Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
346 results about "Skin penetration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Skin penetration can be defined as a procedure where the skin is cut, torn, punctured, shaved or penetrated in any way.
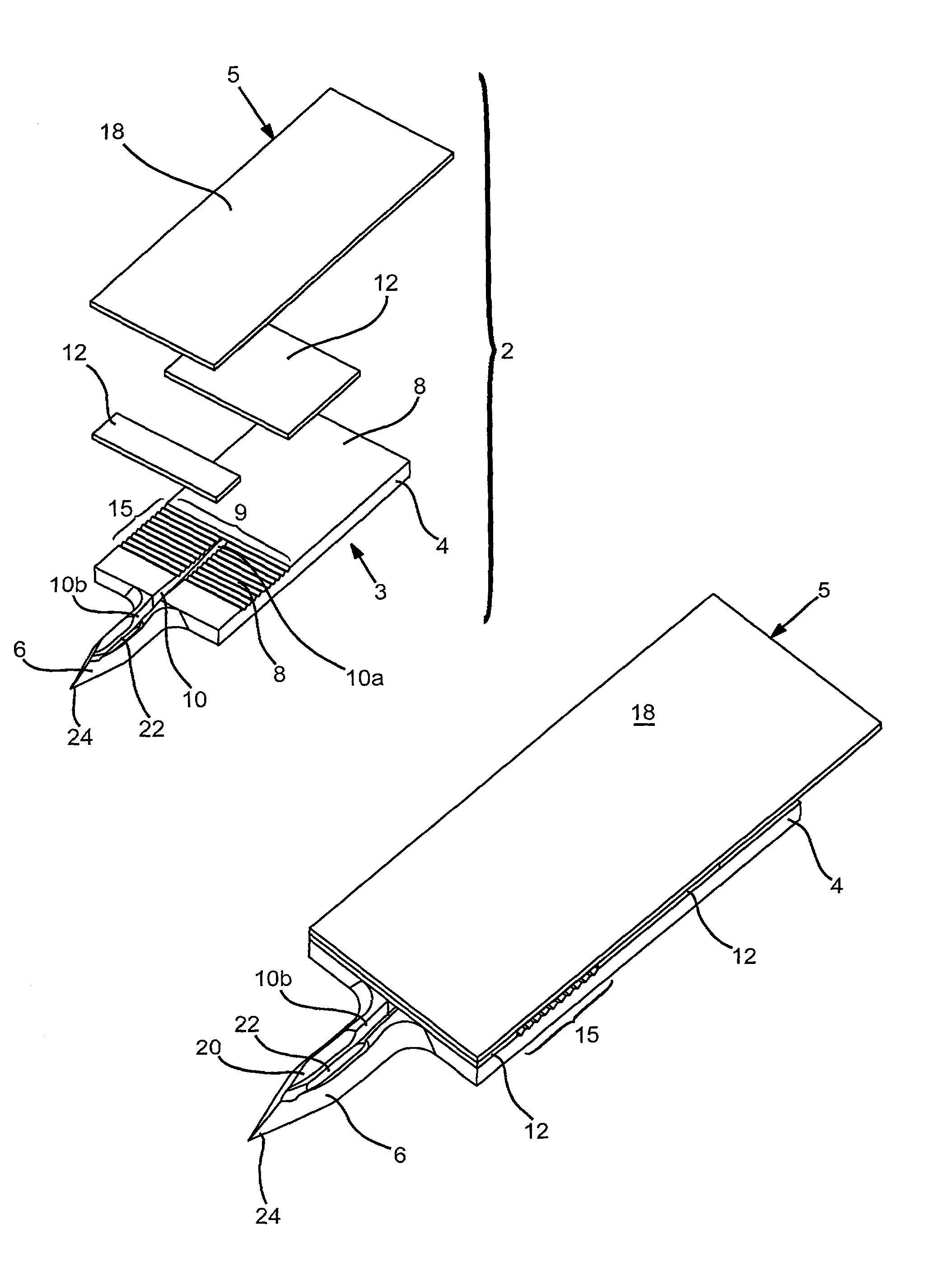
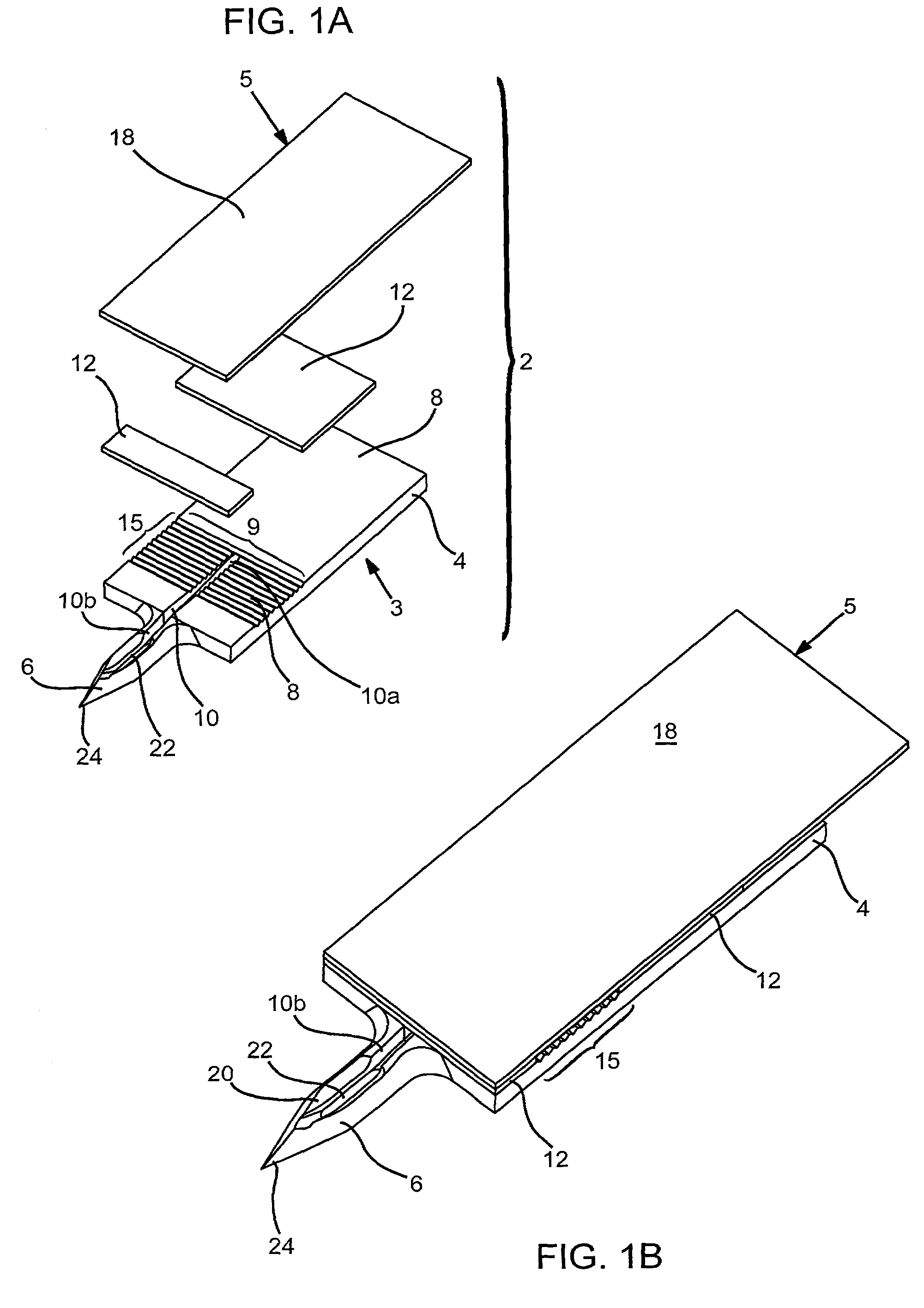
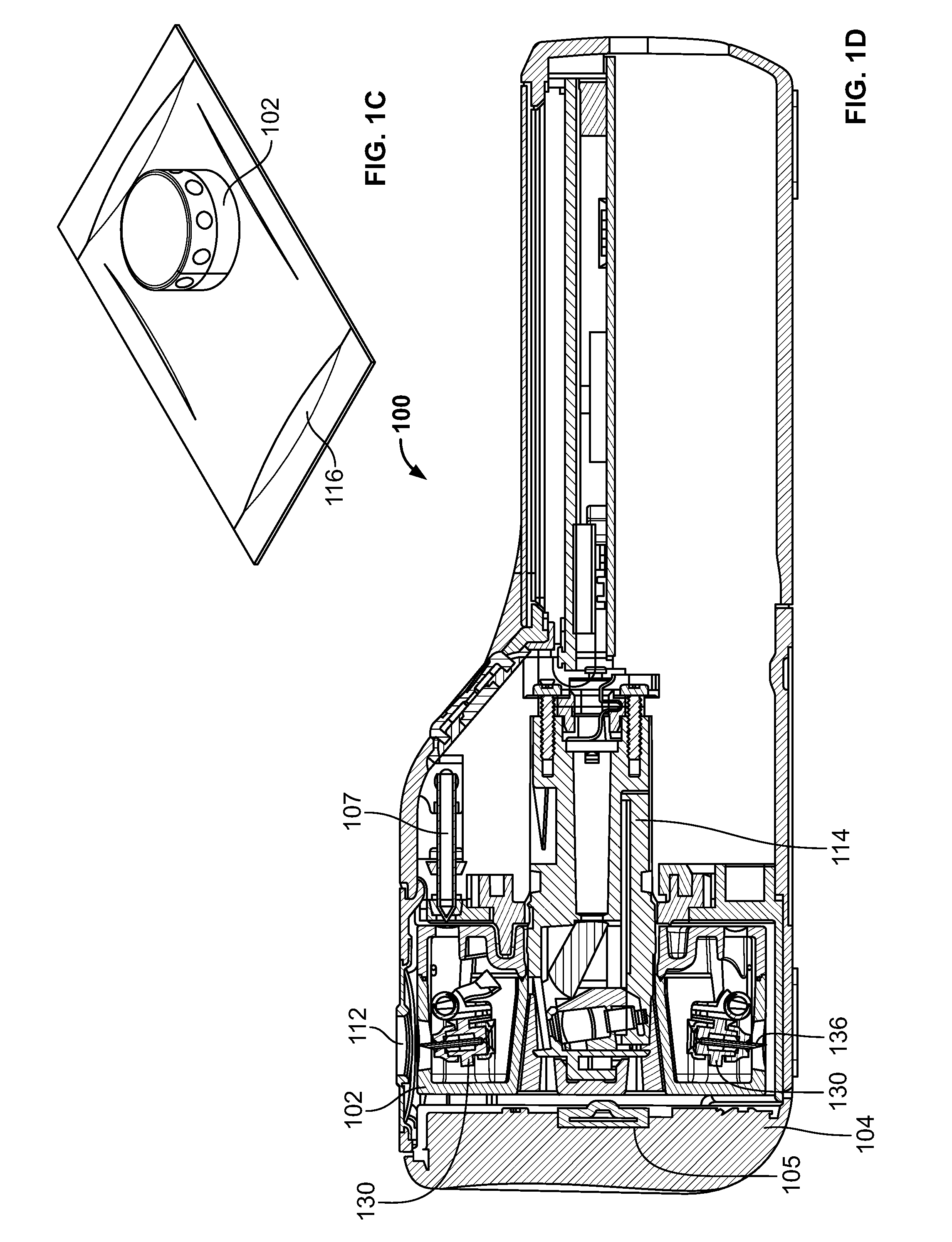
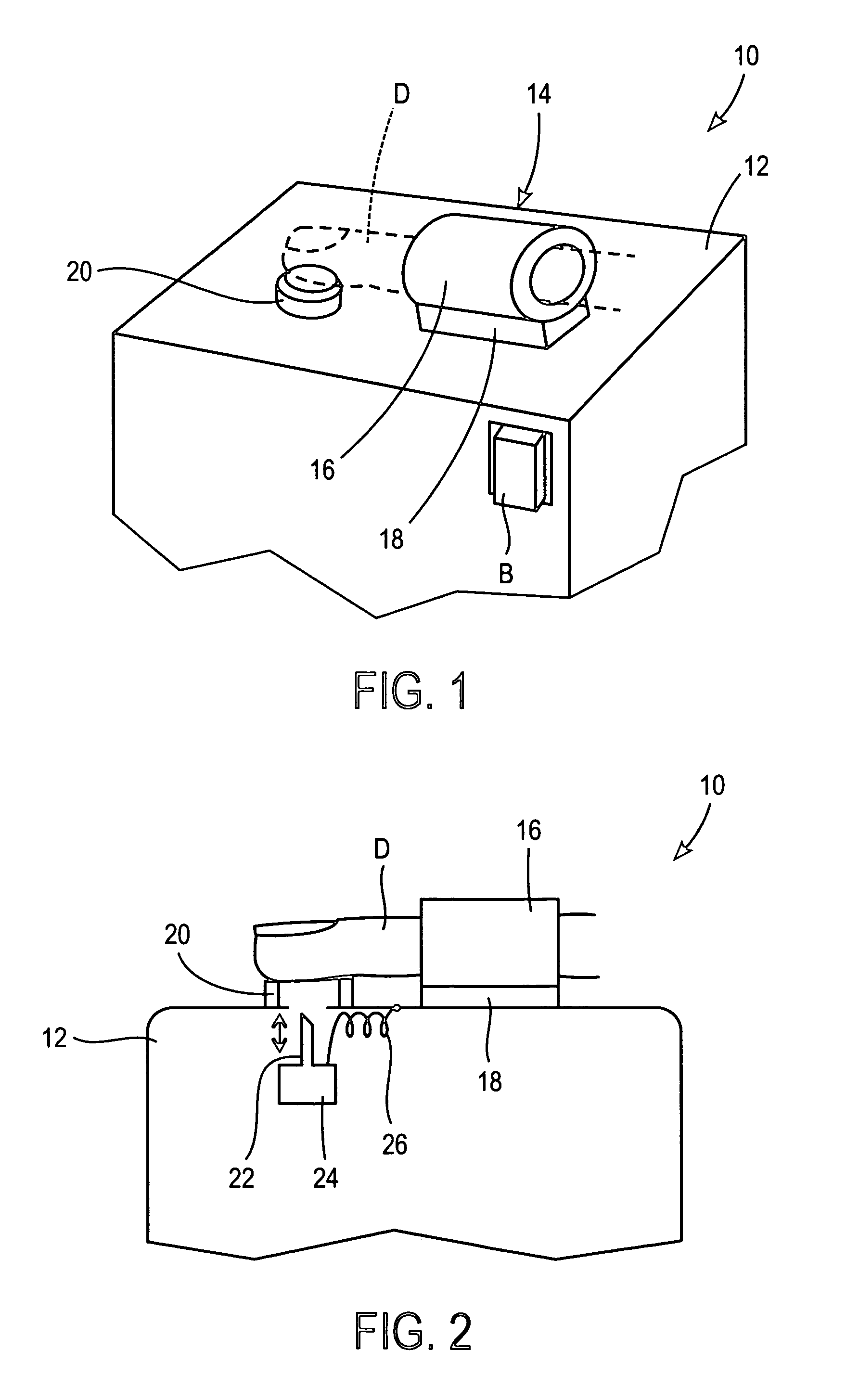
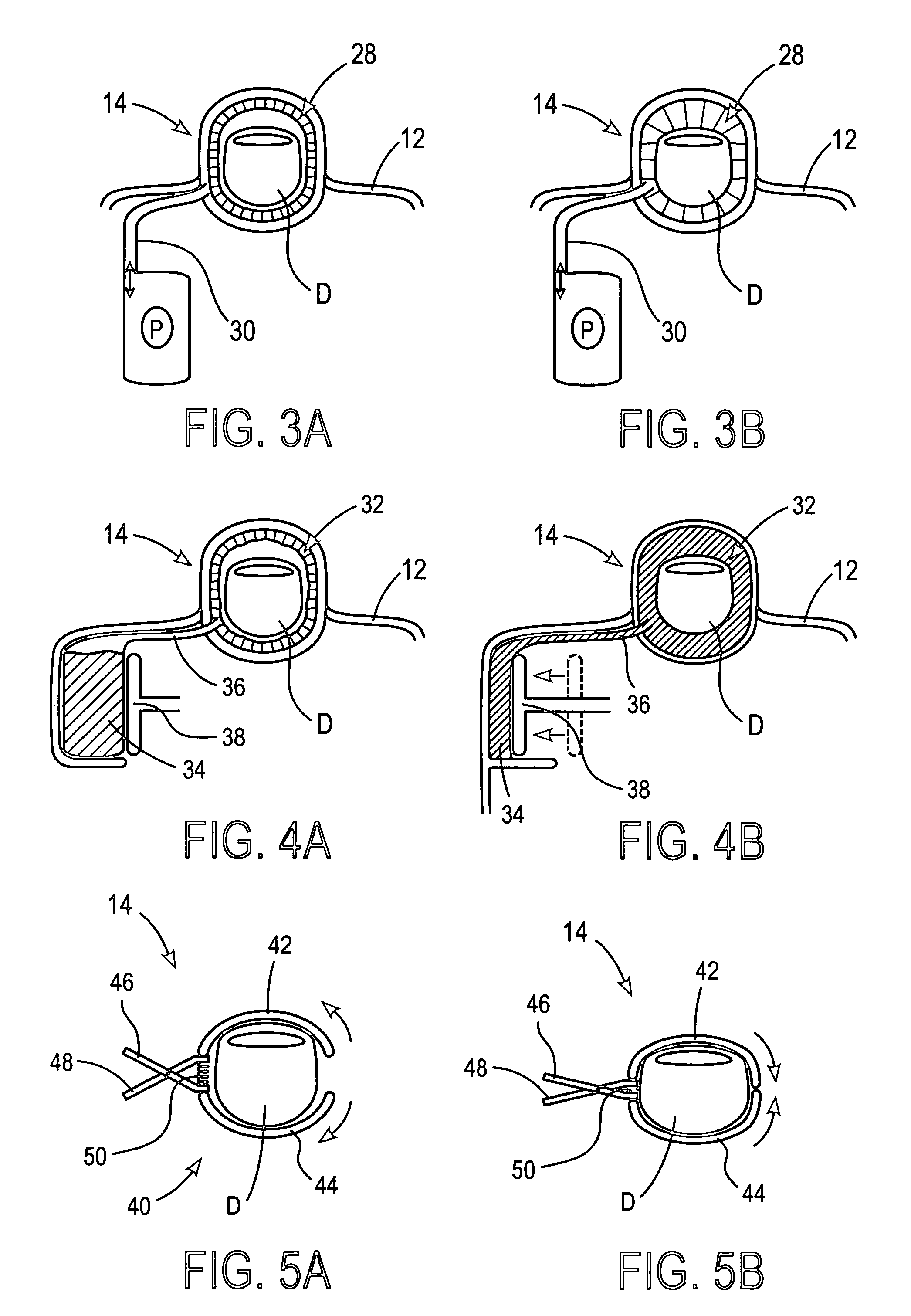
Devices and methods for accessing and analyzing physiological fluid
InactiveUS7343188B2Convenient angleReduce painSensorsBiological testingLiquid glucosePhysiological fluid
Systems, devices and methods for determining the concentration of physiological fluid analytes are provided. The subject systems have a plurality of biosensor devices present on a disposable cartridge. Each biosensor device includes a biosensor and a skin penetration means. In practicing the subject methods, a movement means of the device is used to move each biosensor device in a first direction that provides for penetration of the skin-piercing means into a skin layer followed by movement of the biosensor in a second direction that provides for removal of the skin-piercing means from the skin layer, where this movement profile provides for physiological fluid access and analyte concentration determination by the analyte sensor means. The subject systems, devices and methods for using the same find use in determining the concentration of a variety of different physiological fluid analytes, and are particularly suited for use in detection of physiological fluid glucose concentration.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
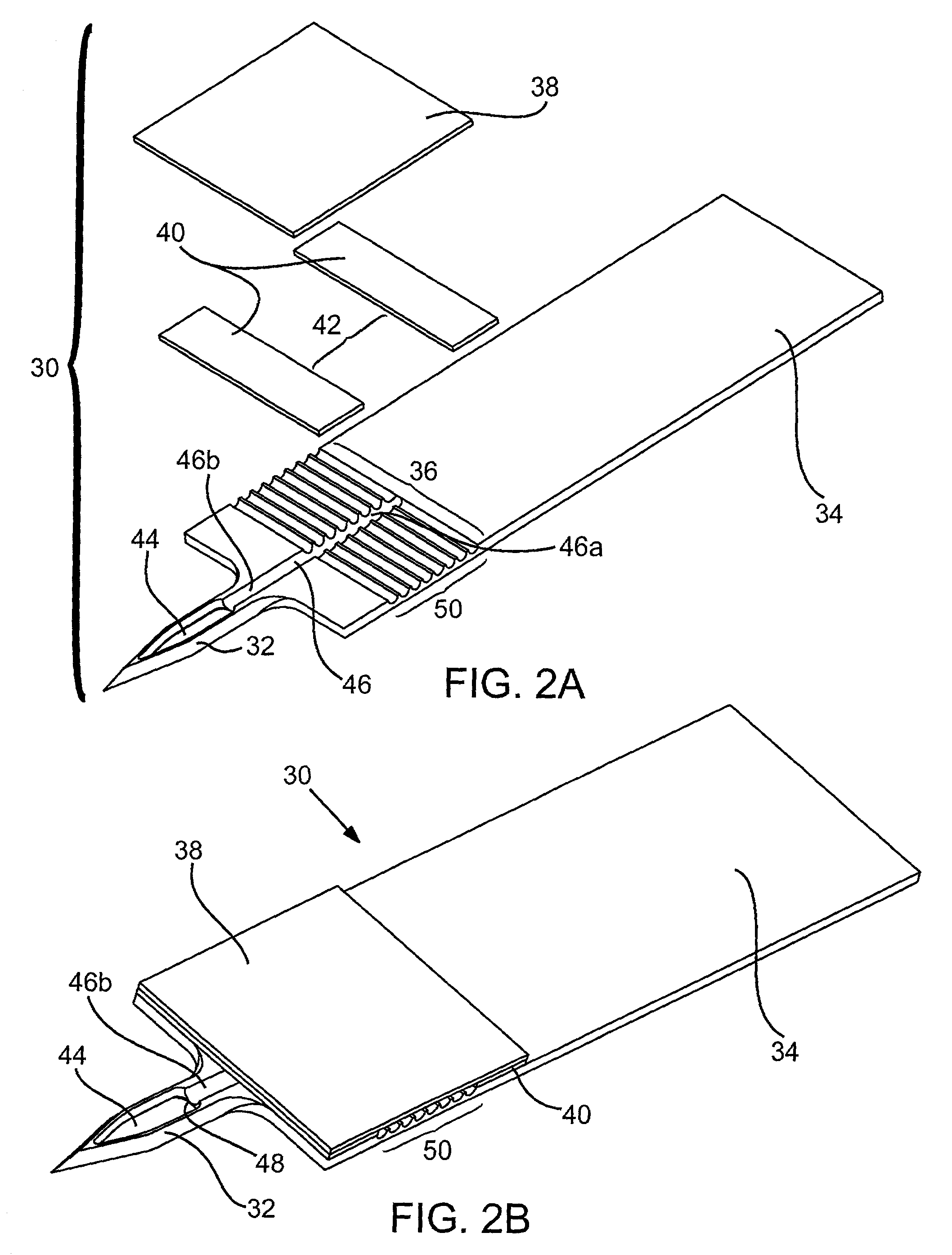
Multi-site body fluid sampling and analysis cartridge
ActiveUS20070179405A1Reduce environmental pollutionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMulti siteAnalyte
An arrangement includes a housing, a plurality of sampling and analysis sites contained within the housing, each of the sampling and analysis sites having a skin-penetration member having a first end configured to pierce the skin, and an inner lumen in communication with the first end, an actuator operatively associated with the skin-penetration member, and an analyte quantification member in fluid communication with the inner lumen of the skin-penetration member. Integrated devices including such arrangements are also described.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Penetrating pharmaceutical foam
ActiveUS20050074414A1Broaden applicationEvenly distributedAntibacterial agentsBiocideAlcohol freeActive agent
The invention relates to an alcohol-free cosmetic or pharmaceutical foam composition comprising water, a hydrophobic solvent, a surface-active agent, a gelling agent, an active component selected from the group of urea, hydroxy acid and a therapeutic enhancer and a propellant. The foam further comprises active agents and excipients with therapeutic properties having enhanced skin penetration.
Owner:VYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
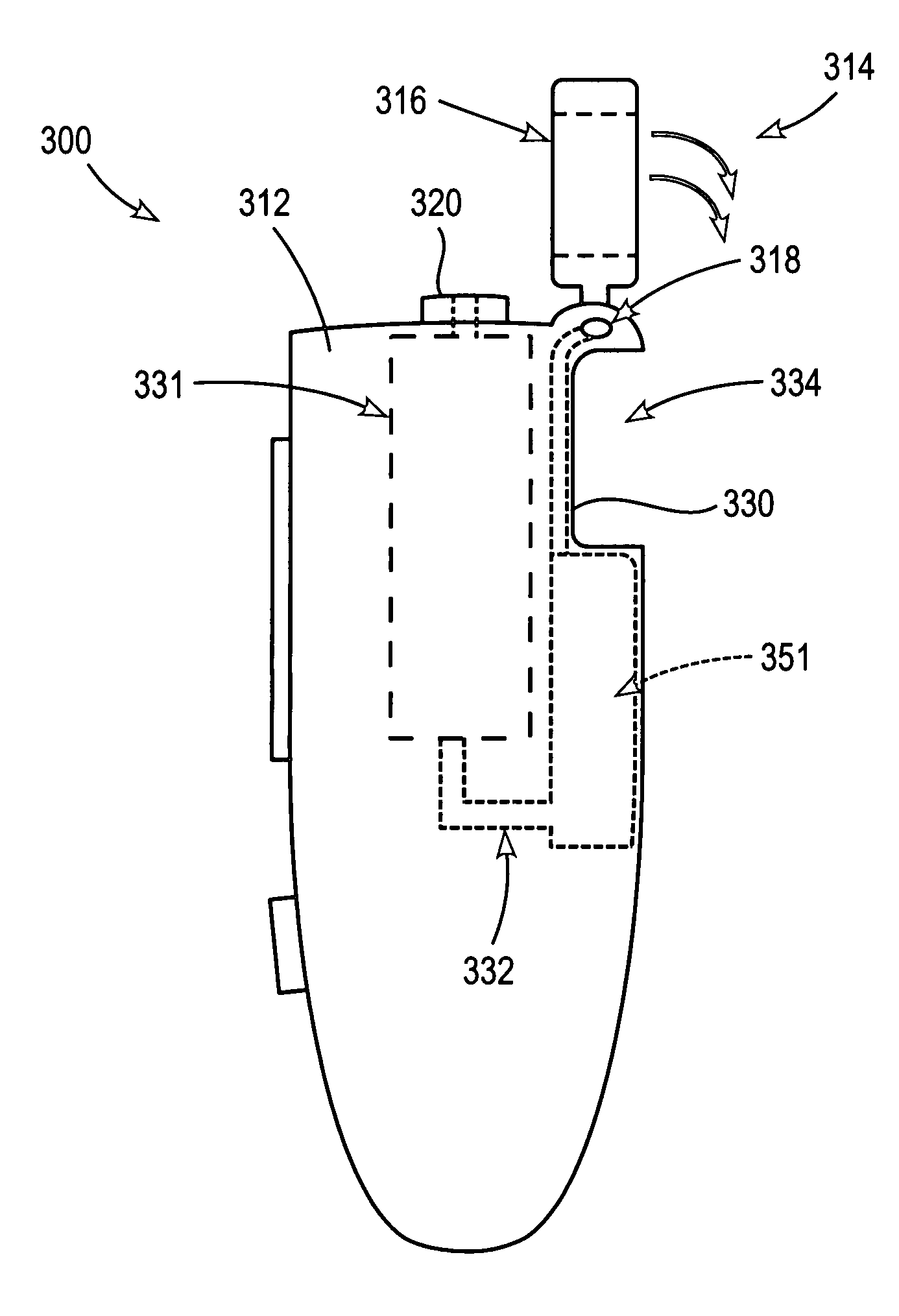
Low-loss multi-lumen injection apparatus
InactiveUS20070073267A1Reduce residual lossInfusion syringesMedical devicesDrug reservoirInjection site
Injection devices, systems and methods are disclosed for injecting two or more medicaments to a patient at a single injection site while preferably minimizing any mixing of the medicaments prior to delivery to the patient. The invention can also be used to sequentially deliver the medicaments to the patient in a repetitive manner. For example, the injection apparatus can sequentially provide a first medicament and then a second medicament to the patient during a first injection procedure. During a second injection procedure, the injection apparatus can again sequentially provide the first medicament and the second medicament to the patient either at the injection site of the first injection procedure or at a different injection site. Multi-lumen manifolds are disclosed for coupling to conventional drug ampoules, to permit the user to sequentially delivery different medicaments via a single skin penetration and to reduce losses associated with usage. Systems including multiple drug reservoirs and filling adaptors are also disclosed.
Owner:MILE CREEK CAPITAL
Process for formulating a customized skin care product
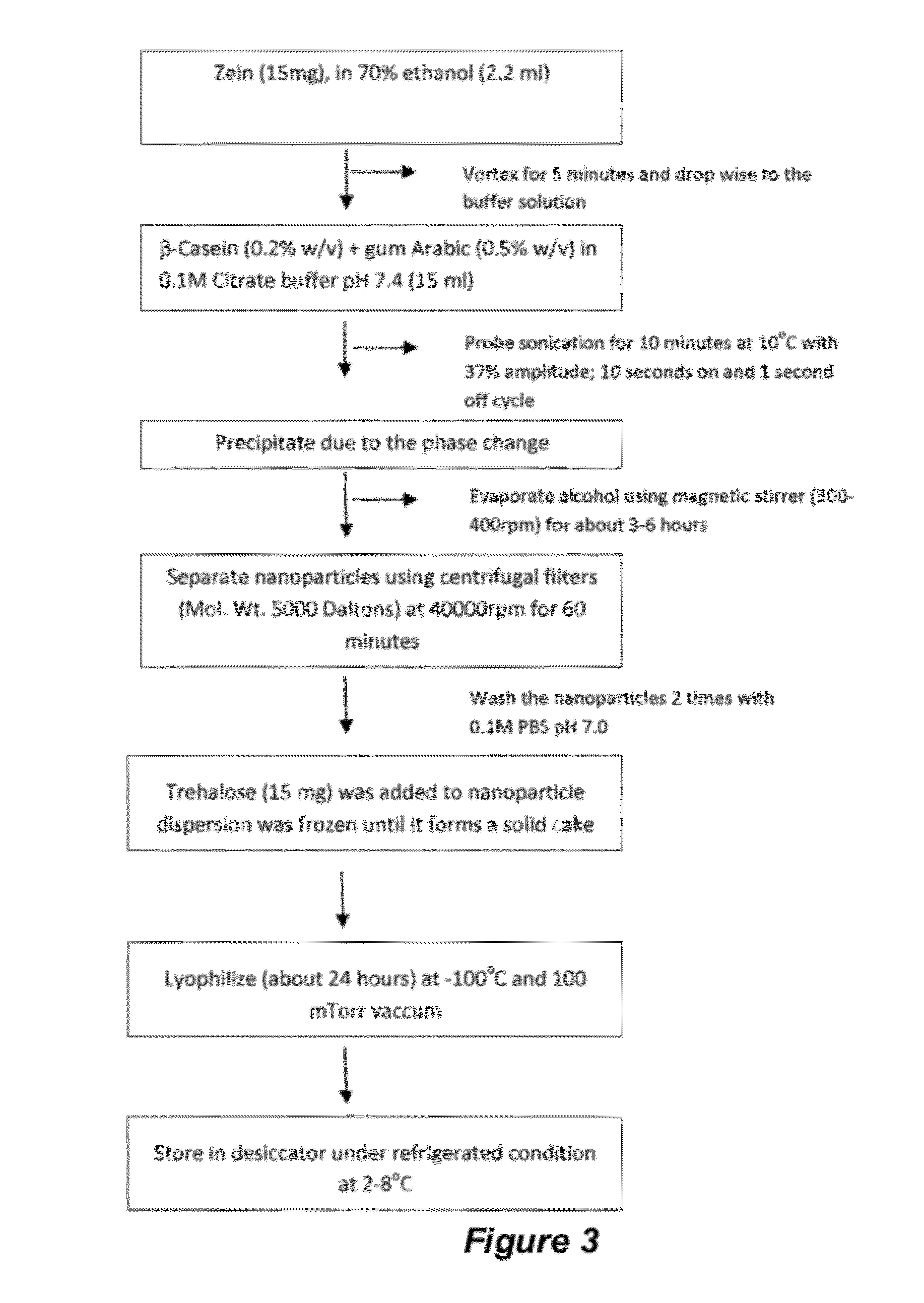
InactiveUS7349857B2Performance advantageStability of product can be controlledPigmenting treatmentVacuum evaporation coatingBiometric dataAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method and a process of determining individual skin structure and function at a point in time for the purpose of determining and formulating skin care products that remedy the deficiencies observed in the skin. Objective and repeatable dermal biometric instrumentation techniques can be used to measure skin moisture content, sebum content, firmness and elasticity properties, skin thickness, transepidermal water loss, skin pH and to perform a photo analysis of the face with UV and visible light. By customizing the skin care products, the individually added active ingredients can be controlled, the diluents can be modified, dermal penetration rates can be controlled, the surfactant systems can be adjusted, and the stability of the product can be controlled. To prevent the loss of active materials in the product, the skin care product is manufactured for an individual consumer and is only sold in a quantity of a three months supply. Additionally, a variety of ingredients can be combined that a mass produced product cannot contain due to stability / compatibility issues. This invention overcomes the limitations in formulating skin products for the mass market by providing a product designed with objective biometric data and created for the specific clinical condition of an individual's skin.
Owner:MANZO ROBERT P
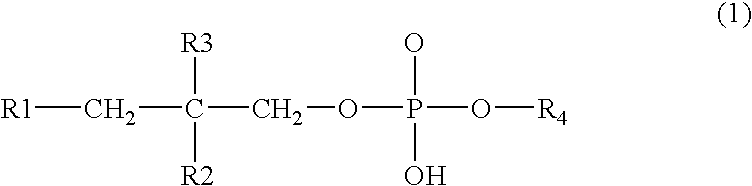
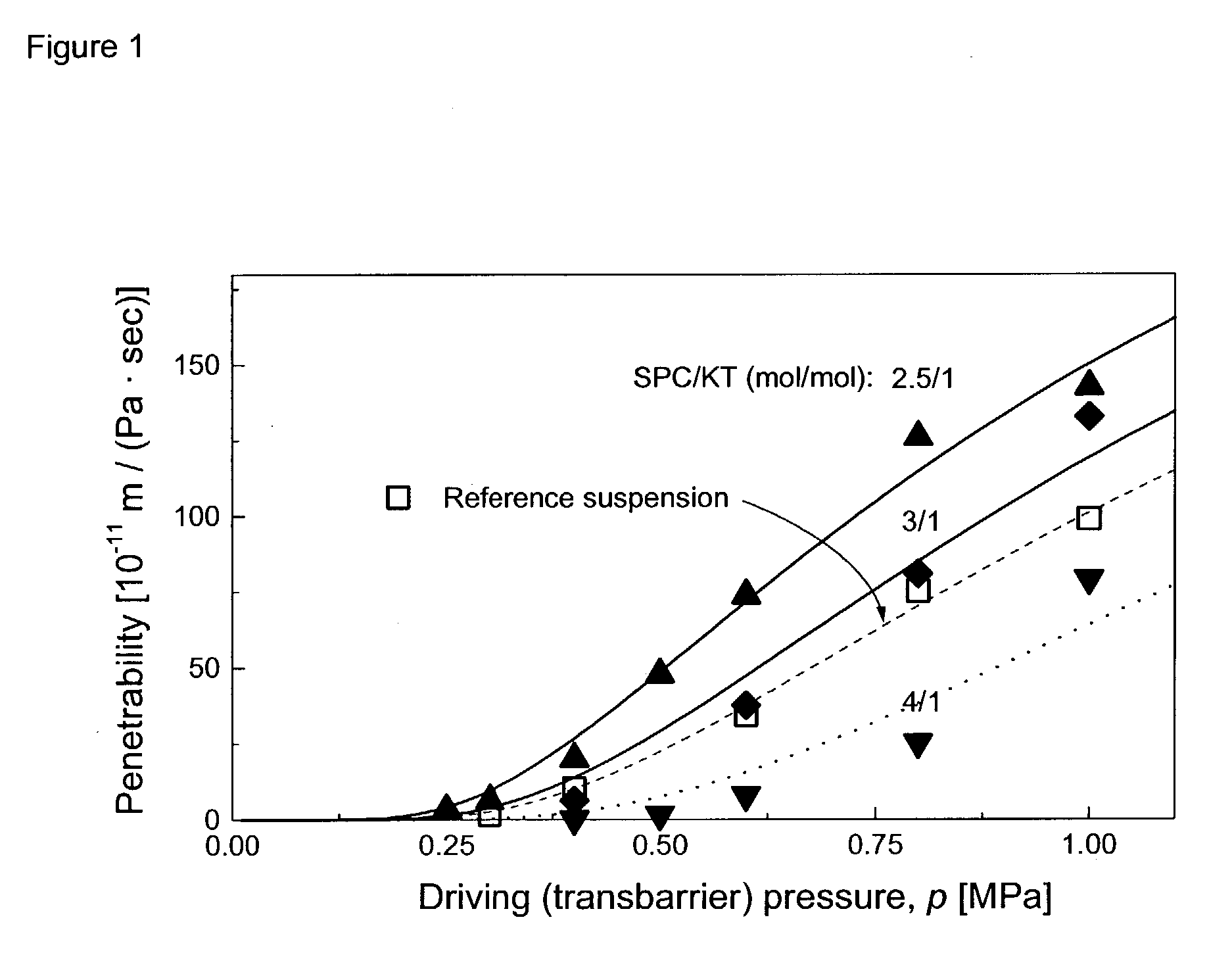
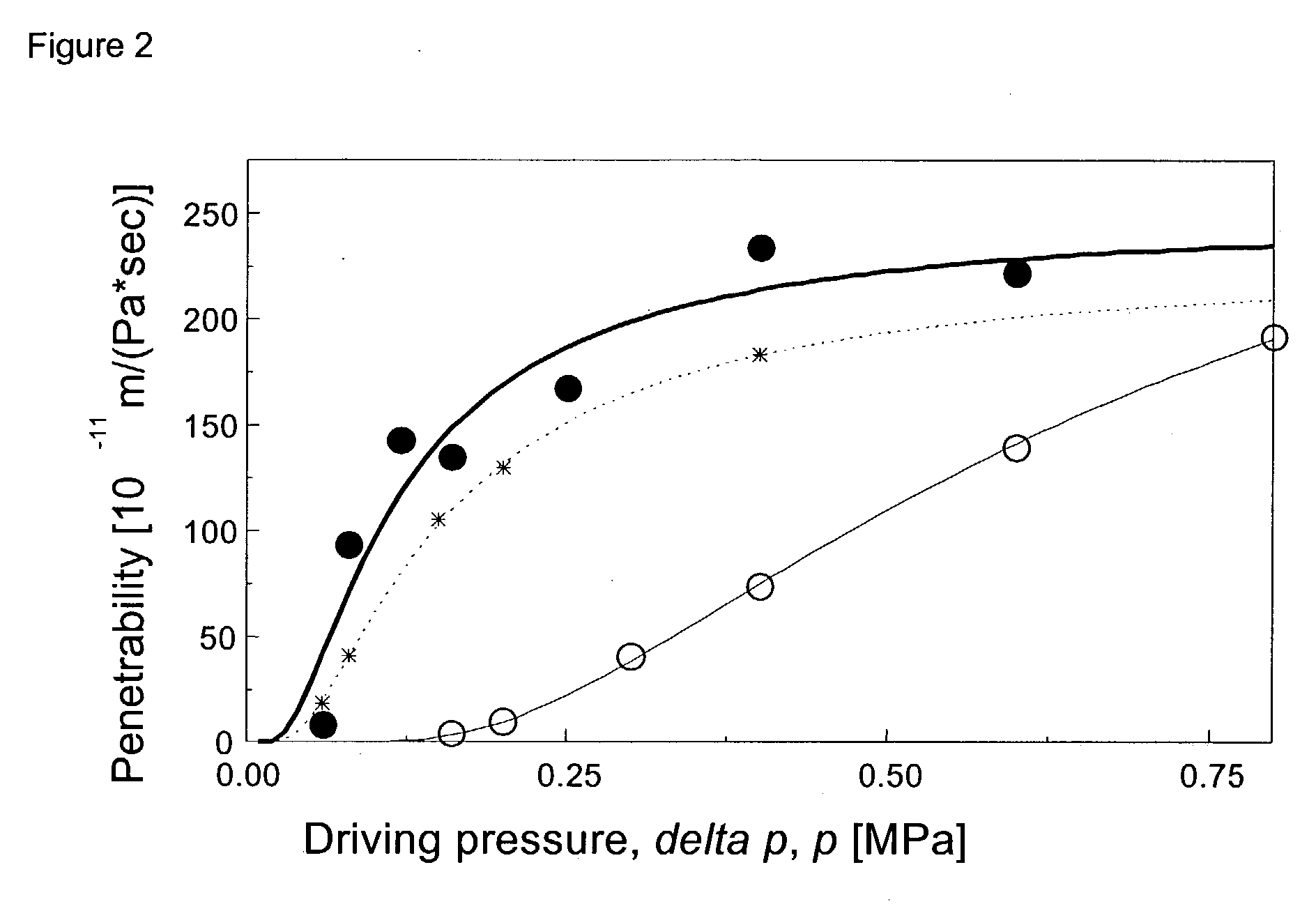
NSAID formulations, based on highly adaptable aggregates, for improved transport through barriers and topical drug delivery
The invention describes novel formulations of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) based on complex aggregates with at least three amphipatic components suspended in a suitable, e.g. pharmaceutically acceptable, polar liquid medium. A suitably ionised NSAID is one of the two, amongst said three, components that tends to destabilise lipid membranes, the other system component with such activity being typically a surfactant. In contrast, the remaining amongst said at least three amphipatic components typically forms a stable lipid membrane on it's own. An essential characteristics of the resulting, relatively large, aggregates is an improved ability to penetrate pores, in a semi-permeable barrier, at least 30%, and often much smaller than the average diameter of the complex aggregate. This enables said aggregates to mediate NSAID transport through semi-permeable barriers including mammalian skin. As a result of the skin penetration by NSAID loaded large aggregates, the drug delivered transcutaneously with such carriers gets deeper into the tissue than the corresponding NSAID from a solution on the skin surface. This is believed to be due to the special ability of suitable large carriers to bypass the local sink of blood capillaries at the epidermal-dermal junction in the skin. The carrier-mediated delivery of locally applied NSAIDs thus allows therapy of deep tissues under the drug administration site, which is medically highly desirable.
Owner:IDEA AG
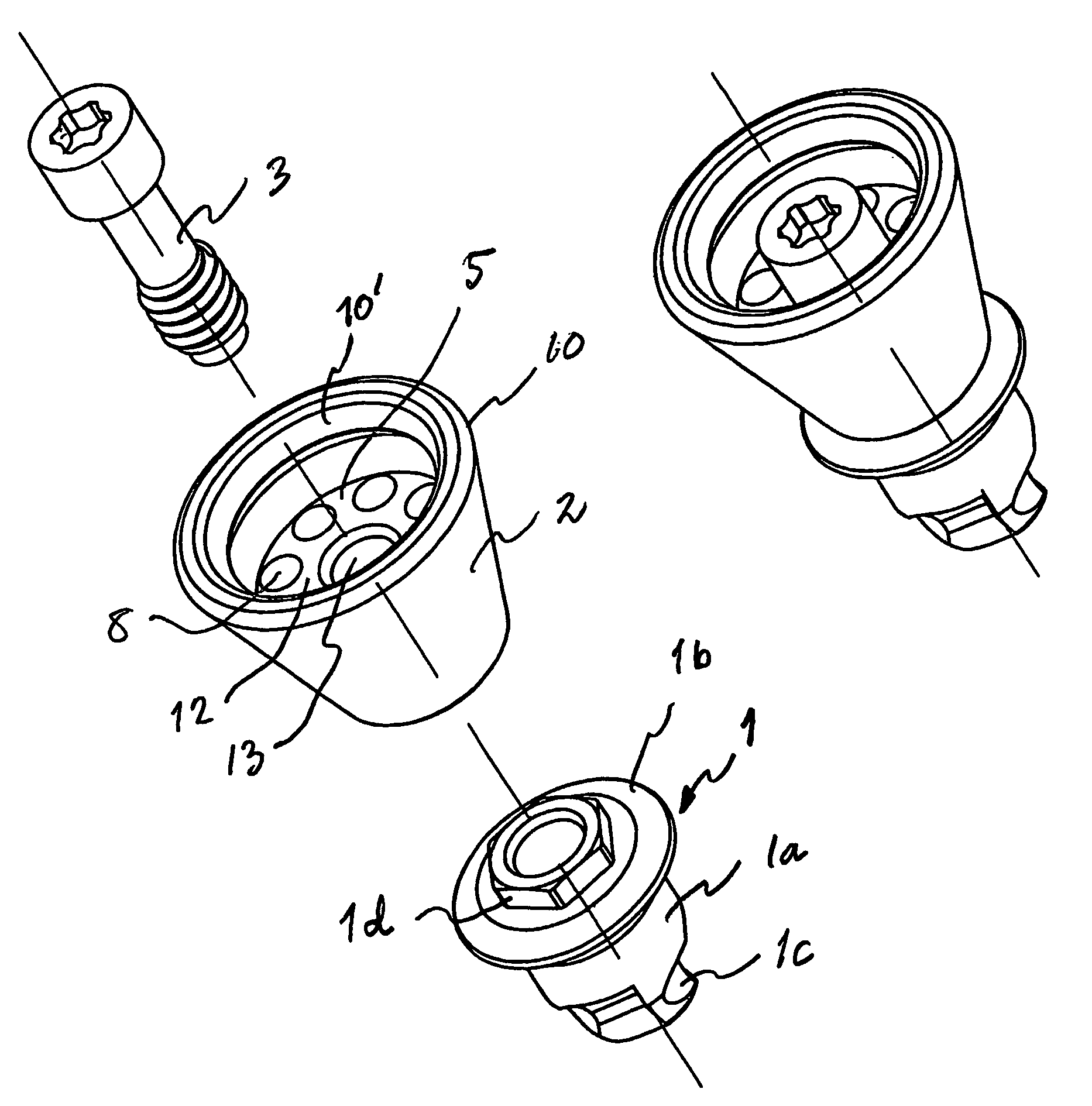
Implant device
ActiveUS7409070B2Incorrect tightening torqueReduce riskSuture equipmentsDental implantsBone-anchored hearing aidBone tissue
An implant device for bone anchored hearing aids of the type that include a screw-shaped anchoring element for anchorage in the bone tissue, an abutment sleeve for skin penetration and arranged to be connected to the fixture with a screw connection and a tool for installing the implant into the bone tissue. The fixture and the abutment sleeve are made as a pre-mounted unit that unit is arranged to be installed in one step by means of the tool, which is arranged to cooperate with a tool engaging portion on the abutment sleeve. This arrangement requires fewer pieces to handle for the surgeon during the installation, which means that the surgical procedure can be carried out in a simpler and predetermined way, at the same time as the advantages inherent in a two-piece implant device are maintained.
Owner:COCHLEAR BONE ANCHORED SOLUTIONS
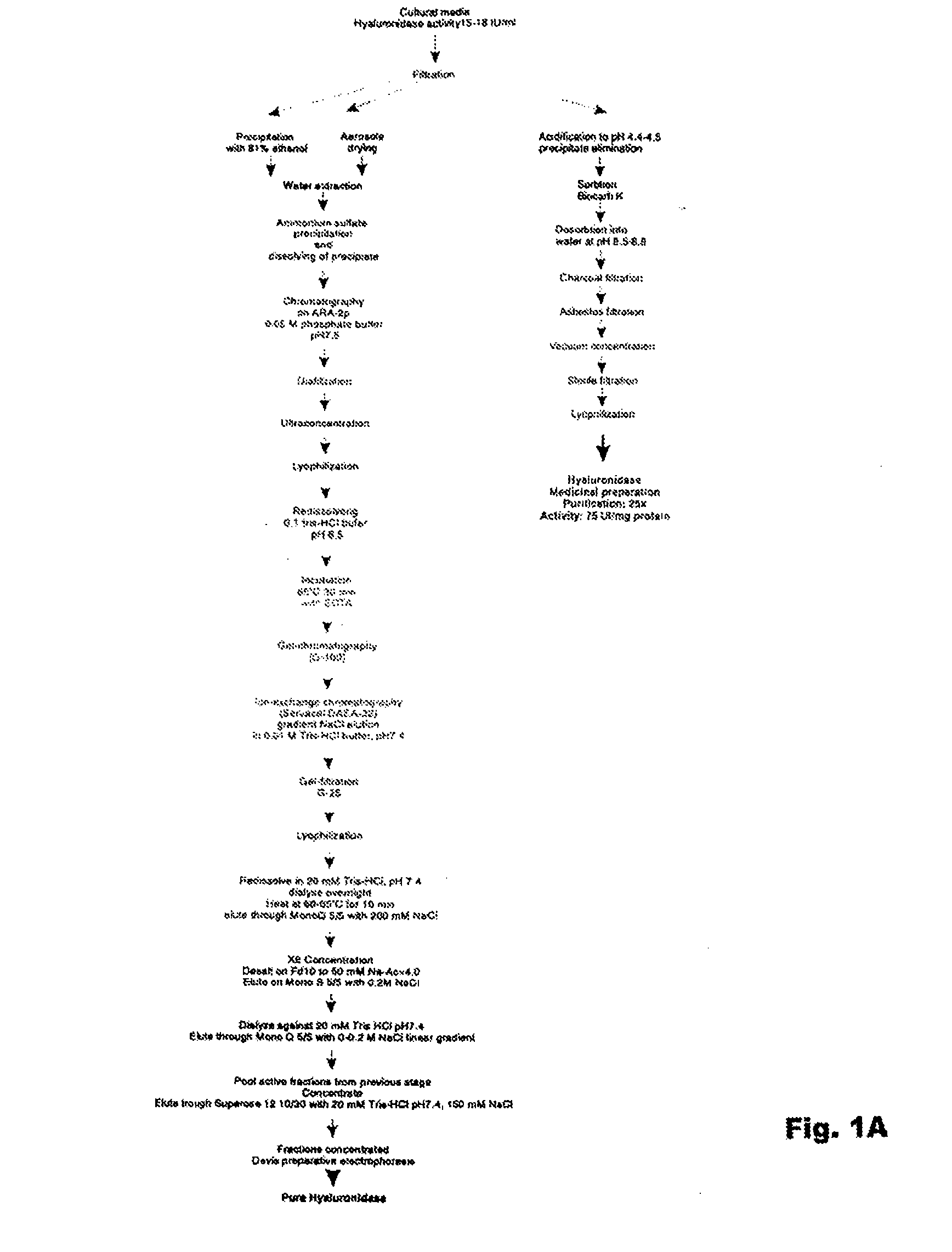
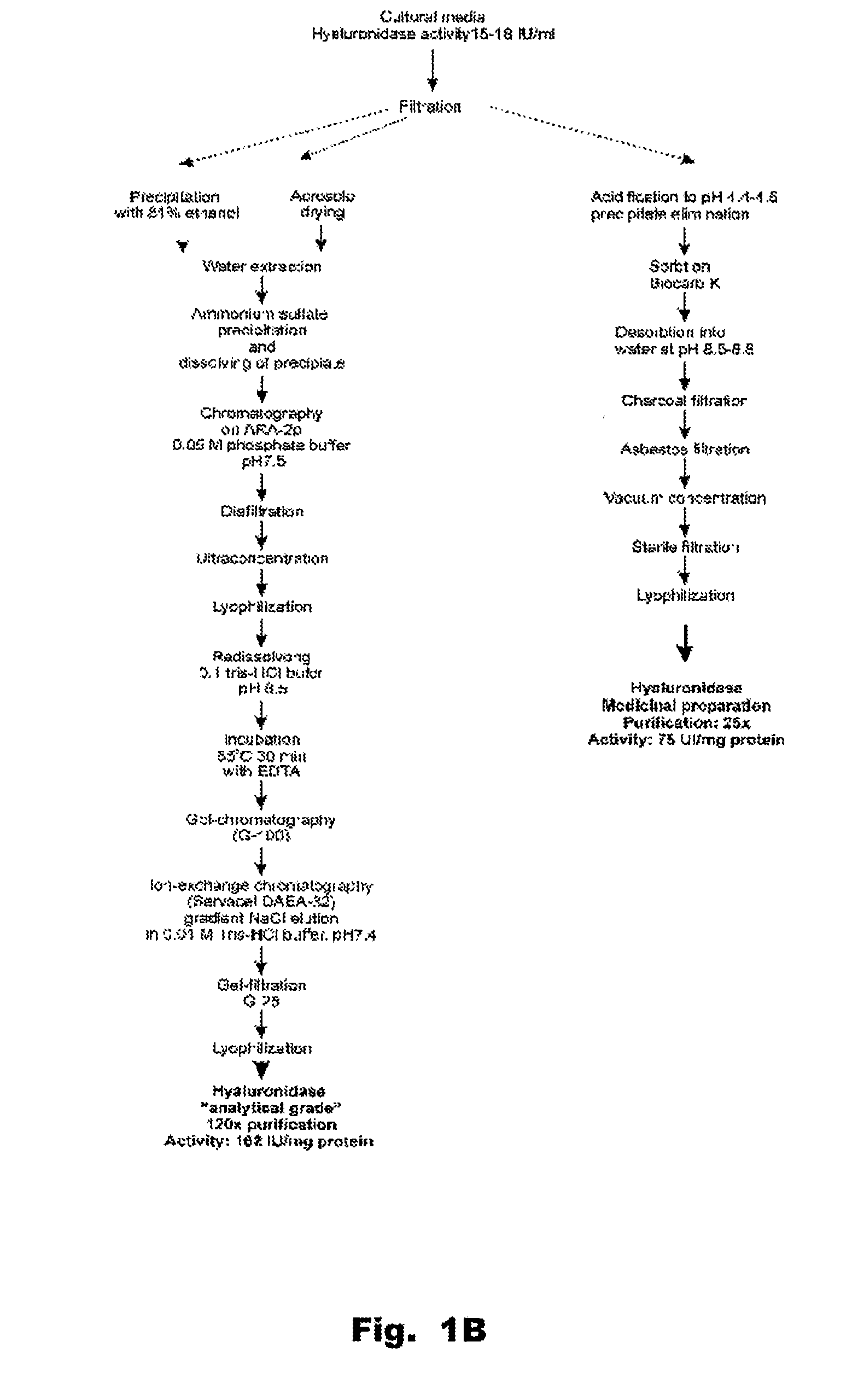
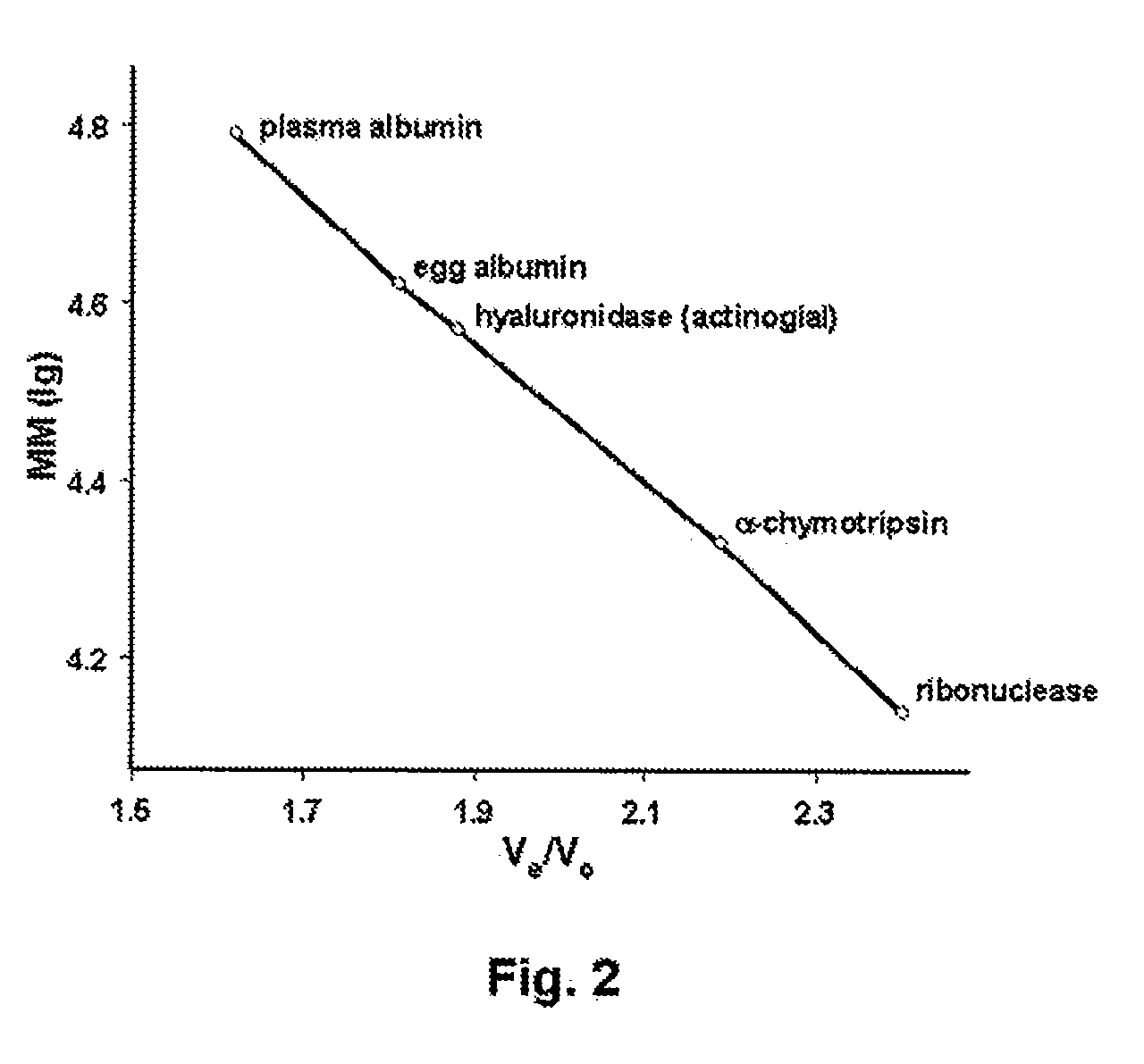
Hyaluronidase and method of use thereof
The present invention provides a tnaluronidase. The hyaluronidase can be produced by the strain Streptomyces aitinocidm 77, Exemplary characteristics of the hyaluronidase include specific C-terminal or other amino acid sequences, including full-length sequences, and improved physico-chemical and actix itj properties as compared to known h> alυronidase preparatkiiis. Described are also various uses of the hyaiurυnidasc, including topical administration of the h> aiuronidasc to improve skin penetration of a co-administered active substance.
Owner:UVARKINA TAMARA P +1
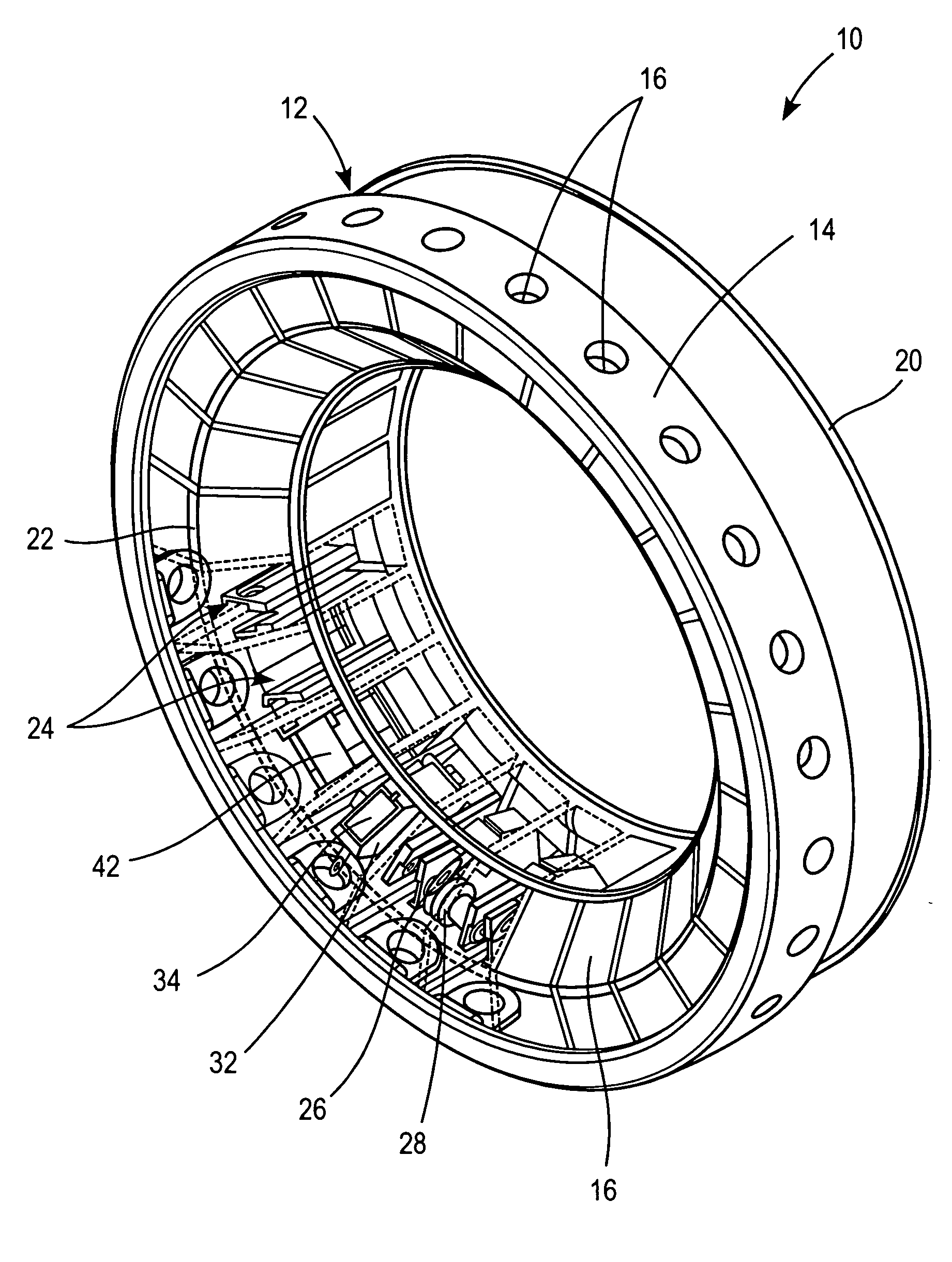
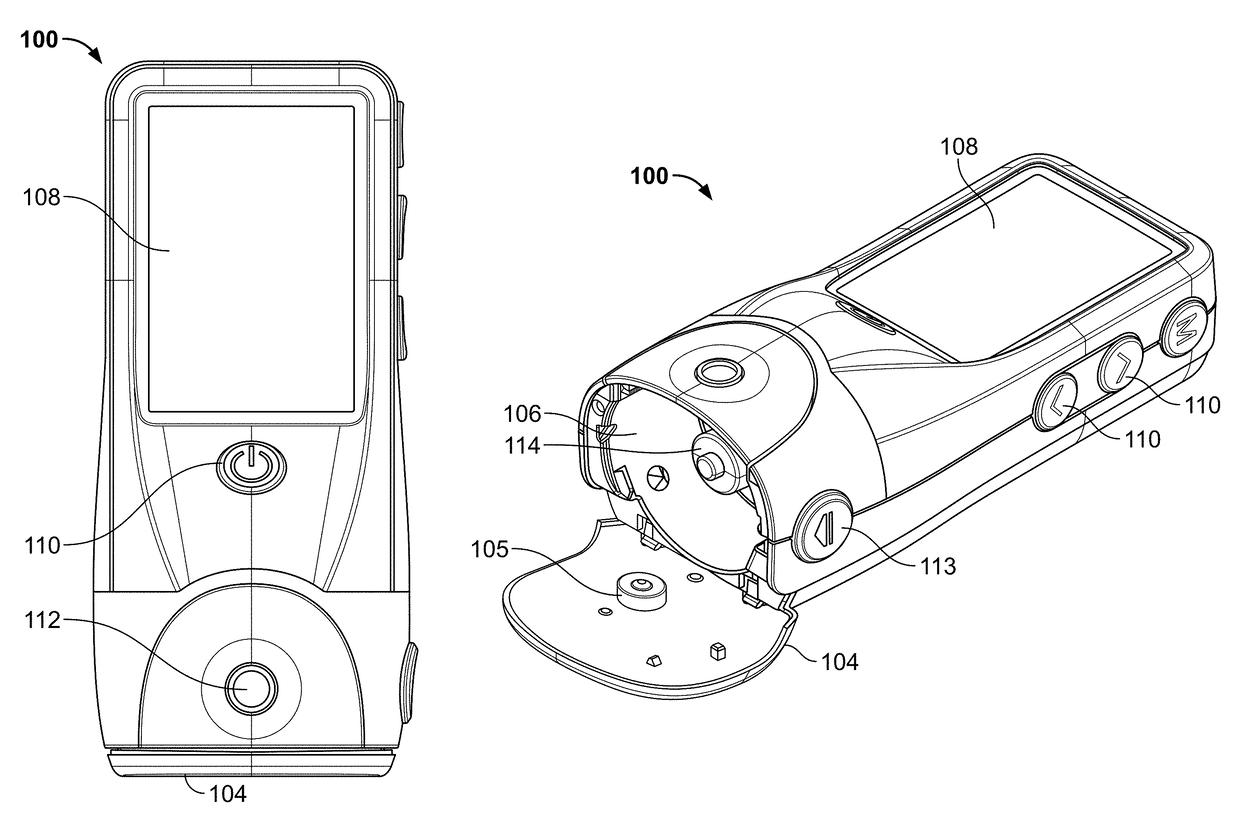
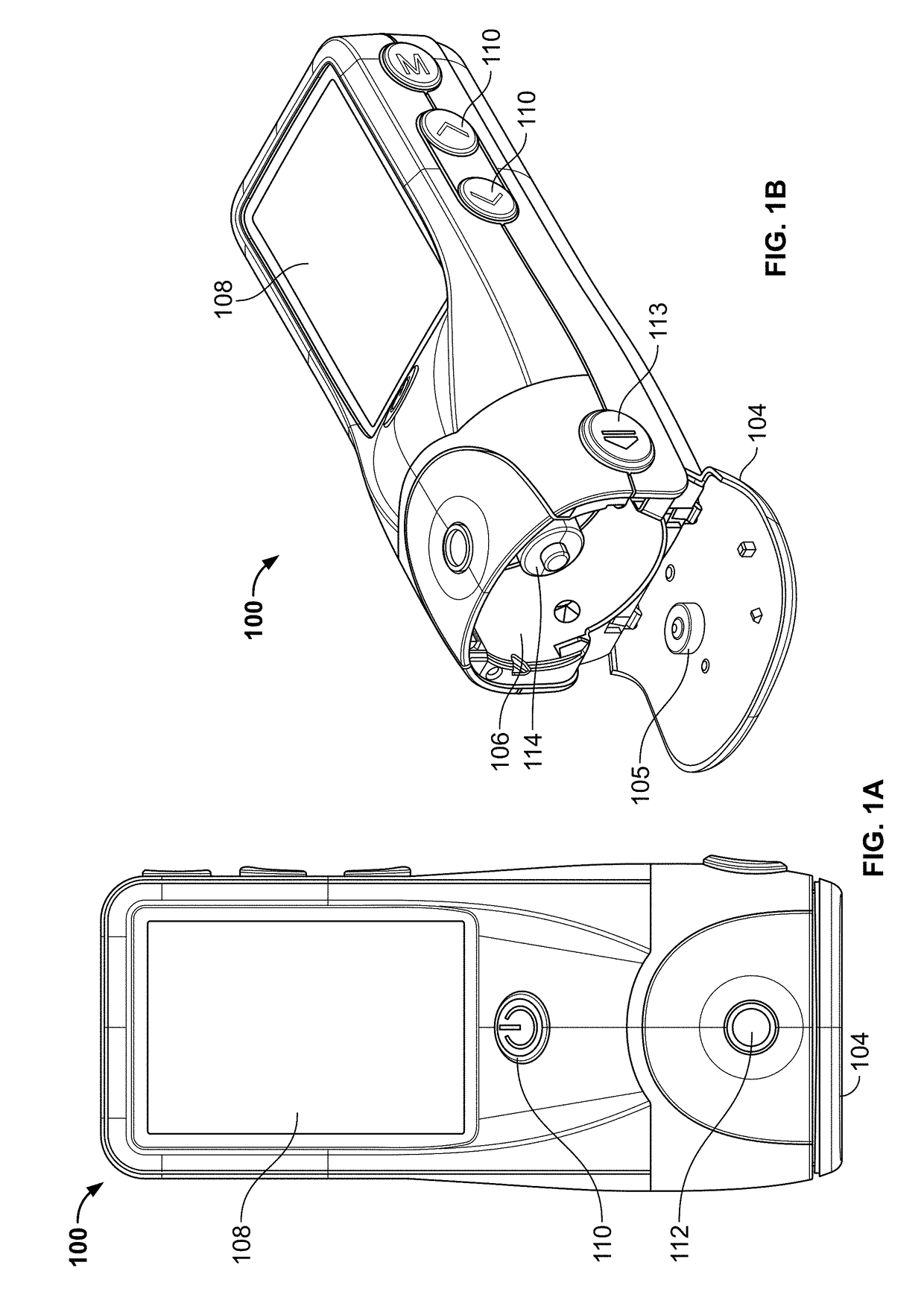
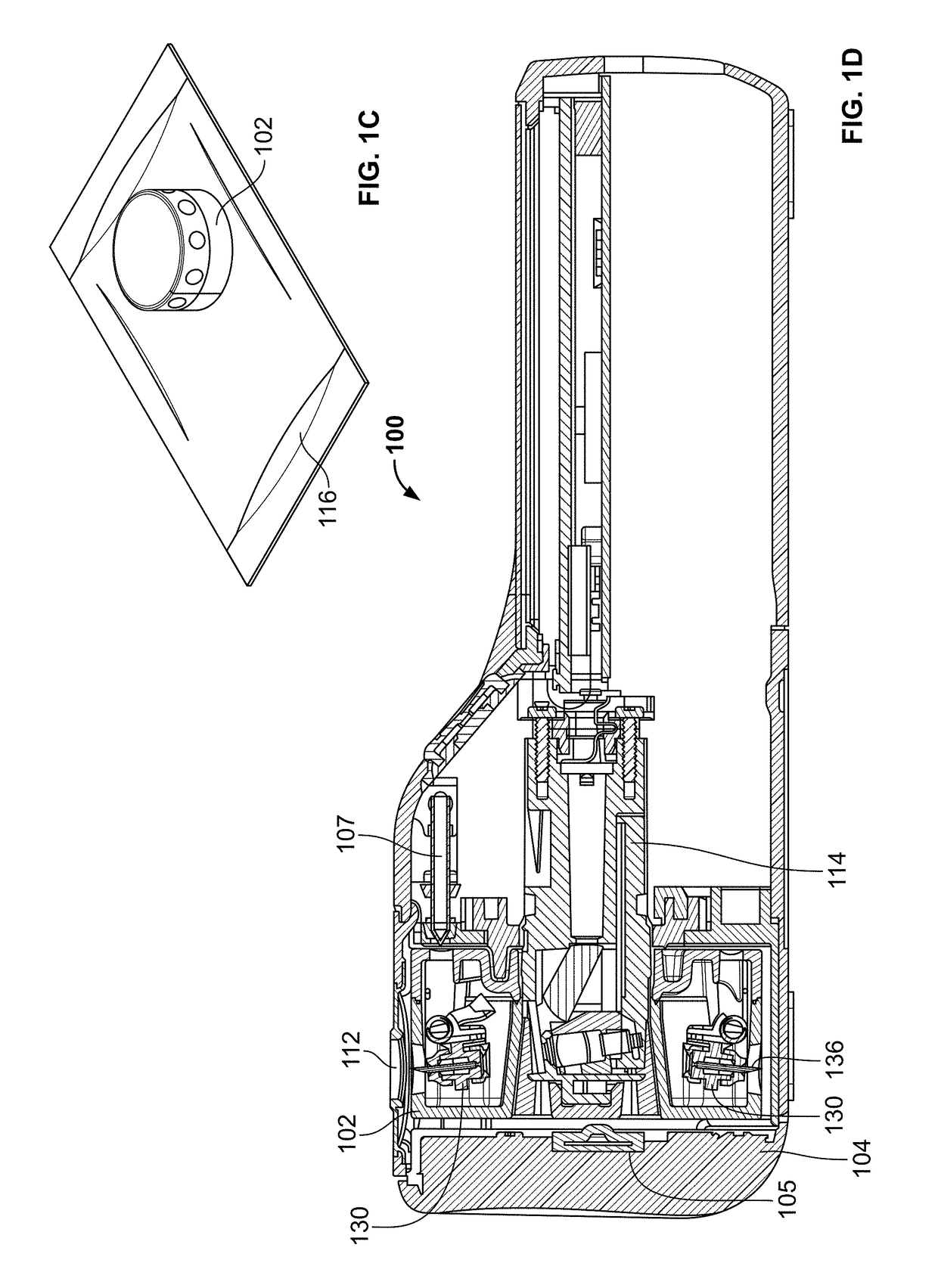
Devices and methods for body fluid sampling and analysis
ActiveUS20130172698A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSensorsSkin penetrationEngineering
Described here are meters and methods for sampling, transporting, and / or analyzing a fluid sample. The meters may include a meter housing and a cartridge. In some instances, the meter may include a tower which may engage one or more portions of a cartridge. The meter housing may include an imaging system, which may or may not be included in the tower. The cartridge may include one or more sampling arrangements, which may be configured to collect a fluid sample from a sampling site. A sampling arrangement may include a skin-penetration member, a hub, and a quantification member.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug formulations for topical application to the skin
InactiveUS20030082226A1Improve performanceSignificant positive effectOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticSkin penetrationAntiinflammatory drug
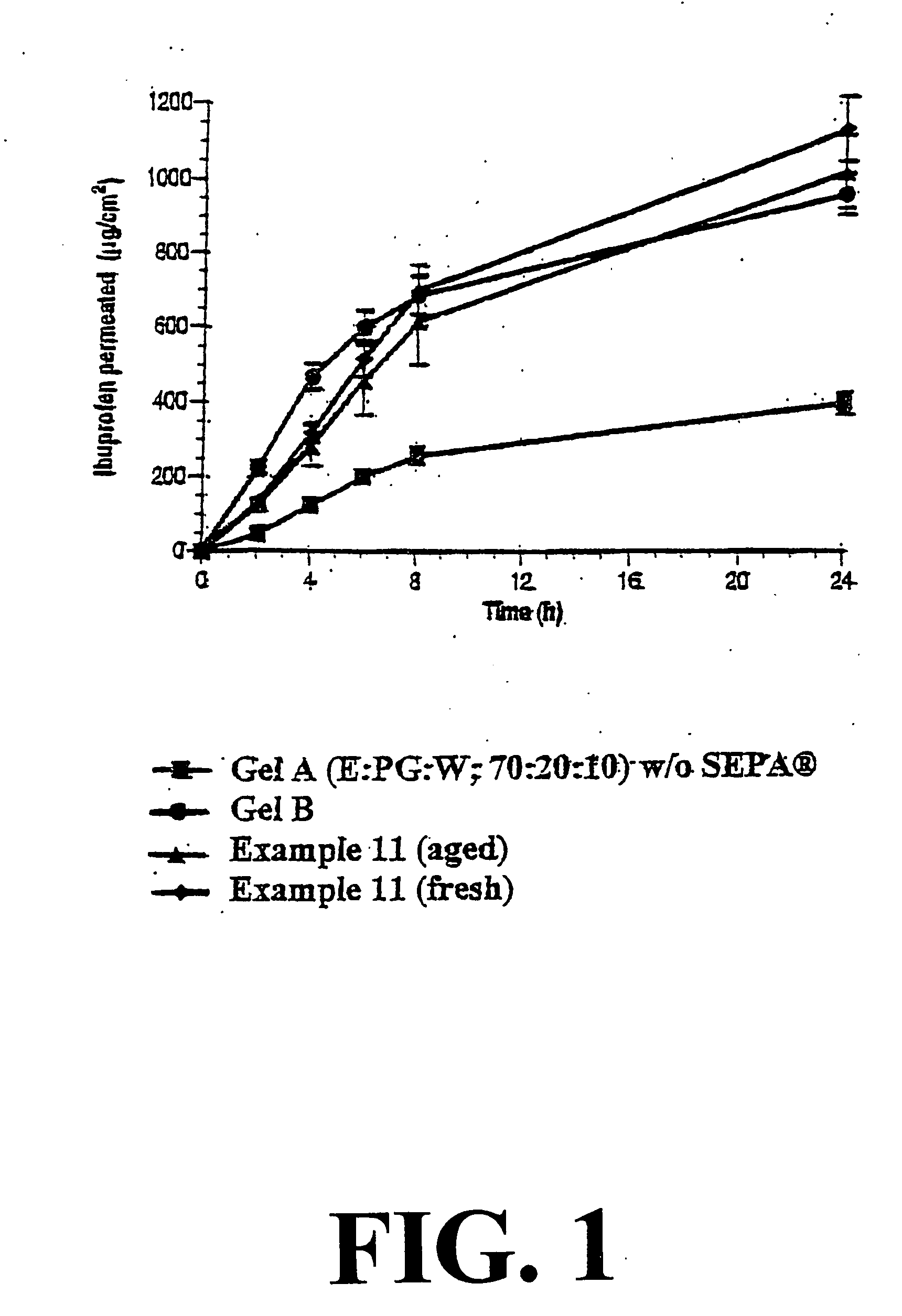
Topical alcoholic or aqueous alcoholic gels containing ibuprofen or other NSAIDs, such as, naproxen, in substantially neutral salt form, have enhanced penetration through skin and may provide rapid pain / inflammation relief by including in the formulation 2-n-nonyl-1,3-dioxolane or other hydrocarbyl derivative of 1,3-dioxolane-or 1,3-dioxane or acetal, as skin penetration enhancing compound. The amount of propylene glycol may be varied to adjust the initial flux of the NSAID through the skin, especially for ibuprofen, naproxen, and ketorolac.
Owner:SAMOUR CARLOS M +2
Body fluid sampling device with pivotable catalyst member
ActiveUS8372015B2Low costEasy to manufactureCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringVacuum pressureIntegrated monitoring
An integrated monitoring and body fluid sampling device constructed to permit digital as well as alternate-site body fluid sampling and analysis, the device comprising: a housing; at least one skin-penetration member; and a member constructed for the application of circumferential or vacuum pressure to an appendage; wherein the member is detachably or retractably connected to the housing in a manner such that the integrated monitoring and body fluid sampling device can perform digital or alternate-site body fluid sampling and analysis. Additional arrangements and techniques are also described.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Pharmaceutical gel formulations
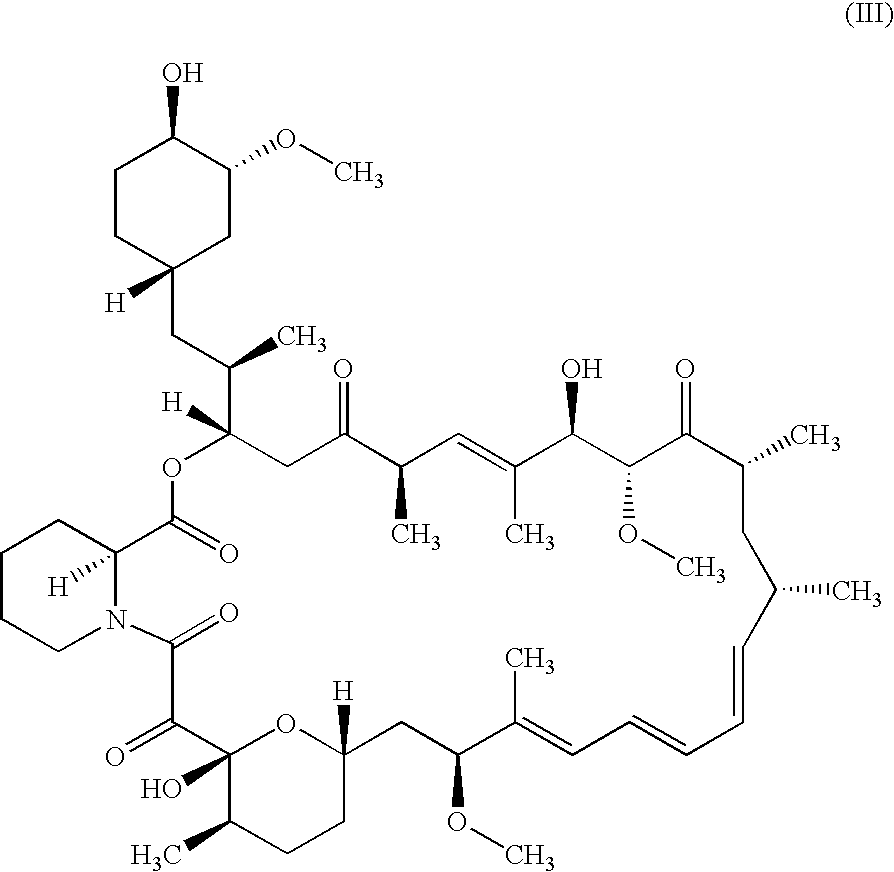
A pharmaceutical gel composition is provided comprising (a) a therapeutically effective amount of one or more active pharmaceutical ingredients comprising one or more macrolide related immunosuppressants or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or esters thereof; (b) one or more gel forming agents; and (c) an effective amount of one or more skin penetration enhancers capable of percutaneous delivery of the macrolide related immunosuppressant through the skin. Also provided is a process for its preparation and methods for delivering a macrolide related immunosuppressant through the skin of a mammal in order to treat conditions situated on and beneath the skin.
Owner:GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LIMITED
Compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles with skin repair function and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN109875910AWith skin repair functionImproves anti-inflammationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin penetrationCholesterol
The invention provides compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles with a skin repair function, and belongs to the technical field of cosmetics. The compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles are prepared from, by weight, 0.01-1 part of regenerated repairing active peptide, 0.01-1 part of antioxidant active peptide, 0.1-5 parts of natural moisturizing active factors, 0.01-1 part of microcirculation-promoting active ingredients, 5-20 parts of lipoid wall materials, 0.1-5 parts of cholesterol, 10-45 parts of polyhydric alcohols and 30-98 parts of water. According to the compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles, repairing components acting on different target spots are provided aiming at different repair mechanisms of the skin barrier; meanwhile, the nanometer vesicles are adopted for covering various hydrophilic and lipophilic active ingredients, a unique closed lipid bilayer structure of the vesicles is utilized, the stability of the repairing compound is significantly improved, the skin penetration amount is increased, slow release of the active ingredients is effectively controlled, and the repairing effect is improved.
Owner:WUHAN BEST CARRIER NANO TECH
Skin Permeation Device for Analyte Sensing or Transdermal Drug Delivery
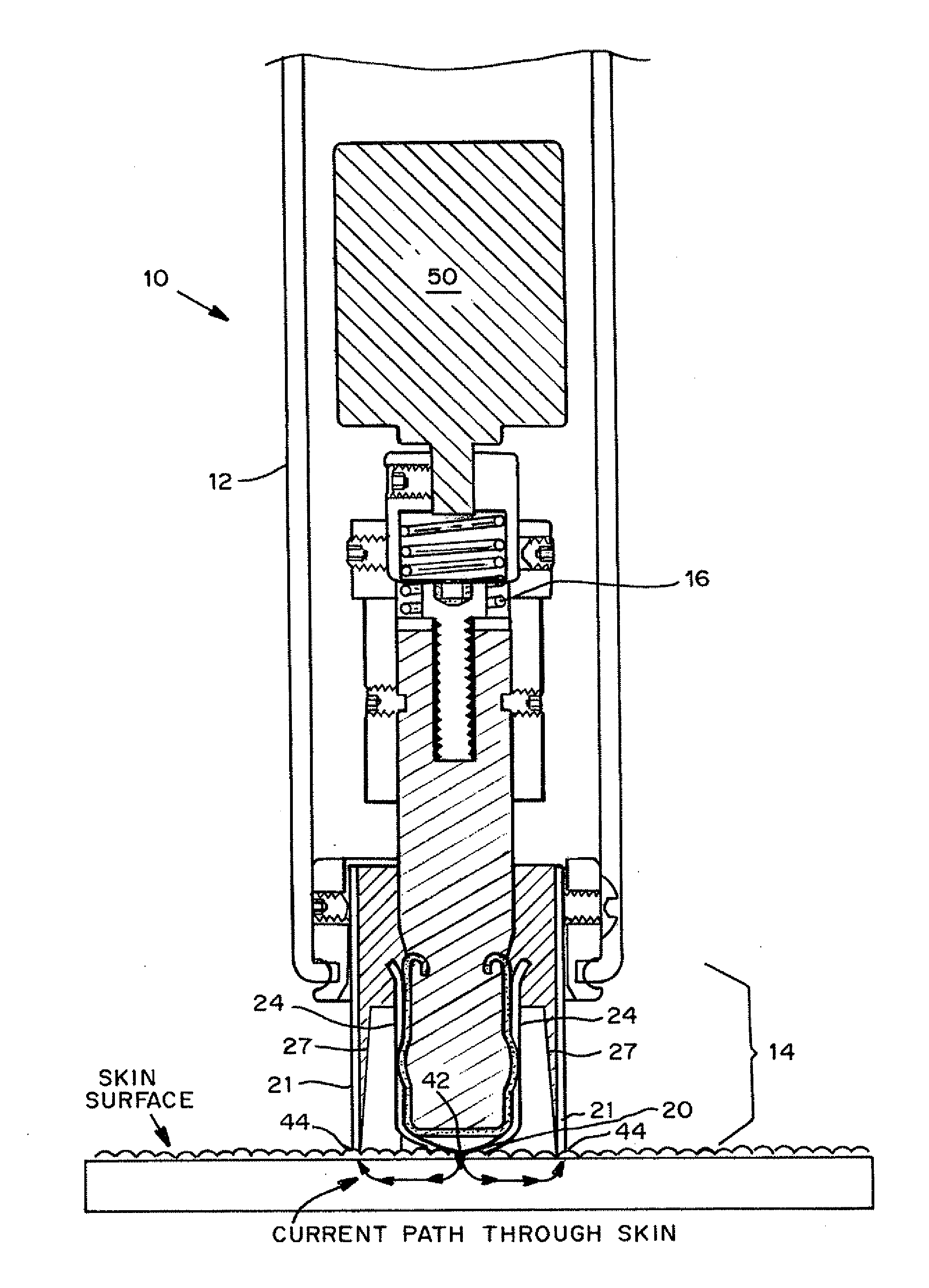
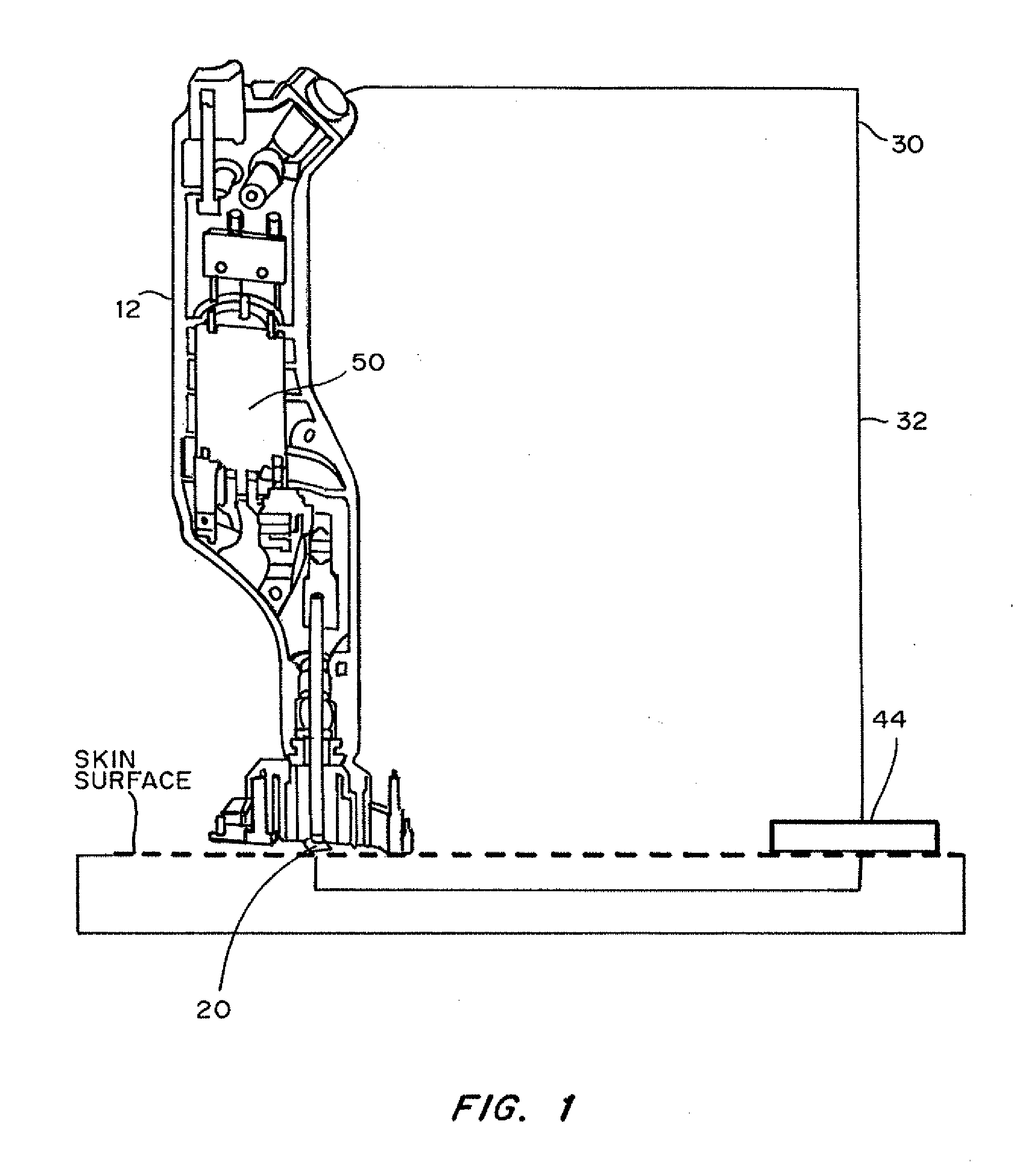
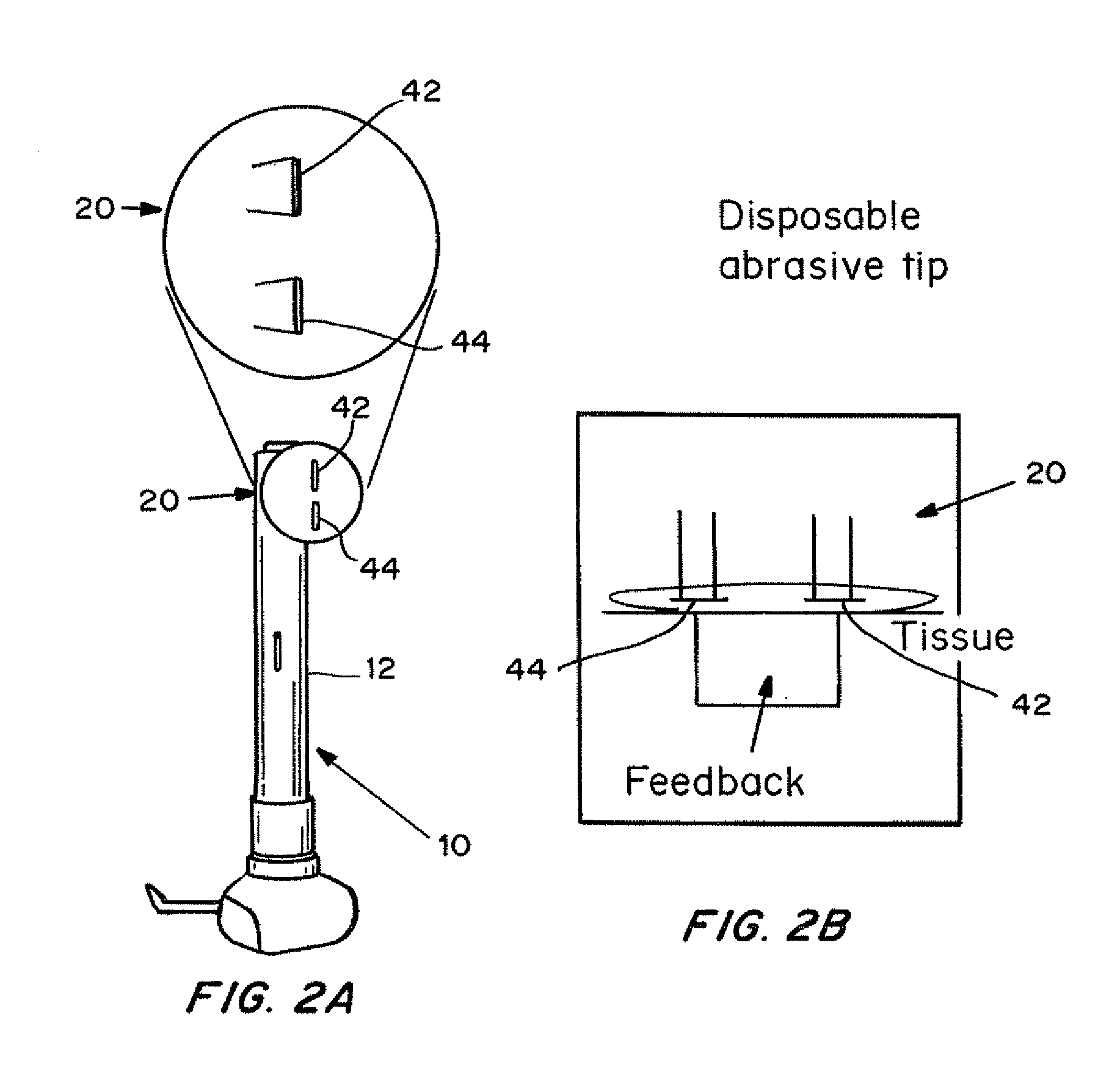
InactiveUS20130137951A1Improve breathabilityElectrotherapyMedical devicesSkin integritySkin penetration
Devices, systems, kits and methods for increasing the skin's permeability controlled by measured skin electrical parameter are described herein. They may be used for transdermal drug delivery and / or analyte extraction or measurement. The controlled abrasion device contains (i) a hand piece, (ii) an abrasive tip, (iii) a feedback control mechanism, (iv) two or more electrodes, and (v) an electrical motor. Preferably the feedback control mechanism is an internal feedback control mechanism. In this embodiment, the abrasive tip contains two electrodes, i.e. both the source electrode and the return electrode. In another embodiment, the feedback control mechanism is an external feedback control. In the preferred embodiment for external feedback control, the device contains a co-axial or concentric arrangement of the two electrodes. In this embodiment, the abrasive tip contains the source electrode and the return electrode is located at the proximal end of the hand piece. The abrasive tip can be made of any material with a surface that can abrade skin. The material can be conductive or non-conductive. The controlled abrasion device may be provided in a kit, where the kit contains the device, one or more abrasive tips, optionally with a wetting fluid. The method for increasing the skin's permeability requires applying the controlled abrasion device to a portion of the skin's surface for a short period of time. The desired level of skin impedance, and thus the resulting permeability of the treated site, can be set at a predetermined value. Alternatively, the level of skin impedance can be selected based on the desired level of skin integrity, the subject's sensation of discomfort, or the duration of the application. The device contains a control mechanism which uses an appropriate algorithm or signal processing on the conductivity information provided by the electrodes to determine when the desired level of skin permeability has been reached. Once the desired level has been reached, the abrasion device is removed and either a drug delivery composition or device or an analyte sensor is applied to the treated site.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
Laminated microneedle system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104338235AImprove stress resistanceRetain hardnessSemi-permeable membranesFixed microstructural devicesSkin penetrationTemperature treatment
The invention relates to a laminated microneedle system and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of medical devices. A laminated structure, namely an outer layer and an inner layer of a needle body, is prepared from a soluble natural polymer material or a high molecular polymer. The outer layer of the needle body for wrapping a target drug has good soundness, can easily penetrate keratoderma, can be rapidly dissolved in a skin environment rich in water, and exerts an effect of releasing the target drug. The inner layer of the needle body cannot penetrate skin and therefore is free of the target drug. The system can strengthen a skin penetration effect of the needle body and reduce waste of the target drug at the same time. A base of the system has better compression resistance, and the problem of frangibility of the base under pressure is improved. The preparation method is easy, avoids high-temperature treatment, facilitates keeping activity of the target drug and is easy and simple to operate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Protein nanocarriers for topical delivery
ActiveUS20120195947A1Low toxicityReduce skin irritationPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsSolubilityNanocarriers
The invention encompasses nanoparticle assemblies and methods for preparing nanoparticle and compositions comprising such nanoparticles for use in topical or skin applications. The invention further encompasses methods of complexing various molecular and cellular entities to the nanoparticles using the resulting nanoparticles of the invention as delivery devices. The nanoparticles can be used for a variety of applications, such as treating cancer, targeting tumors, reducing the toxicity of a drug in vivo, increasing the efficacy of a complexed agent in vivo, protecting a complexed agent against degradation, increasing skin penetration and retention of drugs, and enhancing the water solubility / dispersibility of a drug or other agent.
Owner:SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY
Topical pharmaceutical compositions
A hydroalcoholic topical pharmaceutical composition is provided comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a therapeutic agent comprising one or more selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or esters thereof solubilized in a solubilizing amount of a penetration vehicle system comprising a skin penetration enhancing effective amount of at least one monohydric alcohol and at least two non-volatile organic compounds selected from the group consisting of pyrrolidones, polyol ethers, polyols and mixtures thereof. Also provided is a process for its preparation.
Owner:GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LIMITED
Devices and methods for body fluid sampling and analysis
ActiveUS9782114B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSensorsSkin penetrationEngineering
Described here are meters and methods for sampling, transporting, and / or analyzing a fluid sample. The meters may include a meter housing and a cartridge. In some instances, the meter may include a tower which may engage one or more portions of a cartridge. The meter housing may include an imaging system, which may or may not be included in the tower. The cartridge may include one or more sampling arrangements, which may be configured to collect a fluid sample from a sampling site. A sampling arrangement may include a skin-penetration member, a hub, and a quantification member.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Ibuprofen salt emulsifiers and cream formulations containing same
Emulsions and creams containing ibuprofen effective for topical administration of the ibuprofen are provided without the presence of conventional O / W emulsifying agent. The emulsions and creams are formed by using the ibuprofen, in the form of its salt, as the O / W emulsifying agent. A minor amount of a W / O emulsifying agent may be included in the composition. Percutaneous delivery of ibuprofen is improved by using a skin penetration enhancing compound, such as 2-n-nonyl-1,3-dioxolane or decanaldimethyl acetal, as the oily phase of the emulsion.
Owner:MACROCHEM CORP
Manufacturing method for healthcare pillow pillowcase cloth
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for healthcare pillow pillowcase cloth. The manufacturing method is characterized by including: weaving grey cloth, and adding, by weight, 800-920 parts of water, 15-25 parts of chrysanthemum, 10-20 parts of prepared Sichuan aconite root, 5-15 parts of root of angelica dahurica, 5-15 parts of kudzuvine root, 10-20 parts of Szechuan lovage rhizome, 6-12 parts of root of red-rooted salvia and 8-16 parts of ageratum into a pressure vessel for heating at the temperature ranging from 45 DEG C to 49 DEG C prior to heat preservation for 230-270 minutes; performing final treatment. Various traditional Chinese medicine compositions of natural Chinese herbal medicine for socking a pillowcase are mixed together, so that various medical effects are multiplied and work together, for example, the chrysanthemum has the effect of dispelling wind and clearing heat and improving eyesight and detoxifying; the prepared Sichuan aconite root has the effect of dispelling wind-cold, scattering wind-evil and warming menstruation and relieving pain; the root of angelica dahurica has the effect of relieving swelling and pain and treating neurasthenia headache; the kudzuvine root has the effect of generating Yang and relaxing muscles, relieving restlessness and quenching thirst and treating high blood pressure; the Szechuan lovage rhizome has the effect of promoting circulation of Qi and relieving depression and promoting blood circulation to arrest pain. The effective components of the medicine enter a human body by means of skin penetration, acupuncture point absorption, meridian transmission and the like.
Owner:HUZHOU JINTADI TEXTILE MILL
Devices and methods for body fluid sampling and analysis
ActiveUS20180008178A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSensorsSkin penetrationEngineering
Described here are meters and methods for sampling, transporting, and / or analyzing a fluid sample. The meters may include a meter housing and a cartridge. In some instances, the meter may include a tower which may engage one or more portions of a cartridge. The meter housing may include an imaging system, which may or may not be included in the tower. The cartridge may include one or more sampling arrangements, which may be configured to collect a fluid sample from a sampling site. A sampling arrangement may include a skin-penetration member, a hub, and a quantification member.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Flat magnetic core
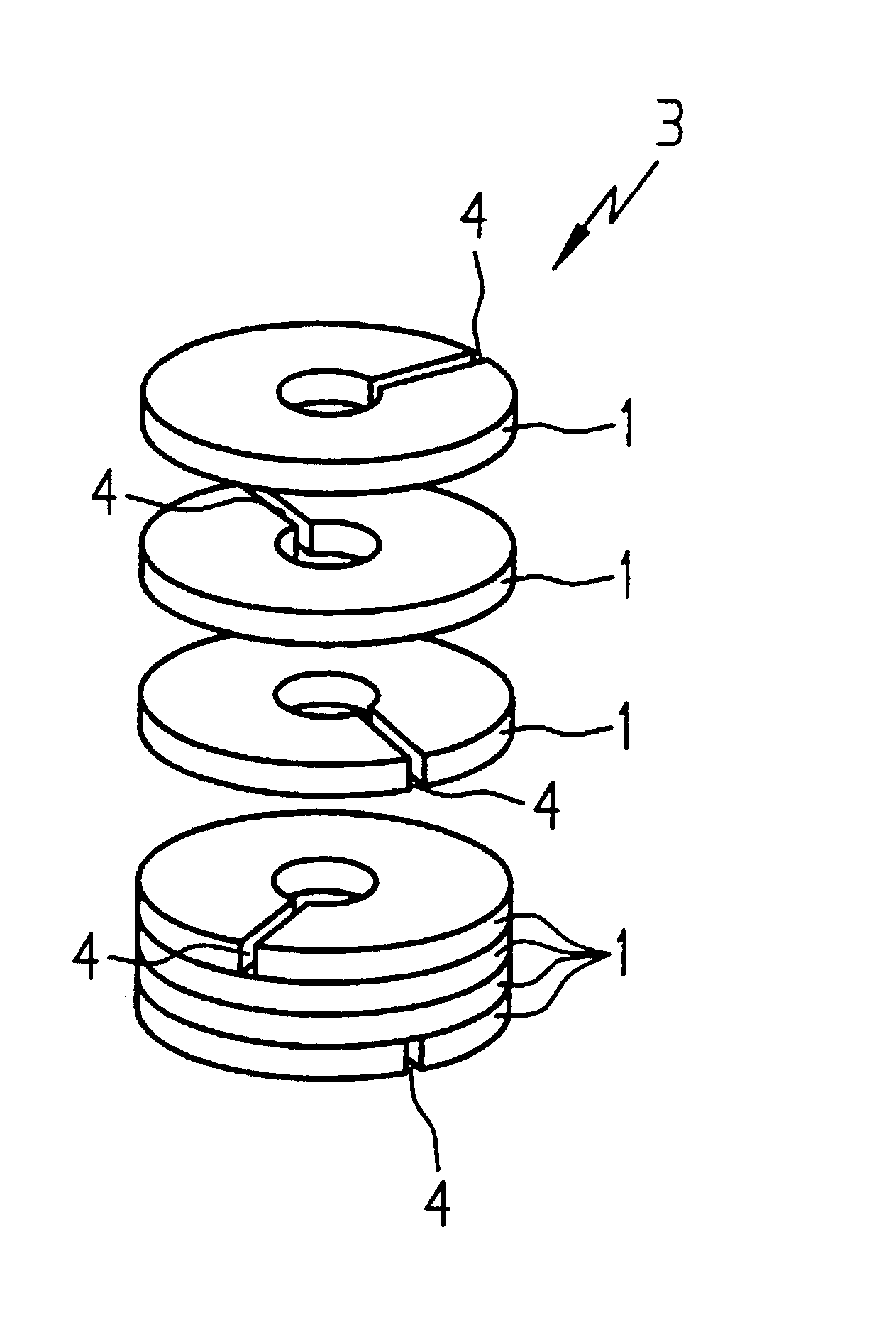
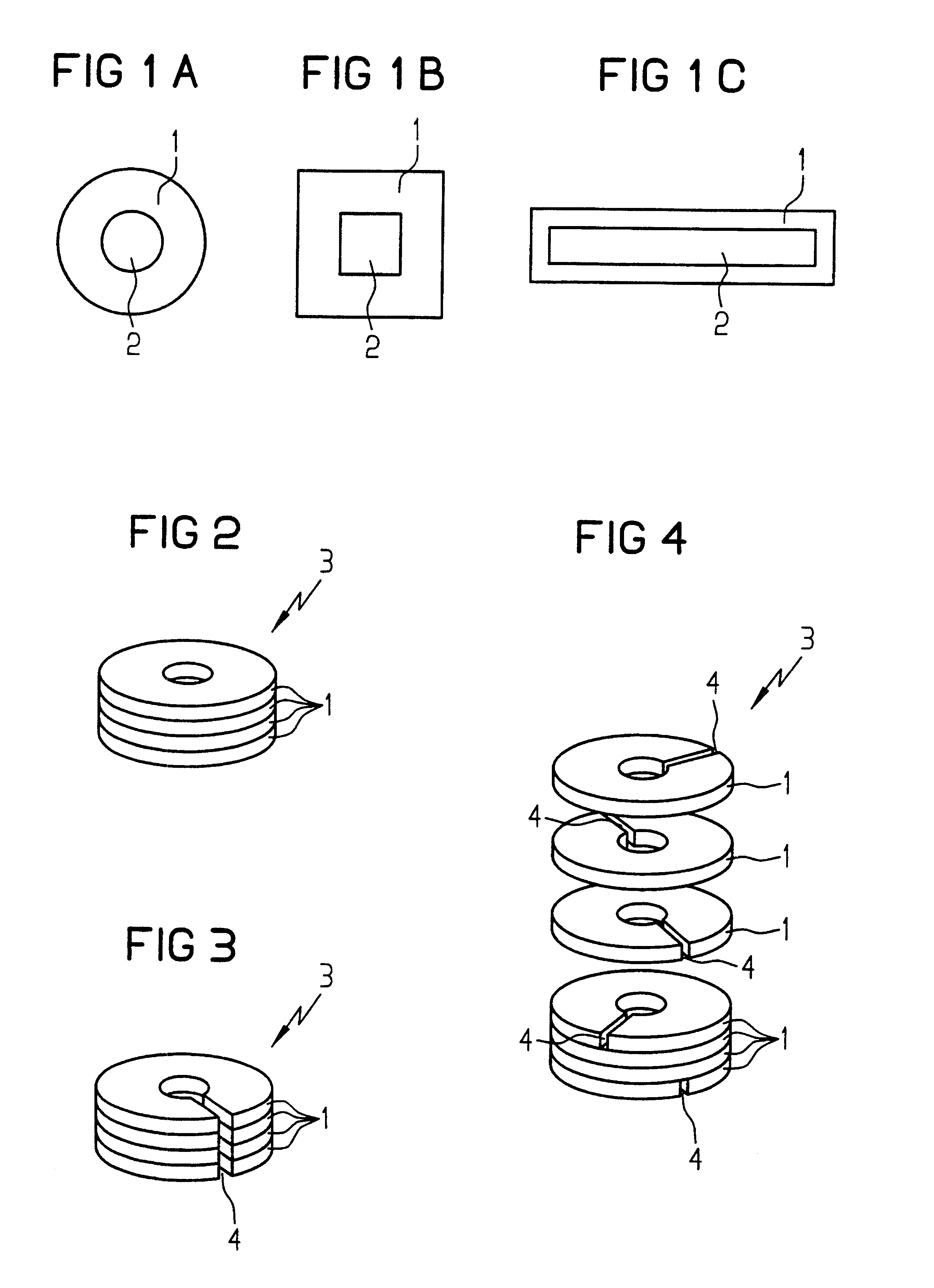
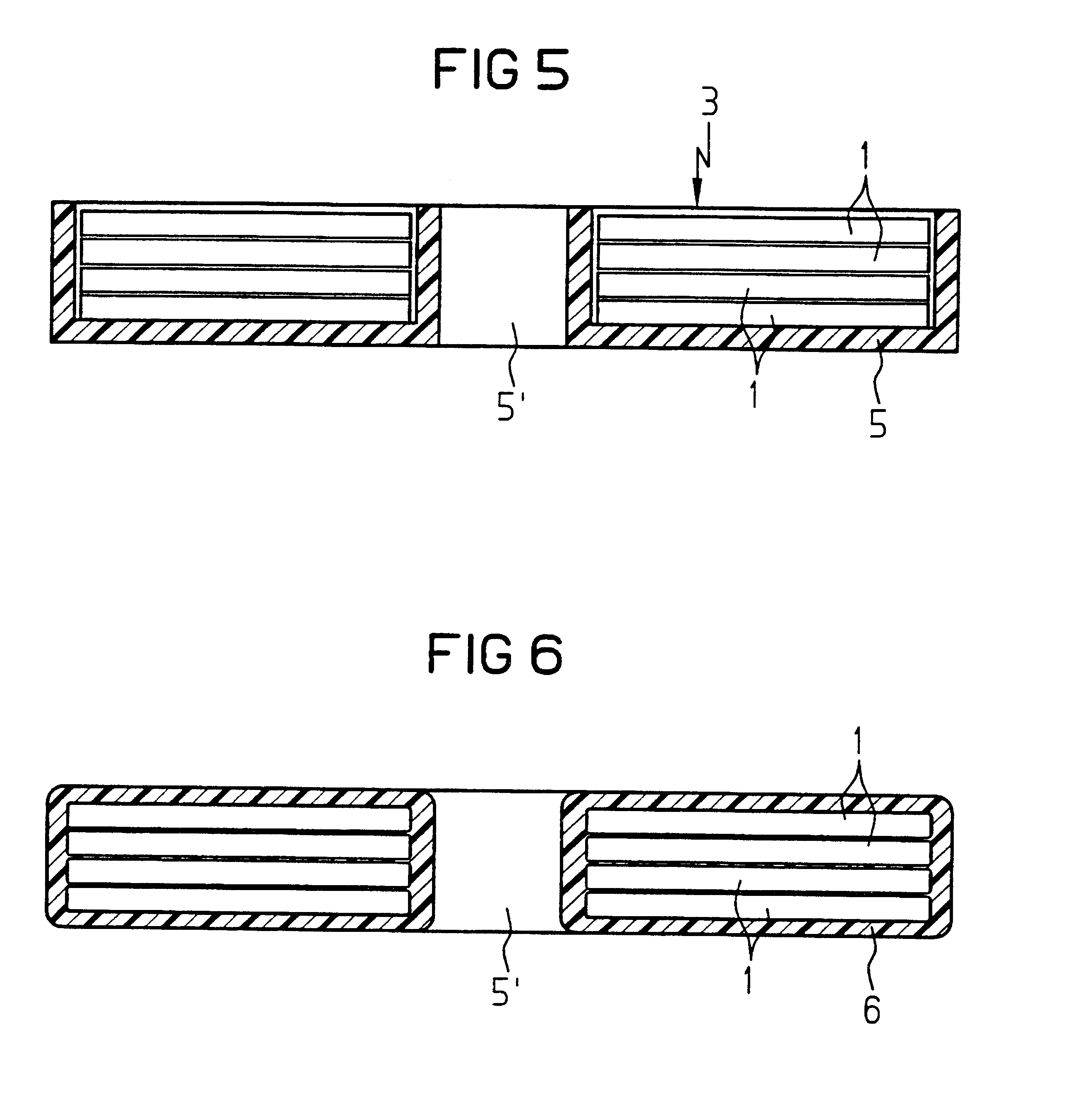
InactiveUS6580348B1Transformers/inductances casingsInorganic material magnetismSkin penetrationSurface roughness
A toroidal tape core is produced from magnetic sheets (1) which may have slits (4). In order to improve the behavior of the toroidal cores (3) at high frequencies, the magnetic sheets (1) have a high surface roughness. The surface roughness of each magnetic sheet (1) is at least equal to the skin penetration depth at the frequency being used.
Owner:VACUUMSCHMELZE GMBH & CO KG
Penetrating pharmaceutical foam
The invention relates to an alcohol-free cosmetic or pharmaceutical foam carrier comprising water, a hydrophobic solvent, a surface-active agent and a gelling agent. The foam carrier further comprises active agents and excipients with therapeutic properties having enhanced skin penetration.
Owner:FOAMIX LTD
Body fluid sampling device—sampling site interface
ActiveUS9833183B2Raise the possibilityReduce decreaseIntravenous devicesTemperature sensorsSkin surfaceSkin penetration
An arrangement for producing a sample of body fluid from a wound opening created in a skin surface at a sampling site includes: a housing, the housing comprising a first opening; a skin interface member disposed in the first opening, the skin interface member comprising an inner member having a second opening, and an outer member at least partially surrounding the inner member and attached to the first opening; and at least one skin-penetration member configured and arranged to project within the second opening. Arrangements having alternatively constructed skin interface members are also described.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Compound clobetasol propionate liposome and preparation thereof
ActiveCN102429913AEasy to storeIncrease resistanceHydroxy compound active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryLipid formationDisease
The invention provides a compound clobetasol propionate liposome and a preparation thereof, which are mainly used for treating diseases such as psoriasis vulgaris, dermatitis, eczema and the like. The liposome prepared from neutral synthetic phospholipids, lipids with positive charges, and cholesterol can coat clobetasol propionate and vitamin A acid simultaneously, and is added with a cream substrate or gel substrate to be prepared into compound clobetasol propionate liposome cream or gel. Compared with the common cream, the liposome preparation has the advantages that: the amount of the medicine retained in skin is larger, the skin penetration rate is lower, the content of the medicine in local skin can be improved, the treatment index is improved, and transdermal absorption dose is reduced, so that the toxic and side effects of the medicine are reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU SEMPOLL PHARMA
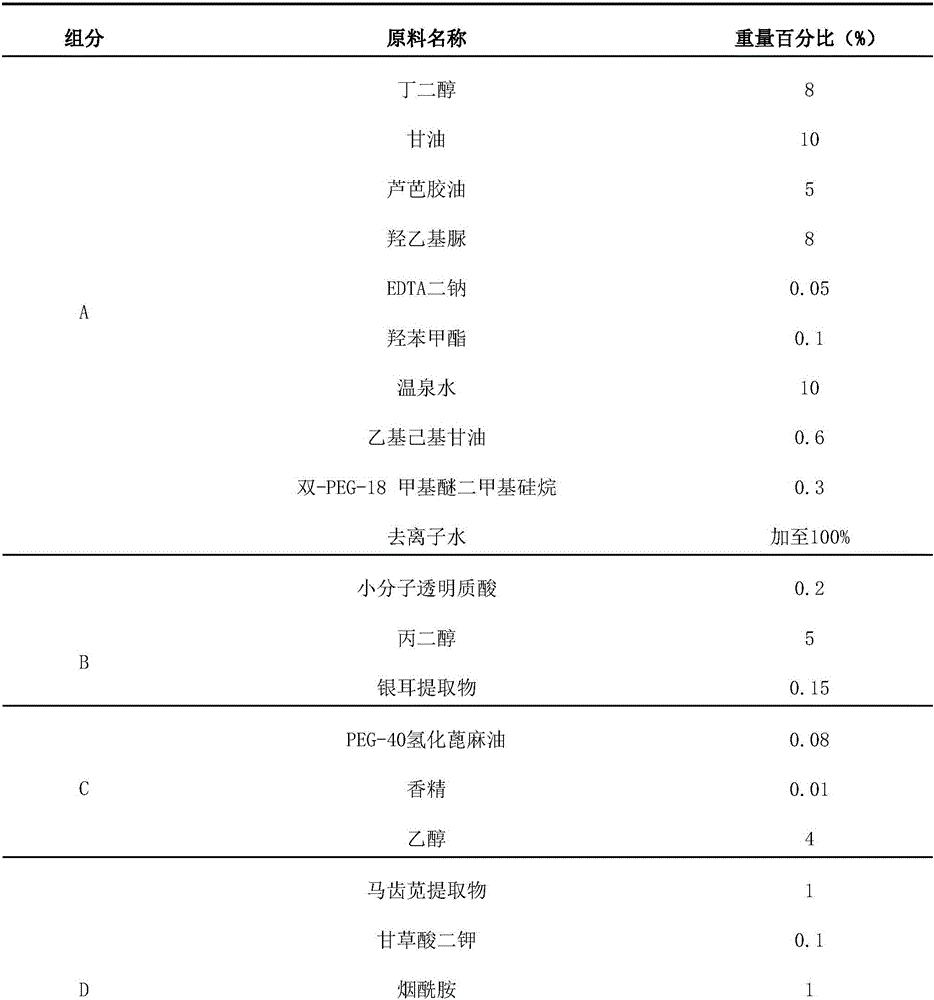
Moistening and moisturizing essence and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105943491AHigh densityReduce penetrationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin penetrationPreservative
The invention relates to a moistening and moisturizing essence, which is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: a component A: 20.1 to 31.3 percent of a moisturizer, 5 to 10 percent of thermal spring water and 0.48 to 0.7 percent of a preservative; a component B: 3.2 to 5.35 percent of a moistening agent; a component C: 0.08 percent of a solubilizer and 2 to 4 percent of an odor remover; a component D: 2.51 to 6.02 percent of a skin conditioning agent and 3.05 to 5.1 percent of a skin penetration promoter. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the moistening and moisturizing essence. The moistening and moisturizing essence is mild and nonirritating in component formula and high in skin penetration, and has synergistic effects, rapid and persistent moisturizing and moisture locking effects and the effects of obviously softening skin and delaying senescence, and the skin can be moistened most rapidly and effectively.
Owner:广州市巧美化妆品有限公司
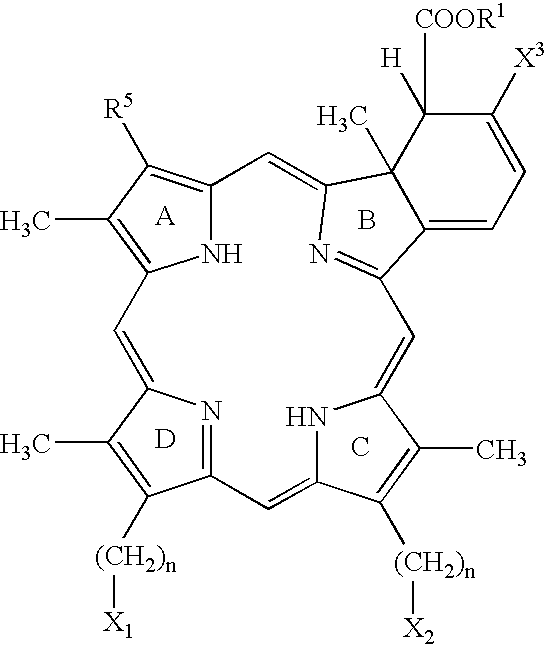
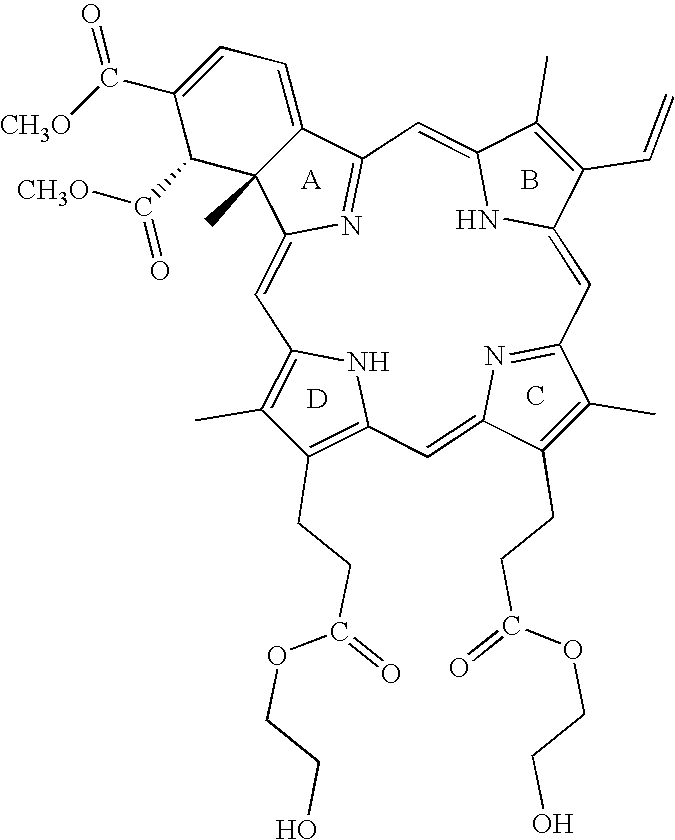
Photodynamic Therapy For The Treatment Of Hyperactive Sebaceous Gland Disorders Using Topically Applied Hydrophobic Green Porphyrins
InactiveUS20080096857A1Small sizeReduced activityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseasePresent method
The present method involves the photodynamic treatment of hyperactive gland disorders. The method involves the topical administration of a photosensitizer composition comprising hydrophobic and / or lipophilic green porphyrins such as lemuteporfin, polyethylene glycol and skin penetration enhancers such as oleyl alcohol and TRANSCUTOL™ to affected skin and subsequent exposure of that skin to energy of a wavelength capable of activating the photosensitizer.
Owner:VALEANT PHARMA INT
Use of penetration enhancers and barrier disruption methods to enhance the immune response of antigen and adjuvant
InactiveUS7378097B2Enhance immunizationEnhance vaccinationSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideAdjuvantWhole body
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
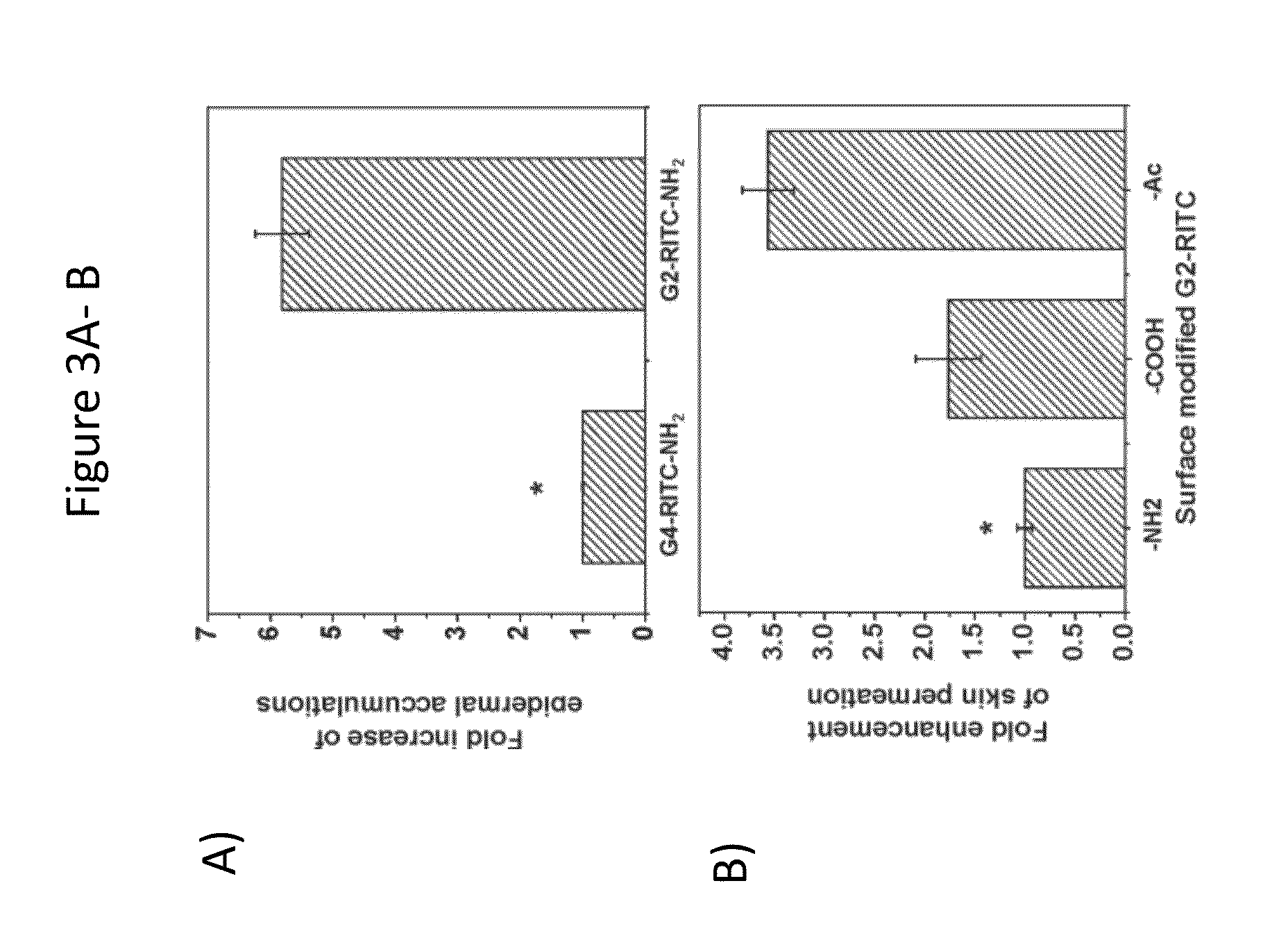
Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutic Agents Using Poly (Amidoamine) Dendrimers
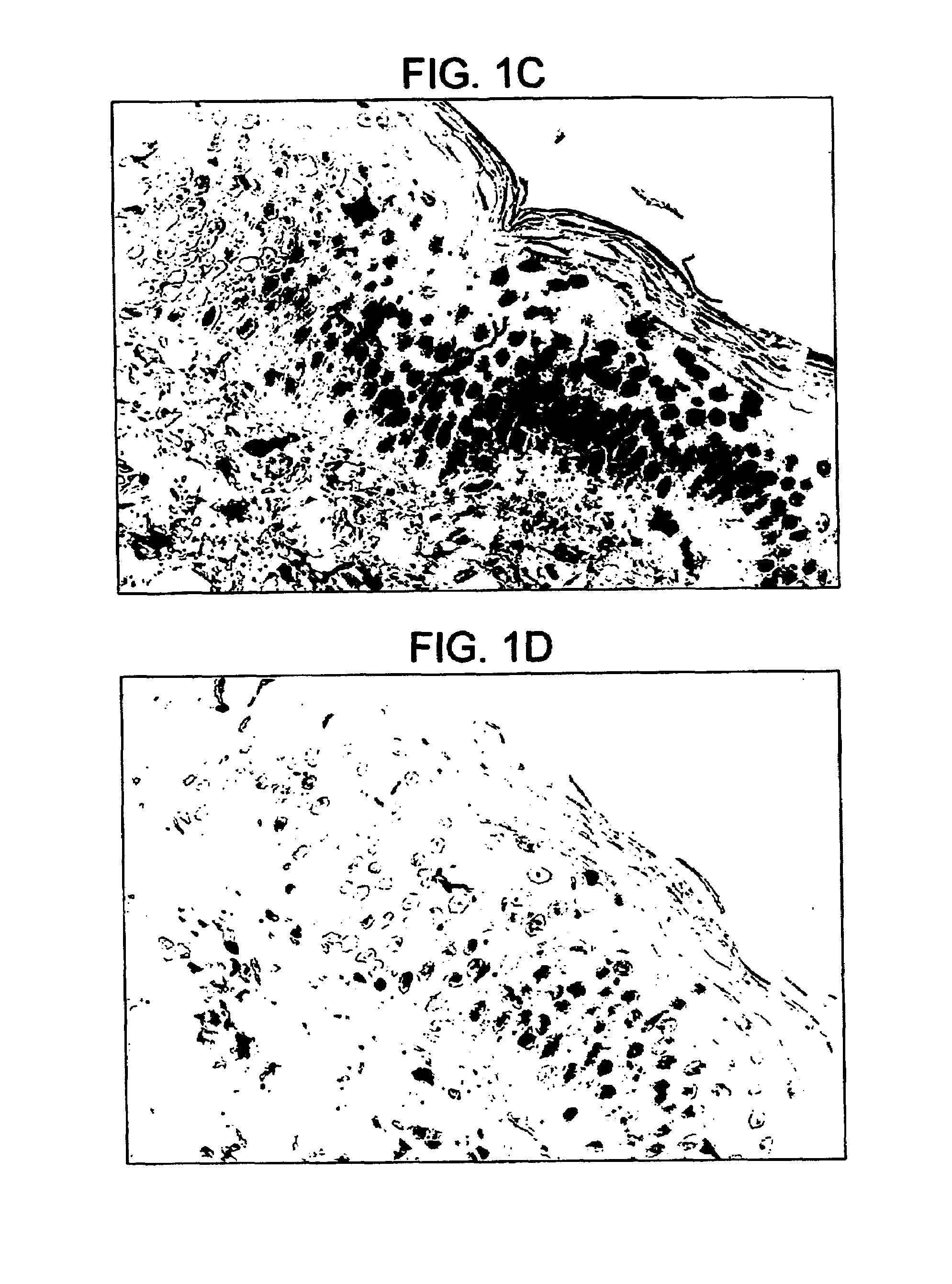
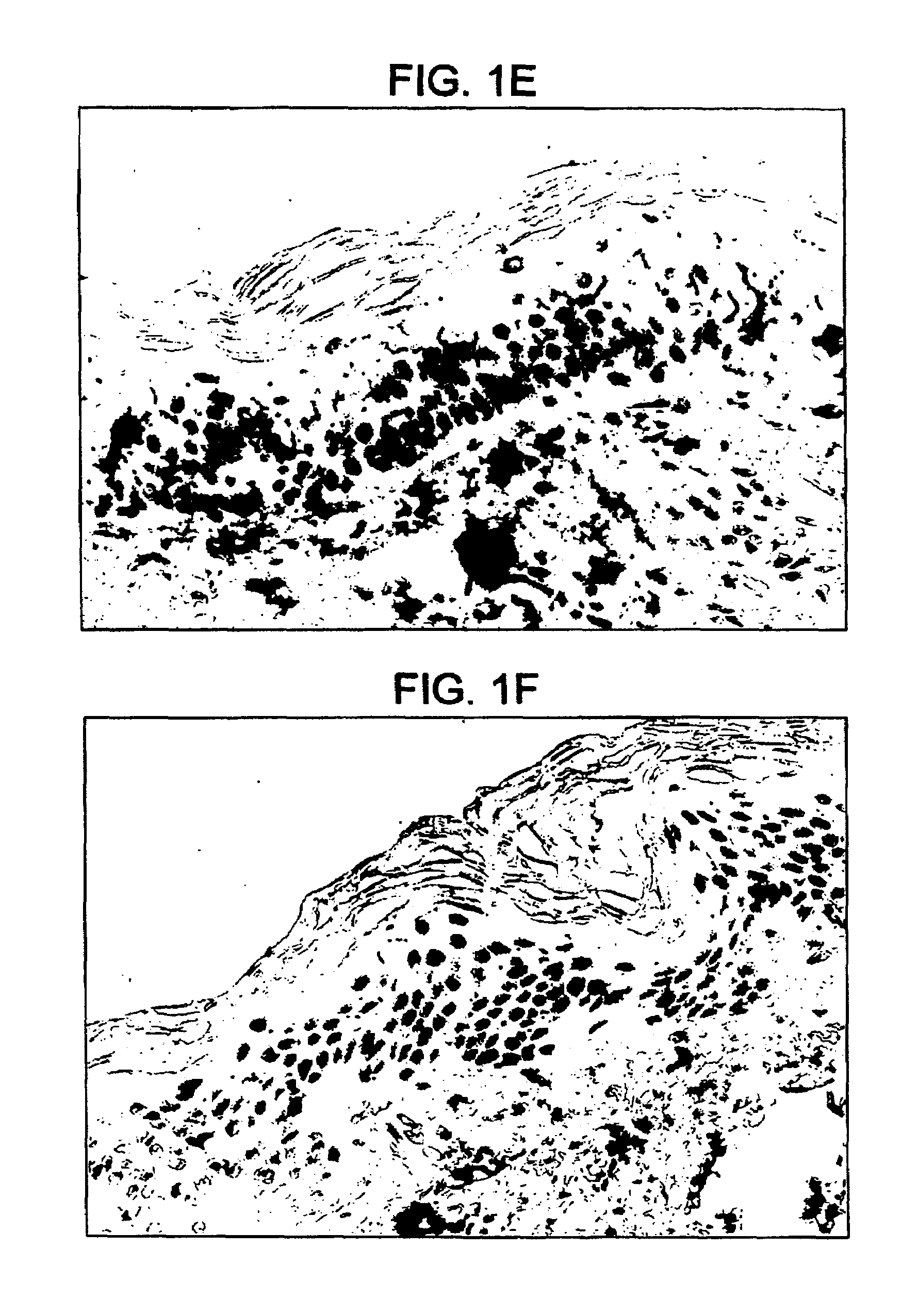
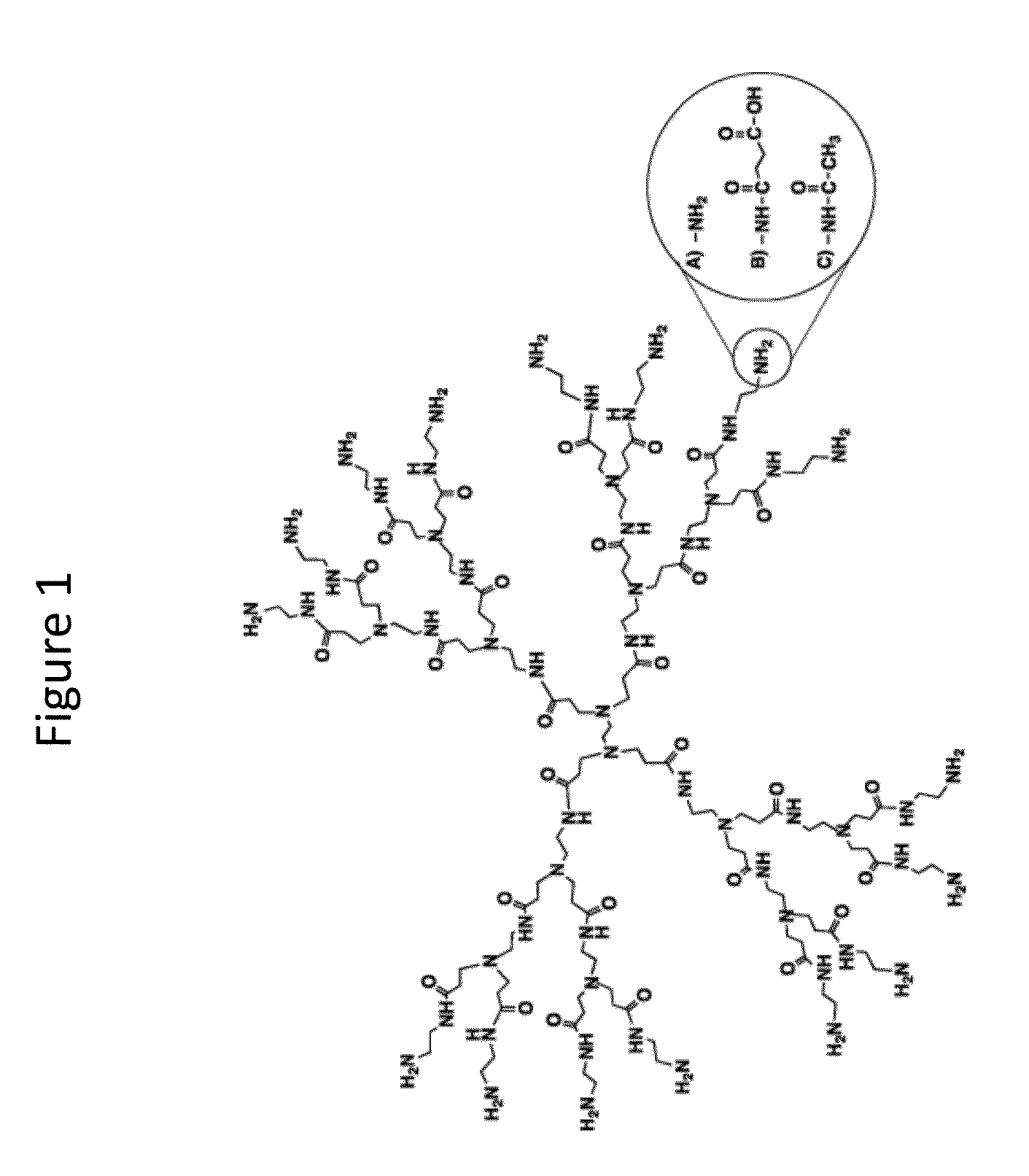
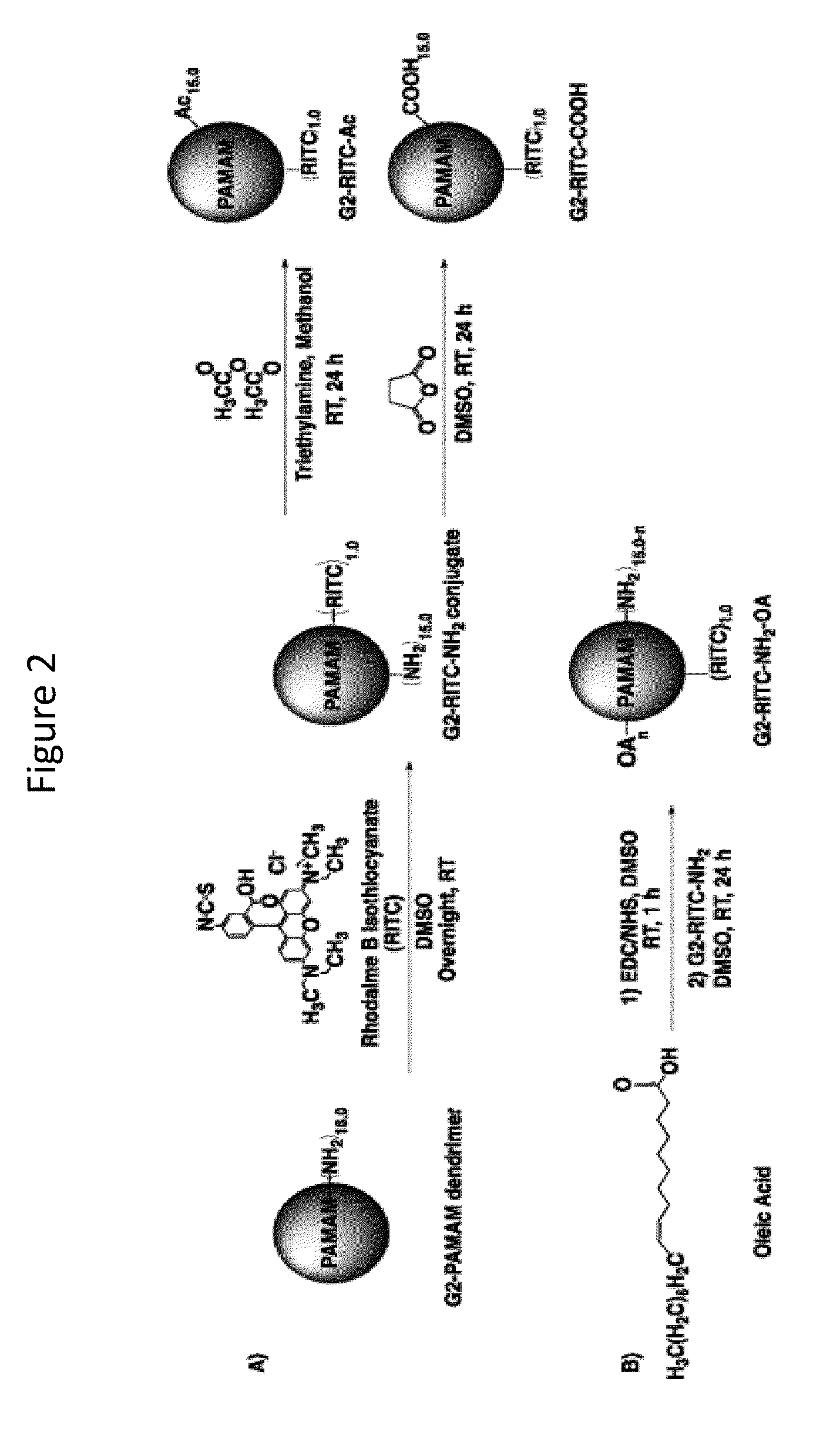
InactiveUS20140018435A1Adverse effect of therapeuticGood skin permeabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAnticarcinogenSkin penetration
The invention provides for compositions for transdermal delivery of a therapeutic agent associated with a surface modified poly(amidoamine) PAMAM dendrimer, wherein the surface modified dendrimer increased skin penetration of the therapeutic agent. The invention particularly provides for compositions and methods for transdermal delivery of anticancer and chemo-preventive agents.
Owner:HONG SEUNGPYO +4
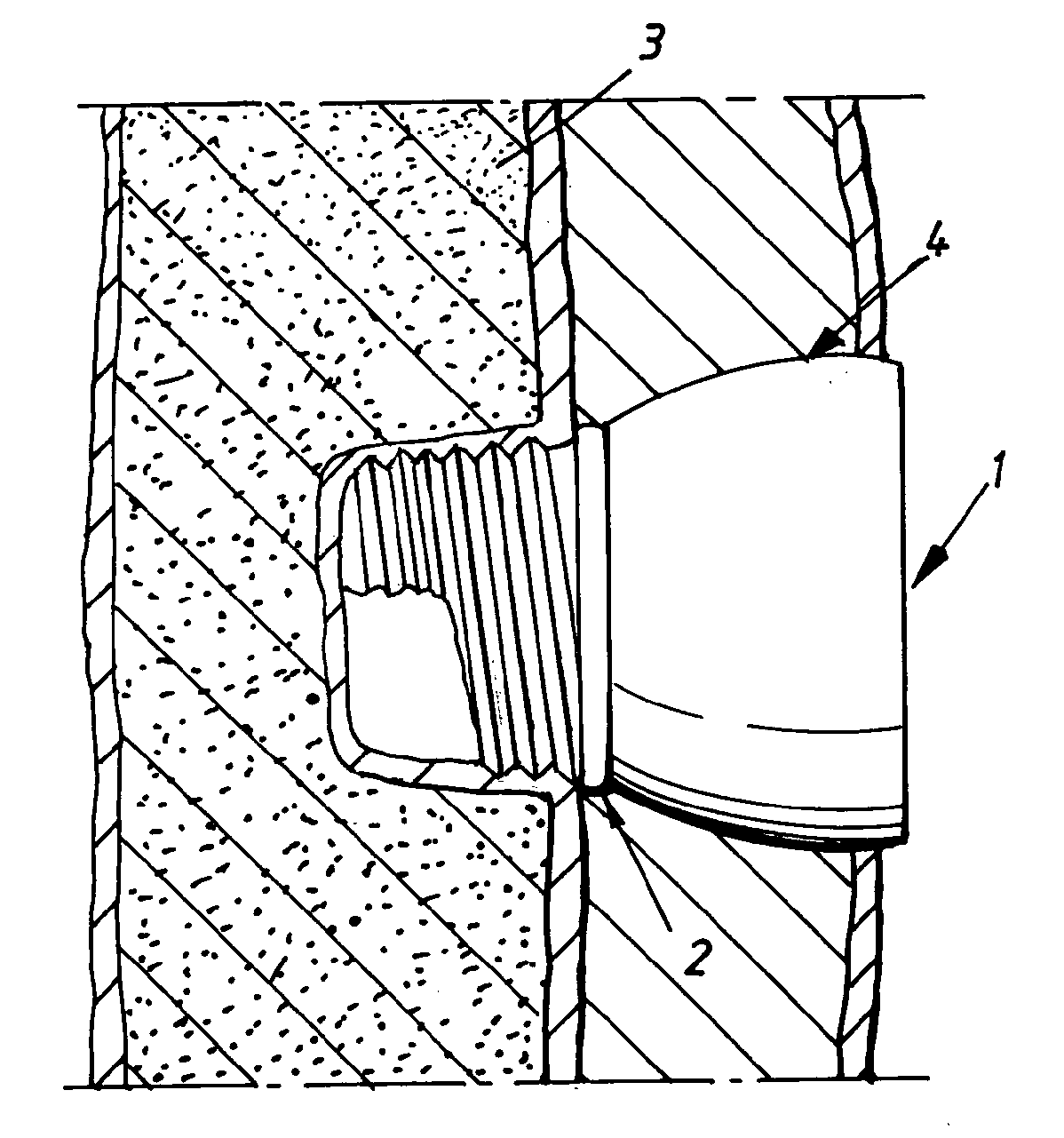
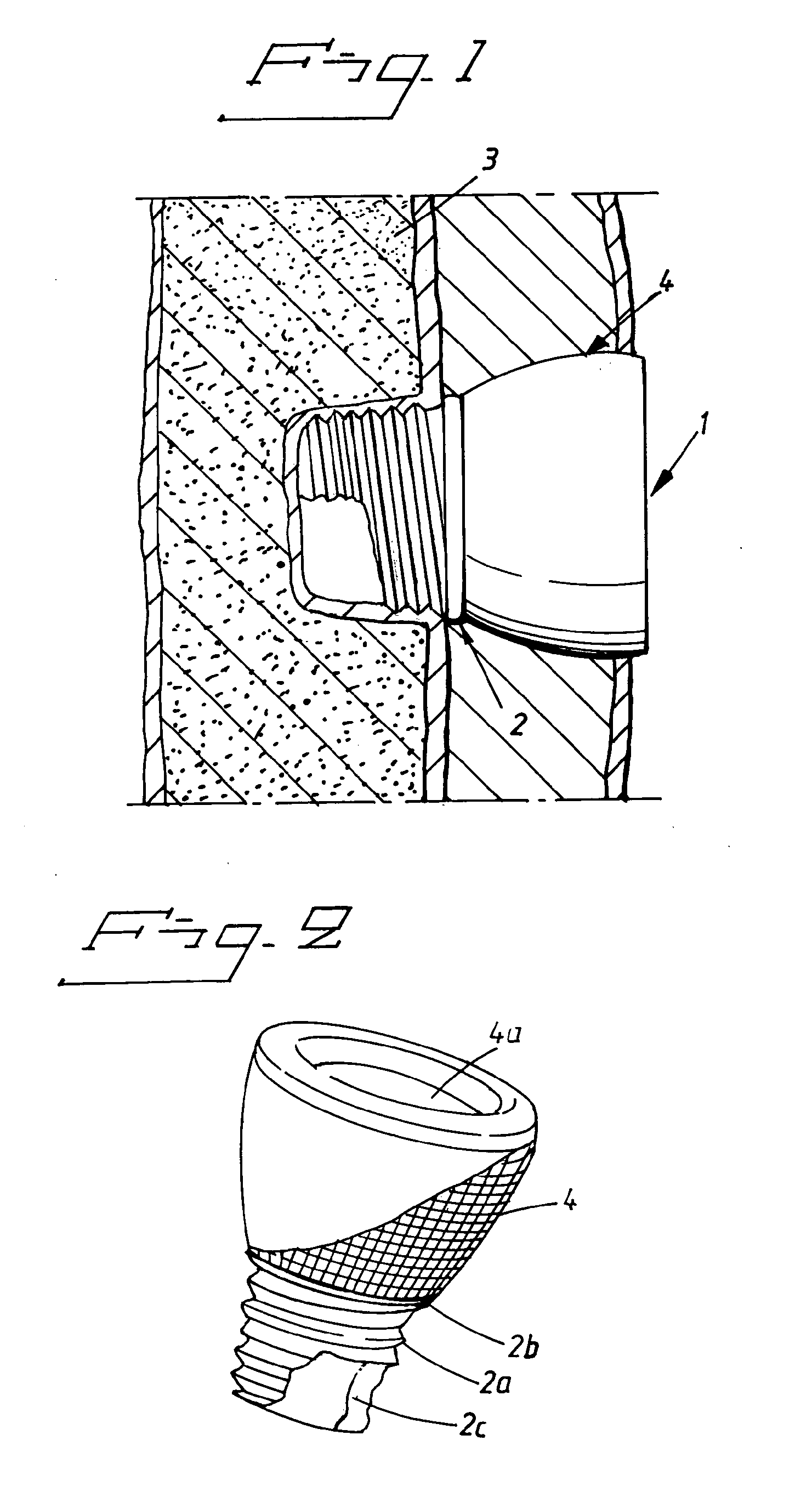
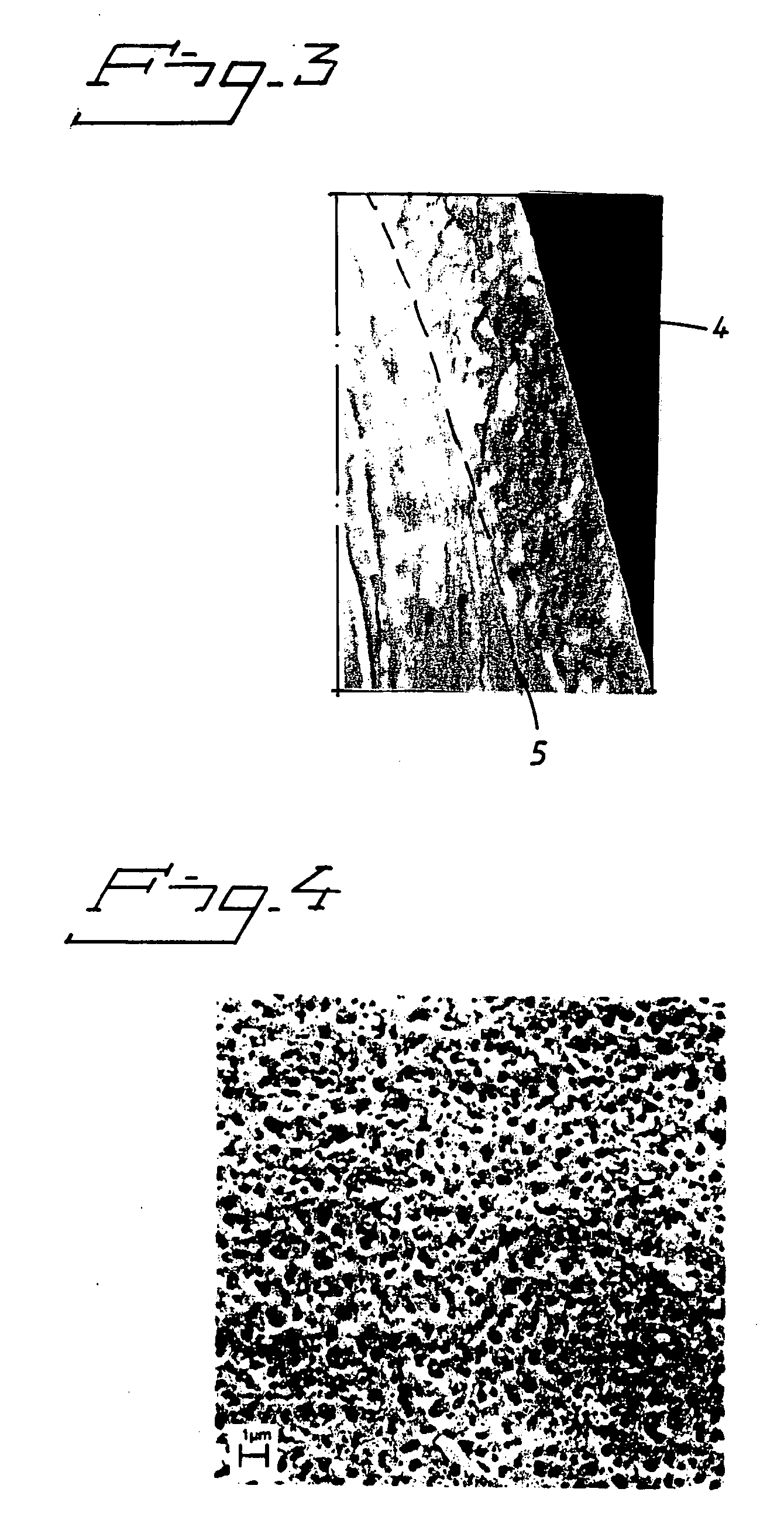
Implant abutment
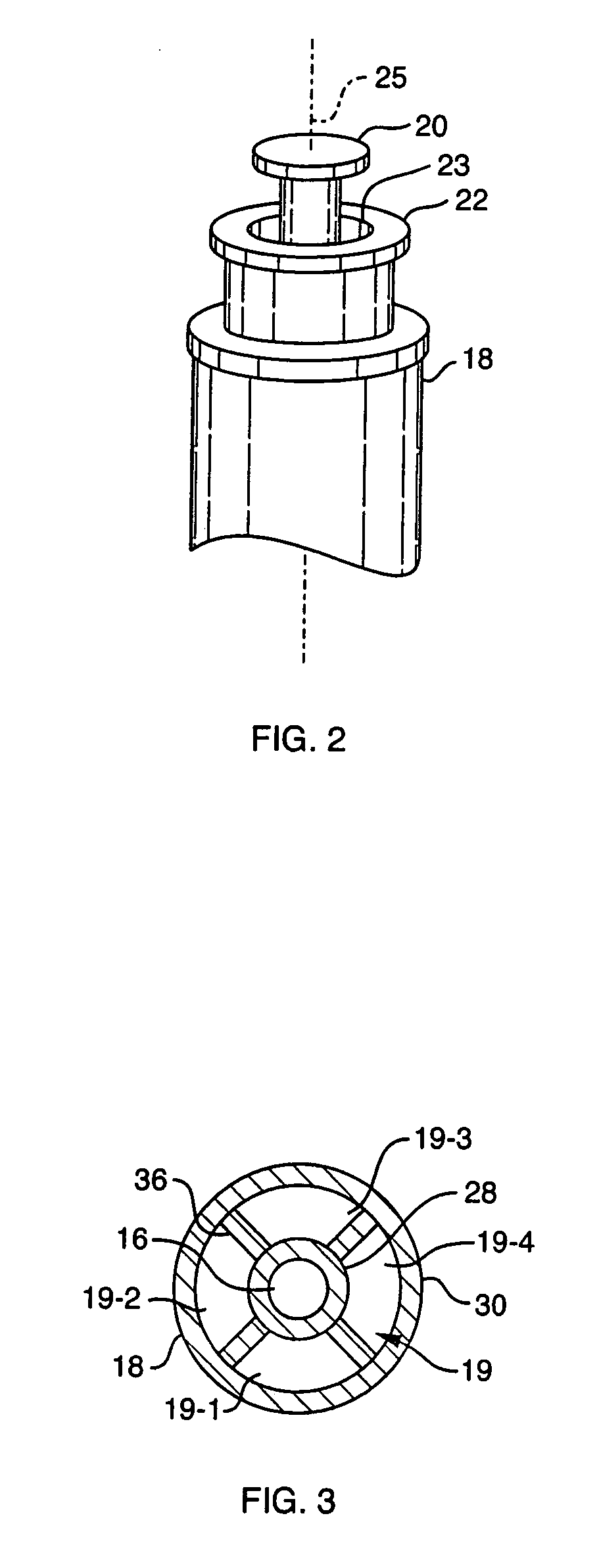
InactiveUS20100249784A1Ear treatmentBone conduction transducer hearing devicesBone-anchored hearing aidSkin contact
The present invention relates to a percutaneous implant abutment for bone anchored implant devices adapted to be anchored in the craniofacial region of a person, such as bone anchored hearing aids. The abutment comprises a skin penetration body having a skin contacting surface. The skin contacting surface has been modified.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com