Blood cell component analysis instrument and method
A component analysis and blood cell technology, applied in the field of medical inspection, can solve problems such as high failure rate, inability to accurately identify cells, and low work efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
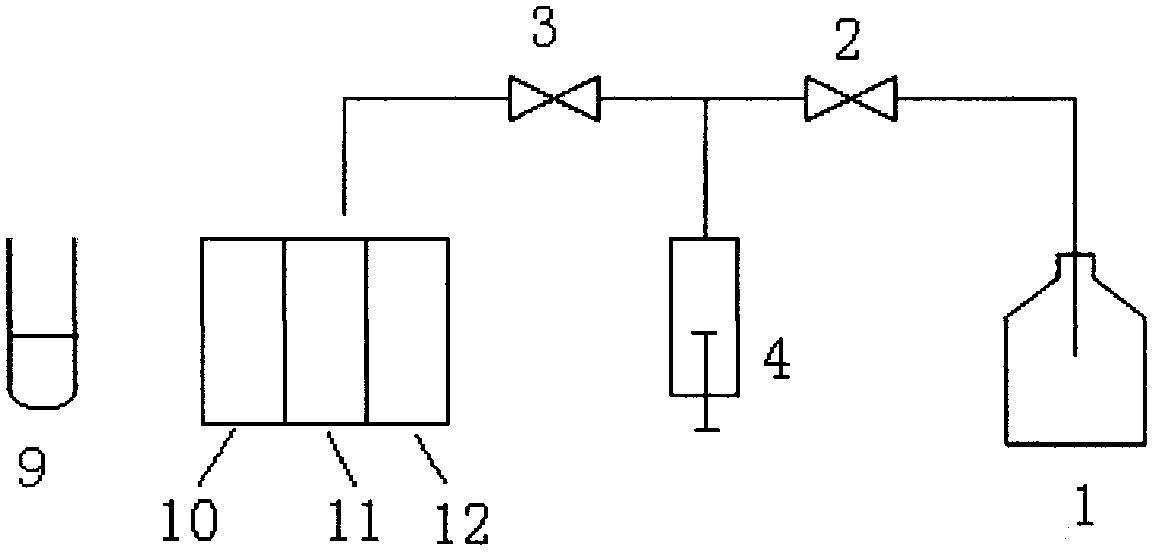
[0047] Such as figure 1 , in this embodiment, the working principle of the sample suction and transfer unit: put the special detection card on the detection card position of the blood cell component analyzer, close the first valve 2, open the second valve 3, pull down the first syringe 4, and the instrument The sample aspirating needle draws an equal amount of sample from the sample tube 9 into the syringe 4, then the aspirating needle is transferred to the top of the test card, the first syringe 4 is pushed up, and the equal amount of sample is transferred to the control tube 10, the first detection tube 11 and the control tube 10. In the second detection tube 12, then turn on the mixing motor under the detection card position, and mix the blood samples in the control tube and the detection tube on the detection card respectively;
[0048] The cleaning needle is transferred to the top of the cleaning pool, the first valve 2 is opened, the second valve 3 is closed, the syringe...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Such as Figure 4 , In this embodiment, the stirring and smearing unit is an inverted T-shaped stirring and smearing unit. When the blood sample and staining solution are added to the slide glass, the inverted T-shaped stirring and smear unit 6 moves vertically above the slide glass, and its cross arm descends to a position greater than 0.1mm from the surface of the slide glass, and the inverted T-shaped stirring and The smear unit rotates to mix the mixture 8 of the blood sample and the staining solution; then the inverted T-shaped stirring and the smear unit continue to descend and rotate close to the glass slide, and then the inverted T-shaped stirring and the smear unit rises and shifts, Cling to the glass slide again and rotate it to spread the blood sample on another smear area of the glass slide, and then move the T-shape stirring and smearing unit to the cleaning tank for cleaning.
Embodiment 3
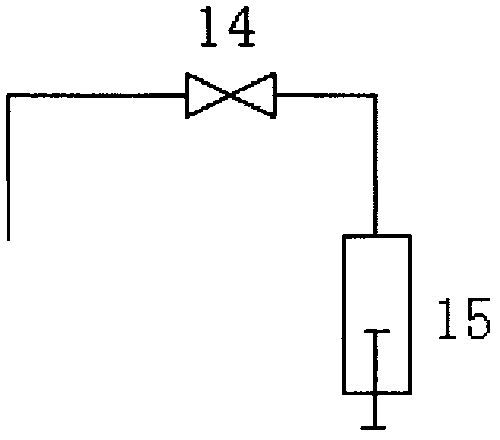
[0053] Such as image 3 , in this embodiment, the instrument is not provided with a cleaning solution bottle, but is provided with a cleaning pool. When the needle is cleaned, the sampling needle is transferred to the cleaning pool, the third valve 14 is opened, the second syringe 15 is pulled down, and the sampling needle is removed from the cleaning pool. The cleaning water is sucked into the second syringe, and then the sampling needle is transferred to the top of the waste liquid collector, the second syringe is pushed up, and the cleaning water is discharged to the waste liquid collector.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com