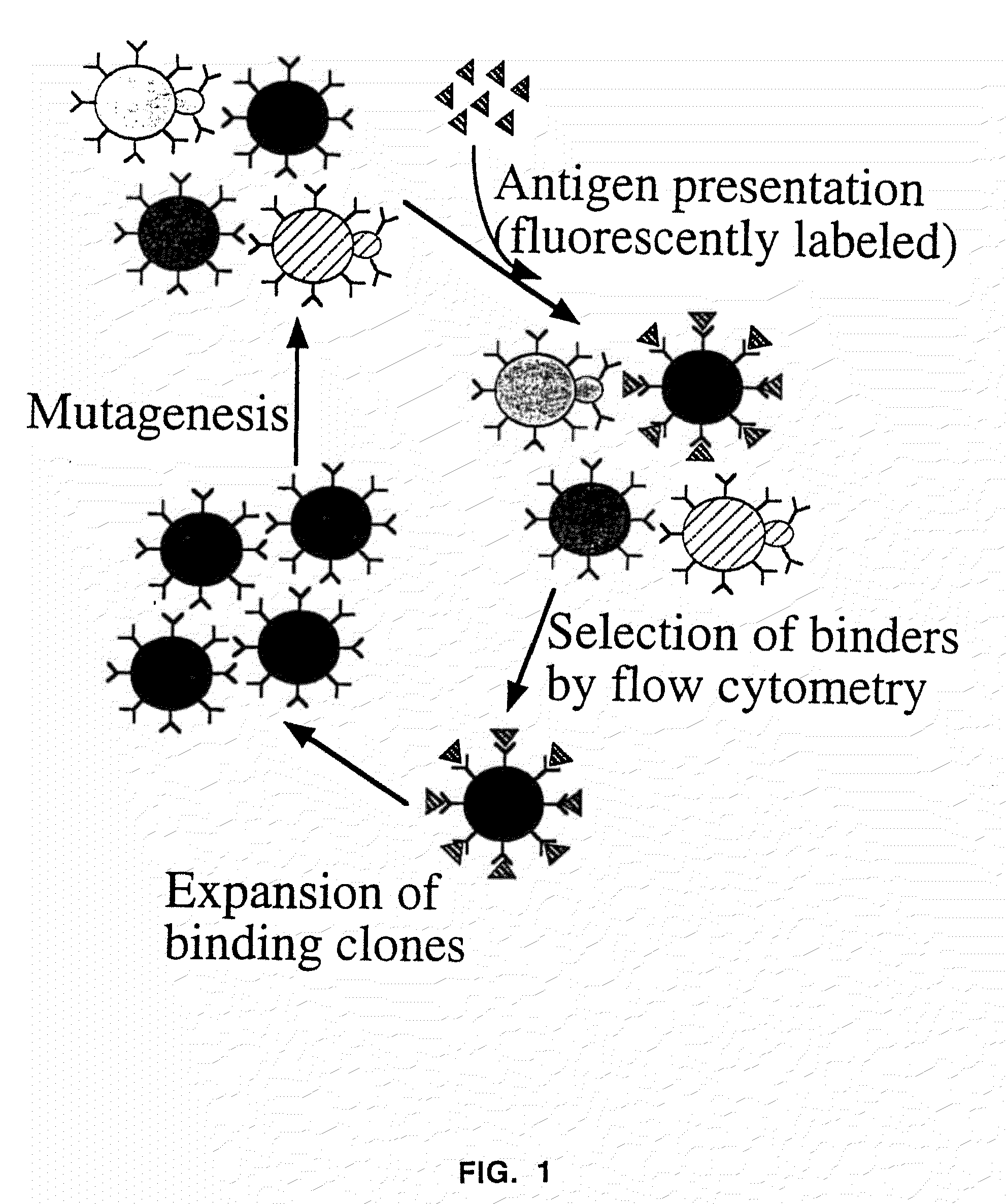
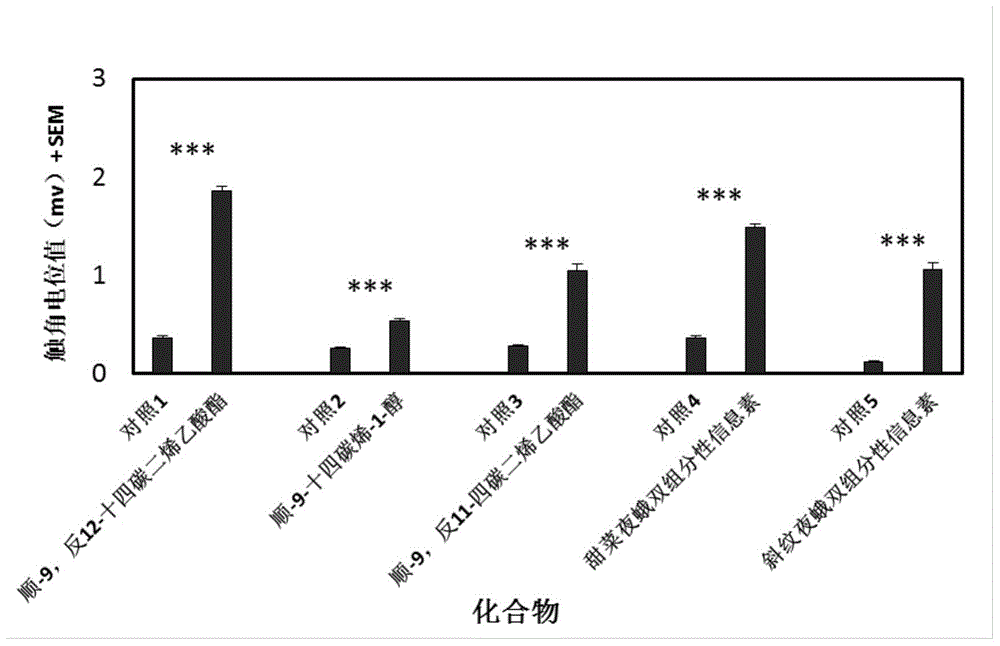
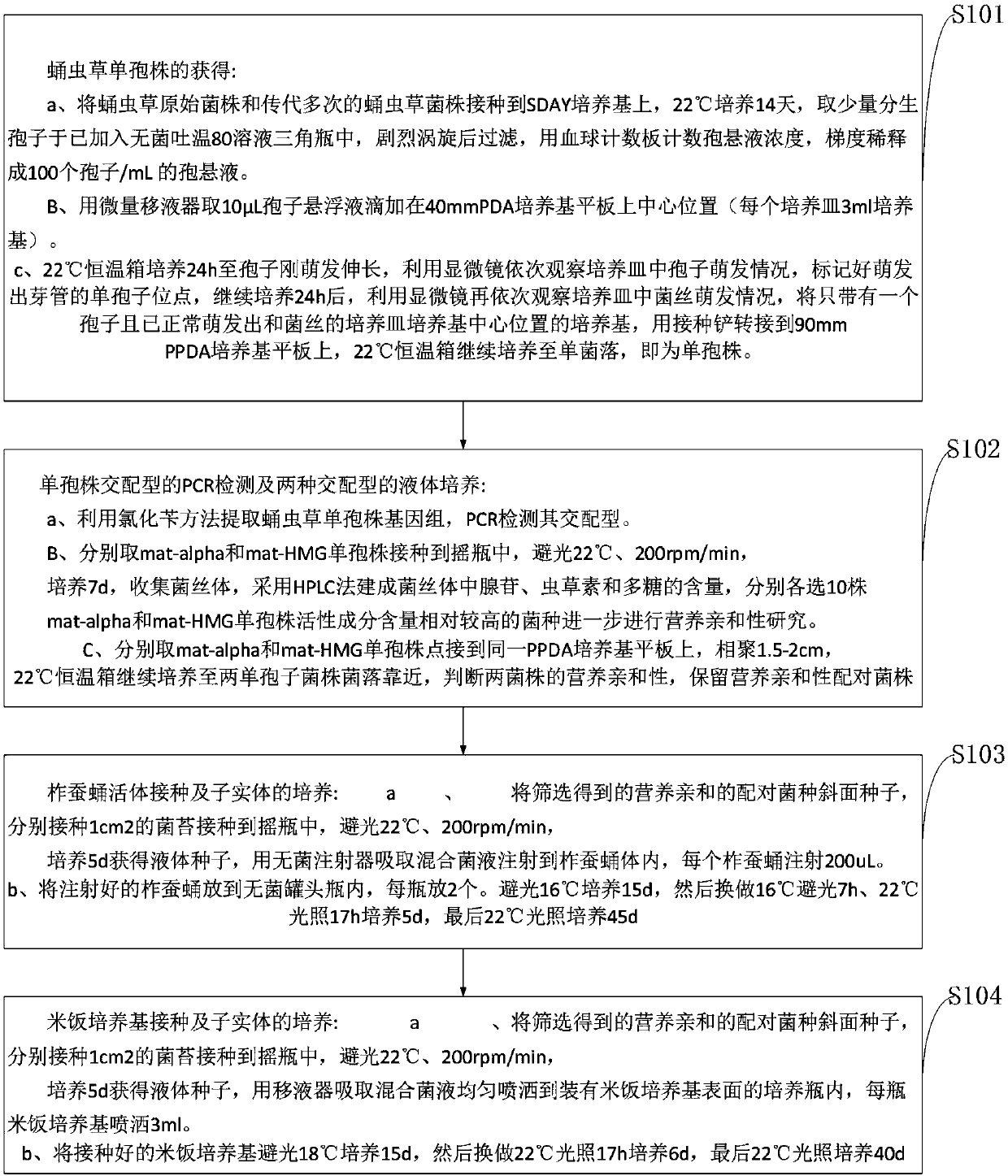
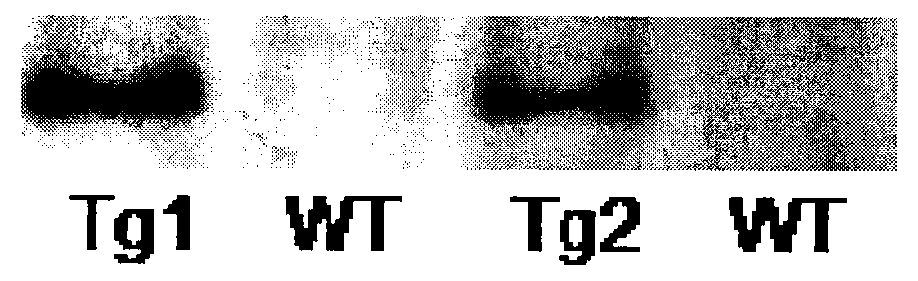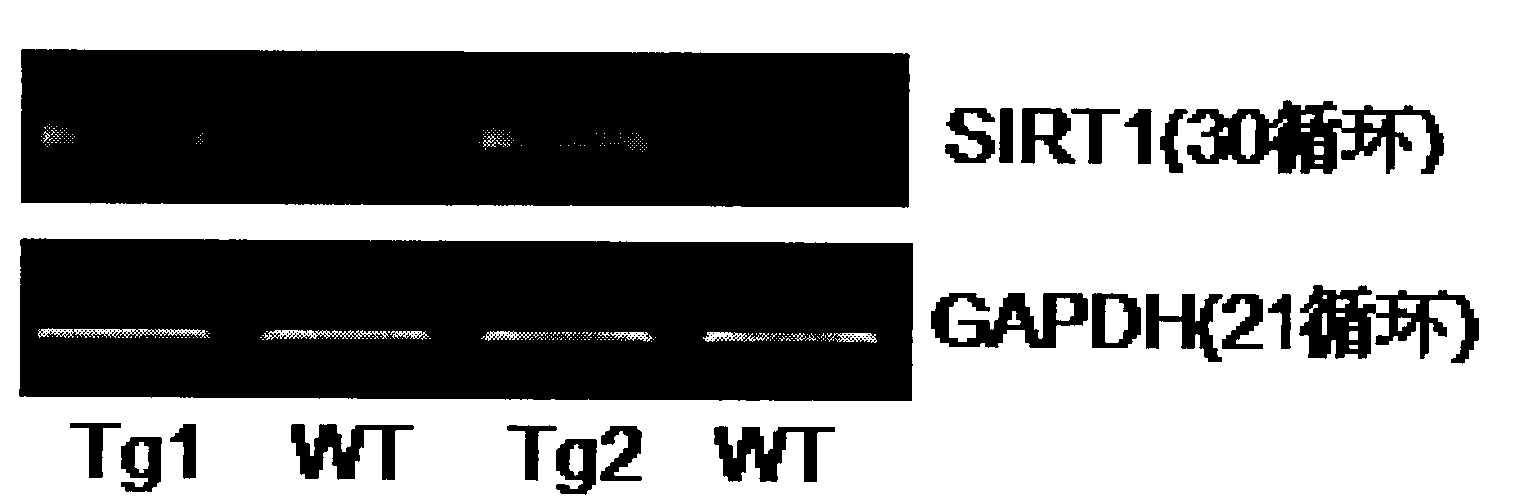Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82 results about "Mating type" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mating types are molecular mechanisms that regulate compatibility in sexually reproducing eukaryotes. They occur in isogamous and anisogamous species. Depending on the group, different mating types are often referred to by numbers, letters, or simply "+" and "−" instead of "male" and "female", that refer to "sexes" or differences in size between gametes. Syngamy can only take place between gametes carrying different mating types.
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and identification of inhibitors of these interactors
InactiveUS6057101AEfficient screeningLess experimentally significant and specific indicationMaterial nanotechnologyFungiDiseaseBinding site
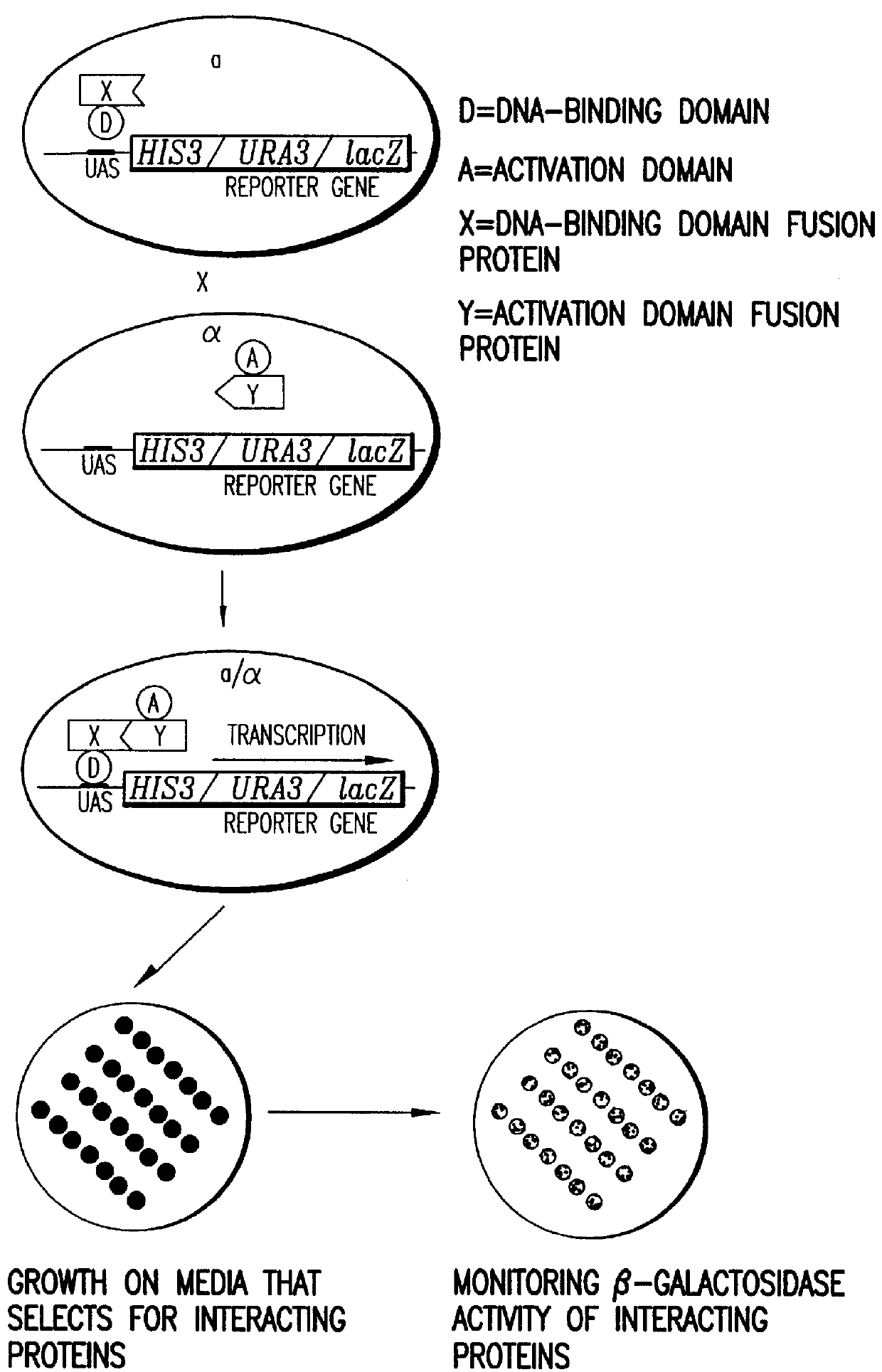
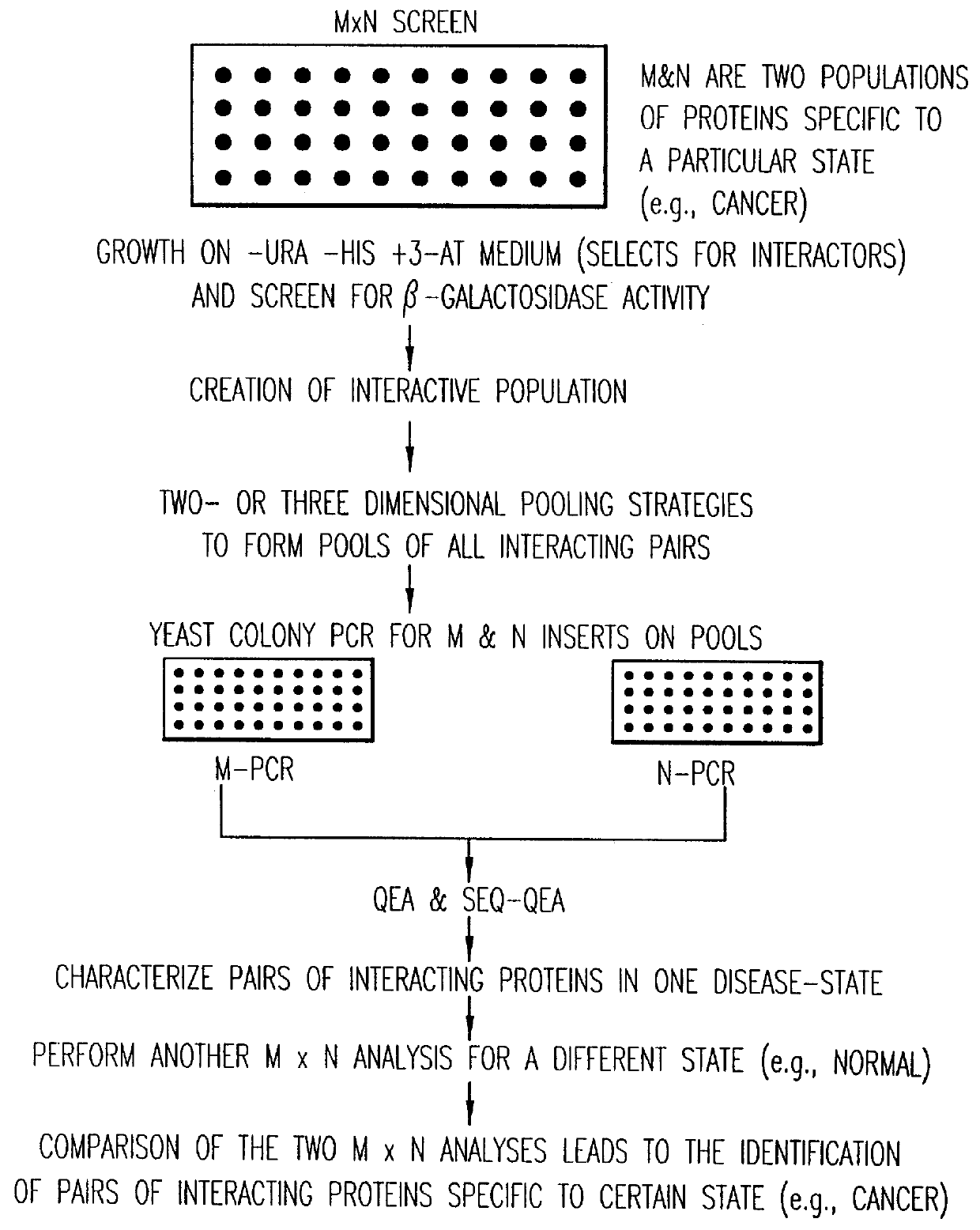
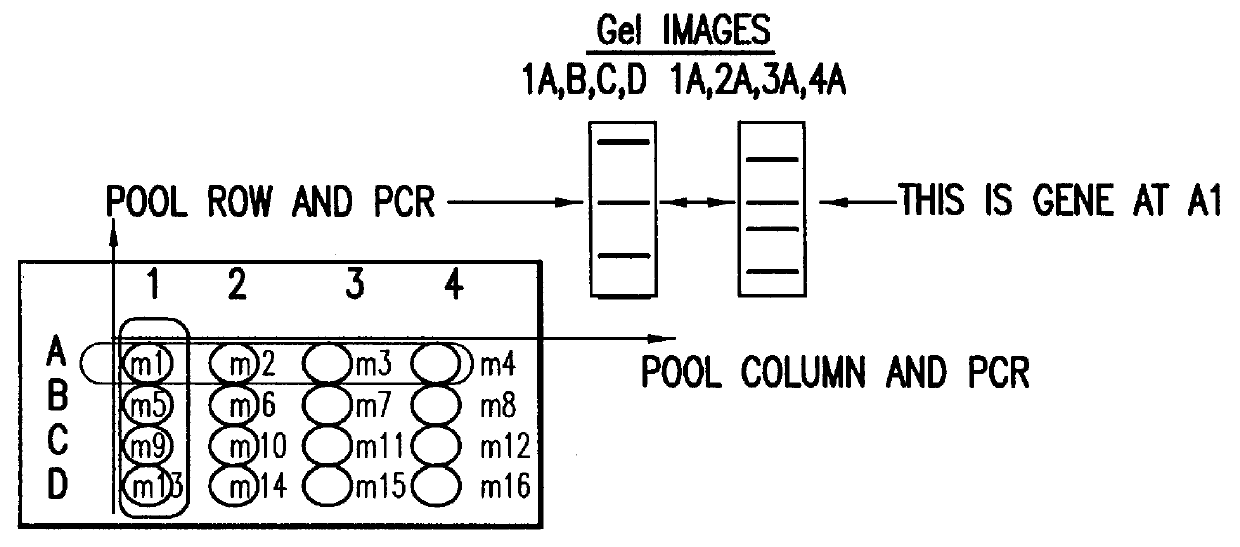
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors. Further, information-processing methods and systems are described. These methods and systems provide for identification of the genes coding for detected interacting proteins, for assembling a unified database of protein-protein interaction data, and for processing this unified database to obtain protein interaction domain and protein pathway information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
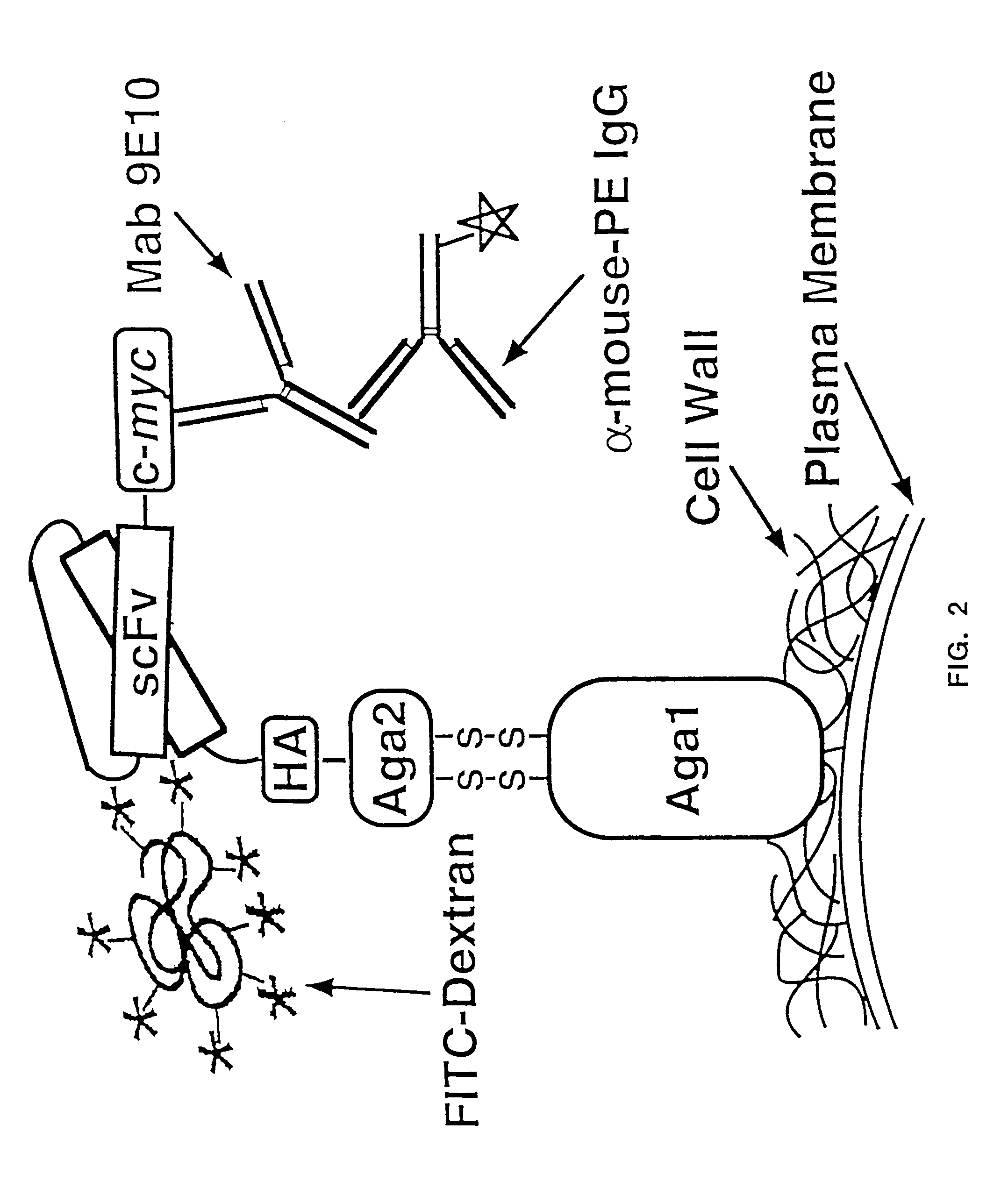
Yeast cell surface display of proteins and uses thereof
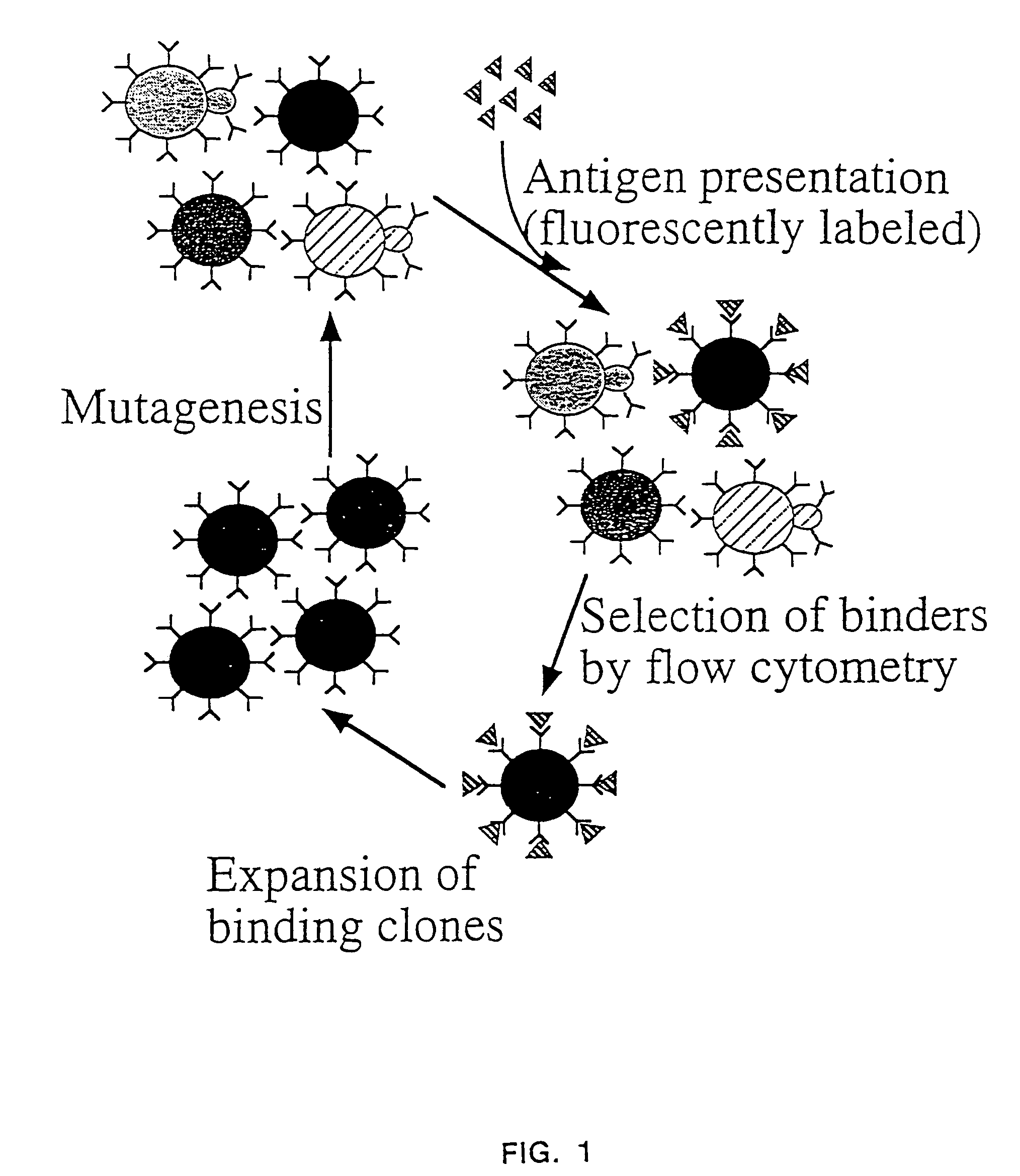
InactiveUS7465787B2Improve the level ofEnhance level of cell surface expression of cellFungiDirected macromolecular evolutionSurface displayAgglutinin-B
The present invention provides a genetic method for tethering polypeptides to the yeast cell wall in a form accessible for binding to macromolecules. Combining this method with fluorescence-activated cell sorting provides a means of selecting proteins with increased or decreased affinity for another molecule, altered specificity, or conditional binding. Also provided is a method for genetic fusion of the N terminus of a polypeptide of interest to the C-terminus of the yeast Aga2p cell wall protein. The outer wall of each yeast cell can display approximately 10 protein agglutinins. The native agglutinins serve as specific adhesion contacts to fuse yeast cells of opposite mating type during mating. In effect, yeast has evolved a platform for protein-protein binding without steric hindrance from cell wall components.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance
InactiveCN102204465AEffectively guide reasonable allocationMeet vaccination needsHorticulture methodsDiseaseTeliospore
The invention relates to the technical field of plant disease resistance, and discloses a method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance. The method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance comprises the steps of: firstly carrying out separate culture to obtain sugarcane smut alien mating type (+or -) haplospores by using a trace amount of fresh sugarcane smut teliospore; and then carrying out the steps of culture enlargement of strains, inoculation, investigation of disease incidence, resistance evaluation and the like. The method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance has the outstanding substantial characteristics and is improved remarkably as follows: 1. the inoculation need can be met by separate culture of only an extremely trace amount of sugarcane smut teliospore, and the working amount is low; 2. the alien mating type strains can be stored at an ultra-low temperature and can be used as the inoculation source after subjected to activation and enlarge culture without repeated taking of strains and separate culture for each time; 3. in the method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance, the resistance identifying period is short, and the sensitivity is high; and 4. the method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance can also be used for identifying the type of smut biological strains resisted by the tested varieties, and effectively guiding smut-resisting seed breeding of sugarcane and reasonable collocation of varieties in a sugarcane area.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST +1
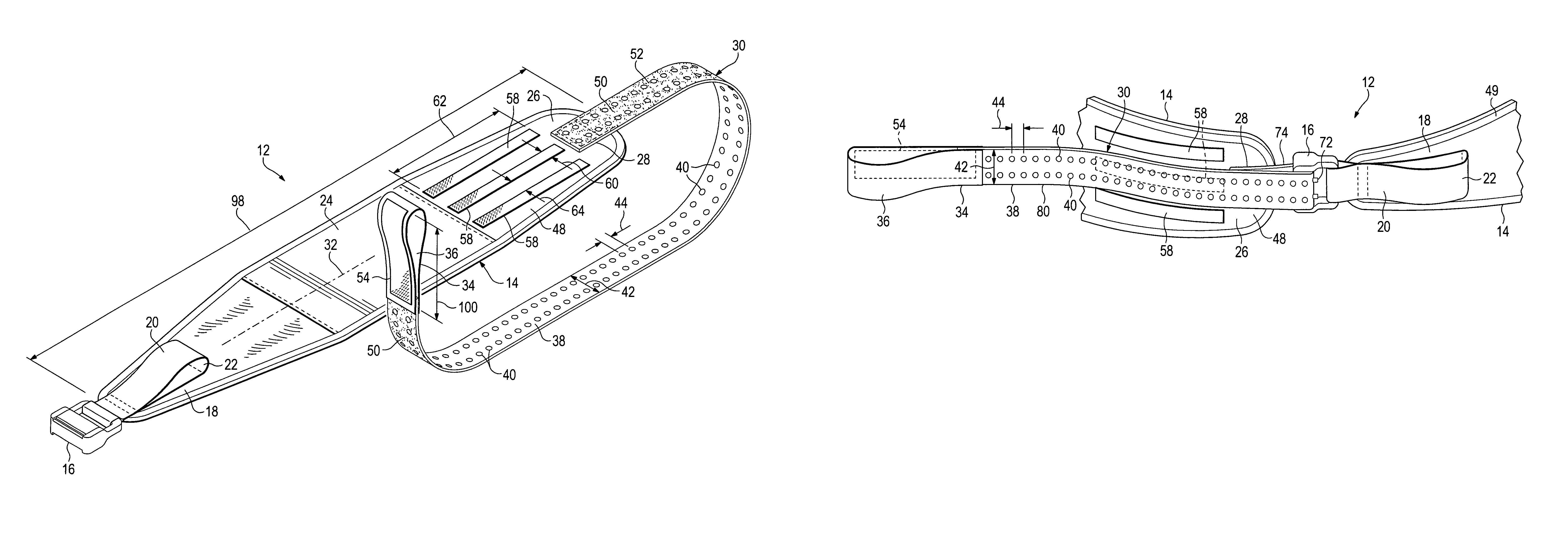
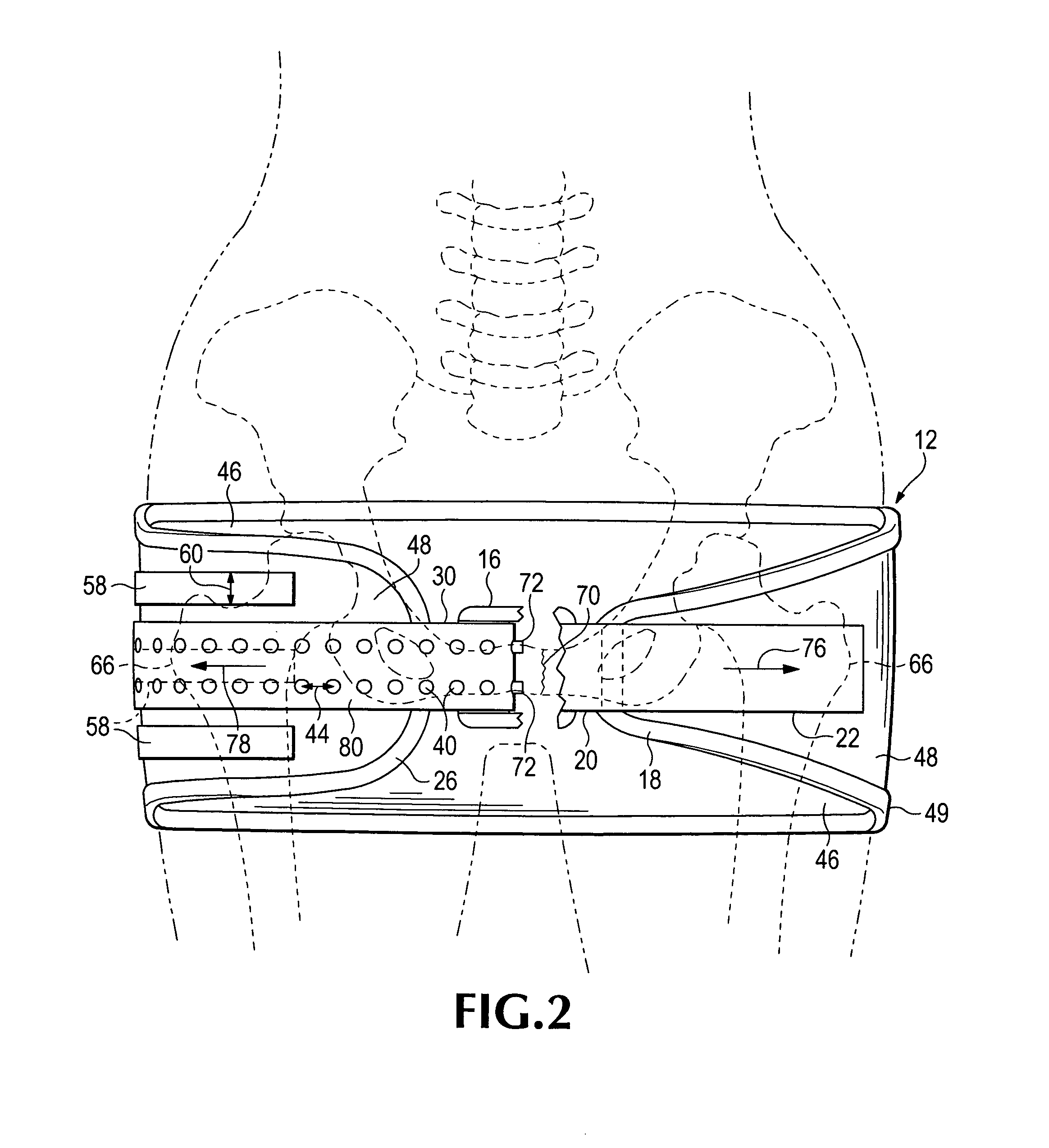
Emergency stabilization of a fractured pelvis
ActiveUS8192383B2Reduce fracturesStabilizing pelvisOrthopedic corsetsGarment beltsPelvic slingEffective length
A hip-girdling pelvic sling device for maintaining a desired amount of tension surrounding a person's hips and pelvis to securely support and stabilize a pelvis that has been fractured. Areas of mating types of fastener material such as mating hook-bearing fastener material and loop pile fastener material are arranged on the device to enable a strap to be secured at various effective lengths to provide a wide range of adjustability to make the device useful for persons of various sizes.
Owner:THE SEABERG
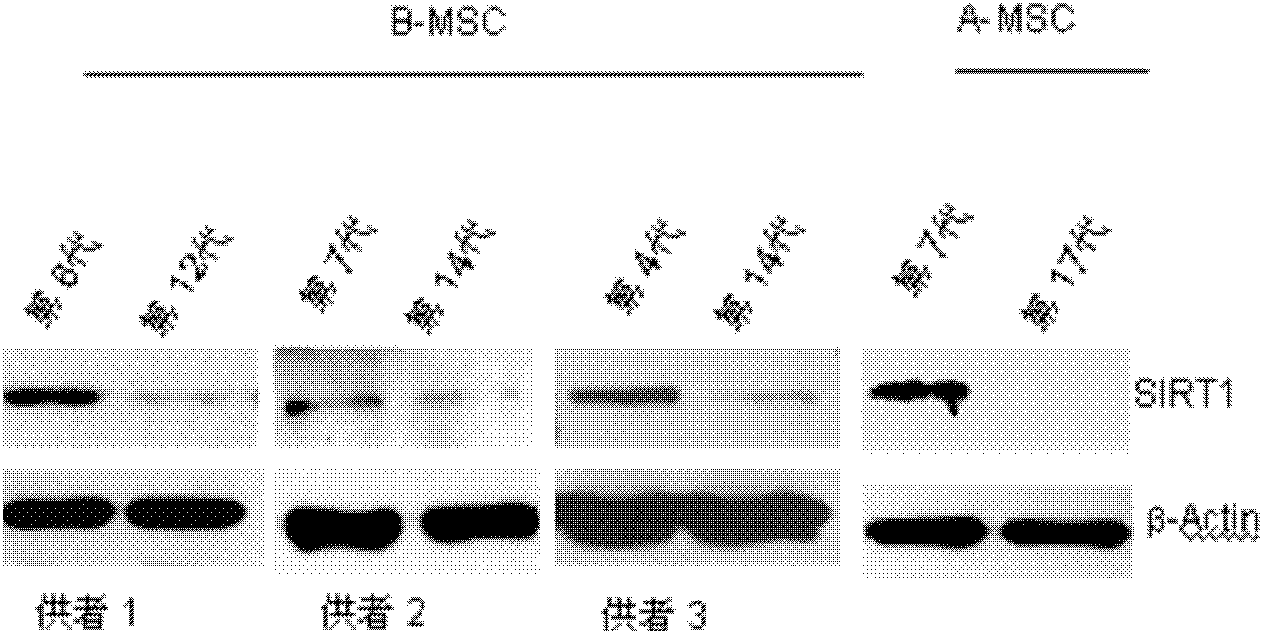
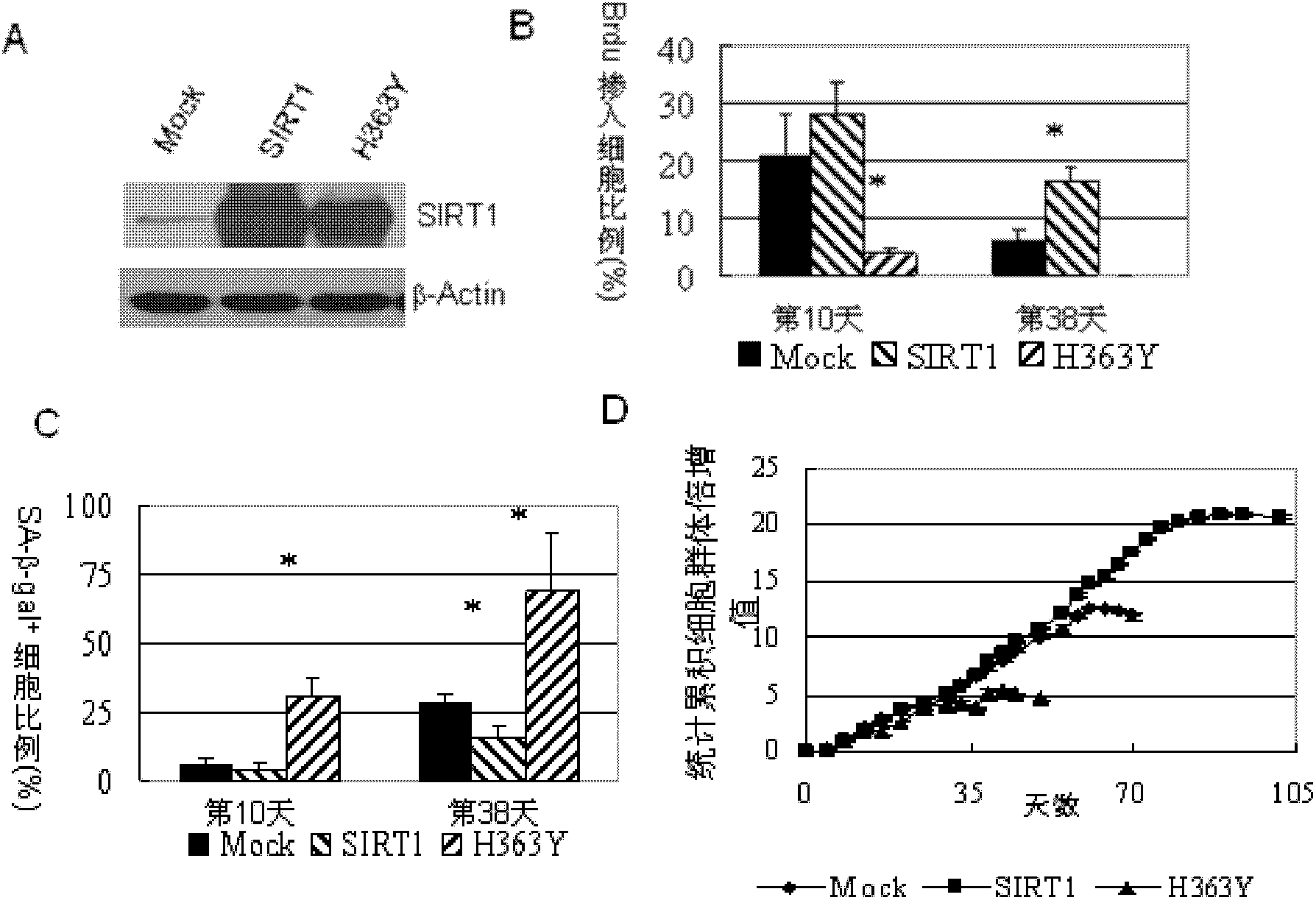
Application of protein acetylation enzyme SIRT1 (Silent Mating type Information Regulation 2Homolog1) in promoting proliferation and delaying senility of mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN102382801APromote proliferationReduce proliferationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGenetic engineeringIn vitro proliferationMesenchymal stem cell proliferation
The invention discloses an application of protein acetylation enzyme SIRT1 (Silent Mating type Information Regulation 2Homolog1), namely promoting proliferation and delaying senility of mesenchymal stem cells. The experimental result shows that the SIRT1 is needed by the in vitro proliferation of the mescenchymal stem cells, and the condition is verified by MSC (mesenchymal stem cells from marrow) and MSC from fat, and the proliferation and the senility of the MSC can be regulated by regulating the expression level of SIRT1 in the MSC. The invention has very important significances on the determination of the regulation mechanism of the proliferation and the senility of the MSC, the prolonging of the service life of the MSC, and the histocyte substitution and repairing treatment based on the MSC, and is broad in application prospect.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
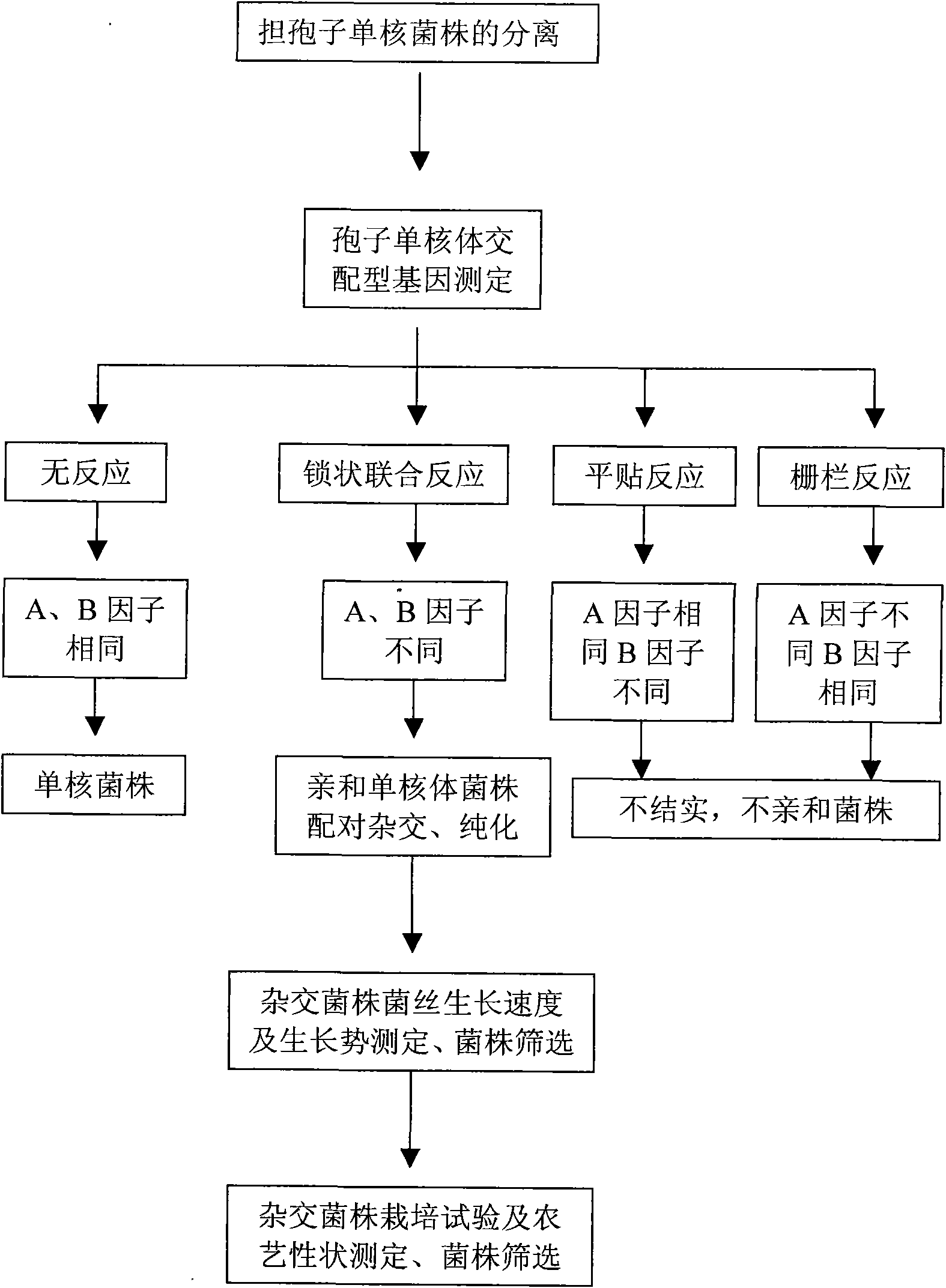
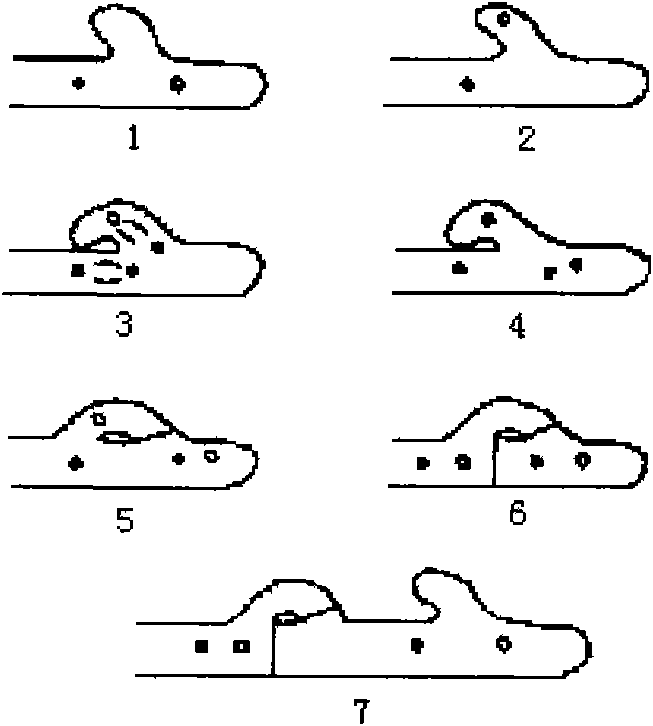
Method for identifying hypsizigus marmoreus mating type gene
InactiveCN101608213AReduced number of contrast screensShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBasidiosporeClamp connection
The invention provides a method for performing mating type gene identification on a basidiospore monocaryon strain which is separated from different hypsizigus marmoreus strains. In the identifying process, in particular application of a flushing reaction, a palisade reaction and transplanting, the method can primarily identify the mating type gene of the hypsizigus marmoreus intuitively and quickly without other instruments and equipment. When the method is applied in cross breeding, the mating type gene of basidiospore monocaryon parent and progeny strains can be identified conveniently so as to improve the purposiveness and the effectiveness of the cross breeding process. The adopted method can shorten the time for identifying the mating type gene for 5 to 10 days, reduce the number of comparing-screening strains by 75 percent theoretically in cross breeding, improve the fecundity, and is more convenient and efficient particularly in application of multiple cross breeding of multiple strains. Then, the method selects the compatible basidiospore monocaryon strain having clamp connection according to the identification result to carry out biparental crossing, and screens hybrid strains according to growth speed, growth potential and economical character index, thereby obtaining stable, high yield and high quality hybrid strains.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Yeast cell surface display of proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090280560A1Effectively mimickedHigh affinityFungiSaccharide peptide ingredientsSurface displayAgglutinin-B
The present invention provides a genetic method for tethering polypeptides to the yeast cell wall in a form accessible for binding to macromolecules. Combining this method with fluorescence-activated cell sorting provides a means of selecting proteins with increased or decreased affinity for another molecule, altered specificity, or conditional binding. Also provided is a method for genetic fusion of the N terminus of a polypeptide of interest to the C-terminus of the yeast Aga2p cell wall protein. The outer wall of each yeast cell can display approximately 104 protein agglutinins. The native agglutinins serve as specific adhesion contacts to fuse yeast cells of opposite mating type during mating. In effect, yeast has evolved a platform for protein-protein binding without steric hindrance from cell wall components. As one embodiment, attaching an scFv antibody fragment to the Aga2p agglutinin effectively mimics the cell surface display of antibodies by B cells in the immune system for affinity maturation in vivo. As another embodiment, T cell receptor mutants can be isolated by this method that are efficiently displayed on the yeast cell surface, providing a means of altering T cell receptor binding affinity and specificity by library screening.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
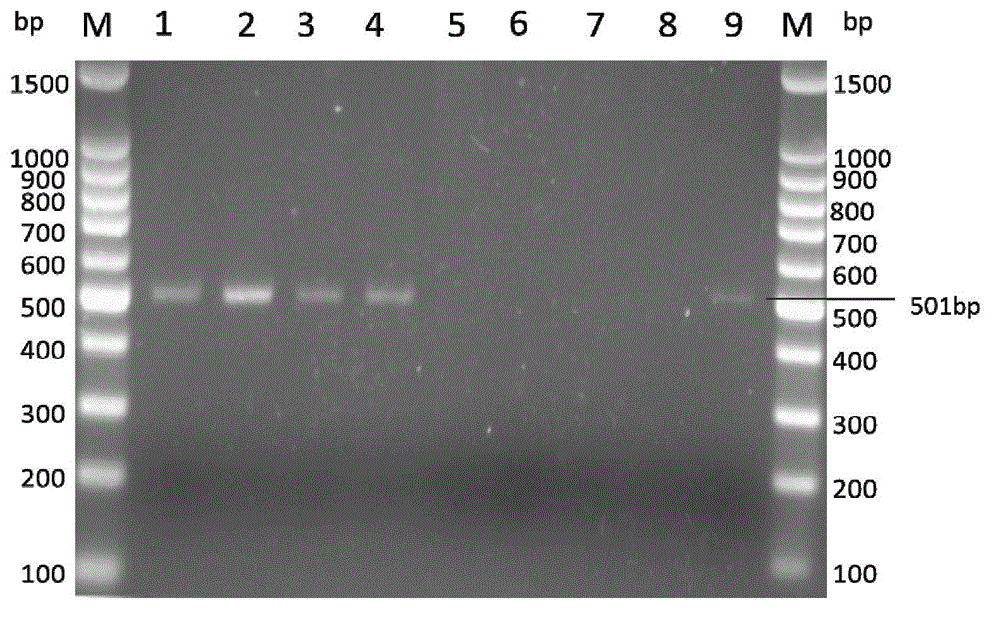
Method for distinguishing mating types of four varieties in black morchella group and primer pair
ActiveCN106282397ASimple methodReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMorchellaMicrobiology
The invention relates to a method for distinguishing mating types of four varieties in black morchella group and a primer pair, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the DNA of a strain to be detected as a template, performing PCR amplification through the primer pair P7-2F / P7-2R or P8-5F / P8-5R to obtain a strain of MAT1-1 mating type of an expected band, performing PCR amplification through the primer pair P10-1F / P10-2R or P10-2F / P10-3R to obtain a strain of MAT1-2 mating type of an expected band, wherein the strain which can be detected by the two expected amplification bands is of two mating types. The four primers can be general to the mating type detection of the four varieties of morchella. A detection result of the method is high in specificity, and the method is stable, reliable and quick, and is applicable to researches on selection, cultivation, mating type genes and system development of strains of the morchella.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
Plutella xylostella sex pheromone directional disruptor
InactiveCN104304247AInterfering with matingInhibition orientationBiocidePest attractantsAlcoholMammal
The invention discloses a plutella xylostella sex pheromone directional disruptor. The directional disruptor is one of the following ingredients: cis-9, trans11-tetradecenoic acetate, cis-9, trans12-tetradecenoic acetate, wherein cis-9, trans11-tetradecenoic acetate and cis-9, trans12-tetradecenoic acetate are mixed in a weight ratio of (12-7): 1; cis-9, trans12- tetradecenoic acetate and cis9- tetradecene-1-alcohol are mixed in a weight ratio of (12-7): 1. The plutella xylostella sex pheromone directional disruptor has advantages of high efficiency, multiple ecological effects, simplicity in preparation, environmental friendliness, safety for mammal and the like, the encountering probability and mating times of male moth and female moth in field can be reduced, and the harm of the plutella on the crucifer can be alleviated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Molecular detection method for rapidly differentiating mating type of Villosiclavavirens
InactiveCN103436605AReduce detection stepsReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesA-DNAGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to a molecular detection method for rapidly differentiating the mating type of Villosiclavavirens. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a mycelium for detection and a tissue sample, extracting the genome DNA of samples for detection through adopting a CTAB process, analyzing through using 0.7% agarose gel electrophoresis, carrying out PCR amplification, recording an electrophoresis result through using a gel imaging system, and utilizing markers to determine the size of a DNA fragment. The detection samples in the invention are Villosiclavavirens conidiophore single-spore strains or ascospore single-spore strains or sclerotes, the PCR amplification is multi-PCR amplification, two pairs of amplimers used in a multi-PCR amplification system comprise Vm1-F / Vm1-R and Vm2-F / Vm2-R, Vm1-F is represented by SEQIDNO.1, Vm1-R is represented by SEQIDNO.2, Vm2-F is represented by SEQIDNO.3 and Vm2-R is represented by SEQIDNO.4.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Primers special for identification of mating type determining genes of morchella and fruiting capability prediction method
ActiveCN106282370AAvoid lostMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular identificationAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular identification, and particularly relates to primers special for identification of mating type determining genes of morchella and a fruiting capability prediction method. The primers and the method aim at solving the technical problem that whether a morchella strain has fruiting capability or not is difficult to judge before planting. According to the technical scheme for solving the technical problem, the primers special for identification of two mating type genes of morchella are invented for the first time. By means of the primers and the method, the fruiting capability of morchella can be confirmed before cultivation, and unnecessary losses caused when morchella has no fruiting capability can be avoided.
Owner:四川省食用菌研究所
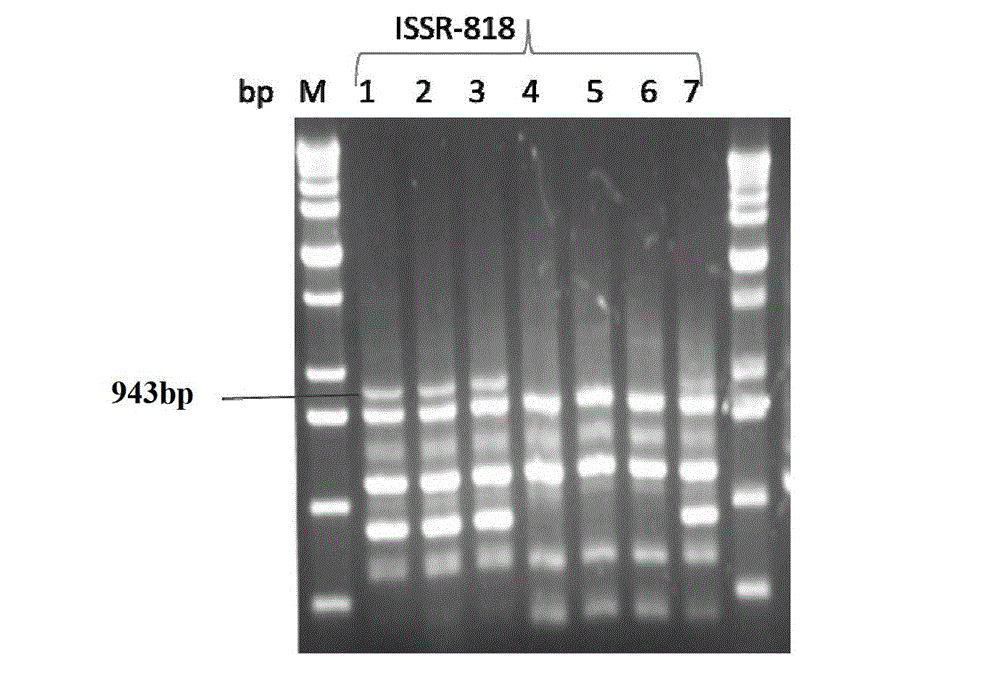
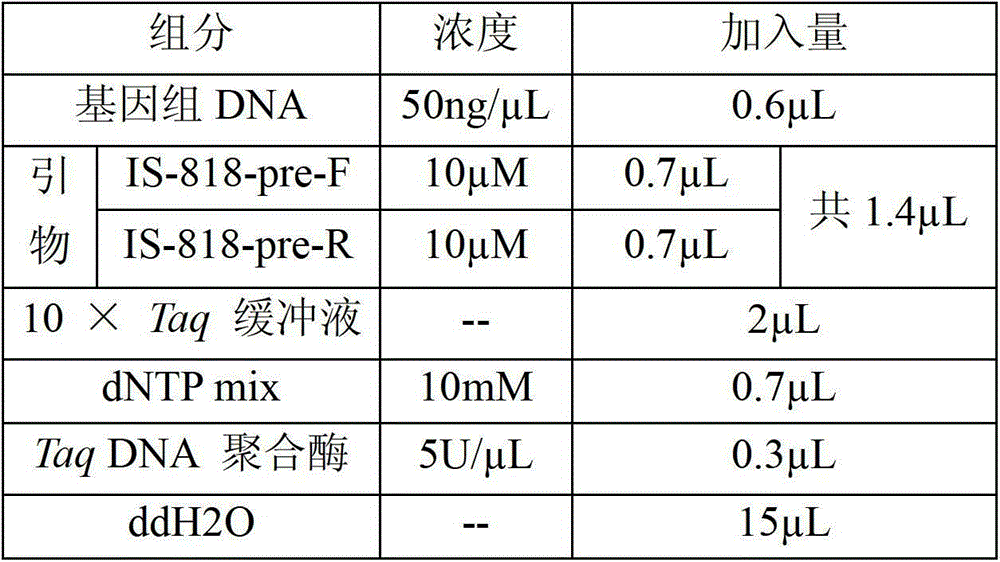
Method for identifying or assisting in identifying mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-818 thereof
ActiveCN103184280AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEtioplastsDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating type of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-818 thereof. The method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of the Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons comprises the following steps: respectively taking the genome DNA of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using PCR primer pairs shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2; detecting the size of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprise 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments or do not comprise 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are identical; and if the PCR product of one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprises 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments and the PCR product of the other one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified does not comprise 800 to 1,000 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
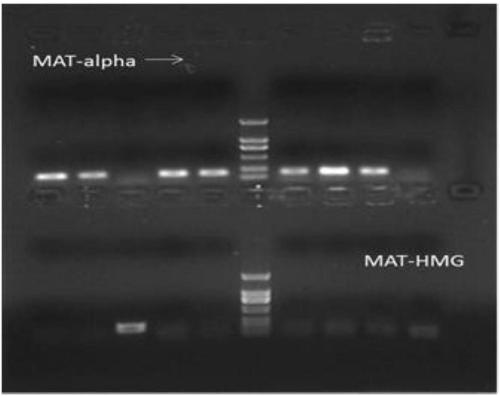
Method for rejuvenating cordyceps militaris strains and increasing sporocarp yield by mating type
ActiveCN103609331AIncrease productionOvercoming the problem of rapidly decreasing yieldHorticultureCordycepsSpore
The invention relates to a method for rejuvenating cordyceps militaris strains and increasing sporocarp yield by a mating type. The method includes performing single spore isolation on cordyceps militaris conidiospores to obtain two different mating-type single-spore strains, and inoculating the mating-type single-spore strains to tussah pupas or a rice medium according to a specific proportion so as to obtain high-yield sporocarps; inoculating the strains subcultured for multiple times to the tussah pupas or the rice medium according to specific proportional quantities of mat-alpha and mat-HMG, wherein mixed strains relatively subcultured for multiple times have high sporocarp yield.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
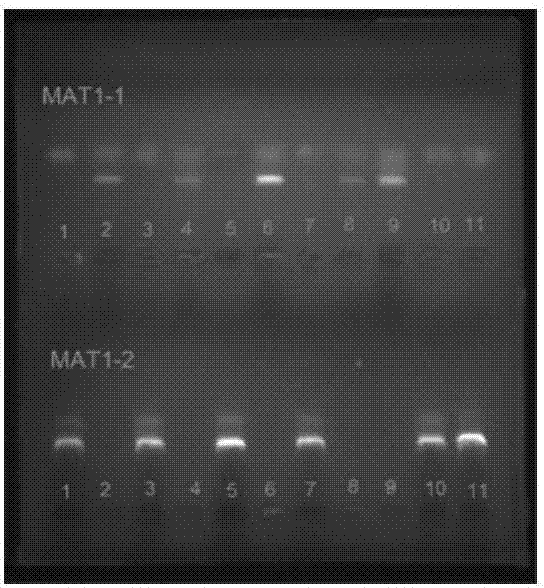
Method for authenticating mating type of eleven varieties in black morchella group
ActiveCN107151698ASimple methodReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhylogenetic studyBiology
The invention provides a method for authenticating the mating type of eleven varieties in a black morchella group. The method includes the steps of firstly, the strain total DNA of a to-be-authenticated strain is extracted to serve as the PCR amplification template; secondly, a primer pair MAT1-1L / MAT1-1R is used to perform PCR amplification to obtain an expected-band strain which indicates that the strain contains the MAT1-1 mating type, a primer pair MAT1-2L / MAT1-2R to perform PCR amplification to obtain an expected-band strain which indicates that the strain contains the MAT1-2 mating type, and the fact that the strain only contains a male parent or a female parent is indicated if only the strain of one mating type is detected, and the strain is poor in fruiting ability or incapable of fruiting; the strains with two expected amplification bands capable being detected have the male parent mating type and the female parent mating type and have fruiting ability. By the primers and detection method for detection the mating type genes of morchella, the high yield and stable yield reliability during morchella cultivation can be increased greatly. The molecular marker of the mating type genes is simple, convenient, easy to operate and applicable to the morchella mating type gene authentication and cultivation, strain breeding, species identification, sexual reproduction evolution and phylogenic studies.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and indentification of inhibitors of these interactors
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Fermentative production of lycopene by blakeslea trispora
InactiveUS20050059134A1Reduce usageIncrease carotenoid contentFungiFermentationBlakeslea trisporaCell culture media
The invention relates to Blakeslea trispora (B. trispora) strains producing at least 0.3 g / l lycopene, when co-cultivated for at least three days with a suitable strain of Blakeslea trispora of the opposite mating type in a suitable medium in the absence of an exogenous cartenogenesis inhibitor, to a natural efficient production process of lycopene by these strains, to a growth medium highly suited for this process and to an isolation process suited for any carotenoid compound.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for rapidly screening hybrid strains of straw mushroom by using molecular marker
InactiveCN103060445AAccelerate research and development workSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyMushroom
The invention relates to a method for rapidly screening hybrid strains of a straw mushroom by using a molecular marker. The method comprises the following steps: (1) synthesis of a primer; (2) mycelium culture of the straw mushroom; (3) determination of the type of a mating type gene of the mononuclear strain; (4) hybridization test of the straw mushroom; and (5) PCR amplification and determination. Compared with methods like conventional morphological detection, antagonism test and fruiting test, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, a short period of detection time and high accuracy; the method can use the molecular marker of the mating type gene to screen the hybrid strains, which is beneficial for crossbreeding of the straw mushroom, so research and development on a novel variety of the straw mushroom are accelerated, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method of using anti-sex pheromone to interfere with mating to prevent and control the green Lygus bug
ActiveCN102273390AHigh activityRaw materials are easy to getBiocideAnimal repellantsLygus hesperusNatural enemies
The invention discloses a method for preventing and treating lygus lucorum by using adverse sex pheromone to interfere mating, belonging to the field of the bionic prevention and treatment technology. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for integrated control of lygus lucorum; the pheromone interferes and stops the mating of lygus lucorum after being released by a pheromone slowly releasing device so as to reduce the mating rate by more than 60%, thus realizing the effect of reducing descendants of lygus lucorum. The method disclosed by the invention has high specifity, causes no influence to natural enemies, is nontoxic, free of residue and environment-friendly, causes no resistance to drugs, is easy to get raw materials of the releasing device, simple and operable, hardly influenced by natural conditions, and has high mating interference capability and long effectiveness duration time.
Owner:QUANZHOU LVPUSEN BIOTECH CO LTD
Rapid identification method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid
InactiveCN102732620AAccurate identificationGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementRapid identificationBiology
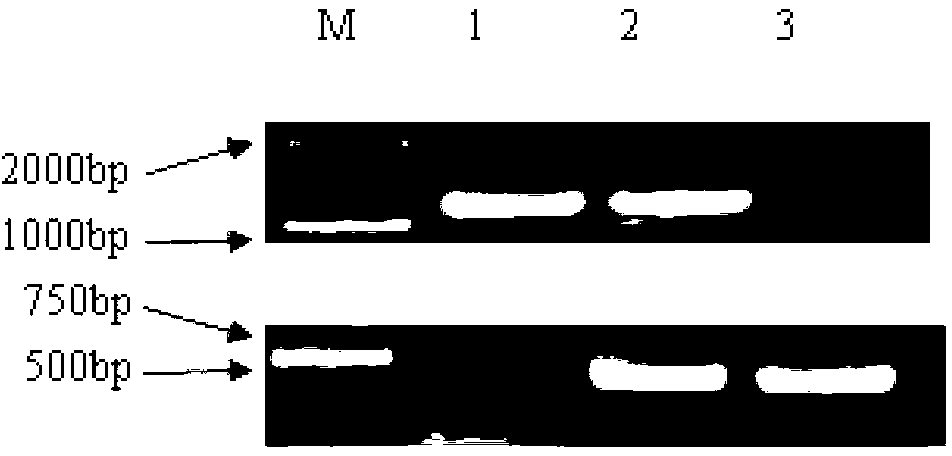
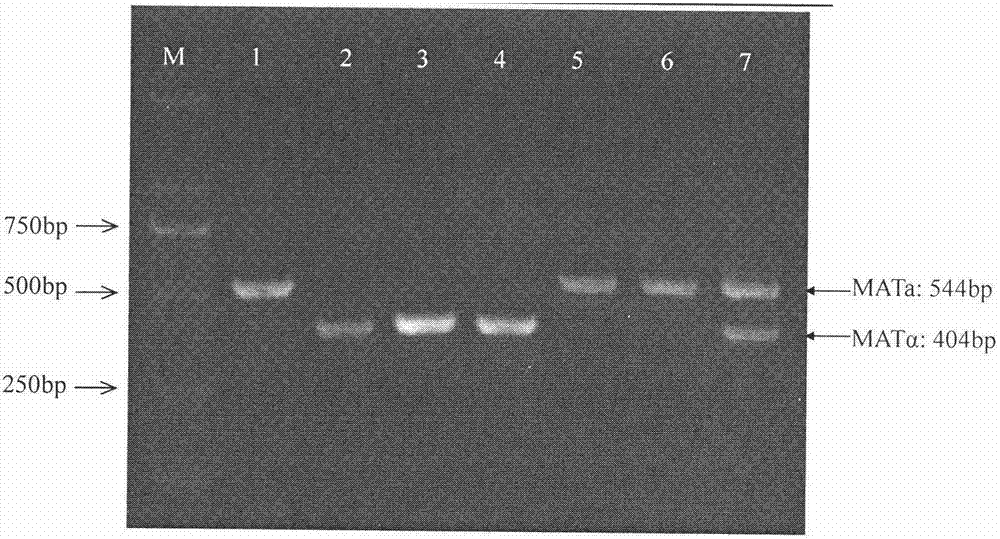
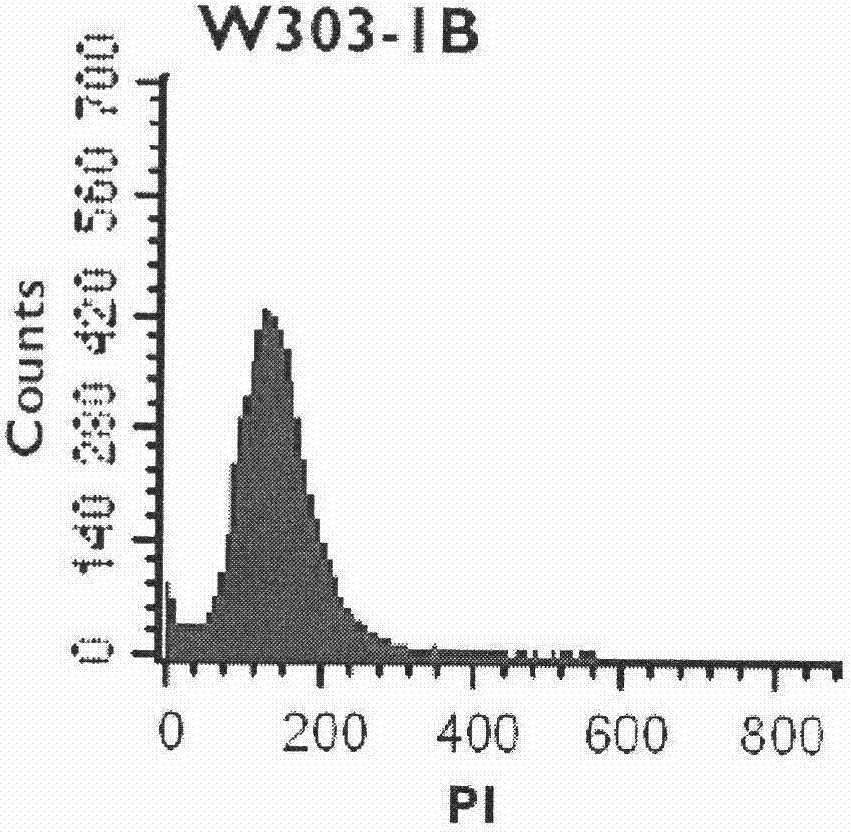
The invention discloses a rapid identification method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid, and belongs to the field of microbial identification. The invention adopts an experimental strategy combining colony PCR and flow cytometry, and has high efficiency, accuracy, and good reproducibility. Compared with a traditional haploid identification method (long time cultivation, staining microscopy), the method of the invention can achieve experimental results in a very short period of time, so as to greatly reduce the workload and the working time, and obtain more reliable experimental results. Moreover, the method of the invention can simultaneously identify mating type ( MATa / MAT alpha) of haploid strains, and can minimize influence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid standard bacteria on the experimental results. In the invention, MAT PCR is not only an identification method for mating types of strains, but also much of a primary judgment means for ploidy identification, and can fast and conveniently exclude the interference of some strains.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of SIRT (Silent Mating Type Information Regulation 2 Homolog 1) to prepare medicine used for regulating down the expression of cyclin D1
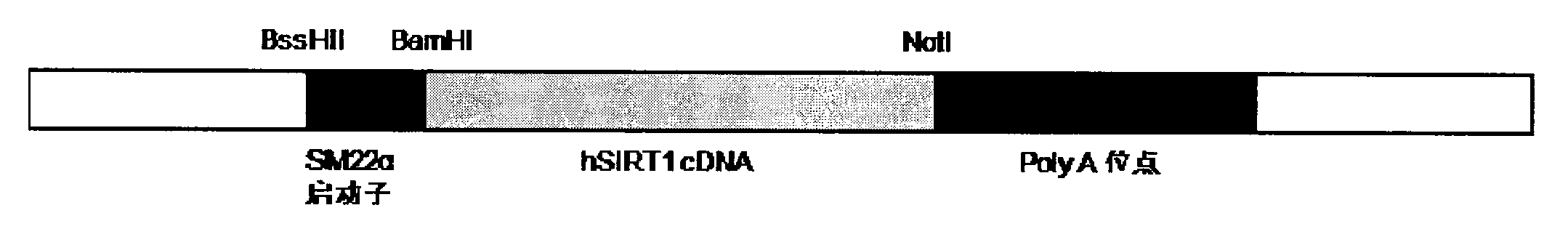
InactiveCN102008718AInhibition formationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCyclin D1Viral vector
The invention relates to the application of SIRT1 (Silence Information Regulator Tuin1) to prepare medicine used for regulating down the expression of cyclin D1. Particularly, the medicine is of a delegiert protein type, and the form of the medicine can be any form suitable for the application of protein medicine. The medicine is a reorganization nucleic acid construction body capable of expressing SIRT1 protein. The expression carrier of the medicine can be any expression carrier which is suitable for gene therapy and comprises a virus carrier, such as a reorganization retrovirus carrier, an adenovirus carrier, an adeno-associated virus carrier, a herpes simplex virus carrier, a vaccinia virus carrier, and the like and a nonviral carrier, such as a bacteriophage carrier, a replicon carrier, and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for identifying mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and special primer pair IS-879b thereof
InactiveCN103276070AShorten identification timeSimplify the identification stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and a special primer pair IS-879b thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking genomes DNA of two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified as templates respectively, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using a PCR primer pair consisting of two single chains DNA shown as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2, and detecting the magnitude of the obtained PCR products, wherein if the PCR products of both the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified contain or do not contain DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are identical; and if the PCR product of one protoplasted monokaryon contains the DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp and the PCR product of the other one does not contain the DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying or assisting in identifying mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-873 thereof
ActiveCN103184281AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEtioplastsDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons and special primer pairs IS-873 thereof. The method for identifying or assisting in identifying the mating types of the Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons comprises the following steps: respectively taking the genome DNA of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on by using PCR primer pairs shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2; detecting the size of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments or do not comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are identical; and if the PCR product of one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified comprises 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments and the PCR product of the other one of the two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons to be identified does not comprise 500 to 600 bp of DNA segments, the mating types of two Lepista sordid protoplast monokaryons are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
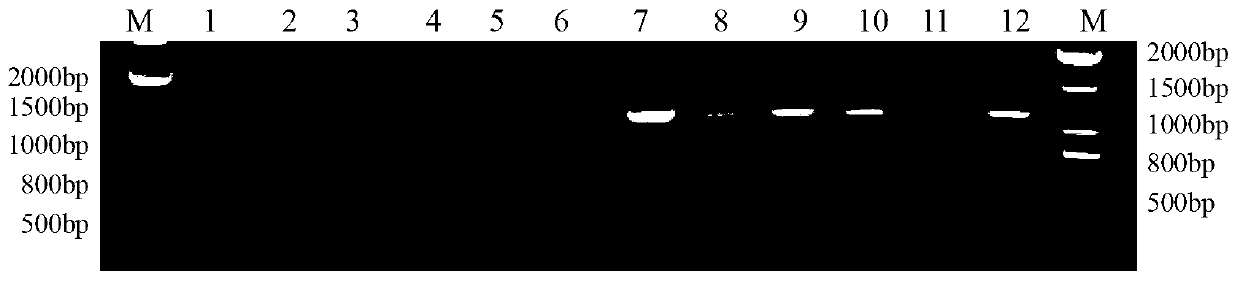
Monocaryon mating type primer set for identifying Shenxiang 215 strains and substantive derivative varieties of shiitake mushrooms, identifying method and application
ActiveCN110029191AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesElectrophoresisGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a monocaryon mating type primer set for identifying Shenxiang 215 strains and substantive derivative varieties of shiitake mushrooms, an identifying method and an application,and relates to the technical field of edible mushroom molecular marked auxiliary breeding. The monocaryon mating type primer set specifically comprises 4 pairs of primers. The identifying method specifically comprises the steps of culturing mycelia, performing quick preparation of genomic DNA, performing mating type PCR detection, and determining the result of electrophoresis detection. Compared with a conventional monocaryon mating type identification method, the identifying method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that detection time is shoter and accuracy is higher; and throughthe adoption of the identifying method disclosed by the invention, the identifying time can be greatly shortened, the false detection rate can be reduced, and dicaryon elimination can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for breeding cordyceps militaris by hybridizing with ascospore on basis of molecular biological technology
InactiveCN107493979AGenetically diverseImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySterile environment
The invention relates to a method for breeding cordyceps militaris by hybridizing with ascospore on the basis of a molecular biological technology. The method specifically comprises the following steps: inducing and isolating cordyceps militaris monospores in a sterile environment and culturing to form colonies; using a PCR technology for detecting mating type genes MAT1-1-1, MAT1-1-2 and MAT1-2-1 of the colonies formed by the isolated monospores; selecting the colonies formed by the monospores containing the mating type genes MAT1-1-1 and MAT1-1-2 but not containing MAT1-2-1 and the colonies formed by the monospores containing the mating type gene MAT1-2-1 but not containing MAT1-1-1 and MAT1-1-2; respectively taking mycelia appropriate in size to be placed in a culture solution for dark culturing; inoculating an appropriate concentration of combination-cultured bacteria solution into an artificial culture medium of cordyceps militaris; culturing for a period of time to grow a new variety of cordyceps militaris sporophore from the artificial culture medium. The new variety of cordyceps militaris cultured by the method is easy to obtain relatively good yield and content of active substances of sporophores; a combination capable of stably producing high-quality cordyceps militaris sporophores can be obtained by counting the yield of sporophores and active substances cultured by different combinations; the method is relatively short in cycle and relatively small in workload, and is an efficient method for breeding cordyceps militaris.
Owner:CHANGDE YANDI BIOTECH LTD CO
Method for identifying agaricus bisporus homonuclear sterile monospore strain and mating type thereof and primer
ActiveCN108611435AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAgaricusEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for identifying an agaricus bisporus homonuclear sterile monospore strain and a mating type thereof and a primer. The method comprises the following steps: extractinggenome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of agaricus bisporus, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a primer ABA1F1 and a primer ABA1R1, carrying out enzyme digestion on the obtained PCR amplification product by using an incision enzyme, and detecting an enzyme digestion product through 1-2% agarose gel electrophoresis; if a DNA fragment ABH1 obtained through amplificationwith a specific primer can only be subjected to incision enzyme digestion of an A<+> factor, judging that the strain is a mating type of the A<+> factor of a homonuclear sterile monospore strain; ifthe DNA fragment ABH1 obtained through amplification with the specific primer can only be subjected to incision enzyme digestion of an A<-> factor, judging that the strain is a mating type of the A<->factor of the homonuclear sterile monospore strain. The method disclosed by the invention is applied to identification on agaricus bisporus homonuclear sterile monospore strains and mating types thereof, and has the advantages of being short tin time, simple and convenient to operate, high in precision, high in mushroom yield and low in cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting clamp connection in edible fungi mating type research
InactiveCN103389306ANormal growthReduce in quantityMaterial analysis by optical meansExperimental researchClamp connection
The invention relates to a method for detecting clamp connection in edible fungi mating type research. The method comprises the steps of preparing a special culture medium; sterilizing the culture medium; separately filling the culture medium into a disposable flat plate by using a liquor separator; closely and pairwise inoculating tested mononuclear strains to the center of the flat plate, placing in a culture room at temperature of 25-26 DEG C for culture; observing whether the clamp connection exists in a hypha growth area or not after 7-8 days. The method disclosed by the invention can very accurately judge whether the clamp connection exists or not, thereby enlarging the confidence interval of experimental research; the method disclosed by the invention is easy and convenient to operate, omits the complex steps of selecting hypha in a junction area, culturing the hypha, inserting slices and carrying out microscopic examination on the hypha inserted with slices in the conventional method, reduces the anthropogenic influence factors in a test to minimum, saves the time and has good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method and specific primer pairs for authenticating Morchella importuna mating types
ActiveCN106282396AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesElectrophoresisMorchella
The invention relates to a method and specific primer pairs for authenticating Morchella importuna mating types, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The primer pairs comprise the specific primer pair P8-4F / P8-4R for detecting the mating type MAT1-1 and the specific primer pair P6-1F / P6-1R for detecting the mating type MAT1-2. The method includes the steps that strain DNA is extracted, and PCR amplification is carried out with the two primer pairs; if expected bands can be obtained in all times of electrophoresis detection, the strain contains two kinds of mating type genes and is an effective cultivation strain; if only one amplified band can be detected, the strain contains only one mating type and can not be used for cultivation. The detection result is high in specificity, detection is stable, reliable and fast, and the method and the specific primer pairs are suitable for research on the aspects of Morchella strain breeding, cultivation, mating type genes and phylogeny.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
Pharmaceutical Composition Having Anti-Aging Properties against High-Glucose
InactiveUS20180318199A1Extend your lifeIncreased proliferationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSenescence-associated beta-galactosidasePresent method
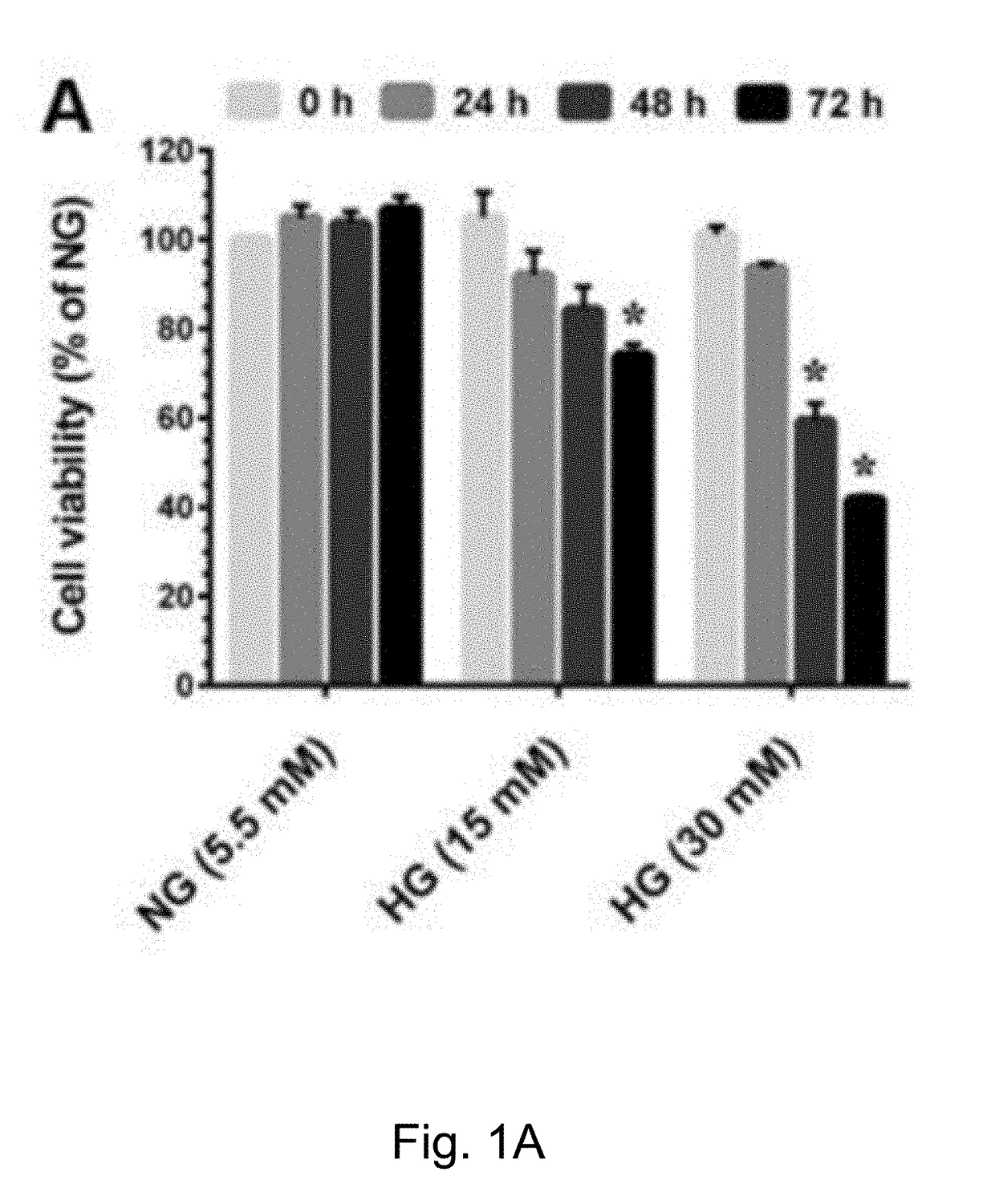
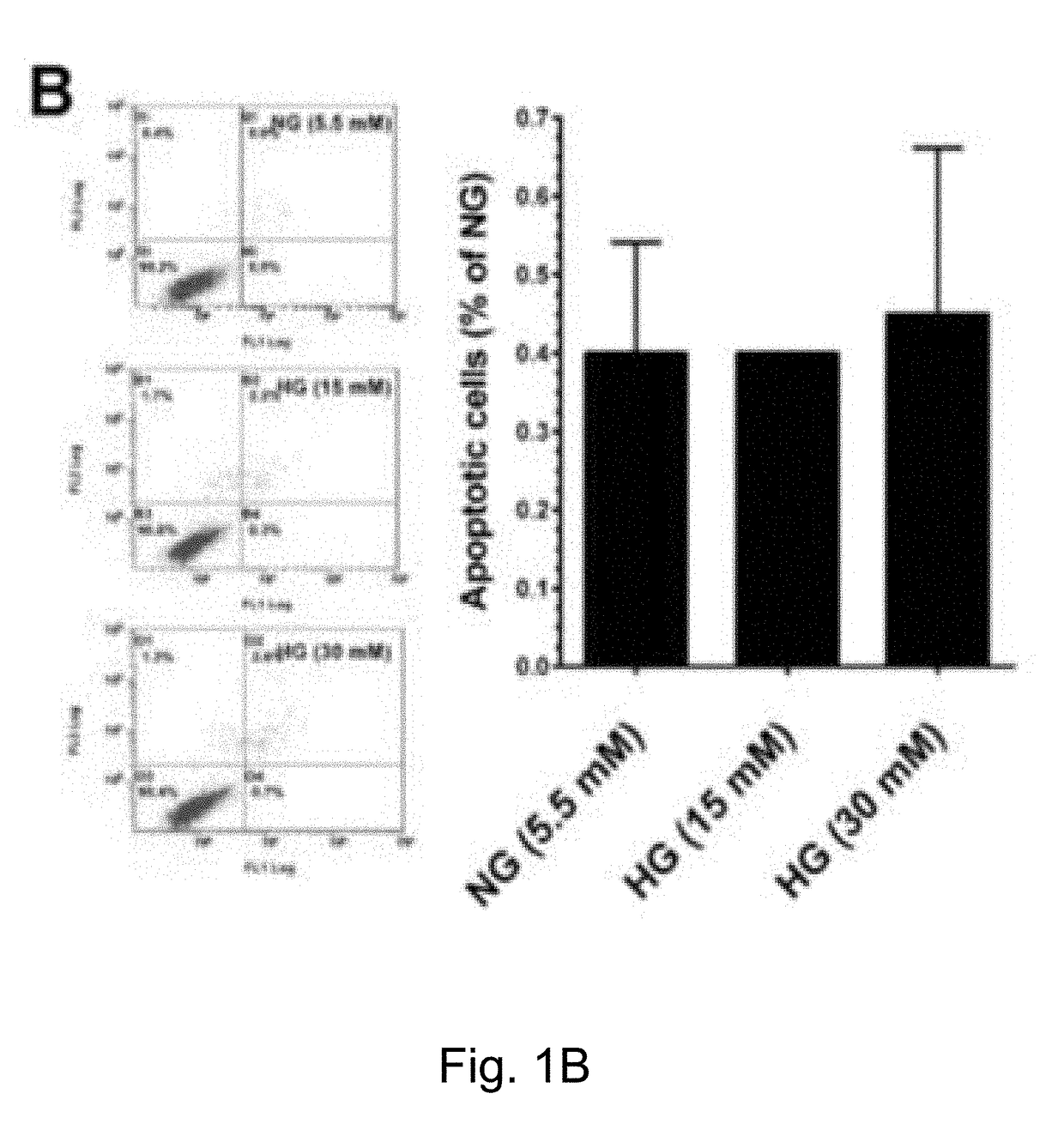
The present method has anti-aging properties against high-glucose. The present invention reveals the anti-aging properties of antcin M (ANM) and elucidates the molecular mechanism underlying the effects. It is found that exposure of human normal dermal fibroblasts (HNDFs) to high-glucose (HG) for 3 days, cell phase arrest and senescence are accelerated. As confirmed through experiments, co-treatment with ANM significantly attenuates HG-induced growth arrest and promotes cell proliferation. In addition, treatment with ANM eliminates HG-induced reactive oxygen species through the induction of anti-oxidant genes via transcriptional activation of NF-E2 related factor-2 (Nrf2). Treatment with ANM abolishes HG-induced stress-induced premature senescence as evidenced by reduced senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity. Also, the HG-induced decline in aging-related marker protein, senescence marker protein-30, is rescued by ANM. Furthermore, treatment with ANM increases expression of silent mating type information regulation 2 homologs 1 (SIRT-1), and prevents SIRT-1 depletion.
Owner:TAIWAN LEADER BIOTECH CORP
SCAR-PCR identification method for mating types of agaricus bisporus homonuclear sterile single spore strains
ActiveCN108070674AShort timeSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSporeAgaricus
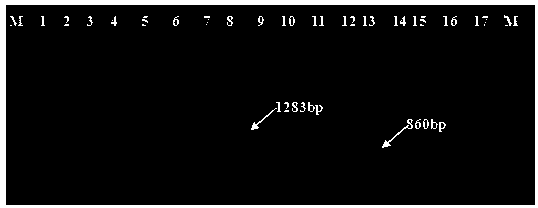
The invention belongs to the field of edible mushroom molecular marker assistant breeding, and particularly relates to an SCAR-PCR identification method for the mating types of an agaricus bisporus homonuclear sterile single spore strains. In the method, an SCAR molecular mark is utilized for performing PCR specific amplification on the agaricus bisporus homonuclear sterile strains with differentmating types. In the method, a complex hybridizing pairing experiment is not needed, and the mating types of the agaricus bisporus homonuclear sterile single spore strains are identified specifically.The method is short in consumed time, easy and convenient to operate and high in specificity. According to existence of a specific amplification product 1283bp band, the sterile single spore strainswith the mating type A+ are identified, and according to existence of a specific amplification product 860bp band, the sterile single spore strains with the mating type A- are identified. With the method, in agaricus bisporus hybridizing breeding, the mating types of the homonuclear sterile strains can be rapidly identified, and therefore the efficiency of hybridizing breeding is greatly improvedfor agaricus bisporus.
Owner:INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method of cordyceps militaris high-activity strain
InactiveCN110157769AAvoid out of grassAvoid YieldMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAdenosine
The invention belongs to the technical field of cordyceps militaris cultivation, and discloses a breeding method of a cordyceps militaris high-activity strain. A cordyceps militaris monospore strain is separated artificially, and gene mating types of cordyceps militaris are distinguished by adopting a molecular biology method; monospore strains of active substances such as high-yield cordycepin and adenosine are screened; through screening of nutritional compatibility, a pair of strains of different gene mating types are selected and paired, and further, a high-yield target strain is obtainedthrough cordyceps militaris outlet verification. The breeding method of the cordyceps militaris high-activity strain has the advantages that a traditional strain breeding technology by changing a culture medium formula and simple mating type pairing is changed, pairing and cordyceps militaris outlet verification are carried out, the technology bottleneck of no quantized investigation parameters inbreeding work is broken through, and the breeding method can be applied to rejuvenation of cordyceps militaris degradation strains, can also be applied to breeding of high-activity strains, gets ridsof the blindness and randomness of a traditional breeding mode, and has important significance for stabilizing the yield of cordyceps militaris in industrial production, inhibiting strain degeneration, rejuvenating the degraded strains and breeding the high-activity strains.
Owner:安徽祥康生物工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com