Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141 results about "Resistant mutants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
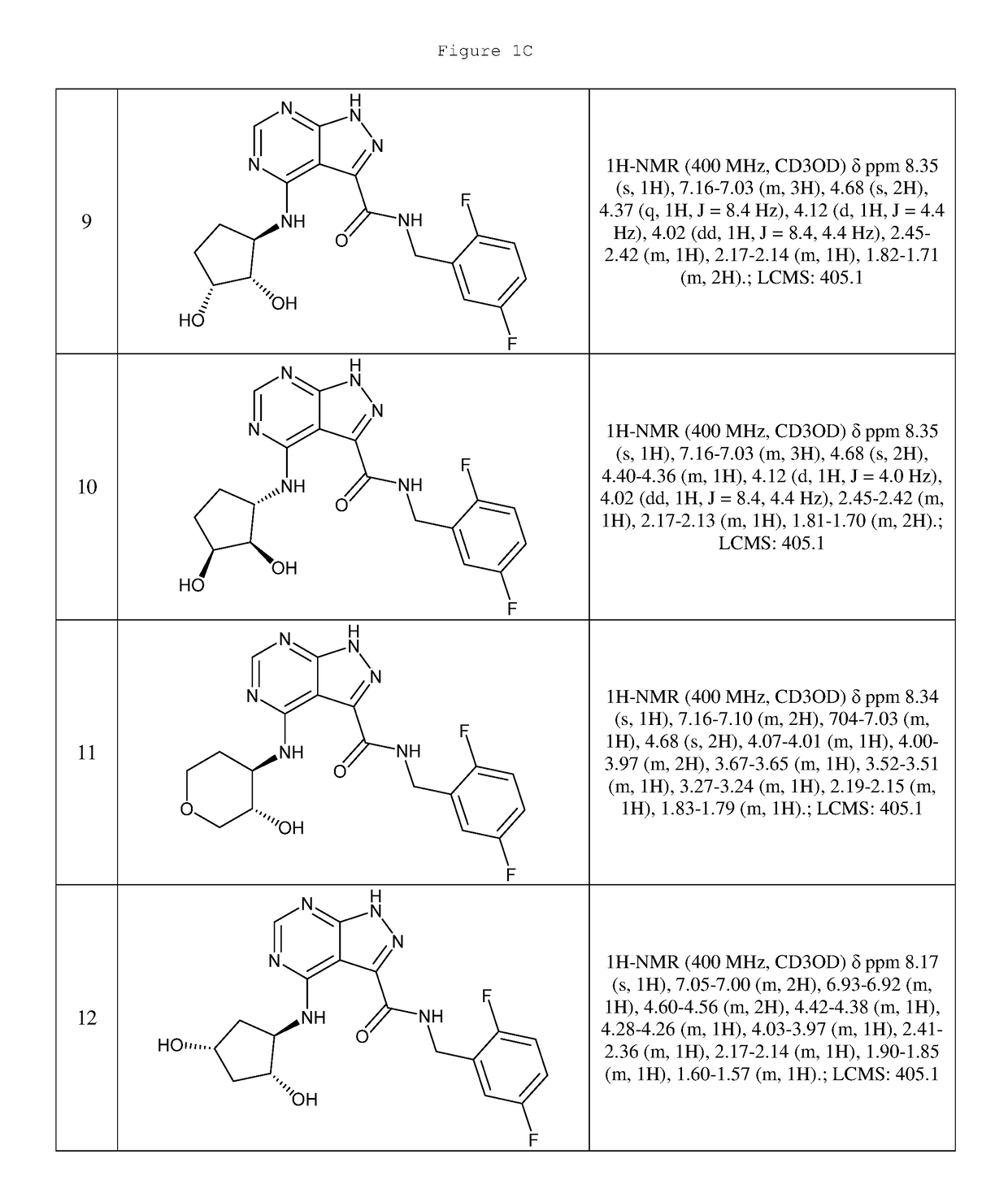
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compounds and compositions useful for treating disorders related to ntrk
ActiveUS20170145018A1Suppression problemOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderWild typeCancer research
This invention relates to inhibitors of NTRK that are active against wild-type NTRK and its resistant mutants.
Owner:BLUEPRINT MEDICINES
Compounds and compositions useful for treating disorders related to ntrk
This invention relates to inhibitors of NTRK that are active against wild-type NTRK and its resistant mutants.
Owner:BLUEPRINT MEDICINES
Acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase, and its gene, engineering bacterium and preparation method
ActiveCN102787130AGood acid stabilityIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisAlpha-amylase
The invention relates to an acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase, and its gene, engineering bacterium and preparation method. A technical proposal of the method consists of: utilizing a recombinant DNA technology for site-directed mutagenesis of a high temperature resistant alpha-amylase gene of Bacillus licheniformis, thus obtaining an acid resistant mutant gene of the high temperature resistant alpha-amylase, i.e. an acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase gene, and making use of a Bacillus subtilis expression system for secreting expression of the acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase. The acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase provided in the invention solves the problem of limited application of current high temperature resistant alpha-amylase due to its poor acid resistance and absence of high temperature resistance and acid resistance at the same time, satisfies some requirements for conducting a starch raw material liquefaction process under an acid and high temperature environment, and can improve product yield and quality as well as simplify the process.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Compositions and methods for treatment of staphylococcal infection while suppressing formation of antibiotic-resistant strains
Co-administration of a lysostaphin or other anti-staphylococcal agent which cleaves cross-links of peptidoglycans of staphylococci cell walls such as lysostaphin and an antibiotic effective against staphylococci due to antibiotic activity mediated by cell-wall activity is effective against staphylococcal infection, even staphylococci that may be resistant to one or other of lysostaphin or the cell-wall active antibiotic. Co-administration simultaneously suppresses the generation of antibiotic-resistant mutant strains. Effective cell-wall active antibiotics include β-lactams and glycopeptides.
Owner:NUTRITION 21 INC
Compounds and compositions useful for treating disorders related to NTRK
This disclosure relates to inhibitors of NTRK that are active against wild-type NTRK and its resistant mutants, such as compounds of Formula (I):
Owner:BLUEPRINT MEDICINES
Compositions and methods for treatment of staphylococcal infection while suppressing formation of antibiotic-resistant strains
Co-administration of a lysostaphin or other anti-staphylococcal agent which cleaves cross-links of peptidoglycans of staphylococci cell walls such as lysostaphin and an antibiotic effective against staphylococci due to antibiotic activity mediated by cell-wall activity is effective against staphylococcal infection, even staphylococci that may be resistant to one or other of lysostaphin or the cell-wall active antibiotic. Co-administration simultaneously suppresses the generation of antibiotic-resistant mutant strains. Effective cell-wall active antibiotics include β-lactams and glycopeptides.
Owner:NUTRITION 21 INC
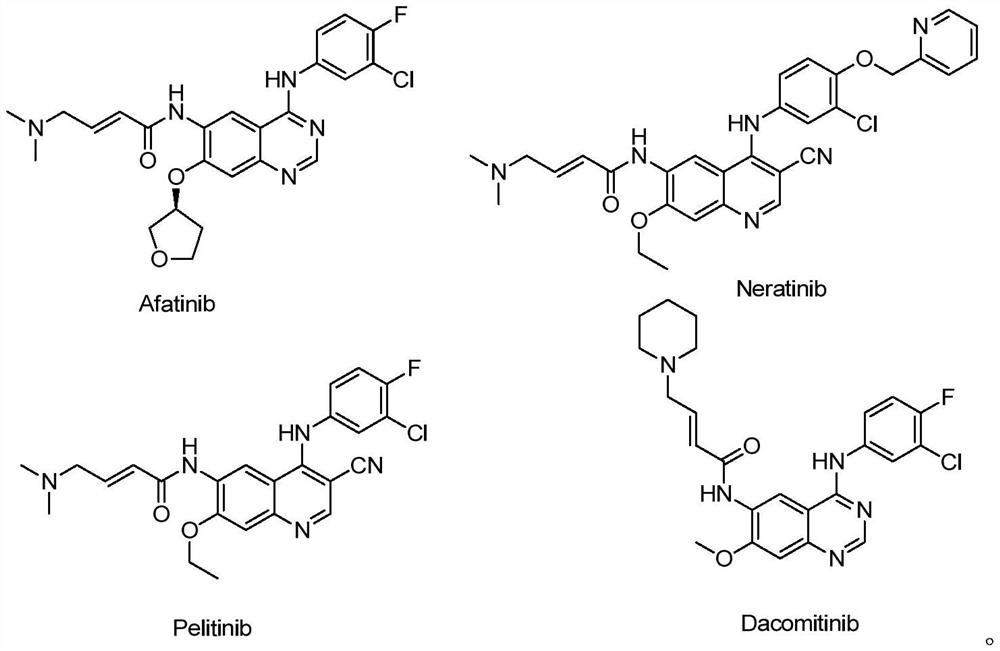
Pyrimidine or pyridine compounds, preparation method therefor and pharmaceutical uses thereof
ActiveUS20170355696A1Strong inhibitory activityReduce inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseActivating mutation
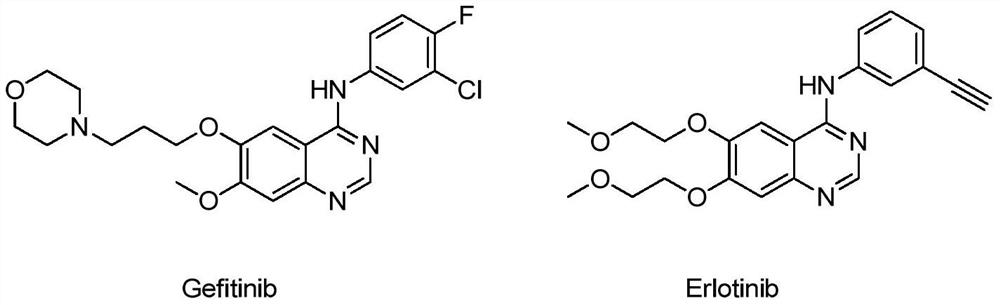
The present invention disclosed a class of pyrimidine or pyridine compounds, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, stereoisomers, prodrugs and solvates thereof, preparation method therefor and pharmaceutical compositions and pharmaceutical uses thereof. The compounds can inhibit the variants of EGFR (Epidermis Growth Factor Receptor) proteinases, and therefore can inhibit the growth of a variety of tumor cells effectively. The compounds can be used to prepare antitumor drugs, used for the treatment, combined therapy or prevention of various different cancers. The compounds can overcome the drug resistance induced by the existing first-generation EGFR inhibitors such as gefitinib, erlotinib and so on. Particularly, the compounds can be used to prepare drugs for treating or preventing diseases, disturbances, disorders or conditions mediated by epidermis growth factor receptor variants (such as L858R activated mutants, Exon19 deletion activated mutants and T790M resistant mutants).
Owner:INVENTISBIO CO LTD
Method for detecting resistant mutant of mycoplasma pneumoniae
InactiveCN102002522AQuick checkoutSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceResistant strainThermal cycler
The invention belongs to the fields of biology and medicines and particularly relates to a method for detecting a resistant mutant of mycoplasma pneumoniae. By adopting Real-time PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and a cycling probe technology for distinguishing the difference of monobases and searching a specific primer aiming at the mycoplasma pneumoniae in an upstream and a downstream sequence of 2063 bit / 2064 bit of the mycoplasma pneumoniae 23SrRNA gene, specific cycling probes aiming at mutation-free sensitive strains, 2063-bit mutant drug-resistant strains and 2064-bit mutant drug-resistant strains can be respectively designed according to the difference of the bases at the 2063 bit / 2064 bit of the mutation-free sensitive strains and mutant drug-resistant 23SrRNA gene of the mycoplasma pneumoniae; the PCR amplification can be carried out by using the specific primer of the mycoplasma pneumoniae; and the fluorescence intensity change can be read by a Real-time PCR thermal cycler in real time to determine the mutant types of samples to be detected. The invention can correctly distinguish the mutation-free sensitive strains from the mutant drug-resistant strains of clinical separation strains of the mycoplasma pneumoniae. The specificity is 100 percent and the sensitivity can reach 102copy / PCR reaction.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase
InactiveCN103070068AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce chanceSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention provides a herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase, which belongs to a plant trait breeding method. The method comprises the following steps of selecting materials needed by production of rape or breeding of the rape, processing seeds with ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS), mutagenizing the seeds to be isolated and propagated to a M2 generation, and directionally screening herbicide-resistant mutant characters in a large group under the selection pressure of the herbicide adopting the ALS as the target esterase. In order to increase the probability for acquiring the mutant characters, the directive screening can be continuously conducted in multiple years, or conducted in multiple places in the same year or conducted in multiple places in multiple years until the needed mutant material is screened out.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Screening method of chlamydomonas reinhardtii heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants
InactiveCN106967749ASimple stepsImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCadmium adsorptionChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a screening method for heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The screening method comprises: selecting a suitable screening concentration for heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants according to the influence of different cadmium chloride concentrations on the growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Transformation to obtain Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutants; screening out heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the screening of heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii includes screening heavy metal cadmium sensitive mutants and screening heavy metal cadmium resistant mutants; identification screening Mutant genes of heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The invention achieves the technical effect of being able to obtain a large amount of Chlamydomonas heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants simply and efficiently.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Method for breeding salt-tolerance mutant of sweet-potato
InactiveCN101002539AGood repeatabilityEasy to operateClimate change adaptationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentMicrobiologySomatic cell
A method for screening the salt-resistant mutant of sweet potato includes such steps as secondary culture of suspended embryonic cells of sweet potato, irradiating them by Co gamma-ray, sequentially culturing in liquid culture media A, B and C, culturing in solid culture medium A to obtain calli, sequentially culturing in solid culture media B, C and D to obtain plantlet, culturing in basic MS culture medium, culturing in liquid culture medium D, and culturing in Hoagland solution containing NaCl.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pyrimidine compound as well as preparation method and medical application of pyrimidine compound
PendingCN106478605AStrong inhibitory activityImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsDiseaseErlotinib
The invention discloses a pyrimidine compound, a pharmaceutically-acceptable salt, a stereoisomer, a prodrug and a solvate thereof, as well as a preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition and medical application of the pyrimidine compound. This type of compound can generate an inhibitory effect on variant forms of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) protease, so that the compound can effectively inhibit the growth of various tumor cells, can be used for preparing antitumor drugs, can be applied to treatment, combined treatment or prevention of many different cancers, and can overcome drug tolerance induced by first-generation EGFR inhibitors including existing drugs of gefitinib, erlotinib and the like. More particularly, this type of compound can be used for preparing medicines for treating or preventing diseases, obstacles, disorders or illness states mediated by certain epidermal growth-factor receptors with variant forms (for example, L858R active mutants, Exon19 deletion active mutants, and T790M resistant mutants).
Owner:INVENTISBIO CO LTD +1
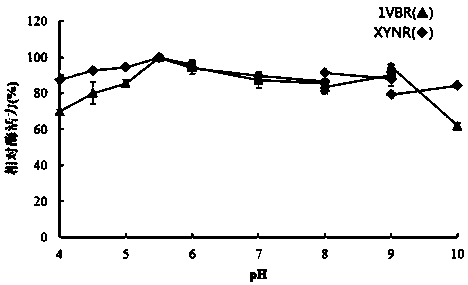
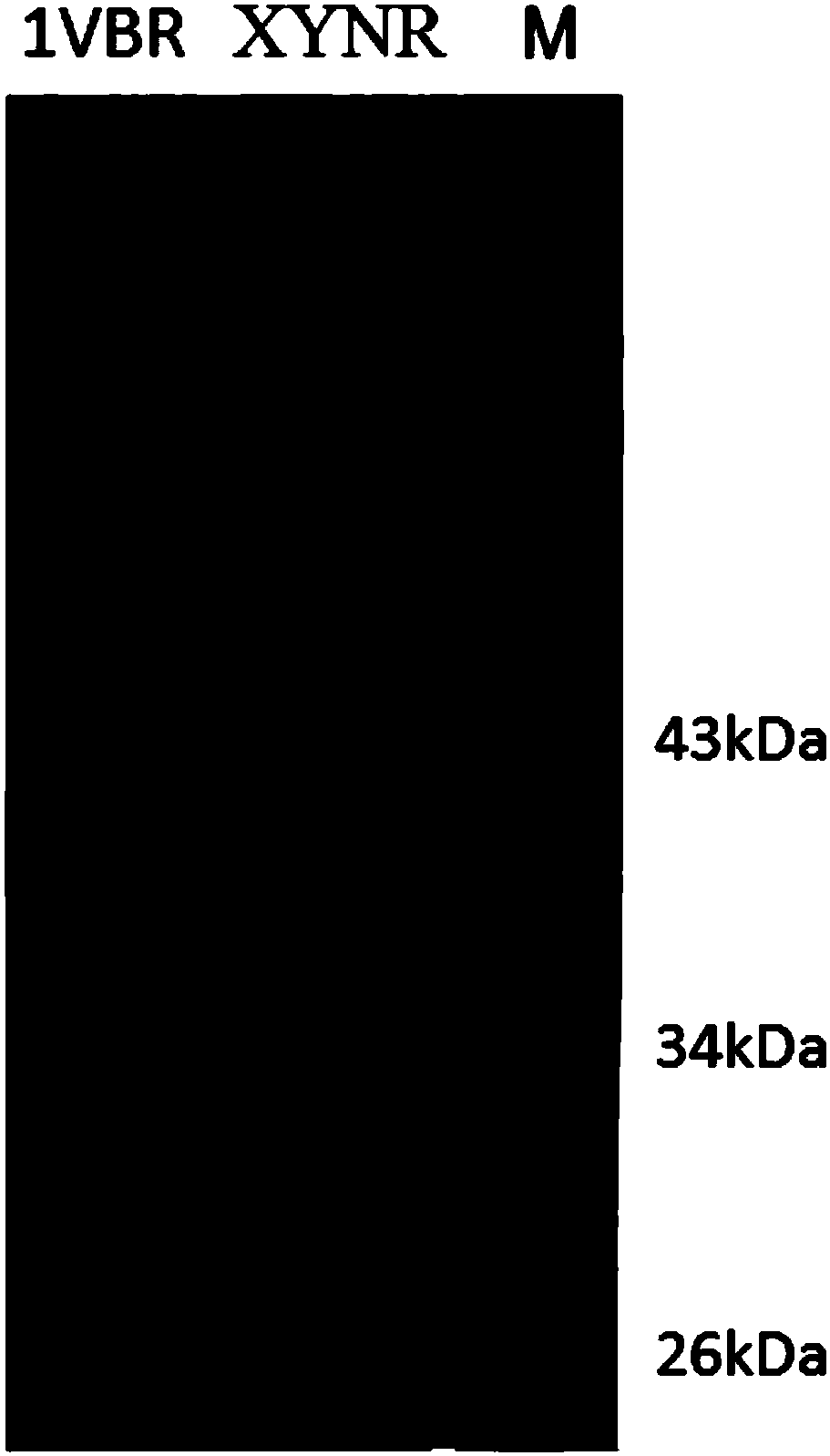
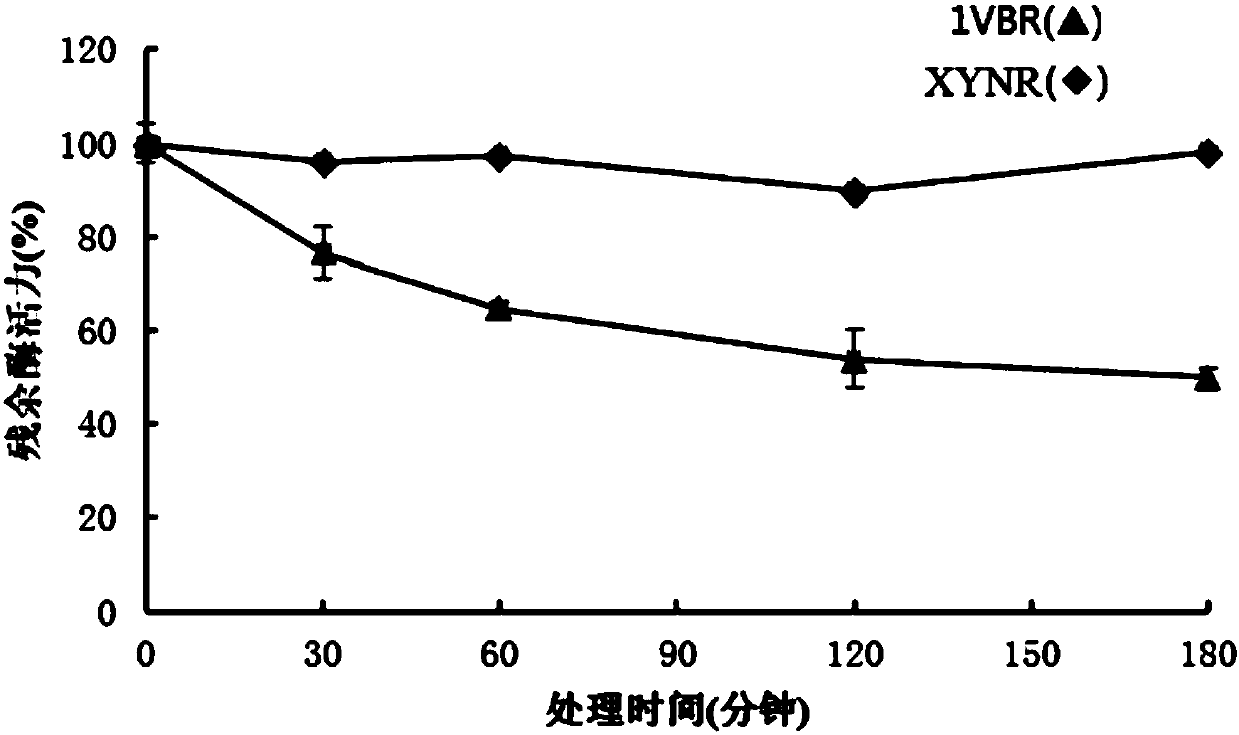
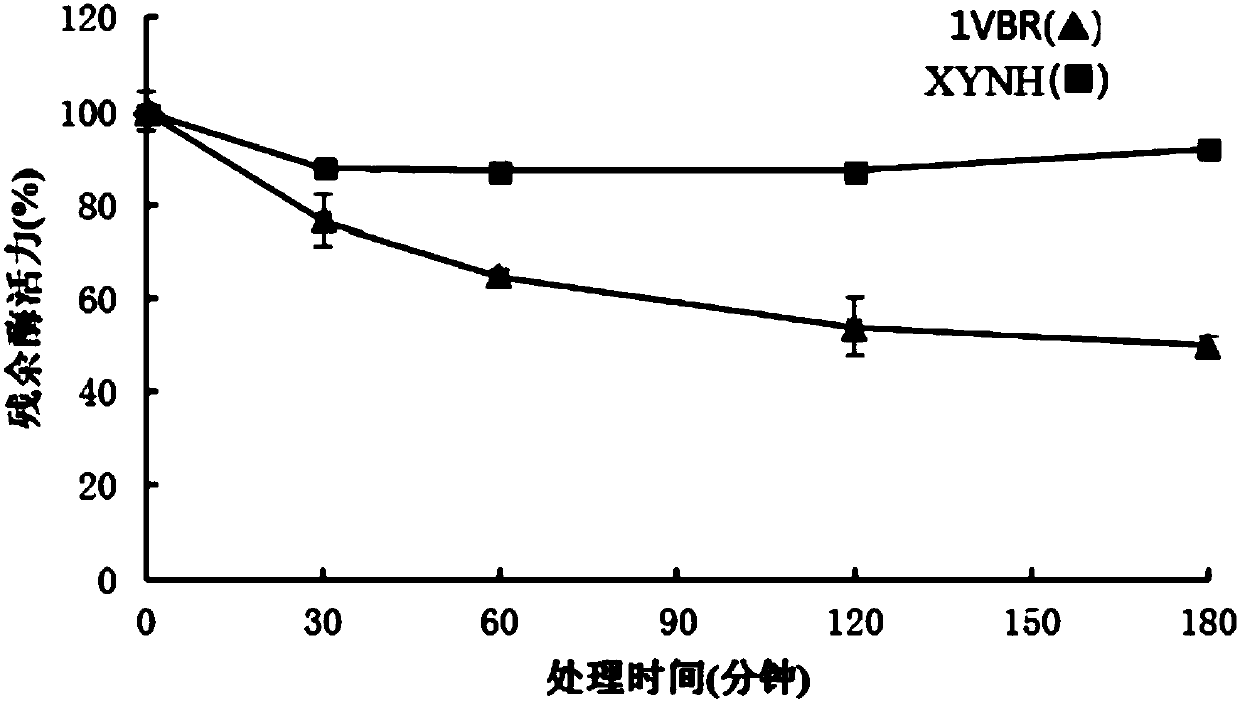
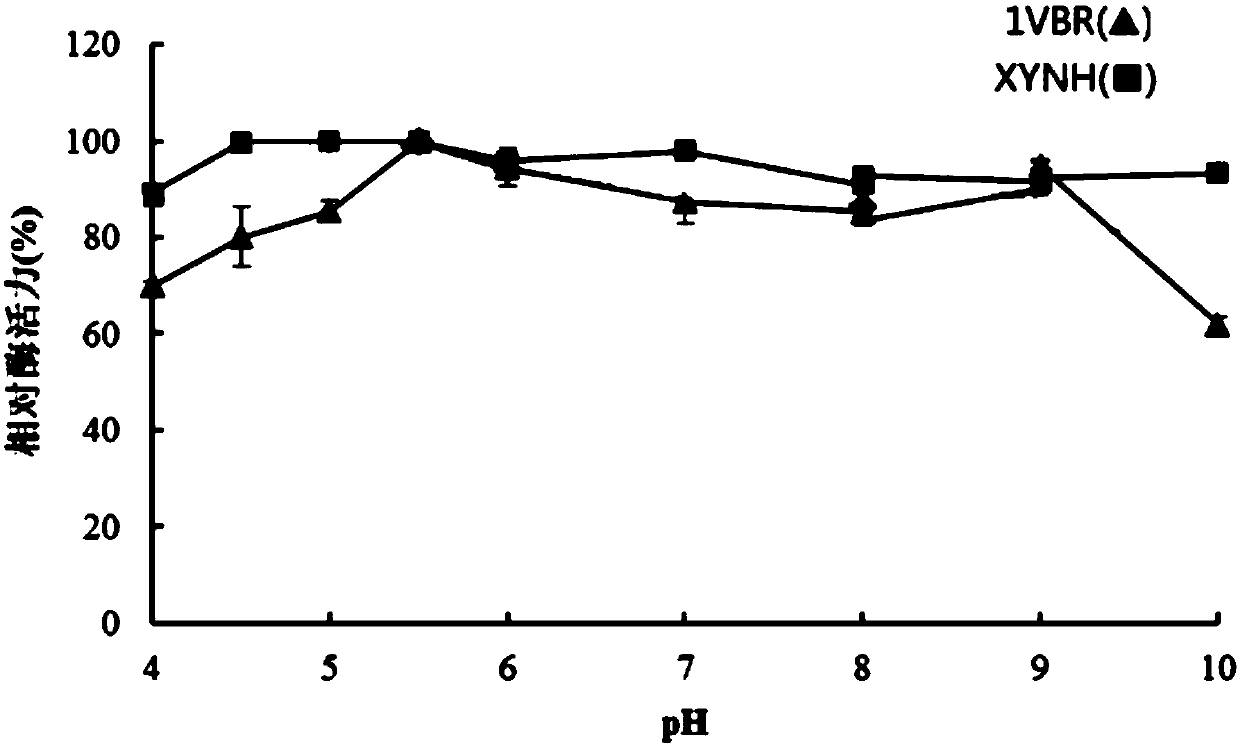
Mutant XYNR of extreme heat-resistant xylanase 1VBR and use thereof
The invention provides a mutant XYNR of an extreme heat-resistant xylanase 1VBR. The mutant XYNR is prepared through mutation of phenylalanine at the 290th of an amino acid sequence of the xylanase 1VBR into valine and has an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.1. The invention also provides a gene for encoding the mutant XYNR. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a recombinant expression vector pPIC9K-XYNR with the gene for encoding the mutant XYNR and a recombinant strain with the recombinant expression vector.After the amino acid sequence of the xylanase 1VBR is subjected to site-directed mutagenesis, the high heat-resistant mutant XYNR is obtained, is highly expressed in a pichia pastoris expression system and has a wide application prospect in the fields of feed additives, health foods, papermaking, washing, brewing, textiles and pharmacy.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Herbicide resistance mutant and application thereof
Owner:深圳洁田模式生物科技有限公司
PNA Probes, Kits, and Methods for Detecting Lamivudine-Resistant Hepatitis B Viruses
InactiveUS20080233557A1High sensitivityStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHbv dna polymeraseLamivudine resistance
Disclosed are peptide nucleic acid (PNA) probes to detect lamivudine resistant mutants of hepatitis B virus (HBV), which causes acute and chronic hepatitis, kits for detecting lamivudine resistant HBV comprising the PNA probes, and methods for detecting lamivudine resistant HBV by using the kits. They can accurately detect mutations of rtL180M, rtM204V, rtM204I and rtV2071 within B and C domains of HBV DNA polymerase gene, the main cause of lamivudine resistance, as well as mixed mutants of more than one mutant. They can detect lamivudine resistant HBV with high specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:PANAGENE INC
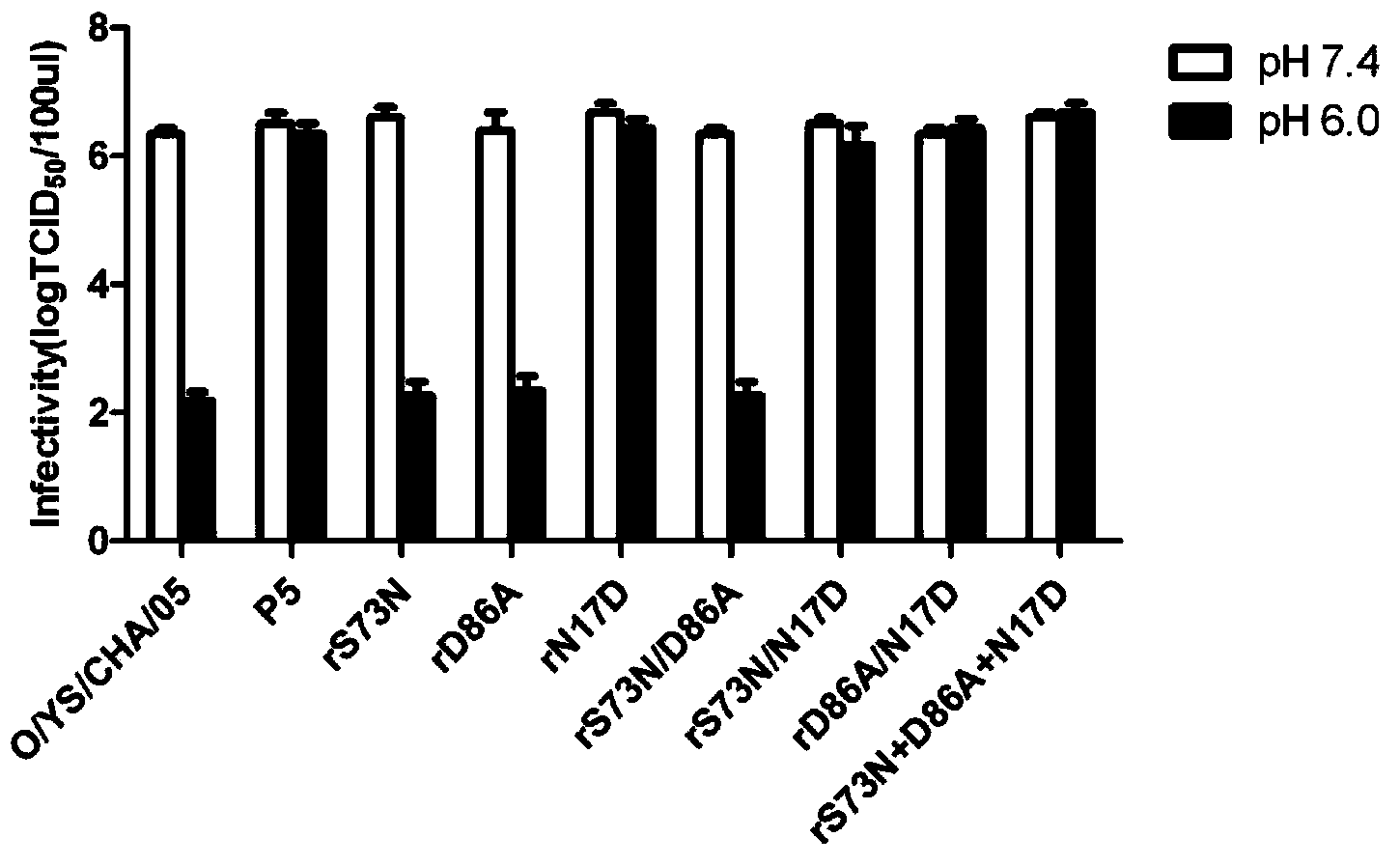
O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant mutant strain, capsid protein carried by O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant mutant strain, coding gene of capsid protein and use of O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant mutant strain and capsid protein
ActiveCN103849637ADecreased immune efficiencyImproving immunogenicityGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesSerial passageVaccine Production
The invention discloses an O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant mutant strain, a capsid protein carried by the O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant mutant strain and a coding gene of the capsid protein and also discloses a key amino acid site for determining O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant characteristics and a use of the key amino acid site. An O-type foot and mouth disease virus parent strain is subjected to serial passage screening under acid stress so that a mutant strain having strong acid resistance is obtained, and an analysis result shows that a VP1 N17D mutational site is a key amino acid site for determining O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant characteristics, the O-type foot and mouth disease virus only with the VP1 N17D mutational site has the acid resistance the same as that of the mutant strain and also has a good replication capability and immunogenicity. The key amino acid site for determining O-type foot and mouth disease virus acid-resistant characteristics can be used for reconstruction of acid resistance of a foot and mouth disease virus vaccine and for exploitation of a novel foot and mouth disease gene engineering vaccine. The acid-resistant mutant strain rN17D can be used as a high-quality inactivated vaccine-production parent strain, can improve content of a 146S effective antigen in the inactivated vaccine and can improve vaccine immune efficacy.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method for resistant super-male polyploidy asparagus based on flow cytometry
InactiveCN102783416AComprehensiveImprove efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeComparative test
The invention discloses a breeding method for resistant super-male polyploidy asparagus based on flow cytometry. The method comprises the following steps: (1) choosing excellent male plants in a field and carrying out indoor planting and microscopic examination; (2) mechanically separating microspores; (3) carrying out flow sorting; (4) carrying out suspension culture; (5) screening resistant mutants; (6) carrying out artificial doubling; (7) carrying out flow analysis; (8) subjecting the microspores obtained in step (7) respectively to field selective matching and cross combination and to in vitro rapid propagation; and (9) carrying out variety comparative tests on plants obtained after field selective matching and cross combination and plants obtained after in vitro rapid propagation, and applying plants obtained in the tests in production in the field. The method provided by the invention has the following beneficial effects: (1) a breeding period is shorter, breeding efficiency is higher, and operation is simpler; (2) an obtained variety has comprehensiveness; and (3) a breeding technology is novel.
Owner:SHAANXI TIANZHENGDA BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for producing mutant of hemerocallis middendorffii by in vitro mutagenesis of ethyl methane sulfonate
InactiveCN106973791AImprove seedling efficiencyImprove the level of breeding technologyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLethal doseNormal growth
Owner:INST OF DRY LAND FARMING SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Acid-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof
ActiveCN111676146AStable traitsPromote growthFungiMicroorganism based processesCell factorySuccinic acid
The invention discloses an acid-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof. The saccharomyces cerevisiae MTPfo-4 disclosed by the invention is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on June 10, 2020, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2020199. According to the invention, exogenous malic acid is used as stress pressure, the S. Cerevisiae acid-resistant mutant strain MTPfo-4 is obtained through directed evolution screening in a laboratory, and the minimum tolerance pH is 2.44 which is also the minimum tolerance pH of currently reported saccharomyces cerevisiae.The mutant strain MTPfo-4 which is tolerant to various organic acids at the same time has the advantage that the tolerance to exogenous malic acid is increased to 86.8 g / L. The obtained mutant strainMTPfo-4 is further identified, is stable in character and good in growth, and can tolerate various organic acids (lactic acid, malic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, citric acid, gluconic acid andtartaric acid) at the same time, also has strong tolerance to inorganic acids (HCl and H2PO3), which is difficult to achieve in current S. Cerevisiae research reports. The acid-resistant saccharomycescerevisiae is expected to be used for producing various short-chain organic acids in an acid-resistant chassis cell factory.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
4,6-pyrimidine diamine compound and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN104844526AGood EGFR activityEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEgfr expressionSynthesis methods
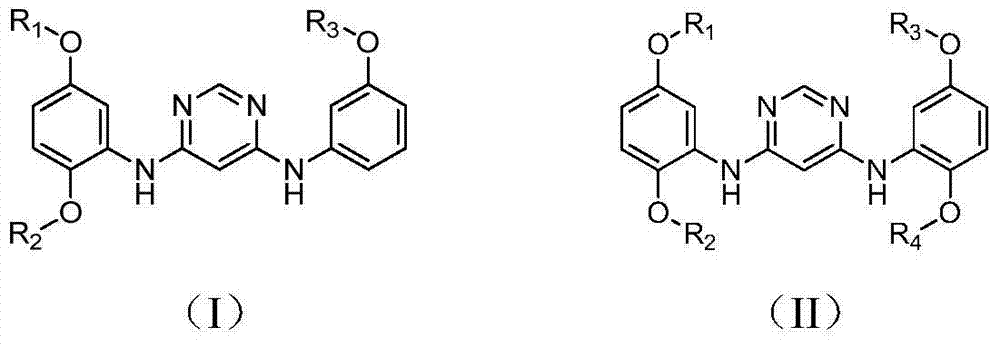
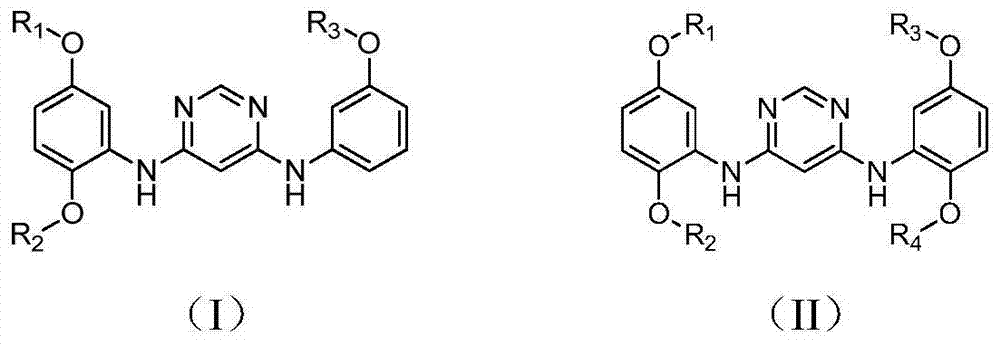
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemistry, and particularly relates to a 4,6-pyrimidine diamine compound and a preparing method and an application thereof; the 4,6-pyrimidine diamine compound is an N4,N6-(2,5-dialkoxy phenyl)-pyrimidine diamine compound or an N4-(2,5-dialkoxy phenyl)-N6-(3-alkoxy phenyl)-pyrimidine diamine compound, and in particular, alkoxy can be C1-C4 alkane. The 4,6-pyrimidine diamine compound can be used for broad-spectrum inhibition of the activity of an EGFR kinase and resisting of EGFR expressed tumor cell activity. The EGFR kinase is a wild-type or drug-resistant mutant EGFR kinase, and provides a basis for new drug screening. And the synthesis method of the 4,6-pyrimidine diamine compound provided by the invention is simple in synthesis process and is in favor of industrialized production.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method of protecting fish against columnaris disease with modified live Flavobacterium columnare
InactiveUS6991793B2Control process safetyReduce economic lossBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunityMicrobiology
Safe and effective live vaccines against Flavobacterium columnare of fish were created through the induction of rifampicin resistance in a native Flavobacterium columnare isolate; these including rifampicin-resistant mutants NRRL B-30303 and B-30304. Single immersion exposure of fish stimulated acquired immunity against virulent F. columnare infection.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Polysubstituted quinazoline compound and application thereof
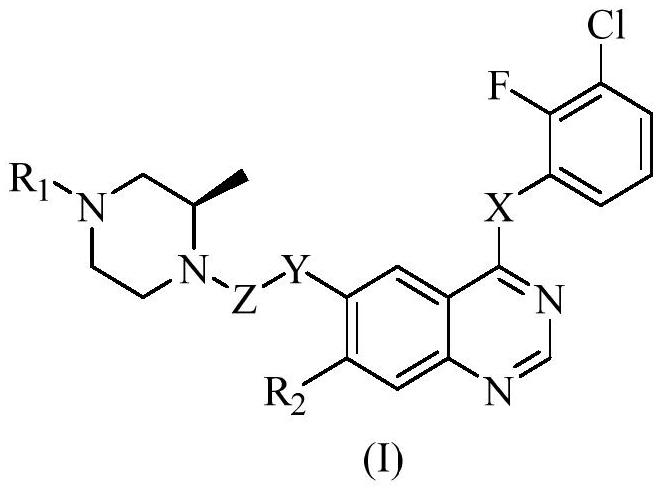
InactiveCN111848584AExcellent brain barrier penetration performanceGood pharmacodynamic propertiesOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySide effectMetabolic stability
The invention discloses a polysubstituted quinazoline compound and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of chemical medicines. The substituted quinazoline compound represented by the general formula (I) and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof have excellent brain barrier permeability, enhanced metabolic stability and longer metabolic half-life period, show higher inhibitory activity on an activated or drug-resistant mutant form EGFR than a wild type EGFR, and can effectively reduce side effects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
2 - (2, 4, 5 - substituted -anilino) pyrimidine derivatives as egfr modulators useful for treating cancer
The present invention relates to certain 2-(2,4,5-substituted-anilino)pyrimidine compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof which may be useful in the treatment or prevention of a disease or medical condition mediated through certain mutated forms of epidermal growth factor receptor (for example the L858R activating mutant, the Exon19 deletion activating mutant and the T790M resistance mutant). Such compounds and salts thereof may be useful in the treatment or prevention of a number of different cancers. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compounds and salts thereof, especially useful polymorphic forms of these compounds and salts, intermediates useful in the manufacture of said compounds and to methods of treatment of diseases mediated by various different forms of EGFR using said compounds and salts thereof.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain and application thereof in production of L-leucine by fermentation method
InactiveCN103031265BIncrease production capacityDefeedback regulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLeucine biosynthesisBio engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of biological engineering, in particular to a corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain and application thereof in production of L-leucine by a fermentation method. The corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain is an L-leucine defect response and alpha-amino-beta-hydroxy valeric acid resistant mutant strain SL-0193 (Leu+AHVr) obtained by implementing DES one-step mutation screening for corynebacterium glutamicum CGMCC1.495 (Leu-); the preservation number of the mutant strain is CGMCC No.7033; the mutant strain effectively relieves the feedback regulation of a target product L-leucine to an L-leucine biologic synthetase system, and has higher L-leucine production capacity; under proper cultivation conditions, 32.0 g / L L-leucine is produced by implementing the fermentation in a shake flask for 48 hours, and 41.3 g / L L-leucine is produced by implementing the fermentation in a self-control fermentation tank for 60 hours.
Owner:XINTAI JIAHE BIOTECH CO LTD
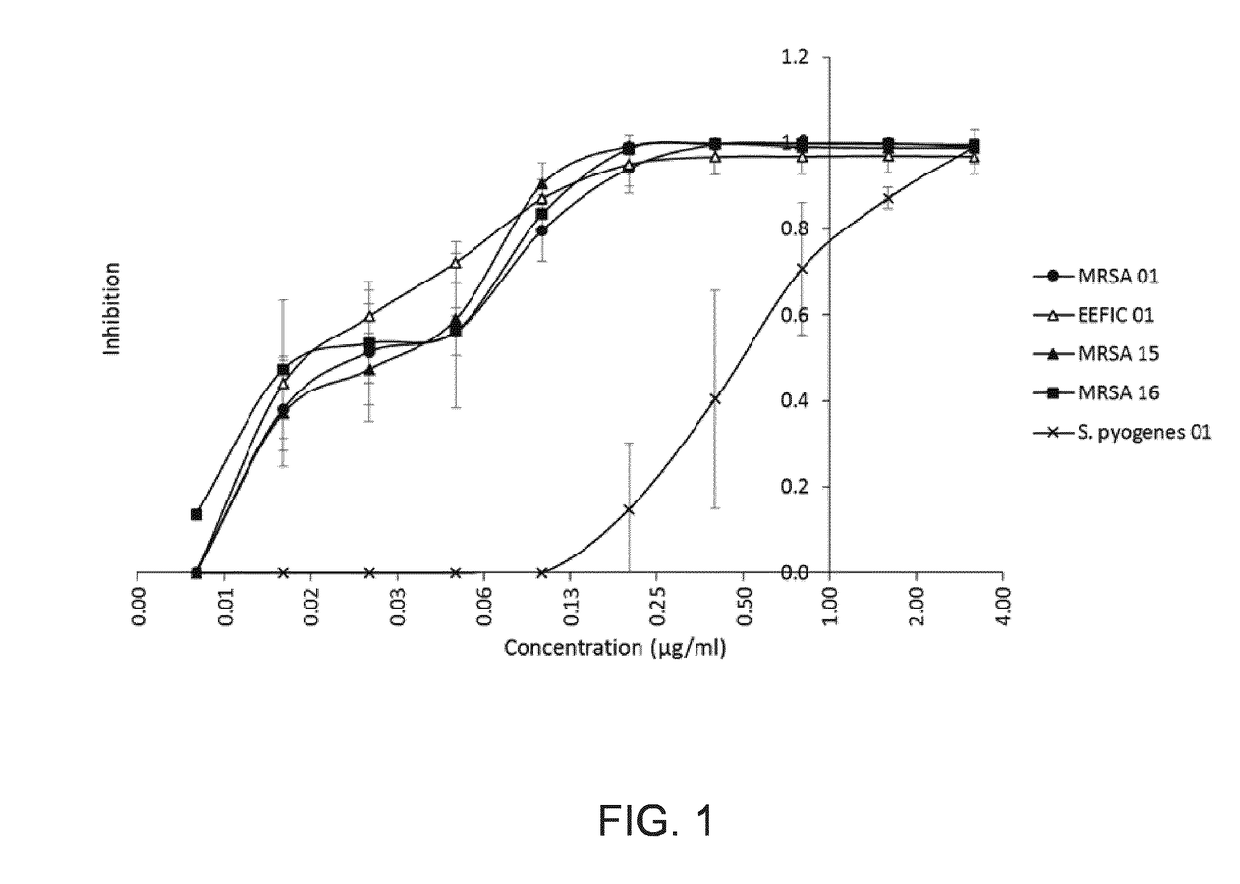
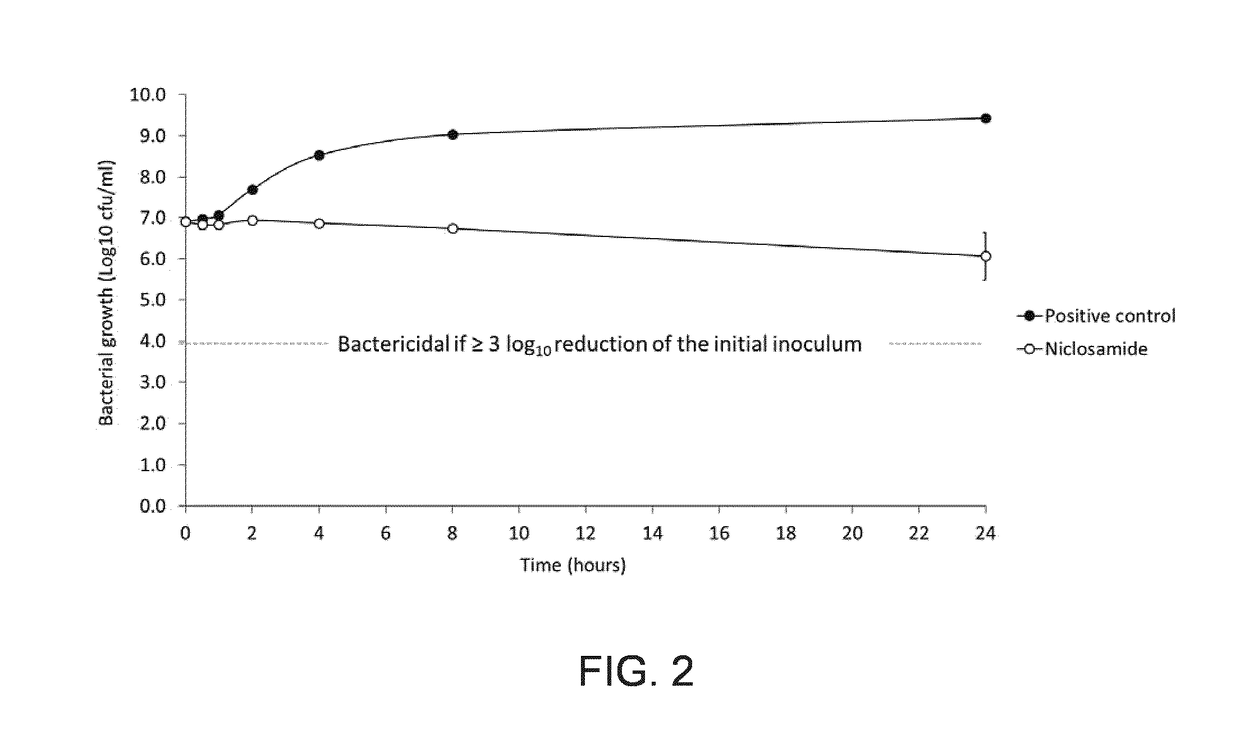
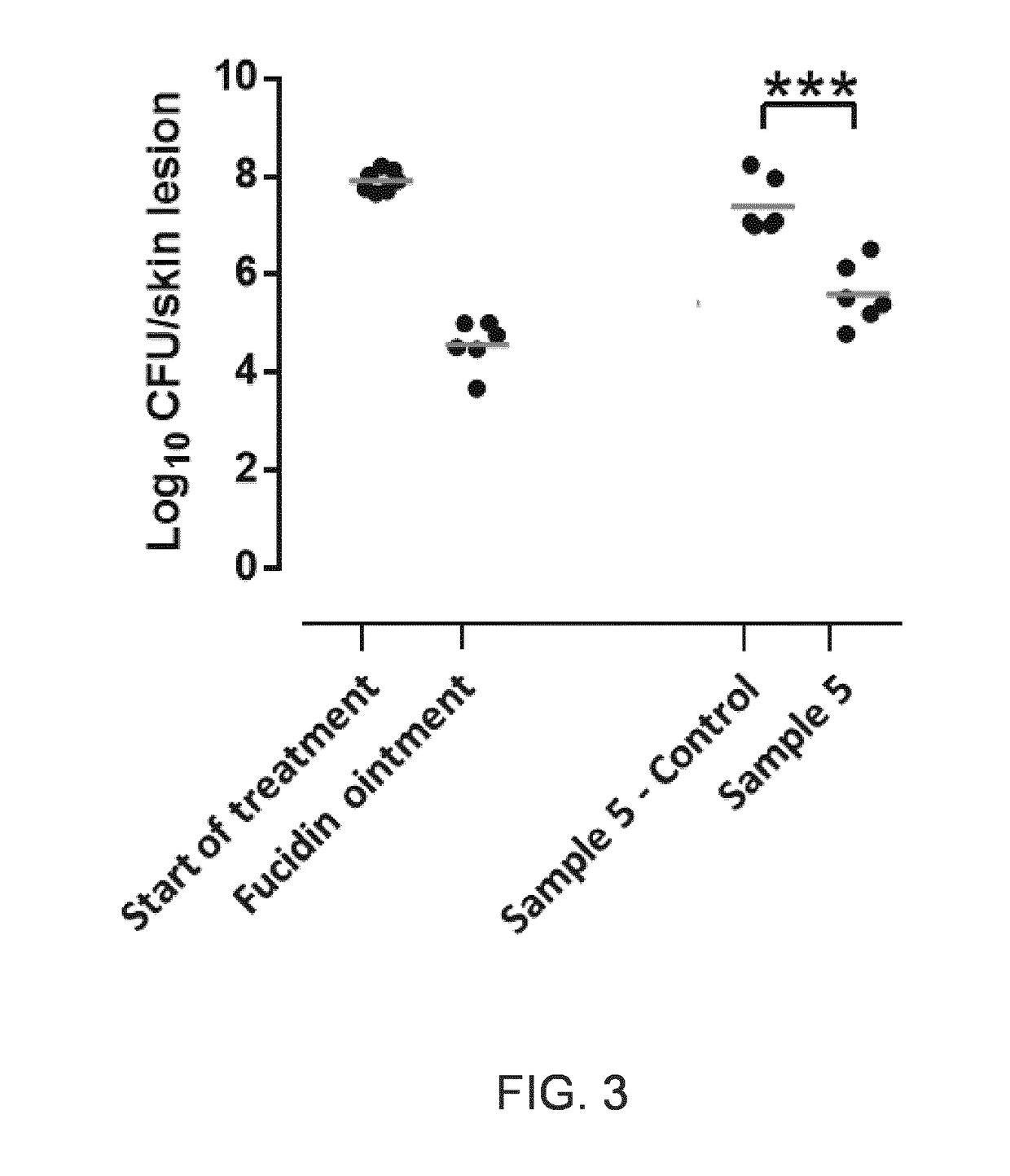
Antibacterial Use of Halogenated Salicylanilides
InactiveUS20170258816A1Reduced rate of appearanceReduce developmentAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStreptococcus pyogenesRafoxanide
The invention relates to a halogenated salicylanilide selected from closantel, rafoxanide, oxyclozanide and niclosamide and derivatives thereof including salts, hydrates, esters and the like for use in the topical treatment or prevention of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus, in particular Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus, in particular Streptococcus pyogenes. Gram positive bacteria treated with the halogenated salicylanilides exhibit a very low frequency of appearance of resistant mutants compared to commonly used topical antibiotics.
Owner:UNION THERAPEUTICS AS
Method for identifying antibiotic targets by complemented sequencing
InactiveUS20140135234A1Easy to detectAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant cloneEssential gene
Disclosed is a method for identifying an essential gene which serves as an antibiotic target in a bacterium, the method comprising the steps of:(a) generating an antibiotic resistant mutant of said bacterium by a method comprising the step of selecting for growth in the presence of said antibiotic to produce an antibiotic resistant mutant clone (AbR mutant);(b) transforming the AbR mutant with: (i) one or more essential genes of said bacterium; and (ii) a transposon which insertionally inactivates bacterial DNA, to produce a pool of transposon mutants which are merodiploid for said one or more essential genes;(c) growing bacteria from the merodiploid pool in the presence of different amounts of said antibiotic to produce two or more test cultures; and(d) comparing the distribution of transposon insertions between test cultures to identify a putative essential gene serving as a target of said antibiotic in said bacterium.
Owner:DISCUVA
Mutant XYNH of extreme heat-resistant xylanase 1VBR and use thereof
The invention provides a mutant XYNH of an extreme heat-resistant xylanase 1VBR. The mutant XYNH is prepared through mutation of phenylalanine at the 290th of an amino acid sequence of the xylanase 1VBR into histidine and has an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.1. The invention also provides a gene for encoding the mutant XYNH. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a recombinant expression vector pPIC9K-XYNH with the gene for encoding the mutant XYNH and a recombinant strain with the recombinant expression vector. After the amino acid sequence of the xylanase 1VBR is subjected to site-directed mutagenesis, the high heat-resistant mutant XYNH is obtained, is highly expressed in a pichia pastoris expression system and has a wide application prospect in the fields of feed additives, health foods, papermaking, washing, brewing, textiles and pharmacy.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
2 -(2,4,5-substituted -anilino) Pyrimidine Derivatives As Egfr Modulators Useful For Treating Cancer
The present invention relates to certain 2-(2,4,5-substituted-anilino)pyrimidine compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof which may be useful in the treatment or prevention of a disease or medical condition mediated through certain mutated forms of epidermal growth factor receptor (for example the L858R activating mutant, the Exon19 deletion activating mutant and the T790M resistance mutant). Such compounds and salts thereof may be useful in the treatment or prevention of a number of different cancers. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compounds and salts thereof, especially useful polymorphic forms of these compounds and salts, intermediates useful in the manufacture of said compounds and to methods of treatment of diseases mediated by various different forms of EGFR using said compounds and salts thereof.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Pyridine amino pyrimidine derivative mesylate crystal forms, preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN107163027AImprove bioavailabilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsPyrimidineSolubility
The invention provides a crystal form I and a crystal form II of mesylate of a compound as shown in a formula (I), a preparation method of the crystal forms, a medicine composition with the crystal forms and an application of the crystal forms to treatment of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) activated or drug-resistant mutant mediated diseases, particularly cancers of mammals, particularly human bodies. The crystal forms of the mesylate of the compound as shown in the formula (I) have good solubility and are high in bioavailability in animal bodies.
Owner:SHANGHAI ALLIST PHARM CO LTD
Screening method of successive cropping obstacle resistant mutants of strawberry
InactiveCN103053415AStable differentiationGenetic stabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyContinuous cropping
The invention relates to a screening method for inducing successive cropping obstacle resistant mutants of strawberry with the mixed liquor of oxysporum toxin and autotoxin p-hydroxybenzoic acid as selection pressure and belongs to the agricultural biological technical field. The strawberry blight caused by fusarium oxysporum and the root system autotoxin p-hydroxybenzoic acid are important factors causing serious successive cropping obstacle of strawberry. The screening method employs seedling leaf sections of a strawberry group as the induction materials; and in the optimal callus induction medium (MS solid culture medium, maltose (10-30 g / L), TDZ (1-4 mg / L) and AgNO3 1mg / L) containing the mixed liquor of the toxin and p-hydroxybenzoic acid in the medial lethal concentration (10% of toxin+1.0*10-4 mol L-1), three resistant mutants high in differentiation rate, good in hereditary stability and high in firmness are selected. The screening method provides new technical way and theoretical support for realizing breakthrough and innovation of resisting continuous cropping germplasm resources under the successive cropping condition of strawberry.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com