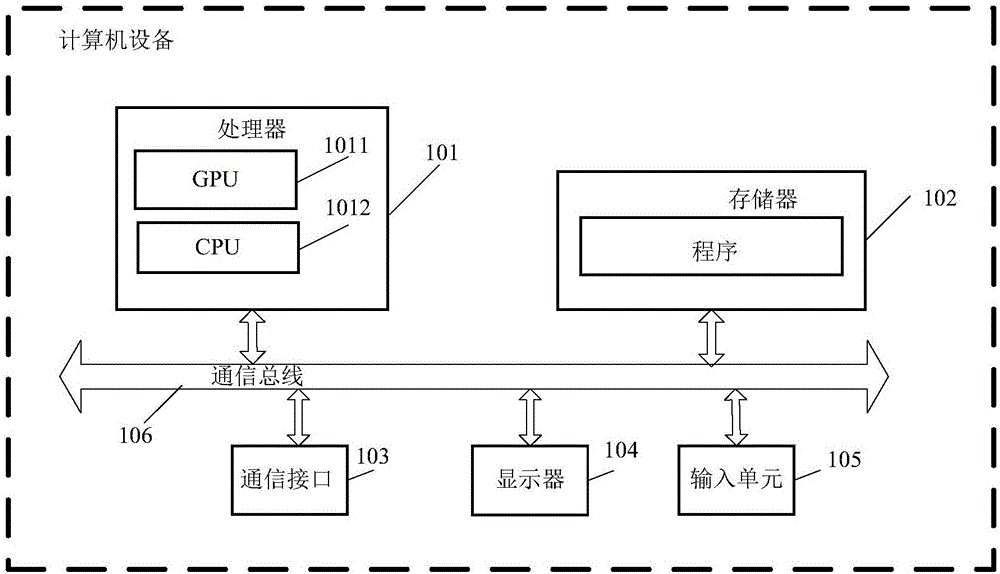
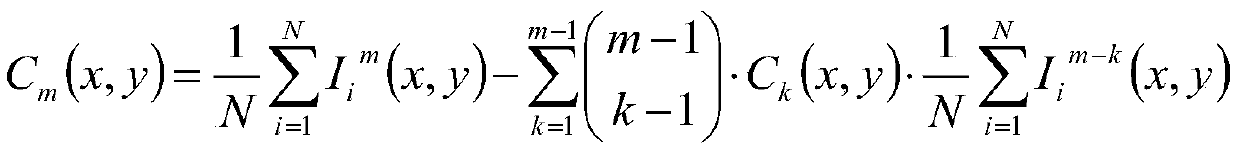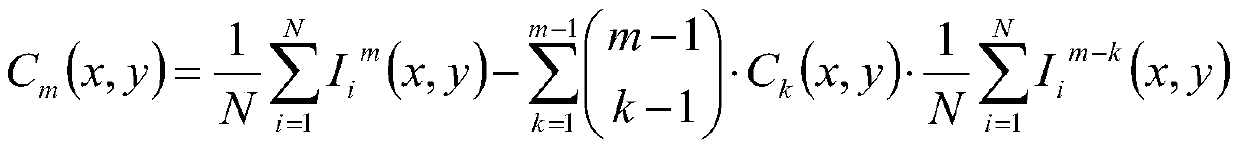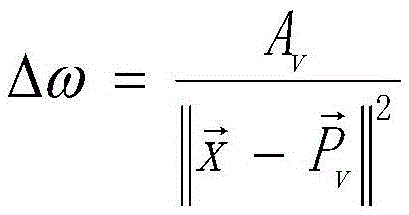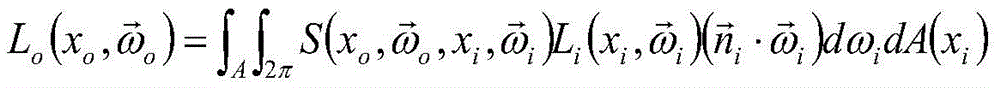Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Subsurface scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
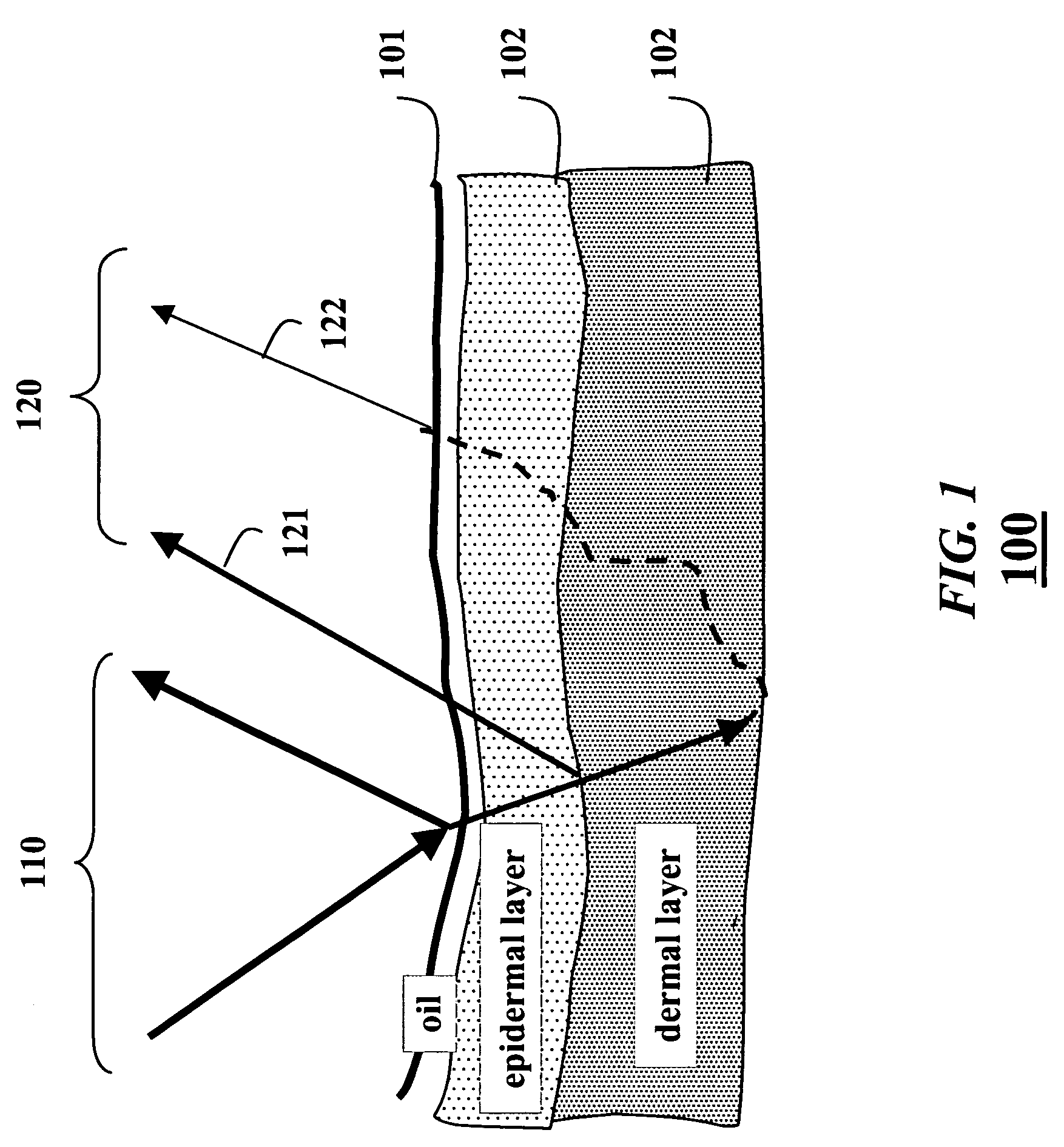
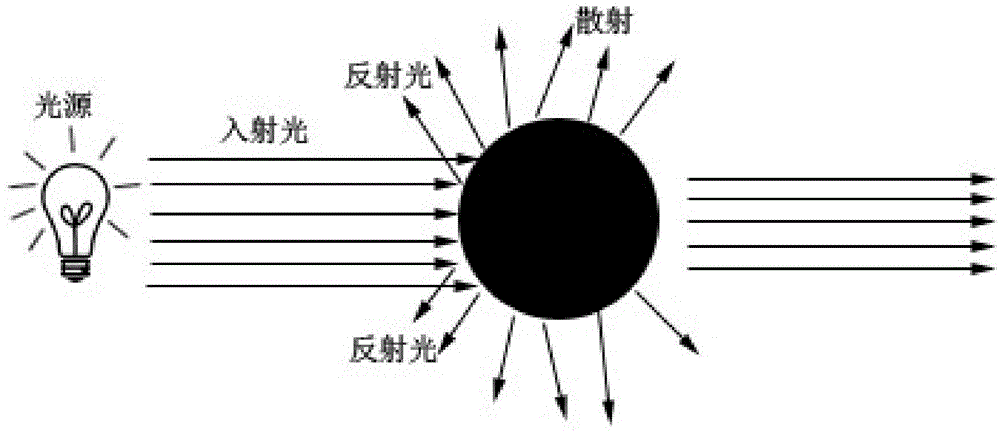
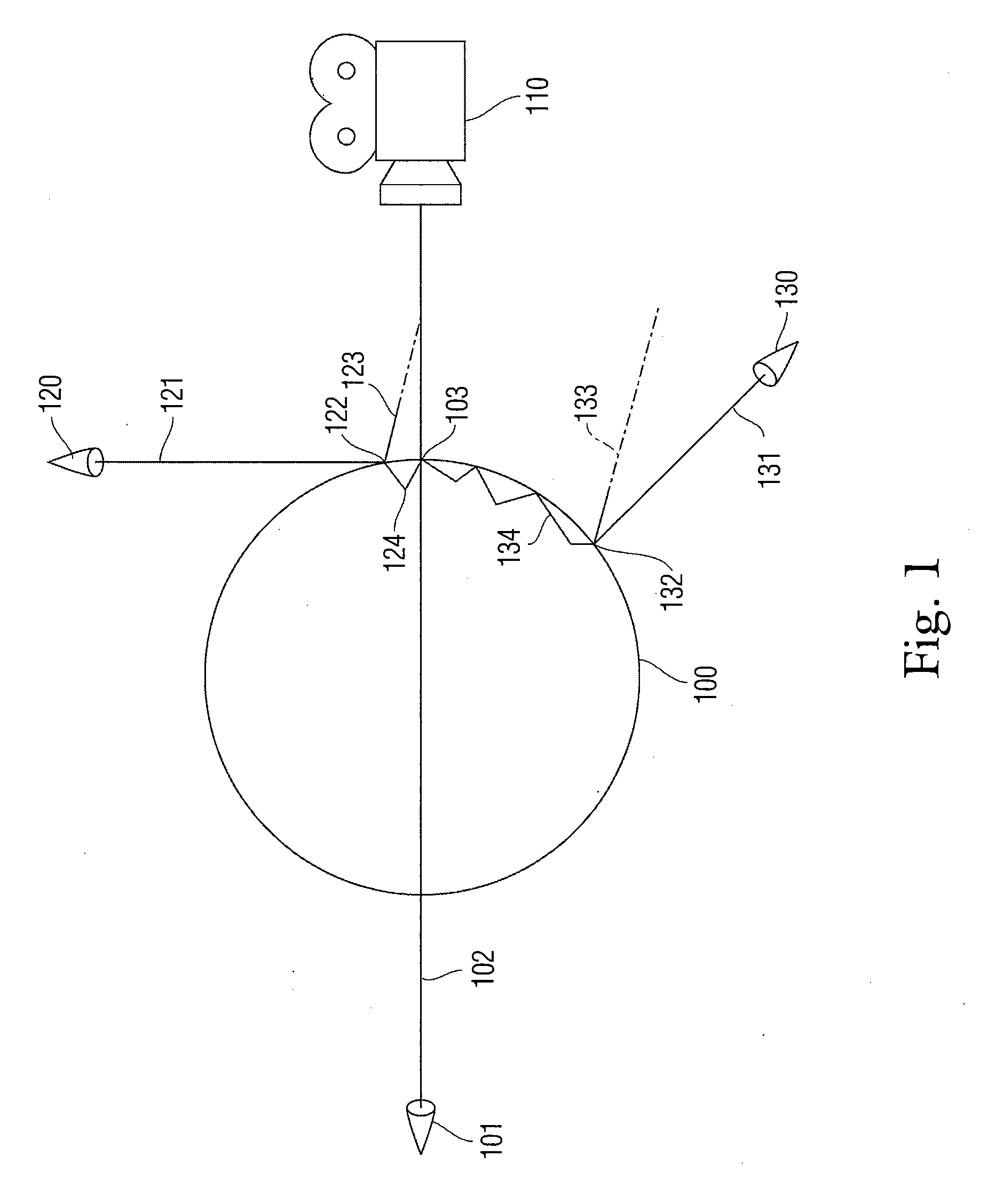
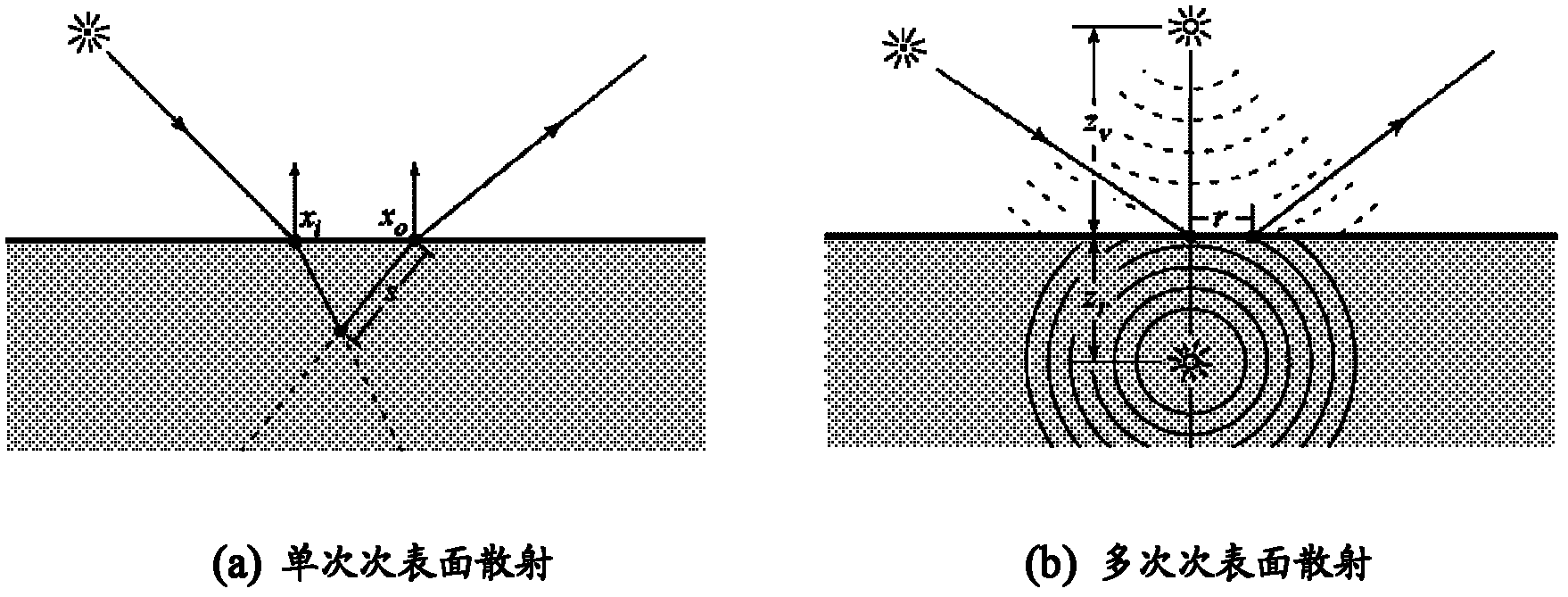
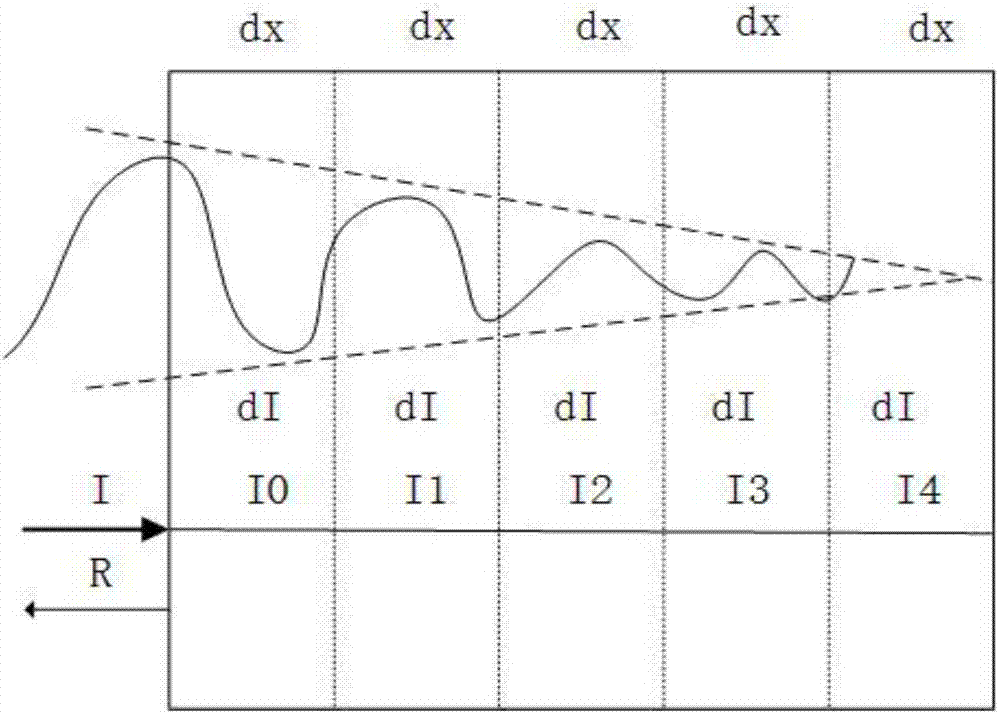
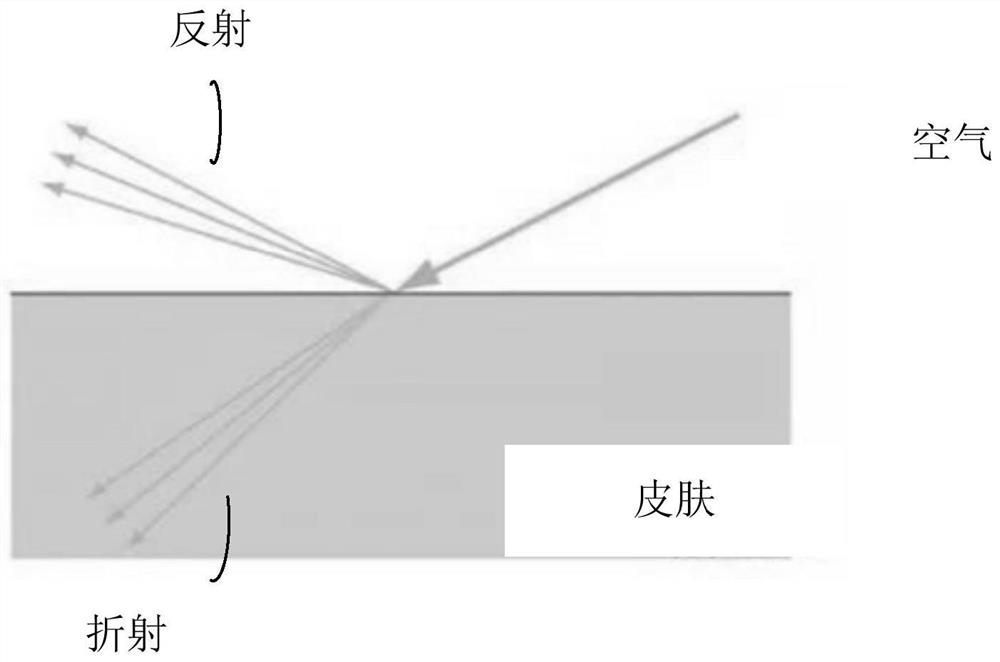
Subsurface scattering (or SSS), also known as subsurface light transport (SSLT), is a mechanism of light transport in which light that penetrates the surface of a translucent object, is scattered by interacting with the material, and exits the surface at a different point. The light will generally penetrate the surface and be reflected a number of times at irregular angles inside the material, before passing back out of the material at an angle other than the angle it would have if it had been reflected directly off the surface. Subsurface scattering is important in 3D computer graphics, being necessary for the realistic rendering of materials such as marble, skin, leaves, wax and milk.
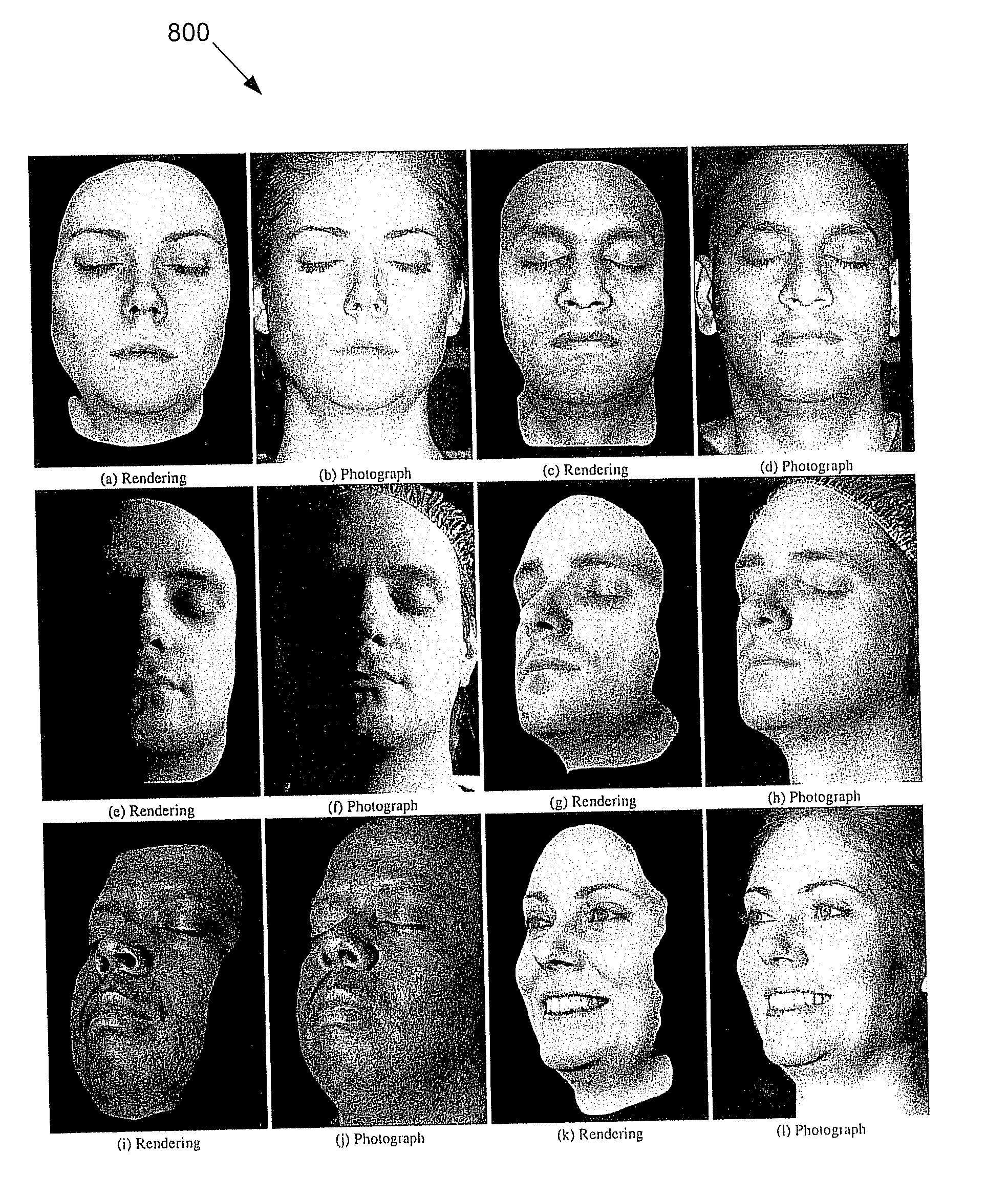
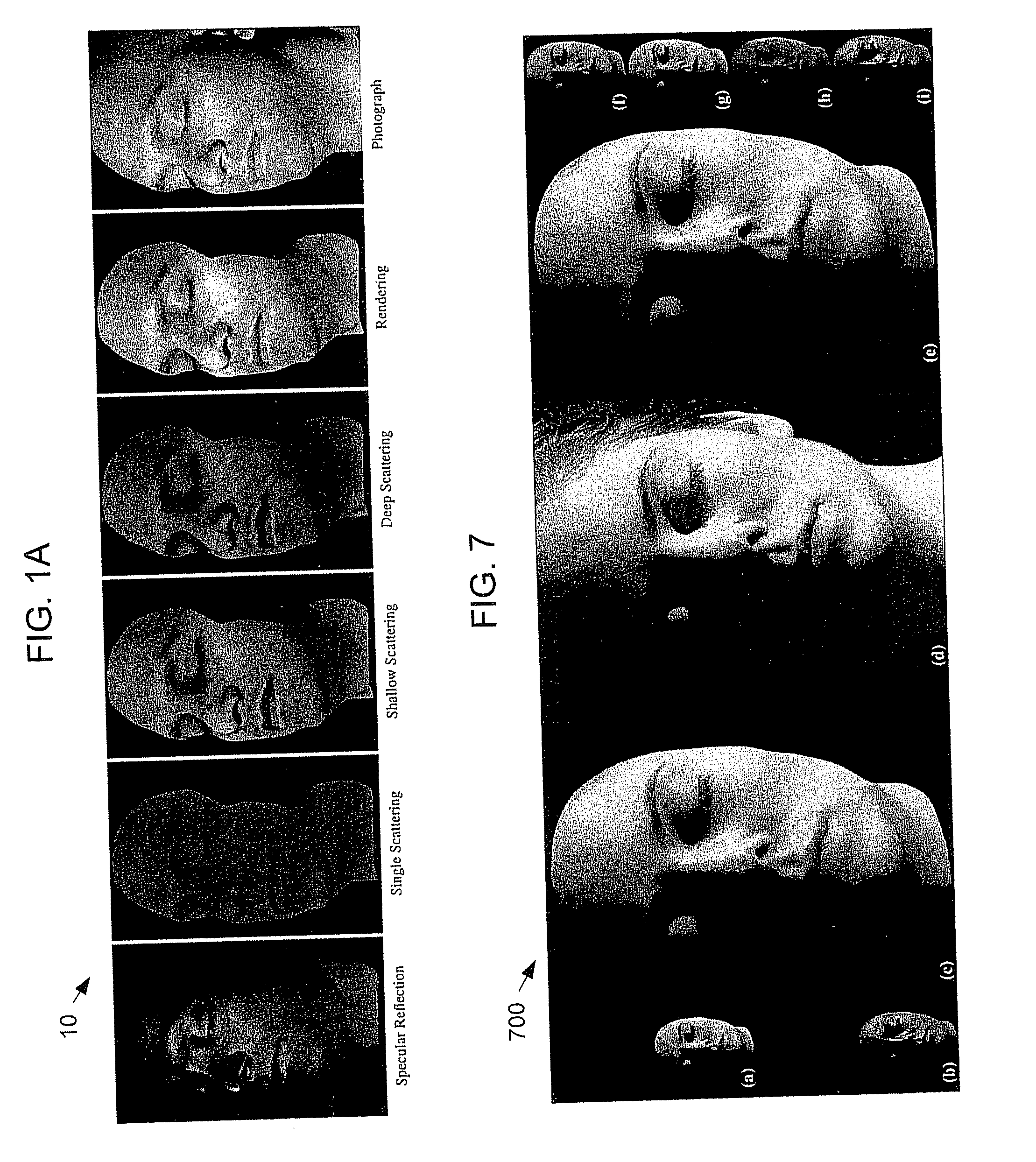
Practical Modeling and Acquisition of Layered Facial Reflectance
ActiveUS20090226049A1Easy to mergeConvenience to workCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsViewpointsDeep level
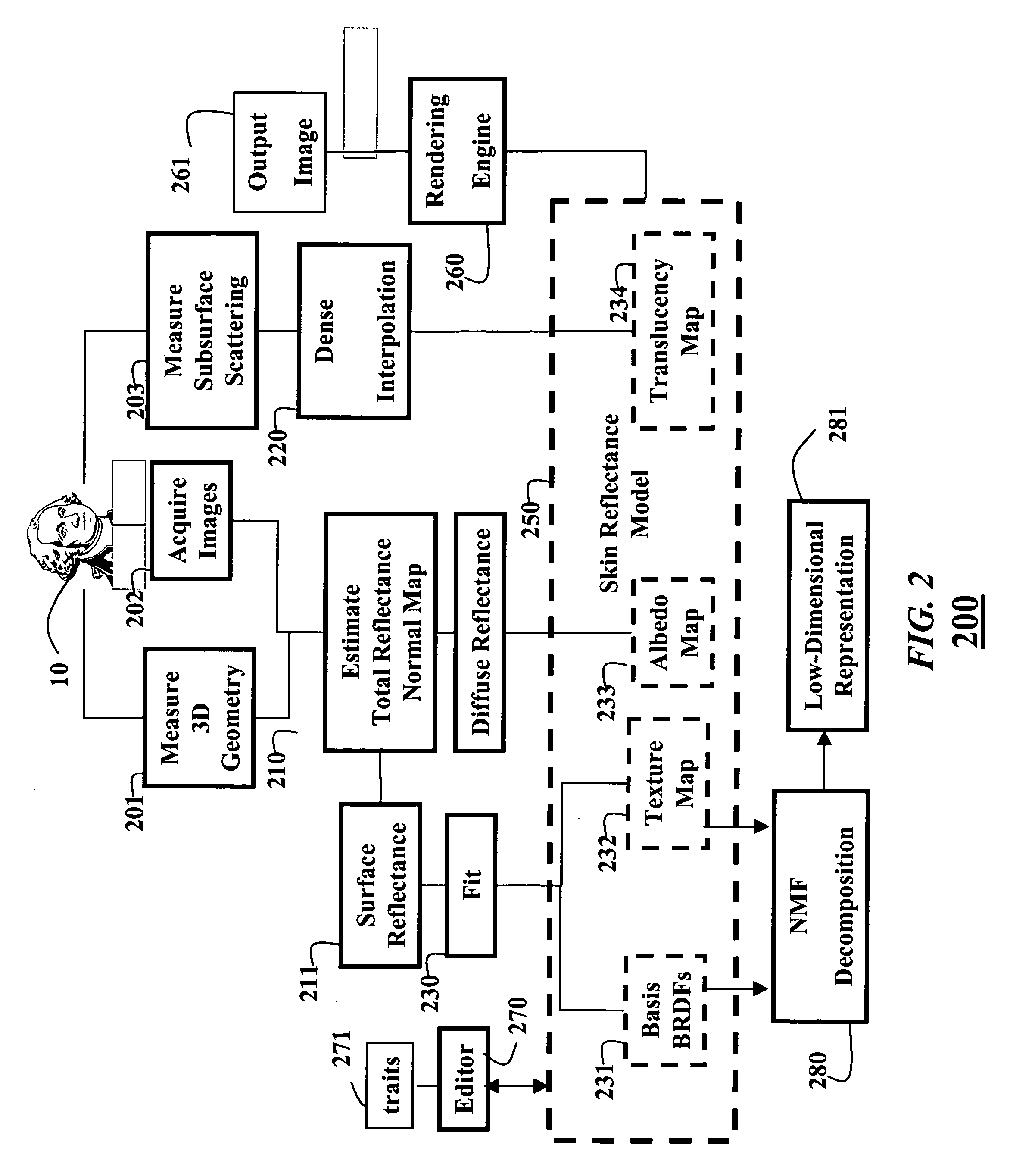
Techniques are described for modeling layered facial reflectance consisting of specular reflectance, single scattering, and shallow and deep subsurface scattering. Parameters of appropriate reflectance models can be estimated for each of these layers, e.g., from just 20 photographs recorded in a few seconds from a single view-point. Spatially-varying specular reflectance and single-scattering parameters can be extracted from polarization-difference images under spherical and point source illumination. Direct-indirect separation can be employed to decompose the remaining multiple scattering observed under cross-polarization into shallow and deep scattering components to model the light transport through multiple layers of skin. Appropriate diffusion models can be matched to the extracted shallow and deep scattering components for different regions on the face. The techniques were validated by comparing renderings of subjects to reference photographs recorded from novel viewpoints and under novel illumination conditions. Related geometry acquisition systems and software products are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
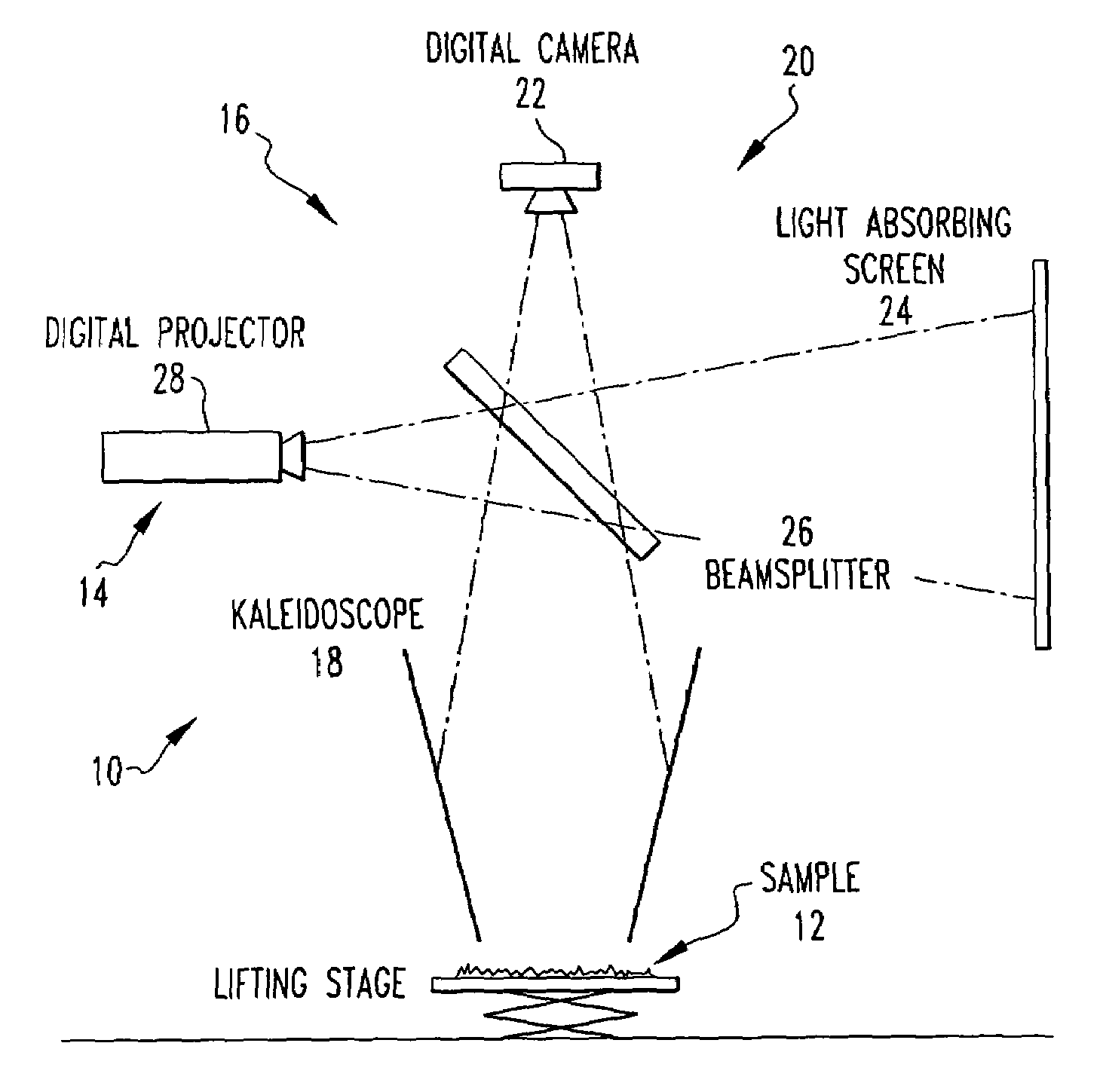
Method and apparatus for determining a bidirectional reflectance distribution function, subsurface scattering or a bidirectional texture function of a subject
InactiveUS7190461B2Scattering properties measurementsSubsurface scatteringBidirectional texture function
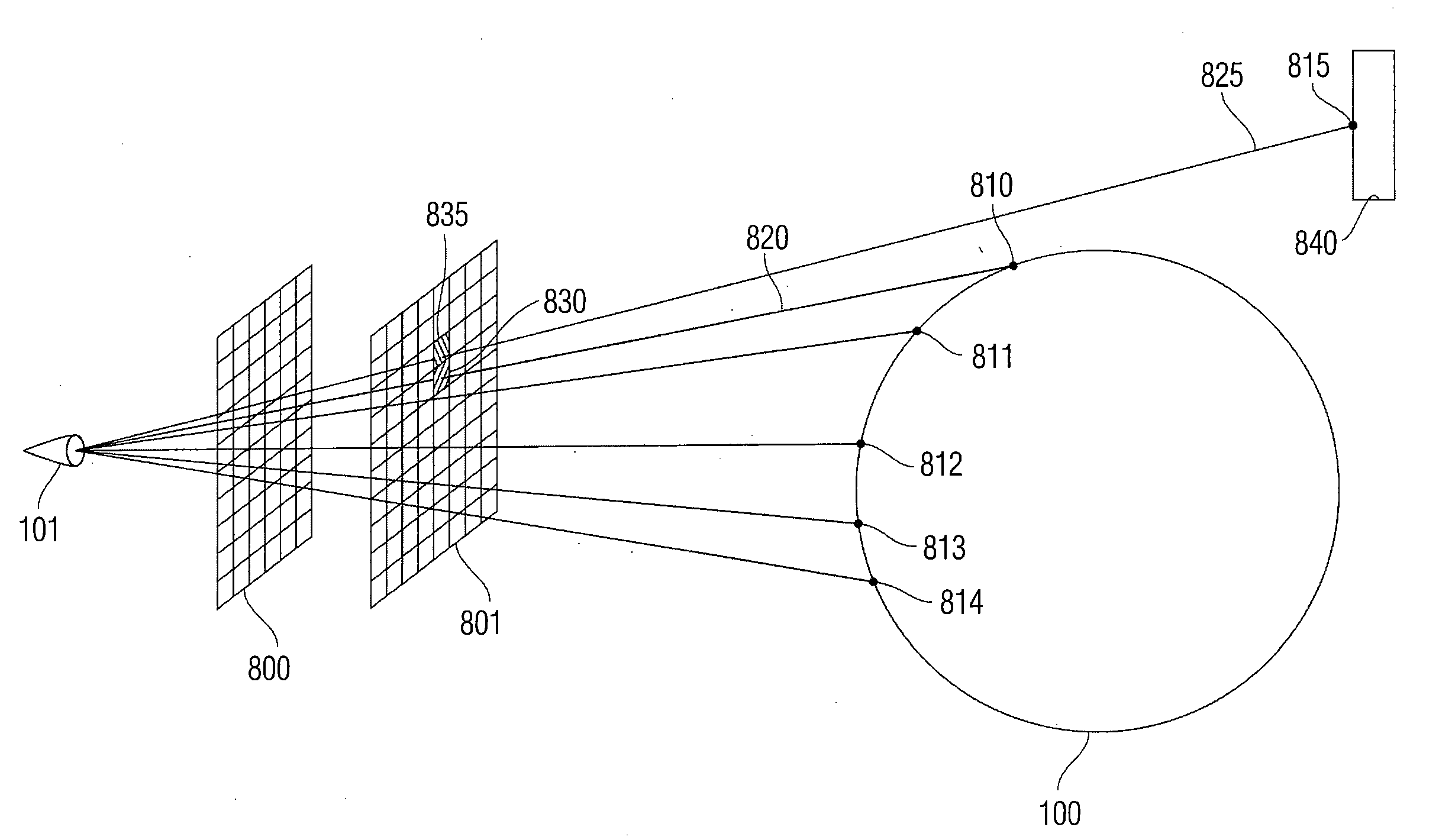
An apparatus for determining a bidirectional reflectance distribution function of a subject. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a light source for producing light. The apparatus includes means for measuring the bidirectional reflectance distribution function of the subject from multiple locations simultaneously with the light. A method for determining a bidirectional reflectance distribution function of a subject.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
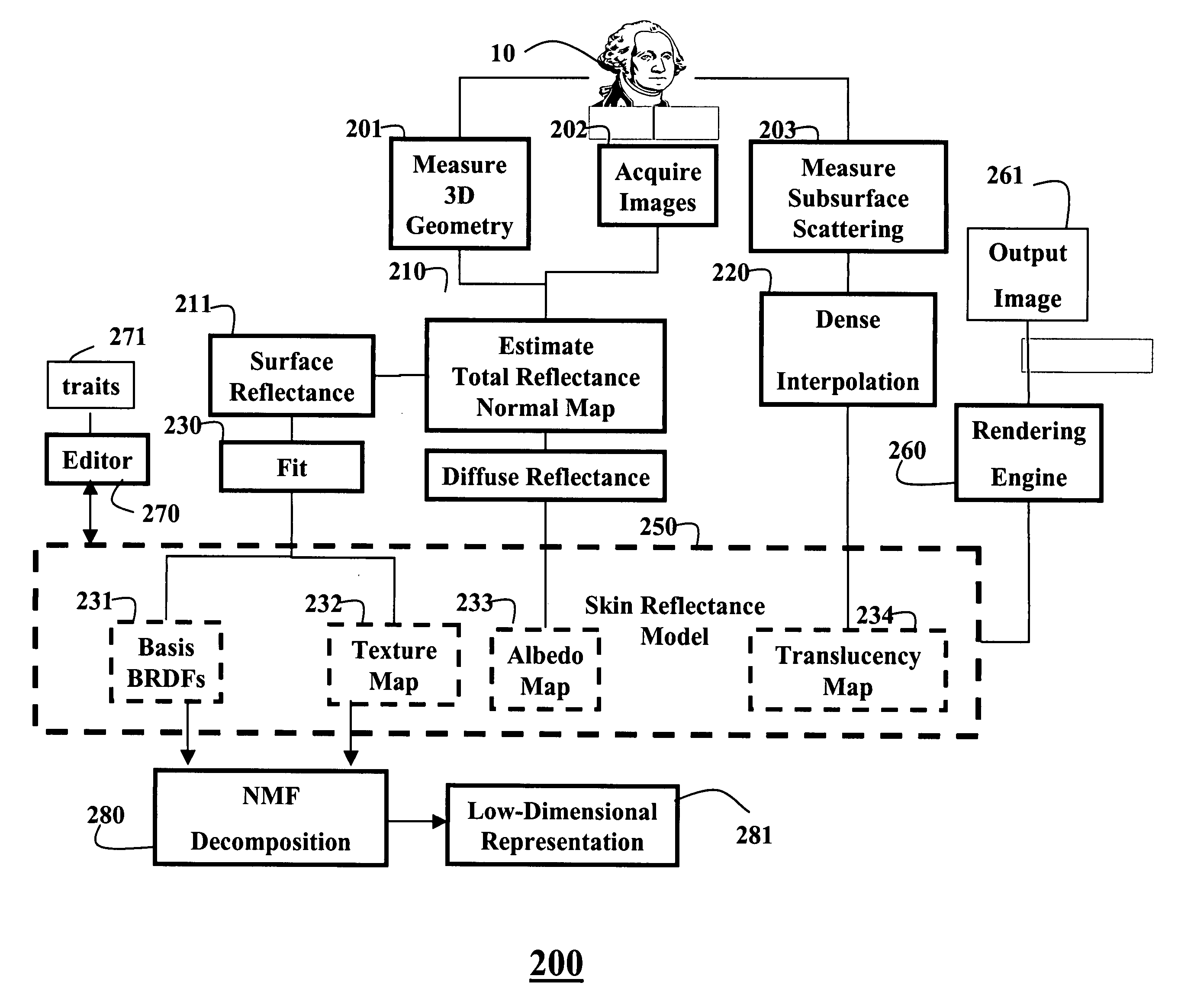
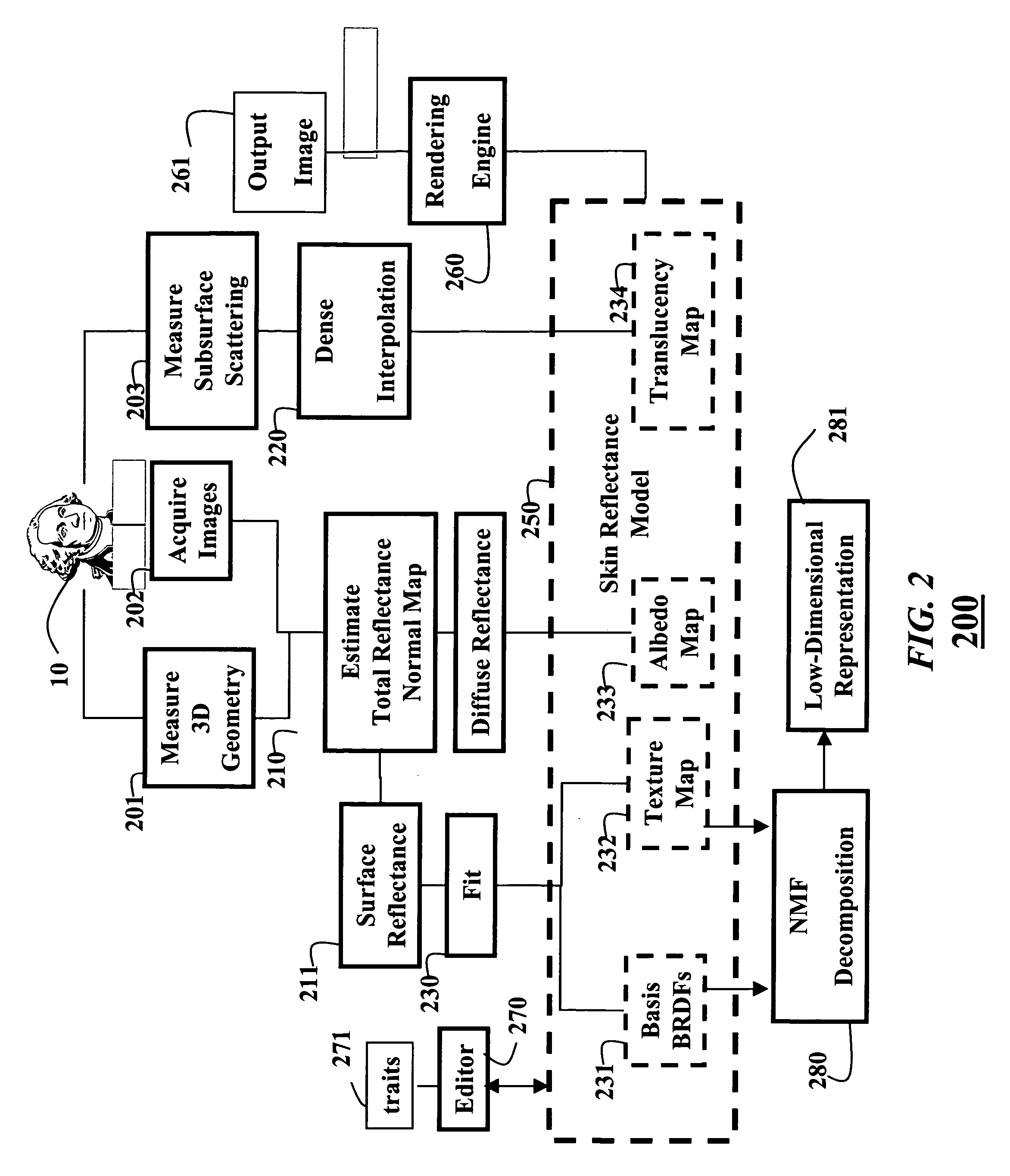
Skin reflectance model for representing and rendering faces
InactiveUS20060227137A1Scattering properties measurements3D-image renderingAlbedoSubsurface scattering
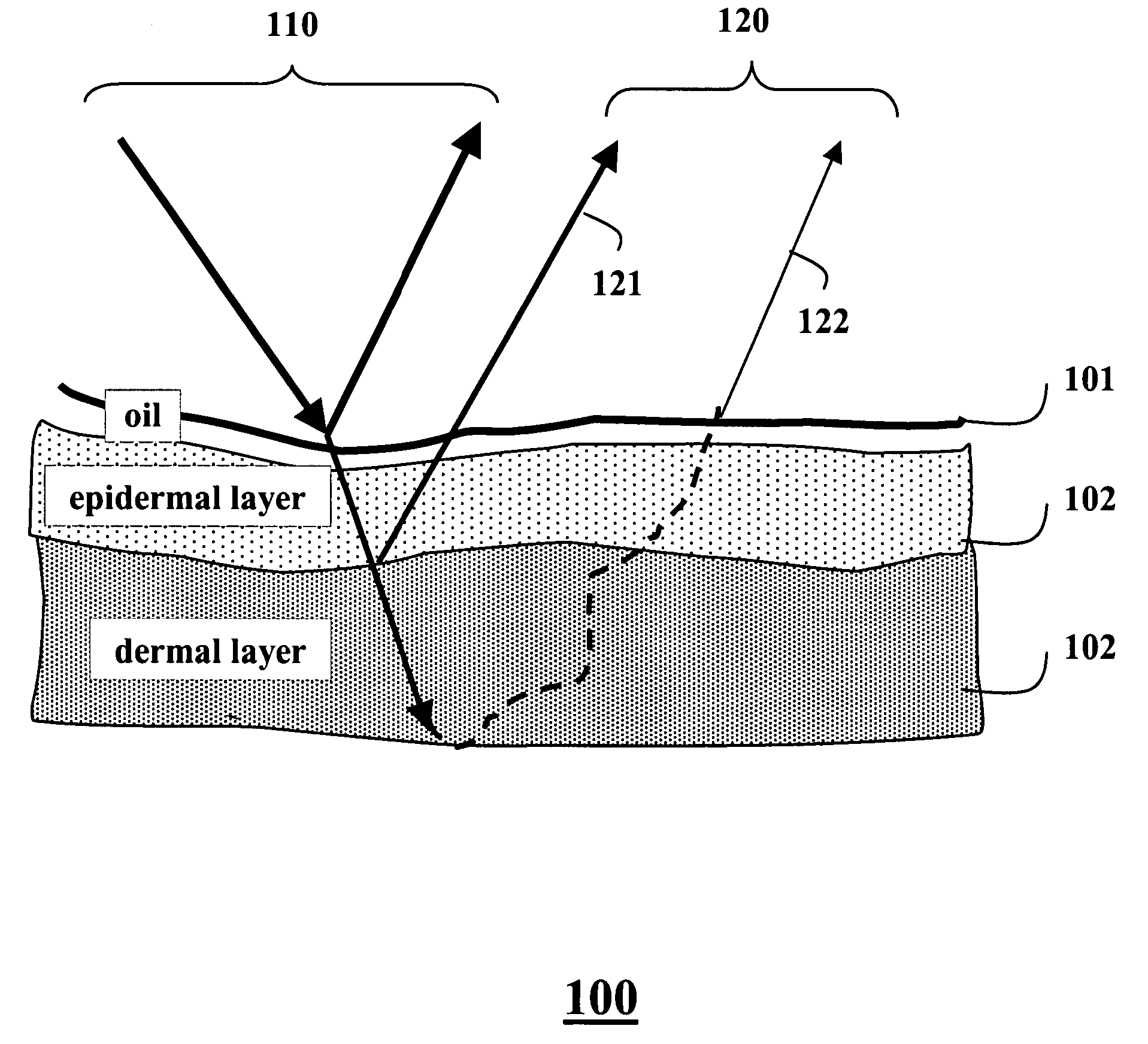
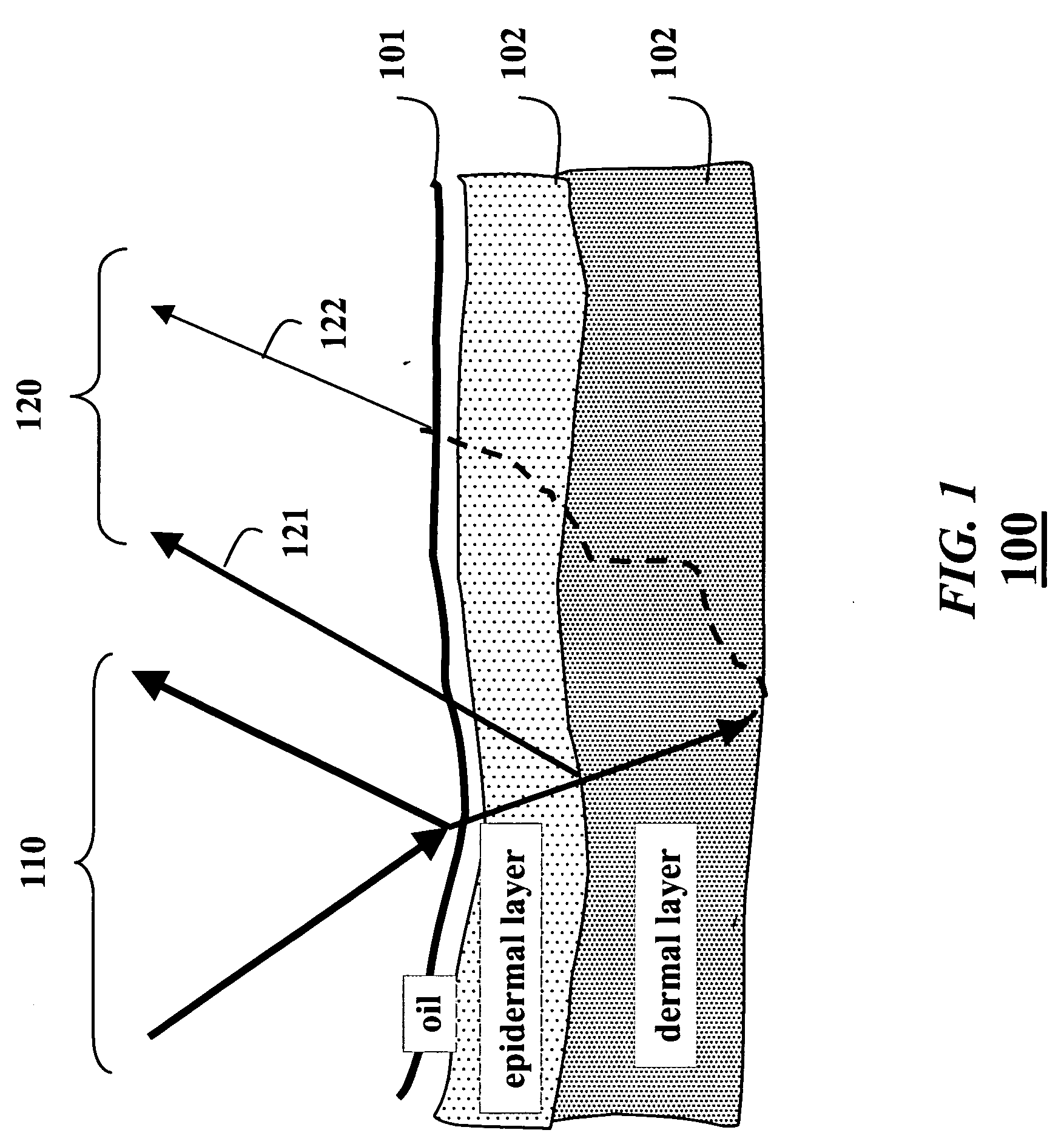
A face is scanned to obtain a three-dimensional geometry of the face, images are also acquired of the face, and subsurface scattering of the face is measured. A translucency map is determined from the subsurface reflectance. A total surface reflectance and a normal map are estimated from the three-dimensional geometry and the images, and diffuse reflectance is estimated using the total reflectance. An albedo map is determined from the diffuse reflectance. The diffuse reflectance is subtracted from the total reflectance to obtain a surface reflectance. A set of bi-directional reflectance functions is fitted to the surface reflectance. Then, the set of bi-directional reflectance distribution functions, the albedo map, and the translucency map are combined to form a skin reflectance model of the face.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
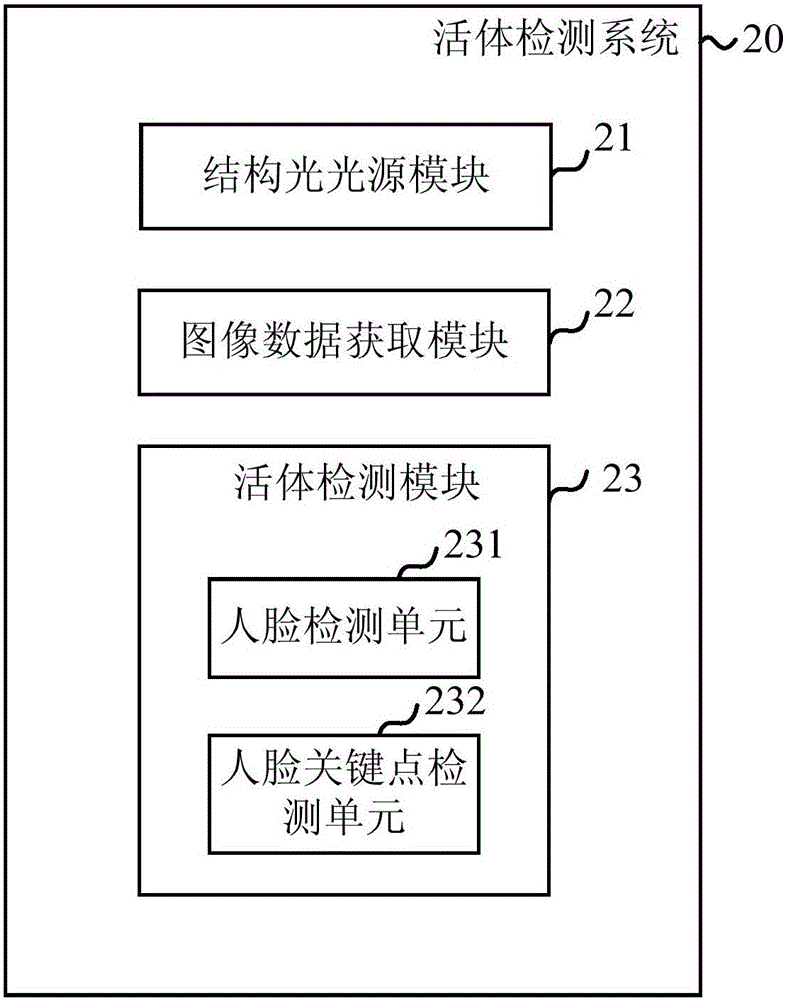
In vivo detection method, in vivo detection system and computer program product
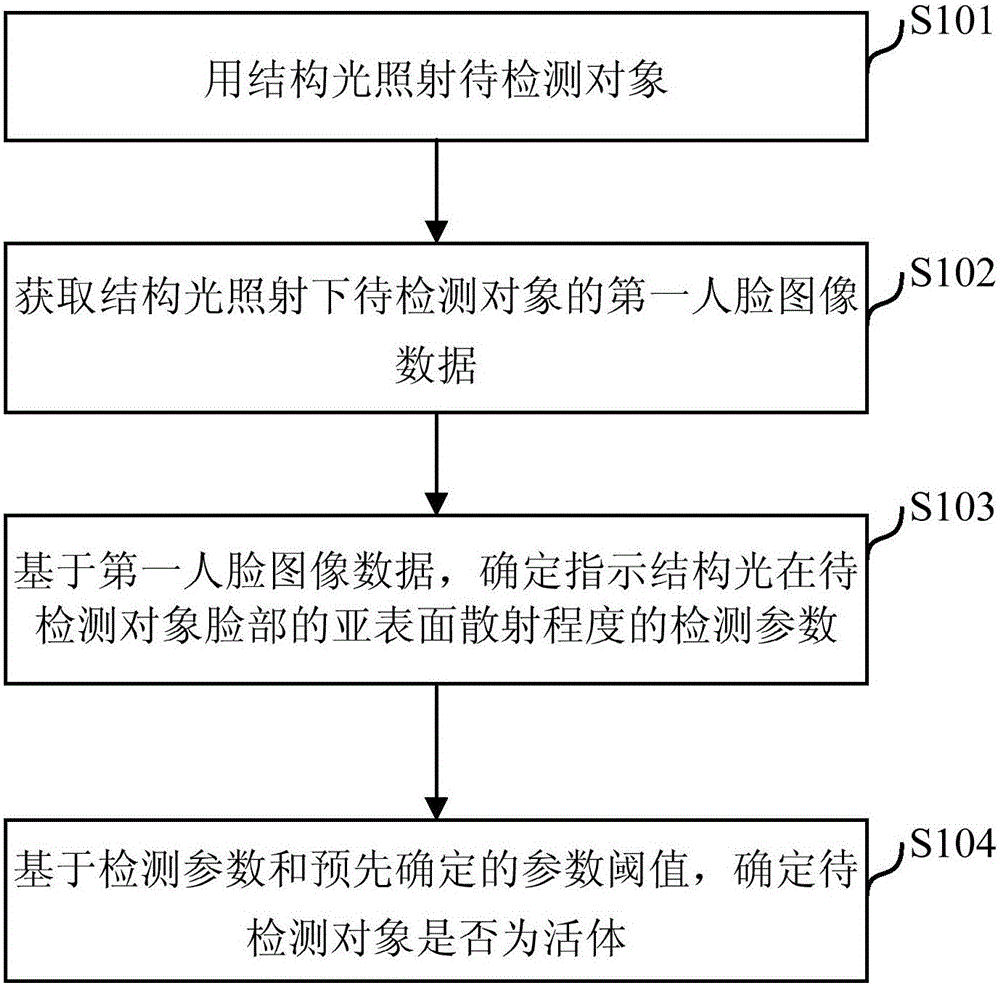
The invention relates to an in vivo detection method capable of realizing human body in vivo detection and an in vivo detection system employing the in vivo detection method. The in vivo detection method comprises steps that the structured light is utilized to irradiate a to-be-detected object; the first face image data of the to-be-detected object irradiated by the structured light is acquired; based on the first face image data, detection parameters indicating a subsurface scattering degree of the structured light on a face of the to-be-detected object are determined; based on the detection parameters and the pre-determined parameter threshold, whether the to-be-detected object is a living body is determined.
Owner:BEIJING KUANGSHI TECH +1
Skin reflectance model for representing and rendering faces
A face is scanned to obtain a three-dimensional geometry of the face, images are also acquired of the face, and subsurface scattering of the face is measured. A translucency map is determined from the subsurface reflectance. A total surface reflectance and a normal map are estimated from the three-dimensional geometry and the images, and diffuse reflectance is estimated using the total reflectance. An albedo map is determined from the diffuse reflectance. The diffuse reflectance is subtracted from the total reflectance to obtain a surface reflectance. A set of bi-directional reflectance functions is fitted to the surface reflectance. Then, the set of bi-directional reflectance distribution functions, the albedo map, and the translucency map are combined to form a skin reflectance model of the face.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
Physical method based on environment mapping for simulating human skin subsurface scattering
ActiveCN104484896AOvercoming processingOvercome space3D-image renderingSubsurface scatteringPhysical approach
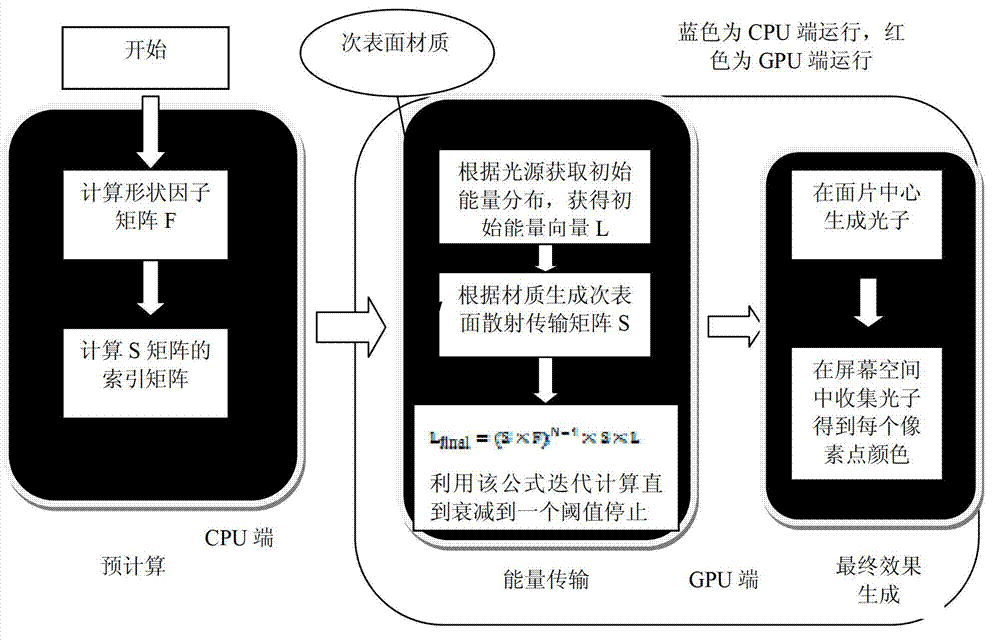
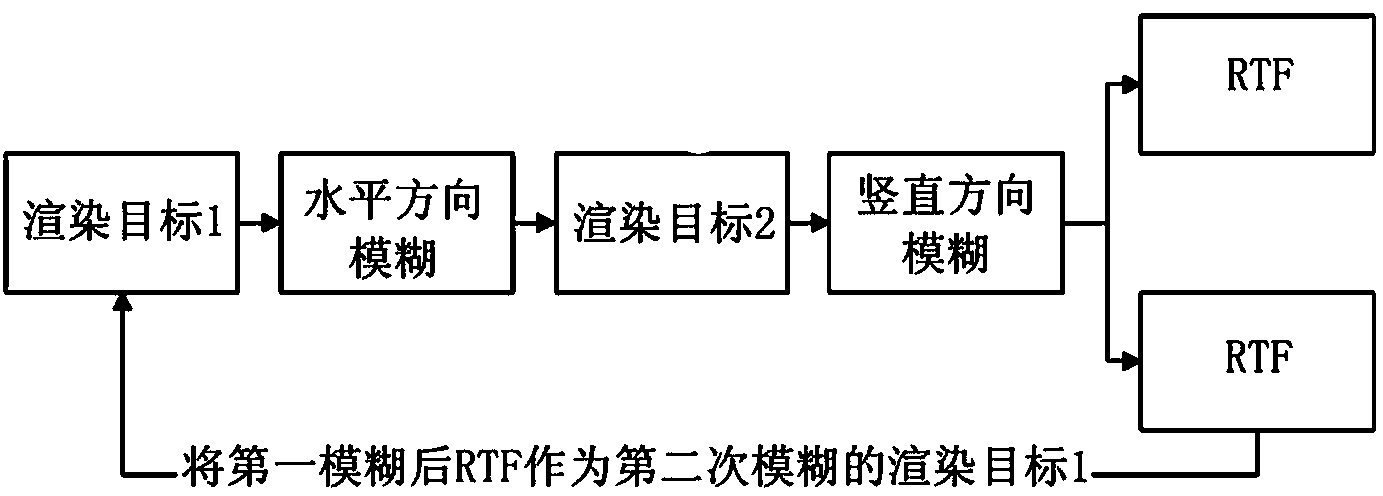
The invention discloses a physical method based on environment mapping for simulating human skin subsurface scattering. The method comprises steps that, a legendre formula is utilized to project and disintegrate an illumination integration equation in a to-be-simulated scene to acquire a luminance value of each pixel; the luminance value of each pixel is multiplied with an overflow color value to acquire a scattering value of each pixel at a back light face. The physical method based on environment mapping for simulating human skin subsurface scattering solves problems of large data processing workload, large occupation storage space and low processing efficiency existing in the prior art and has advantages of small data processing workload, small occupation storage space and high processing efficiency.
Owner:WUXI FANTIAN INFORMATION TECH
Rendering of Subsurface Scattering Effects in Translucent Objects
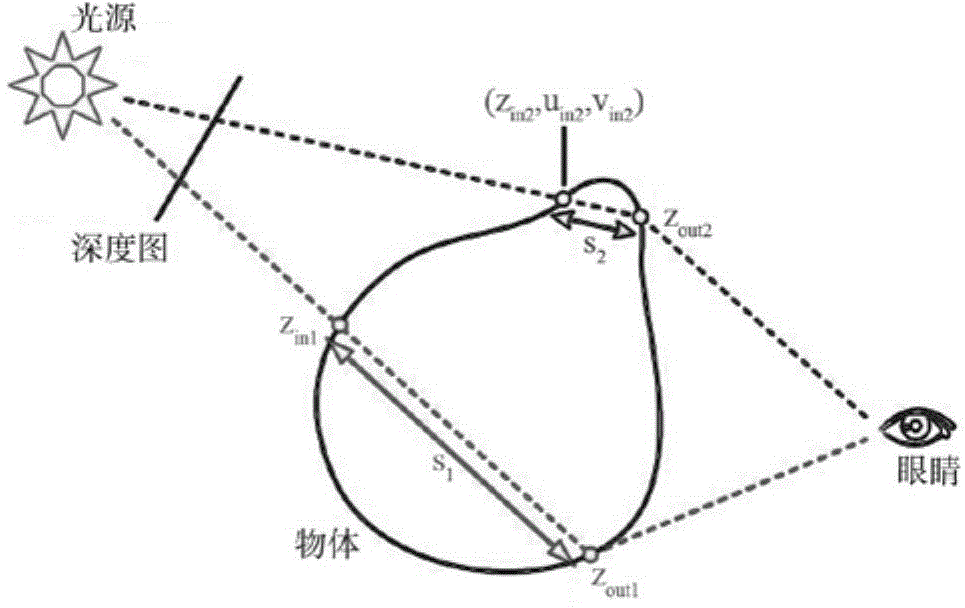
ActiveUS20090254293A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceColor measuring devicesSubsurface scatteringDepth map
Embodiments are directed to modifying an existing scheme for providing translucent illumination in order to take account of subsurface scattering. The color of a selected point of a translucent object can be determined using existing methods. The existing methods need not take subsurface scattering into account. Then, a contribution to the color at the selected point due to subsurface scattering may be calculated. The contribution due to subsurface scattering may be calculated based on a photon map. Embodiments of the invention also include the use of different types of photon maps. In some embodiments, a standard photon map may be used. In other embodiments, a photon map may be defined in a manner similar to a depth map. Thus, the entries of a photon map may be defined in terms of an angle from a light source and a distance between an object's surface and a light source.
Owner:DREAMWORKS ANIMATION LLC
Subsurface Rendering Methods and Apparatus
InactiveUS20090109220A1Quickly solve transportEfficient indexing3D-image rendering3D modellingVoxelSubsurface scattering
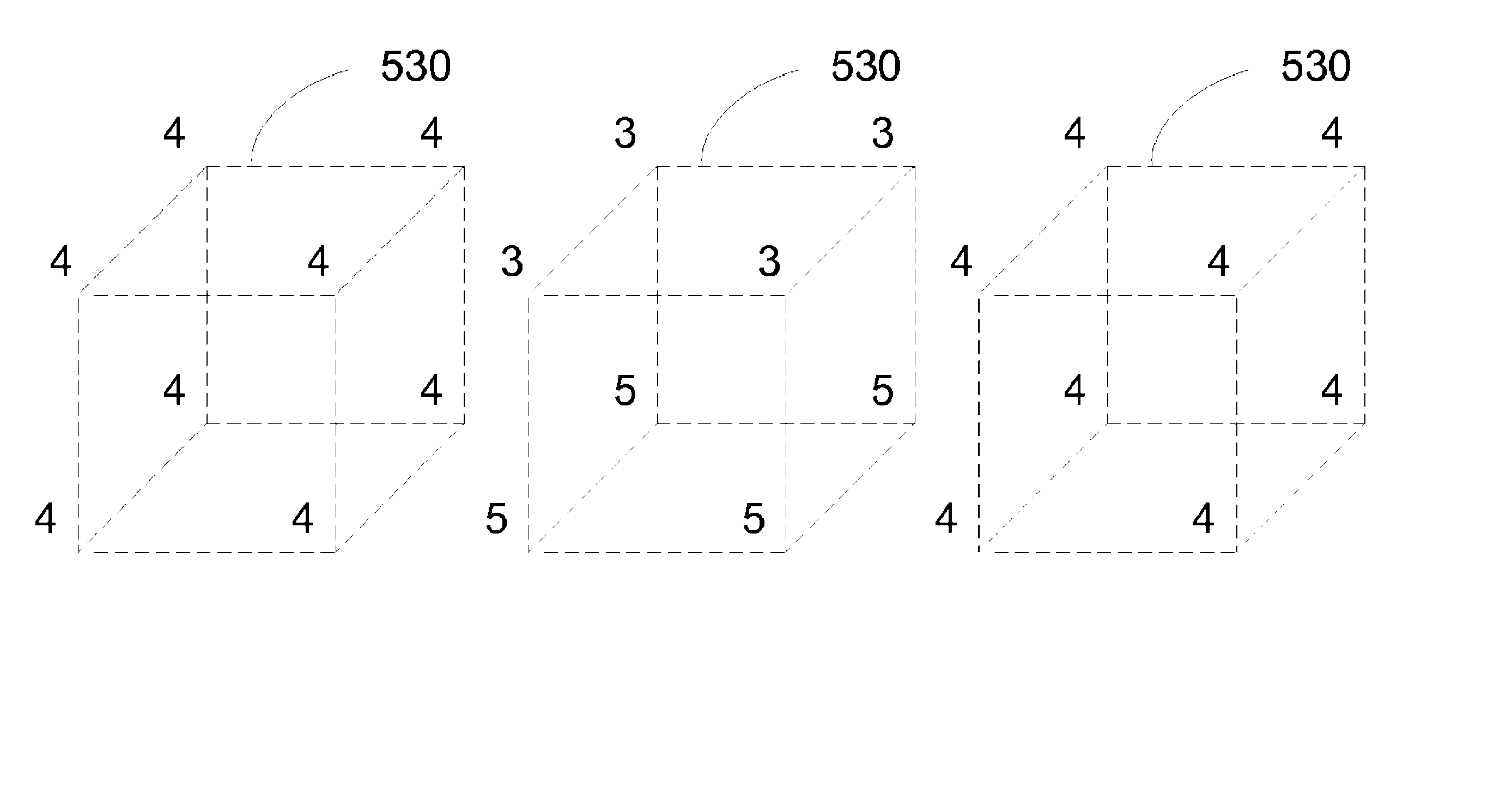
A method for a computer system includes receiving a three-dimensional model of an object, wherein the object includes a surface region, determining an incident irradiance associated with the surface region, determining a plurality of voxels associated with the three-dimensional model of the object, wherein a first plurality of voxels is associated with the surface region, and wherein a second plurality of voxels is associated with a sub-surface region of the object, associating the incident irradiance with the second plurality of voxels, and determining a subsurface scattering contribution associated with the surface region of the object in response to the incident irradiance associated with the second plurality of voxels.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
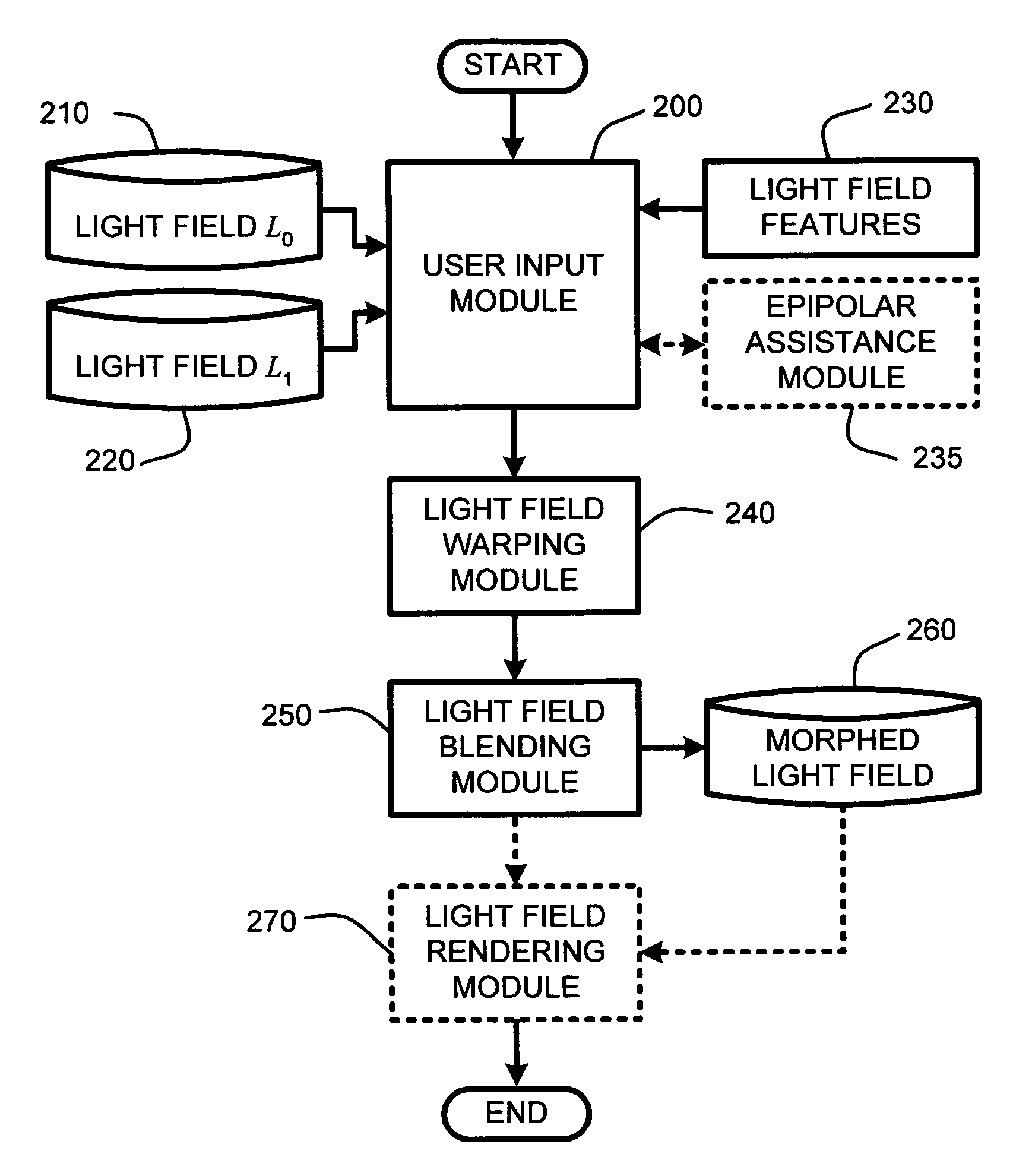
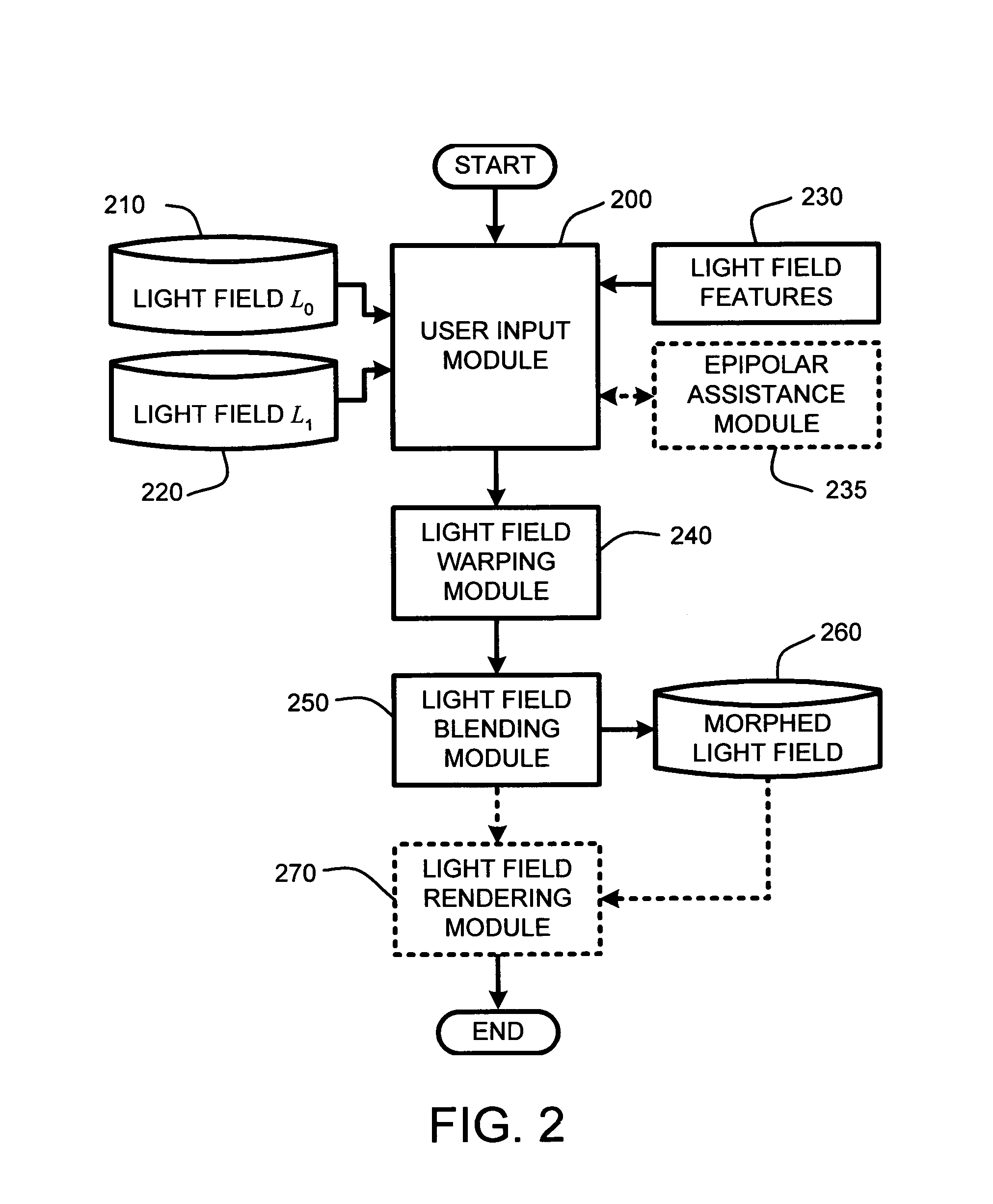
System and method for feature-based light field morphing and texture transfer
InactiveUS7129943B2Simple working processShorten the timeGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsMorphing
A “light field morpher,” as described herein, provides a computationally efficient system and method for image-based three-dimensional (3D) morphing and texture transfer of 3D objects by morphing “light fields” or “lumigraphs,” associated with source and target 3D objects. The light field morpher is applicable to morphing of objects having either or both Lambertian, or non-Lambertian surfaces, including surfaces having complex properties such as fur, subsurface scattering, and hypertextures, without the need for object modeling, or otherwise recovering detailed object geometry. Light field morphing begins by first specifying corresponding 2D and 3D feature elements, such as, “feature lines,”“feature polygons,” and “background edges,” in the input light fields representing the source and target light fields. Once the feature elements have been specified, “ray-space warping” of both light fields then warps those light fields to produce feature alignment. These warped light fields are then blended to produce a light field morph.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Shell texture functions
InactiveCN1741070AImage data processing detailsFilling planer surface with attributesShadowingsSubsurface scattering
Techniques are provided for at least modeling any one of mesostructure shadowing, masking, interreflection and silhouettes on a surface, as well as subsurface scattering within a non-homogeneous volume. Such techniques include, at least, acquiring material parameters for a material sample, determining irradiance distribution values for the material sample, synthesizing the material sample onto a mesh of an object. The synthesized object may then be rendered by one of plural rendering techniques.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP
BRDF (bidirectional reflectance distribution function) -based real-time subsurface scattering rendering method
InactiveCN102314704ASmall amount of calculationGuaranteed image quality3D-image renderingSubsurface scatteringComputer graphics (images)
A BRDF (bidirectional reflectance distribution function) -based real-time subsurface scattering rendering method includes the following steps: firstly, decomposing an illumination model into a Phone model, a scattering model and compensated illumination; secondly, improving a subsurface scattering model: adopting the BRDF method to approximate single subsurface scattering in subsurface scattering, and by simplifying an integral, simplifying a great deal of calculation load brought by the conventional illumination model to increase the rendering efficiency; and finally, rendering subsurface scattering in real time: by introducing the idea of deferred shading and adopting the GPU (graphics processing unit) technology, rendering subsurface scattering in an image space in real time is completed. The BRDF-based real-time subsurface scattering rendering method adopts the BRDF approximation method, realizes the real-time property of subsurface scattering rendering, and enhances the calculation performance while guaranteeing realistic rendering.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
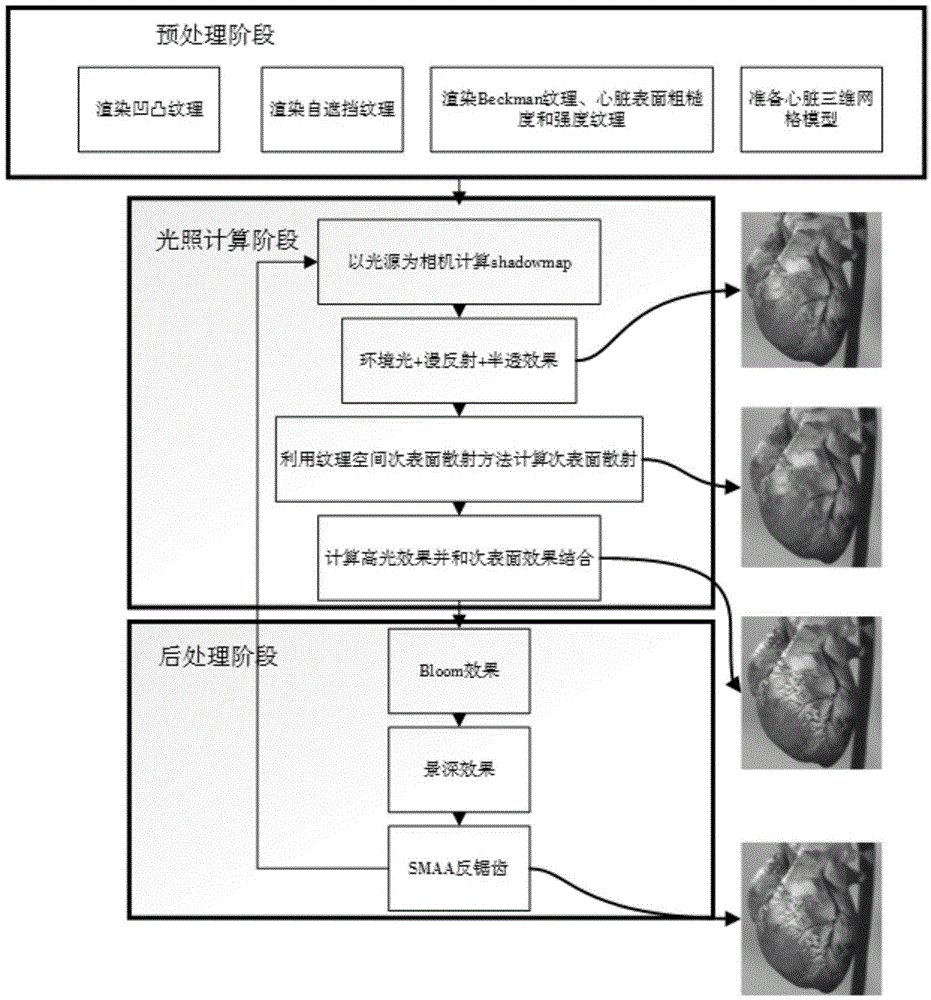
Real-time realistic drawing method of human heart
ActiveCN104599326ARealistic drawingWith subsurface scattering effect3D-image rendering3D modellingSubsurface scatteringMedicine
The invention discloses a real-time realistic drawing method of a human heart. The method comprises the steps of effectively drawing the surface and sub-surface effects by the texture space sub-surface drawing method and the semitransparent transmission method; combining a concave-convex map and a Kelemen / Szirmay-Kalos lighting model, so as to achieve the effect the heart surface is covered with mucus; combining sub-frame scattering, mucus coverage and other foundation effect of the heart surface to obtain the heart surface drawing effect. The experiment result shows that the real-time realistic drawing method of the human heart is relatively high in drawing efficiency and realistic performance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and device for emulating secondary surface dispersion effect of non-physical model
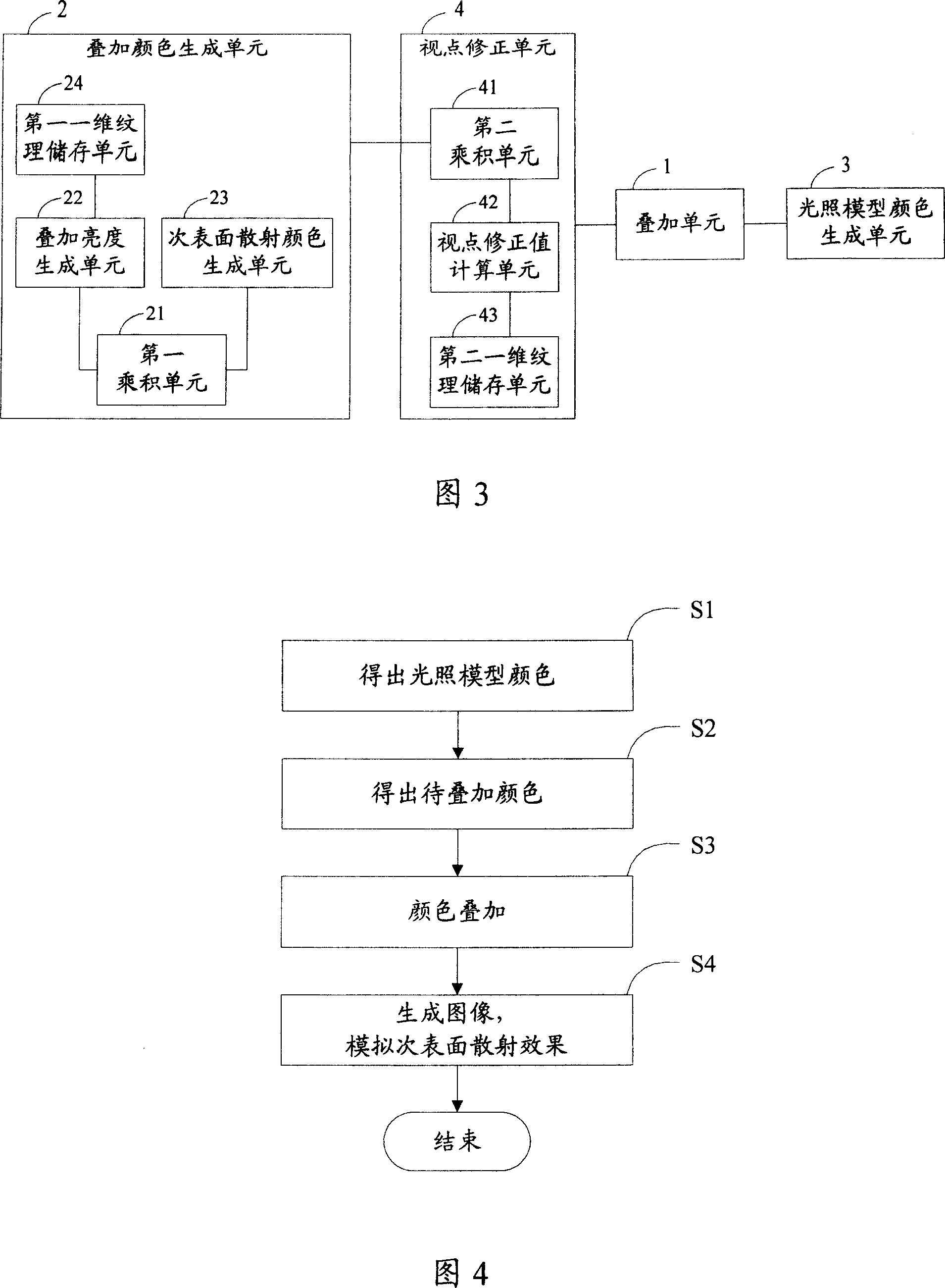
ActiveCN101127126ARealize simulationCutting costs3D-image renderingSubsurface scatteringComputer graphics (images)
The utility model discloses a method a device for non-physical model simulation secondary surface scattering result, which aims to solve the problems of strict realizing condition of simulating secondary surface scattering result using simplified physical model in prior art. The method of the utility model comprises: A. The illumination model color and the color waiting for superposition are get; B. The color waiting for superposition is superposed with the illumination model color to simulate secondary surface scattering result. The device of the utility model comprises: an illumination model color generation unit, a superposition three color generation unit which is used for generating the color waiting for superposition, a color waiting for superposition which is used for generating the superposition color generation unit and a superposition unit of the illumination model color superposition which is generated with the illumination model color generation unit. The utility model has the advantages of lower cost and reasonable theory compared with the predicted light ray transmission method of realizing secondary surface scattering result.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Rendering method and device
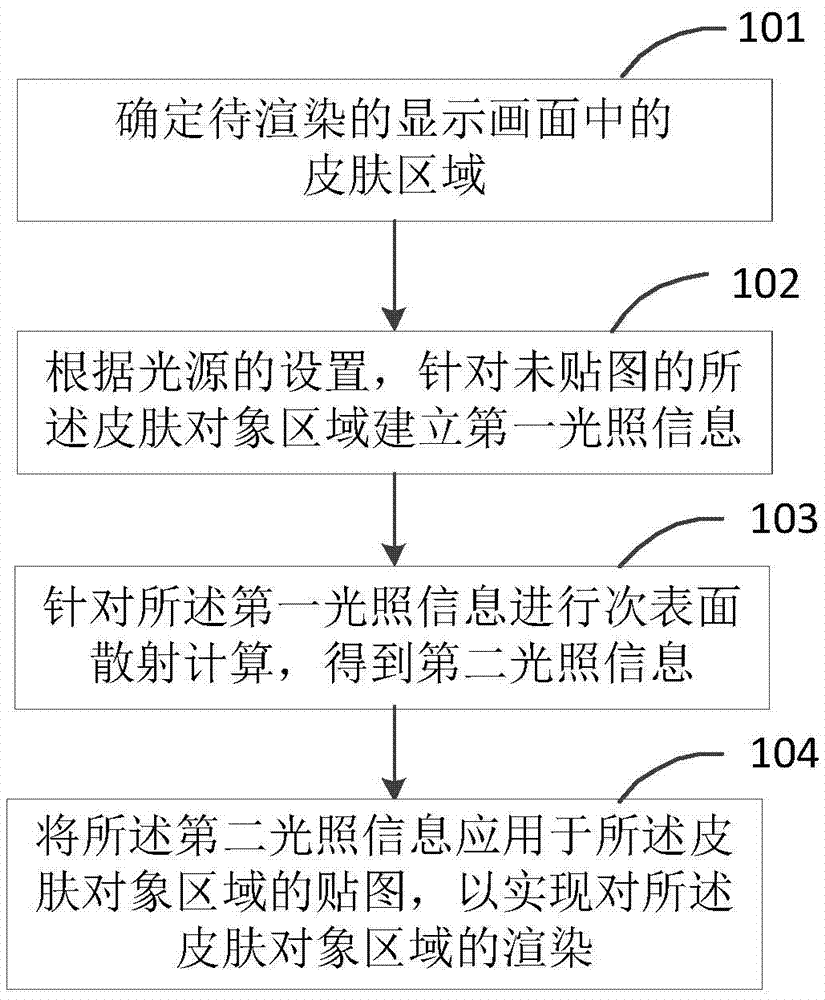
ActiveCN107204029AQuality improvement3D-image renderingSubsurface scatteringComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a rendering method and device, and the method and device are used for the rendering of a skin region in a three-dimensional game display frame. The rendering method comprises the steps: determining a skin region in a to-be-rendered frame; building first illumination information for an unmapped skin region according to the setting of a light source; carrying out the subsurface scattering calculating of the first illumination information, and obtaining second illumination information; and applying the second illumination information to a map of the skin region, so as to achieve the rendering of the skin region.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Real-time global illumination method for sub-surface scattering object on the basis of radiosity
InactiveCN102819860AReal-time Global Illumination EffectsReal-time replacement3D-image renderingDipole modelSubsurface scattering
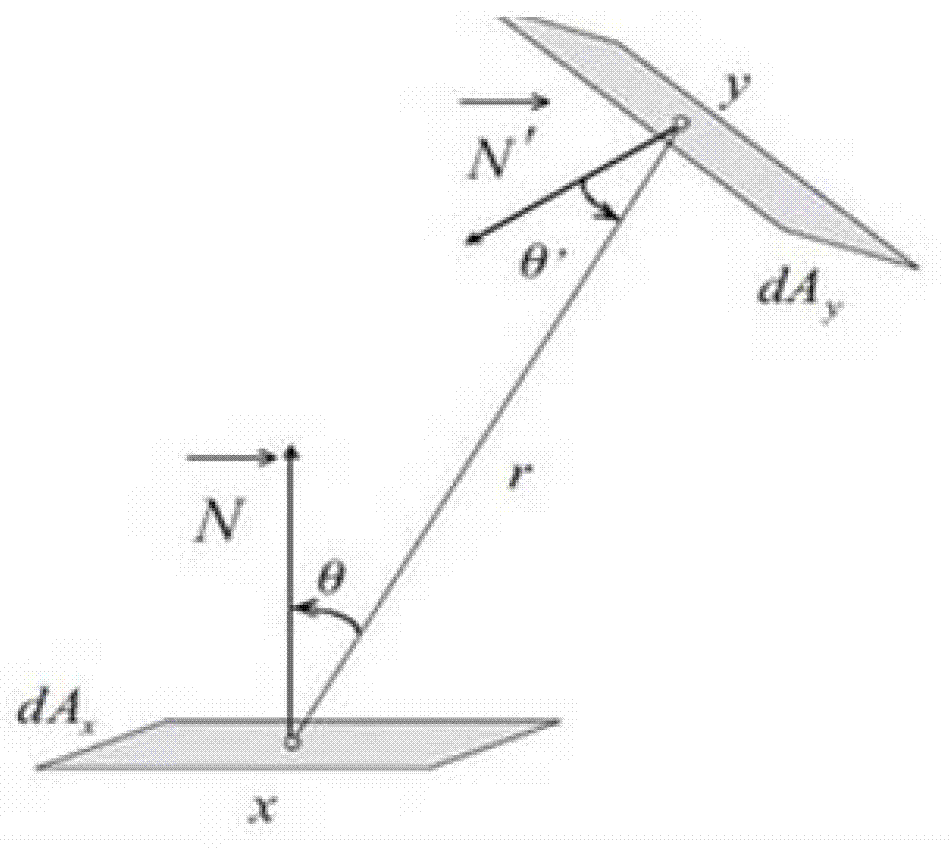
The invention provides a real-time global illumination method for a sub-surface scattering object on the basis of the radiosity, which is mainly divided into three steps of: 1) pre-calculating: pre-calculating an energy transmission matrix of a scene by the traditional approximate dipole model and the radiosity, and storing in a sparse matrix mode; 2) calculating an energy transmission process by a quick sparse matrix library of a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), and obtaining energy acquired by each surface patch; and 3) obtaining the final global illumination effect by a quick photon collection algorithm. On the basis of the certain pre-calculation basis, the real-time global illumination effect for the sub-surface scattering object can be obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Snow covered path of travel surface condition detection
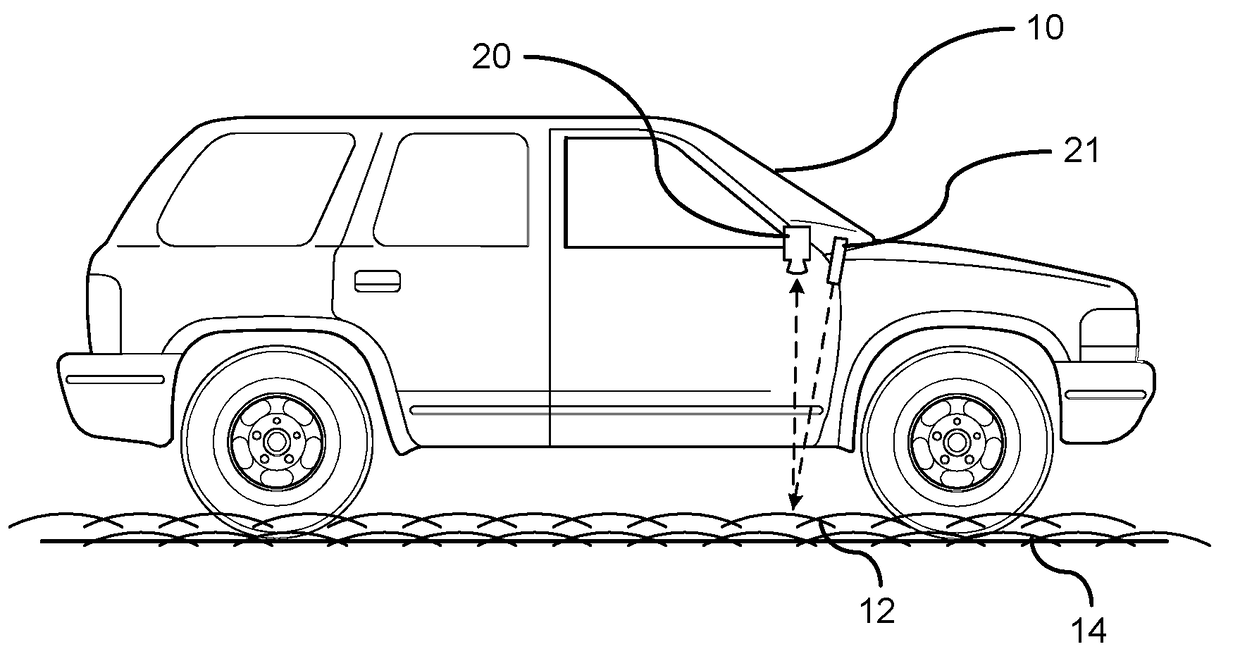
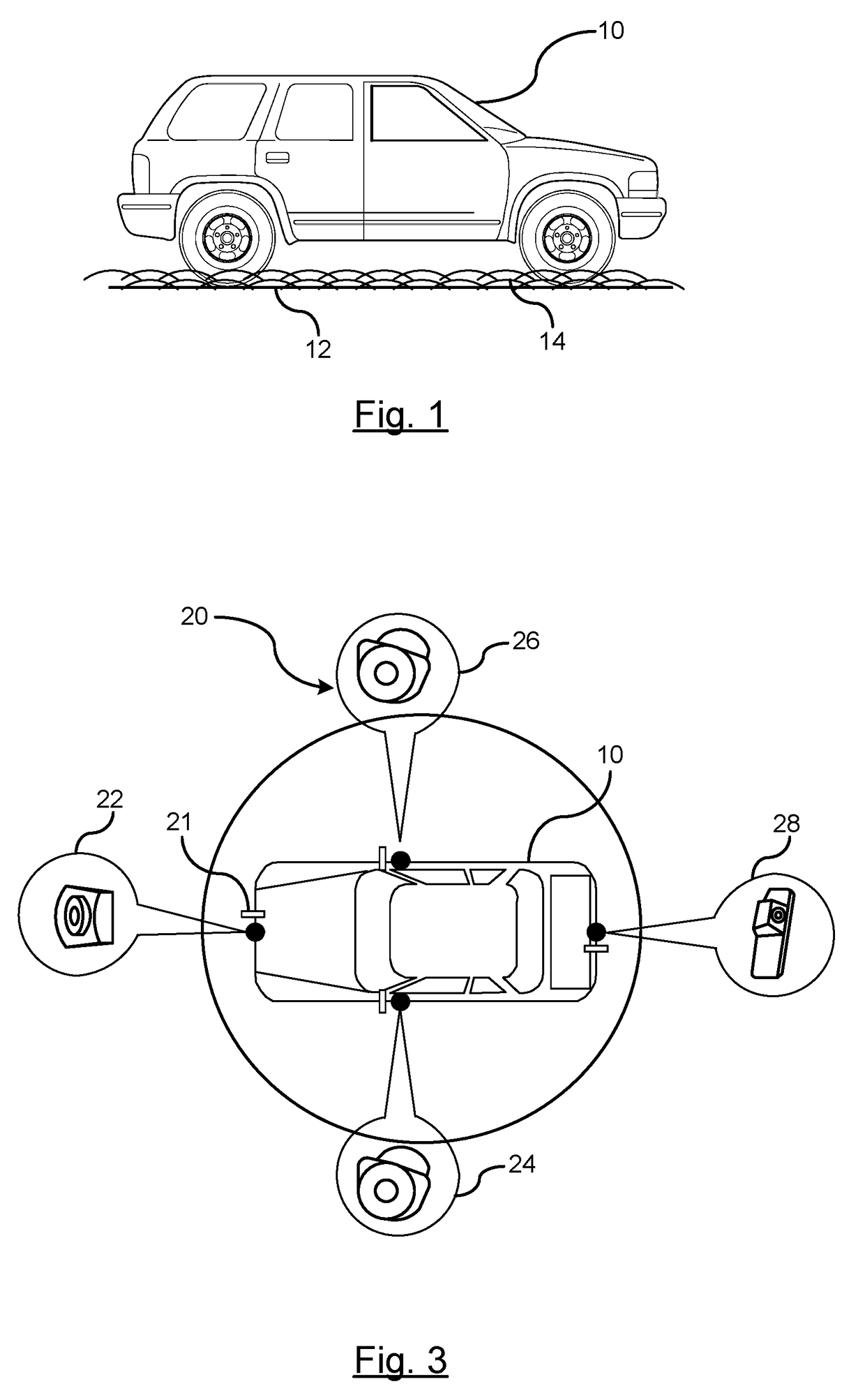
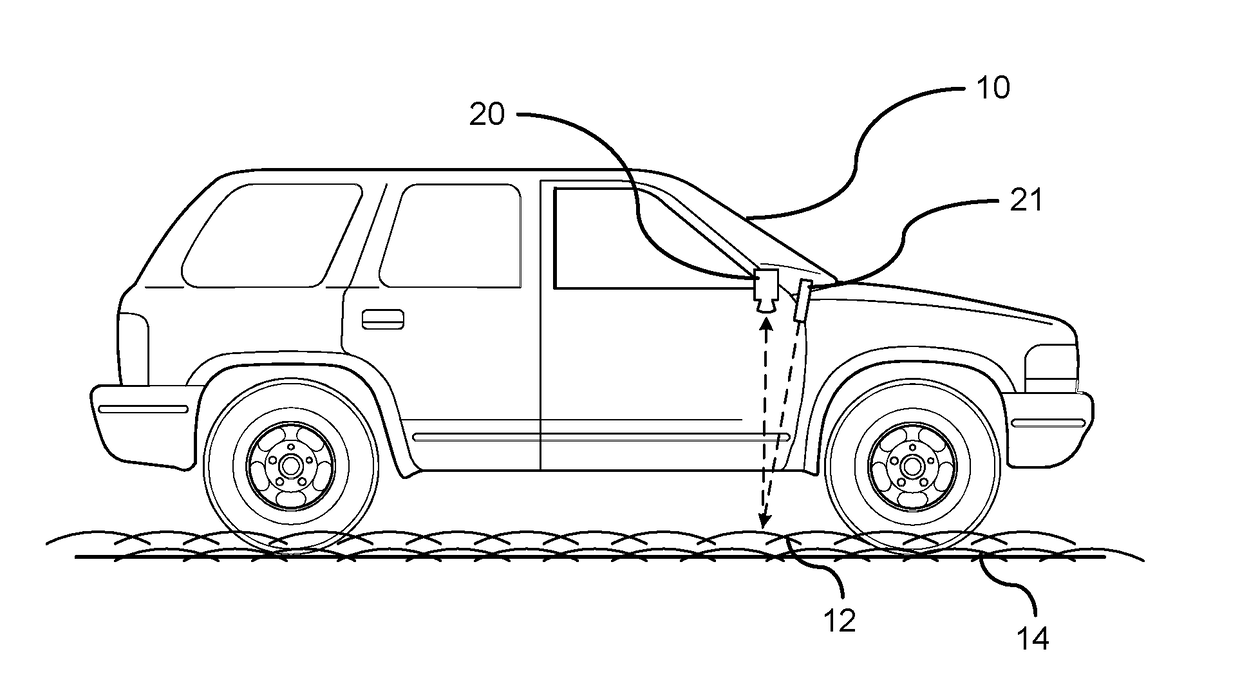
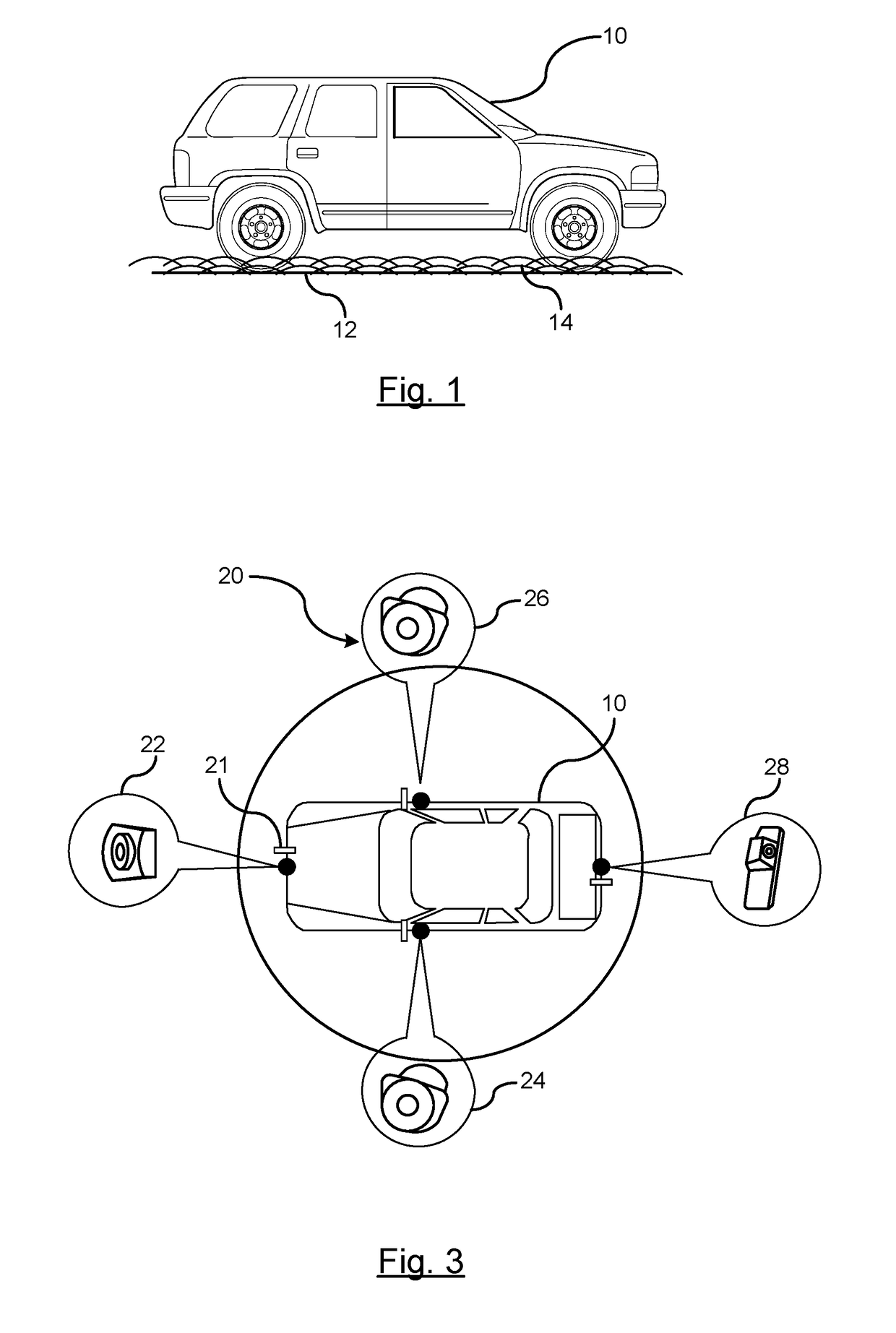
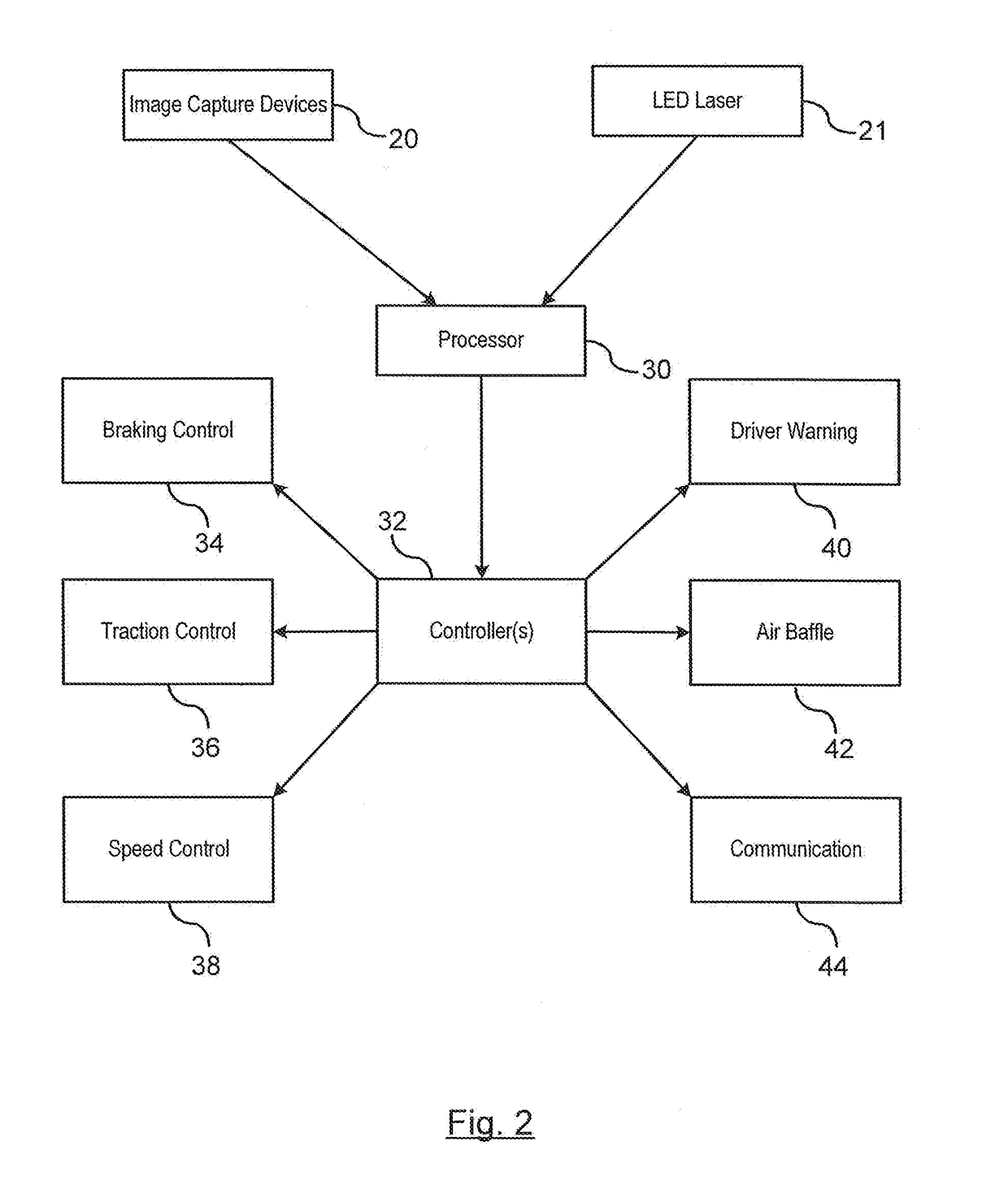
ActiveUS20170161571A1Broad blurring of diffused lightingImage enhancementImage analysisSnowpackSubsurface scattering
A method for determining a snow covered surface condition of a path of travel. A beam of light is emitted at a surface of the path of travel by a light emitting source. An image of a path of travel surface is captured by an image capture device. The image capture device is mounted on the vehicle and captures an image in a downward direction. The captured image captures the beam of light emitted on the path of travel surface. Analyzing a subsurface scattering of the light generated on the path of travel surface by a processor. A determination is made whether snow is present on the path of travel. A snow covered path of travel surface signal is generated in response to the identification of snow on the path of travel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
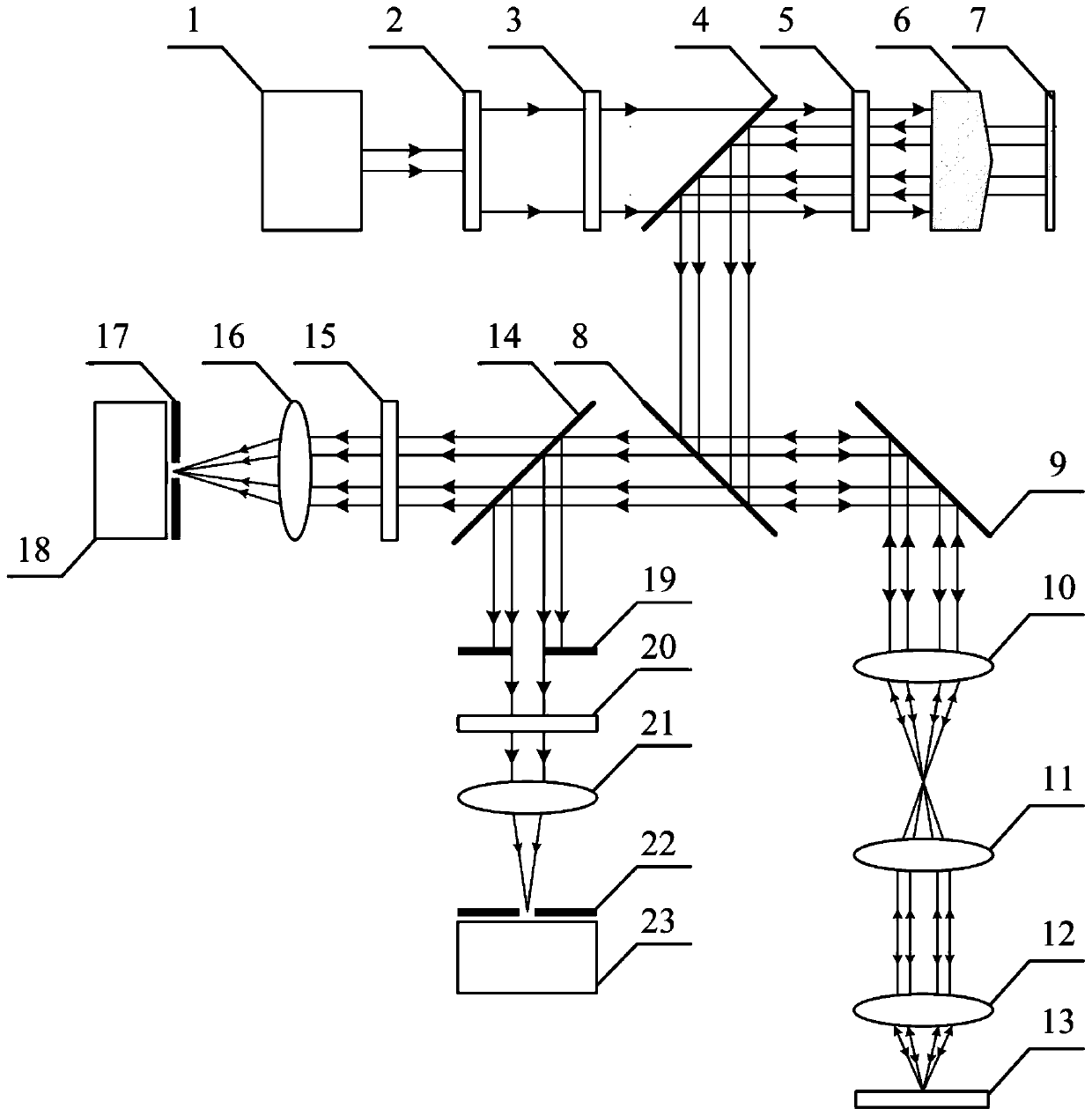
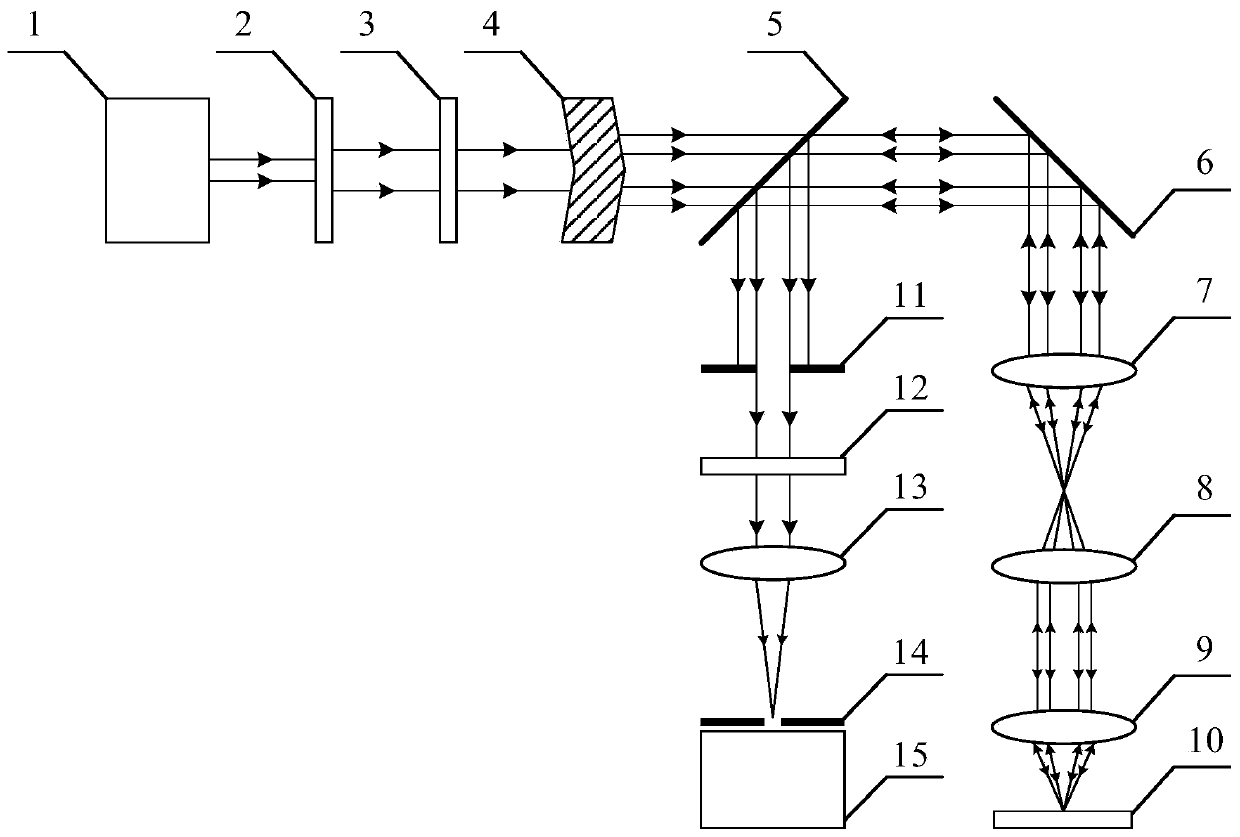
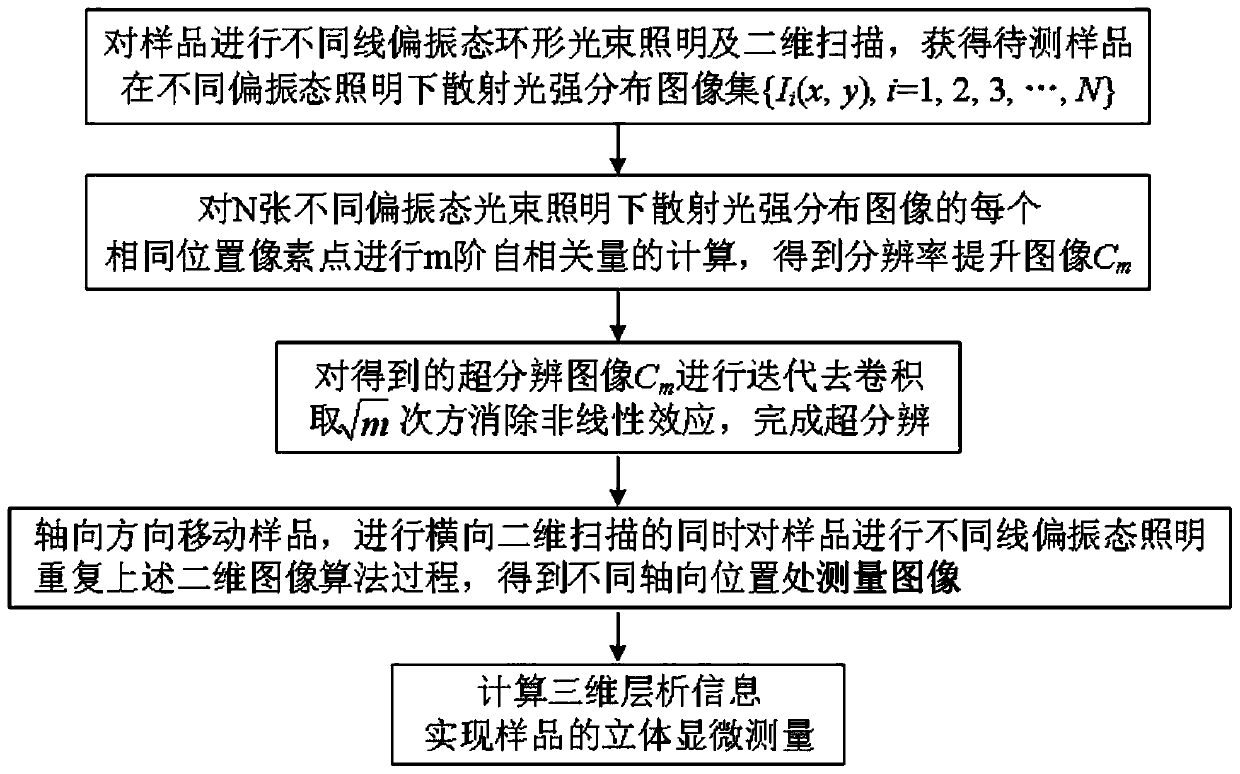
Surface and subsurface integrated confocal microscopic measurement device and method
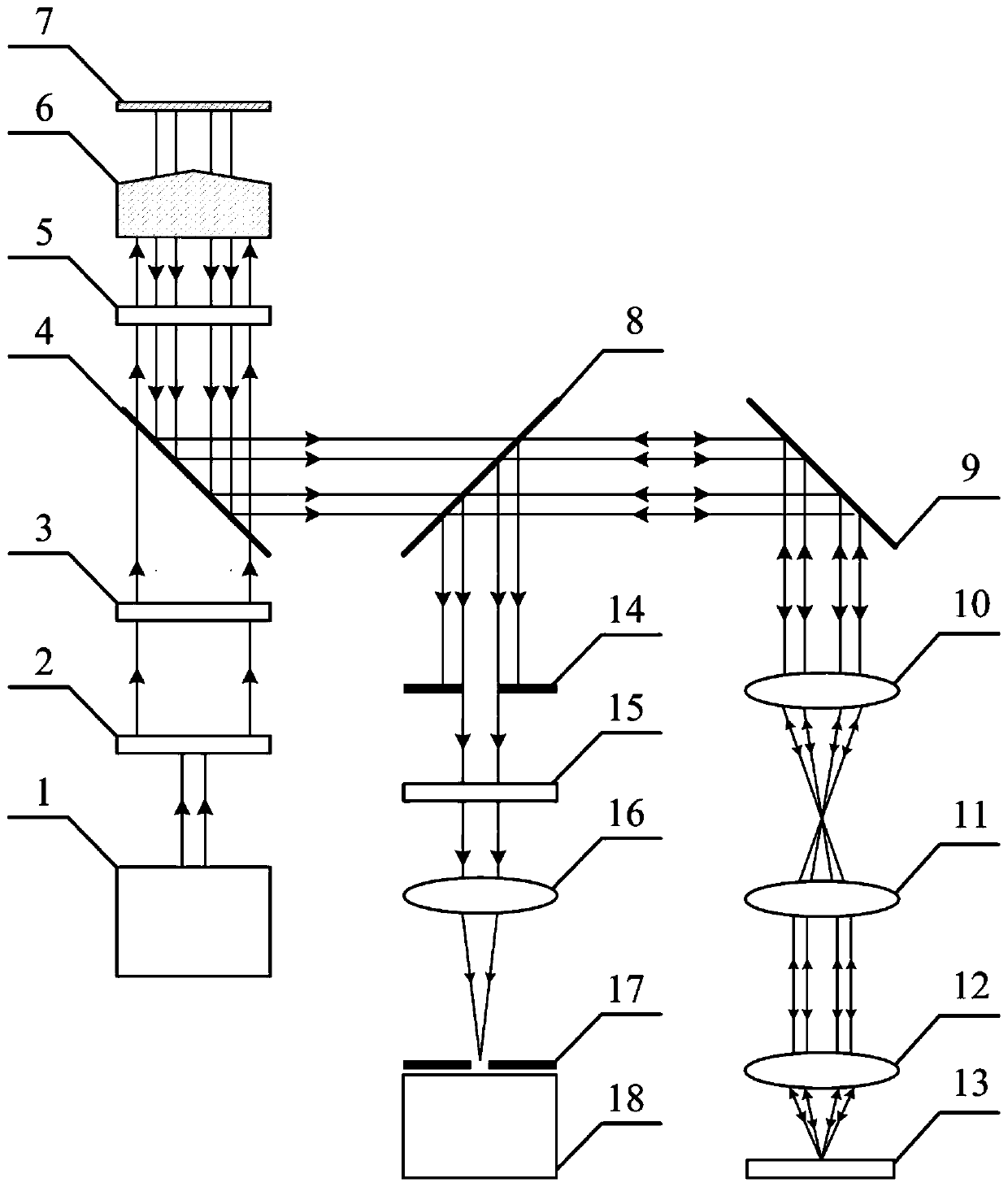
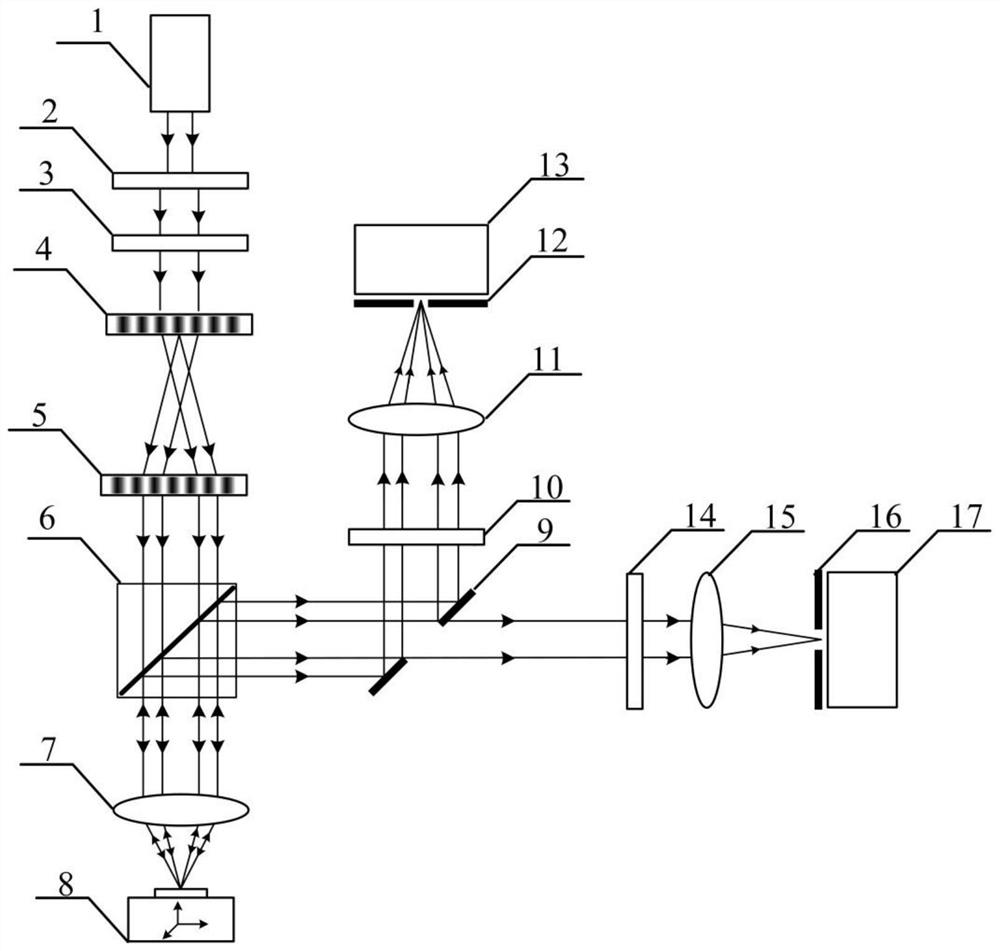
PendingCN111220624AEfficient separationWith integrated detection functionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansPlane mirrorBeam splitting
The invention discloses a surface and subsurface integrated confocal microscopic measurement device and a surface and subsurface integrated confocal microscopic measurement method. The surface and subsurface integrated confocal microscopic measurement comprises an annular light illumination module, an annular light scanning module, a reflective confocal detection module and a dark field confocal detection module, wherein the annular light illumination module comprises a laser, a beam expander, a polarizing film I, a polarizing beam splitting film, a quarter-wave plate, a conical lens and a plane mirror; the annular light scanning module comprises a transflective film I, a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a scanning lens, a tube lens, an objective lens and a to-be-detected sample; thereflective confocal detection module comprises a transflective film II, a polarizing film II, a focusing lens I, a pinhole I and a camera I; and the dark field confocal detection module comprises a diaphragm, a polarizing film III, a focusing lens II, a pinhole II and a camera II. By means of illumination beam shaping and complementary aperture shielding detection, the surface and subsurface integrated confocal microscopic measurement device effectively separates a sample surface reflection signal and a subsurface scattering signal, can obtain three-dimensional distribution information of defects such as nanoscale surface scratches, abrasion, subsurface cracks and bubbles at the same time, and has a surface and subsurface defect integrated detection function.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +2
Body rendering method and system of semitransparent material
ActiveCN106023300ASolve the problem of time-consuming and memory-consuming3D-image renderingVoxelSubsurface scattering
The invention discloses a body rendering method of a semitransparent material. The method comprises the following steps: step one, obtaining light source attribute data and material parameter data of a semitransparent module body; step two, for each light color spectrum, through combination with the light source attribute data and the material parameter data of the semitransparent module body, generating a body light quantity model; and step three, based on a conventional light projection algorithm, an influence exerted by voxels around a sampling point on the sampling point is added, and a rendering formula of the semitransparent module body is obtained. The invention also discloses a body rendering system of a semitransparent material, comprising structures of such three portions, i.e., a data collection unit, a body light quantity model generation unit and a rendering unit. According to the invention, little extra memory is consumed based on a conventional light projection three-dimensional rendering algorithm, real-time subsurface scattering simulation is realized, and the problem of too much consumption of time and memory in conventional simulation subsurface scattering is well solved.
Owner:深圳市瑞恩宁电子技术有限公司
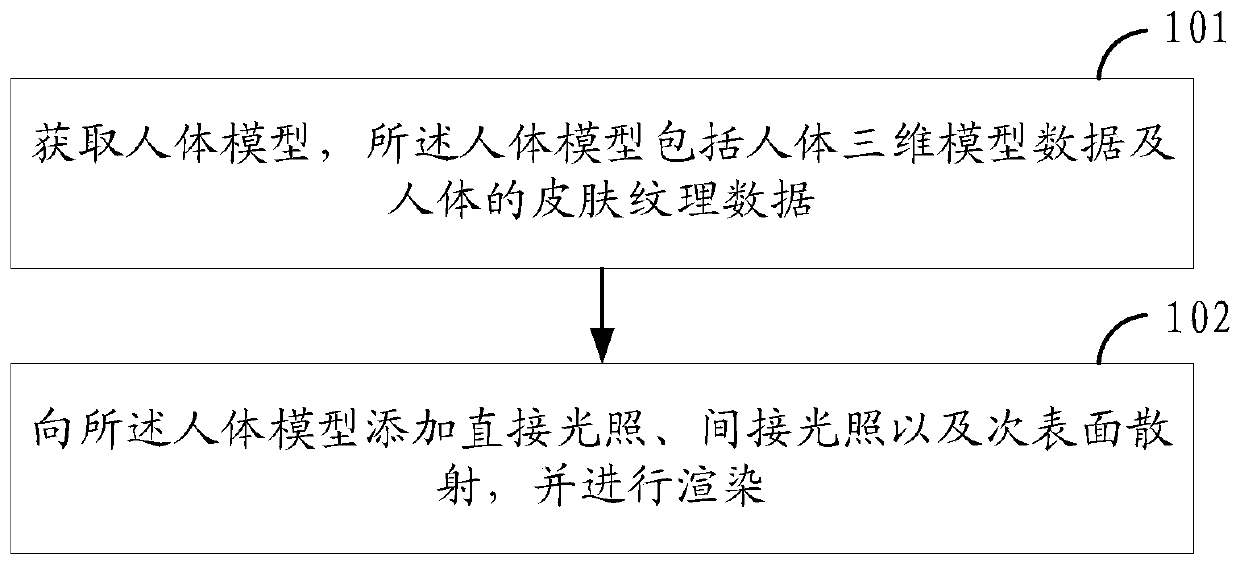
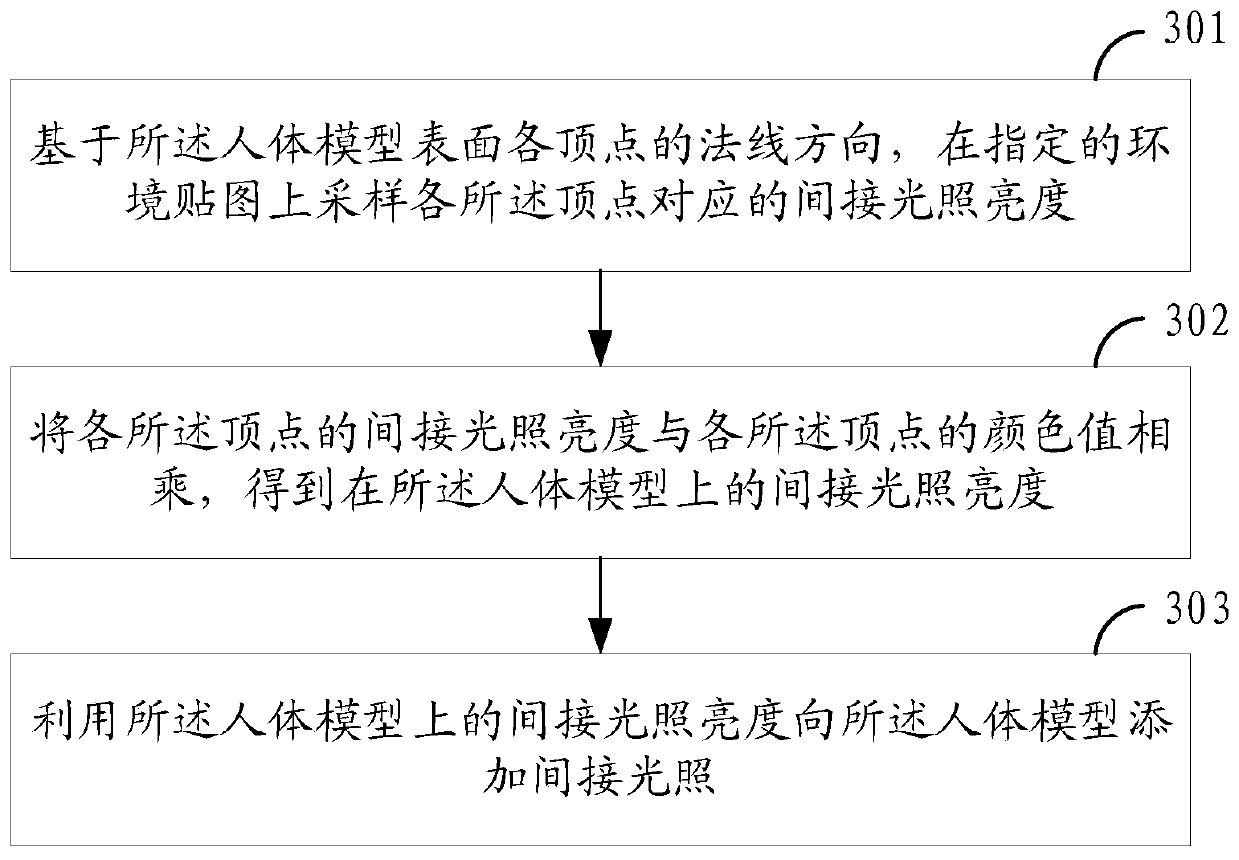
Human body model rendering method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN111145330AWith three-dimensional effectRealistic3D-image renderingHuman bodyDirect illumination
The invention provides a human body model rendering method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps that a human body model is acquired, wherein the humanbody model comprises human body three-dimensional model data and human body skin texture data; and direct illumination, indirect illumination and subsurface scattering are added to the human body model, and rendering is carried out. Direct illumination, indirect illumination and sub-surface scattering are added to a human body model, the human body model comprises human body three-dimensional model data and skin texture data, and the effects of reflecting highlight and projecting shadows can be generated on the human body model by adding the direct illumination, so that the human body model ismore stereoscopic, and details of skin textures of the human body model are displayed; the indirect illumination and the direct illumination are superposed, so that the brightness reflected by the human body model has a softer rendering effect; and part of the human body model has a transmission effect by adding subsurface scattering. Therefore, the rendered human body model can reflect skin texture details, so that the human body has a three-dimensional effect and a sense of reality.
Owner:广州方硅信息技术有限公司
Dark field confocal microscopic measurement device and method based on polarization autocorrelation
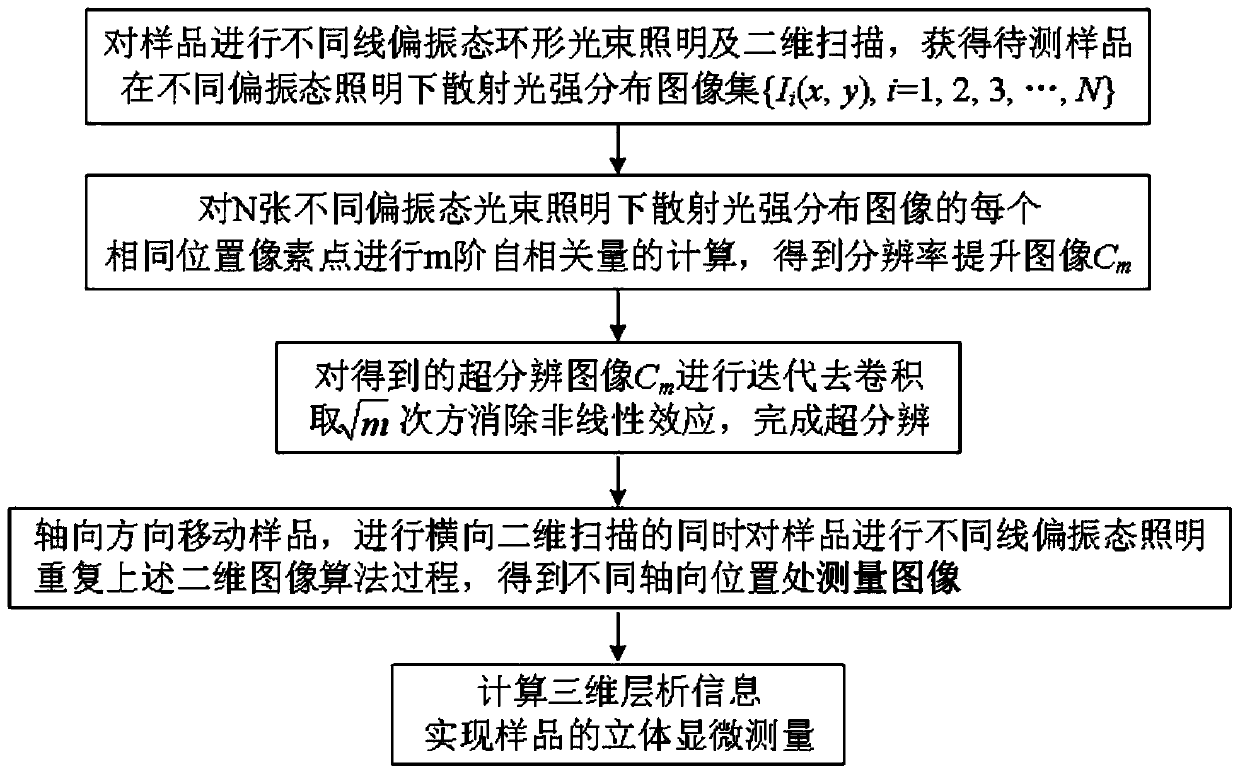
ActiveCN111257227AEnabling Nanoscale Defect MeasurementEfficient separationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesSubsurface scatteringObservation point
The invention discloses a dark field confocal microscopic measurement device and method based on polarization autocorrelation. The device comprises a polarization annular light illumination module, apolarization annular light scanning module and a confocal polarization detection module. A sample surface reflection signal and a subsurface scattering signal are effectively separated through illumination beam shaping and complementary aperture shielding detection, three-dimensional distribution information of nanoscale surface scratches, abrasion, subsurface cracks, bubbles and other defects canbe obtained at the same time, and the function of integrated detection of surface and subsurface defects is achieved. Meanwhile, polarity scattering and autocorrelation cumulant difference of adjacent observation points are generated by exciting single-wave vector illumination light fields in different directions by utilizing asymmetry of a sample structure so that super-resolution measurement isrealized. The device and the method have the advantage that nanoscale subsurface three-dimensional defect detection can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING HENGRUI PRECISION INSTR CO LTD
Method and device for rendering subsurface scattering effect
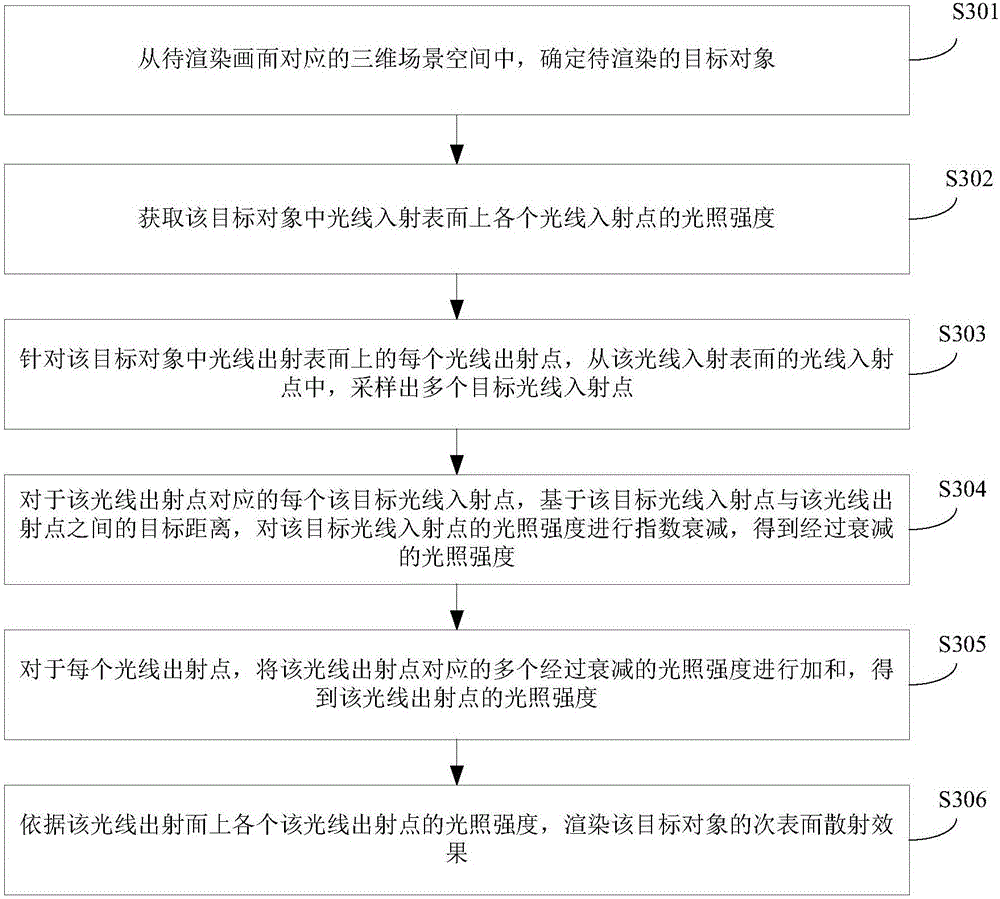
ActiveCN106846447AHigh precisionIncrease authenticity3D-image renderingUltrasound attenuationSubsurface scattering
The invention discloses a method and device for rendering the subsurface scattering effect. According to the scheme, after a target object to be rendered is determined, and aiming at each light emission point on a light emission surface in the target object, a plurality of target light incidence points are sampled from a light incidence surface; for each target light incidence point corresponding to the light emission points, based on the target distance between the target light incidence points and the target light emission points, the illumination intensities of the target light illumination intensity points is subjected to index attenuation, and attenuated illumination intensities is obtained; for each light emission point, multiple attenuated illumination intensities corresponding to the light emission points are summed up, and the illumination intensities of the light emission points are obtained; the subsurface scattering effect of the target object is rendered according to the illumination intensities of the light emission points on the light emission face. According to the scheme, the truthfulness of the rendered subsurface scattering effect of the object in a picture can be improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
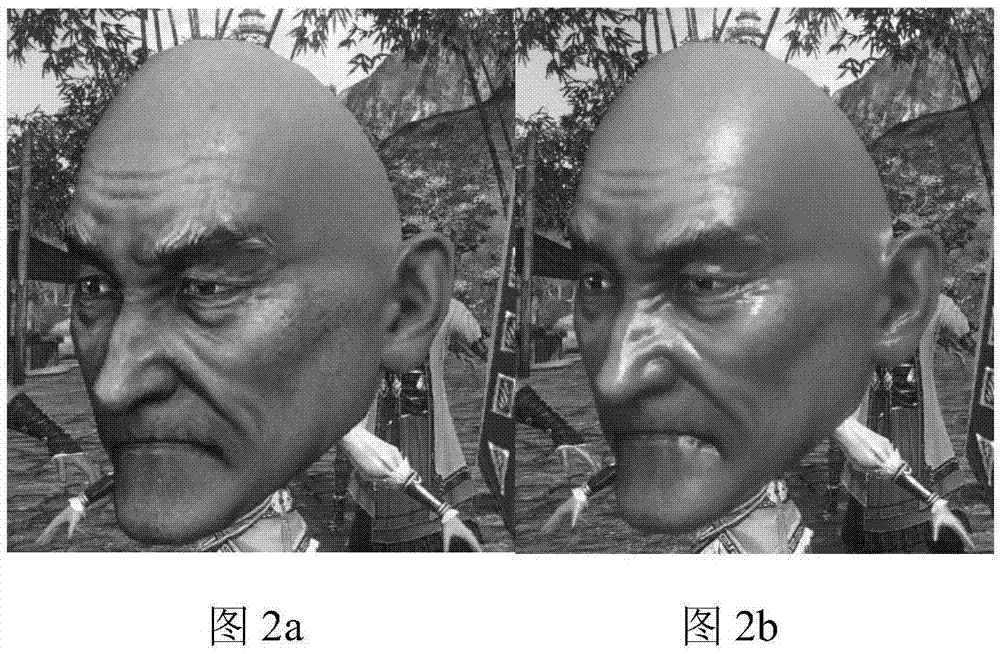
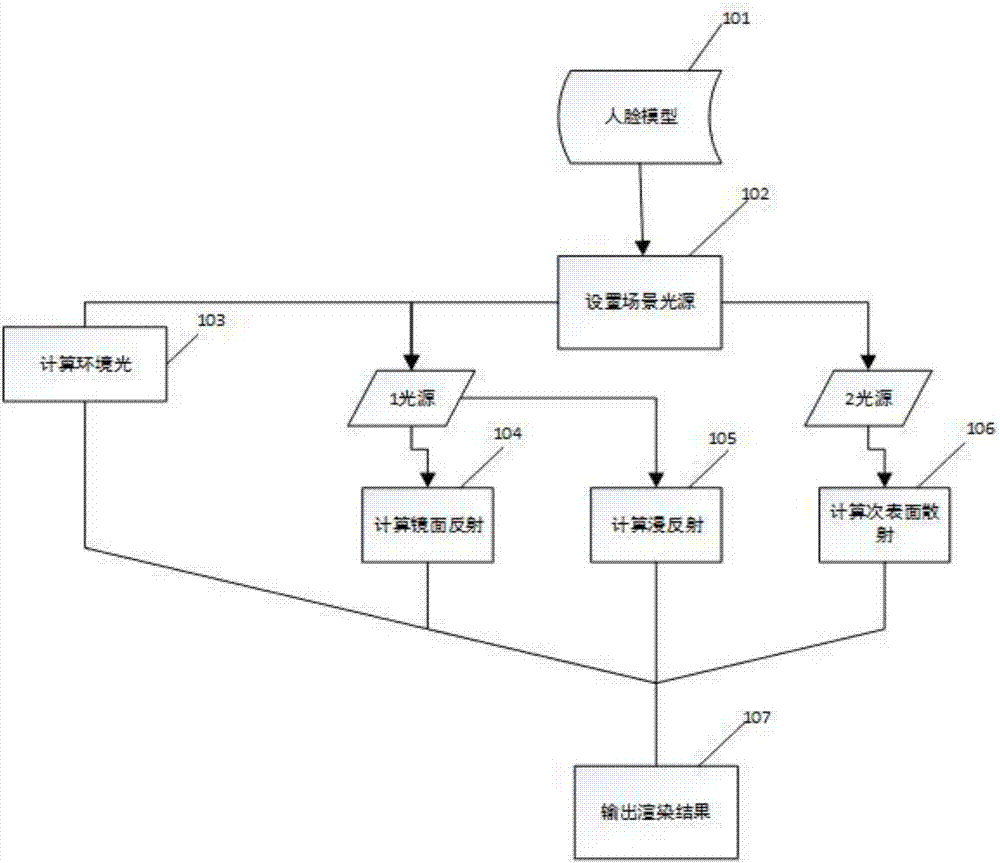
Realistic rendering method for face model of layered structure
ActiveCN107170036AExpress translucencyImprove realism3D-image renderingSubsurface scatteringComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a realistic rendering method for a face model of a layered structure. The method comprises the steps that 1, face data is prepared, wherein the face data comprises a face three-dimensional model, diffuse reflection texture of a face, normal texture of the face and skin detail texture; and 2, the sum of ambient light intensity I<am>, specular reflection light intensity I<sp> of a sebum layer, diffuse reflection light intensity I<diff> of an epidermal layer and subsurface scattering light intensity of a corium layer (I<R2>, I<G2> and I<B2>) is output to the face model to obtain a final rendering effect I. Through the method, the semitransparent characteristic of the face model can be better displayed, and the sense of reality of the rendering effect is improved while real-time rendering is guaranteed.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
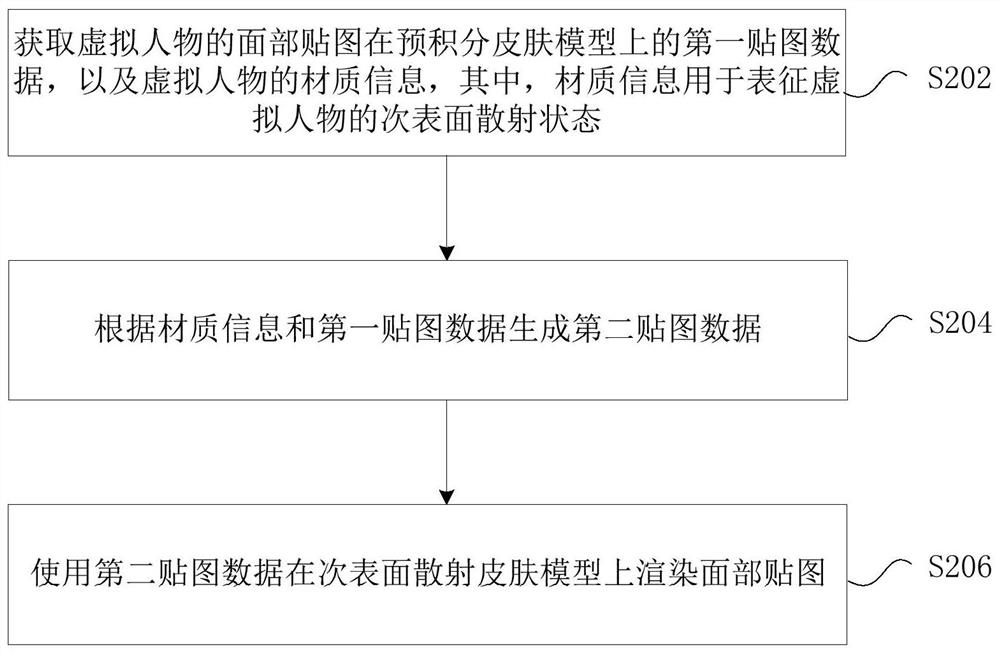
Character skin rendering method and device, storage medium and electronic device
PendingCN111862285AEnhance layeringSolving rigid technical problems3D-image renderingSubsurface scatteringComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a character skin rendering method and device, a storage medium and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps that first mapping data of a face map of a virtual character on a pre-integration skin model and material information of the virtual character are acquired, and the material information is used for representing the sub-surface scattering state of the virtual character; second mapping data is generated according to the material information and the first mapping data; the facial map is rendered on a sub-surface scattering skin model using the second map data. The technical problem that the face of the virtual character is stiff and stiff in the prior art is solved, so that the face of the virtual character is more vivid, natural, flexible and real.
Owner:BEIJING PERFECT WORLD SOFTWARE TECH DEV CO LTD
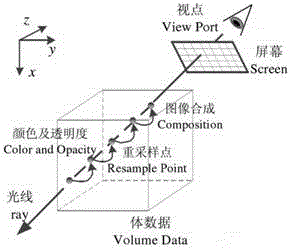
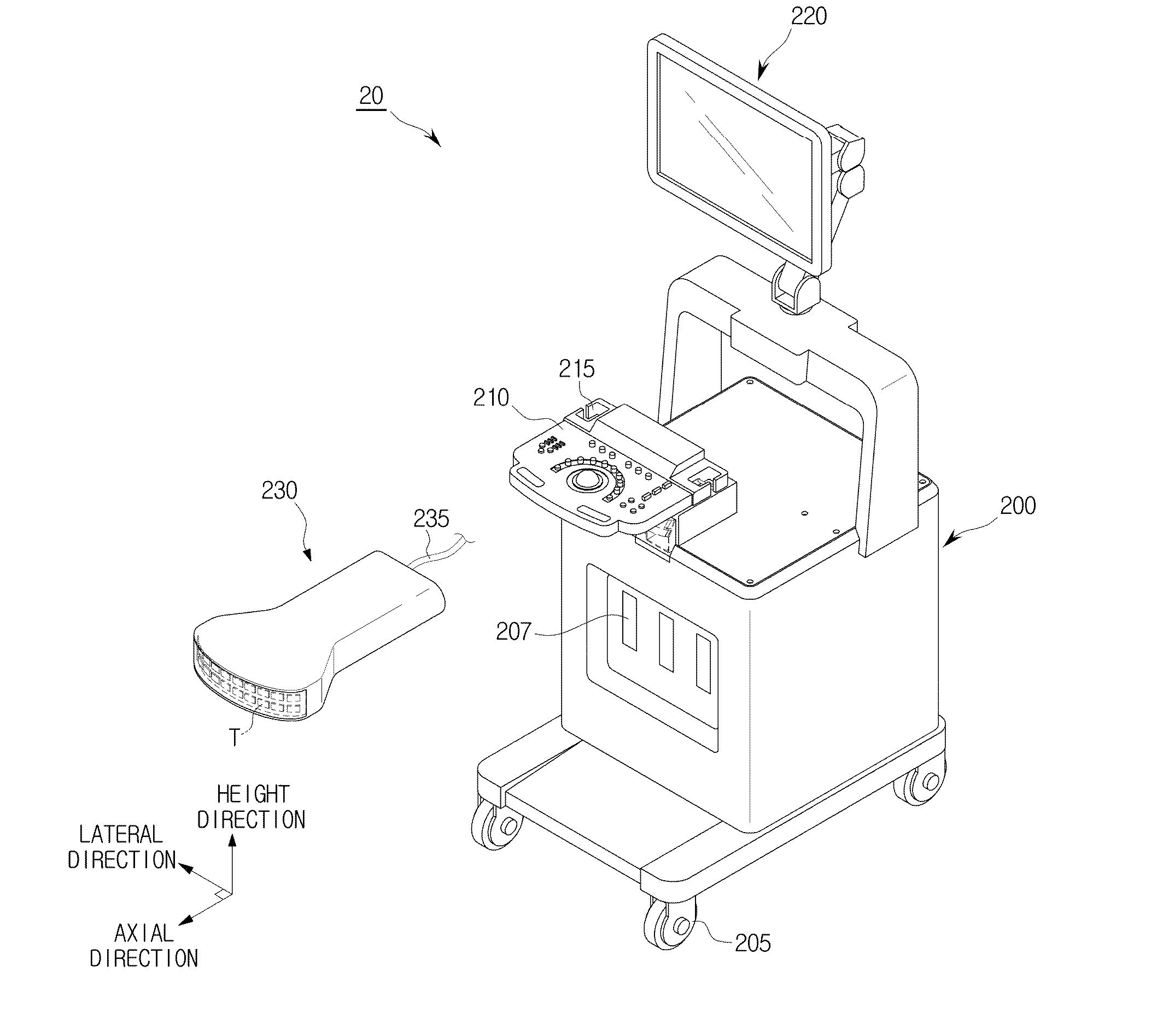
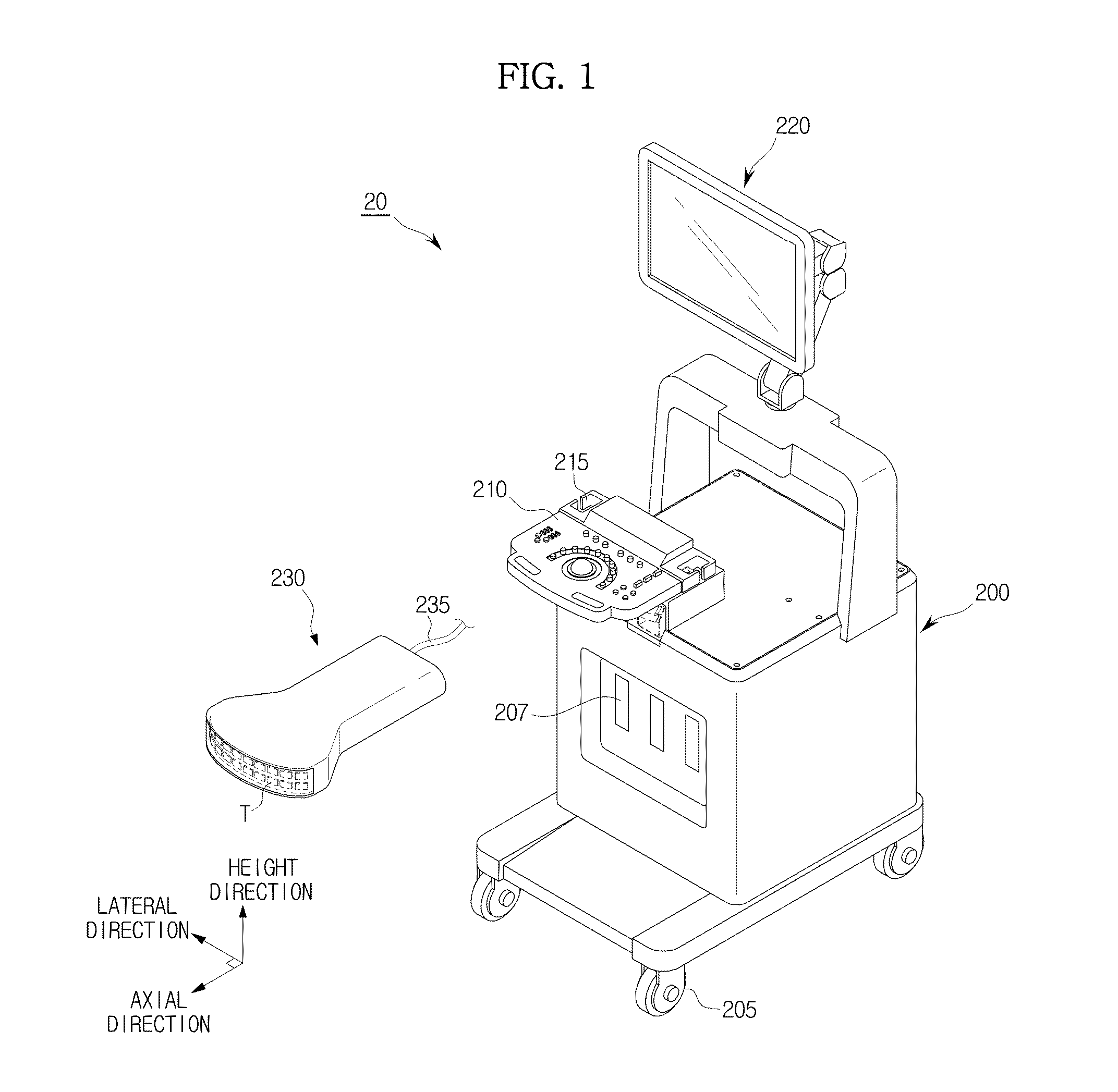
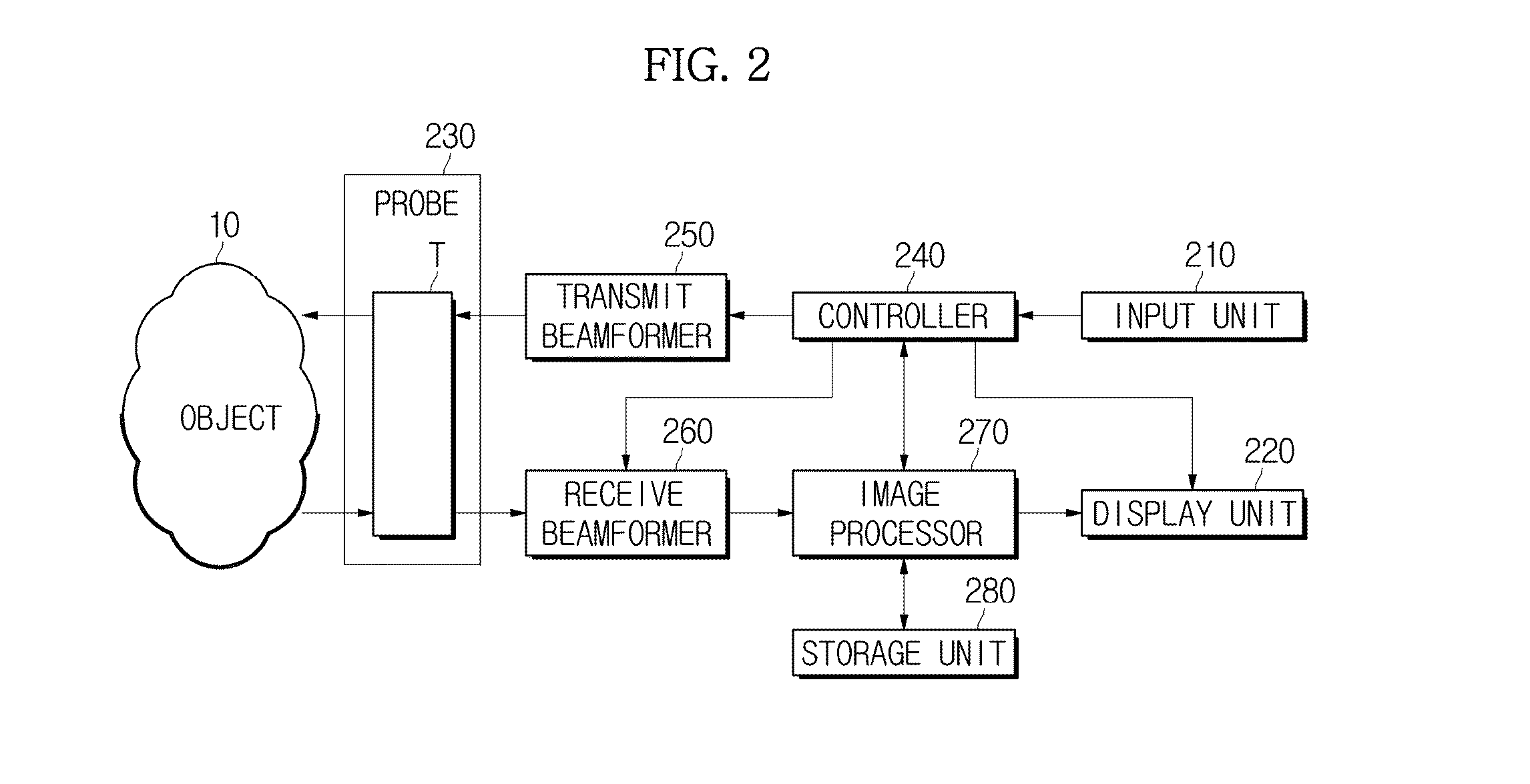
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
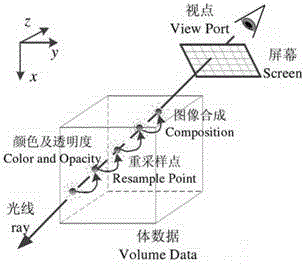
Disclosed herein are an image processing apparatus and an image processing method for realistically expressing an object. The image processing apparatus includes a volume data generator configured to generate volume data using received signals of an object, and a volume rendering unit configured to perform volume rendering using the volume data to acquire a projection image, and apply a subsurface scattering effect according to virtual lighting information, to the projection image with respect to a user's viewpoint to produce a final image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Snow covered path of travel surface condition detection
A method for determining a snow covered surface condition of a path of travel. A beam of light is emitted at a surface of the path of travel by a light emitting source. An image of a path of travel surface is captured by an image capture device. The image capture device is mounted on the vehicle and captures an image in a downward direction. The captured image captures the beam of light emitted on the path of travel surface. Analyzing a subsurface scattering of the light generated on the path of travel surface by a processor. A determination is made whether snow is present on the path of travel. A snow covered path of travel surface signal is generated in response to the identification of snow on the path of travel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Dark field confocal microscopic measurement device and method based on polarization autocorrelation
ActiveCN111257226AEnabling Nanoscale Defect MeasurementEfficient separationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansSubsurface scatteringObservation point
The invention discloses a dark field confocal microscopic measurement device and method based on polarization autocorrelation. The device comprises a polarization annular light illumination module, apolarization annular light scanning module and a confocal polarization detection module. A sample surface reflection signal and a subsurface scattering signal are effectively separated through illumination beam shaping and complementary aperture shielding detection, three-dimensional distribution information of nanoscale surface scratches, abrasion, subsurface cracks, bubbles and other defects canbe obtained at the same time, and the function of integrated detection of surface and subsurface defects is achieved. Meanwhile, polarity scattering and autocorrelation cumulant difference of adjacent observation points are generated by exciting single-wave vector illumination light fields in different directions by utilizing asymmetry of a sample structure so that super-resolution measurement isrealized. The device and the method have the advantage that nanoscale subsurface three-dimensional defect detection can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING HENGRUI PRECISION INSTR CO LTD
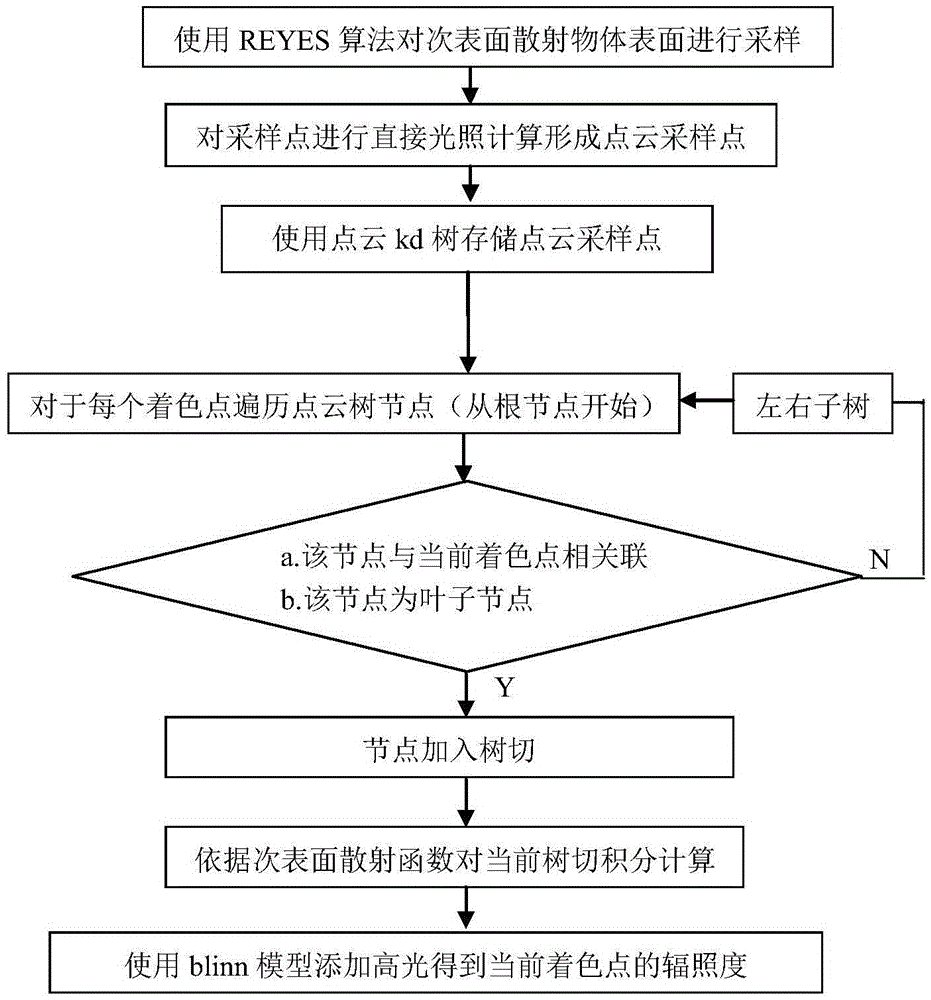
Point cloud based method for calculating emergent irradiance of sub-surface scattering object
InactiveCN105488843AFast renderingImprove efficiencyDetails involving 3D image data3D-image renderingIlluminanceSubsurface scattering
The invention discloses a point cloud based method for calculating emergent irradiance of a sub-surface scattering object. The method comprises the steps of (1): sampling the surface of the sub-surface scattering object, then performing direct illumination calculation on a sampling point on the surface of the sub-surface scattering object to form a point cloud sampling point, and organizing the point cloud sampling point into a point cloud tree for storage; and (2): performing a light ray tracing and rendering process for rendering, wherein a cross point of each light ray and a scene containing a plurality of three-dimensional objects is a coloring point; when the coloring point falls on the sub-surface scattering object, traversing the point cloud tree to obtain a tree cut associated with the emergent irradiance of the current coloring point, performing integration on the incident irradiance of the current coloring point by each node on the tree cut, and performing calculation according to a sub-surface scattering function to obtain the emergent irradiance of the current coloring point in any direction.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Subsurface rendering methods and apparatus
InactiveUS7859530B2Quickly solve transportEfficient indexing3D-image rendering3D modellingVoxelSubsurface scattering
A method for a computer system includes receiving a three-dimensional model of an object, wherein the object includes a surface region, determining an incident irradiance associated with the surface region, determining a plurality of voxels associated with the three-dimensional model of the object, wherein a first plurality of voxels is associated with the surface region, and wherein a second plurality of voxels is associated with a sub-surface region of the object, associating the incident irradiance with the second plurality of voxels, and determining a subsurface scattering contribution associated with the surface region of the object in response to the incident irradiance associated with the second plurality of voxels.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Screen-space-based method for simulating real skin of figure through sub-surface scattering
InactiveCN104240276ATrue AccuracyReal picture effectFilling planer surface with attributes3D-image renderingSubsurface scatteringFiltration
The invention discloses a screen-space-based method for simulating the real skin of a figure through sub-surface scattering. The method mainly includes the steps of conducting filtration and screening on a finger skin object to be rendered and other objects in a scene; rendering the skin of the figure first time to obtain Alpha mixing to obtain a mixed image; rendering the scene second time to obtain a semi-transparent effect image for a thinner part of the skin; stacking the semi-transparent image with the mixed image to obtain a final rendering effect image. By means of the screen-space-based method for simulating the real skin of the figure through sub-surface scattering, the shortcomings that in the prior art, the rendering difficulty is large, the drawing accuracy is poor and the image effect is untruthful can be overcome; the screen-space-based method has the advantages of being small in rendering difficulty, good in drawing accuracy and real in image effect.
Owner:WUXI FANTIAN INFORMATION TECH
Surface and subsurface integrated confocal microscopic measurement device and method
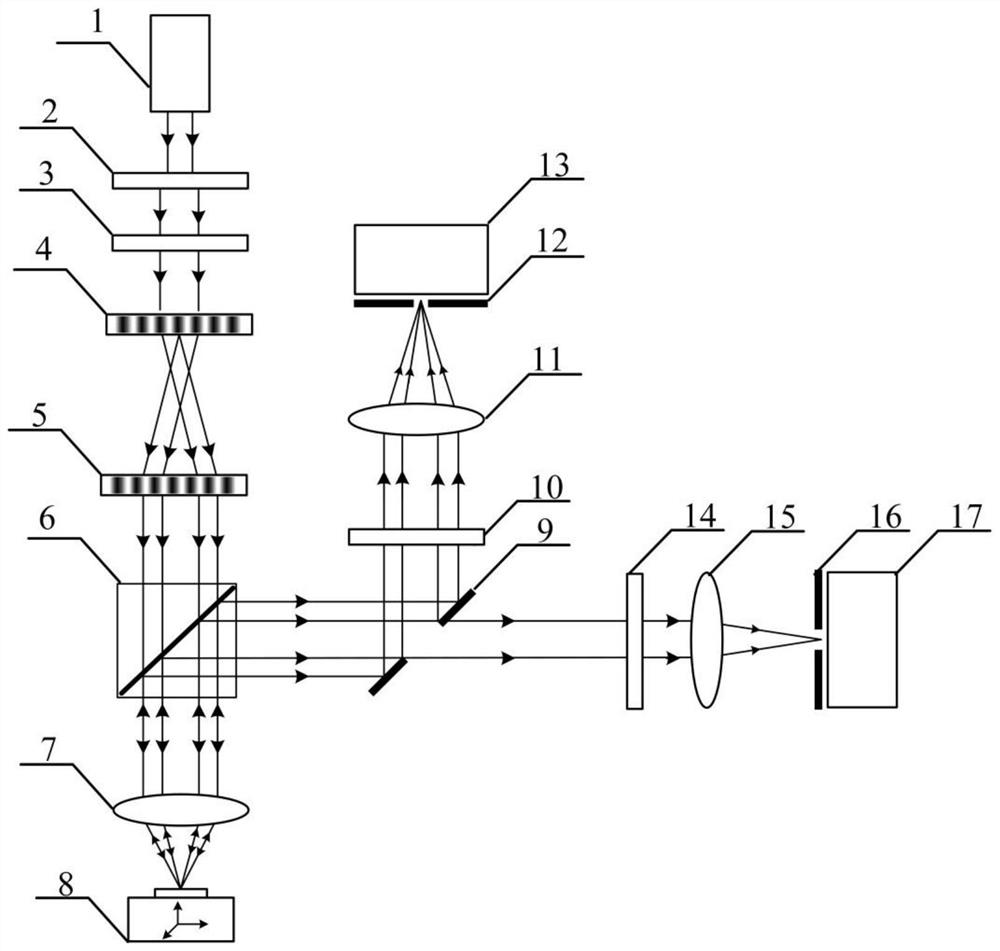
PendingCN113959357AEfficient separationWith integrated detection functionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansSubsurface scatteringBeam splitting
The invention discloses a surface and subsurface integrated confocal microscopic measurement device and method. The device comprises an annular light illumination scanning module, a dark field confocal detection module and a reflection confocal detection module, wherein the annular light illumination scanning module comprises a laser, a beam expanding lens, a first polaroid, a first diffraction type flat plate conical lens, a second diffraction type flat plate conical lens, a beam splitting prism, an objective lens and a three-dimensional displacement table; the reflection confocal detection module comprises a reflector with a light through hole, a polarizing film I, a focusing lens I, a pinhole I and a camera I; and the dark field confocal detection module comprises a polarizing film II, a focusing lens II, a pinhole II and a camera II. Through illumination beam shaping and complementary aperture shielding detection, a sample surface reflection signal and a subsurface scattering signal are effectively separated, three-dimensional distribution information of defects such as nanoscale surface scratches, abrasion, subsurface cracks and bubbles can be obtained at the same time, and the surface and subsurface defect integrated detection function is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com