Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
184 results about "Primer dimer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
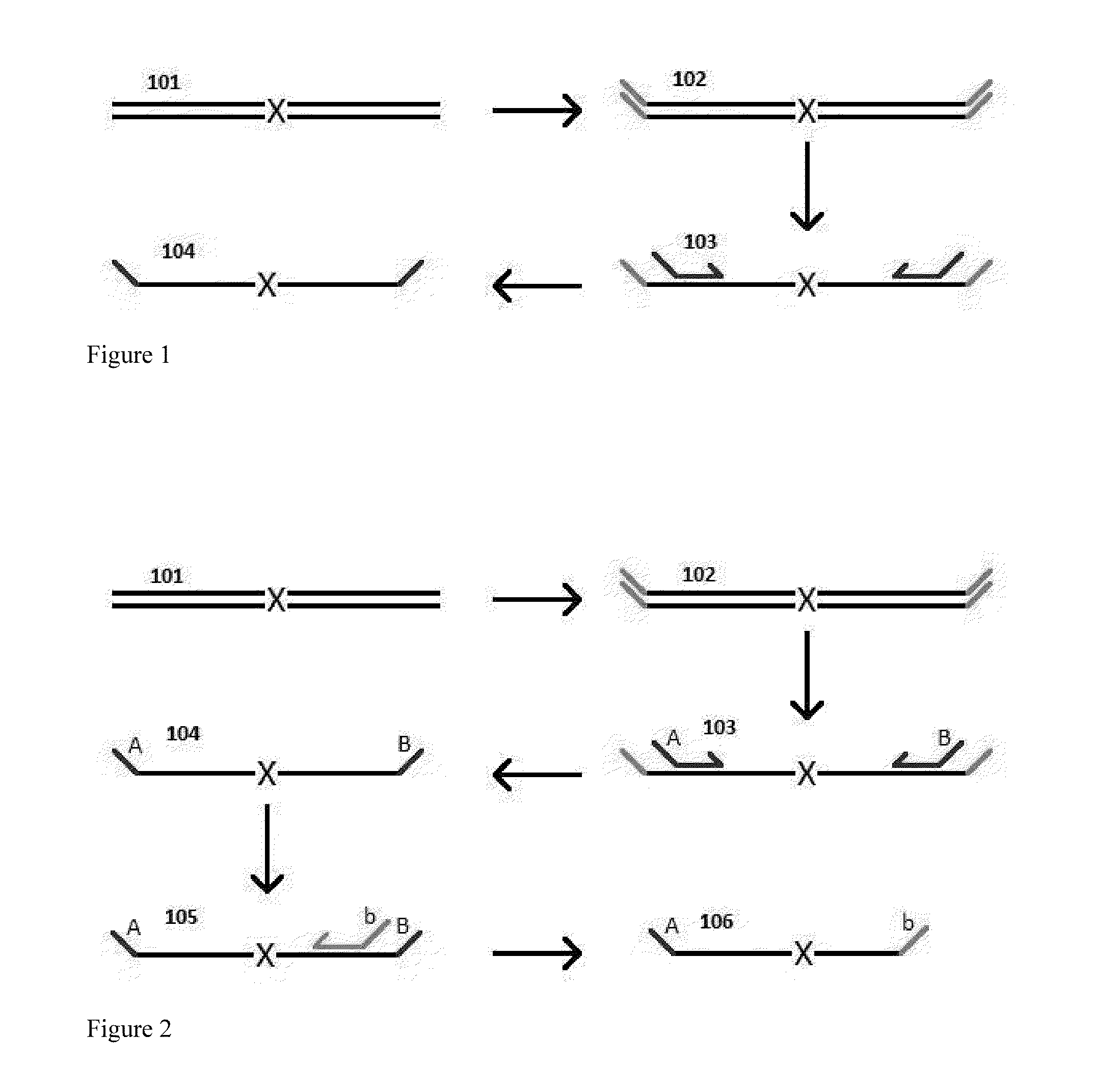
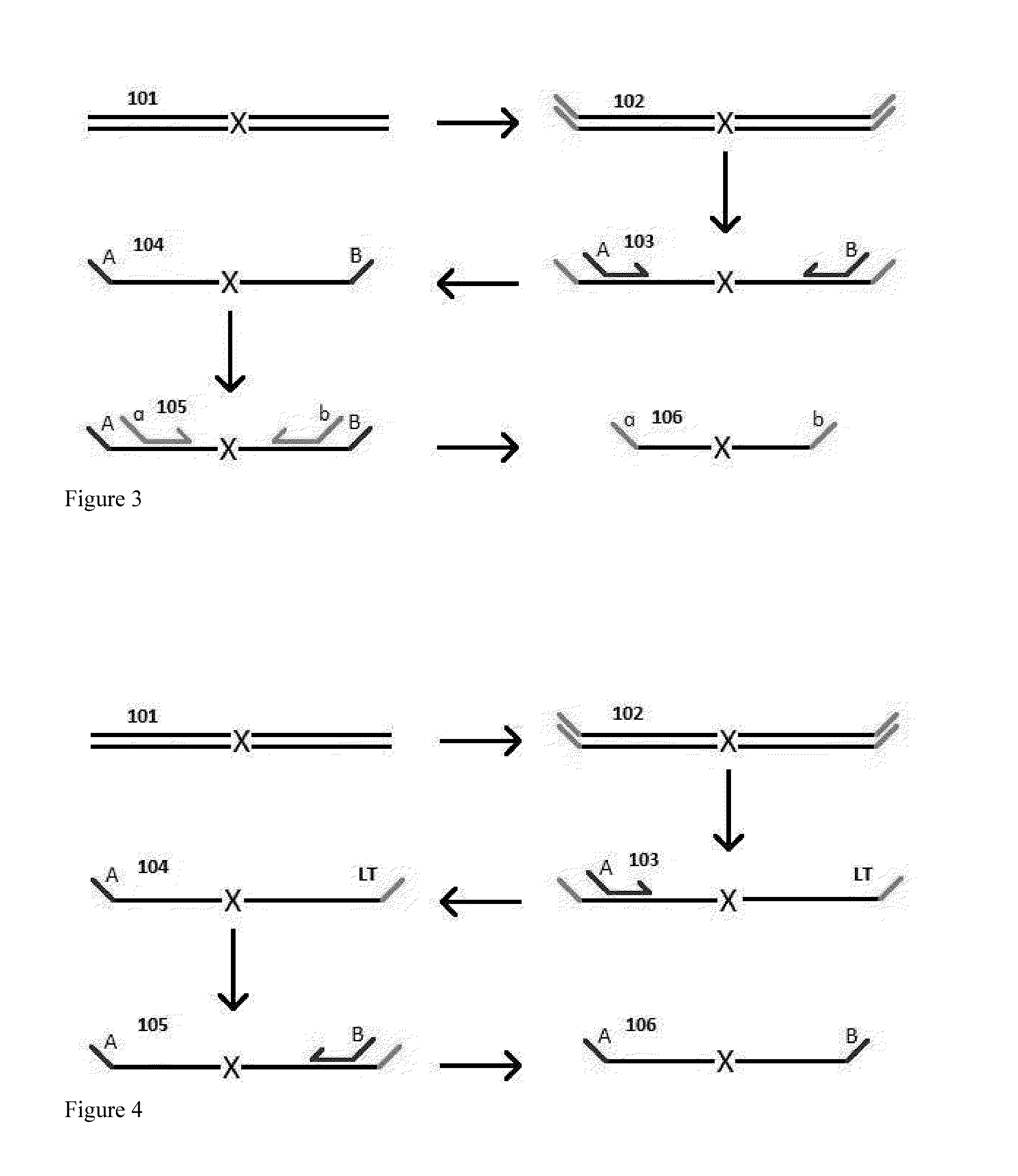
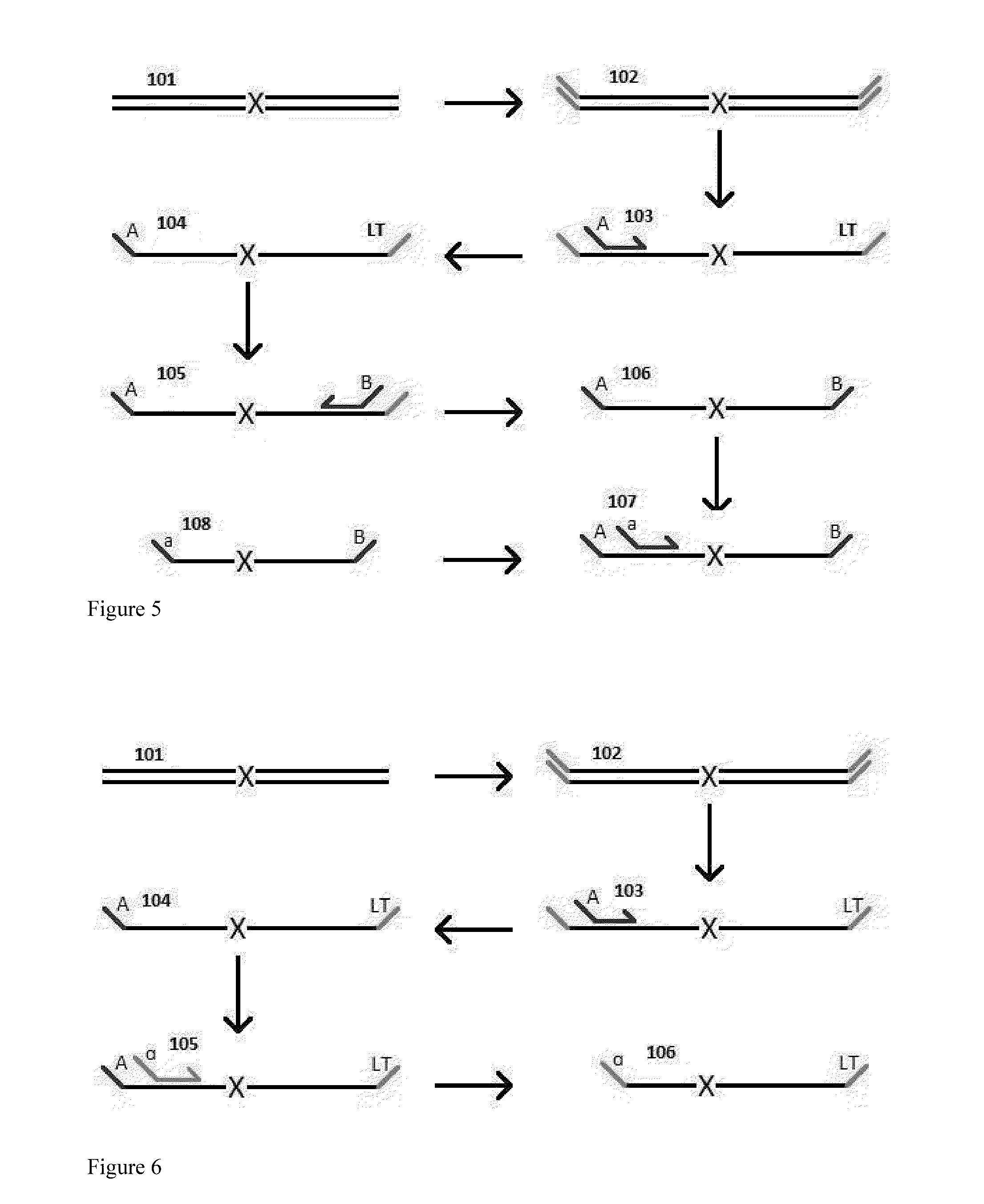
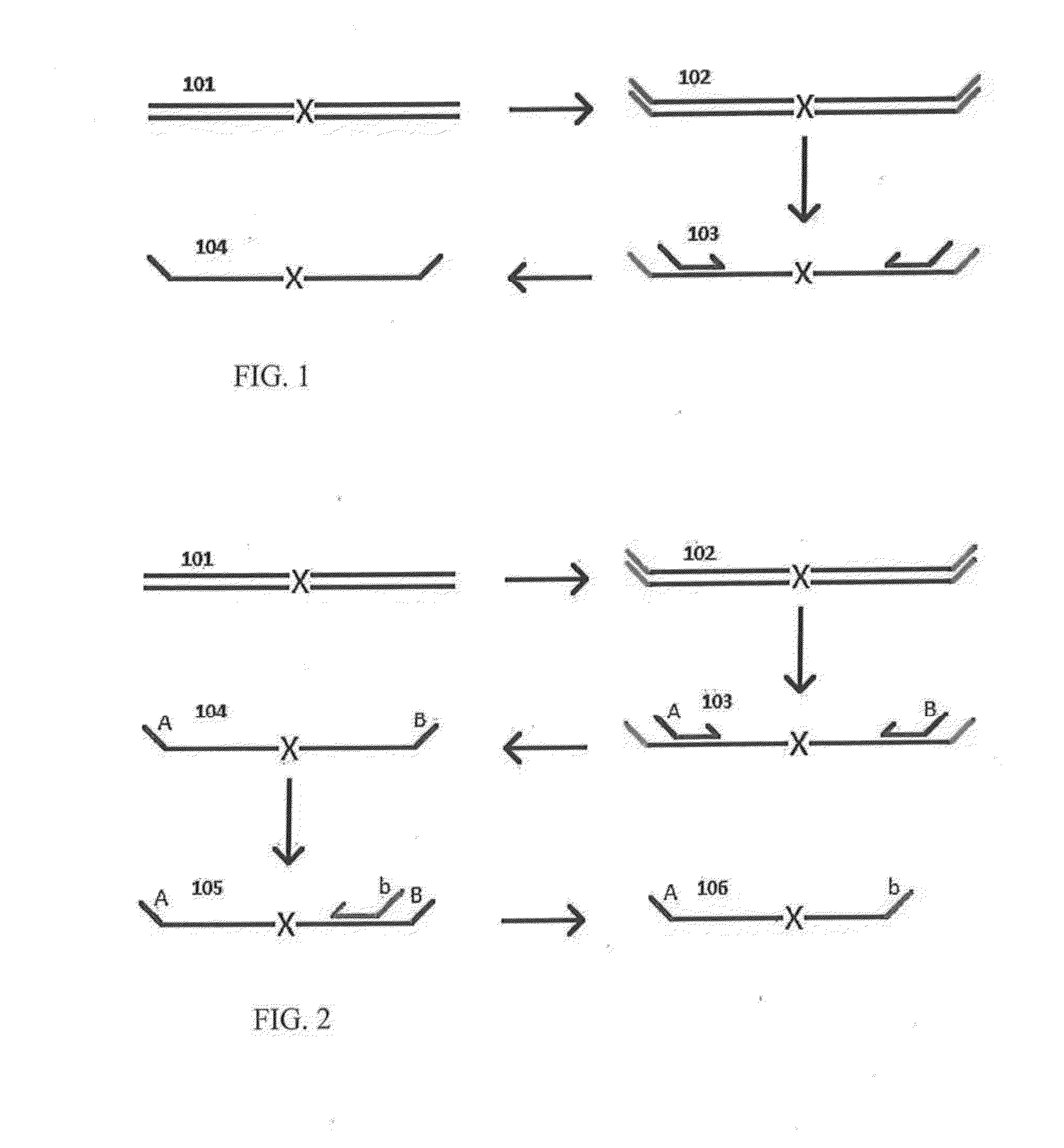
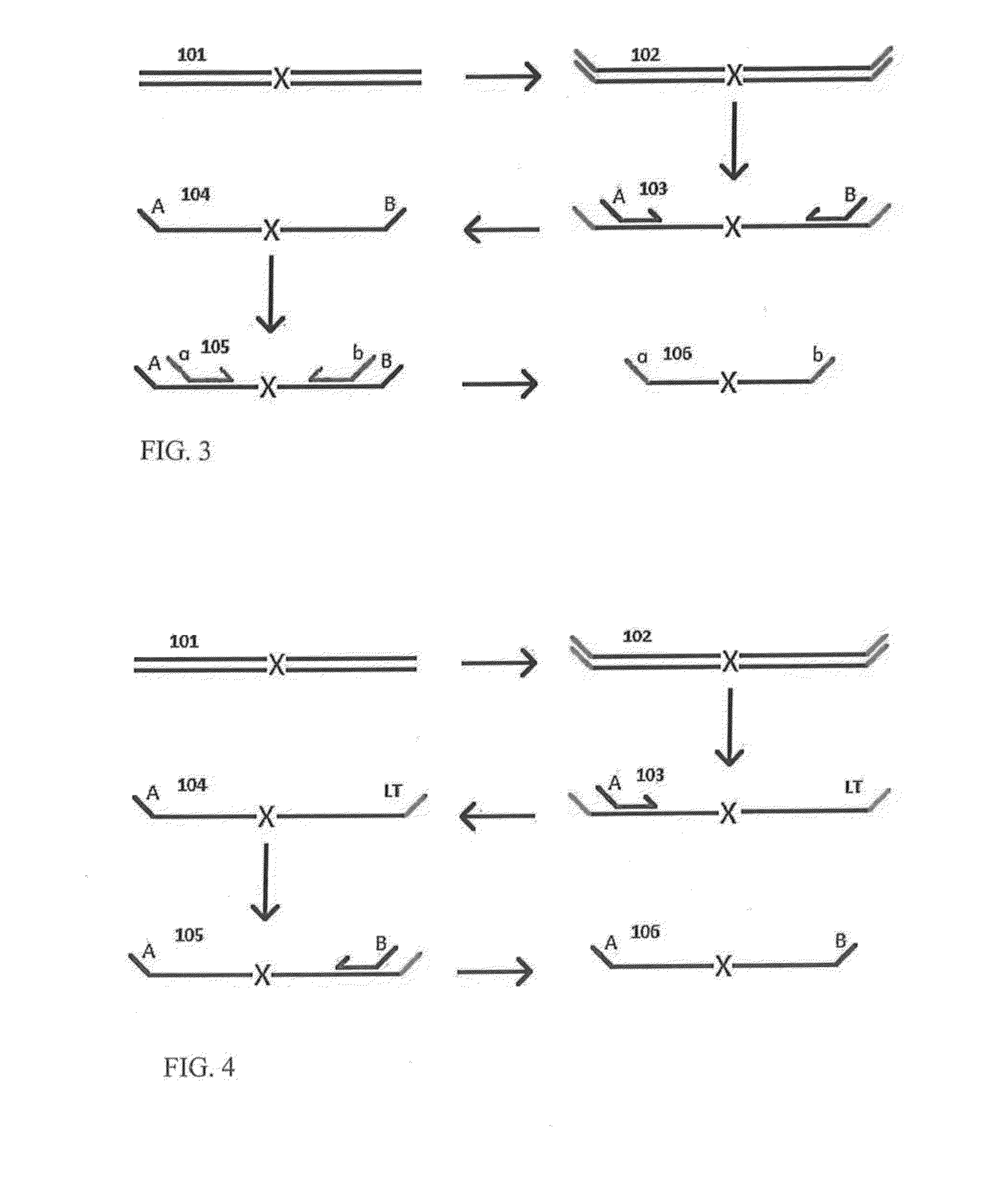
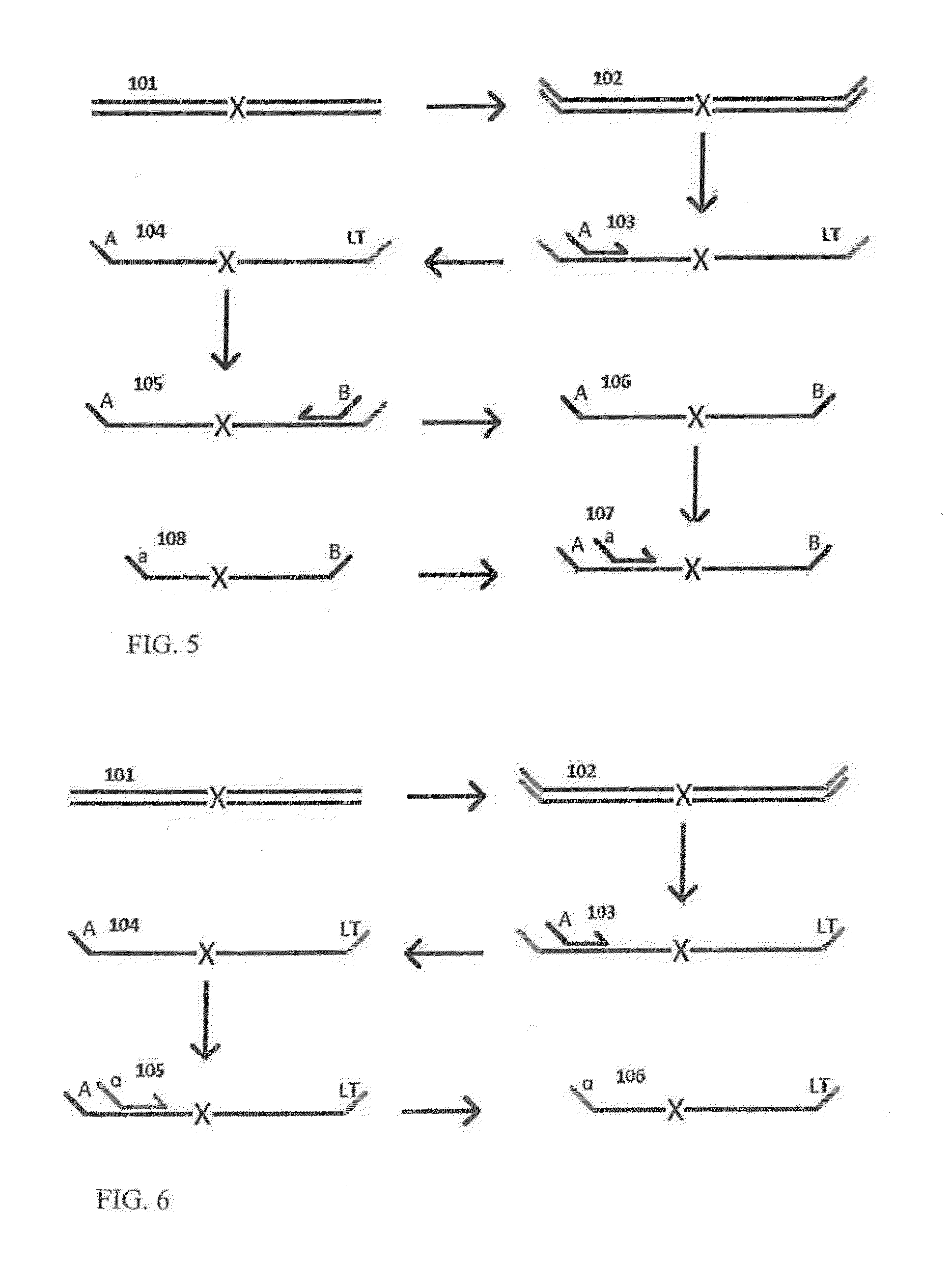
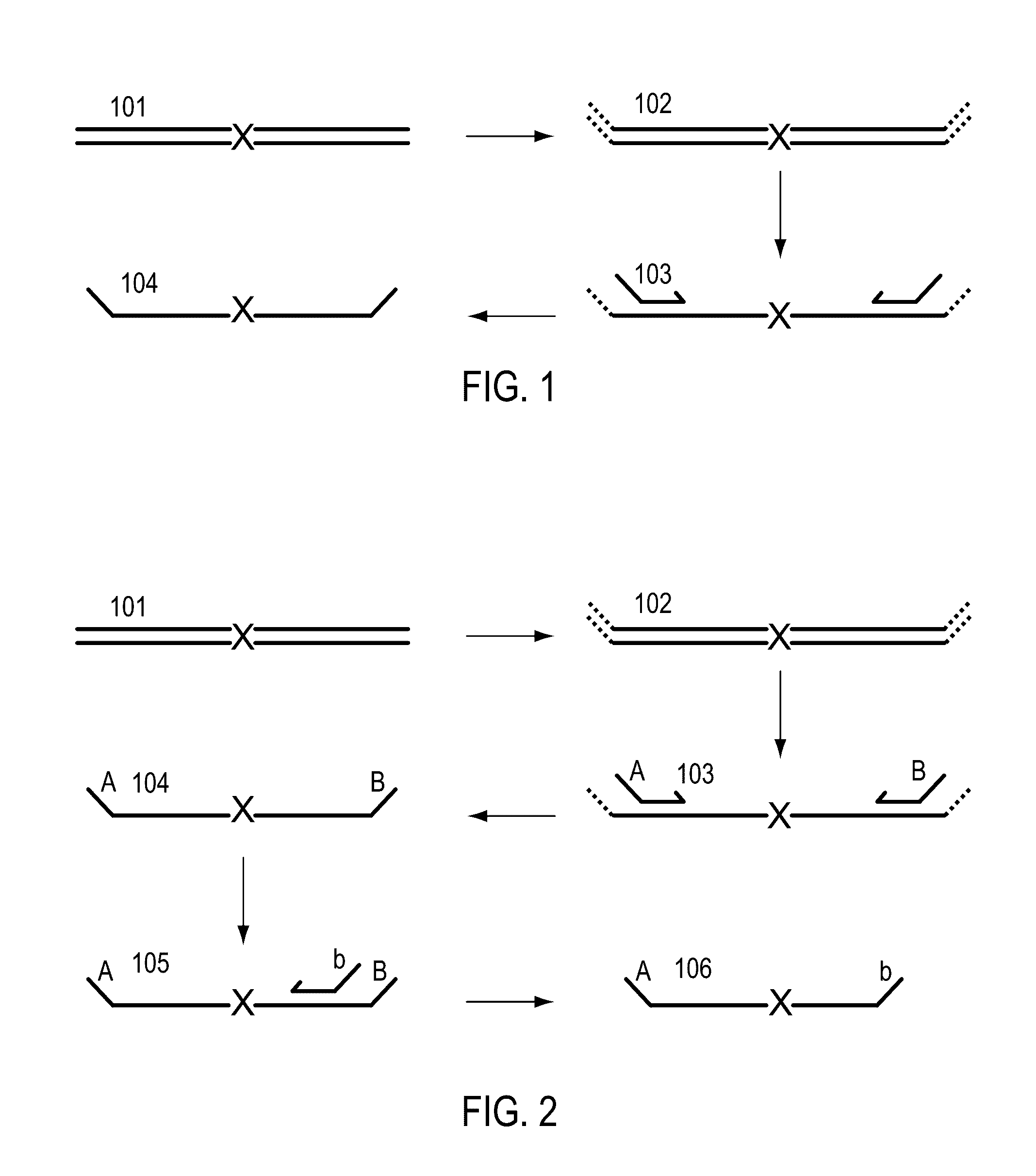
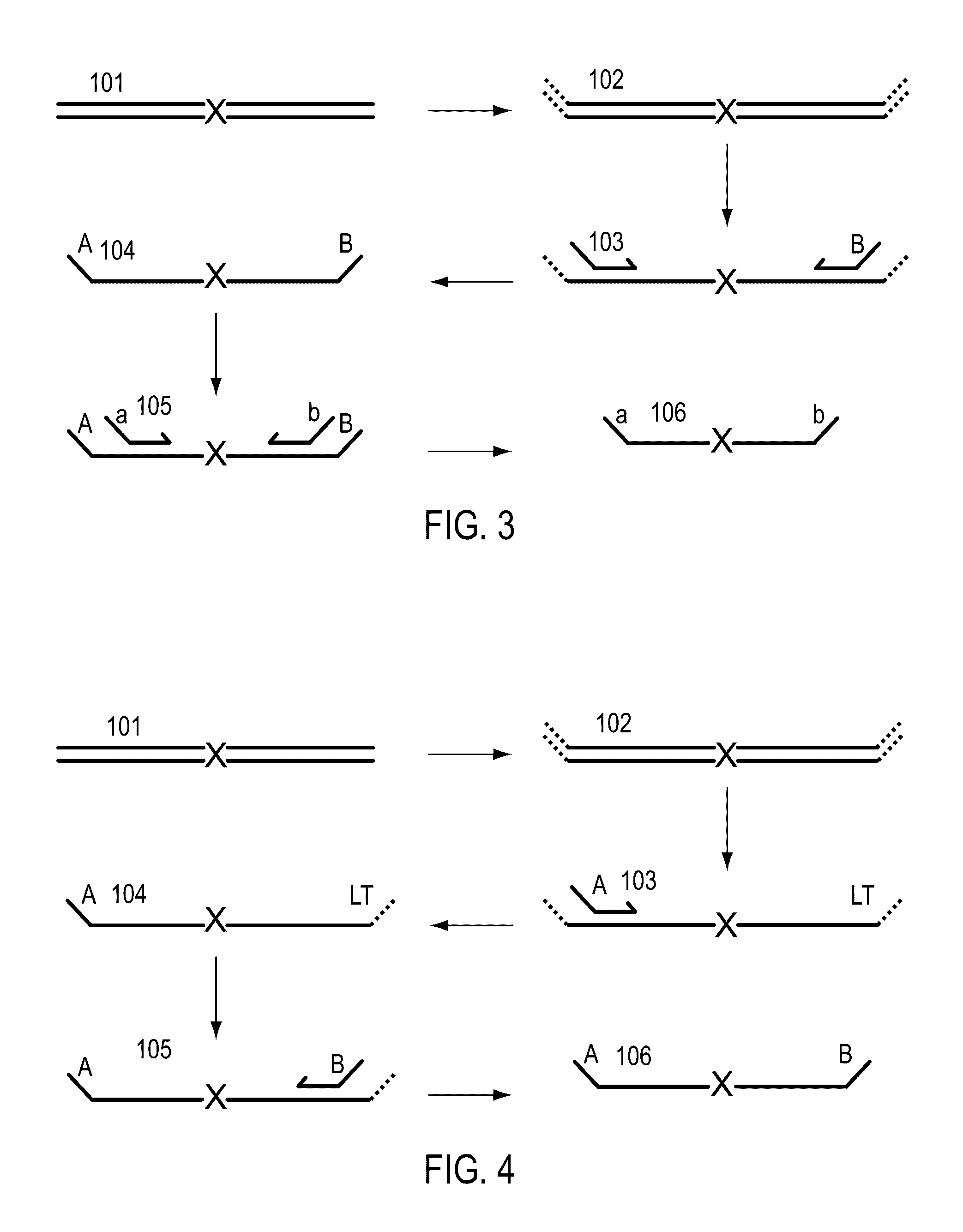
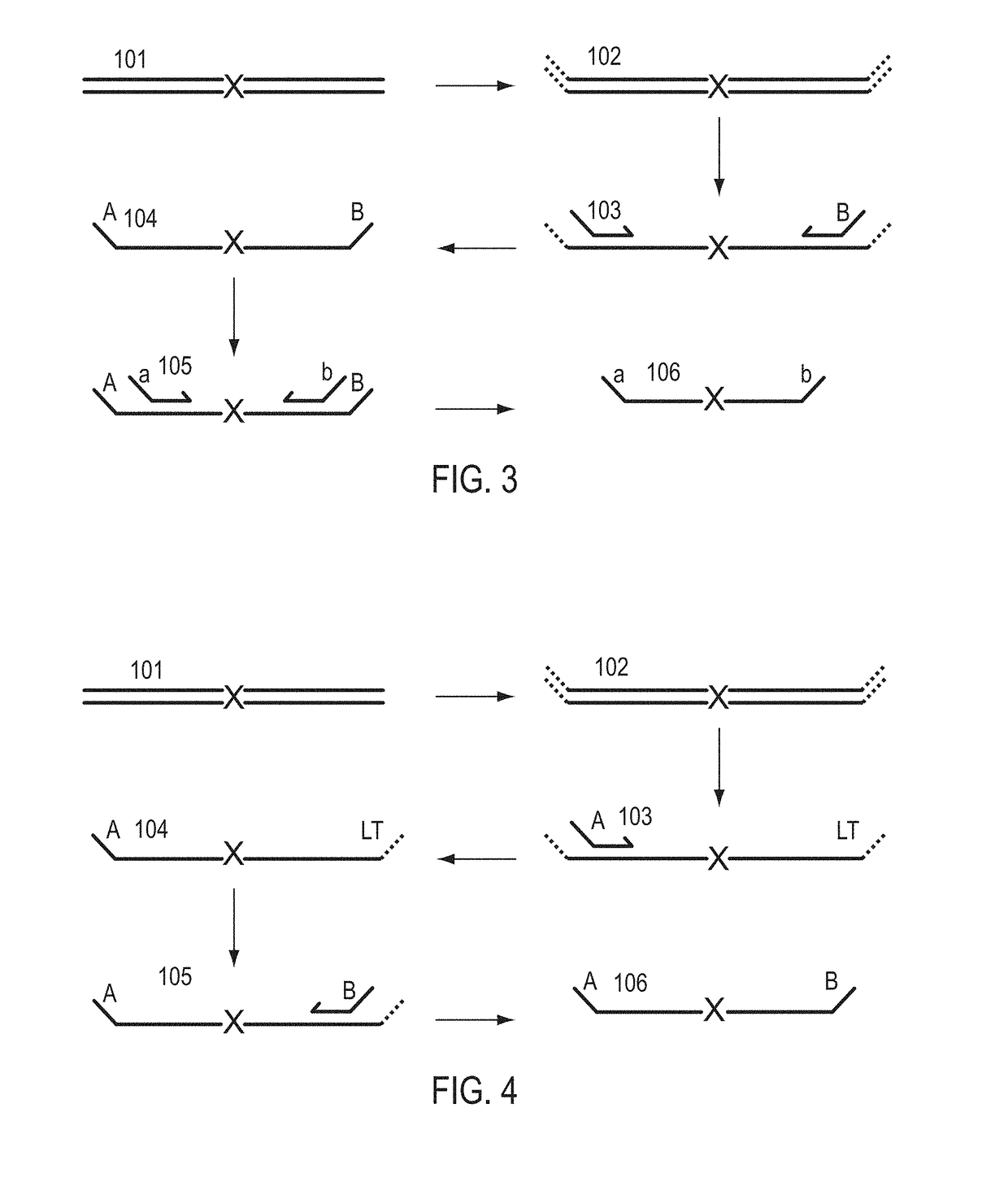
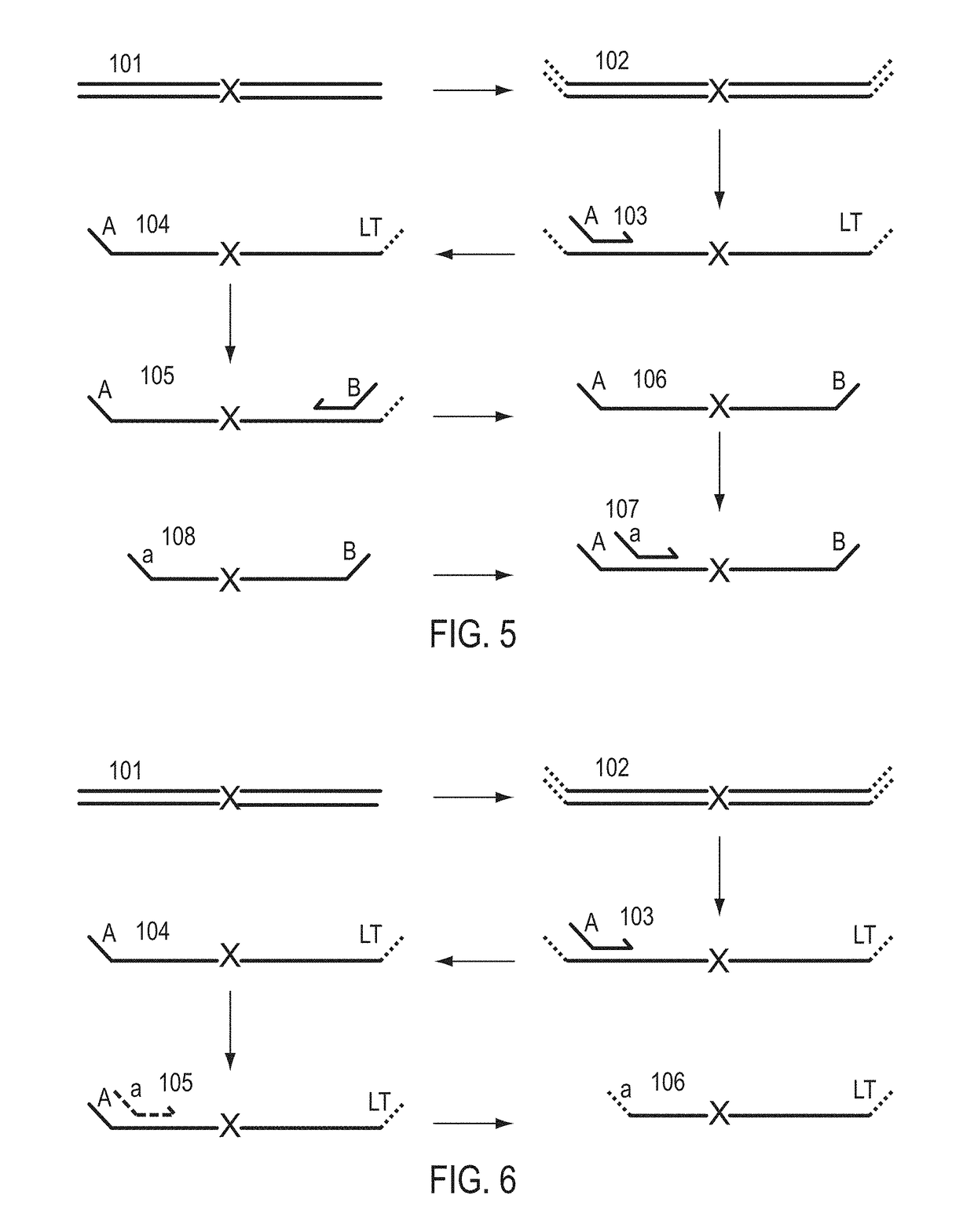
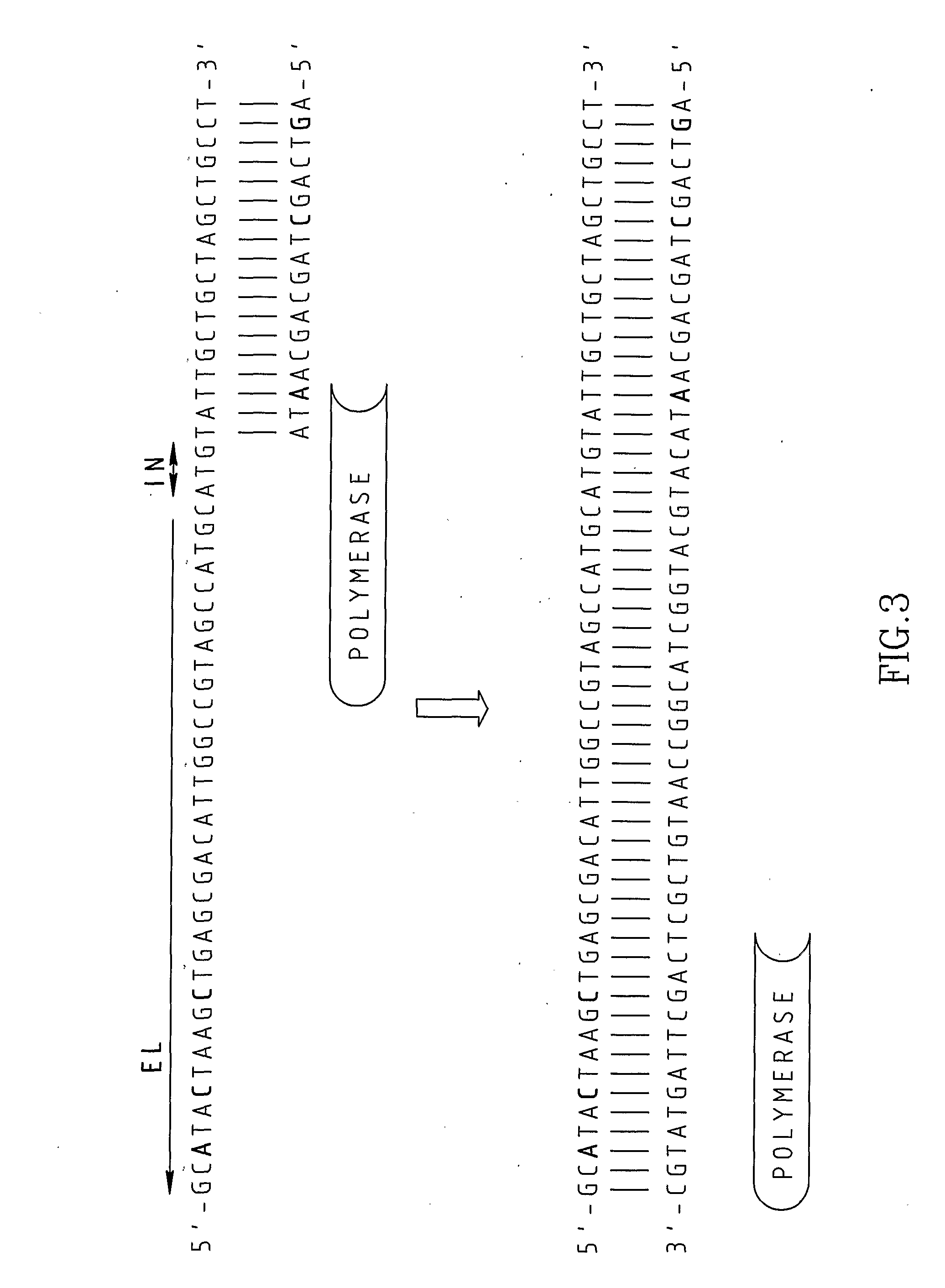
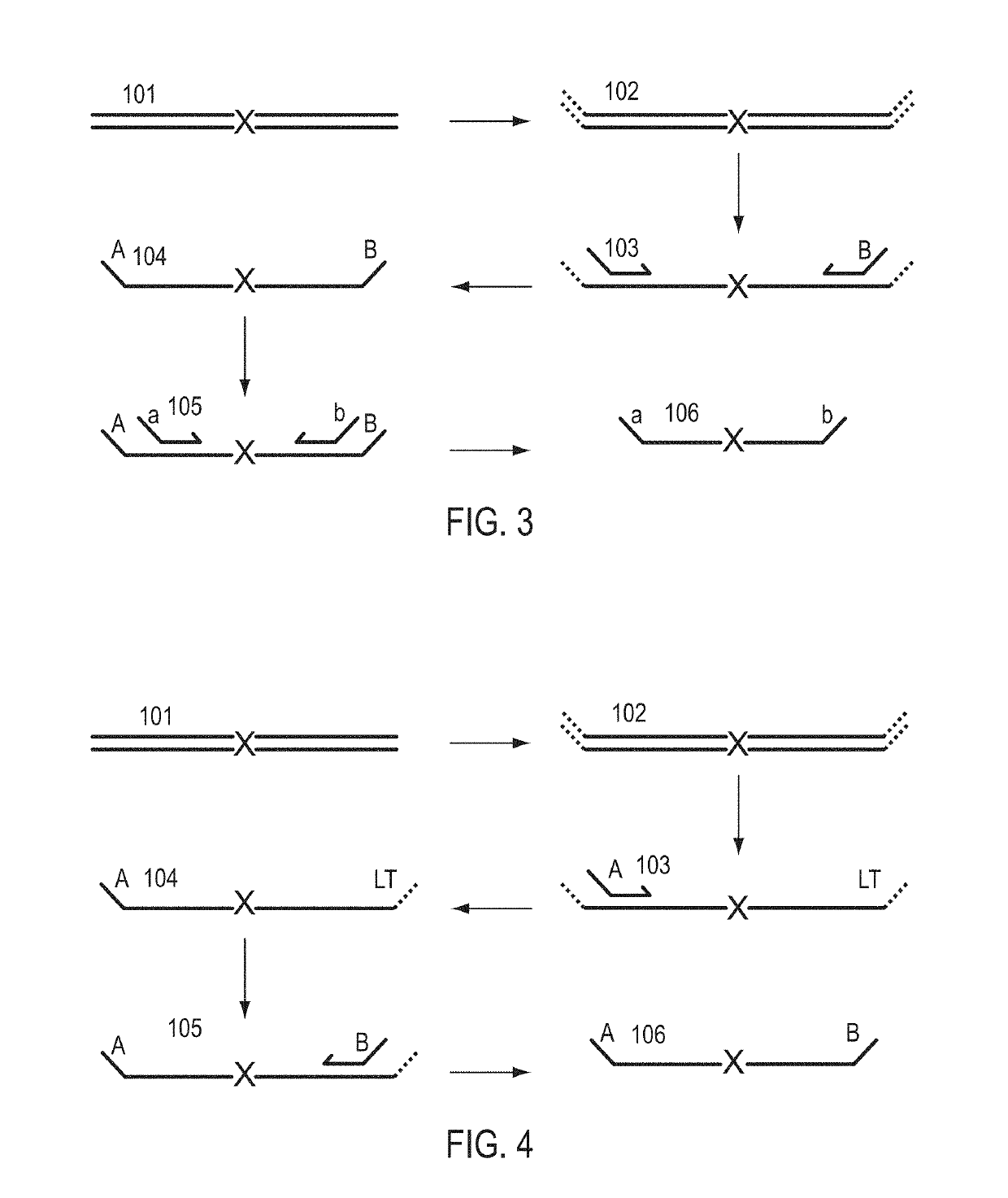
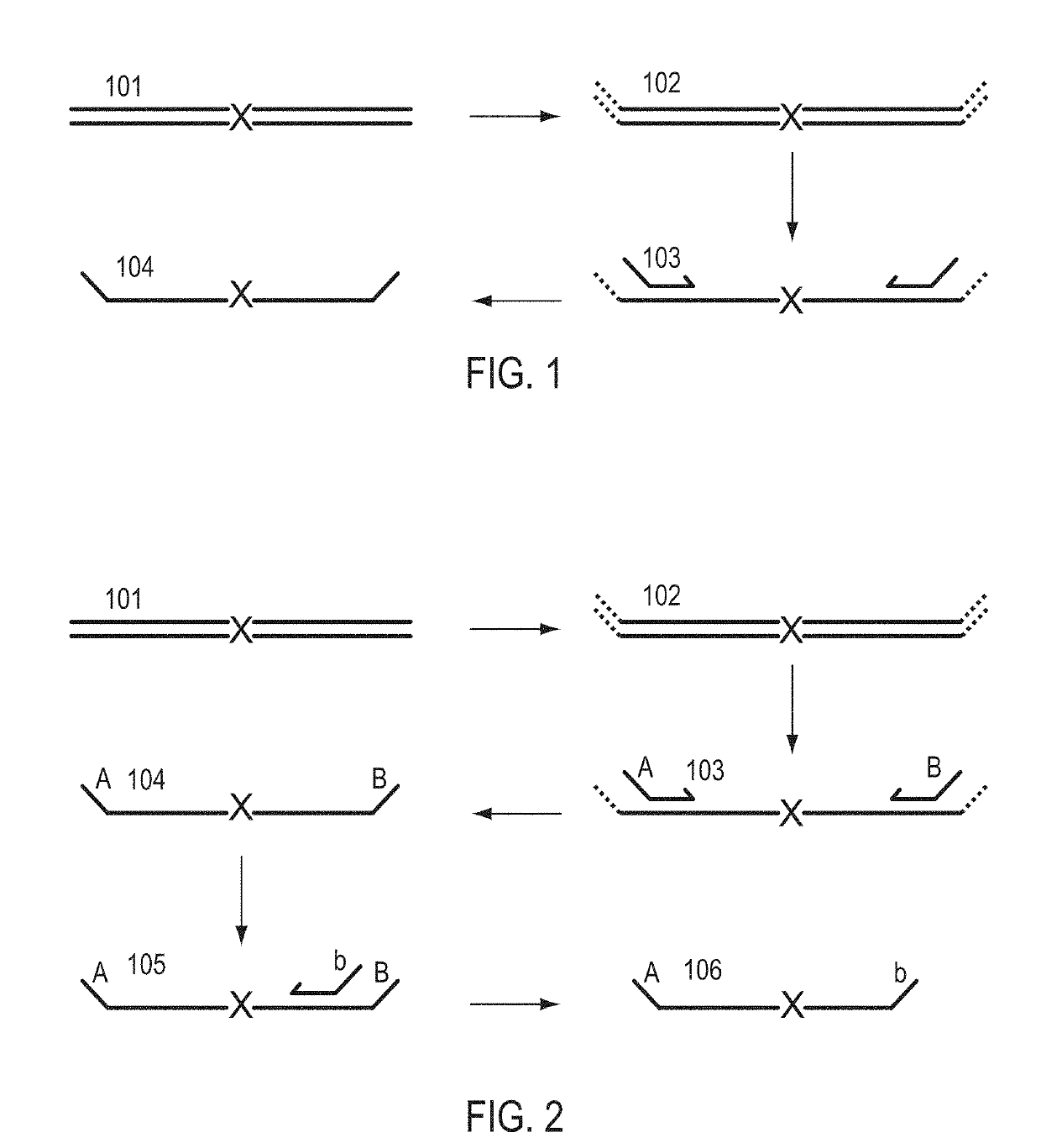
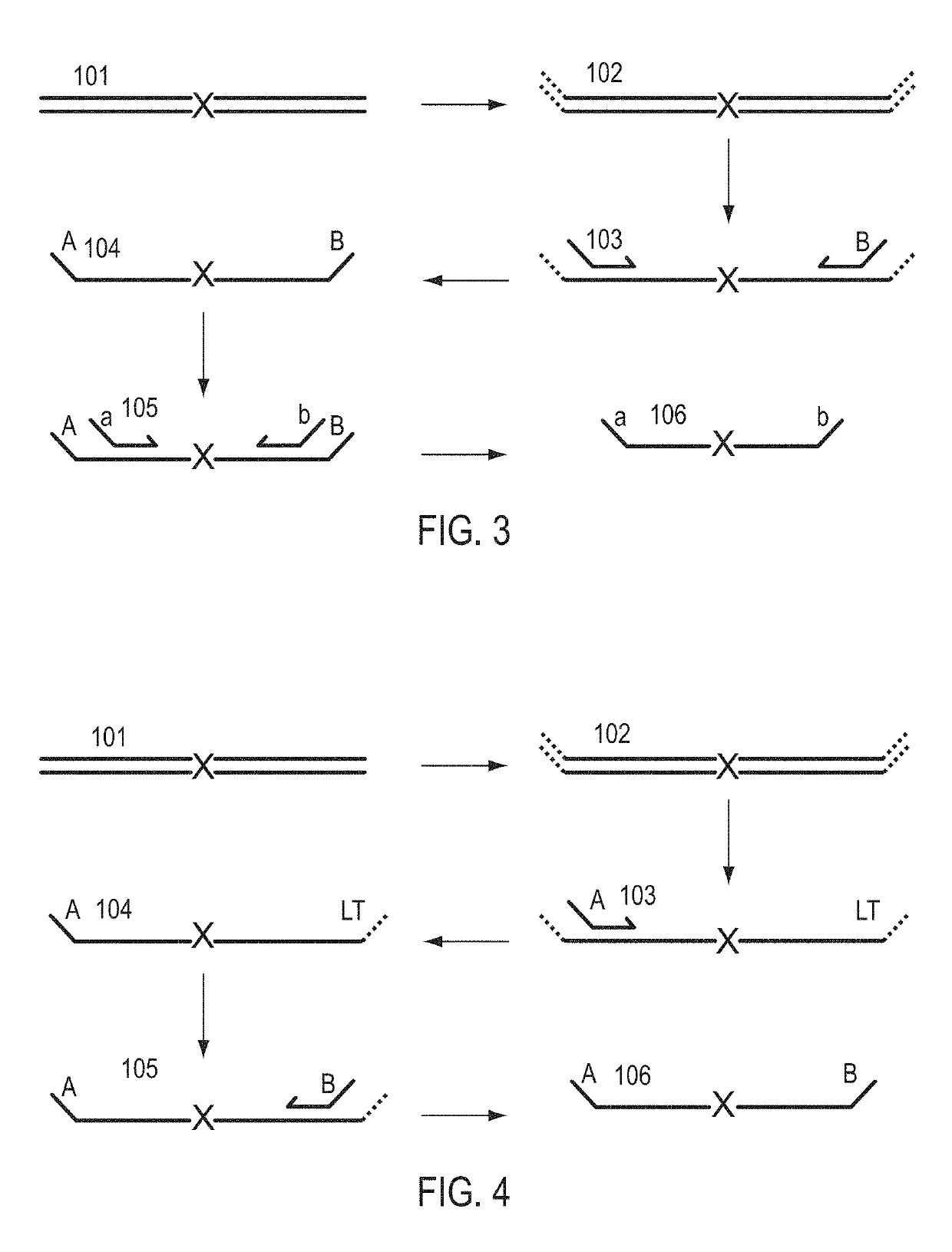
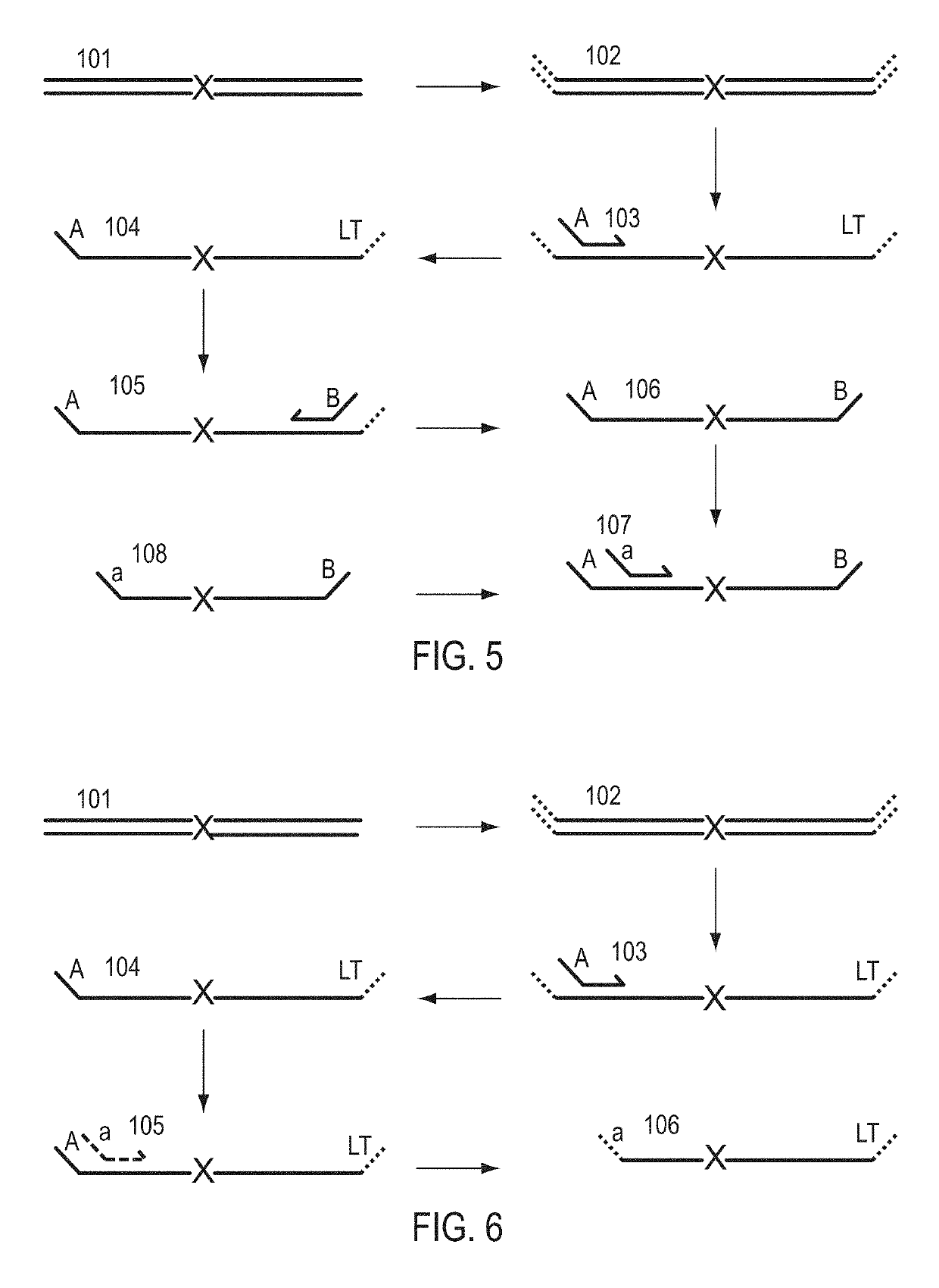
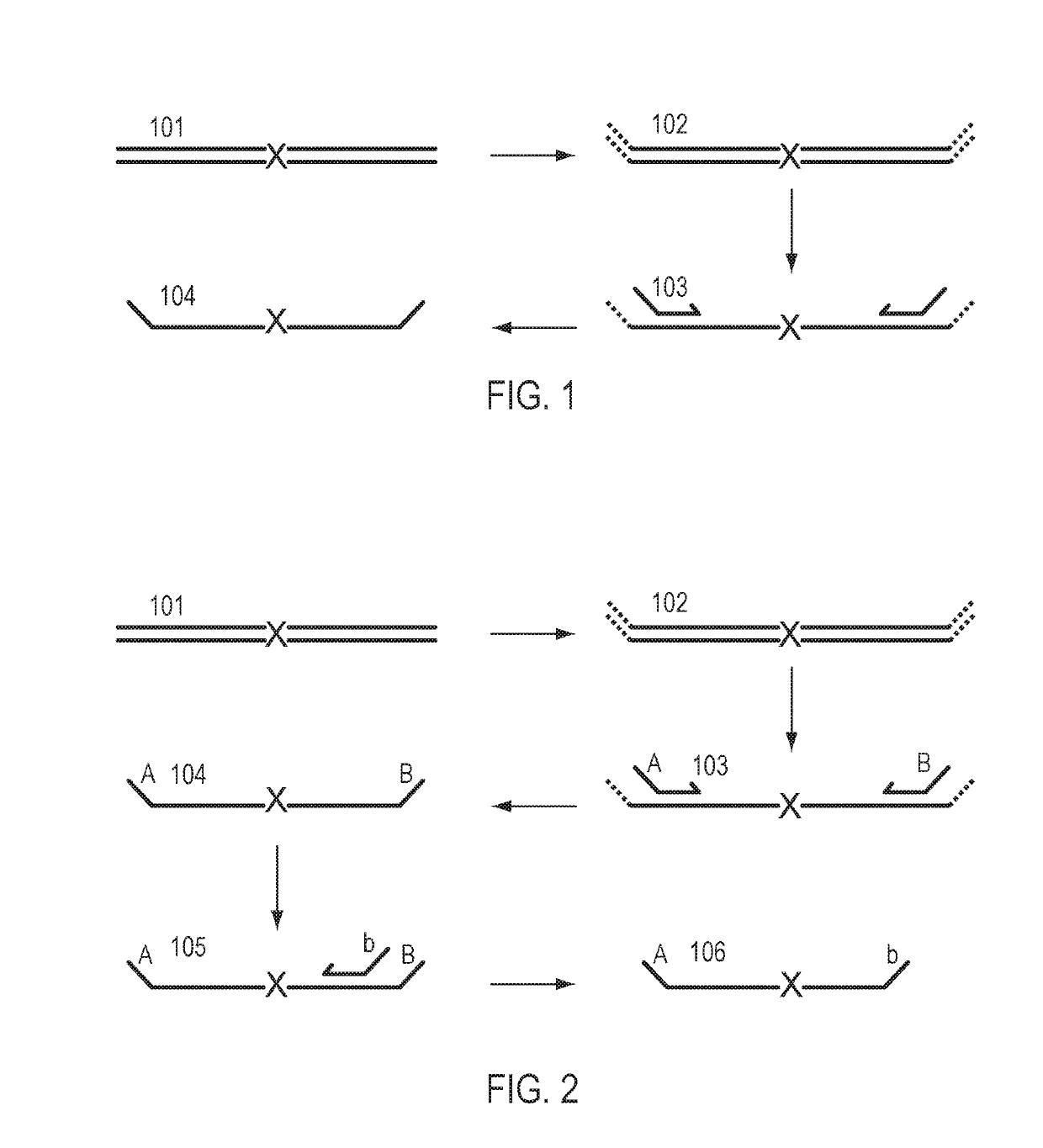
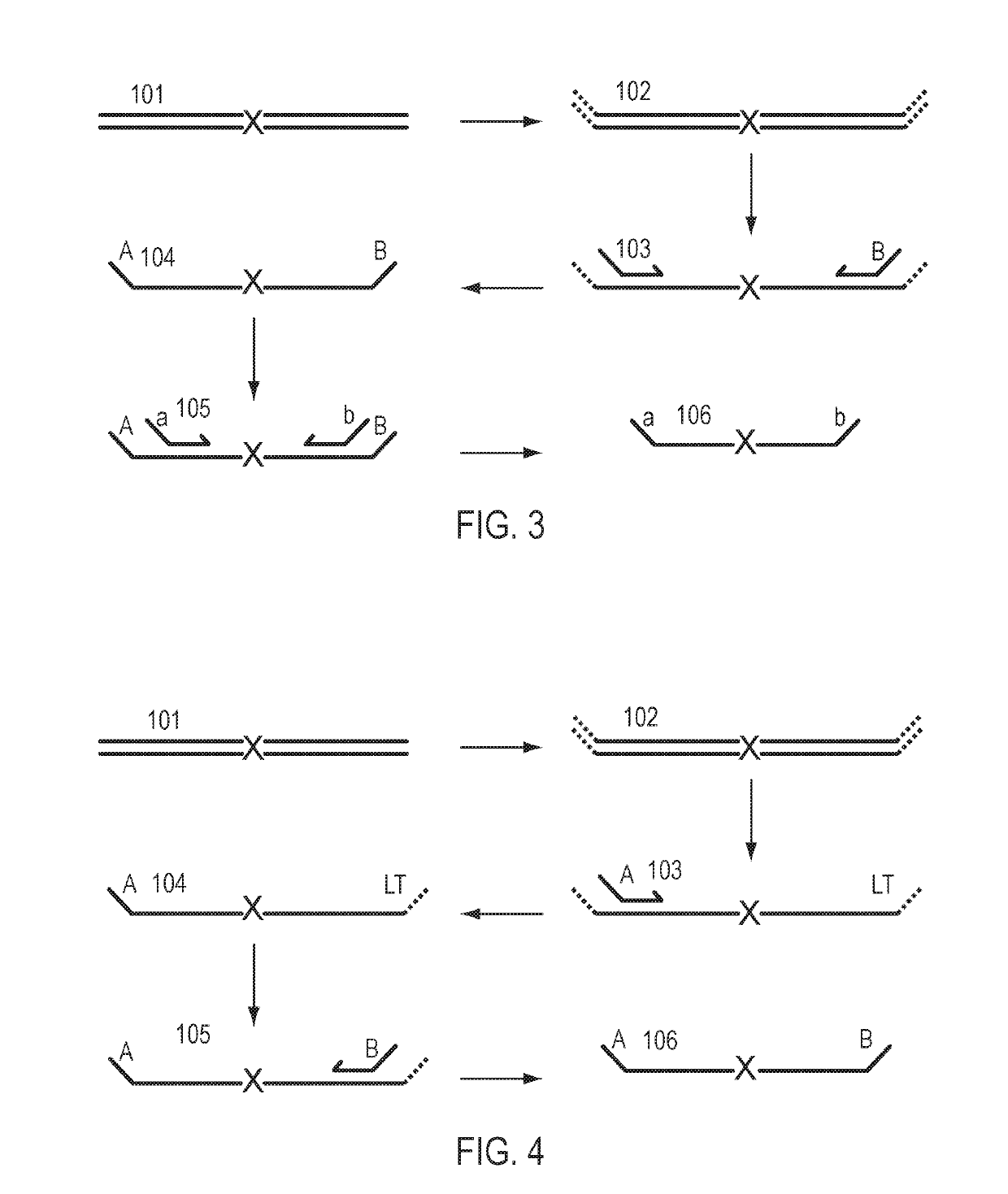
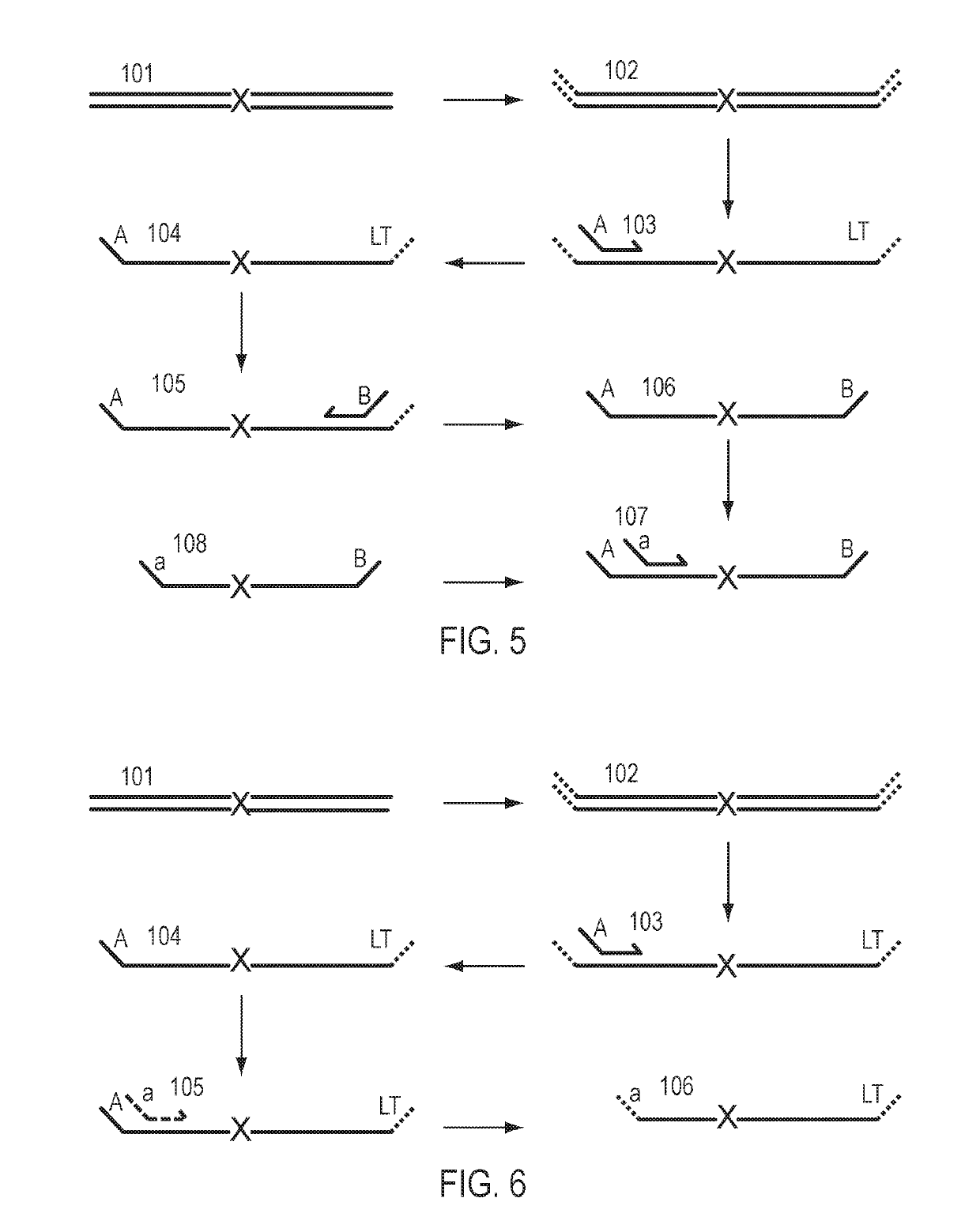
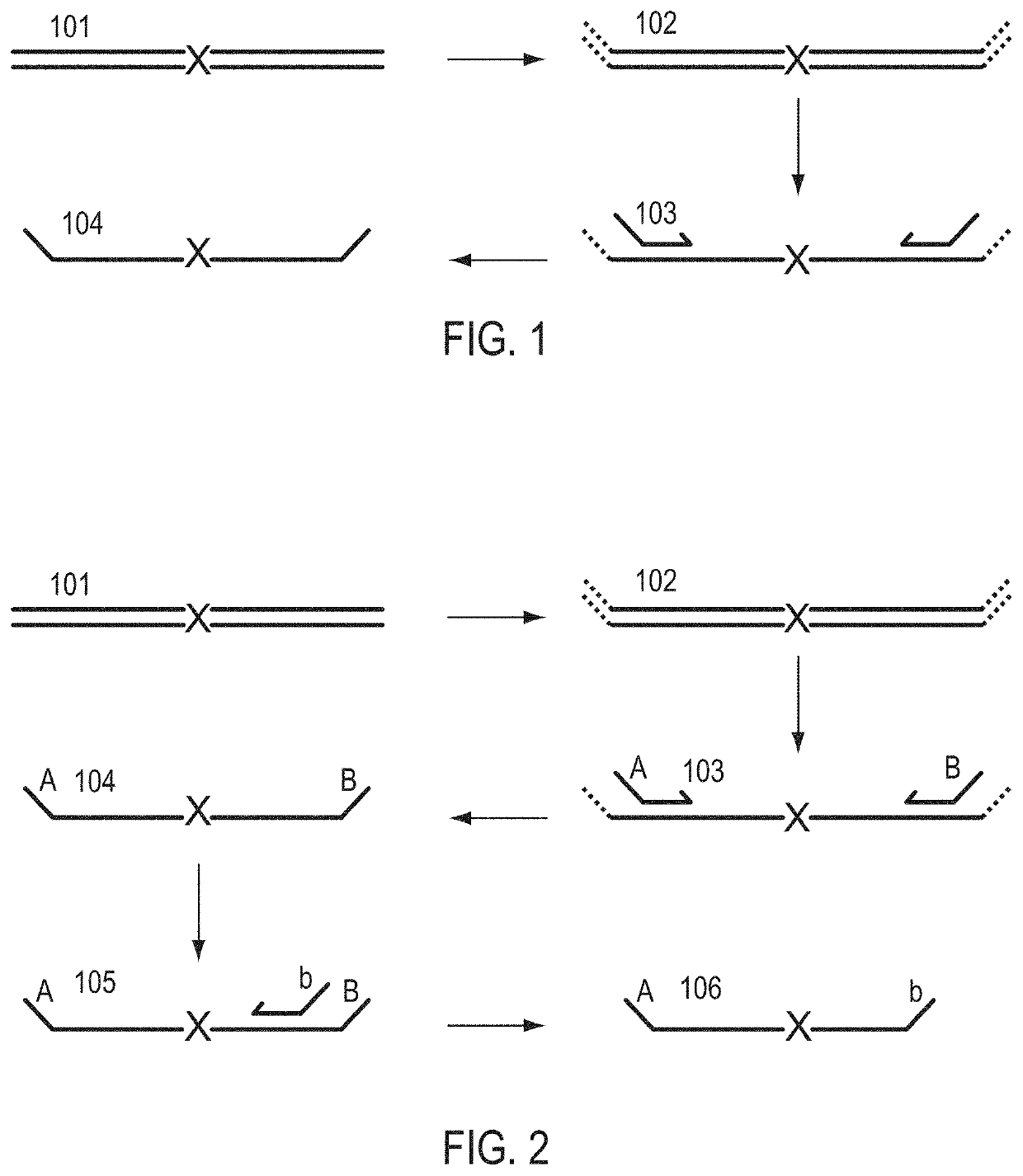
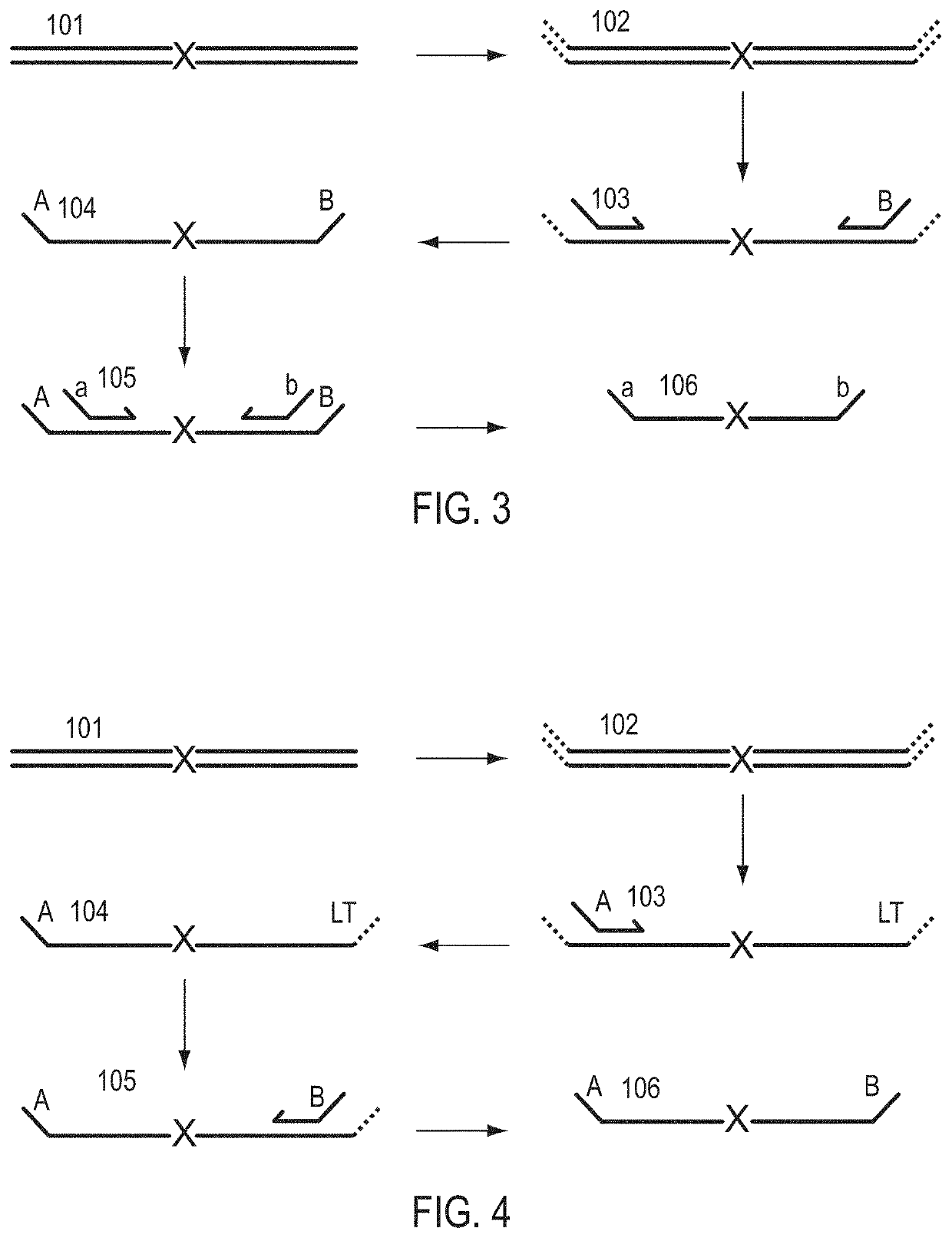
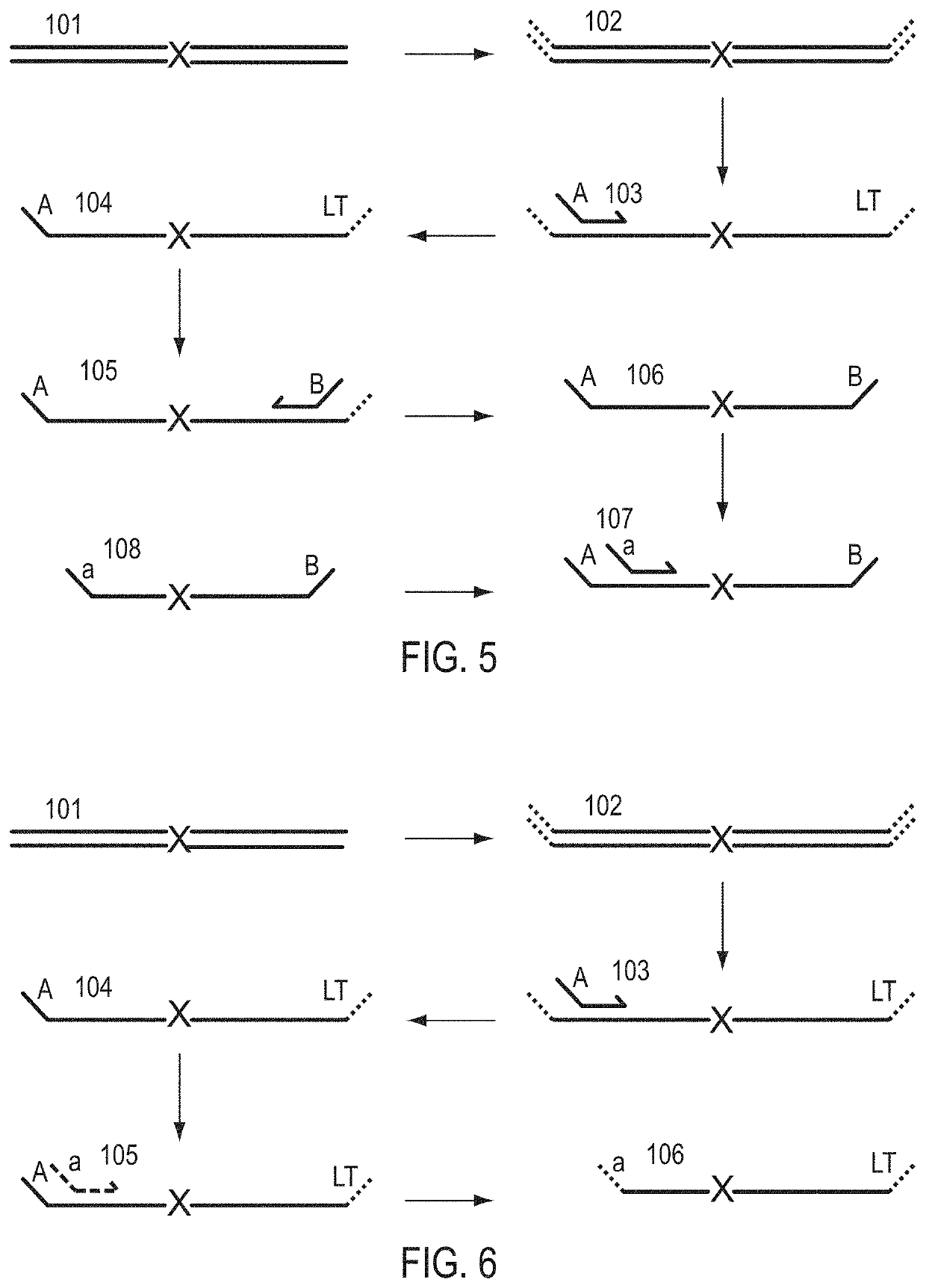
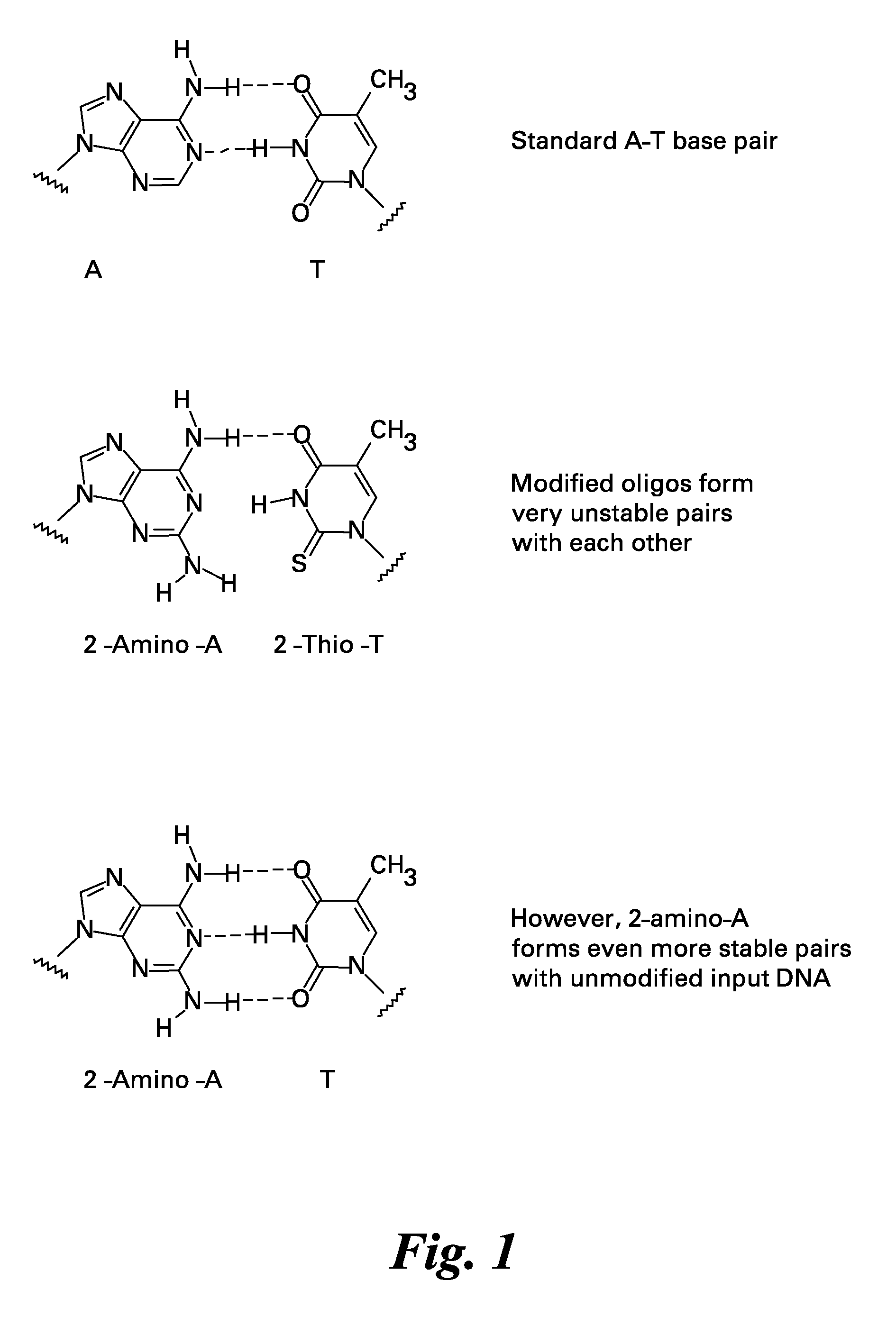
A Primer dimer (PD) is a potential by-product in PCR, a common biotechnological method. As its name implies, a PD consists of primer molecules that have attached (hybridized) to each other because of strings of complementary bases in the primers. As a result, the DNA polymerase amplifies the PD, leading to competition for PCR reagents, thus potentially inhibiting amplification of the DNA sequence targeted for PCR amplification. In quantitative PCR, PDs may interfere with accurate quantification.
Highly Multiplex PCR Methods and Compositions
InactiveUS20130123120A1Increase opportunitiesHigh copy numberNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexDimer
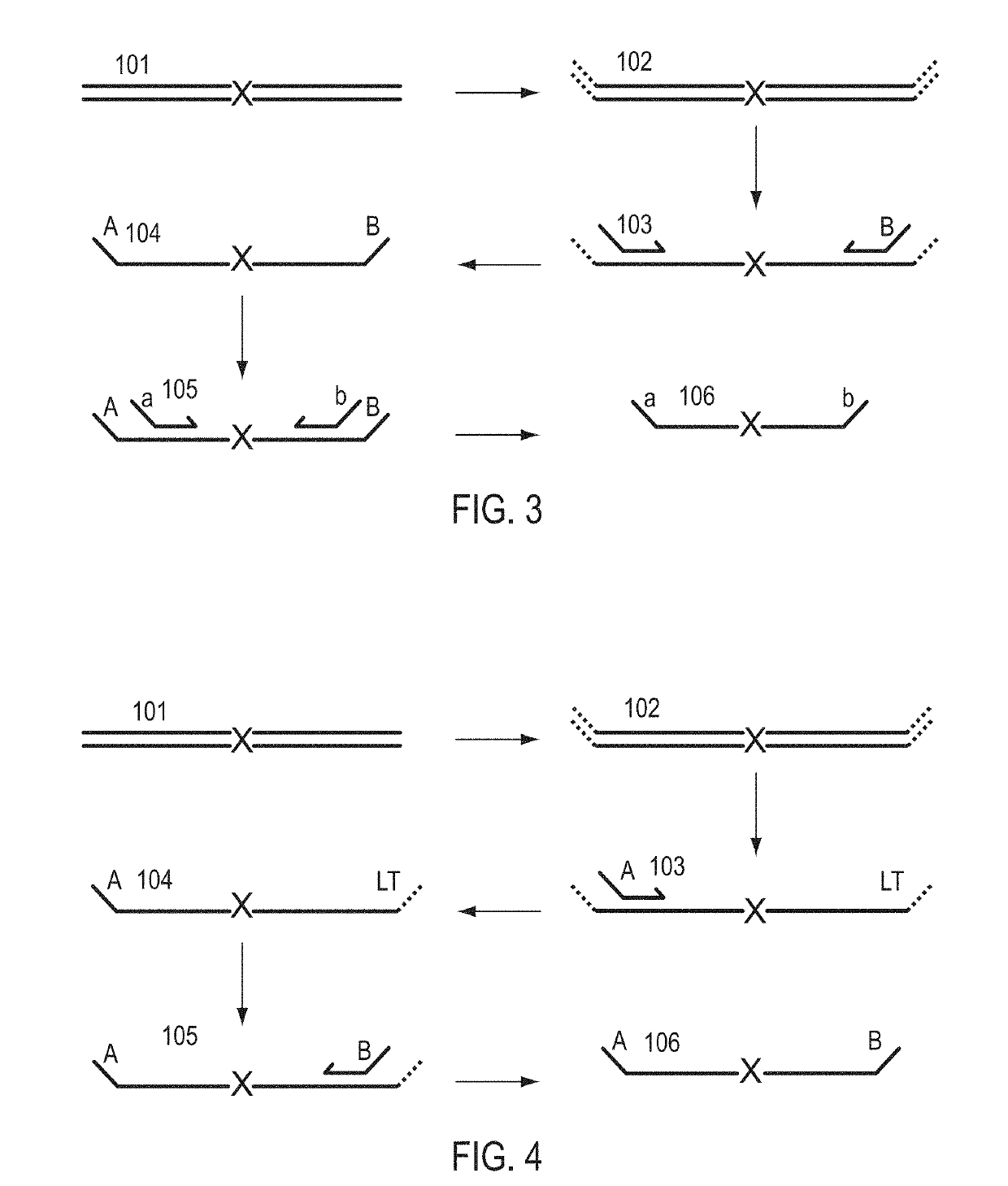
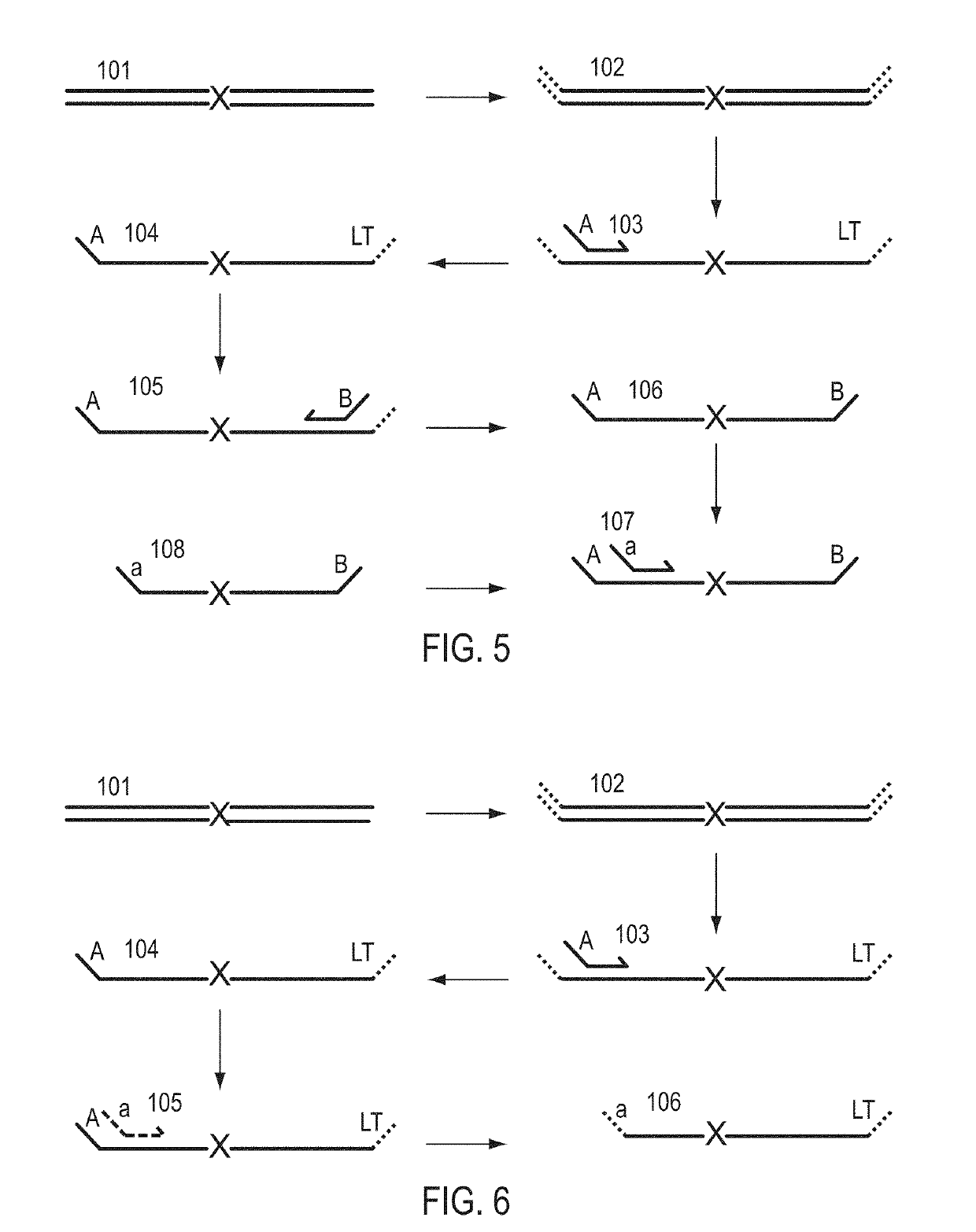
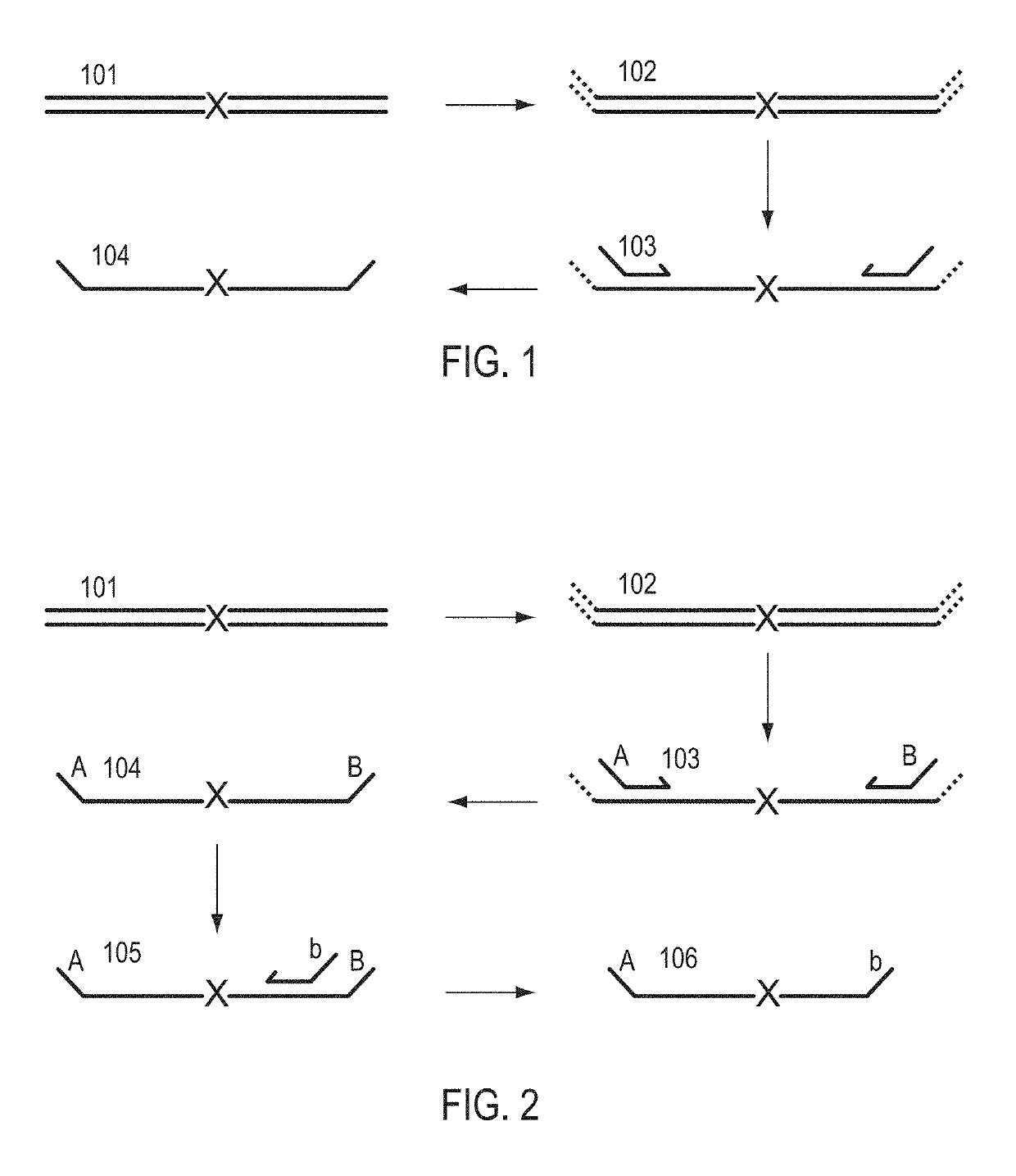
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Highly multiplex PCR methods and compositions
InactiveUS20140094373A1High copy numberMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMultiplexDimer
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
ActiveUS20160369333A1Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerBioinformatics
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
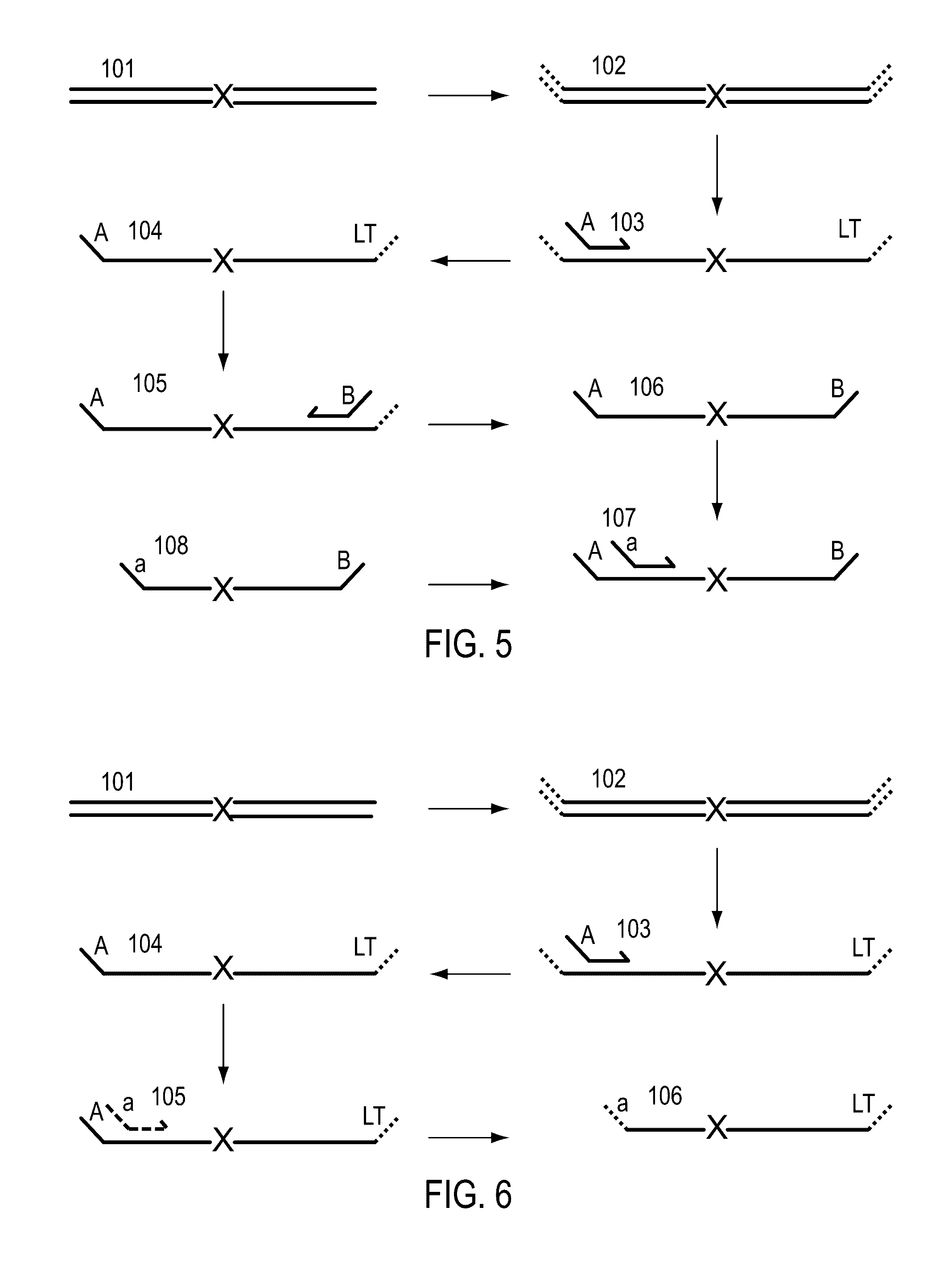
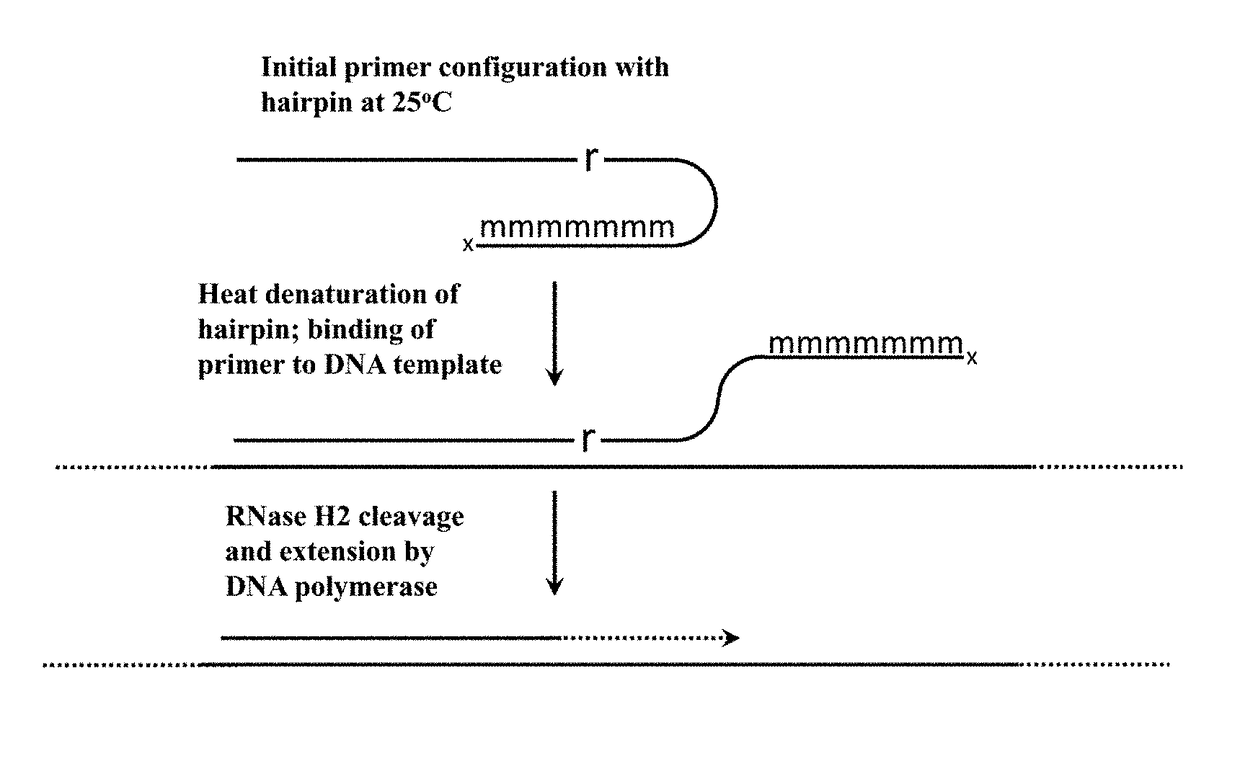
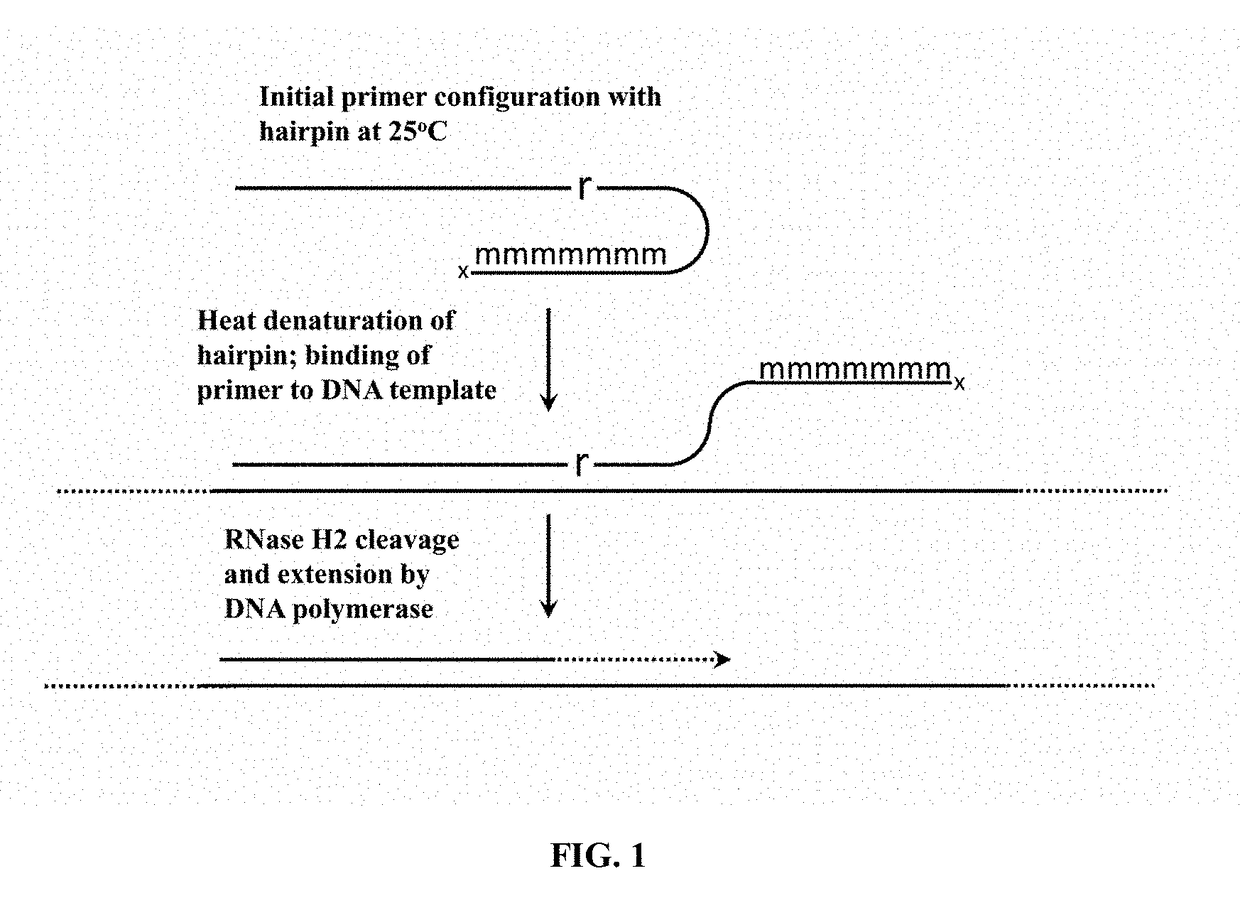
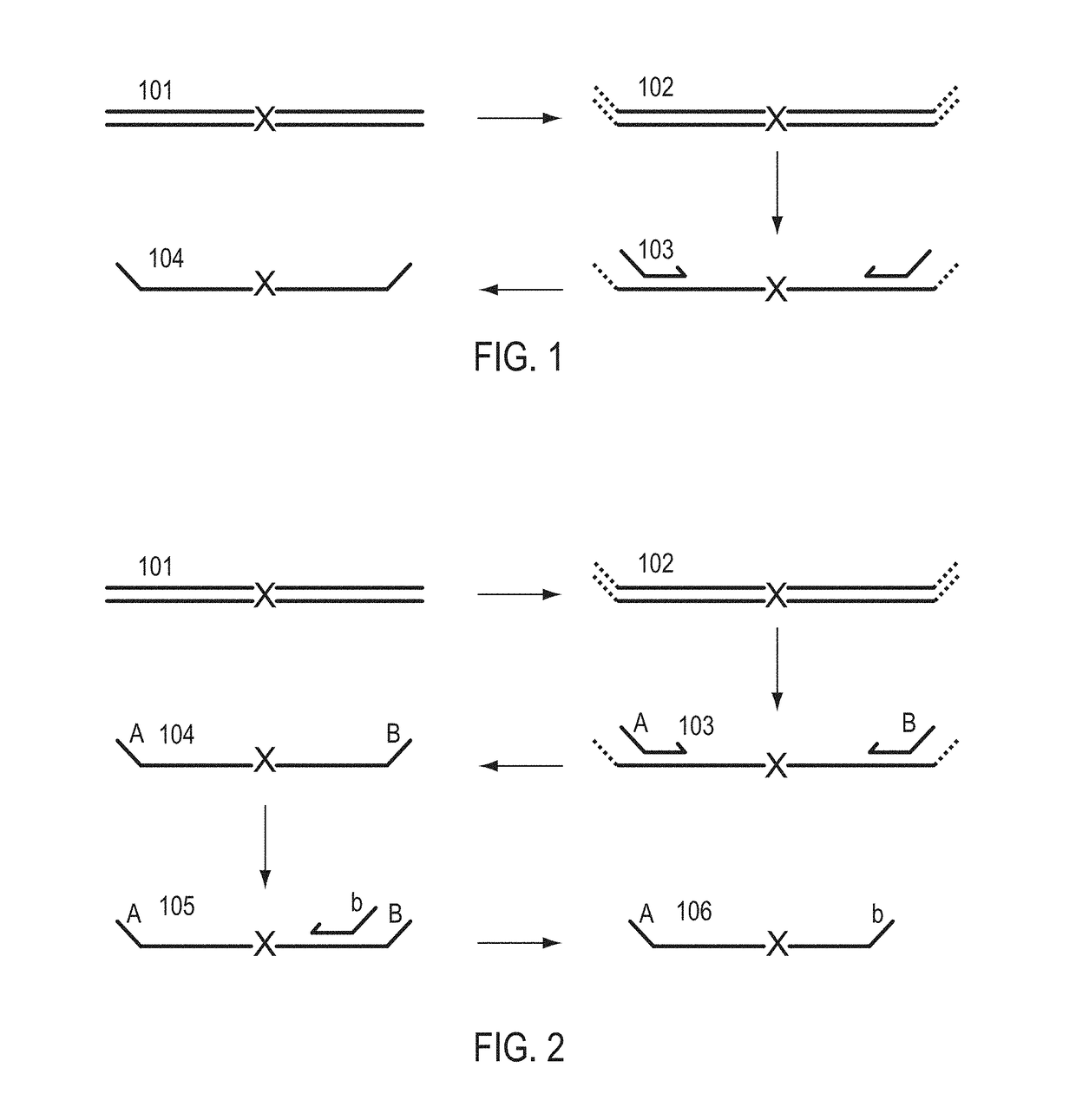
Cleavable hairpin primers
ActiveUS20180057868A1Improve reaction efficiencyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringSingle-Stranded RNASingle strand
The invention describes composition and methods of use for novel hairpin blocked-cleavable primers. In one embodiment unblocking occurs through action of RNase H2. The method improves the specificity of PCR and reduces primer dimer events, enabling higher level multiplex reactions. Additionally, the invention protects RNA-containing primers from attack by single-strand RNases.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
InactiveUS20190010543A1Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerBioinformatics
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Chimeric primers for improved nucleic acid amplification reactions
ActiveUS20100291635A1Reduce formationLow efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesRibonucleotide synthesisNucleic acid sequencing
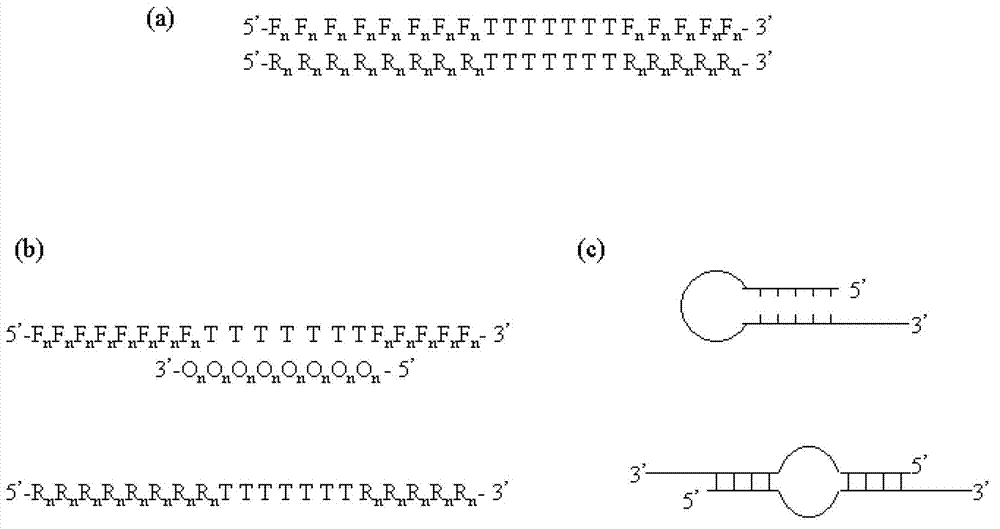
Methods are provided for amplification of a nucleic acid sequence. The method use RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotides as primers. The primers have RNA residues scattered along their length and no two ribonucleotides in the prime are adjacent to one another. The methods are useful for reducing non-specific amplification products, such as primer dimers. The invention also provides kits comprising RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotide primers for practicing the amplification methods.
Owner:INFINIPLEX LTD
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
ActiveUS20190185936A1Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerBioinformatics
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
ActiveUS20190203294A1Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerBioinformatics
Owner:NATERA
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
ActiveUS10316362B2Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementNon targetedNon target
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
ActiveUS20190256919A1Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerBioinformatics
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
ActiveUS20200157629A1Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerBioinformatics
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Methods and kits for reducing non-specific nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS20090130720A1Efficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesNucleotidePrimer dimer
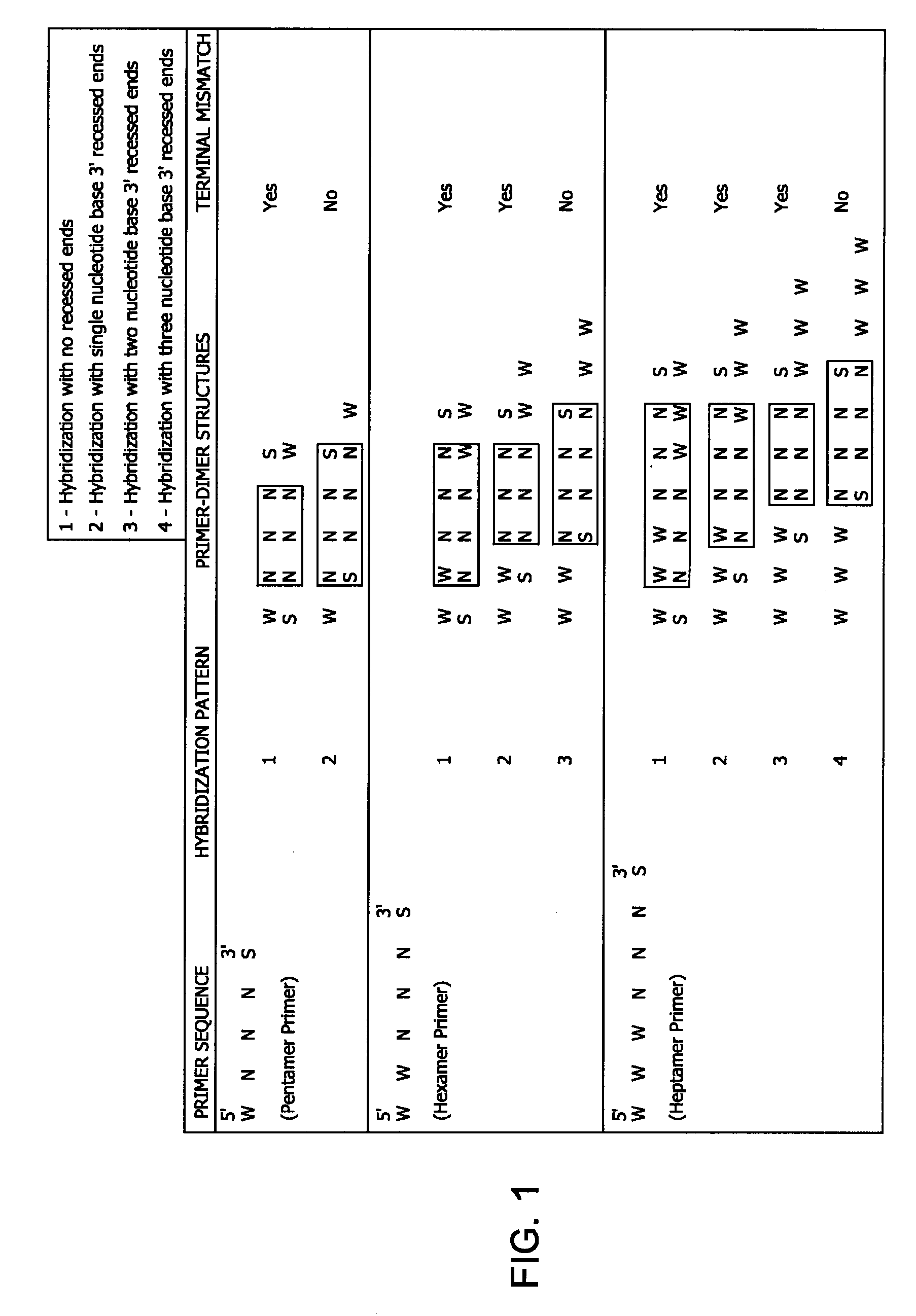
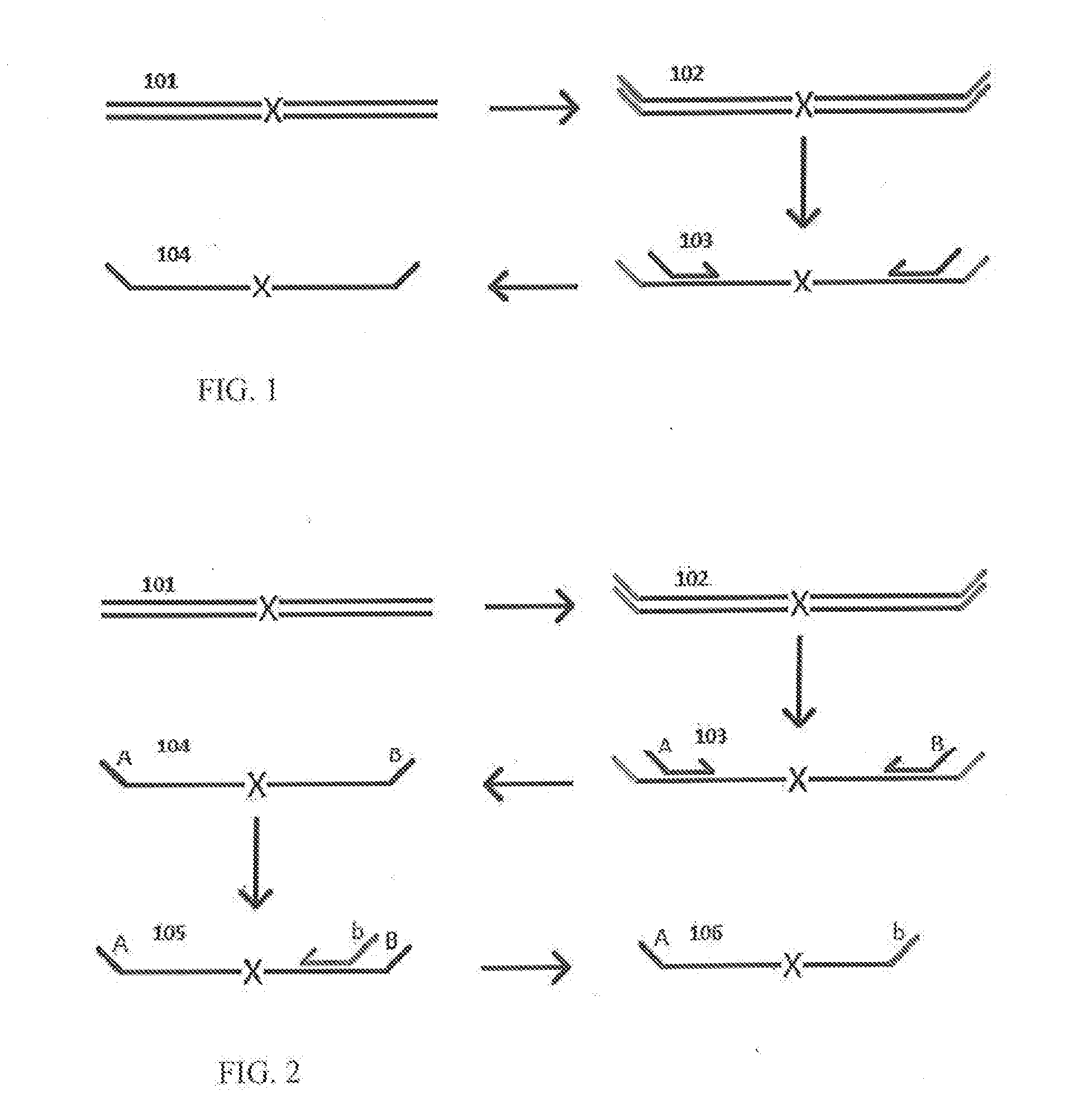
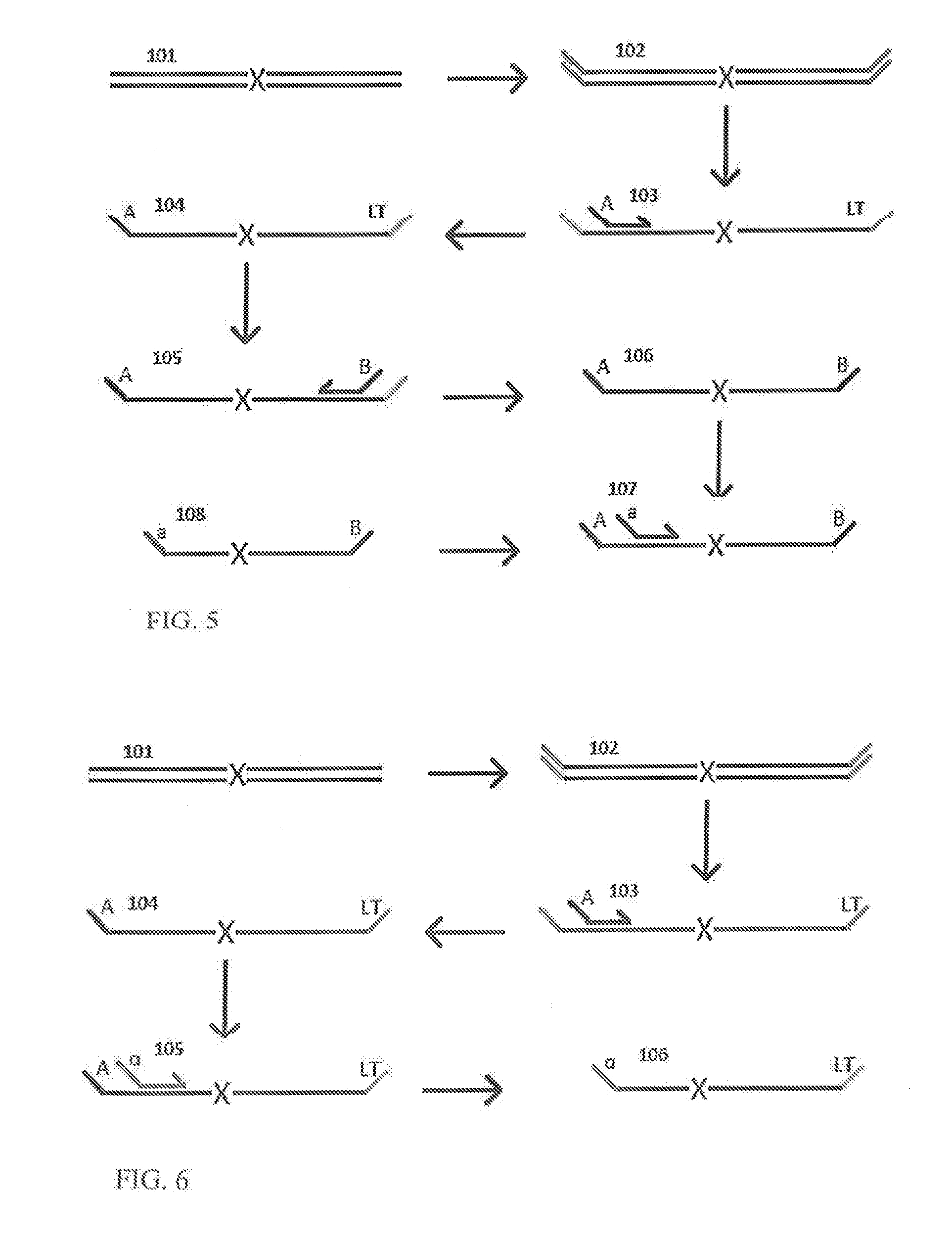
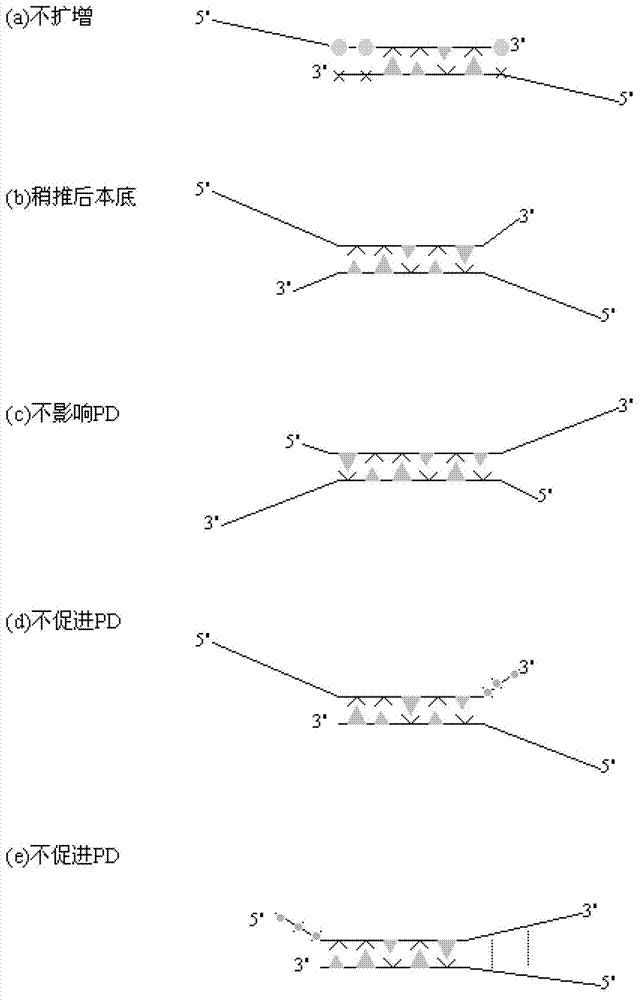
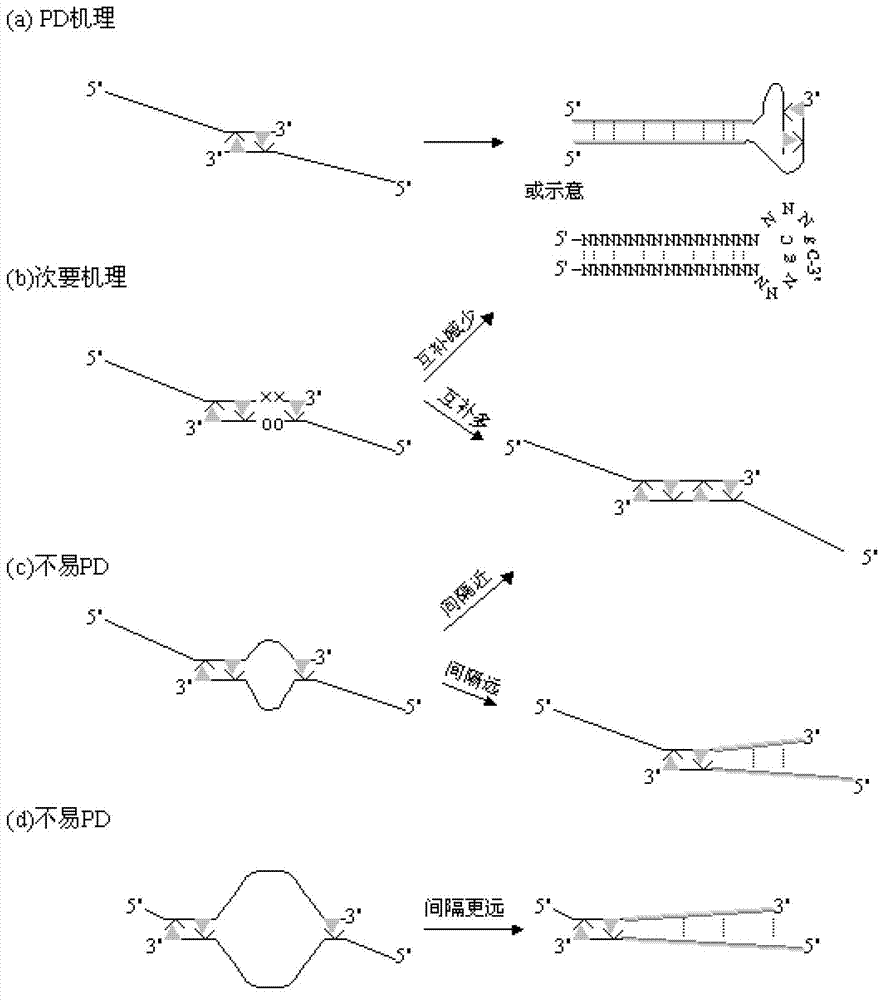
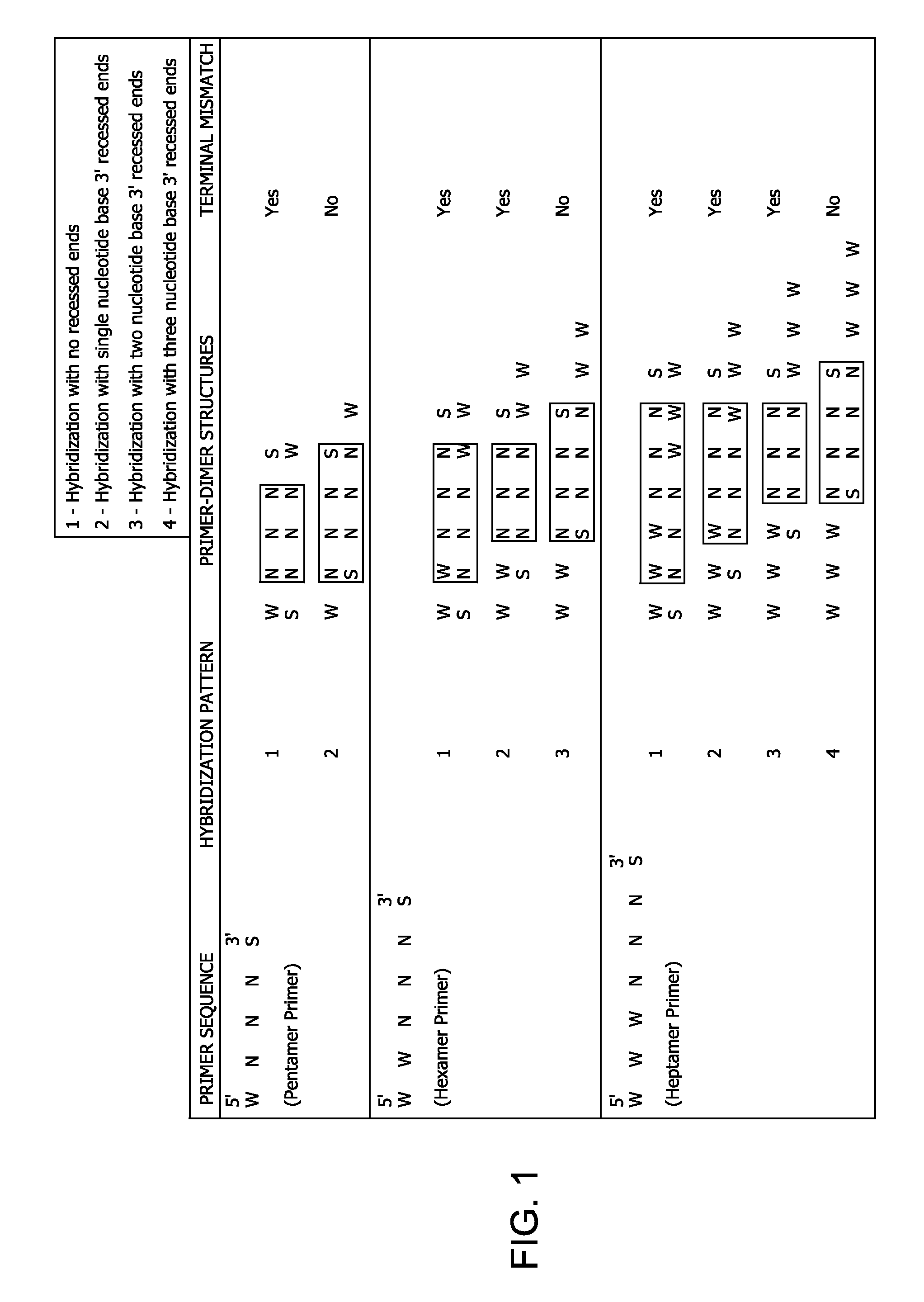
Methods and kits for efficient amplification of nucleic acids are provided. The methods comprise in-vitro amplification of a nucleic acid template employing partially constrained primers having terminal mismatch primer-dimer structure. The methods also comprise in-vitro amplification of a nucleic acid template employing partially constrained primers having nucleotide analogues. The methods enhance efficiency of nucleic acid amplification reaction by reducing non-specific amplification reactions.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Methods for simultaneous amplification of target loci
ActiveUS20150322507A1Minimize the numberImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerBioinformatics
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Amplification using modified primers
InactiveUS20030044817A1Promote cloningExtension of timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
The present invention provides modified primers for use in the amplification of a nucleic acid sequence. Amplifications carried out using the modified primers result in less template-independent non-specific product (primer dimer) compared to amplifications carried out using unmodified primers.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit for detecting expression level of HER2 genes
ActiveCN102719547AAvoid formingLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceEnzyme system
The invention provides a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit for detecting the expression level of HER2 genes and relates to a PCR kit. The real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR kit comprises PCR reaction liquid of the HER2 genes, PCR reaction liquid of ACTB genes, a Taq enzyme system, a control product and a packaging object; and the adopted primer is an annular primer, 3-8 self-designed basic groups are at the 5' end, and can be combined with the sequence at the 3' end under proper conditions so as to form double chains. The real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR kit has the advantages that the non-specific amplification products especially primer dimer generated by nonspecific amplification products especially the primer can be effectively prevented from being formed, the specificity is increased; and a relative-quantitative RT-PCR method is utilized for detecting the expression level of the HER2 genes of a patient with the breast cancer, adopts a 2-delta deltaCt value method for quantifying the detected result, and can be used for diagnosis of early stage and transferring of the breast cancer and assisting multiple fields such as clinicalmedicine selection and prognosis.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
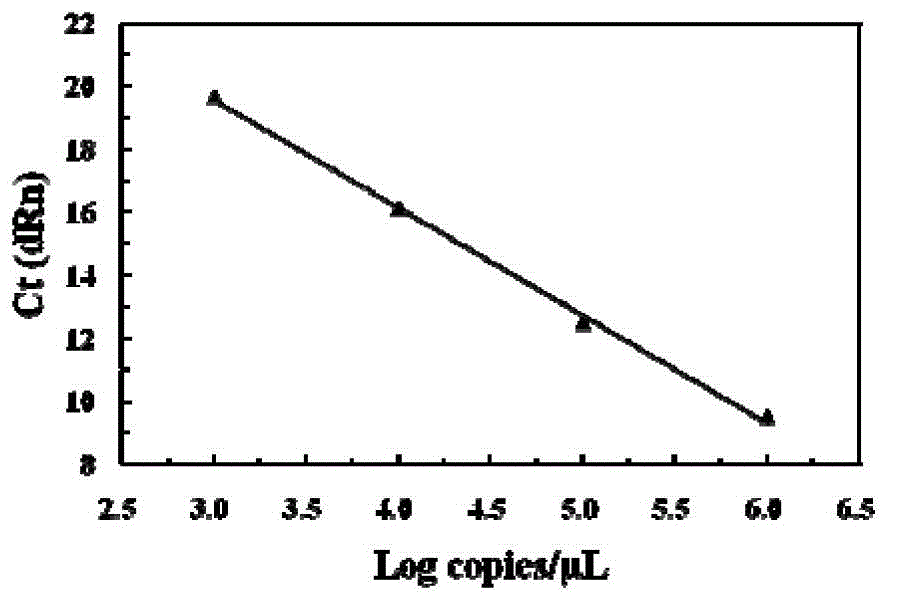
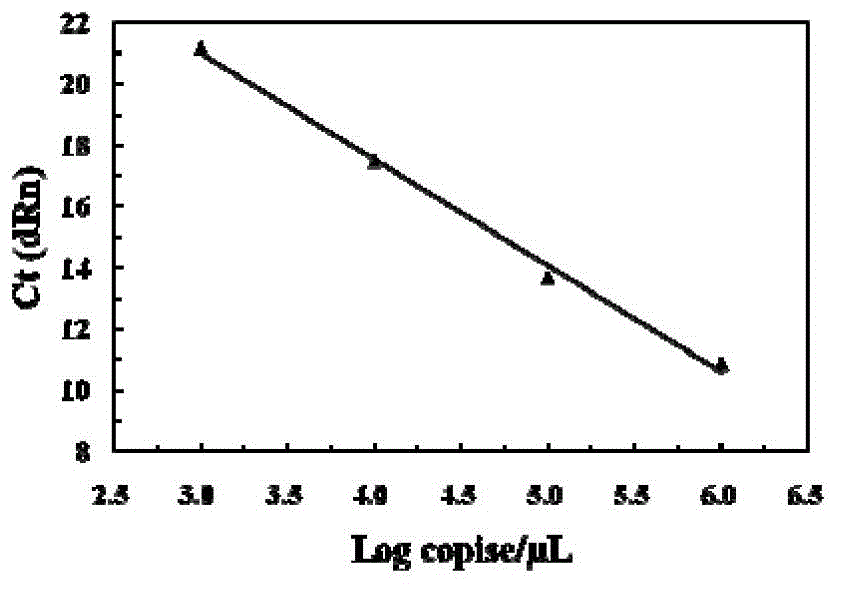
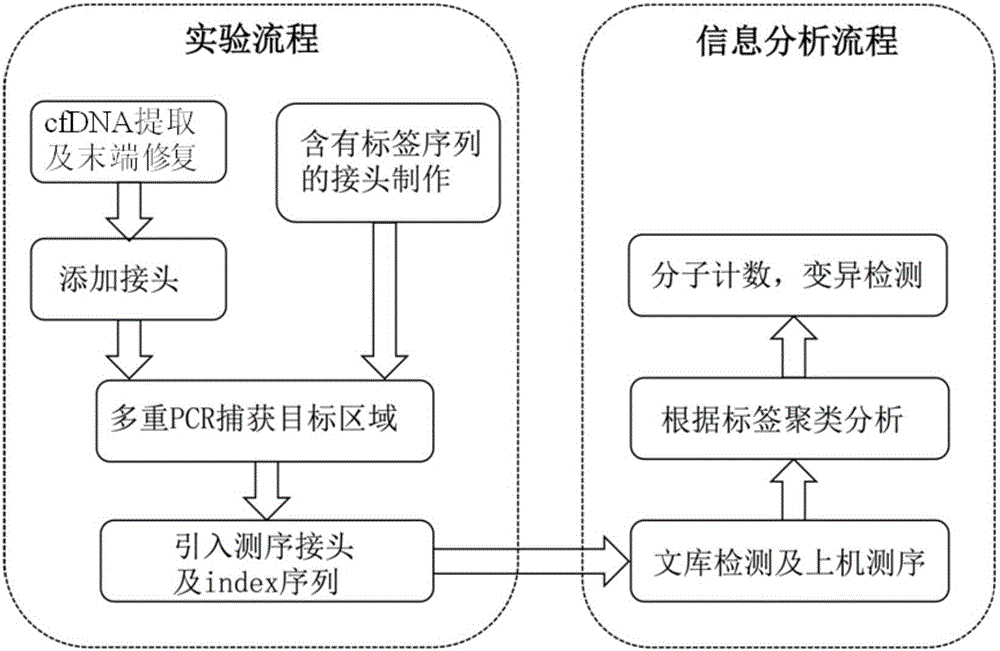
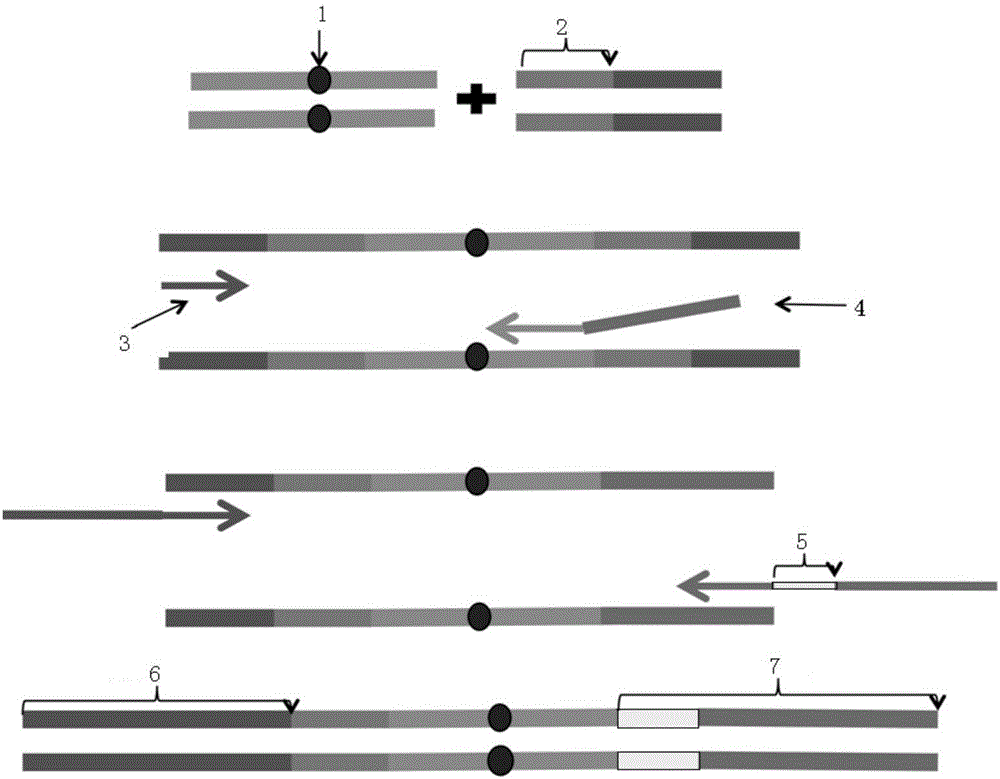
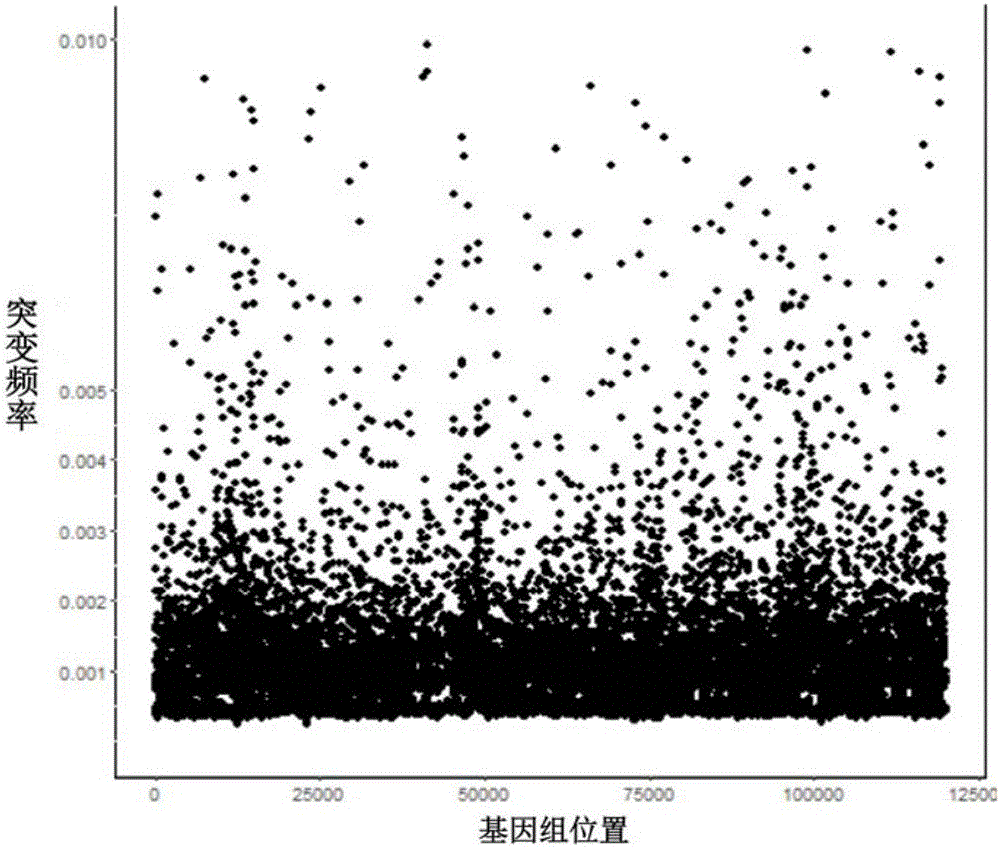
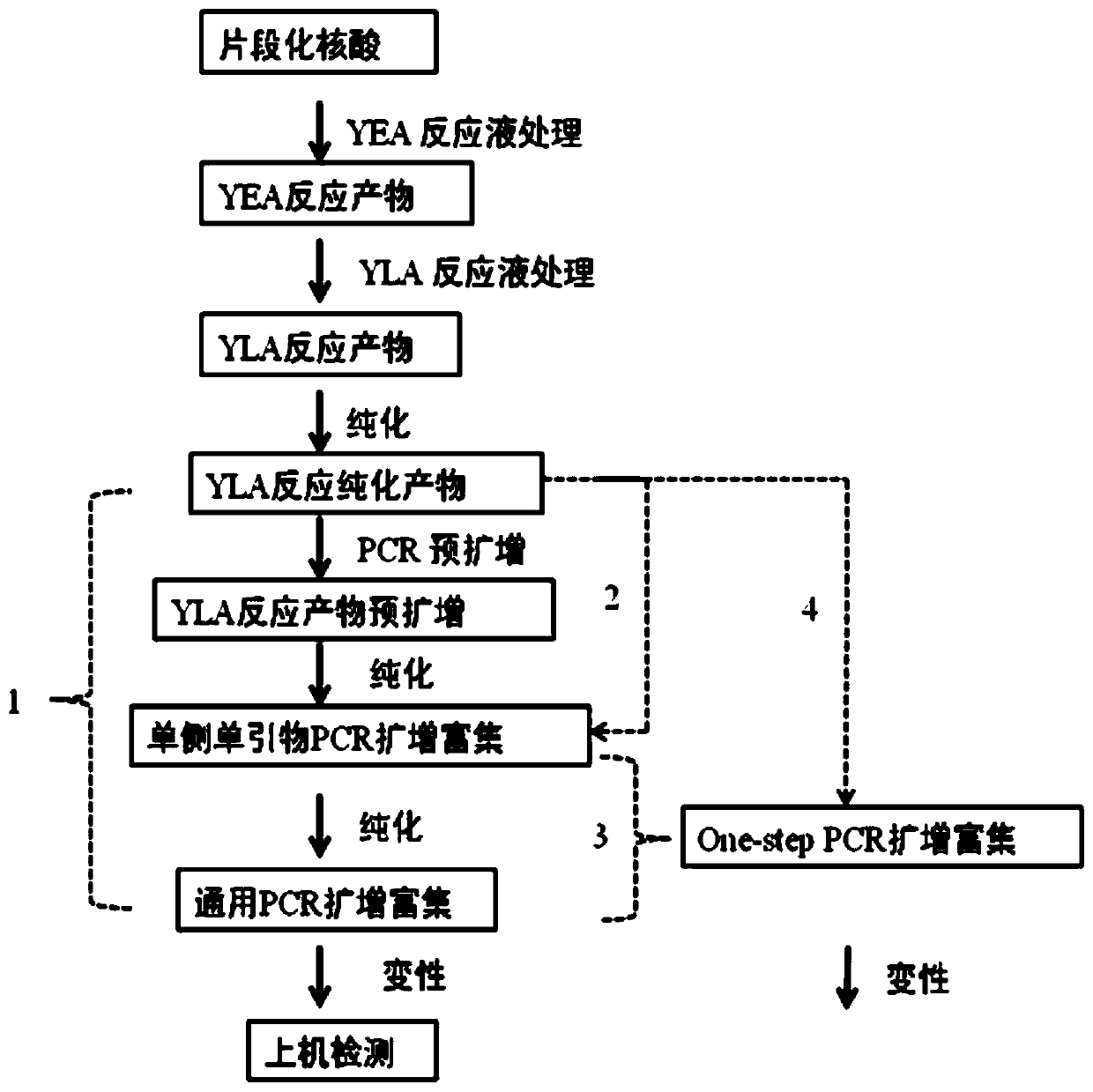
Construction method of ctDNA ultra-low-frequency mutation detection library, kit and analysis method of library detection data
InactiveCN106834275AIncrease diversityEasy to solveMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsMagnetic beadSmall fragment
The invention discloses a construction method of a ctDNA ultra-low-frequency mutation detection library, a kit and an analysis method of library detection data. The construction method comprises steps as follows: S1, cfDNA is extracted from whole blood; S2, the terminal of cfDNA is restored and an A basic group is added to the 3'terminal; S3, the terminal of the cfDNA obtained in S2 is connected with connectors containing random label sequences; S4, primers for multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) are designed according to the sequences of the connectors and an object region for object region capturing; S5, a PCR product in S4 is subjected to magnetic bead purification, and small-fragment DNA not subjected to non-specific amplification and primer dimer are removed; S6, a product in S5 is subjected to PCR amplification, an index sequence is introduced, and the ctDNA ultra-low-frequency mutation library is obtained. According to the method, PCR mistakes and sequencing mistakes are eliminated, and the detection specificity is improved.
Owner:天津诺禾医学检验所有限公司
Primer middle sequence interference PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology
InactiveCN103114131AHigh Sensitivity FeaturesQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceFluorescence
The invention relates to a primer middle sequence interference PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology. The improved PCR technology is characterized in that one segment of relatively non-complemented or same-sequence basic group primer molecules in the intermediate domain of primers perform the antisense interference inside and outside so as to competitively destroy the polymerization among the primers to selectively inhibit the primer dimer (PD) from being amplified. For the interference of the intermediate domain of the primers, based on the primers optimally selected by the conventional design principle, the technology that the intermediate domain (ID) of a pair of the primers are in parallel but are not complemented with each other or are in the same sequence or / and the technology that ID antisense oligonucleotides (Oligo) are added into the primers to perform the interference action or / and the Oligo antonymy is carried out in the primer molecules via the ID so as to perform the interference action are adopted, or the combined technology of the three types of the technologies is adopted. As a result, only the ID of the primers is interfered while the target specific amplification is not influenced; the combining force acting on the minority of base-group pairing hydrogen bonds at the tail end and the base-group hydrogen bonds outside the tail end due to the action of the primers is dispersed to a maximum extent, so that the PD is selectively inhibited. Therefore, the PD accumulation in the PCR system is avoided. If the mineral oil is additionally used, the sealed primers can slowly release the hot starting and the UDG pretreatment so as to prevent aerosol glue as a byproduct of the PCR system from causing the pollution. Consequently, the nucleic acid is amplified reliably and the real-time fluorescence PCR is quantified accurately.
Owner:珠海市坤元科技有限公司
Methods and kits for reducing non-specific nucleic acid amplification
Methods and kits for efficient amplification of nucleic acids are provided. The methods comprise in-vitro amplification of a nucleic acid template employing partially constrained primers having terminal mismatch primer-dimer structure. The methods also comprise in-vitro amplification of a nucleic acid template employing partially constrained primers having nucleotide analogues. The methods enhance efficiency of nucleic acid amplification reaction by reducing non-specific amplification reactions.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Chimeric primers for improved nucleic acid amplification reactions
ActiveCN101842494AMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleotide synthesisNucleic acid sequencing
Methods are provided for amplification of a nucleic acid sequence. The method use RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotides as primers. The primers have RNA residues scattered along their length and no two ribonucleotides in the prime are adjacent to one another. The methods are useful for reducing non-specific amplification products, such as primer dimers. The invention also provides kits comprising RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotide primers for practicing the amplification methods.
Owner:INFINIPLEX LTD
Low-frequency gene fusion detection method and device
ActiveCN106676182ASolving the False Negative/False Positive ProblemBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSmall fragmentMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a low-frequency gene fusion detection method and a low-frequency gene fusion detection device. The detection method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting cfDNA from whole blood; S2, performing tail end repairing on the cfDNA and adding A basic group at the 3' end; S3, connecting a joint containing a random label sequence; S4, designing a multiplex-PCR primer and performing target area capture; S5, performing magnetic bead purification on the PCR product in the S4, removing small fragment DNA not subjected to non-specific amplification and a primer dimer, and introducing an index sequence to obtain a ctDNA ultralow-frequency mutation library; S7, performing computer sequencing; S8, performing clustering analysis on data after library sequencing through the random label sequence; and S9, entering variation detection analysis after the quality control of the remaining data is qualified. By application of the technical scheme of the invention, the low-frequency mutation detection sensitivity is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Methods and kits for reducing non-specific nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS20130210078A1Efficient amplificationMinimize and prevent productionMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPrimer dimerComputational biology
Methods and kits for efficient amplification of nucleic acids are provided. The disclosure generally relates to methods and kits for nucleic acid amplification of target nucleic acids of interest. The methods described herein promote the synthesis of the target nucleic acid (i.e., template nucleic acid) by reducing the production of undesirable primer-dimer structures and chimeric nucleic acid products during the amplification process by using novel modified primers.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Methods and kits for reducing non-specific nucleic acid amplification
Methods and kits for efficient amplification of nucleic acids are provided. The methods comprise in-vitro amplification of a nucleic acid template employing partially constrained primers having terminal mismatch primer-dimer structure. The methods also comprise in-vitro amplification of a nucleic acid template employing partially constrained primers having nucleotide analogues. The methods enhance efficiency of nucleic acid amplification reaction by reducing non-specific amplification reactions.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Construction method, kit and application of plasma free DNA methylation detection library
InactiveCN107541791AImprove recycling efficiencyReduce the initial amount of conventional trace methylation library constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMagnetic beadSmall fragment
The invention discloses a construction method, a kit and application of a plasma free DNA methylation detection library. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1 of extracting plasmafree DNA from a blood sample; S2 of performing tail end repair and 3' terminal A base addition on the plasma free DNA; S3 of connecting the tail ends of the plasma free DNA obtained in the S2 with C methylation modified connectors; S4 of performing bisulfite conversion on a product obtained in S3 and performing PCR expansion; S5 of performing magnetic bead purification on the PCR product of S4 andremoving small-fragment DNA which is not amplified in a non-specific mode and primer dimer; S6 of performing PCR amplification on a product of S5 and performing magnetic bead purification to obtain aplasma free DNA methylation detection library. By means of the technical scheme of the construction method disclosed by the invention, an initial amount of general microscale methylation library construction is reduced, library construction steps are simplified, library recycling efficiency is improved, and a foundation is established for sequentially screening tumor diagnosis markers through plasma free DNA methylation difference locus.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
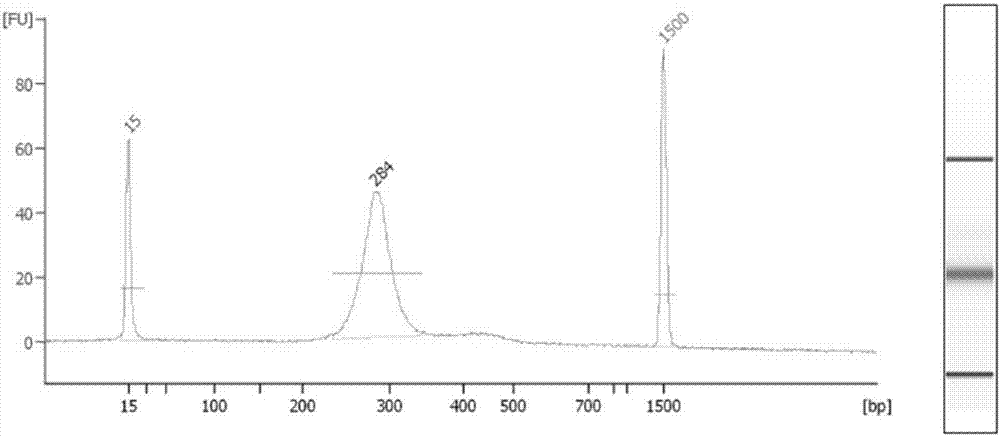
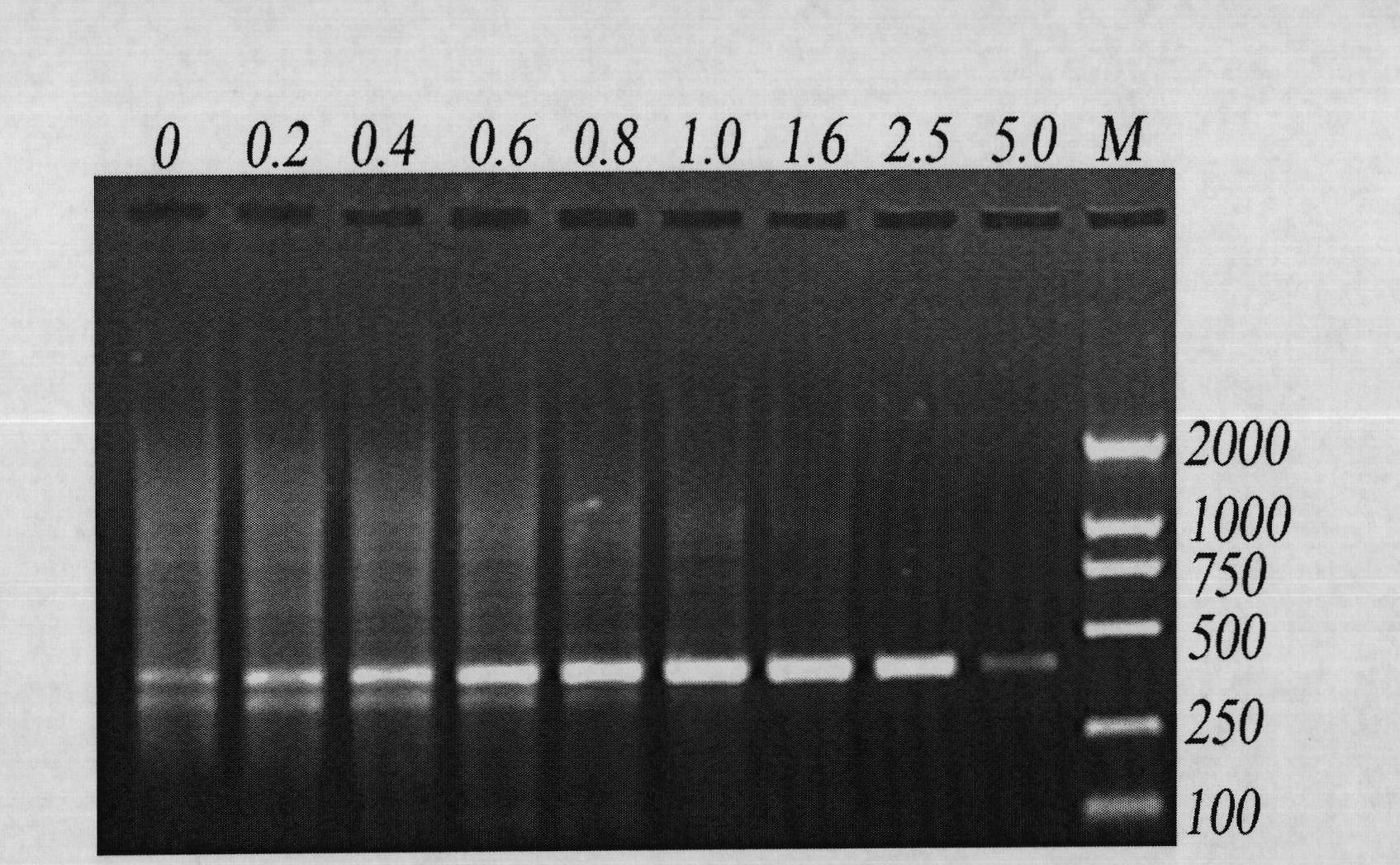
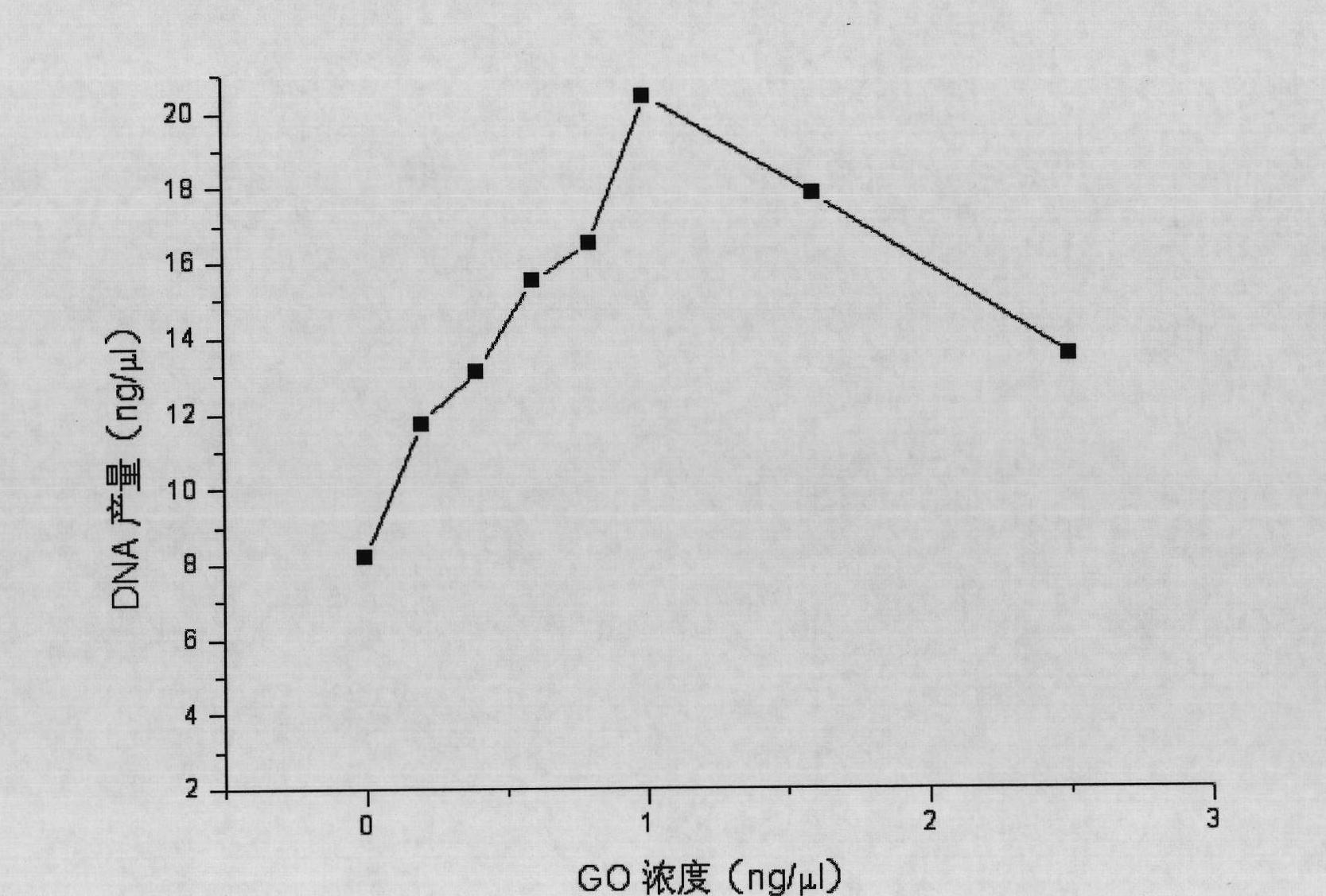
Application of graphene oxide
InactiveCN102465163AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPcr ctppCarbon nanomaterials
The invention discloses application of graphene oxide to polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The application is implemented according to the method that the PCR is carried out under the action of the graphene oxide. The invention finds that the graphene oxide has the advantages of obviously increasing the specificity and the sensitivity of PCR and amplifying the yield by being applied to the PCR technology for the first time and can eliminate a primer dimer formed in amplification, in addition, the graphene oxide has a wide optimization interval and can be widely applied to DNA templates of various concentrations and complex degrees. Compared with other carbon nanomaterials applied to the PCR technology, the graphene oxide has a more excellent comprehensive effect on optimizing the PCR. In addition, the graphene oxide is low in cost, mature in preparation process, and simple to operate when applied to the PCR technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
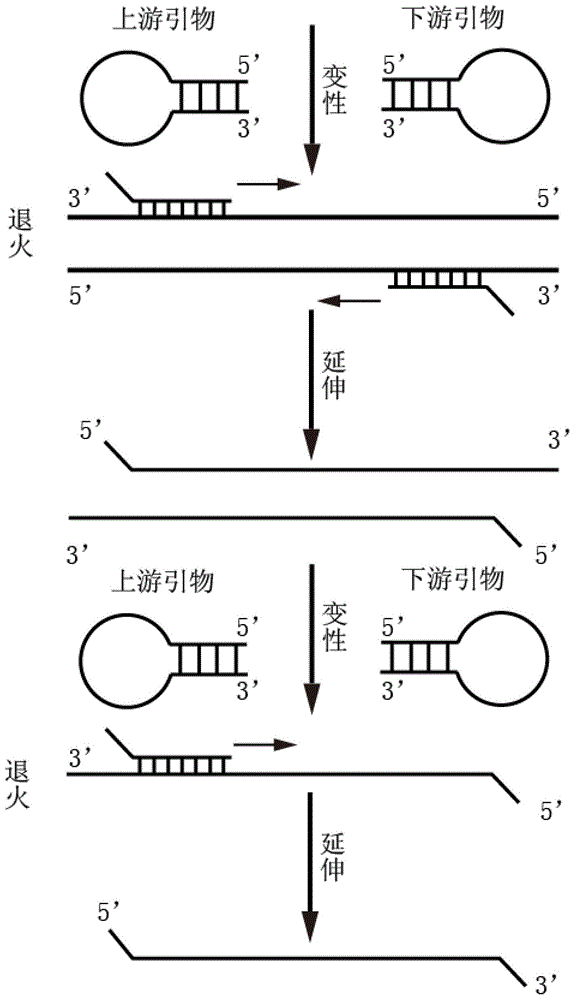
Method for performing multiplex PCR by utilizing hairpin primers
ActiveCN106282353AImprove efficiencyImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBarcodeBiology
The invention relates to a method for performing multiplex PCR by utilizing hairpin primers and a kit as well as application thereof to the establishment of a second-generation sequencing platform library. A specific sequence at the 3'end of each of the hairpin primers is completely paired with a target segment, the melting temperature is 80 DEG C or higher, and a hairpin structure is only opened in the degeneration process when the PCR is performed. The non-specific amplification and the primer dimer formation can be effectively reduced, so that the uniformity of multiple PCR products is improved. The method and the kit as well as the application thereof provided by the invention have the benefits that the two rounds of reaction is performed by utilizing the multiple hairpin primers, so that the second-generation sequencing library is quickly and conveniently established; different templates are distinguished through joint primers carrying different bar code sequences, and the different joint primers carry a same universal amplification primer, so that the difference among different template amplification products is reduced.
Owner:上海翼和应用生物技术有限公司
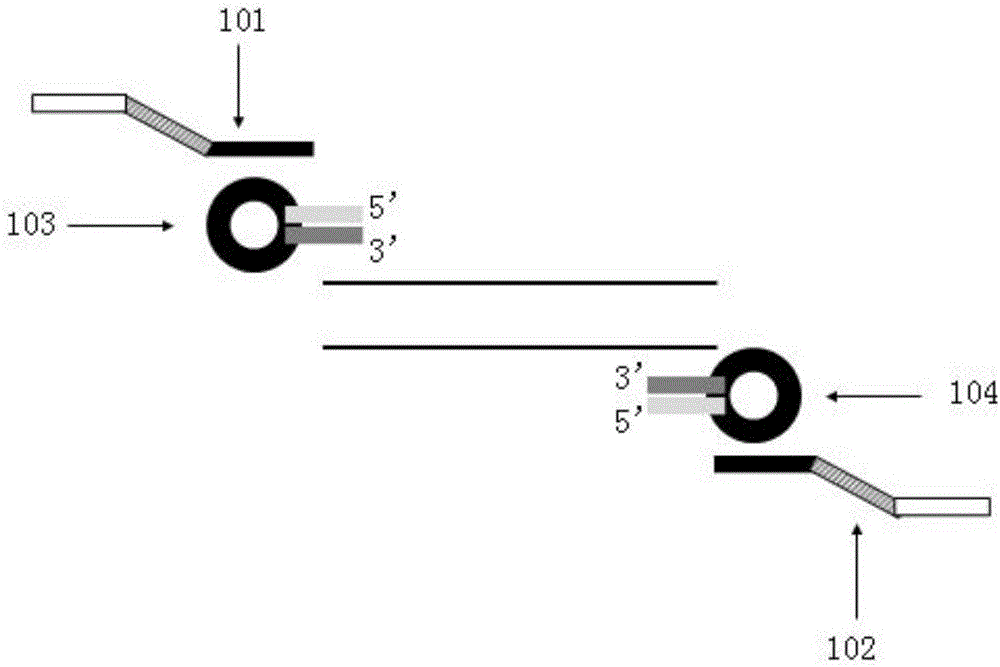
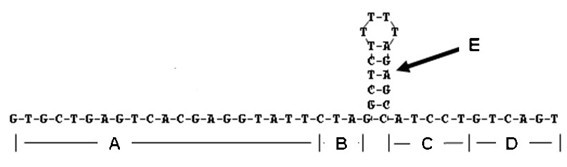
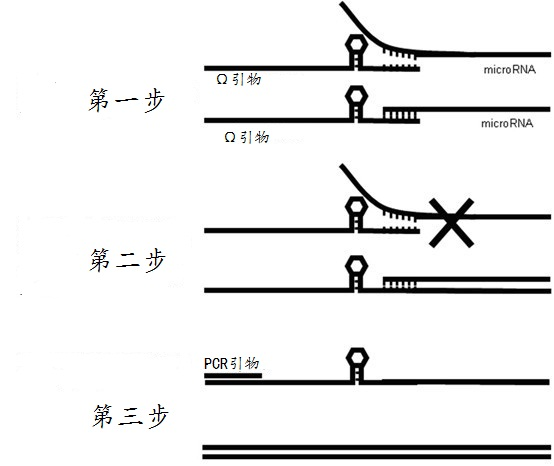
Omega structure oligonucleotide primer for detecting short chain ribonucleic acid (RNA) and application thereof
ActiveCN102618651AHigh RT efficiencyAvoid dimerizationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses an omega structure oligonucleotide primer for detecting short chain RNA. The oligonucleotide primer sequentially comprises a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer target area containing 20-30 basic groups, a variable coding area containing 0-50 basic groups, an omega stem-loop, a probe spacer region containing at least one basic group, and a probe region containing 4-11 basic groups from a 5' end to a 3' end. The length of stems of the omega stem-loop is that of 4-12 paired basic groups, and the length of loops of the omega stem-loop is that of 3-20 unpaired basic groups. According to the omega structure oligonucleotide primer for detecting the short chain RNA and an application thereof, starting inside chains and primer dimmer can be avoided, target hybridization accuracy of a probe at the 3' tail end can be increased, transcription specificity and sensitivity can be improved, high reverse transcriptase (RT) efficiency and good specificity can be achieved with few primers, a plurality of primers capable of detecting different targets can be added into a reaction system simultaneously, and PCR resultants obtained from different detected targets can be distinguished simultaneously, therefore multi-channel and high-flux detection is achieved, and detection efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:CHENGDU NUOEN BIOLOGICAL TECH
Visual detection method of isothermal amplification products of nucleic acids
InactiveCN103725750ASolve pollutionRealize closed cover detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerPyrophosphate
The present invention relates to two visual detection reagents of isothermal amplification products of nucleic acids, the two visual detection reagents are that 1-(1-hydroxy-2-naphthalene azo)-6-nitro-2-naphthol-4-sodium sulfonate or derivatives thereof (hereinafter referred to as the reagent 1) and 4-(2-pyridine azo) resorcinol sodium salt or derivatives thereof (hereinafter referred to as the reagent 2), the two visual detection reagents are used alone, at the beginning of a reaction, the reagent 1 combines with magnesium ions to become red, and the reagent 2 combines with the magnesium ions to form an orange complex, with the reaction, by-product pyrophosphate groups combines the magnesium ions to form a precipitation, the reagent 1 or loses the magnesium ions to become blue from red, the reagent 2 becomes yellow from orange, amplification reaction results can be judged by color change, detection without opening of a cover can be realized by the method, the aerosol pollution can be overcome, and the false positive problem caused by primer dimmers can be solved.
Owner:HARBIN DEGE BIOTECH
Ultra-low frequency mutant nucleic acid fragment detection method, library construction method, primer design method and reagent
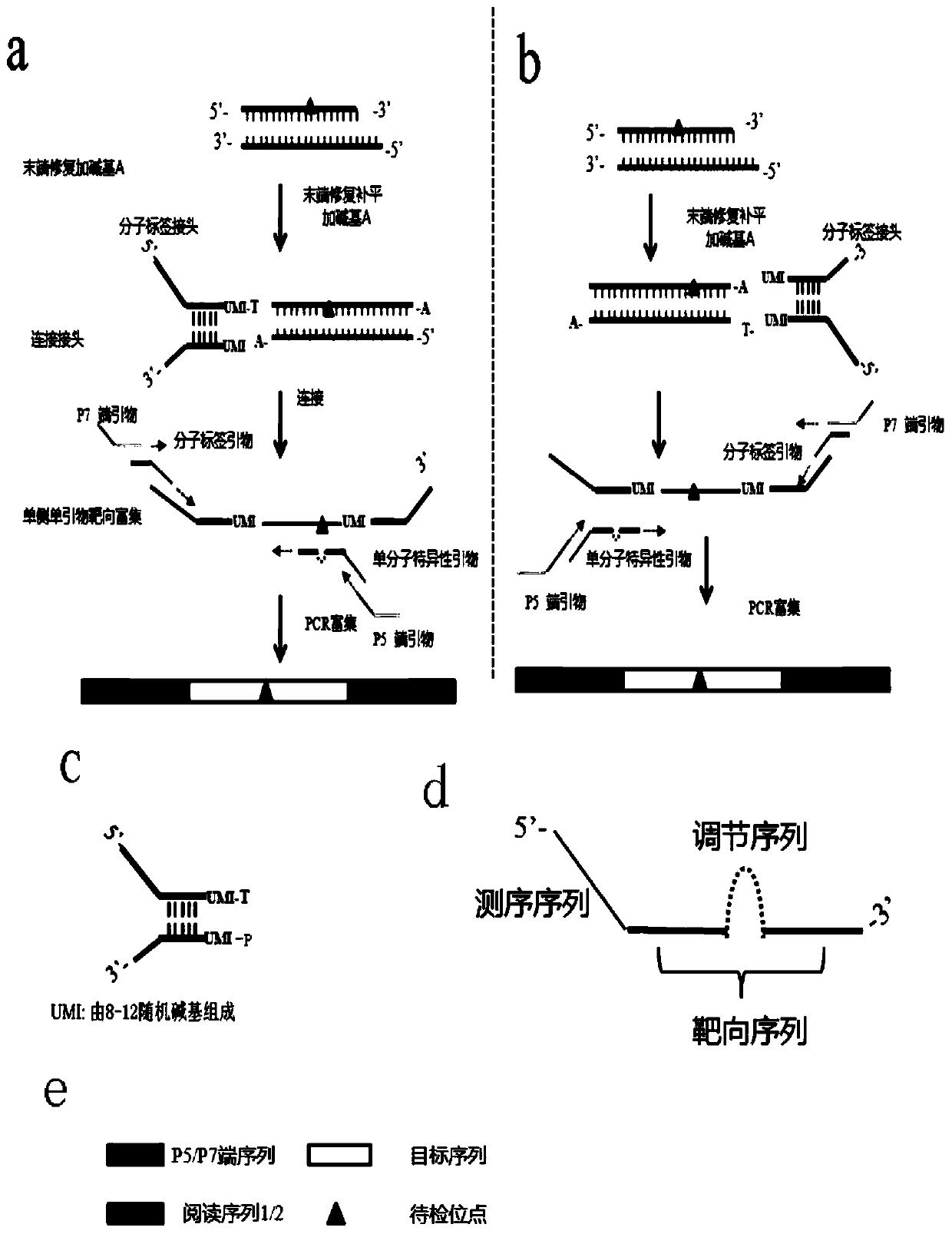
PendingCN110656156AImprove effective formwork utilizationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerTarget enrichment
The invention discloses an ultra-low frequency mutant nucleic acid fragment detection method, a mutant nucleic acid fragment library construction method, a primer design method and a reagent. Firstly,the fragmented nucleic acid of the sample to be tested is subjected to terminal repair, end-filling and adding A; connecting molecular tag joints; using the combination of molecular tag primers and single molecule specific primers to carry out amplicon targeted enrichment on the connection jointer product; finally, performing PCR amplification and enrichment. The single molecule specific primer designed by the invention obviously improves the number of available effective templates, and the carried adjustment sequence can obviously reduce the probability of forming primer dimers among specific primers, and the utilization rate of templates can be also obviously improved. The ultra-low frequency mutation nucleic acid fragment detection method of the invention uses one-sided single primer amplicon enrichment method and molecular label technology, improves the utilization rate of effective templates, reduces noise sources, reduces false positives, improves detection sensitivity and specificity, and is especially suitable for detection of trace ultra-low frequency mutation samples. At the same time, the invention can also carry out high-efficiency library construction.
Owner:HUNAN YEARTH BIOTECHNOLOGICAL CO LTD
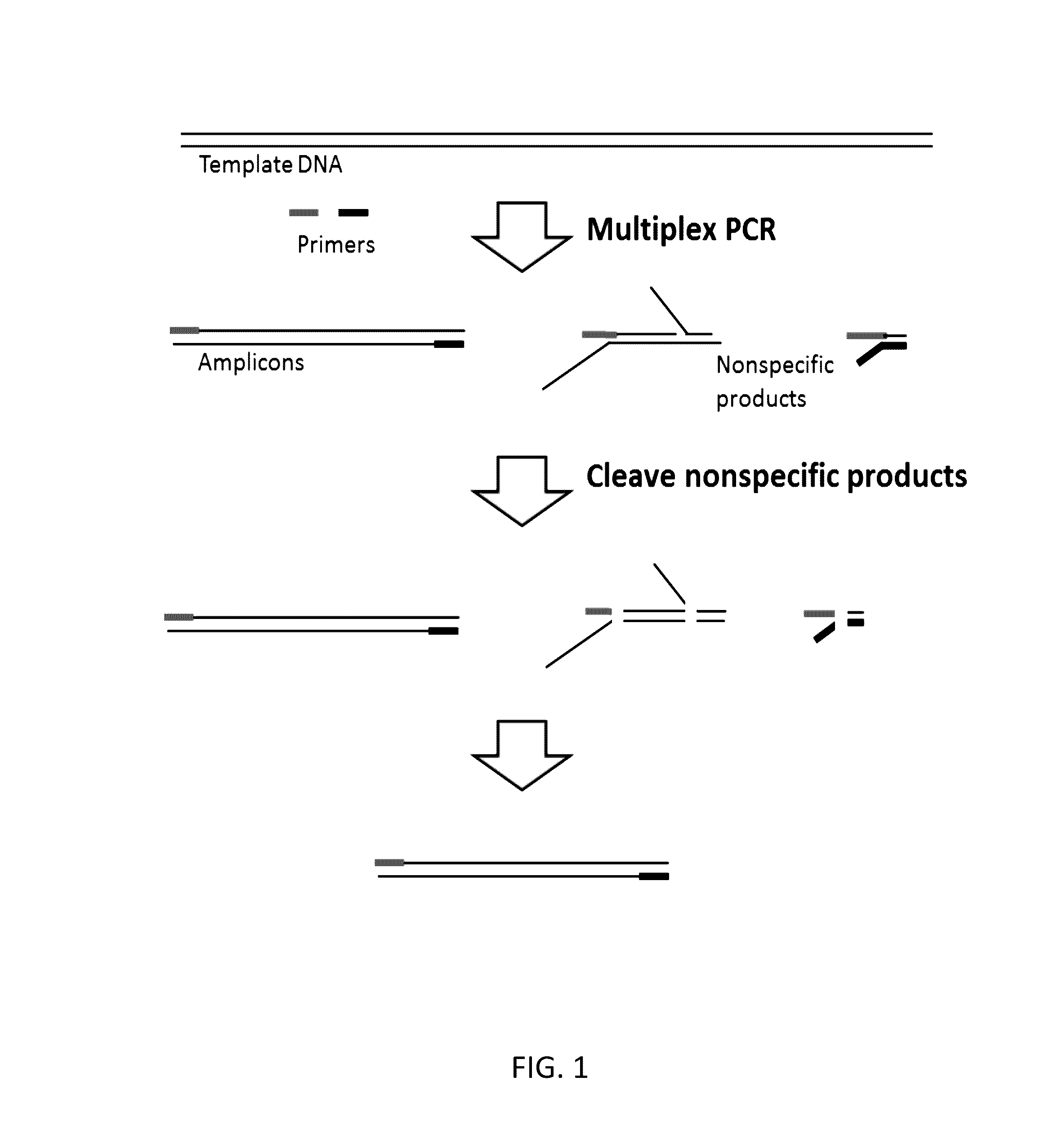
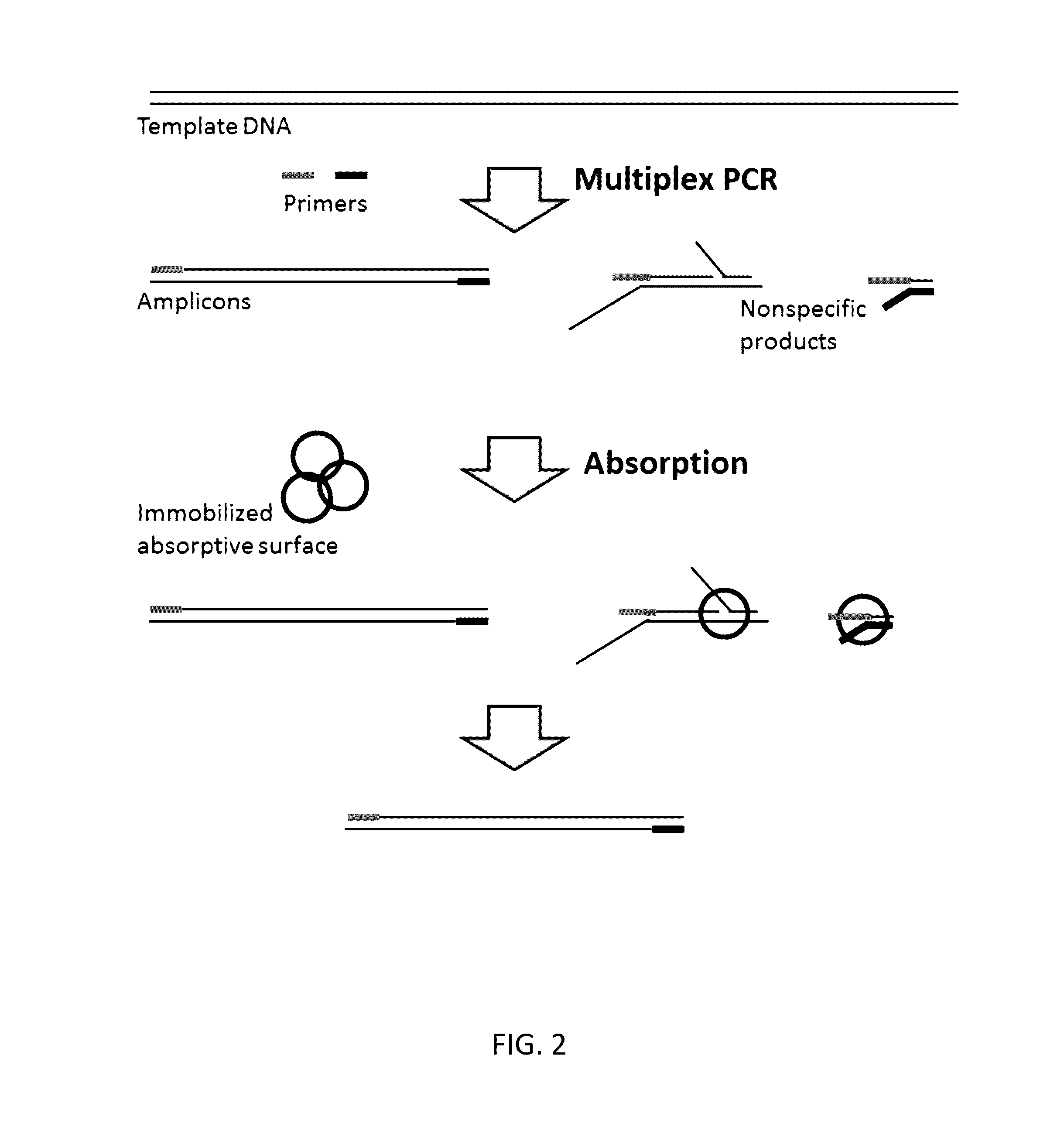
Methods and compositions for reducing non-specific amplification products
ActiveUS20170022551A1Effectively and efficiently cleaveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNAPrimer dimer
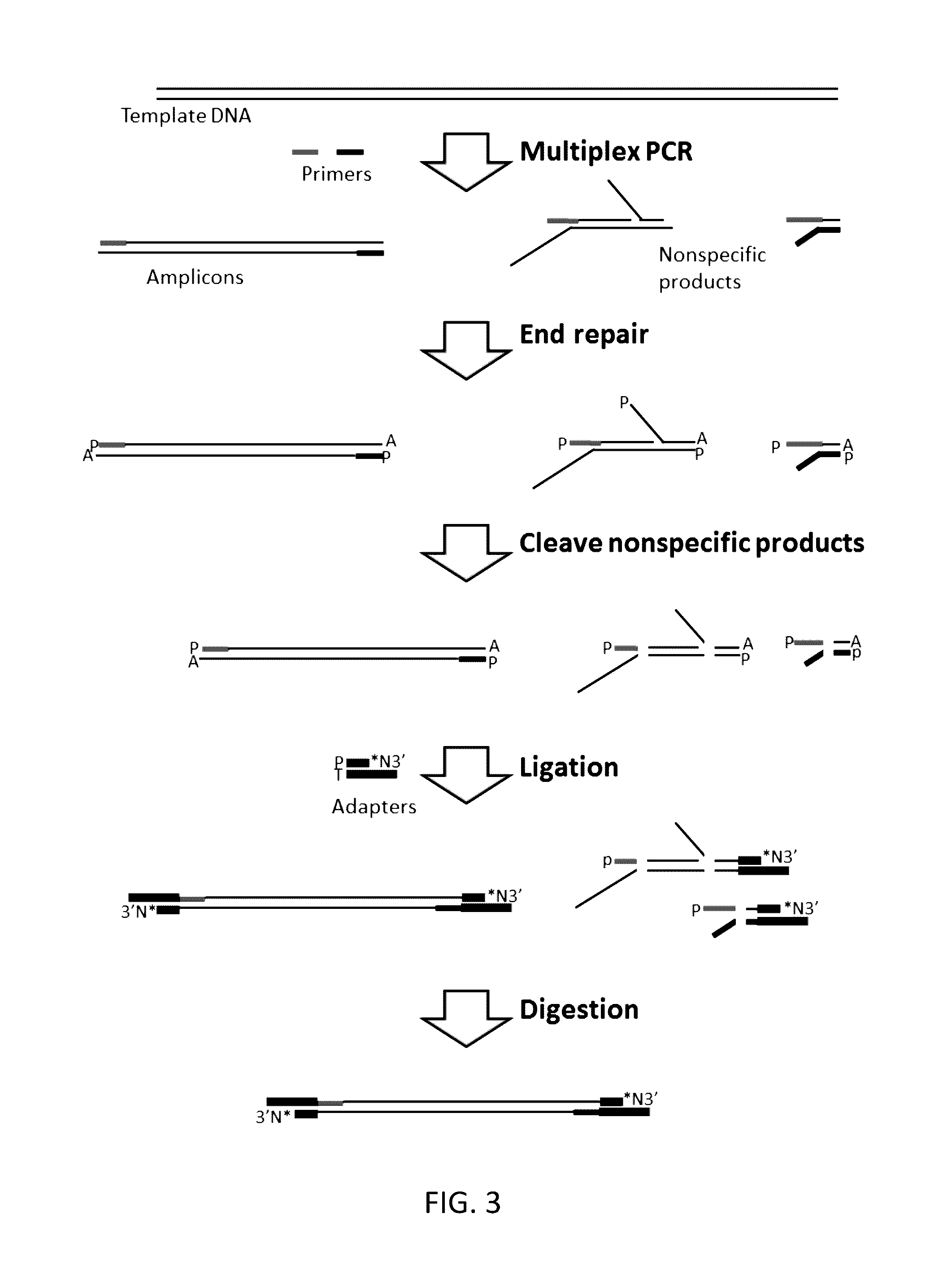
Methods, compositions, systems and kits to amplify or improve amplification of target-specific amplification products by reducing non-specific amplification products (e.g., primer-dimers) when amplifying multiple different nucleotide regions. The methods, compositions, systems and kits described herein may include, or include the use of, one or more resolvases that recognize and bind to and / or cut an aberrant DNA structure.
Owner:PARAGON GENOMICS INC
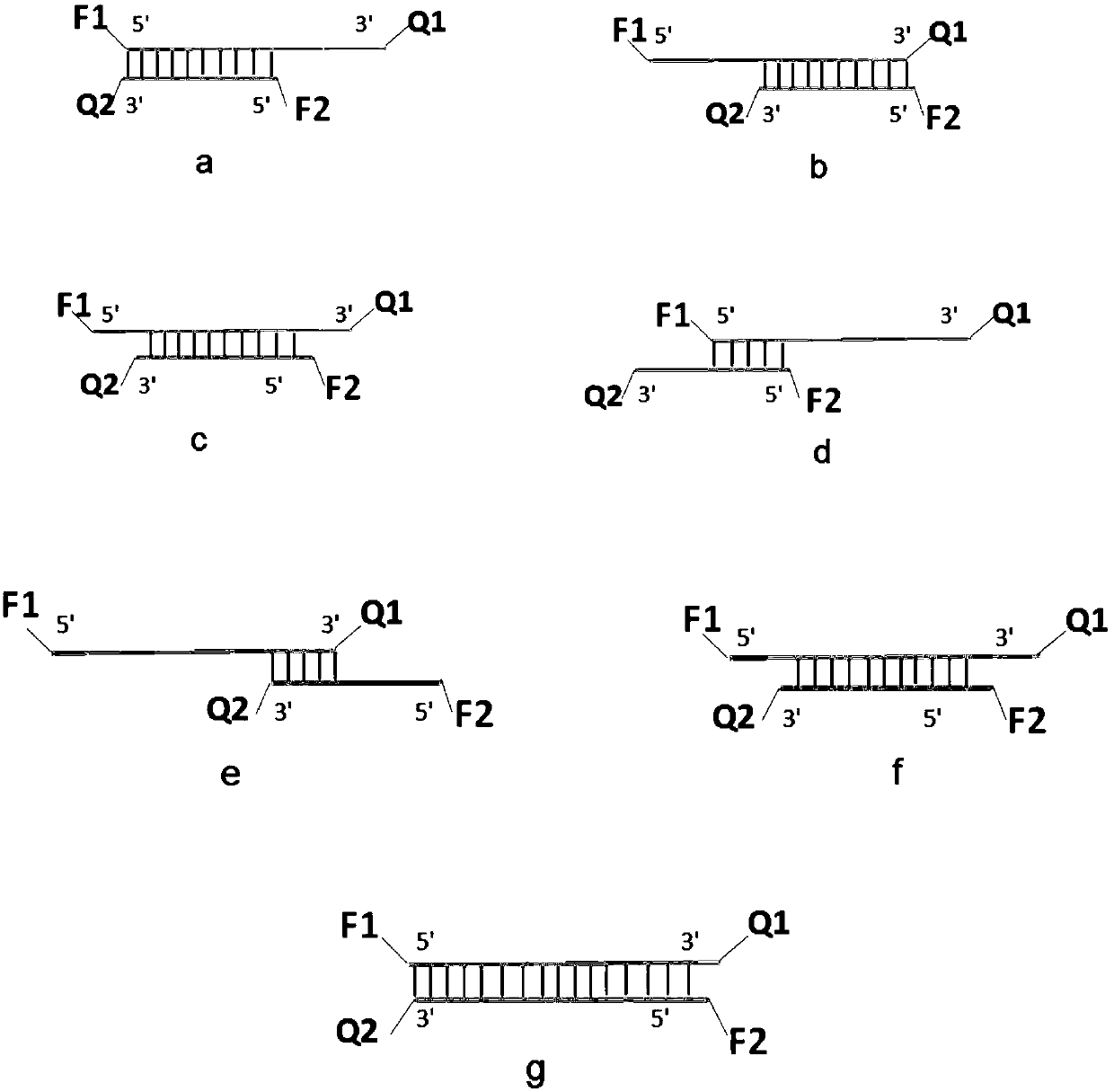
Structure and application of double-stranded oligonucleotide nucleic acid probe
PendingCN109652516ANearbyQuenched completelyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideNucleic Acid Probes
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com