Cell detection and identification system and method
A technology for identifying systems and cells, applied in the field of cell detection and identification systems, and can solve problems such as affecting identification accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
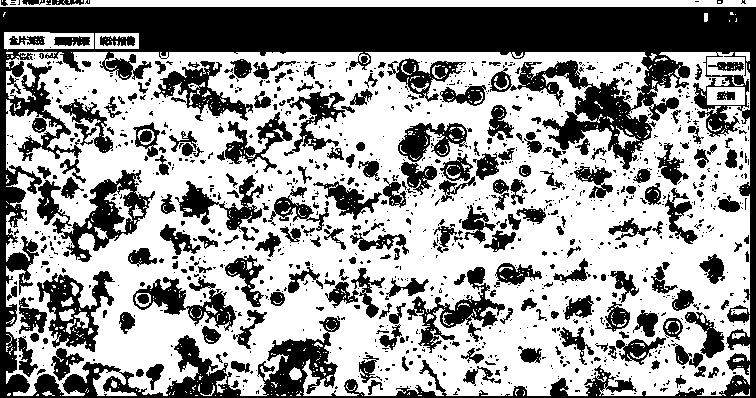
[0157] Such as Figure 1~6 Among them, a cell detection and identification system, which includes a microscopic scanning device, and the microscopic scanning device is used to obtain microscopic images;
[0158] In the computer, multiple images of a single sample are stitched together, such as Figure 10a , 10b As shown in , extract according to the features of cell nuclei in the spliced image to obtain a microscopic image of a single cell nuclei;
[0159] According to the labeled cells, the artificial intelligence program after model training is used to classify the microscopic images of single cell nuclei;
[0160] Such as Figure 11 As shown in , the artificial intelligence program preferably uses a convolutional neural network with a learning rate of 0.001. The number of result categories adopts num_classes = 3, corresponding to positive, negative and garbage respectively. Number of training rounds epochs = 300; image size: img_cols = 128 img_rows = 128; regularizat...
Embodiment 2
[0163]On the basis of Example 1, the preferred scheme is as Figure 3~6 In , the process of stitching images includes: field of view sub-block matching, field of view position fitting and block extraction;
[0164] Such as Figure 4 , Figure 10a As shown in , the process of visual subblock matching is:
[0165] Sa01, input, result set initialization M;
[0166] Sa02. Set the current field of view i as the first field of view;
[0167] Sa03. Find all adjacent visual field sets J of the current visual field i;
[0168] Sa04. Set the current adjacent field of view j as the first field of view in J;
[0169] Sa05. Find the possible overlapping areas Ri and Rj of the field of view i and field of view j;
[0170] Sa06. Rasterizing the template region Ri into a template sub-block set Pi;
[0171] Sa07. Arranging the template sub-block set Pi in descending order according to the dynamic range of the sub-blocks;
[0172] Sa08. Set the current template sub-block P as the first ...
Embodiment 3
[0217] On the basis of embodiment 1~2, preferred scheme is as figure 2 , Figure 7~9 In , the process of obtaining a microscopic image of a single nucleus is:
[0218] Sa100, detecting the characteristic points of the cell nucleus;
[0219] Reduce the image to multiple different ratios, preferably, the reduction ratios are: 0.3, 0.15, 0.08; extract feature points respectively;
[0220] Sa101. Preliminary screening, using the coordinates of the feature points to filter out the feature points that are too close to reduce the repeated extraction of cells; this step greatly improves the efficiency of recognition, especially the diagnosis efficiency of doctors.
[0221] In this example, if the distance of the feature points does not exceed half the radius of the cell, and half the radius is greater than 32, it is considered too close if the distance is less than 32 pixels, otherwise it is considered too close if it is less than half the cell radius. That is cell.Center.L1Distan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com