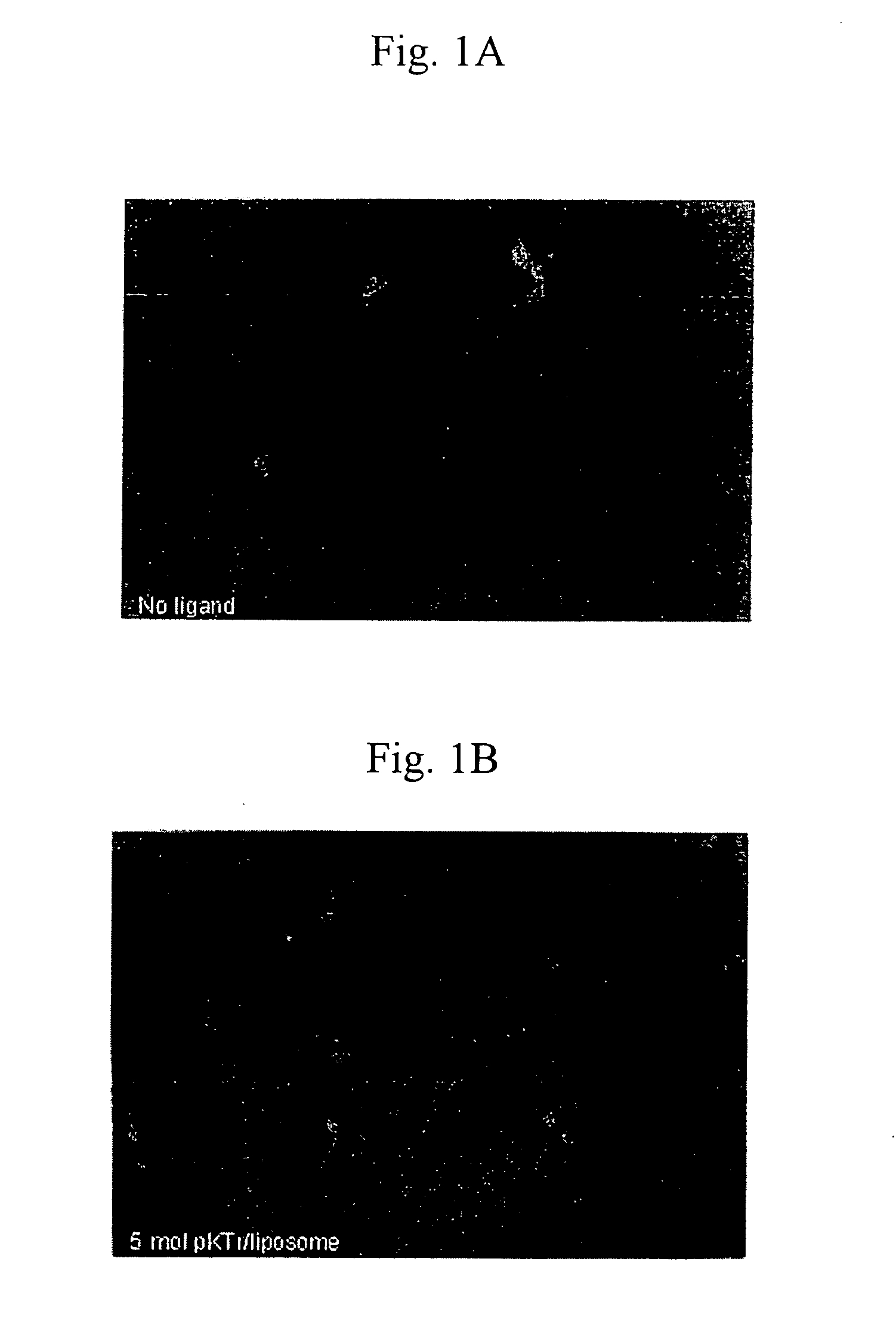
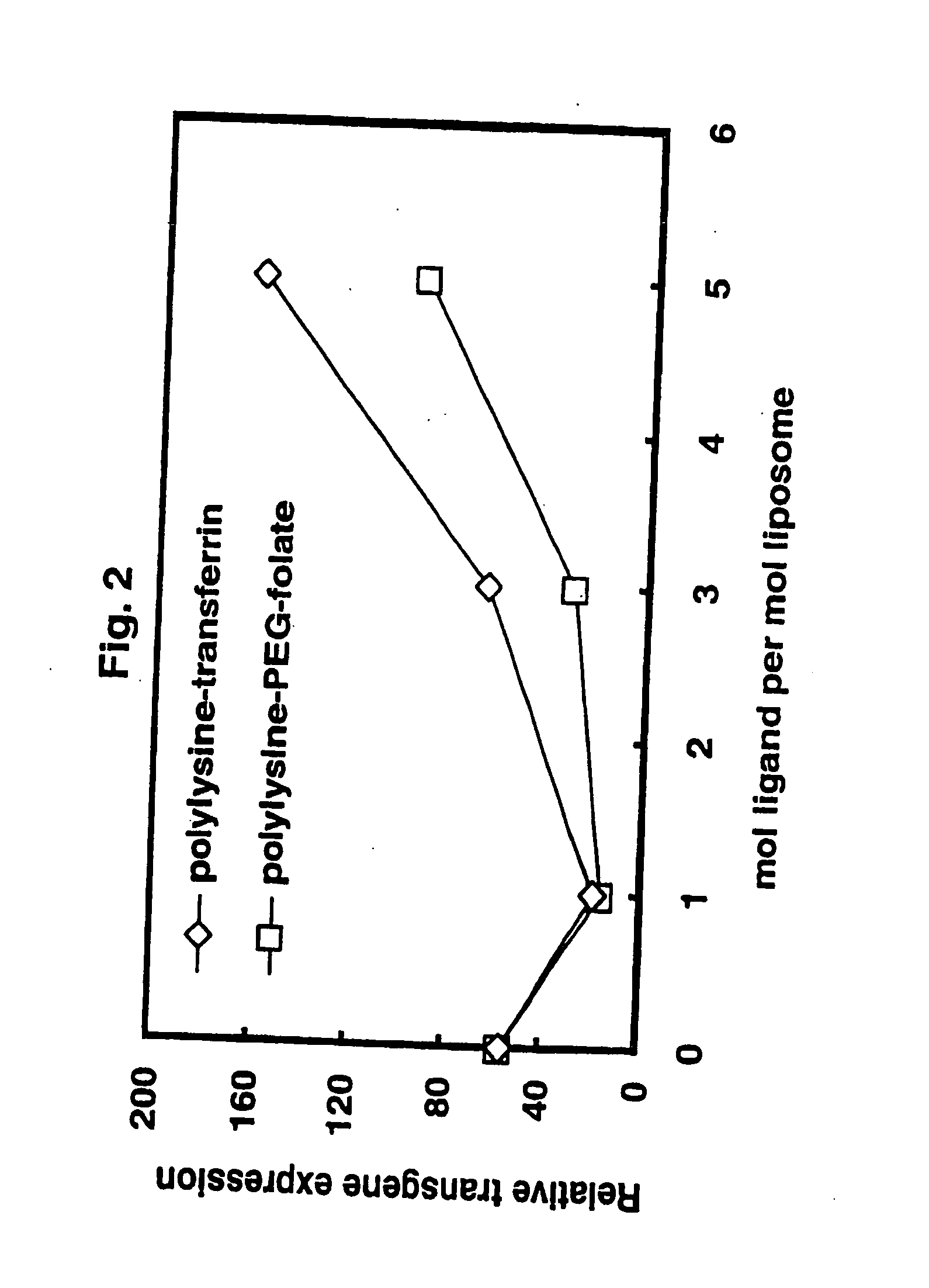
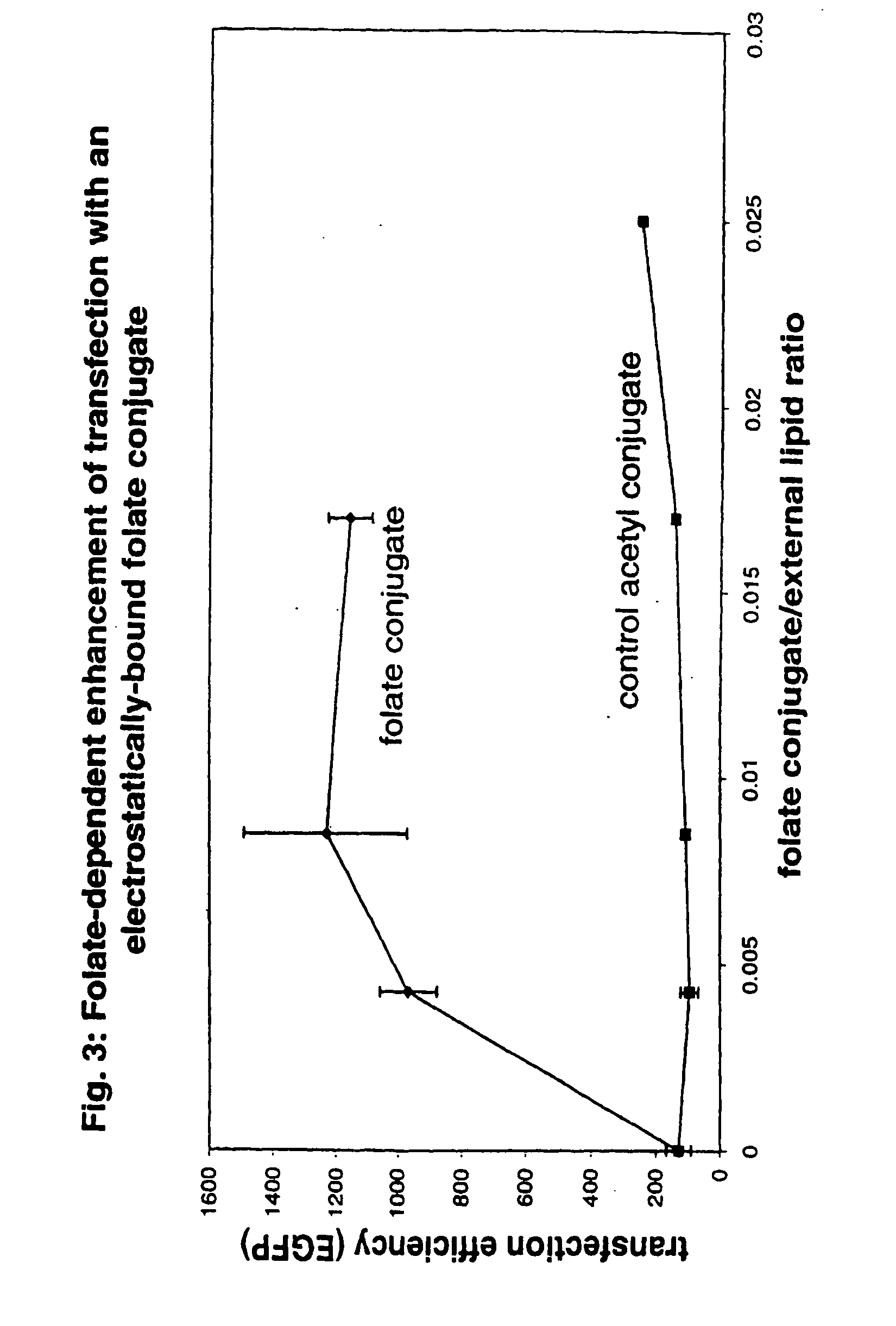
Modular targeted liposomal delivery system
a liposome and module technology, applied in the field of targeted liposomes, can solve the problems of reducing the amount of bioactive agents available to the target site, reducing the ability of the liposome, and difficult to deliver intact bioactive agents to the target site. the effect of liposome ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Formulations
Preparation of Liposomes for Delivery of Nucleic Acids:
[0052] Preferably, for the delivery of nucleic acids to cells, liposomes are prepared according to the method described in U.S. Provisional Application Ser. No. 60 / 122,365 entitled “Encapsulation of Bioactive Complexes in Liposomes”, filed on Mar. 2.1999. One embodiment is described below.
[0053] Plasmid Purification: Two plasmids were used in this study: the pZeoSVLacZ plasmid which is 6.5 kb, and expresses the IacZ gene for β-galactosidase in mammalian cells from the SV40 early enhancer-promoter, allowing selection in mammalian cells and E. coli using the antibiotic zeocin; and, the pEGFP-Cl plasmid, which is 4.7 kb and expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) from a human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter, allowing selection in E. coil using kanamycin, and in mammalian cells using G418. Plasmids were purified from E. Coli (Baumann and Bloomfield, 1995; or by Qiagen kit per manufacturer's inst...
example 2
Synthesis of Targetingistabilizing Moiety—Linker Conjugates
[0059] Targeting / stabilizing modules were synthesized to use with liposomes prepared as in example 1. Targeting / stabilizing moieties may be covalently coupled to a linker for electrostatic interaction, such as polylysine (pK), by any method known in the art. Examples of processes for coupling polylysine to targeting agents such as folic acid, transferrin and antibodies are provided herein for exemplary purposes only. Methods for coupling a linking agent such as polylysine to a stablizing agent such as PEG or to a stabilizing agent and a targeting moiety are also provided herein.
a. Preparation of Folic acid, PEG and Polylysine Without Glutaric Acid (FA-NH-PEG-CO-PL or FPK)
Preparation of FAA
[0060] Folic acid (50 mg, 0.11 mmole) was dissolved in 6 ml of DMF:PY (5:1; v / v). To this solution dicylohexylcarbodiimide (DCC, 140 mg, 0.68 mmoles) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2-3 h. Dicyc...
example 3
Assay Methods and Materials:
a. Cell Cultures for Measurements of Liposome Binding and Transfection
[0091] OVCAR-3 cells were plated at 2×105 cells per ml in 96-well plates in 0.1 ml per well of RPMI 1640 with 10% heat inactivated fetal bovine serum. Cells were allowed to grow for two days (approximately 4048 hours) before transfections were performed; at this point the cells were at confluency. In the case of pHdependent liposomes described below, the cells were allowed to grow for only one day before transfection.
b. Measure of Cell Number (CBAM, Calcein Blue Acetoxy Methyl Ester)
[0092] Cell number in terms of total intracellular esterase activity was determined by washing the cells with phosphate buffered saline (PBS), staining with calcein blue acetoxy methyl ester (CBAM-5 μM in PBS for approximately 3045 minutes at room temperature), and then rinsing the plates with PBS). 100 μ / well of detergent solution (1% Cl2E8, TE, pH 8) was added to each well. Cell number was determine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com