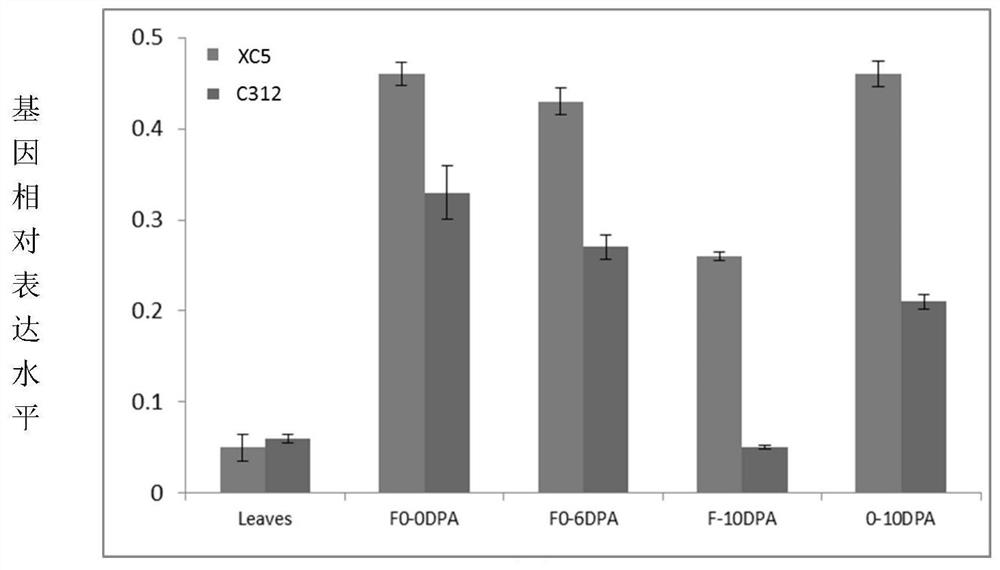
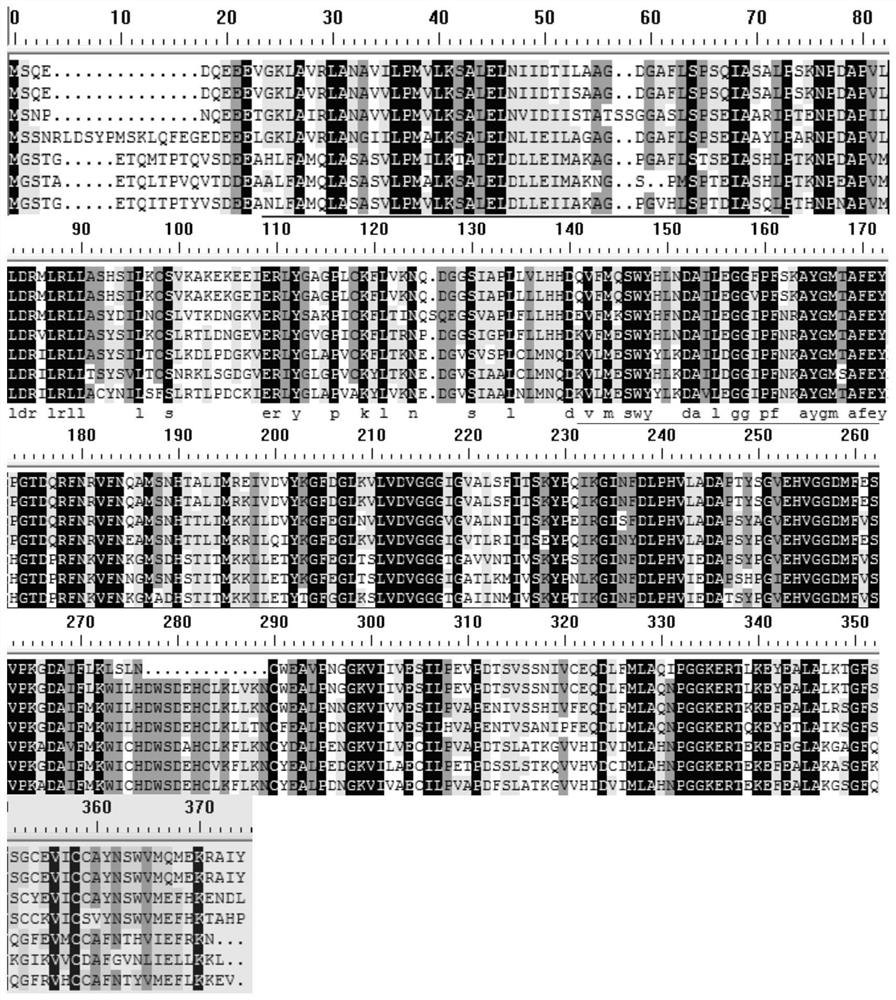
A method for improving cotton properties
A cotton and trait technology, applied in the field of cotton trait improvement, can solve the problems of the complexity of cotton genetic background, the loss of spontaneous mutant pool resources, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 Acquisition and Gene Cloning of Cotton Violet Senescence-Resistant Mutants
[0053] 1. Acquisition of purple senescence-resistant mutants in cotton
[0054] The constructed T-DNA expression vector (pBI121) was transferred to Agrobacterium LB4404 for expanded culture, and the hypocotyls of cotton C312 seedlings were mixed with Agrobacterium LB4404 loaded with T-DNA vector in induction medium (MSB5 medium + 2,4- D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) 0.1 mg / L + KT (cytokinin) 0.1 mg / L) at 23°C for 36-48 hours. The embryogenic callus was washed with sterile water containing cephalosporin (500 mg / L). The embryogenic callus after cleaning is transferred to the resistance selection medium (MSB5 medium+IBA (indole acetic acid) 0.5mg / L+KT0.15mg / L+kanamycin 50mg / L) to screen for successful transformation Embryogenic callus. Inoculate the different callus pieces that differentiated and grown on the subculture medium (MSB5 medium+IBA0.5mg / L+KT 0.2mg / L) respectively, pick ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Example 2 Using RNAi to interfere with the GhOMT1 gene to cultivate purple senescence-resistant transgenic cotton
[0094] (1) Cloning the full-length GhOMT1 gene (shown in SEQ ID NO.1) according to Example 1, inserting the GhOMT1 gene forward into the plant expression vector pBI121-35S-NOS, using the CaMV35S promoter to promote expression, and constructing a GhOMT1 gene containing Gene plant expression vector pBI21-35S-GhOMT1-NOS, such as Figure 4 .
[0095] Insert the GhOMT1 gene fragment (shown in SEQ ID NO.1) into the plant interference expression vector pB7GWIWG2(II), use the CaMV35S promoter to promote expression, and construct the plant interference expression vector pB7GWIWG2(II)-GhOMT1-F- containing the GhOMT1 gene T35S, such as Figure 5 .
[0096] The constructed vector was heat-shocked to transform DH-5α Escherichia coli competent, and during this process, kanamycin LB medium was used to cultivate the recombinant. The plasmid pB7GWIWG2(II)-GhOMT1 extract...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3 Using CRISPR-Cas9 Technology to Knockout the GhOMT1 Gene to Cultivate Violet Senescence-resistant Transgenic Cotton
[0100] 1. CRISPR / Cas9 system gene knockout vector of cotton GhOMT1 gene
[0101] 1) In order to obtain the 18-23bp guideRNA of the target gene GhOMT1 sequence, the only restrictive conditions for determining the target site according to the CRISPR / Cas9 system are the PAM site at the 3' end and the 18-22bp gRNA sequence at the front of the PAM. Look for the 23bp site, the standard recognition site form is GN19NGG, where NGG is the PAM sequence required for protein binding to the genome, and does not need to appear on the constructed vector, only the 20bp of GN19 in front of NGG needs to be placed in the vector. The first G in GN19 is the initiation signal required for small RNA transcription.
[0102] The guideRNA (gttccttttagtaaggcata) of the target gene GhOMT1 sequence was used to synthesize upstream and downstream primers (5'-GATTGN19-3', 3'...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com