Sintering process method and device for producing microcrystalline glass by using blast furnace slag
A technology of blast furnace slag and glass ceramics, which is applied in the field of metallurgy and inorganic non-metallic materials, can solve the problems of melting energy consumption, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing excessive consumption, improving economic profits, and good application treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
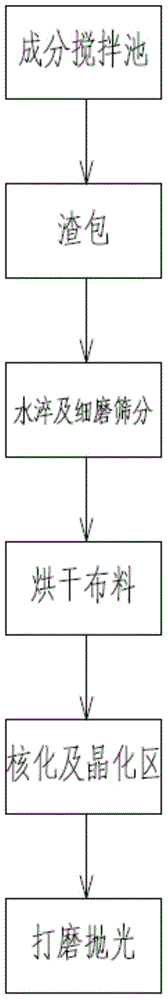
[0055] The blast furnace slag provided by the present embodiment prepares glass-ceramic comprising the following steps:
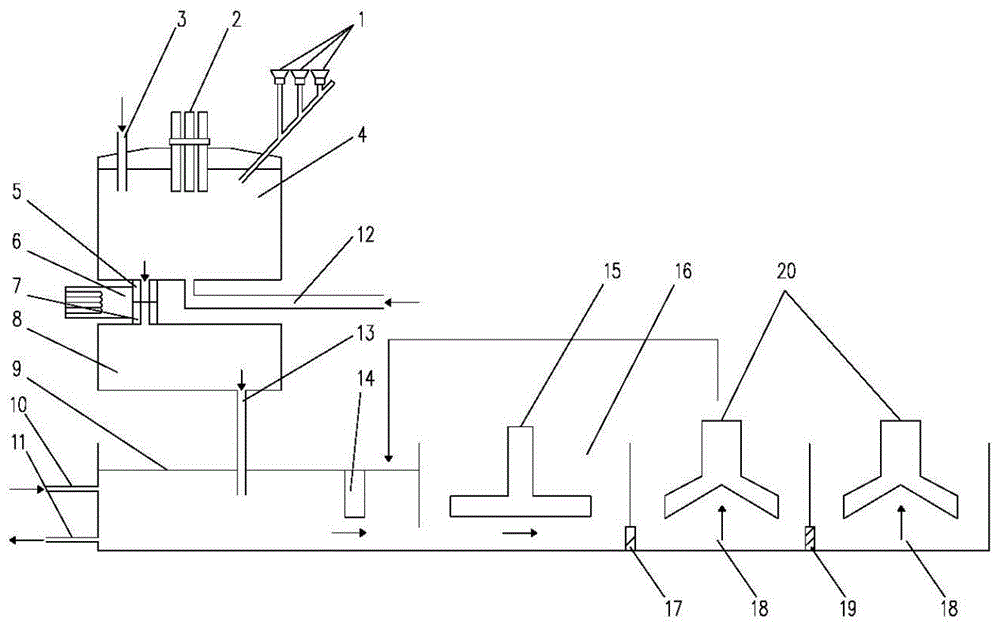
[0056] (1) The 1500°C molten slag flowing out of the blast furnace is transferred to the composition quenching and tempering stirring pool through the iron mixing furnace for heating and heat preservation;
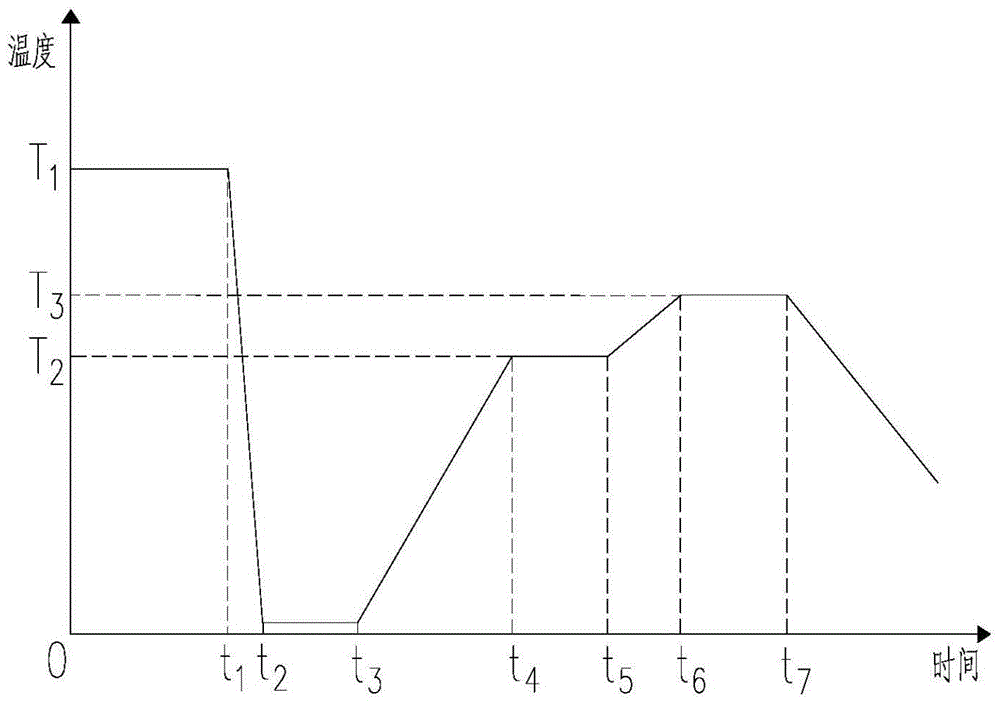
[0057] (2) Add the component modifying agent into the component tempering stirring tank, blow inert gas and coal powder from the top and bottom to mix the components evenly, and keep warm at 1450-1500°C for 1 hour;
[0058] (3) The slag enters the slag ladle through the slag port at the bottom of the composition quenching and tempering mixing tank to adjust the flow of the slag, and enters the water quenching pool from the slag port below the slag ladle for water quenching treatment to form glass particles;
[0059] (4) The obtained glass particles are finely ground and sieved, and the glass particles on the sieve are sent to the dryer for drying treatm...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The blast furnace slag provided by the present embodiment prepares glass-ceramic comprising the following steps:
[0067] (1) The 1500°C molten slag flowing out of the blast furnace is transferred to the composition quenching and tempering stirring pool through the iron mixing furnace for heating and heat preservation;
[0068] (2) Add component modifiers, nucleating agents, etc. into the component conditioning and tempering stirring tank, blow inert gas and coal powder from the top and bottom to mix the components evenly, and keep warm at 1450-1500°C for 1 hour;
[0069] (3) The slag enters the slag ladle through the slag port at the bottom of the composition quenching and tempering mixing tank to adjust the flow of the slag, and enters the water quenching pool from the slag port below the slag ladle for water quenching treatment to form glass particles;
[0070] (4) The obtained glass particles are finely ground and sieved, and the glass particles that meet the requir...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The blast furnace slag provided by the present embodiment prepares glass-ceramic comprising the following steps:
[0078] (1) The 1500°C molten slag flowing out of the blast furnace is transferred to the composition quenching and tempering stirring pool through the iron mixing furnace for heating and heat preservation;
[0079] (2) Add component modifiers, nucleating agents, etc. into the component conditioning and tempering stirring tank, blow inert gas and coal powder from the top and bottom to mix the components evenly, and keep warm at 1450-1500°C for 1 hour;
[0080] (3) The slag enters the slag ladle through the slag port at the bottom of the composition quenching and tempering mixing tank to adjust the flow of the slag, and enters the water quenching pool from the slag port below the slag ladle for water quenching treatment to form glass particles;
[0081] (4) The obtained glass particles are finely ground and sieved, and the glass particles that meet the requir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com