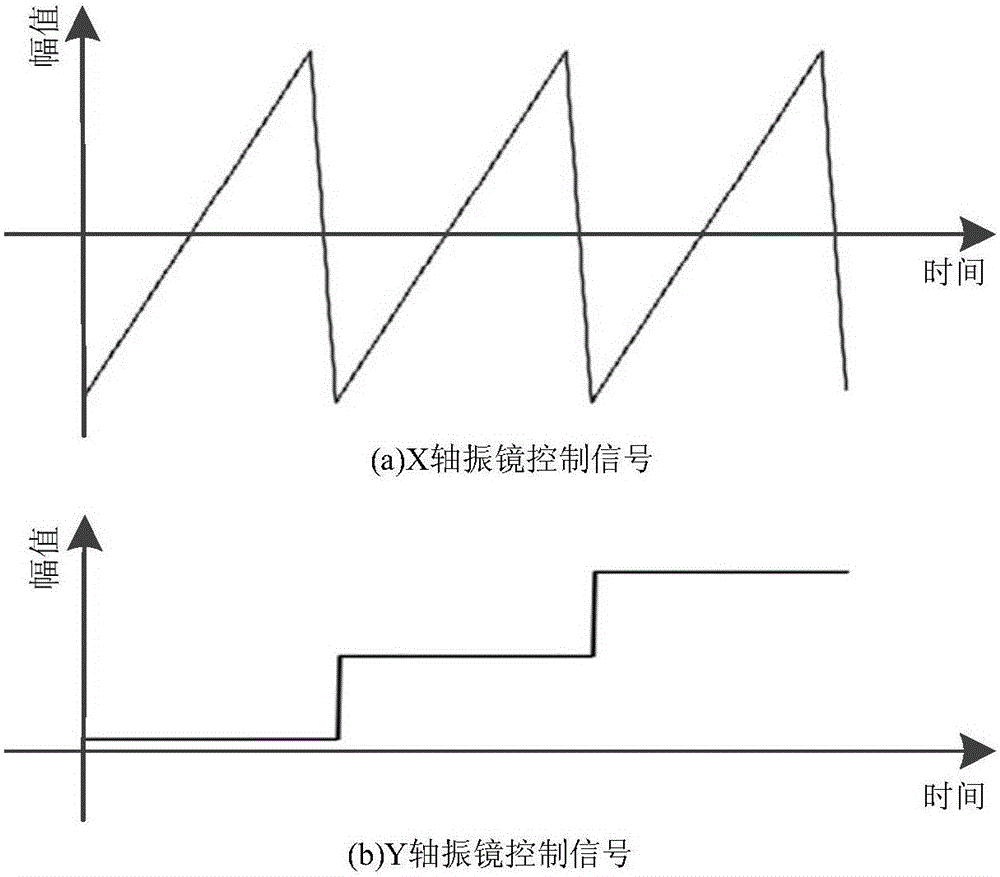
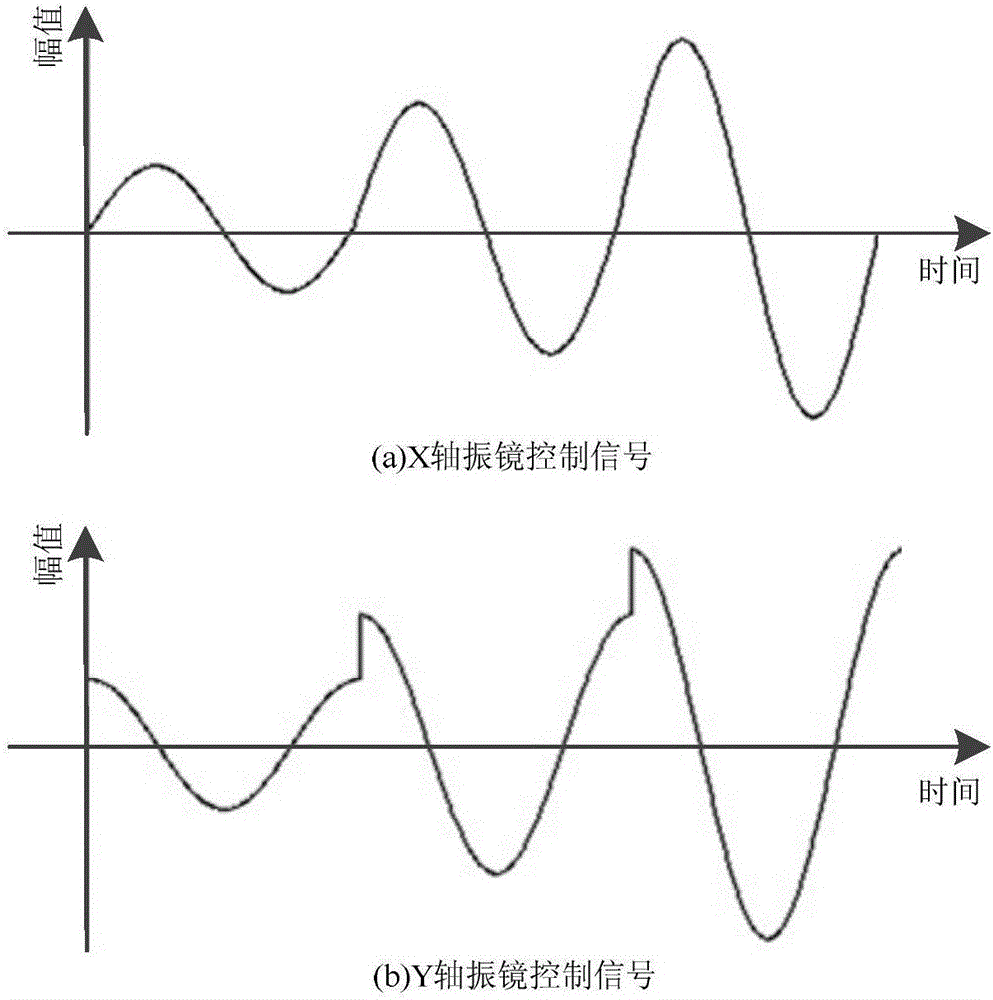
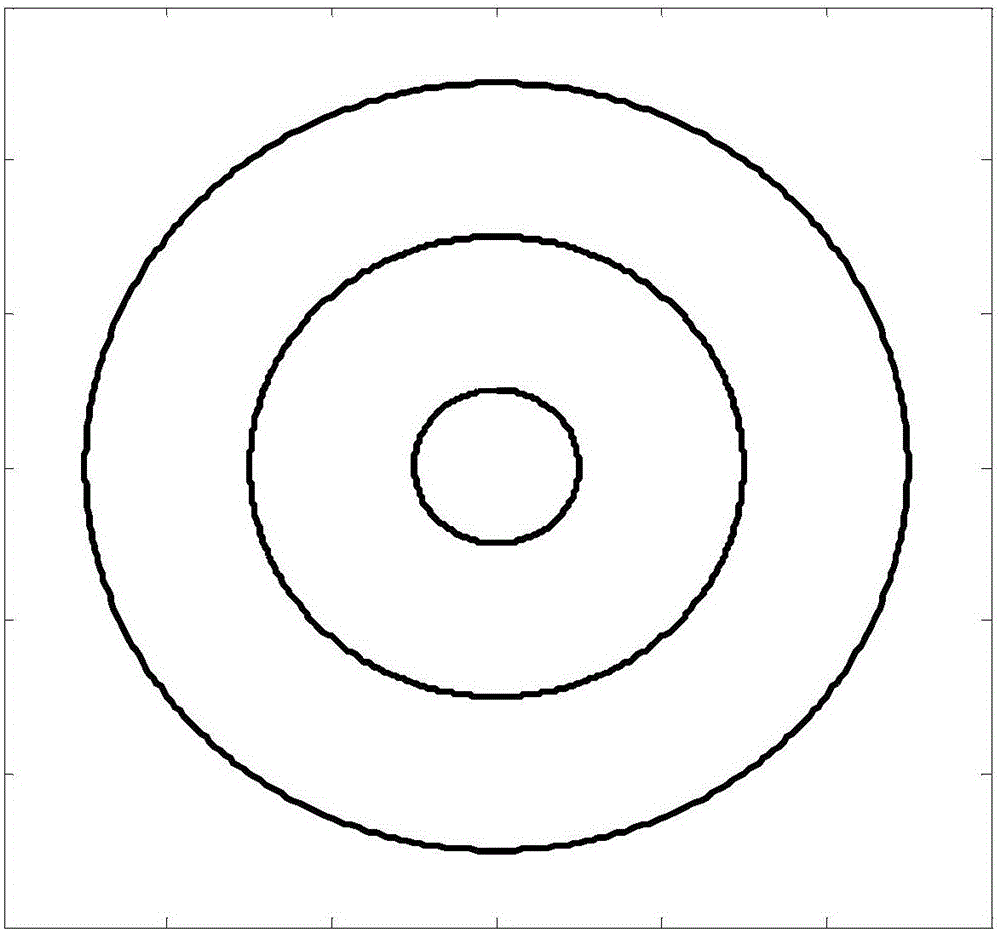
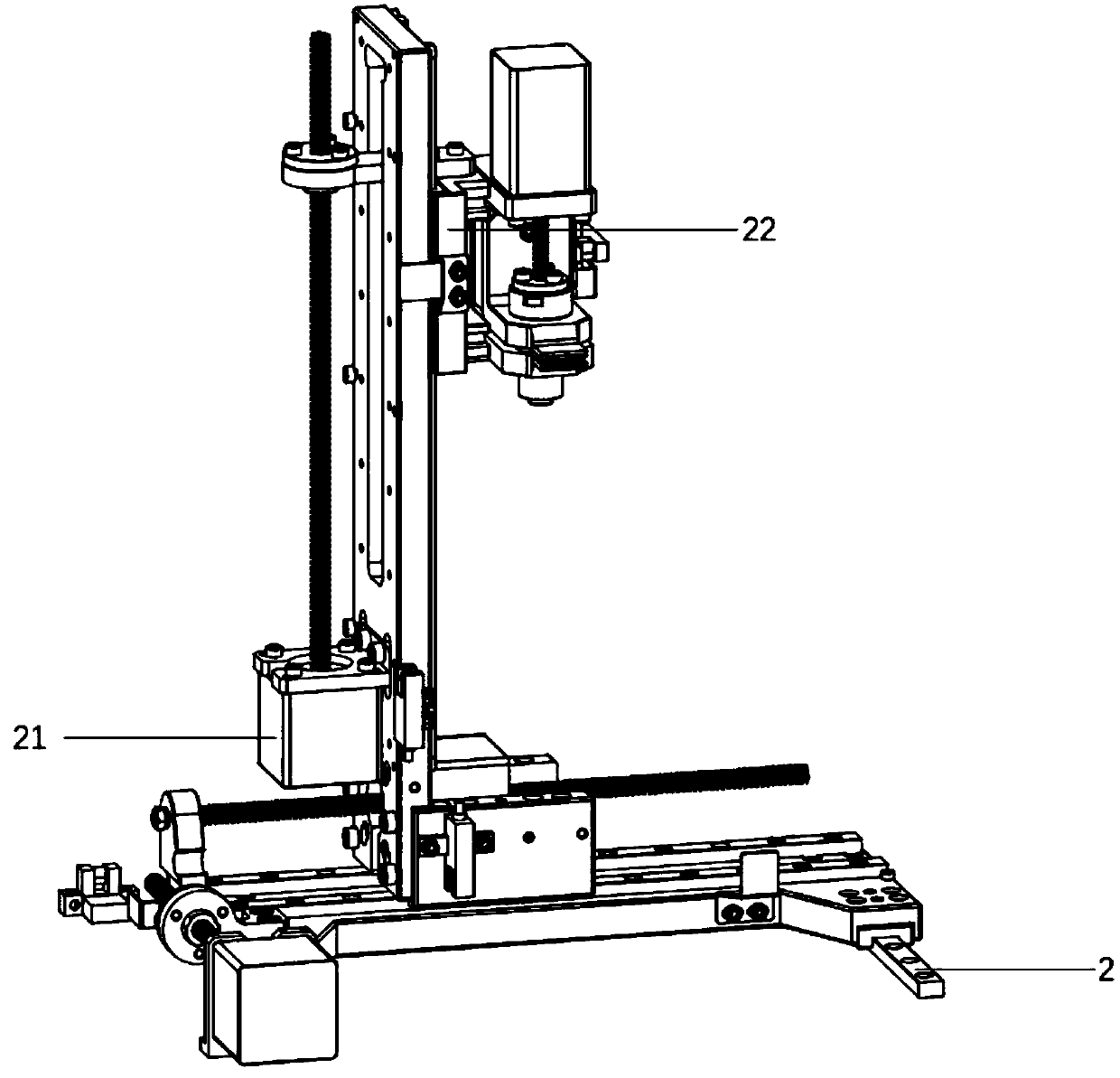
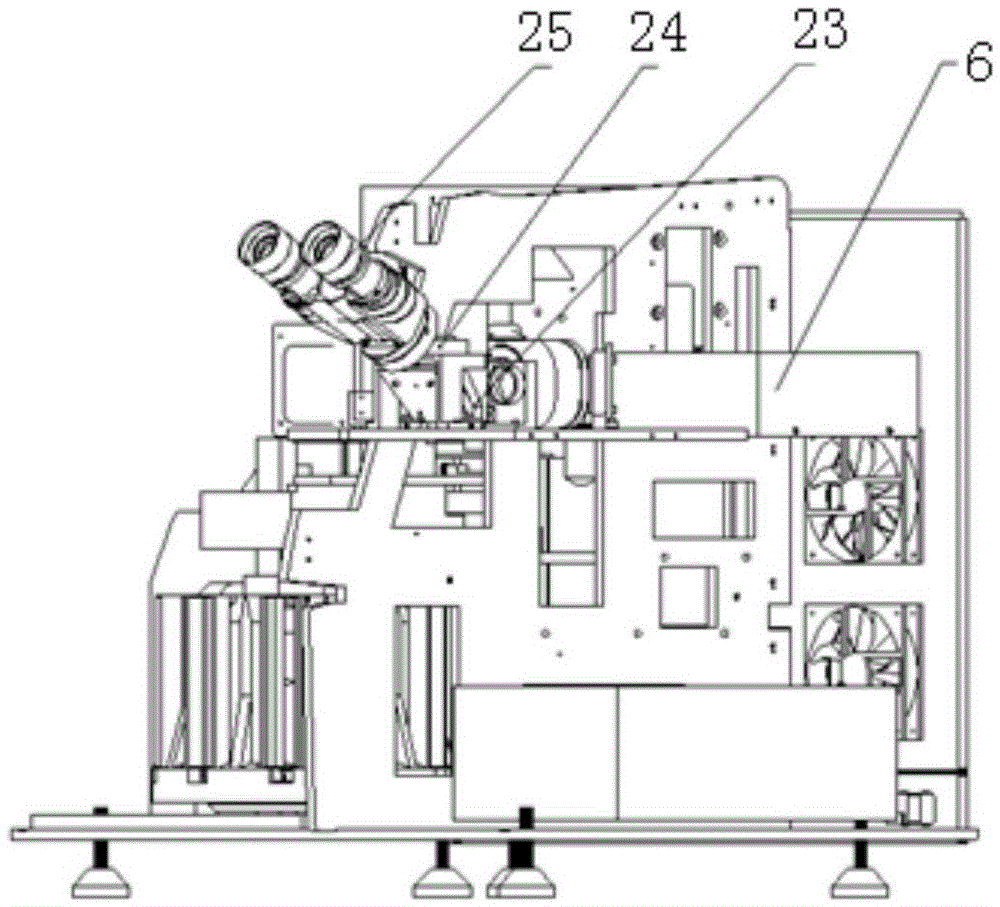
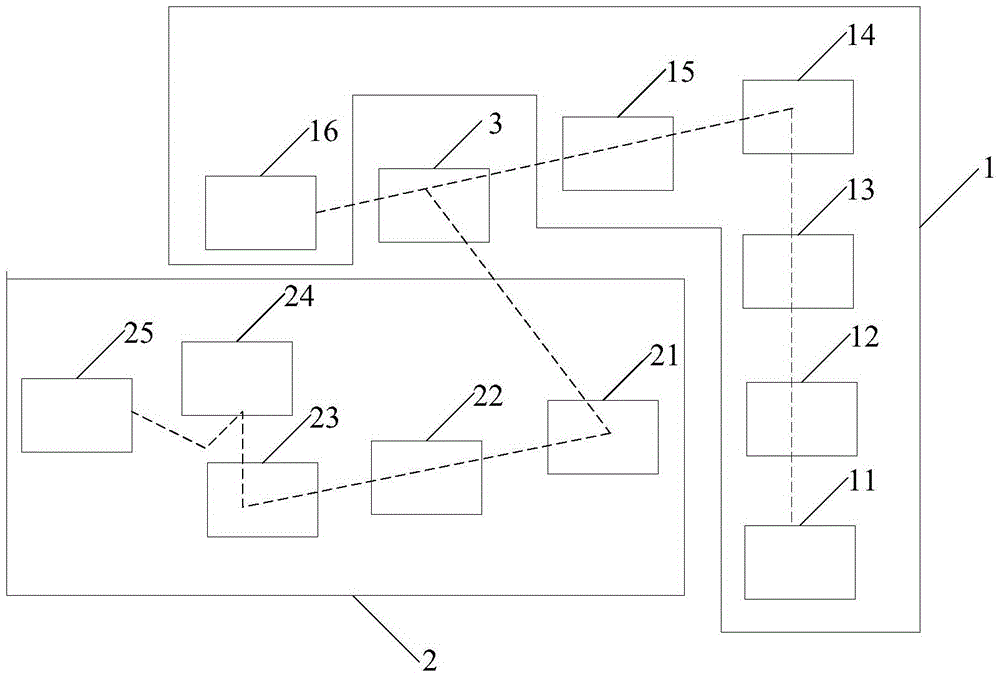
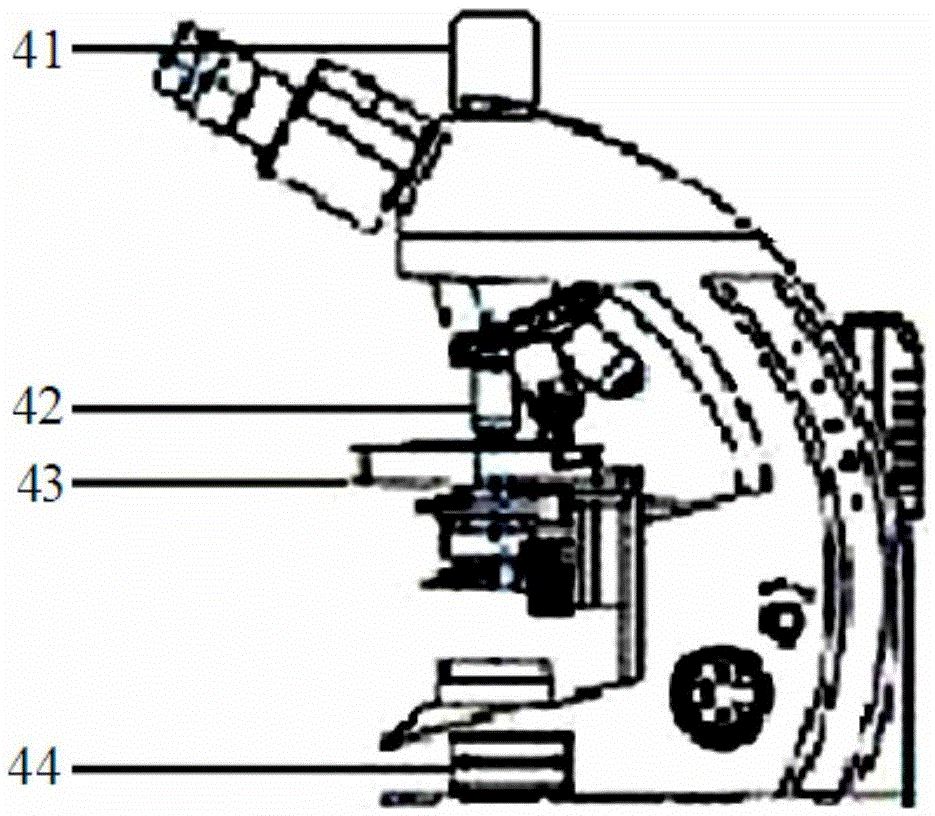
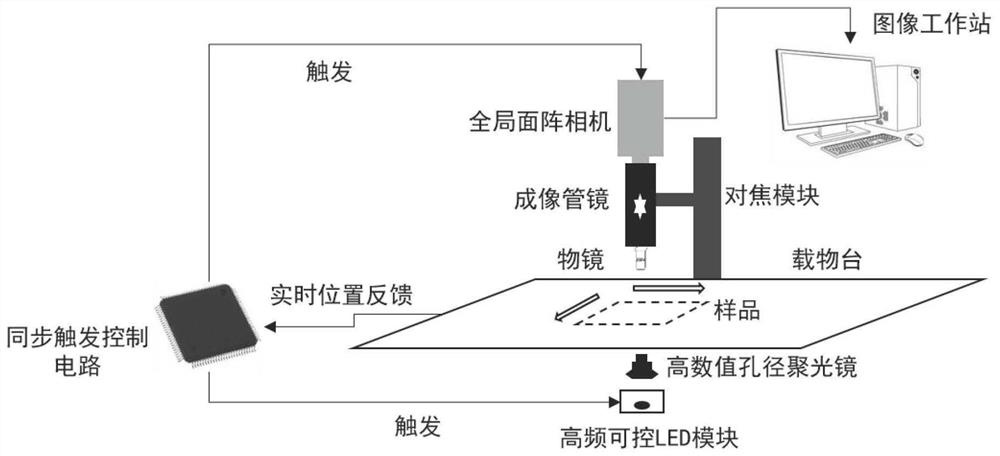
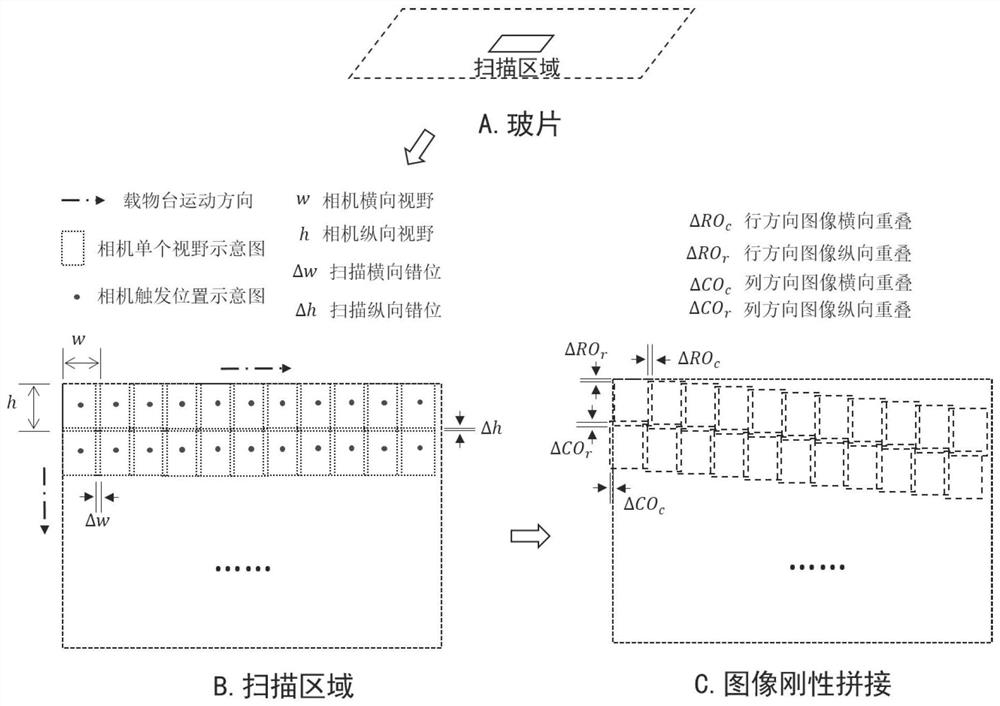
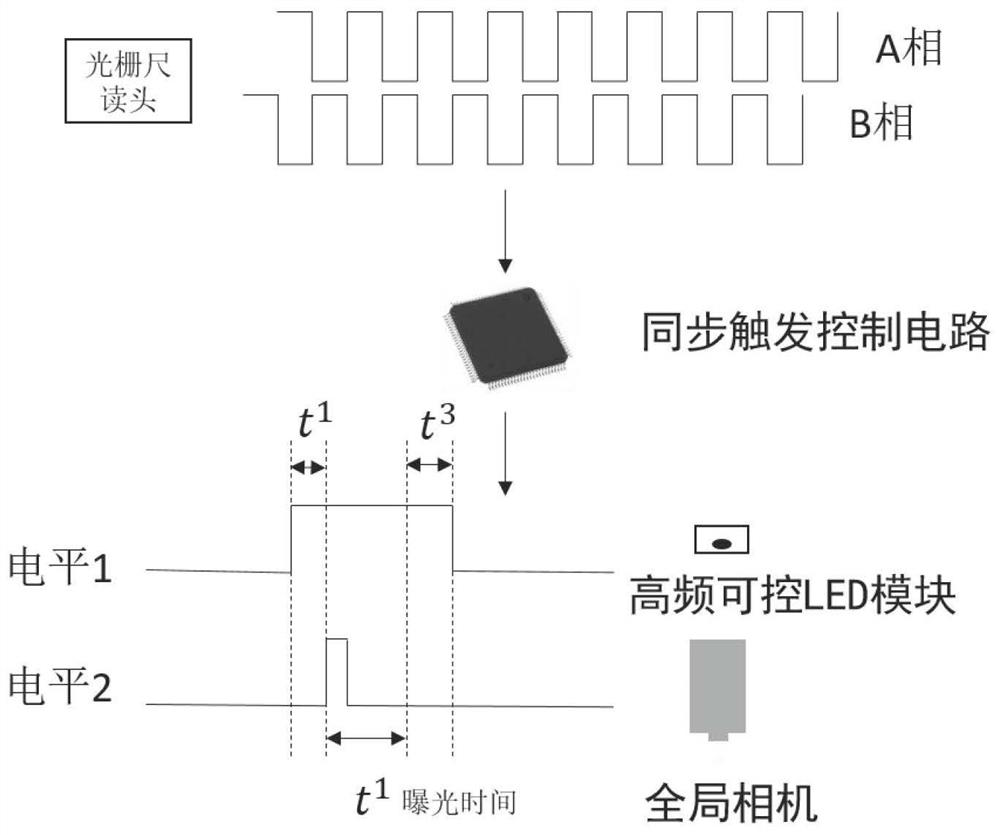
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Microscanning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
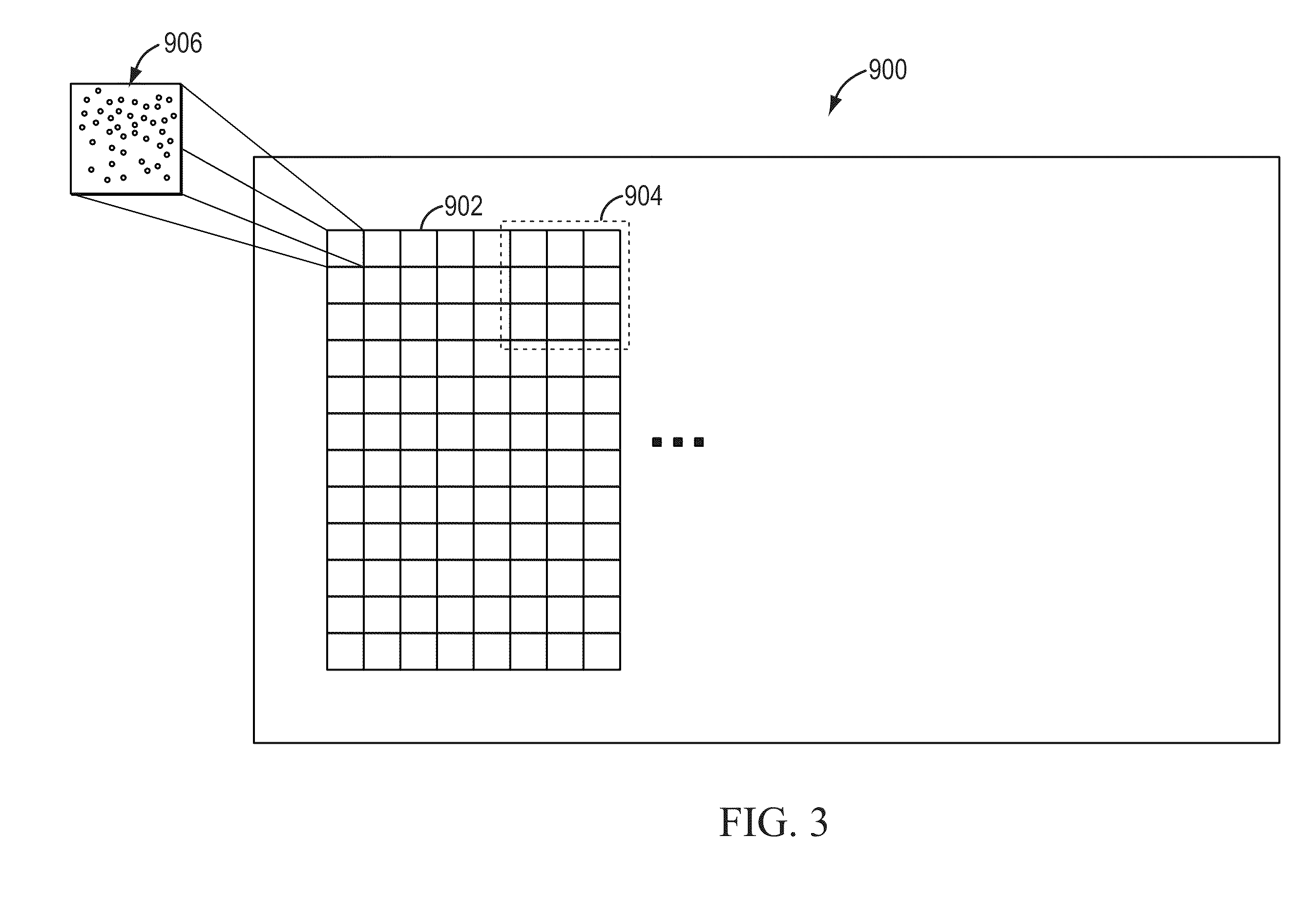
Microscanning is a method for increasing resolution of digital cameras. With the color co-site sampling identically colored pixels in several frames of the specimen, obtained by moving the sensor with a piezo mechanism in a regular raster, are combined to a sharp resulting image. The detector, however, can also be translated by a fraction of the pixel pitch: this way also the interstitial space between sensor pixels gets scanned and the number of pixels in the final image is increased. Three positions on the x and y axes increase the image size by a factor of 9, for instance from the common 1388 x 1040 pixels to 4164 x 3120 pixels (see Sony ICX285 series). The color co-site sampling used at the same time ensures correct reproduction of colors at the pixel density produced.
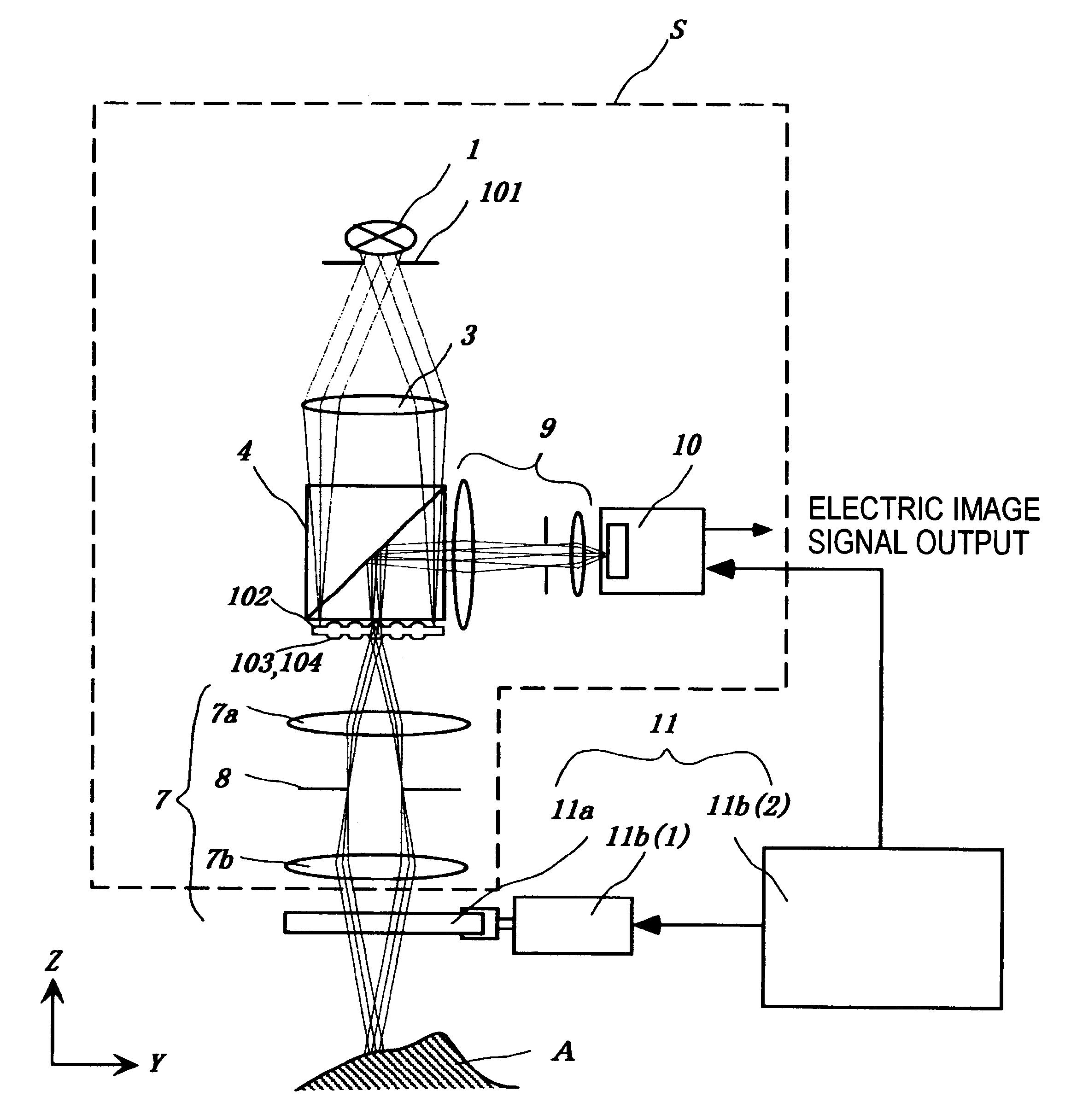
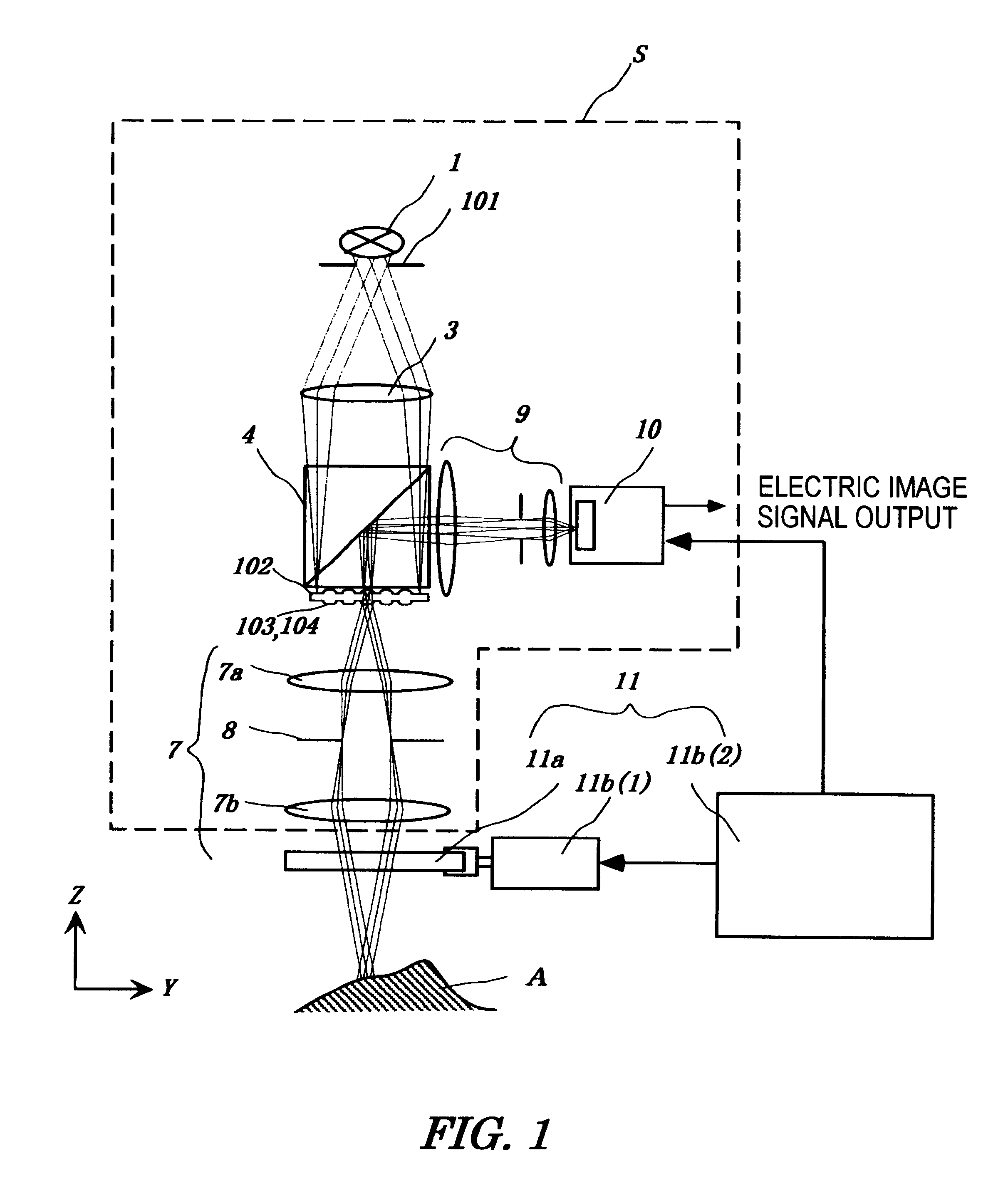
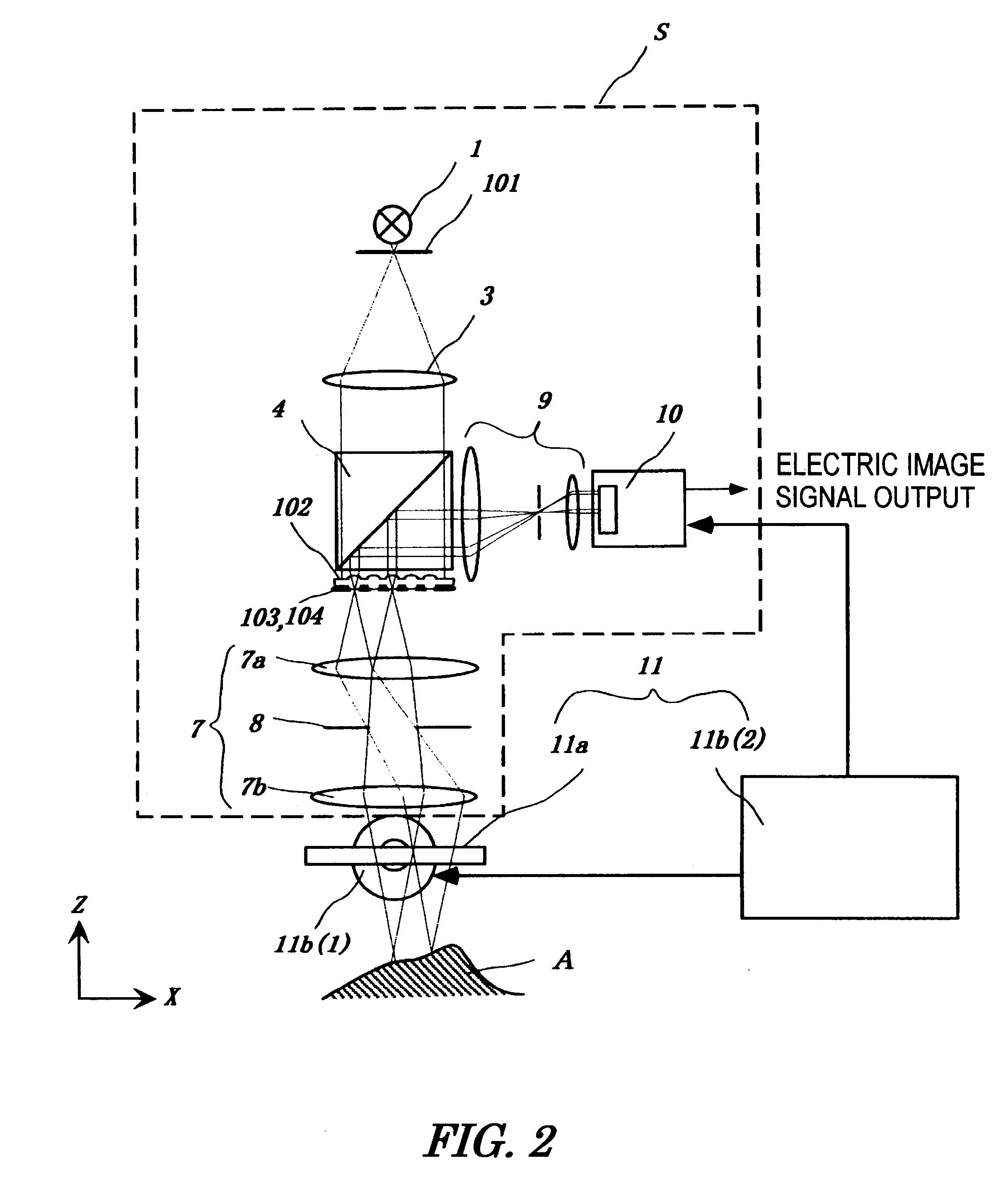
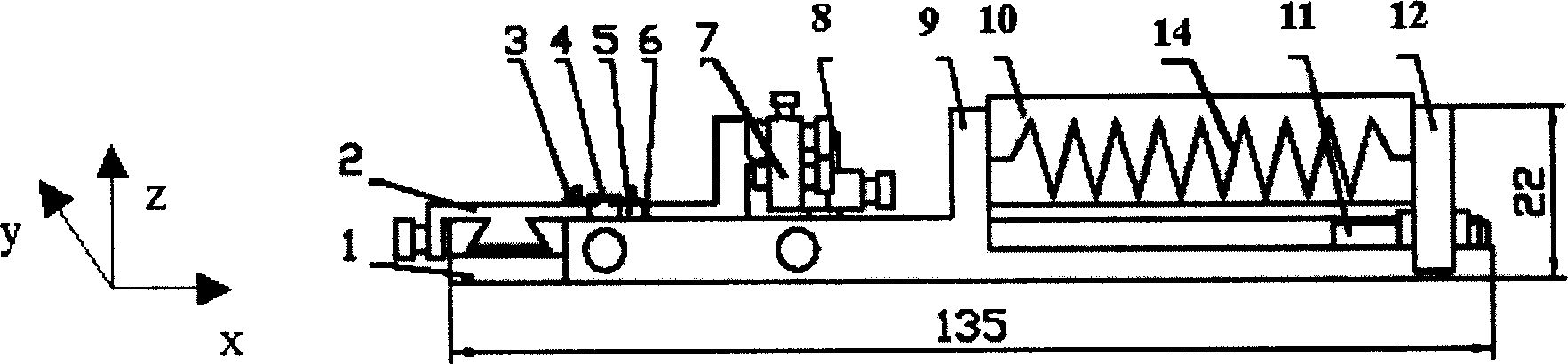
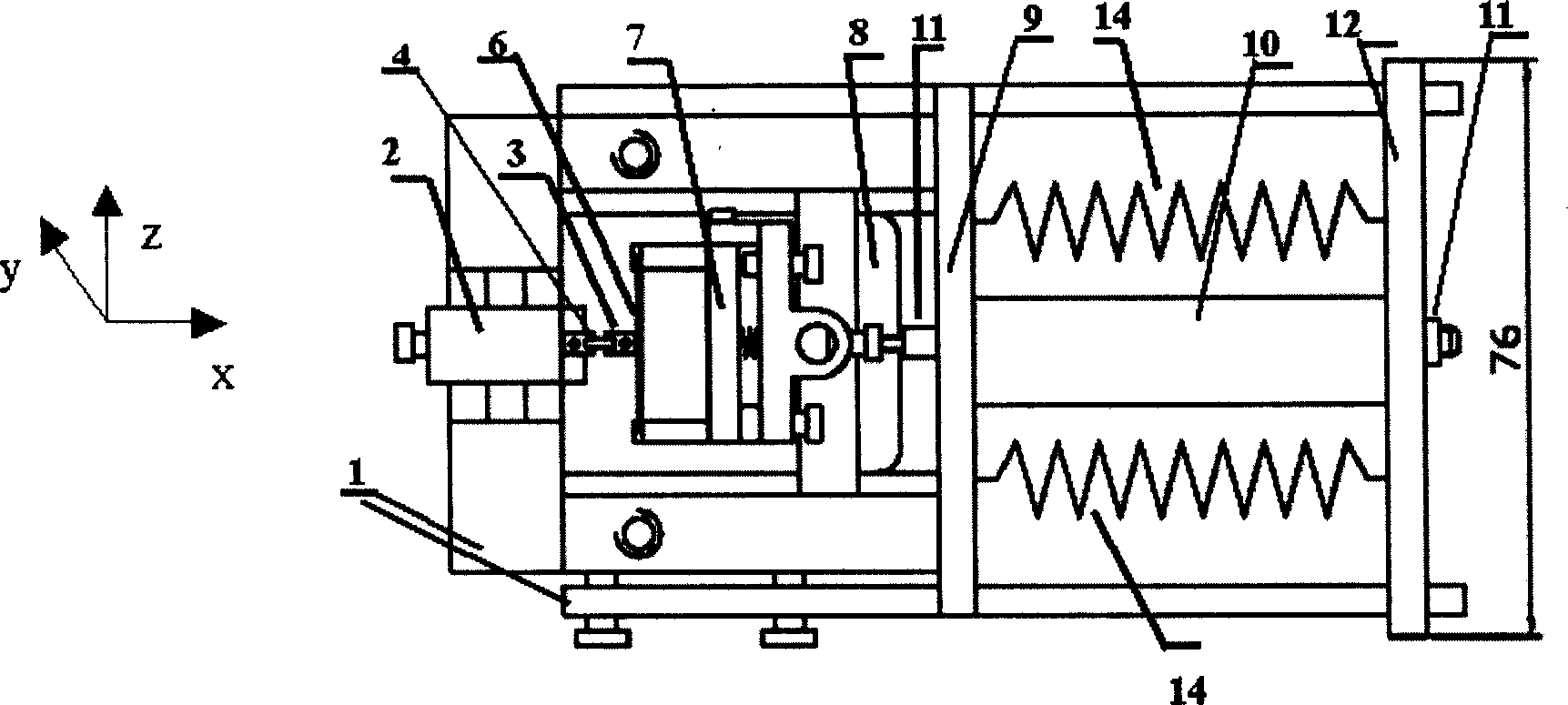
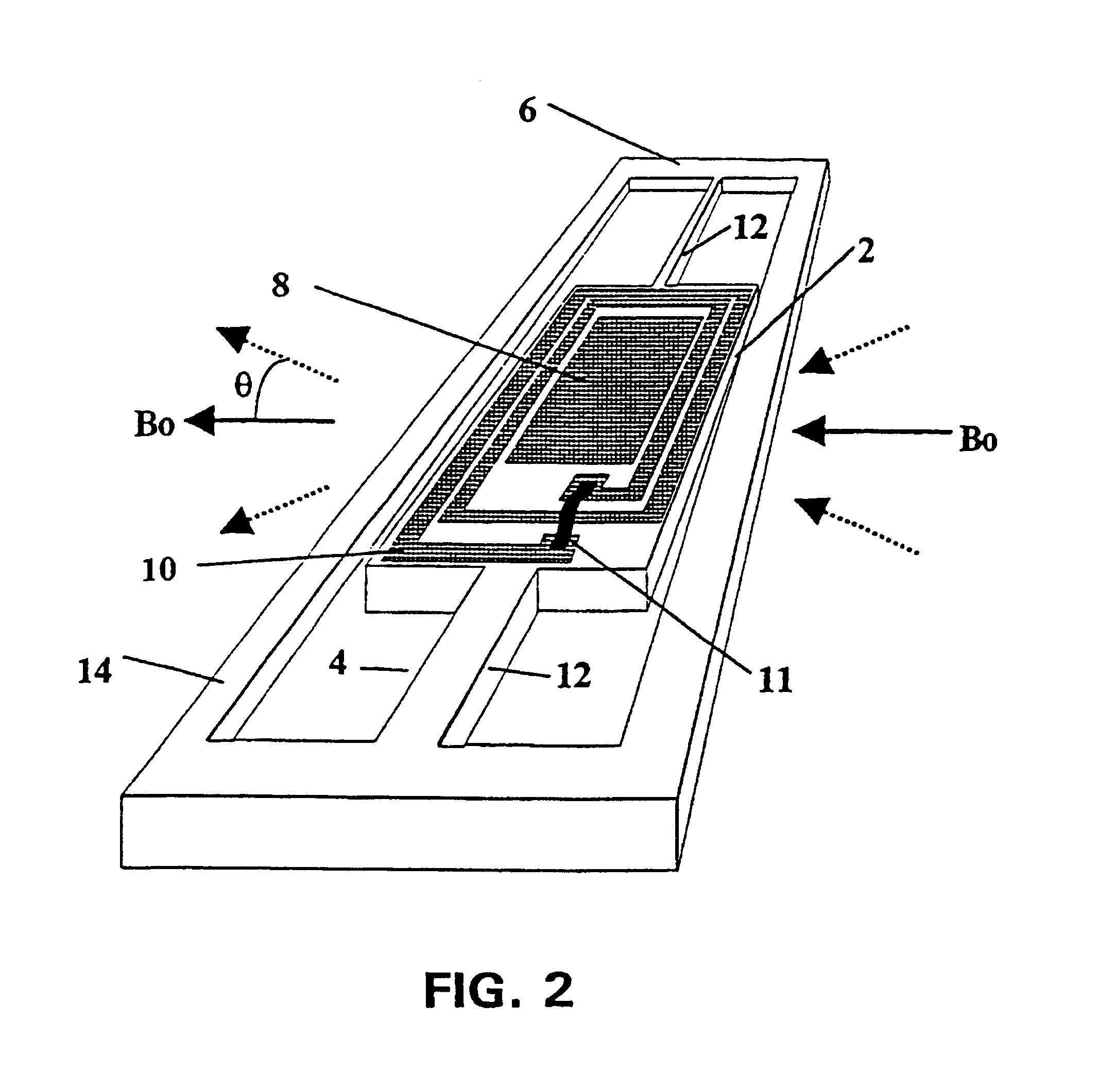
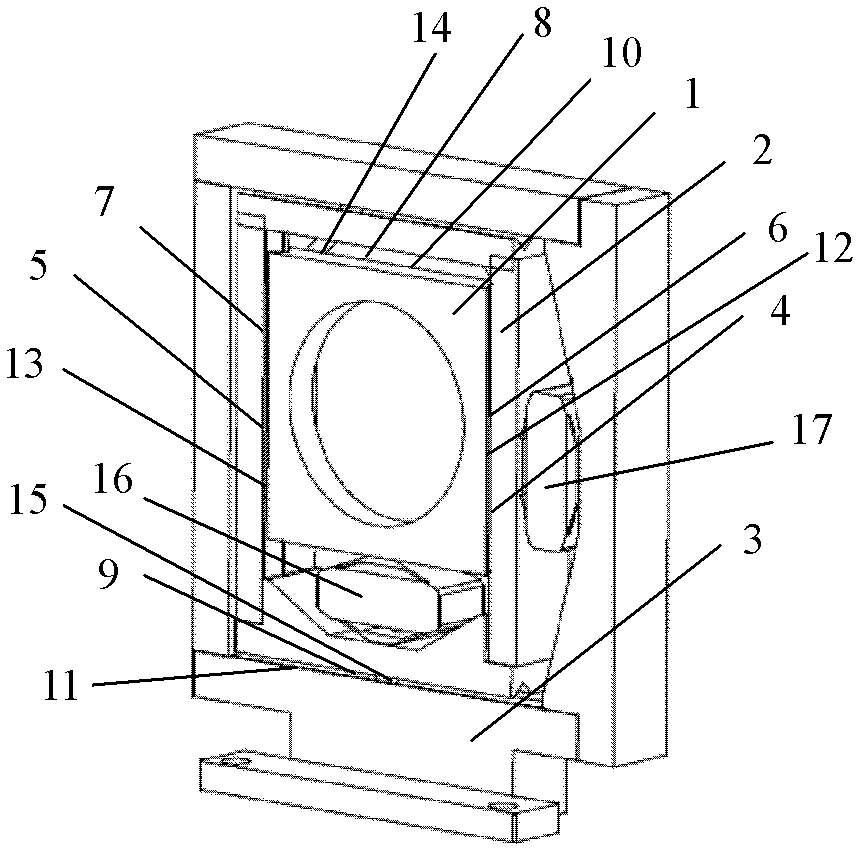
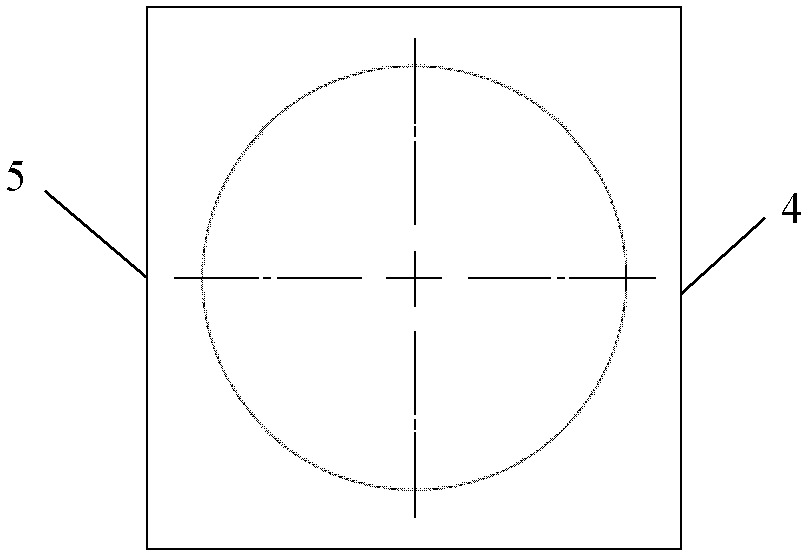
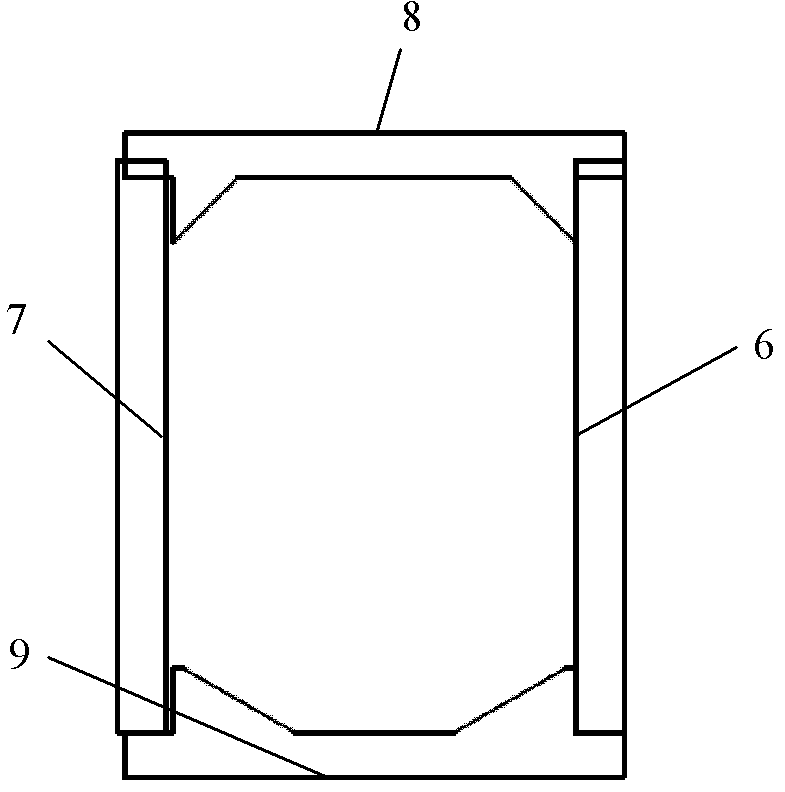
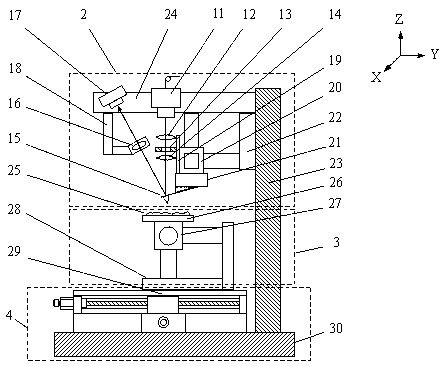
Micro-scanning multislit confocal image acquisition apparatus
InactiveUS6288382B1Reduce the impactReduce impactRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The micro-scanning multislit confocal image acquisition apparatus of the present invention is a confocal image acquisition apparatus that comprises a nonscanning multislit confocal image acquisition system using a slit array instead of a pinhole array and a multislit-image microscanning mechanism for moving the image of the slit array in a small back and forth motion with respect to the object during each exposure of the two-dimensional arrayed photodetector in one complete measurement. Microscanning the image of the slit array with an amplitude equal to half the distance between adjacent slits increase the aperture ratio of the pixels to 100 percent, reducing blind regions to zero. As a result, this apparatus can measure a small object that cannot be measured by a conventional nonscanning confocal image acquisition apparatus because of blind regions. Microscanning the image of the slit array can also reduce the effect of speckles, another problem of a conventional nonscanning confocal image acquisition apparatus, by averaging the reflected light passing through each aperture of the slit array.
Owner:TAKAOKA ELECTRIC MFG
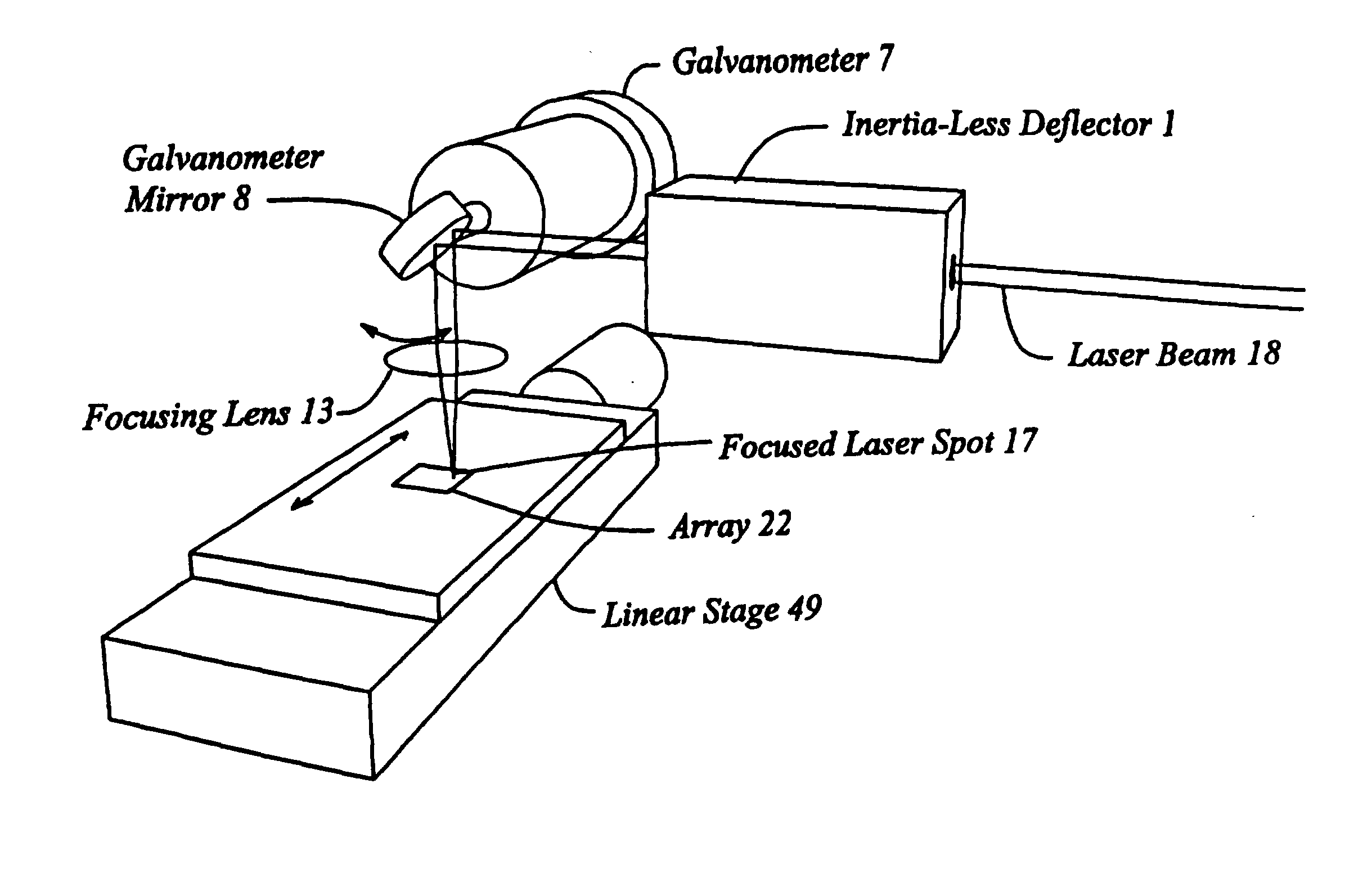
Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning
InactiveUS20030156323A1Diameter of to varyEnsure high efficiency and accuracyMirrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansWide areaGrating
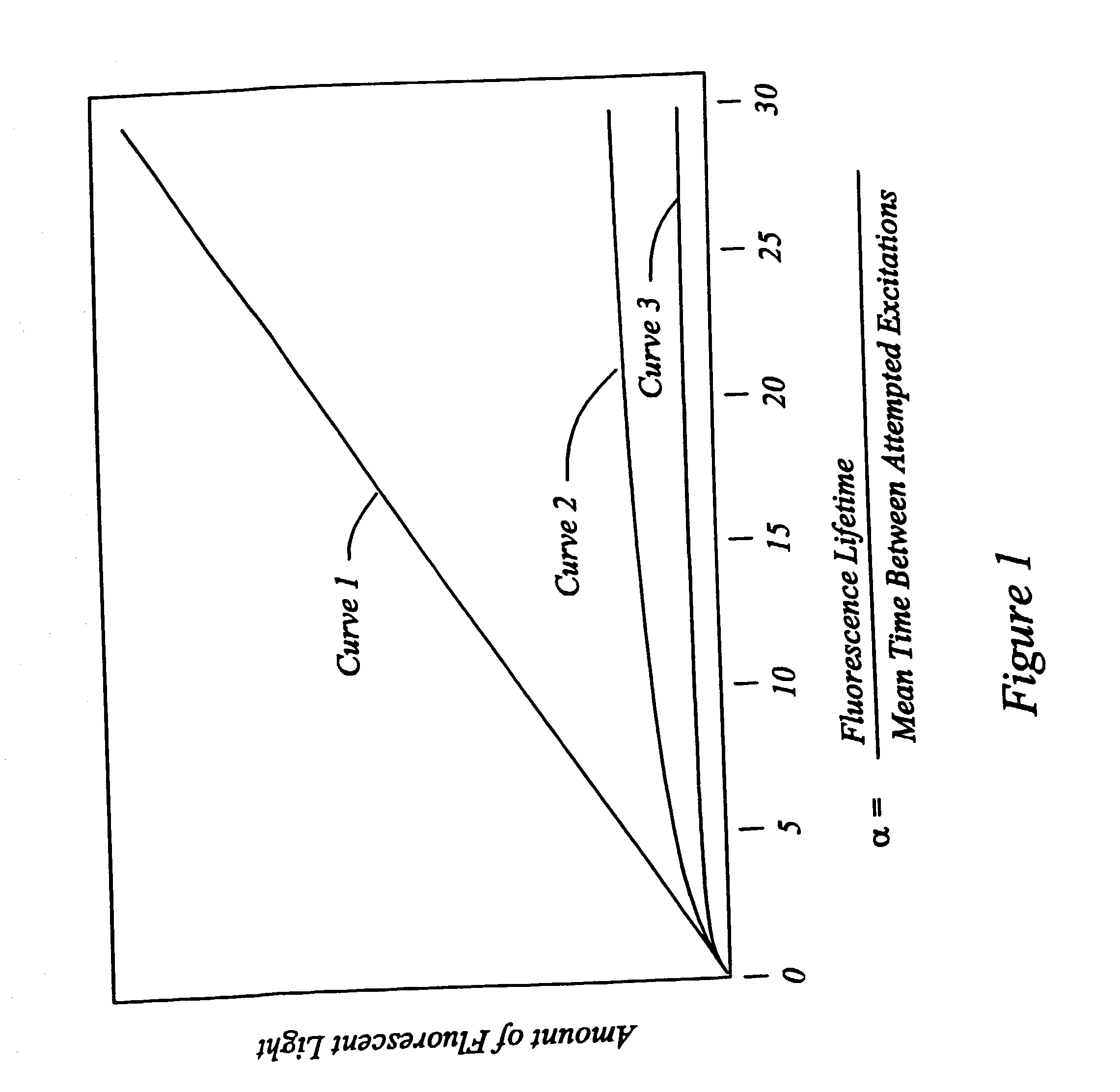
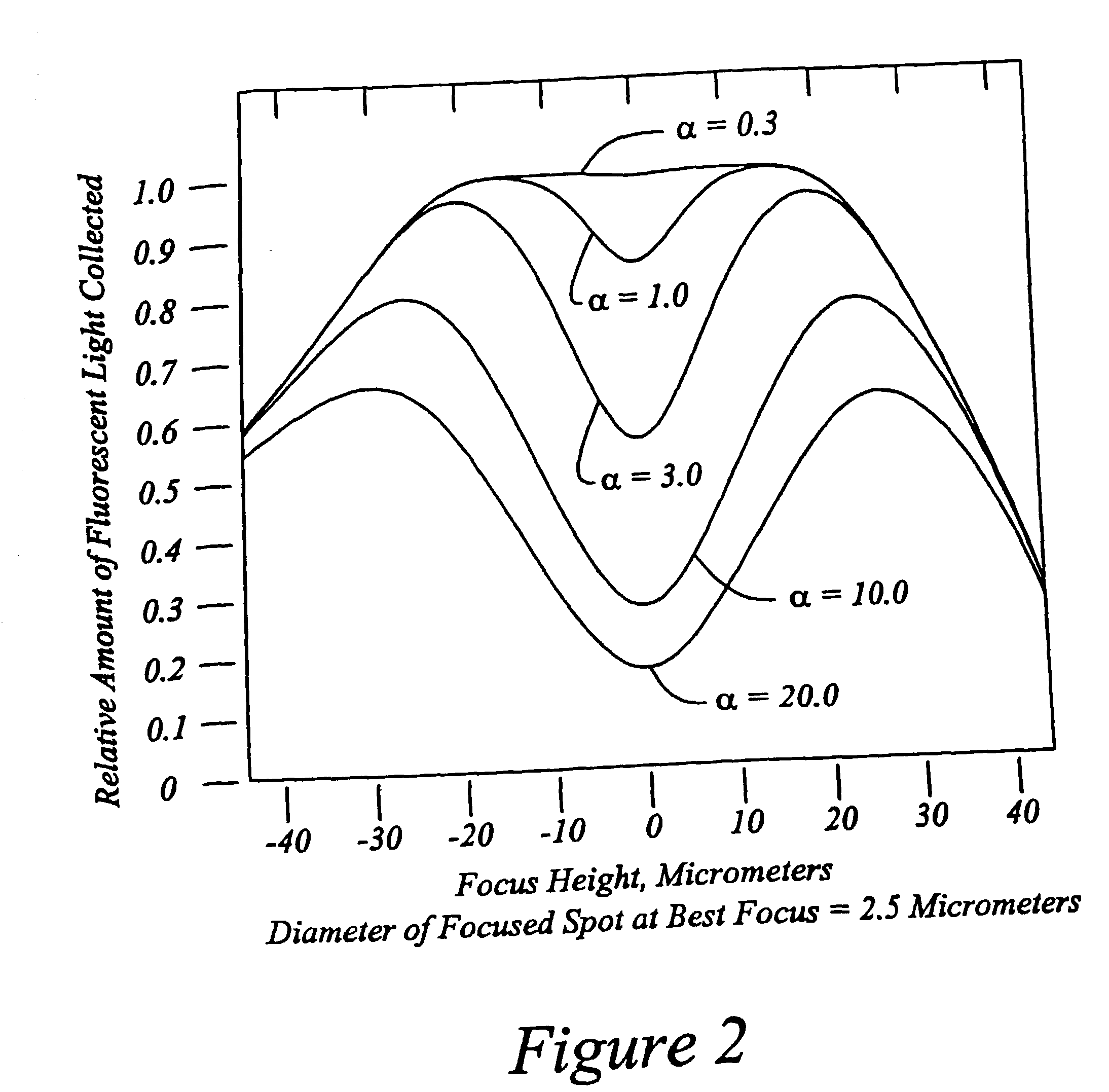
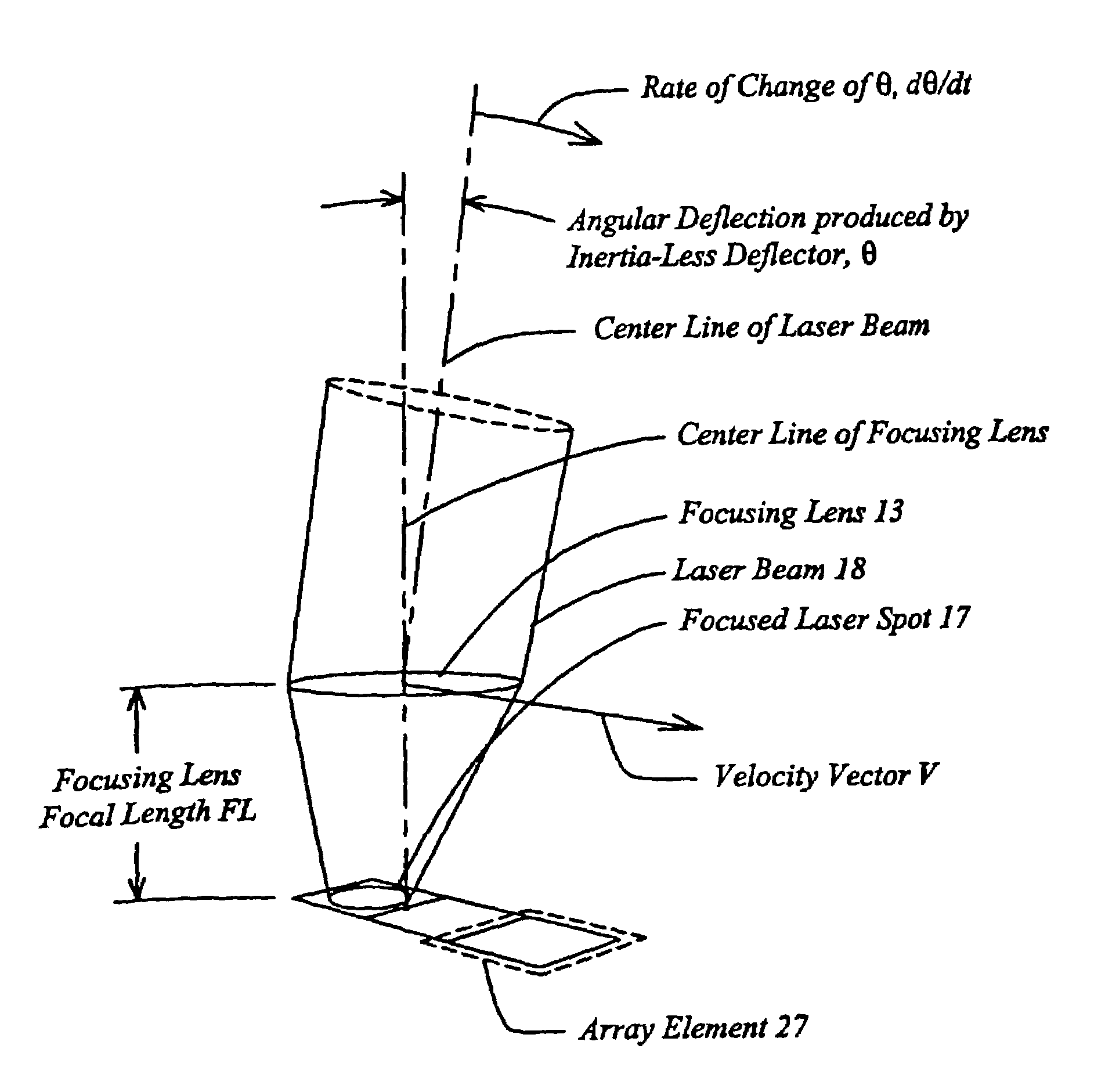
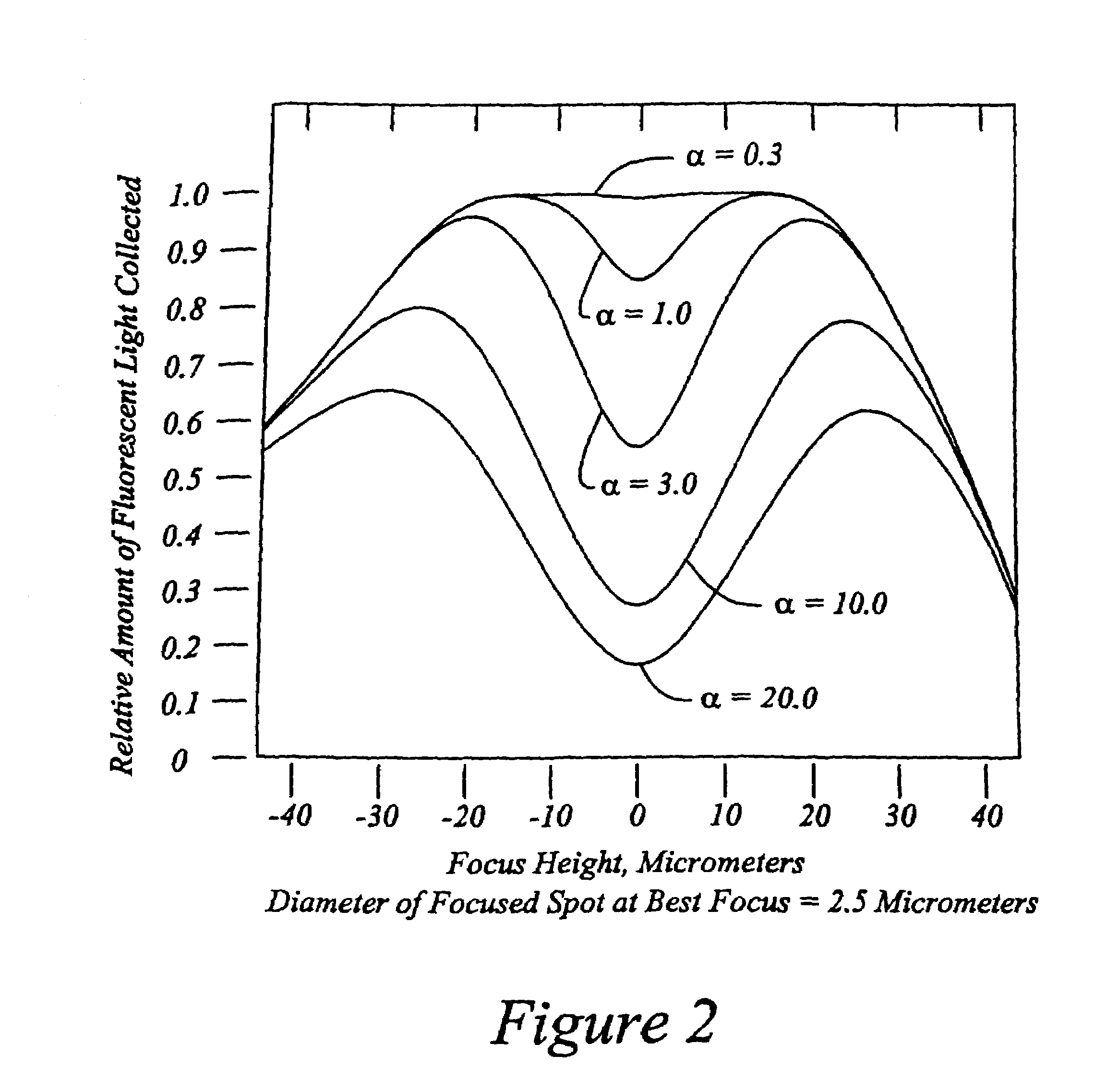
High speed, wide area microscopic scanning or laser positioning is accomplished with an inertia-less deflector (for example an acousto-optic or electro-optic deflector) combined with a high speed wide area microscopic scanning mechanism or laser positioner mechanism that has inertia, the motion of the inertia-less deflector specially controlled to enable a focused spot to stabilize, for example to stop and dwell or be quickly aimed. It leads to improved data acquisition from extremely small objects and higher speed operation. In the case of fluorescence reading of micro-array elements, dwelling of fluorophore-exciting radiation in a spot that is relatively large enables obtaining the most fluorescent photons per array element, per unit time, a winning criterion for reducing fluorophore saturation effects. The same inertia-less deflector performs stop and dwell scanning, edge detection and raster scans. Automated mechanism for changing laser spot size enables selection of spot size optimal for the action being performed.
Owner:OVERBECK JAMES W
Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning
InactiveUS7050208B2Increase ratingsAdd dimensionMirrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringFluorophore
High speed, wide area microscopic scanning or laser positioning is accomplished with an inertia-less deflector (for example an acousto-optic or electro-optic deflector) combined with a high speed wide area microscopic scanning mechanism or laser positioner mechanism that has inertia, the motion of the inertia-less deflector specially controlled to enable a focused spot to stabilize, for example to stop and dwell or be quickly aimed. It leads to improved data acquisition from extremely small objects and higher speed operation. In the case of fluorescence reading of micro-array elements, dwelling of fluorophore-exciting radiation in a spot that is relatively large enables obtaining the most fluorescent photons per array element, per unit time, a winning criterion for reducing fluorophore saturation effects. The same inertia-less deflector performs stop and dwell scanning, edge detection and raster scans. Automated mechanism for changing laser spot size enables selection of spot size optimal for the action being performed.
Owner:OVERBECK JAMES W
Film stretching loading device under scanning microscopy environment and film distortion measurement method
InactiveCN1731135ARealize online detectionSurface/boundary effectUsing mechanical meansMicrometerBeam scanning
The invention relates to a film-stretching loading device in scanning microscope environment and a film-deformation measuring method in the field of microscope scanning nondestructive inspection and precision machine. The device uses the designed mechanic structure, pressure ceramic driving system, force buffer system and so on which can do three-space location and angle adjustment to finish film deformation measuring on atom force scanning microscope and electron beam microscope detecting table. It can dose quantity detecting to deformation field of all region or localized region of the micro size film; the thickness of the detected film is from several micrometers to sub-micros; it can finish film original location and on line detecting under the high spacing resolution microscope atom force scanning microscope or electron beam scanning microscope environment combined with the double-exposure digital spot technique, the image related technique or micro-labeling technique.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Induction microscanner
InactiveUS6285485B1Consumes less powerIncrease deflection angleDynamo-electric machinesOptical elementsControl electronicsPhysics
A micro-electromechanical scanner is disclosed for the efficient, controlled deflection of light beams. The device comprises a moving rotor, a suspension system, and a stator. The rotor comprises a closed-circuit coil and a mirror. The suspension system may be, for example, a set of torsion bars on which the rotor is mounted. The stator may be, for example, a rectangular frame holding the suspension system. When placed in a constant magnetic field and excited by an alternating magnet field, the rotor oscillates at the frequency of the alternating magnetic field, All else being equal, the highest deflection angles occur at the natural mechanical resonance frequency of the rotor-suspension combination. Compared to conventional devices, the novel device can be smaller, can be less expensive, can consume less power, and may exhibit higher deflection angles over a given time scale than other micromechanical devices operating on different actuation principles. The novel device may be used, for example, to replace the scanning devices currently used in laser printers, laser bar-code readers, and laser image projectors (e.g., large screen televisions). The control electronics may optionally be manufactured on the same device, eliminating the need for a separate controller and reducing costs.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Micro-scanning platform, shooting method and work area flatness calibration method
InactiveCN104730702AContinuous scan implementationEasy to adjustMicroscopesContinuous scanningShooting method
The invention discloses a micro-scanning platform, a shooting method and a work area flatness calibration method. Continuous scanning on a low precision platform can be achieved. The method mainly comprises the steps that a scanning coordinate system is set up in a work area; through a plane formula A1X+B1Y+C1Z+D1=0 and a standard slide, the calibration values En of the flatnesses of all scanning points in the work area of an objective table are determined; then, in actual sample slide shooting, the actual focusing position of each scanning point is determined according to the corresponding En. In this way, all scanning points can be adjusted to be in place before a camera shoots all the scanning points. The continuous scanning on the low precision platform can be achieved. Moreover, the scanning precision is high, scanning efficiency is high, and shot photos are clear. Due to the fact that high-precision continuous scanning is achieved on the low precision platform, the manufacturing cost of a high-precision scanning device is remarkably reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU CHUANGJI BIOLOGICAL TECH
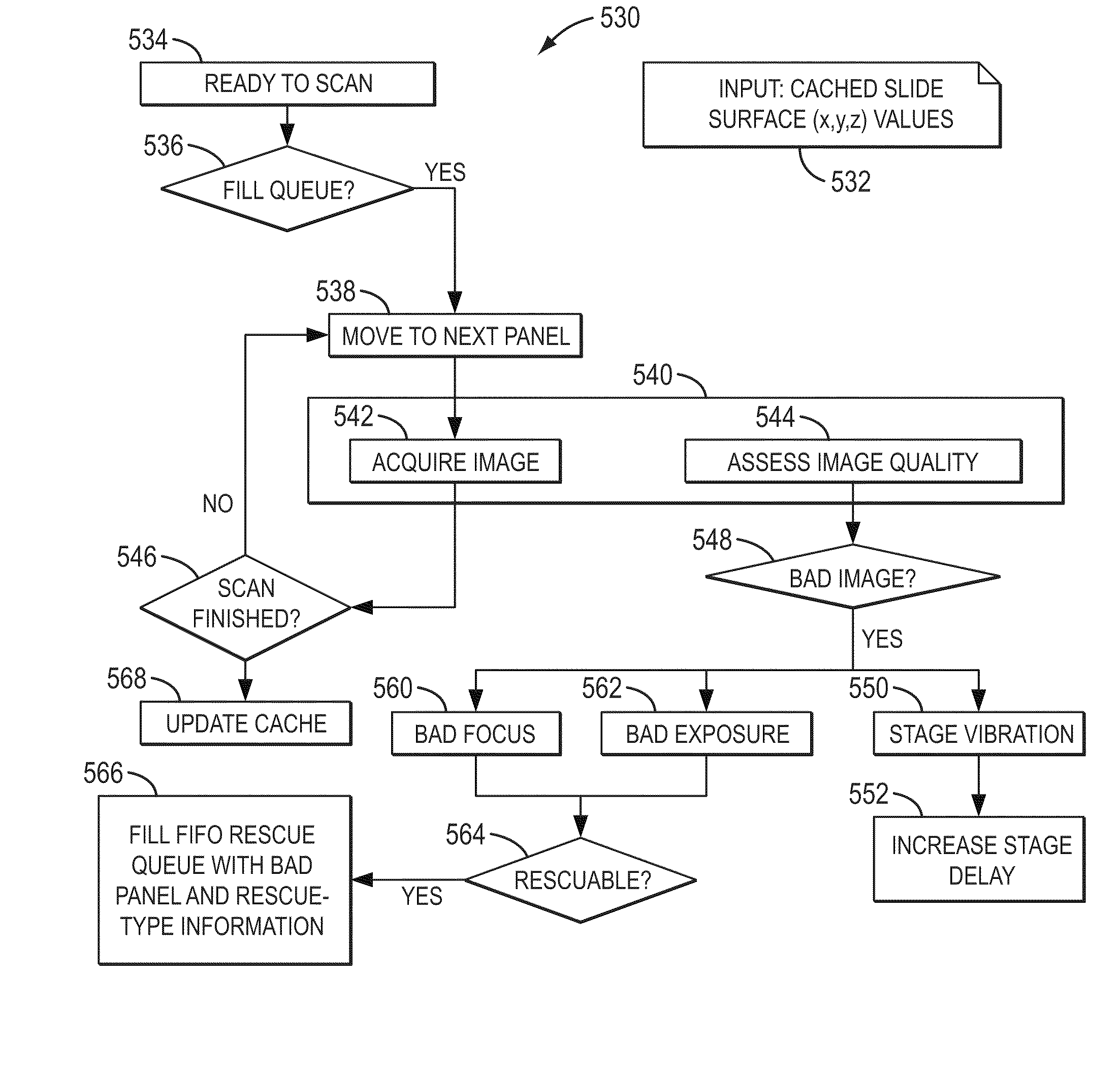
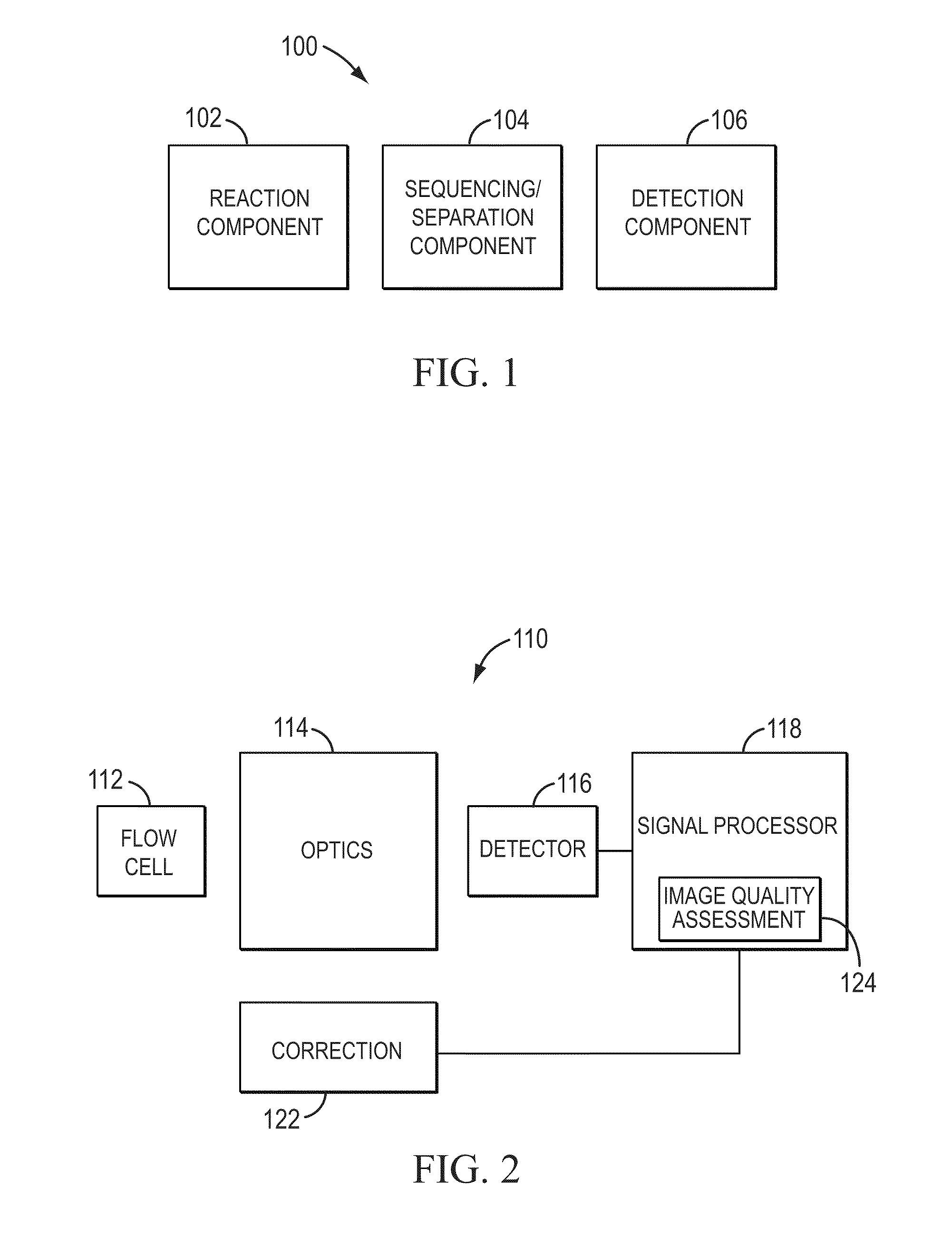
Systems and methods for assessing images
ActiveUS8929630B2Promote formationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityNucleic acid sequencing
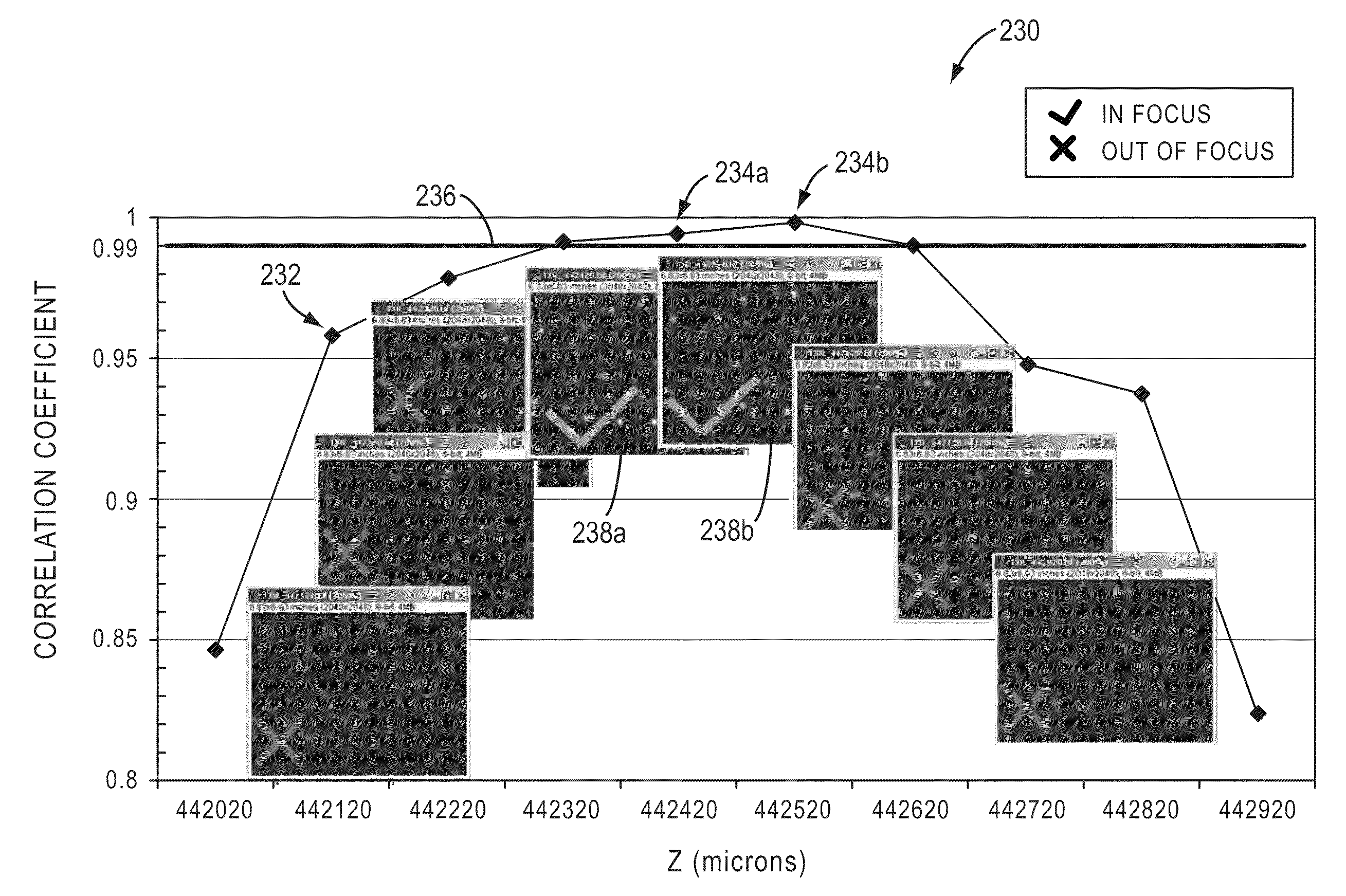
Disclosed are systems and methods for assessing images in applications such as microscopic scanning of a slide having light emitting objects. In certain embodiments, such scanning can involve objects such as sequencing beads disposed on the slide to facilitate biological analysis such as nucleic acid sequencing. Also disclosed are certain embodiments where images of light emitting objects are assessed for image quality so as to facilitate a feedback response such as a corrective action. In certain embodiments, such assessment and correction can be performed in real-time during the scanning process, and can include re-acquisition of the assessed image. Also disclosed are certain embodiments where such assessment and correction can be triggered dynamically during the scan, or before start of the scan, so as to enhance the scanning performance, including scanning time and throughput.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Double beam plate lighting microscan imaging method and microscope
ActiveCN104155274ALose weightReduce distractionsMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceImaging qualityEffect light
The invention belongs to technical field of microscan, and discloses a double beam light sheet lighting microscan imaging method. The method comprises the steps: dividing scanning laser output by an identical light source into first directional scanning laser and second directional scanning laser; ensuring that the two paths of scanning laser are vertically projected onto a sample to motivate sample fluorescent light, and the projection directions are opposite; detecting and collecting fluorescent light motivated by the sample and performing exposure imaging; shifting the sample, and repeating the process till a complete sample image is obtained through scanning, wherein the two paths of scanning laser are synchronous, a light sheet laser sample is produced, and the projection direction is in the x-axis direction; the scanning direction is in the y-axis direction; the fluorescent light collected direction of the sample is in the z-axis direction; scanning initial positions of the two paths of scanning laser are in the center line of a scanning array plane; scanning directions of the two paths of scanning laser are opposite. The method performs light sheet lighting imaging on the transparent sample through double beam scanning laser, so as to obtain higher imaging speed, and enhances the imaging quality through image frequency domain weighted superposition.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fully-automatic microscopic scanner
InactiveCN107065160AFlexible adjustmentQuality improvementMicroscopesMountingsCamera lensFully automatic
The invention discloses a fully-automatic microscopic scanner. The fully-automatic microscopic scanner comprises an image acquisition mechanism, a microscopic scanning mechanism, an object-carrying platform mechanism and a light source mechanism. The image acquisition mechanism is connected with the microscopic scanning mechanism, the microscopic scanning mechanism and the image acquisition mechanism achieve X / Y / Z shaft movements under the action of a power control mechanism, and the object-carrying platform mechanism and the light source mechanism are fixed. The light source mechanism comprises a flat panel light source with a collecting lens, the flat panel light source is disposed right below a material disk of the object-carrying platform mechanism, and the light source area of the flat panel light source is greater than or equal to the total area of the material disk Flexible adjustments of a microscopic scanning mechanism lens is achieved through the arranged power control mechanism, and then the microscopic scanning mechanism lens can move in forward and backward directions, left and right directions and up and down directions. The unique light source mechanism is disposed, so the object-carrying platform mechanism and the light source mechanism are fixed during scanning, flexible and rapid microscopic scanning and real-time accurate focusing are achieved, a microscopic scanning range is expanded infinitely, and scanning efficiency and the scanning quality are improved.
Owner:李昕昱
Fully Automatic Microscopic Scanner
ActiveUS20190033568A1Quick costOptimizationTelevision system detailsMicroscopesEngineeringLine array
A fully automatic microscopic scanner, comprising an image acquisition mechanism (IAM) with a line array camera. The IAM and the microscopic scanning mechanism can move along X / Y / Z axis under the action of a power control mechanism and the stage mechanism and the light source mechanism are fixed and not moved. The light source mechanism comprises a flat light source with a condenser and the flat light source area is greater than or equal to the total area of the tray. The light source mechanism comprises a cooling fan and a water cooling unit. It also comprises a general control mechanism and a laser pre-focus system connected to it. The invention also discloses a fully automatic microscopic scanner which links the microscopic scanning mechanism and the IAM with the light source mechanism. According to the present invention, flexible adjustment of lens can be achieved to make the lens move forwards and backwards, leftwards and rightwards and up and down. In addition, with the unique light source mechanism and laser pre-focus system, the stage and the light source are fixed and not moved during the scanning process so that real-time accurate and fast focusing might be fulfilled. In such a way, unlimitedly extended microscopic scanning range, improved scanning efficiency and improved quality of scanning can be accomplished.
Owner:LI XINYU
Method for calibrating flatness of X-Y plane of microscopic scanning platform
InactiveCN105334612AGuaranteed flatnessRealize high-precision continuous scanningMicroscopesComputer scienceControl unit
The invention discloses a method for calibrating flatness of an X-Y plane of a microscopic scanning platform. The method comprises the following steps: (1) defining a coordinate system of a plane of the microscopic scanning platform through a control unit; (2) selecting a standard stripe slide, calculating a scanning height corrected value of each scanning point, and storing the corrected value corresponding to each calculated coordinate point into a storage unit in the control unit; (3) calculating the coordinate of a scanning corrected value of each coordinate point n in the coordinate system of the scanning platform, and recording a corrected coordinate value corresponding to the standard stripe slide into storage unit in the control unit; (4) reversely loading a scanning corrected coordinate of the standard stripe slide corresponding to the coordinate point recorded in the storage unit of the control unit, or calculating a theoretical plane scanning height according to the corrected value, and transmitting a corrected actual scanning focusing height value to the control unit; and (5) issuing an instruction by the control unit to drive a driver to carry out scanning imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU CHUANGJI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Blood cell component analysis instrument and method
InactiveCN108844906APreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsFailure rateImaging processing
The invention provides a blood cell component analysis instrument and a method. The instrument comprises a sample absorbing and transfer unit, a dyeing liquid adding unit, a stirring and smearing unit, a cleaning unit, a microscanning unit, an image processing unit and a control unit. The sample absorbing and transfer unit is used for absorbing a quantitative blood sample to a glass slide; the dyeing liquid adding unit is used for adding the dyeing liquid to dye cells and dilute the blood sample; a reverse T-shaped stirring and smearing unit is used for mixing the blood sample and the dyeing liquid uniformly and smearing the mixed blood sample; the microscanning unit is used for performing microscopic examination on the smear; the instrument automatically and continuously performs axial scanning on the unclear targets for many times; the image processing unit processes the scanning image and selecting the images with clearest cells or granules in the multi-focus images into a whole image; and the analysis instrument is simple to operate, low in failure rate, accurate in result and few in consumed material reagent, and can perform quantitative analysis on the blood cells conveniently and accurately.
Owner:CLINDIAG SYSTEMS CO LTD
Microscopic scanning imaging acquisition device for vertical optical element surface damage and method thereof
InactiveCN106338524AHigh-precision image stitchingHigh-precision detectionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDisplay deviceImage acquisition
The invention discloses a microscopic scanning imaging acquisition device for vertical optical element surface damage and a method thereof. The device comprises a two-dimensional scanning motion platform, a one-dimensional focusing shaft, a automatic zoom microscope, a area array color CCD, a coaxial light source, a ring light source, a dispersion confocal displacement sensor, a system controller, an industrial control computer, a seismic isolation platform and a display. The device of the invention can automatically acquire and store images, can automatically complete image splicing, has image analysis capability, and can count quantity and dimension of damage spots in an image. According to the invention, online rapid high-precision microscopic scanning imaging acquisition and damage detection of vertical optical element surface in an optical path can be realized. The device of the invention has a wide application prospect and considerable social and economic benefits.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frequency domain imaging method of ultrasonic scanning microscope
InactiveCN103018331AImprove scanning imaging accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalTime domainSonification
The invention relates to a frequency domain imaging method of an ultrasonic scanning microscope, being applicable to the field of ultrasonic scanning microscope detection and ultrasonic C-scanning detection and capable of improving the C-scanning imaging precision in ultrasonic micro-scanning and revealing details which are difficultly discovered in time-domain imaging. The frequency domain imaging method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out full-wave acquisition on an A-scanning signal generated in the C-scanning process; secondly, carrying out fast Fourier transform on signals in data gates of each A-scanning waveform, finding out the maximum amplitudes in the signals, normalizing the maximum amplitudes and expressing the intensities by using corresponding color gray levels; and finally, drawing pixel points on a screen so as to accomplish the frequency domain imaging in ultrasonic micro-scanning.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Large visual field non-diffracting Bessel light sheet microscopic scanning imaging method and system
InactiveCN108303402ASolve the problem of lost optical powerImprove throughputFluorescence/phosphorescenceRight visual fieldImaging quality
The invention discloses a large visual field non-diffracting Bessel light sheet microscopic scanning imaging method and system. The method comprises following steps: generating two collimated Gauss laser beams with same intensity by a laser source; converting two Gauss laser beams into two Bessel beams by a Bessel light generating element respectively; aligning two Bessel beams, projecting the Bessel beams on two sides of a scanned sample to excite the sample to generate fluorescence; collecting the fluorescence by a detector with an electron slit, using the fluorescence to carry out exposureimaging to obtain the image of the sample, and adopting a detection object lens with a low value aperture to carry out large visual field imaging by the detector. Two Bessel beams are used to enhancethe transmission depth in a same visual field, the position of the electron slit is opposite to the center of two Bessel beams, under a condition of large depth of field, the side lobe effect is eliminated, and the depth of the electron slit is matched with the diameter of the center of two Bessel beams. The provided method and system can realize large visual filed and large depth of field imagingand improves the imaging quality of sample images.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH RES INST SHENZHEN +1
Systems and methods for assessing images
ActiveUS20100246977A1Increase delayPromote formationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed are systems and methods for assessing images in applications such as microscopic scanning of a slide having light emitting objects. In certain embodiments, such scanning can involve objects such as sequencing beads disposed on the slide to facilitate biological analysis such as nucleic acid sequencing. Also disclosed are certain embodiments where images of light emitting objects are assessed for image quality so as to facilitate a feedback response such as a corrective action. In certain embodiments, such assessment and correction can be performed in real-time during the scanning process, and can include re-acquisition of the assessed image. Also disclosed are certain embodiments where such assessment and correction can be triggered dynamically during the scan, or before start of the scan, so as to enhance the scanning performance, including scanning time and throughput.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
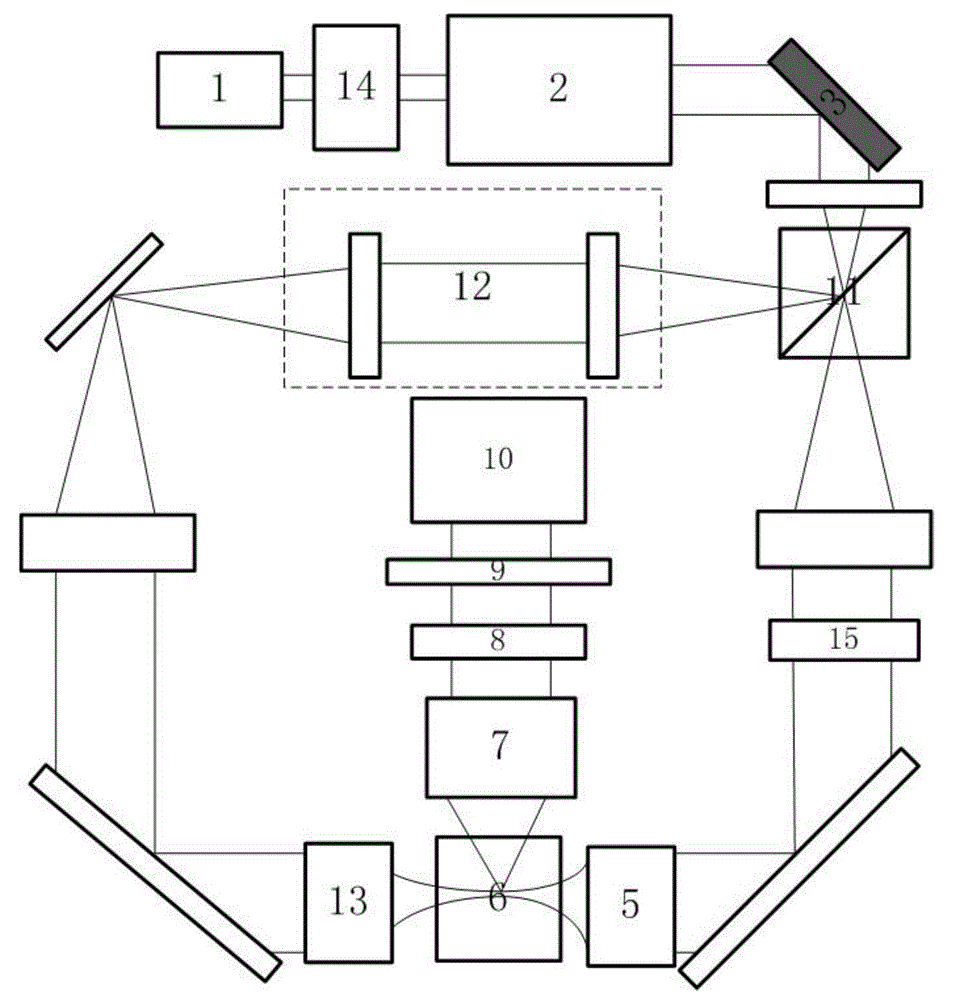
Confocal laser microscope based on self-mixing interference and scanning method of confocal laser microscope
ActiveCN104729424AEasy to adjustSimple structureUsing optical meansOpto electronicConfocal laser microscope
The invention discloses a confocal laser microscope based on self-mixing interference. The confocal laser microscope based on self-mixing interference comprises a helium-neon laser, an expanding collimating lens group composed of a concave lens and a convex lens, a variable neutral-density filter, an objective lens, a bidimensional moving platform, an one dimensional moving platform, a high-precision moving platform controller, a photoelectric detector, an electric current / voltage switching circuit, a filter, an amplifier, an analogue-to-digital conversion circuit and a computer unit. According to the confocal laser microscope based on self-mixing interference, a method of conducting microscanning with laser self-mixing interference and the confocal principle is adopted, the advantages of the laser self-mixing technology that the structure is simple, the collimation is easy and the characteristics of the confocal microscope that the axial resolving power is high and the antijamming capability is strong are combined, the automatic focusing problems and the measuring vision enlarging problem of the confocal laser microscope are solved, the structure of a traditional confocal microscope is simplified, the adjusting difficulty of reflected light path in a confocal measuring system is lowered, the defects of the traditional confocal microscope that the number of the needed optical element is large, the requirement on the optical element is high, the light path is complicated and adjusting is difficult are overcome.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
High-precision controllable microscanning device based on piezoelectric ceramics and sliding guide rail
InactiveCN102384787AImprove accuracyImprove consistencyRadiation pyrometryEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a design method of a high-precision controllable microscanning mechanism based on piezoelectric ceramics and a sliding guide rail, which belongs to the field of the design of high-performance photoelectronic imaging systems. By utilizing the relation that the expansion amounts of the piezoelectric ceramics are in proportion to driving voltages of the piezoelectric ceramics, the invention provides the high-precision controllable microscanning mechanism which uses the piezoelectric ceramics as driving devices and uses the sliding guide rail as a translation element to control the marching direction. The mechanism comprises two piezoelectric ceramics, a vertical movable framework, a horizontal movable framework, four pairs of dovetail grooves, a microscanning mechanism framework and four groups of balls. The piezoelectric ceramic for realizing displacement driving in the vertical direction is connected with a two-dimensional translation element and is arranged atthe inner part of a vertical sliding guide rail component. The piezoelectric ceramic for realizing displacement driving in the horizontal direction is connected with the outer wall of the microscanning mechanism and the vertical sliding guide rail component to realize horizontal displacement driving. The displacement amounts of the piezoelectric ceramics can be controlled in a high-precision manner through the amplitude values of the driving voltages.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and device for detecting atomic force microscopic scanning of tri-scanner atomic
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting atomic force microscopic scanning of a tri-scanner atomic. The detecting method combines a sample scanning manner with a probe scanning manner, so that high-precision micro nano detection of small light samples and large heavy samples can be realized at the same time. The method for detecting atomic force microscopic scanning of the tri-scanner is provided with a atomic force microscopic detecting head of the tri-scanner formed by a probe scanning and photoelectric detecting unit, a sample scanning unit, a two-dimensional stepping scanning unit, and the like, and a scanning and feedback control system formed by a preamplifier, a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) feedback unit, an XYZ control module I, an XYZ control module II, a stepping control module, a computer, an interface, and the like. The method for detecting atomic force microscopic scanning of the tri-scanner has the advantages that three probes and three sample scanning manners are provided, nano scale scanning accuracy is kept, single width image scanning in the range of 1 Mum to 100 Mum and image splicing in the range of 0.1mm to 1mm are realized on samples of different sizes and different weights, limitations of a conventional atomic force microscope (AFM) are overcome, and a new way is provided for the realization of high-precision, large-range and multi-scanning-manner micro nano scanning imaging of micro nano samples of various sizes and weights.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Alpha-beta scanning method for confocal microscopic system
InactiveCN105806255AIncreased scanning field of viewHigh frequencyUsing optical meansLight spotControl signal
The invention relates to a confocal microscopic scanning method and discloses an alpha-beta scanning method for a confocal microscopic system to solve the problems that a confocal scanning method in the prior art can not fully utilize an effective field of view of an optical system, the measuring efficiency is low, and reliability is hard to improve.A signal alpha and a signal beta are constructed through upper computer software and sent into a streaming detection type galvanometer system through two channels of a data collecting card respectively to be taken as control signals of the streaming detection type galvanometer system; the streaming detection type galvanometer system conducts scanning according to the signal alpha and the signal beta, and two-dimensional scanning is finished for a scanning light spot according to a concentric circle track; scanning light spot track information is acquired through calculation; the streaming detection type galvanometer system and an axial micropositioner are controlled to achieve three-dimensional scanning measurement of a sample to be detected; the collected data is processed, and by combining the scanning light spot track, the three-dimensional shape of the sample to be detected is reconstructed.According to the method, the effective field of view of the optical system can be fully utilized, and the scanning field of view of the confocal microscopic system is enlarged to the maximum extent.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Panoramic stitching system and method for microscopic images
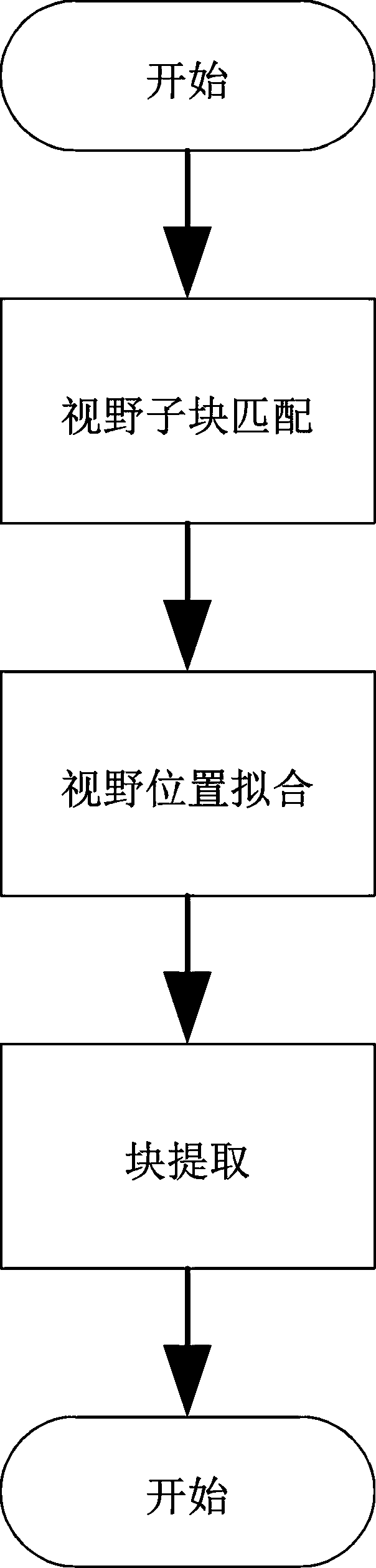
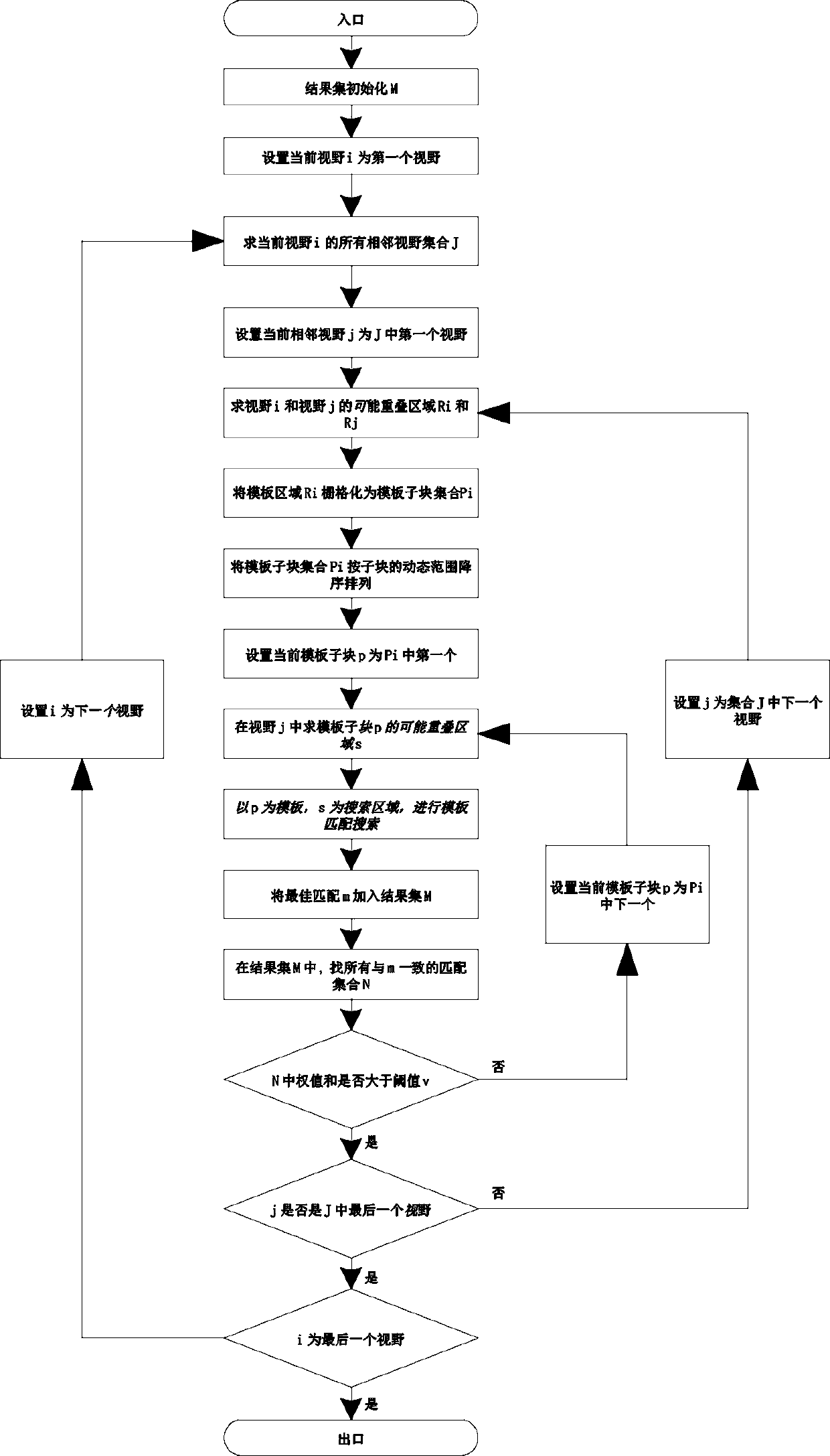
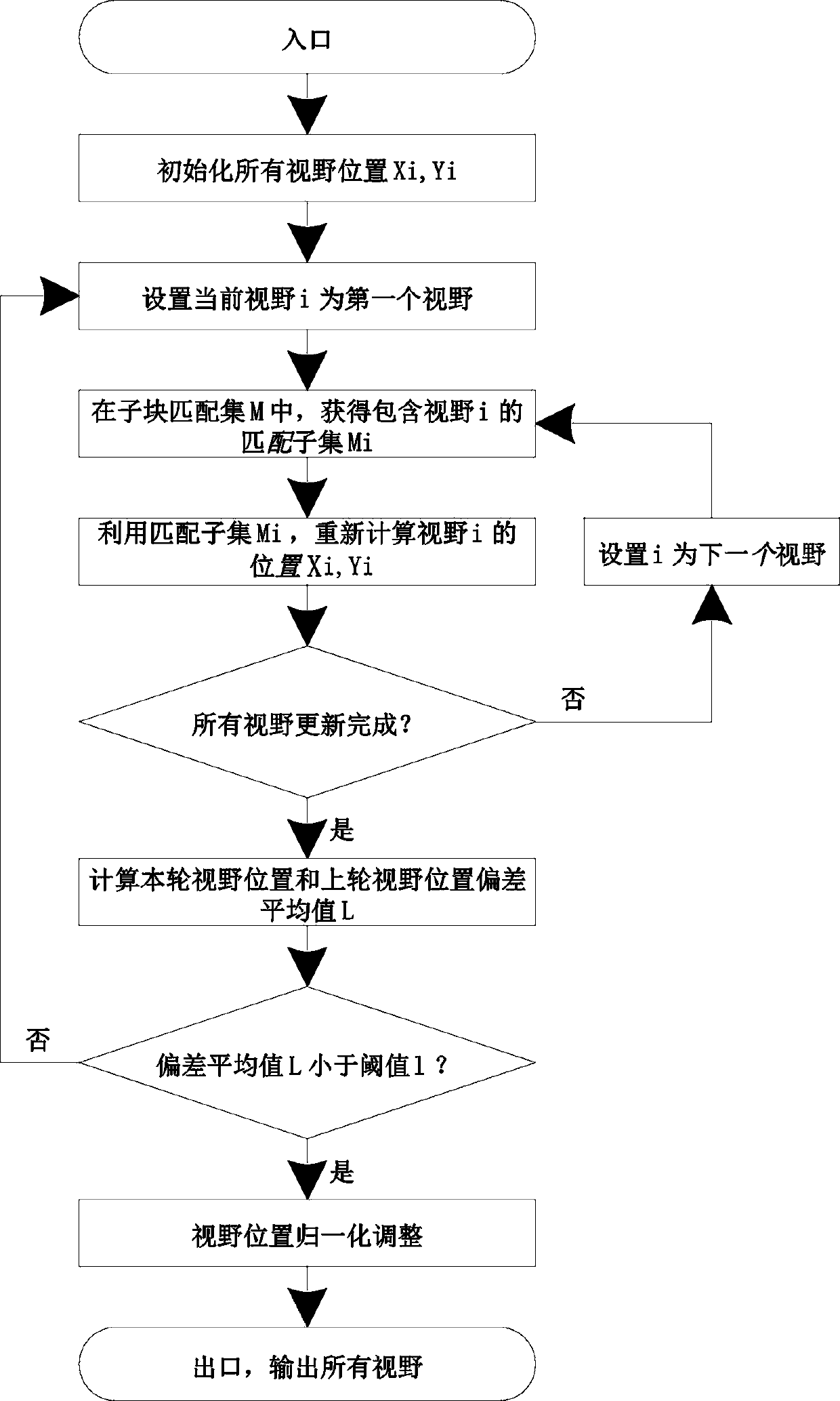
ActiveCN110807732AImprove clarityRealize automatic splicingImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageRadiology
The invention provides a panoramic stitching system and method for microscopic images. The panoramic stitching system comprises a view sub-block matching module, a view position fitting module and a block extraction module, the view sub-block matching module is used for identifying an overlapping region between the images and judging an adjacent position relationship between the sub-images, so that the sub-images acquired by the microscopic scanning device are automatically arranged according to a splicing sequence of the images; the visual field position fitting module is used for finely adjusting the position according to the overlapping area between the sub-images so as to accurately splice the cell positions; and the block extraction module is used for automatically extracting a completely spliced image. By the adoption of the scheme, automatic splicing can be achieved, high-definition images can be obtained, in the splicing process, the method can adapt to disorderly-arranged images without clearly scanning the sequencing problem of the images, high compatibility is achieved, and labor intensity is greatly reduced. The splicing process of the method can be completed in a second-level range so as to adapt to the data processing intensity of large-scale diagnosis on the cloud.
Owner:WUHAN LANDING INTELLIGENCE MEDICAL CO LTD
Full-automatic mycobacterium tuberculosis microscanning analyzer
PendingCN111272659AFully automatedReduce labor intensityMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesMicroscopic imageStaining
The invention discloses a full-automatic mycobacterium tuberculosis microscanning analyzer which comprises a rack, a slide conveying device, a slide rack, a scanning device, a nozzle clamping mechanism, an optical instrument, a computer and an oil injection system; according to the invention, the slide conveying device is adopted to realize extraction and storage of slide samples between the sliderack and the objective table; a scanning device is adopted to accurately send the sample to a detection position specified by an optical instrument, and microscopic scanning is carried out; a computer and a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) are used for controlling a first three-dimensional driving power head, a second three-dimensional driving power head and a clamping nozzle driving head to operate and controlling switching of a fluorescence switcher on a fluorescence-Candida mechanism, realizing scanning of Ziehl-Neelsen acid-fast staining and fluorescence staining slides, and operational analysis of microscopic images is performed by adopting a computer and a CPU (Central Processing Unit) to finish full-automatic microscopic scanning work of a detected slide sample. The full-automatic mycobacterium tuberculosis microscanning analyzer has the advantages of high automation degree, large slide rack capacity and high image scanning precision.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Microscopic scanner and microscopic scanning method
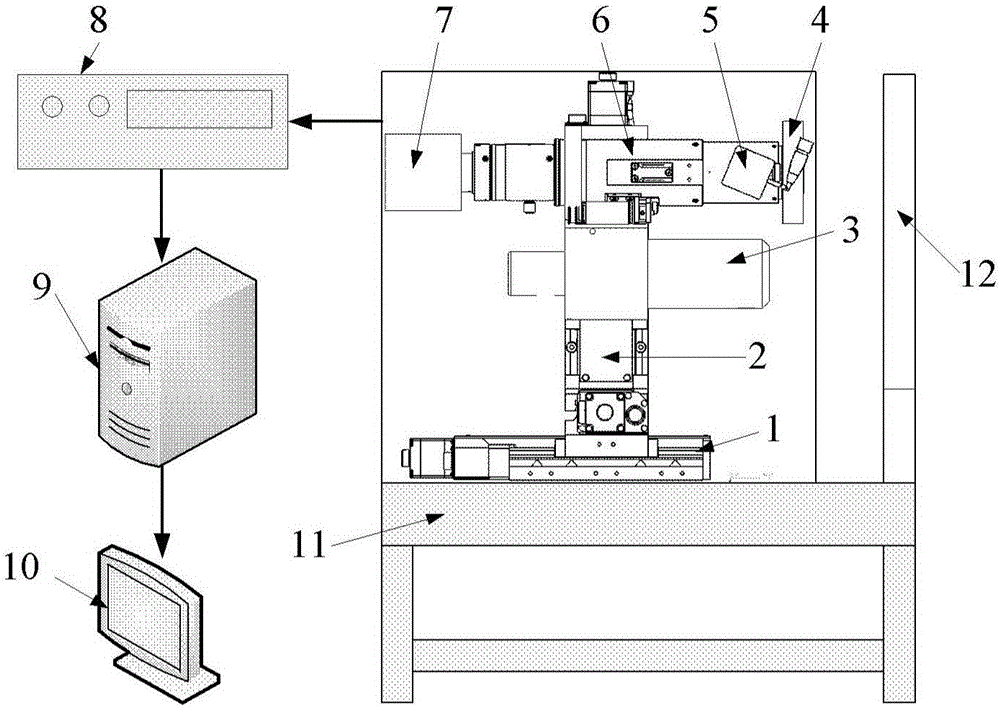
The invention discloses a microscopic scanner and a microscopic scanning method. The microscopic scanner comprises a scanner main body, an ocular lens device and a switching device for realizing switching of the optical paths. A first optical path is formed by a light source device in the scanner body, a platform for placing a slice, an object lens set, a third reflector set, a second auxiliary lens set, a switching device, a first reflector set, a first auxiliary lens set, a second reflector set, a turning prism and an ocular lens, wherein the first reflector set, the first auxiliary lens set, the second reflector set, the turning prism and the ocular lens are arranged in the ocular lens device; a second optical path is formed by a light source device in the scanner body, the platform for placing the slice, the object lens set, a third reflector set, a second auxiliary lens set, the switching device and a microscopic camera. The microscopic scanner can be used for performing slice scanning and can be used for microscopic observation through the switching device. The invention avoids using the box type microscopic scanner and the traditional microscope to realize the above two functions, improves the working efficiency of the microscopic scanning and reduces the cost.
Owner:NINGBO SUNNY INSTR
Remote microscope system
The invention discloses a remote microscope system. The system comprises a microscopic scanner, a client, a first communication unit and a control unit, wherein the microscopic scanner is used for scanning a slice; the client is used to receive a control instruction input by a user or a scanning image; the first communication unit is remotely connected to the client and is used to carry out data transmission with the client; the control unit is connected to the microscopic scanner and the first communication unit respectively and is used to make the microscopic scanner carry out microscopic amplification on the slice according to the control instruction and scan the slice so as to acquire the scanning image; and the first communication unit sends the scanning image to the client so as to carry out display. The control unit is used to make the microscopic scanner carry out microscopic amplification and scanning on the slice according to the received control instruction. Through the first communication unit, the scanning image is sent to the client to be displayed so that a purpose of remote control of slice scanning and reading is realized and a range of application is increased.
Owner:KONFOONG BIOTECH INT
Microscopic scanning platform and working area flatness calibration method
PendingCN111122583AEasy to scanEasy to adjustMaterial flaws investigationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationRapid scanWorkspace
The invention relates to the technical field of microscope scanning, especially, to a microscanning platform comprising a scanning platform being a workbench. An XY coordinate system is arranged on the surface of the workbench, and zero points of an X axis and a Y axis are connected to a corner of the scanning platform, so that an area formed by the X axis and the Y axis is located in a first quadrant of the coordinate system, and coordinate values of the X axis and the Y axis are positive values. Besides, the invention also provides a working area flatness calibration method of a microscanning platform. According to the invention, the X axis and the Y axis are adopted to carry out rapid and comprehensive scanning on the scanning platform; the defect position of the scanning platform is determined through the coordinate system; the defect position is marked and recorded, workers can conveniently adjust the scanning platform and correct the defect; and problems that the existing microscopic scanning platform and the existing working area flatness calibration method cannot quickly scan the scanning platform and cannot determine and adjust the specific position of the defect are solved at the same time.
Owner:HANGZHOU JUNHUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Short-exposure high-speed surface scanning rigid splicing microscopic imaging system and method
ActiveCN113031242AAchieving Distortion CancellationLow destructive scanMicroscopesMicroscopic imageImaging processing
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
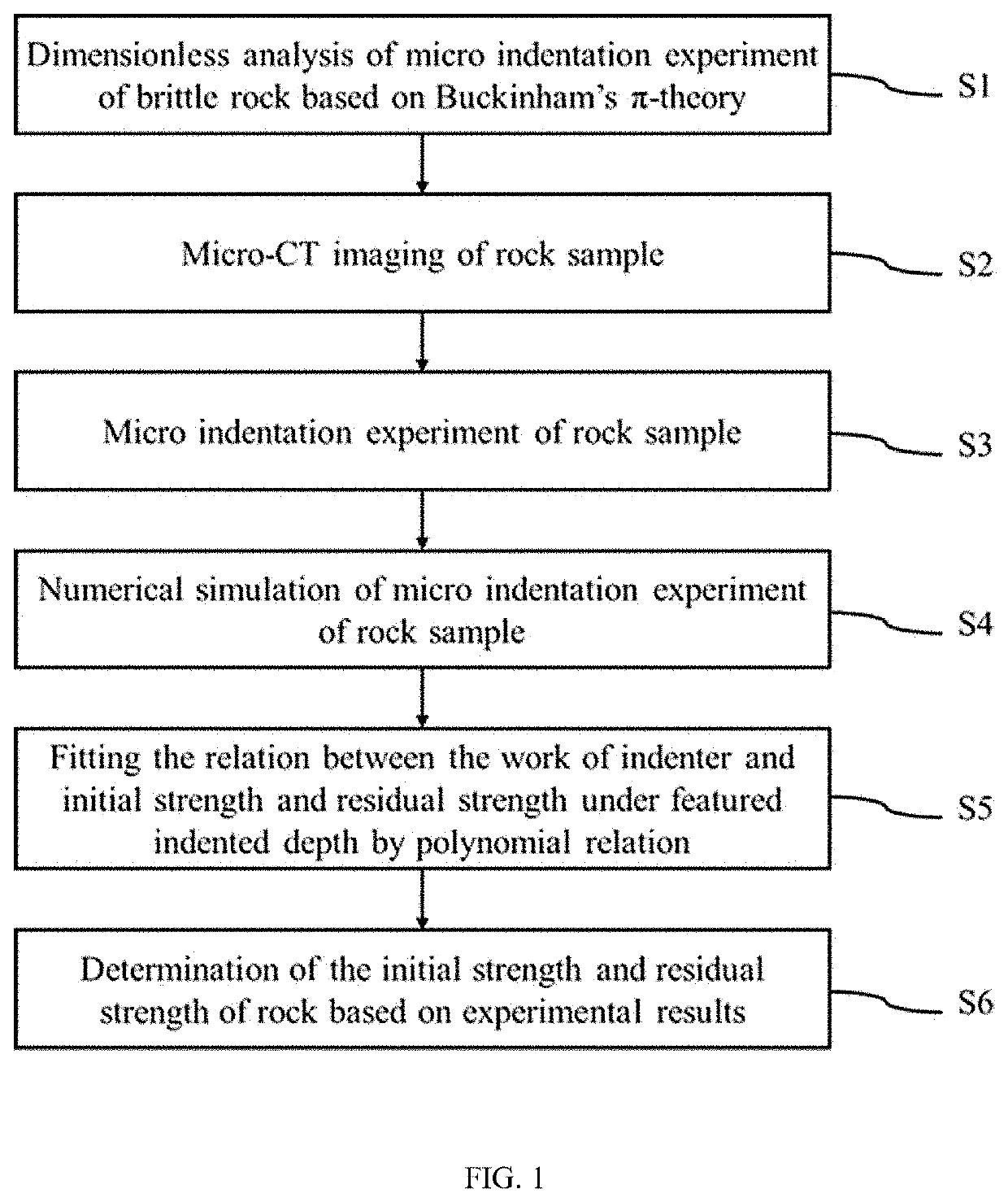
Method for measuring micro-scale strength and residual strength of brittle rock
InactiveUS20210088428A1High feasibilityImprove accuracyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEarth material testingClassical mechanicsSimulation based
A method for measuring micro-scale strength and residual strength of brittle rocks, including: performing micro-CT scanning on a target area; obtaining loading and unloading curves and an elastic modulus of the rock via micro indentation experiment; performing dimensionless analysis based on Buckinham's π-theorem to obtain relation between the loading and unloading curves and elastic modulus, indentation depth, initial and residual strengths; reconstructing a grid model of micro rock matrix at the target area and indenter; performing micro indentation numerical simulation based on Mohr-Coulomb criterion to obtain loading and unloading curves under different strengths and residual strengths; fitting a formula between simulated work of the indenter and initial and residual strengths at h / R of 0.1 and 0.15; and substituting experimental values of the work into the formula to plotting curves of initial and residual strengths under two indentation depths, where coordinates of an intersection point represent micro-scale initial and residual strengths.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Cell detection and identification system and method
PendingCN110766668AImprove recognition accuracyShorten judgment timeImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageBioinformatics
The invention provides a cell detection and identification system and method. The invention relates to the field of intelligent cell identification by using a computer, and discloses a cell identification system, which comprises a microscopic scanning device used for acquiring microscopic images. In a computer, multiple images of each sample are spliced in the computer, and extraction is made inspliced images according to cell nucleus characteristics to obtain a single cell nucleus microscopic image, According to marked cells, the single cell nucleus microscopic images are classified by using an artificial intelligence program after model training; and obtaining classified cell data based on the target. According to the invention, the identification accuracy and the identification efficiency can be greatly improved, especially the judgment time of doctors can be reduced, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:WUHAN LANDING INTELLIGENCE MEDICAL CO LTD
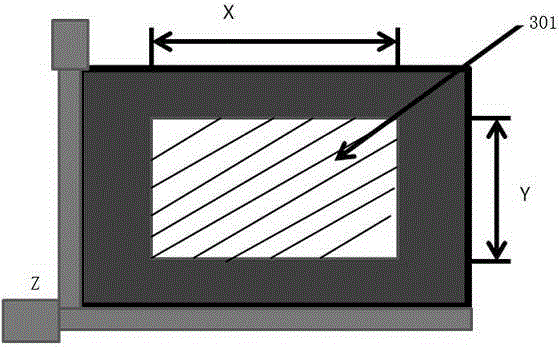
Microscanning platform
The present invention relates to a microscanning platform. It is formed from base, X-axis slide block and its bidirectional movement traction mechanism and Y-axis slide block and its bidirectional movement traction mechanism. Said invented microscanning platform can be mounted on the existent microscope.
Owner:重庆天海医疗设备有限公司
Rotary demodulation type multi-mode high-efficiency microscanner
InactiveCN102507010AMultiple micro scan modesImprove conversion efficiencyRadiation pyrometryCircular discCamera lens
The invention discloses a rotary demodulation type multi-mode high-efficiency microscanner, which comprises a strong rotating disk, a retaining plate, an actuating motor, an actuating motor driving circuit, a coupler and a photoelectric coupler, wherein the rotating disk arranged between an optical lenses and an array detector and panel components on the rotating disk are driven to rotate by the actuating motor, the panel components sequentially cut in a light path to ensure that positions of images change a little, so that a microscanning image is obtained, a synchronizing signal is generated, and all optical images obtained through microscanning are transformed into electronic images; and the electronic images are arranged according to space positions by using frames as units in a process of processing the synchronizing signal and finally synthesized into a high-definition image, thus microscanning imaging is completed.
Owner:成都军区昆明总医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com