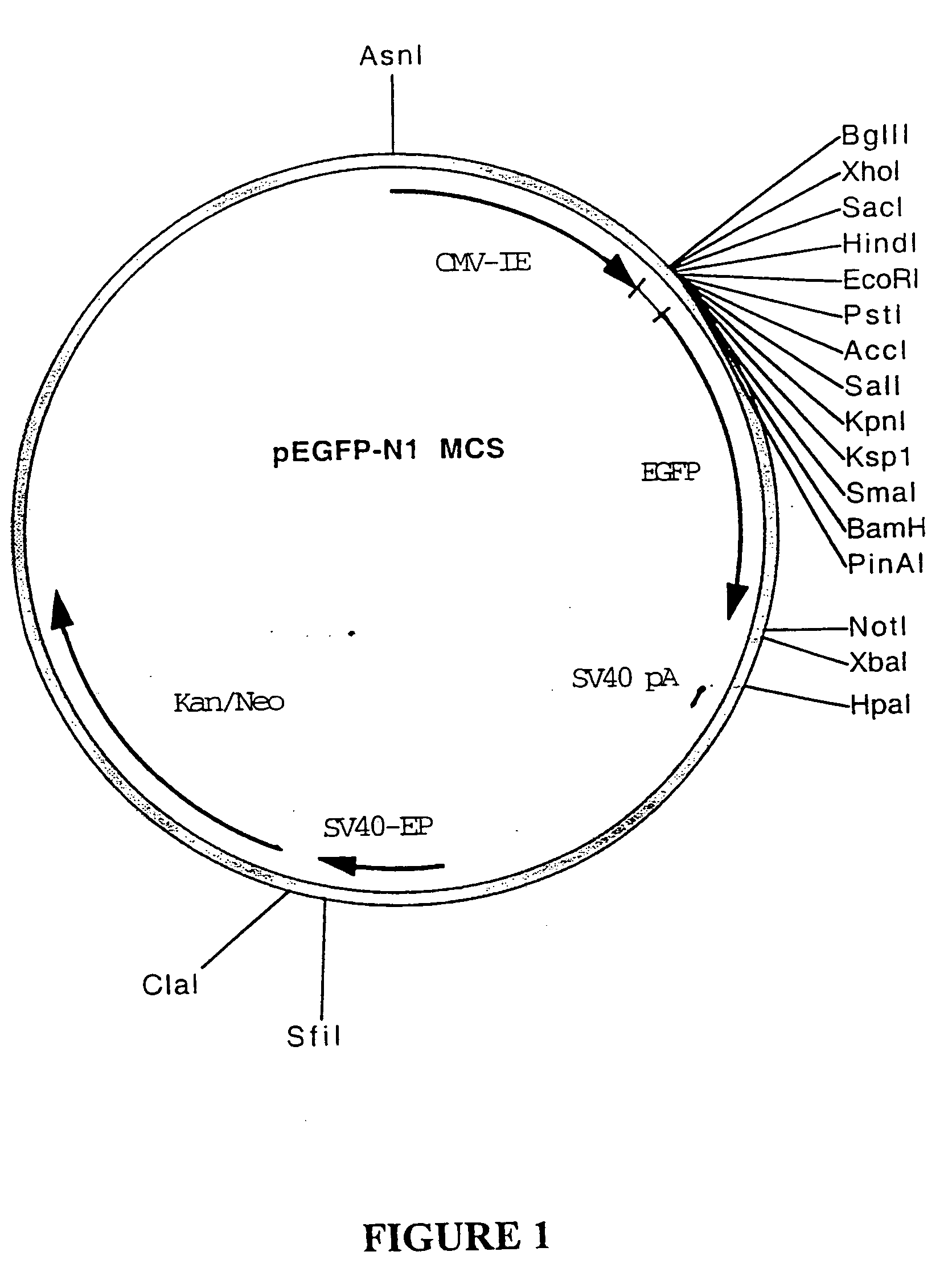
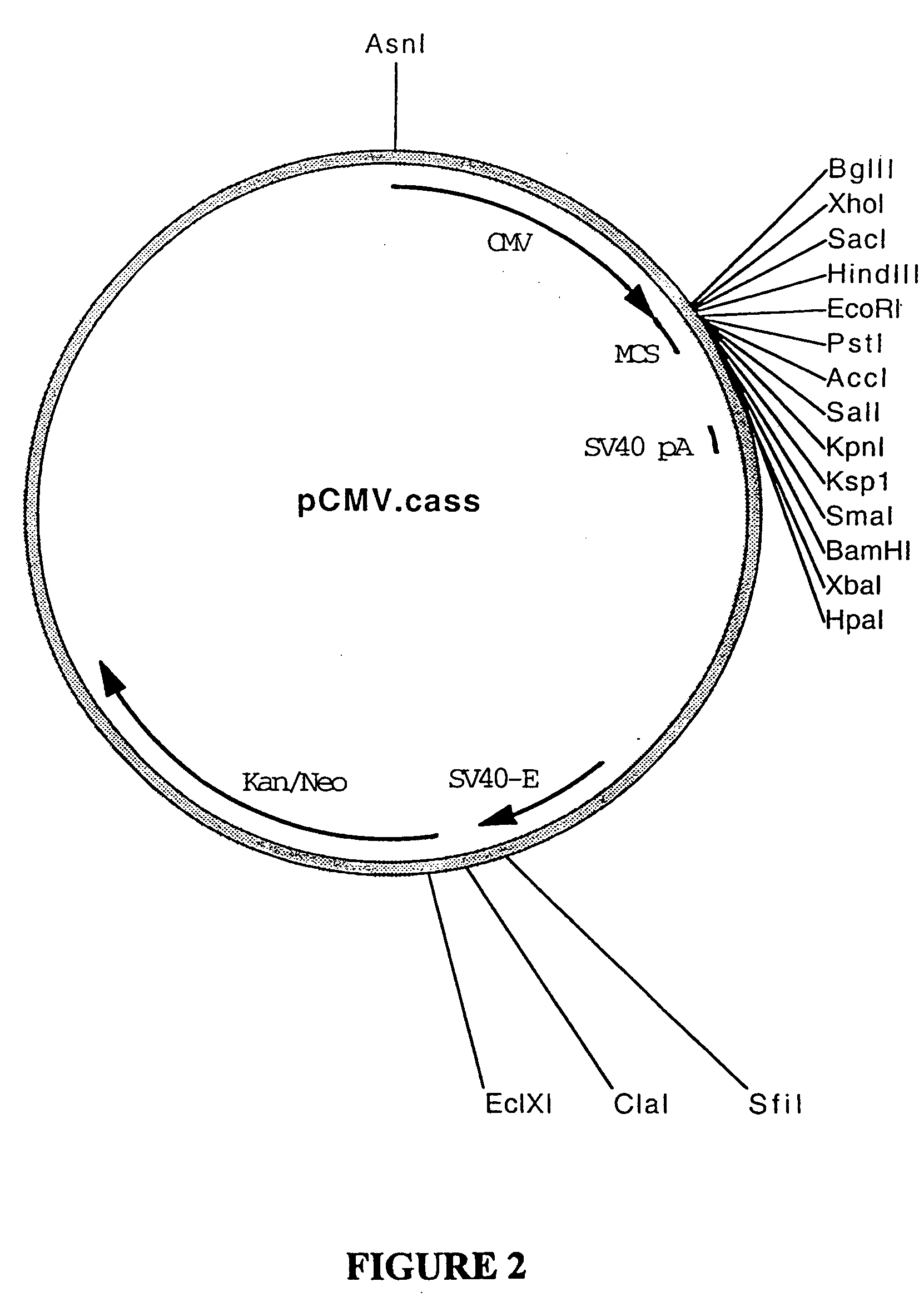
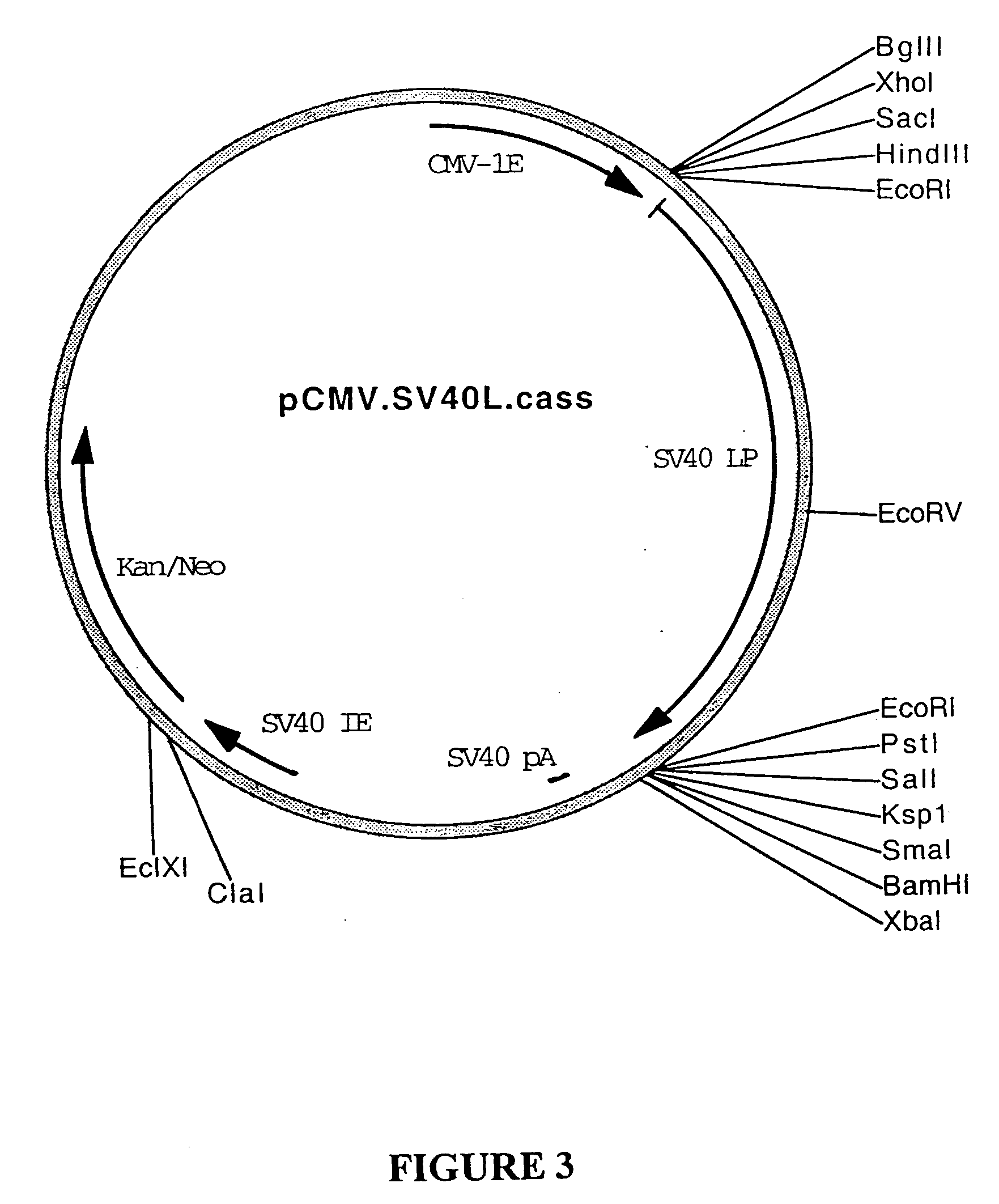
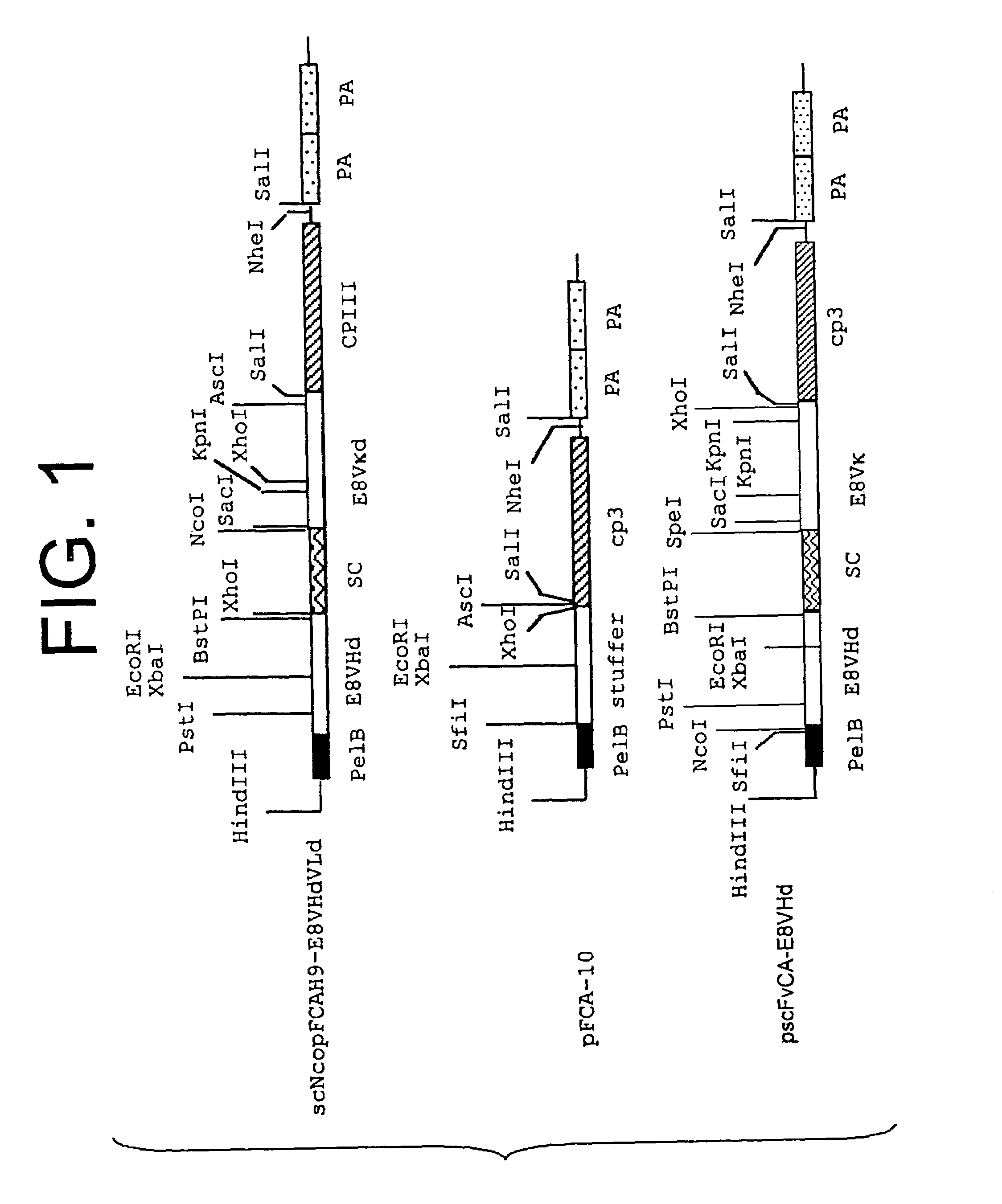
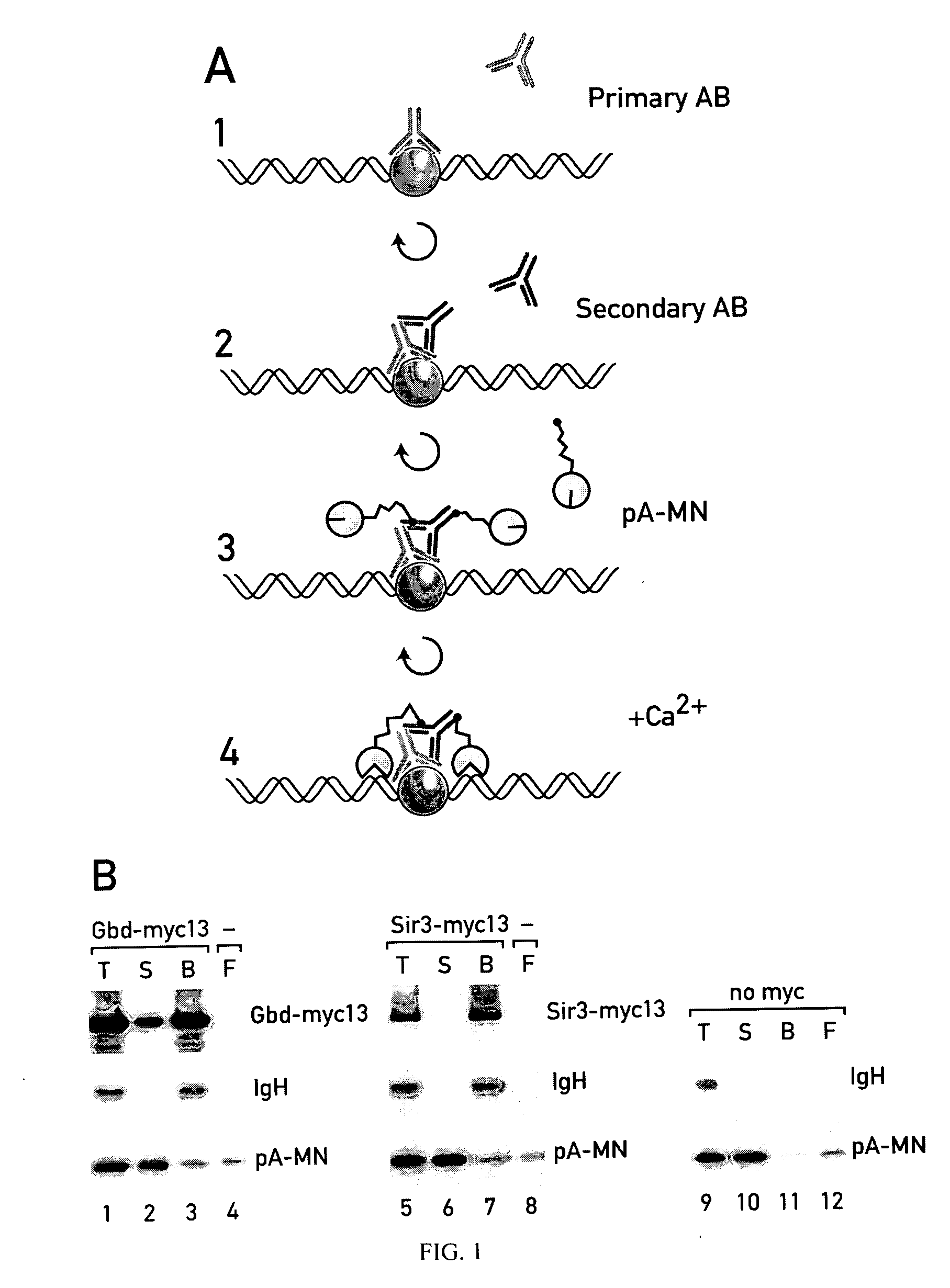
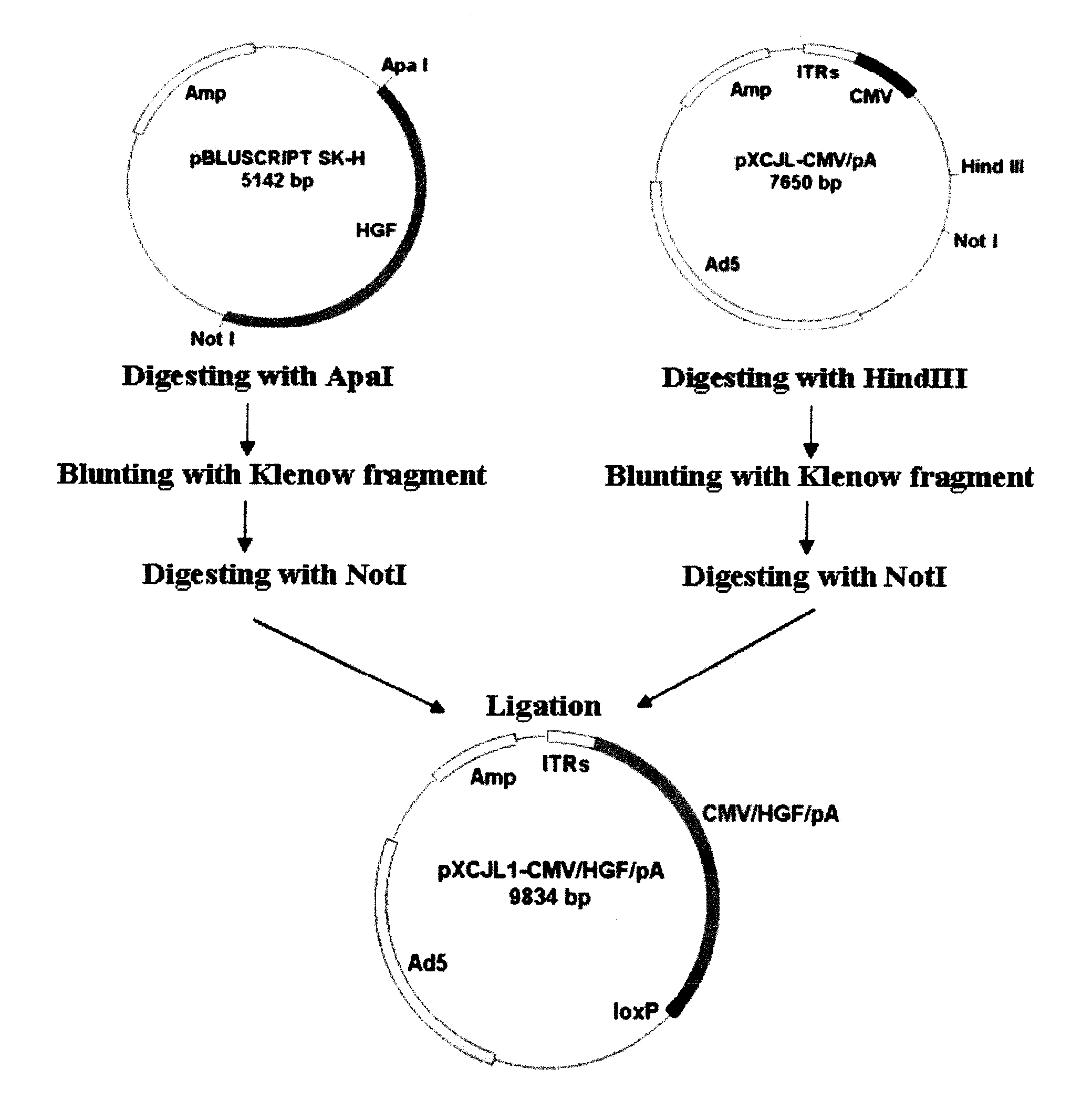
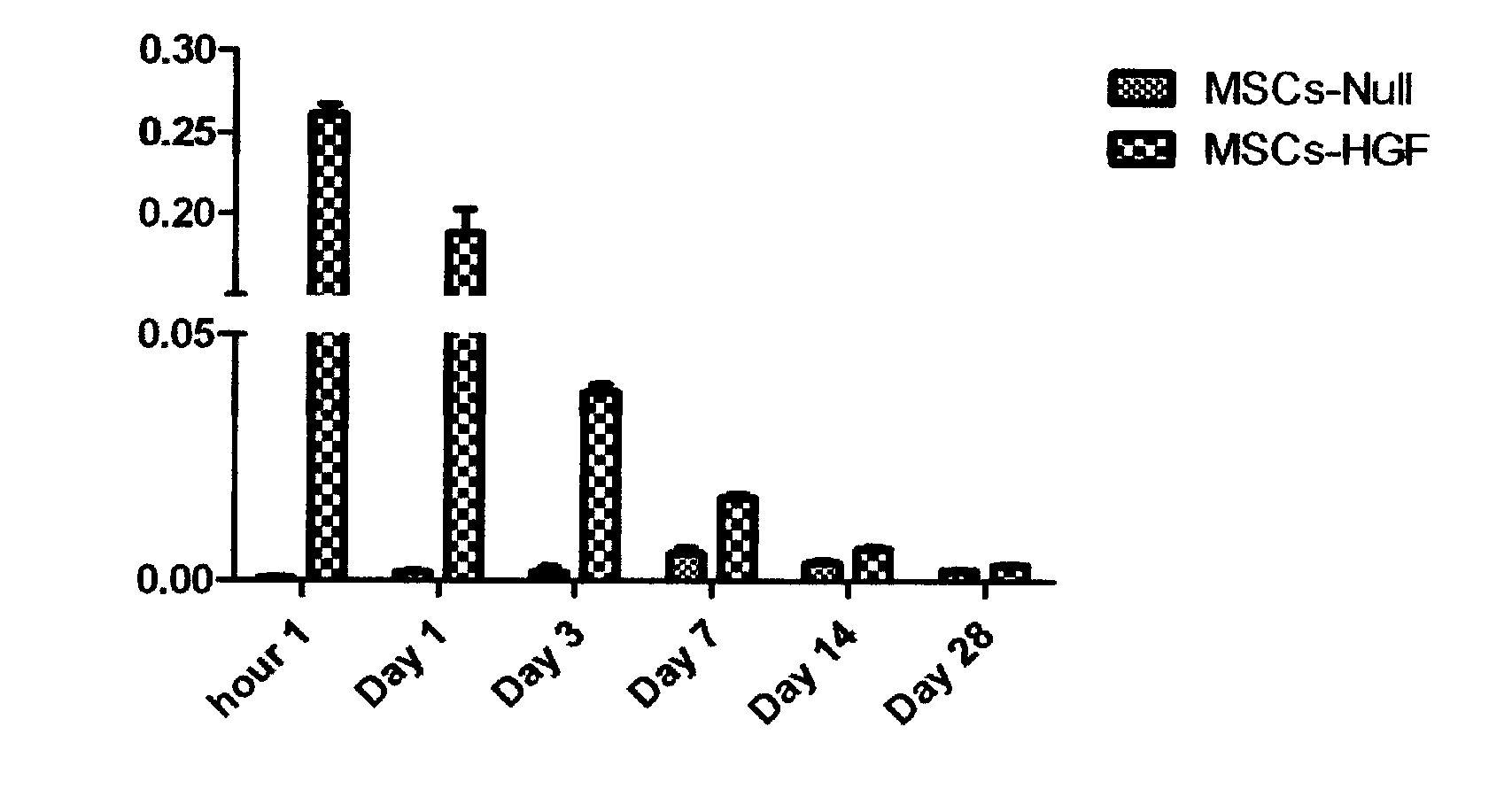
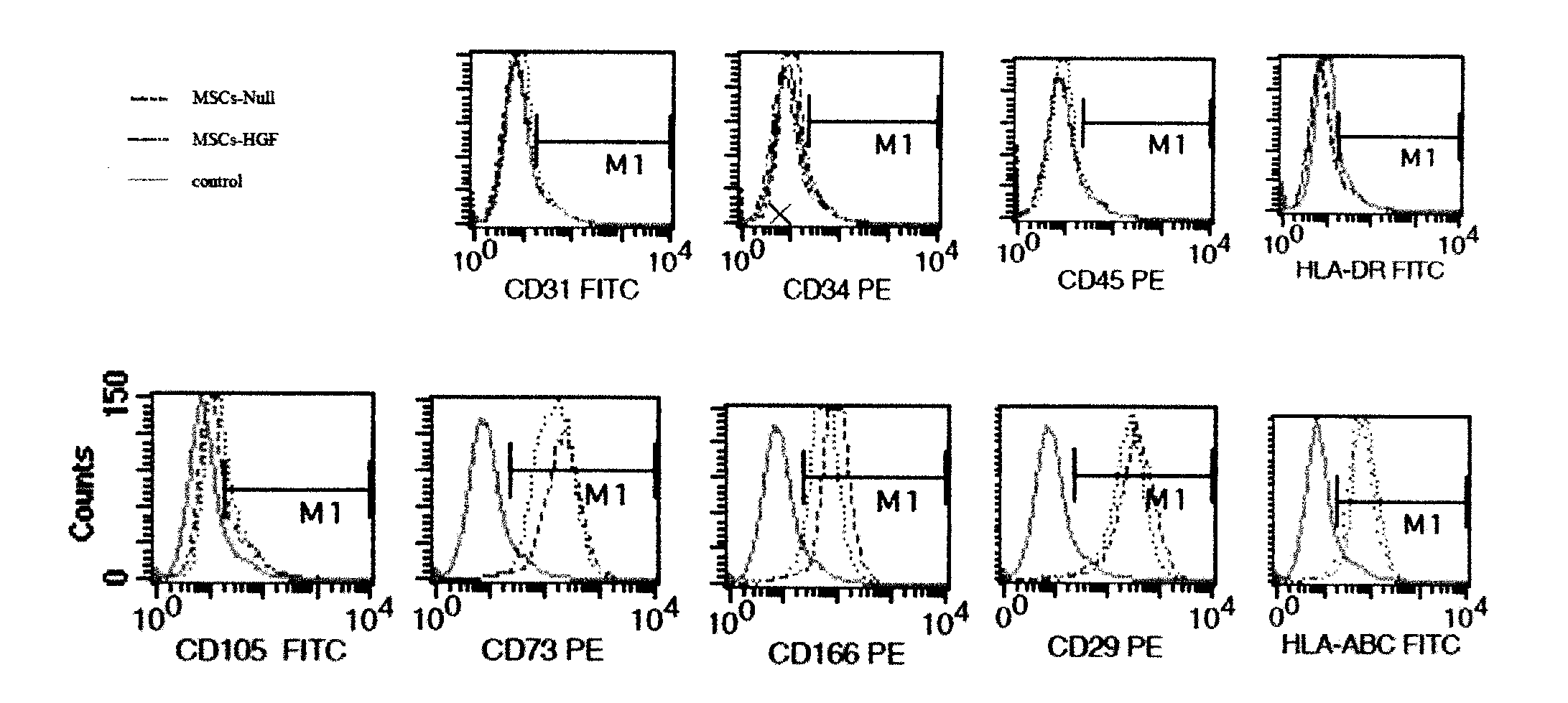
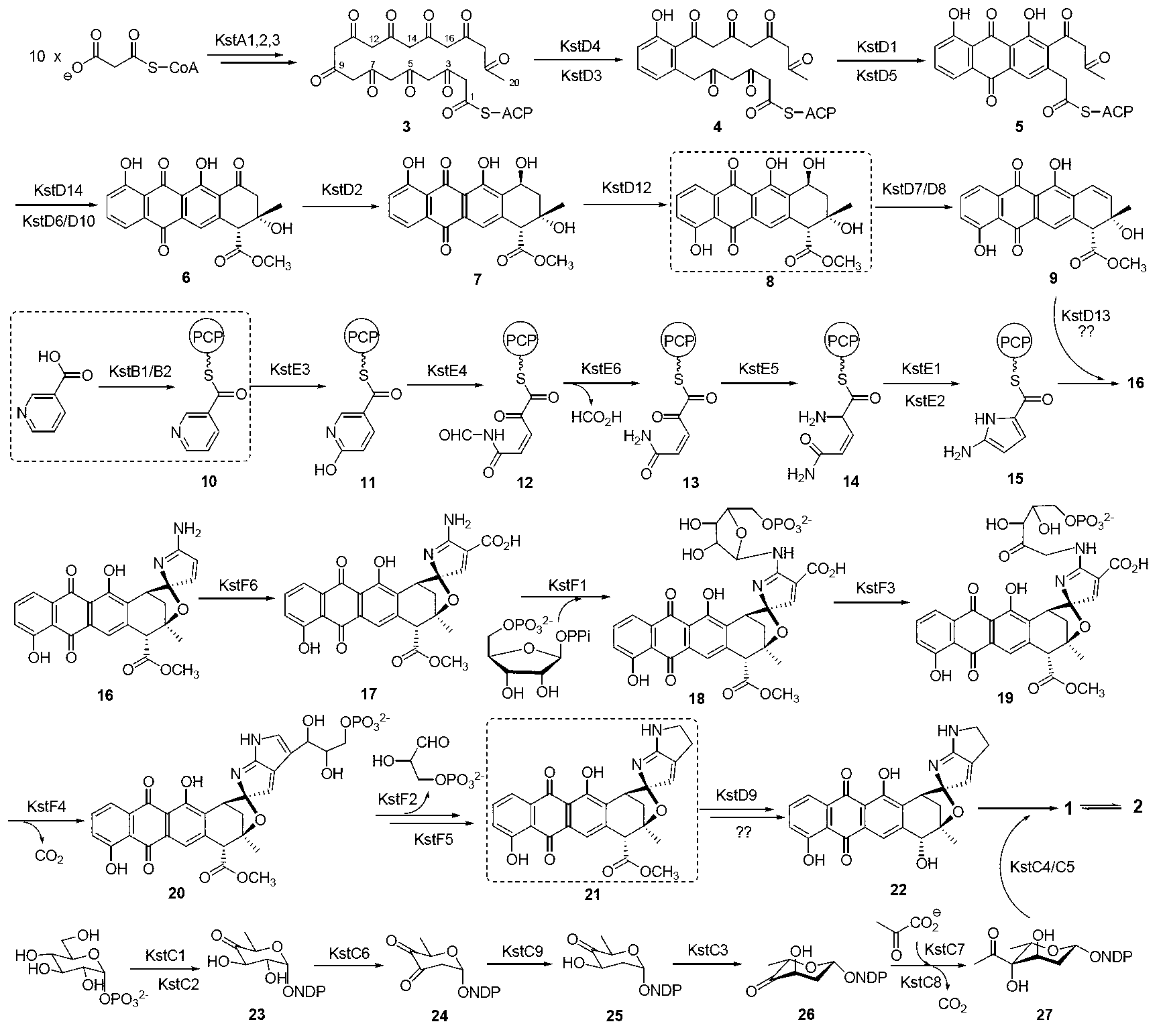Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
165 results about "Modifying genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Modifying gene. a gene that alters or influences the expression function of another gene, including the suppression or reduction of the usual function of the modified gene. Also called modification allele. modifying gene. A gene that influences or alters the expression of other genes.
Control of gene expression
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Methods of constructing camel antibody libraries
InactiveUS7371849B2Deleterious effect can be avoidedAvoid developmentPeptide librariesSugar derivativesSolubilityAntigen
The present invention provides camel antibody libraries that maintain in vivo diversity of camelid antibody variable region genes. The in vivo diversity of antibody variable region genes can be accomplished by, for example, mixing genes derived from a plurality of animals or modifying gene amplification conditions. Conventional methods yield only VHHs with limited repertoire diversity. However, the present invention provides libraries comprising genes encoding functional VHHs with sufficient repertoire size. According to the present invention, libraries that enable to freely obtain VHHs against arbitrary antigens are provided. VHHs have excellent solubility and stability, and show a reactivity that usually cannot be expected from tetrameric IgGs.
Owner:INST FOR ANTIBODIES
Methods and compositions for modifying genomic DNA
PendingUS20170029805A1Improve toleranceReduce DNA-induced toxicity of cellAntipyreticGenetic material ingredientsGenomic DNAA-DNA
Compositions and methods concern the sequence modification of an endogenous genomic DNA region. Certain aspects relate to a method for site-specific sequence modification of a target genomic DNA region in cells comprising: transfecting the cells by electroporation with a composition comprising (a) a DNA oligo and (b) a DNA digesting agent wherein the donor DNA comprises: (i) a homologous region comprising nucleic acid sequence homologous to the target genomic DNA region and (ii) a sequence modification region; and wherein the genomic DNA sequence is modified specifically at the target genomic DNA region.
Owner:MAXCYTE
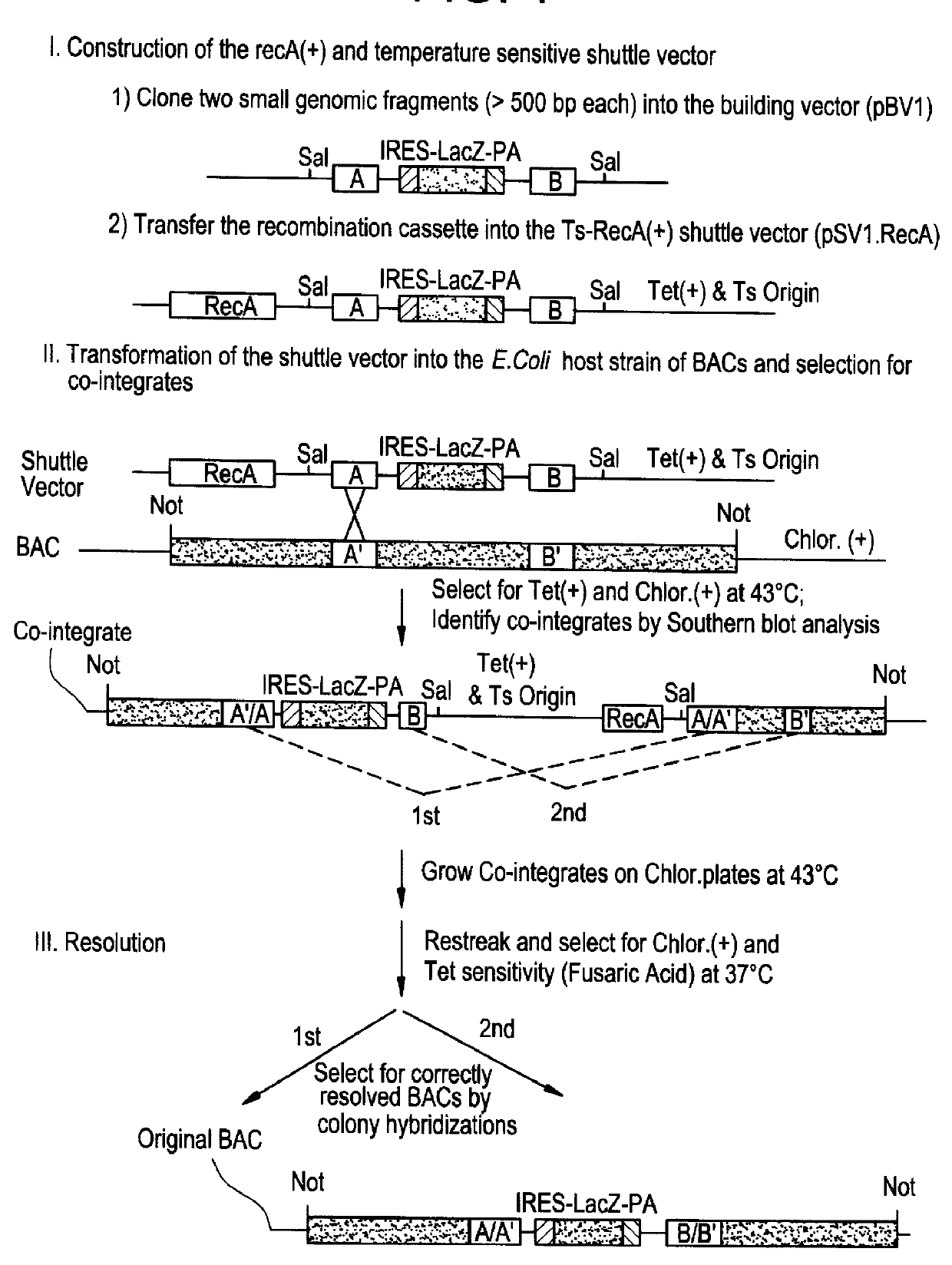
Methods of performing homologous recombination based modification of nucleic acids in recombination deficient cells and use of the modified nucleic acid products thereof
A simple method for modifying genes in a recombination deficient host cell is disclosed. Such modifications include generating insertion, deletions, substitutions, and / or point mutations at any chosen site in the independent origin based cloning vector. The modified gene can be contained in an independent origin based cloning vector that is used to introduce a modified heterologous gene into a cell. Such a modified vector may be used in the production of a germline transmitted transgenic animal, or in gene targeting protocols in eukaryotic cells.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Controlled nucleic acid delivery systems
InactiveUS7030097B1Facilitates continued incorporationLow efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsModifying genesDelivery system
One aspect of the present invention relates to a nucleic acid delivery system including a polymeric structure formed of a biocompatible polymer and a mixture comprising one or more nucleic acid molecules and a first co-dispersant, the mixture being contained within the polymeric structure, wherein the first co-dispersant is present in an amount effective to control diffusion of the one or more nucleic acid from the polymeric structure. Compositions including the nucleic acid delivery system and a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier are disclosed. Methods of making the nucleic acid delivery system and their use in delivering nucleic acid into a patient and modifying gene expression in a target cell are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Nucleic acid detection assay
A method for determining the methylation status of a potential methylation site in genomic nucleic acid comprising treating genomic nucleic acid with an agent which modifies cytosine bases but does not modify 5methyl-cytosine bases under conditions to form a. modified nucleic acid template containing a potential methylation site; providing a first clamp containing a first capture sequence complementary to a region flanking one side of the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template, providing a second clamp containing a second capture sequence complementary to a region flanking the other side of the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template; allowing the first clamp and the second clamp to hybridise to the modified nucleic acid template; ligating the hybridised first and second clamps to form a probe spanning the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template; digesting the modified nucleic acid template to obtain the probe; and detecting the probe and determining the methylation status of the potential methylation site in the modified genomic nucleic acid.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Methods and compositions for determining gene function
InactiveUS20040048264A1Improve , robustImproved and robustCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBioinformaticsComputer program
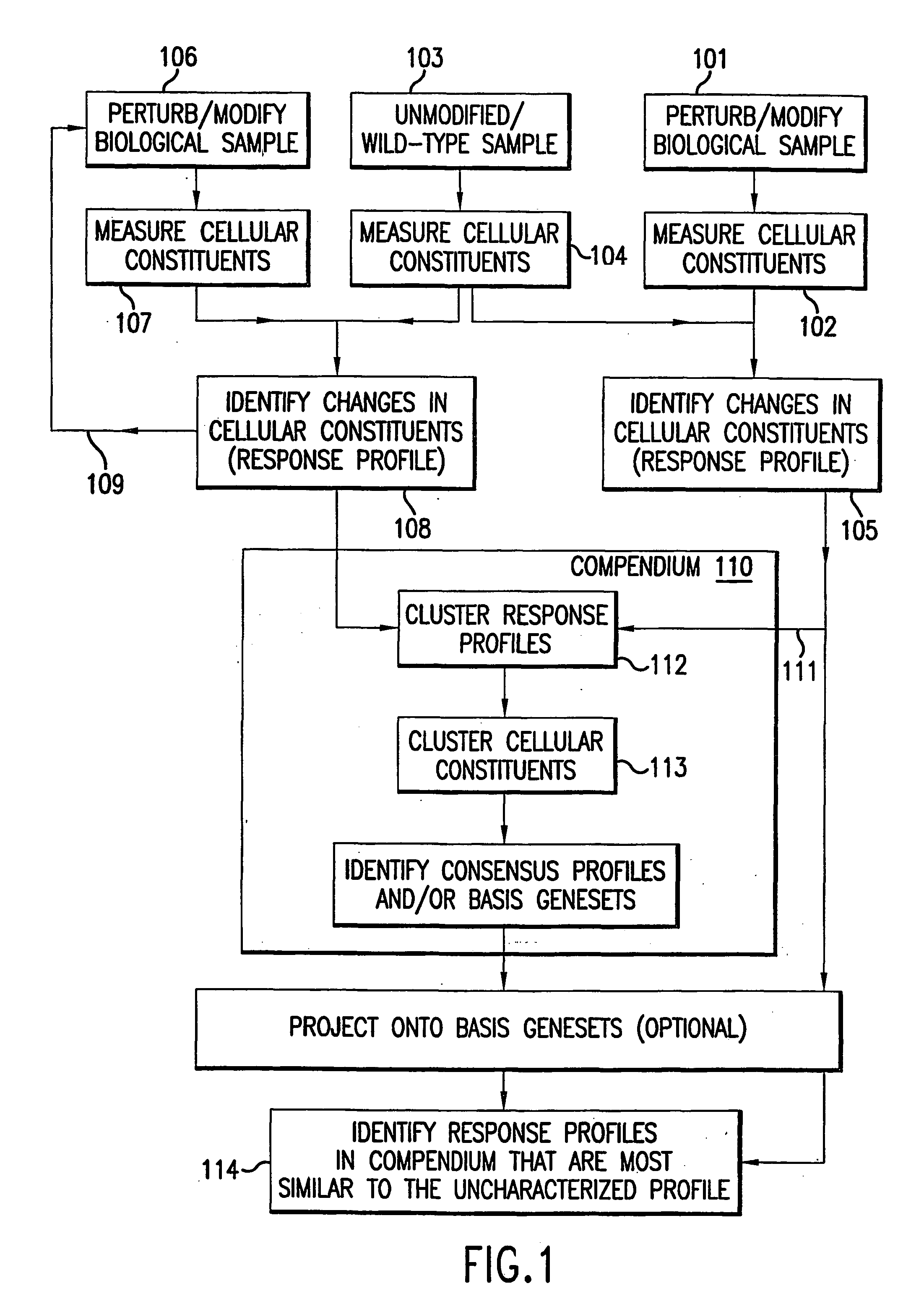
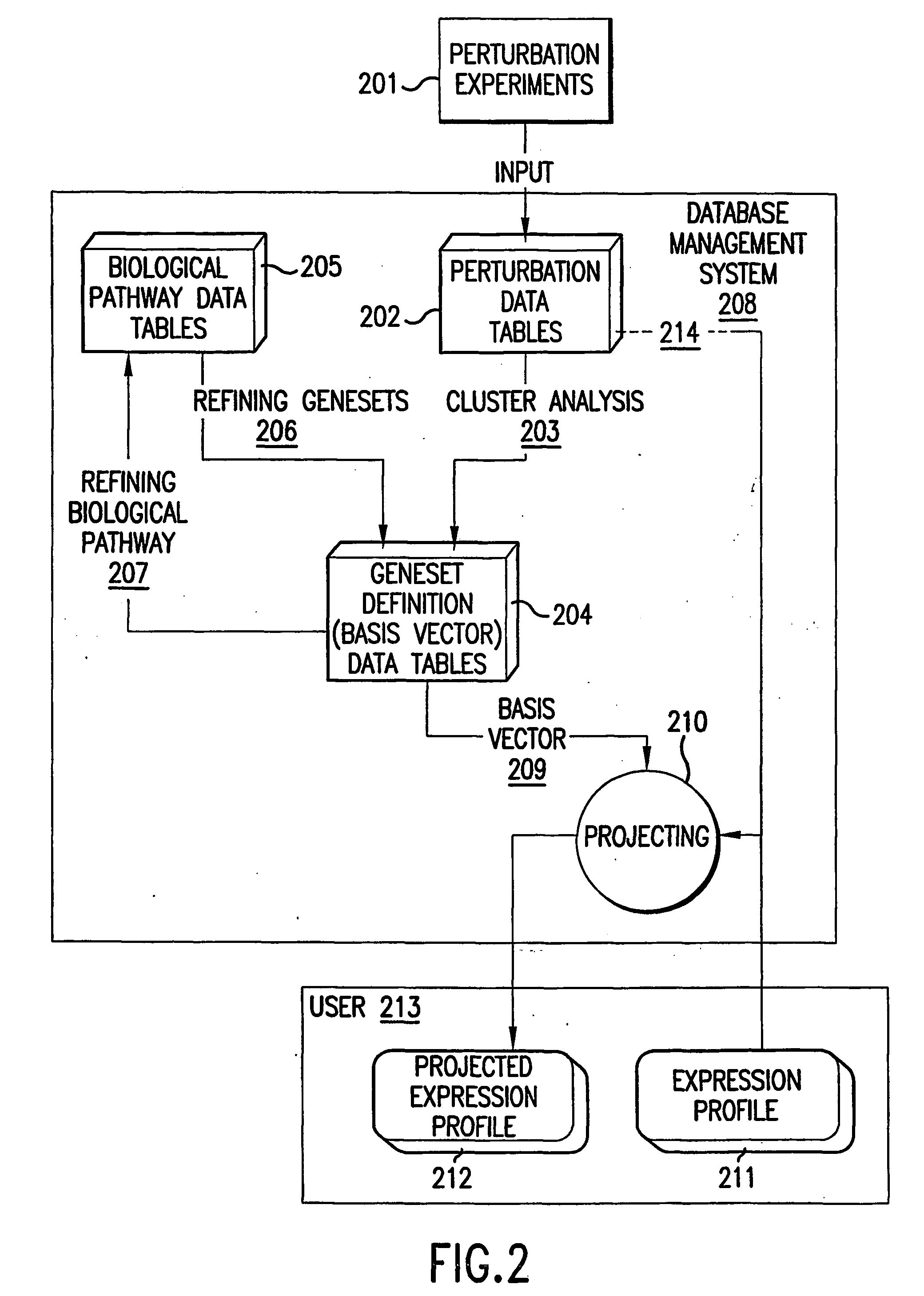
The invention relates to methods and systems (e.g., computer systems and computer program products) for characterizing cellular constituents, particularly genes and gene products. In particular, the invention provides methods for assigning or determining the biological function of uncharacterized genes and gene products by using "response profiles," i.e., measurements of pluralities of cellular constituents in cells having a modified gene or gene product, as phenotypic markers for the gene or gene product. Methods are provided for clustering such response profiles so that similar or correlated response profiles are organized into the same cluster. The invention also provides databases or "compendiums" of response profiles to which the response profile of an uncharacterized gene or gene product can compared.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and compositions for the identification and treatment of neurodegenerative disorders
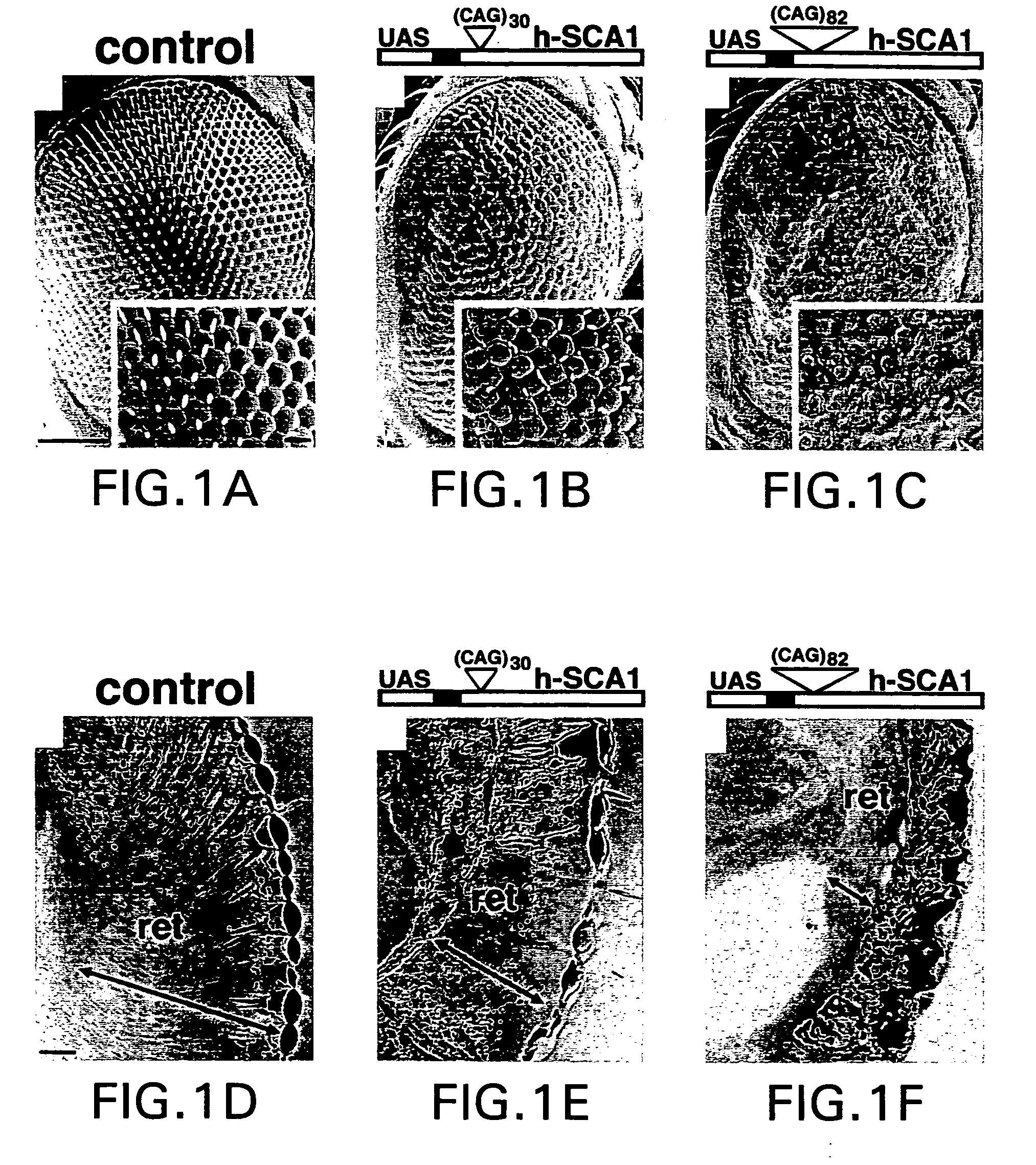
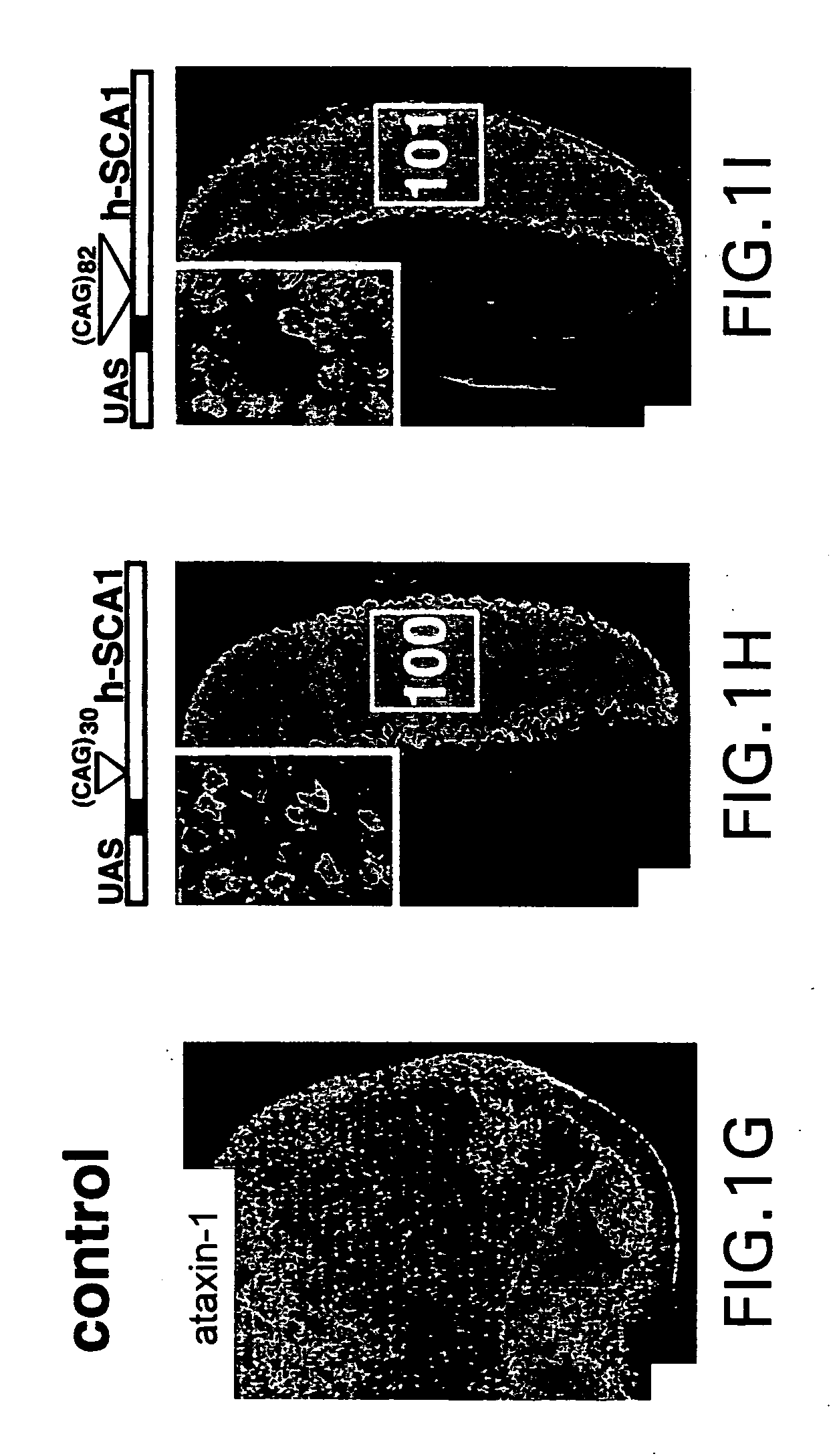
InactiveUS20040177388A1Valuable toolImpaired clearanceOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseAtaxin 1
The present invention relates to Drosophila models of the neurodegenerative disorder spinocerebellar ataxia 1 (SCA-1). In particular, the invention relates to transgenic Drosophila which express normal human ataxin-1 or mutant human ataxin-1 with expanded polyglutamine repeats for SCA-1 therapeutics. The invention further relates to the diagnosis of predispositions to developing SCA-1. The invention further relates to methods of using the transgenic Drosophila to screen for therapeutics of SCA-1 and other neurodegenerative disorders. The invention further relates to the identification of modifier genes of the SCA-1 phenotypes produced by overexpression of ataxin-1, for therapeutic and diagnostic uses and for screening for therapeutics of SCA-1 and other neurodegenerative disorders. The invention further relates to the diagnosis of a predisposition to SCA-1 comprising detecting the overexpression of normal ataxin-1.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Enhancement of adenoviral oncolytic activity by modification of the E1A gene product
ActiveUS7662795B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTranscriptional Regulatory ElementsCytotoxicity
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for enhancing the oncolytic activity of replication-competent, target cell-specific adenovirus vectors by modification of the E1A gene product. The target cell-specific replication-competent adenovirus vectors comprise a chimera of an adenovirus gene essential for replication, preferably an early gene, and the Androgen receptor (or a portion thereof) under the transcriptional control of a cell type-specific transcriptional regulatory element (TRE). By providing for cell type-specific transcription through the use of one or more cell type-specific TREs, the adenovirus vectors effect prostate-specific cytotoxicity due to selective replication.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Somatic hypermutation systems
InactiveUS20120028301A1Avoid problemsDecrease and increase in rateImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminaseIn vivo
The present application relates to somatic hypermutation (SHM) systems and synthetic genes. Synthetic genes can be designed using computer-based approaches to increase or decrease susceptibility of a polynucleotide to somatic hypermutation. Genes of interest are inserted into the vectors and subjected to activation-induced cytidine deaminase to induce somatic hypermutation. Proteins or portions thereof encoded by the modified genes can be introduced into a SHM system for somatic hypermutation and proteins or portions thereof exhibiting a desired phenotype or function can be isolated for in vitro or in vivo diagnostic or therapeutic uses.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
Codon modified immunogenic compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS8772256B2High expressionFunction increasePowder deliveryAnimal cellsVirus ProteinViral infection
The present invention features immunogenic compositions comprising codon modified genes that encode viral proteins and / or glycoproteins or fragments. The immunogenic compositions of the invention are useful in various methods of treatment, such as preventing or treating viral infection. Also provided in the present invention are kits and instructions for use.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
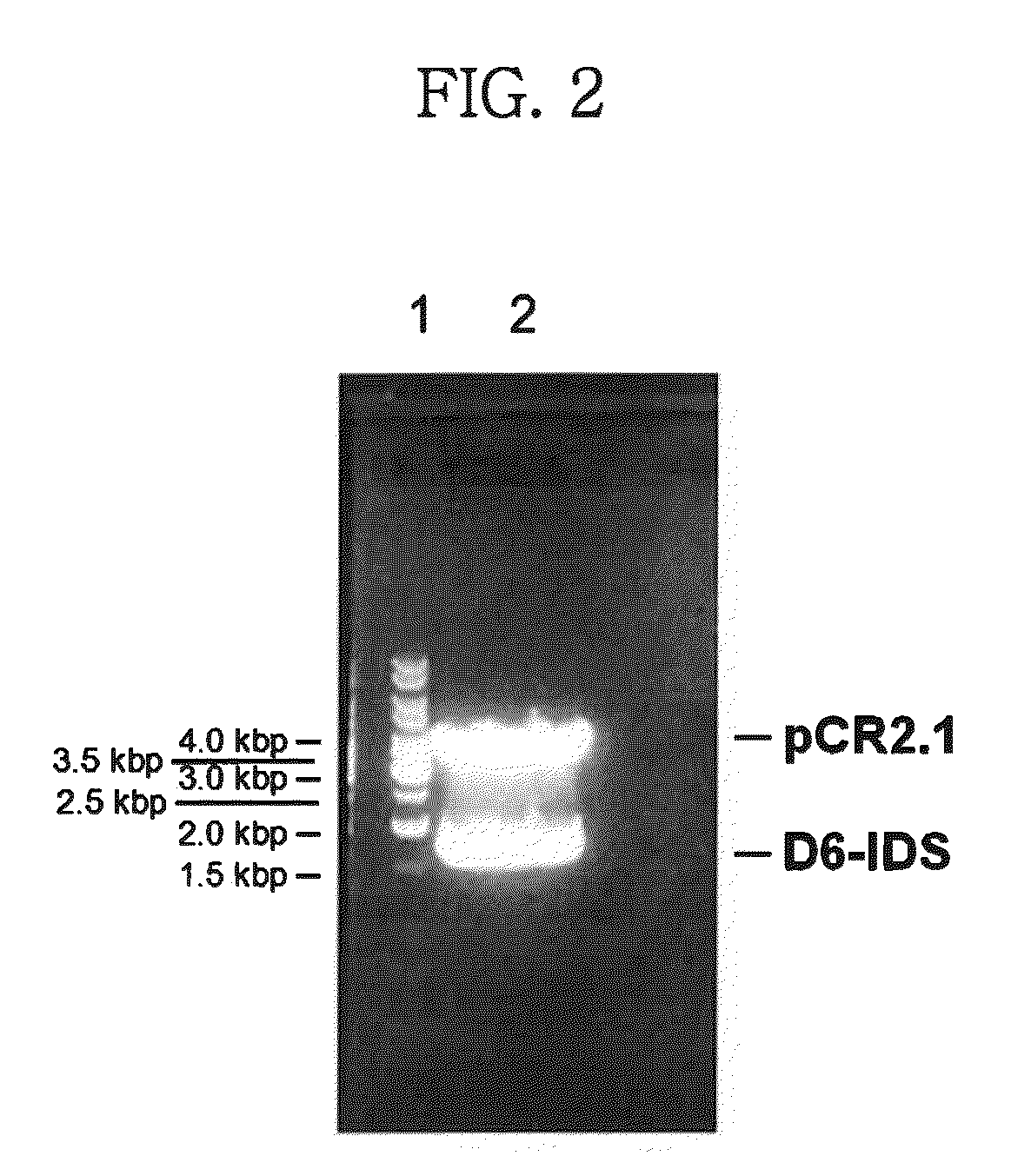
Iduronate-2-sulfatase and use thereof
Disclosed is a modified iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene constructed by inserting the nucleotide of SEQ ID NO: 2 into a wild-type IDS gene. In addition to being negatively charged, the improved IDS enzyme encoded by the modified gene exhibits a sufficient retention time in blood to target the bone, so that it is more effective for treating Hunter syndrome.
Owner:THE GREEN CROSS CORP
Mapping of proteins along chromatin by chromatin cleavage
ActiveUS20070009937A1Accurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProteaseProteinase activity
The present invention is directed to a method for localising, in chromatin or DNA, the binding loci of a chromatin or DNA binding protein comprising the following steps: a) tethering, directly or indirectly, an enzyme with regulatable activity to said chromatin binding protein, b) transiently activating the regulatable enzymatic activity bound to the targeted chromatin and c) mapping the enzymatically-modified genomic sites introduced by the enzyme into the chromatin. According to an embodiment of the invention, the regulatable enzyme is a regulatable protease. The mapping step may be carried out on specific DNA fragments, or on a chromosome-wide scale or a genome-wide scale. The present invention is also directed to kits for carrying out the methods of the invention.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Application of gene modified mesenchymal stem cell in pulmonary fibrosis treatment
InactiveCN103203025AHigh activityPromote proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBone marrowFactor ii
Relating to the fields of biotechnologies and gene therapy, the invention provides application of a gene modified mesenchymal stem cell in pulmonary fibrosis treatment. The gene modified mesenchymal stem cells are obtained through: in-vitro isolated culture and amplification of a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) deriving from bone marrow and an umbilical cord, and recombinant adenovirus Ad-HGF mediated in-vitro modification of the MSC by a hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). By transplanting the gene modified MSC to a C57 mouse to intervene in radiation induced lung injury and fibrosis, exudation of a plurality proteins including albumin, IgM and the like from an alveolar space can be reduced, local inflammatory responses of the lung can be alleviated, and expression of TNF-alpha, soluble ICAM-1 and multiple factors is inhibited, expression of the profibrotic factor TGF-beta, the collagen gene col1 alpha 1 and col 3 alpha 1 can be inhibited, and pulmonary tissue collagen fiber deposition is reduced. The expression results of endogenous HGF and its receptor cmet show that endogenous HGF expression can be induced and endogenous MSC can home to injured parts. Therefore, the employment of HGF modified MSC in treatment of lung injury and fibrosis brought by various pathogenic causes is of great significance.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
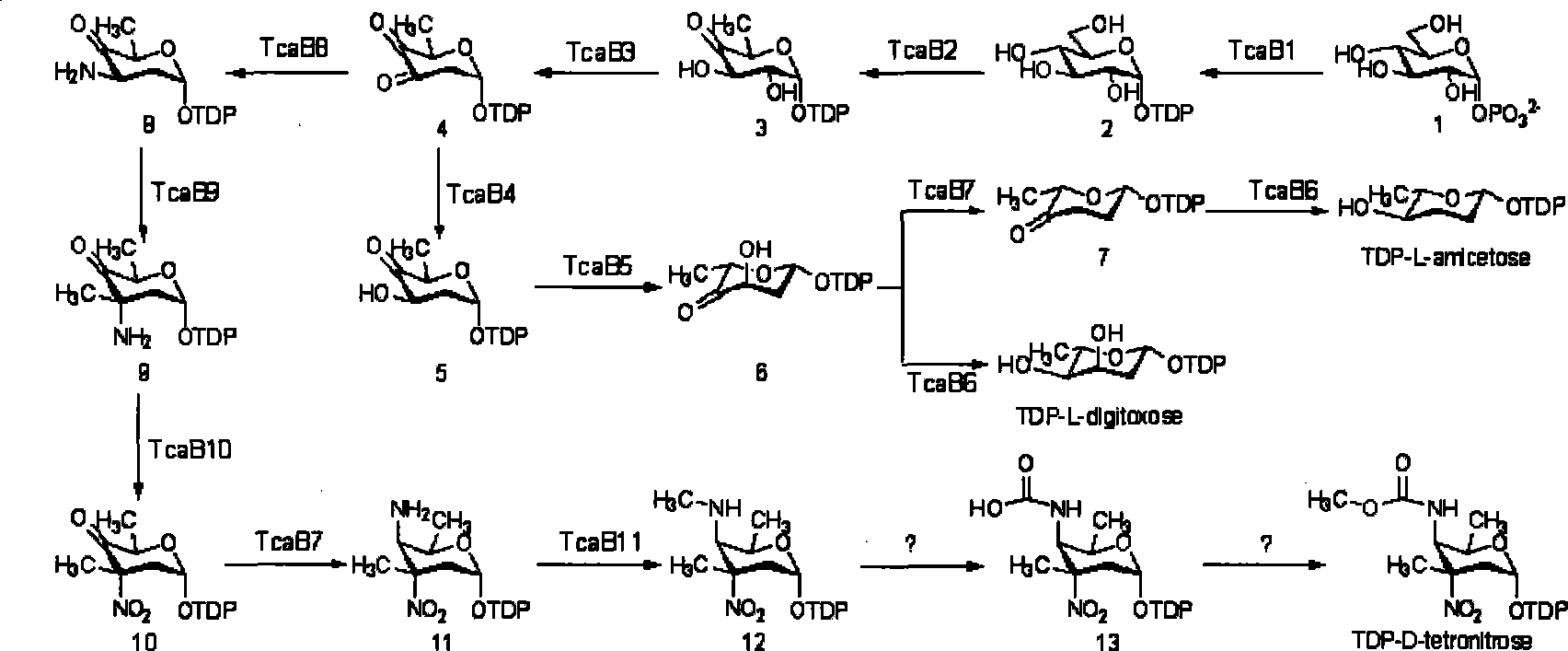
Trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline hydroxylase modifying gene with high transformation rate and application thereof
ActiveCN103146720ALess quantityEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxyprolineProline Hydroxylase
The invention discloses a trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline hydroxylase modifying gene with high transformation rate and application thereof. An expression carrier of an optimization gene is constructed by optimizing nucleotide sequence of trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline hydroxylase (GenBankID:D78338.1) in Dactylosporangiumsp.RH1; the thallus is collected as the enzyme source of the transformation reaction through the prokaryotic expression. The experiment result expresses that the transformation rate of generating the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline by using L-proline as a substrate is as high as 91%. The gene can be applied to biologically generating trans-4-hydroxy-L-hydroxyproline and has good industrial application value.
Owner:HEBEI BOLUNTE PHARMA +1
Modified pig propagation and respiratory syndrome virus ORF5 gene and use thereof
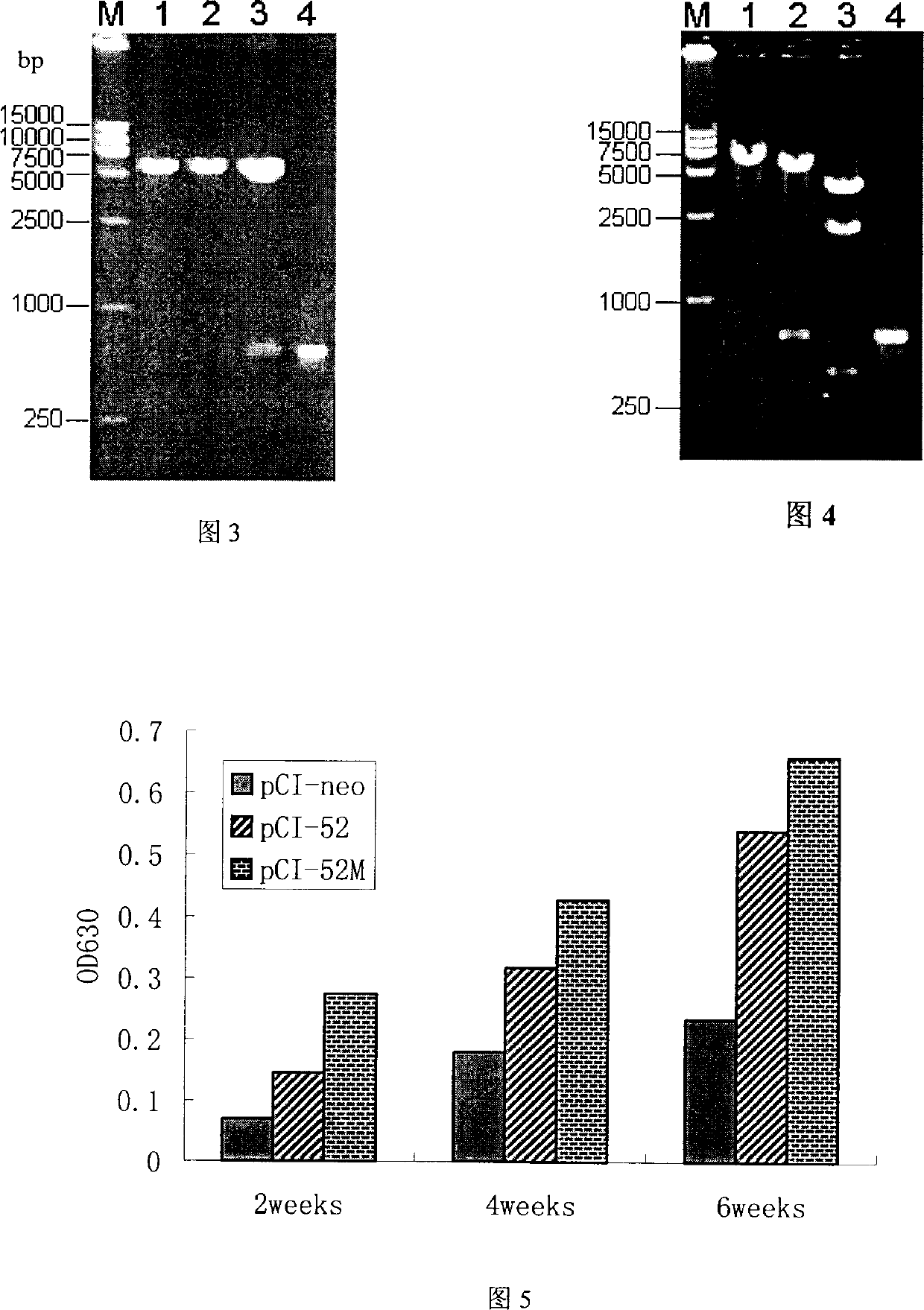
The invention belongs to the animal gene engineering technology field. It is about a gene and its application, the gene is modificatory porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus ORF5. Its attribute is to insert nucleotide sequence between the neutralization and cover list of GP5, the nucleotide sequence is artificial synthesis coding accessorial T-lymph cell list. The sequence of this nucleotide is just as the sequence list of SEQ ID NO:1 and attached figure 1. This modificatory gene is included in eukaryotic expression plasmid, and the Escherichia coliDH5 / pCI-52M, which includes the plasmid, is conserved in CCTCC, and the number is CCTCC NO: M204080. This invention also presents the use of this gene in the preparation of pig bread and respiratory syndrome DNA vaccineíú
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods and Compositions for Modifying Gene Regulation and Dna Damage in Ageing
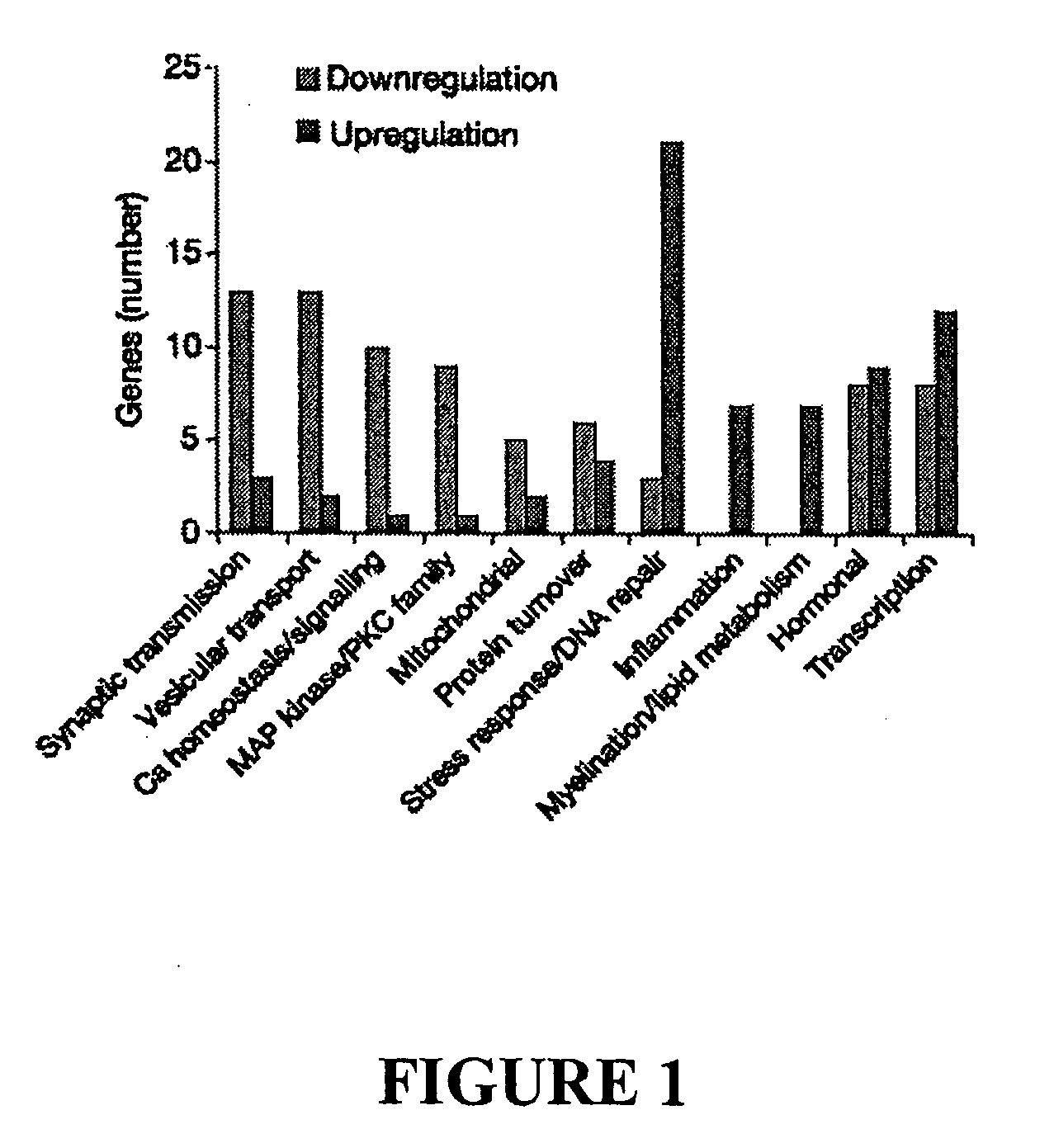
The invention relates to gene regulation in ageing, and age-related cognitive decline. The invention, in particular relates to methods for screening a subject for a propensity to develop diseases associated with oxidative stress, and for age-related conditions, by examining the up-regulation and / or down-regulation of at least one gene associated within the central nervous system.
Owner:YANKNER BRUCE +1
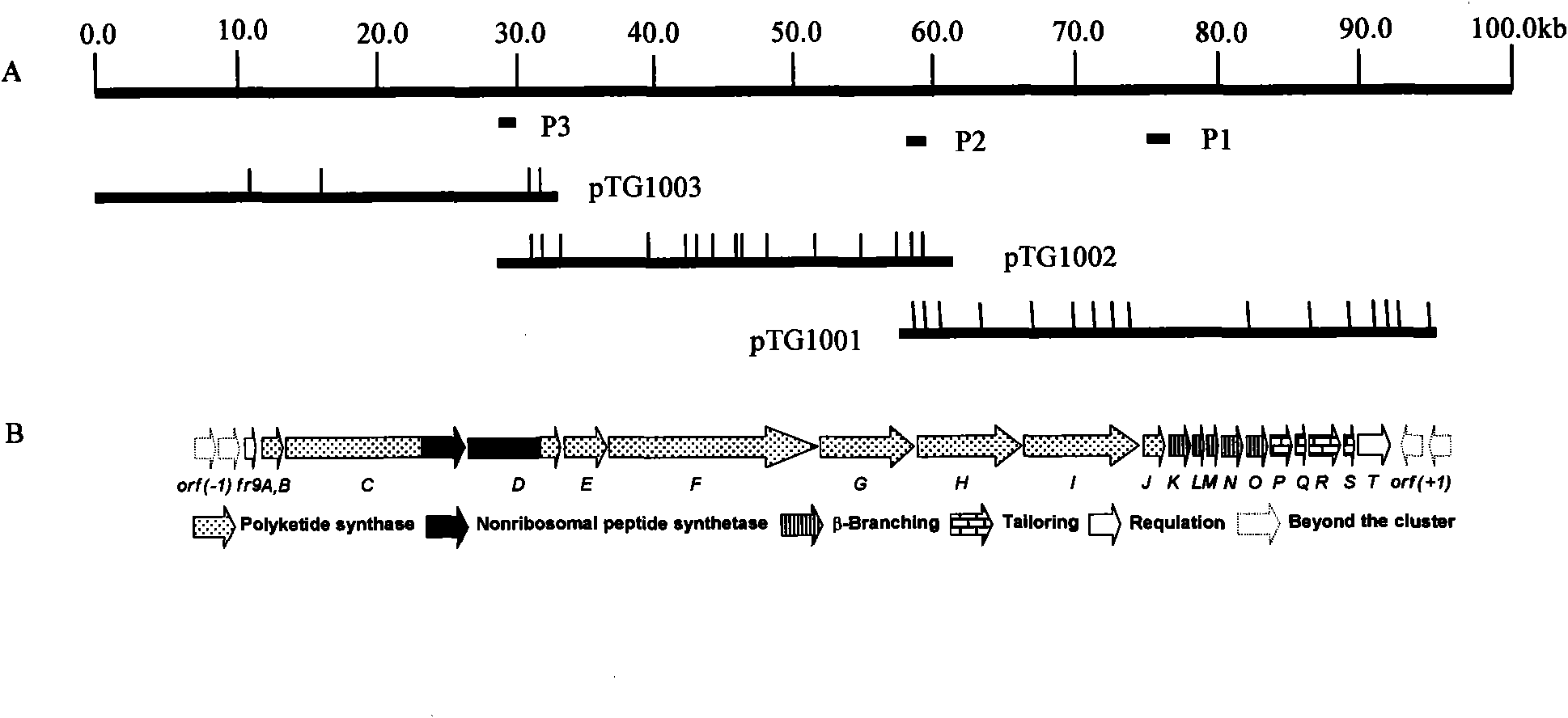
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
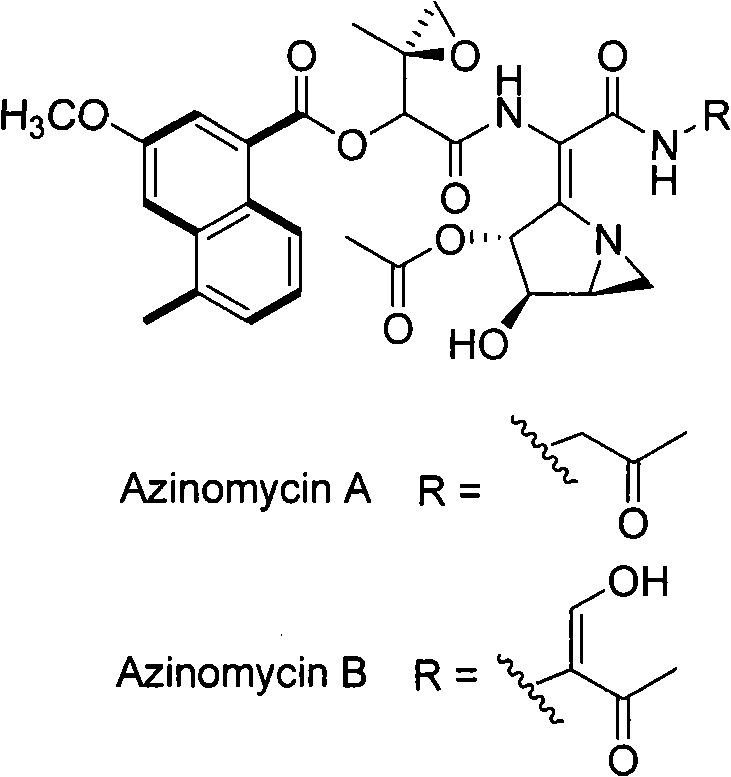
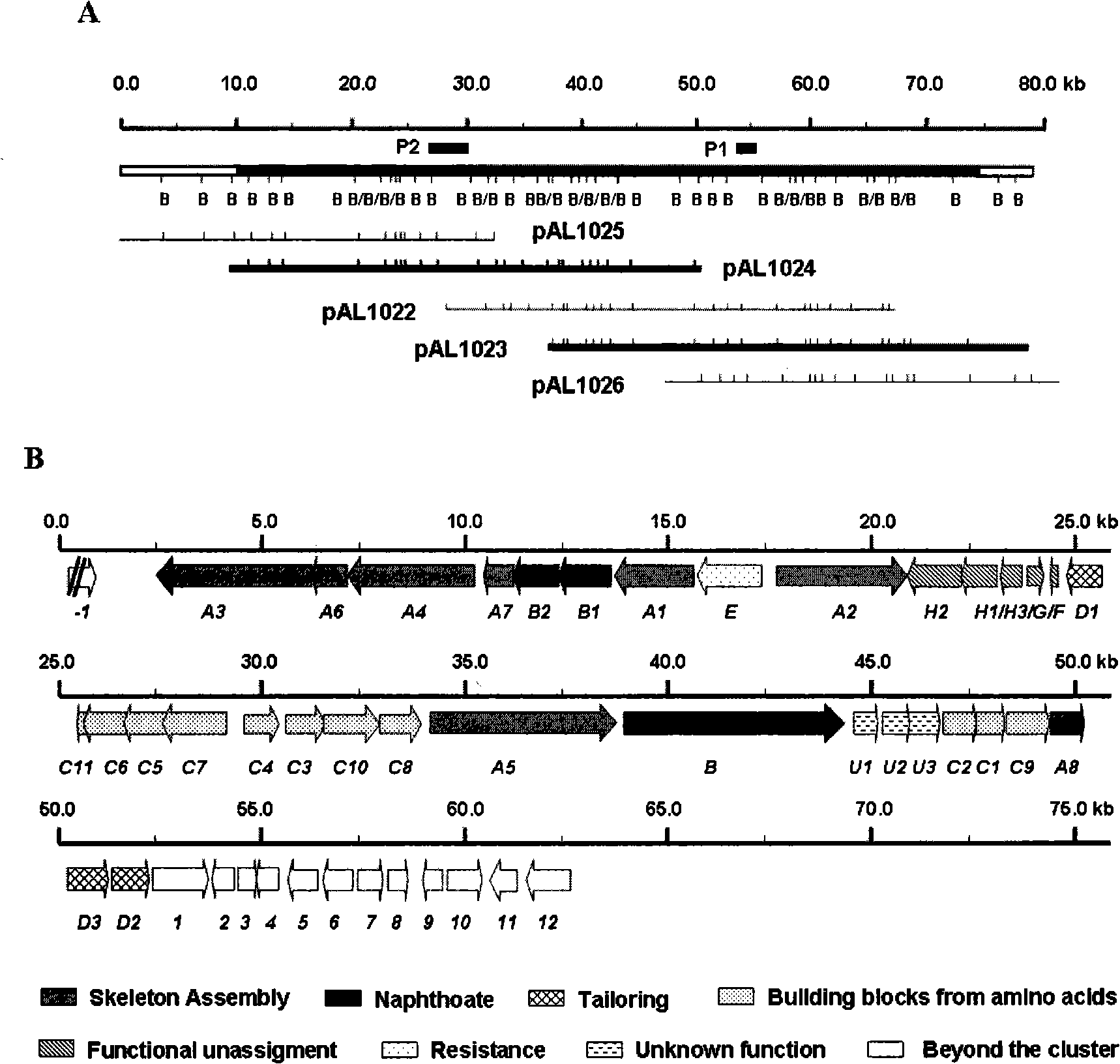
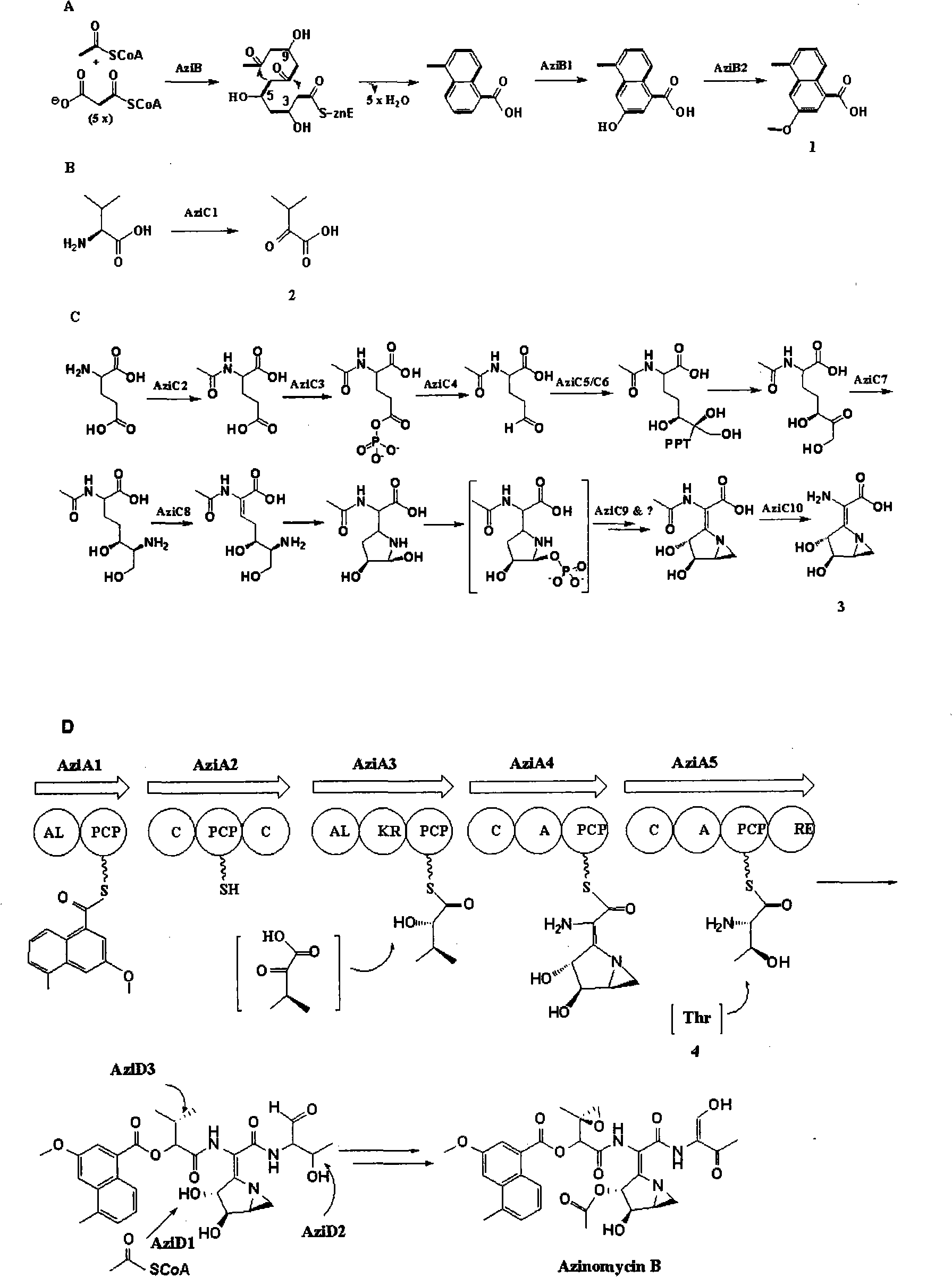
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System for capturing and modifying large pieces of genomic DNA and constructing organisms with synthetic chloroplasts
The functional analysis of genes frequently requires the manipulation of large genomic regions. A yeast-bacteria shuttle vector is described that can be used to clone large regions of DNA by homologous recombination. Also described is a method for isolating entire genomes, including chloroplast genomes, or large portions thereof, and manipulating the same. Also described are methods for determining minimal genomes, minimal pathway requirements, and minimal organelle genomes.
Owner:SAPPHIRE ENERGY
Retrons for gene targeting
The invention provides methods and nucleic acid constructs that may be used to modify a nucleic acid of interest at a target locus within the genome of a host. In some aspects, the invention contemplates producing in vivo a gene targeting substrate (GTS), which may be comprised of both DNA and RNA components. The gene targeting substrate may comprise a gene targeting nucleotide sequence (GTNS), which is homologous to the target locus, but comprises a sequence modification compared to the target locus. The gene targeting substrate may be produced by reverse transcription of a gene targeting message RNA (gtmRNA). The gene targeting message RNA may be folded for self-priming for reverse transcription by a reverse transcriptase. The gene targeting message RNA may in turn be the product of transcription of a gene targeting construct (GTC) encoding the gene targeting message RNA. The gene targeting construct may for example be a DNA sequence integrated into the genome of the host, or integrated into an extrachromosomal element. Following expression of the gene targeting systems of the invention, hosts may for example be selected having genomic modifications at a target locus that correspond to the sequence modification present on the gene targeting nucleotide sequence. In some embodiments, the structure of retrons may be adapted for use in the gene targeting systems of the invention.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Gene involved in quorum-sensing system of acetic acid bacterium, acetic acid bacterium bred by modification of the gene and method for production of vinegar by using the acetic acid bacterium
ActiveUS20100137641A1Improve fermentation effectEfficient productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeHigh concentrationBacteroides
The object of the present invention is to provide a method for efficiently producing vinegar that contains a higher concentration of acetic acid, wherein a gene involved in the acetic acid fermentation ability is obtained, the acetic acid fermentation ability of an acetic acid bacterium is improved by reducing or deleting the function of the protein encoded by the gene. An acetic acid bacterium with a remarkably improved acetic acid fermentation ability was obtained by obtaining genes encoding an acyl homoserine lactone synthase and an acyl homoserine lactone receptor-type transcription factor that are involved in the quorum-sensing system in the acetic acid bacterium, and modifying the genes so as to reduce or delete the function of the quorum-sensing system. Further provided is a method for more efficiently producing vinegar containing a higher concentration of acetic acid by using the acetic acid bacterium.
Owner:MITSUKAN GROUP CORP +1
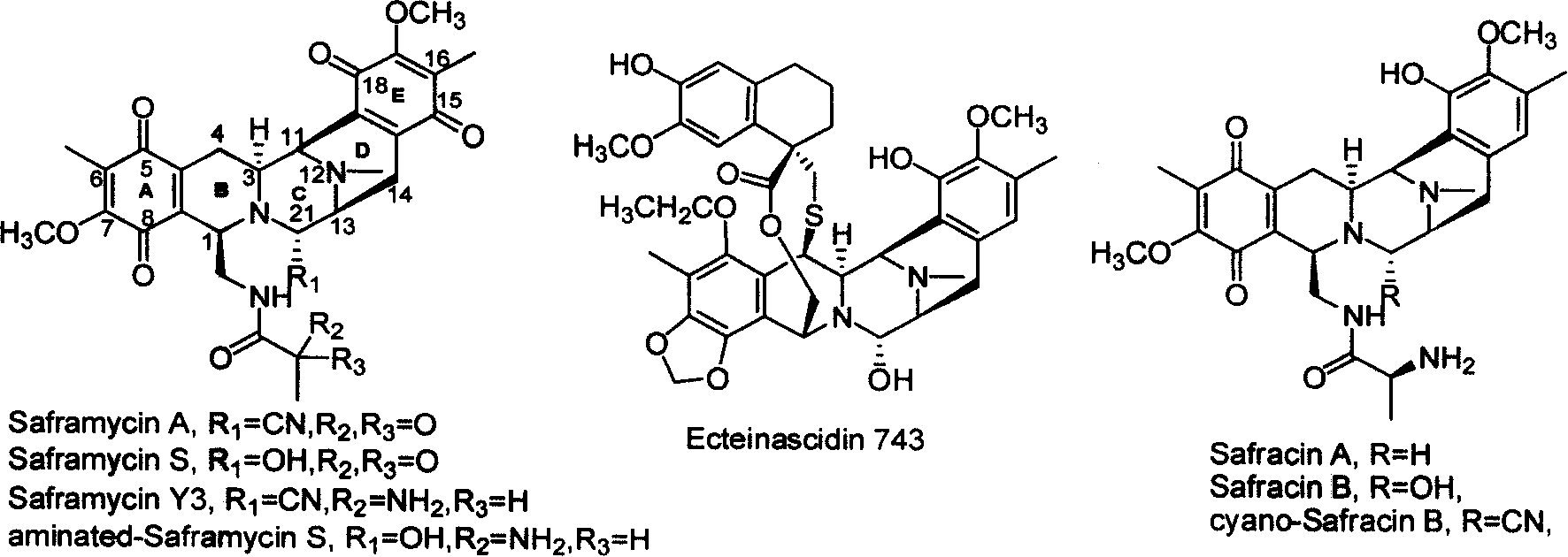
Safraninemycin biological synthesis gene cluster
The invention relates to the cloning, sequencing, analyzing, functional study of biological synthetic gene cluster of erythromycin produced by streptomycete in tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid family which has the antineoplastic activity and application thereof. The whole gene cluster contains 30 genes: 3 nonribosome polypeptide synthetase genes, 4 antecedent molecule synthetic genes of 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-O-methyl-tyrosine, 2 peptid ring skeleton synthetic genes, 7 erythromycin modifying genes, 5 genes related to S-adenosine methionine synthesis, 3 regulation genes, 2 resistance genes and 4 genes with uncertain function. Genetic manipulation of the genes can block the synthesis of erythromycin, change the output and get analogue of erythromycin. The gene cluster can be used for gene engineering, protein expression, enzymic catalytic reaction, etc. of tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid family and finding out compounds or genes being suitable for medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions and methods for the modification of gene expression
InactiveUS7518034B2High expressionReduce expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPolynucleotide
Novel isolated plant polynucleotide promoter sequences are provided, together with genetic constructs comprising such polynucleotides. Methods for using such constructs in modulating the transcription of DNA sequences of interest are also disclosed, together with transgenic plants comprising such constructs.
Owner:RUBICON FORESTS HLDG LTD
Method for gene editing
ActiveUS20190002869A1Microencapsulation basedVector-based foreign material introductionGene ModificationModifying genes
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods for modifying a gene sequence, and for systems for delivering such compositions. For example, the disclosure relates to modifying a gene sequence using a CRISPR-Cas9 or other nucleic acid editing system, and methods and delivery systems for achieving such gene modification, such as viral or non-viral delivery systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
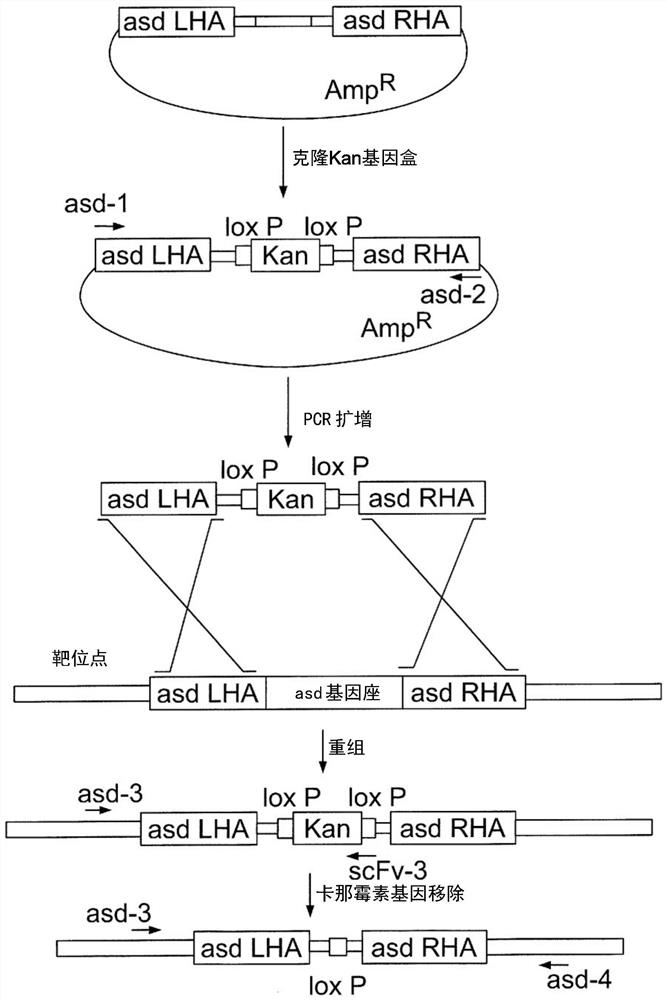
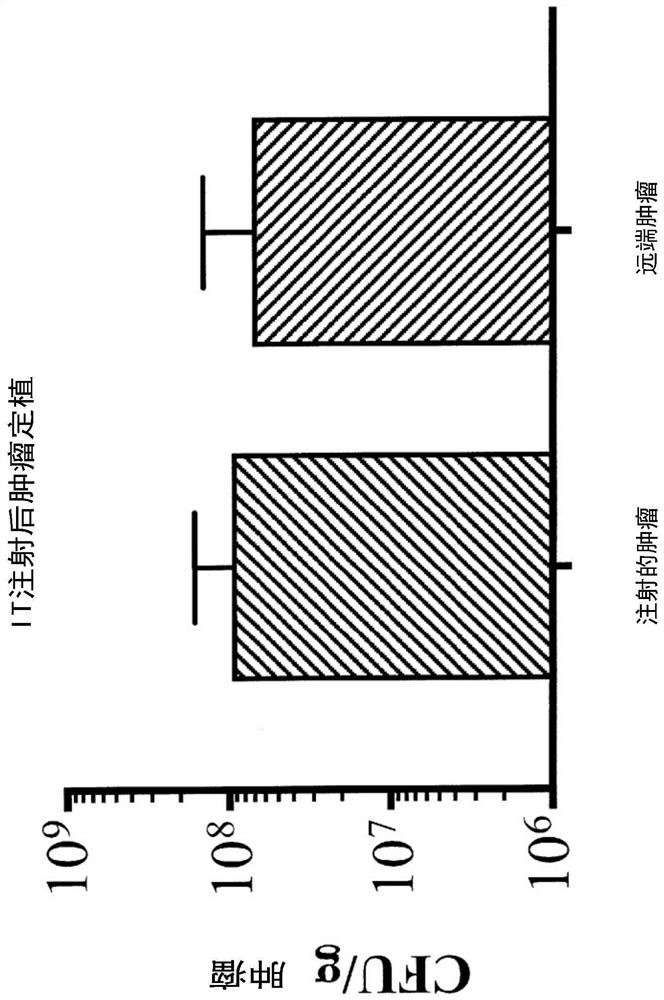
Engineered immunostimulatory bacterial strains and uses thereof
Provided are delivery immunostimulatory bacteria that have enhanced colonization of tumors, the tumor microenvironment and / or tumor-resident immune cells, and enhanced anti-tumor activity. The immunostimulatory bacteria are modified by deletion of genes encoding the flagella or modification of the genes so that functional flagella are not produced, and / or are modified by deletion of pagP or modification of pagP to produce inactive PagP product. As a result, the immunostimulatory bacteria are flagellin- and / or pagP -. The immunostimulatory bacteria optionally have additional genomic modifications so that the bacteria are adenosine or purine auxotrophs. The bacteria optionally are one or more of asd -, purI - and msbB -. The immunostimulatory bacteria, such as Salmonella species, are modified to encode immunostimulatory proteins that confer anti-tumor activity in the tumor microenvironment, and / or are modified so that the bacteria preferentially infect immune cells in the tumor microenvironment or tumor-resident immune cells and / or induce less cell death in immune cells than in other cells. Also provided are methods of inhibiting the growth or reducing the volume of a solid tumor by administering the immunostimulatory bacteria.
Owner:阿克蒂姆治疗有限公司
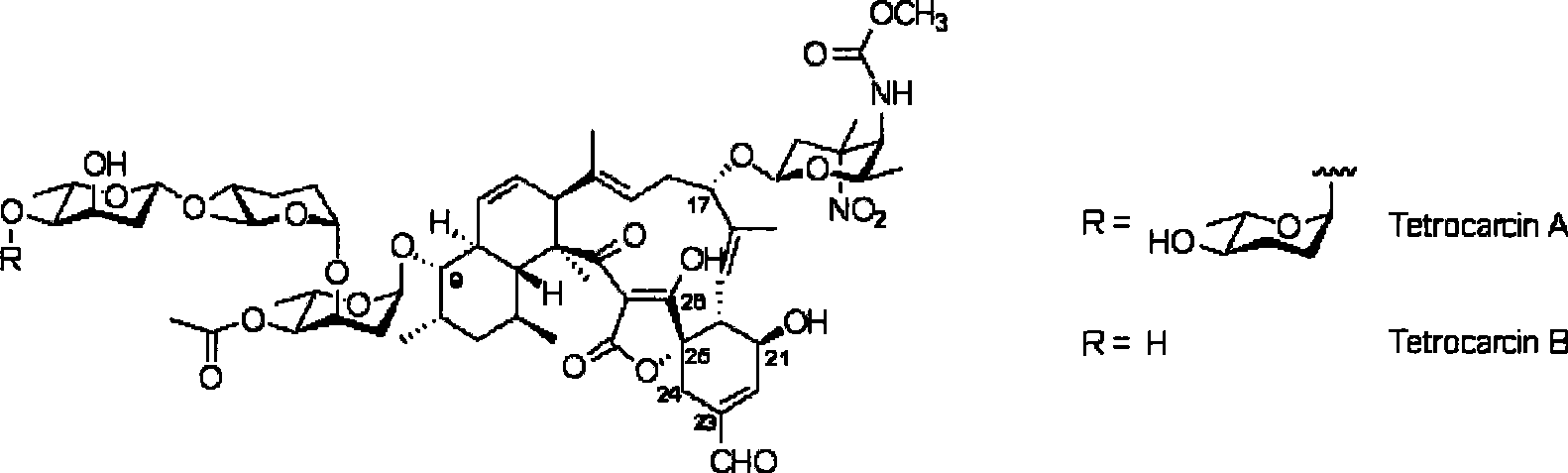
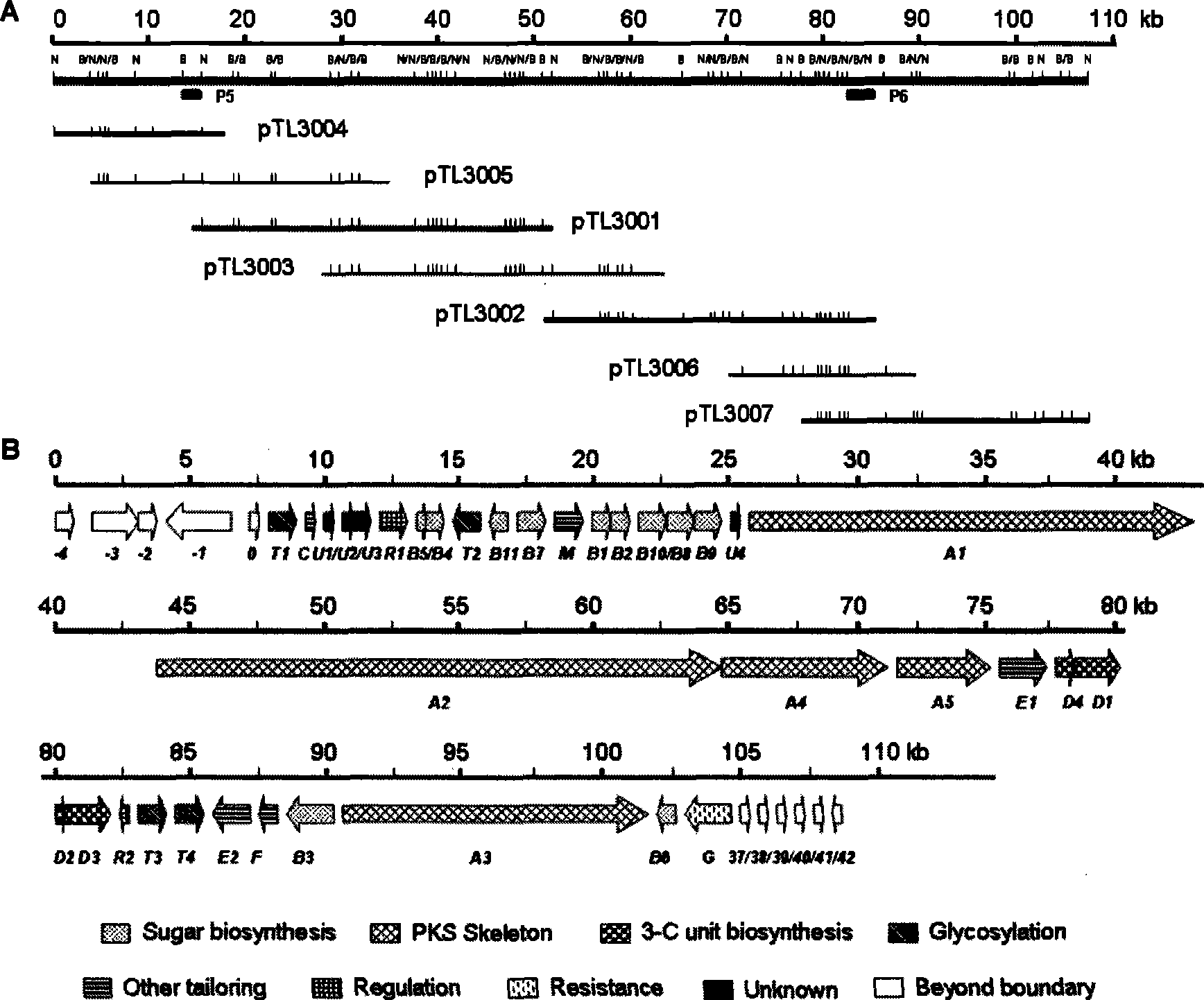
Biological synthesis gene cluster of tetrokacin A and use thereof
The invention relates to a clone, sequencing, analysis and function study of biosynthesis gene cluster of antibiotics-Tectrocarcin A which has anti-tumor activity and is generated by Micromonospora chalcea NRRL11289 and the application thereof. The whole gene cluster contains 36 genes: 5 non-reused I type polyketone synthetase genes; 4 special three-carbon biosynthesis genes; 11 desoxy sugar biosynthesis genes; 9 post modifying genes; 2 regulator genes; 1 resistance gene; and 4 genes with uncertain function. Due to the genetic manipulation of biosynthesis genes, the biosynthesis of Tectrocarcin A can be prevented. The genes and the proteins thereof which are provided by the invention can also be used for searching and discovering the compounds, genes or proteins that can be applies in medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthetic gene cluster of FR901464
ActiveCN101818158AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsDepsipeptidesFermentationBiosynthetic genesGenetic engineering
The invention relates to cloning, sequencing, analysis and functional study of a biosynthetic gene cluster of a natural product FR901464 which has anti-tumor activity and is generated from pseudomonas as well as the application thereof. The whole gene cluster contains 20 genes: five polyketide synthase genes, one hybrid polyketide / non-ribosomal polypeptide synthase gene, one non-ribosomal polypeptide synthase gene, three independent acyltransferase genes, four genes related to polyketide backbone alkylation, four post-modification genes and two control-related genes. The genetic operation of the biosynthetic gene can block the biosynthesis of FR901464. The provided gene and protein thereof can be used for genetic engineering, protein expression, enzyme catalysis reaction, and the like of the compound and can also be used for searching and discovering compounds that can be used in medicines, industry or agriculture or genes and proteins thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthesis gene cluster of kosinostatin and application thereof
The invention relates to a biosynthesis gene cluster of kosinostatin, and in particular relates to cloning, sequencing, analysis, functional study and application of the biosynthesis gene cluster of the kosinostatin, which is an antharcycline antibiotic with antitumor activity and generated from micromonospora sp.TP-A0468. The whole gene cluster comprises 55 genes in all, that is, 17 II-type polyketone synthetase (PKS) related genes, 8 non-ribosome polypeptide synthetase (NRPS) related genes, 9 glycosyl synthetic related genes, 6 special post-modifying genes, 7 antibiotic genes, 5 conditioning genes and 3 genes without definite functions. Through the genetic manipulation of the biosynthesis genes, the biosynthesis of kosinostatin can be blocked, the output is changed, or novel compounds are produced. The gene cluster can be applied to gene engineering, protein expression, enzymatic catalytic reaction and the like of antharcycline compounds, and can also be used for finding and discovering compounds, genes or proteins for medicines, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantitative detection method and reagent kit of GSTP1 (Glutathione S-Transferase P1) methylation for predicting hepatic failure prognosis
InactiveCN103805699AGuaranteed specificityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceReference genesGenomic DNA
The invention provides a quantitative detection method and a reagent kit GSTP1 (Glutathione S-Transferase P1) methylation for predicting hepatic failure prognosis. The invention relates to quantitative detection for gene methylation, and in particular relates to a quantitative detection method and a reagent kit f GSTP1 (Glutathione S-Transferase P1) methylation for predicting hepatic failure prognosis. The reagent kit contains a reagent for extracting genomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), a reagent for modifying the genomic DNA, a 5x premixing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) system, a standard substance, positive and negative control, a methylation-specific primer pair aiming at a target gene GSTP1 promoter, a specific primer pair of a reference gene ALU-C4, and a corresponding Taqman fluorescent probe. By extracting peripheral blood genomic DNA and carrying out real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, a quantitative value of the gene GSTP1 methylation is obtained through calculation. The reagent kit provided by the invention can help doctors to determine the pathogenetic condition and prognosis of hepatic failure patients so as to make effective treatment plans.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
High throughput cancer pharmaceutical screening using drosophila
InactiveUS20060010505A1Easy to practiceEasy to adaptOncogene translation productsGenetic engineeringAbnormal tissue growthTumour suppressor gene
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com