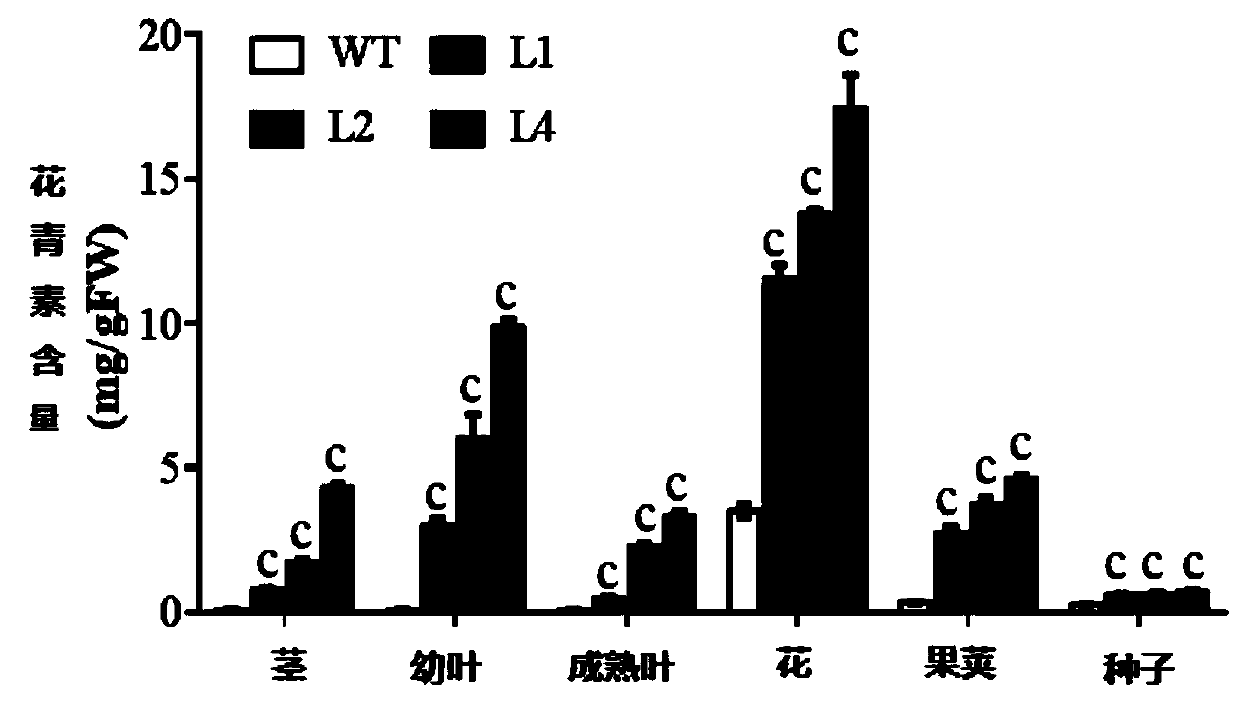
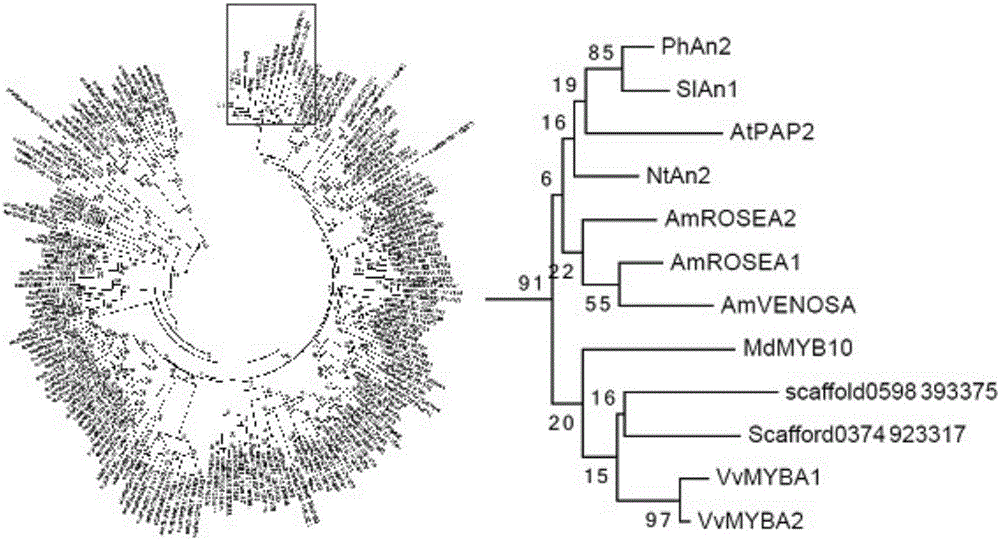
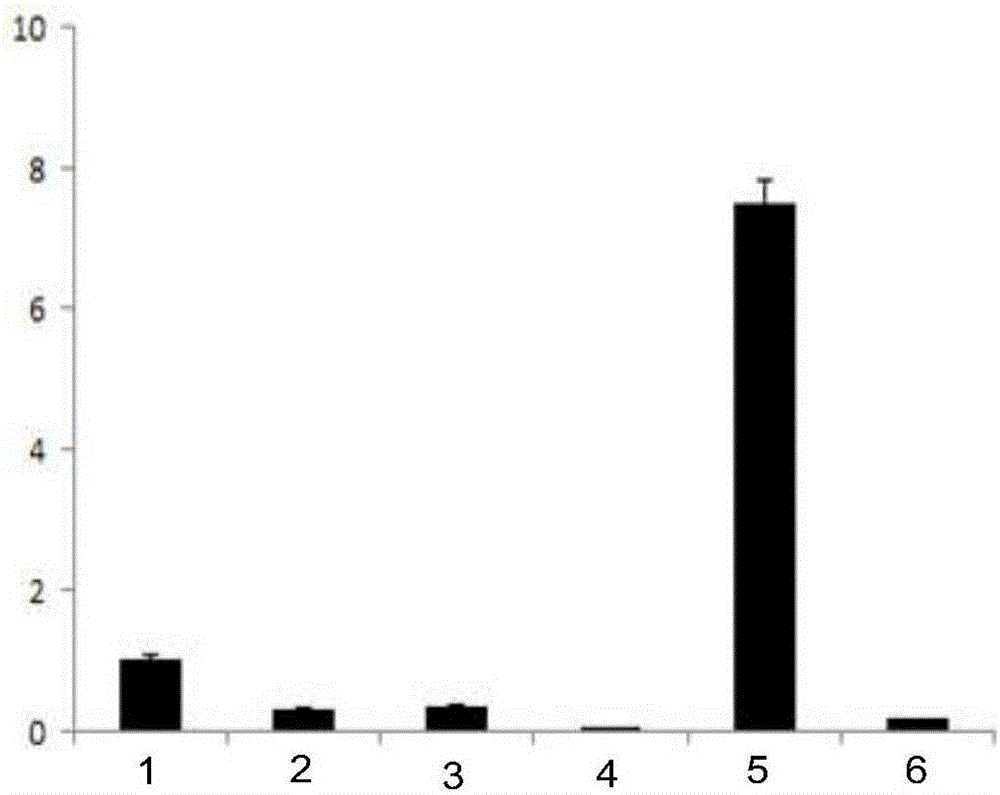
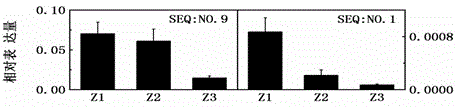
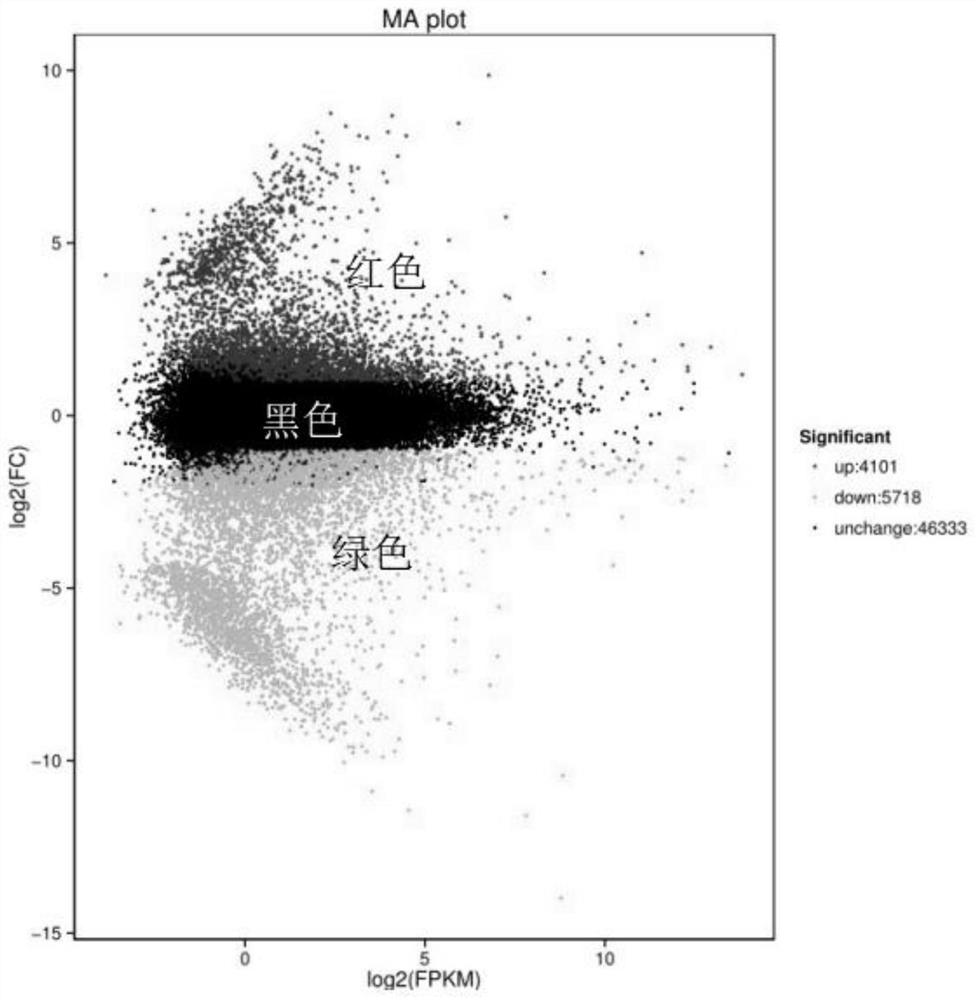
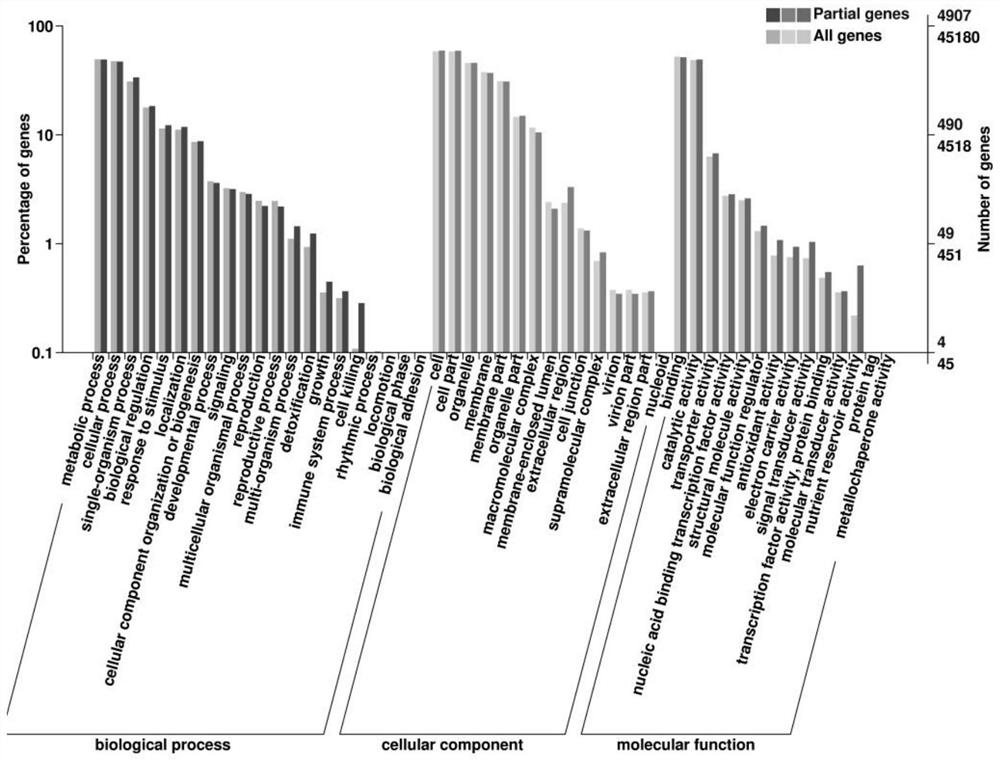
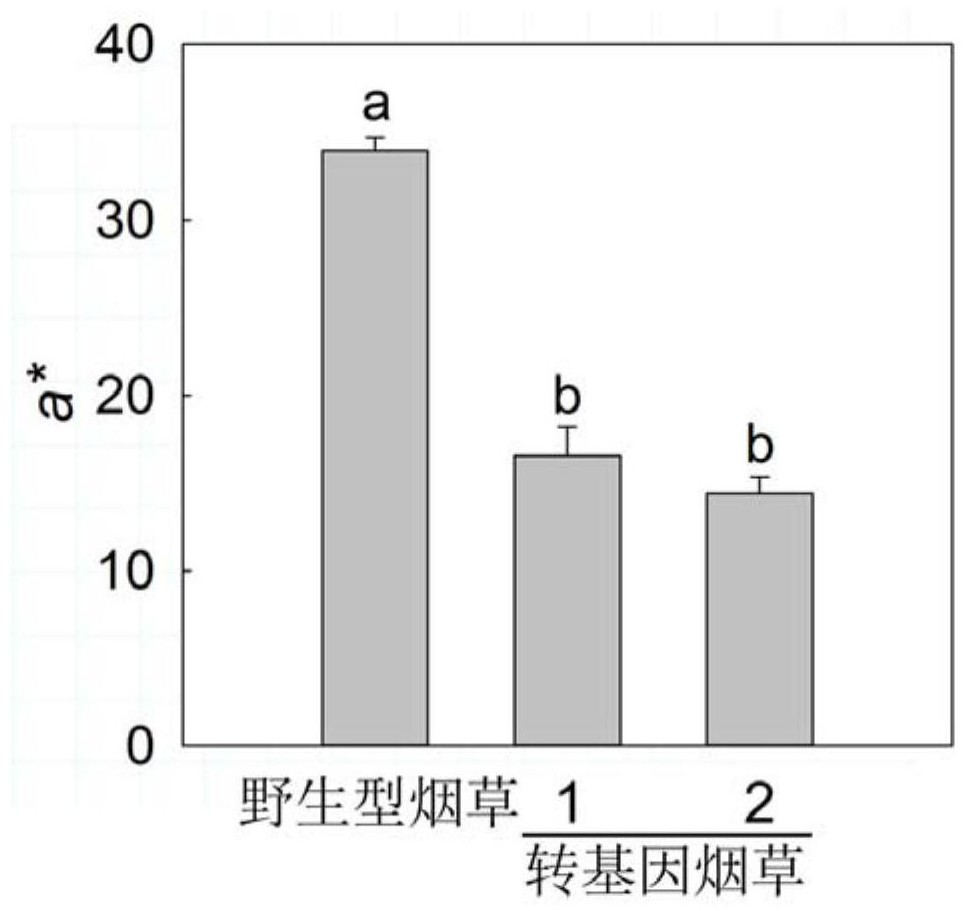
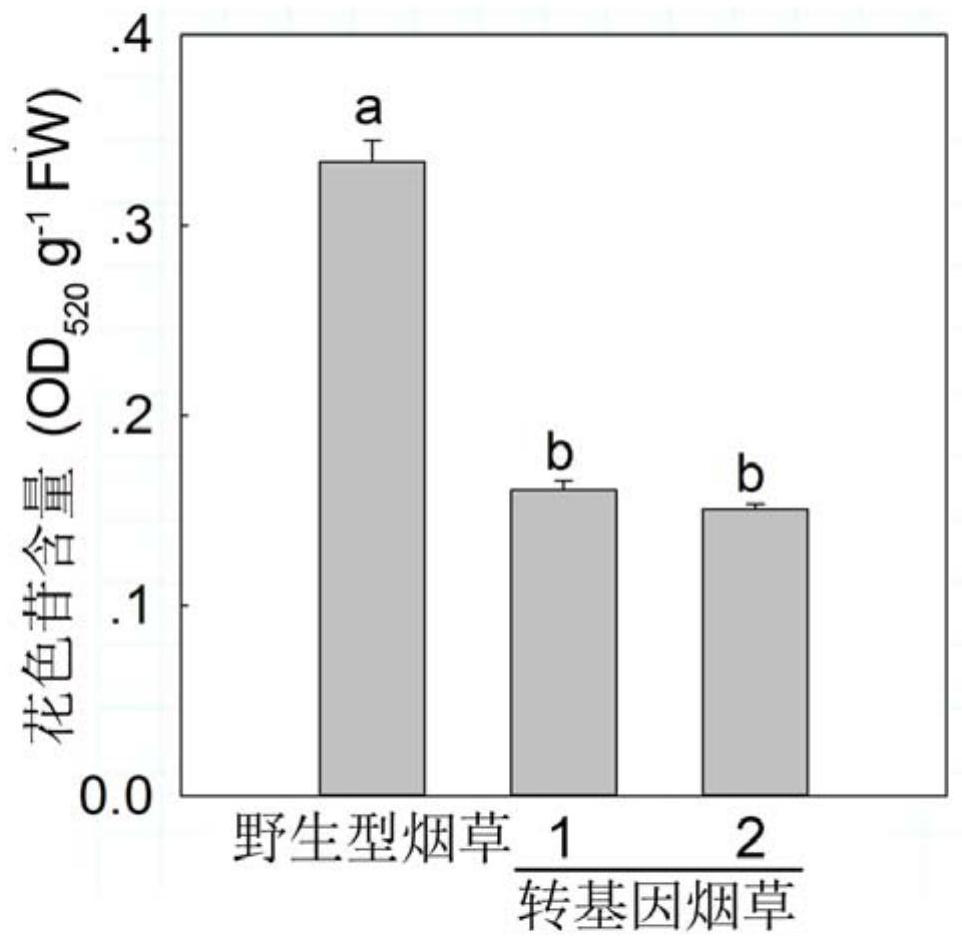
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Anthocyanin synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Streptomycin enhances the synthesis of anthocyanins and inhibits the synthesis of chlorophylls and the development of chloroplasts in dark-grown seedlings of cabbage (Brassica oleracea), mustard (Sinapis alba), tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum), and turnip (Brassica rapa) exposed to prolonged periods of irradiation in various spectral regions.
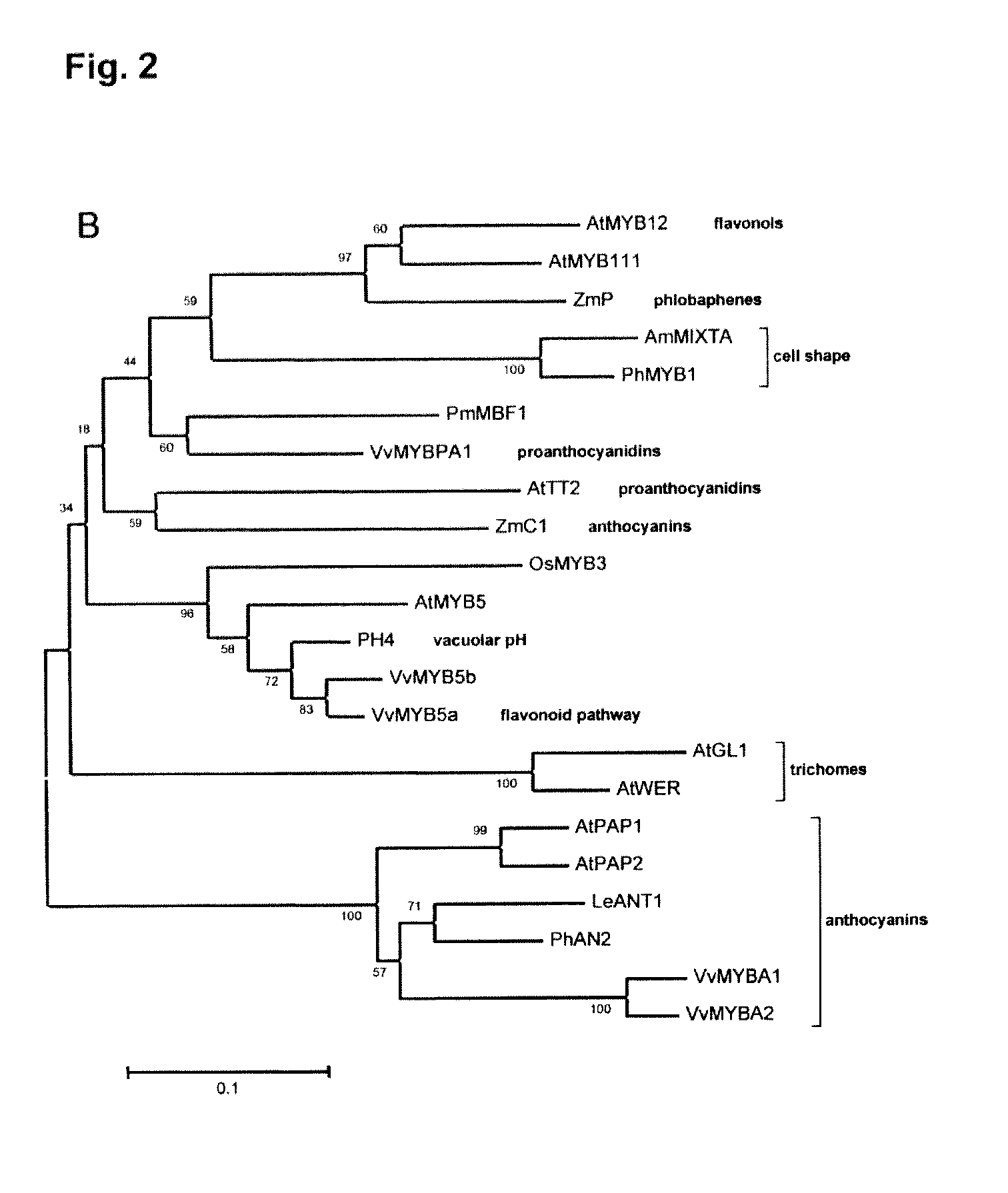
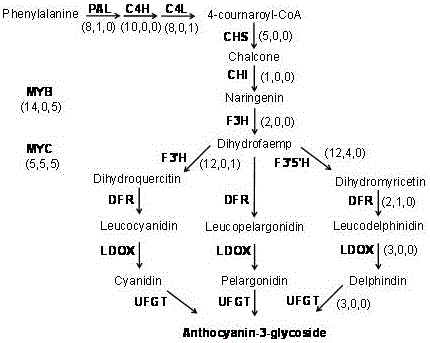
MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation
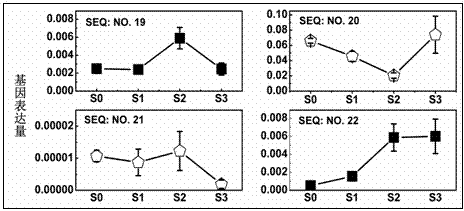
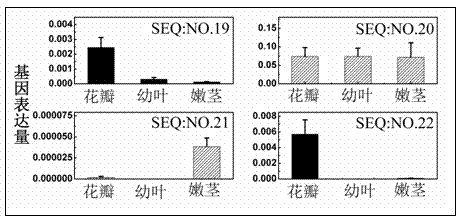
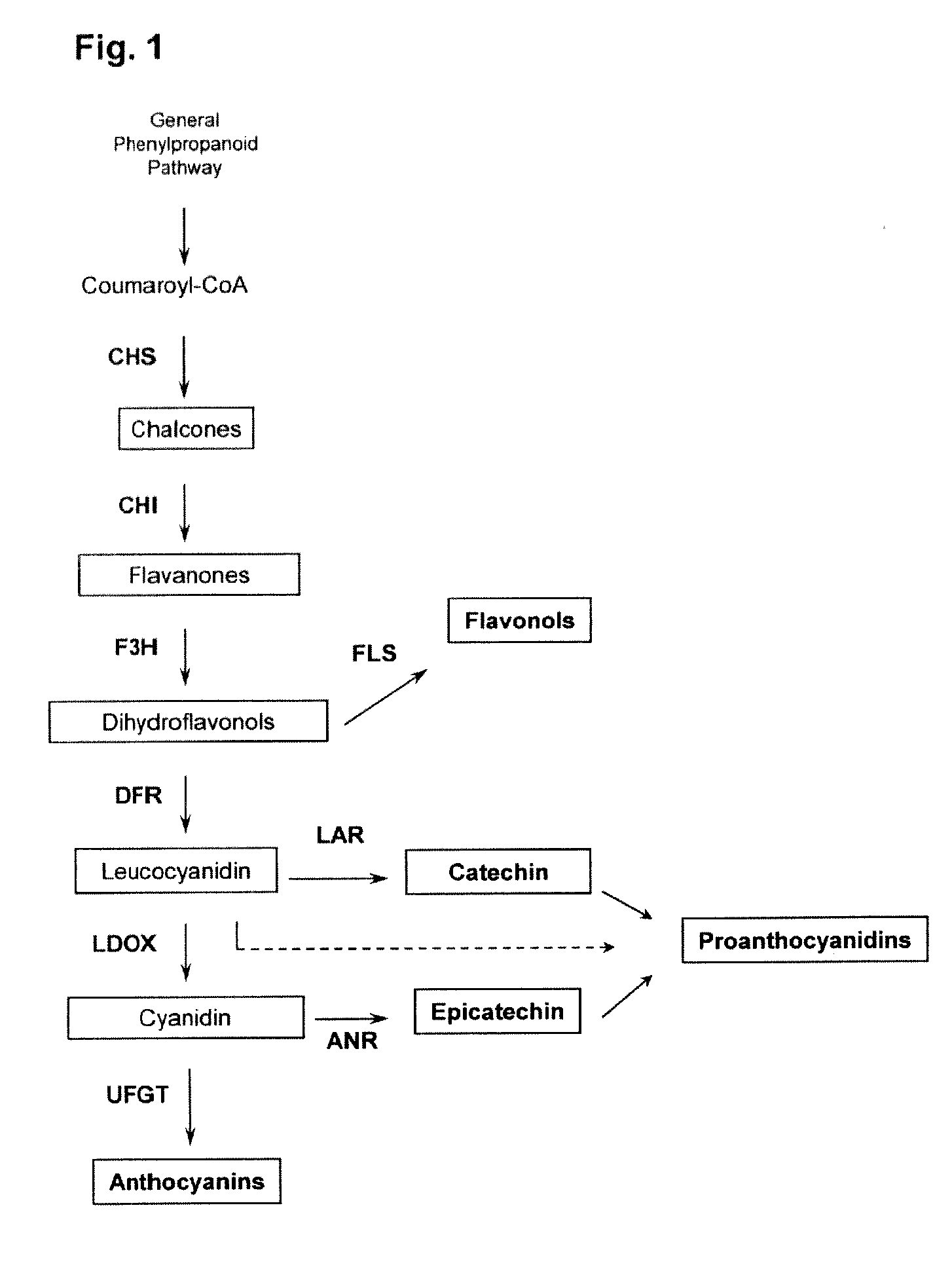
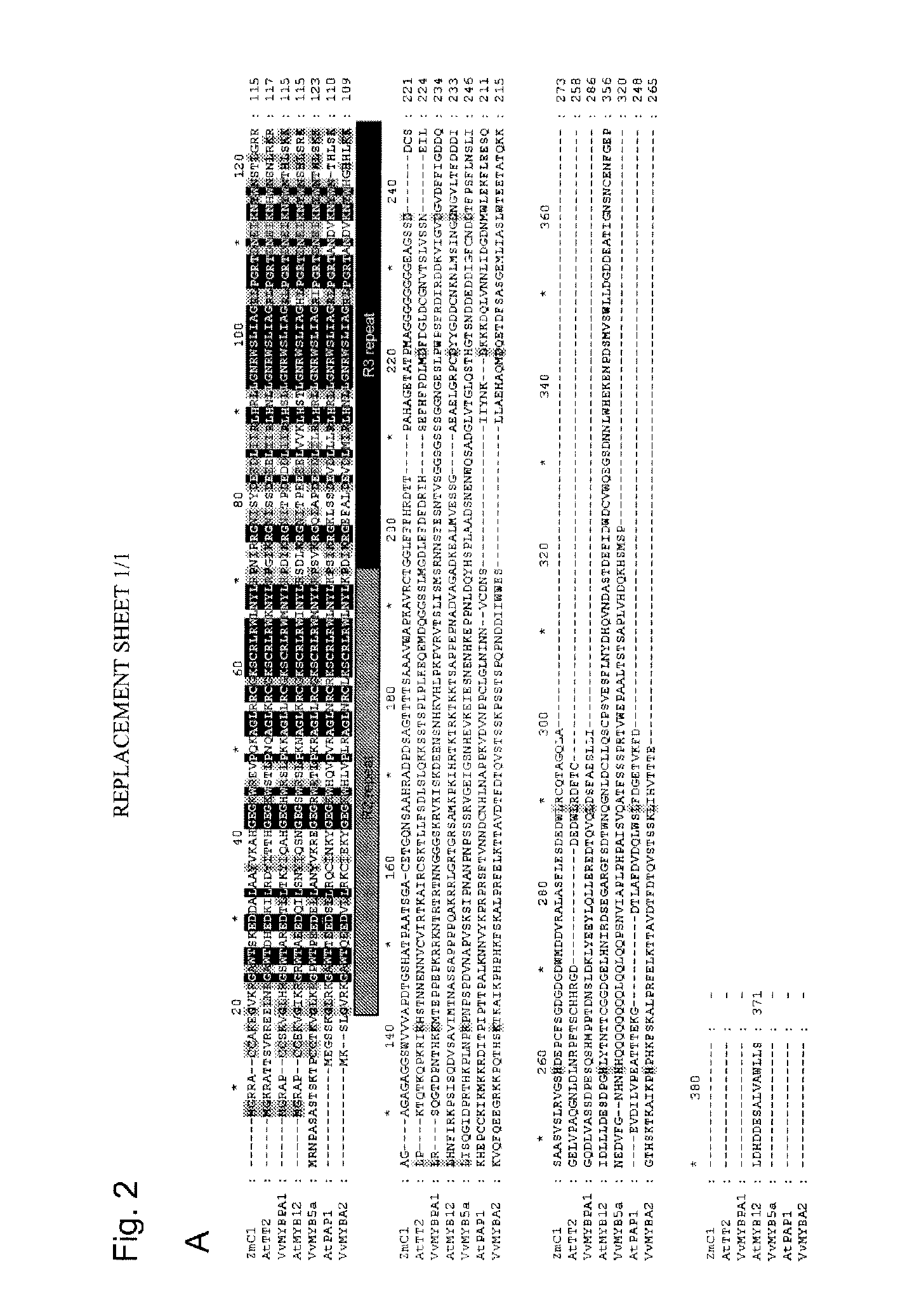
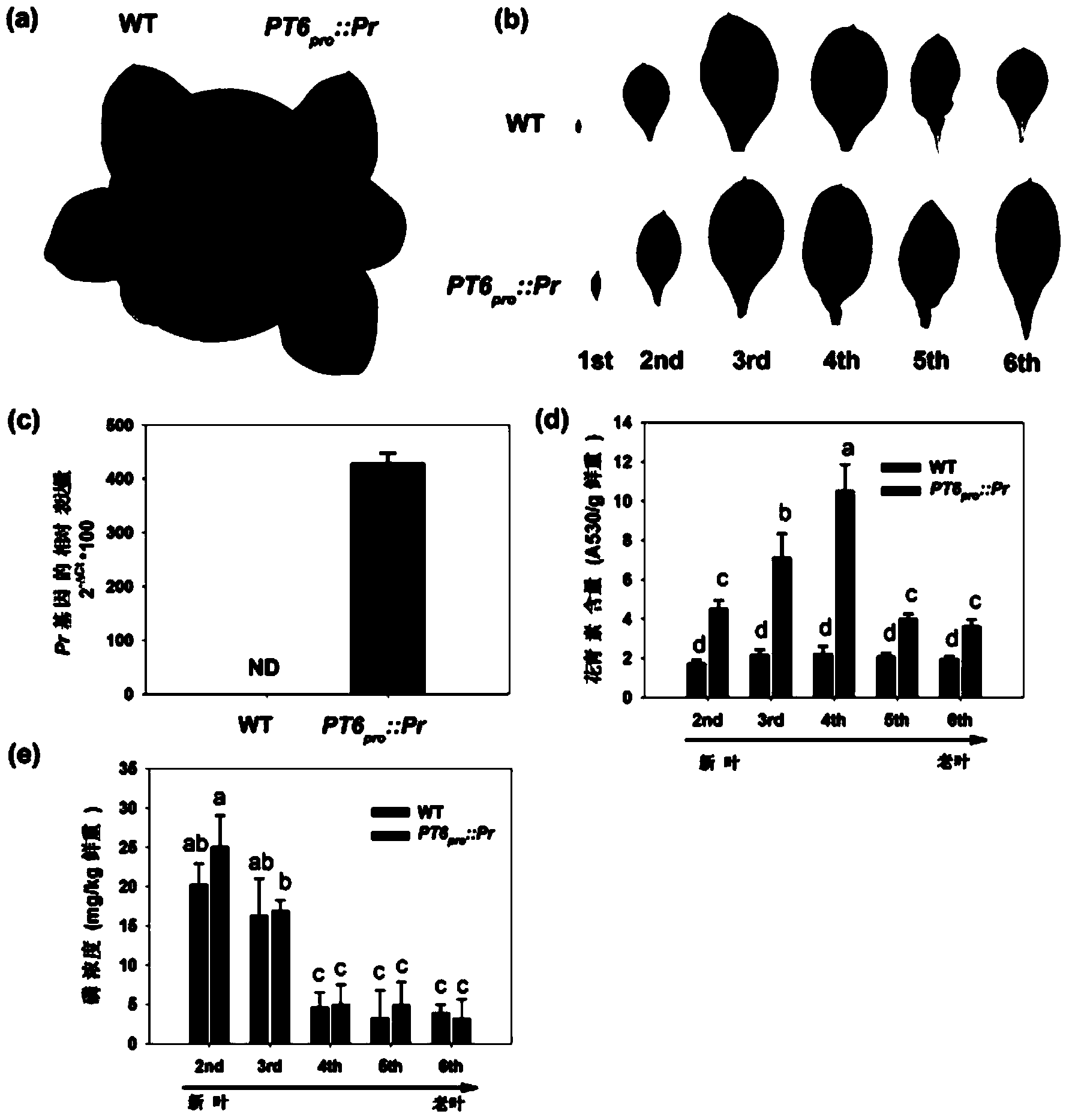
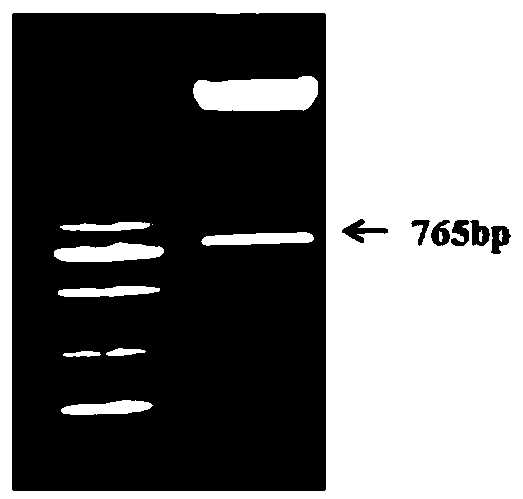
The invention provides an MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 implicated in chrysanthemum petal anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The coding region sequence of the MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 contains 765 nucleotides. A CmMYB6 amino acid sequence contains a conserved R2R3 MYB domain, a [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif and an ANDV motif exist in the R3 domain, the [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif can interact with bHLH, and the ANDV motif is the characteristic motif of the MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The gene expression of CmMYB6 rises in the petal growth process and is significantly and positively correlated with anthocyanin synthesis the CmMYB6 can induce the activity of synthesis of a key gene CmDFR promoter from anthocyanin, and the CmMYB6 has substantially enhanced induction usefulness and can strongly induce accumulation of tobacco leaf anthocyanin during cooperative expression of the CmMYB6 and MrbHLH1. The MYB transcription factor can be used in transcription regulation of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis and plant color modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel gene encoding myb transcription factor involved in proanthocyanidin synthesis
InactiveUS20120208198A1Improve propertiesImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAnthocyanin synthesisNovel gene
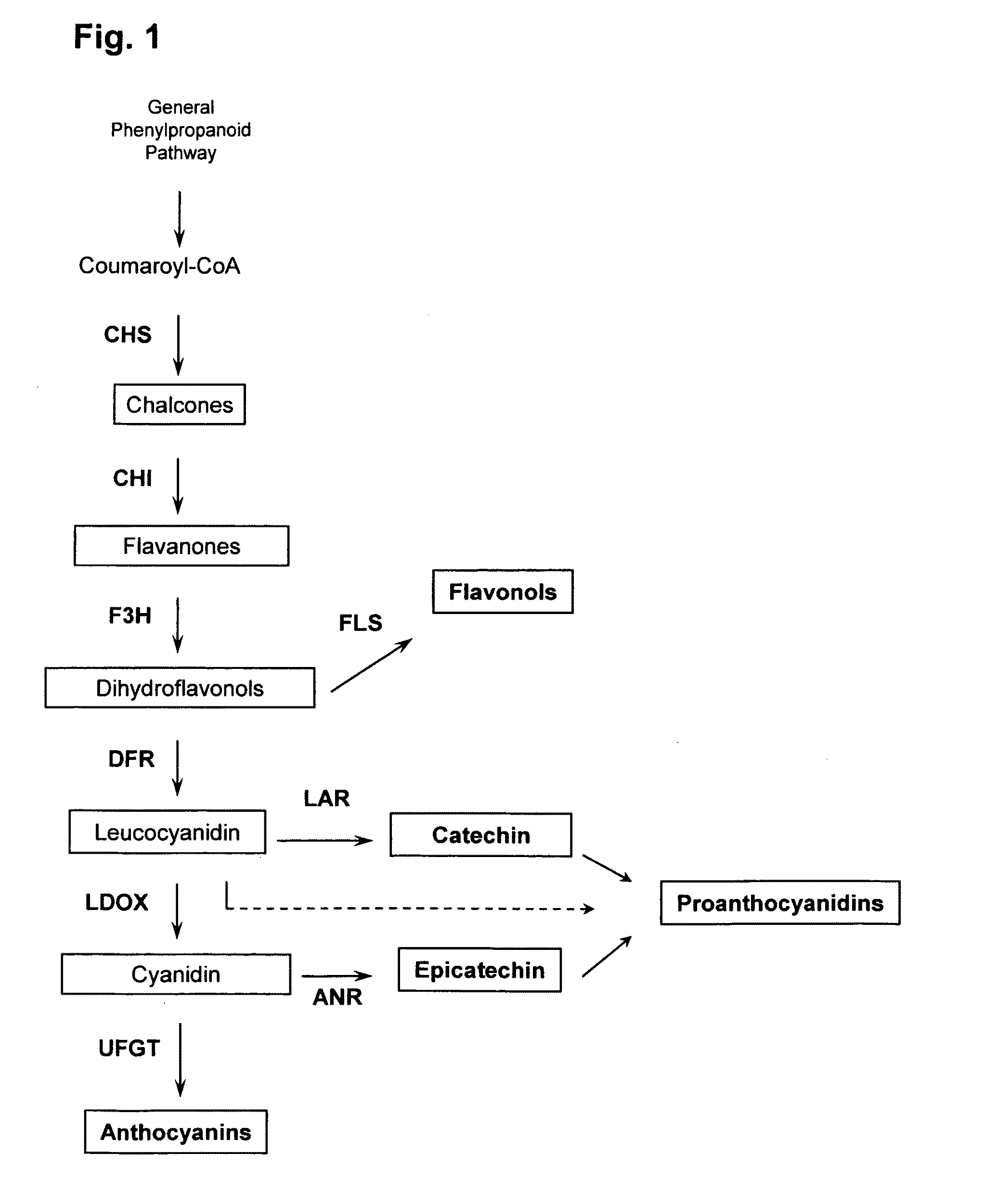
An isolated or recombinant MYB polypeptide having activity as a transcription factor in the synthesis of proanthocyanidins in plants, and nucleic acid molecule encoding same, wherein the polypeptide activates in the plants (a) promoters of the leucoanthocyanidin (LAR) and anthocyanidid reductase (ANR) genes, and (b) promoters of at least two of the genes of the general flavonoid pathway. Use of the polypeptide and nucleic acid molecule in regulating the biosynthesis and accumulation of proanthocyanidins in plants, such as in modifying pasture quality of legumes, is also disclosed.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for cultivating tobacco rich in anthocyanin and application thereof
ActiveCN103045642AReduce health hazardsFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
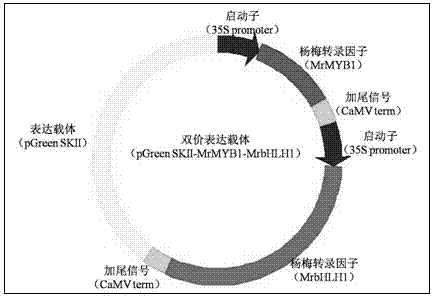
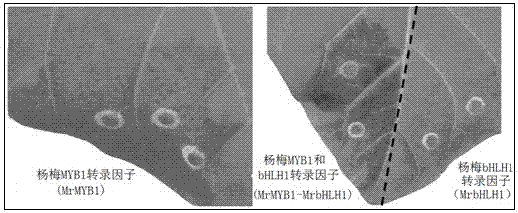
The invention provides a method for cultivating tobacco rich in anthocyanin and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of recombining two confirmed genes, namely MrMYB1 and MrbHLH1 which can be used for regulating and controlling anthocyanin synthesis in red bayberry fruits, establishing an expression plasmid, screening genes capable of regulating and controlling anthocyanin synthesis by using a tobacco leaf transient expression technique, converting genes with confirmed functions into the tobacco, and cultivating tobacco rich in anthocyanin. The invention provides a method for cultivating tobacco rich in anthocyanin, so that health hazard caused by smoking is alleviated; and the method is also applicable to MYB and bHLH genes in other fruits besides red bayberry.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for establishing tomato nuclear male sterile line with green stem marker
InactiveCN109735563AHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceTransgenesis
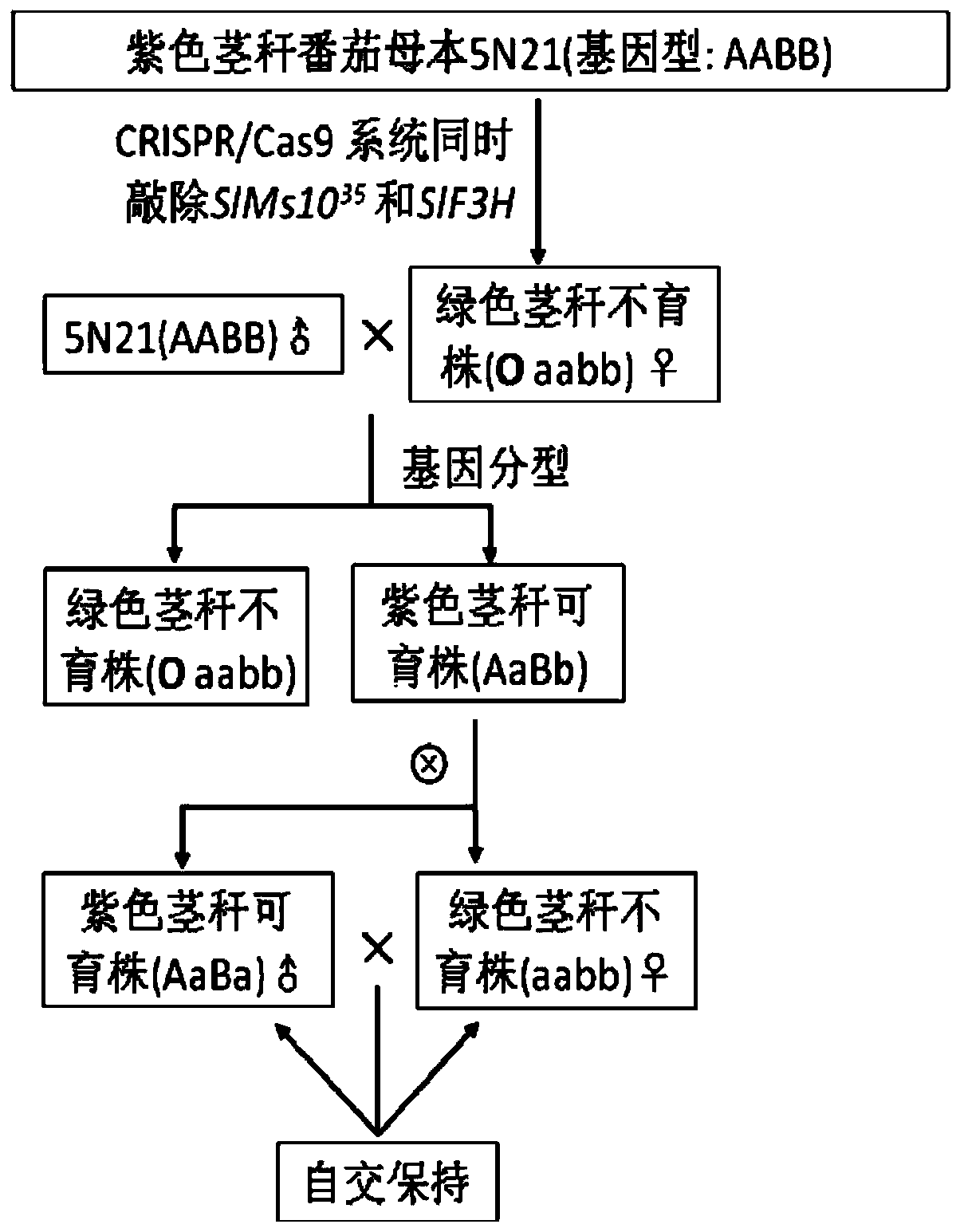
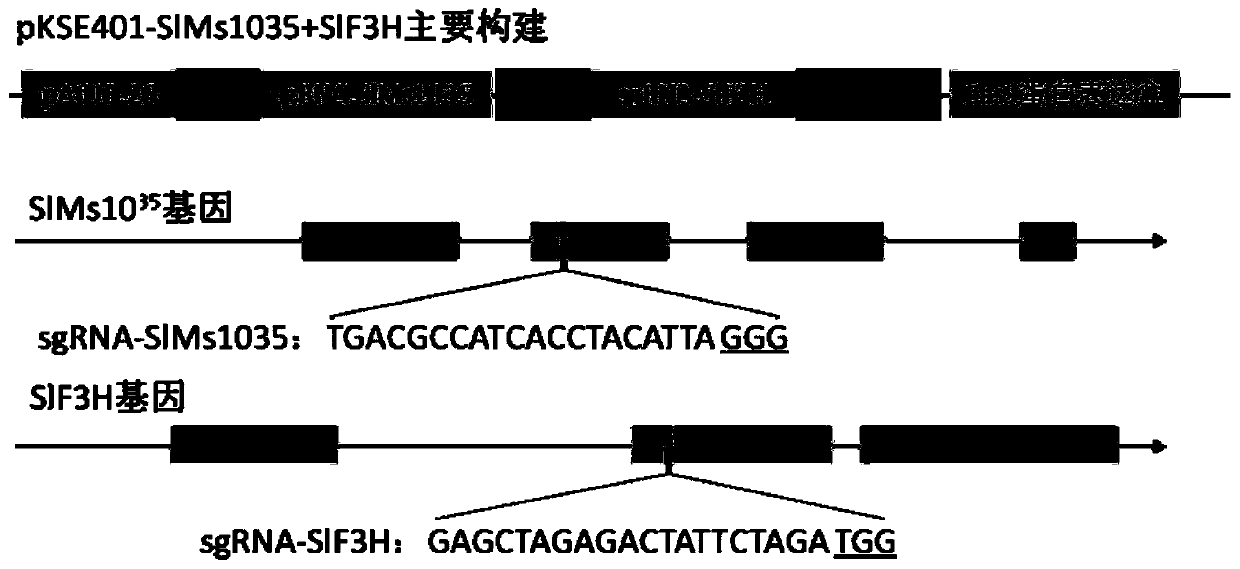
The invention discloses a method for establishing a tomato nuclear male sterile line with a green stem marker, which comprises the following steps: simultaneously editing a fertility gene SlMs1035 ina receptor tomato genome and a linked marker gene SlF3H thereof by using a CRISPR / Cas9 system so as to cause the two genes to lose functions, and the tomato material obtained with the SlMs1035 and theSlF3H simultaneously losing function through ridding the transgene structure by carrying out selfing or hybridization is the tomato nuclear male sterile line with the green stem mark; wherein the marker gene SlF3H is an anthocyanin synthesis gene. As the stem of the sterile plants is green at the seedling stage, the sterile plants can be selected before the plants blossom. The method for establishing tomato nuclear male sterile line with the green stem marker adopts a molecular design breeding method to obtain a tomato nuclear male sterile line with a non-transgenic seedling stage marker character, and can be applied to transforming a tomato hybrid female parent into a nuclear sterile line with a green stem marker for tomato seed production through hybrid.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Anthocyanin synthesis related protein IbMYB113 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN113621039AGood yield and qualityEasy to synthesizeBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to an anthocyanin synthesis related protein IbMYB113 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the IbMYB113 protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; the nucleotide sequence of the coding gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the invention, IbMYB113 protein and a coding gene thereof are cloned from red sweet potato peel, the IbMYB113 gene is connected to a plant expression vector, a transgenic tobacco plant over-expressing IbMYB113 is obtained through agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation, pigment accumulation of the whole plant is shown, and the content of delphinidin and cornflower pigment is detected to be obviously increased by high performance liquid chromatography. The IbMYB113 protein and the coding gene thereof provided by the invention have important theoretical significance and application value for promoting synthesis and accumulation of plant anthocyanin.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Pear anthocyanin synthesis transcription factor PbMYB109 and application thereof
The invention discloses a pear anthocyanin synthesis transcription factor PbMYB109 and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the transcription factor is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and theamino acid sequence of protein encoded by the transcription factor is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. By an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method, pear fruits are transiently transformed andArabidopsis thaliana is stably transformed by a PbMYB109 gene, obtained transgenic plants are subjected to phenotype identification, results indicate that the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana has obvious anthocyanin accumulation on rosette leaves, seed pods and main stems as compared with mild types, the clonal PbMYB109 gene is a new transcription factor participating in anthocyanin synthesis, andanthocyanin synthesis can be promoted. Discovery of the transcription factor provides an important gene resource for gene engineering of exploration of anthocyanin synthesis routes and improvement offruit quality.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Novel gene encoding MYB transcription factor involved in proanthocyanidin synthesis
InactiveUS20100064383A1Improve securityImprove propertiesFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAnthocyanin synthesisNovel gene
An isolated or recombinant MYB polypeptide having activity as a transcription factor in the synthesis of proanthocyanidins in plants, and nucleic acid molecule encoding same, wherein the polypeptide activates in the plants (a) promoters of the leucoanthocyanidin (LAR) and anthocyanidid reductase (ANR) genes, and (b) promoters of at least two of the genes of the general flavonoid pathway. Use of the polypeptide and nucleic acid molecule in regulating the biosynthesis and accumulation of proanthocyanidins in plants, such as in modifying pasture quality of legumes, is also disclosed.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Eggplant anthocyanin synthesis-related gene SmMYB1 as well as recombinant expression vector thereof and application of gene SmMYB1 in purple tomato culture
InactiveCN103966235AIncrease anthocyanin contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses an eggplant anthocyanin synthesis-related gene SmMYB1 as well as a recombinant expression vector thereof and an application of the gene SmMYB1 in purple tomato culture. The nucleotide sequence of the eggplant anthocyanin synthesis-related gene SmMYB1 is as shown in SEQ ID No.3; the gene is constructed into a recombinant expression vector which is used for transforming tomato by use of agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation and then a transgenic tomato is obtained; the phenotypes of petals, stigma, anther, fruits, root, stem and leaves of the obtained transgenic tomato are purple, and therefore, the transgenic tomato can be cultured as an ornamental plant; the content of anthocyanin in the fruits of the transgenic tomato is relatively high and the anthocyanin can be used for reducing the risk of suffering from cancers and cardiovascular diseases, and in short, the transgenic tomato has excellent ornamental and edible values.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
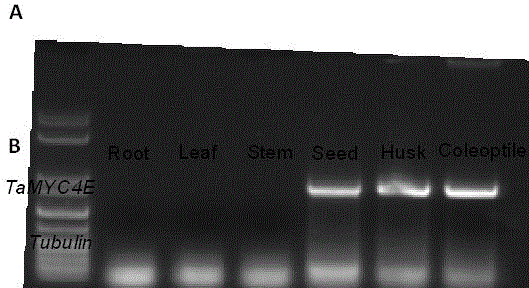
Wheat new gene ThMYC4E for regulating anthocyanin synthesis and metabolism
The invention relates to a wheat new gene ThMYC4E for regulating anthocyanin synthesis and metabolism. The gene ThMYC4E has a nucleotide sequence shown by the 1st-1,707th site of SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. In the invention, the obtained gene can be used for cultivating transfection plants so as to regulate anthocyanin synthesis.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
Peony PsMYB12 transcription factor as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a peony PsMYB12 transcription factor as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The peony PsMYB12 transcription factor is a protein of (a) or (b) which is described as follows: (a) a protein consists of an amino acid sequence shown by a sequence 1 in a sequence table; (b) proteins which are derived from (a), are associated with peony color spot formation and / or anthocyanin synthesis and are formed by replacing and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues in the amino acid sequence shown by the sequence 1 in the sequence table. By means of VIGSsilencing and heterologous excess transformation analysis, the results show that the peony PsMYB12 transcription factor can regulate the expression of key enzyme genes in an anthocyanin synthesis route. The peony PsMYB12 transcription factor is speculated to play an important role in the synthesis and accumulation of anthocyanin in peony flower spots and the formation of color spots. The specifically expressed gene is cloned for the first time and the functions of the gene are verified, so that a foundation is laid for the molecular mechanism of the formation of the color spots, and technicalbasis and thought are provided for further analysis of the synthesis and regulation of flavonoids in peony flowers.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Strawberry glutathione-transferase FaGST gene of, express protein thereof and application thereof
The invention discloses a strawberry glutathione-transferase FaGST gene, an express protein thereof and an application thereof, wherein the base sequence of the strawberry glutathione transferase FaGST gene is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The strawberry glutathione-transferase FaGST gene is cloned, and the FaGST1 is found to be related to the accumulation of anthocyanin in strawberry fruit through an infection, and after the gene is silenced, the expression amount is reduced, and the expression amount of main anthocyanin synthesis genes such as CHS1, F3H1, ANS1, UGT1 and the like are inhibited. Therefore, the FaGST gene will be widely used in anthocyanin synthesis.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Thellungiella salsuginea transcription factor EsMYB41 for controlling plant anthocyanin synthesis and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN110066326AEasy to synthesizeImprove antioxidant capacityPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumWild type
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology, and particularly relates to a thellungiella salsuginea transcription factor EsMYB41 for controlling plant anthocyanin synthesis and an encoding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the thellungiella salsuginea transcription factor EsMYB41 for controlling plant anthocyanin synthesis is shown in SEQ ID No.1. Byconstructing an EsMyb41 containing over expression vector, tobacco and arabidopsis are transferred, and EsMYB41 transgenic tobacco and arabidopsis are obtained; results find that the transgenic planthas the almost whole-plant claret-colored phenotype; the anthocyanin content of different tissues of transgenic plants and the expression of the anthocyanin synthesis structure gene are both remarkably higher than the wild type, and meanwhile under the salt stress, the anti-oxidase capability of the transgenic plant is improved remarkably.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Transcription factor capable of regulating rubber tree anthocyanin synthesis and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to molecular biology and specifically discloses an R2R3-MYB transcription factor HbAn1 capable of positively regulating rubber tree anthocyanin synthesis and an encoding gene and application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the transcription factor HbAn1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. According to the invention, an encoding gene sequence of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor HbAn1 capable of regulating anthocyanin synthesis is separated from rubber trees for the first time, and functions and an application range of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor HbAn1 are determined. Researches and analysis find that the expression of HbAn1 is gradually reduced along with leaf senescence and anthocyanin fading; meanwhile, HbAn1 expression in dark-culture tender stems is higher than that in light-culture tender stems, and the HbAn1 expression has positive correlation with the anthocyanin content. The transcription factor can positively regulate rubber tree anthocyanin synthesis and achieves the purpose of increasing an anthocyanin accumulation amount through self overexpression.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulation
The invention provides a chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor (CmbHLH2) involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulation. A nucleotide sequence of the chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor is shown as SEQ: NO.1. When the CmbHLH2 and a CmMYB6 coordinate to perform instantaneous over-expression in tobacco leaves, anthocyanin accumulation can be strongly induced to change the original green color of the leaves into a red color. Therefore, by means of transgenosis, over-expression of the CmbHLH2 in a plant is achieved or expression of the CmbHLH2 in the chrysanthemum plant is inhibited so that anthocyanin synthesis enhanced and inhibited transgenic plants can be obtained respectively, and the colors and luster of the transgenic plants can change with anthocyanin synthesis change.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Lycium barbarum gene, and coding protein, recombinant vector and application thereof
ActiveCN113337635AIncrease contentMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a lycium barbarum gene, and a coding protein, a recombinant vector and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the lycium barbarum gene is disclosed as SEQ ID NO. 1 or SEQ ID NO. 2. The nucleotide sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO. 3 or SEQ ID NO. 4. The invention also discloses a recombinant vector, expression cassette, transgenic cell line, recombinant bacterium or host cell containing the gene. The invention also discloses application of the gene in regulating anthocyanin synthesis, and a method for regulating anthocyanin synthesis in plants. The black lycium barbarum LMH1 and red lycium barbarum Ningqi7 fruit transcriptome is selected for sequencing, and the major gene for controlling the black fruit characters of the black lycium barbarum is analyzed and predicted, thereby providing foundation for researching the lycium barbarum anthocyanin synthesis mechanism. The invention also provides a direction and target for improving the anthocyanin content by modifying plants by gene engineering means.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
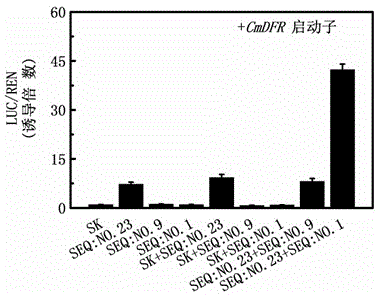
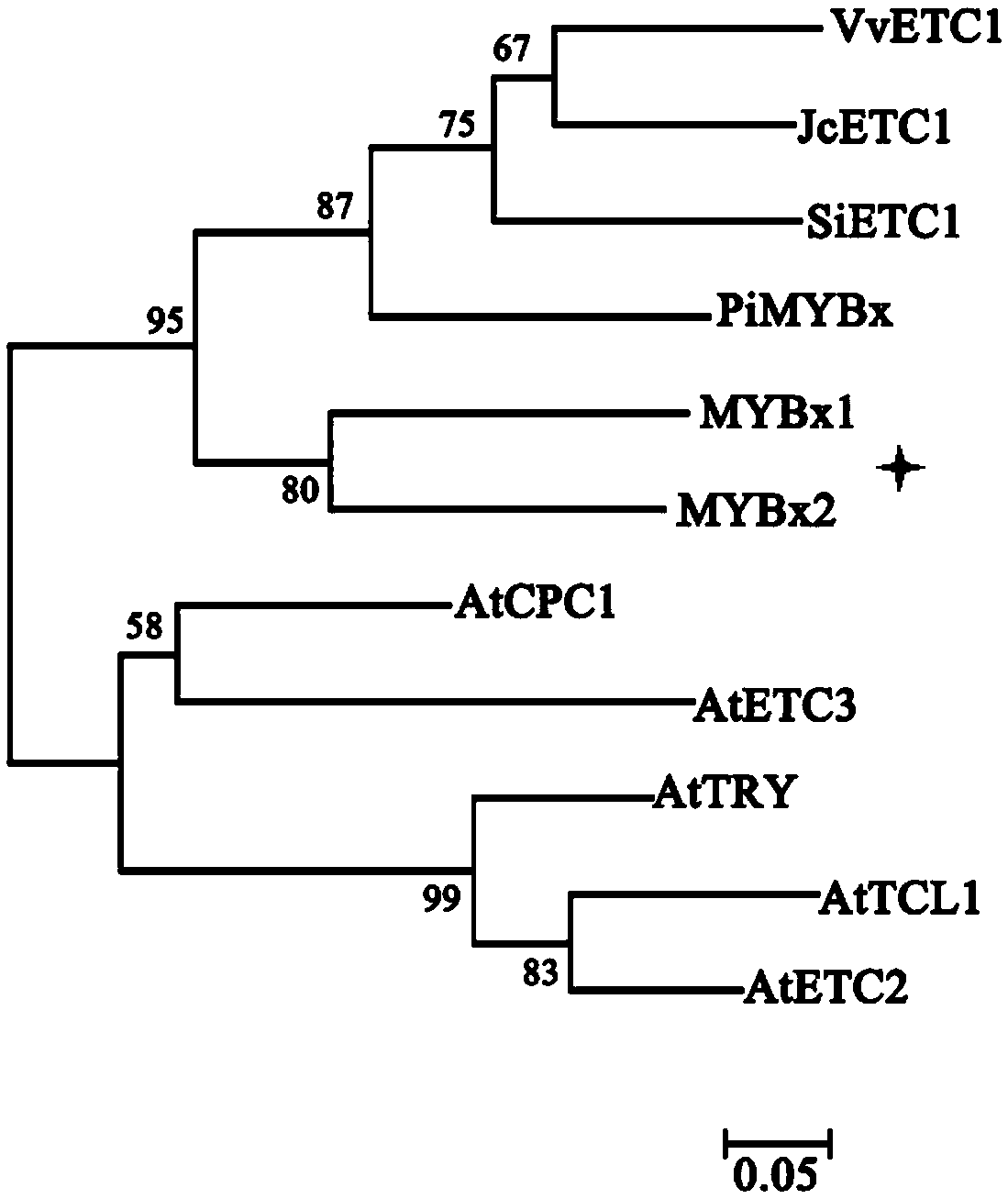
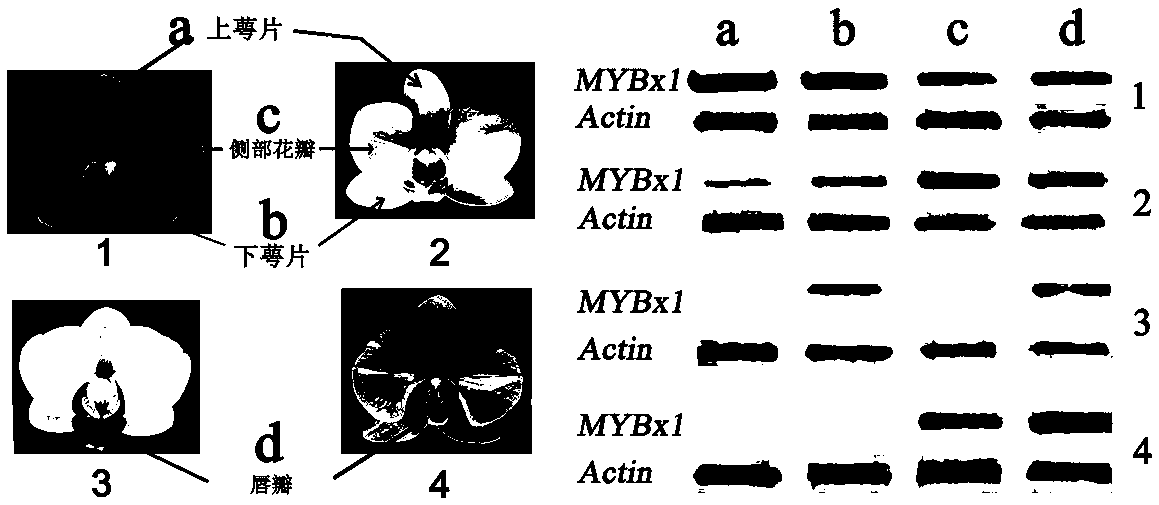
Phalaenopsis aphrodite R3-MYBx1 gene and application thereof in flower color adjustment
ActiveCN107723297AObvious degradation functionInhibit synthesisPlant peptidesFermentationOpen reading framePetal
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant variety cultivation, and specifically relates to a phalaenopsis aphrodite R3-MYBx1 gene and application thereof in flower color adjustment. An open reading frame of the gene contains a 162bp base, and a base sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The MYBx1 gene participates in a petal coloration process, but the MYBx1 gene can express both white petals and red petals; phalaenopsis aphrodite petal coloration can be affected by a plurality of transcription factors, and the MYBx1 is one of regulation factors and participates in the petal coloration process. Application of the gene in overexpression in petunia shows that the gene is related to an anthocyanin content, and the stronger expression of the gene is, the stronger anthocyanin synthesis inhibition capacity is. The MYBx1 is the gene which is researched and shown for the first time to have an obvious and specific anthocyanin degrading function. Through overexpression in plants, the gene can create novel varieties with novel petal coloration characteristics.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Biological activator for promoting fruit coloring, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111559937AStable mature coloringColoring firmBiocideAnimal repellantsPotassium hydroxideFruit development
Owner:潍坊真维农生物工程有限公司
Anthocyanin synthesis related proteins and application in regulating anthocyanin content of plants
ActiveCN110857316AAnthocyanin content can be used to regulatePlant peptidesFermentationAnthocyanin synthesisOrganic chemistry
The invention discloses an anthocyanin synthesis related protein and its application in regulating anthocyanin content of plants. The anthocyanin synthesis related protein disclosed by the invention is as shown in the following A1), A2) or A3): A1) a protein with its amino acid sequence being sequence 1; A2) a protein obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or several aminoacid residues of the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence table and having the same functions; or A3) a fusion protein obtained by connecting a tag at the N-terminal or / andC-terminal of A1) or A2). The anthocyanin synthesis related protein of the invention can regulate the anthocyanin content of plants, can be used to cultivate plants with increased or decreased anthocyanin content, and can also be used to regulate the color of plants.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
cDNA sequence of MYB transcription factors for positively regulating anthocyanin synthesis
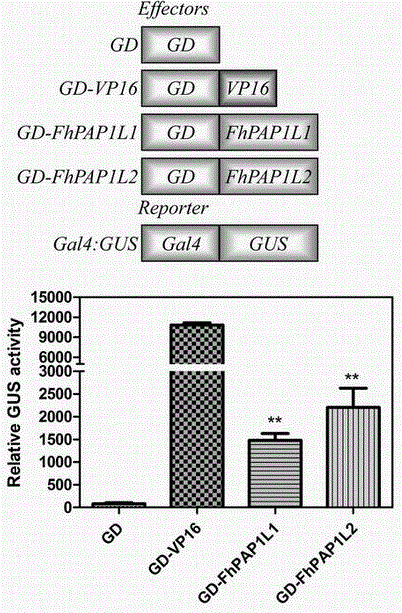
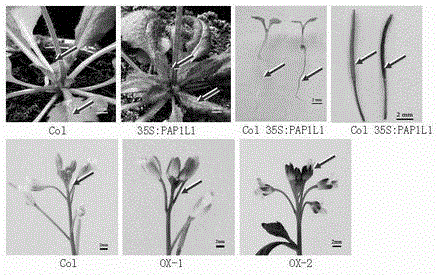
The invention discloses a cDNA sequence of two MYB transcription factors (FhPAP1L1 and FhPAP1L2) which are cloned from petals of freesia refracta for the first time and are used for positively regulating anthocyanin synthesis, and a coded amino sequence is obtained through conjecture. Through over-expression of FhPAP1L1 and FhPAP1L2 in arabidopsis thaliana and tobacco, coloring of plant tissues can be significantly enhanced, so that the function of the FhPAP1L1 and FhPAP1L2 of participating in the positive regulation for plant anthocyanin synthesis is determined.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
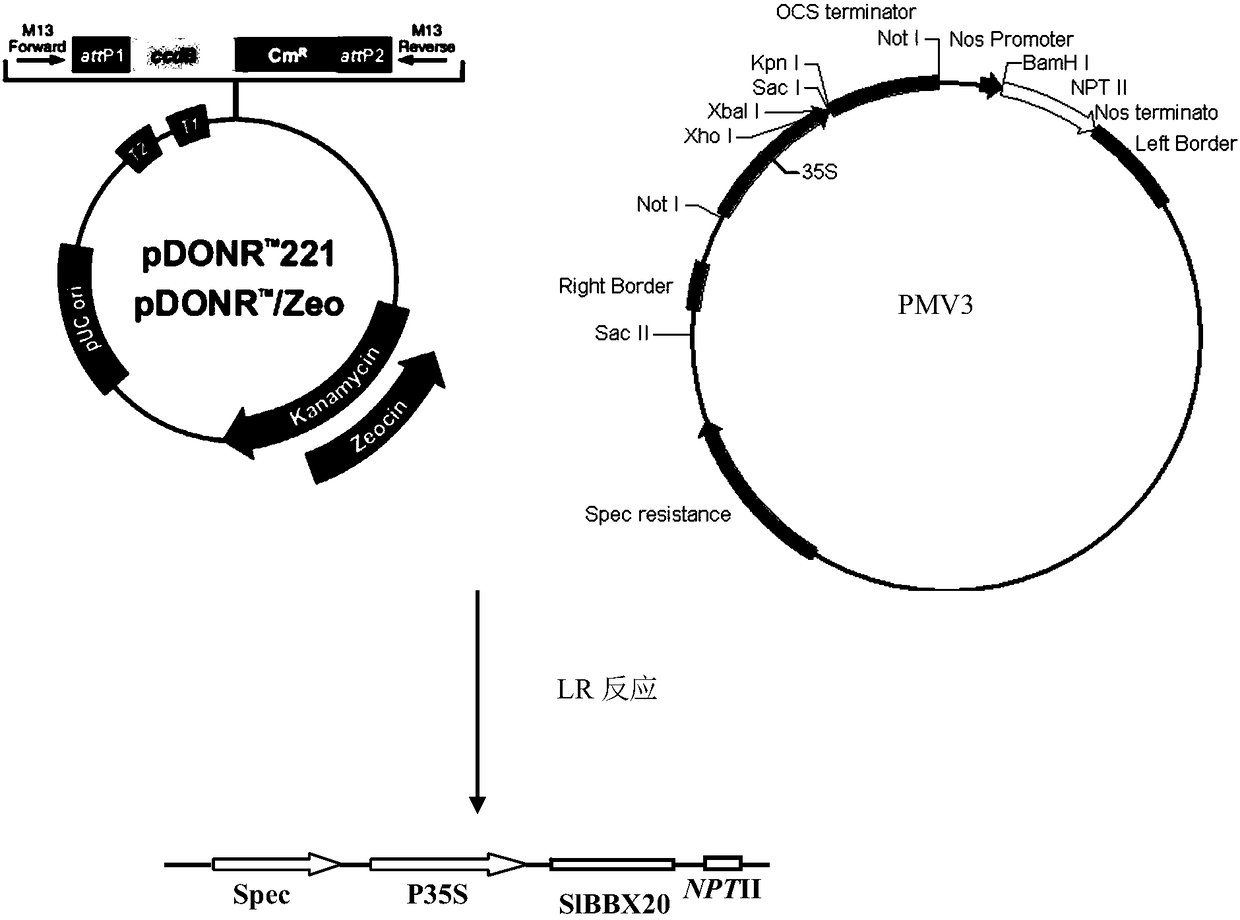
Overexpression transcription transcription factor SlBBX20 for improving the content of tomato anthocyanin
ActiveCN109136233AAccelerate the accumulation processPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural sciencePlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to an overexpression transcription factor SlBBX20 for improving the content of tomato anthocyanin. The method of the invention clones a key gene SlBBX20 for controlling anthocyanin synthesis in tomato leaves, and performs biological function identification. The cDNA sequence of the gene is shown inSEQ ID NO: 1 of the sequence table and the sequence of the encoded protein is shown as SEQ ID NO: 3. The transgenic function verification shows that the overexpression of the gene in tomato can significantly regulate the function of anthocyanin content in tomato leaves.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Wild wheat blue grain character major gene as well as molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN113549631AIncrease contentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a wild wheat blue grain character major gene as well as a molecular marker and application thereof. The gene is a wild wheat grain gene identified in a common wheat-wild wheat grain 4Ab (4B) substitution line, the gene is a major gene for regulating and controlling the wild wheat blue grain character, and anthocyanin synthesis can be regulated and controlled. The nucleotide sequence of the wild wheat blue grain major gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein of the major gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention provides a basis for researching an anthocyanin synthesis mechanism of the wild wheat, and also provides a direction and a target spot for improving the content of anthocyanin by transforming plants through a genetic engineering means.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Potato tuber anthocyanin synthesis transcription inhibitor StMYB44-1 and application thereof
PendingCN109988772AIncrease contentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyRNA extraction
The invention discloses a potato tuber anthocyanin synthesis transcription inhibitor StMYB44-1 and application thereof, wherein a gene sequence of the StMYB44-1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. A preparationmethod of the potato tuber anthocyanin synthesis transcription inhibitor StMYB44-1 comprises the following steps of: selecting plant materials; selecting reagents; extracting RNA and qPCR; constructing an expression vector; and cloning the StMYB44-1 gene sequence according to a designed primer of a potato database, and obtaining a complete coding sequence of the StMYB44-1 from potato meat of a black beauty potato by using cDNA as a template through PCR amplification. The invention discloses the transcription factor StMYB44-1 for inhibiting the potato tuber anthocyanin synthesis at high temperature; and the potato tuber anthocyanin synthesis transcription inhibitor StMYB44-1 has important significance for clarifying a regulation and control mechanism of the potato tuber anthocyanin under the influence of temperature and improving the content of the potato anthocyanin on the basis of the regulation and control mechanism.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Application of a Paeonia lactiflora PlTDC gene in changing plant flower colors
ActiveCN111826379AChange colorReduce anthocyanin contentPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses an application of a Paeonia lactiflora PlTDC gene in changing plant flower colors. The accession number of the Paeonia lactiflora PlTDC gene is KY765554. The constructed PlTDCgene overexpression vector is transformed into tobacco for expression, so that the anthocyanin content in plants, particularly in tobacco petals, is reduced, anthocyanin synthesis related gene expression is inhibited, and a novel light pink tobacco germplasm is created.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
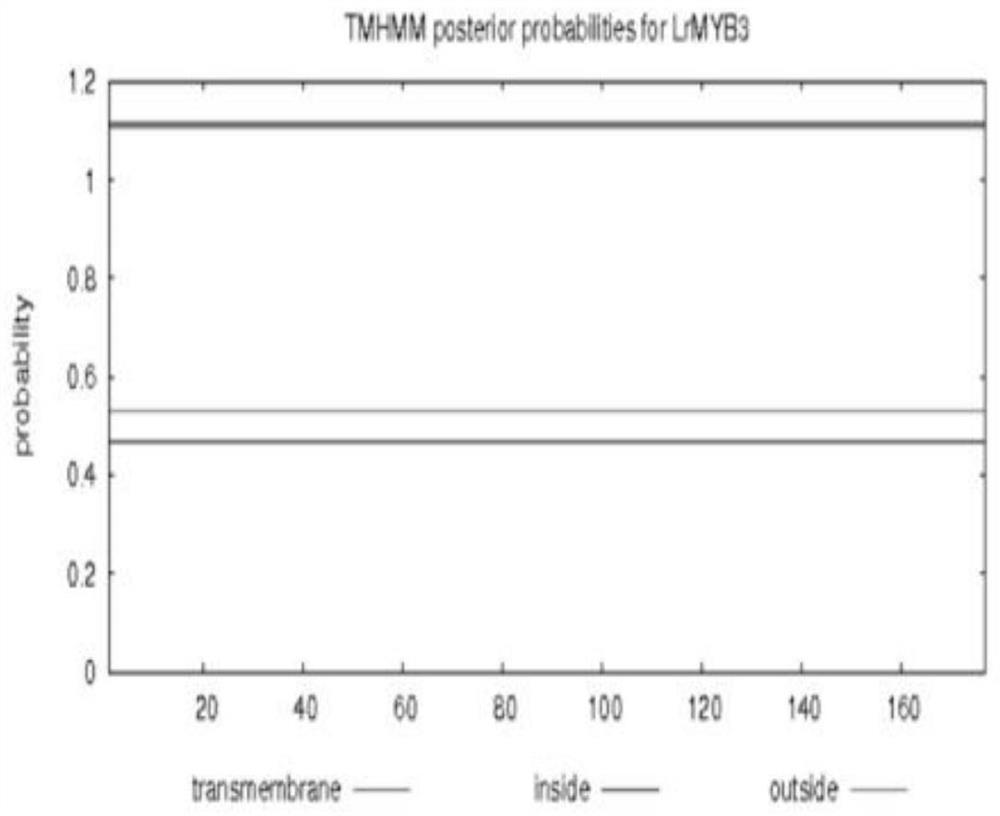
MYB transcription inhibition factor LrMYB3 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof
The invention discloses an MYB transcription inhibition factor LrMYB3 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to transcriptome data of lycium ruthenicum, the MYB transcription inhibition factor LrMYB3 participating in anthocyanin synthesis is screened and cloned according to annotation results and expression quantity differences of MYB transcription factors, and belongs to a R2R3 type MYB transcription factor. Multiple sequence alignment and evolutionary tree analysis show that the transcription inhibition factor belongs to a FaMYB1-like transcription inhibition factor. QRT-PCR analysis shows that: the LrMYB3 is expressed in each tissue of the lycium ruthenicum, and the expression level is gradually increased along with ripening of the lycium ruthenicum. Subcellular localization and transcriptional activity detection experiments show that the LrMYB3 is a transcription factor which is localized in a cell nucleus and has no activation function.
Owner:WOLFBERRY SCI INST NINGXIA ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Methylpyrane anthocyanin preparation method and application of methylpyrane anthocyanin
ActiveCN106432384AHigh yieldEasy to synthesizeSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationState of artCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
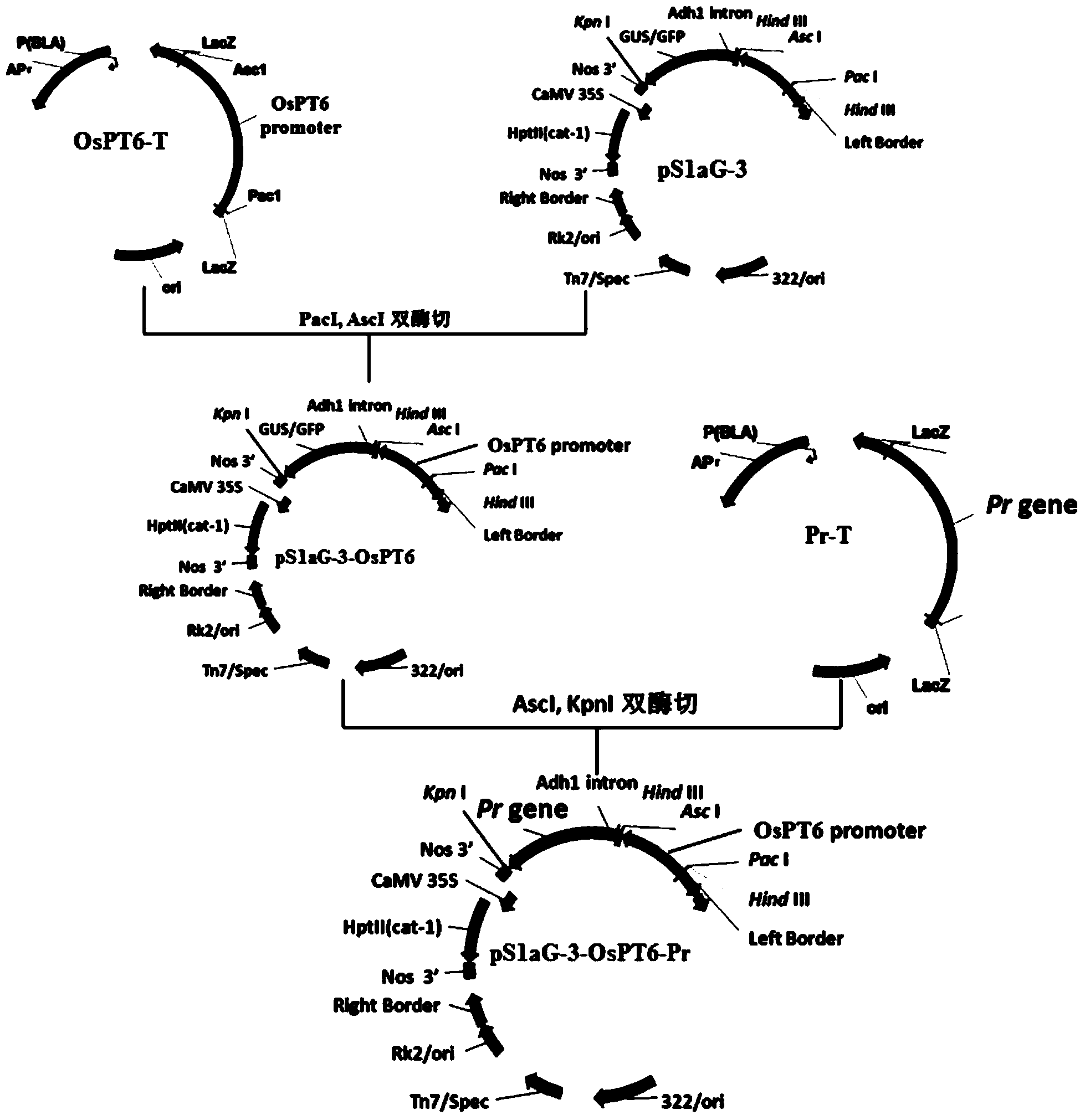
Rapid plant phosphorus nutrition diagnosis and visual dynamic monitoring method and application of recombinant expression vector
ActiveCN103509821AConserved regulatory functionSo as not to damageColor/spectral properties measurementsFermentationDynamic monitoringAnthocyanin synthesis
The invention discloses a rapid plant phosphorus nutrition diagnosis and visual dynamic monitoring method and application of a recombinant expression vector. A promoter which specifically responds to a phosphorus deficiency signal is used for regulating and controlling a recombinant expression vector for plant anthocyanin synthetic route gene expression to be converted into a plant so as to obtain a transgenic plant; when sufficient phosphorus is supplied, the leaves of the transgenic plant are maintained to be original green; when the plant is lack of the phosphorus, the promoter specifically drives overexpression of the anthocyanin synthesis gene, the anthocyanin is greatly accumulated on the leaves of the transgenic plant, and then the leaves of the plant are turned into dark pulp; when sufficient phosphorus is supplied again, the transgenic plant can be recovered to be green within a short time, so that the purpose of visual dynamic monitoring of the phosphorus of the plant is achieved. Due to the adoption of the method, the dynamic change of the phosphorus inside the plant can be sensitively and specifically monitored, and meanwhile with the application of the remote sensing technique, the supply state of the plant phosphorus supply condition can be rapidly monitored in large area, so that instruction of rational application of fertilizers in the field can be realized.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Strawberry anthocyanin-related gene FvMYB17 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering in molecular biology, and specifically relates to a strawberry anthocyanin-related gene FvMYB17 and an application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the FvMYB17 is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:2; the gene is indicated to have the function of promoting arabidopsis thaliana anthocyanin synthesis through research. A theoretical basis and technical means are provided for regulation of fruit color by using a genetic engineering technology, and great application value is achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
InDel molecular marker closely linked with eggplant anthocyanin synthesis gene as well as primer and application of InDel molecular marker
ActiveCN111910013AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyAnthocyanin synthesis
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, particularly relates to the field of molecular genetics, and particularly relates to an InDel molecular marker closely linked with an eggplantanthocyanin synthesis gene as well as a primer and application of the InDel molecular marker. For developing the molecular marker for controlling eggplant anthocyanin synthesis epistatic genes, the molecular marker InDel87335789 closely linked with the eggplant anthocyanin synthesis mutant pw gene is developed from a small associated region for restraining the eggplant anthocyanin synthesis mutantpw gene, wherein the eggplant anthocyanin synthesis mutant pw gene is positioned on the chromosome 8 of an eggplant, and the genetic distance between the molecular marker and a target gene P is 0.65cM. The molecular marker is expected to be applied to molecular marker assisted breeding of the eggplant anthocyanin synthesis mutant pw gene; and the molecular marker and the amplification primer ofthe molecular marker can be simply, conveniently and quickly applied to eggplant fruit color breeding practice with high throughput, and lay a good foundation for cloning an eggplant mutant pw gene and researching functions of the eggplant mutant pw gene.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for improving quality of grape fruits by using compound anti-transpiration agent
ActiveCN109699387AReduce weight lossReduce water evaporationCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsFruit setEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for improving the quality of grape fruits by using a compound anti-transpiration agent. In the period of fruit bearing, a hyaluronic acid solution is sprayed; from the initial period of maturation in the beginning to the initial period of maturation, the compound anti-transpiration agent is sprayed onto the surfaces of the fruits, hyaluronic acid can form an edible covered membrane on the surface of the grape skin, and the covered membrane maintains the local environmental humidity of the tissue while hindering the transpiration, thereby increasing the growthspeed of the grape fruits in the first expansion growth period, reducing the weight loss ratio of the fruits, reducing the water evaporation of the fruits, and enhancing the drought resistance ability. In the initial period of maturity of grapes in the beginning, ABA mixing treatment can obviously advance and improve the expression and expression quantity of a VvCWI (cell wall acid invertase) generelated to sugar accumulation and VvUFGT gene related to anthocyanin synthesis in the maturation process, and finally, the content of sugar, anthocyanin and other important quality factors in ripe grape fruits is increased.
Owner:山东济清科技服务有限公司
MYB transcription inhibition factor LrETC1 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof
ActiveCN113444731AMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesSequence databaseTranscription Repressor
The invention discloses an MYB transcription inhibition factor LrETC1 related to lycium ruthenicum anthocyanin synthesis and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the invention, the MYB transcription inhibition factor LrETC1 participating in the anthocyanin synthesis is screened and cloned, the total cDNA of the gene is 240bp, and 79 amino acids are encoded; protein sequence database analysis shows that the transcription factor belongs to R3 type MYB; and multiple sequence alignment and evolutionary tree analysis show that the transcription inhibition factor belongs to AtCPC-like transcription inhibition factors, and is a transcription factor which is located in a cell nucleus and does not have an activation function. A LrETC1 transgenic arabidopsis thaliana strain is obtained through agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation, compared with a wild type, seed coats of seeds are light brown, arabidopsis thaliana seedlings are free of pigment accumulation under the stress condition of high sucrose concentration, and the expression level of related structural genes is remarkably reduced.
Owner:WOLFBERRY SCI INST NINGXIA ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com