diamond like coating has better comprehensive performance than a piston of which the skirt is treated by MoS2, and can meet the requirements on high speed, high efficiency and low emission of a modern engine.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
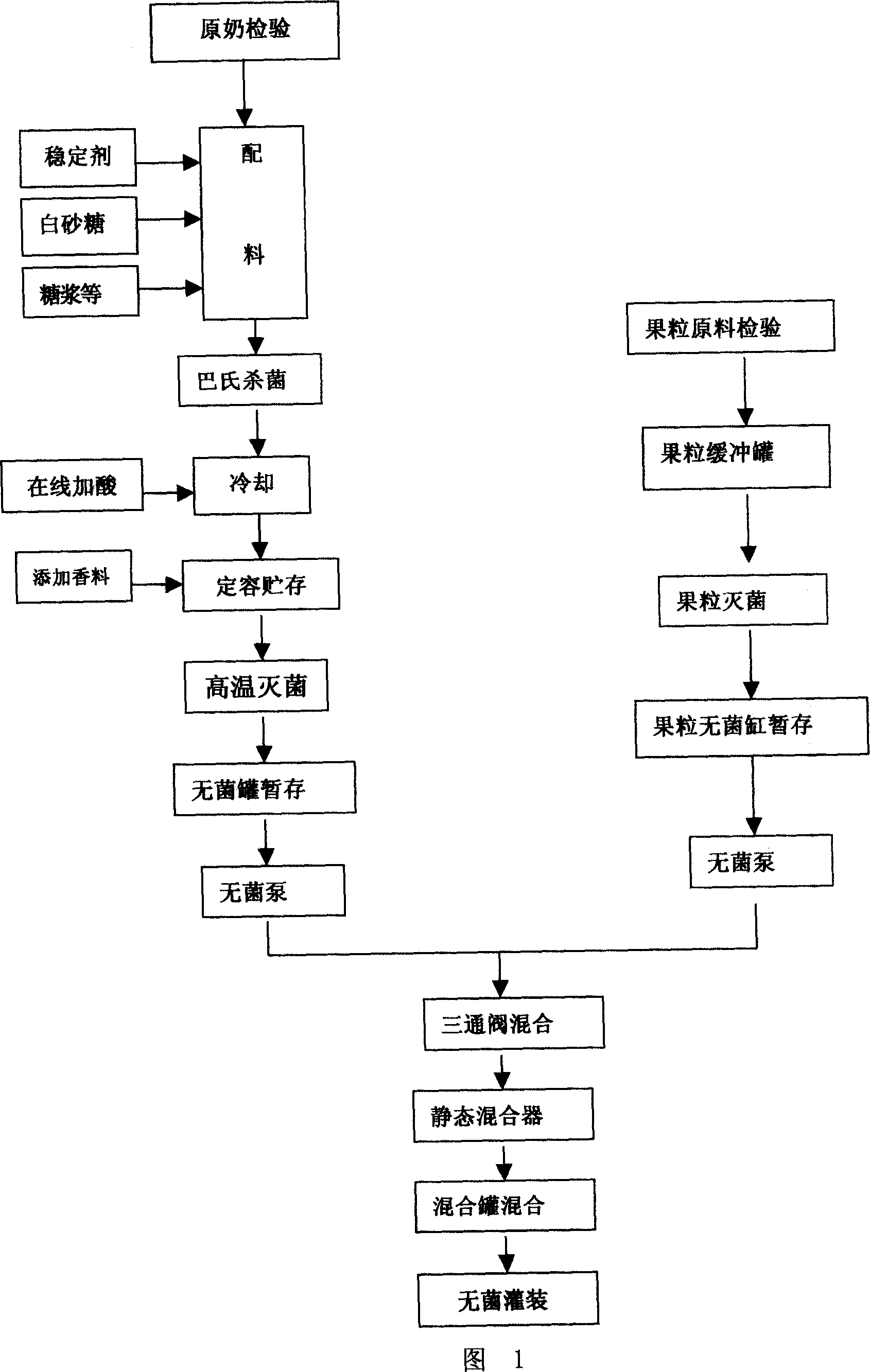
Method for producing lactic acid drink containing flesh grains
ActiveCN101040634ASolve incomplete sterilizationProtect fruit typeMilk preparationMilk preservationCow milkChemistry
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA MENGNIU DAIRY IND (GRP) CO LTD
Process for preparing natural magnesium aluminium silicate gel
InactiveCN1363515AAvoid pollutionFe <sub>2</sub> o <sub>3</sub> Low contentAluminium silicatesInorganic saltsSodium Bentonite
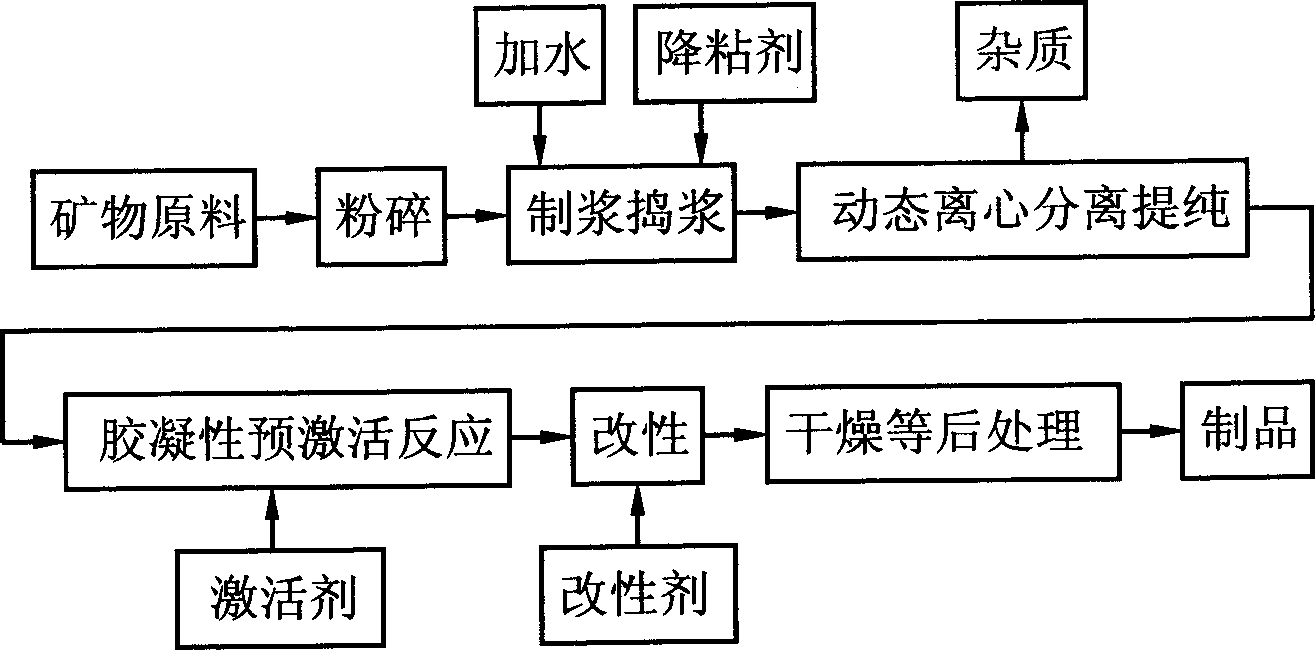
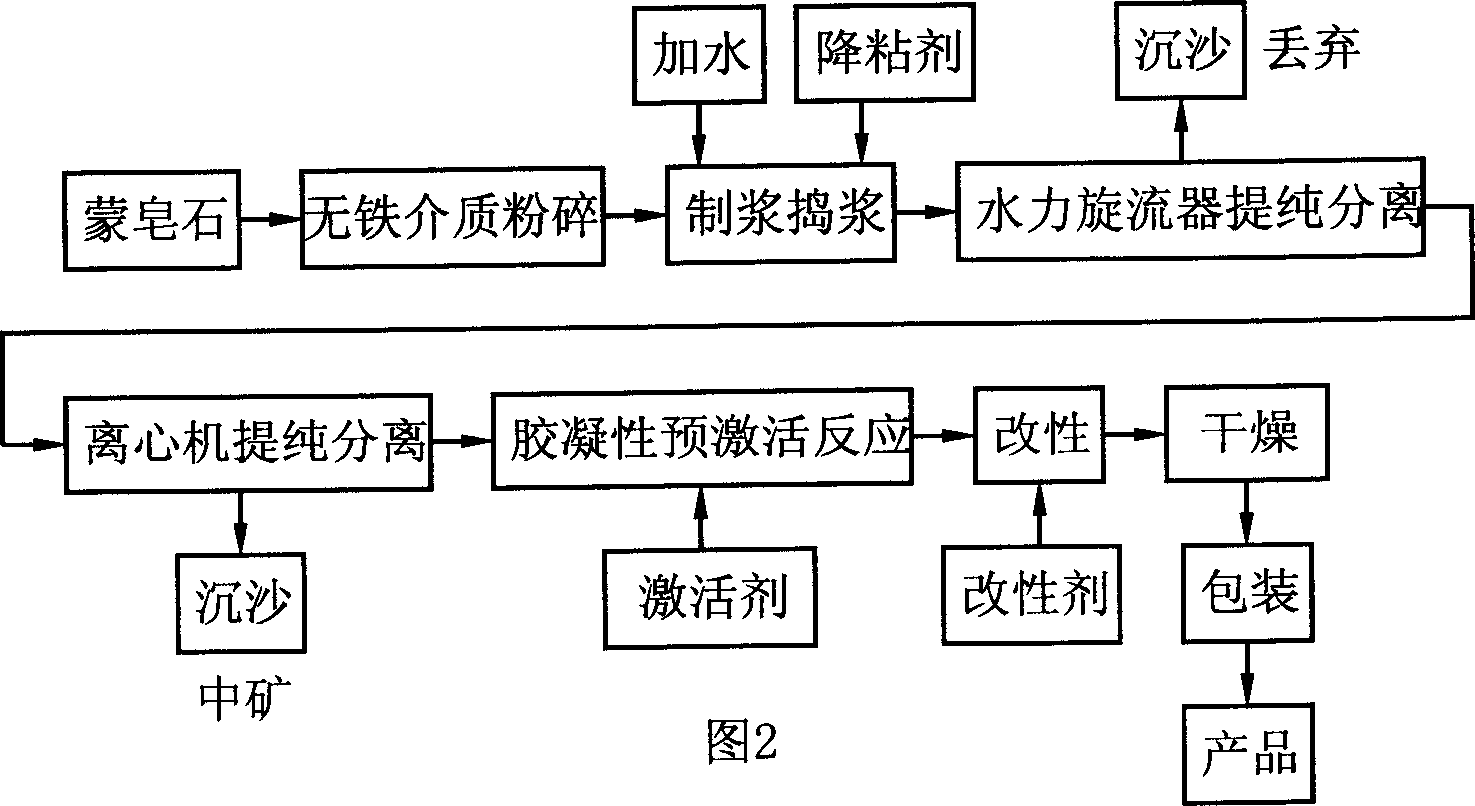
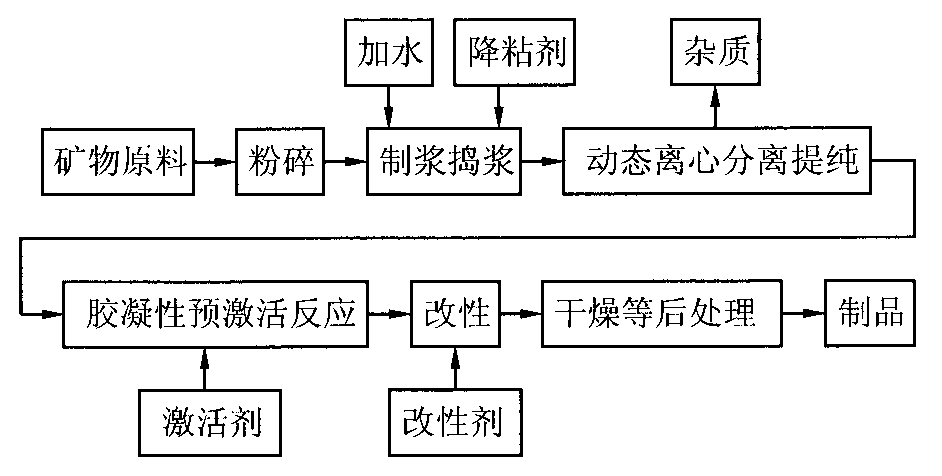
A process for preparing natural gel of magnesium aluminium silicate from bentonite, attapulgite, bentone, etc includes such steps as pulverizing, preparing slurry, adding pour depressor, stirring, dynamic centrifugal separation, adding inorganic salt containing one-valence metal ions, stirring, pre-activating, adding organic salt containing at least Na ions, stirring for modifying, and post-treating.
Owner:国家非金属矿深加工工程技术研究中心
Preparation method and application of electrochemical micro-fluidic sensing chip
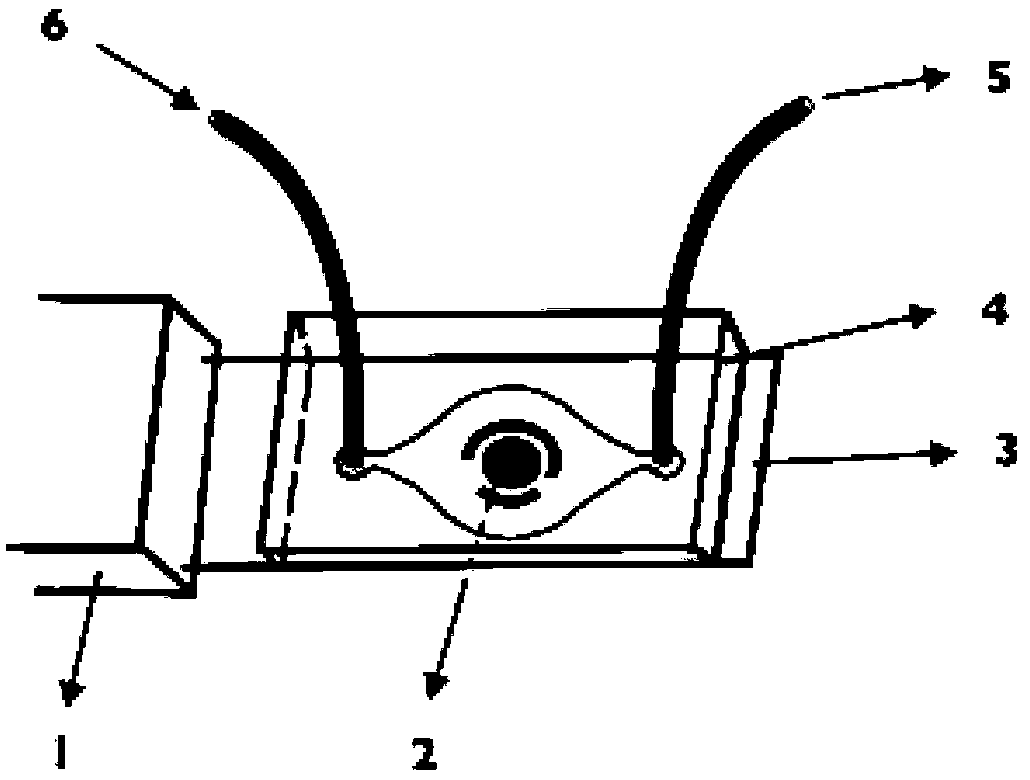
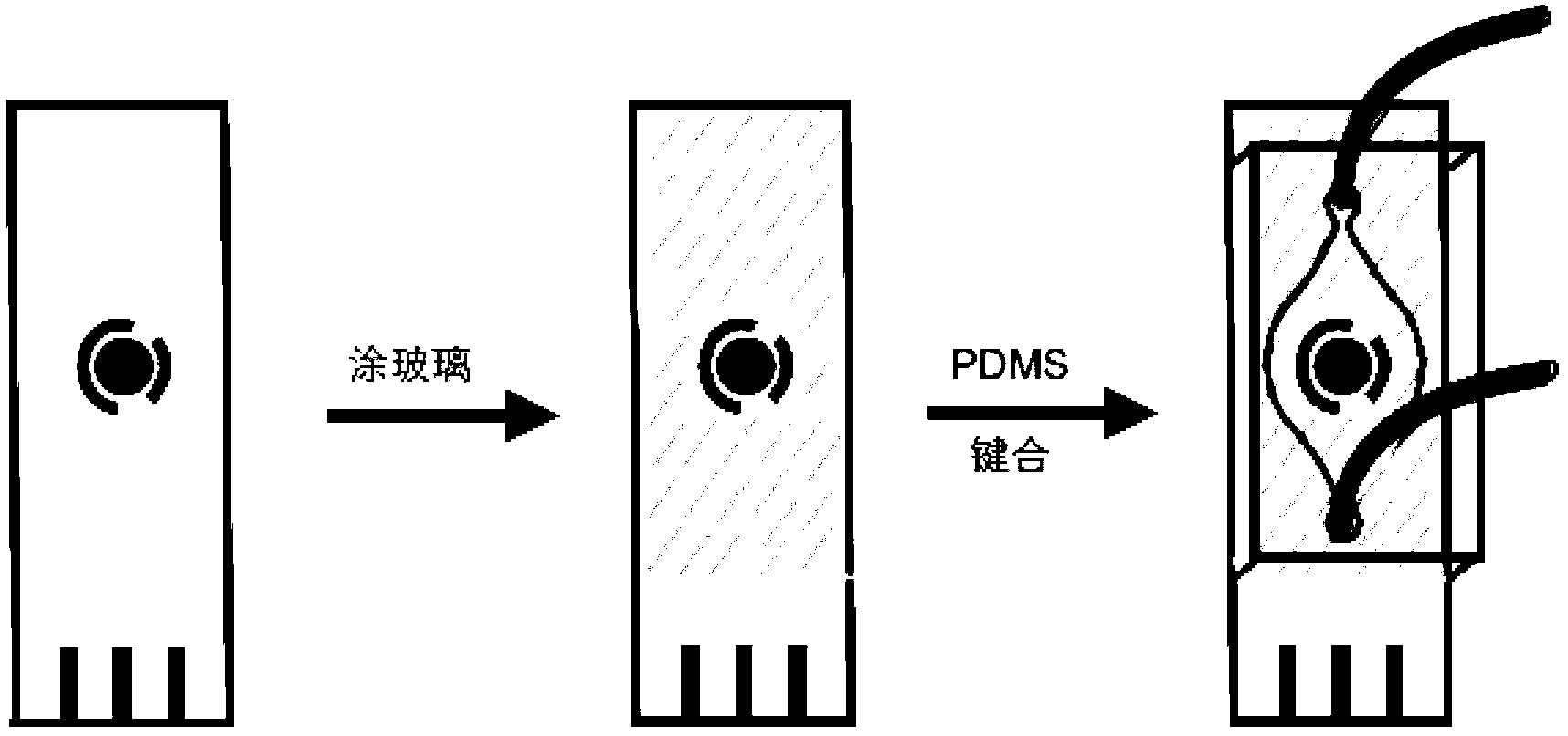
ActiveCN103182334AEasy to manufactureReduce weightMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresElectrochemical detectorStandardization
The invention provides a preparation method and the application of an electrochemical micro-fluidic sensing chip. The preparation method comprises the following steps: directly coating an improved glass solution on a commercial standard printed electrode; and performing vacuum plasma treatment on a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) chip with pre-designed pipelines and the printed electrode coated with the glass solution together, and directly bonding the PDMS chip on the commercial standard printed electrode to form a novel electrochemical microfluidic sensing platform. A sensor provided by the invention can perform ultrasensitive detection on various sample analytes in a biological fluid sample, taking the detection of a prostate cancer marker PSA (Prostate-specific Antigen) in human serum as an example, a coulomb amperometry is used for detection, and a result shows that the detection sensitivity can reach 0.84 pg / mL which is improved by two magnitudes than the standardized clinical testing requirement of 0.1 ng / mL, so that the sensor has superhigh detection sensitivity and accuracy, which are higher than those of other electrochemical detection devices, is convenient in operation, and can integrates sample processing, separation and the like on one micro electrochemical microfluidic sensing chip.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
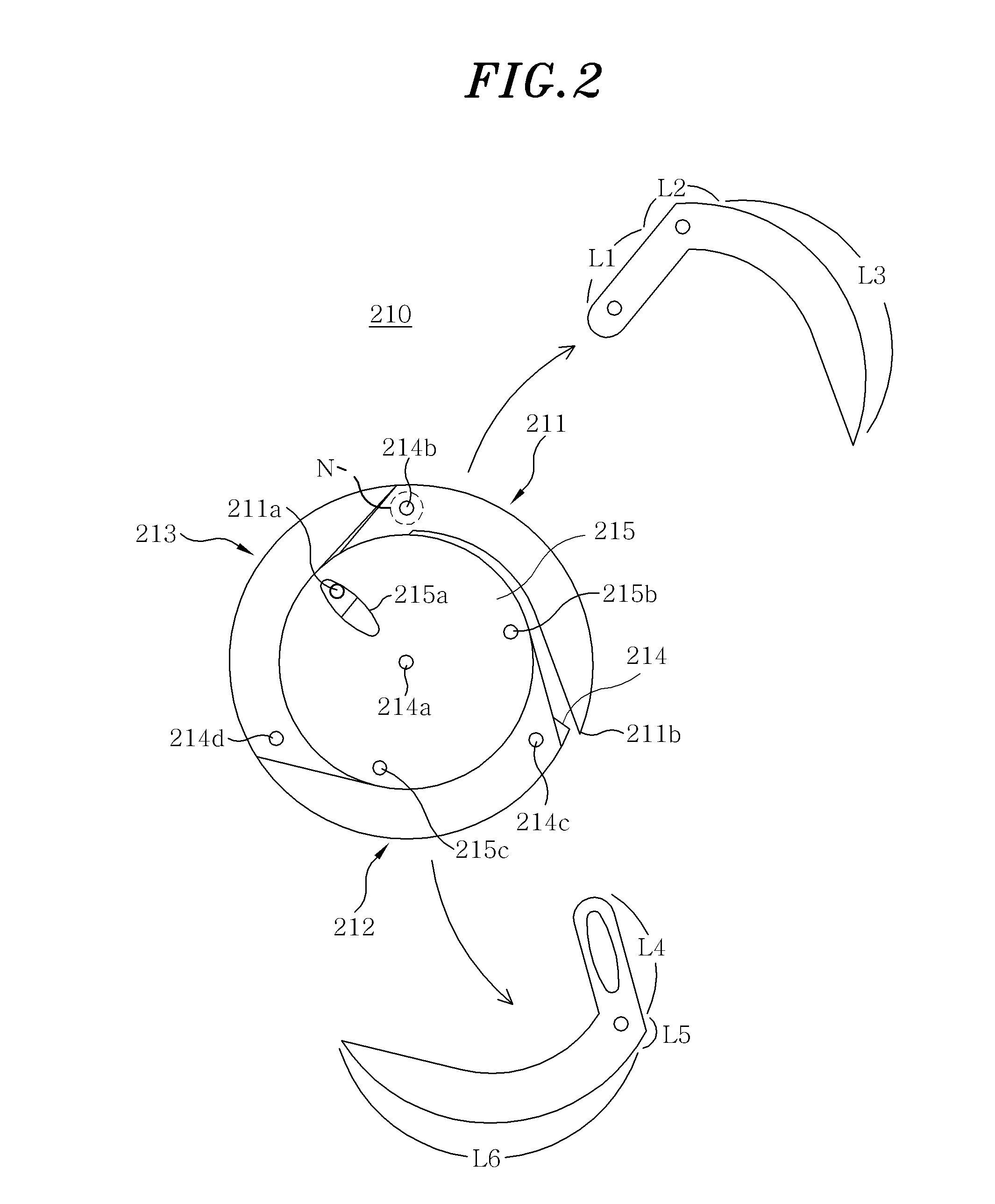
Passive transformable wheel and robot having the wheel
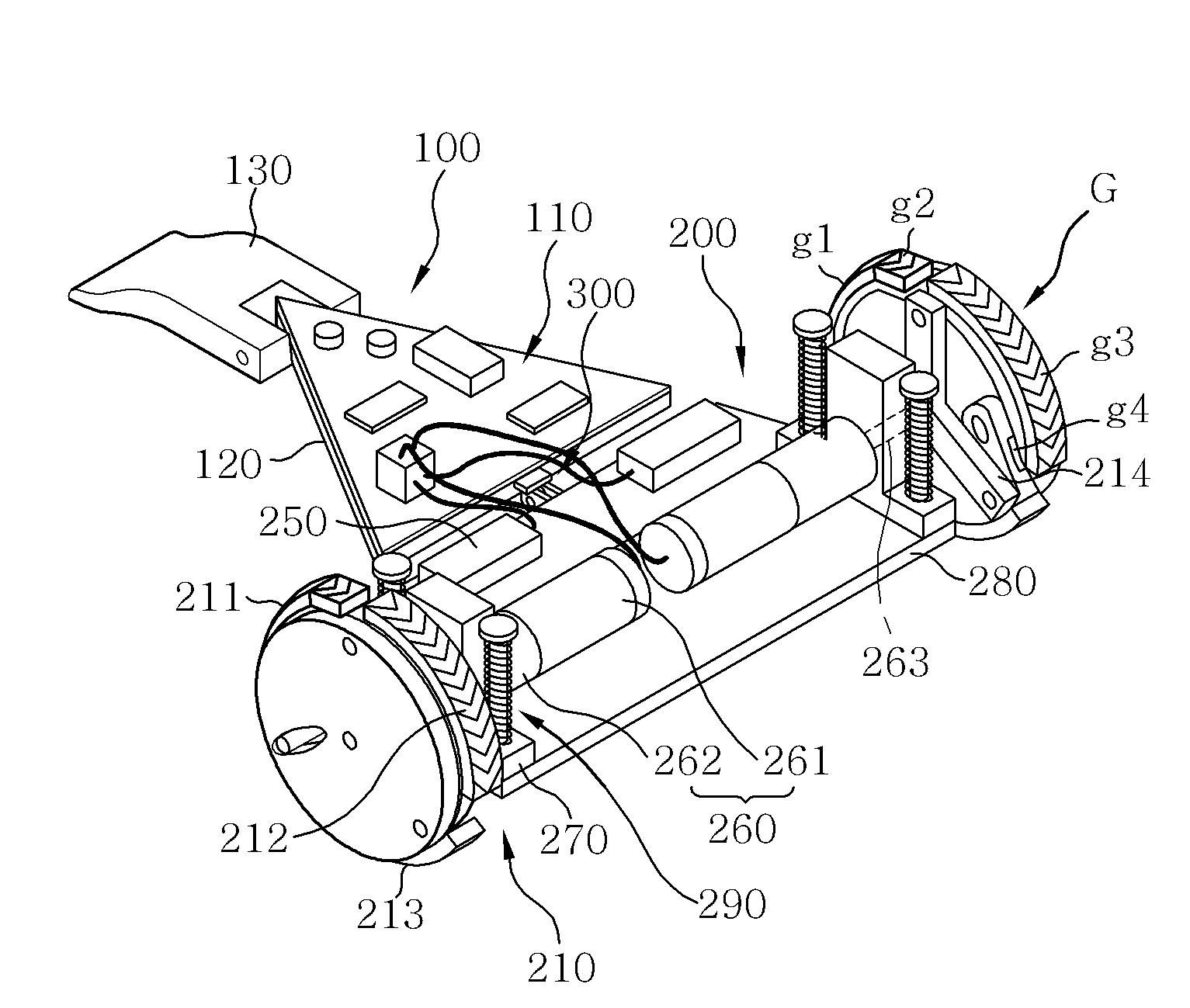
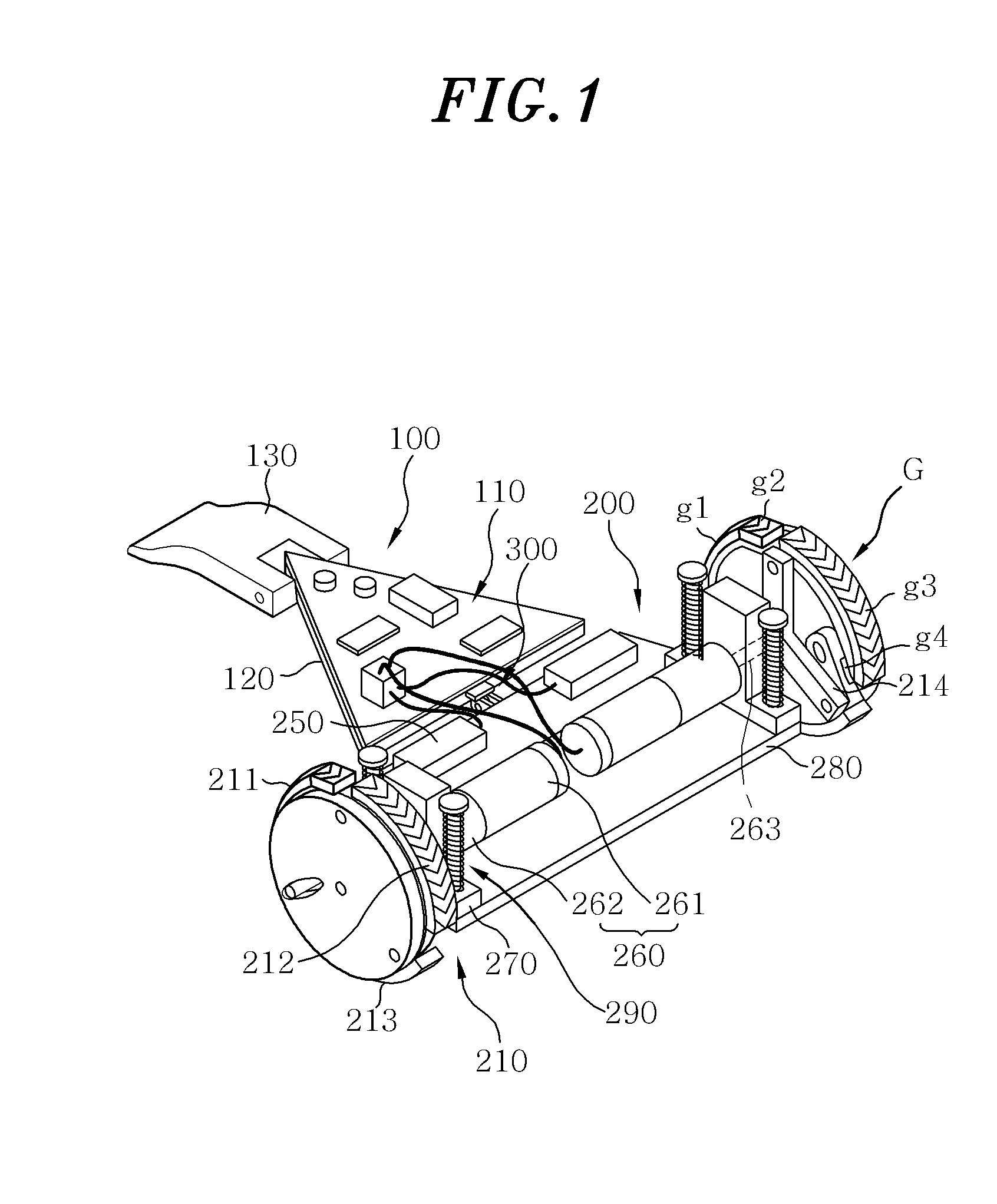
ActiveUS20140158439A1Simple structureReduce manufacturing costCarriage/perambulator accessoriesRimsJoint spacesMechanical engineering
A passively transformable wheel includes a wheel base including a centrally positioned transmitter rotation shaft and one or more passive leg rotation shafts positioned in the outer periphery; a force transmitter rotatably coupled to an end of the transmitter rotation shaft, the force transmitter including a trigger slide and one or more passive leg joints spaced apart from one another; a trigger leg arranged between the wheel base and the force transmitter and rotatably coupled to the trigger leg rotation shaft, the trigger leg including a trigger joint fitted to the trigger slide; andone or more passive legs arranged between the wheel base and the force transmitter so as not to interfere with the trigger leg and rotatably coupled to the passive leg rotation shafts, the passive legs including one or more passive leg slides engaging with the passive leg joints of the force transmitter.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
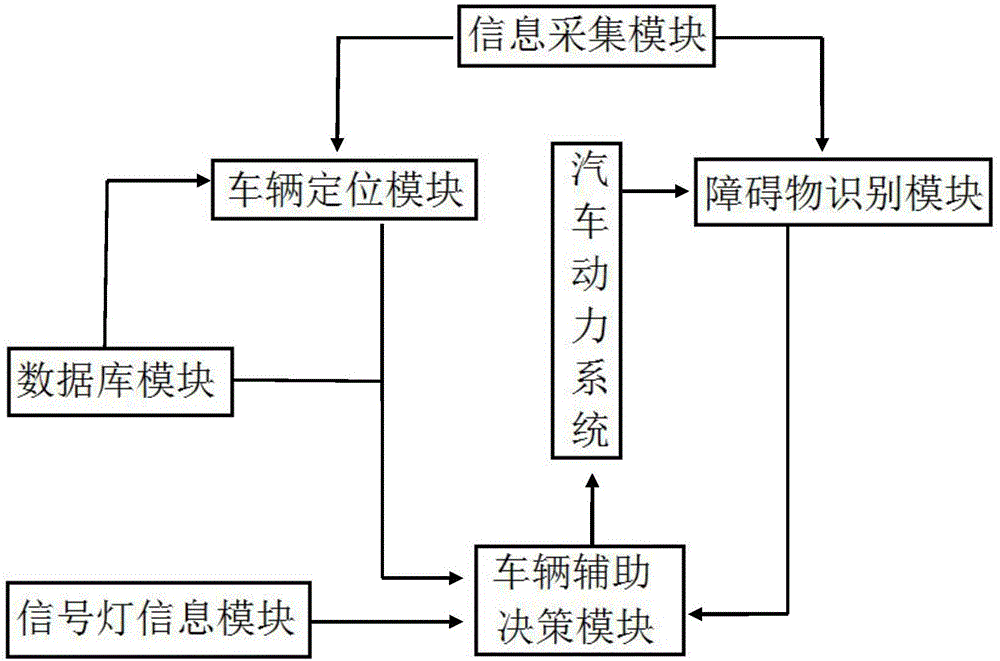
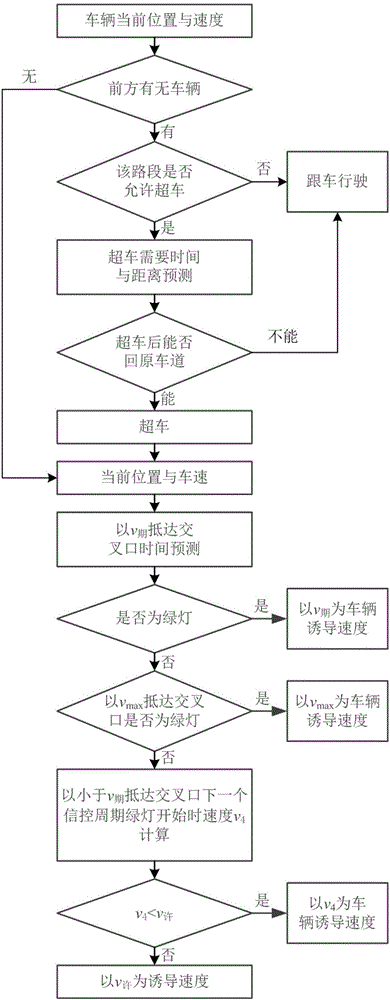
Auxiliary driving system and method for rapid passing of vehicle in crossing
InactiveCN106485931ATo achieve the purpose of energy savingReduce pollutionRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer moduleThe Internet
The invention discloses an auxiliary driving system and method for rapid passing of a vehicle in a crossing. The system comprises an information collection module, a vehicle positioning module, a barrier identification module, a database module, a signal lamp information module, a vehicle auxiliary decision module and an automobile power system. According to technical features of road traffics and physical features of drivers, a method including guiding information through which each crossing can be passed rapidly and smoothly and a vehicle in front can be overtaken is provided for the driver in the driving process, the guiding information including whether to overtake, the concrete driving speed and the like, and thus, when the vehicle is driven according to the guiding speed and manner, the crossing can be passed without stop, and core technical support is provided for development of Internet of vehicles and automatic driving technologies.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
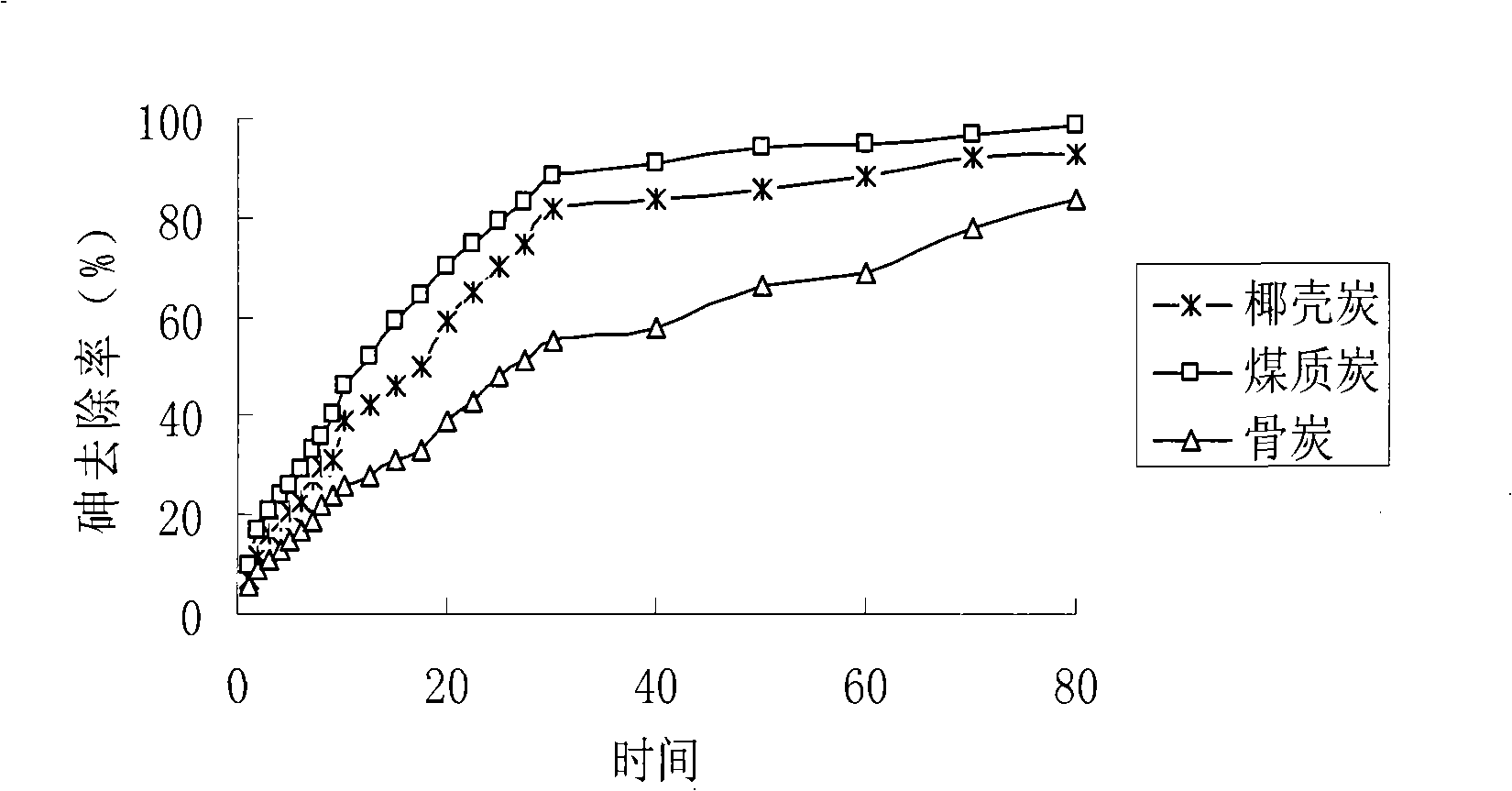
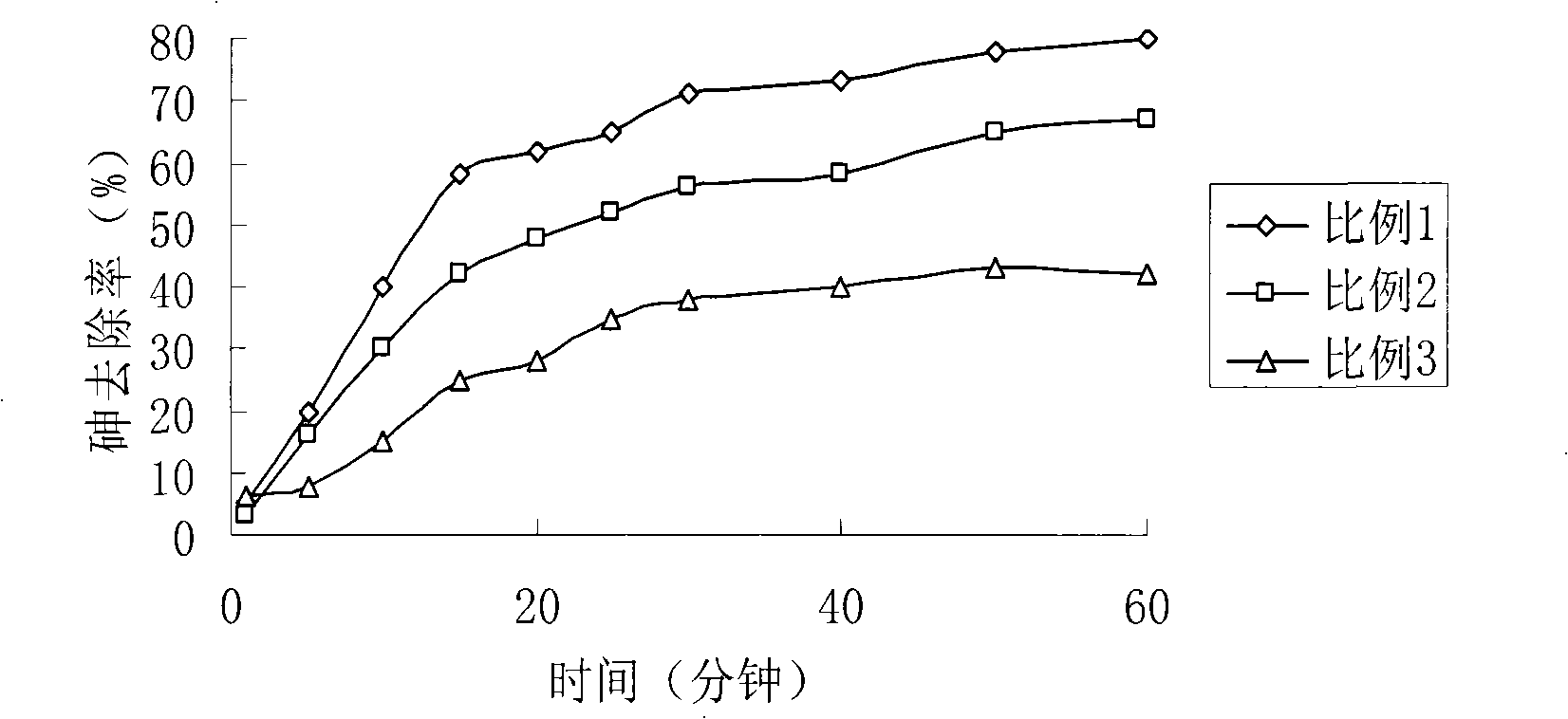
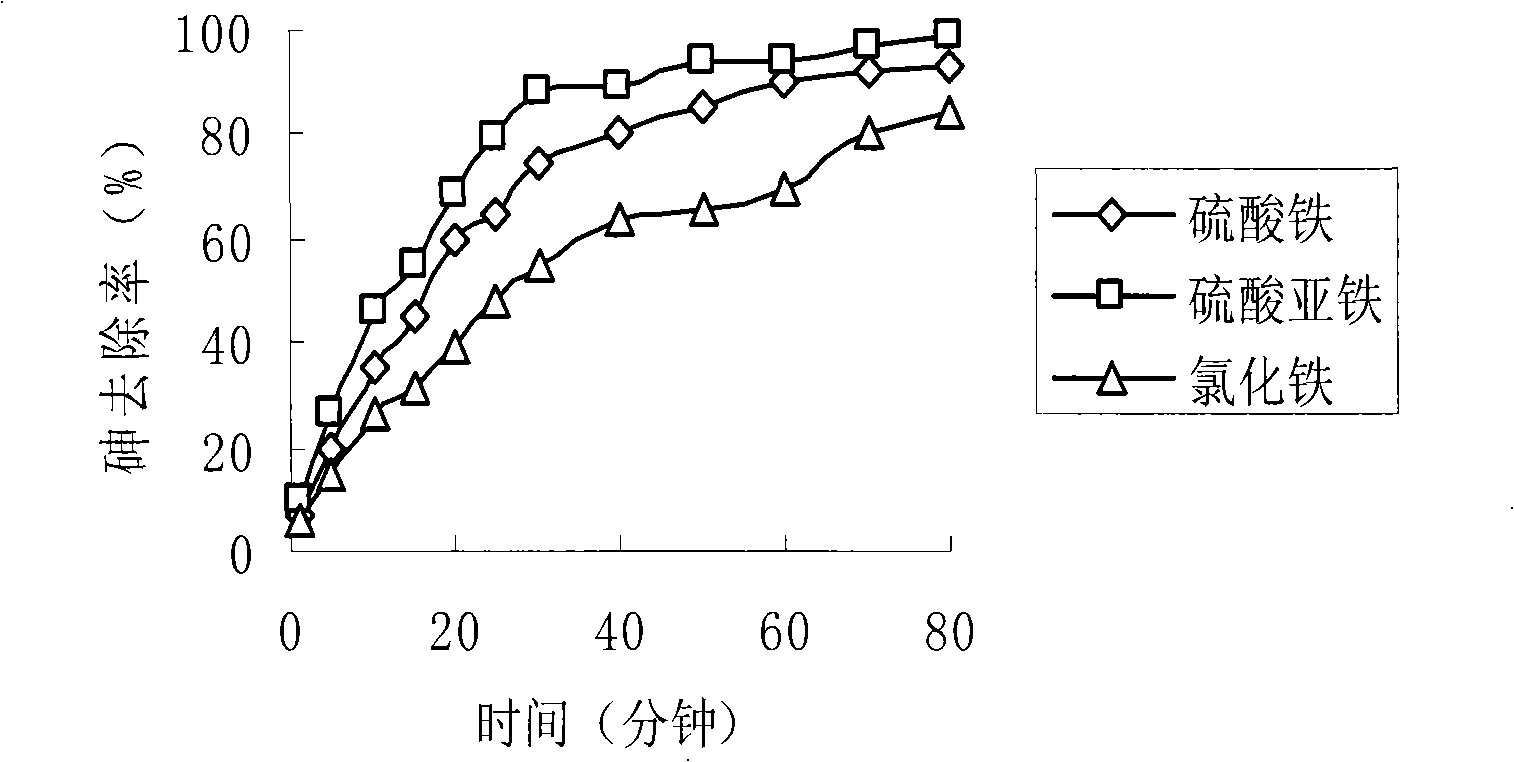
Method for preparing load type nano arsenic-removing sorbent for drinking water
InactiveCN101347717ALarge adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPotassium borohydrideSorbent
The invention relates to the elimination of the arsenic in drinking water, in particular to a preparation method of a supported type nano-adsorbent for removing arsenic from drinking water; the method includes the following steps: (1) activated carbon material with pore volume of 0.100-0.500cm<3> / g is selected for pretreatment; (2) soluble ferric salt solution is firstly used for soaking the activated carbon for 10-120 min; (3) alcoholic solution is taken as a dispersant to be added into the ferric salt solution; (4) under the protection of inert gases at room temperature, a strong reductant, potassium borohydride or sodium borohydride, is used for titrating the ferric salt, and agitation is carried out under the protection of inert gases; after the titration of potassium borohydride or sodium borohydride solution, agitation lasts for 10-120 min; (5) after agitation, centrifugation is carried out; oxygen-free water is firstly used for washing for 1-3 times, then organic solvent is adopted for washing for 1-3 times, and vacuum drying is done at 40-100 DEG C for 12-48h to obtain the product. The adsorbent of the invention has large adsorption capacity and small volume and is safe, stable and easy to store and transport.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flexible stretchable conductive circuit and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN108668431AReduce dosageAchieve mass productionLithography/patterningConductive pattern formationWire widthImage resolution
The invention provides a flexible stretchable conductive circuit, a preparation method and use thereof. The invention also provides double-sided wiring, multilayer board, flexible display, flexible electronics, and / or sensor comprising the flexible stretchable circuit described above. The method for preparing flexible stretchable conductive circuit provided by the invention is simple and rapid, and is generally applicable to various substrate materials, the liquid metal is used in a small amount, does not require additional external force, and the pattern does not generate cracks, the wire width is controllable, has a high resolution and it's very suitable for mass production.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Mesoporous graphene foam as well as preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103482611AStable structureLarge specific surface areaGrapheneNanotechnologyDraw ratioElectric properties
The invention belongs to the technical fields of a novel material as well as preparation, and particularly relates to mesoporous graphene foam as well as a preparation method thereof. The invention realizes hydrothermal preparation of a magnesium oxide texture structure and preparation of the mesoporous graphene foam by using textured magnesium oxide as a template. The mesoporous graphene foam material has abundant mesoporous structures and excellent electric property and can be used as an electrode material of batteries and supercapacitors, so that the energy density and the power density of the batteries or the supercapacitors are expectedly improved to a great extent. The cycling stability of the mesoporous graphene foam material is increased, and the mesoporous graphene foam material combined with materials with high draw ratio or the mesoporous graphene foam material can soften energy storage apparatuses. The advantages have important meaning for realization of commercialization of a new generation of energy storage apparatuses for electromobiles and development of smaller, lighter and flexible portable mobile power supplies. The business prospect is wide. Meanwhile, preparation processes of the high temperature hydrothermal method and a fluidized bed can realize engineering enlargement, so that the method is expected to be industrialized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
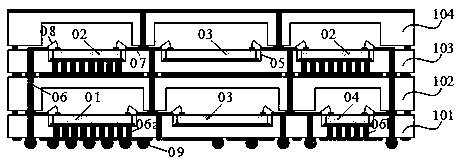
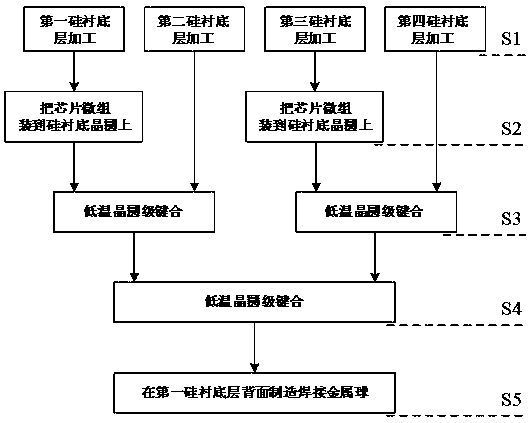
Silica-based three-dimensional heterogeneously-integrated radio frequency microsystem and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN108083223AImprove performanceAchieve mass productionDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesLow noiseHigh resistance
The invention discloses a silica-based three-dimensional heterogeneously-integrated radio frequency microsystem and a manufacturing method thereof. The silica-based three-dimensional heterogeneously-integrated radio frequency microsystem comprises a first silica substrate layer, a second silica substrate layer, a third silica substrate layer, a fourth silica substrate layer, a radio frequency power amplification chip, a radio frequency low noise amplification chip, a radio frequency filter and a radio frequency switch, wherein the silica substrate layers are high-resistance silicon wafers; radio frequency chips and devices are made of different substrate materials through different processes; the radio frequency chips and devices are assembled inside cavities pre-etched in the first silicasubstrate layer and the third silica substrate layer; the first silica substrate layer, the second silica substrate layer, the third silica substrate layer and the fourth silica substrate layer are processed through low-temperature wafer-scale bonding into a whole and vertically connected through silicon through holes to form the silica-based three-dimensional heterogeneously-integrated radio frequency microsystem. The silica-based three-dimensional heterogeneously-integrated radio frequency microsystem achieves tree-dimensional integration of heterogeneous radio frequency chips and devices,thereby reducing the size, increasing the packaging density, reducing transmission loss of wire connection and enhancing the properties.
Owner:GREAT MICROWAVE TECH CO LTD
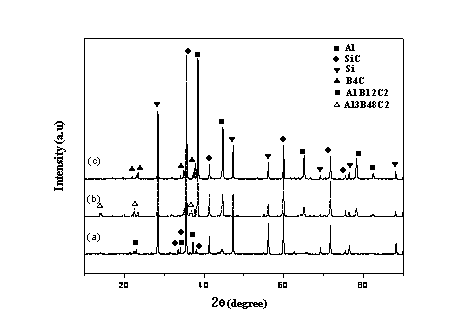
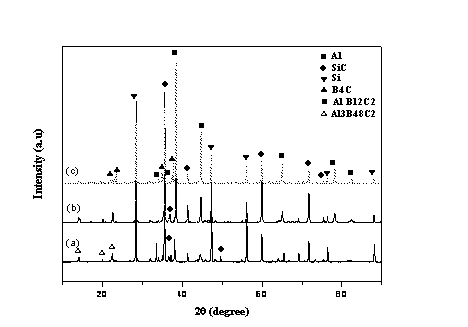
Boron carbide-silicon carbide complex ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of ceramic materials and in particular relates to a boron carbide-silicon carbide complex ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The boron carbide-silicon carbide complex ceramic is prepared through the following steps: degreasing a boron carbide and carbon mixed powder preform and then carrying out alloy infiltration reactive sintering on the degreased preform, wherein the boron carbide and carbon mixed powder preform comprises 85wt%-98wt% of boron carbide, 1.0wt%-14.0wt% of carbon and an organic bonding agent with a use amount for prefabrication and formation; and alloy is composed of 12.5wt% of silicon and 5wt%-87.5wt% of aluminum. According to the invention, a technology combining infiltration with reactive sintering is adopted, and a bidirectional interconnection microstructure is formed, so that the product has high mechanical property and can resist shooting of bullets; and the complex ceramic is low in density, is an optimal bulletproof and armour material, and is mainly applied to low-density high-property materials in the bulletproof and armour fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LIGHT TOUGH COMPOSITE MATERIALS
Preparation method of hydrolysis-resistant modified polylactic acid fibers
InactiveCN102660797AFeel goodGood flexibilityMelt spinning methodsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolyesterHydrolysis
The invention relates to a preparation method of hydrolysis-resistant modified polylactic acid fibers. The preparation method comprises the following steps of uniformly mixing 70 to 98.9 parts by weight of polylactic acid, 1 to 30 parts by weight of one or more low-molecular weight polyesters and 0.1 to 5.0 parts by weight of multifunctional polycarbodiimides, carrying out melt blending granulation of the mixture to obtain master batches, carrying out vacuum drying of the master batches, carrying out melt spinning and winding to obtain winded wires, and carrying out drafting to obtain the hydrolysis-resistant modified polylactic acid fibers. The preparation method is simple, has a low cost and is suitable for large-scale production. The hydrolysis-resistant modified polylactic acid fibers have excellent handle and softness, realize low temperature dying, have high dye-uptake in high temperature dying and have good hydrolysis resistance so that the problem of mechanical property degradation produced in high temperature treatment is avoided.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com