Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
261results about How to "Increase sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
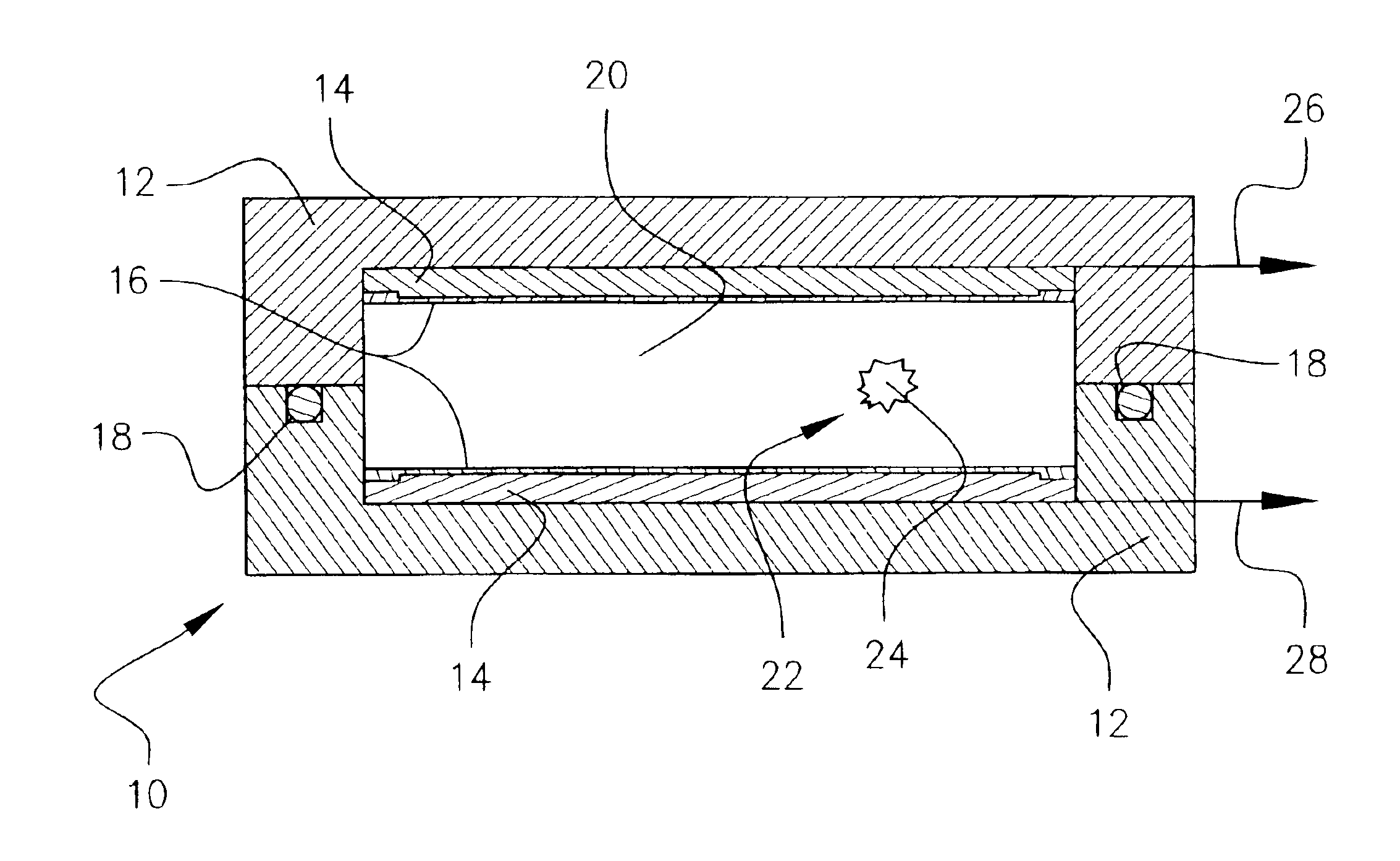
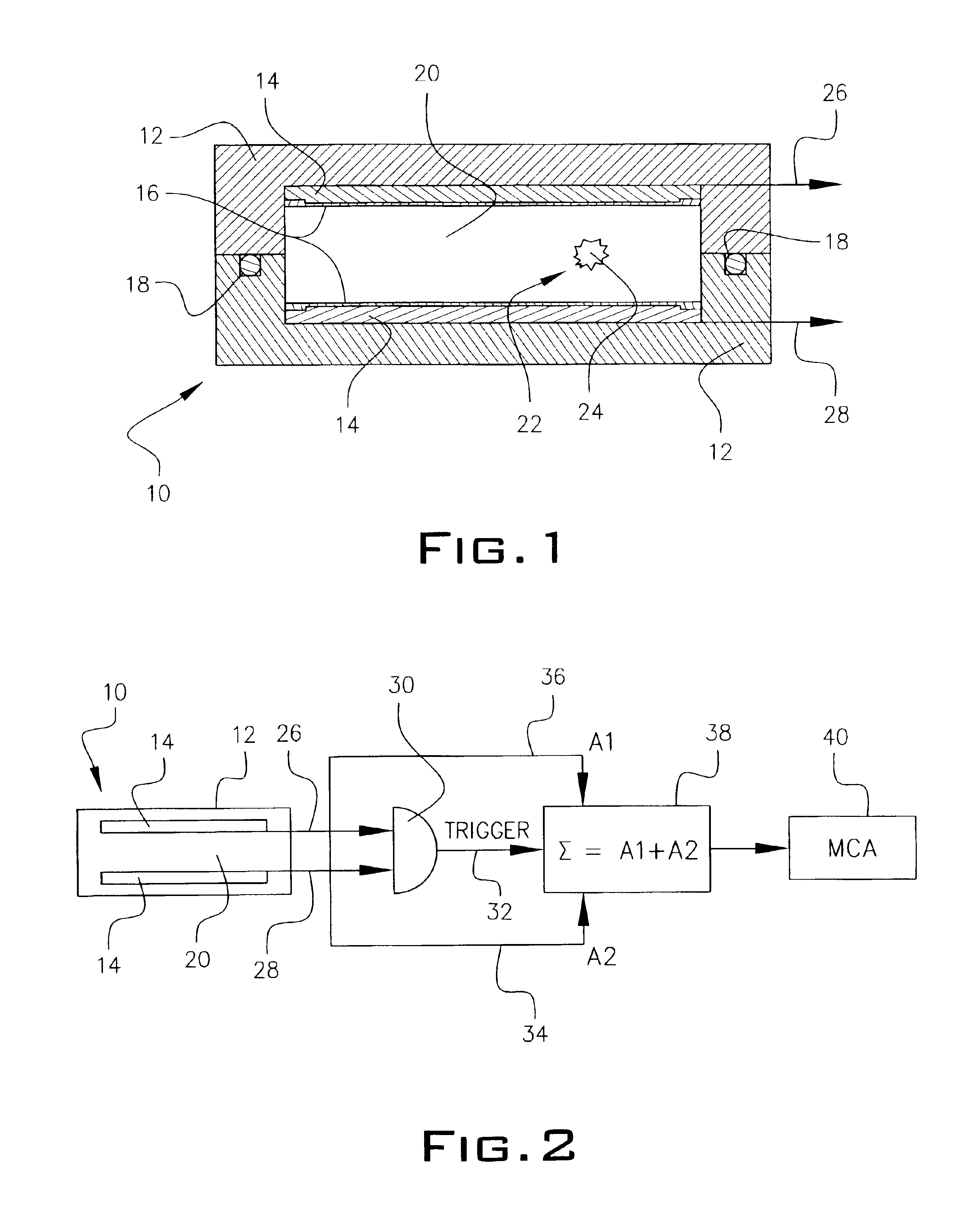
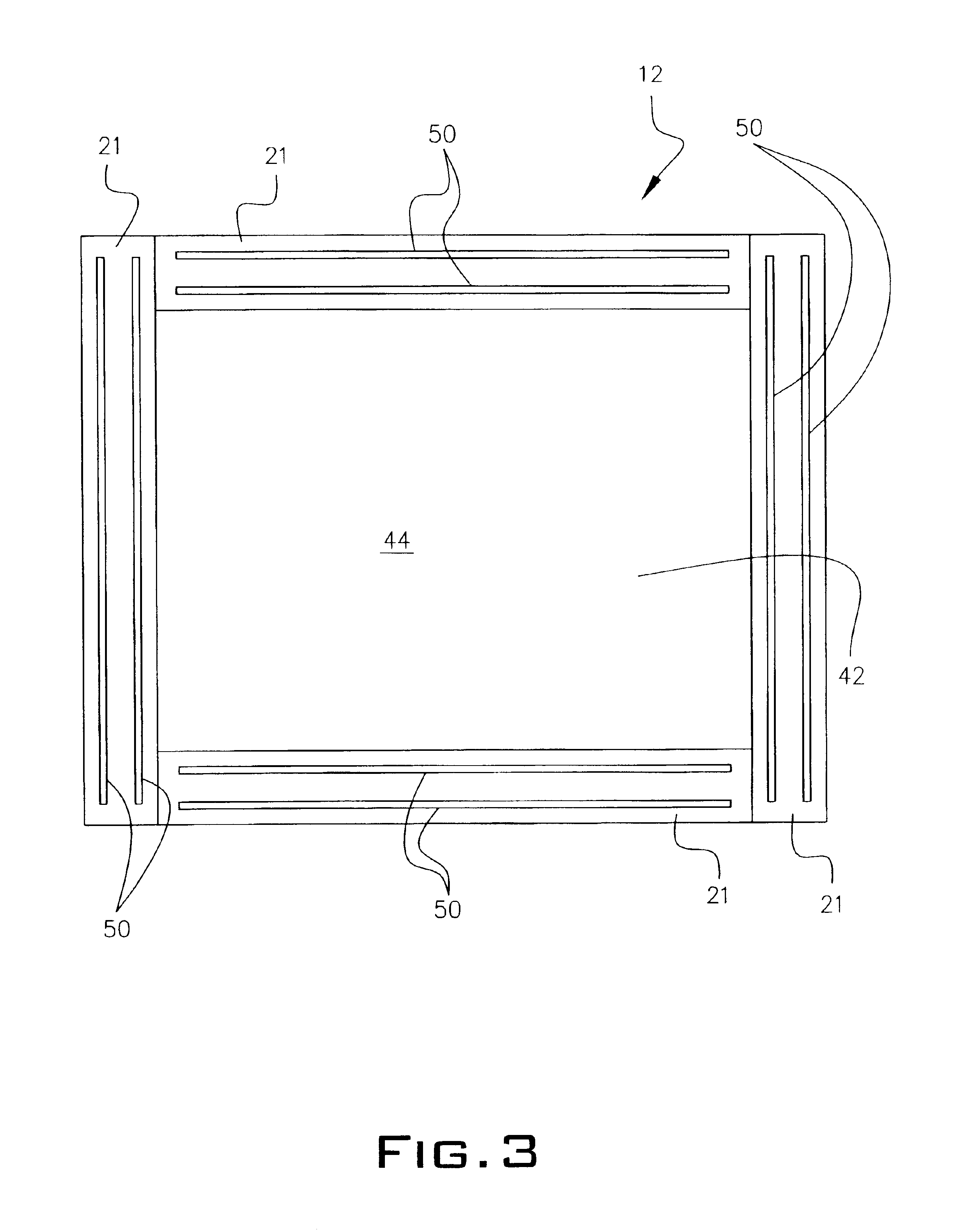
Microfabricated crossflow devices and methods
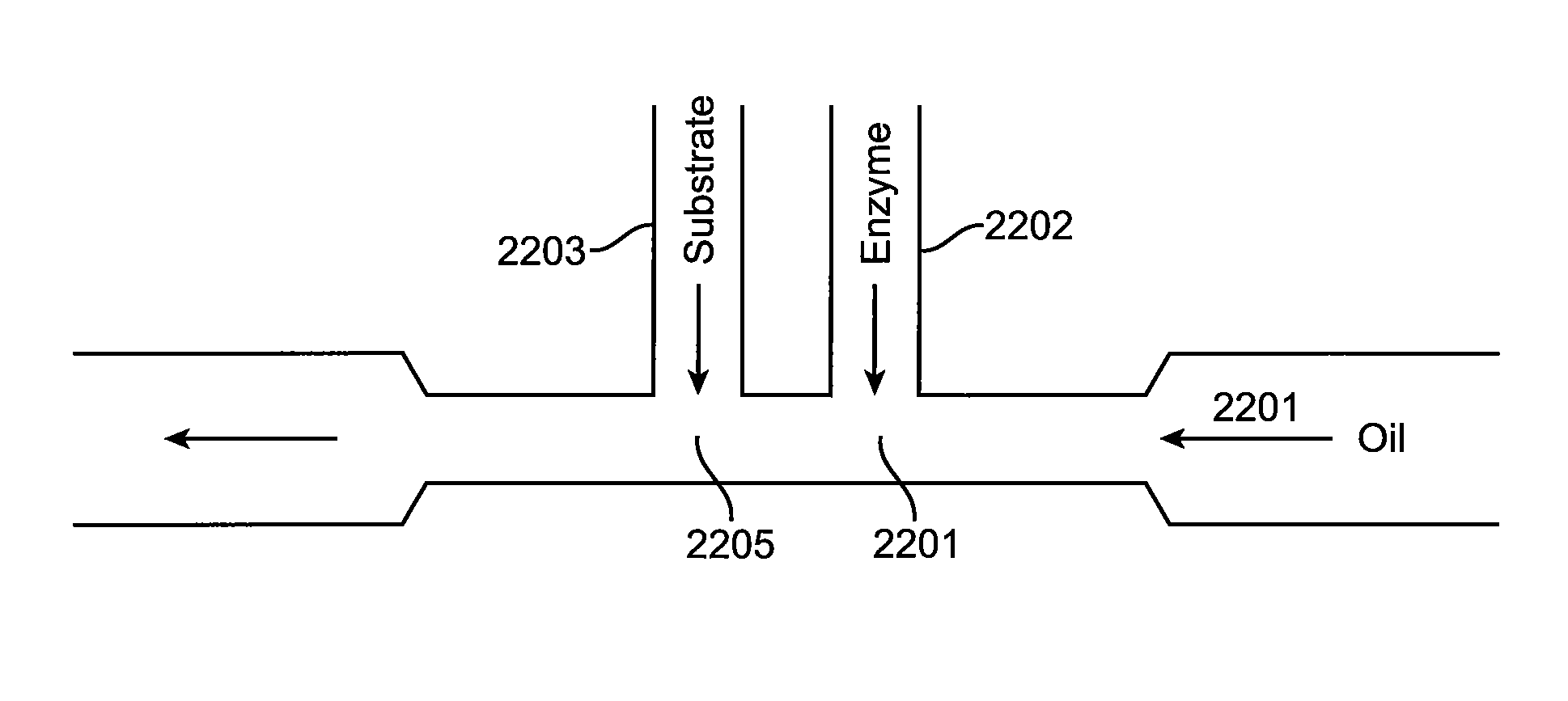
InactiveUS7294503B2Increase sensitivityHigh numberSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesMain channelEnzyme
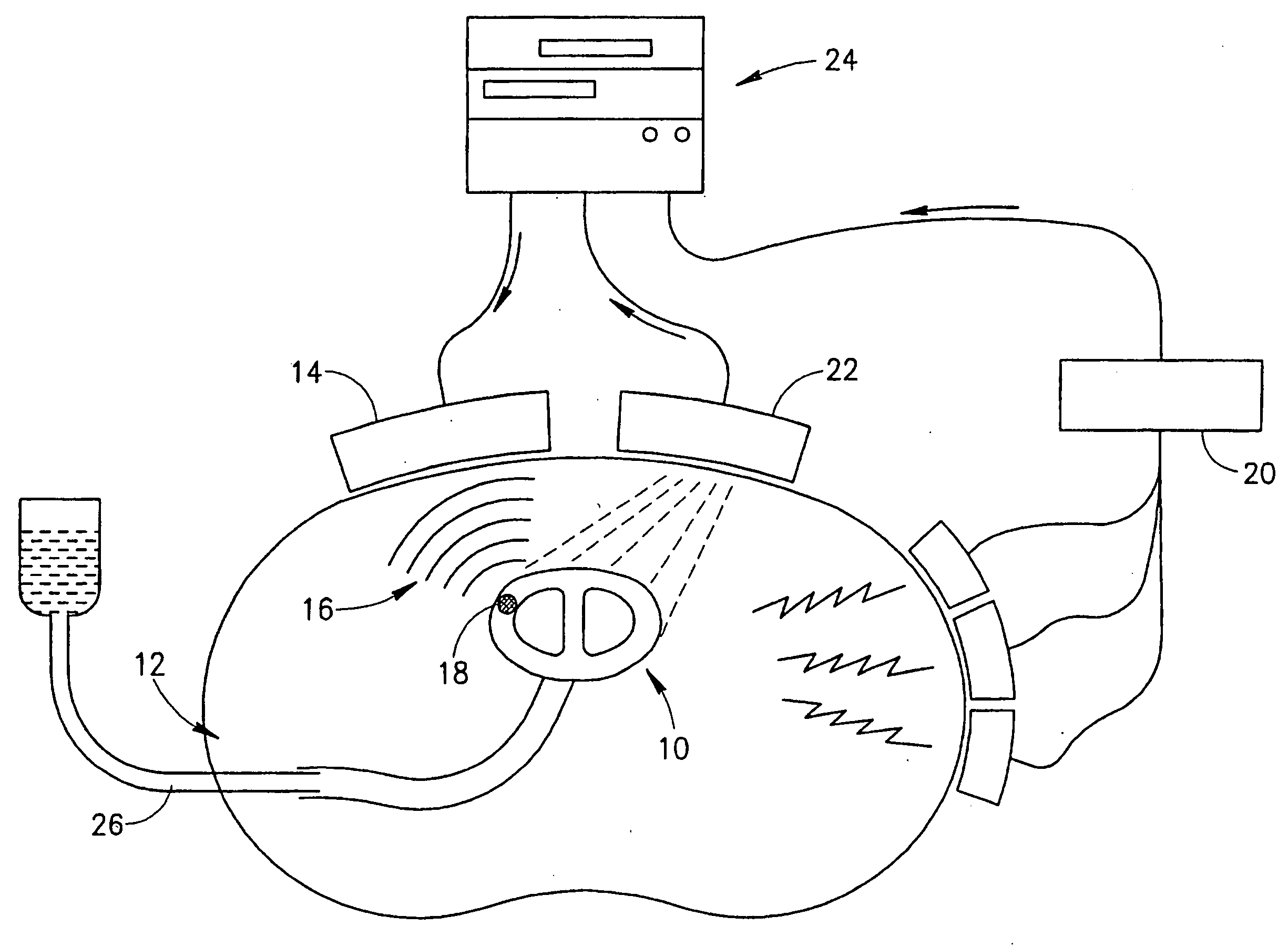
A microfluidic device for analyzing and / or sorting biological materials (e.g., molecules such as polynucleotides and polypeptides, including proteins and enzymes; viruses and cells) and methods for its use are provided. The device and methods of the invention are useful for sorting particles, e.g. virions. The invention is also useful for high throughput screening, e.g. combinatorial screening. The microfluidic device comprises a main channel and an inlet region in communication with the main channel at a droplet extrusion region. Droplets of solution containing the biological material are deposited into the main channel through the droplet extrusion region. A fluid different from and incompatible with the solution containing the biological material flows through the main channel so that the droplets containing the biological material do not diffuse or mix. Biological material within the droplets can be analyzed and / or sorted by detecting a predetermined characteristic of the biological sample in each droplet and sorting the droplet accordingly.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
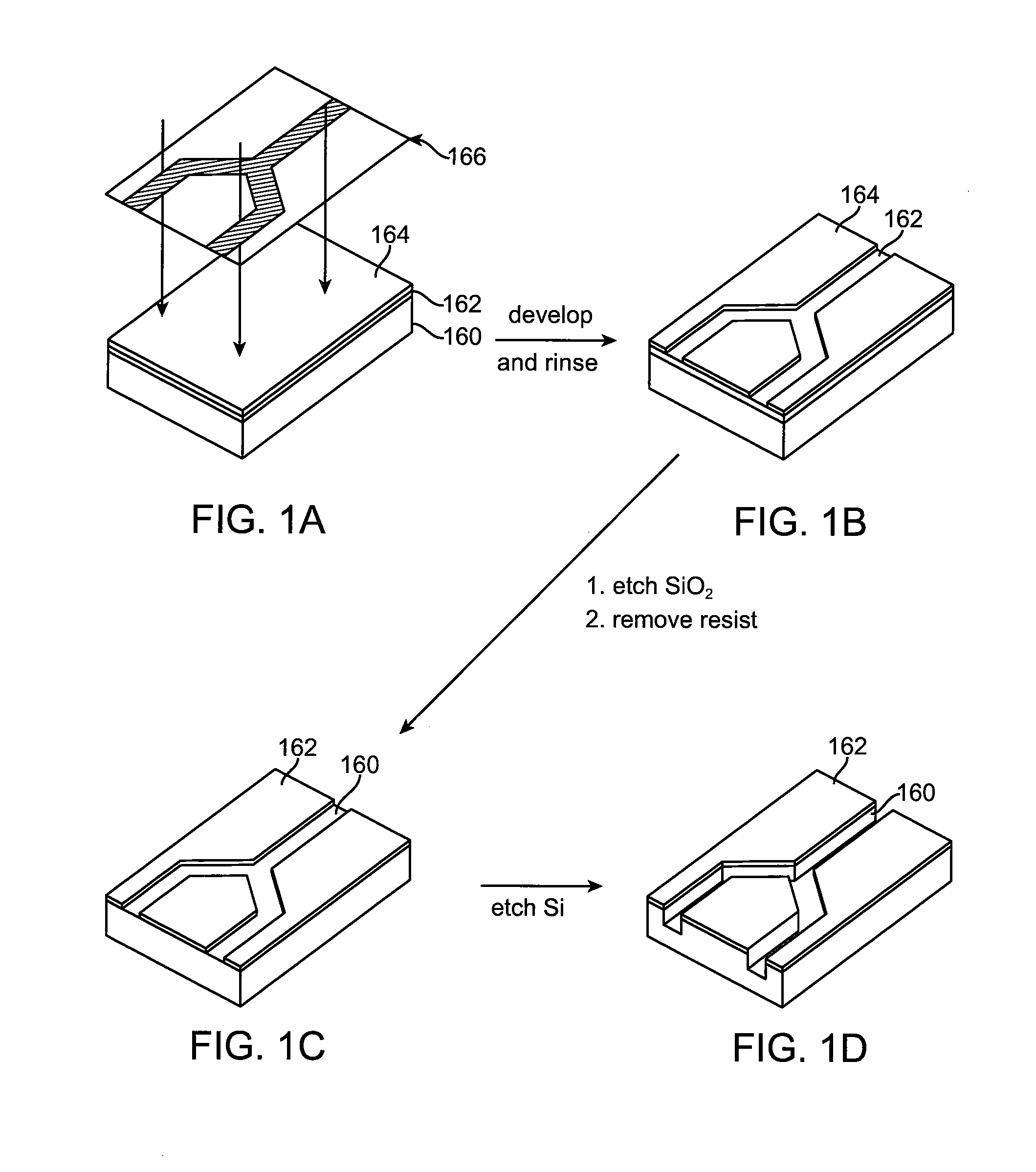
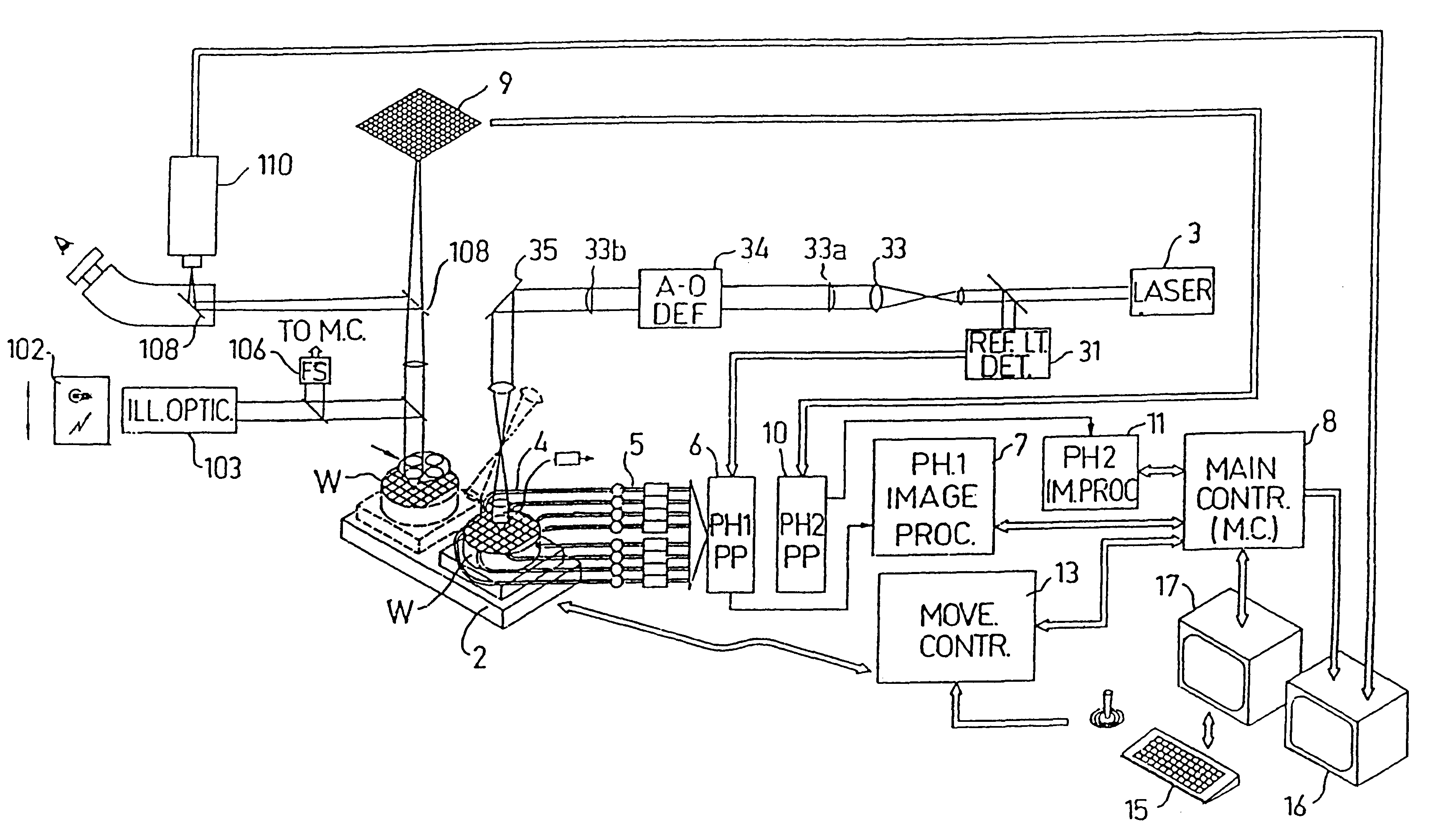
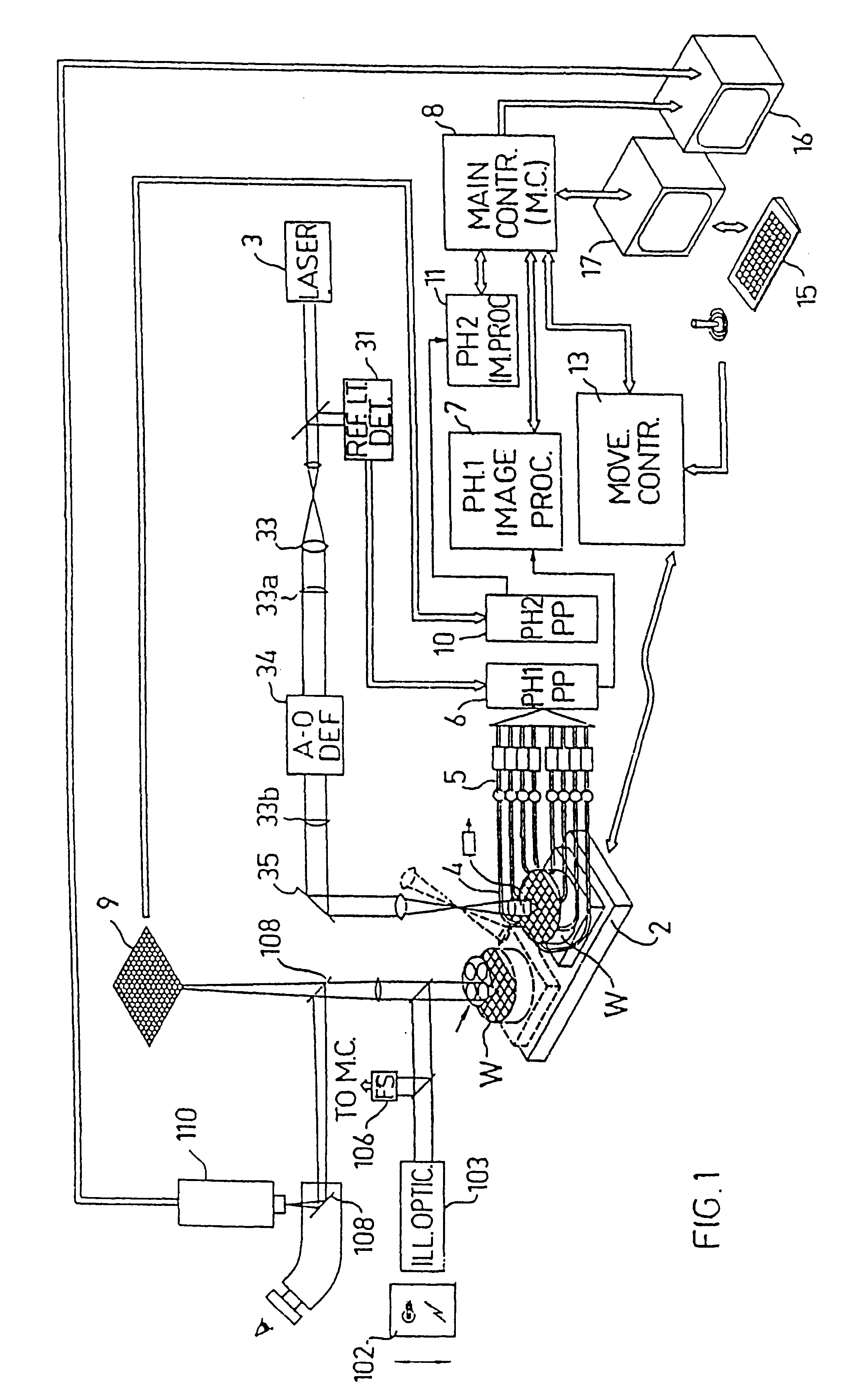
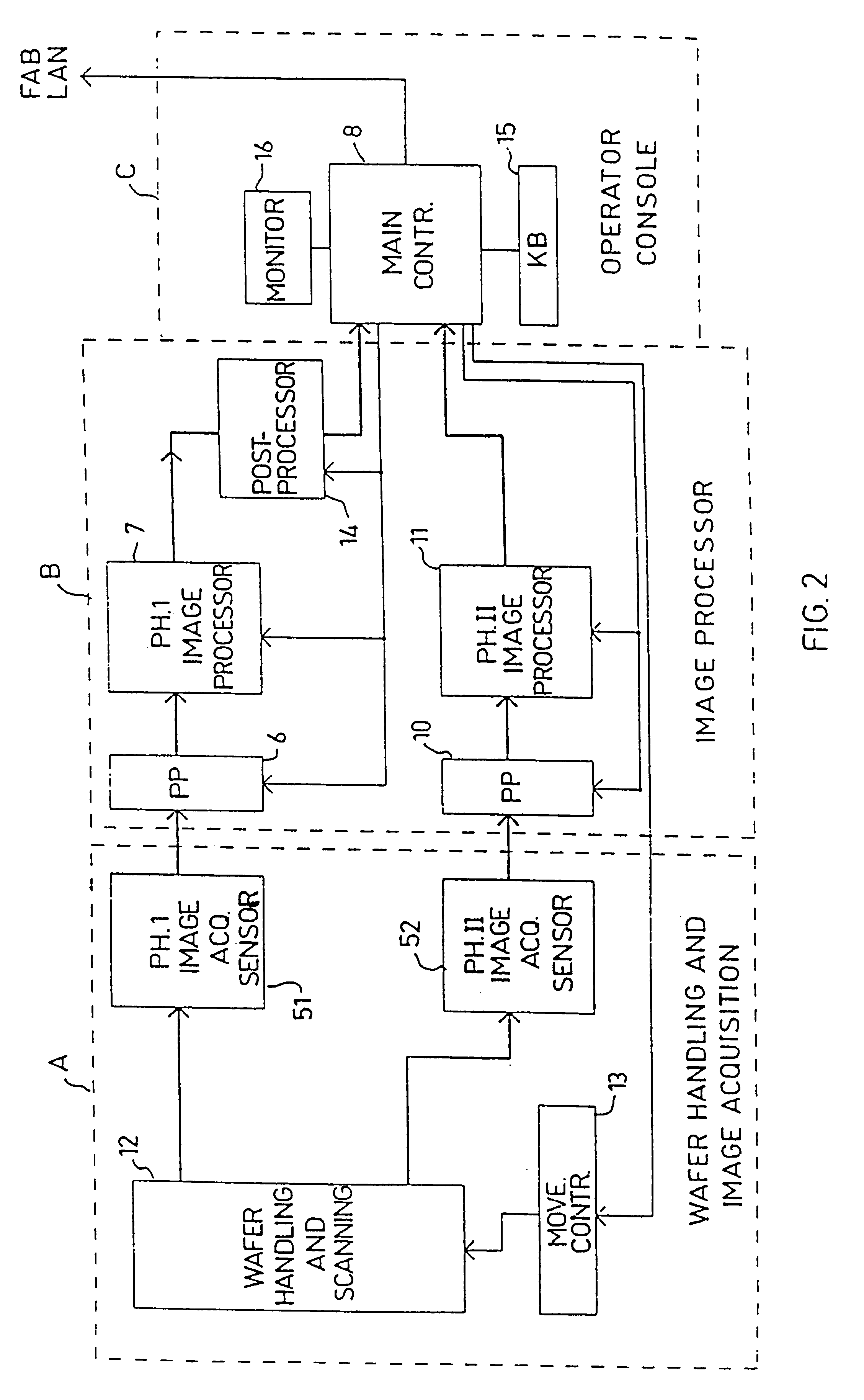
Substrate inspection method and apparatus
InactiveUS6178257B1High throughputIncrease sensitivityCharacter and pattern recognitionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A method and apparatus for inspecting the surface of articles, such as chips and wafers, for defects, includes a first phase of optically examining the complete surface of the article inspected at a relatively high speed and with a relatively low spatial resolution, and a second phase of optically examining with a relatively high spatial resolution only the suspected locations for the presence or absence of a defect therein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
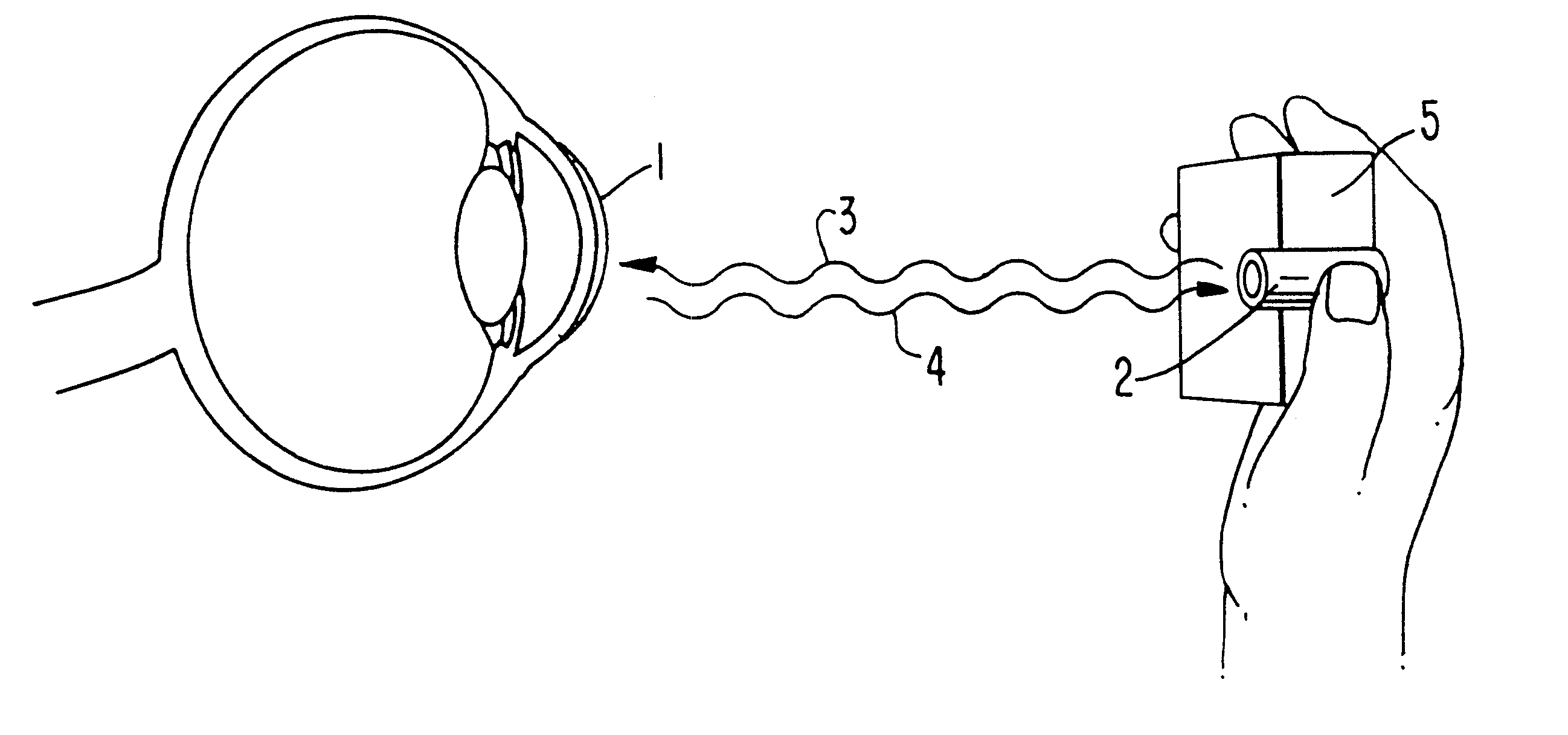
Ocular analyte sensor
InactiveUS6681127B2Increase rangeIncrease sensitivityNanotechMedical devicesInterstitial fluidIntracellular Fluid
An ophthalmic lens comprising a receptor moiety can be used to determine the amount of an analyte in an ocular fluid. The receptor moiety can bind either a specific analyte or a detectably labeled competitor moiety. The amount of detectably labeled competitor moiety which is displaced from the receptor moiety by the analyte is measured and provides a means of determining analyte concentration in an ocular fluid, such as tears, aqueous humor, or interstitial fluid. The concentration of the analyte in the ocular fluid, in turn, indicates the concentration of the analyte in a fluid or tissue sample of the body, such as blood or intracellular fluid.
Owner:EYESENSE AG
Communications within population of wireless transceivers based on common designation
InactiveUS20060018274A1Increase sensitivityIncrease rangeEnergy efficient ICTPosition fixationReceiptPopulation
A method of forming an ad hoc hierarchical communication network among a plurality of wireless transceiver includes assigning to each of the transceivers one or more common designations. A network organization routine of the transceivers operates to establish hierarchical networks based on the transceivers' common designations, resulting in a logical network organization that provides efficiencies for acquiring information from particular transceivers that share a common designation. Each transceiver's common designation is used by a digital processor of the transceiver to selectively receive data packets that are intended for receipt by transceivers sharing the particular common designation. Such a “common designation” network reduces power consumption and signal interference, which increases battery life in the transceivers. The transceivers may include a query handling routine in communication with a memory of the transceiver for serving as a dynamic distributed hierarchical database system of information such as, for example, sensor-derived information and time-sensitive information.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
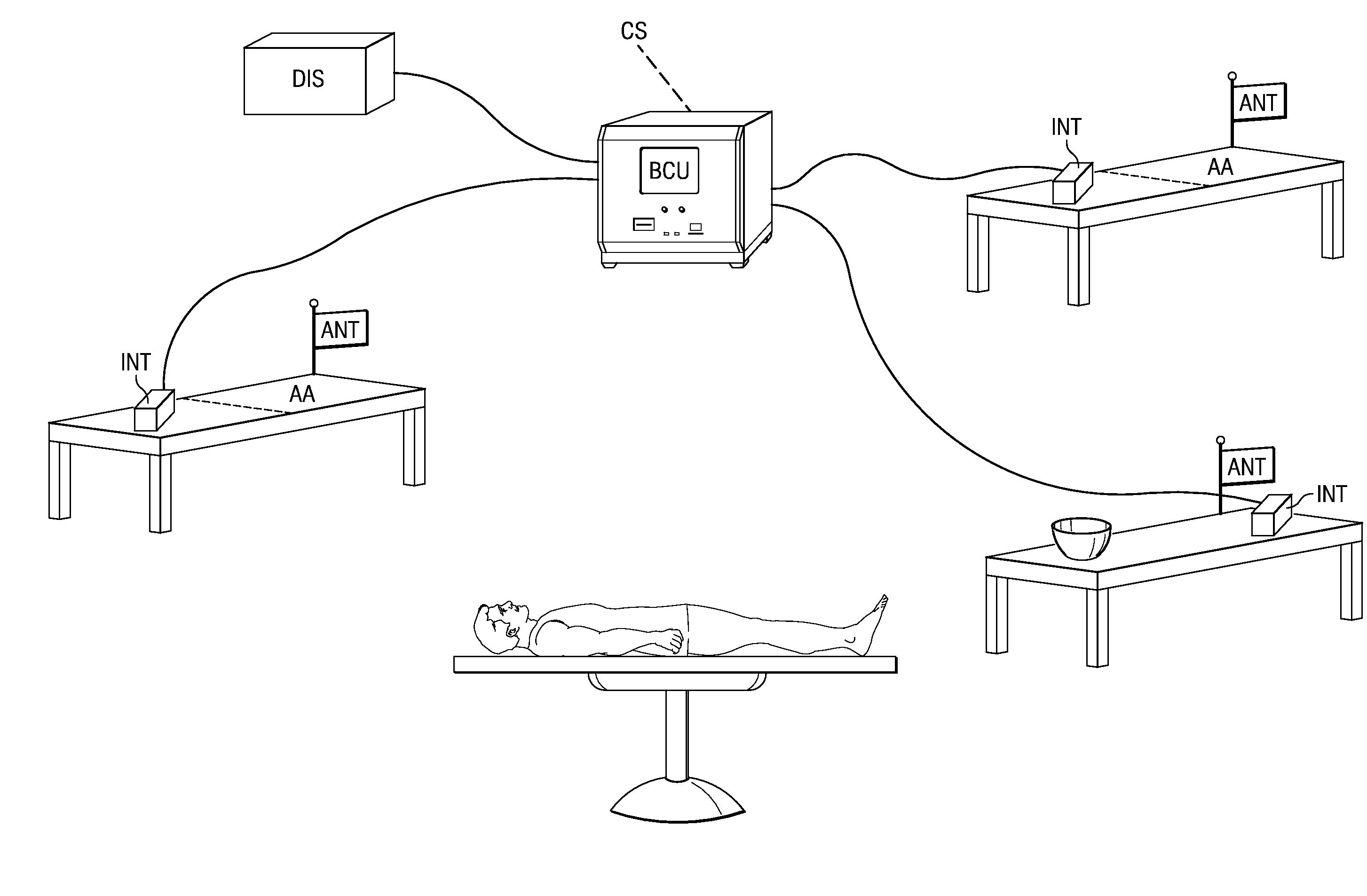
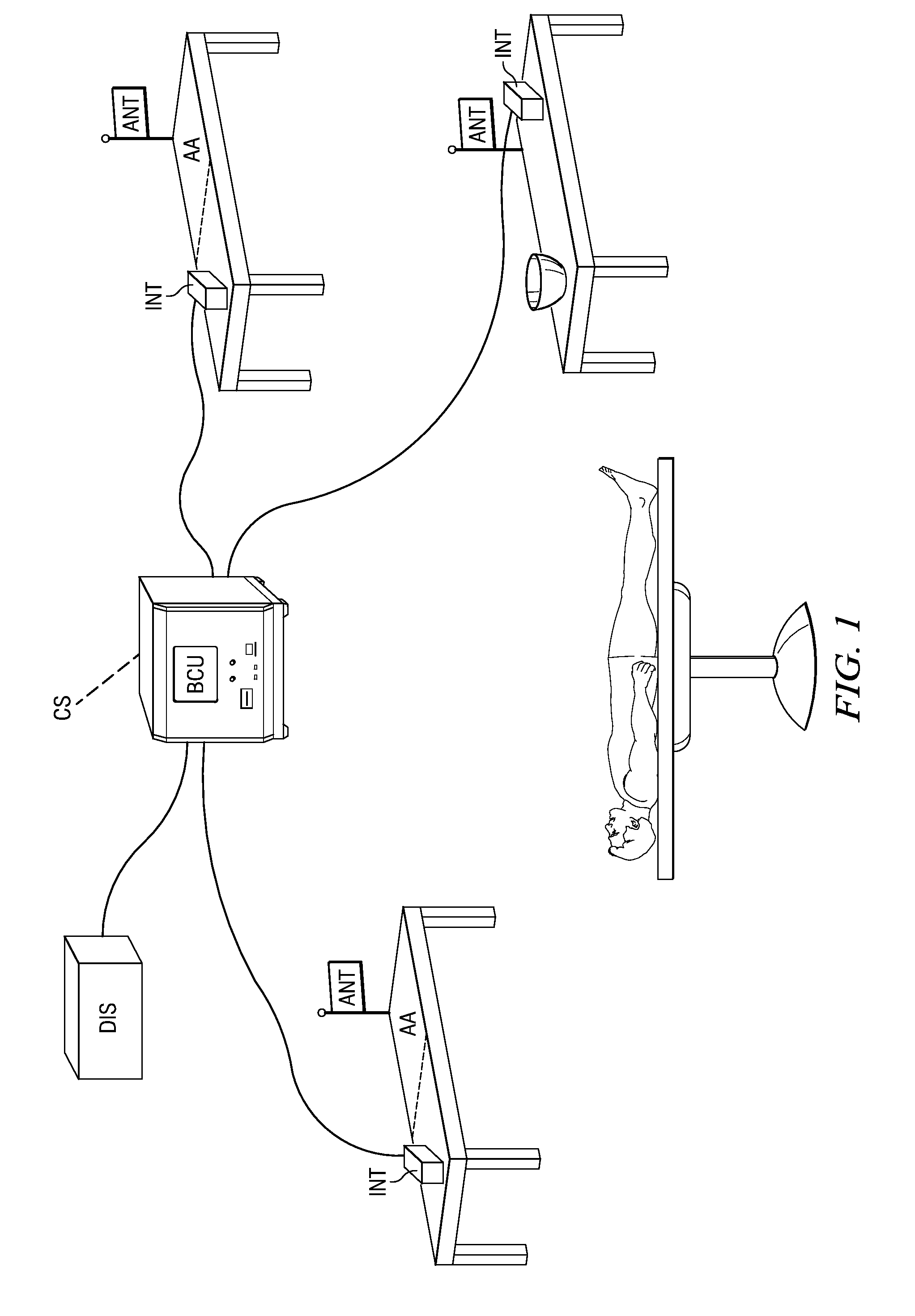
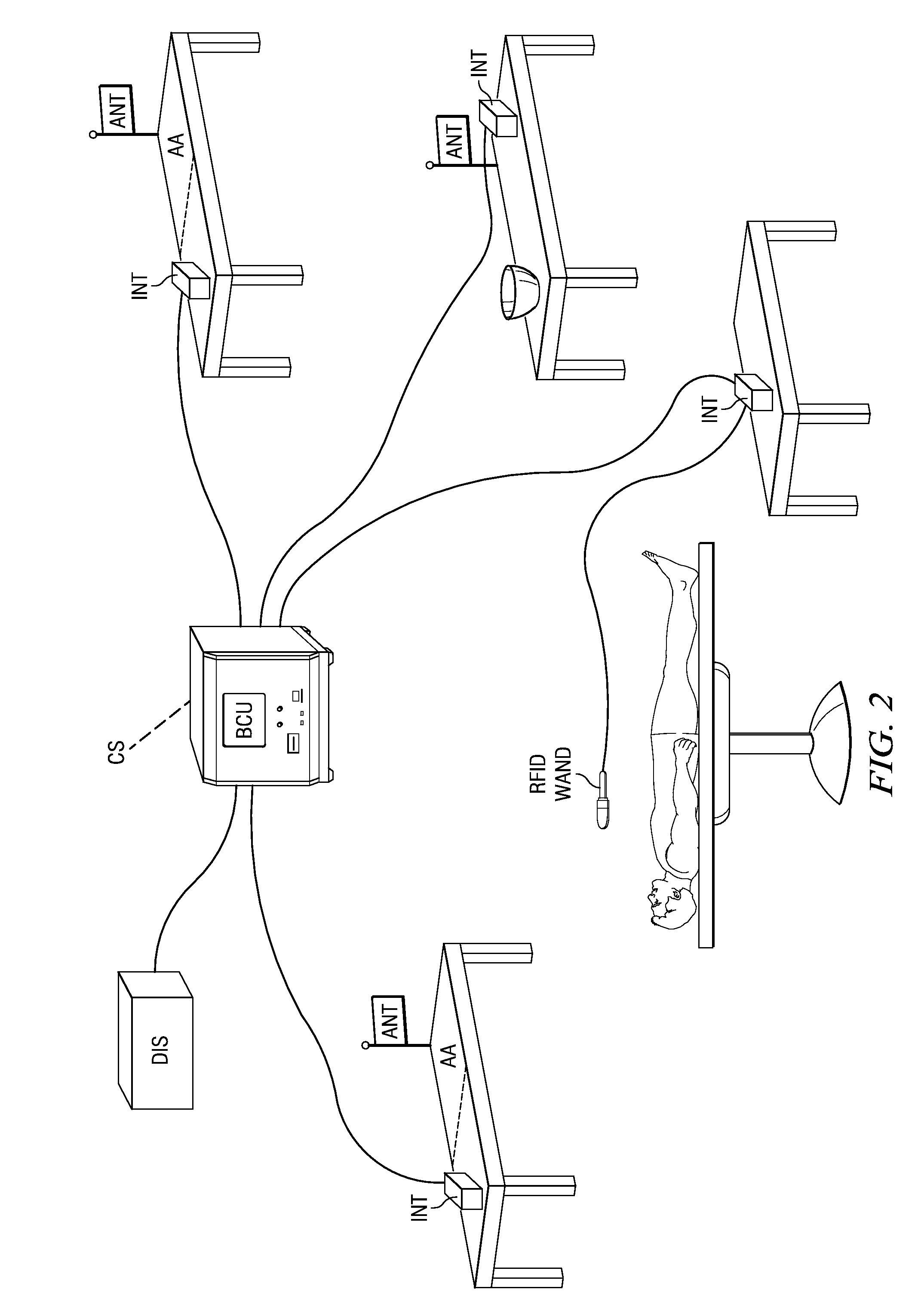
Interrogator and Interrogation System Employing the Same
An interrogator, methods of discerning the presence of an object, and interrogation systems employing the same. In one embodiment, the interrogation systems include multiple interrogators that communicate with a base command unit to track a location of an object. In another embodiment wherein the object is an RFID object (e.g., an object with an RFID tag), the interrogators employ signal processing techniques such as precharging the RFID object, and correlating a reference code with a reply code from the RFID object using selected techniques to increase a sensitivity of the interrogator, especially for adverse environments. In other embodiments, the interrogation systems include variations of metal instruments and sponges employed therewith. In yet another embodiment, the interrogation system includes metal interrogators capable of discerning the presence of a metal object, especially in a presence of another metal object.
Owner:LONE STAR SCM SYST LP
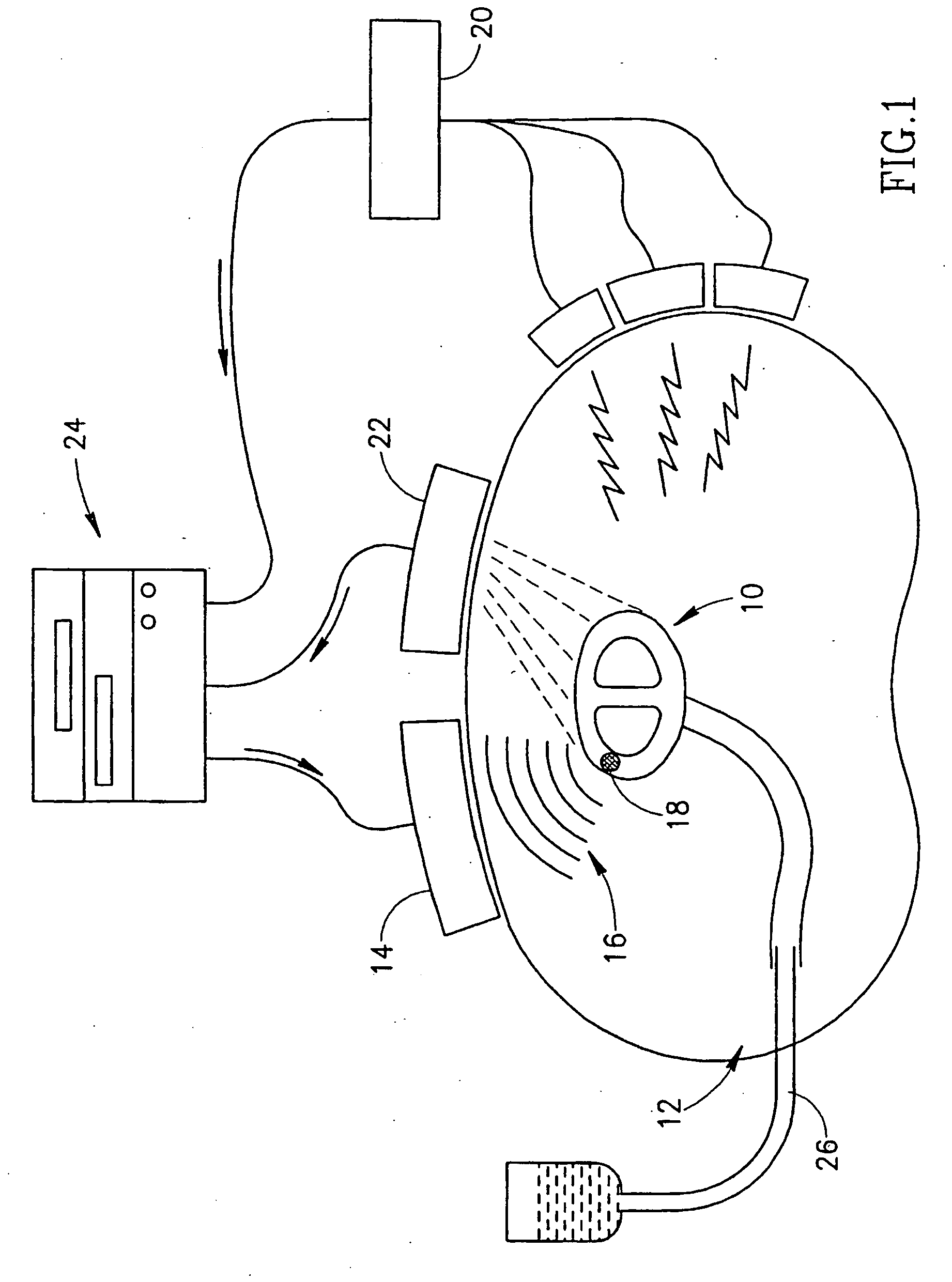
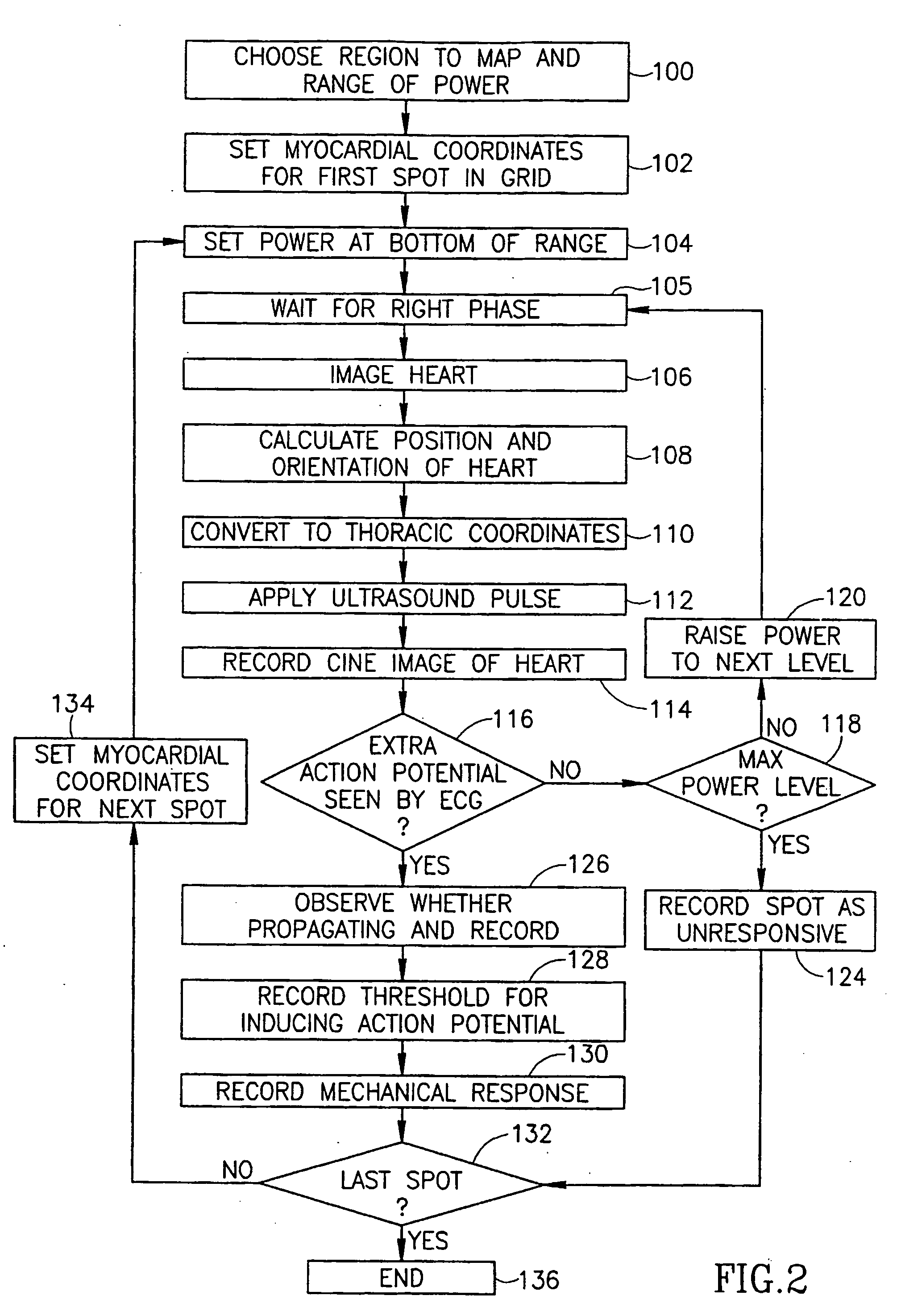
Ultrasound cardiac stimulator
InactiveUS20060052695A1Enhance procedureIncrease sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectricityPower level
An ultrasound cardiac stimulation system comprising: a spatially selective ultrasound source comprising at least one ultrasound transducer located outside the circulatory system; and a controller; where the controller generates an electrical response in the heart by directing the ultrasound source to transmit a high enough power level of ultrasound to one or more locations in the heart.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
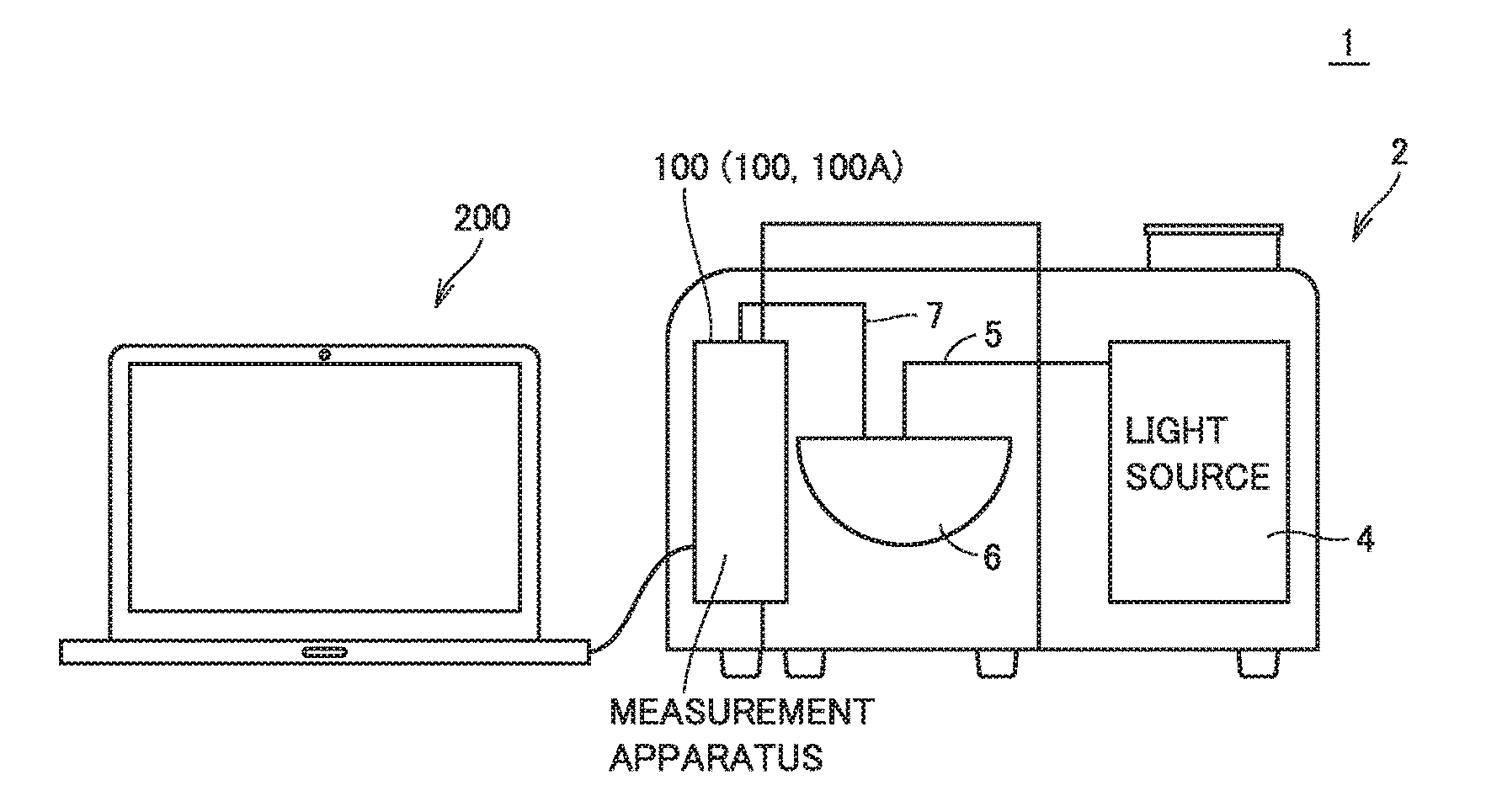
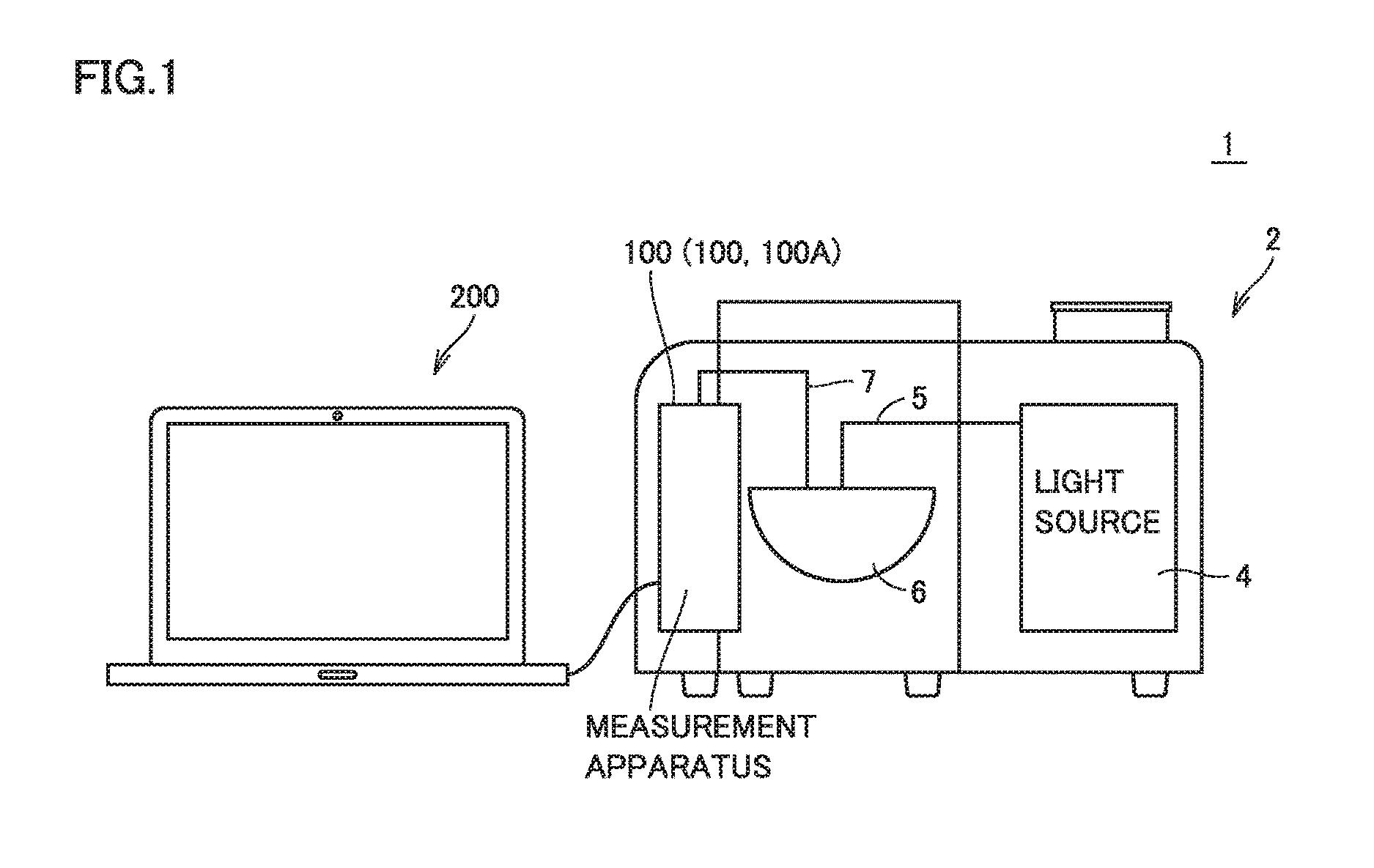
Optical characteristic measurement system and calibration method for optical characteristic measurement system
ActiveUS20170010214A1Increase sensitivityShort timeSpectrum investigationPhotometryMeasurement deviceCooling Units
There is provided an optical characteristic measurement system that can be set up in a relatively short time and can increase a detection sensitivity. The optical characteristic measurement system includes a first measurement apparatus. The first measurement apparatus includes: a first detection element arranged in a housing; a first cooling unit at least partially joined to the first detection element that cools the detection element; and a suppression mechanism that suppresses temperature variations occurring around the detection element in the housing.
Owner:OTSUKA DENSHI CO LTD
MTJ sensor including domain stable free layer
ActiveUS20080258721A1Cost reductionIncrease sensitivityNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsMagnetic detector
By subdividing the free layer of a GMR / TMR device into multiple sub-elements that share common top and bottom electrodes, a magnetic detector is produced that is domain stable in the presence of large stray fields, thereby eliminating the need for longitudinal bias magnets. Said detector may be used to measure electric currents without being affected by local temperature fluctuations and / or stray fields.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Neutron detector
InactiveUS6924487B2Increase sensitivityEfficiently measureLaser detailsMeasurement with semiconductor devicesPhotodetectorAmount of substance
A neutron detector is provided which is able to measure thermal neutron radiation within a gap filled with a substance that permits scintillation in the absorption of thermal neutron radiation, the gap being formed between at least a first and second spaced apart photodetector working in electrical coincidence. The substance disposed within the gap can be either a gas, liquid or solid. In the case of a gas, a shell is used so that the gas can be retained and kept under pressure. The neutron detector is able to differentiate between gamma radiation and neutron energy. An alternate embodiment of the novel detector includes a device which employs a plurality of detectors surrounding a moderator which can be used to measure both thermal and high energy neutrons.
Owner:CONSTELLATION TECH
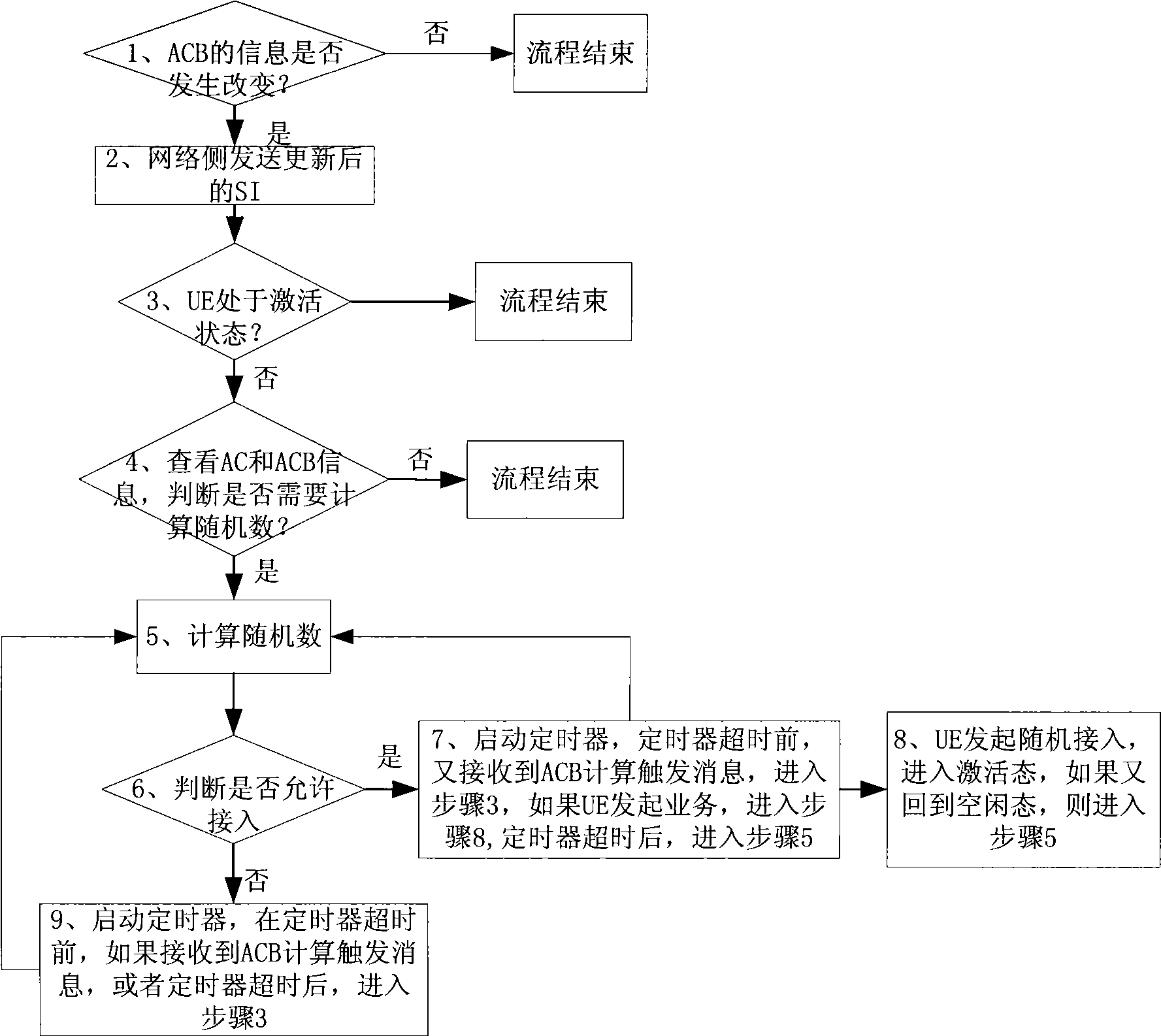
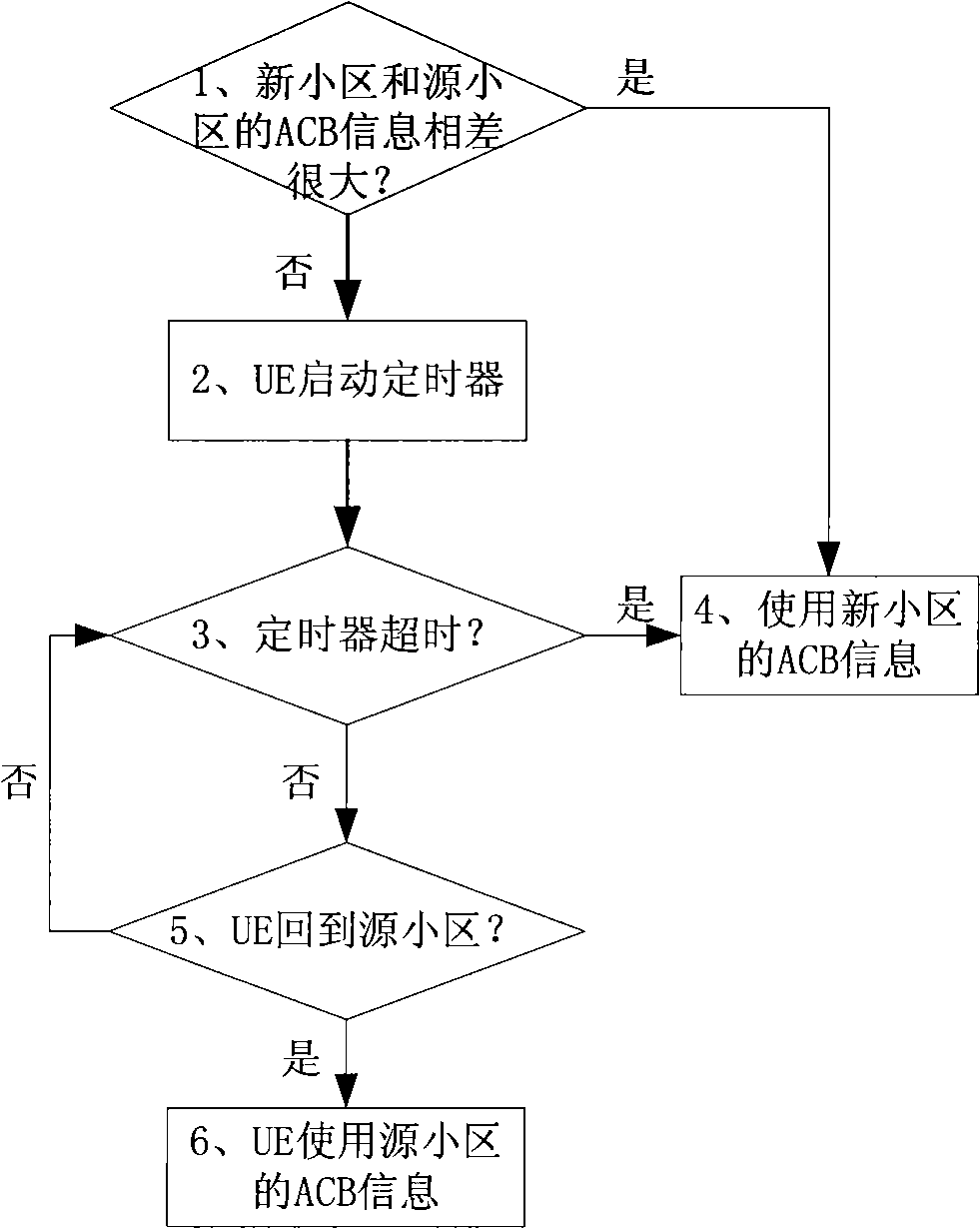
Method for barring access class
InactiveCN101547492AImprove user experienceIncrease sensitivityAssess restrictionAccess stratumTelecommunications
The invention discloses a method for barring access class. The method comprises the following steps that: user equipment UE receives system information SI transmitted by a network side, wherein the SI contains Access Class Barring ACB information; and the UE calculates random number according to the ACB information, when the UE cannot be accessed to a network according to the random number, an access stratum AS of the UE transmits interlayer primitive to a non-access stratum NAS, and the interlayer primitive contains a cause value. The invention also discloses user equipment, which comprises a receiving unit and an executing unit. By the method and the device provided by the embodiment of the invention, barring of the network on the access class of a user can be fairer, and the sensitivity of the user can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
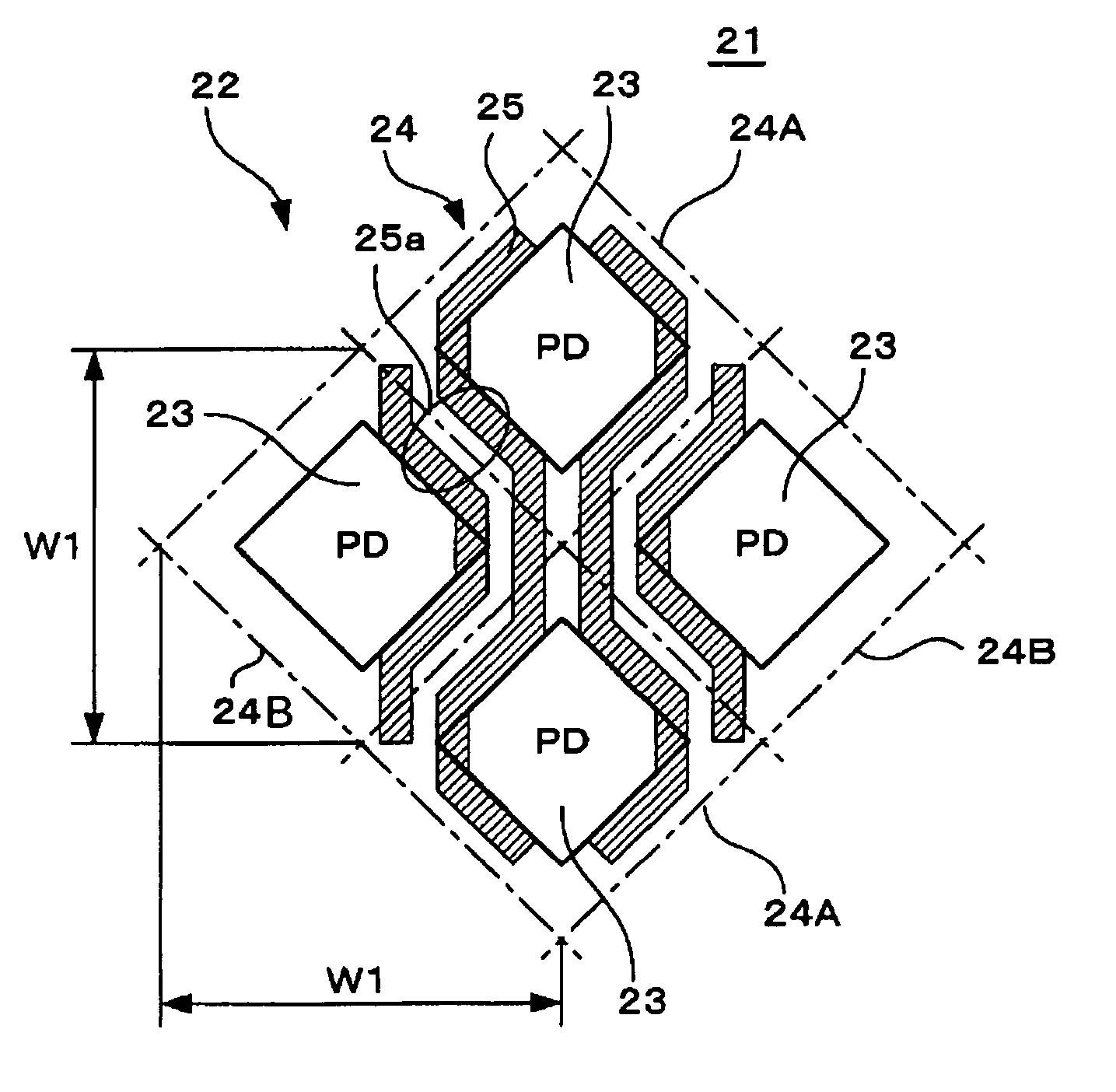
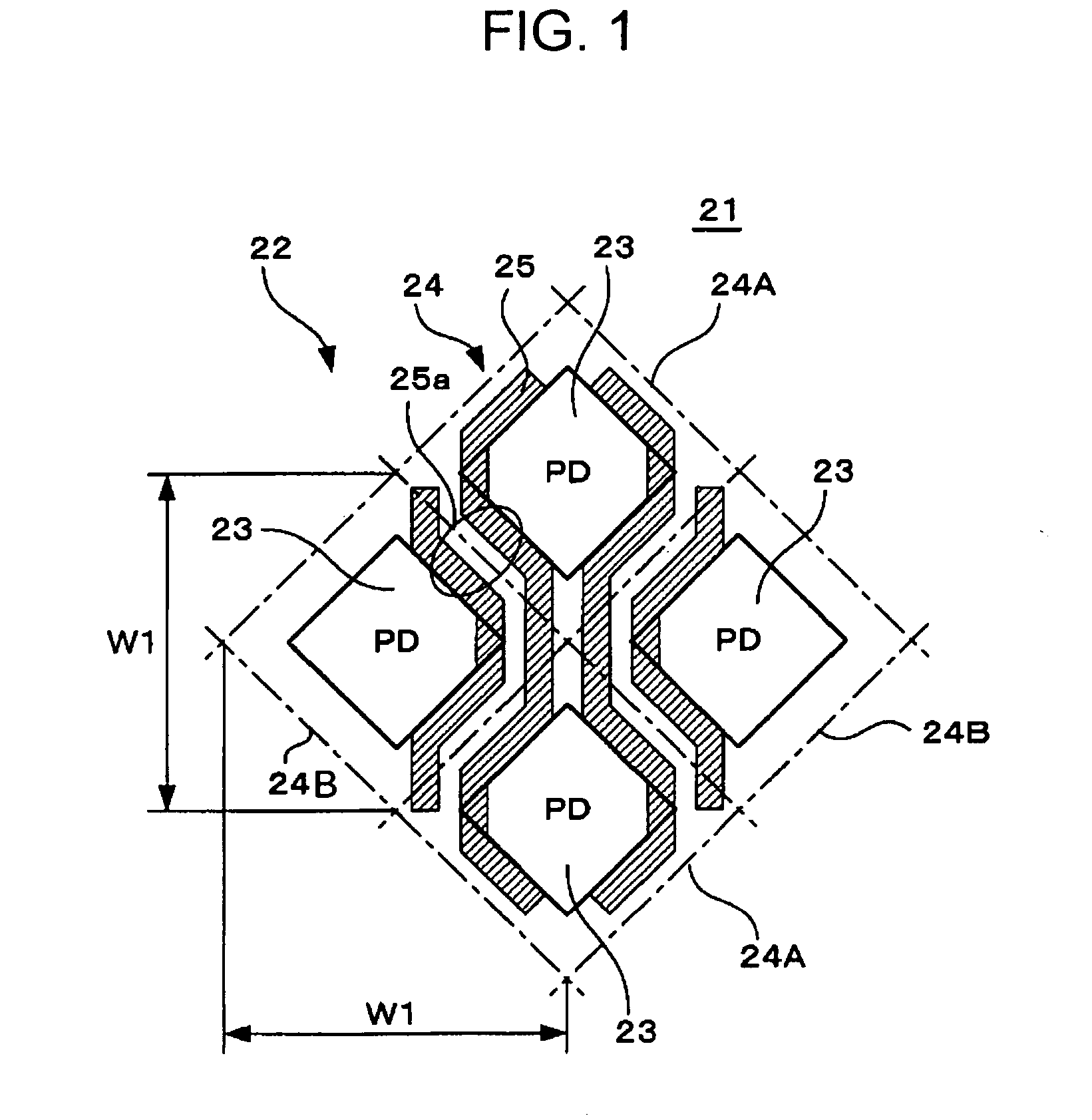
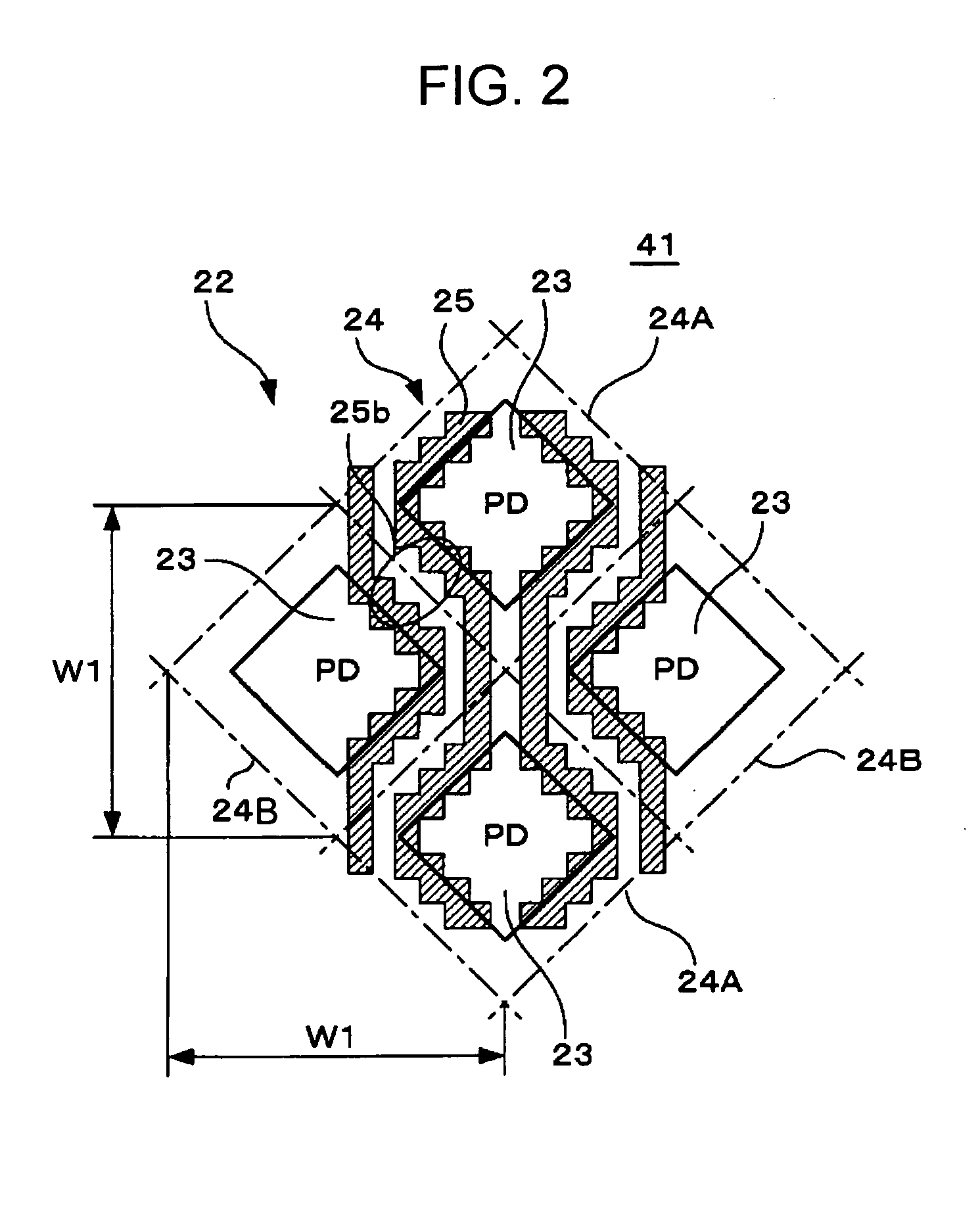
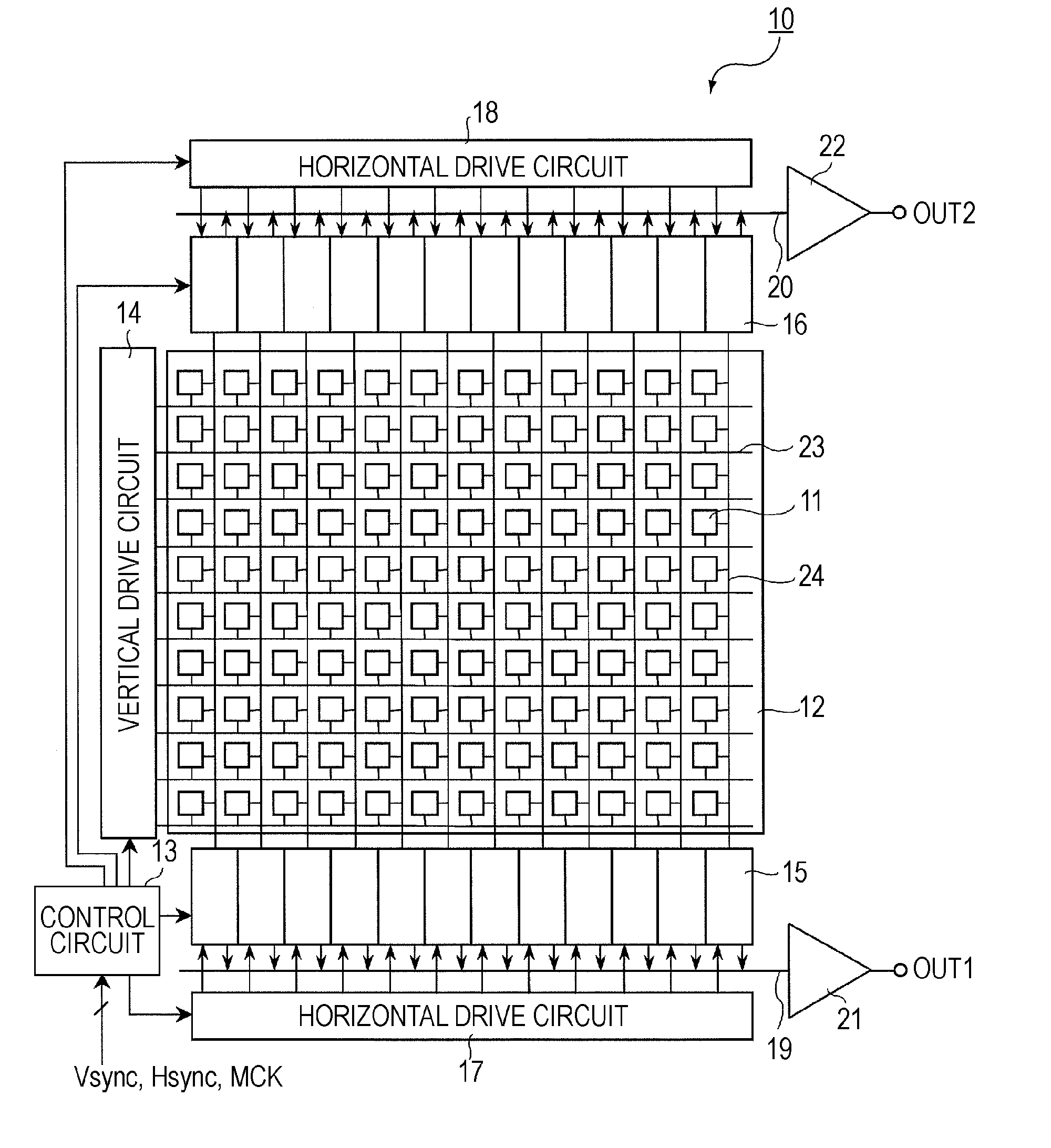
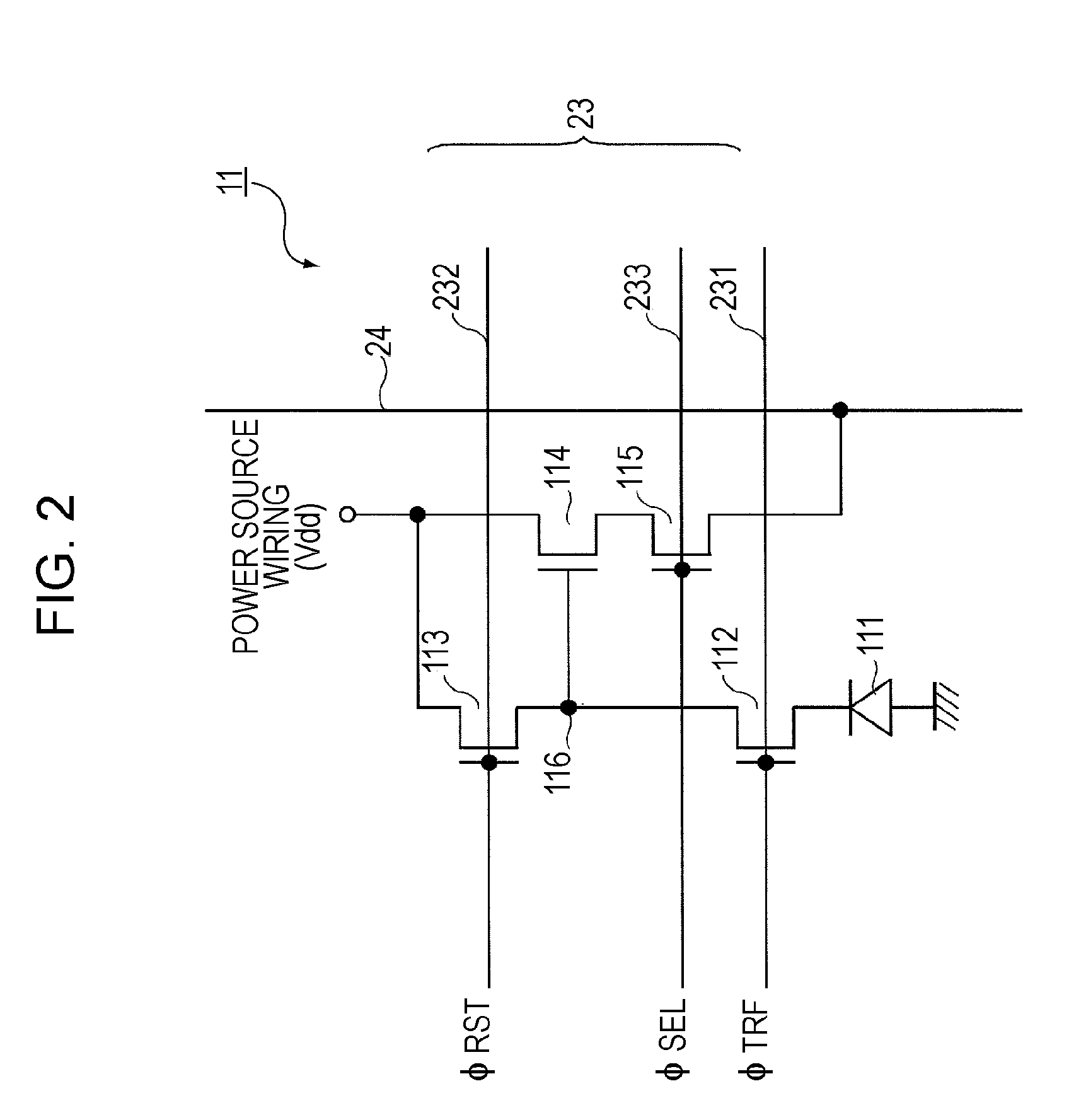
Solid-state image pickup device
ActiveUS20070177044A1Improve efficiencyIncrease sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsTransducing UnitSolid-state
A solid-state image pickup device includes pixels diagonally arranged, each including a photoelectric conversion unit and a plurality of transistors and wiring extending in the vertical and horizontal directions which is diagonally arranged around the photoelectric conversion unit in each of the pixels so that at least one portion of the wiring is arranged along at least one side of the photoelectric conversion unit.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Metamaterial Particles for Near-Field Sensing Applications
InactiveUS20120086463A1High sensitivityIncrease sensitivityNanomagnetismResistance/reactance/impedenceSplit-ring resonatorElectricity
A method and structure for designing near-field probes with high sensitivity used in detecting a wide variety of materials and objects such as biological anomalies in tissues, cracks on metallic surfaces, location of buried objects, or composition of material such as permittivity and permeability . . . etc., is disclosed. The present invention includes using single or multiple metamaterial unit cells or metamaterial particles as near-field sensors. Metamaterial unit cells are defined as the building blocks used for fabricating metamaterials that provide electrical or magnetic properties not found in naturally occurring media. Metamaterial unit cells or particles include split-ring resonators, complementary split-ring resonators, or a variety of other electrically-small resonators made of conducting wires or conducting flat surfaces. Metamaterial unit cells are excited by appropriate excitations such as small loops, microstriplines, etc. depending on the electromagnetic properties of the metamaterial unit cell. Once the metamaterial unit cell is excited, the reflection and transmission coefficients from the excitation mechanism can be measured.
Owner:BOYBAY MUHAMMED S +1
Selection, segmentation and analysis of exhaled breath for airway disorders assessment
InactiveUS20150265184A1Increase sensitivityGood sensitivityUser/patient communication for diagnosticsRespiratory organ evaluationAssessment methodsAsthma
Methods and systems are described to automatically obtain and analyze a lung airway gas sample from the breath of a person for compositional analysis. These techniques may provide an improved method for example for accurately and reliably measuring nitric oxide for asthma assessment in young children and non-cognizant patients.
Owner:CAPNIA INC
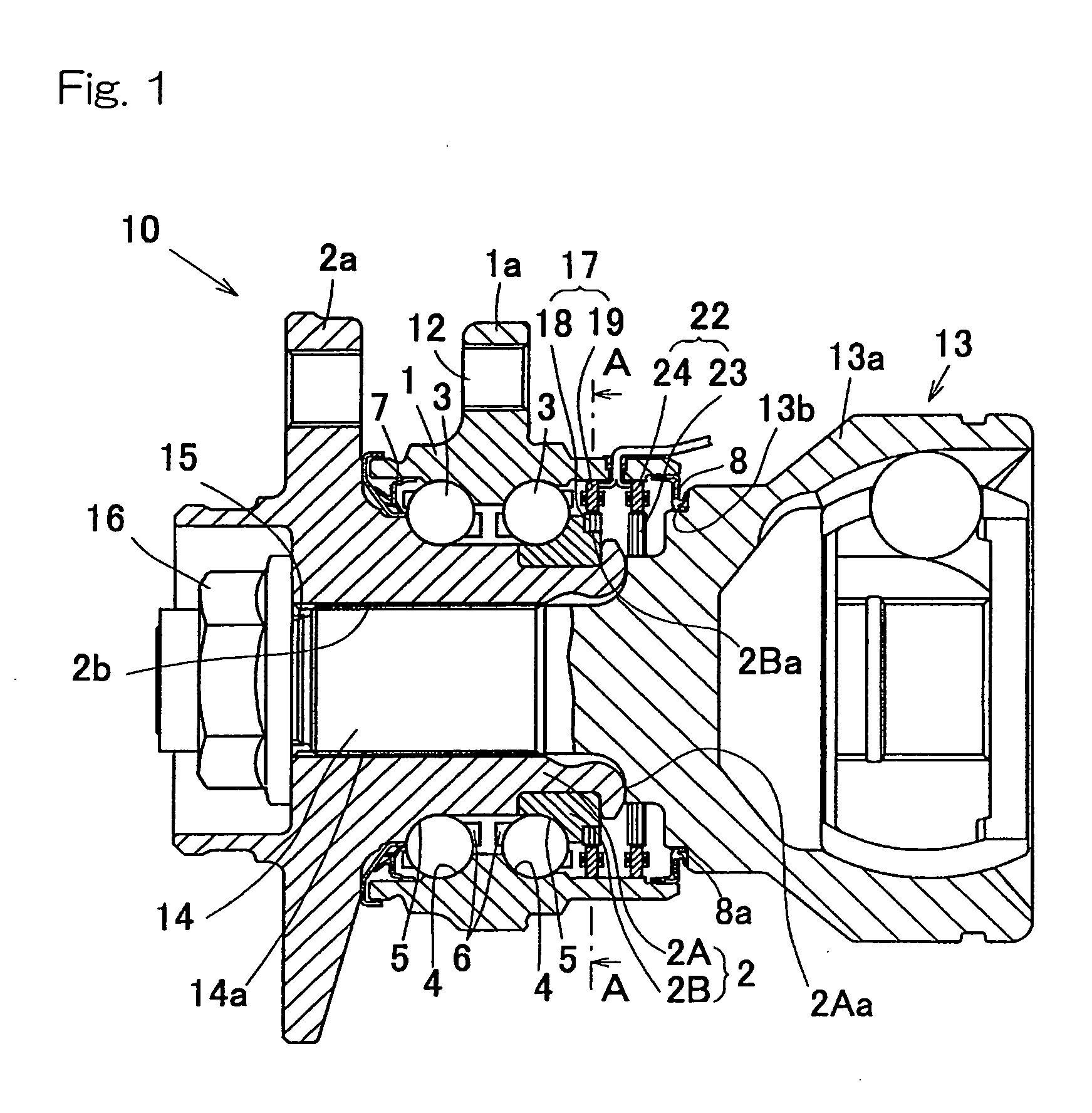
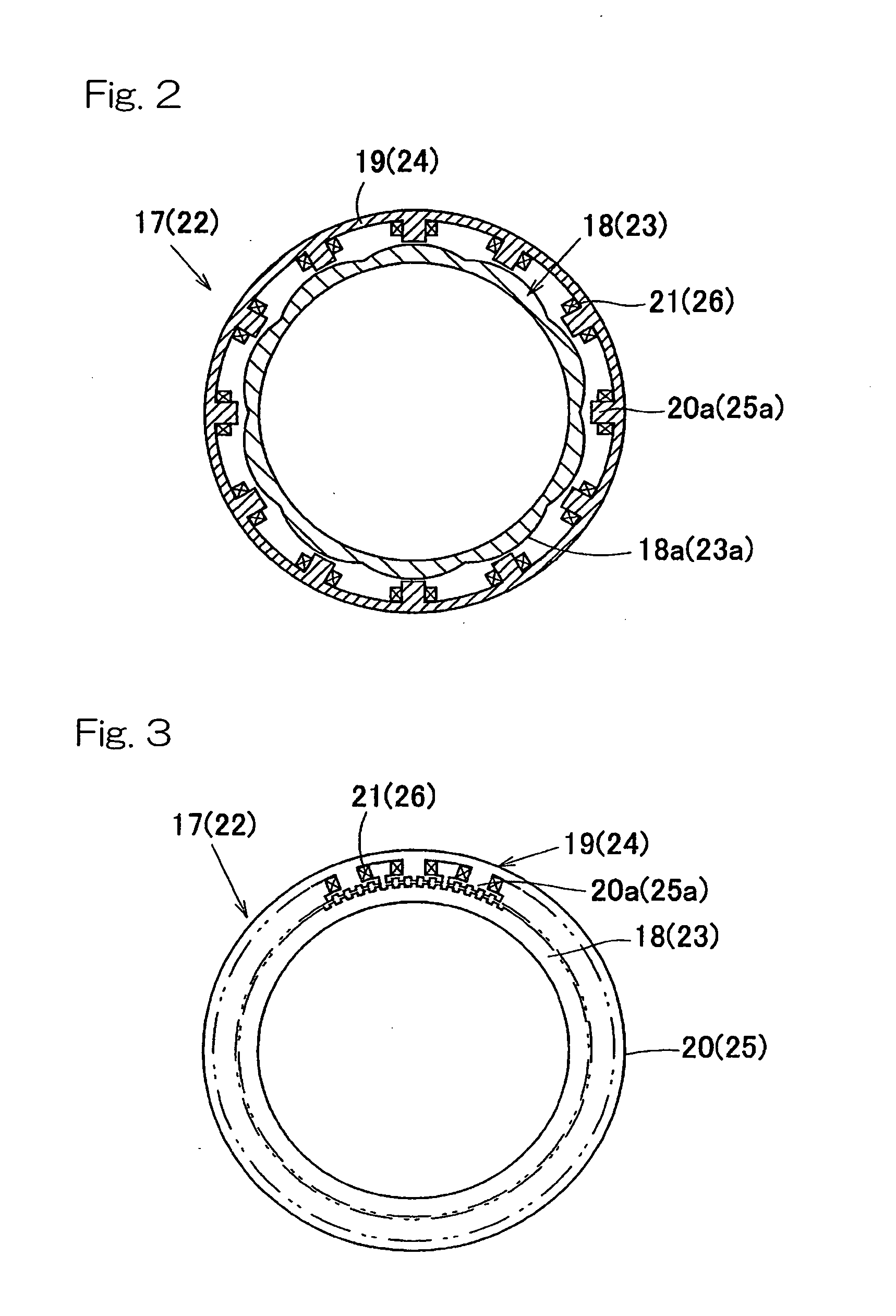
Wheel Support Bearing Assembly with Built-In Load Sensor
ActiveUS20080285901A1Increase sensitivityEasily developRoller bearingsBearing assemblyConstant-velocity jointAngular difference
A wheel support bearing assembly comprises a stationary outer member and a rotatable inner member. The to-be-detected parts of angle detection sensors are fixed to the inner member and an outer race of a constant velocity joint connected to the inner member, respectively. Detecting parts of the angle detection sensors are fixed to the outer member in face-to-face relation with the to-be-detected parts. The bearing assembly also includes a load conversion unit detecting a relative angular difference between the inner member and the constant velocity universal joint by comparing the detection signals from the detecting parts to detect the load acting on the bearing assembly.
Owner:NTN CORP
Biochemical ultrasensitive charge sensing
InactiveUS20050218464A1Increase signal outputIncrease sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsActive sensingCompound s
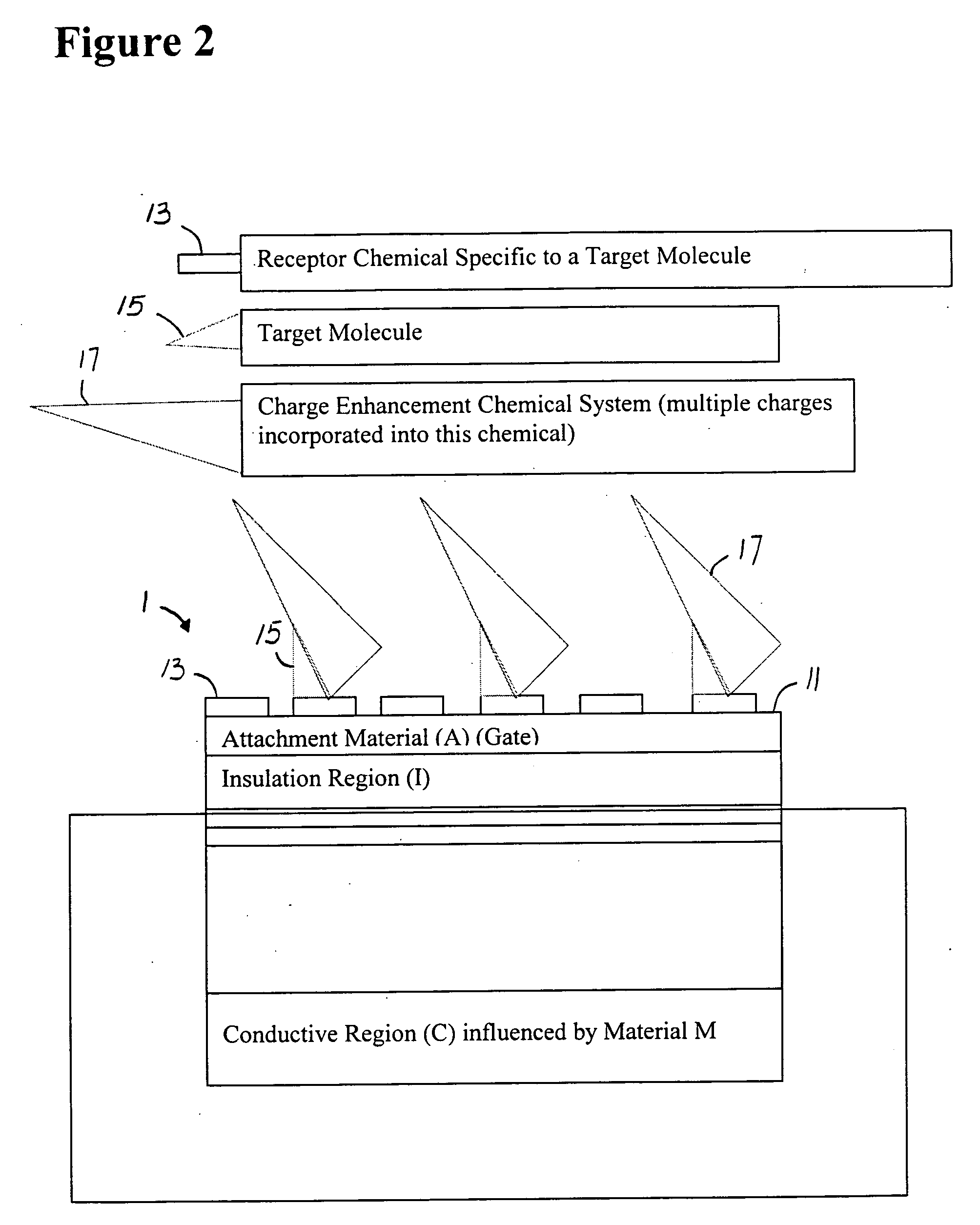
Chemical sensors for detecting chemicals are provided using surface and bulk selective chemical reactions. Large charge complexes are bound to the bound target and provide ultrasensitive sensing detection of the original target. In particular embodiments, the sensing device is affected by a change in the resistance of some key part of the device. In certain embodiments, the invention employs beads and other systems to provide a significantly enhanced sensor detection signal. In other embodiments, the invention employs chemical reactions with a pre-selected surface integrated with a suitable semiconductor sensor devices where material coats the top active sensing region of a sensor, and a reaction results in a new compound.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Ocean bottom seismometer package with distributed geophones
ActiveUS20050259516A1Increase sensitivityIncrease net sensitivitySeismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasGeophoneCollections data
A seismic data collection unit having multiple separate geophones / geophone packages positioned in a housing wherein the geophones are offset from a vertical axis so that summing of the geophones' respective outputs minimizes certain noise in the unit's output. Specifically, the offset geophones are physically positioned or mathematically configured so as to be symmetrical about a selected vertical axis in order to cancel out certain noise in a seismic signal. The particular placement of the geophones within the housing is preferably selected so that the vertical axis around which the geophones are positioned passes through the center of gravity of the unit.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Solid-state image pickup apparatus, drive method for the solid-state image pickup apparatus, and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20090273695A1Low luminanceIncrease sensitivityAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsSolid-statePixel array
In a solid-state image pickup apparatus having a pixel array unit composed by two-dimensionally arranging pixels for detecting a physical quantity in a row-column manner, pixel signals of a plurality of systems having different sensitivities are read from the pixel array unit in an analog manner, the pixel signals of the plurality of systems are amplified at respective basis amplification rates when a gain setting of the analog pixel signals is lower than a predetermined gain, and a pixel signal of at least one system having a high sensitivity among the plurality of systems is amplified at a plurality of amplification rates including an amplification rate higher than a basis amplification rate of the system having the high sensitivity when the gain setting is equal to or higher than the predetermined gain.
Owner:SONY CORP
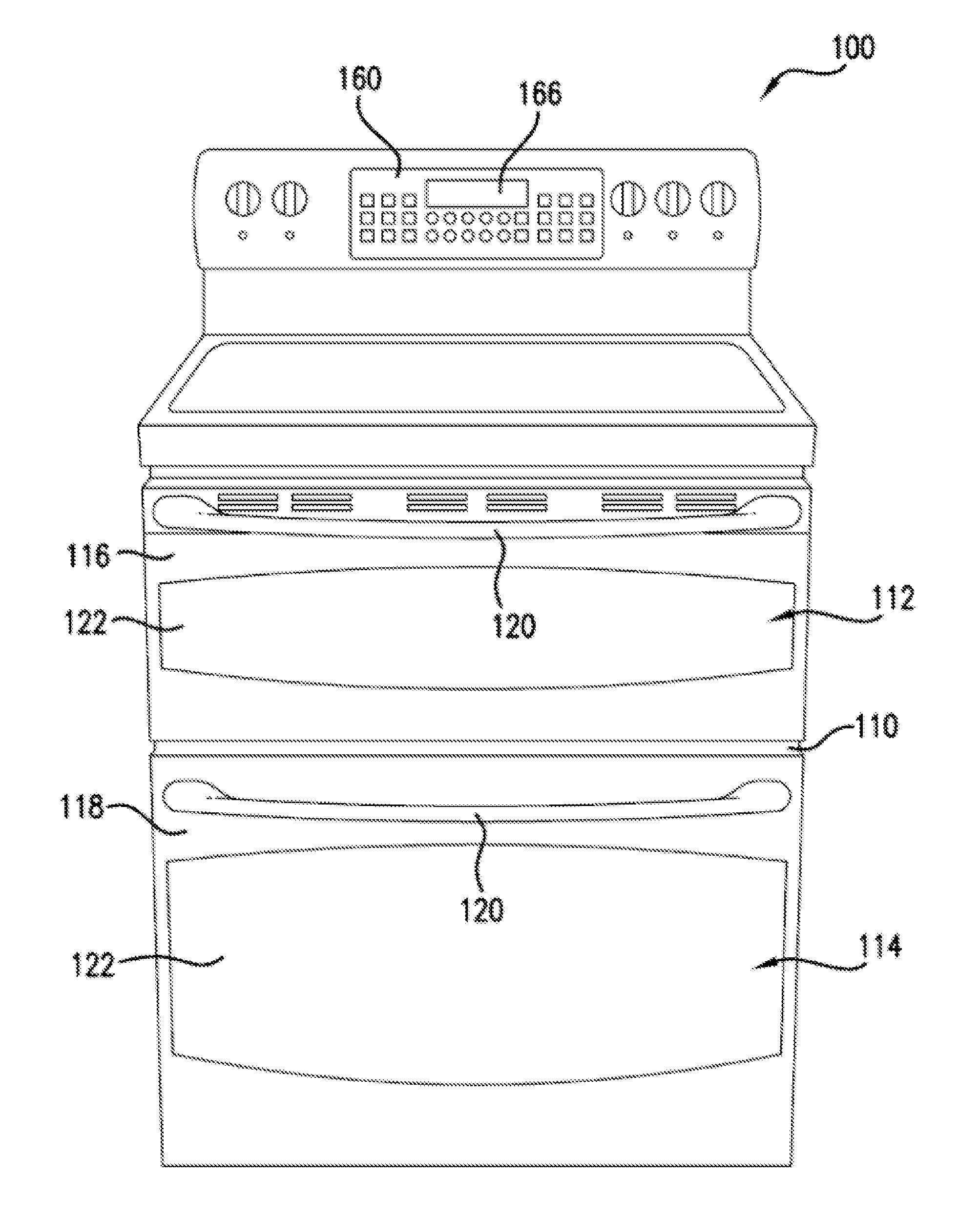
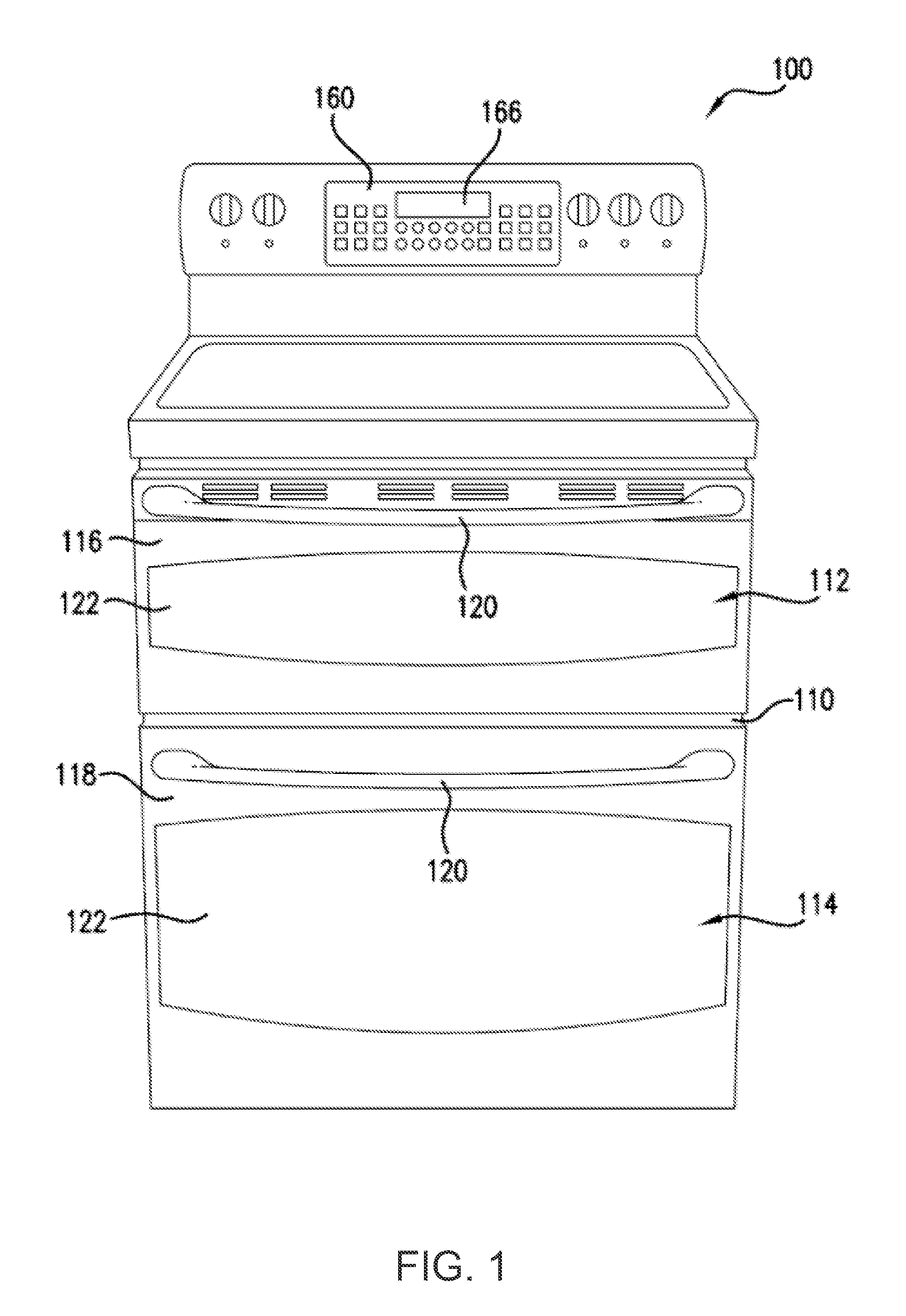
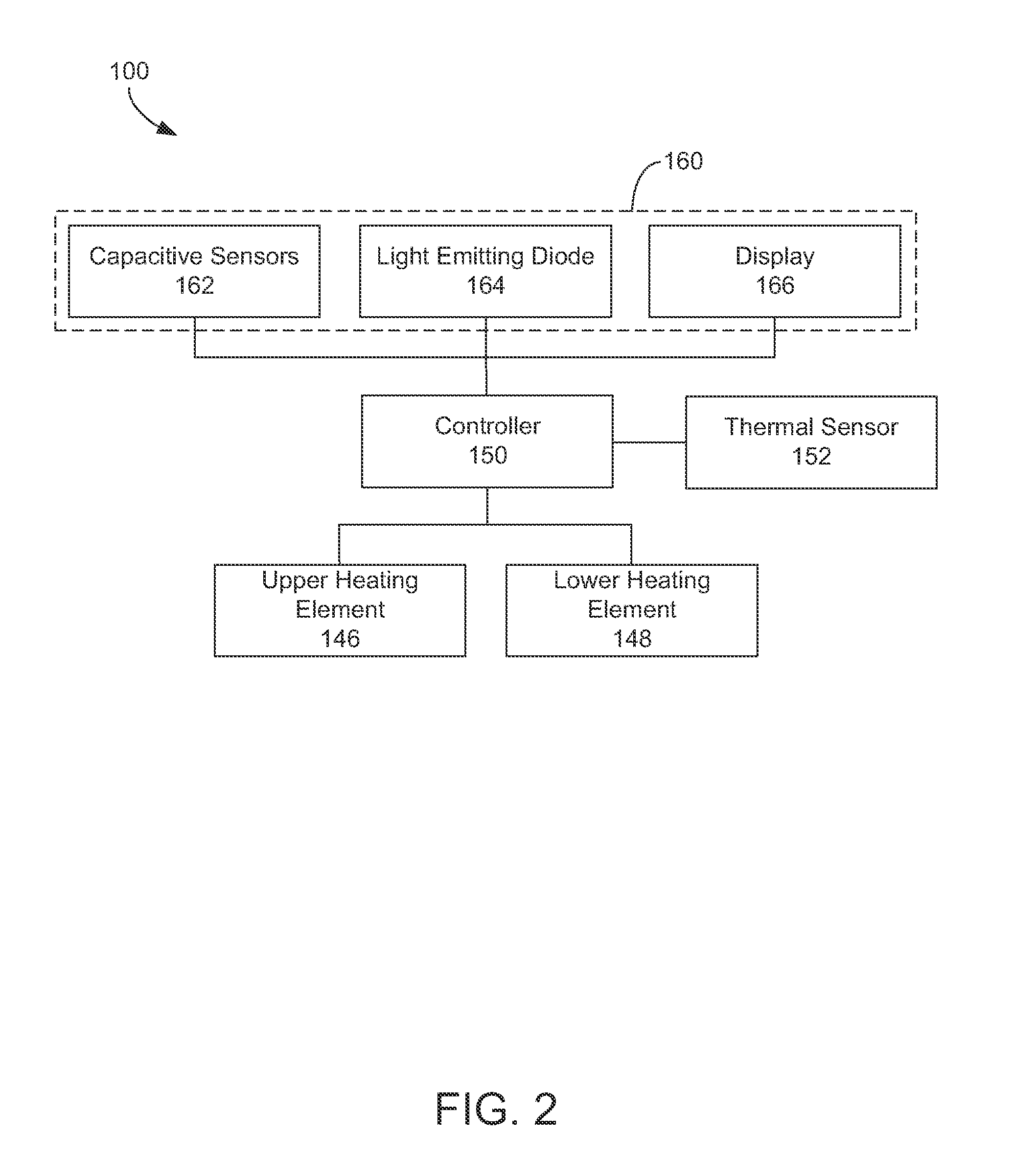
Appliance and a method for operating a control panel of the same
ActiveUS20140203863A1Increase sensitivityDecrease in sensitivityElectronic switchingControl theoryEngineering
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
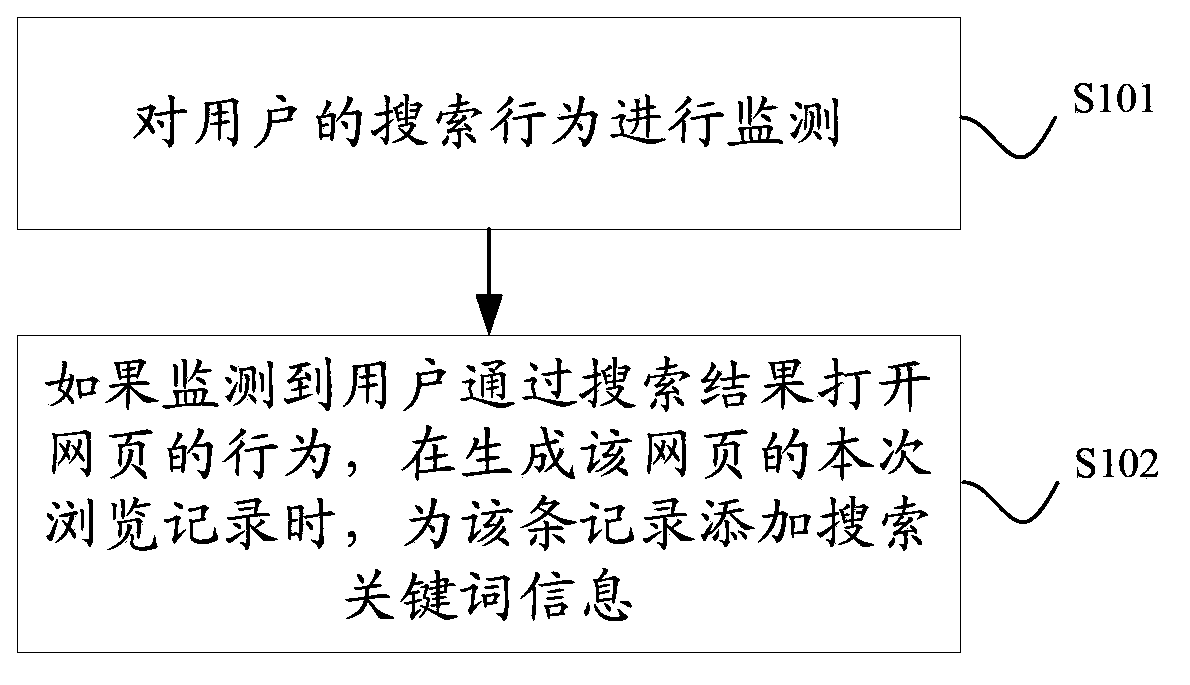
Method and device of searching web browsing history
InactiveCN103577489AMeet browsing needsImprove query performanceSpecial data processing applicationsWeb data retrieval using information identifiersUser inputText matching
The invention discloses a method and a device of searching a web browsing history. The method of searching the web browsing history comprises the following steps of receiving a search text which is input by a user; obtaining a pre-generated web browsing history record; judging whether the record is matched with the search text according to search keyword information carried in each record; and generating a search result by utilizing the record clause with the successful matching. In comparison with the prior art, the scheme of the invention is based on a text matching manner, the search effect is remarkably better than the scheme of searching according to a browsing period. In addition, the matching basis is the search keyword, which is more sensitive to the user, so that the search keyword is easier to remember than contents such as a web URL or a web title, and the corresponding search result conforms to the browsing requirements of the user well.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Asymmetrical positron emission tomograph detectors
InactiveUS20070080295A1Increase sensitivityGreat amount of attenuationMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyPhysicsPositron emission
An apparatus for detecting a greater number of lines of response (LOR) within a subset of azimuthal angles of a positron emission tomography scanner. In a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner, the detectors are configured to detect a greater number of lateral LORs than the number of anterior / posterior LORs passing through a patient. The increased sensitivity to the lateral LORs compensates for the increased distance that the lateral LORs travel through the patient than the anterior / posterior LORs. In one embodiment, at least one pair of partial rings are positioned adjacent fixed detector rings. In another embodiment, panel detectors with a longer length than the other detectors are positioned to be responsive to the lateral LORs. In still another embodiment, detectors rotated with a variable angular speed, spending more time measuring lateral LORs than measuring anterior / posterior LORs.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Digital camera for changing a recording size to a high-sensitivity compatible recording size
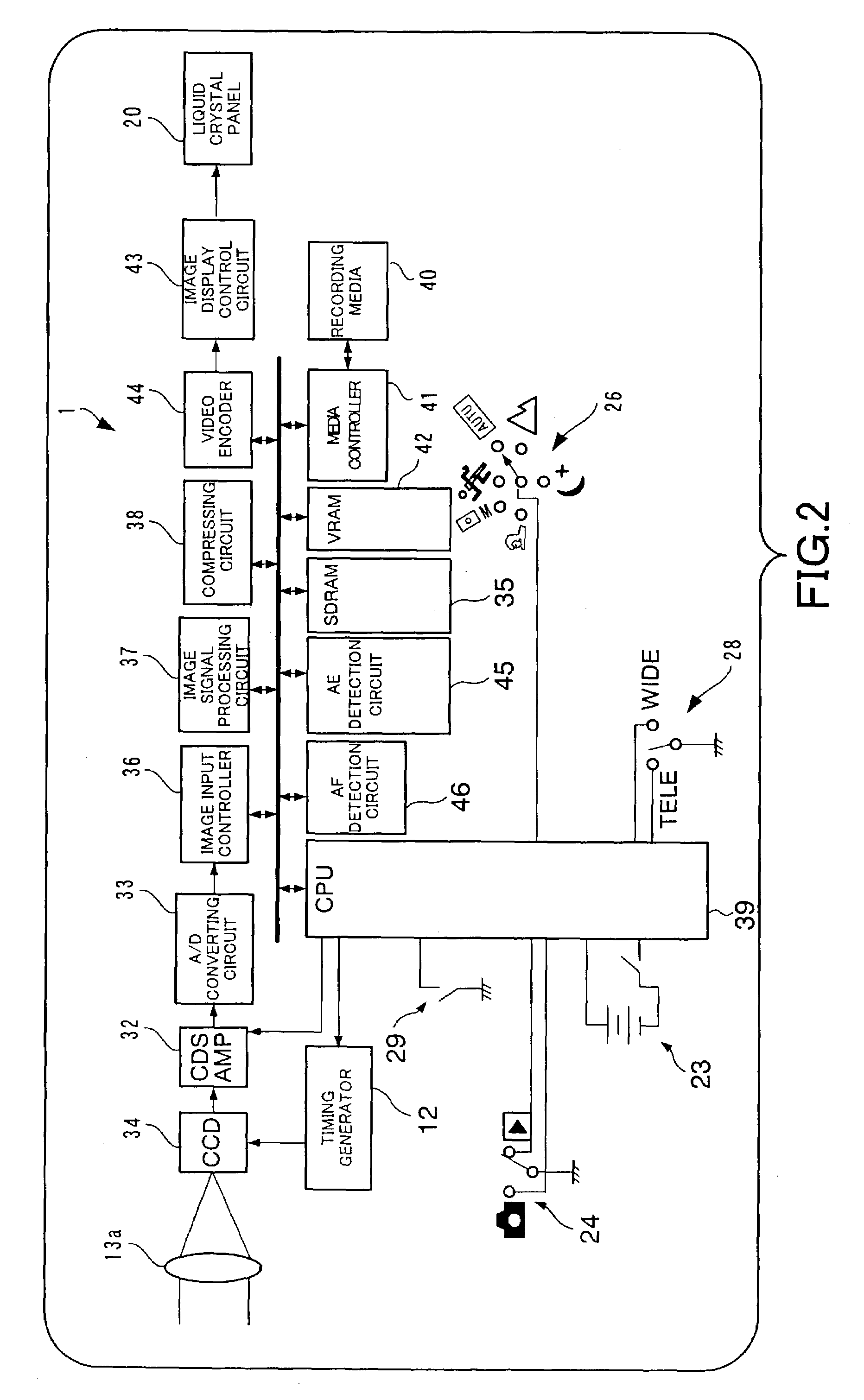
ActiveUS7268810B2Prevent errorIncrease sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital cameraComputer graphics (images)
The present invention provides a digital camera that prevents photographing errors attributed to an increase in sensitivity effected by reducing the recordable image size. In a digital camera that allows a high sensitivity to be set by pixel mixture, a display is provided to prevent photographing errors caused by restrictions or the like resulting from setting of a high sensitivity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for detecting contaminants in pharmaceutical products
InactiveUS20050059156A1Increase sensitivityHigh sensitivityComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementPollutantChromatography
The present invention relates to a quantitative, highly sensitive analytical procedure capable to control at part per billion (ppb) detection level the possible presence of undesired chemical contaminants, especially β-lactam antibiotics, in anthracycline products.
Owner:PHARMACIA ITAL SPA
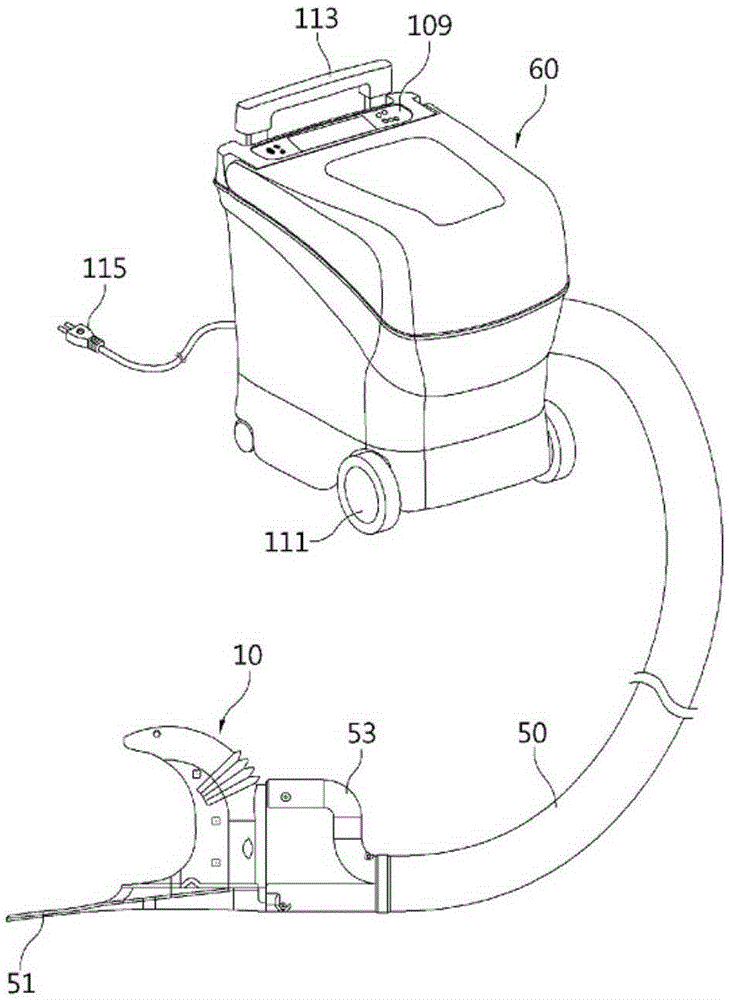
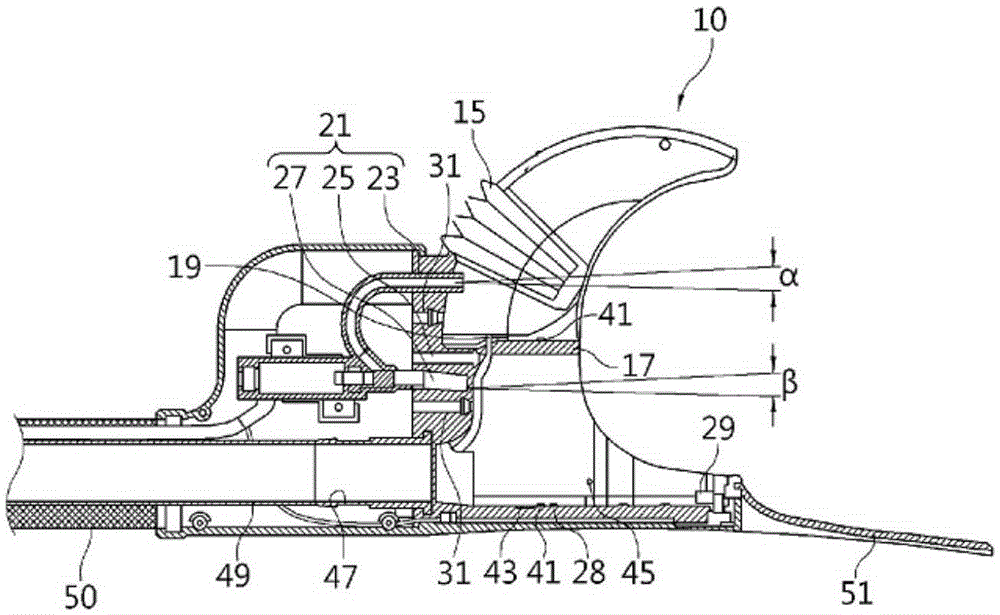
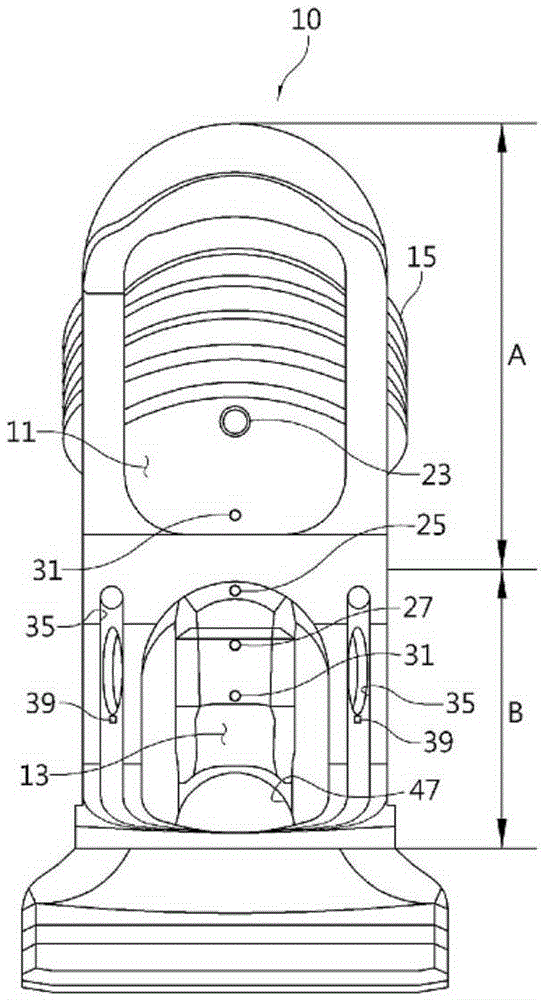
Automatic excrement processing device
The present invention relates to an automatic excrement processing device comprising: a cup unit (10) worn on a portion of a user at which the excretory organs are located, and forming a space (11) in which urine is suctioned that is partitioned from a space (13) in which feces is suctioned; an excrement processing main body (60) connected to the cup unit (10) and suctioning excrement discharged into the cup unit (10) and storing same; a sensor unit provided on the cup unit (10), connected to the excrement processing main body (60), and sensing excrement; a washing nozzle unit (21) performing a washing function; a suctioning nozzle unit (49) suctioning excrement; and a drying nozzle unit (31) performing a drying function. The present invention has the advantages that the device provides a good feeling when worn, and clean excrement processing is possible through accurate sensing of excrement.
Owner:ANGELWINGS
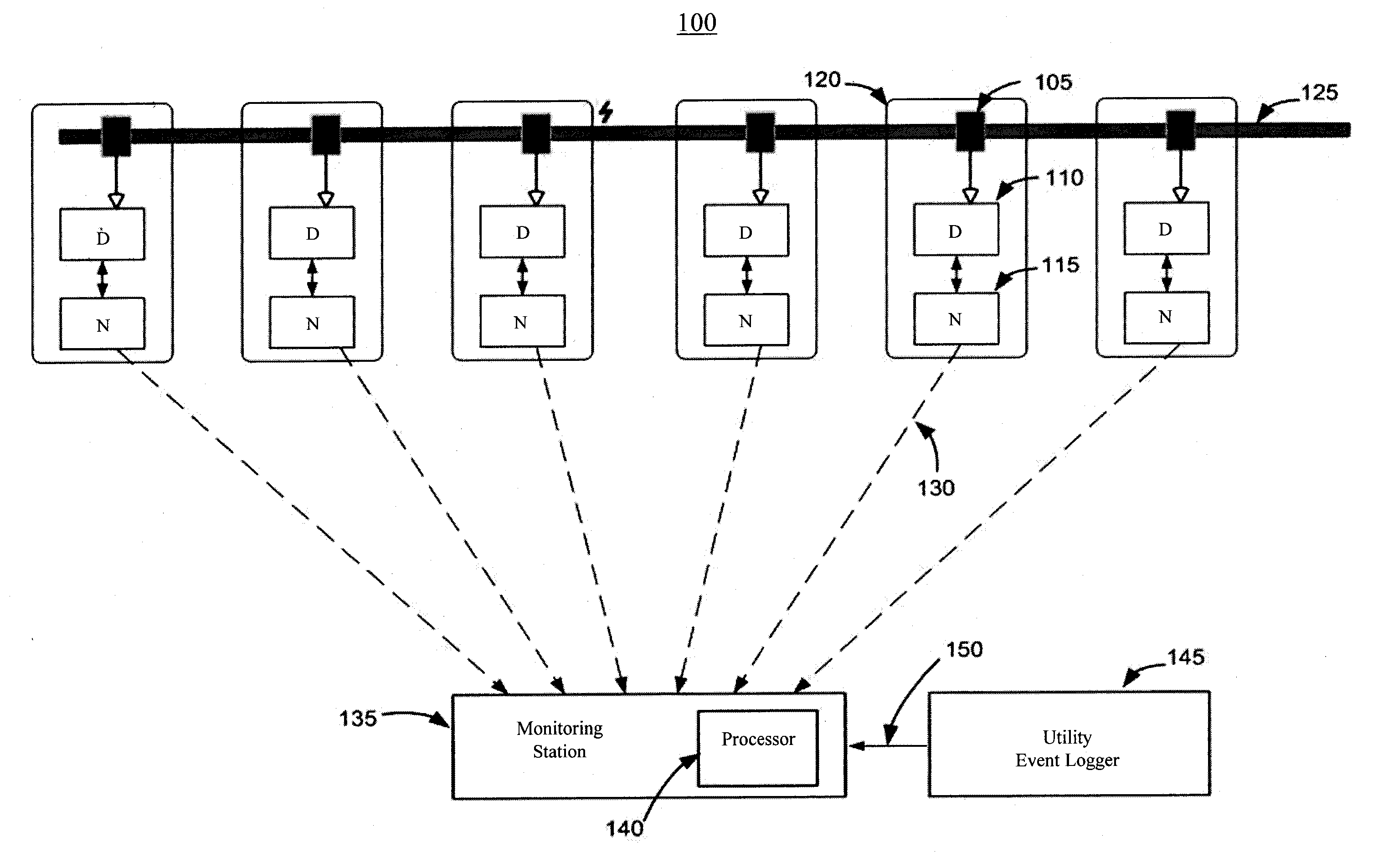
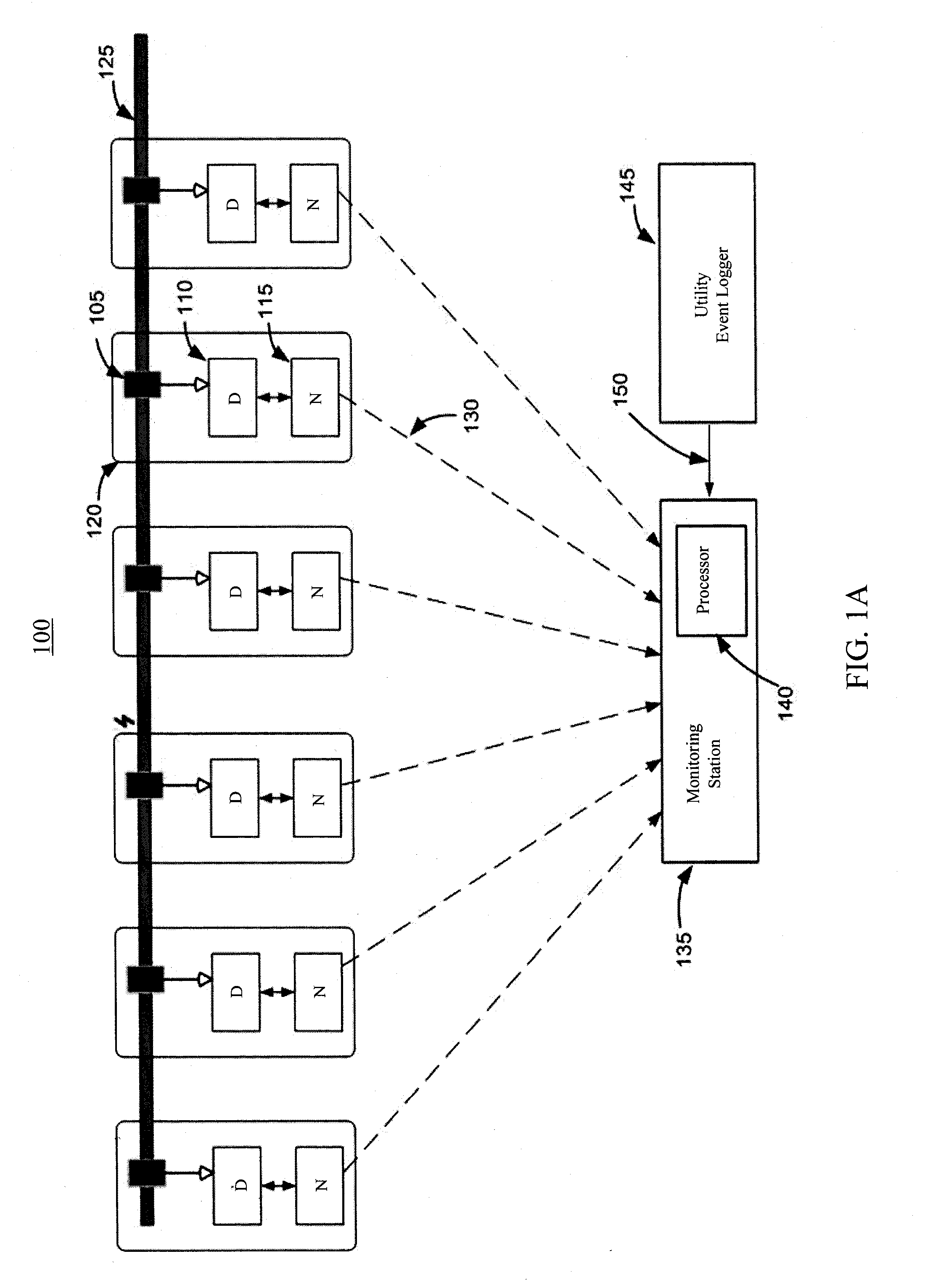
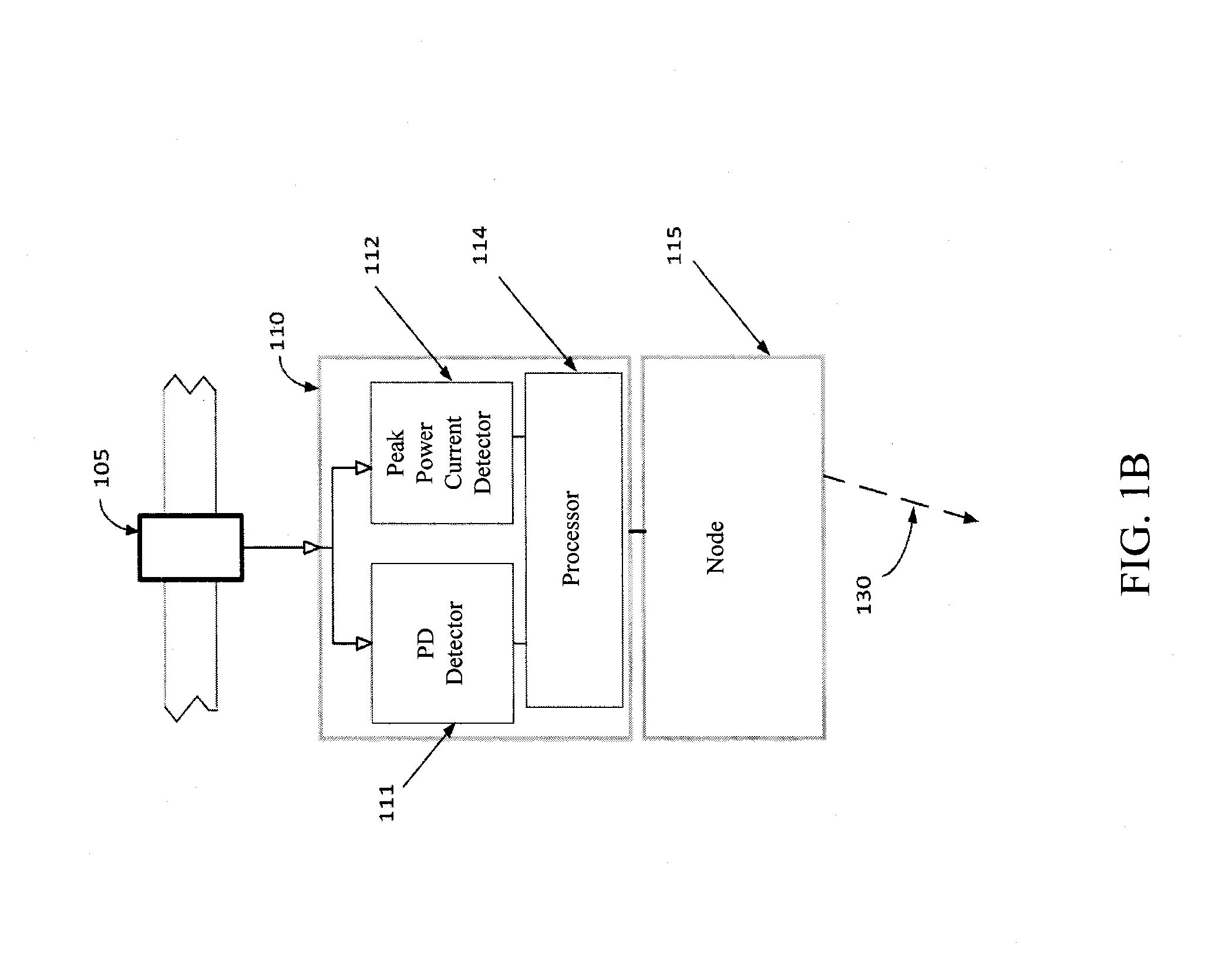
Analyzing partial discharge in an electric power distribution system
ActiveUS20150160284A1Increase sensitivityTesting dielectric strengthElectric switchesElectric power distributionPartial discharge
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
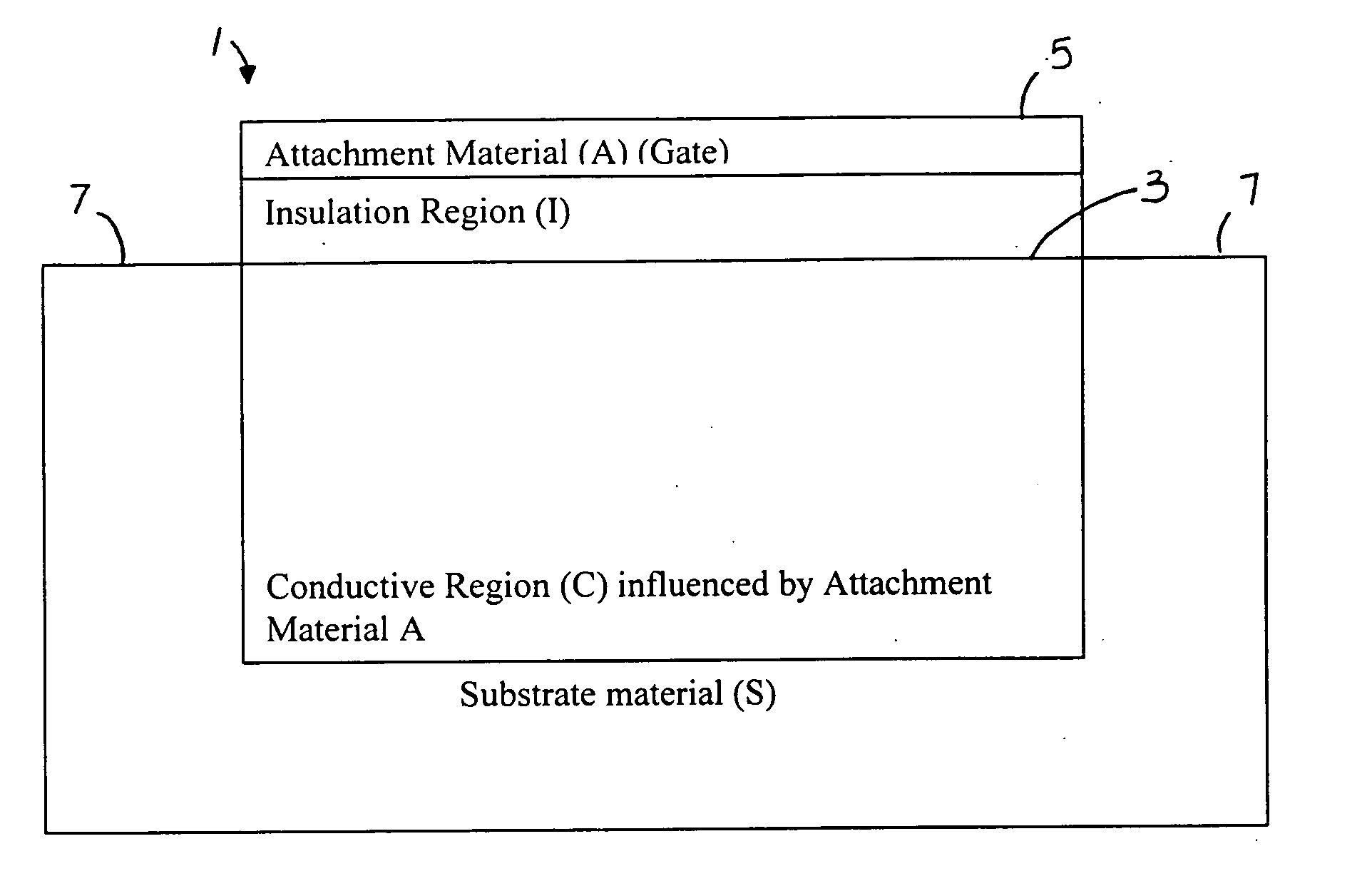
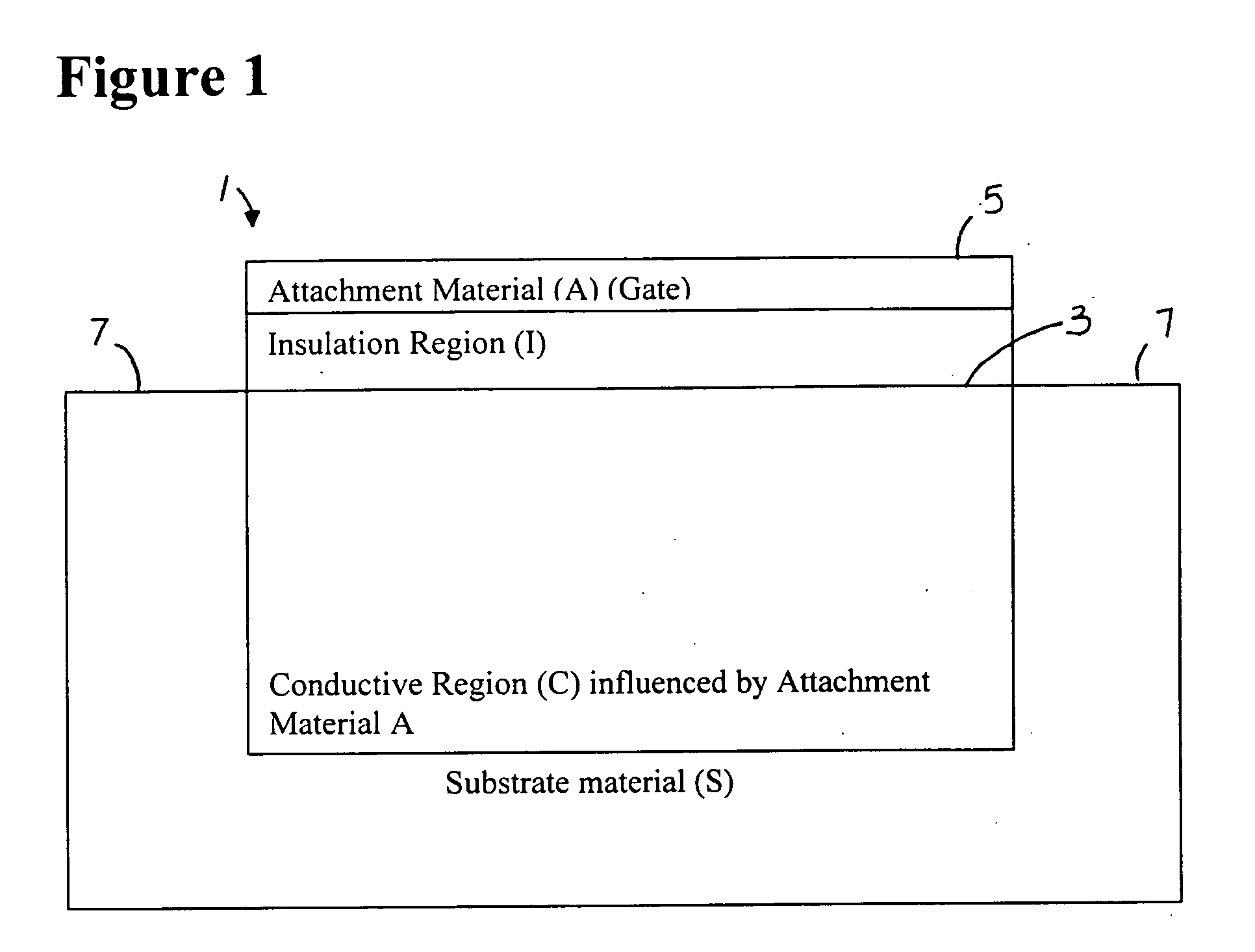
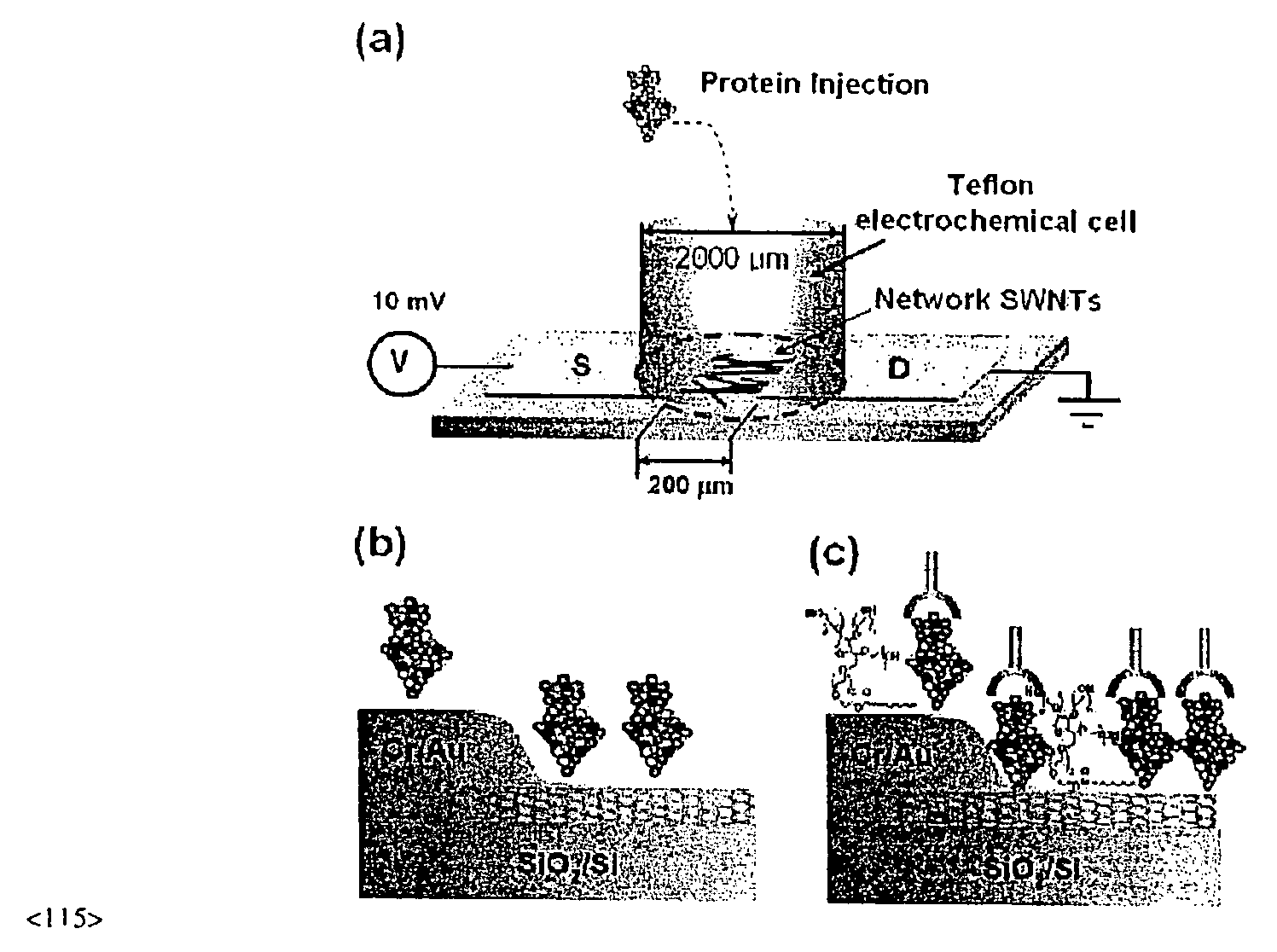
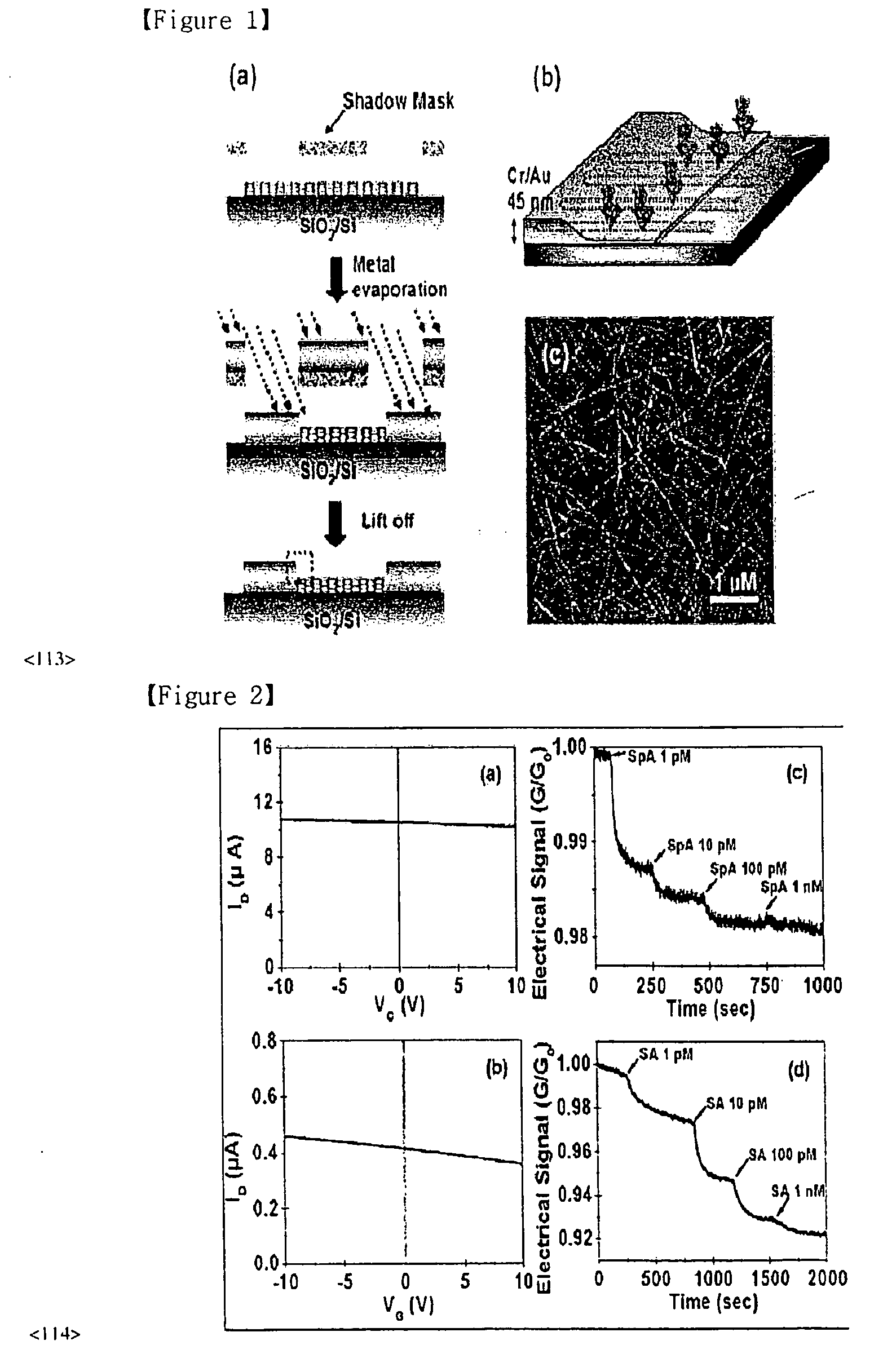
Fet based sensor for detecting biomolecule, method for preparing the same, and method for detecting biomolecule using the fet based sensor
InactiveUS20090208922A1Increase sensitivityHigh sensitivityResistance/reactance/impedenceMicrobiological testing/measurementNon specificChemistry
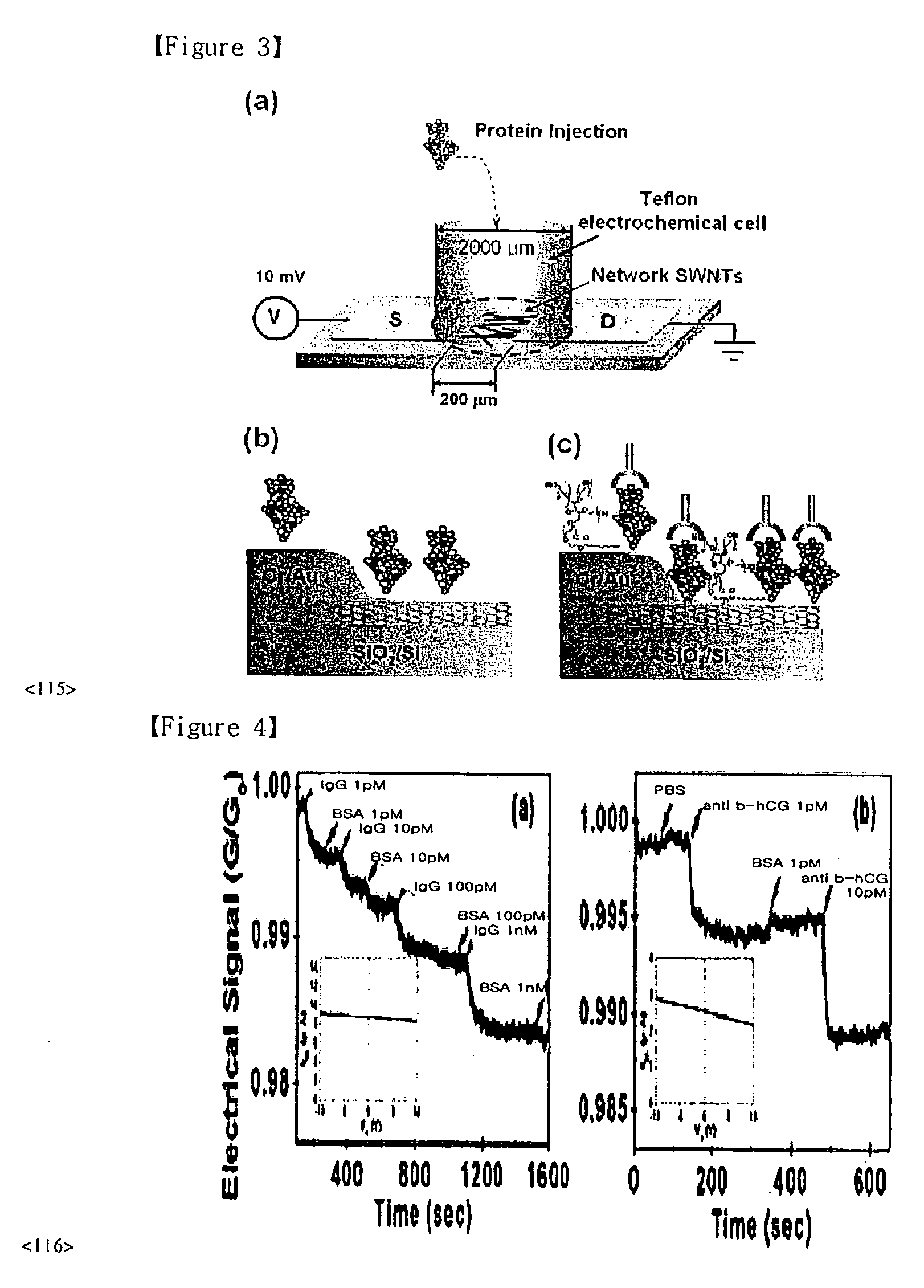
Provided is a SWNT-FET-based sensor for detection of biomolecules including an increased Schottky contact area, a method for preparing the same, and a method for detection of biomolecules using the SWNT-FET-based sensor. According to the method of the present invention, a SWNT-FET-based sensor for detection of biomolecules having a thin and increased Schottky contact area can be obtained. The biomolecule detection sensor exhibits a superior detection sensitivity, and can effectively detect both nonspecific adsorption of biomolecules and specific biomolecule-biomolecule interactions, even at a low concentration of 1 pM, for example.
Owner:CHOI HEE CHEUL +1
Methods and compositions for the treatment of cancer
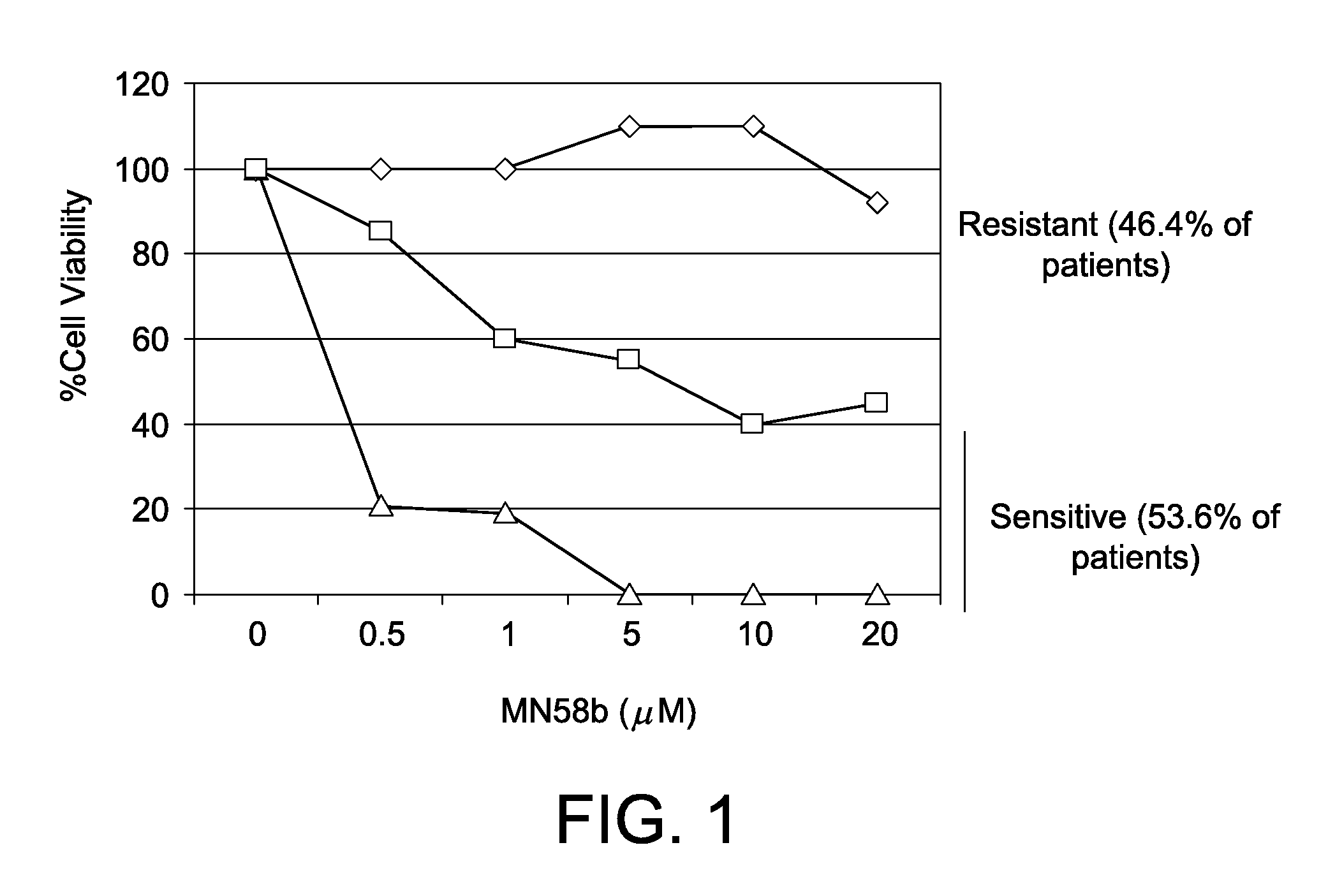
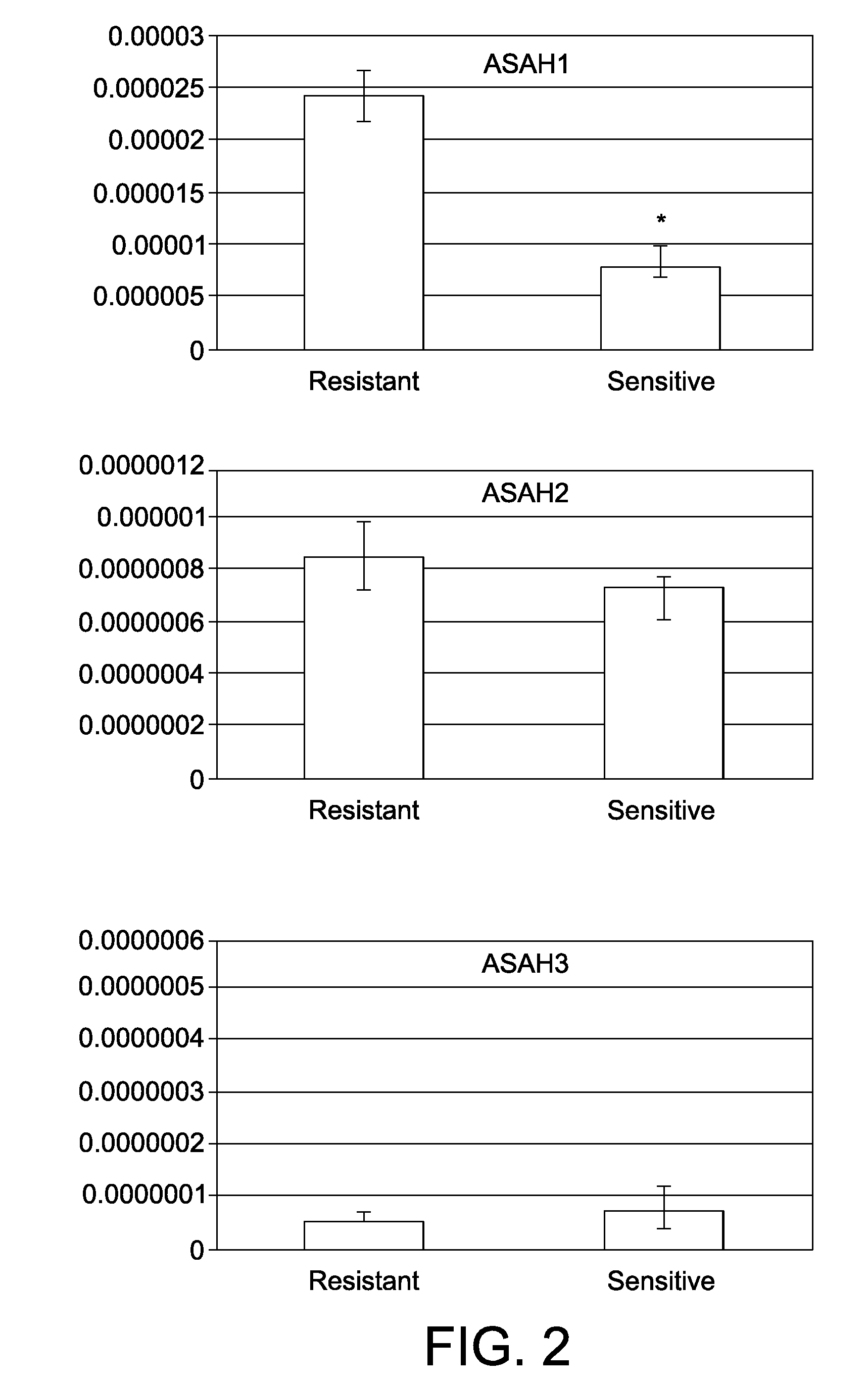
InactiveUS20100068302A1Increase sensitivityHigh sensitivityCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsAcid CeramidaseCancer
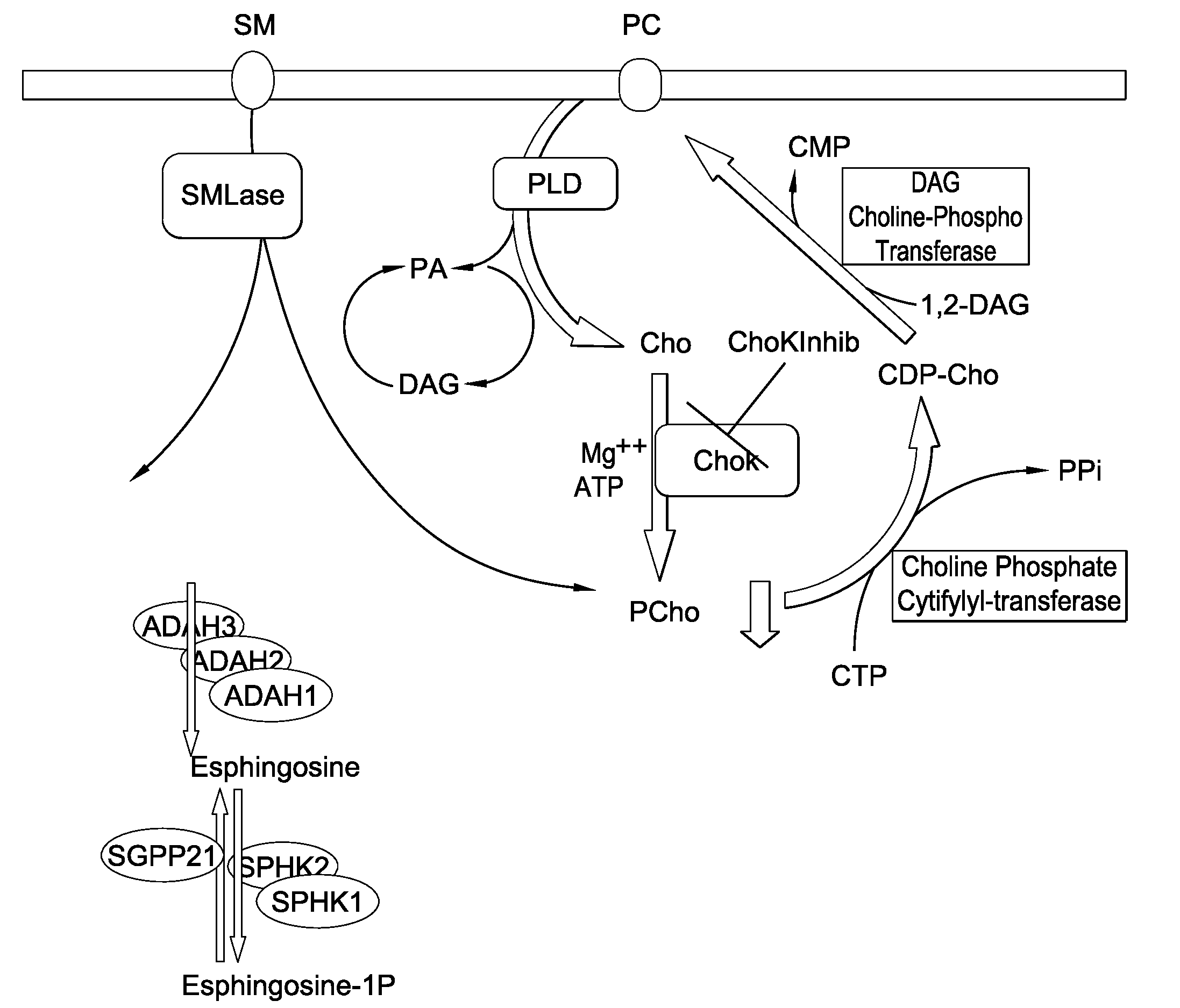
The invention relates to compositions comprising an acid ceramidase inhibitor and a choline kinase inhibitor as well as to the uses thereof for the treatment of cancer. The invention also relates to methods for the selection of an individualised therapy of a cancer patient based on the detection of the acid ceramidase levels. Moreover, the invention also relates to compositions comprising a choline kinase inhibitor and an alkylating agent and uses thereof for the treatment of cancer. Finally, the invention also relates to compositions comprising a choline kinase inhibitor and an alkylating agent or a death receptor ligand and uses thereof for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:TRASLATIONAL CANCER DRUGS PHARMA SL
Mass spectrometer and mass spectrometric method
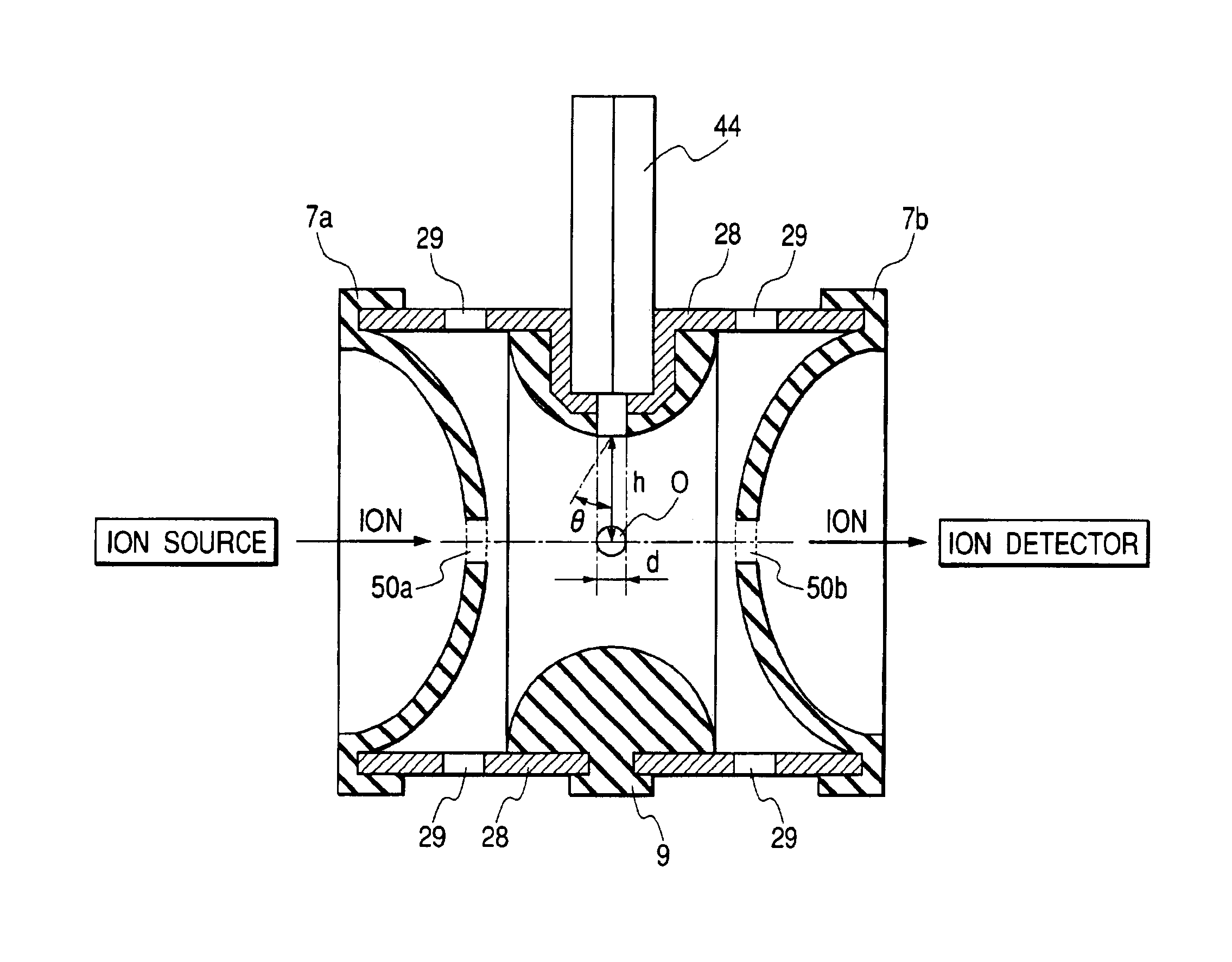
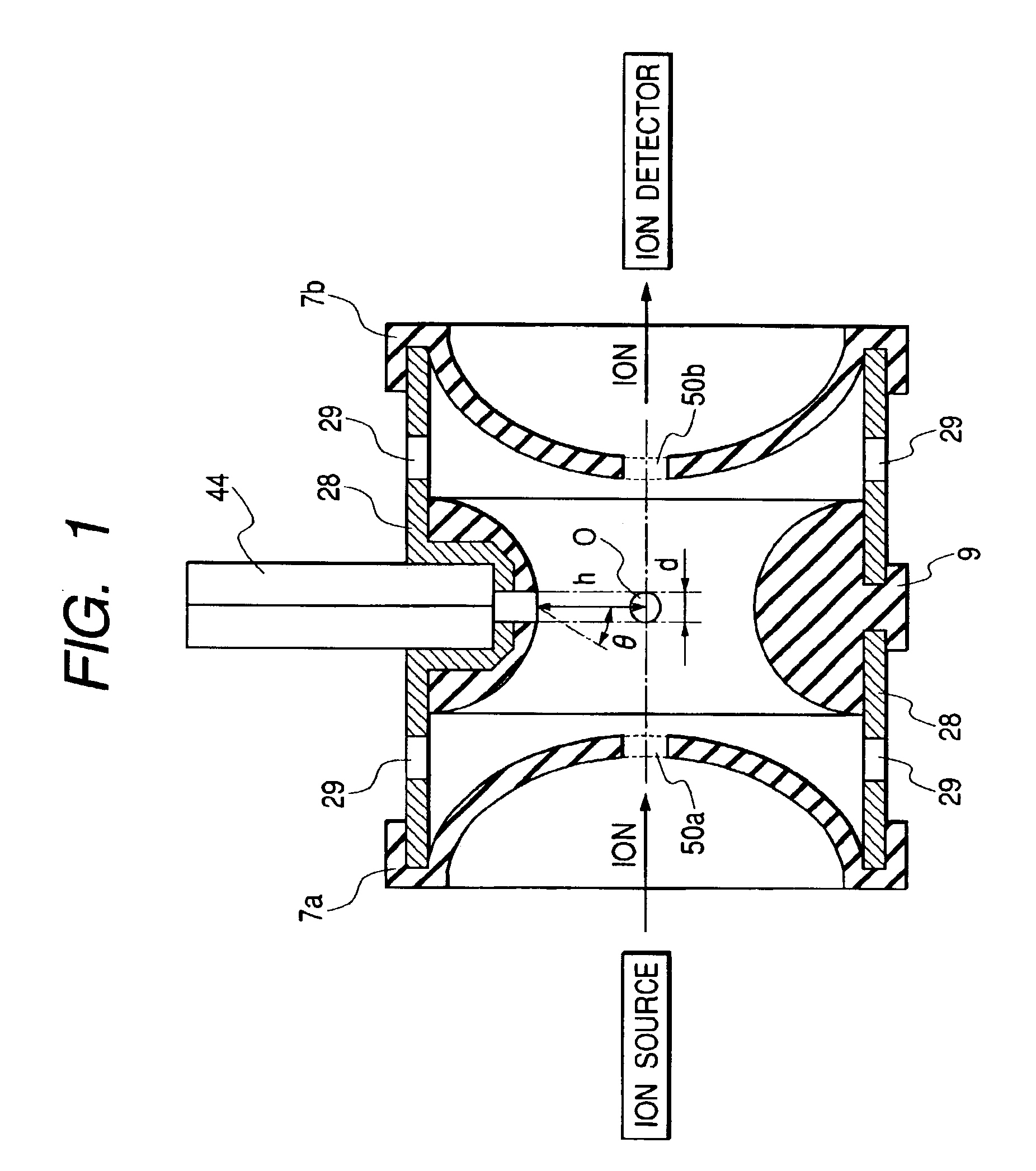
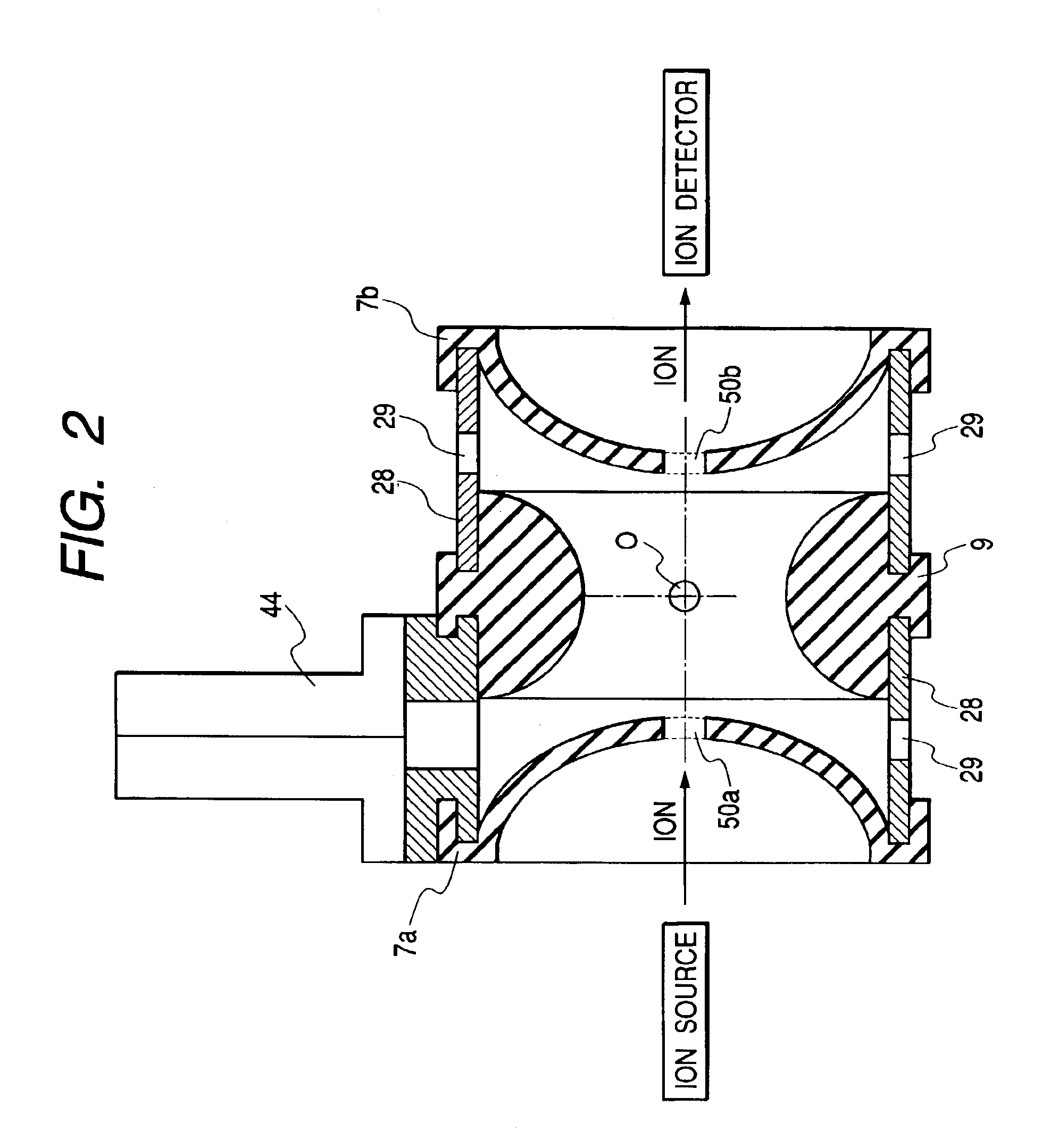
InactiveUS6888134B2Increase sensitivityLow utilization efficiencyStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryIon source
There is provided an ion trap mass spectrometer which can detect fragment ions having a low mass and enables high-sensitivity measurement. A mass spectrometer has an ion source generating sample ions; an ion trap having a pair of and endcap electrodes and a ring electrode and accumulating ions generated by the ion source and isolating precursor ions from the accumulated ion and dissociating the isolated precursor ions and ejecting the dissociated ions from the ion trap. A gas introduction hole is arranged in the endcap electrode or the ring electrode for introducing in intermittently-introduced bath gas therethrough into the ion trap. A detector detects the ions ejected from the ion trap. The center axis of the gas introduction hole is arranged so as to pass through a region near the center of gravity of the ion trap.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
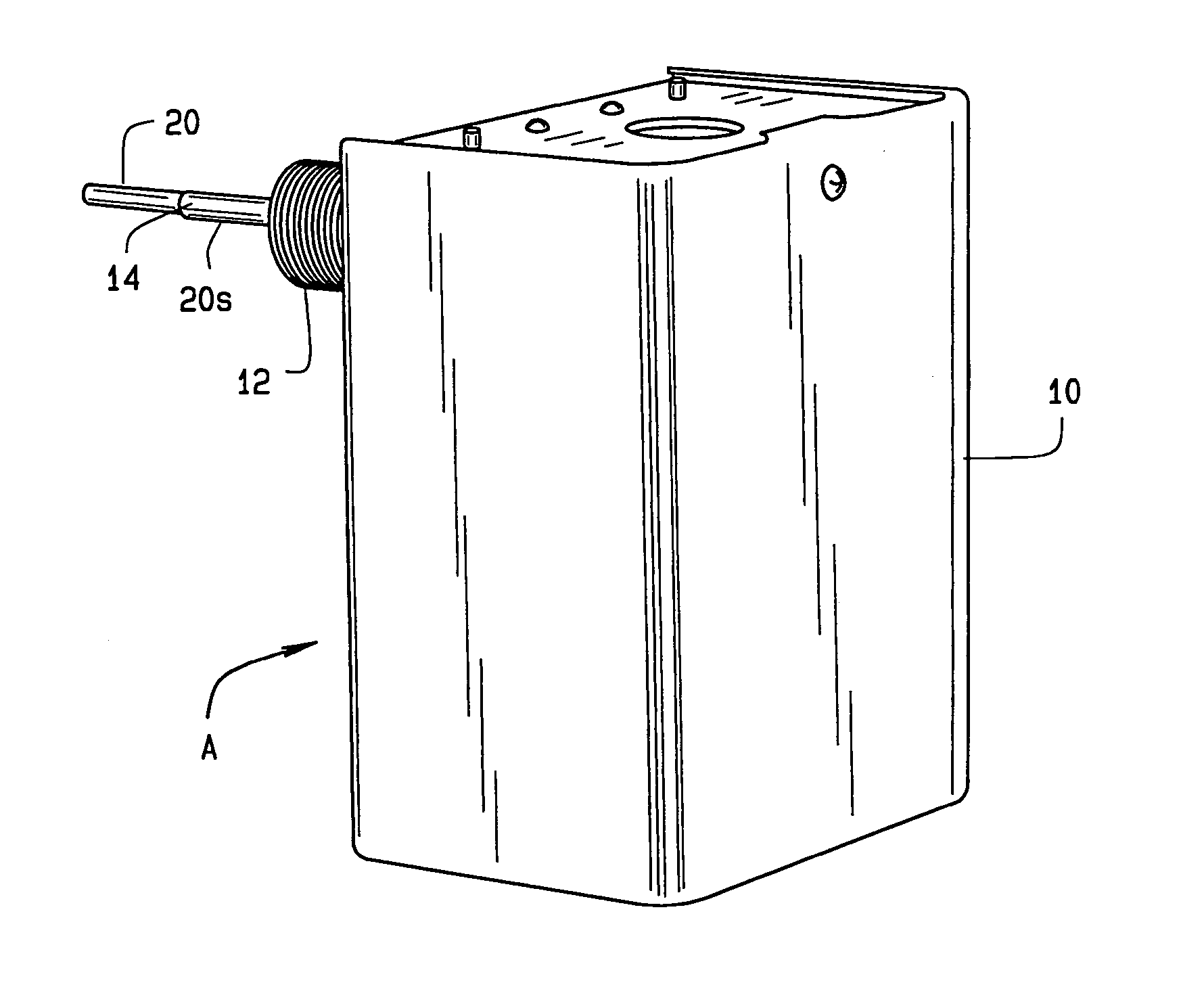
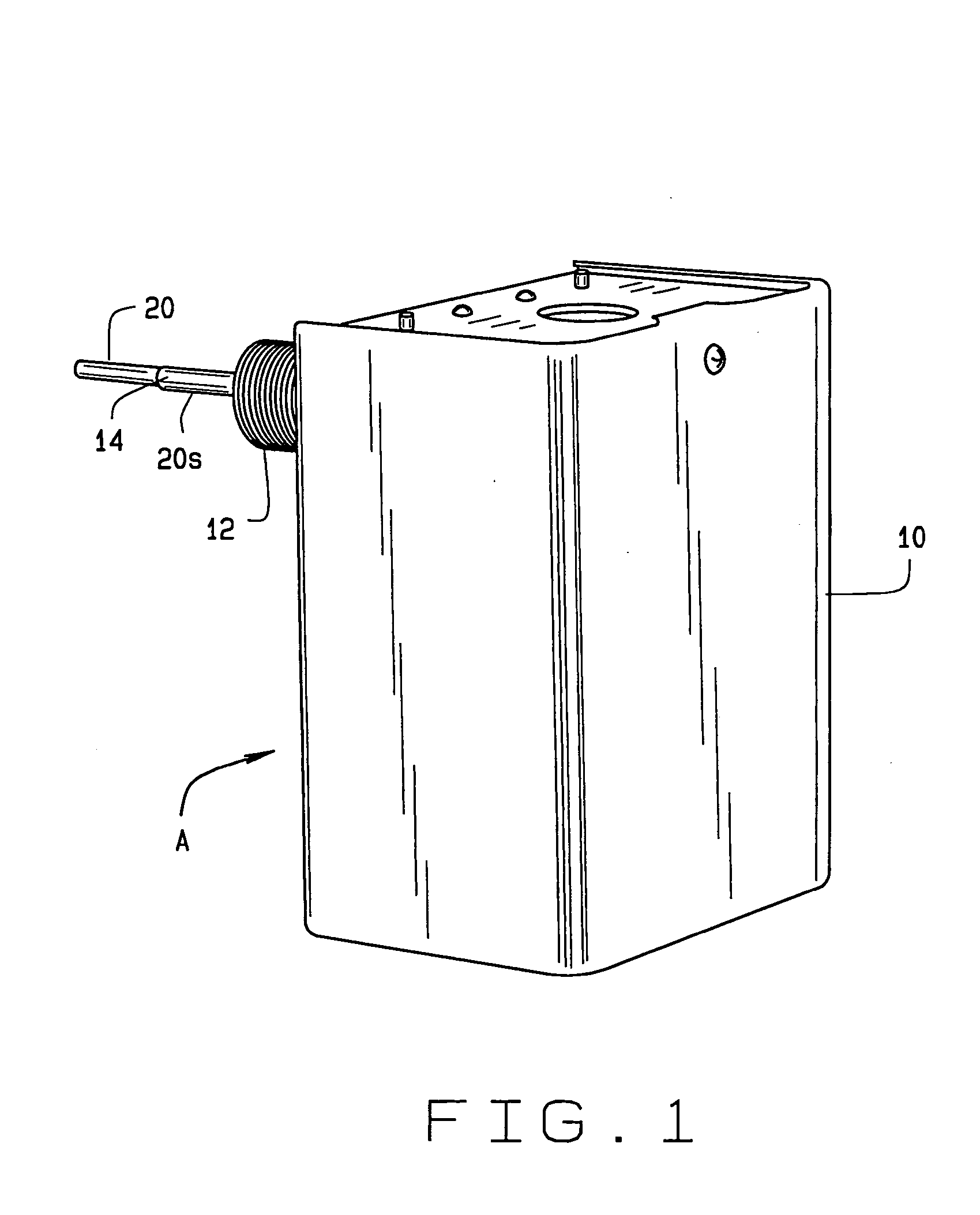
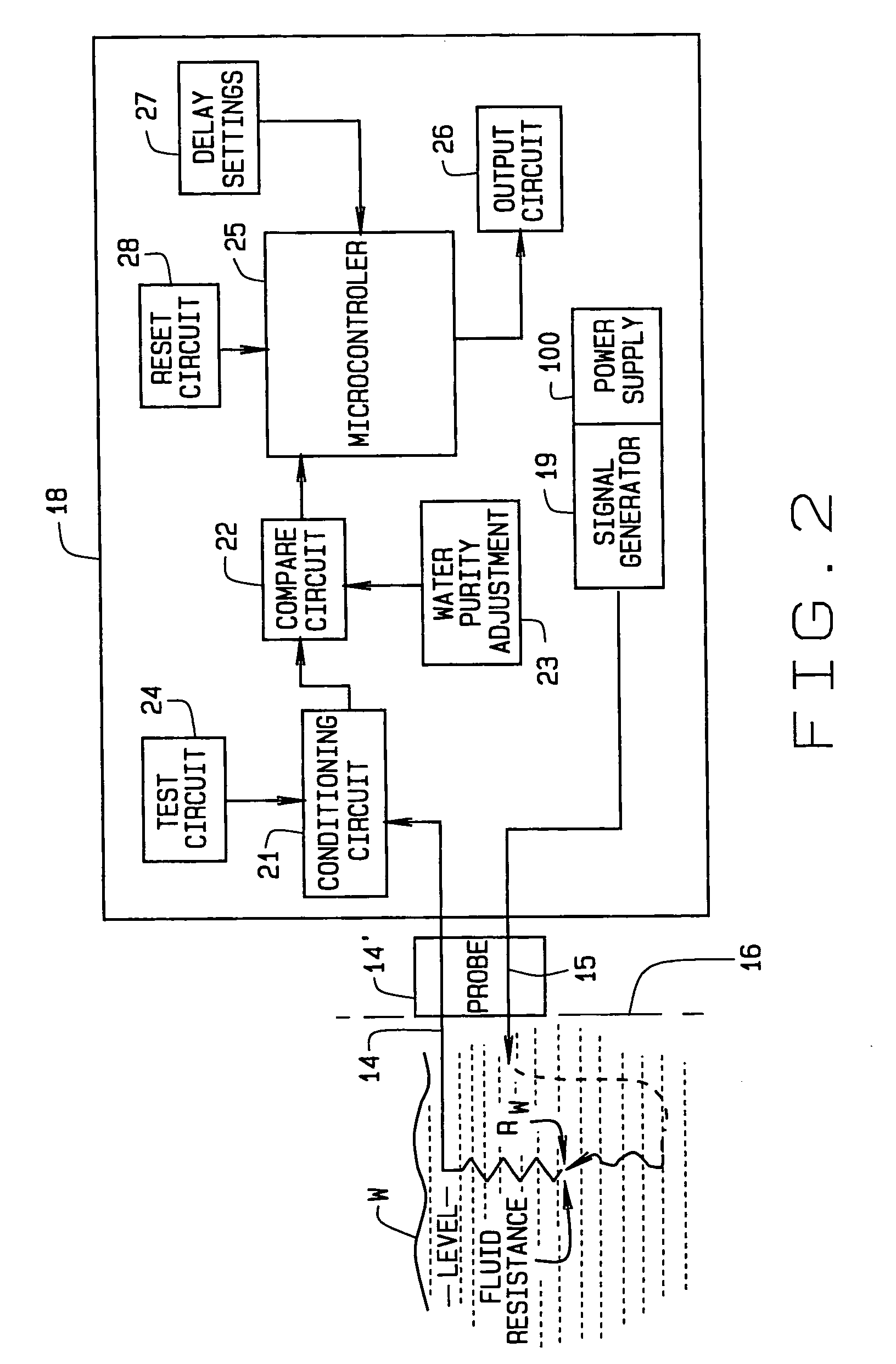
Low-water cut-off system
InactiveUS20040123659A1Increase sensitivityGuaranteed uptimeTesting/calibration apparatusFluid pressure measurementTime delaysControl function
A low-water cut-off system [A] determines if fluid [W] within a boiler or other enclosure drops below a predetermined level within the enclosure. A signal generator introduces a signal into the enclosure so that the signal is present for sensing at the predetermined level, where a probe is provided for sensing the signal if present as occurs if the water is at the predetermined level. A control, which includes a microcontroller, is responsive to the probe for providing a control function in response to whether the signal is so sensed by the probe, and so to determine if water has dropped below the predetermined level. The function may be causing alarm signalling or boiler heating cut-off. Self-test and time delay features are also included. Provision is made so that the control compensates for variation in electrical conductivity of the water through which the probe signal is sent, including circuitry to adjust for a wide range of possible purity levels. Provision is included such that the low water cut-off system is fault tolerant no matter at what water purity it is adjusted to operate.
Owner:NAT CITY BANK CO
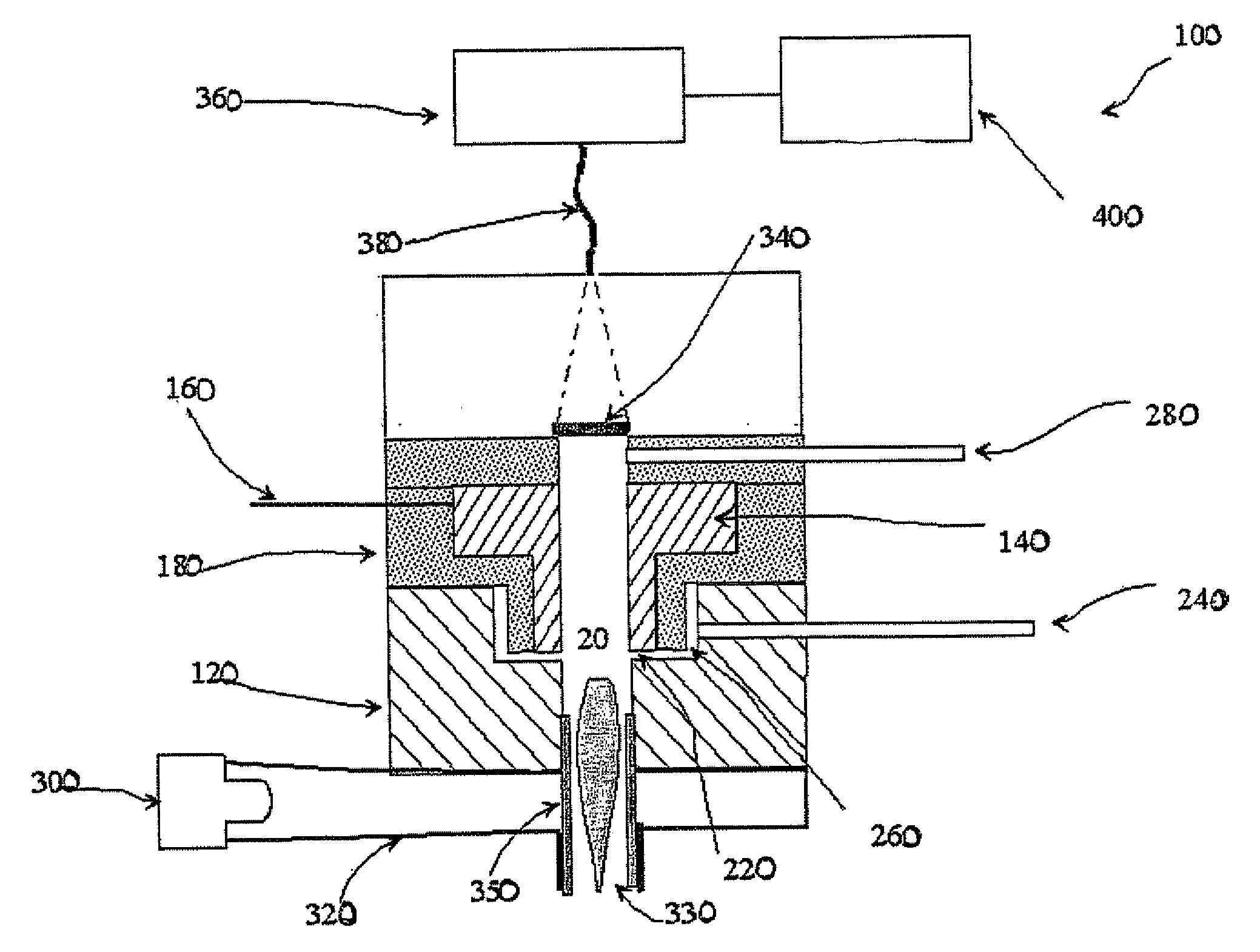
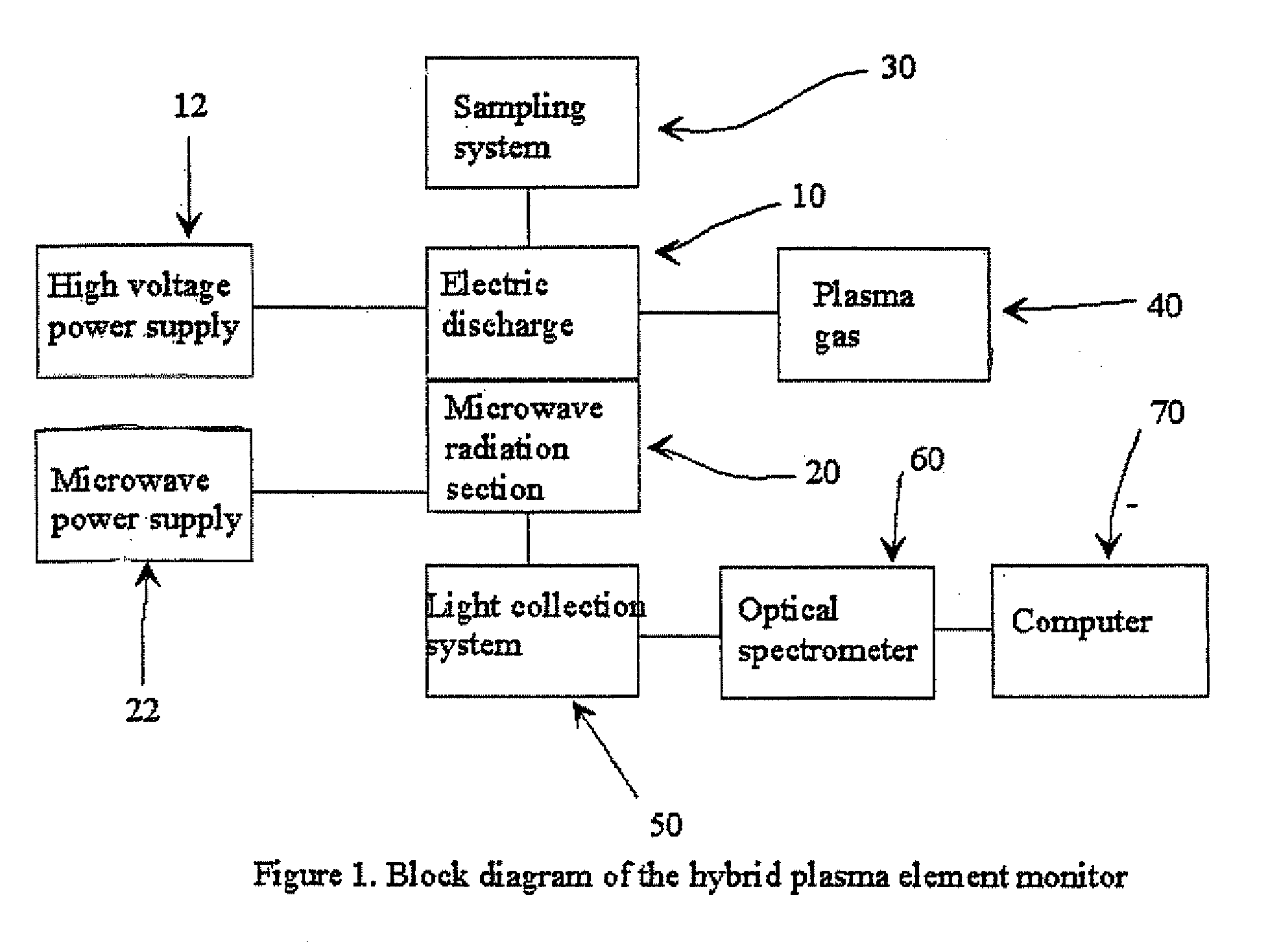
Hybrid plasma element monitor
InactiveUS20080055594A1Reduce background noiseIncrease sensitivityEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryRadiationMicrowave
Hybrid plasma monitor. A ground electrode is spaced apart from a high voltage electrode supporting an electric discharge therebetween to generate a plasma. The ground electrode and the high voltage electrode form an annular region into which a sample is introduced for generating a plasma. Microwave radiation couples into the plasma to sustain the plasma. A light detector such as a spectrometer receives light resulting from atomic emissions from the sample to analyze elements in the sample.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Glossy ganoderma spore oil and its supercritical prepn process
The present invention discloses one kind of glossy ganoderma spore oil, and belongs to the field of Chinese medicine technology. The glossy ganoderma spore oil is measured to contain total triterpene in 25-35 % and unsaturated fatty acids in 60-80 %, and has density of 0.85-1.0, refractive index at 25 deg.c of 1.45-1.50, and acid value of 15-25. The present invention also discloses the supercritical preparation process of the glossy ganoderma spore oil, and the preparation process has high extracting rate, and is favorable to the stability of the glossy ganoderma spore oil and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:吴逸芳
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com