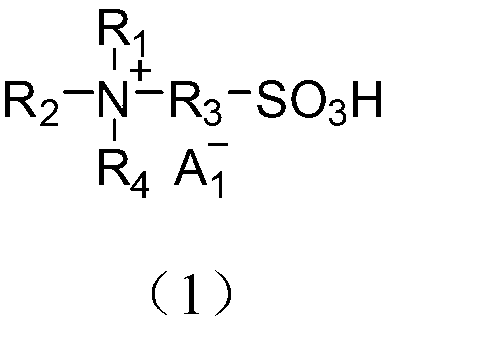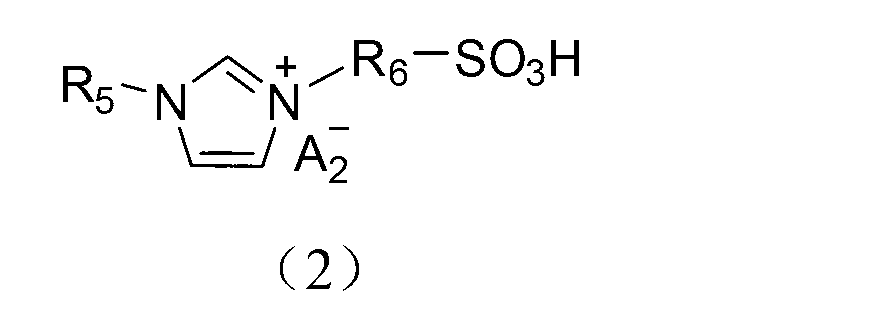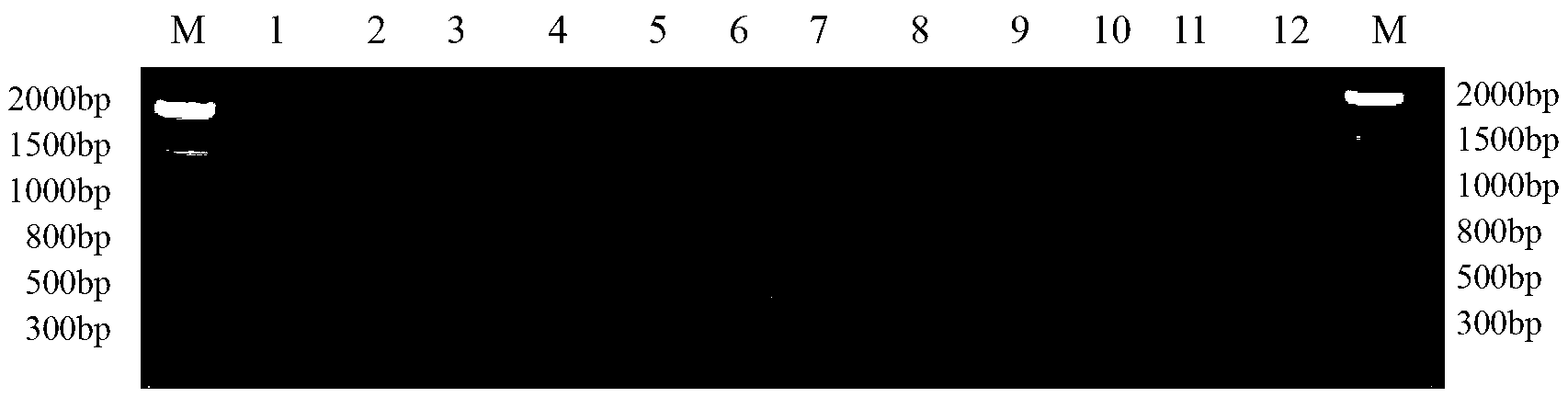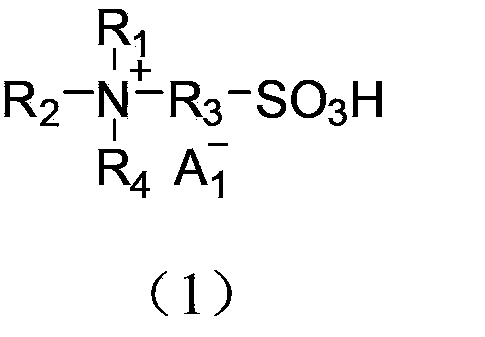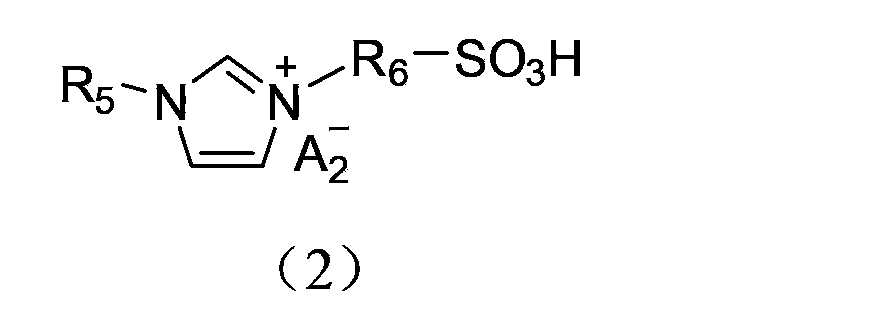Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Monokaryon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
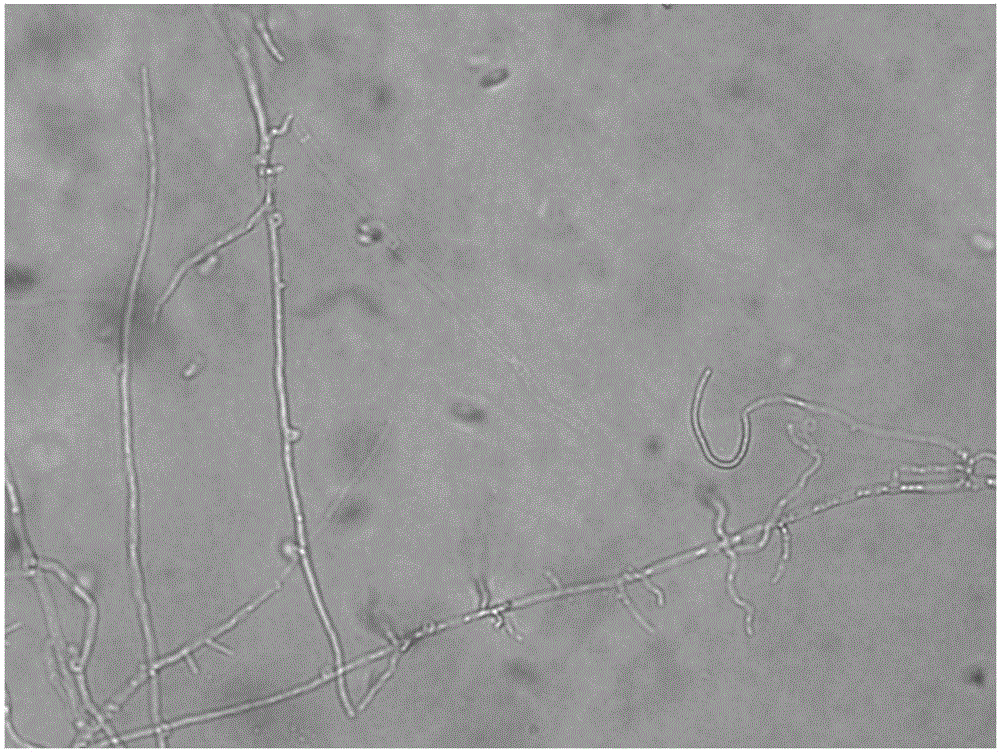
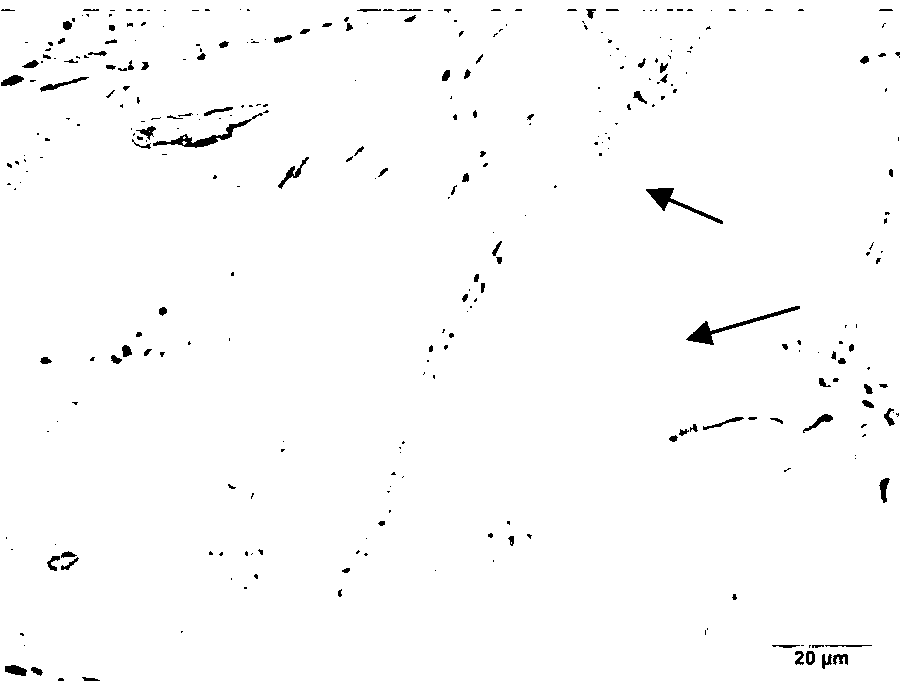
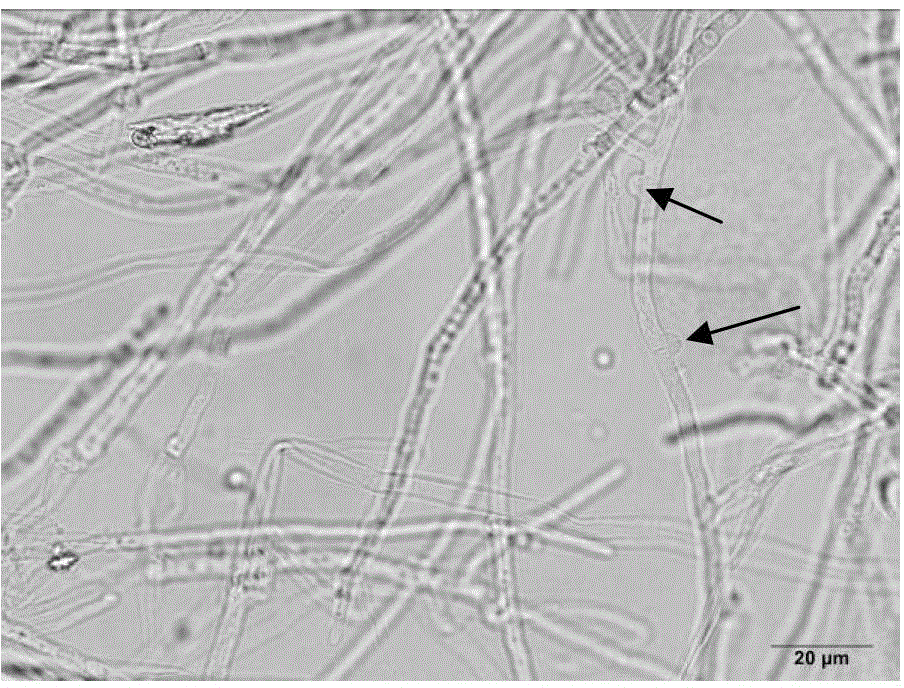
A monokaryon is a fungal mycelium or hypha in which each cell contains a single nucleus. It also refers to a mononuclear spore or cell of a fungus that produces a dikaryon in its life cycle.
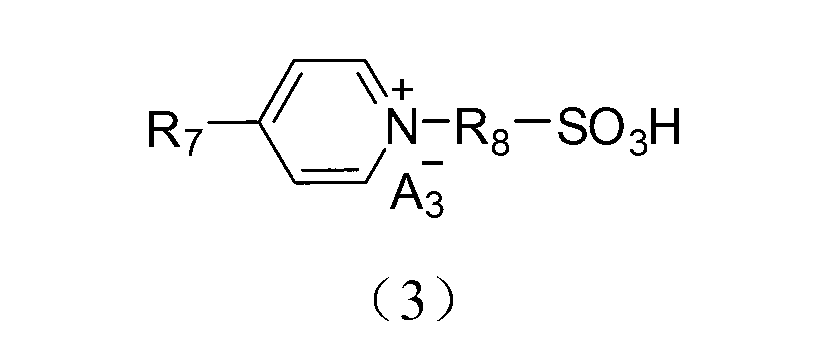
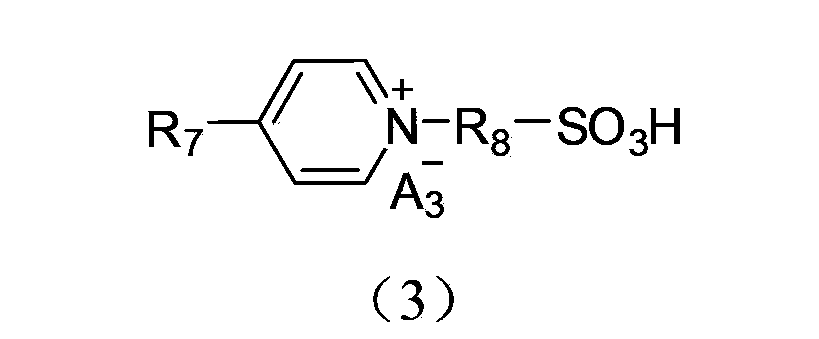
Application of acidic ionic liquid in catalyzing and synthesizing diphenolic acid and/or diphenolic acid ester
InactiveCN102701955AHigh catalytic yieldEasy to separateOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPropanoic acidSolvent
The invention discloses a method utilizing acidic ionic liquid in catalyzing and synthesizing diphenolic acid and / or diphenolic acid ester. The method comprises heating and stirring 1-100 parts of the acidic ionic liquid, 1-200 parts of levulinic acid and 1-500 parts of phenol for 5-60 hours' reaction under the protection of nitrogen to obtain the diphenolic acid; and continuously adding alcohols into the reacted mixture, stirring and heating the mixture to obtain the corresponding diphenolic acid ester. The acidic ionic liquid utilized in the method is sulfonic acid ion liquid including tertiary amine base monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, imidazolyl monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, pyridyl monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, ditertiary amine base dikaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, diimidazolyl dikaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid or dipyridyl monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid. The method successfully enables the acidic ionic liquid to serve as a catalytic agent to prepare the diphenolic acid and / or the diphenolic acid ester and is simple in preparation process and high in yield. According to the method, the separation of the catalytic agent and the reaction substrate is achieved through a solvent extraction method, and the catalytic agent can be repeatedly used and has no significant inactivation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene and application
The invention discloses a rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene. The nucleotide sequence of the rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene is shown as SEQID NO:1, and an amino acid sequence asshown in SEQID NO:2 is coded. A glucosyltransferase gene sequence is screened out according to a CDS sequence provided by a rhizoma gastrodiae transcriptome, a nest type PCR primer is designed, and through amplification and splicing, an overall length sequence of the glucosyltransferase gene is obtained; a prokaryotic expression vector pGEX4T-UGT is constructed, proteins are obtained through expression and purification, a eukaryotic expression vector is constructed, subcellular localization is performed on expression of a UGT gene, glucosyltransferase is transferred into monokaryon honey mushroom mycelia by an agrobacterium tumefaciens infection method for the constructed eukaryotic expression vector pH2GW7.0 35S-UGT, transgene honey mushrooms are obtained, biosynthetic gastrodin is used,the rhizoma gastrodiae is artificially cultured by the transgene honey mushrooms, the content of gastrodin in the rhizoma gastrodiae is increased, and besides, the gastrodin can also be produced through culturing genetic engineering honey mushrooms.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for protecting lentinus edodes strain through uracil auxotroph
ActiveCN105802952AUnable to reproduce normallyNormal growth and reproductionFungiHybrid cell preparationSporeCross breeding
The invention relates to a method for protecting a lentinus edodes strain through uracil auxotroph.The method comprises the steps that a lentinus edodes uracil auxotroph monokaryon 423-9 and a lentinus edodes monokaryon wild-type strain are crossbred, and single spore isolation is carried out after fruiting to obtain a monokaryon strain; a 5-fluororotic acid screening medium is inoculated with the monokaryon strain for culture, authentication is carried out to obtain a uracil auxotroph monokaryon strain, and then a uracil auxotroph dikaryon strain is obtained by means of mon-mon cross breeding.The method is simple, cost is low, a strain obtained through a conventional strain separation method cannot grow or reproduce normally, and the lentinus edodes strain can be effectively protected through the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
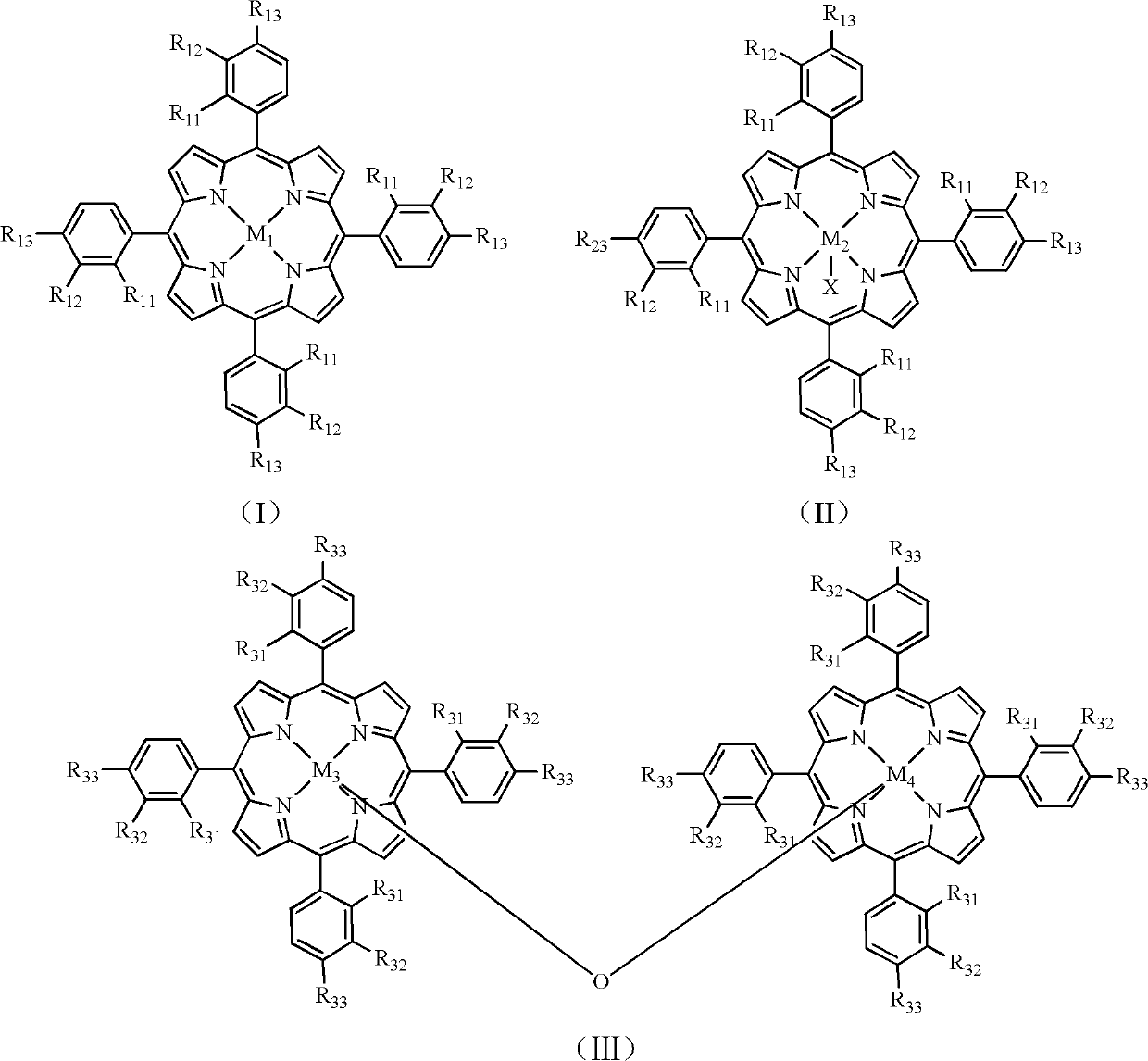
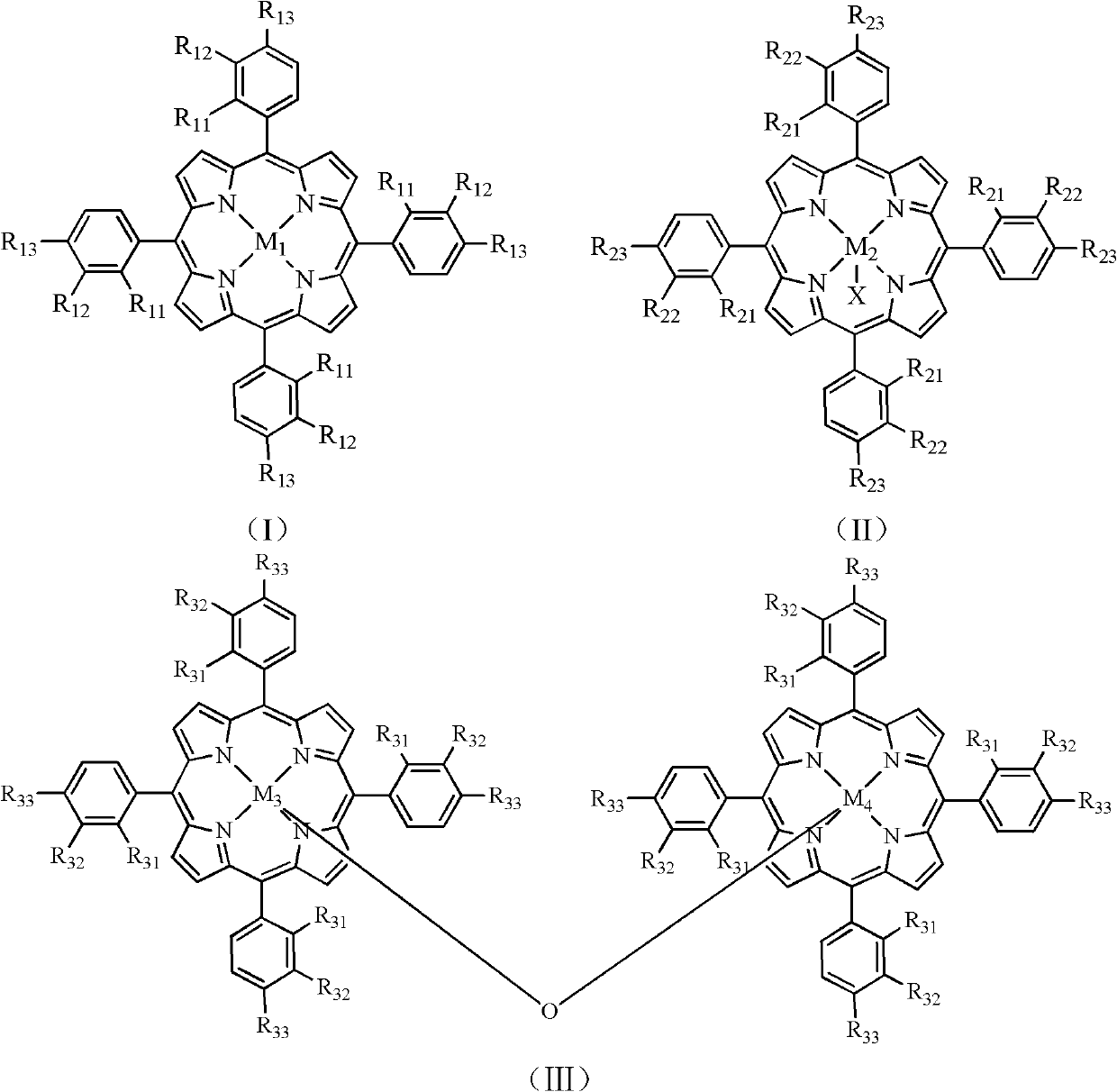
Process for preparing pyrazine-2-formic acid through metalloporphyrin catalytic oxidation of 2-methylpyrazine
The invention relates to a process for preparing pyrazine-2-formic acid through metalloporphyrin catalytic oxidation of 2-methylpyrazine. The process comprises the steps of using 2-methylpyrazine as raw materials; using a mixed solution of ethanol or 60% - 90% (by volume) of ethanol and water as a solvent; using monokaryon metalloporphyrin having a structure represented by formula (I) or formula (II) or dicaryon metalloporphyrin having a structure represented by formula (III) as a catalytic agent with the using amount accounting for 0.02% - 0.07% of raw material weight; reacting for 0.5 - 8 hours at a temperature between 80 DEG C - 140 DEG C under the oxygen pressure of 0.5 - 2.5 MPa in the presence of alkali sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide; subjecting the reacted product to acidification, filtration, extraction and hot water recrystallization; and obtaining the pyrazine-2-formic acid finally. According to the process, a small amount of the catalytic agent is consumed and the catalytic agent does not require to be separated, the reaction temperature is low, the solvent environment is friendly, and the process has wide application prospects in industry.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
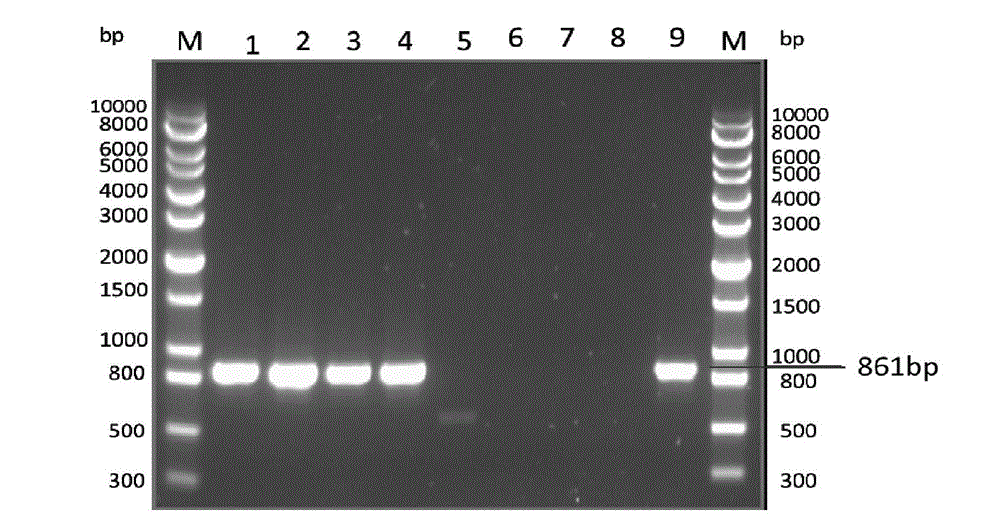
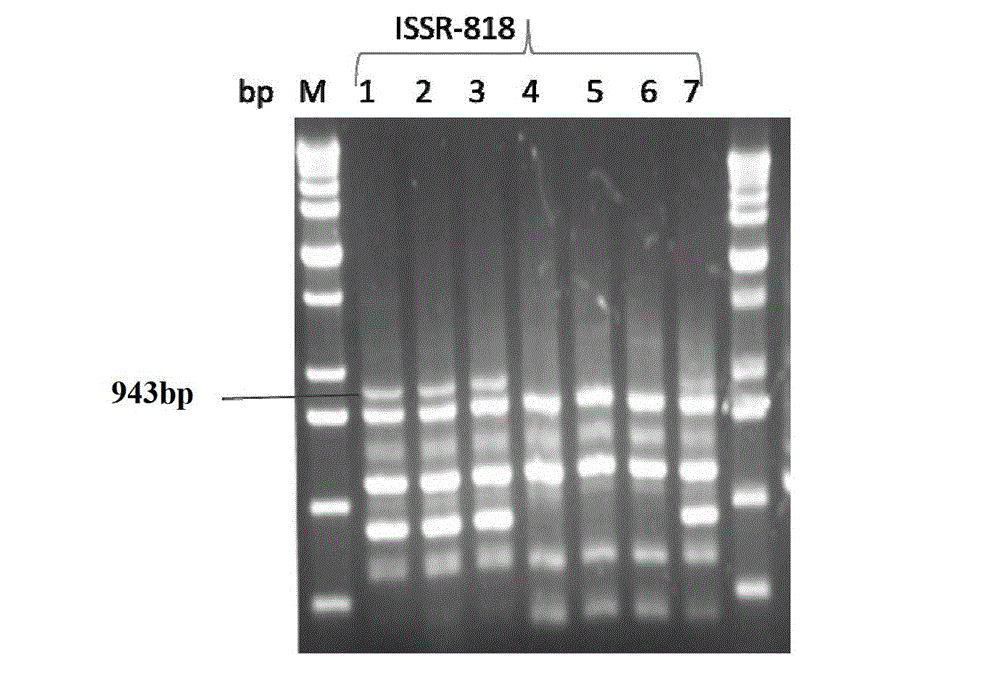
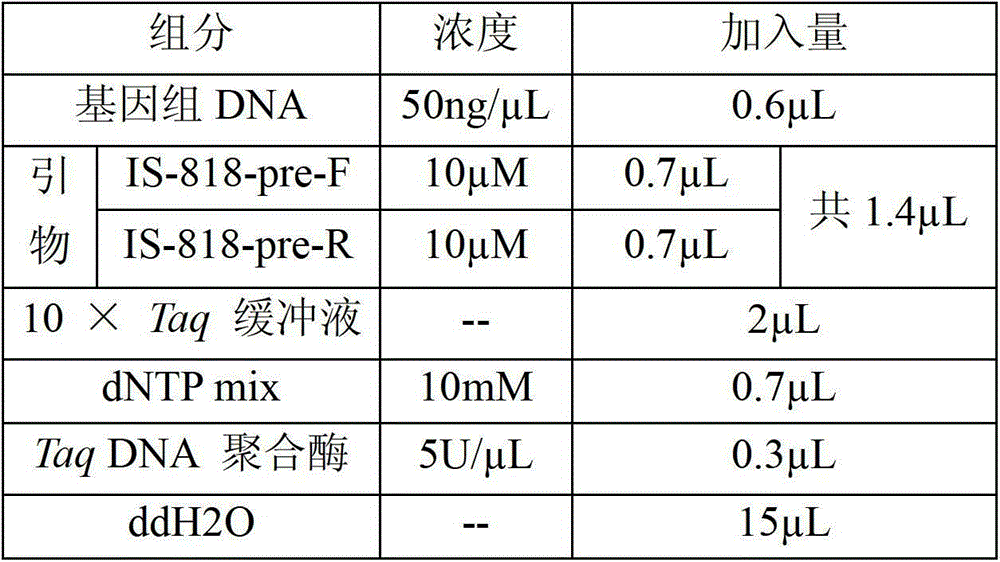
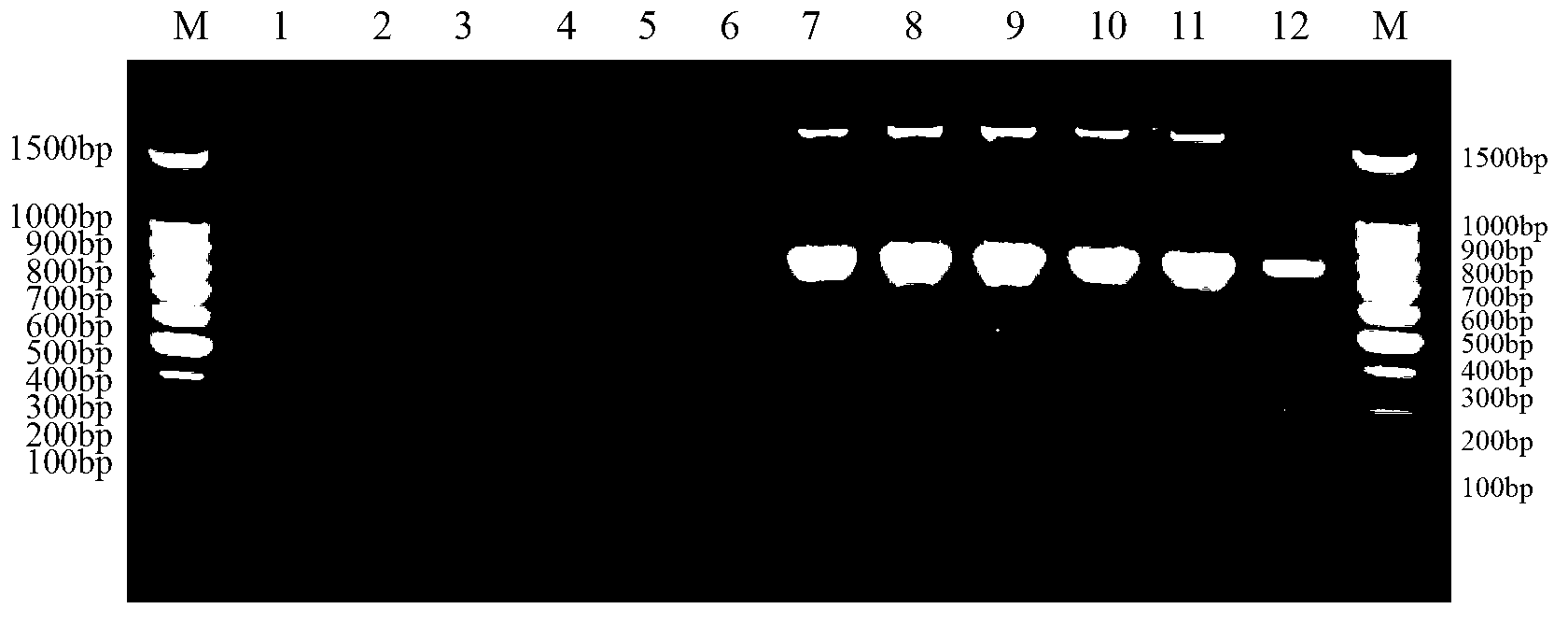
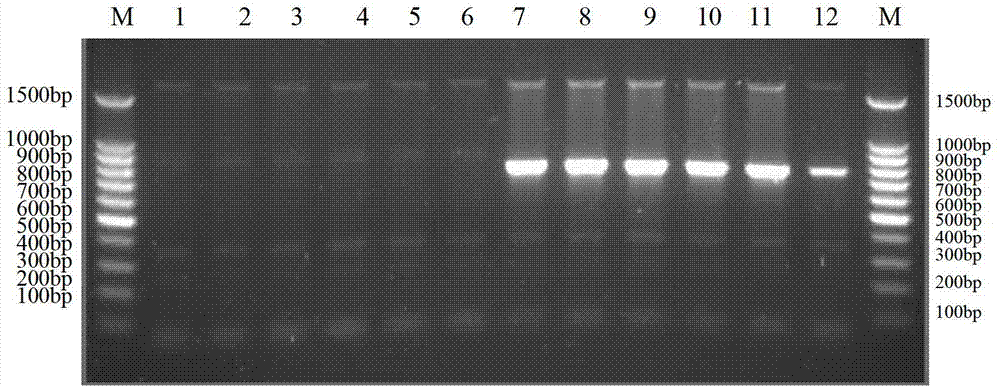
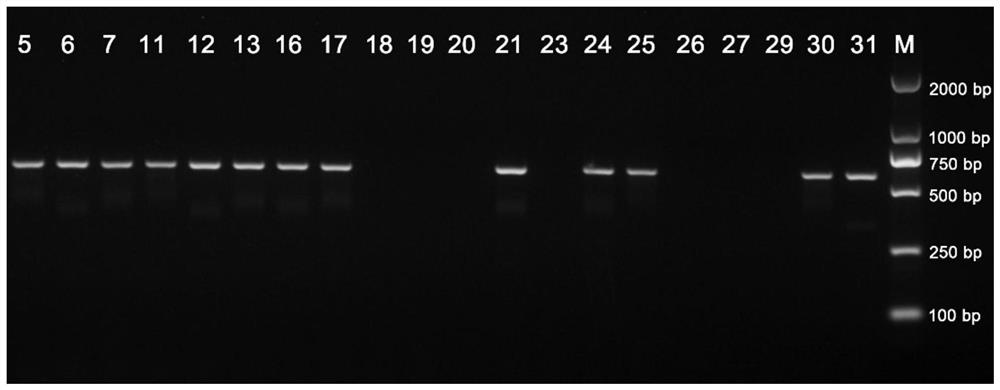
Method for identifying or assisting in identifying mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-818 thereof
ActiveCN103184280AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEtioplastsDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating type of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-818 thereof. The method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of the Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons comprises the following steps: respectively taking the genome DNA of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using PCR primer pairs shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2; detecting the size of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprise 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments or do not comprise 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are identical; and if the PCR product of one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprises 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments and the PCR product of the other one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified does not comprise 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Planting method for increasing yield of late-maturing litchis
InactiveCN106613650APromote growthIncrease productionSuperphosphatesSeed and root treatmentChemical controlEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a planting method for increasing the yield of late-maturing litchis. The method comprises the steps that slightly acidic soil which facilities drainage and irrigation, is deep in soil layer and achieves ventilation and light transmitting is selected, large core seeds are immediately sown after being washed and soaked with clear water, and after radical of the seeds is exposed, monokaryon is taken out for seedling growing; from the first ten days of February to the last ten days of March, planting is carried out in windless and warm weather, and the seeds are watered with enough rooting water; regular trimming is carried out, planting water supplementing is carried out to maintain the humidity of the soil, and biological control and chemical control are adopted as auxiliary means for controlling plant diseases and insect pests; 2-3 years after planting, the litchis are harvested from the middle ten days of August to the middle ten days of October after being mature. The late-maturing litchi planting method has the advantages of being low in cost, easy to operate and easy to popularize, increasing the yield and the like, and has good economic benefits.
Owner:盈江县富民红荔枝种植专业合作社
Method for protecting flammulina velutipes strain by utilizing uracil auxotroph
ActiveCN106978413AUnable to reproduce normallyNormal growth and reproductionFungiHybrid cell preparationSporeScreening cultures
The invention relates to a method for protecting the flammulina velutipes strain by utilizing uracil auxotroph. The method comprises the following steps: hybridizing uracil auxotroph monokaryon NG1-92 of flammulina velutipes with a monokaryon wild type strain of flammulina velutipes, and after fruiting, carrying out single spore isolation, thus obtaining a monokaryon strain; inoculating the monokaryon strain to 5-fluoroorotic acid screening culture medium for culturing, carrying out identification, thus obtaining the uracil auxotroph monokaryon strain, and carrying out mon-mon crossing to obtain a uracil auxotroph dikaryon strain. The method provided by the invention is simple and is low in cost, the strain obtained by adopting the conventional strain separation method can not grow and propagate normally, and thus the flammulina velutipes strain is effectively protected.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for identifying mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and special primer pair IS-879b thereof
InactiveCN103276070AShorten identification timeSimplify the identification stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and a special primer pair IS-879b thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking genomes DNA of two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified as templates respectively, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using a PCR primer pair consisting of two single chains DNA shown as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2, and detecting the magnitude of the obtained PCR products, wherein if the PCR products of both the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified contain or do not contain DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are identical; and if the PCR product of one protoplasted monokaryon contains the DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp and the PCR product of the other one does not contain the DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
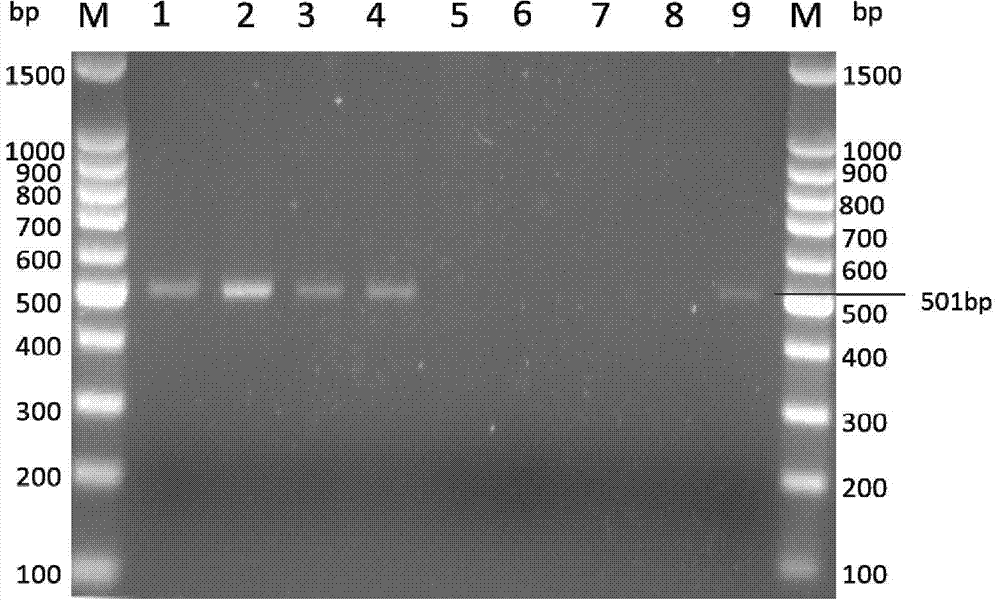
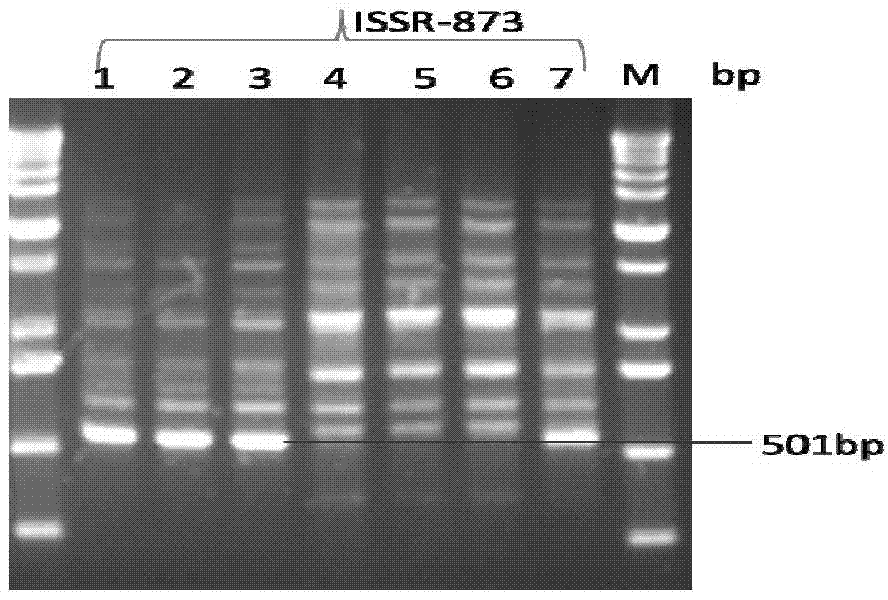
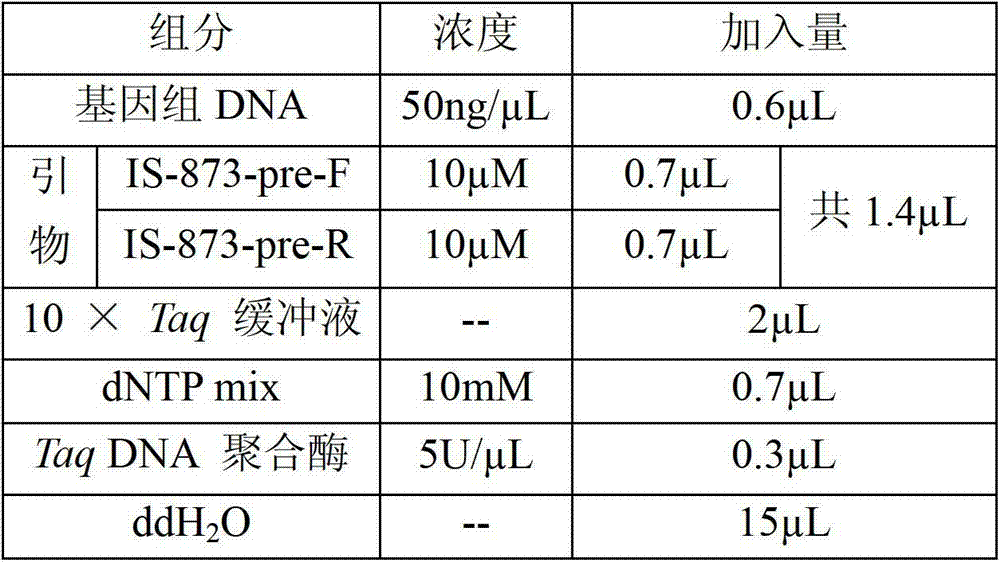
Method for identifying or assisting in identifying mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-873 thereof
ActiveCN103184281AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEtioplastsDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-873 thereof. The method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of the Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons comprises the following steps: respectively taking the genome DNA of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on by using PCR primer pairs shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2; detecting the size of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments or do not comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are identical; and if the PCR product of one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprises 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments and the PCR product of the other one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified does not comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
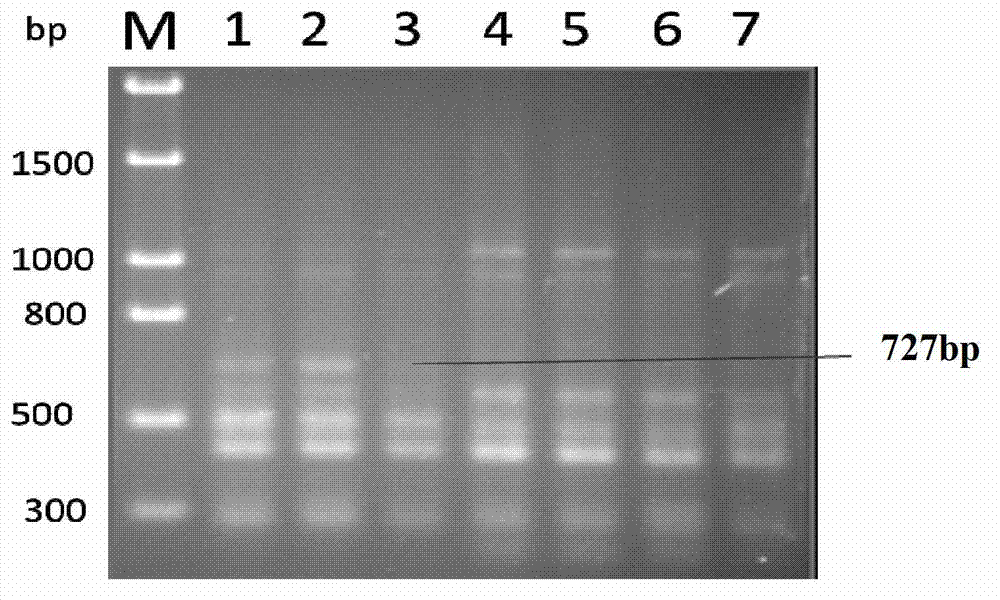
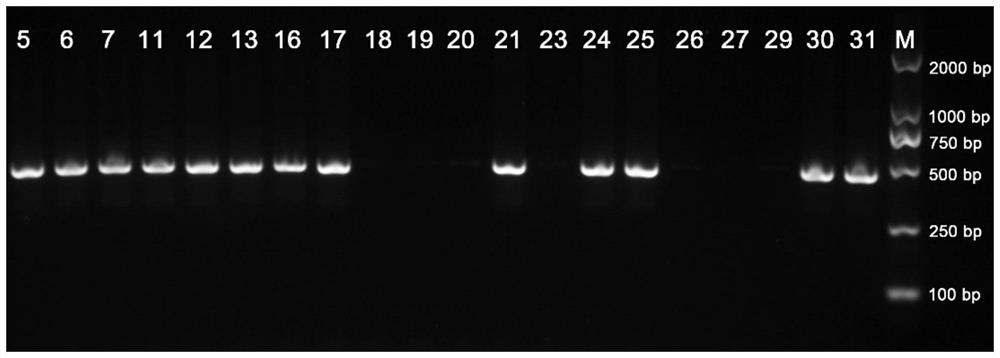
Monocaryon mating type primer set for identifying Shenxiang 215 strains and substantive derivative varieties of shiitake mushrooms, identifying method and application
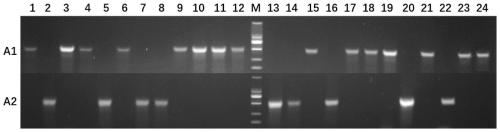
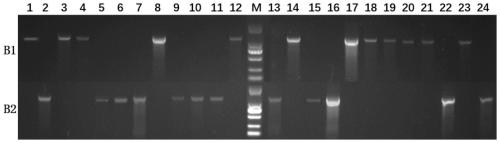
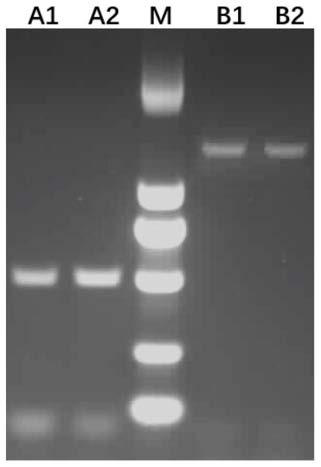
ActiveCN110029191AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesElectrophoresisGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a monocaryon mating type primer set for identifying Shenxiang 215 strains and substantive derivative varieties of shiitake mushrooms, an identifying method and an application,and relates to the technical field of edible mushroom molecular marked auxiliary breeding. The monocaryon mating type primer set specifically comprises 4 pairs of primers. The identifying method specifically comprises the steps of culturing mycelia, performing quick preparation of genomic DNA, performing mating type PCR detection, and determining the result of electrophoresis detection. Compared with a conventional monocaryon mating type identification method, the identifying method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that detection time is shoter and accuracy is higher; and throughthe adoption of the identifying method disclosed by the invention, the identifying time can be greatly shortened, the false detection rate can be reduced, and dicaryon elimination can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing precocious white needle mushroom strain
The invention discloses a method for preparing a precocious white needle mushroom strain. In the method, a yellow needle mushroom strain 'gold wire' and a white needle mushroom strain F092 are used as parents; and by using a di-monad hybridization method, the white needle mushroom strain F212-1 is prepared. The method comprises the following steps of separation and identification of a mononuclearbody, hybridization matching, screening of hybrids and construction of a hybrids selfing strain. The white needle mushroom strain prepared by using the method has the following characteristics that afruit body is white and precocious; the root of prostheca has no tomenta; not only are the characters of precocity and no tomenta at the root of the prostheca of a yellow needle mushroom maintained, but also the character that the fruit body of the white needle mushroom is white is maintained; the cultivating time is shortened; and the method is suitable for production in various cultivation technical modes.
Owner:INST OF SOIL FERTILIZER SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-6*6 therefor
InactiveCN103233081AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingDNA fragmentation
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
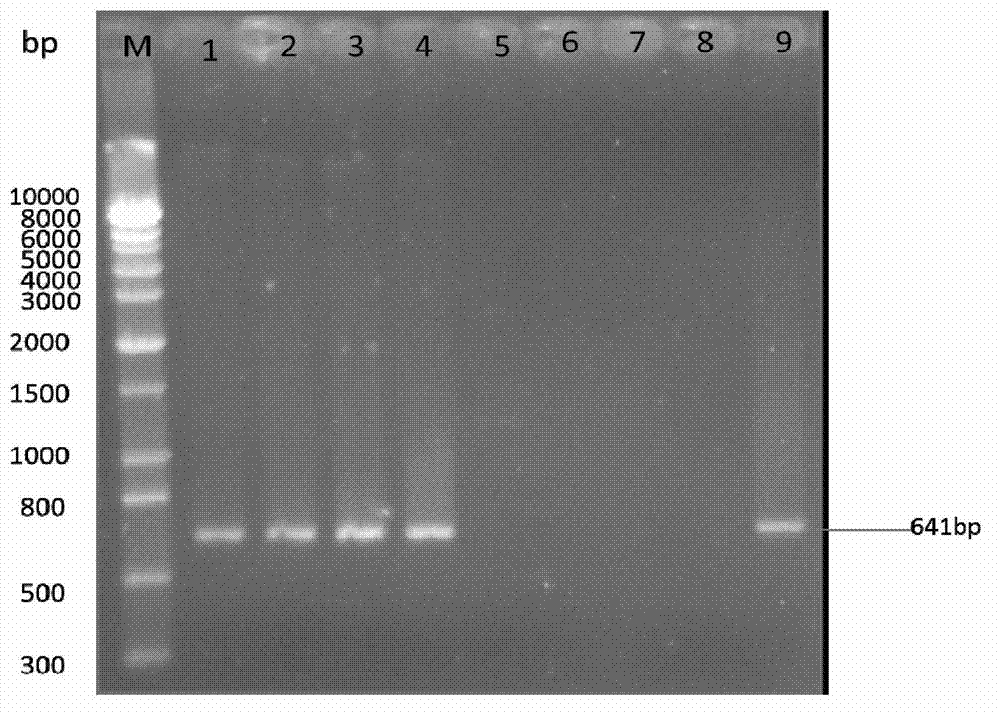
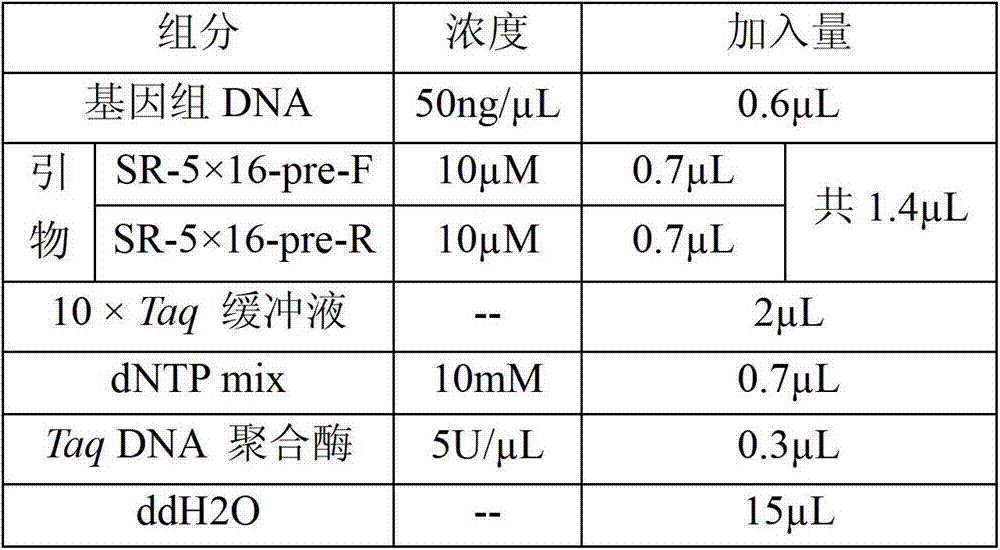
Method for identification or auxiliary identification of mating type of protoplast monokaryon of Lepista sordid and special primer pair SR-5*16 used therein
ActiveCN103194535AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationProtoplastGenome
The invention discloses a method for identification or auxiliary identification of the mating type of the protoplast monokaryon of Lepista sordid and a special primer pair SR-5*16 used therein. The method comprises the following steps: with genome DNAs of the protoplast monokaryon of two to-be-identified Lepista sordid strains as templates respectively, carrying out PCR amplification by using a PCR primer pair as represented by SEQ ID No. 1 and 2; and detecting the size of obtained PCR products, determining that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryon of the two to-be-identified Lepista sordid strains are identical if both PCR products of the protoplast monokaryon of the two Lepista sordid strains contain or do not contain 500 bp to 800 bp DNA fragments, and determining that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryon of the two to-be-identified Lepista sordid strains are different if the PCR product of the protoplast monokaryon of one of the two Lepista sordid strains contains 500 bp to 800 bp DNA fragments while the PCR product of the protoplast monokaryon of the other of the two Lepista sordid strains does not contain 500 bp to 800 bp DNA fragments.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Mutagenization method for Aspergillus oryzae with hereditary stability
InactiveCN111218442AGet quicklyMaintain genetic stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAspergillus oryzae
The invention discloses a mutagenization method for Aspergillus oryzae with hereditary stability. The mutagenization method comprises the following steps: filtering mutagenized Aspergillus oryzae suspension by virtue of a sterile membrane, so as to obtain a monokaryon Aspergillus oryzae strain; and further breeding the obtained monokaryon Aspergillus oryzae strain, so as to obtain a monokaryon Aspergillus oryzae mutant strain with hereditary stability. The Aspergillus oryzae strain processed by virtue of the method has good hereditary stability, so that an application value of the Aspergillusoryzae strain can be remarkably increased.
Owner:QIANHE CONDIMENT & FOOD CO LTD
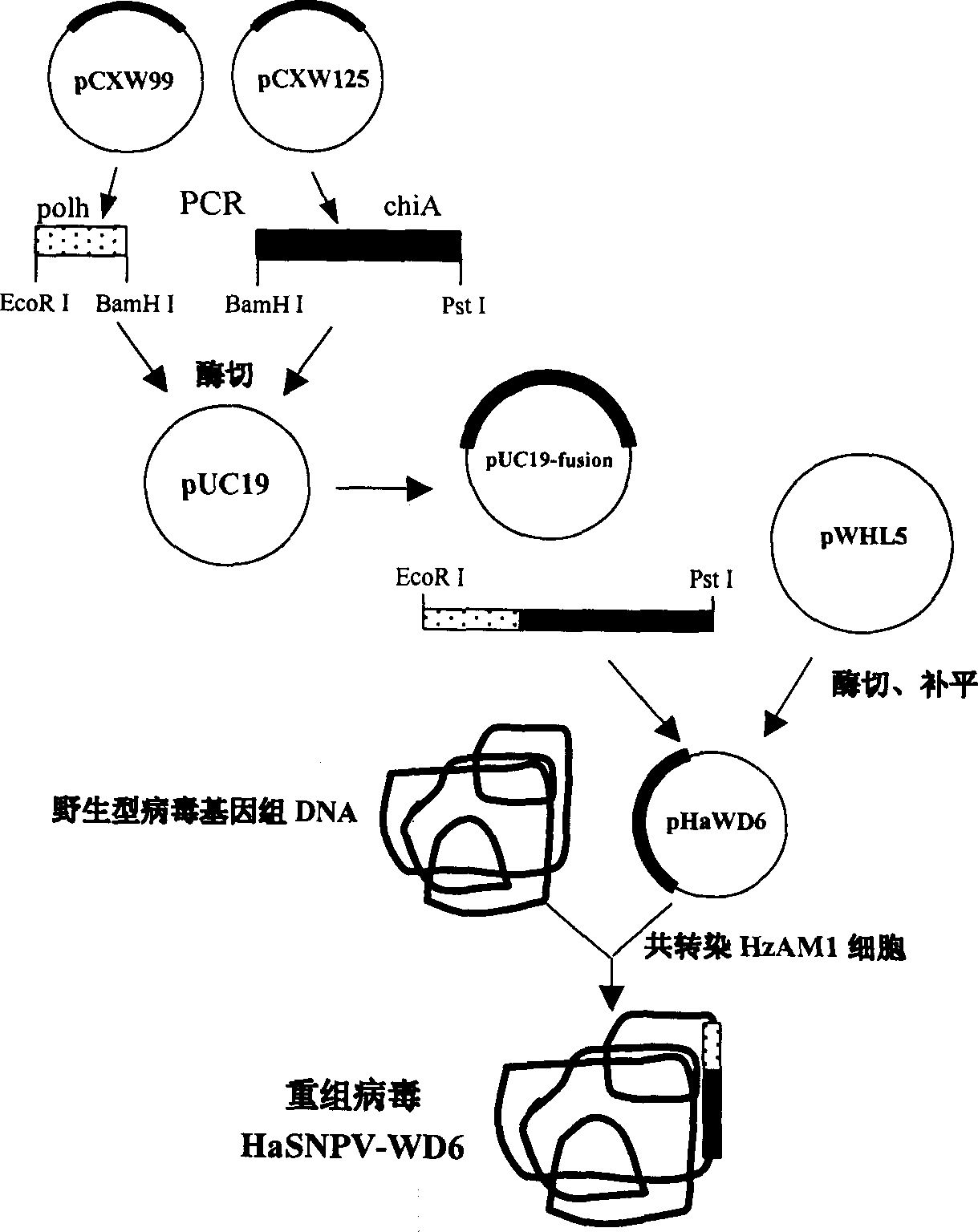
Recombination bollworm monokaryon capsid polyhedrosis virus for expression polghedrosis and chitinase fusion protein and its preparation method
InactiveCN1429902AIncreased efficiency of infecting the midgutSolve the shortcomings of late expression and slow onsetBiocideViruses/bacteriophagesPUC19Wild type
A recombinant mononuclear capsid nucleopolyhedrovirus of bollw orm able to express polyhedron and chitinase fusion protein is prepared through PCR amplification of polyhedron gene HaSNPV and chitinase gene, cloning to carrier pUC19 to configure fusion gene, inserted it in eukaryotic carrier pHaWHL5 to obtain eukaryotic transfer carrier pHaWD6, transfecting insection cell by it along with wild virus DNA, and homologous recombination.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
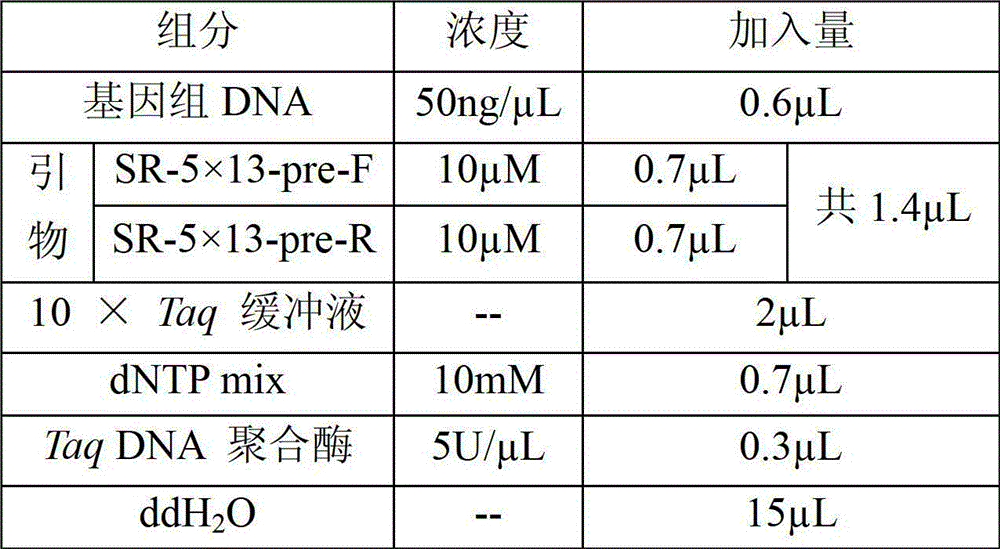
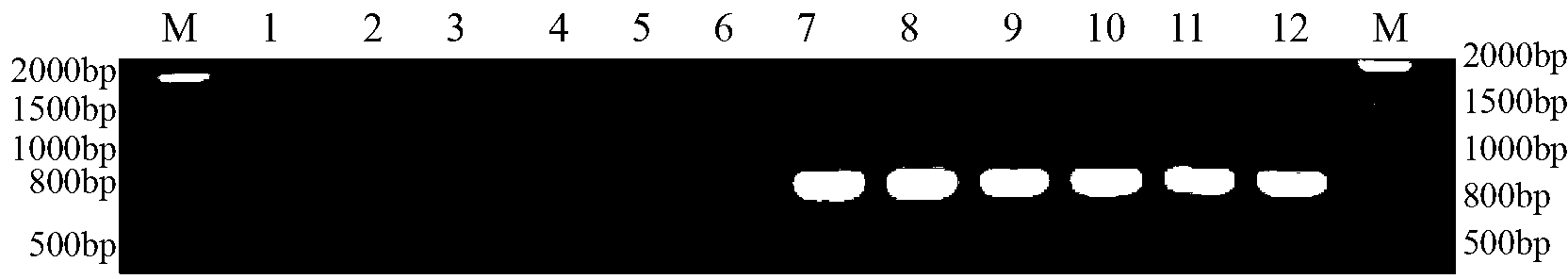
Method and special primer SR-5*13 for differentiating and auxiliarily differentiating mating types of bioplast monokaryons of lepista sordida (Fr) sings
ActiveCN103184282AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationMatingDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method and a special primer SR-5*13 for differentiating and auxiliarily differentiating mating types of bioplast monokaryons of lepista sordida (Fr) sings. The method comprises the following steps: genome DNAs of bioplast monokaryons of two lepista sordida (Fr) sings to be differentiated are respectively taken as templates; PCR primers shown by SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2 are used for PCR increase; the sizes of the obtained PCR products are detected; if the PCR products of the bioplast monokaryons of both the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings to be differentiated contain DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp or don't contain the DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp, the mating types of the bioplast monokaryons of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings are same; and if the PCR product of the bioplast monokaryon of one of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings contains DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp, and the PCR product of the bioplast monokaryon of the other of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings dose not contain the DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp, the mating types of the bioplast monkaryones of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for protection of pleurotus eryngii strain by using uracil auxotrophy
ActiveCN107557354AUnable to reproduce normallyNormal growth and reproductionHybrid cell preparationMicroorganism based processesSporeBacteroides species
The invention relates to a method for protection of a pleurotus eryngii strain by using uracil auxotrophy, which comprises the following steps of hybridizing a pleurotus eryngii uracil auxotrophy monokaryon NX2-0 with a pleurotus eryngii monokaryon strain, and after fruiting, performing single spore isolation to obtain a monokaryon strain; inoculating the monokaryon strain on a 5-fluororotic acidscreening medium for culture and identification, so as to obtain a uracil auxotrophy monokaryon strain, and then performing mon-mon crossing to obtain a uracil auxotrophy dikaryon strain. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simpleness and low cost, and the strain obtained by the conventional strain isolation method cannot grow and multiply normally, and the pleurotus eryngii strain can be effectively protected.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for identifying mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof
InactiveCN103305606AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologySingle strand
The invention discloses a method for identifying a mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: by taking the genome DNAs of the protoplasted monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida as templates, respectively, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-stranded DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2; detecting the sizes of the PCR products obtained; if the PCR products of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp or not, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are the same; if one plant contains the DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp while the other plant contains no DNA segment of 500 bp-800 bp, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof
InactiveCN103290117AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingGenome
The invention discloses a method for identifying the protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: with genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) of the protoplast monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida to be identified as templates, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain or do not obtain 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are the same; and if one plant contains 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, while the other plant contains no 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof
InactiveCN103290117BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method for identifying the protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: with genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) of the protoplast monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida to be identified as templates, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain or do not obtain 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are the same; and if one plant contains 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, while the other plant contains no 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof
InactiveCN103305606BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologySingle strand
The invention discloses a method for identifying a mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: by taking the genome DNAs of the protoplasted monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida as templates, respectively, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-stranded DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2; detecting the sizes of the PCR products obtained; if the PCR products of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp or not, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are the same; if one plant contains the DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp while the other plant contains no DNA segment of 500 bp-800 bp, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and special primer pair SR-2x8 thereof
InactiveCN103276072AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-2x8 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking genomes DNA of two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified as templates respectively, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using a PCR primer pair consisting of two single chains DNA shown as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2, and detecting the magnitude of the obtained PCR products, wherein if the PCR products of both the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified contain or do not contain DNA fragments of 300bp-500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are identical; and if the PCR product of one protoplasted monokaryon contains the DNA fragments of 300bp-500bp and the PCR product of the other one does not contain the DNA fragments of 300bp-500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor
InactiveCN103224992BSimplify the identification stepsShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor. The method comprises the following steps: respectively taking genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acid) of two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if both or neither of the PCR products of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are the same; and if one of the two contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp and the other does not contain a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
A method for protecting mushroom strains by using uracil auxotroph
ActiveCN105802952BUnable to reproduce normallyNormal growth and reproductionFungiMicroorganism based processesSporeCross breeding
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor
InactiveCN103224992ASimplify the identification stepsShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor. The method comprises the following steps: respectively taking genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acid) of two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if both or neither of the PCR products of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are the same; and if one of the two contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp and the other does not contain a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
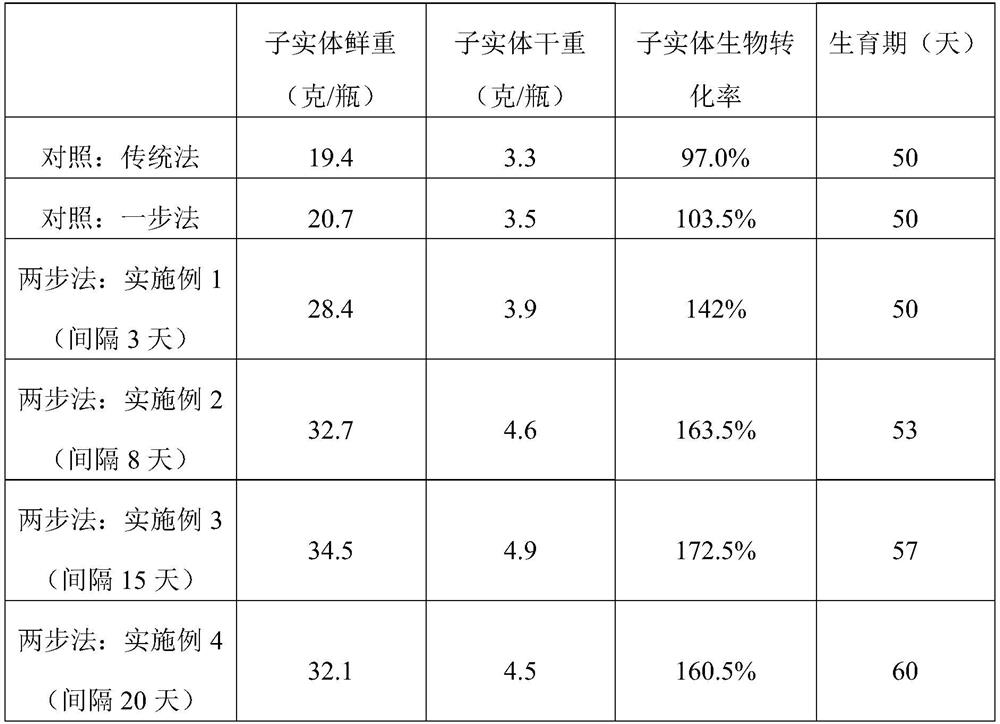
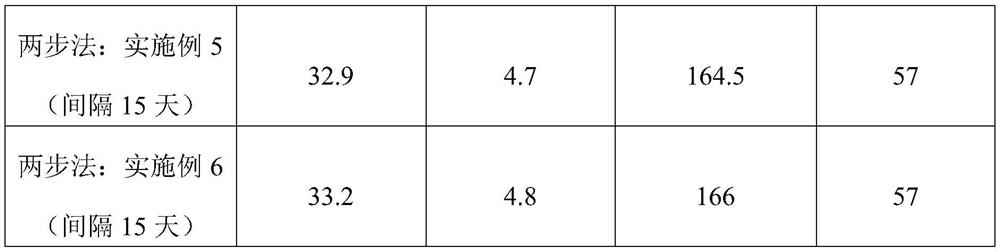
A method of two-step inoculation to increase fruiting bodies of Cordyceps militaris
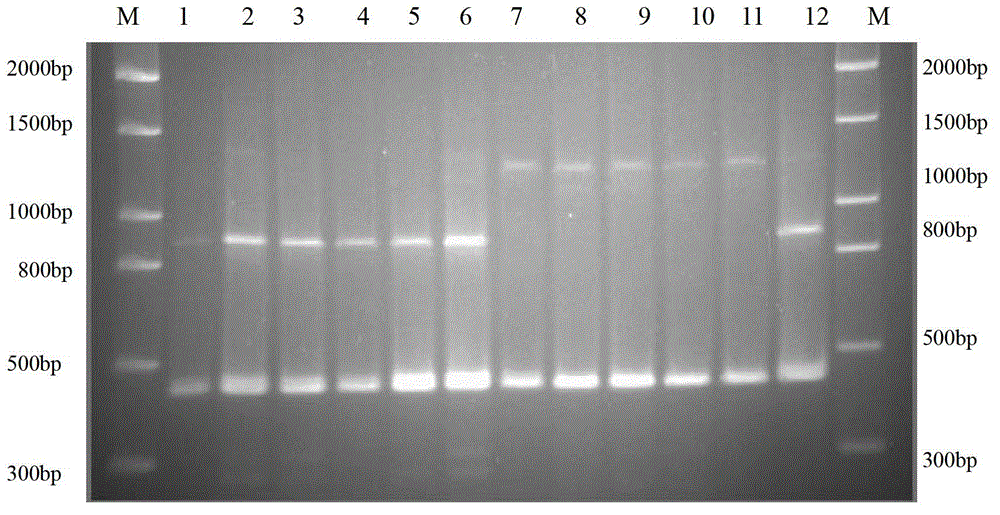
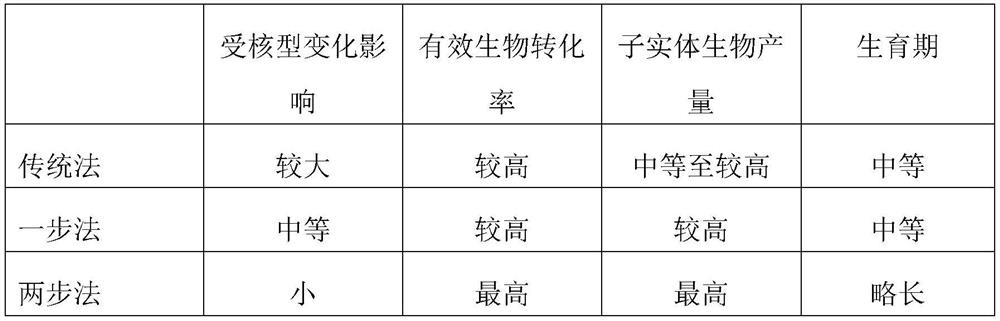
ActiveCN111527987BIncrease productionHigh biotransformation rateCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologyCordyceps
The invention discloses a two-step inoculation method for increasing the fruiting body yield of Cordyceps militaris. The method comprises first inoculating the monokaryotic strain of Cordyceps militaris on the culture medium of Cordyceps militaris and cultivating it for a period of time; Inoculate the Cordyceps militaris monokaryon, heterokaryon or homokaryon strains of the opposite mating type gene of the inoculated monokaryotic strain to the culture of Cordyceps militaris inoculated for the first time, and continue to cultivate until the fruiting body of Cordyceps militaris is harvested . The two-step inoculation method adopted in the present invention can not only reduce the impact of strain degeneration caused by karyotype changes in large-scale production, but also greatly improve the biotransformation rate of the fruiting body of Cordyceps militaris, so the biological yield of the fruiting body of Cordyceps militaris can be effectively improved, The invention is an important innovation in the field of edible fungus strain inoculation.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of acidic ionic liquid in catalyzing and synthesizing diphenolic acid and/or diphenolic acid ester
InactiveCN102701955BHigh catalytic yieldEasy to separateOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPropanoic acidNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a method utilizing acidic ionic liquid in catalyzing and synthesizing diphenolic acid and / or diphenolic acid ester. The method comprises heating and stirring 1-100 parts of the acidic ionic liquid, 1-200 parts of levulinic acid and 1-500 parts of phenol for 5-60 hours' reaction under the protection of nitrogen to obtain the diphenolic acid; and continuously adding alcohols into the reacted mixture, stirring and heating the mixture to obtain the corresponding diphenolic acid ester. The acidic ionic liquid utilized in the method is sulfonic acid ion liquid including tertiary amine base monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, imidazolyl monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, pyridyl monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, ditertiary amine base dikaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid, diimidazolyl dikaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid or dipyridyl monokaryon sulfonic acid ion liquid. The method successfully enables the acidic ionic liquid to serve as a catalytic agent to prepare the diphenolic acid and / or the diphenolic acid ester and is simple in preparation process and high in yield. According to the method, the separation of the catalytic agent and the reaction substrate is achieved through a solvent extraction method, and the catalytic agent can be repeatedly used and has no significant inactivation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-6*6 therefor
InactiveCN103233081BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingA-DNA
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Primer pairs and kit for identifying mating type of Coriolopsis trogii protoplast monokaryon and application of primer pairs
ActiveCN112126701AFast and accurate identificationSimplify identification stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses primer pairs and kit for identifying the mating type of Coriolopsis trogii protoplast monokaryon and an application of the primer pairs. The invention discloses two primer pairs PMD_1 and PMD_2 for identifying the mating type of the Coriolopsis trogii protoplast monokaryon. According to the invention, genomic DNA of the to-be-identified Coriolopsis trogii protoplast monokaryon is used as a template, the primers PMD_1 and PMD_2 are used for amplification, and the mating type of the Coriolopsis trogii protoplast monokaryon is determined according to the size of a PCR product obtained by detection. The method provided by the invention is simple and easy to implement, shortens the identification time, simplifies the identification steps, has high accuracy, and can be suitable for research in the related fields of genetic breeding, genomics and the like of edible and medicinal fungi, especially Coriolopsis trogii.
Owner:广东省科学院生物与医学工程研究所
Method for identifying or assisting in identifying mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-873 thereof
ActiveCN103184281BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingProtoplast
The invention discloses a method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-873 thereof. The method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of the Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons comprises the following steps: respectively taking the genome DNA of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on by using PCR primer pairs shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2; detecting the size of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments or do not comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are identical; and if the PCR product of one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprises 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments and the PCR product of the other one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified does not comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com