Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
426results about How to "Sufficient effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
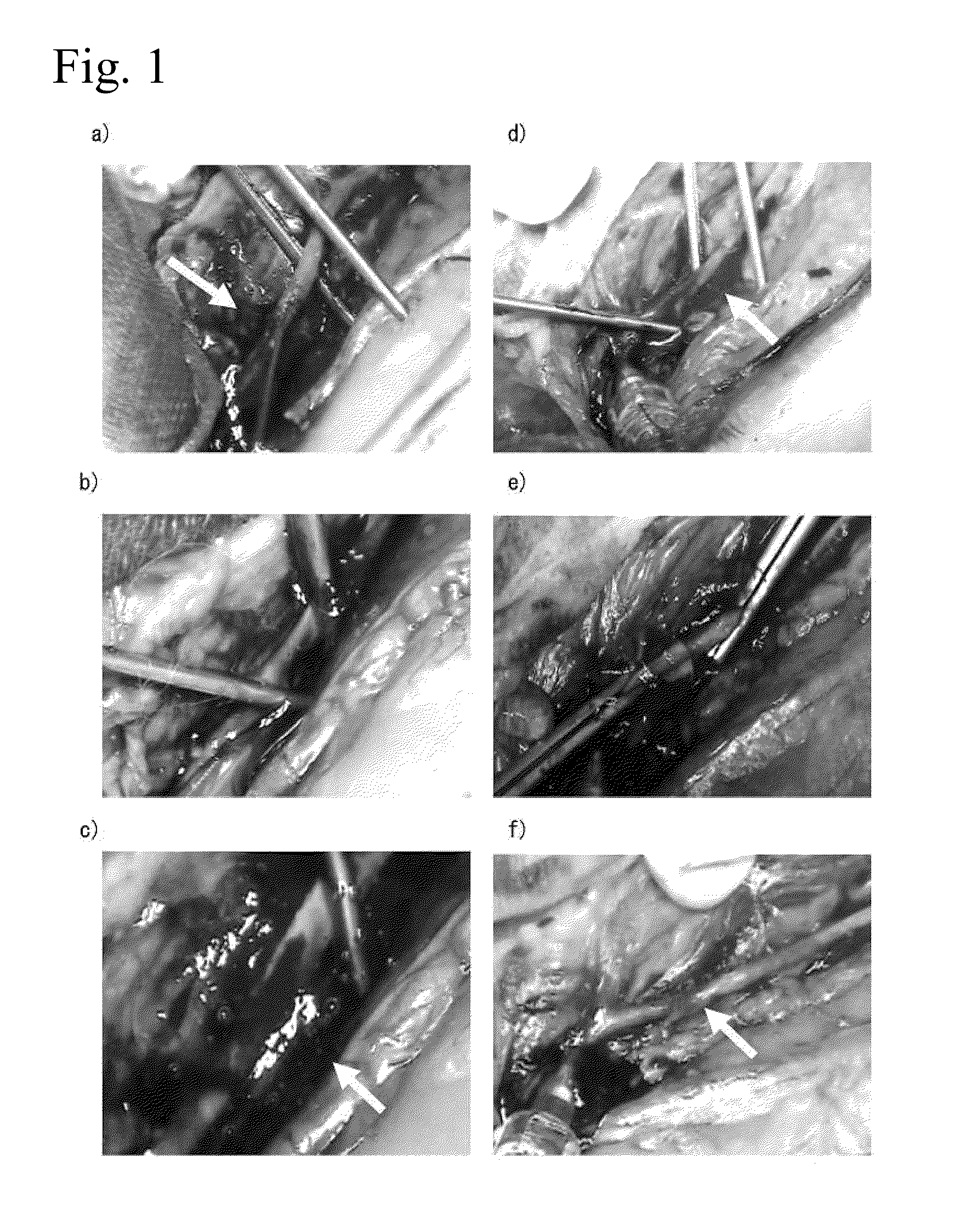
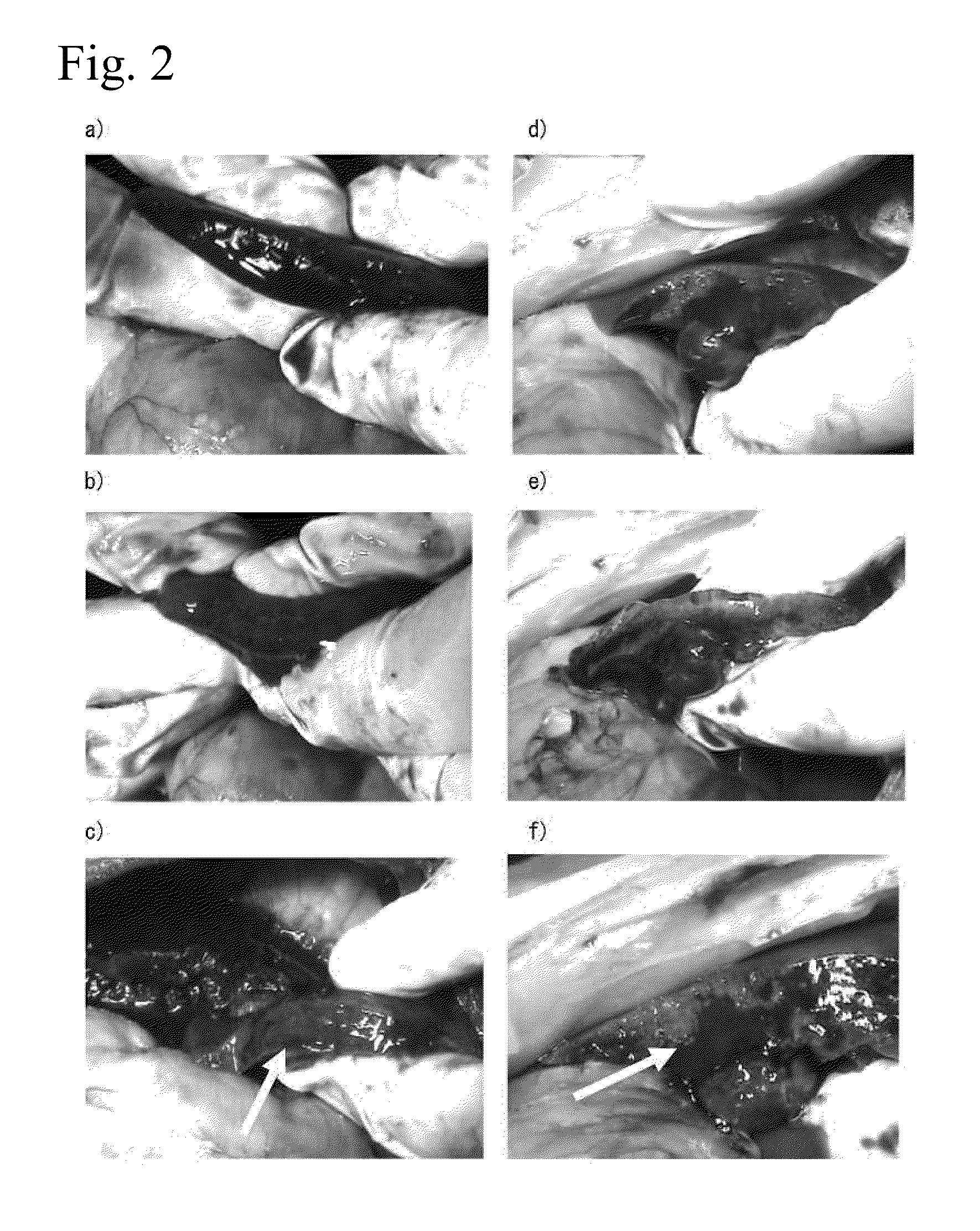
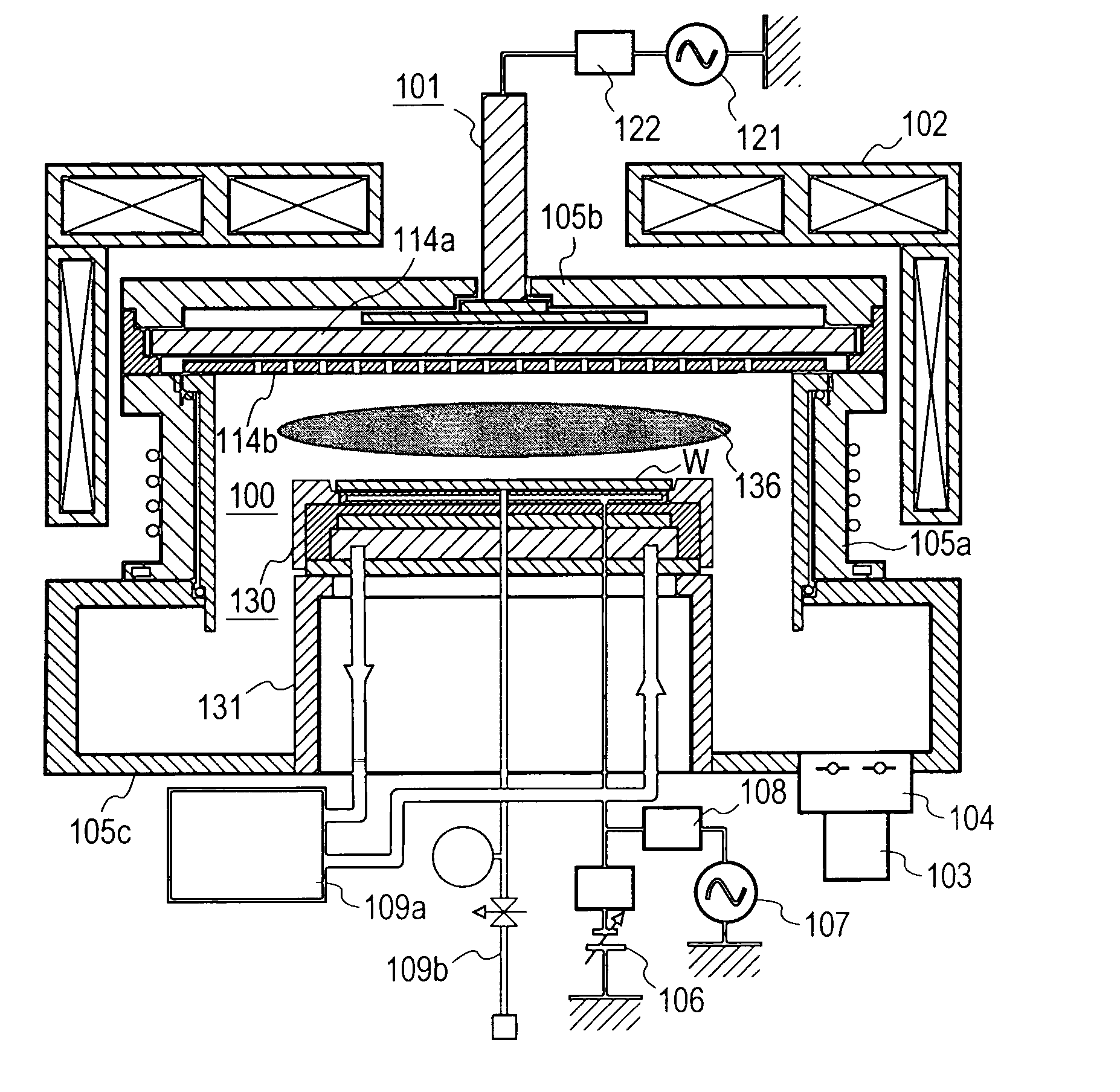
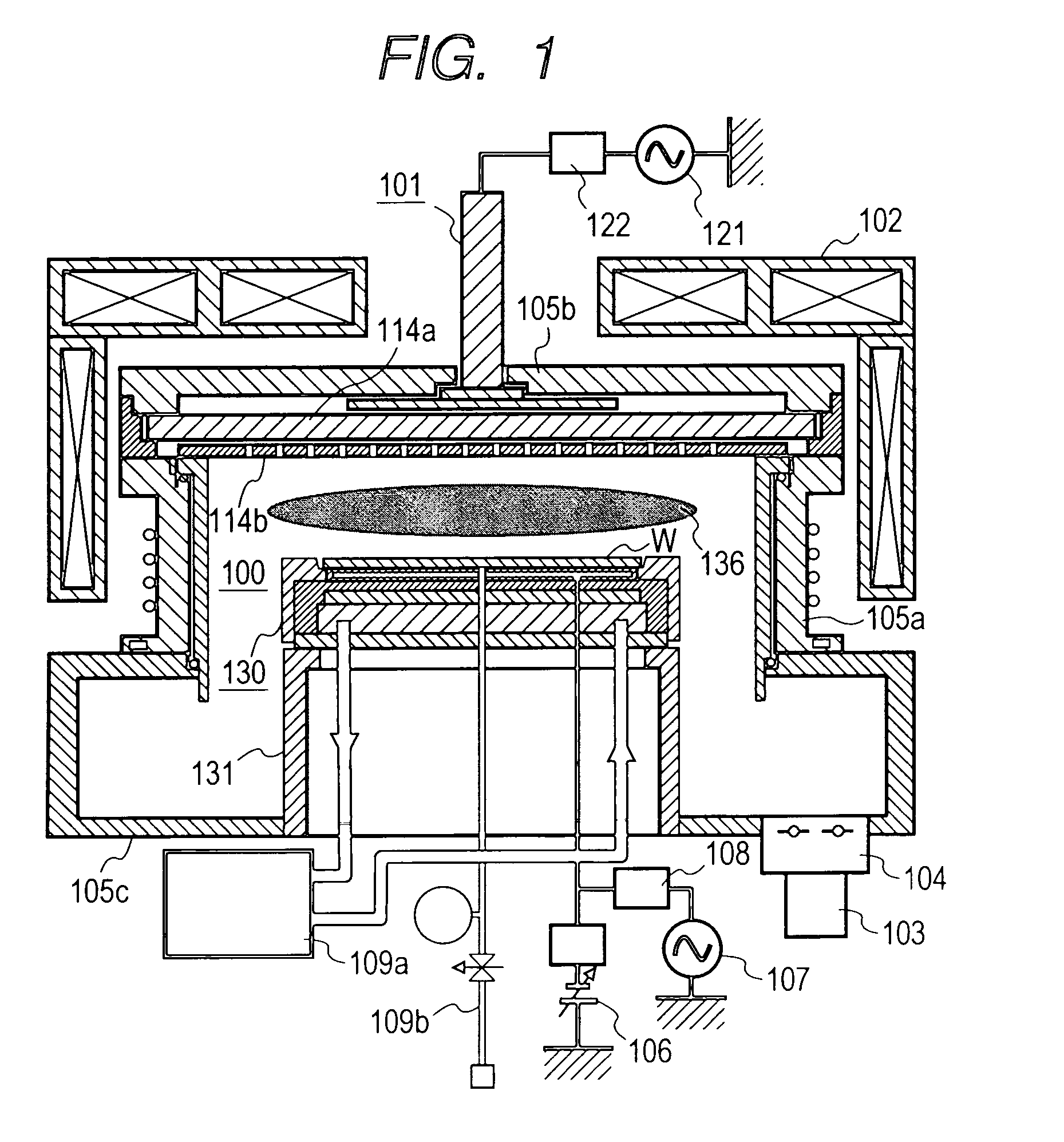
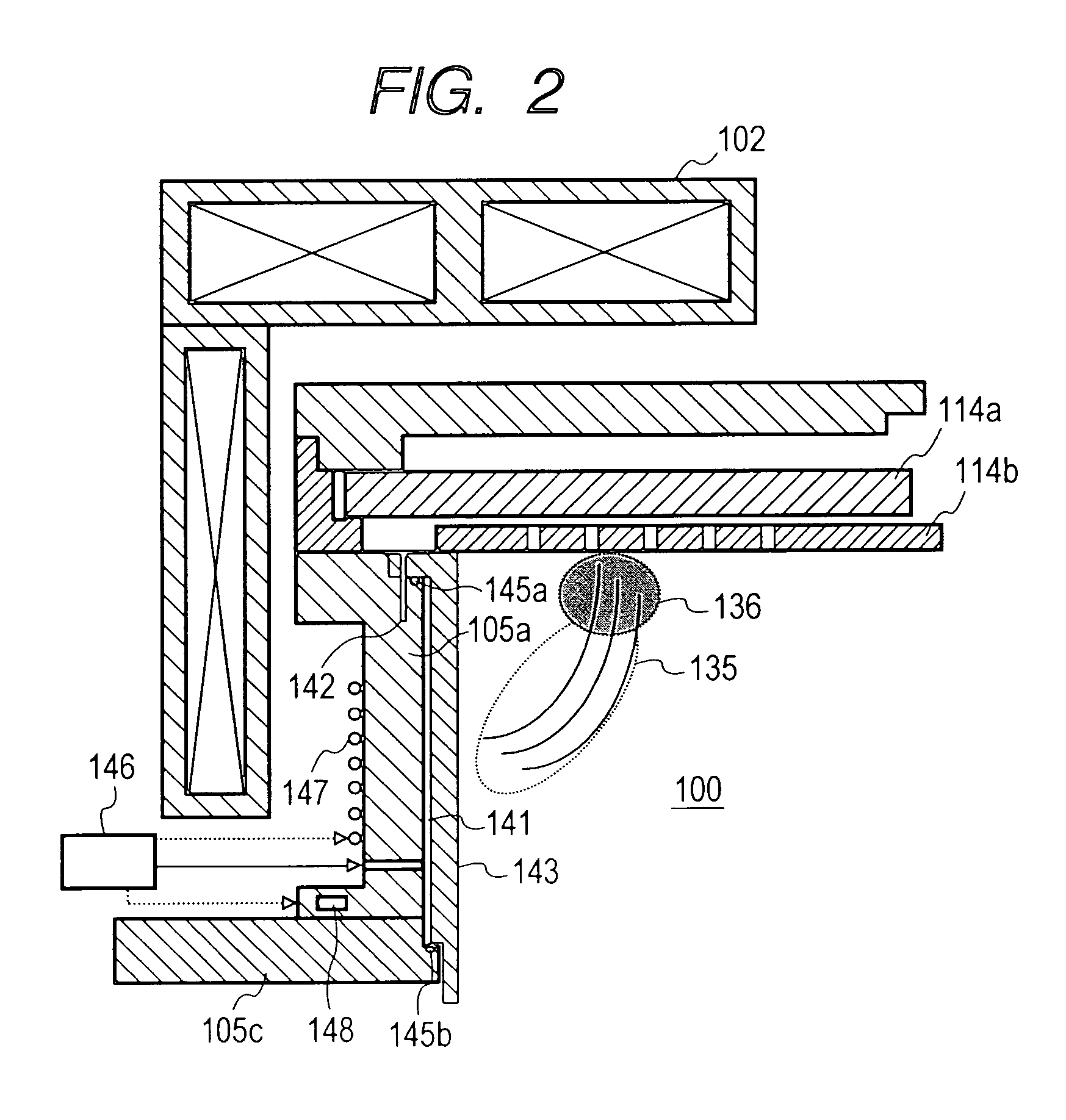
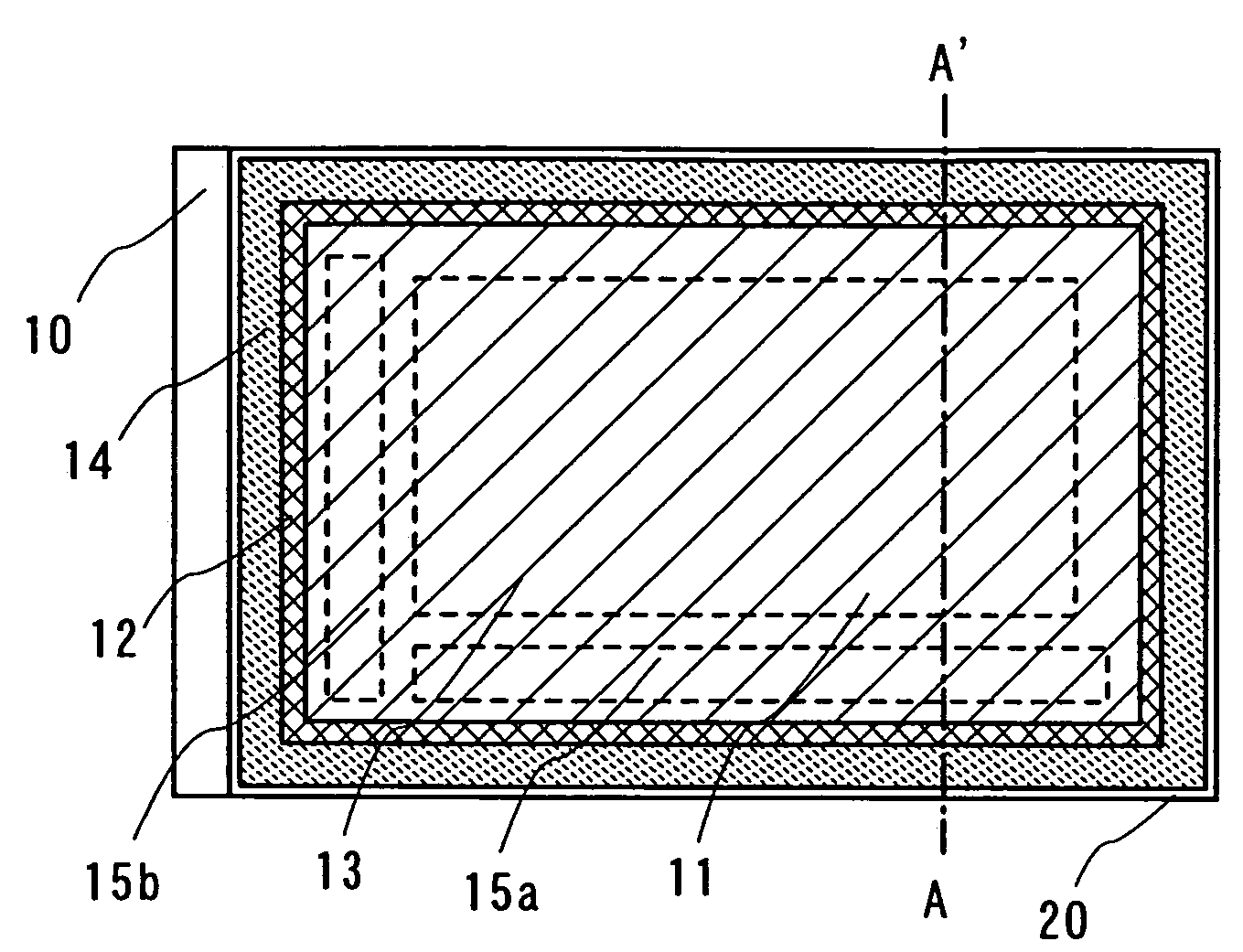
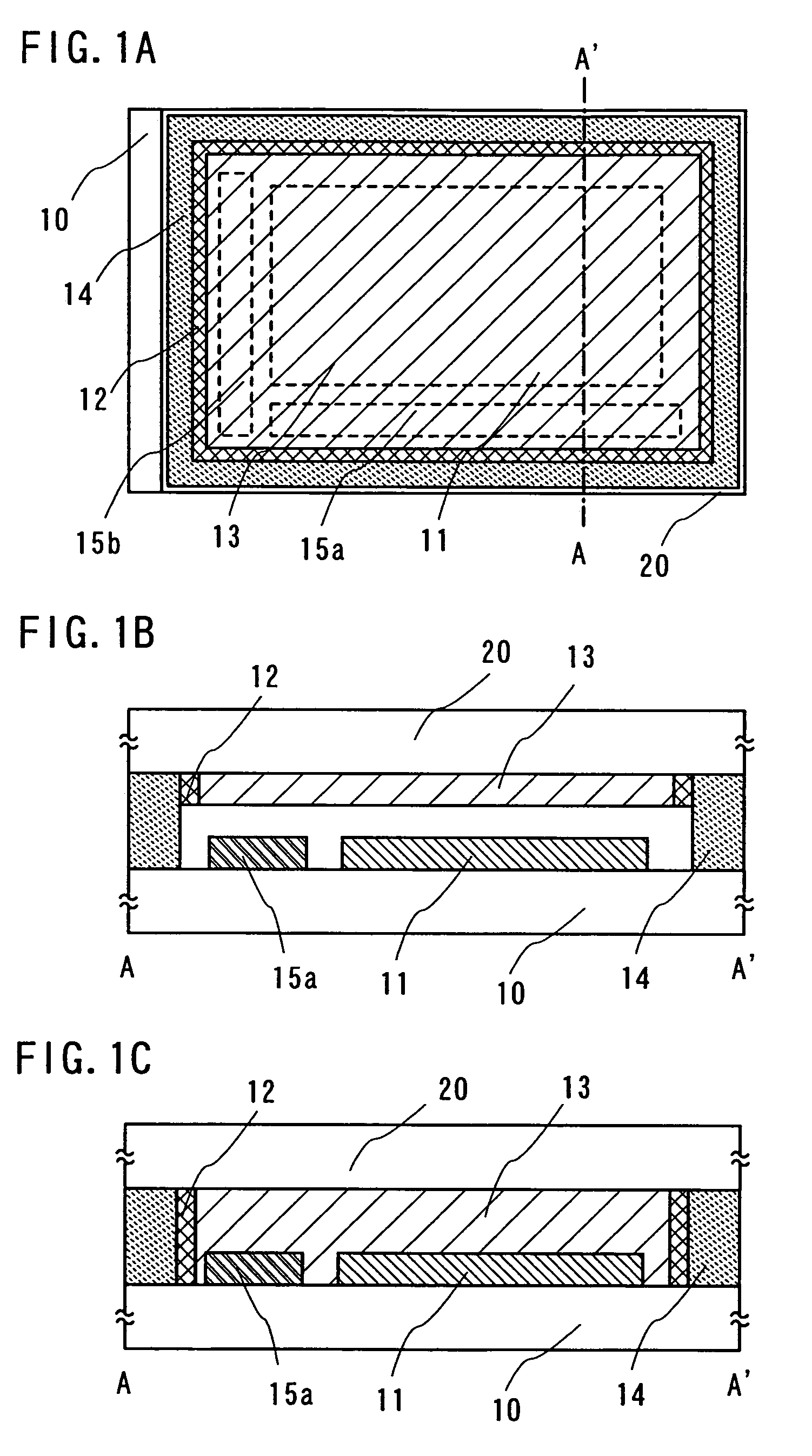
Plasma etching apparatus and method for forming inner wall of plasma processing chamber
InactiveUS20070215278A1Reduce corrosionDecreasing amountElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateHeat resistance
A plasma etching apparatus is provided which can prevent corrosion of an aluminum substrate constituting an etching processing chamber or an inside component thereof, thereby avoiding a reduction in productivity due to scattering of a sprayed coating. In the plasma etching apparatus, an anodic oxide film is disposed between a ceramic sprayed coating with excellent resistance to plasma, and the etching processing chamber and the inside component thereof made of aluminum alloy. The anodic oxide film has a thickness of 5 μm or less to have heat resistance.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
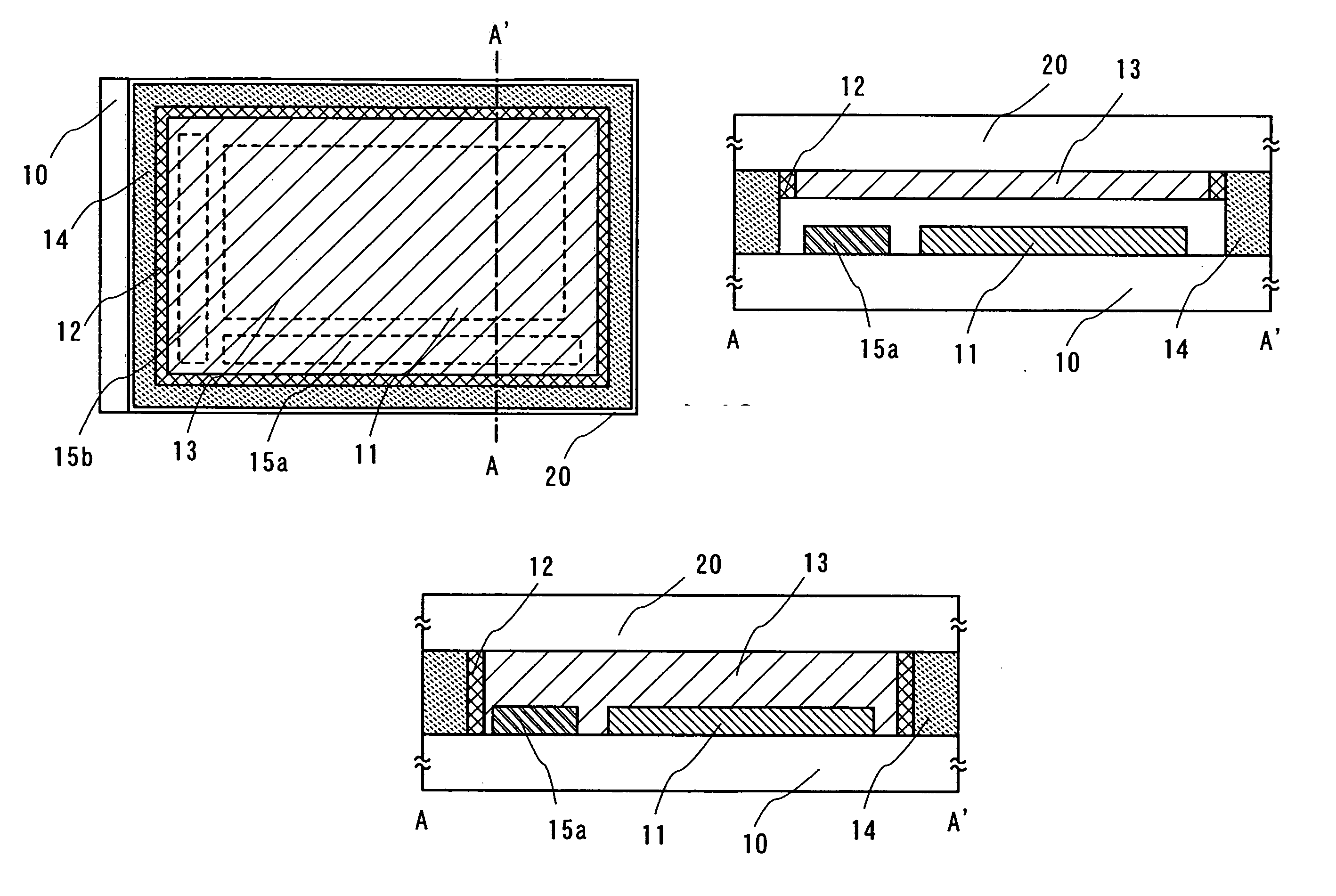
Display device and method for manufacturing display device
InactiveUS20050140265A1Inhibit deteriorationImprove reliabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceSealant
An object of the present invention is to provide a highly reliable display device and a method for manufacturing the display device with a much easy way. According to one aspect of a method for manufacturing a display device of the invention, it comprises the steps of forming a light-emitting element over a first substrate; forming a frame to surround the light-emitting element; dropping a composition containing a liquid hygroscopic substance in a region surrounded with the frame; and forming a layer containing a hygroscopic substance by solidifying the composition, wherein the first substrate and a second substrate are adhered to each other with a sealant so that the light-emitting element, the layer containing a hygroscopic substance, and the frame are sealed between the pair of substrates.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
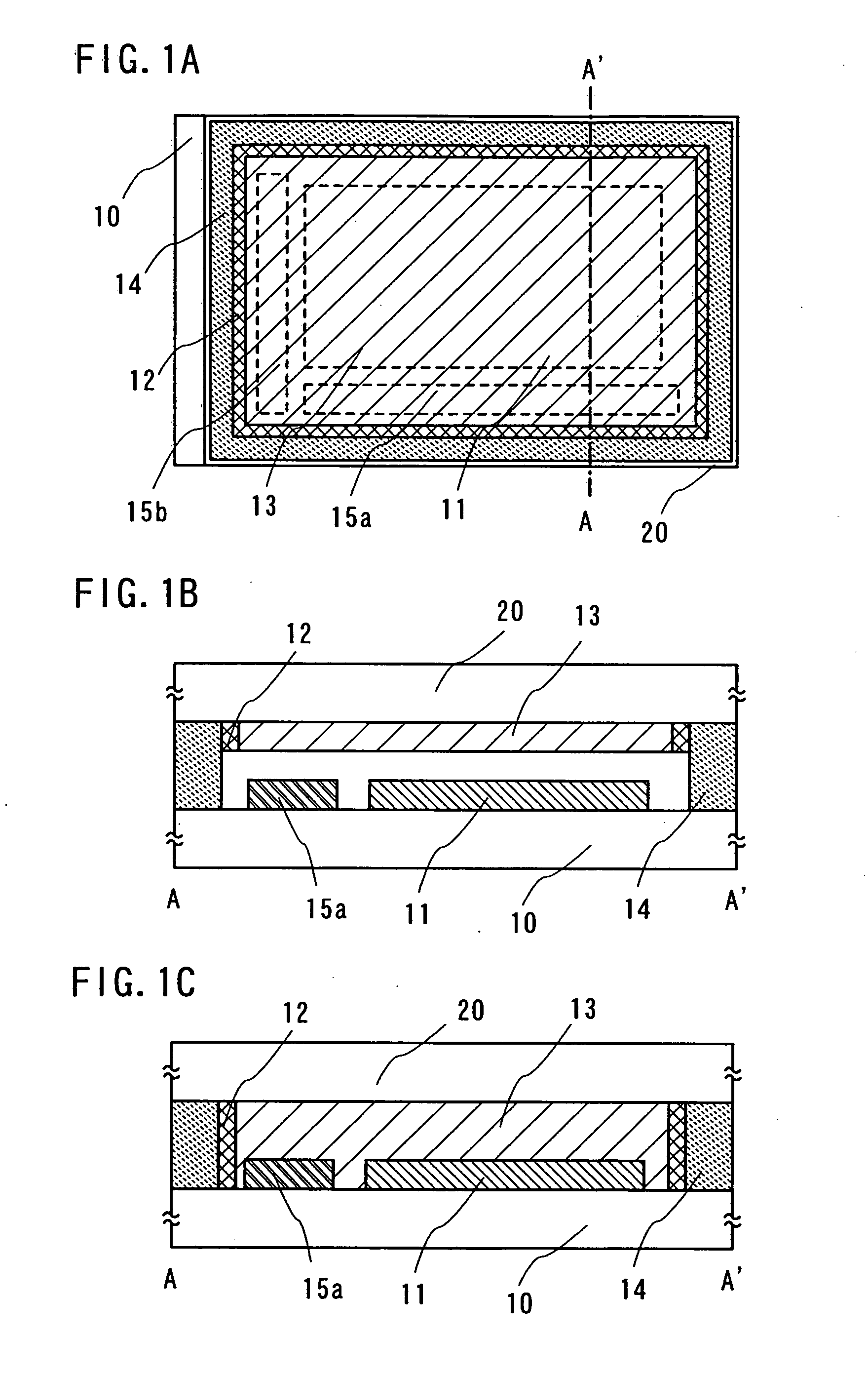
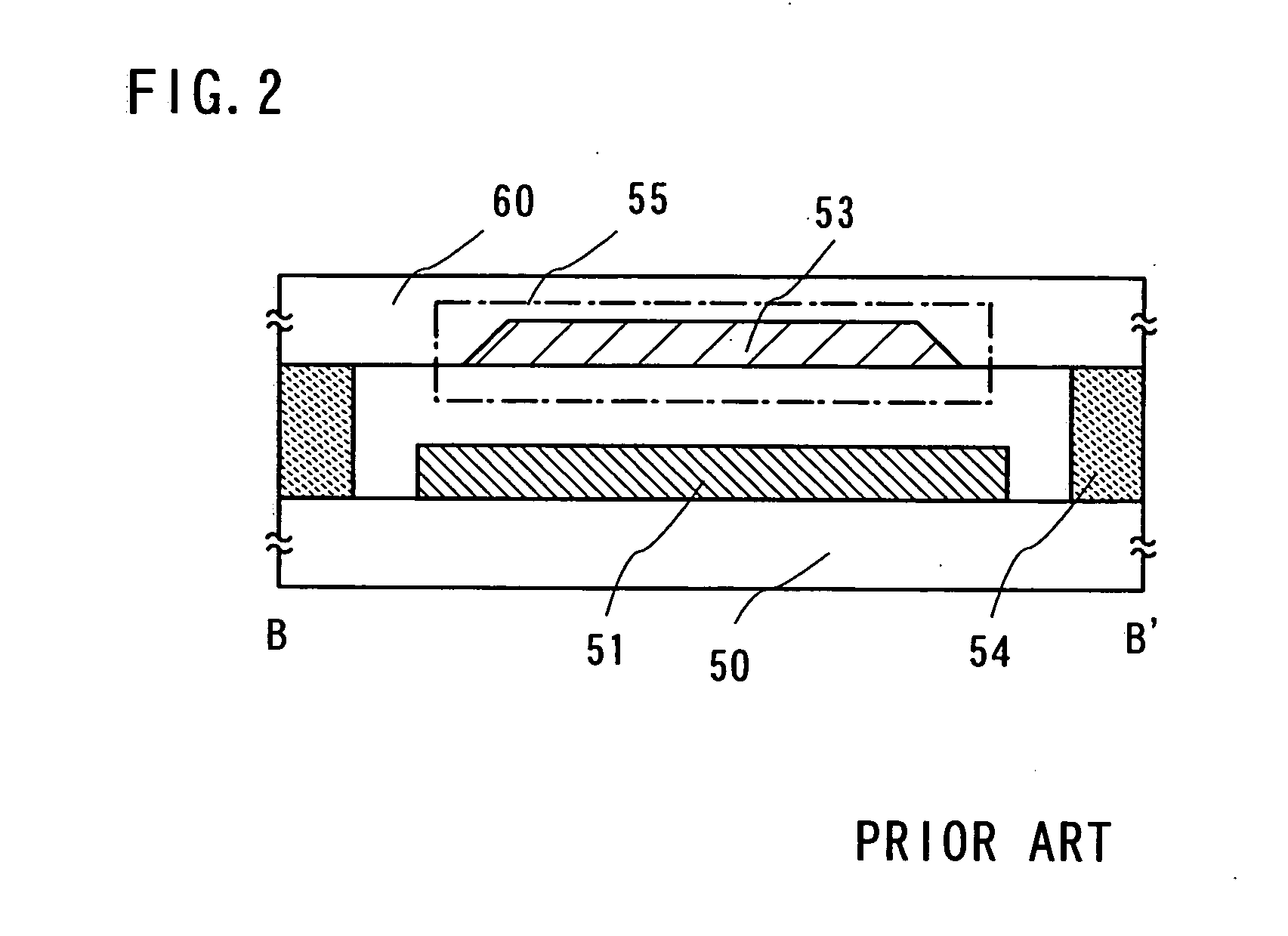
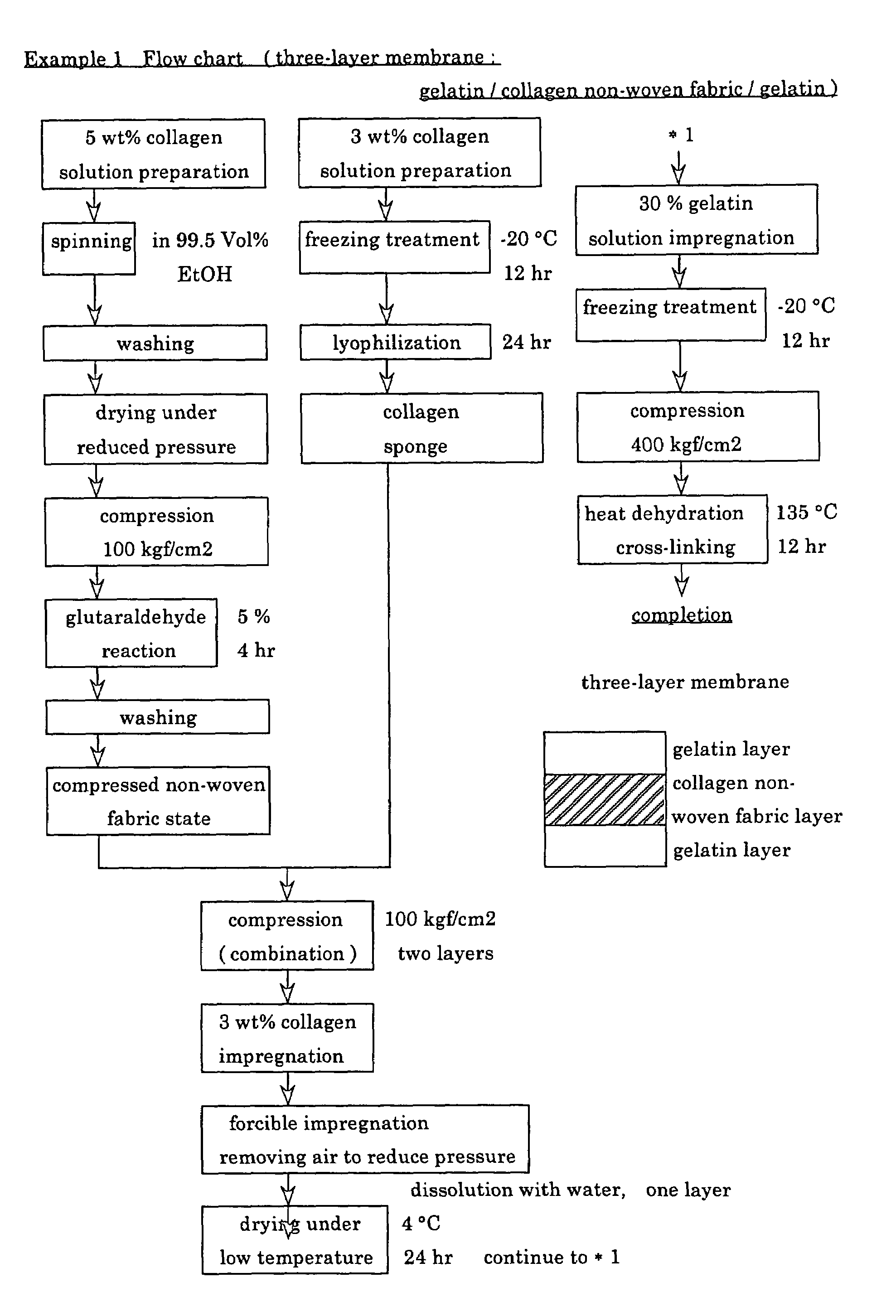
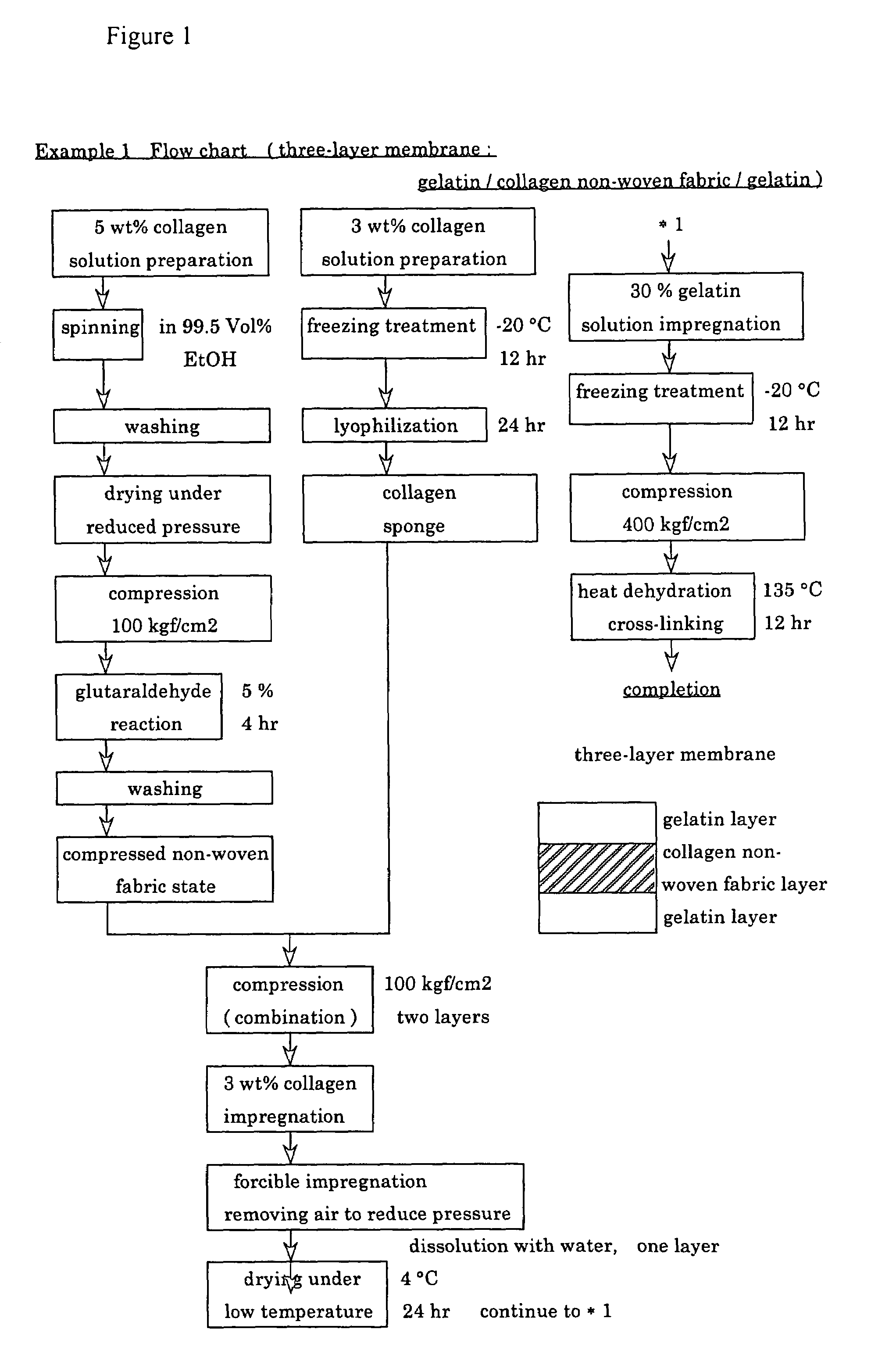
Suturable adhesion-preventing membrane
InactiveUS6977231B1High strengthGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkDecomposition
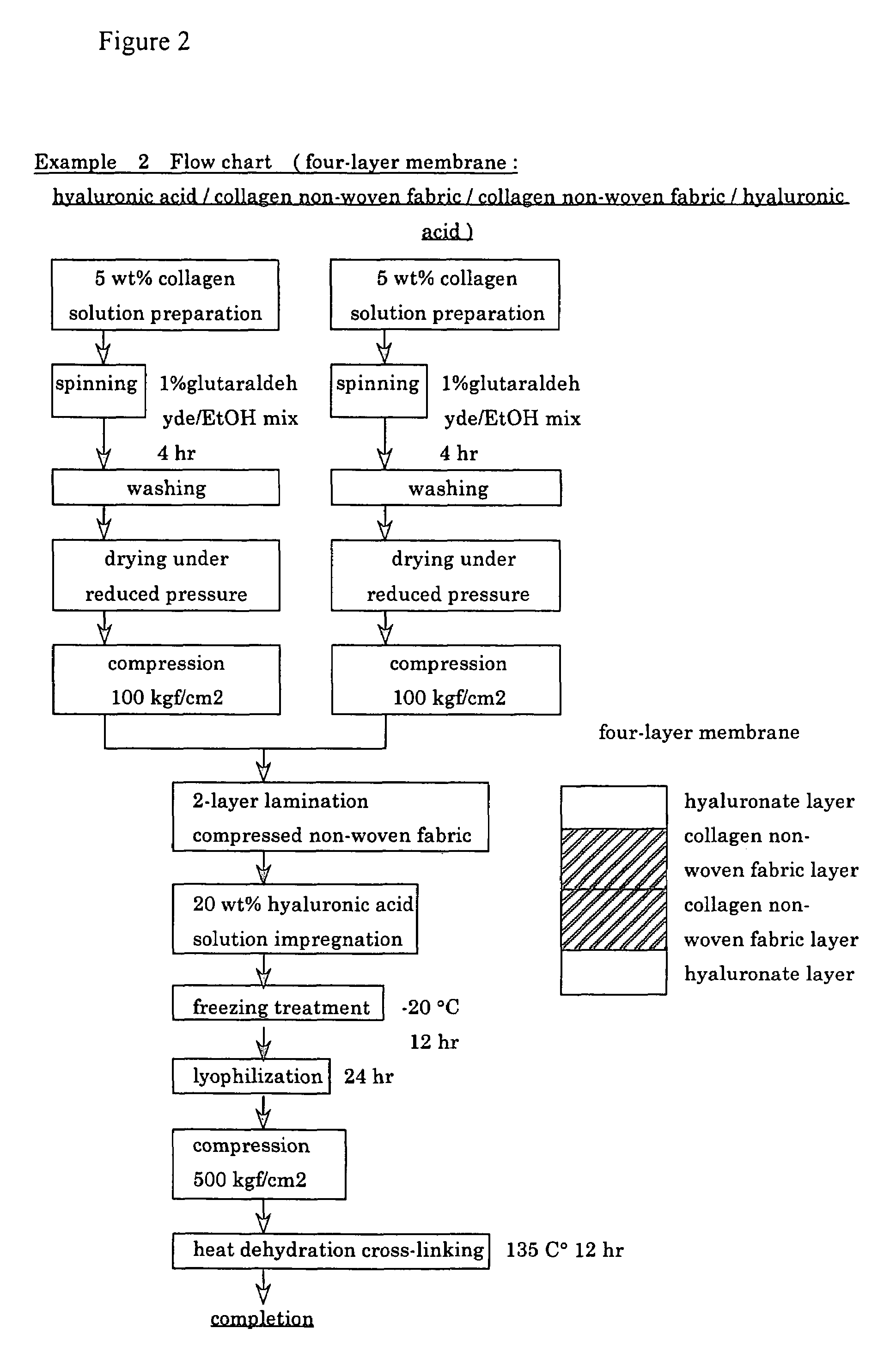
A suturable adhesion-preventing membrane has high suture strength, good biocompatibility, decomposition and absorption in a living body, sufficient adhesion-preventing effect, and desirable guided tissue regeneration. The membrane is composed of at least one non-woven fabric layer made of collagen fibers, or a laminated membranous substance consisting of at least one non-woven fabric layer made of collagen fibers and at least one sponge layer made of collagen, and a coating layer of gelatin or hyaluronic acid on the surface or surfaces of the above membrane. Preferably, the membrane comprises one to six compressed cross-linked collagen non-woven fabric layers wherein a layer has a fibers having a fiber diameter of 0.05 mm to 1.0 mm, a bulk density of 5.0×10−4 to 5 g / cm3 and a thickness of 0.1 mm to 50 mm, and a coating layer containing gelatin or hyaluronic acid and having a thickness of 0.05 mm to 20 mm, wherein the coating layer covers one or both sides or a part or whole of the surface of the membrane.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD +1
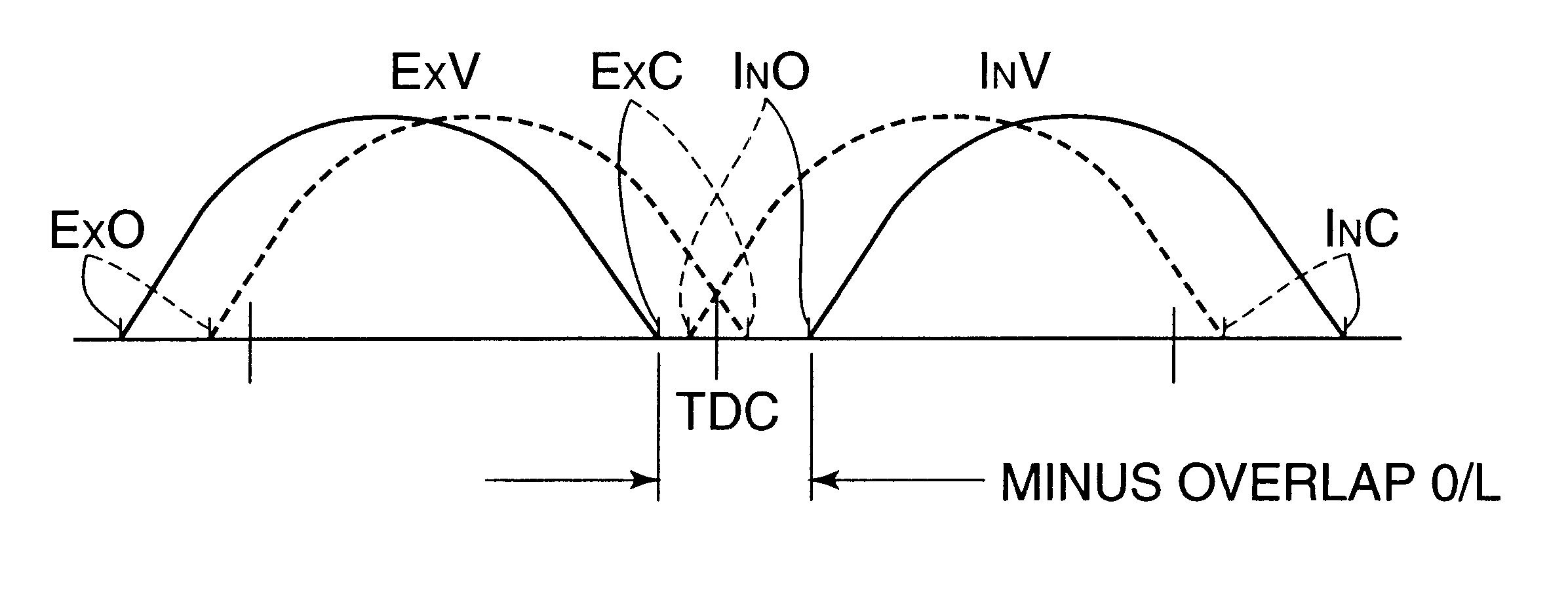
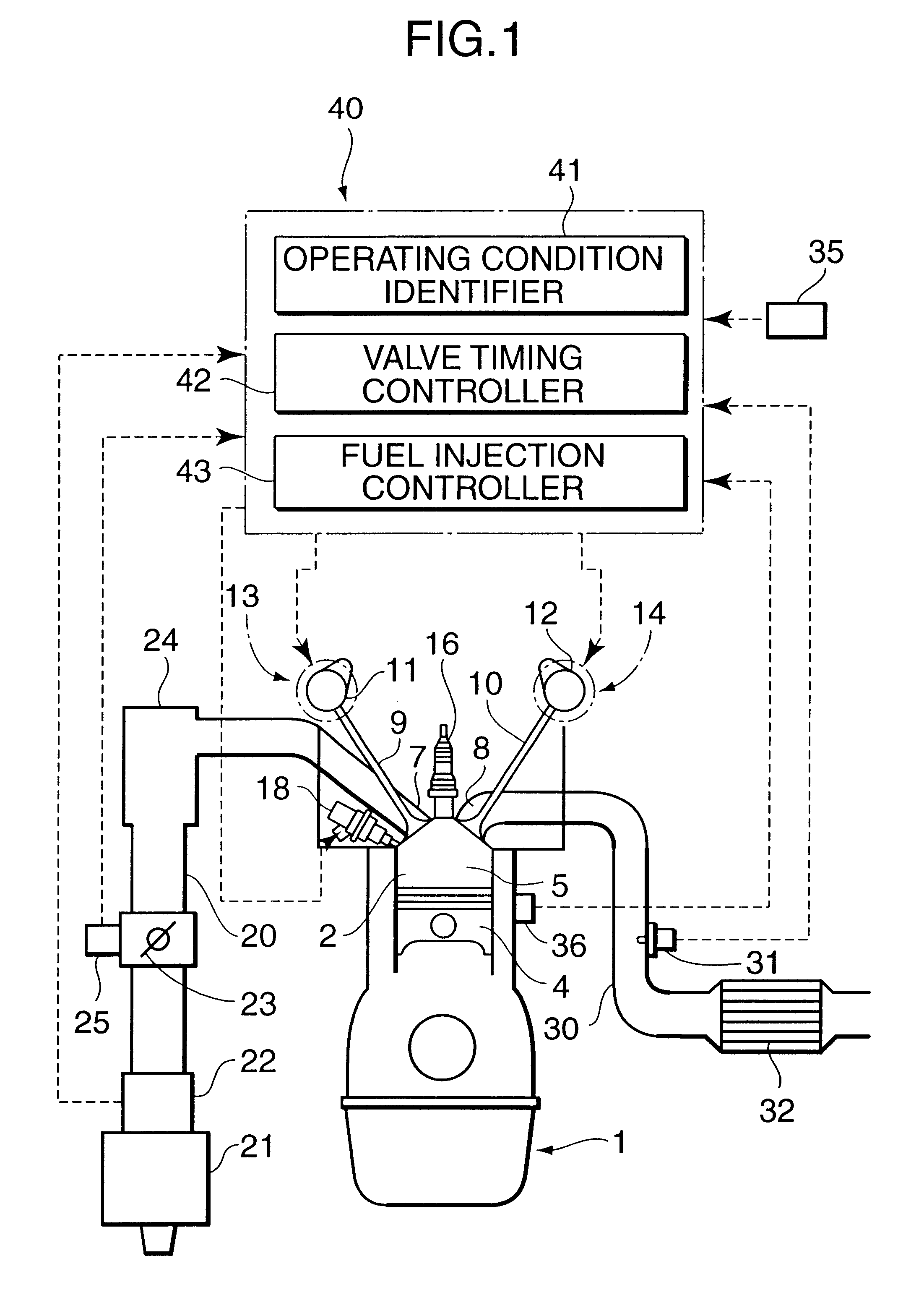
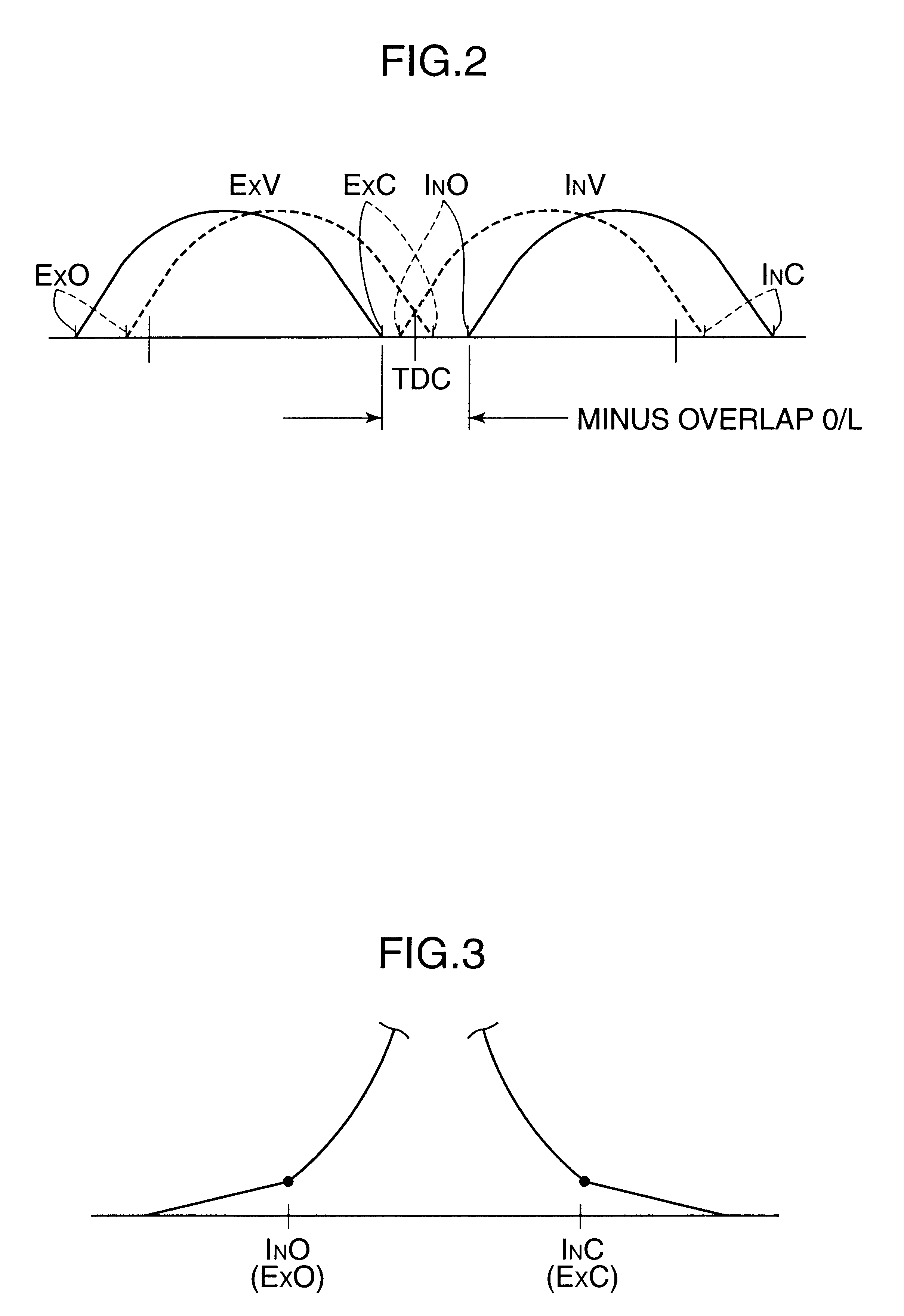
Automotive four-cycle engine
InactiveUS6626164B2Sufficient effectAvoid increase in combustion temperature and exhaust gas temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
A four-cycle engine is provided with valve timing adjusters for adjusting opening and closing timing an and an exhaust valve. In medium- to high-speed ranges in medium- to high-load regions of the engine, a closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve defined as a point of transfer from an acceleration portion to a constant speed portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point a specific period before an intake top dead center, and an opening point (InO) of the intake valve defined as a point of transfer from a constant speed portion to an acceleration portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point after the intake top dead center. In addition, the period from the closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve to the opening point (InO) of the intake valve is made longer in the medium-speed range than in the high-speed range in the medium- to high-load regions of the engine.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Electrode for lithium ion secondary battery and lithium ion secondary battery
ActiveUS20100248026A1Excellent characteristicReduce impedanceSecondary cellsActive material electrodesLithiumPoly(methyl methacrylate)
An electrode for a lithium ion secondary battery having a collector, an active-material layer formed on the collector and a protecting layer formed on the active-material layer, in which the protecting layer contains an organic particle formed of poly(methyl methacrylate) having a crosslinked structure, and the organic particle has an average particle size (D50) of 0.5 to 4.0 μm.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
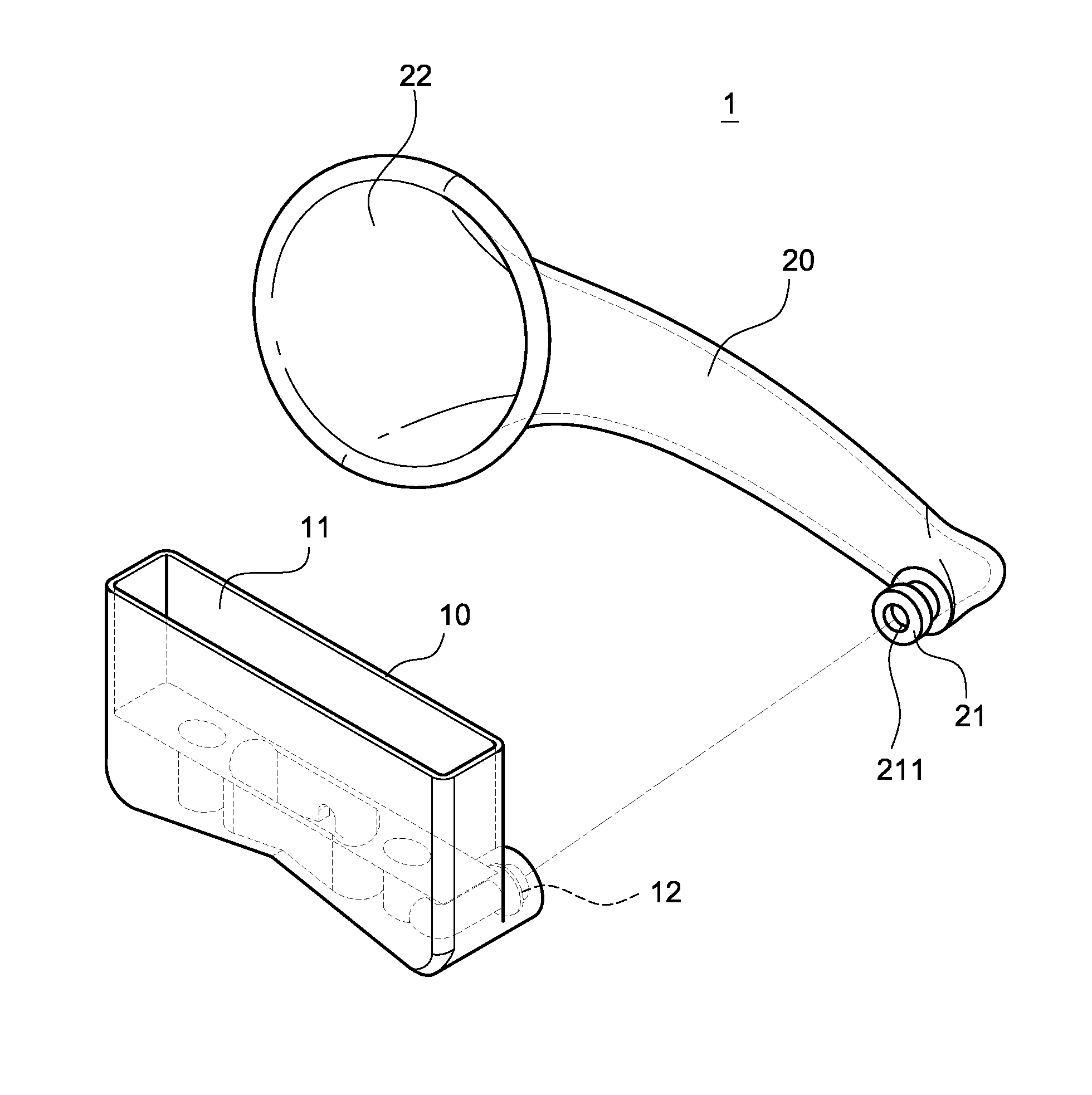
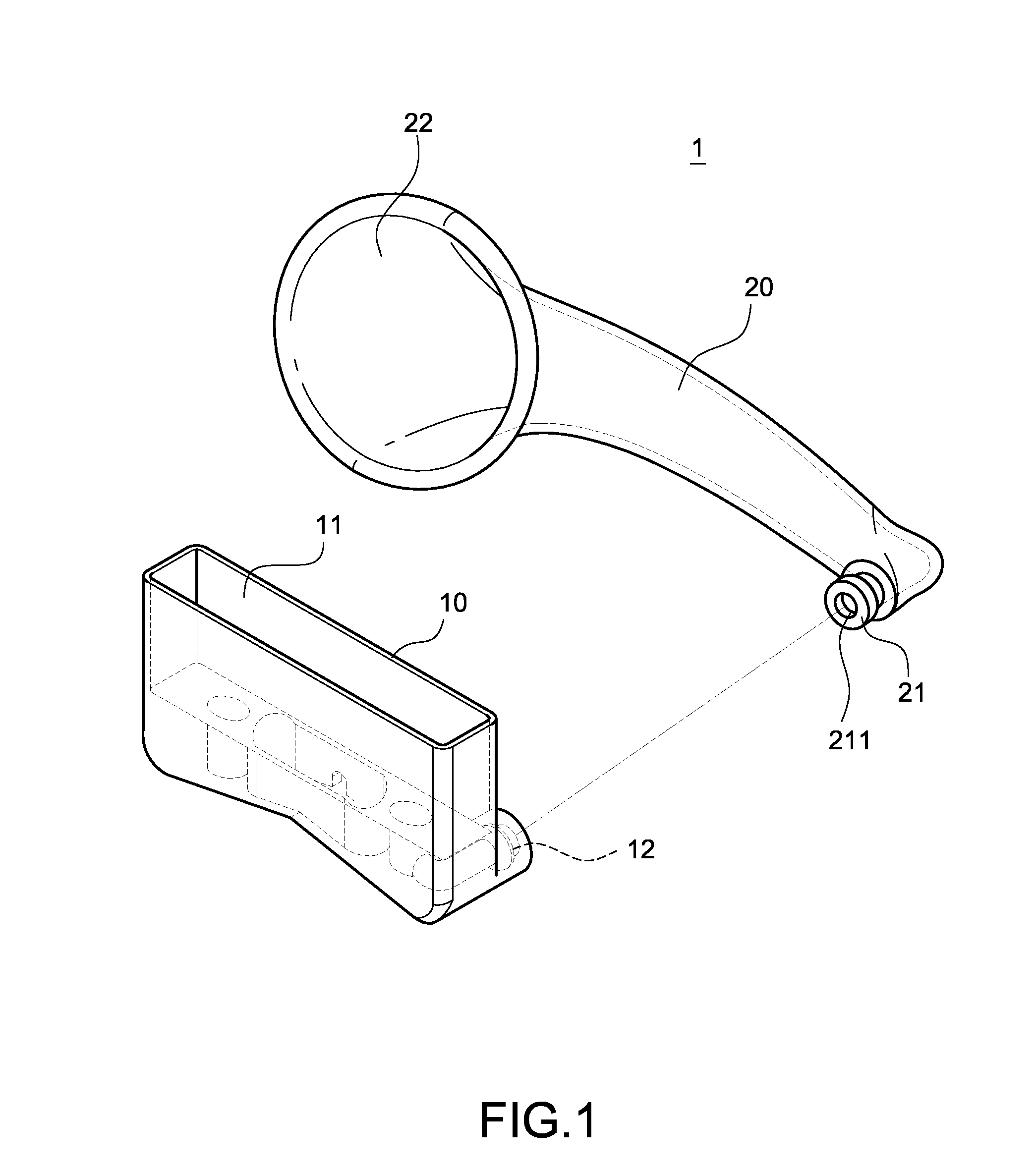
Protective sleeve having a built-in sound-amplifying channel
InactiveUS20120027237A1Improve functionalityGreat practicabilityFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringLoudspeaker
Owner:LIN CHIN SHENG
All solid lithium ion secondary battery and a solid electrolyte therefor
ActiveUS20070048619A1Sufficient effectSmall particle sizeSolid electrolyte cellsElectrolytesLithiumElectrical battery
An all solid type lithium ion secondary battery which has high heat resistance and can be used over a broad temperature range, has a high battery capacity and an excellent charging discharging characteristic, and can be used stably for a long period of time includes an inorganic substance including a lithium ion conductive crystalline and is substantially free of an organic substance and an electrolytic solution. The inorganic substance comprising a lithium ion conductive crystalline preferably is lithium ion conductive glass-ceramics.
Owner:OHARA
Method for generating sterilizing wash water and a portable apparatus thereof
InactiveUS6926819B2Sufficient effectImprove efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesLiquid separation by electricityIonHalogen
In a method and an apparatus for generating a portable sterilizing water that can be easily used at, for example, hospitals, cafeterias of nursing facilities, restaurants, hair salons or homes, an electrolyzer is structured such that a tubular-shaped ferrite anode and a cathode are arranged alternately in a concentric manner with an inter-electrode distance, and integrated with a pressurizable solution container containing halogen ions and a power control apparatus so that it can be carried and operated by one hand.
Owner:OMEGA CO LTD
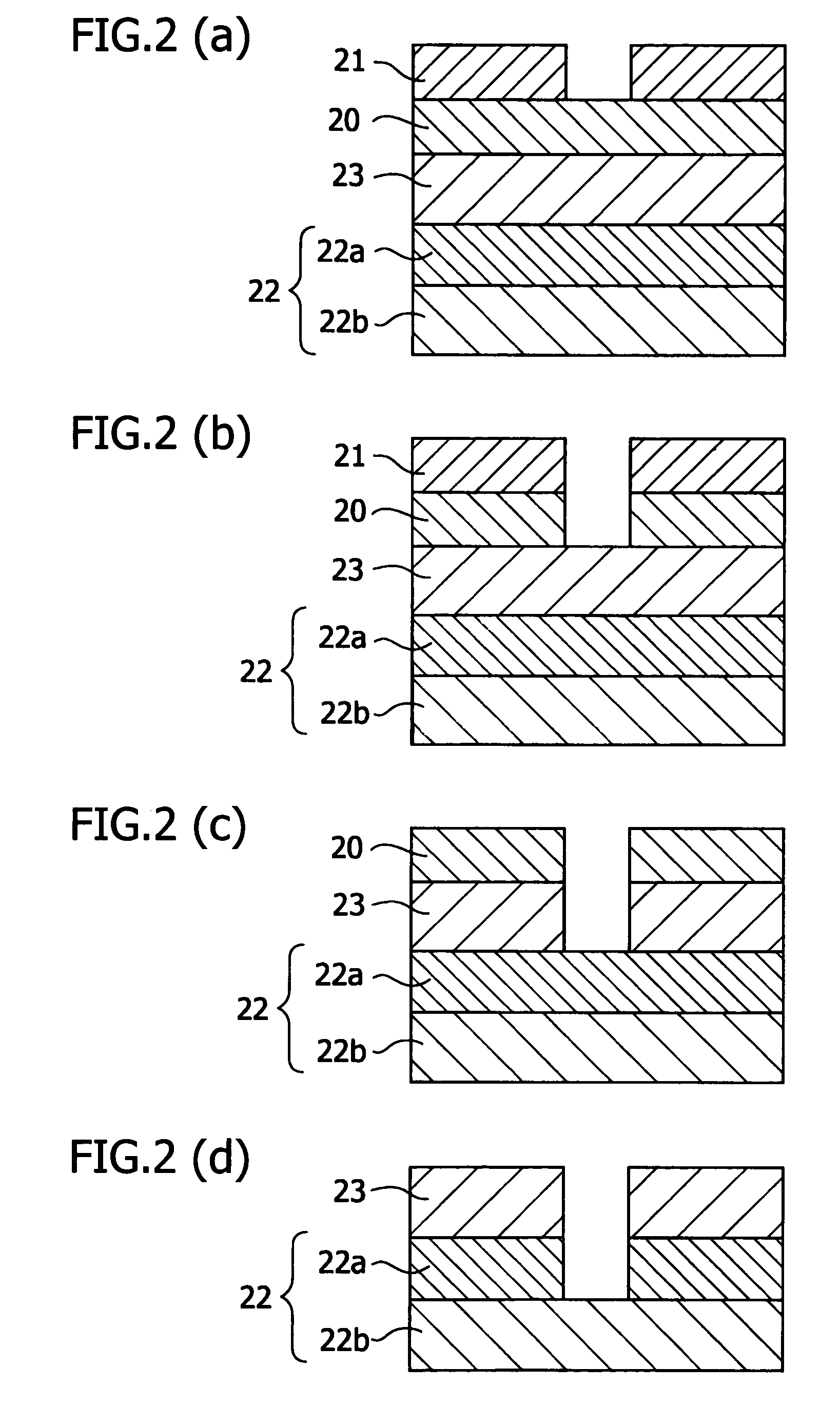
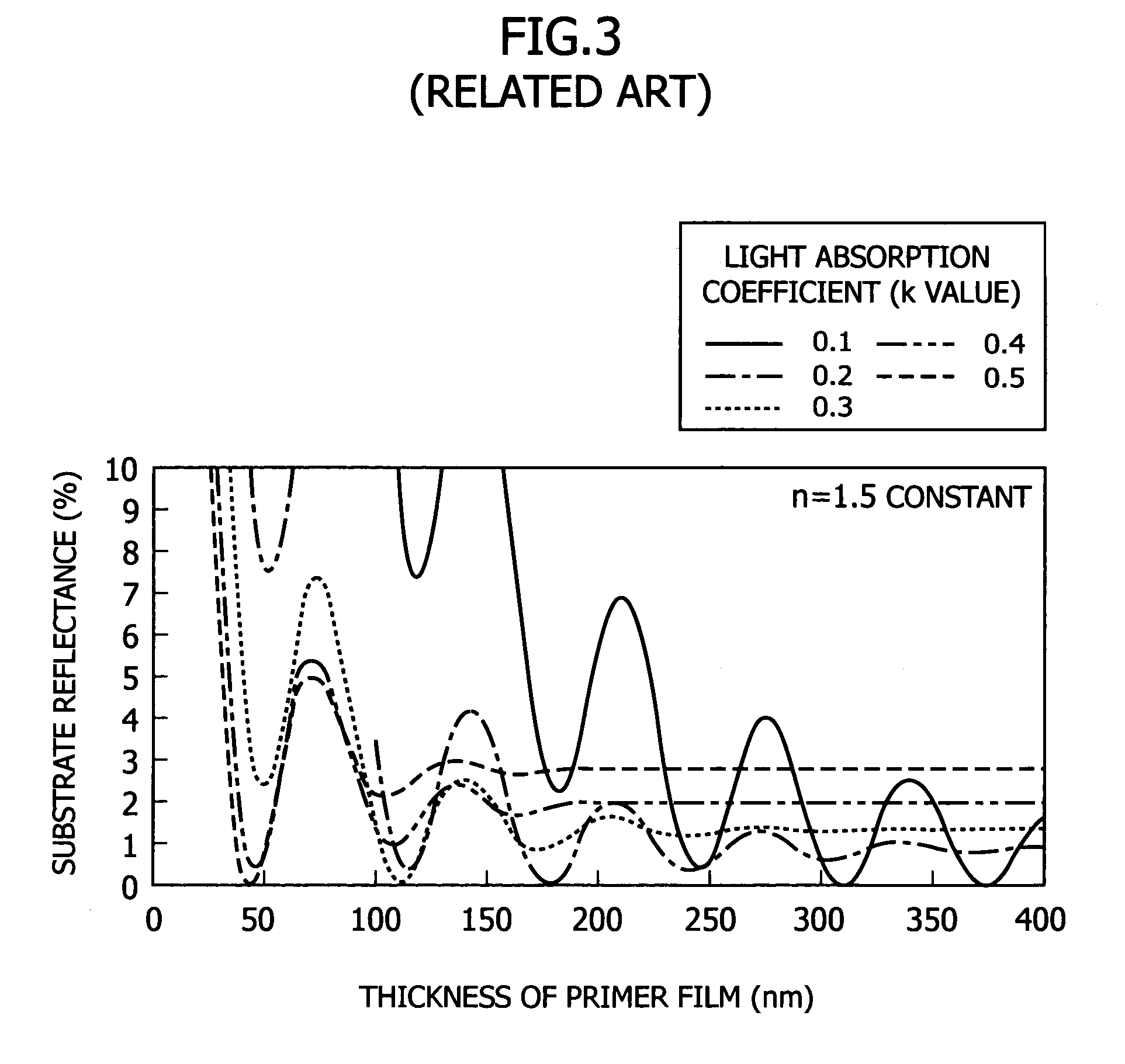
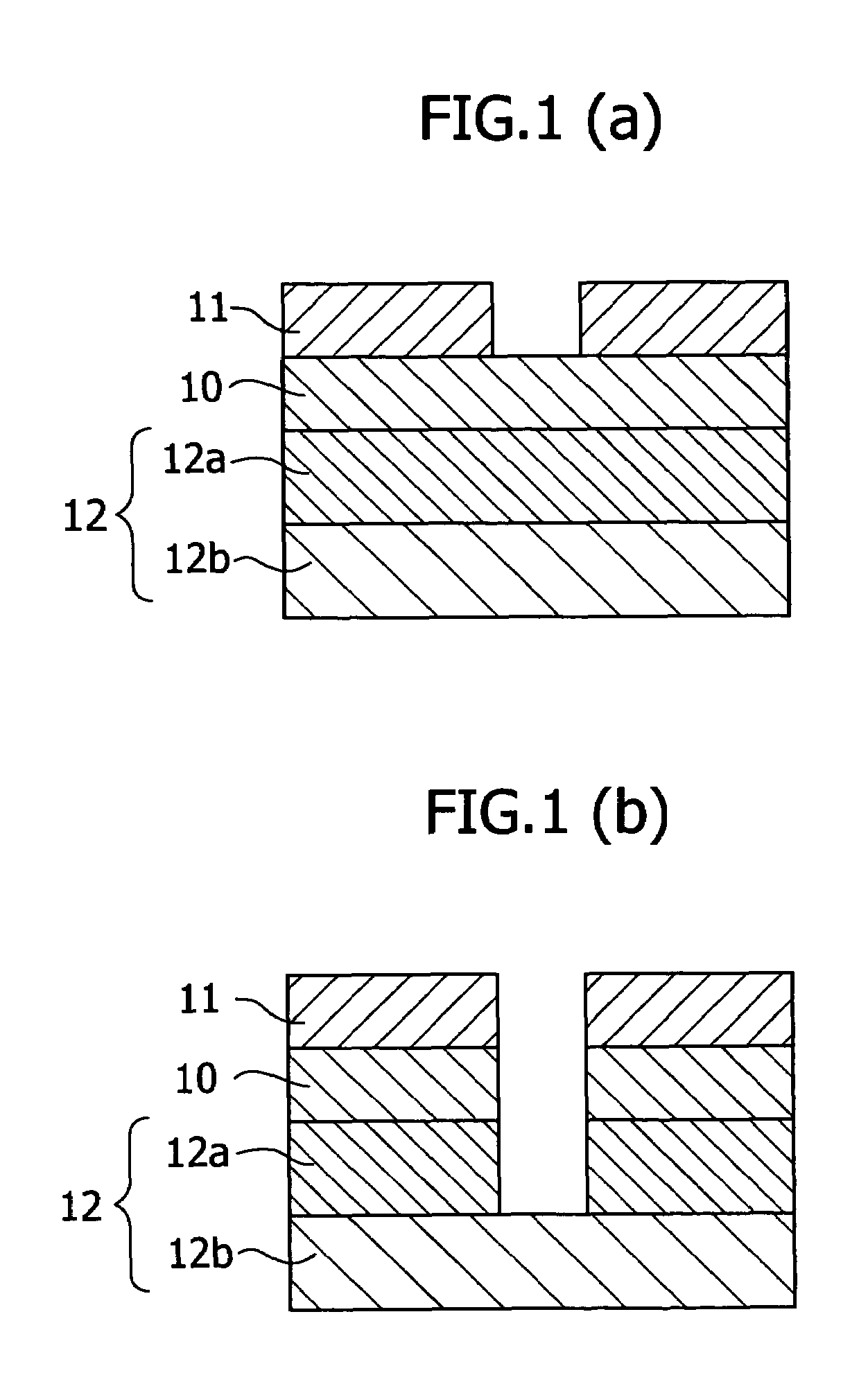
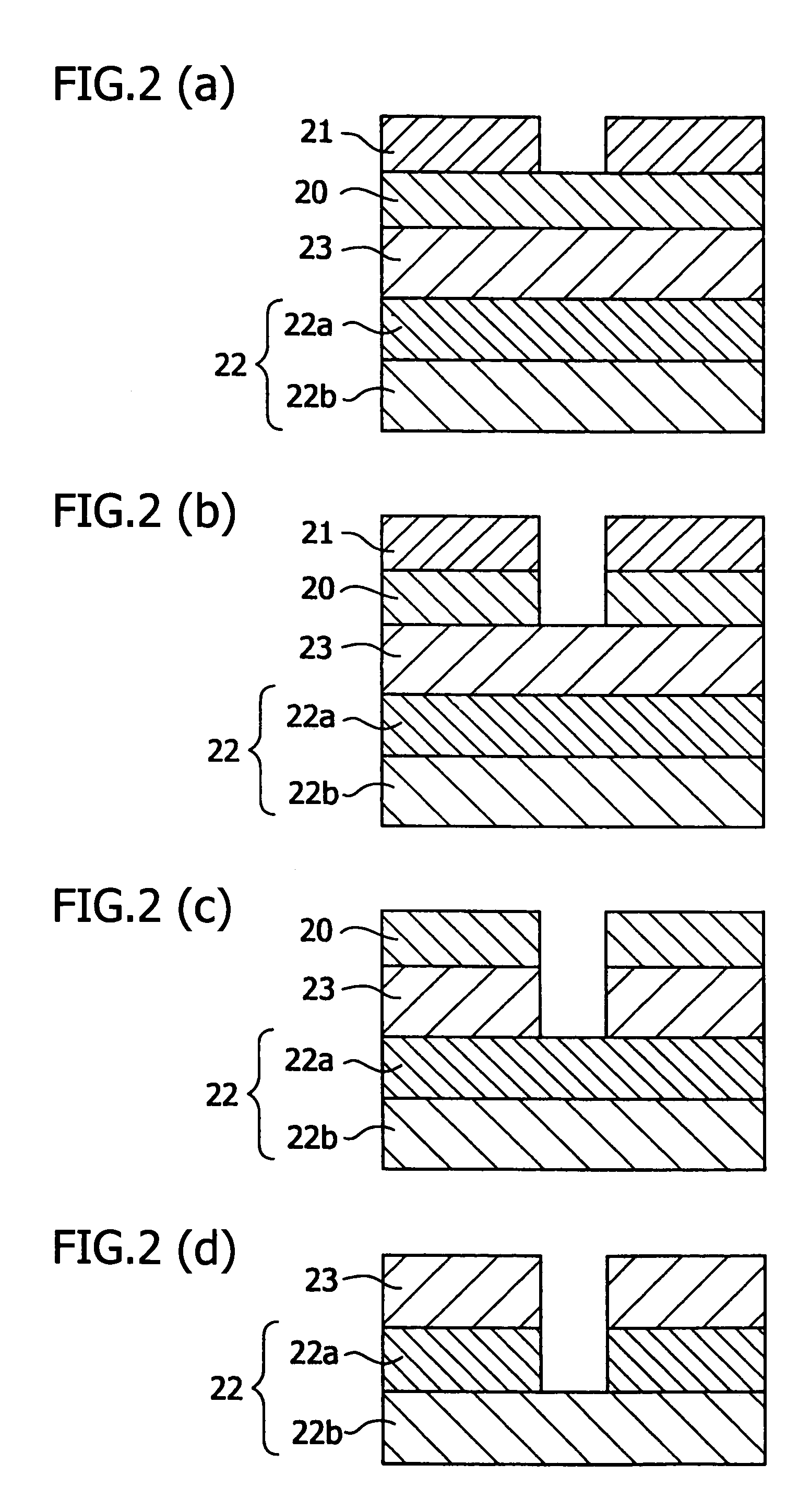
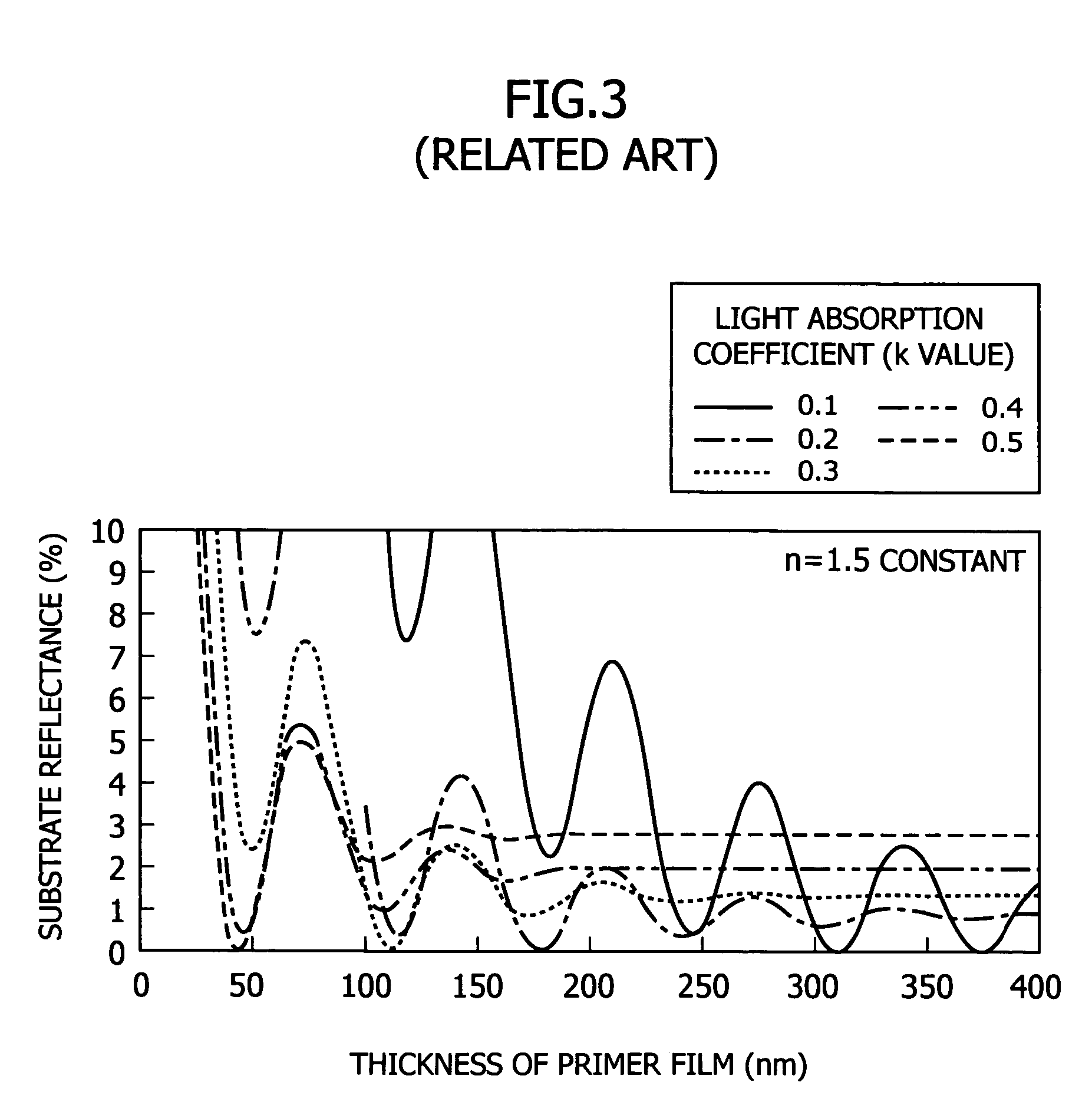
Antireflective film material, and antireflective film and pattern formation method using the same
ActiveUS7202013B2Sufficient antireflective effectImprove etch selectivityPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesResistOrganic solvent
It is an object of the present invention to provide a material for an antireflective film that has high etching selectivity with respect to the resist, that is, that has a faster etching speed than the resist, a pattern formation method for forming an antireflective film layer on a substrate using this antireflective film material, and a pattern formation method using this antireflective film as a hard mask for substrate processing.The present invention provides an antireflective film material comprising a polymer (A) comprising copolymerized repeating units expressed by the Formula (1) and / or the Formula (2), an organic solvent (B), an acid generator (C) and an optional crosslinking agent (D)
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
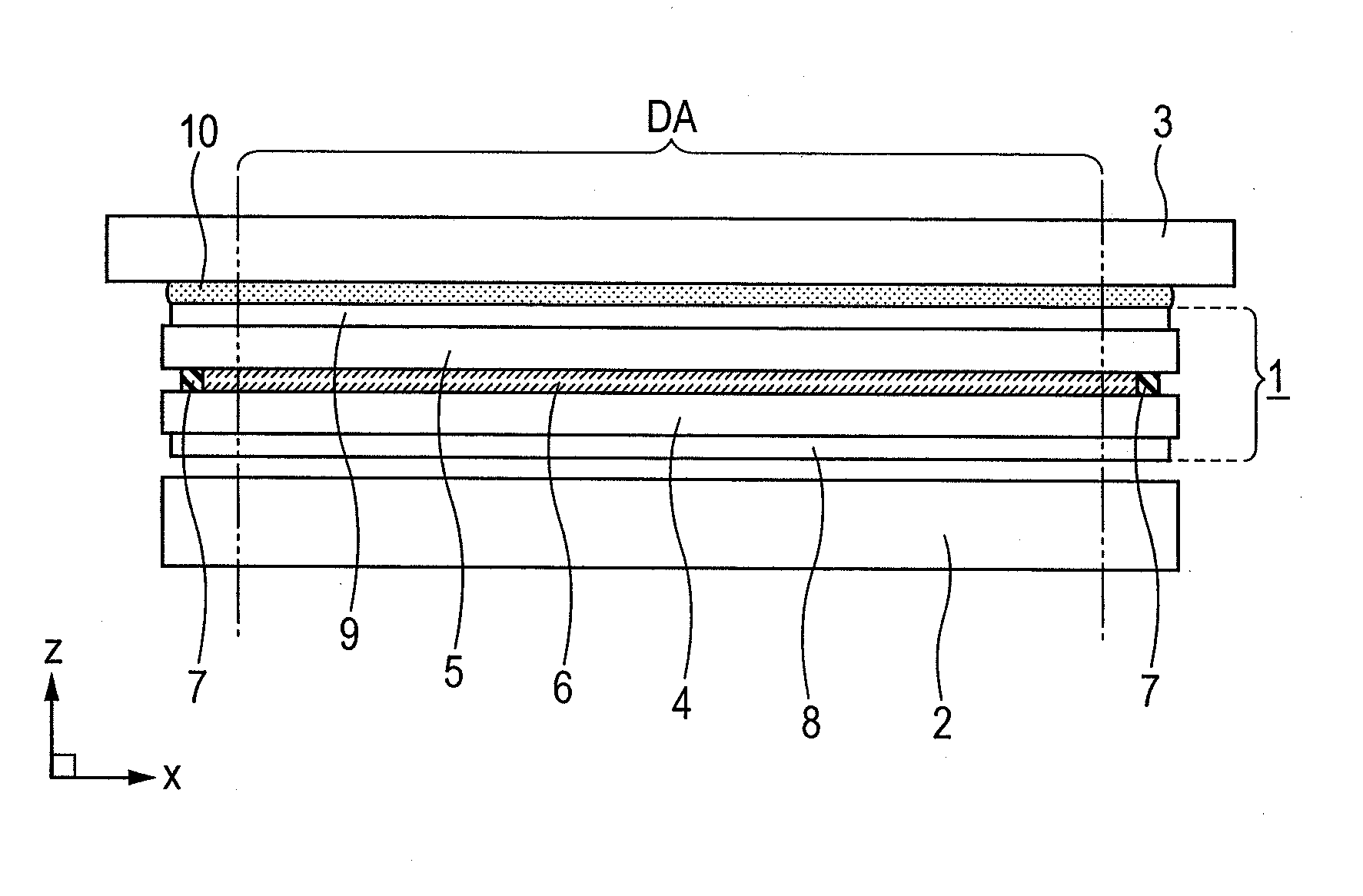
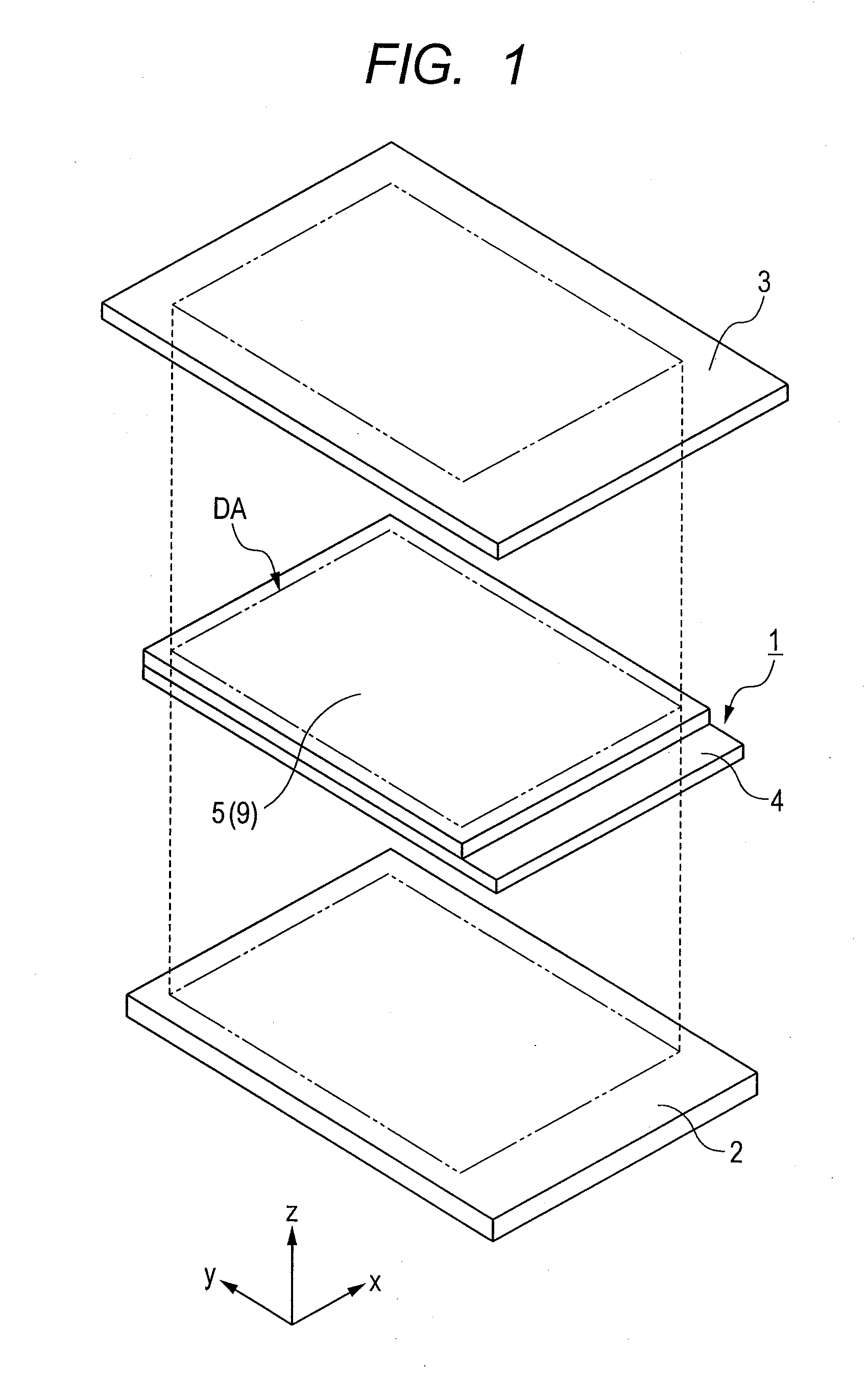
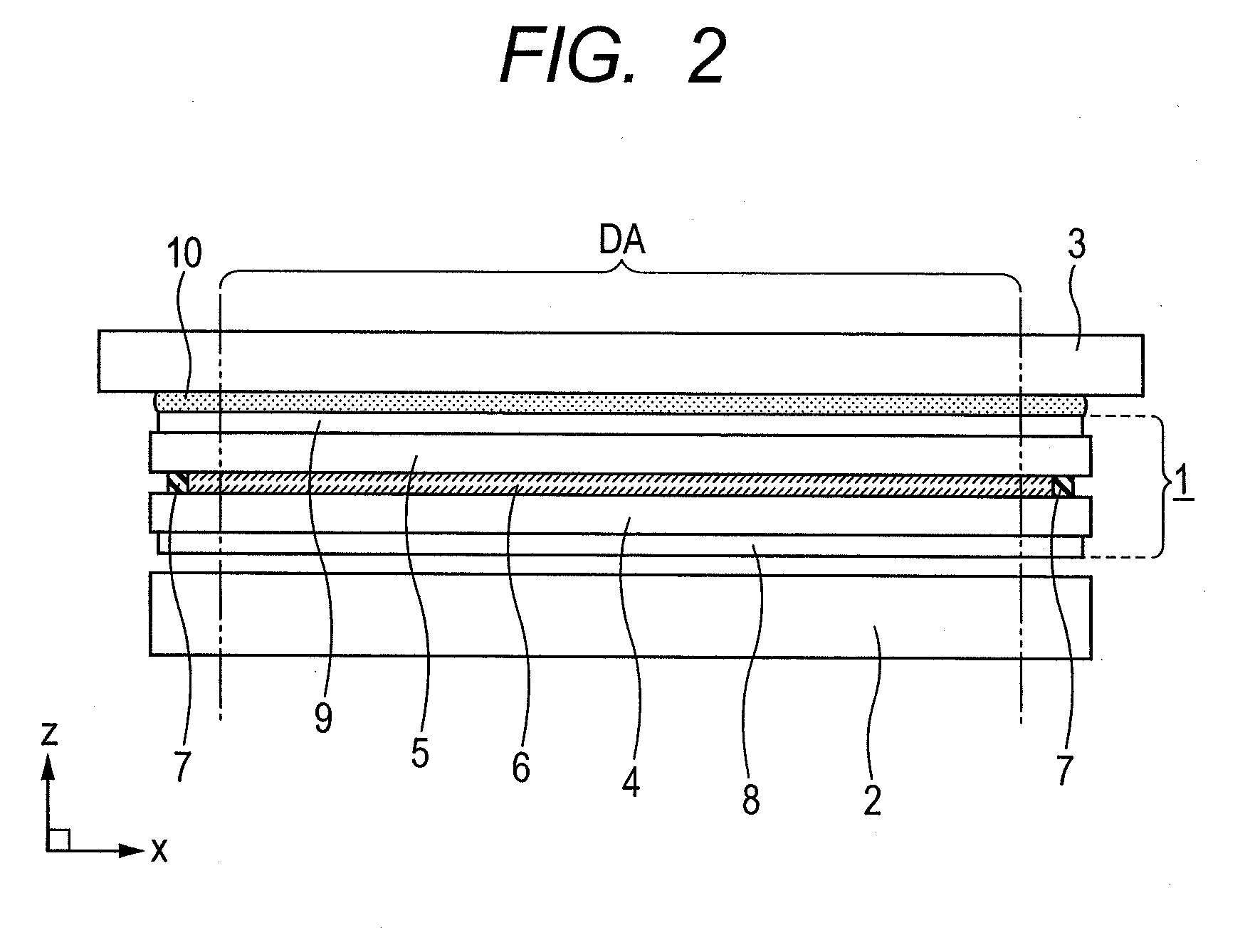
Display device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110187960A1Sufficient effectReduce bond strengthTube/lamp screens manufactureNon-linear opticsUV curingDisplay device
Disclosed is a display device in which reliable bonding strength and high reparability are compatible when a panel-like member is bonded to a display panel.The display device comprises: a display panel; and a panel-like member bonded to the display panel with an adhesive made of an ultraviolet curable resin; wherein the adhesive includes a first adhesive portion and a second adhesive portion, the first adhesive portion being provided outside of a display area of the display panel and formed in a circular shape to surround the display area, the second adhesive portion prevailing in an area surrounded by the first adhesive portion, the first adhesive portion being different in a modulus of elasticity from the second adhesive portion, and wherein the modulus of elasticity of the second adhesive portion is smaller than the modulus of elasticity of the first adhesive portion.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
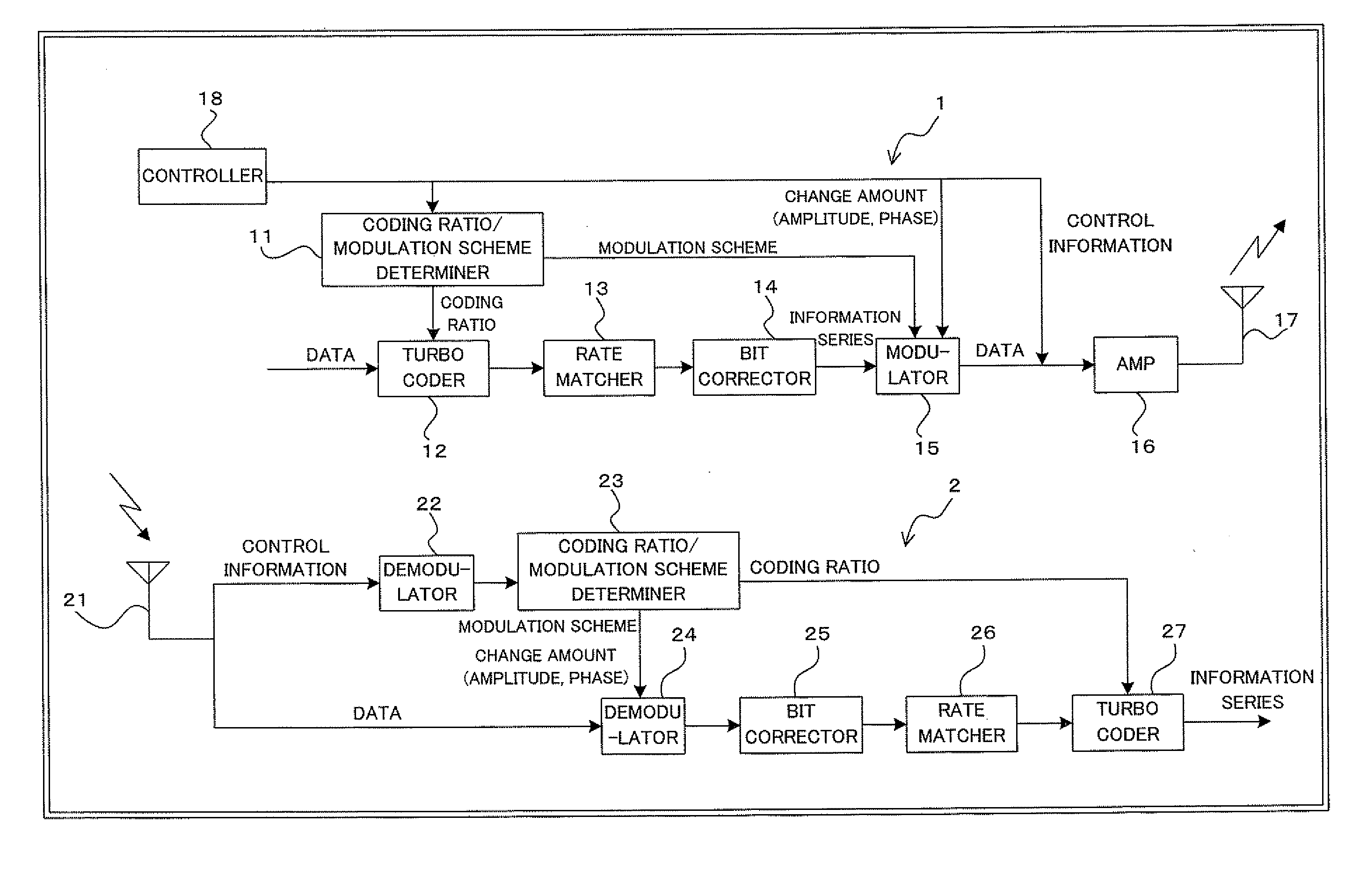
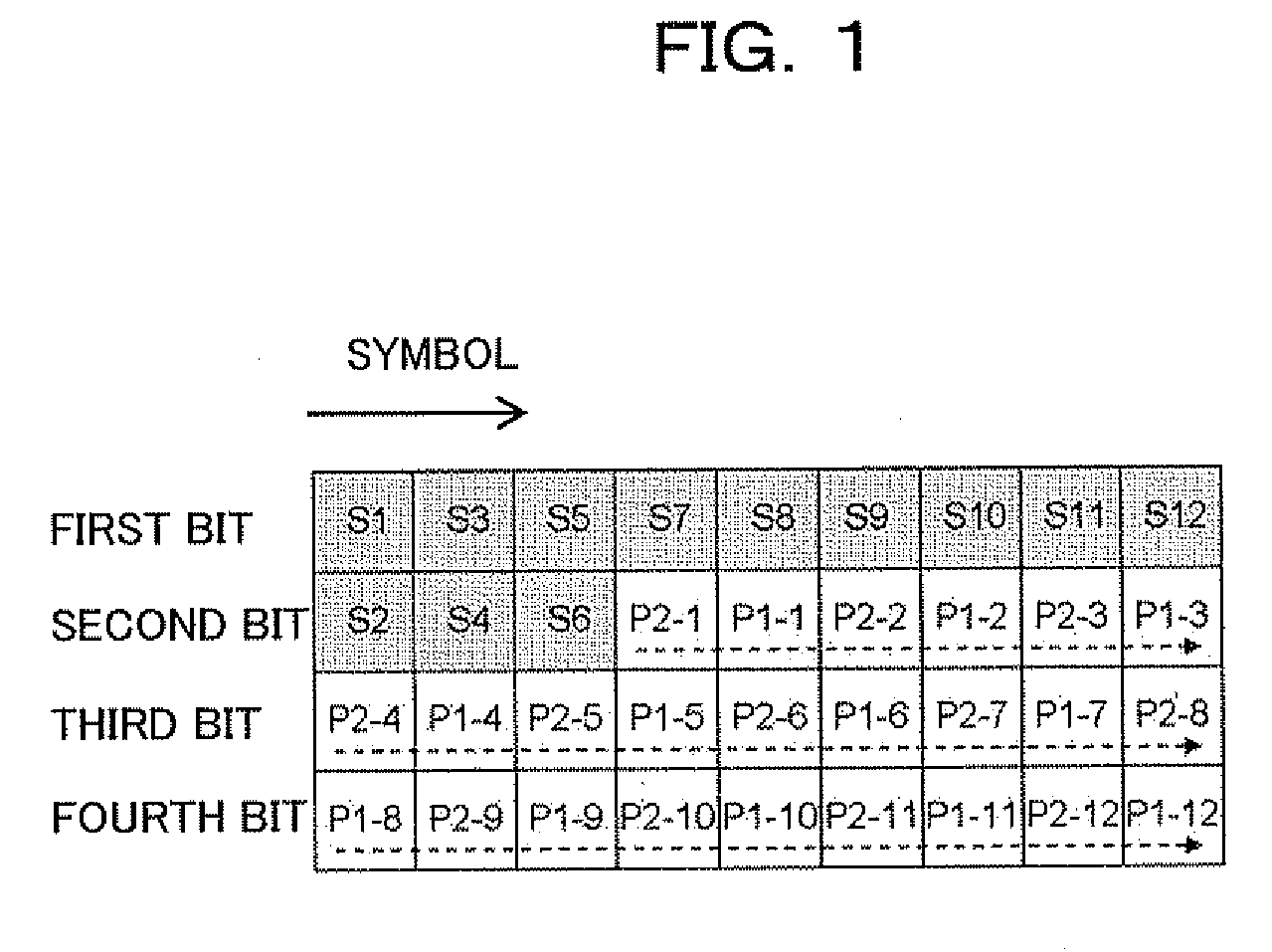
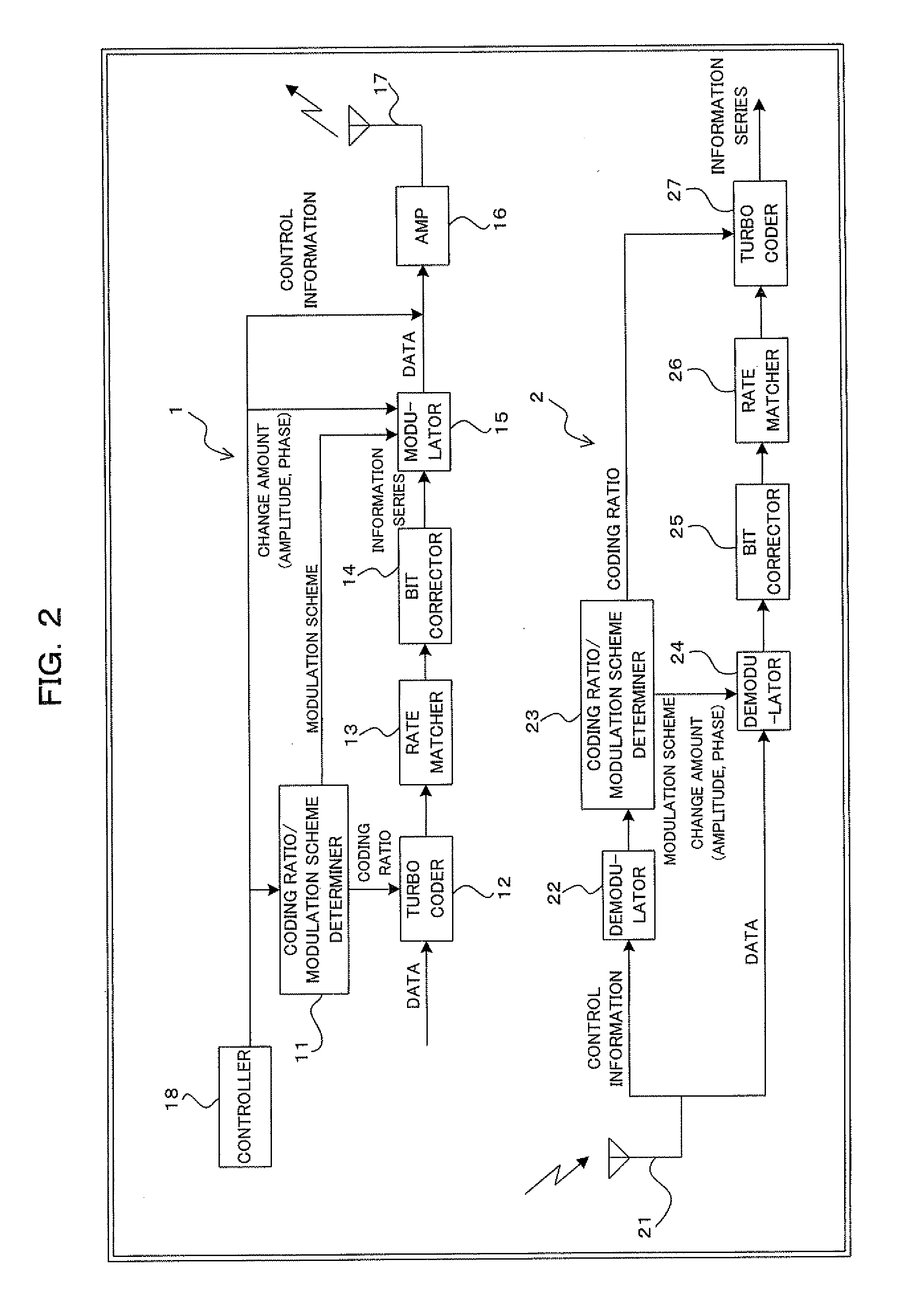
Digital radio communications method using multi-level modulation scheme and transmitter and receiver
InactiveUS20090161786A1Sufficient effectHigh error rateError correction/detection using trellis codingCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
A transmitter for use in digital radio communications systems includes: a bit corrector controls bit arrangement in such a manner that a code having high significance, out of multiple codes obtained by coding, is allocated with high priority to a bit having a tendency that the likelihood enlarges at the time of symbol decision on a receiver; a multi-level modulator allocates the code to the multiple bits in accordance with a predetermined symbol arrangement; and a symbol arrangement controller controls the symbol arrangement from equal distance arrangement to another arrangement in accordance with a ratio of the codes different in significance. To control symbol arrangement increases the effect of bit correction and improves an error rate on the receiver.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Member for electronic device
A member for electronic device includes polylactic acid and polycarbonate. The member for electronic device is made not from fossil resource, but mainly from a carbon-neutral material, and exhibits excellent impact resistance and heat resistance.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Display device and method for manufacturing display device
InactiveUS7495644B2Inhibit deteriorationImprove reliabilityStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceSealant
An object of the present invention is to provide a highly reliable display device and a method for manufacturing the display device with a much easy way. According to one aspect of a method for manufacturing a display device of the invention, it comprises the steps of forming a light-emitting element over a first substrate; forming a frame to surround the light-emitting element; dropping a composition containing a liquid hygroscopic substance in a region surrounded with the frame; and forming a layer containing a hygroscopic substance by solidifying the composition, wherein the first substrate and a second substrate are adhered to each other with a sealant so that the light-emitting element, the layer containing a hygroscopic substance, and the frame are sealed between the pair of substrates.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
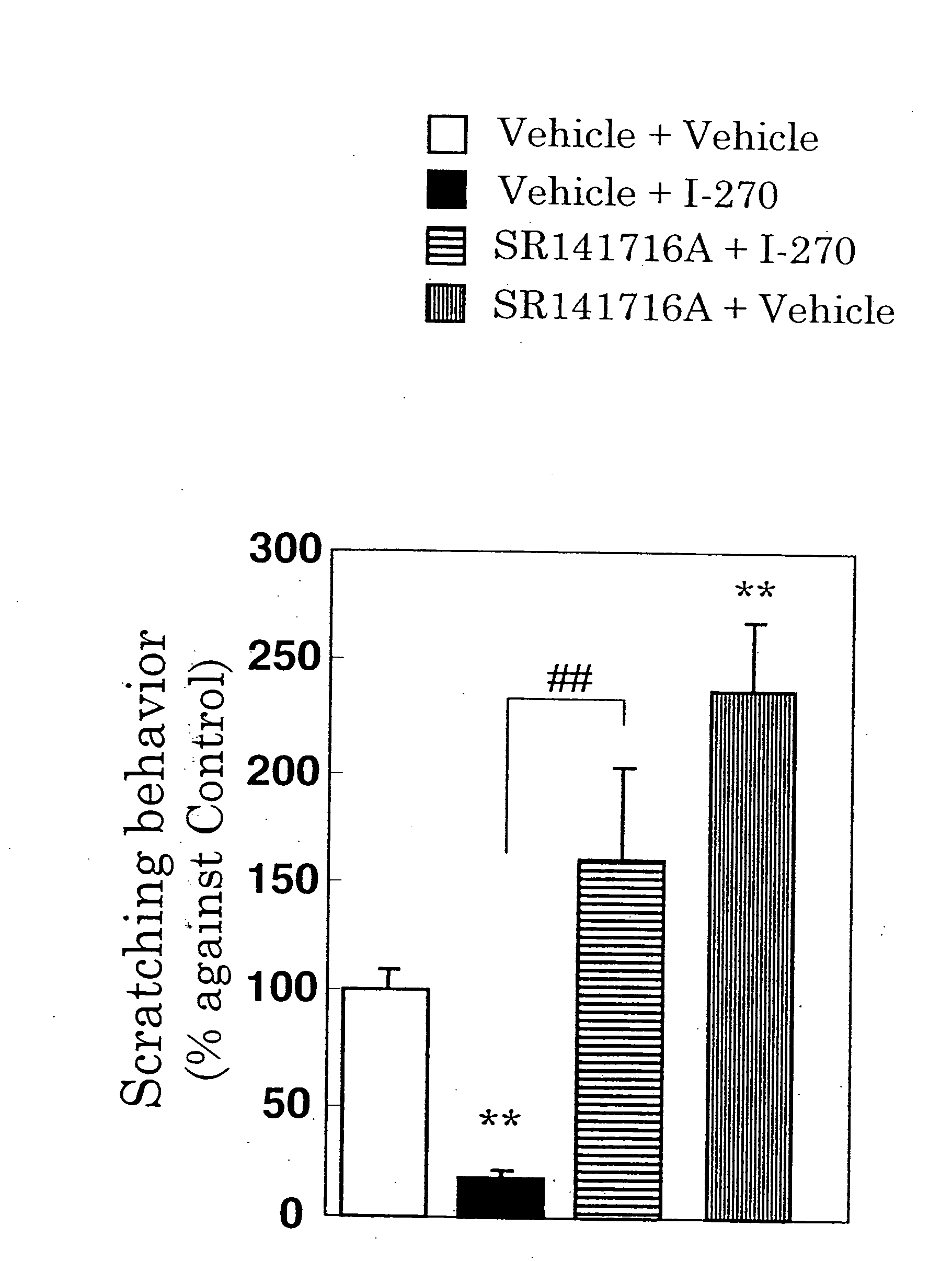
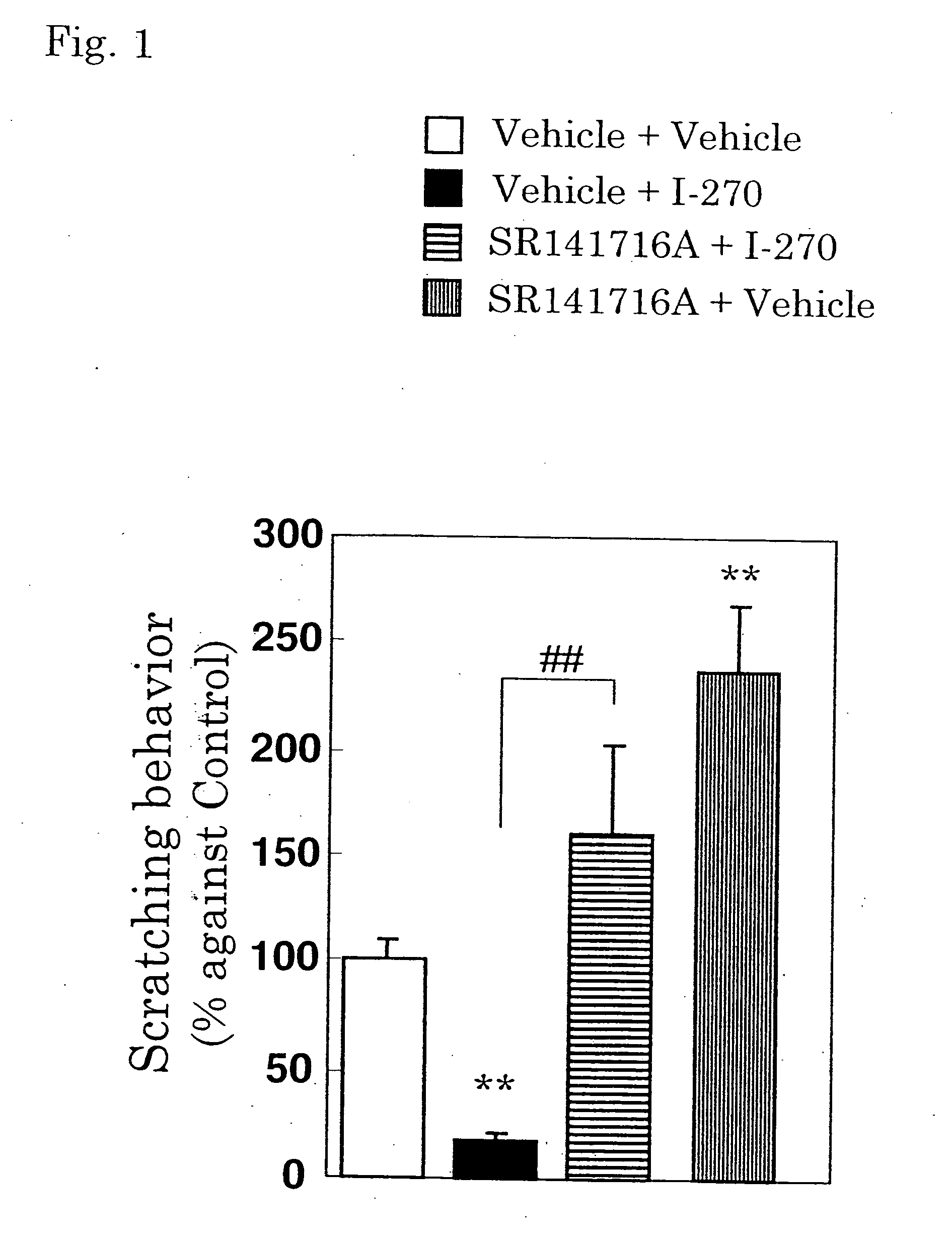
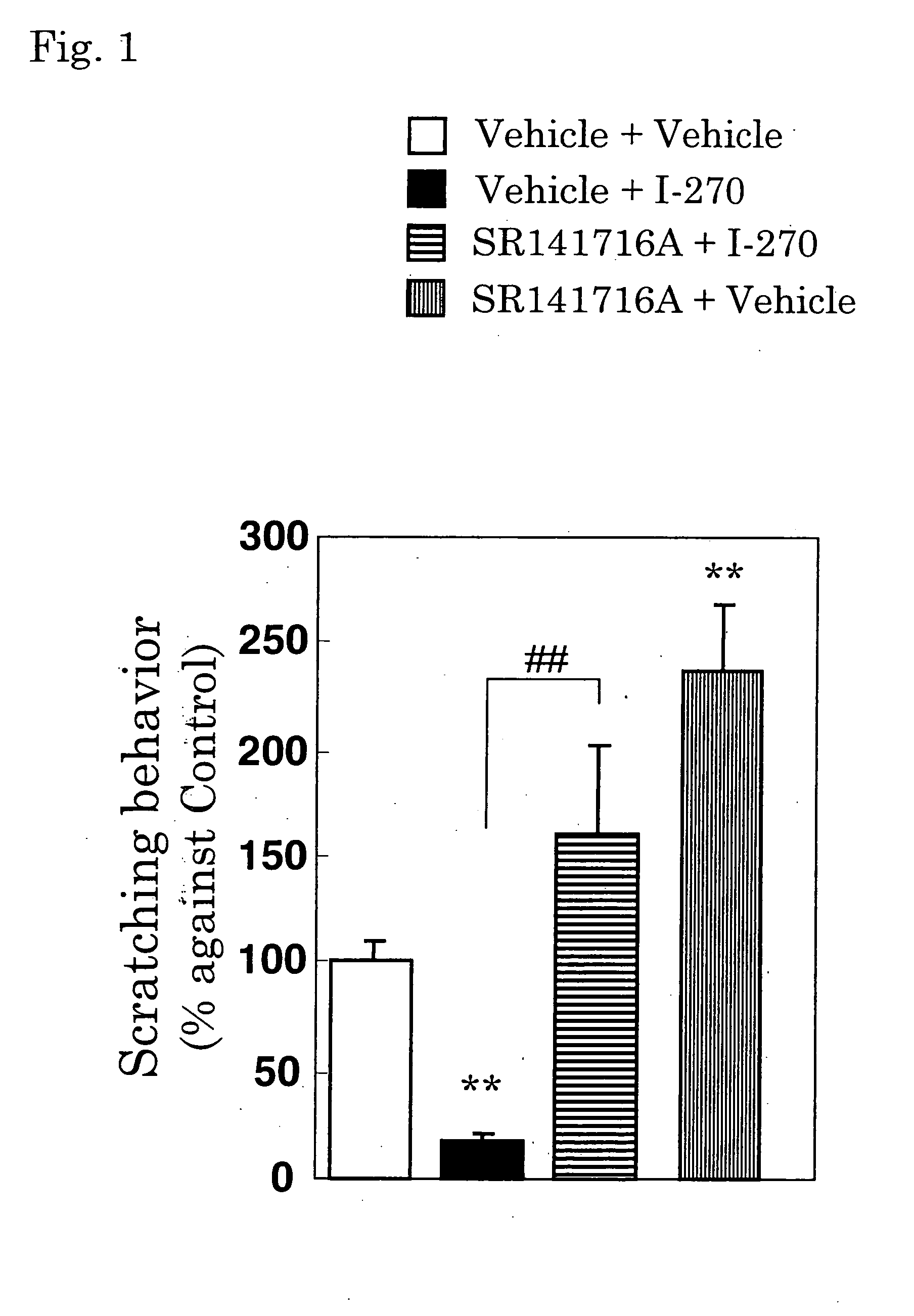
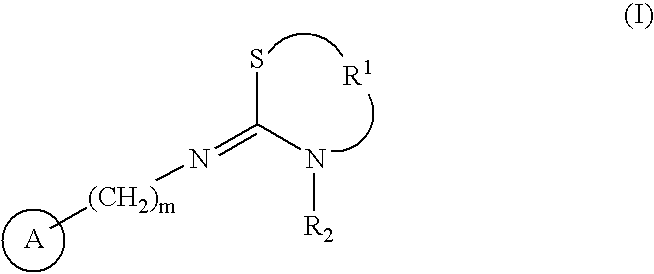
Antipruritics
It is intended to provide antipruritics (drugs to control itching, antiitch agents and drugs to stop itching). It is found out that a compound having an agonistic activity to the cannabinoid receptor shows an antipruritics effect.
Owner:YASUI KIYOSHI +2
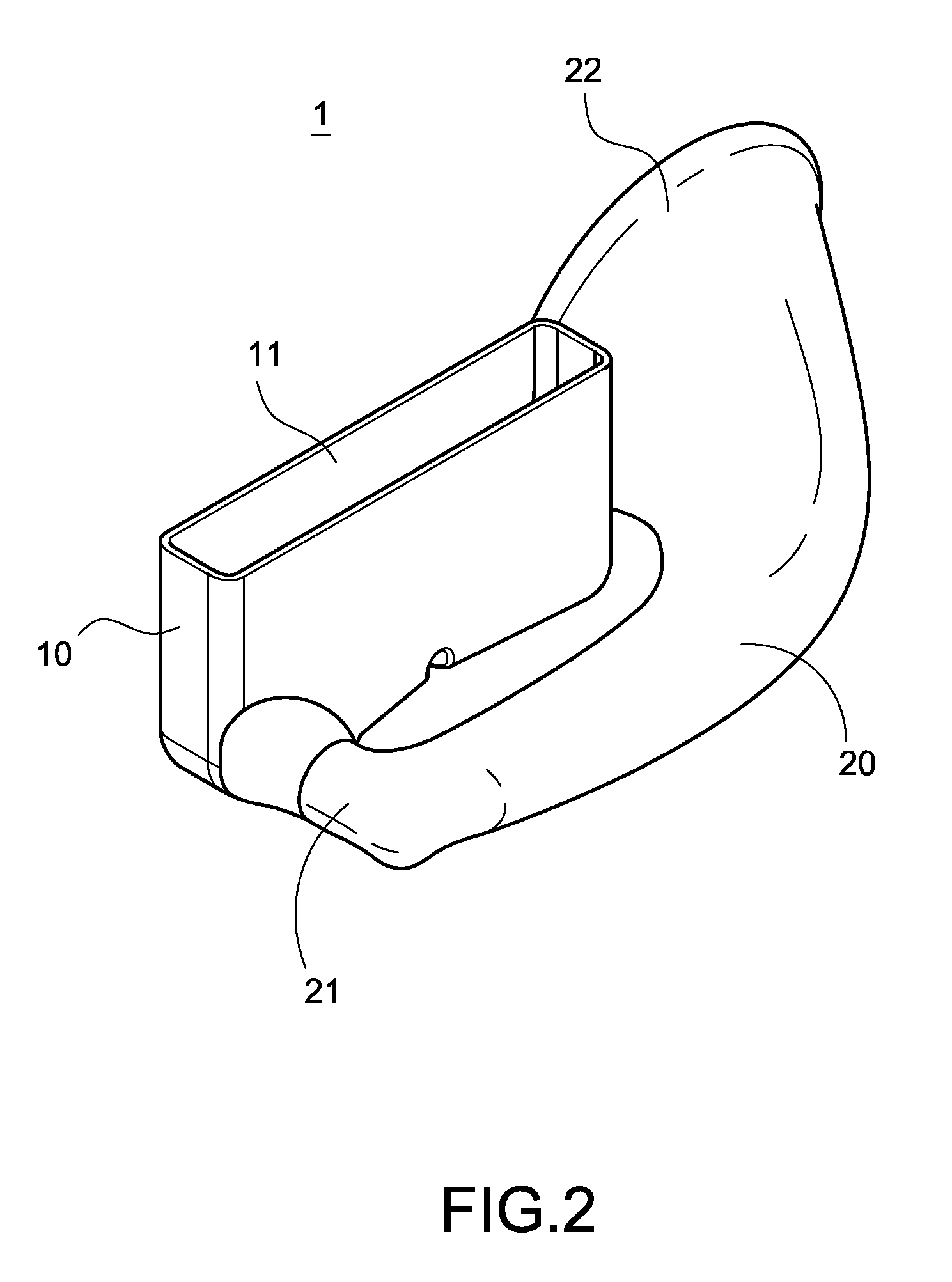
Protective sleeve having an external sound-amplifying member
InactiveUS8256568B2Improve functionalityGreat practicabilityTransducer detailsSound producing devicesLoudspeakerAudio frequency
A protective sleeve having an external sound-amplifying member is configured to cover a portable electronic product having an audio port, and it includes a covering element covering the portable electronic product and a sound-amplifying member. A surface of the covering element is provided with a connecting hole in communication with the audio port. The sound-amplifying member is hollow and connected to the outside of the covering element. One end of the sound-amplifying member is formed into an insertion section inserted into the connecting hole, and the other end thereof is formed into a sound-amplifying section. The sound of the portable electronic product is emitted from the audio port and amplified through the sound-amplifying member and the sound-amplifying section. By this structure, an external loud speaker is unnecessary, and the protective sleeve itself can generate a sufficient sound-amplifying effect, thereby increasing the functionality and practicability of the protective sleeve.
Owner:LIN CHIN SHENG
Touch panel device and electronic device having the same
ActiveUS20120249459A1Enhance haptic effectSmall force outputDigital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingTouch panelEngineering
A touch panel device, includes a transparent protective substrate disposed on a front side of the touch panel, the protective substrate being configured by joining a first glass substrate residing on a front side and a second glass substrate residing on a touch panel side, wherein either one of the first and second glass substrates is configured to have one or more stepped portions formed either on a rear surface of the first glass substrate or a front surface of the second glass substrate, the rear surface of the first glass substrate and the front surface of the second glass substrate facing one another; and one or more piezo vibration elements each disposed within one of the stepped portions so as to be acoustically coupled with the first glass substrate, wherein each of said one or more stepped portions is configured thicker than the corresponding piezo vibration element.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Stent for blood vessel and material for stent for blood vessel
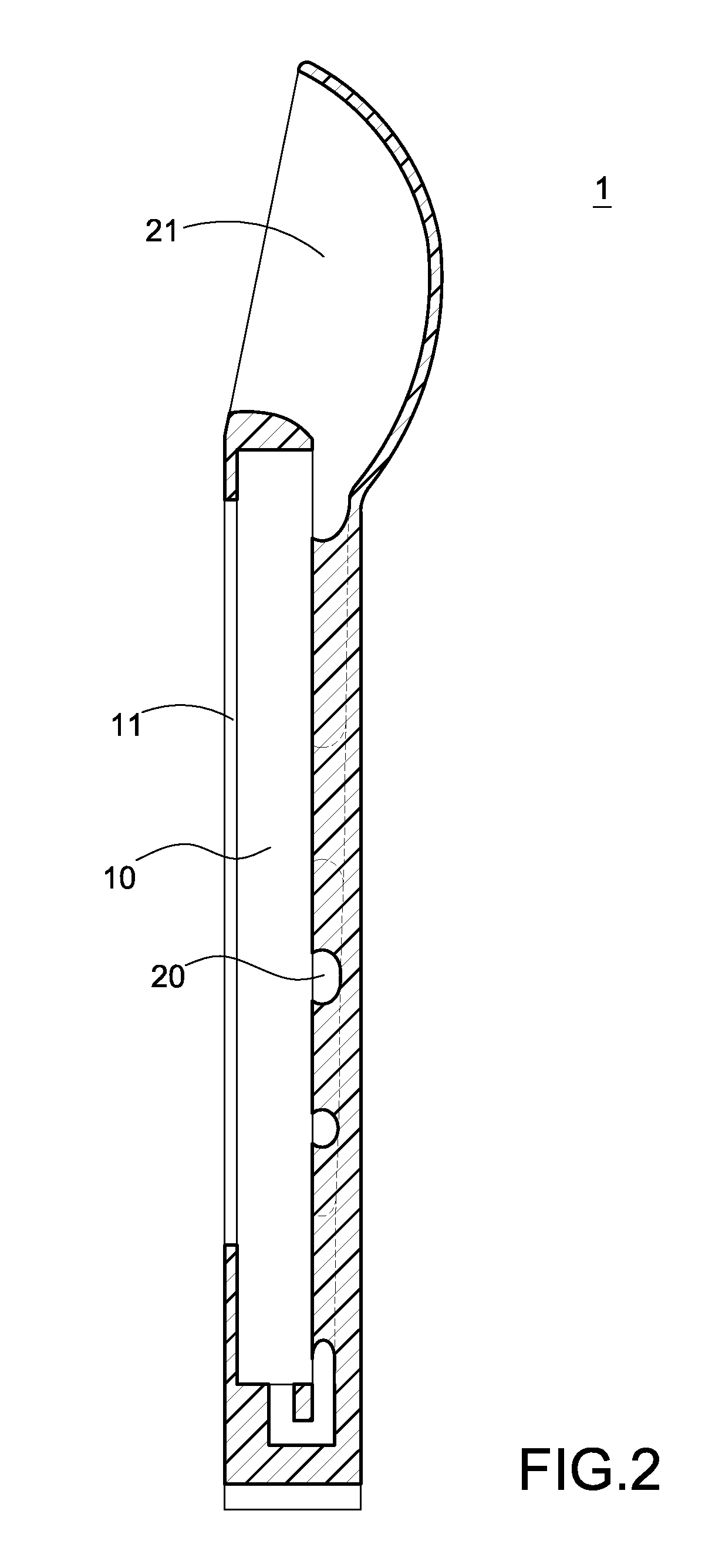
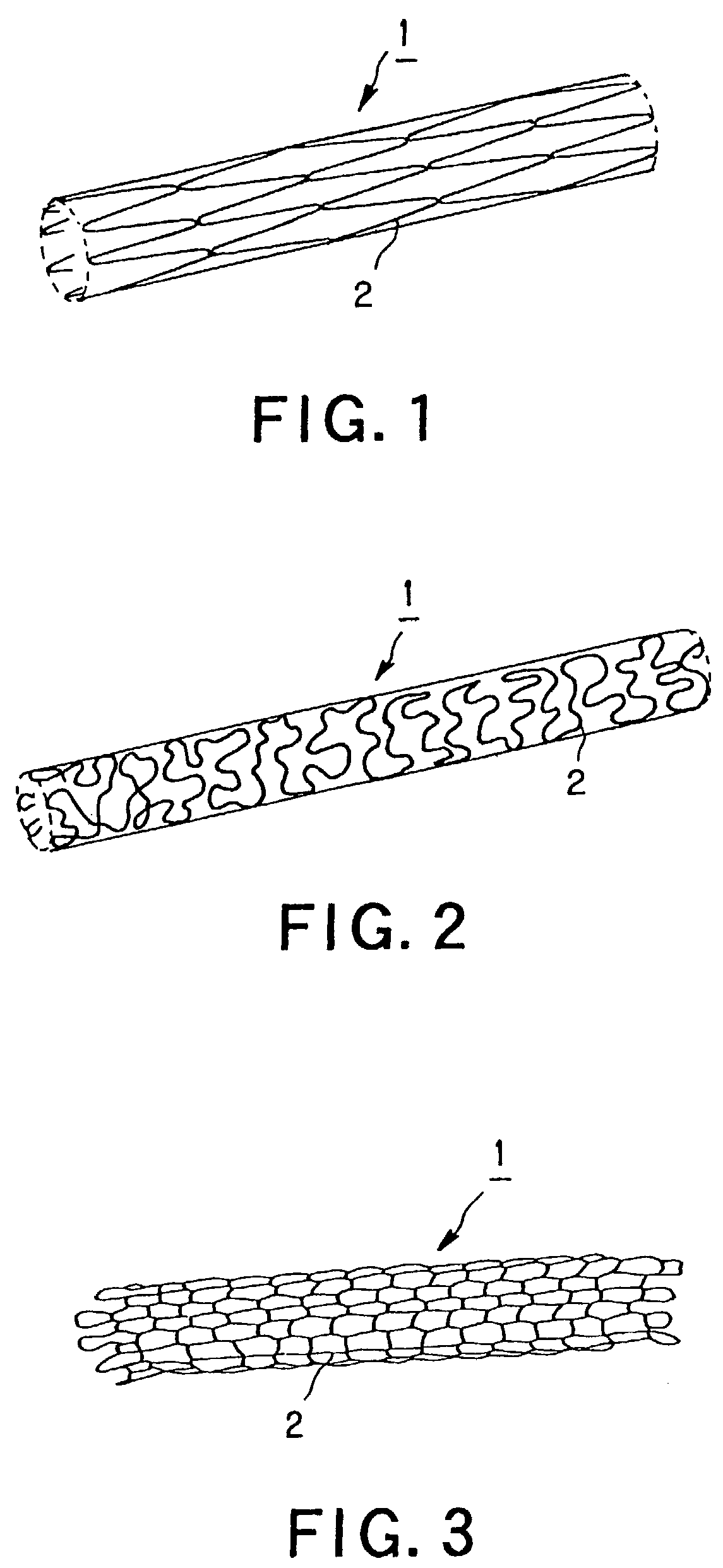
A luminal stent, implanted and implanted and left in the blood vessel, is disclosed. By permitting a stent (1), formed of a biodegradable polymer material (2), to be swollen, and by impregnating the swollen stent (1) with a drug, a sufficient quantity of the drug is impregnated in the stent. This drug is continuously released into the blood vessel over a prolonged time. A biodegradable polymer layer is formed on the surface of the stent (1) impregnated with the drug, and the release rate of the drug impregnated in the stent is controlled.
Owner:KYOTO MEDICAL PLANNING
Exhaust gas system
InactiveUS6938729B2Sufficient effectIncrease powerExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusExternal combustion engineExhaust fumes
An exhaust gas system for an internal combustion engine, in particular, of a motor vehicle has two mufflers through which the exhaust gas is able to flow in a parallel fashion. A switching unit makes it possible to selectively convey the exhaust gas flow of the internal combustion engine only or almost exclusively through the first muffler, or only or almost exclusively through the second muffler, or through both mufflers in a parallel fashion. The two mufflers are realized differently with respect to their muffling effect and / or flow resistance.
Owner:EBERSPACHER EXHAUST TECH GMBH & CO KG
Tissue occluding agent
ActiveUS20110201541A1Higher curative effectImprove adhesionSuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineAqueous solution
There is provided a bioabsorbable peptide tissue occluding agent that can be applied to large mammals including humans, the peptide tissue occluding agent being obtained by artificial synthesis to avoid concerns of infection by viruses and the like.The tissue occluding agent contains a peptide, wherein the peptide is an amphiphilic peptide having 8-200 amino acid residues with the hydrophilic amino acids and hydrophobic amino acids alternately bonded, and is a self-assembling peptide exhibiting a β-structure in aqueous solution in the presence of physiological pH and / or a cation.
Owner:3 D MATRIX
Antireflective film material, and antireflective film and pattern formation method using the same
ActiveUS7303785B2Etching speed is fastSmall fluctuationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPhoto-taking processesResistOrganic solvent
It is an object of the present invention to provide a material for an antireflective film that has high etching selectivity with respect to the resist, that is, that has a faster etching speed than the resist, a pattern formation method for forming an antireflective film layer on a substrate using this antireflective film material, and a pattern formation method using this antireflective film as a hard mask for substrate processing. The present invention provides a silicone resin for preventing reflection comprising an organic group comprising a carbon-oxygen single bond and / or a carbon-oxygen double bond; a light-absorbing group; and a silicon atom whose terminal end or ends are Si—OH and / or Si—OR. It also provides an antireflective film material comprising this silicone resin (A) for preventing reflection film, an organic solvent (B) and an acid generator (C).
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Aluminum alloy of excellent machinability and manufacturing method thereof
An aluminum alloy containing Si: 1.5-12% (mass % here and hereinafter), Mg: 0.5-6% and, optionally, at least one of Mn: 0.5-2%, Cu: 0.15-3% and Cr: 0.04-0.35% and, further, containing Ti: 0.01-0.1% and the balance of Al and inevitable impurities, in which the average grain size of crystallized grains of Si system compounds is from 2 to 20 mu m and an area ratio thereof is from 2 to 12%. The alloy is melted to obtain a cast ingot having DAS (Dendrite Arm Spacing) of 10 to 50 mu m, which is then put to a soaking treatment at 450 to 520 DEG C. and then to extrusion molding. The aluminum alloy has excellent machinability with no addition of low melting metals.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
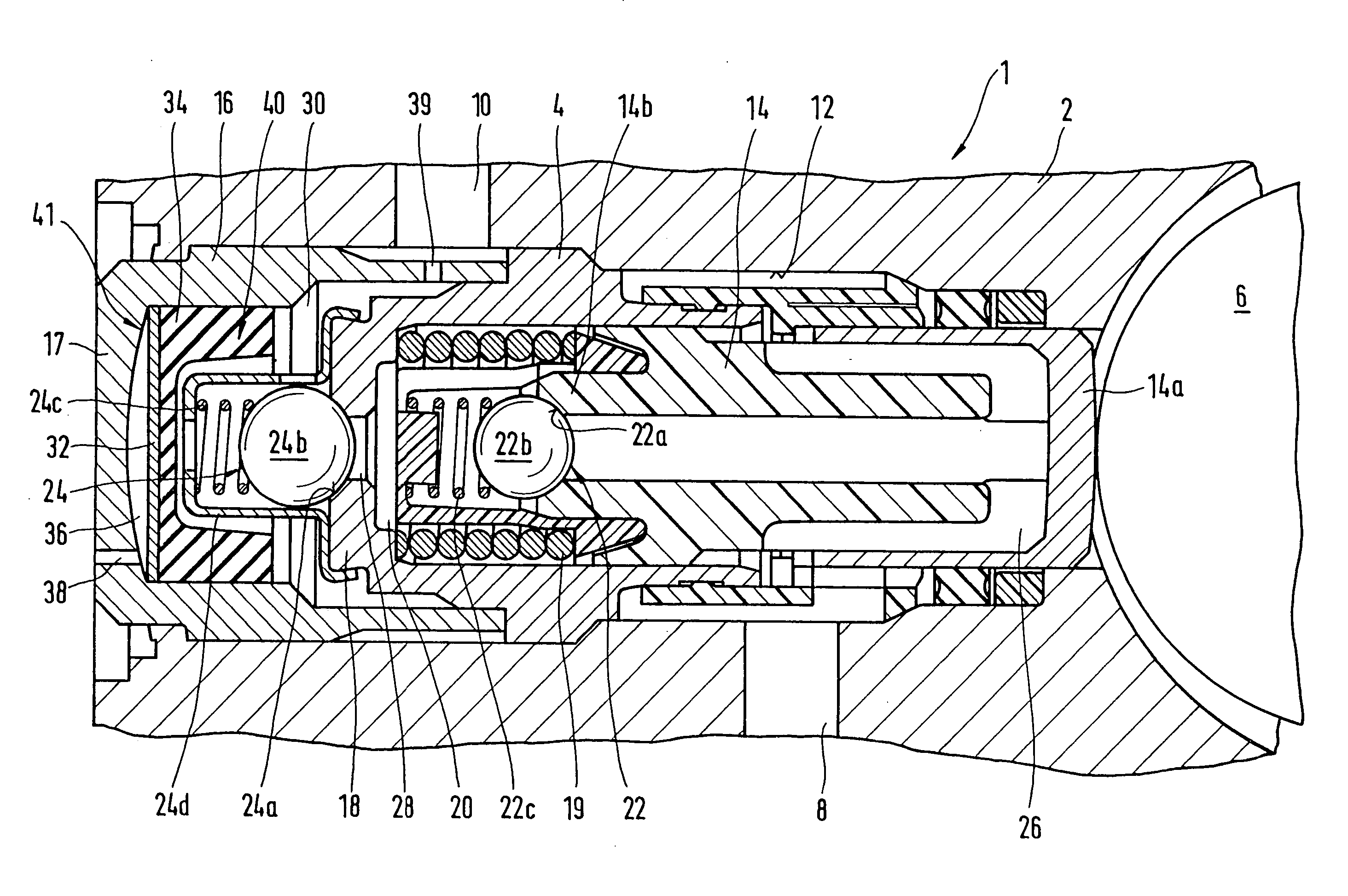
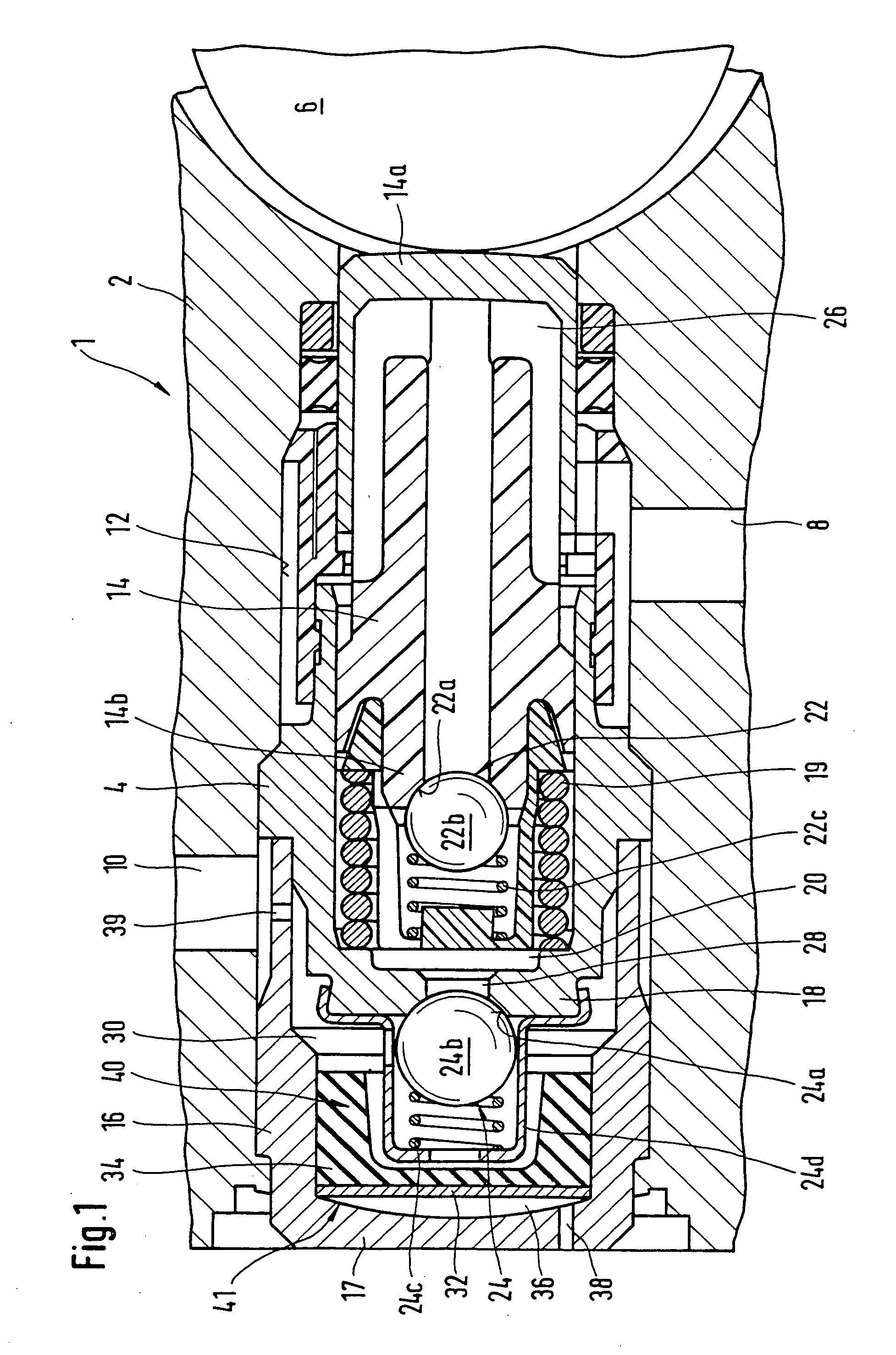
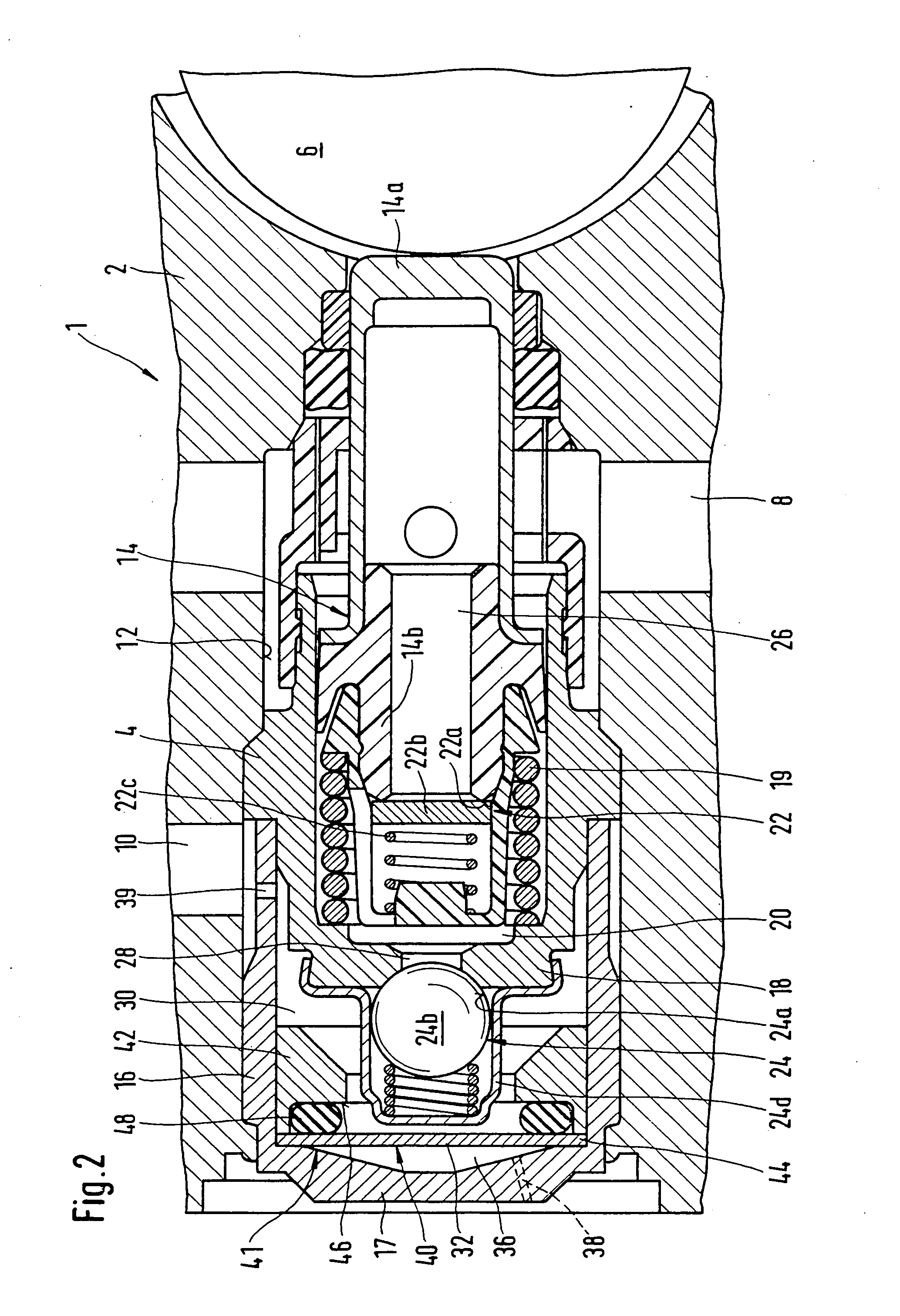
Piston pump
InactiveUS20040166004A1Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyPositive displacement pump componentsPipe elementsMobile vehicleControl theory
In piston pumps for brake systems used until now, there were often noise problems, from pressure pulsations. In the piston pump for brake systems proposed here, a pulsation-smoothing device (40) that functions effectively well is provided in the region of the outlet valve (24). As a result, substantially less noise occurs, and the durability of the piston pump (1) is substantially better. The piston pump is used essentially in traction-controlled motor vehicle brake systems.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Antipruritics
It is intended to provide antipruritics (drugs to control itching, antiitch agents and drugs to stop itching). It is found out that a compound having an agonistic activity to the cannabinoid receptor shows an antipruritics effect.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Water-based surface-treating agent for metallic material
InactiveUS6447620B1Raise the ratioIncreased insolubilityOther chemical processesSolid state diffusion coatingWater basedMetallic materials
A water-based surface-treating agent for metallic materials which gives a film highly satisfactory in corrosion resistance, blackening resistance, wet secondary adhesion to topcoatings, low-pollution characteristics (amount of fixed chromium), chemical resistance (especially acid resistance and alkali resistance), etc., while retaining the intact practical liquid stability of conventional chromate-containing resinous coating agents. The water-based surface-treating agent comprises a synthetic resin emulsion and hexavalent chromium ions and has a pH of 5 or lower, the synthetic resin emulsion being one obtained by emulsion-polymerizing the following ingredients using a nonionic polymerizable emulsifier and a nonionic nonpolymerizable emulsifier: (1) an ethylenic carboxylic acid, (2) a functional acrylic monomer having at least one of N-((un)substituted methylol)carbamoyl, phosphonate, alkoxy, cyano, and carbamoyl groups, and (3) a third monomer which is different from the ingredients (1) and (2) and forms the skeleton of the copolymer to be obtained.
Owner:HENKEL CORP
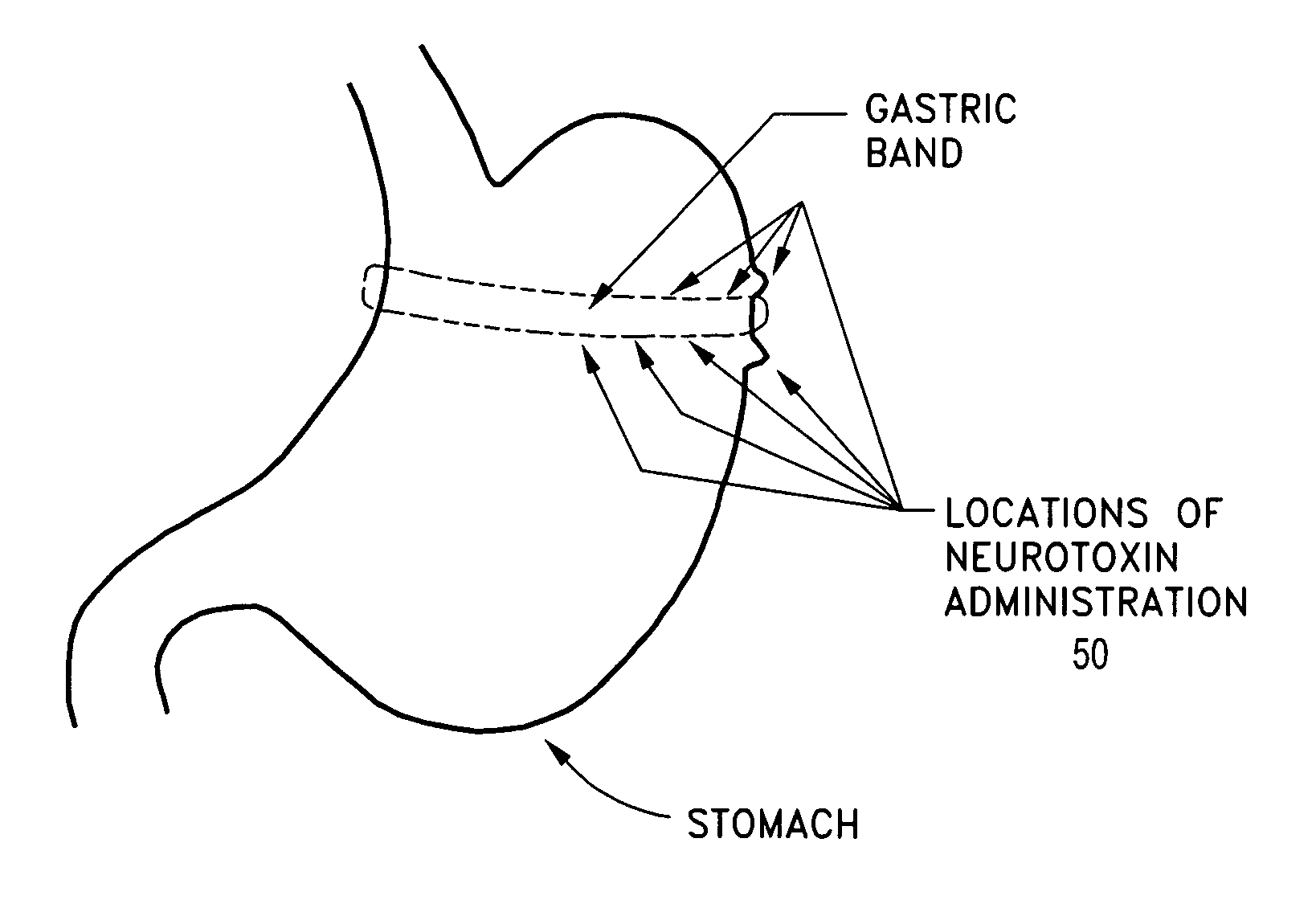
Apparatus and method for treating obesity using neurotoxins in conjunction with bariatric procedures
InactiveUS20080092910A1Inhibit diseaseArrest it developmentPeptide/protein ingredientsDiagnosticsBariatric patientVomiting
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
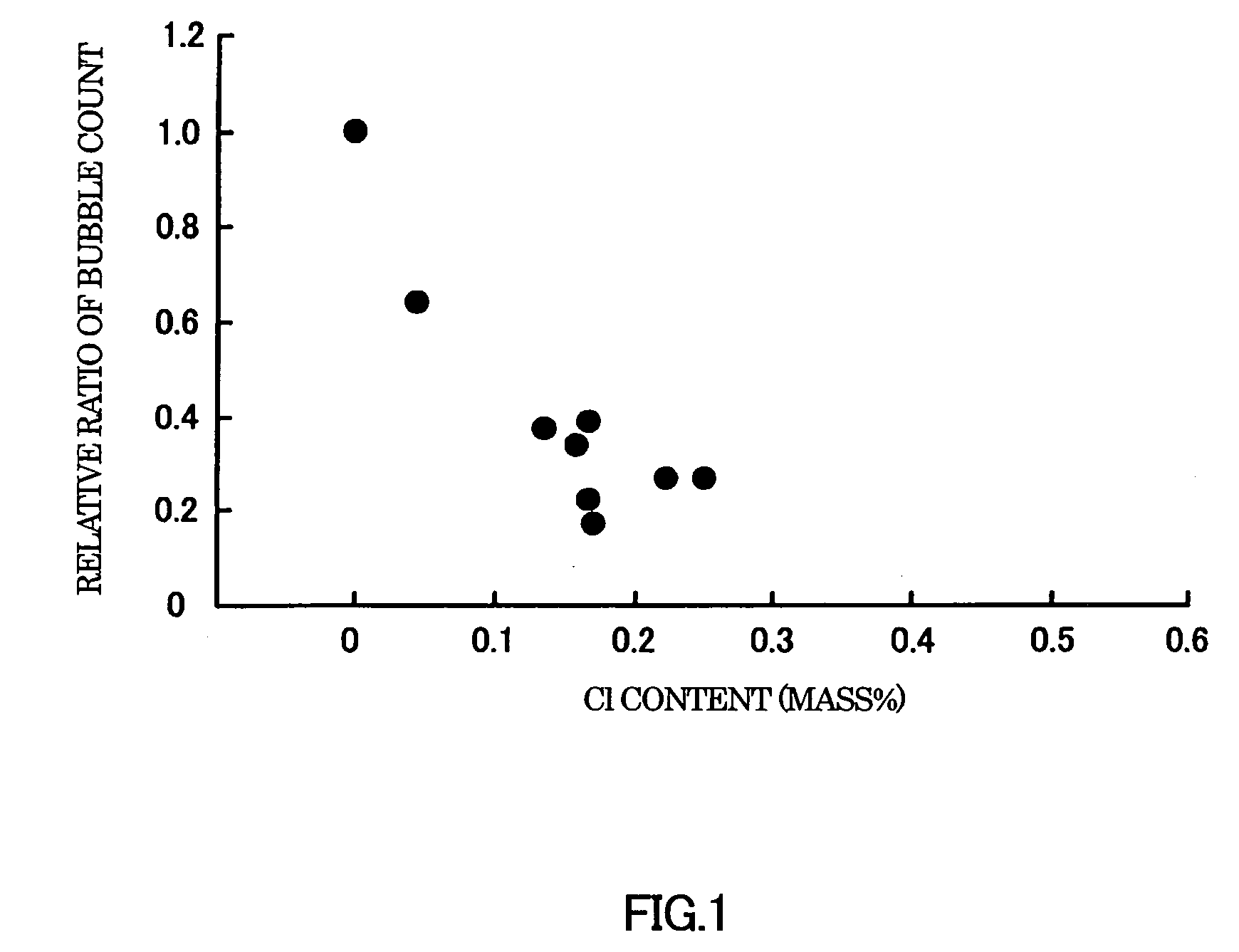
Glass composition
ActiveUS20090143214A1Improve glass fining effectSufficient fining effectNon-linear opticsIdentification meansArsenic oxideChemistry
A glass composition which is reduced in the amount of residual bubbles and is produced using smaller amounts of an environmentally unfriendly component such as arsenic oxide and antimony oxide. This glass composition comprises, in terms of mass %: 40-70% SiO2; 5-20% B2O3; 10-25% Al2O3; 0-10% MgO; 0-20% CaO; 0-20% SrO; 0-10% BaO; 0.001-0.5% Li2O; 0.01-0.5% Na2O; 0.002-0.5% K2O; and 0-1.0%, excluding 0%, Cl
Owner:AVANSTRATE INC
Radical polymerizable composition and lithographic printing plate precursor using the same
ActiveUS20050031986A1Enhance layeringHigh sensitivityRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer sciencePlanographic printing
A radical polymerizable composition comprising (A) an alkali-soluble resin containing a radical polymerizable group, (B) a radical polymerizable compound, and (C) a radical initiator, wherein reactivity of a polymerizable group of the polymerizable compound 4B) to a polymerizable group of the polymerizable compound (B) is larger than reactivity of a polymerizable group of the polymerizable compound (B) to a radical polymerizable group of the alkali-soluble resin (A), and a reactivity of a radical polymerizable group of the alkali-soluble resin (A) to a polymerizable group of the polymerizable compound (B) is larger than reactivity of a radical polymerizable group of the alkali-soluble resin (A) to a radical polymerizable group of the alkali-soluble resin (A).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Polycarboxylic acid copolymer, production method and use thereof
InactiveUS6864337B2Improves water reducing capacityImprove workabilityHigh strength concreteUltimate tensile strength
It is an object of the present invention to provide a polycarboxylic acid copolymer which improves the water reducing capacity and workability of cement compositions and the like and making them easier to handle when the fluidity and water reducing capacity are at the same levels, a method of producing the copolymer, and a cement additive and a cement composition comprising the copolymer. The present invention is further to provide a polycarboxylic acid copolymer and a cement additive which are capable of improving the strength and durability of hardening products of cement compositions, hence can advantageously be used in ultrahigh strength concrete. The present invention is still further to provide a method of producing polycarboxylic acid copolymers having high water reducing capacity, reducing the viscosity of cement compositions and improving the workability in applying cement.The present invention is directed to a polycarboxylic acid copolymer which is obtained by copolymerization of monomer components comprising a polyalkyleneimine unsaturated monomer (A1) and an unsaturated carboxylic acid monomer (B).
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
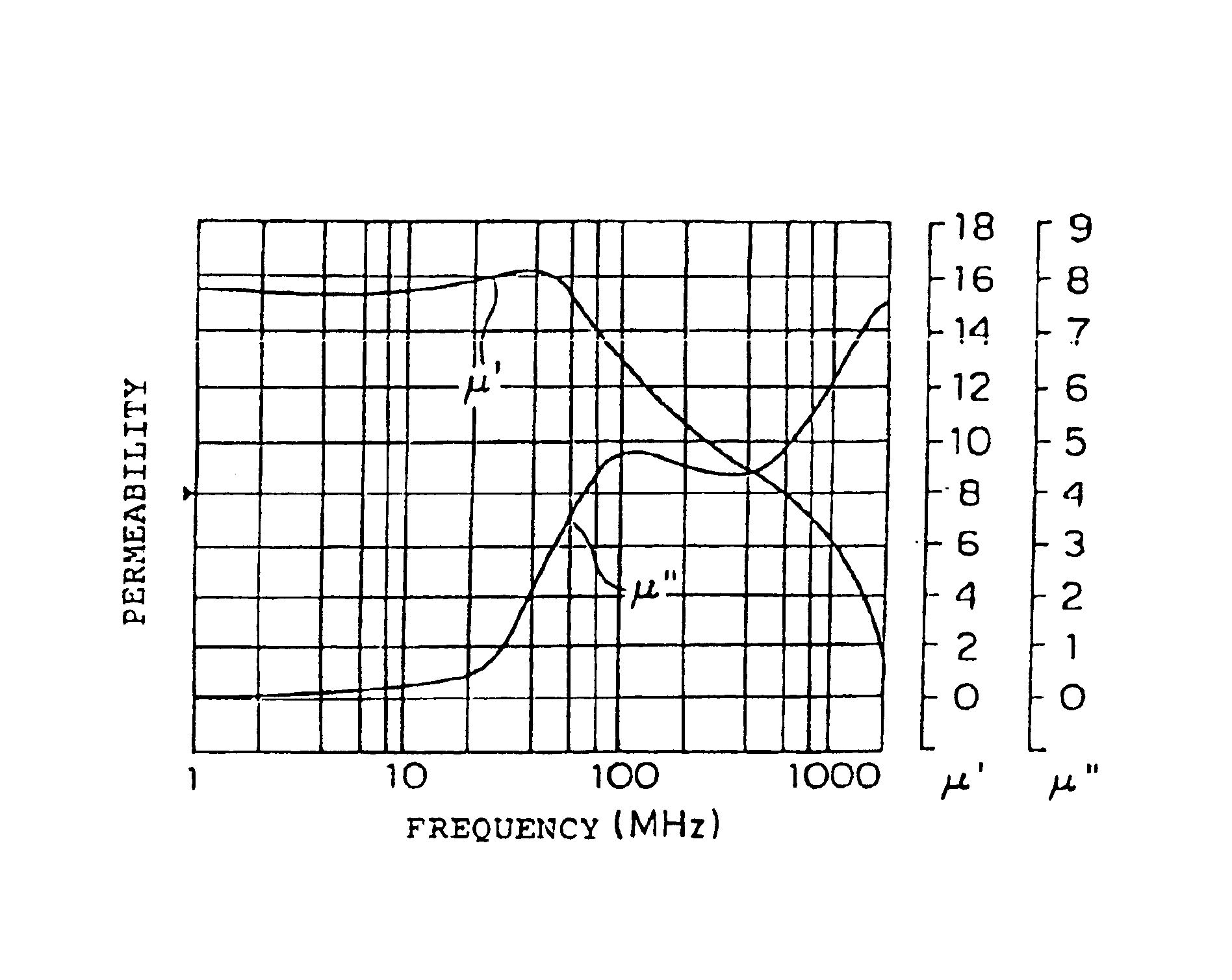
Composite magnetic material and electromagnetic interference suppressor member using the same
InactiveUS6972097B2Complex shapeGood flexibilityMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsResonanceSuppressor
A composite magnetic material is provided for use as an electromagnetic interference suppressing body for effectively suppressing an electromagnetic interference within a high frequency apparatus including a mobile communication terminal. The composite magnetic material consists essentially of a soft magnetic powder and an organic binder and is electrically non-conductive and has at least two magnetic resonances caused by at least two anisotropic magnetic fields (Hk). In the composite magnetic material, the anisotropic magnetic fields (Hk) are different in strength from each other.
Owner:TOKIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com