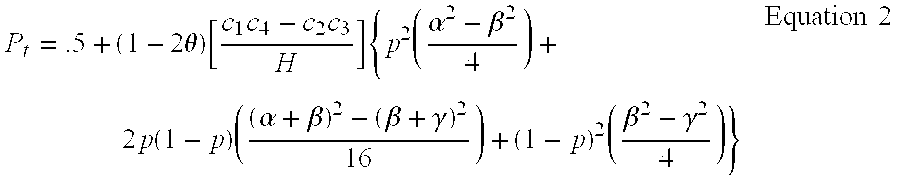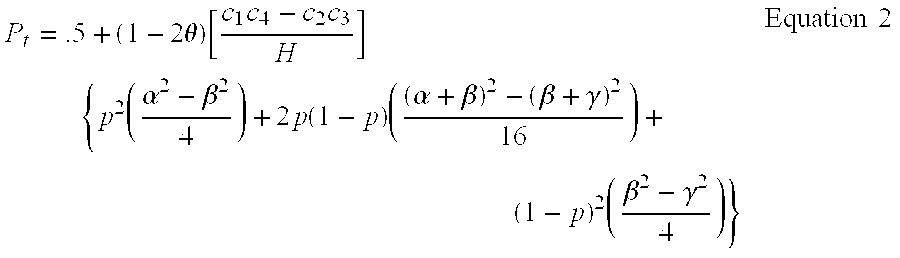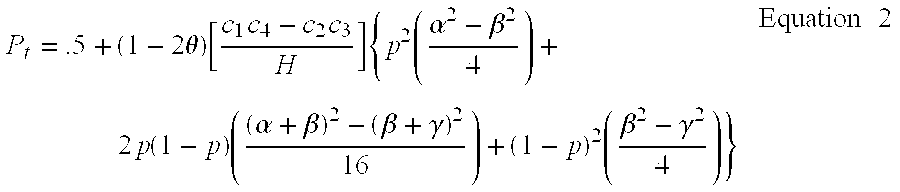Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Chromosome localisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parallel methods for genomic analysis
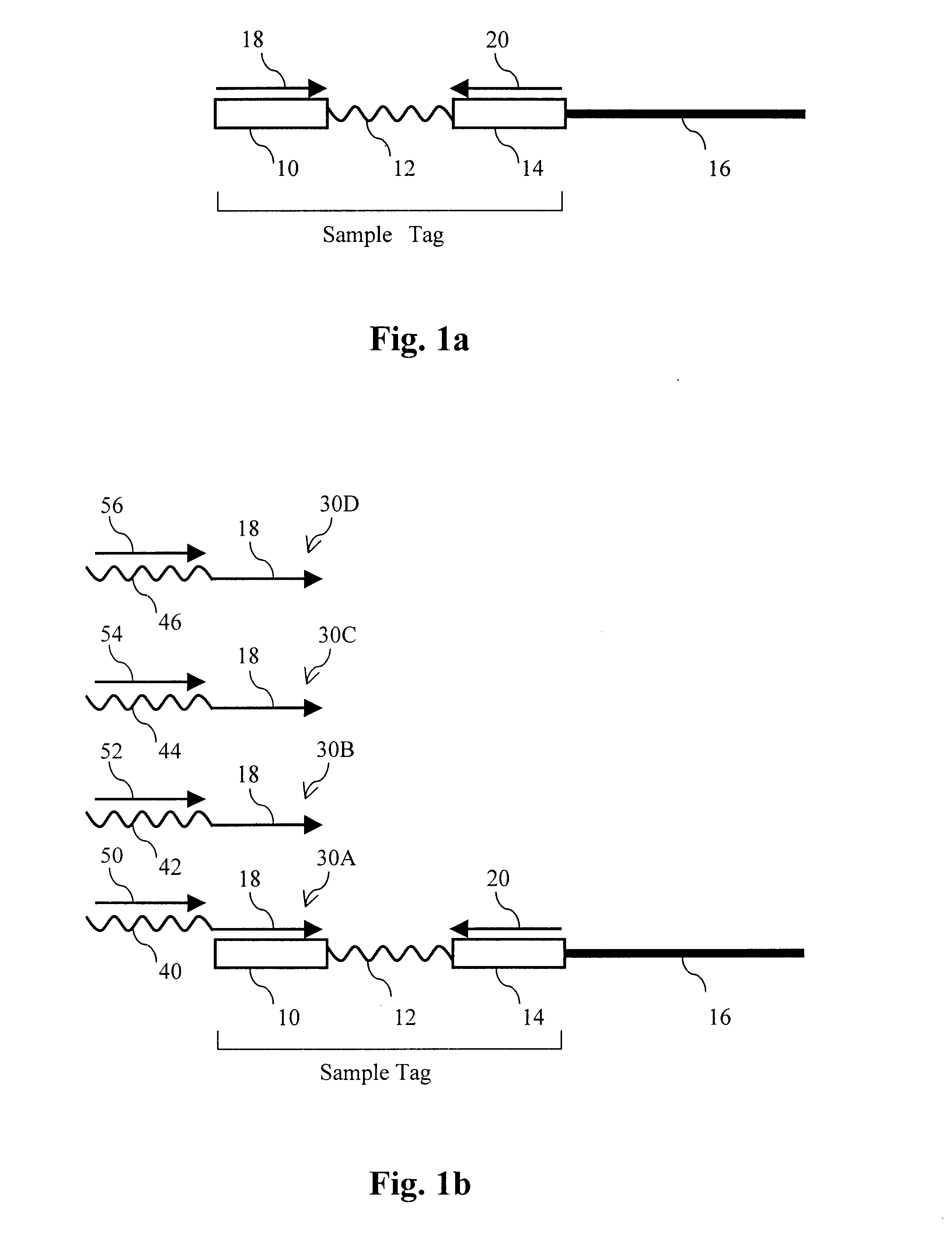
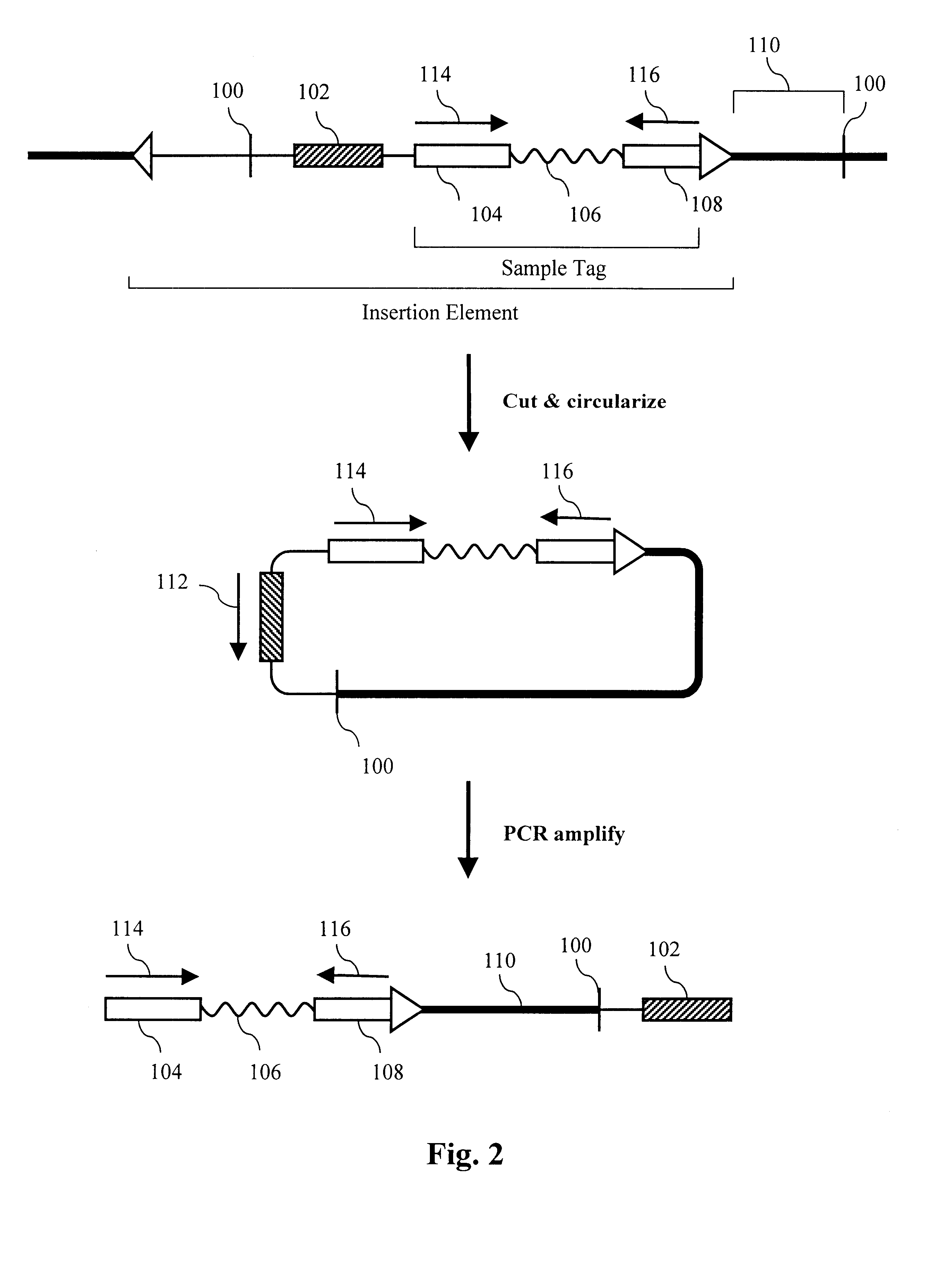
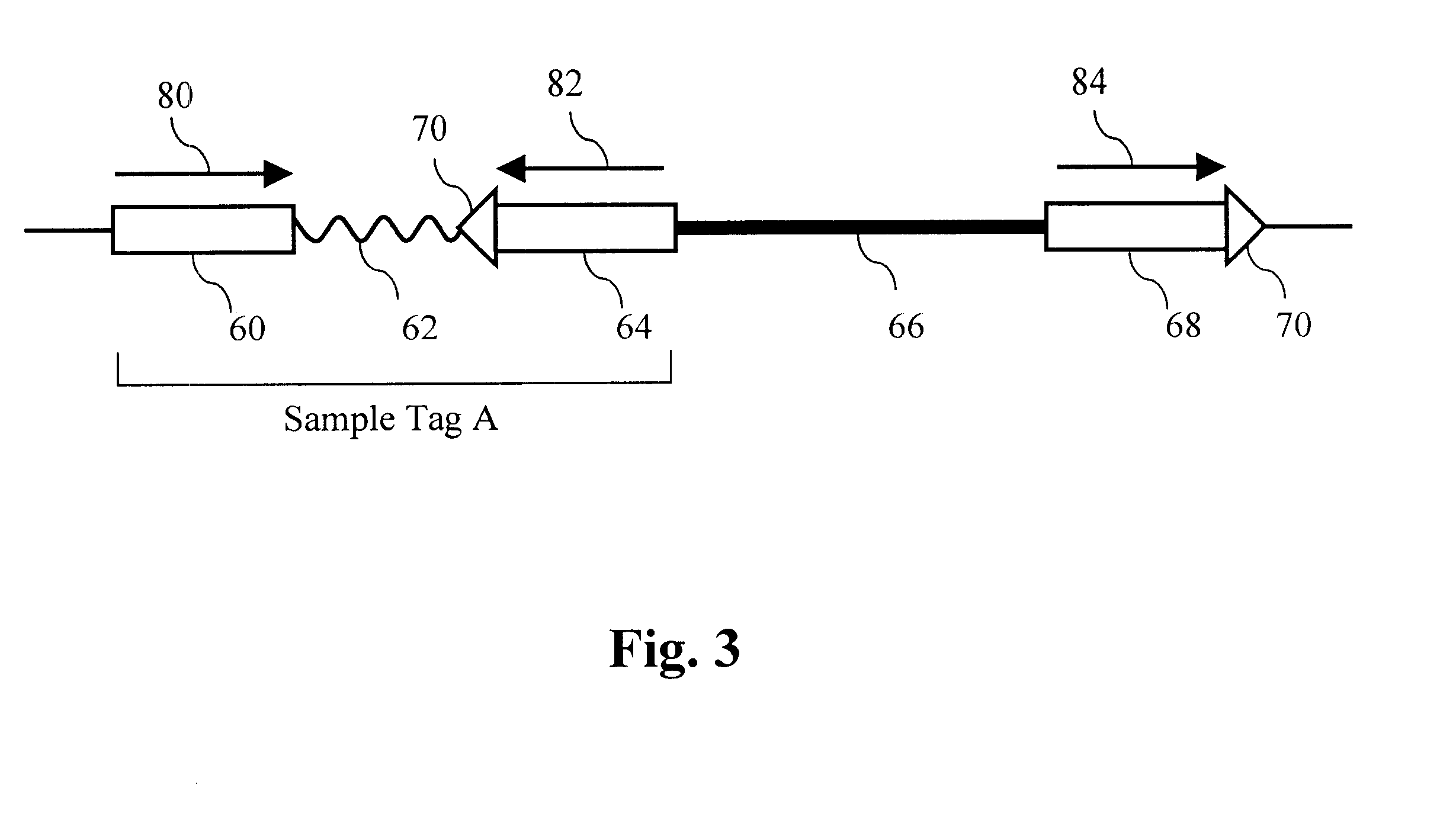
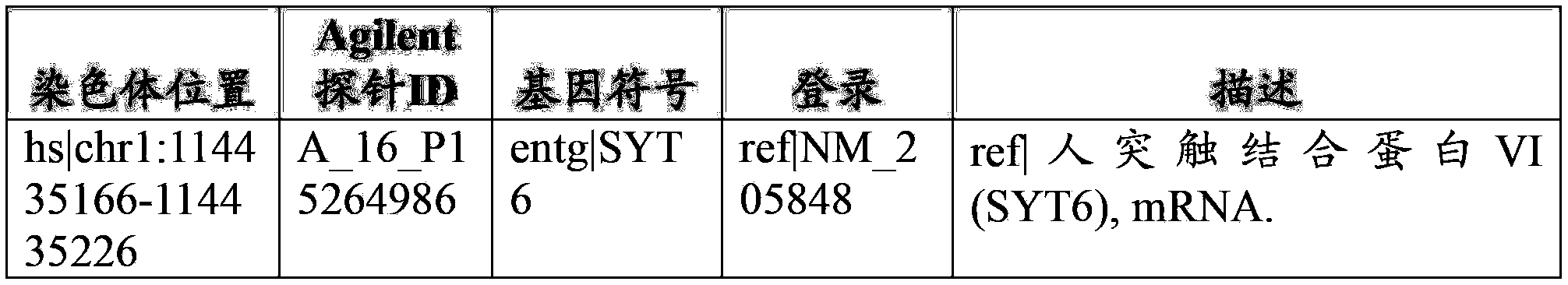
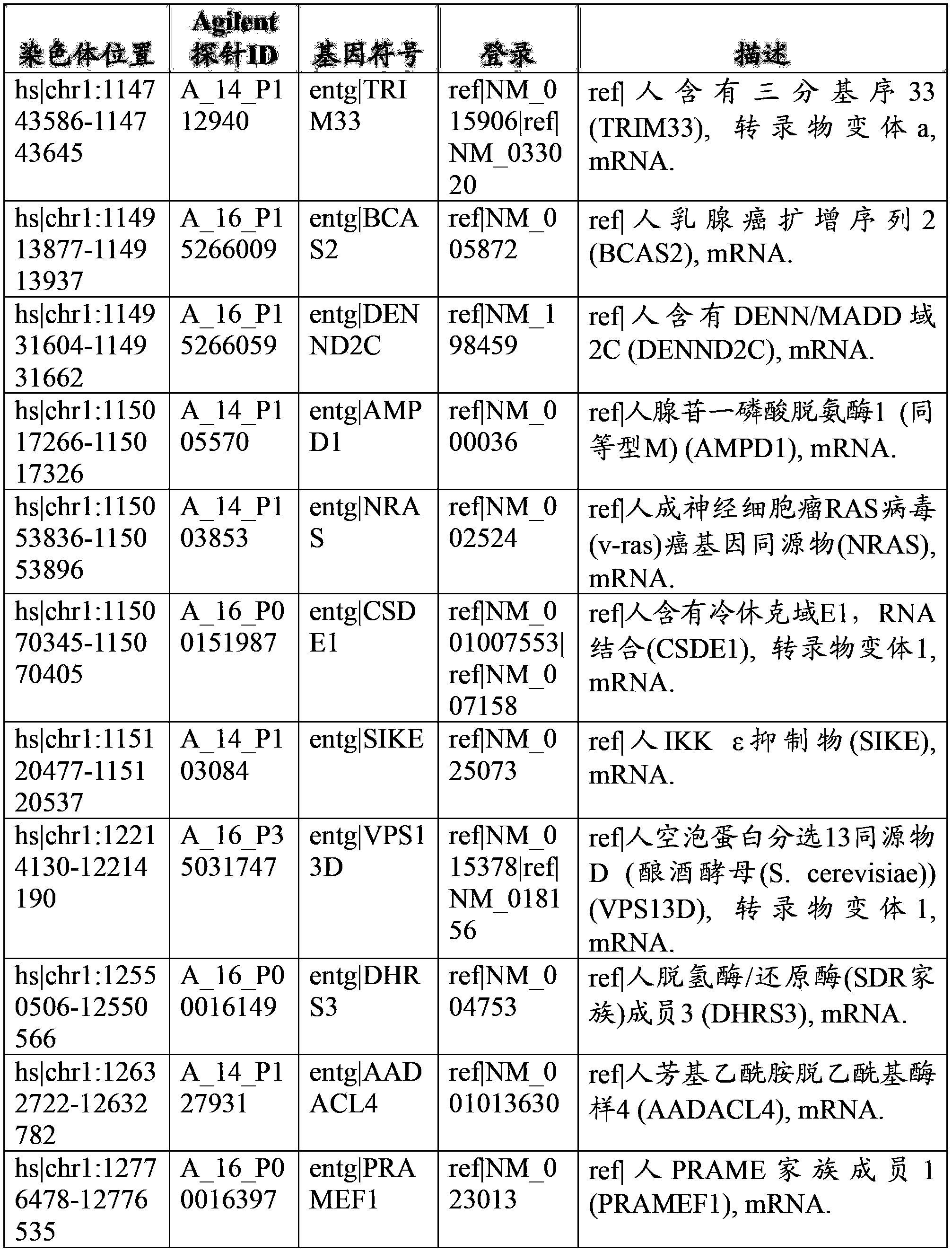
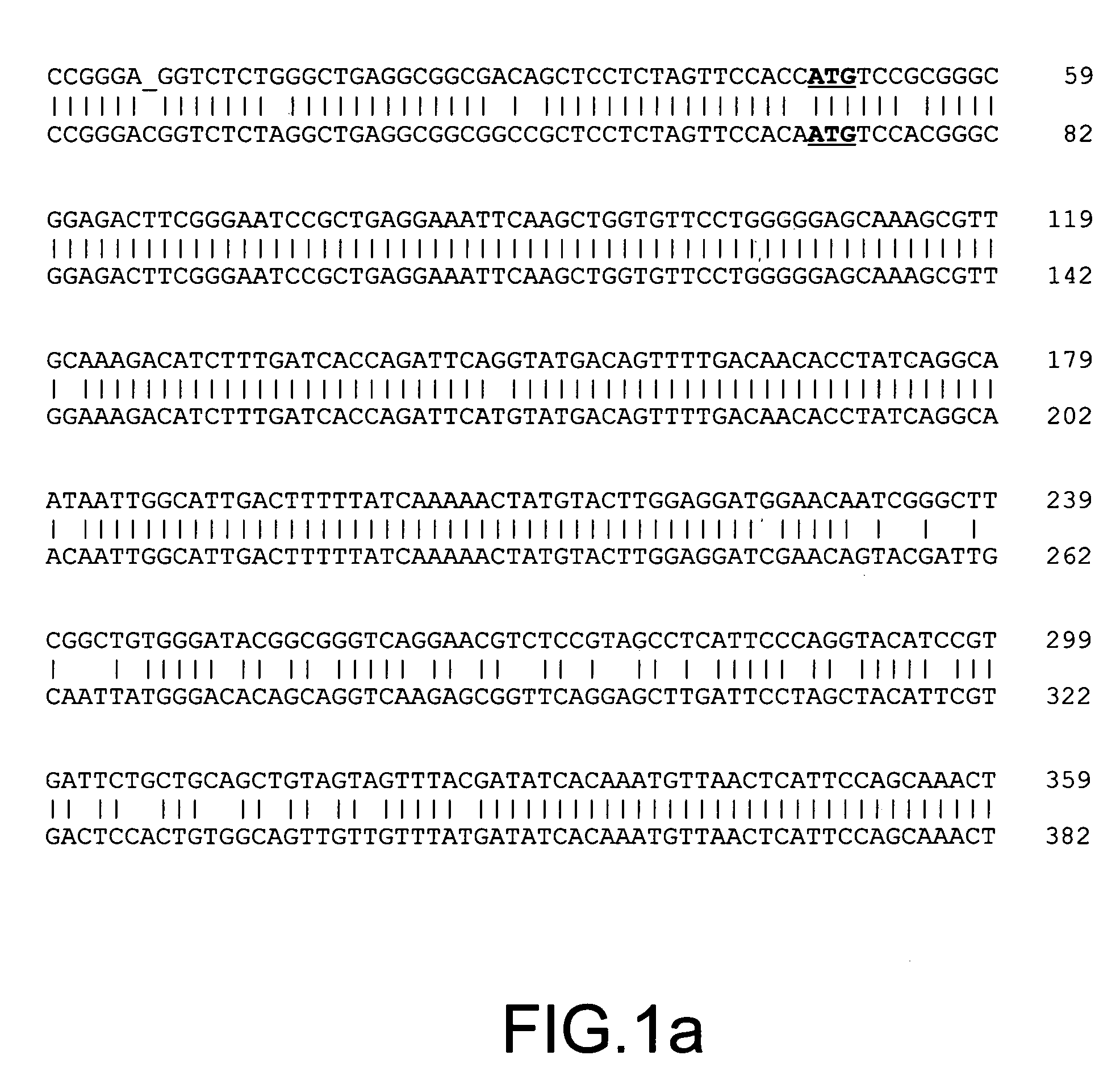
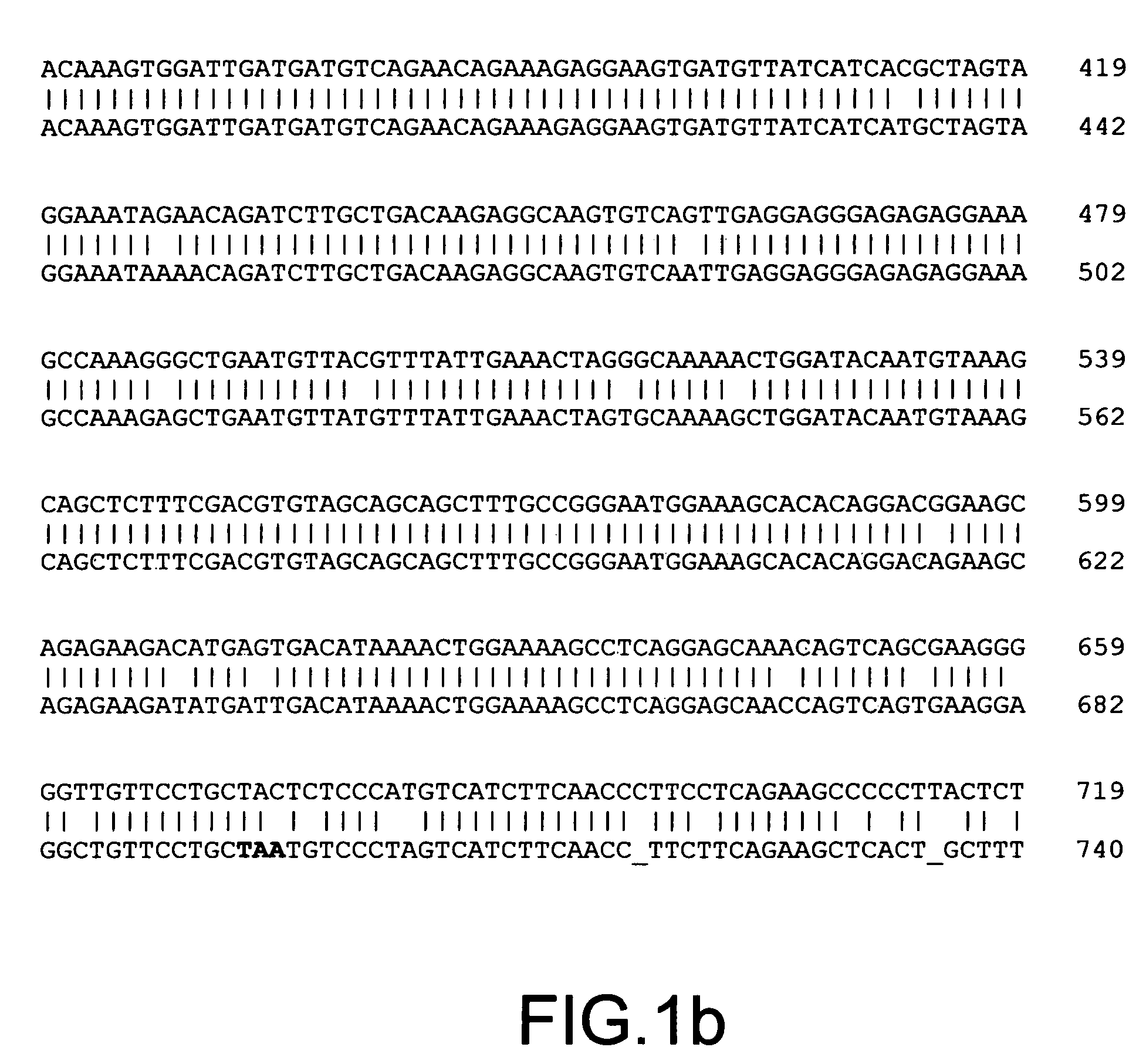
The present invention provides parallel methods for determining nucleotide sequences and physical maps of polynucleotides associated with sample tags. This information can be used to determine the chromosomal locations of sample-tagged polynucleotides. In one embodiment, the polynucleotides are derived from genomic DNA coupled to insertion elements. As a result, the invention also provides parallel methods for locating the integration sites of insertion elements in the genome.
Owner:STRATHMANN MICHAEL P
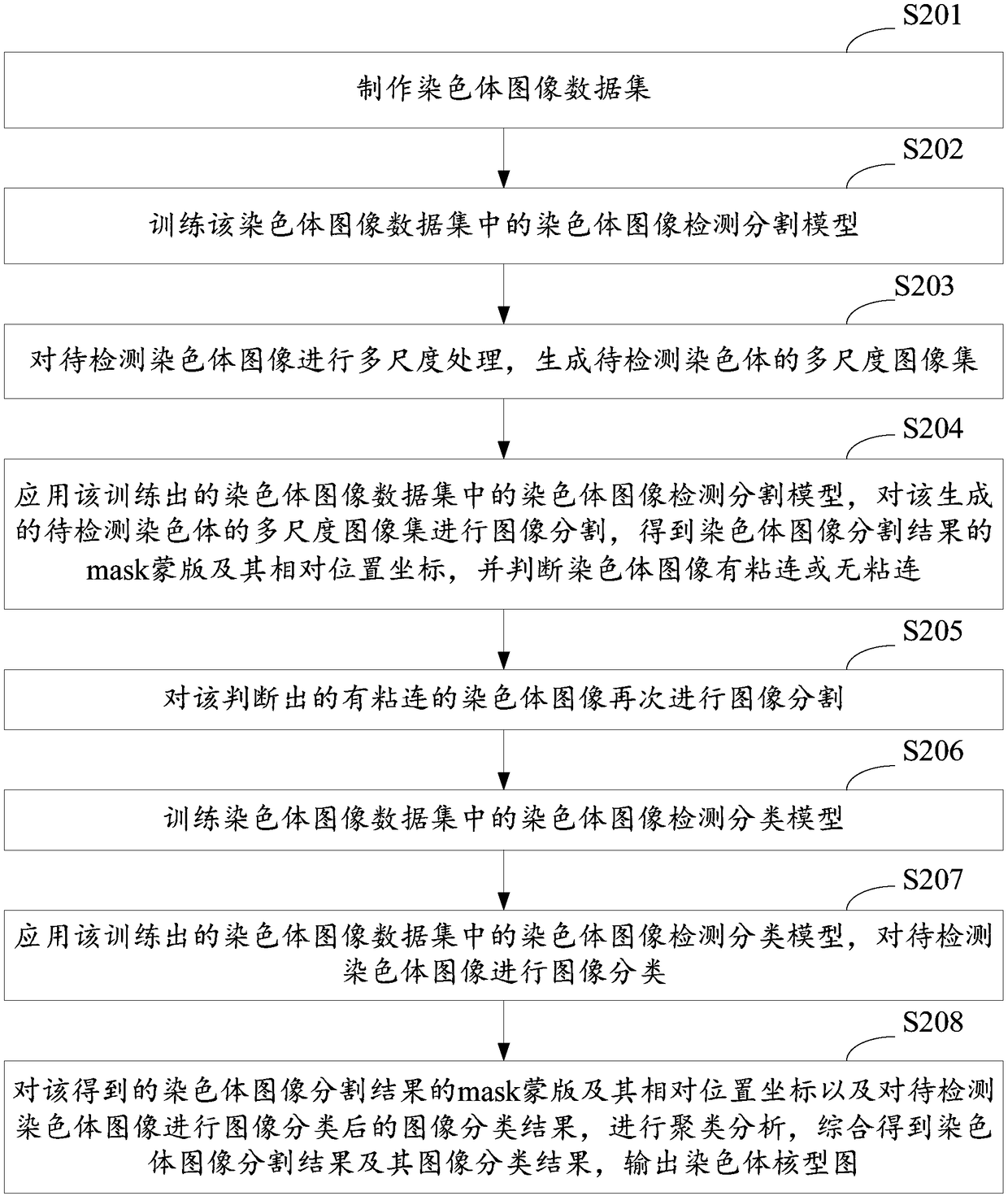
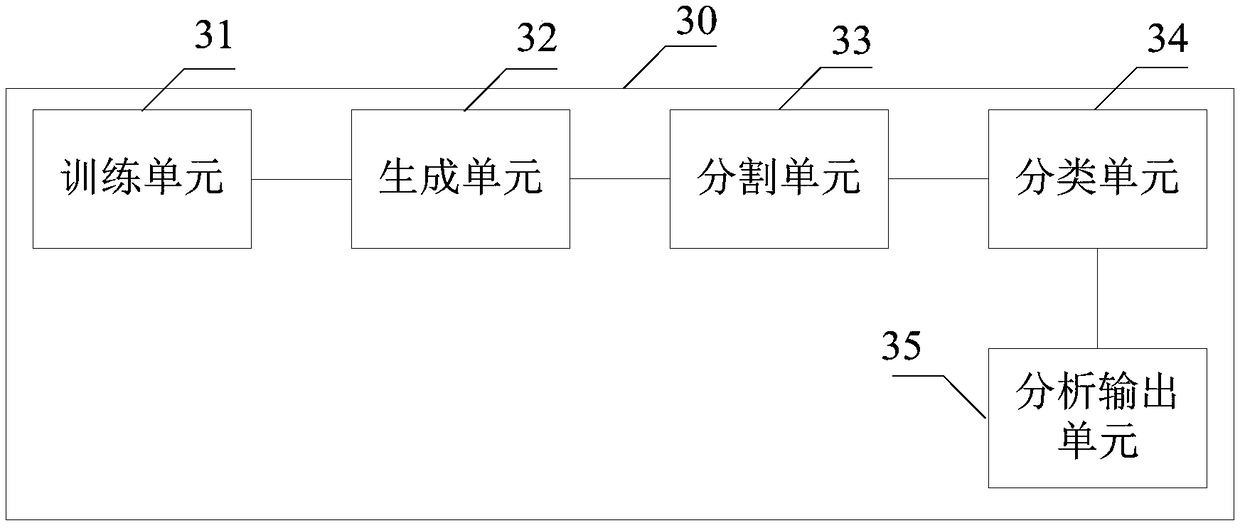
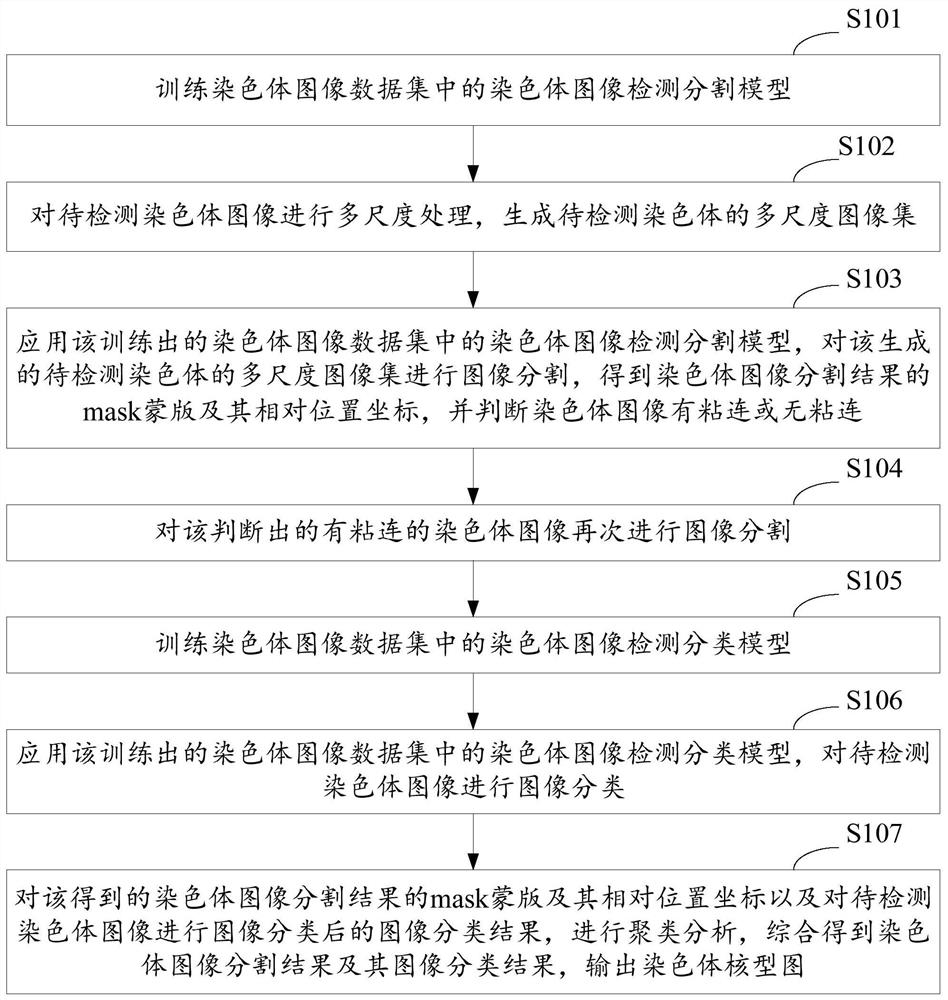
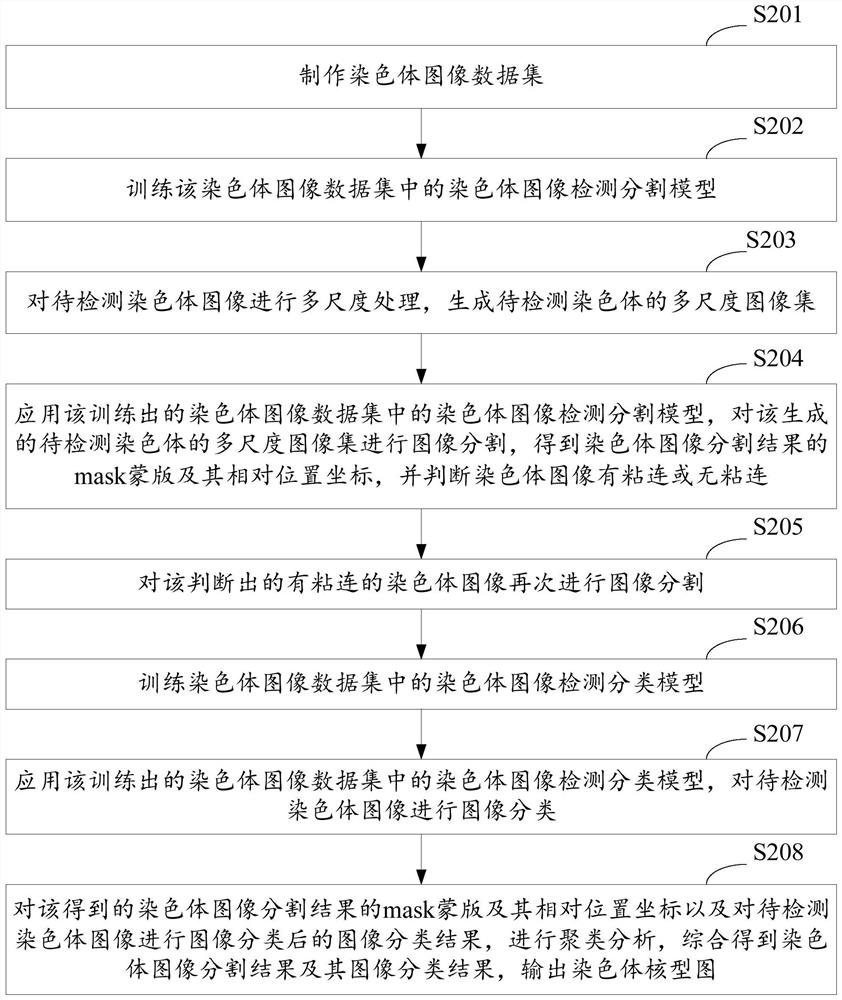
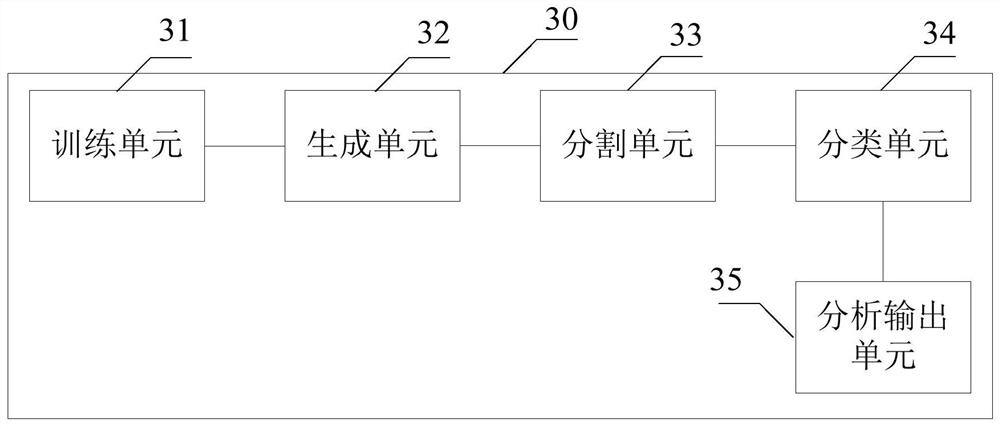
A method and system for automatic chromosome analysis based on depth learning
ActiveCN109344874ATaking into account the overall shapeTaking into account featuresImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionChromosome localisation
The invention discloses a chromosome automatic analysis method and a chromosome automatic analysis system based on depth learning, which can adopt multi-level processing, stratify the independent formand overlapping form of chromosomes, and perform cluster analysis on chromosome position coordinates, classification labels and classification confidence to output a karyotype map. In this manner, the method of chromosome segmentation based on depth learning can be adopted, independent of specific chromosomal morphological patterns, The method has high generalization ability, can adopt chromosomeclassification method based on depth learning, take into account the global morphology and banding characteristics of chromosomes, improve classification accuracy, can adopt multi-scale processing, more fully utilize the detected images, and effectively improve the segmentation effect in the case of chromosome overlap and adhesion.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
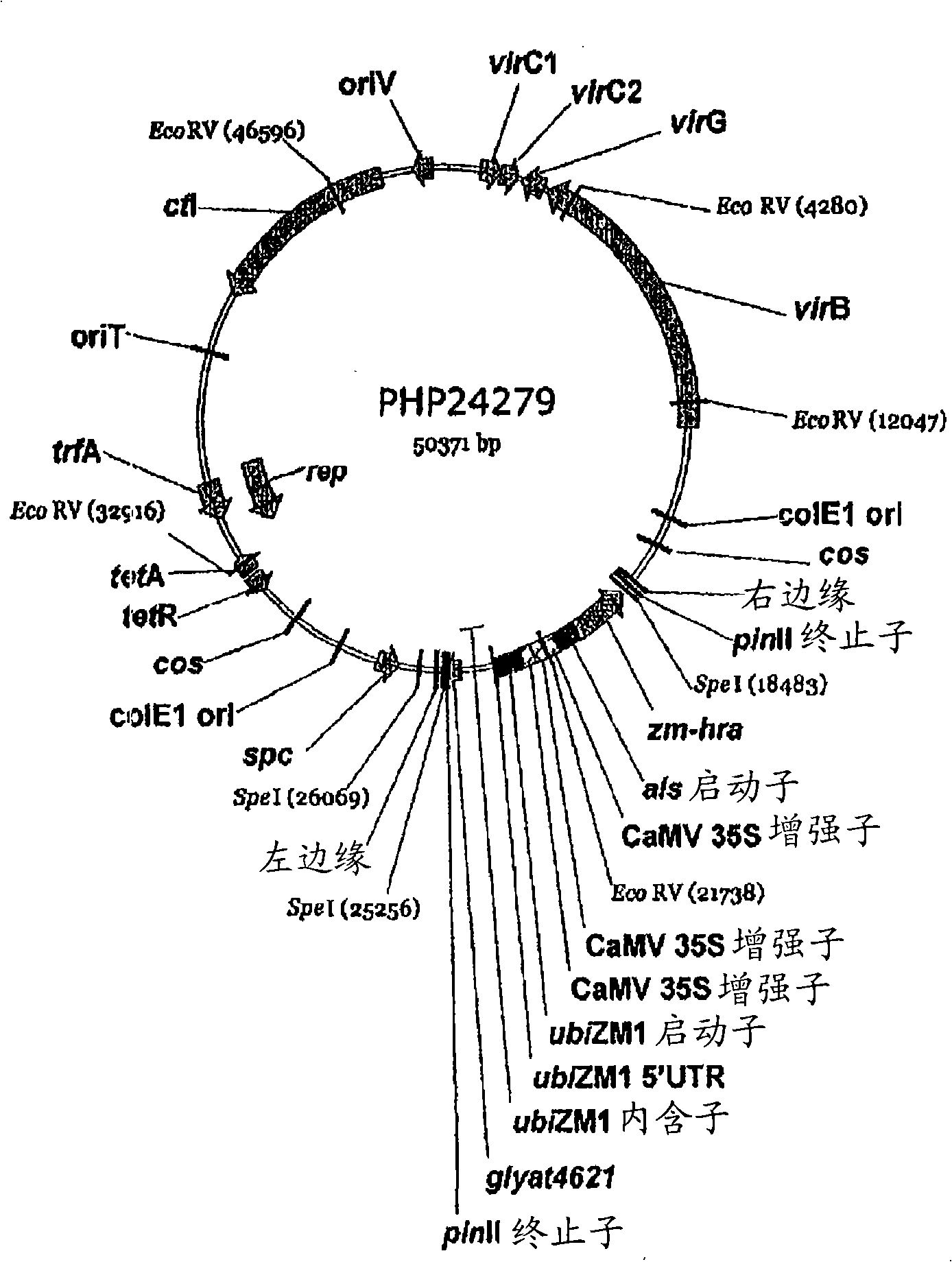
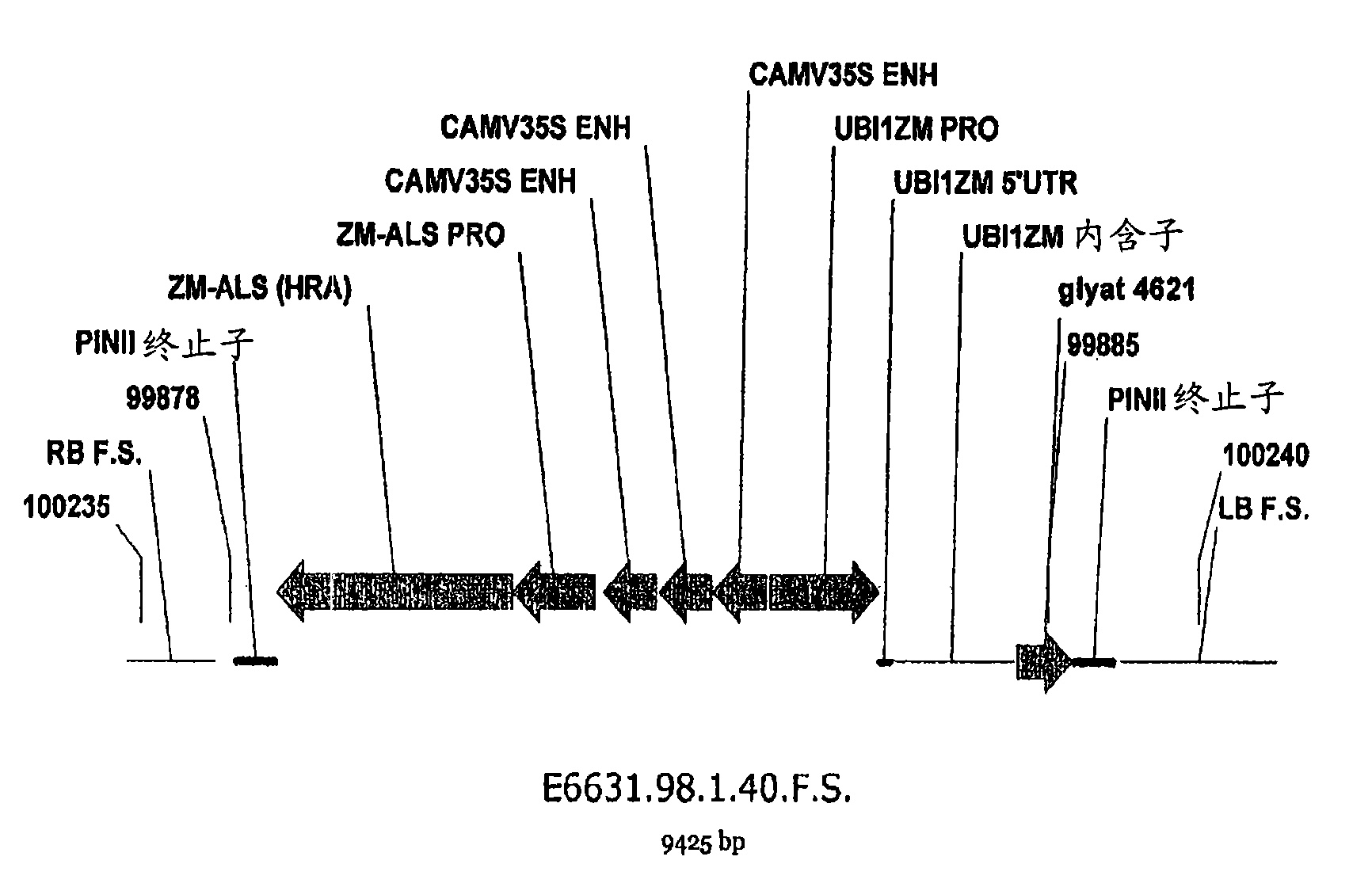
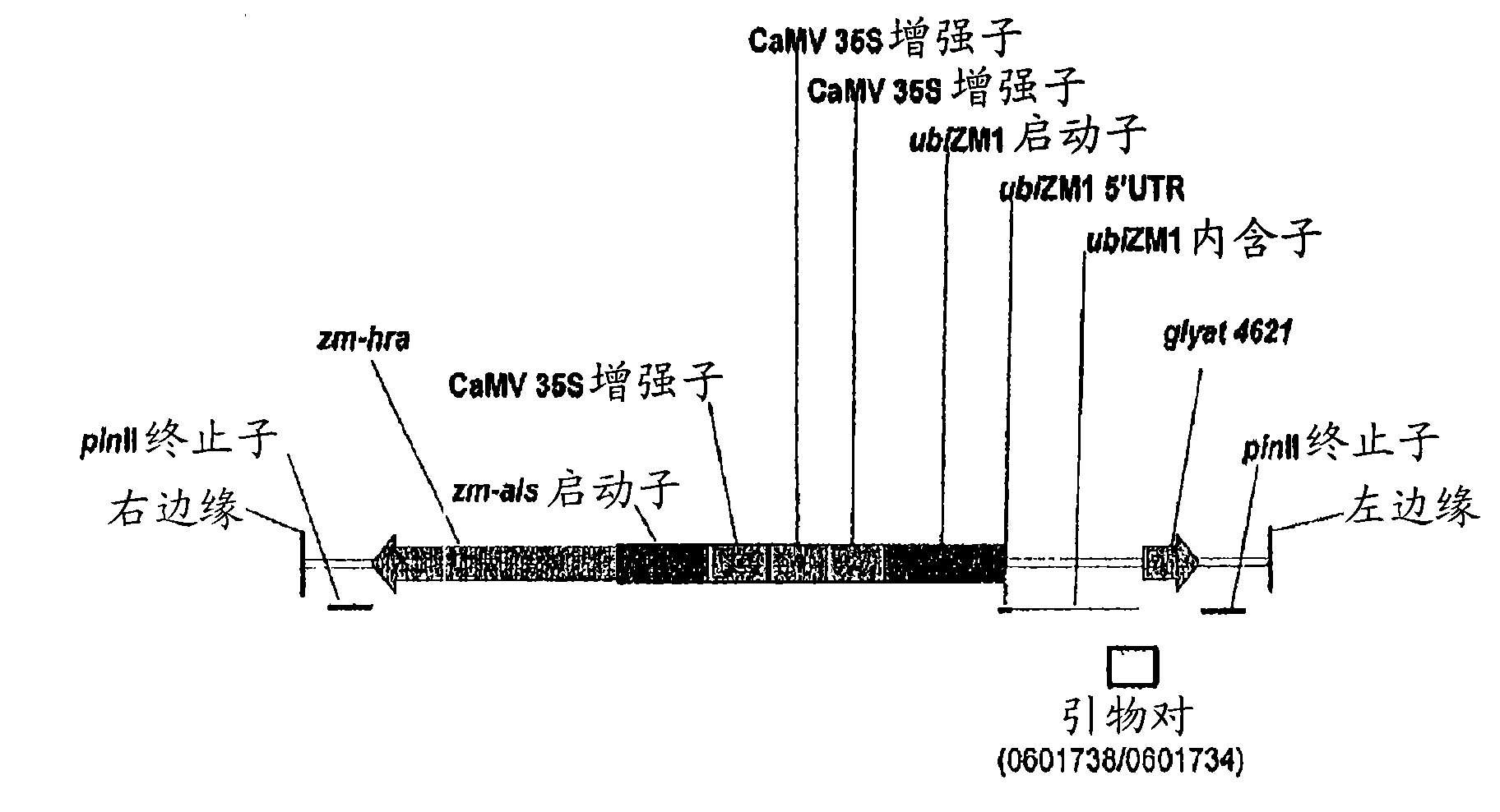
Maize event dp-098140-6 and compositions and methods for the identification and/or detection thereof
InactiveCN101641443AImprove breeding efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsChromosome localisationGlyphosate
Compositions and methods related to transgenic glyphosate / ALS inhibitor-tolerant maize plants are provided. Specifically, the present invention provides maize plants having a DP-098140-6 event which imparts tolerance to glyphosate and at least one ALS-inhibiting herbicide. The maize plant harboring the DP-098140-6 event at the recited chromosomal location comprises genomic / transgene junctions having at least the polynucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO:5 and / or 6. The characterization of the genomic insertion site of the DP-098140-6 event provides for an enhanced breeding efficiency and enables the use of molecular markers to track the transgene insert in the breeding populations and progeny thereof. Various methods and compositions for the identification, detection, and use of the maize DP-098140-6 events are provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Method for developing genome simple sequence repeats (SSR) molecular marker
InactiveCN104313146ALower Sequencing CostsMeet the requirements of finding a large number of SSR molecular markersMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosome localisationContig
The invention discloses a method for developing genome simple sequence repeats (SSR) molecular marker. The method comprises the steps of taking two plant samples, respectively establishing banks for DNA of the samples, thereby obtaining two corresponding libraries; respectively sequencing the libraries by an Illumina sequencing technology, then carrying out micropackaging, seeking in Contigs obtained through micropackage so as to obtain the SSR of the samples, and screening the common SSR in the two samples, wherein the common SSR has the same chromosomal location and the same repetitive unit; and carrying out polymorphism screening on the two samples according to the common SSR, and judging whether the two samples are in porlymorphism according to the difference of times of the repetition of the SSR of the two samples. The method not only meets the requirement of seeking a lot of SSR molecular markers, but also has low cost; due to the advantages of high polymorphism, dominant heredity, wide distribution and few template DNA, the SSR molecular markers can be widely used in genetic diversity analysis, genetic mapping, quantitative trait loci (QTL) location, molecular marker assisted breeding and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
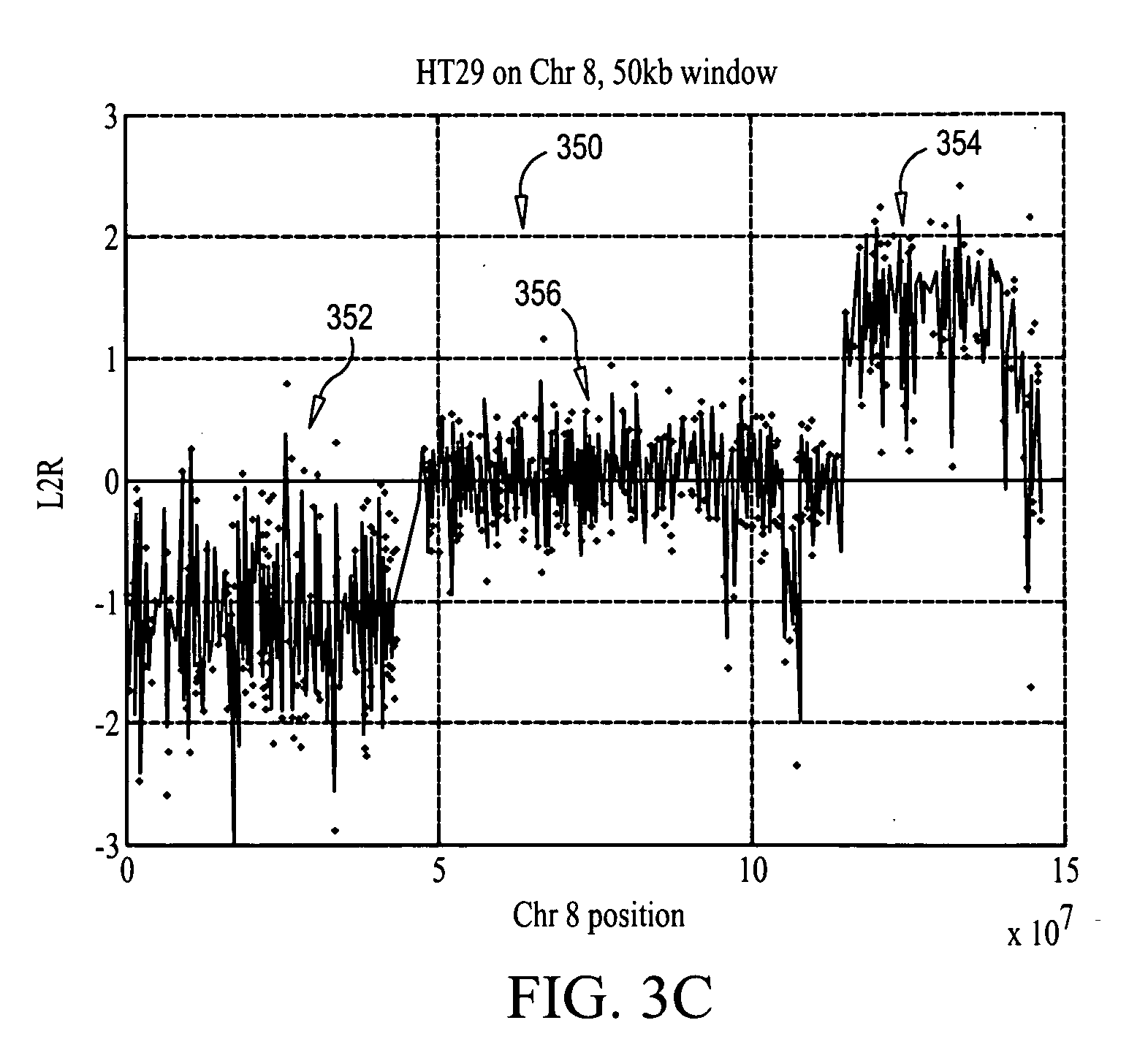
Analyzing CGH data to identify aberrations
InactiveUS20070031883A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsReference sampleChromosome localisation
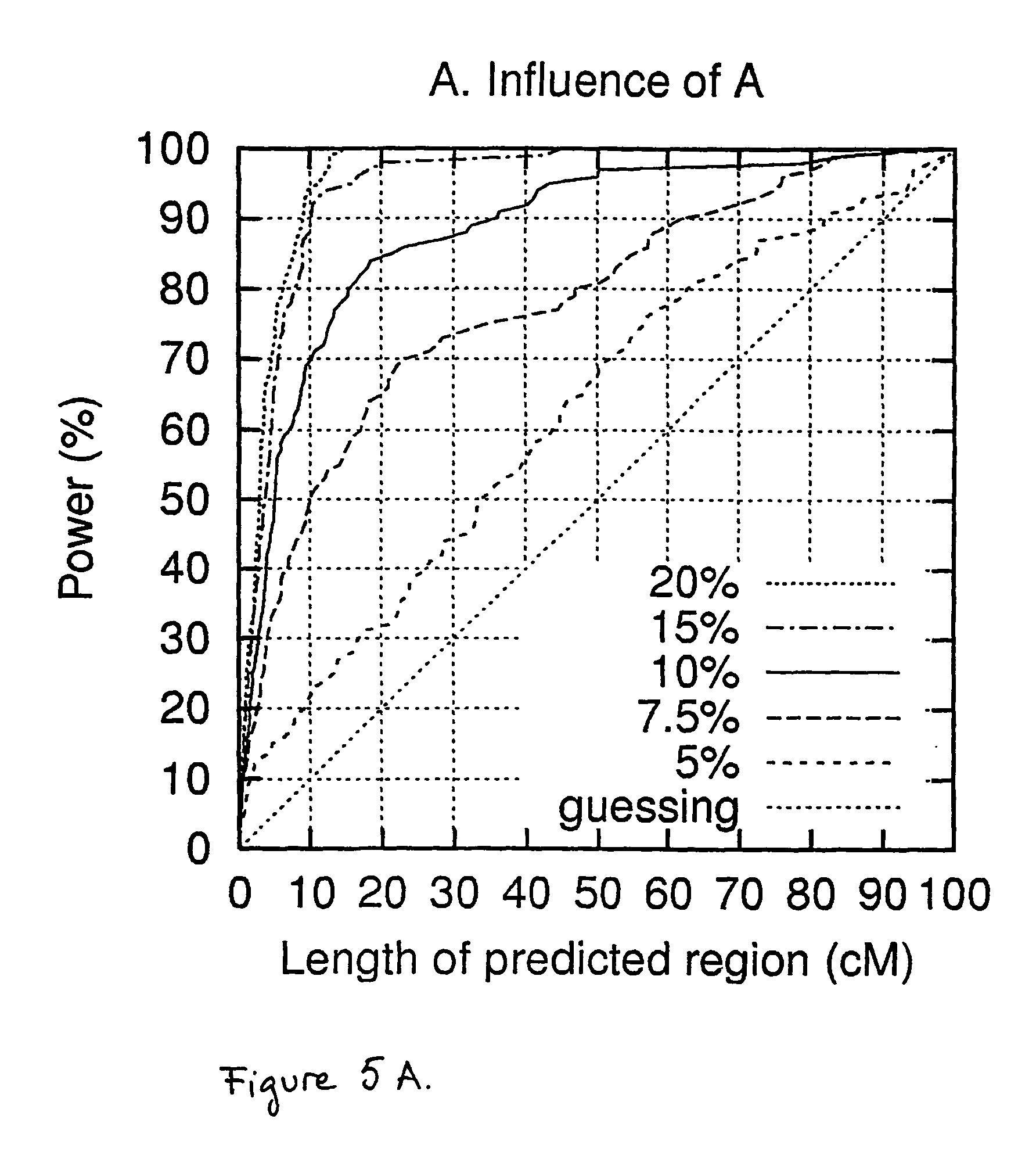
Methods, systems and computer readable media for calling out genetic aberrations. Log ratio noise associated with log ratio signals read from respective probes on at least one array for signals representative of the same chromosomal locations in a test sample of nucleic acids and a reference sample of nucleic acids applied to the at least one array are estimated. Outliers for log ratio values from the reference sample to outliers for log ratio values from the test sample are compared. A copy number of one or more of the chromosomal locations in the test sample is outputted relative to the reference sample for viewing by a user.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
SSR molecular markers for identifying resistance and susceptibility of apple on glomerella leaf spot as well as application of SSR molecular markers
ActiveCN105624280ASpeed up excavationImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationChromosome localisationAgricultural science
The invention provides SSR molecular markers for identifying resistance of apple on the glomerella leaf spot. The molecular markers are S0607039, S0607001, S0506206, S0506078, S0506001, S0405195, S0405127, S0304673 and S0304011 respectively. The invention further provides primers used for multiplying the SSR molecular markers for identifying the resistance of apple on the glomerella leaf spot. The genes, resistant to glomerella leaf spot, of the apple are subjected to molecular marking through the self-designed SSR markers, so that the position of chromosomes and the genetic distance can be determined, and a tightly linked genetic map is established. The molecular marker closest to the resistance gene can be used for accurately identifying the resistance of apple on the glomerella leaf spot, so that an effective tool is provided for apple production practice and resistance breeding, and a good basis is laid for next cloning and functional verification of the resistance gene.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Primers and kit for detecting molecular marker linked to major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength, detection method for detecting corn stalk strength, and applications of primers, kit and detection method
InactiveCN109295248AEasy to operateThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceUltimate tensile strength
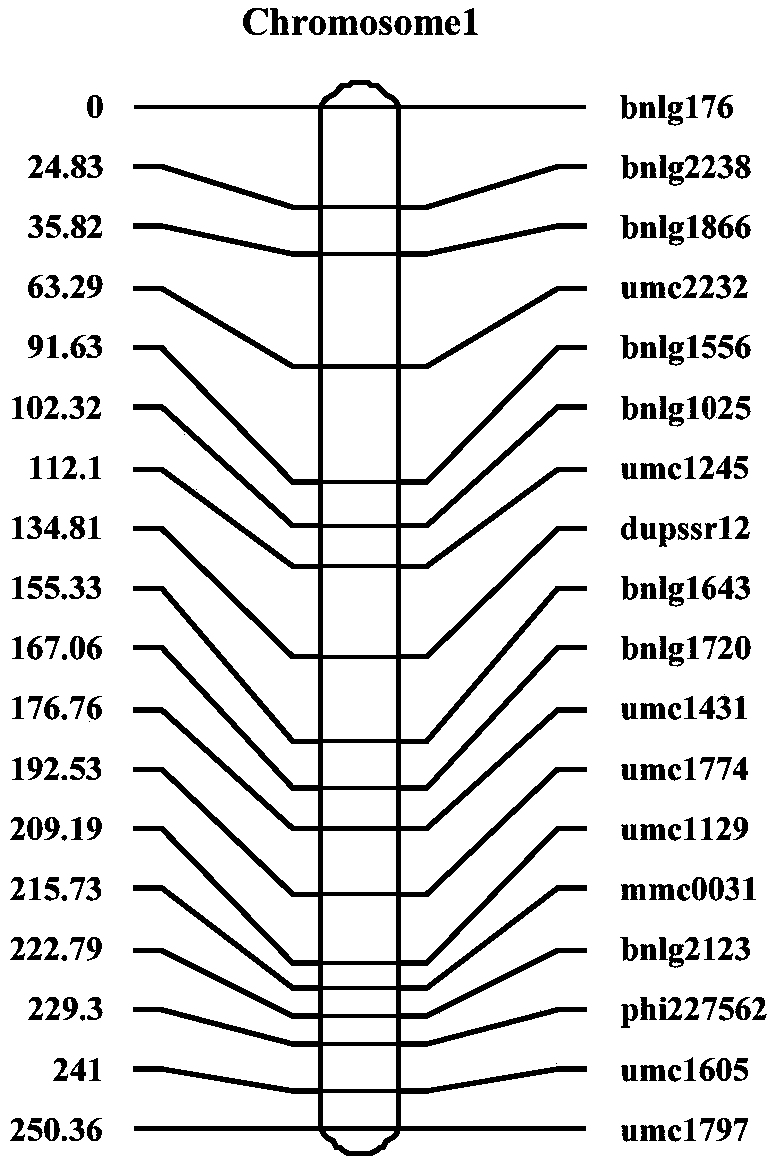
The invention relates to primers and a kit for detecting a molecular marker linked to major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength, a detection method for detecting corn stalk strength, and applications of the primers, the kit and the detection method, and belongs to the technical field of corn genetic breeding and molecular biology. According to the present invention, a recombinant selfing linepopulation containing 241 families is constructed through Zheng 58*D863F, and genetic linkage map analysis is performed, such that four QTL for controlling corn stalk strength are detected, wherein the high stalk strength major QTL qRPR1.07 is identified simultaneously at the position 1.07 of the chromosome 1 of the corn from Hainan Ledong and Henan Yuanyang Demonstration Base, and is positioned between two SSR markers bnlg1556 and umc2232 so as to explain nearly 20% of genetic variation; and the molecular marker linked to the major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength can directionally andprecisely screen corn materials with high stalk strength at the early stage of growth so as to save the breeding cost and the breeding time, and is used for lodging-resistant breeding of corn.
Owner:河南省农业科学院作物设计中心
Method for detecting klenow fragment repetition position in saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome
ActiveCN105624306AQuick checkEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementYeast chromosomeGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to a method for detecting a klenow fragment repetition position in a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome.By combining genomic sequencing with endoreduplication backcrossing, the position of repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the chromosome is confirmed quickly.Through the endoreduplication backcrossing method, the position of the repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome can be detected efficiently and quickly and repaired, repeated klenow fragment genome DNA is deleted, there is no need to precisely confirm the position of a klenow fragment repetition site or conduct cumbersome experimental data analysis on saccharomyces cerevisiae to be detected, operation is easy, and the experimental period is short.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data
InactiveUS20050064408A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsGene mappingGenetic linkage disequilibrium
The present invention relates to a method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data, which utilizes linkage disequilibrium between genetic markers mi, which are polymorphic nucleic acid or protein sequences or strings of single-nucleotide polymorphisms deriving from a chromosomal region. The method according to the invention is based on discovering and assessing tree-like patterns in genetic marker data. It extracts, essentially in the form of substrings and prefix trees, information about the historical recombinations in the population. This infor-mation is used to locate fragments potentially inherited from a common diseased founder, and to map the disease gene into the most likely such fragment. The method measures for each chromosomal location the disequilibrium of the prefix tree of marker strings starting from the location, to assess the distribution of disease-associated chromosomes.
Owner:LICENTIA OY
Defining diagnostic and therapeutic targets of conserved free floating fetal DNA in maternal circulating blood
InactiveCN103370456ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosome localisationCell-free fetal DNA
Owner:BIO DX
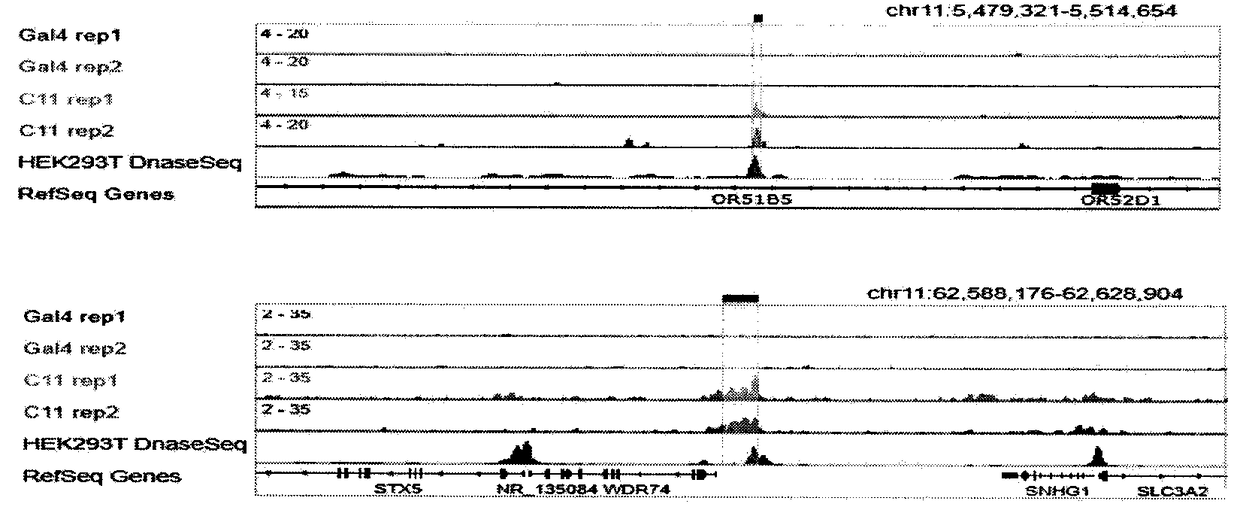
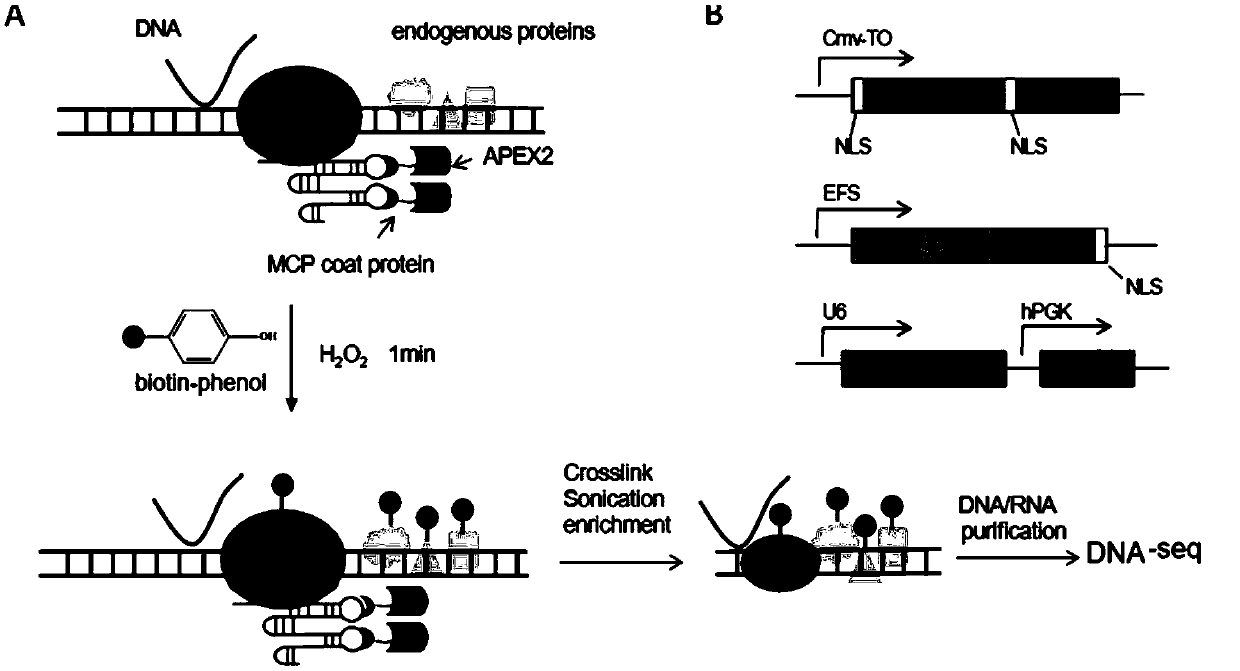
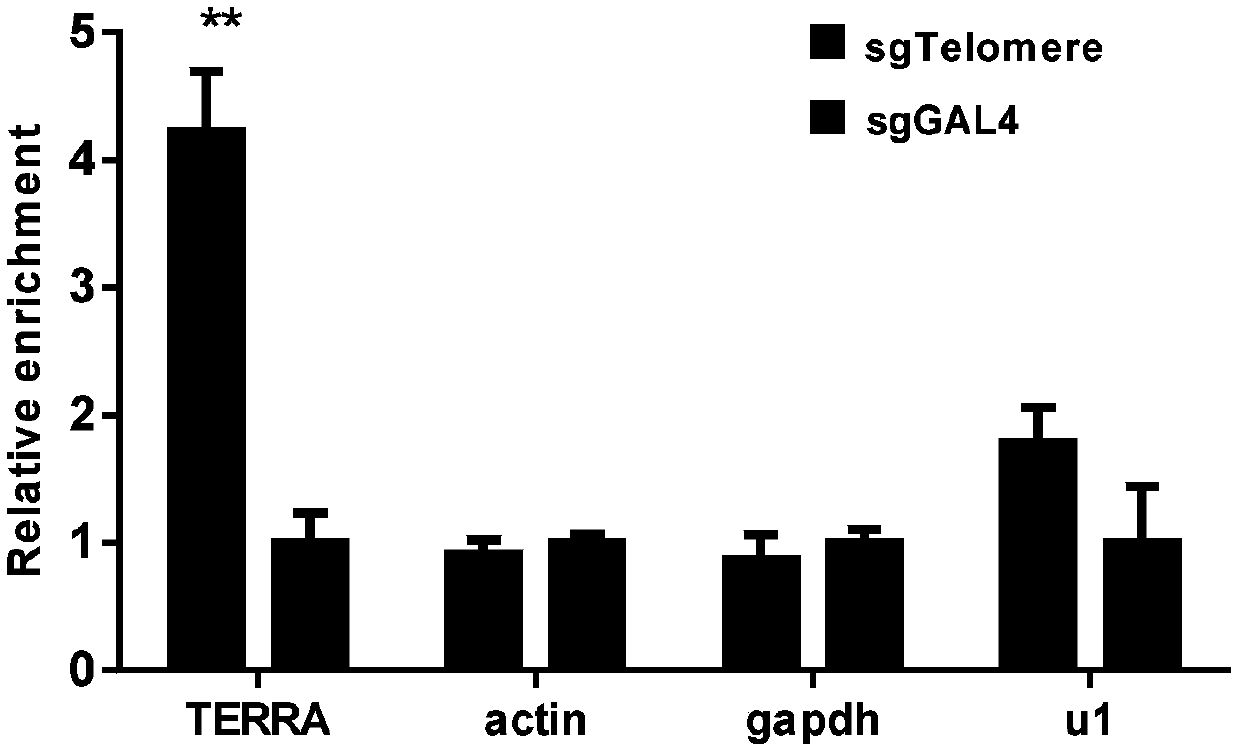
Method for identifying and analyzing specific locus interaction proteins on basis of CRISPR/cas9 and peroxidase APEX2 system
InactiveCN109507429AAchieve highly specific enrichmentEasy to operateBiological testingMagnetic beadInteractions protein
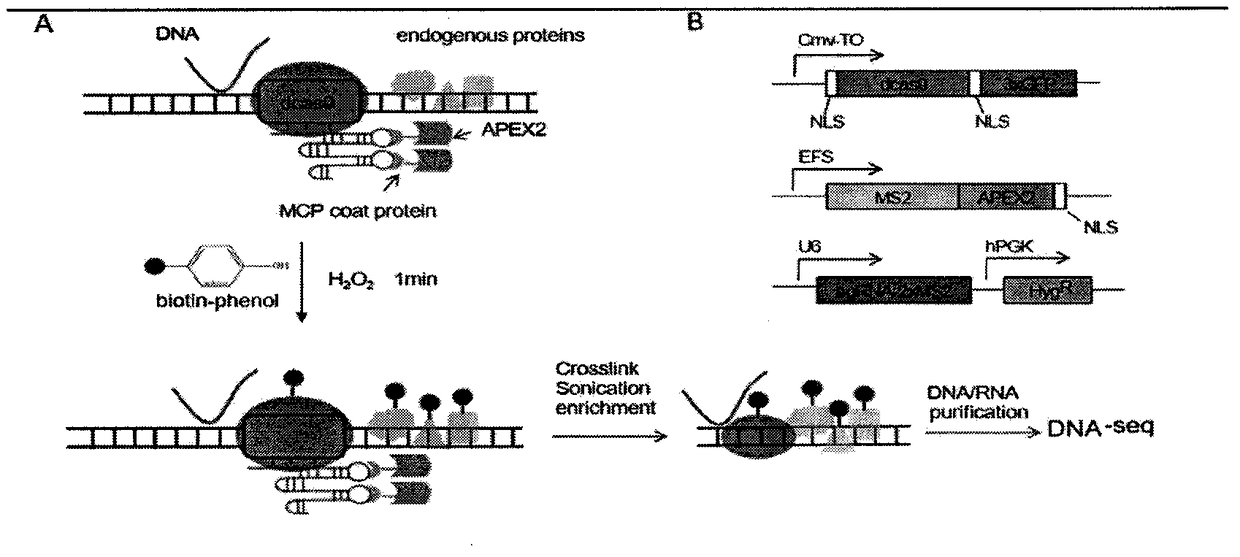
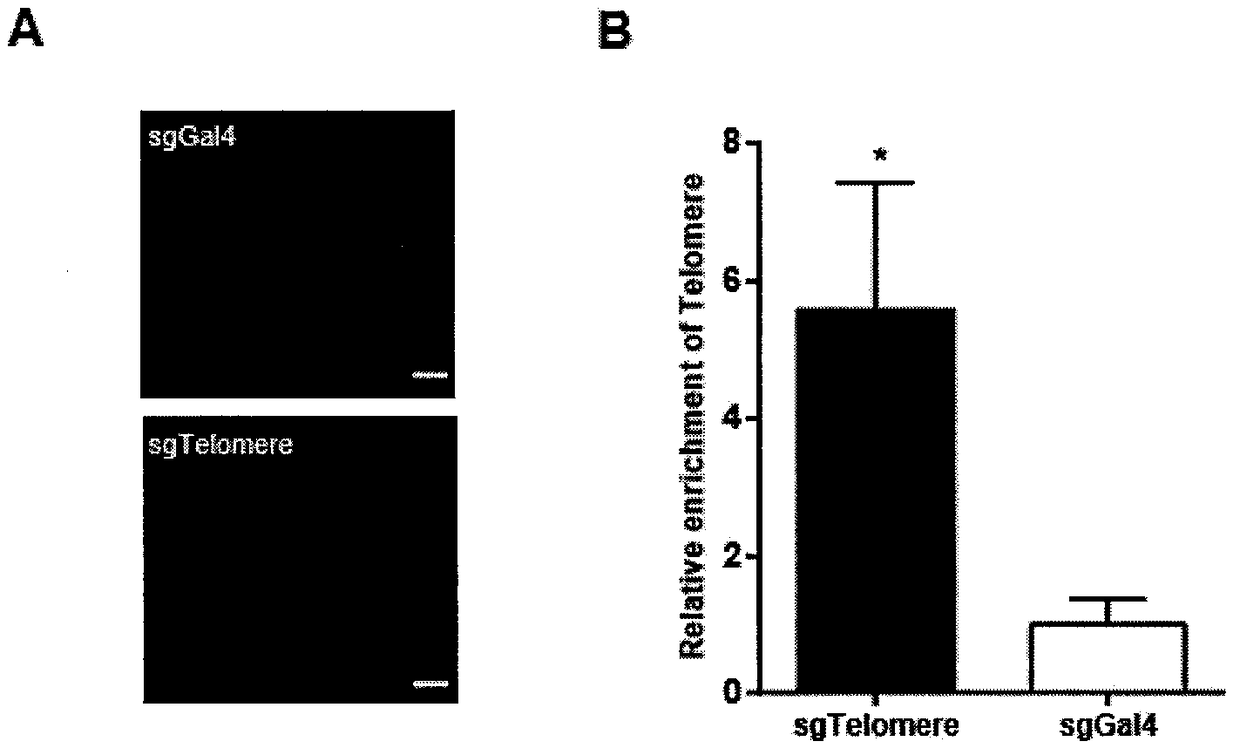
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for identifying and analyzing specific locus interaction proteins on the basis of a CRISPR / cas9 and peroxidase APEX2 system. The method comprises the following steps: plasmid transformation; biotin labeling of specific locus binding protein complex; enrichment of biotin-labeled protein complex by utilizing streptomycin magnetic beads; and assay and analysis of enriched proteins. An experimental analysis result shows that the method is applicable to the research and analysis of protein at any given chromosomal location, and meanwhile, the idea that the method combines the CRISPR gene editing system with APEX2 to carry out specific locus protein analysis is also applicable to the combination of other genome editing methods (such as TALEN) and the APEX2. The method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high sensitivity, high specificity, good repeatability and adaption to the requirement of the research of local chromatin interaction at any given chromosomal location.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for identifying and analyzing specific genomic locus interaction DNAs on basis of CRISPR/cas9 and peroxidase APEX2 system
InactiveCN109504711AEfficient enrichmentHigh resolutionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMagnetic bead
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for identifying and analyzing specific genomic locus interaction DNAs on the basis of a CRISPR / cas9 and peroxidase APEX2 system. The method comprises the following steps: plasmid transformation, biotin labeling of specific locus binding protein complex, enrichment of biotin-labeled protein and DNA complex by utilizingstreptomycin magnetic beads and sequencing and analysis of enriched DNAs. An experimental analysis result shows that the method is applicable to the analysis of any genomic locus, and can obtain theinformation of genomic loci interacting with the genomic locus, and meanwhile, the idea that the method combines the CRISPR gene editing system with APEX2 to carry out specific locus DNA analysis is also applicable to the combination of other genome editing methods (such as TALEN) and the APEX2. The method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high sensitivity, high specificity, good repeatability and adaption to the requirement of the research of local chromatin interaction DNAs at any given chromosomal location.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
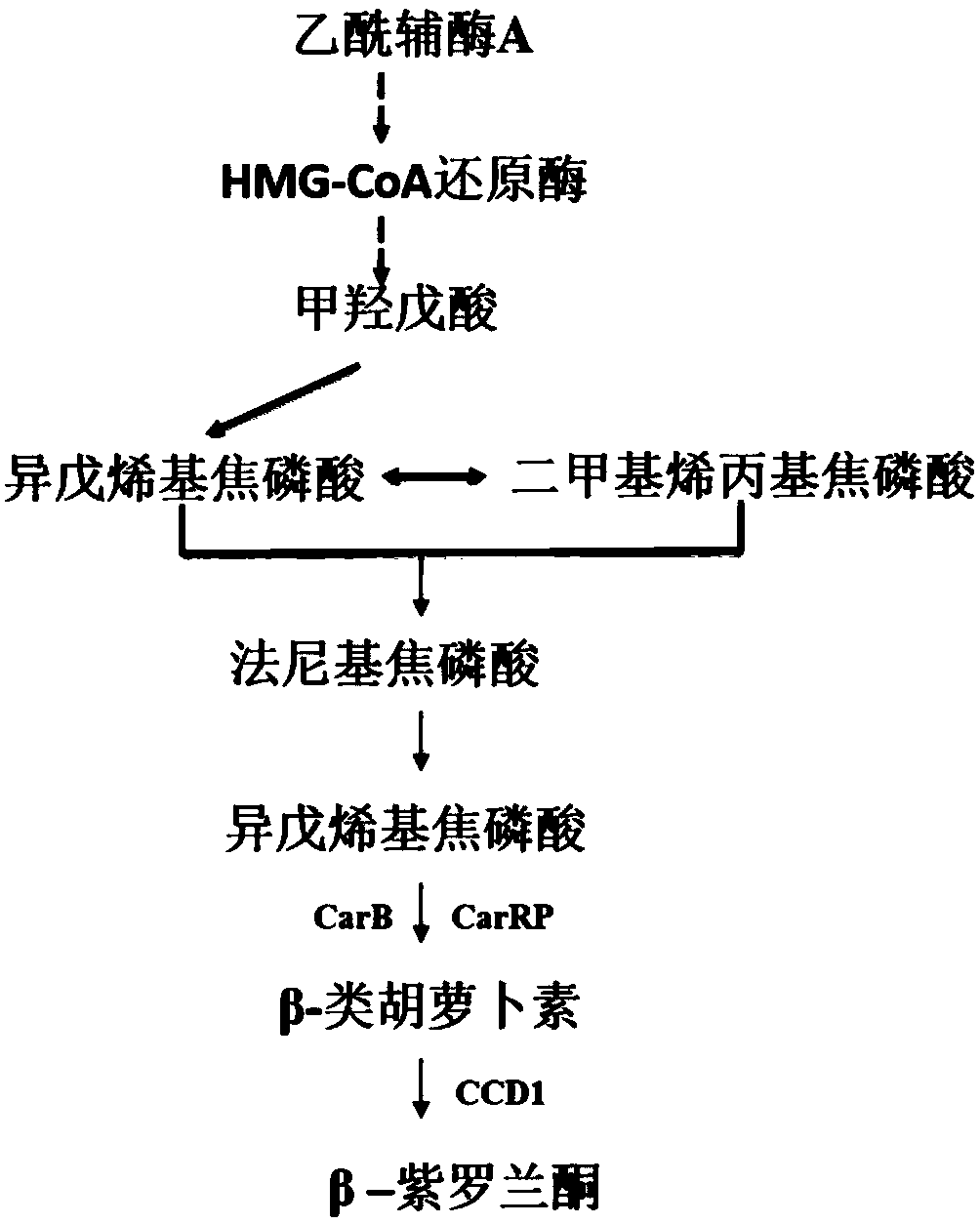
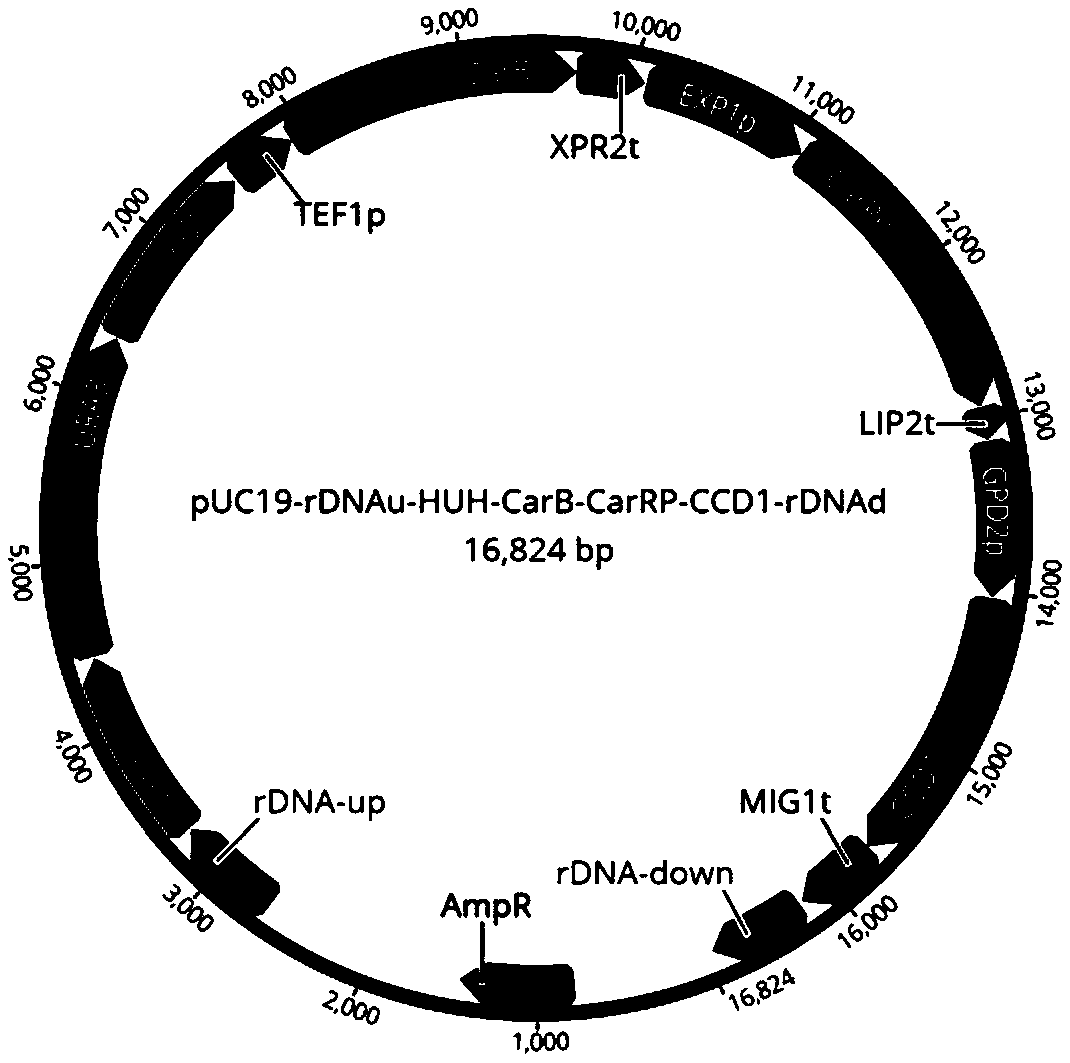
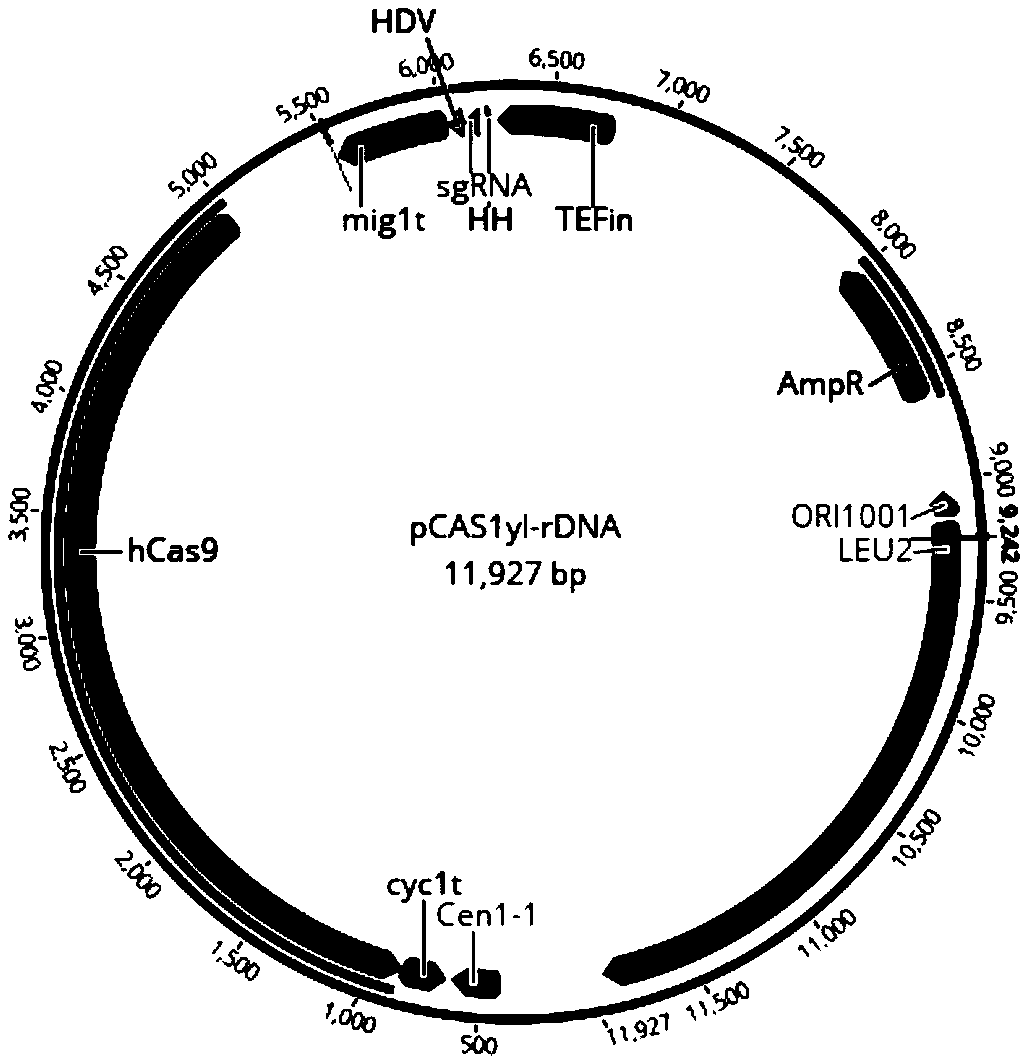
Genetically engineered bacterium for production of beta-ionone and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN108949599AShort build cycleReduce build timeFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIntegrated engineering
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacterium for production of beta-ionone and a construction method and application thereof. According to the invention, by using Yarrowia lipolytica as achassis cell, the beta-ionone expression module (about 14.5 kb) is firstly linearized and then transformed into Yarrowia lipolytica. Then the expression module is integrated into a designed chromosomal location mediated by a CRISPR / cas9 technology. The construction method is simple, fast and efficient. A large fragment integrated engineering strain can be obtained within 2-3 weeks, and the construction period of the engineering bacterium is obviously shortened. The beta-ionone initial output of shaking-flask fermentation of the genetically engineering bacterium obtained according to the methodof the invention can reach about 6.3 mg / L. According to the invention, a simple medium can be used for fermentation production of the perfume beta-ionone, one-time high-efficiency transformation andintegration of multiple genes can be realized, and the construction time of the engineering bacterium can be obviously shortened. The obtained engineering bacterium can be used to perform fermentationto produce the perfume beta-ionone by the use of simple carbon sources such as glucose, glycerin, etc., and has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
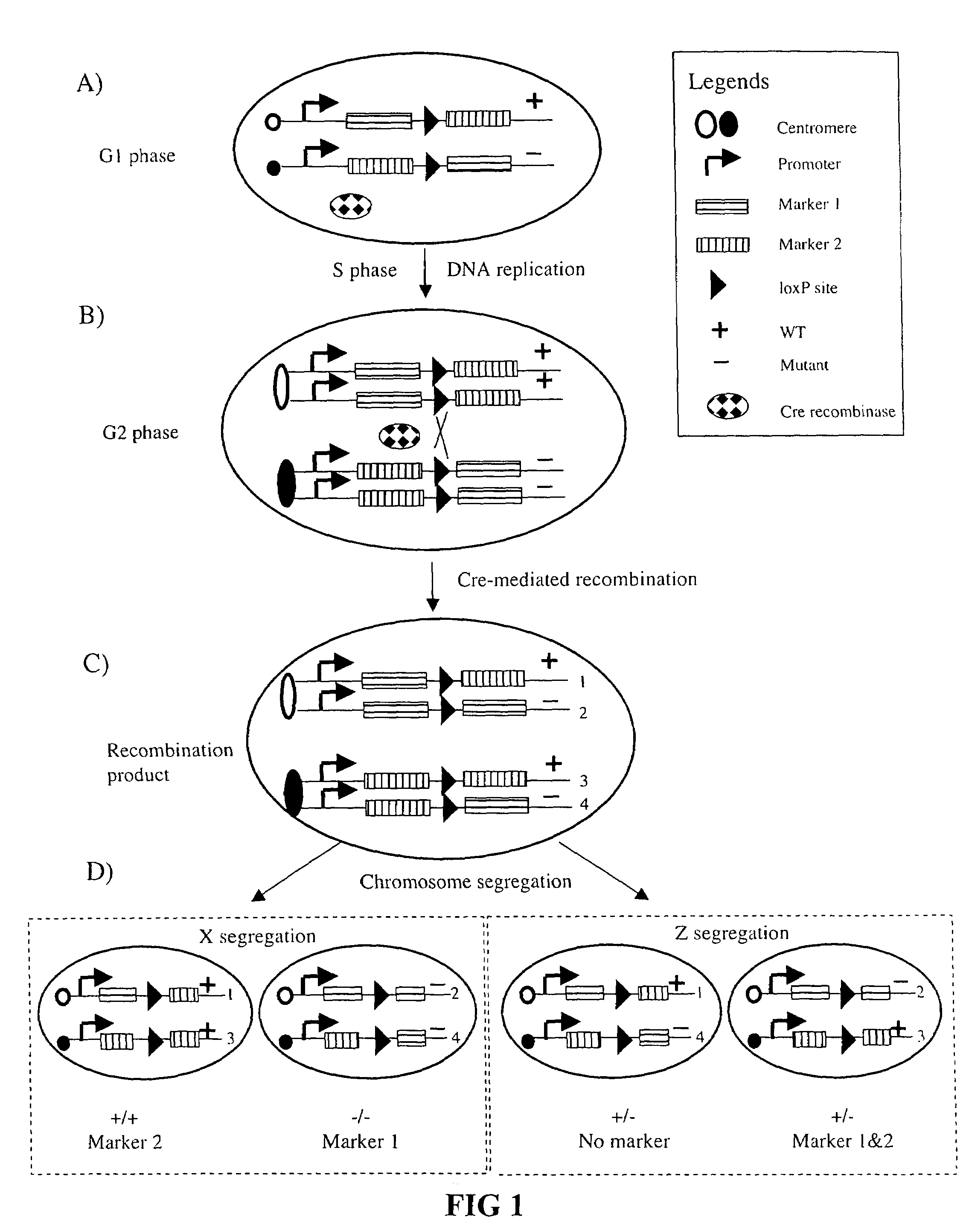
Somatic recombination
InactiveUS7282621B2High sensitivity detectionEasily resolvedStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorMammalCell sensitivity
Recombination in mammalian somatic cell chromosomes is promoted and marked by a method called mosaic analysis with double marker (MADM). Mouse “knock-in” techniques are used to create pairs of chromosomes in which recombinase target sites are placed at homologous chromosomal locations. The knock-in constructs are engineered so that cellular markers, such as green or red fluorescent protein (GFP or RFP), are only expressed after recombinase-induced recombination. This system provides high-sensitivity detection of recombinase-induced mitotic recombination, even down to the single cell level. When this recombination is induced in a mouse heterozygous for a mutation in a gene distal to the “knock-in” locus on the same chromosome, it results in homozygosity of this mutation in the labeled cells. This allows the analysis in singly-labeled neurons of genes whose pleiotropic effects might otherwise result in early lethality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
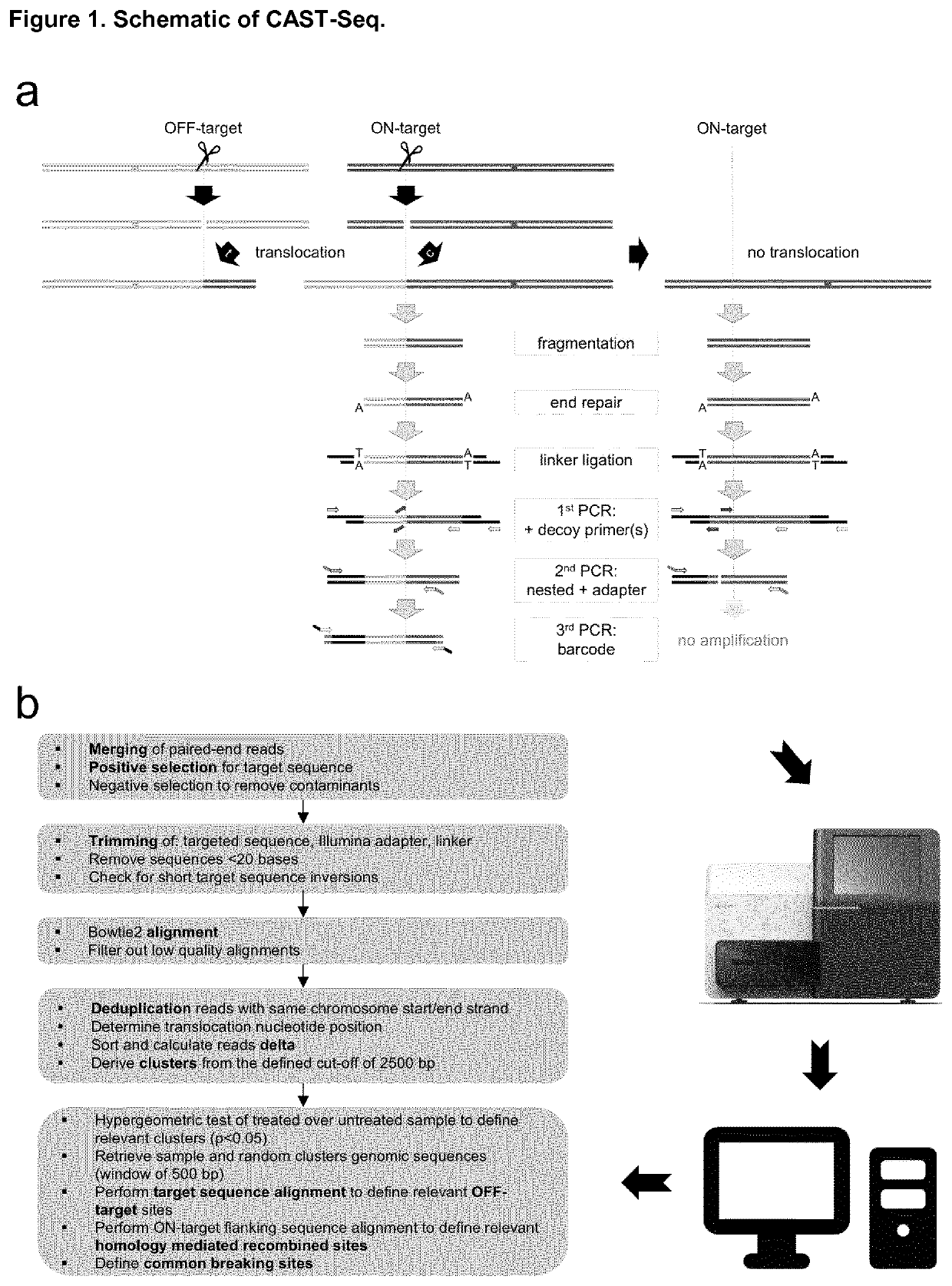
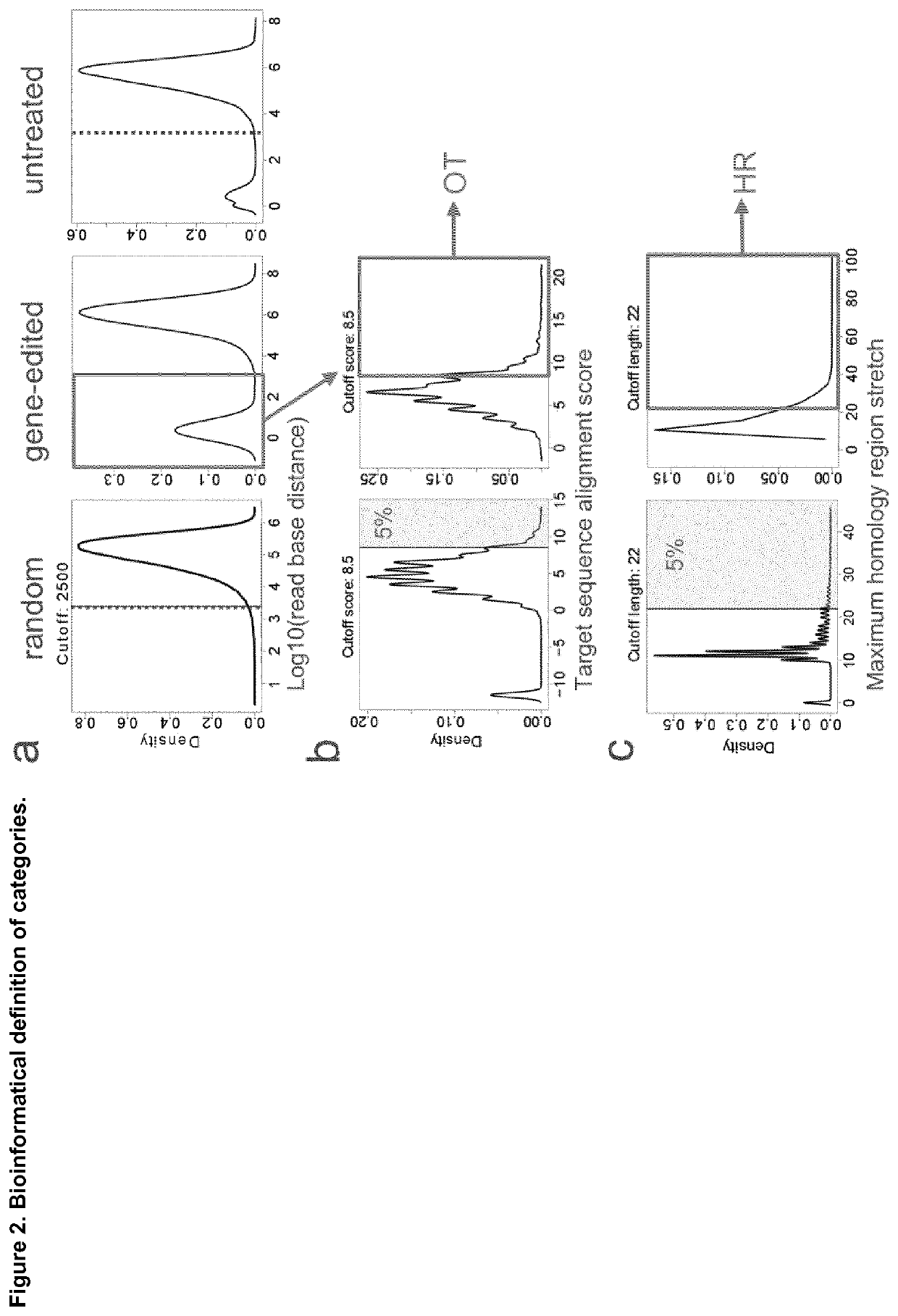
Method for characterization of modifications caused by the use of designer nucleases
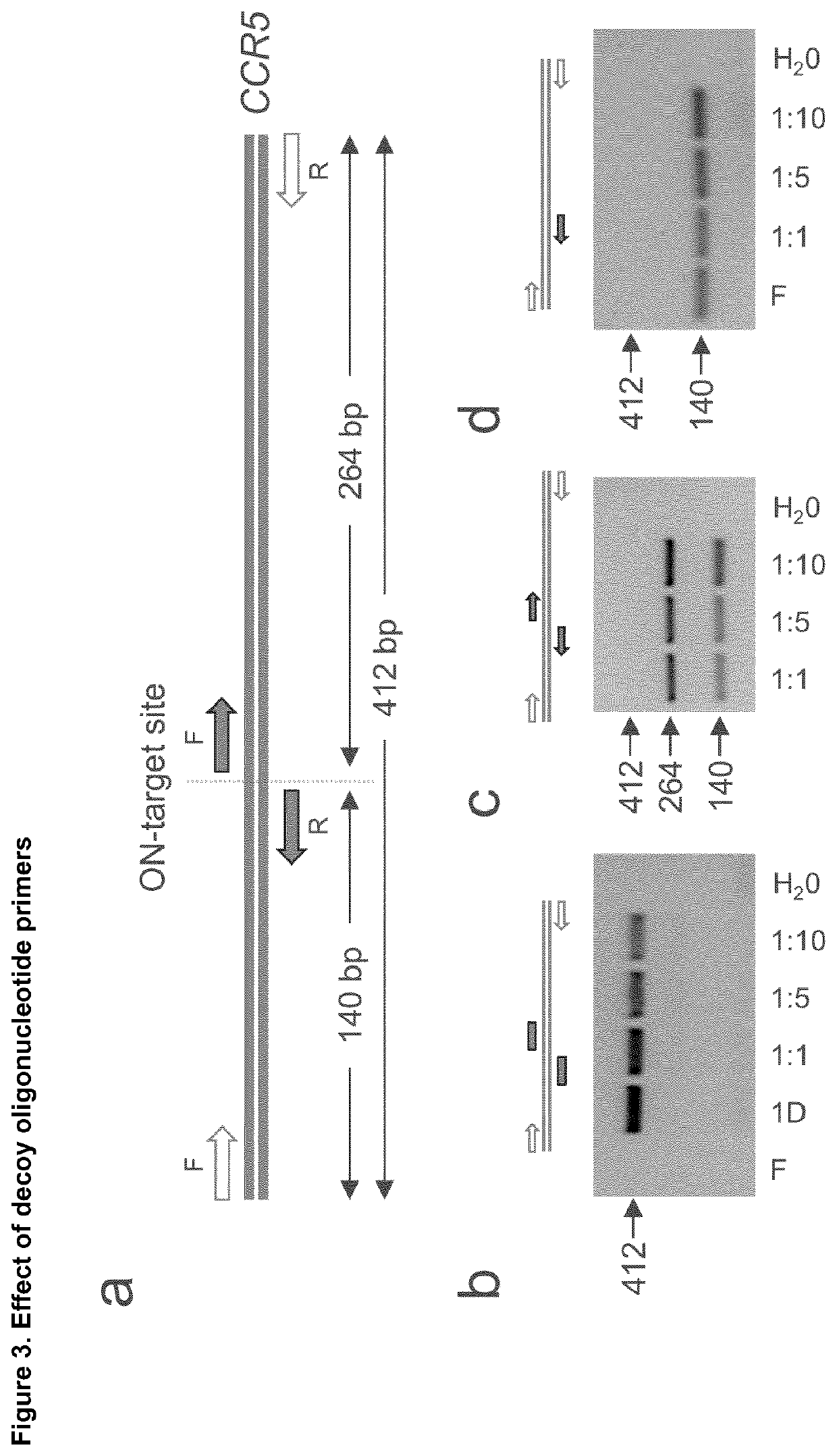
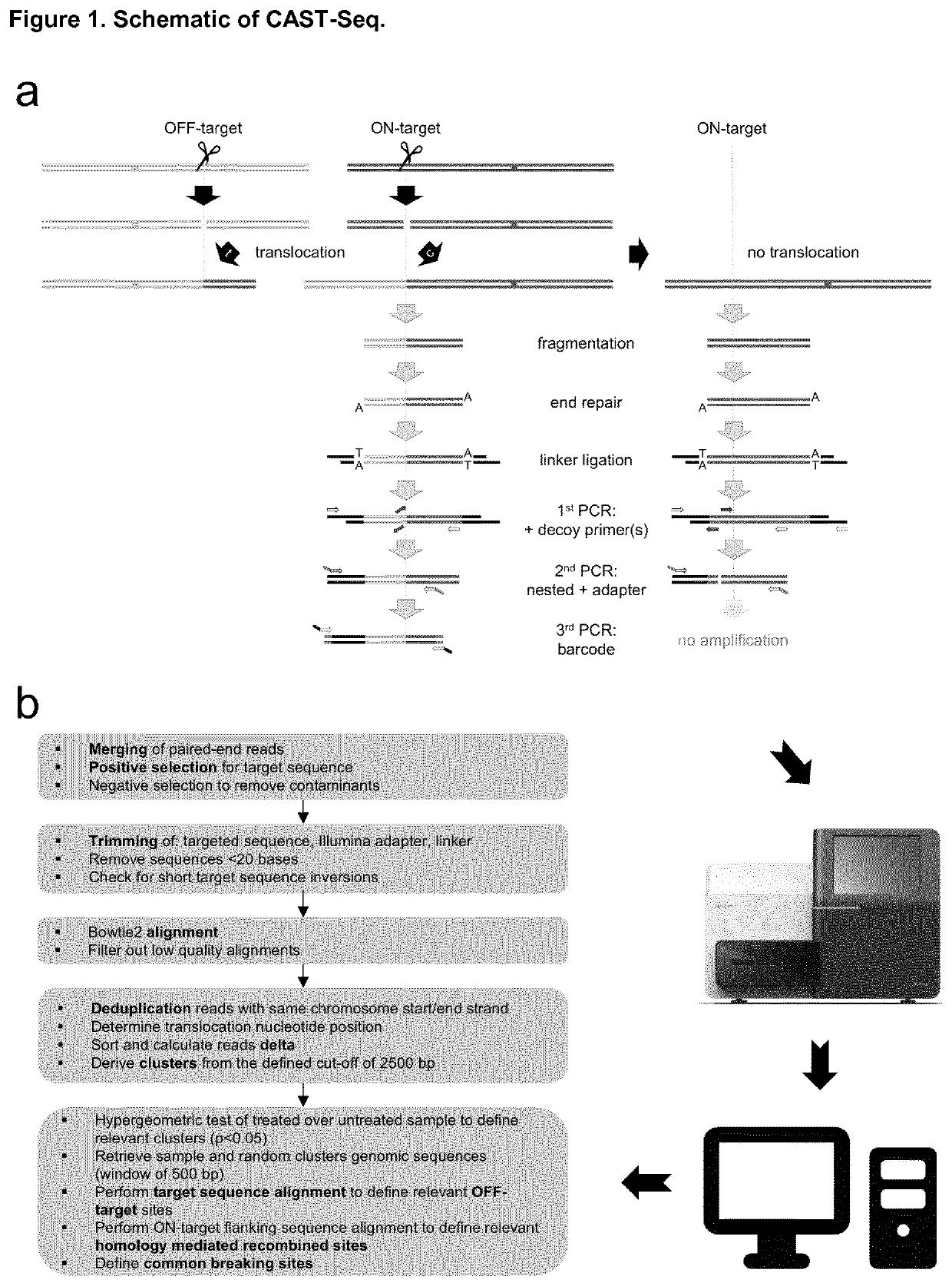
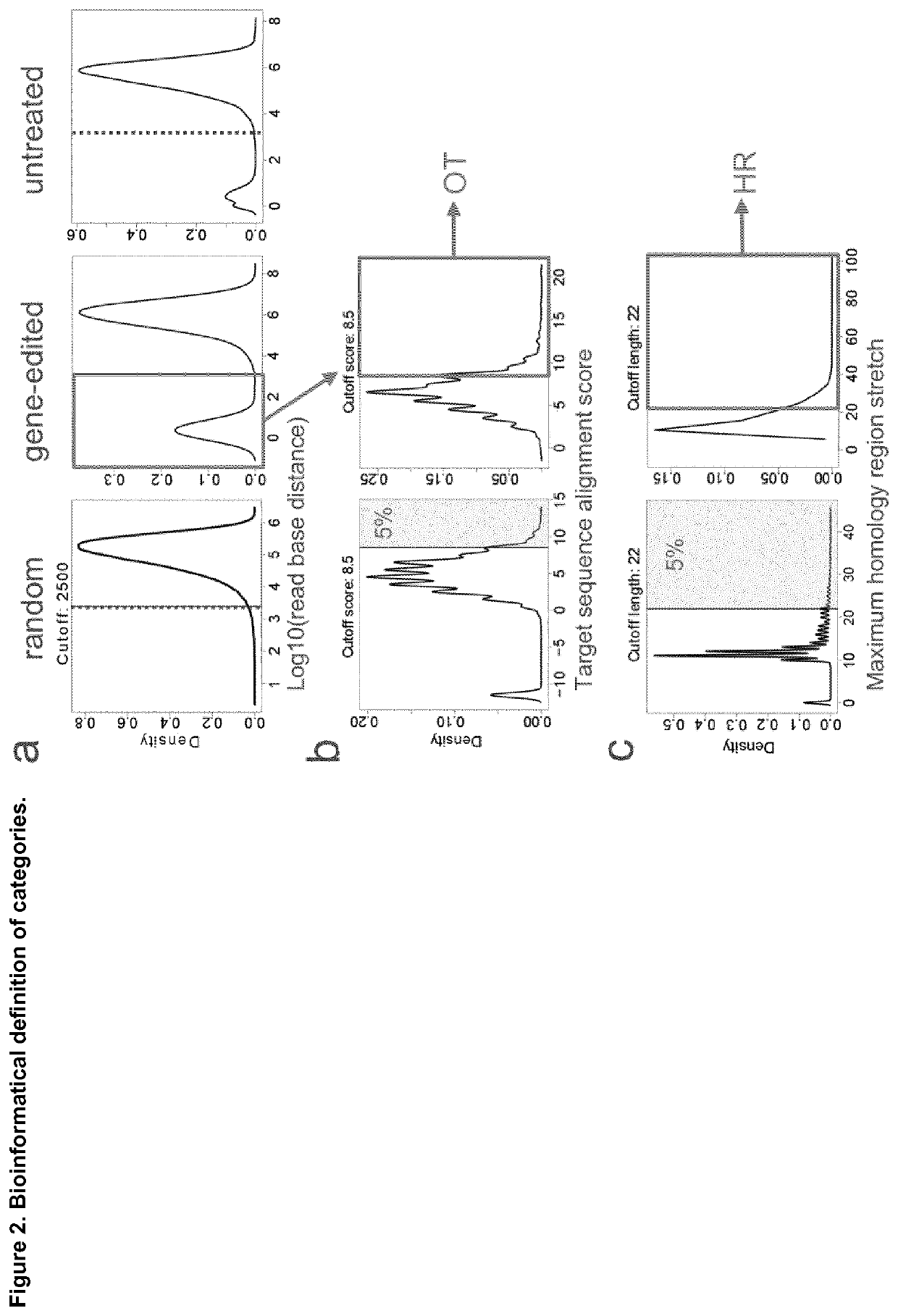
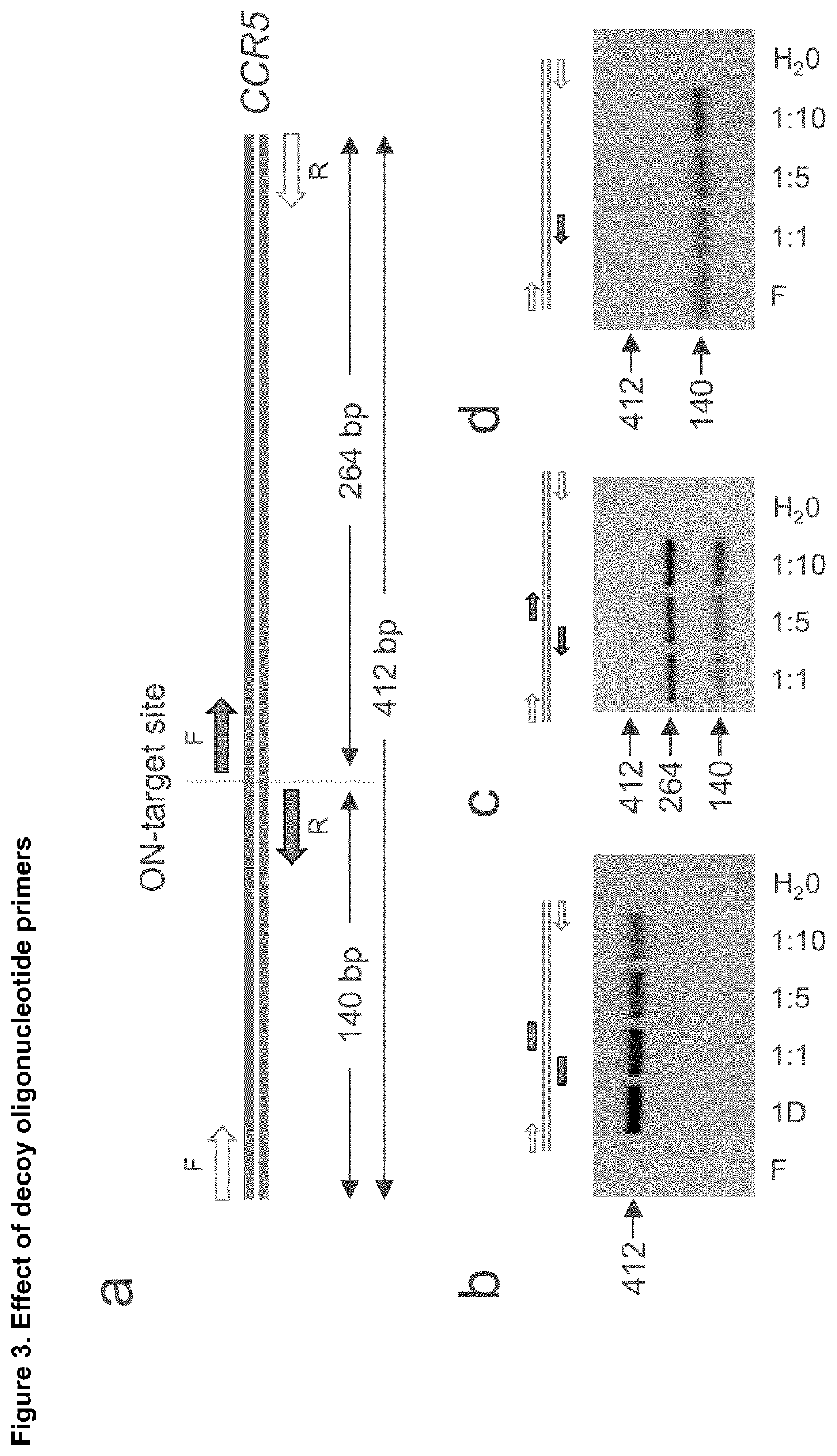
Disclosed is a method for high-throughput detection of genome-wide modifications in a nucleic acid genome obtained from a cell or tissue caused by the activity of a designer nuclease comprising the following steps:a) Extraction of the genomic DNA from cells that were exposed to a designer nuclease under conditions which allow the designer nuclease to introduce a DNA double-strand break (DSB) in the genomic DNA of the cell,b) fragmentation of the nucleic acid to obtain random fragments,c) performing an end repair in order to obtain blunt ends,d) ligation with a linker comprising a sequence complementary to a so called “linker primer”,e) performing a first nucleic acid amplification reaction with a “linker primer” and a so called “ON-target primer”, whereby one primer is located upstream and one primer is located downstream of the on-target site, wherein at least one decoy primer is present in the reaction mixture,f) performing a second nucleic acid amplification reaction whereby so called “nested primers” are added to the reaction mixture, whereby one primer is complementary to the on-target locus and one primer complementary to the linker sequence,g) performing a further nucleic acid amplification reaction whereby at least one code containing primers are added to the reaction mixture,h) sequencing of the nested and barcoded amplification product, andi) aligning the sequenced products with suitable bioinformatic means to a reference sequence to identify a chromosomal location that contains a genomic modification based on at least one DNA double strand break.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG +1
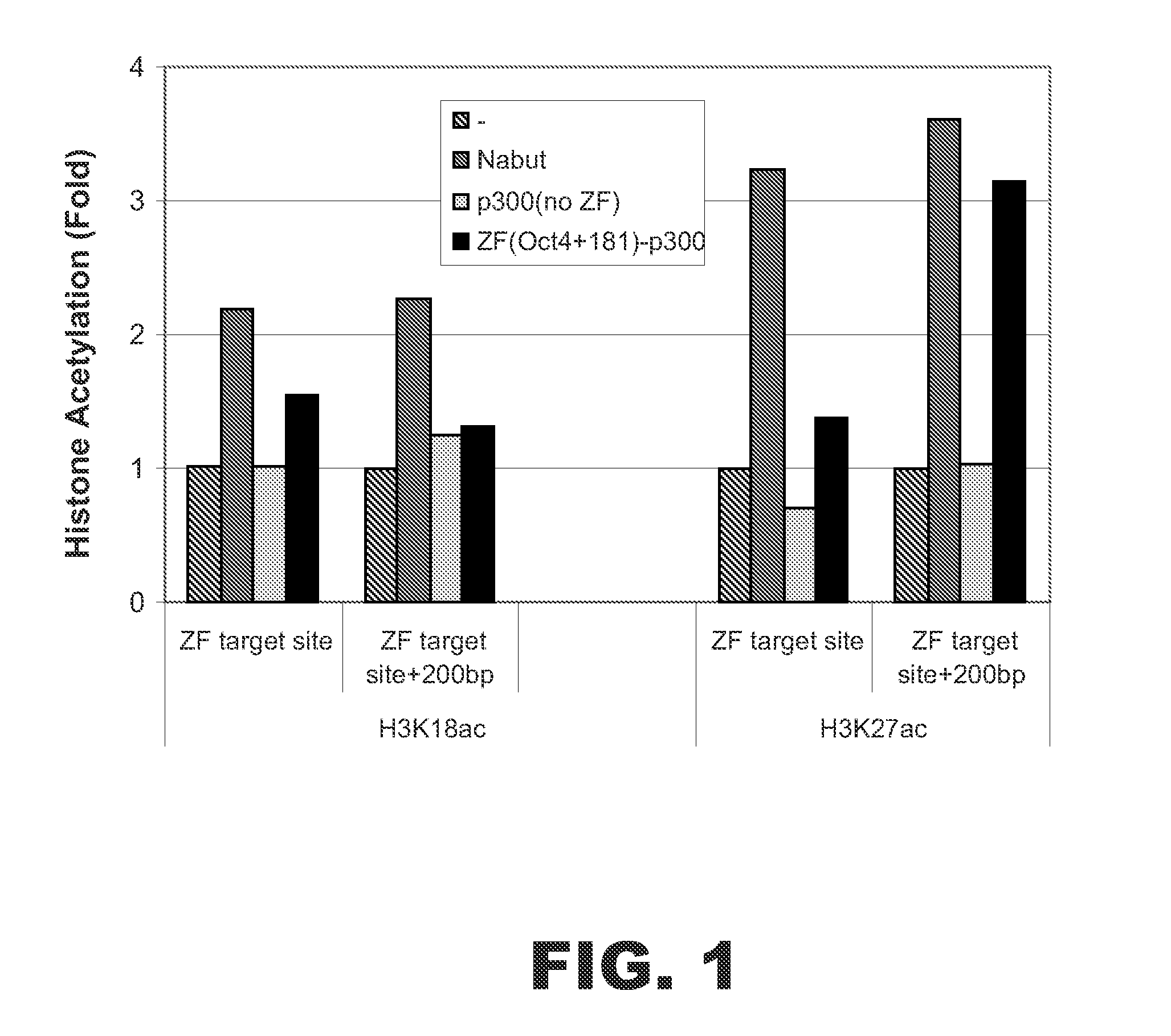
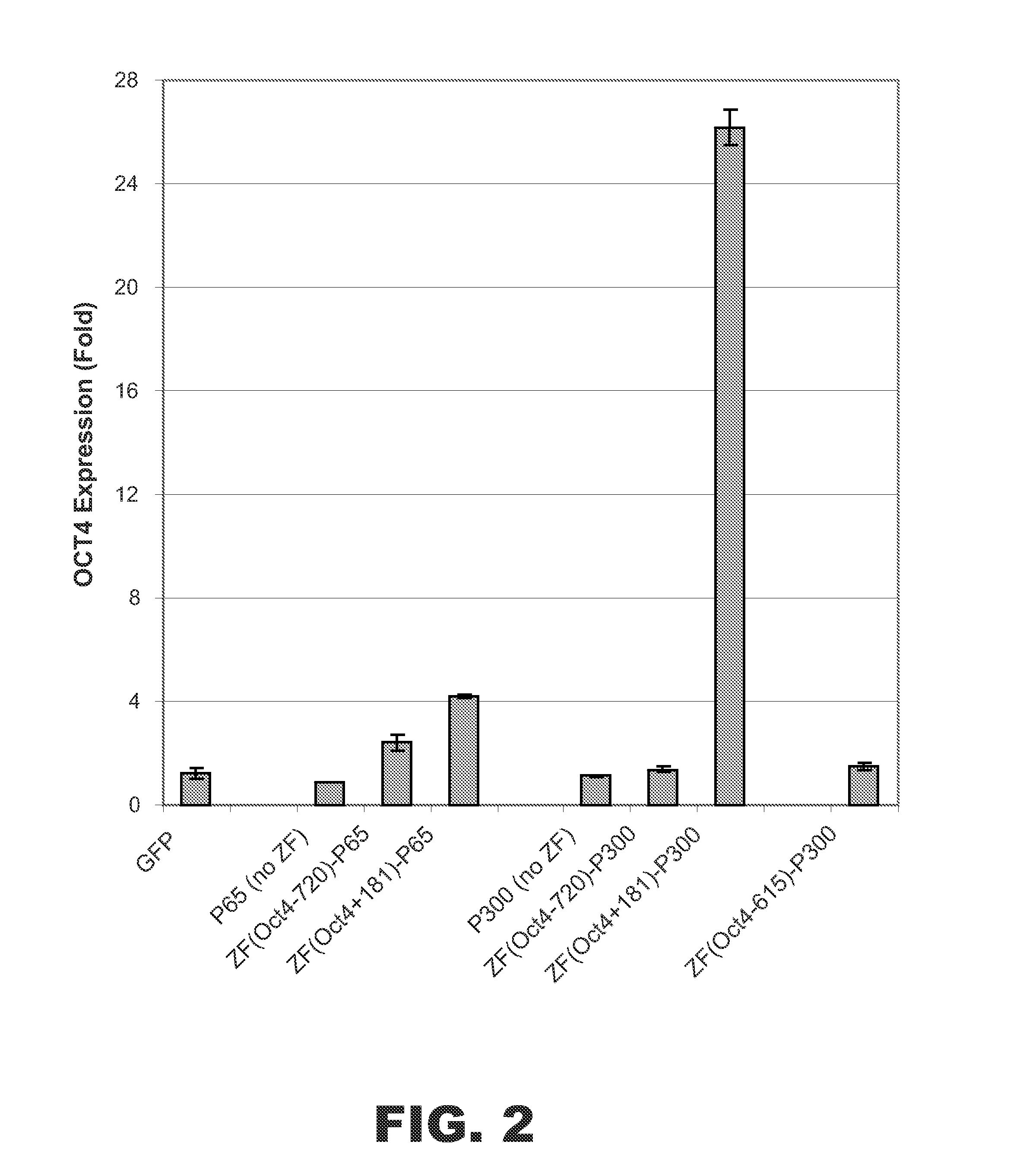
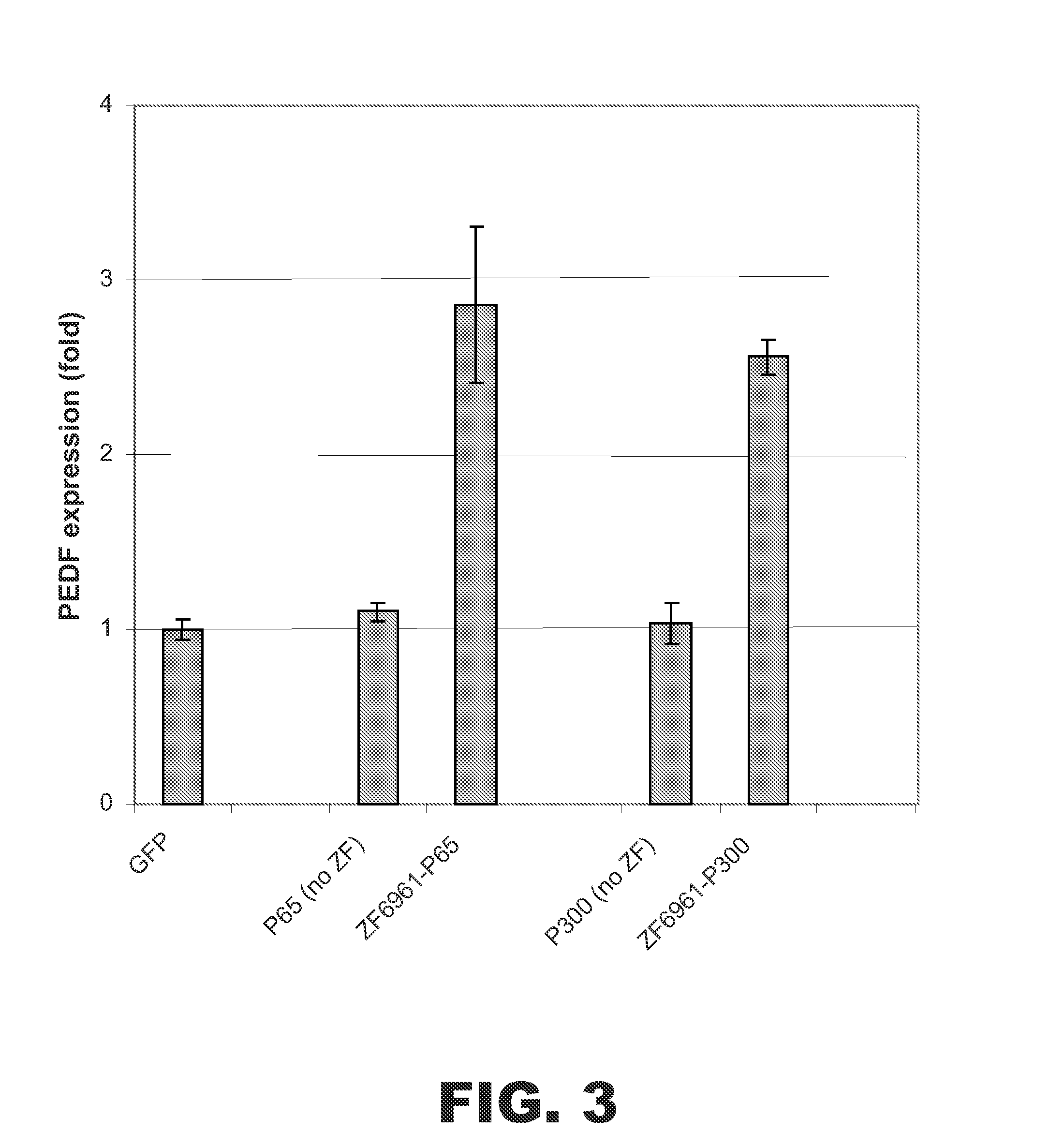
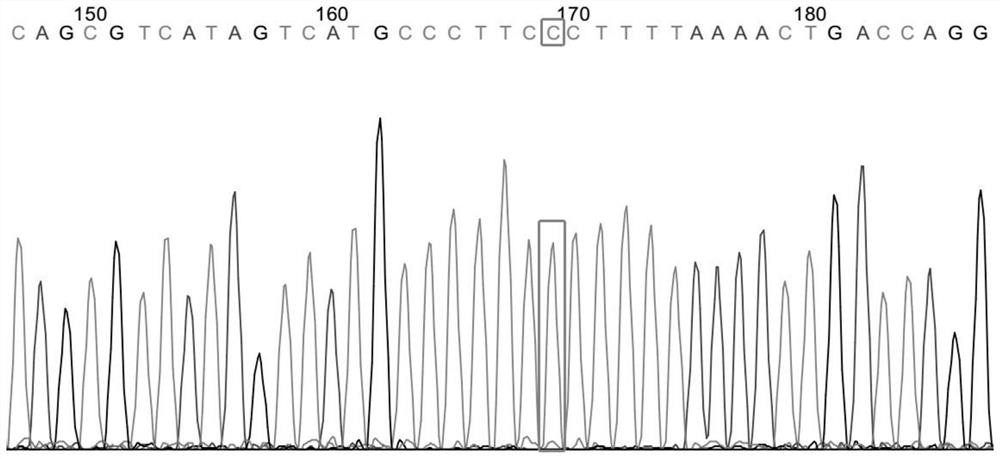
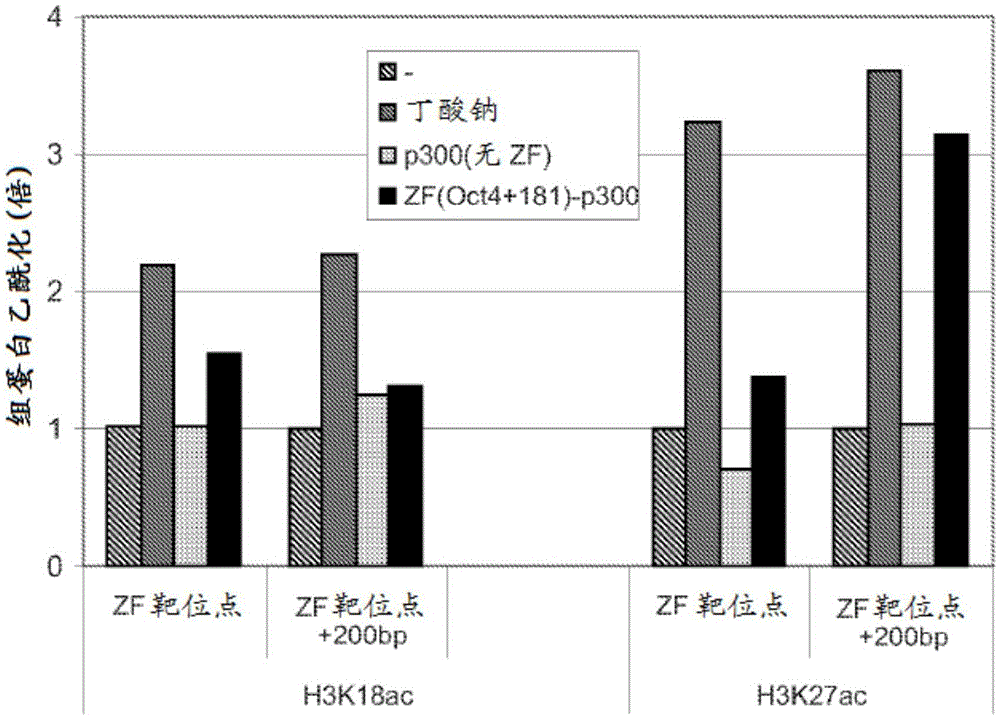
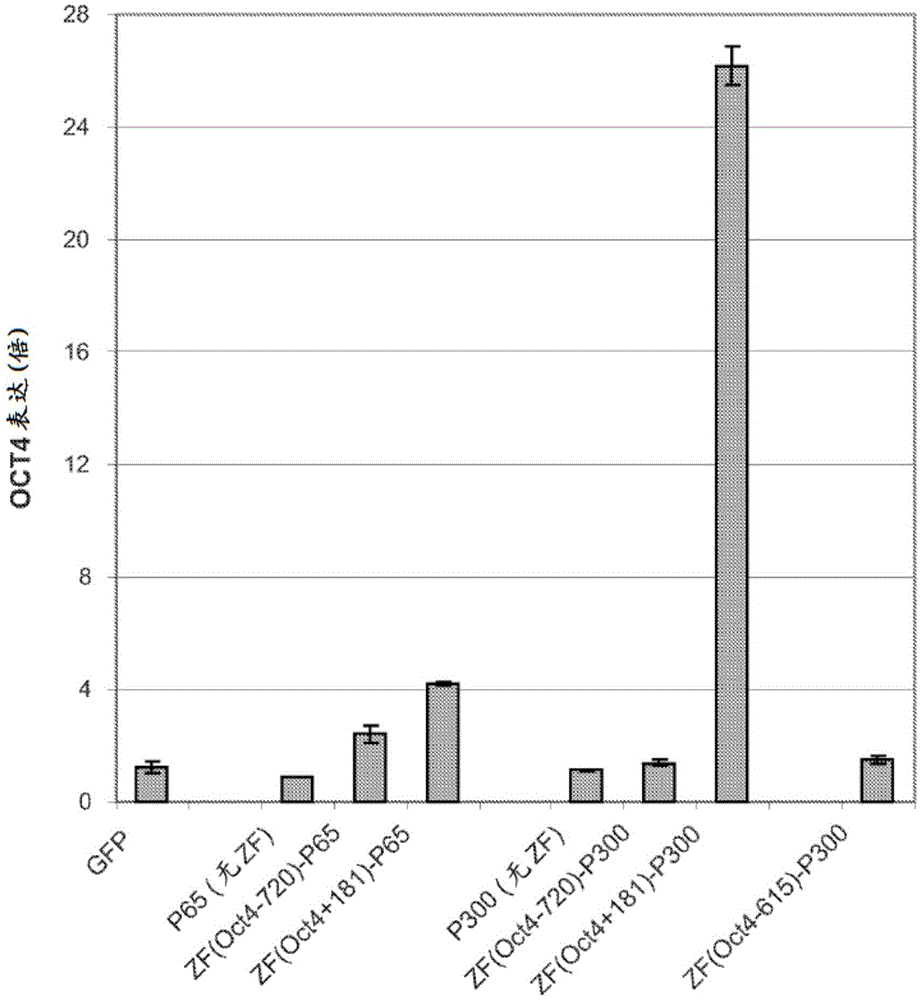
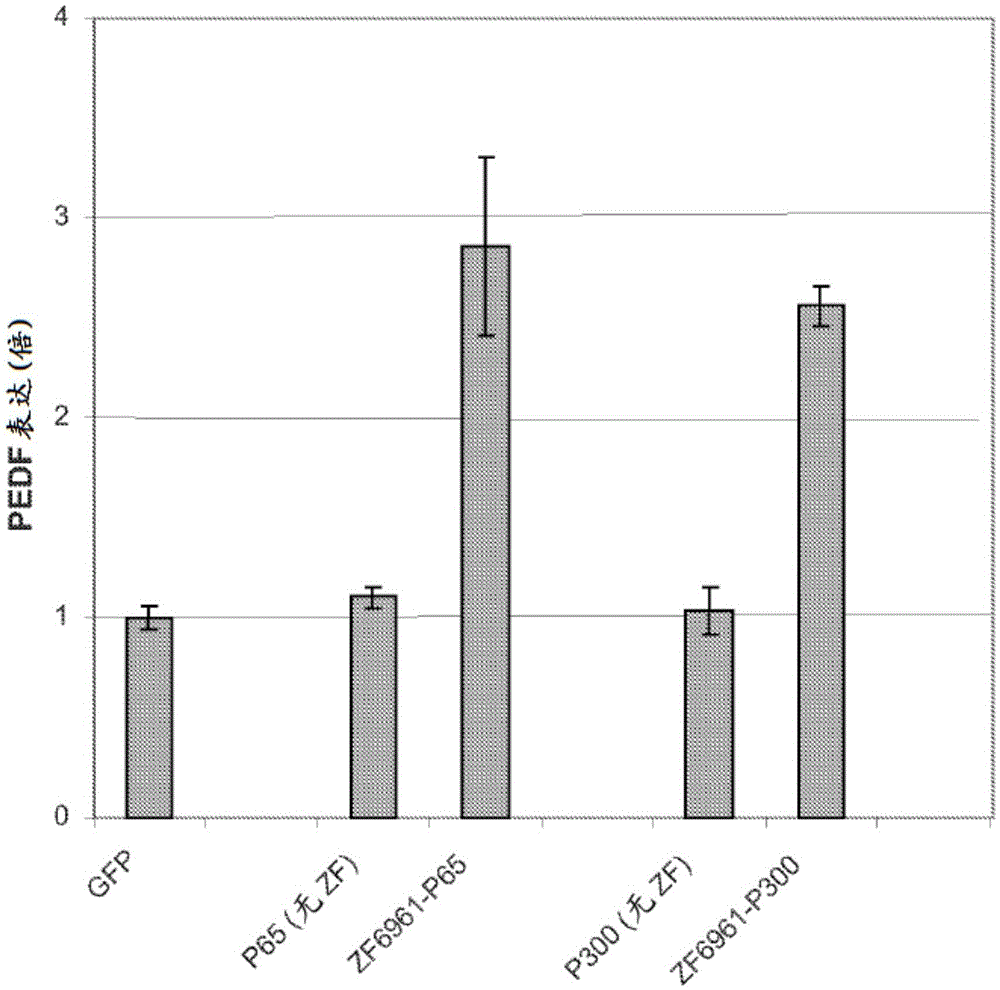
Targeted histone acetylation
ActiveUS20150079657A1Enhanced level of transcriptionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainChromosome localisationDNA-binding domain
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for acetylating histones at targeted chromosomal locations in a cell. In particular, the disclosure provides a fusion protein comprising a DNA binding domain and at least one histone acetyltransferase (HAT) domain, such that the DNA binding domain targets the fusion protein to a targeted chromosomal location and the HAT domain acetylates histones at the targeted location.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
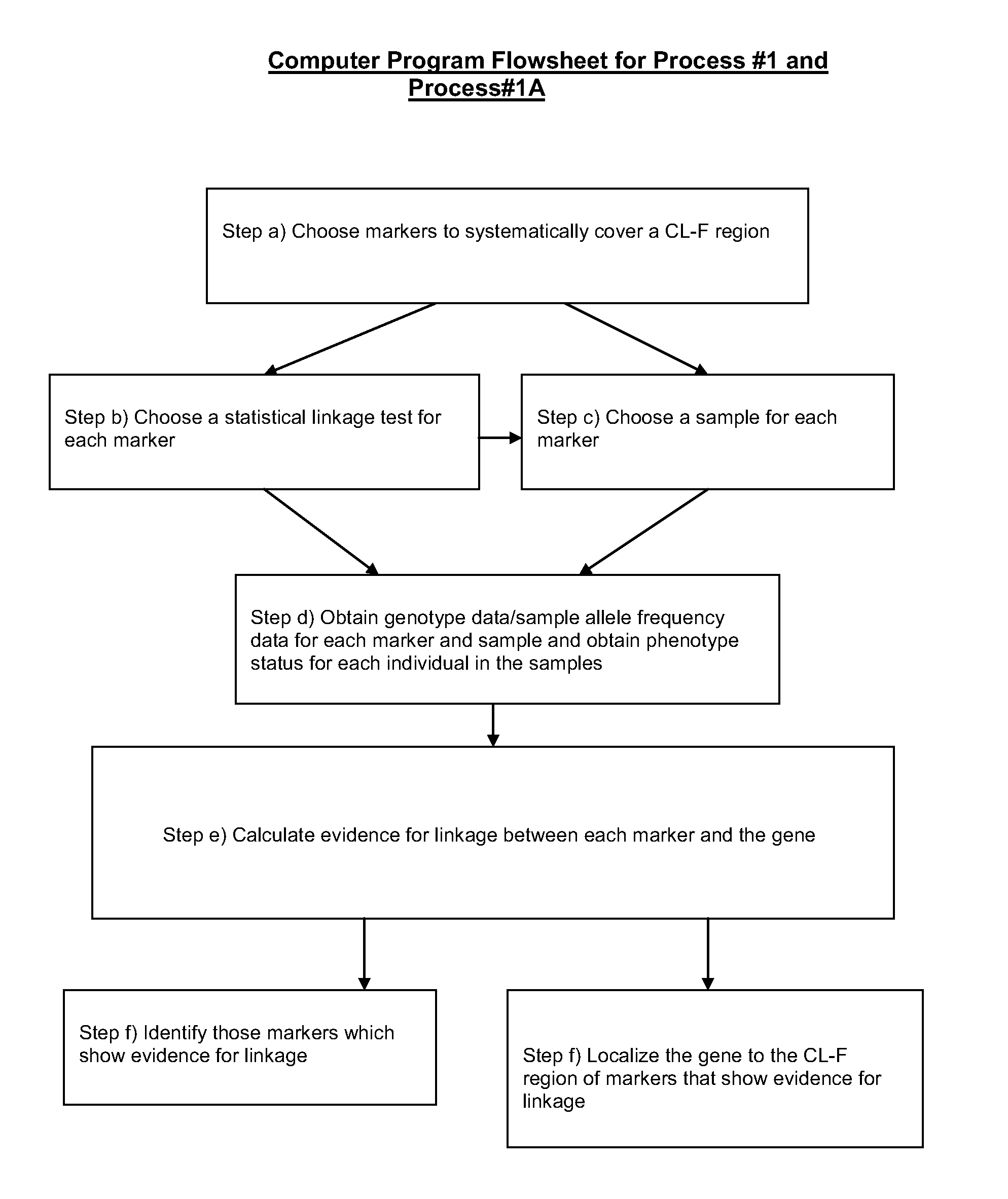
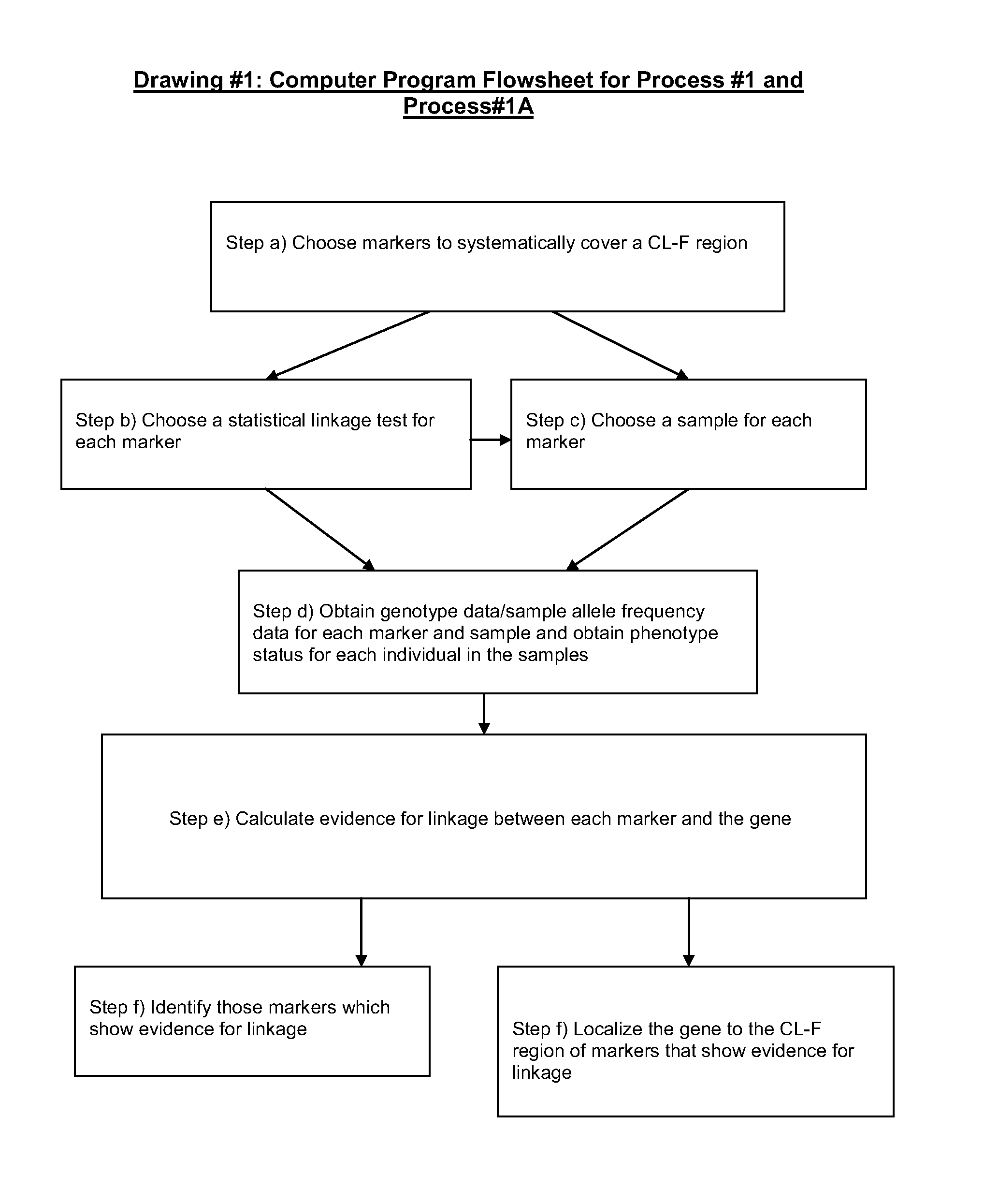
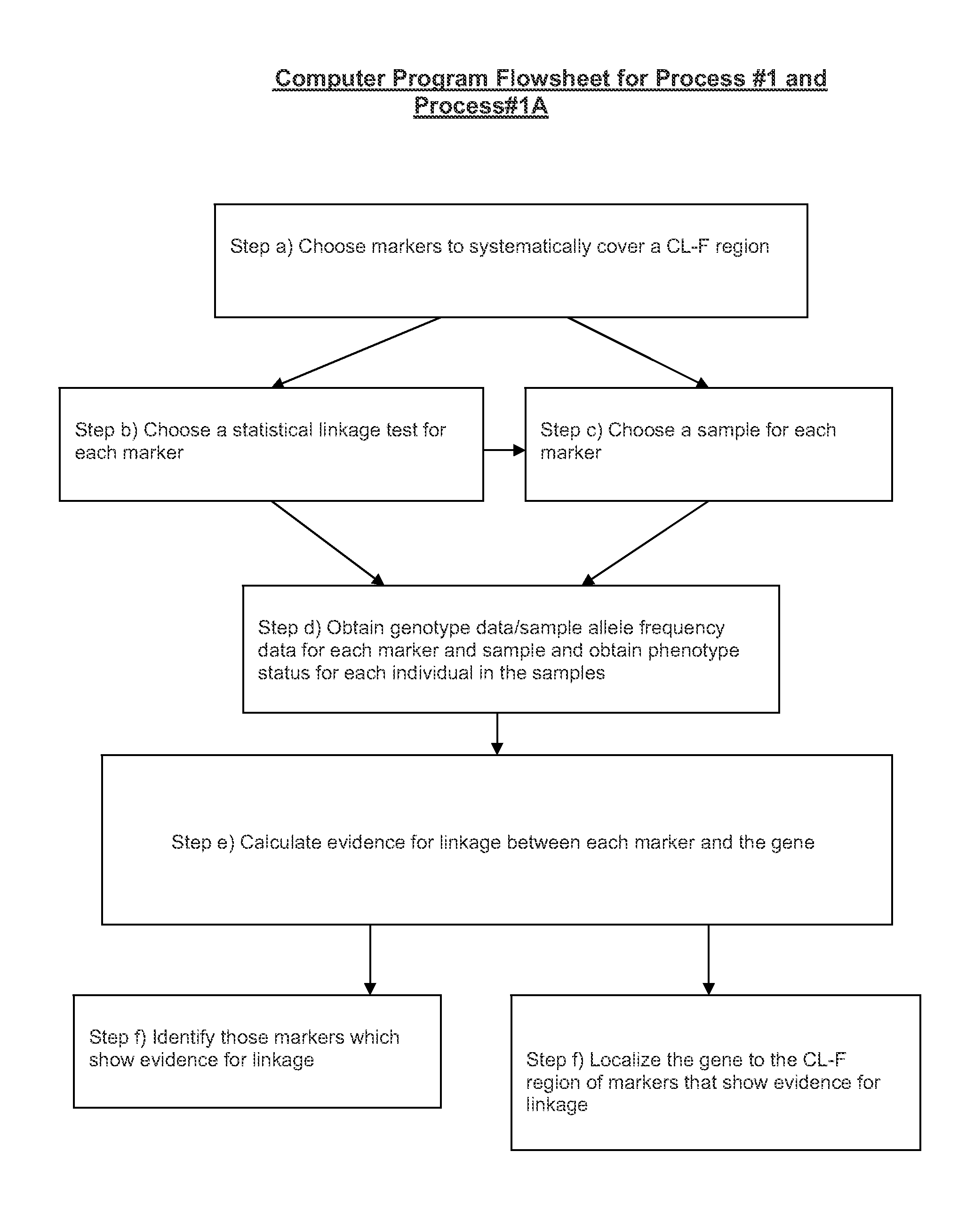
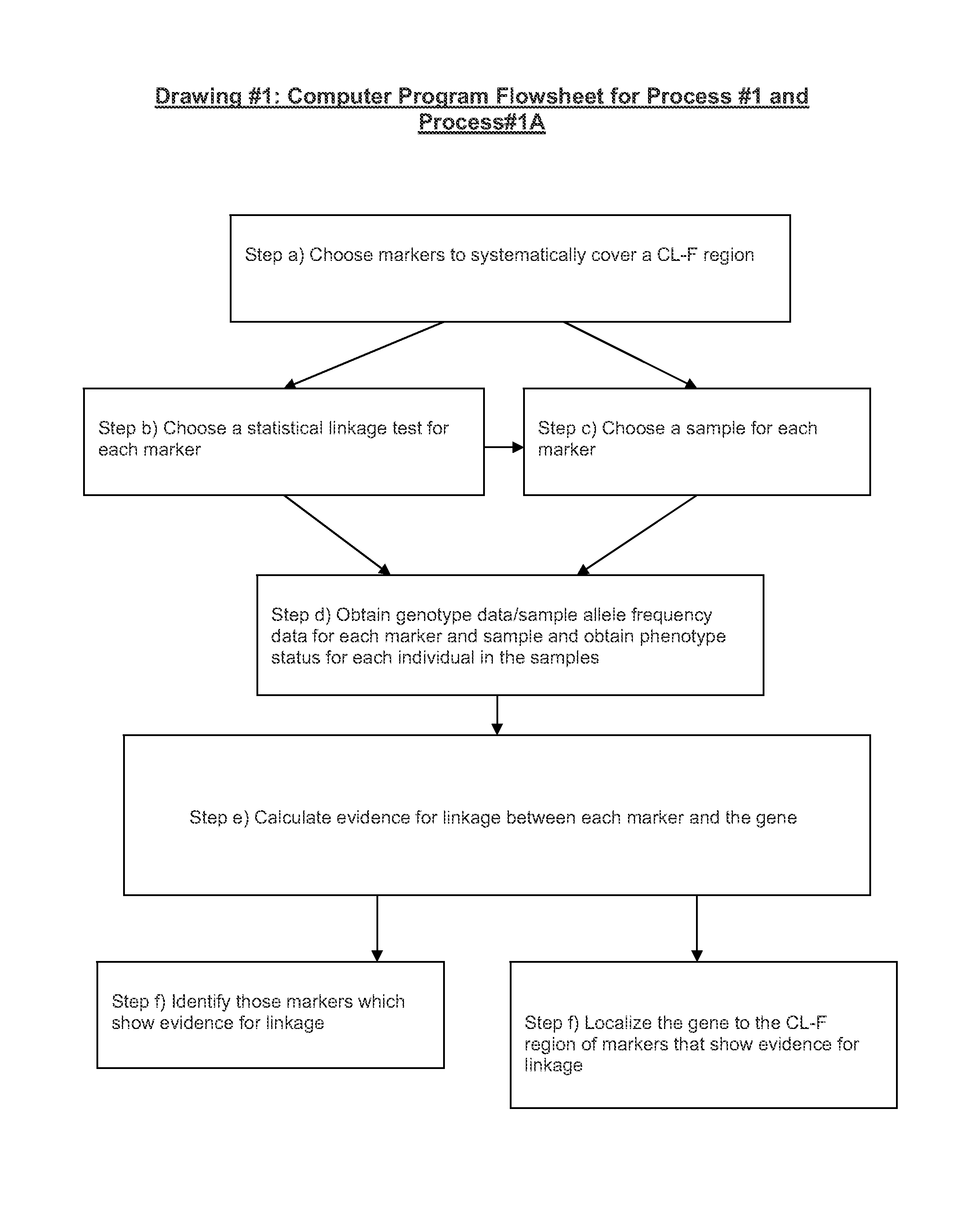
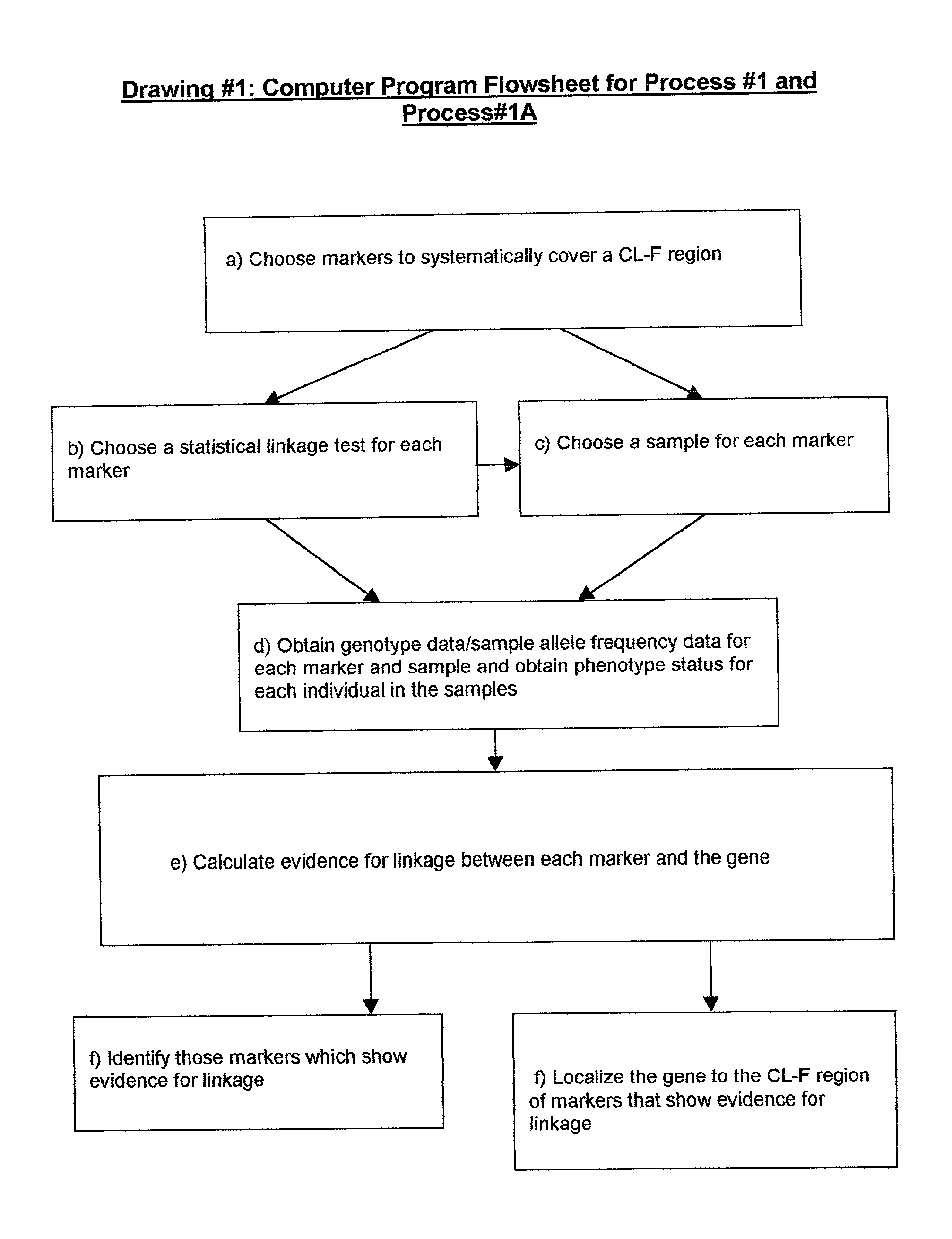
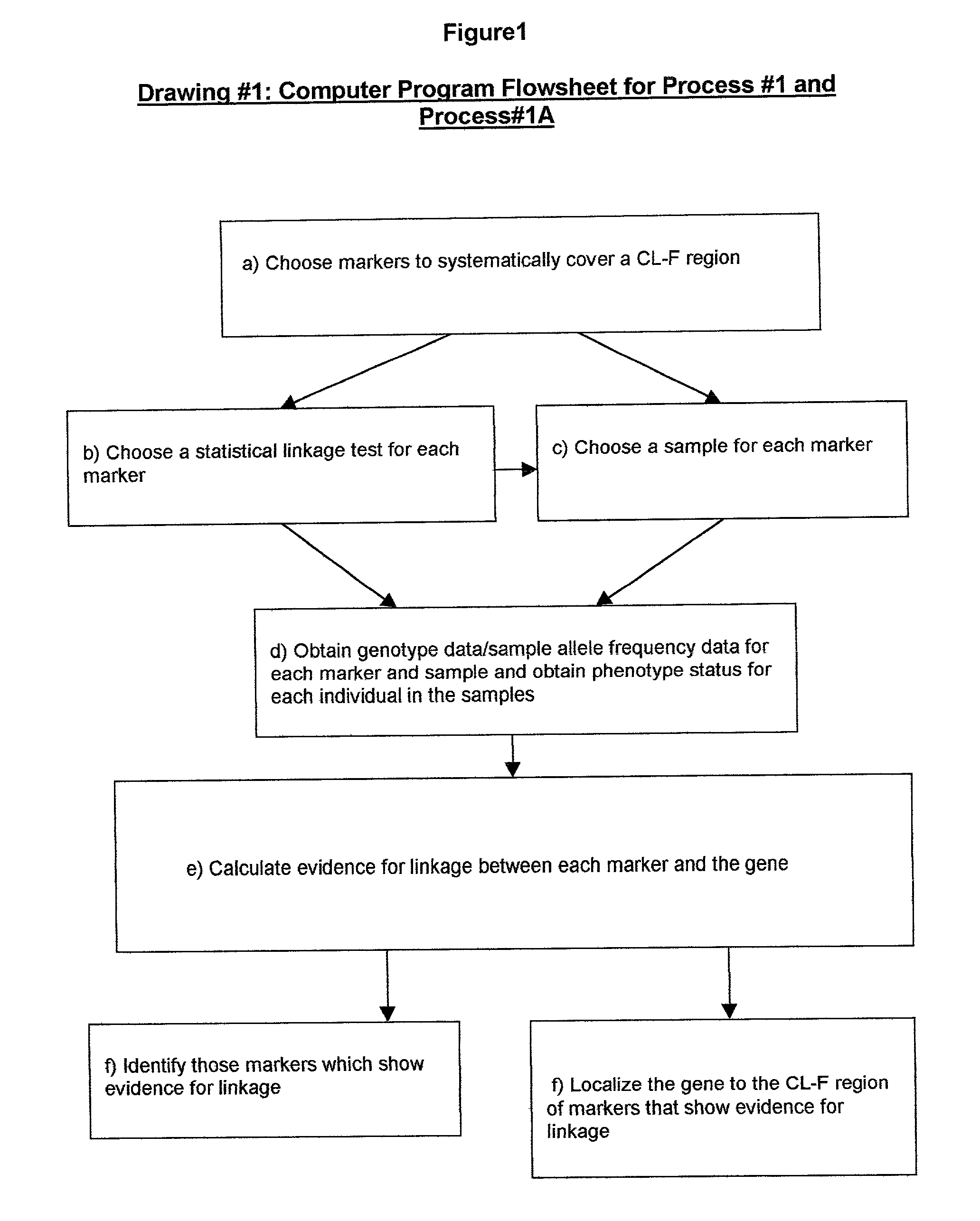
Two-Dimensional Linkage Study Methods
InactiveUS20120053846A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsChromosome localisationAllele frequency
Versions of the invention are directed to methods and apparatus for a new type of association-based linkage study technique using bi-allelic markers. The markers used in this technique are chosen so that the least common allele frequencies of the markers vary systematically over a range or subrange of least common allele frequency and the chromosomal location of the markers vary systematically over one or more chromosomal regions or chromosomes to achieve a systematic distribution of the markers over a two-dimensional region that has the orthogonal dimensions of chromosomal location and least common allele frequency. By using the two characteristics or two dimensions of marker chromosomal location and marker allele population frequency in this way, the power and systematic nature of genetic linkage studies using association-based linkage tests is greatly increased. These two-dimensional linkage study techniques increase the power of association studies to localize trait-causing polymorphisms of modest effect.
Owner:MCGINNIS RALPH EVAN +1
hla-related snp markers and its detection primer pair and determination method
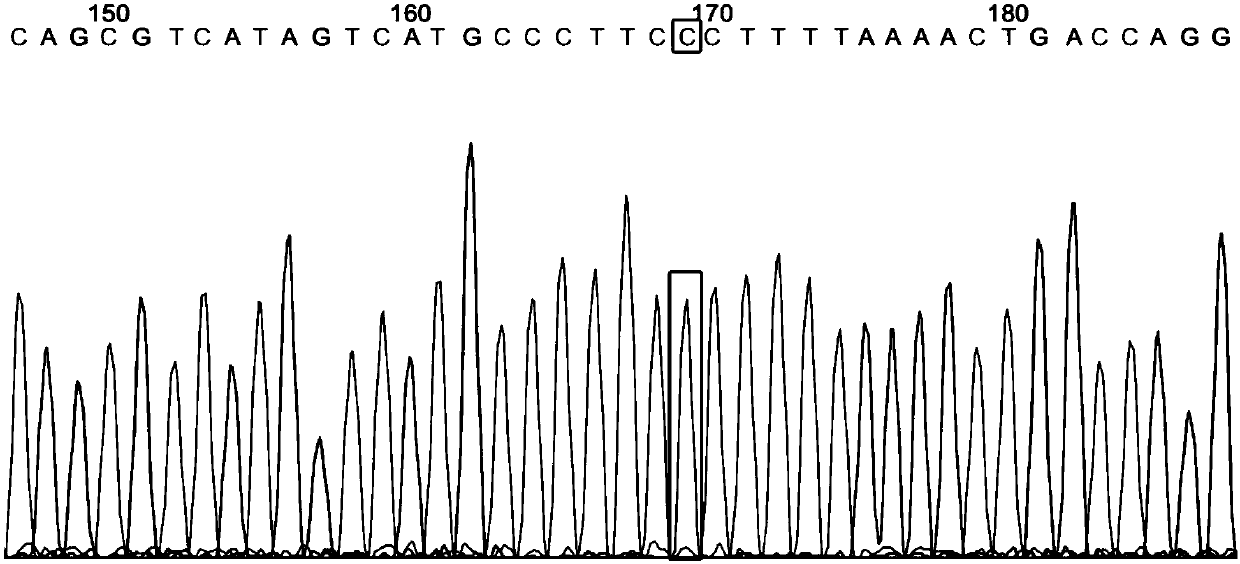
ActiveCN107893113BHigh expressionIncrease or decrease expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JNucleotide
The invention provides an HLA related SNP marker and a detection primer pair and a determination method thereof, and aims to provide a primer and method for evaluating transplantation risk. An SNP marker related with HLA is disclosed and is the base C or T on 32610275th site of human No.6 chromosome. A primer pair for detecting the SNP marker described by the claim one has nucleotide sequences represented by SEQ ID No1-2 or SEQ ID No3-4. A method of determining the SNP site comprises following steps: (1) extracting genome DNA of a host cell; (2) subjecting the template DNA to PCR amplification, and purifying the PCR product (SAP / Exon I); and (3) subjecting the purified PCR product to forward and / or backward sequencing amplification by using a sequencing primer, purifying the sequencing product, and carrying out ABI 3730x1 capillary electrophoresis sequencing to determine the SNP site and genotype thereof.
Owner:广州博富瑞医学检验有限公司
Targeted histone acetylation
ActiveCN105658792APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainChromosome localisationDNA-binding domain
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for acetylating histones at targeted chromosomal locations in a cell. In particular, the disclosure provides a fusion protein comprising a DNA binding domain and at least one histone acetyltransferase (HAT) domain, such that the DNA binding domain targets the fusion protein to a targeted chromosomal location and the HAT domain acetylates histones at the targeted location.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Two-Dimensional Linkage Study Techniques
InactiveUS20120053844A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningChromosome localisationAllele frequency
Owner:MCGINNIS RALPH EVAN +1
A method for detecting the position of large segment repeats in Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome
ActiveCN105624306BQuick checkEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingKlenow fragment
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to a method for detecting a klenow fragment repetition position in a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome.By combining genomic sequencing with endoreduplication backcrossing, the position of repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the chromosome is confirmed quickly.Through the endoreduplication backcrossing method, the position of the repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome can be detected efficiently and quickly and repaired, repeated klenow fragment genome DNA is deleted, there is no need to precisely confirm the position of a klenow fragment repetition site or conduct cumbersome experimental data analysis on saccharomyces cerevisiae to be detected, operation is easy, and the experimental period is short.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Identification of differentially methylated multiple drug resistance loci
The present invention provides genomic loci which are hypermethylated and differentially expressed in drug resistant cells compared to non-drug resistant cells. These genomic loci are homologous to the rab6 locus but map to a different chromosomal position. The present invention also provides nucleic acids isolated from these genomic loci by Methyl-Differential Display (MDD) methods, including genomic DNAs and cDNAs. The present nucleic acids are useful as probes for detecting mutations and the methylation patterns of the newly identified genomic loci, and of homologous nucleic acids. Nucleic acids of the present invention are also useful for detecting expression of mRNA from herein identified genes, for measuring expression of those and homologous genes sequences, and for determining suitability of therapeutic treatment. The disclosed nucleic acids and their homologs are useful for inhibition of multiple drug resistance. Cells are disclosed which are useful for identification or modulators of multidrug resistance.
Owner:NORTH SHORE LONG ISLAND JEWISH RES INST
SSR Molecular Marker and Its Application for Identifying Resistance and Susceptibility to Anthracnose Leaf Blight of Apple
ActiveCN105624280BSpeed up excavationImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationChromosome localisationAgricultural science
The invention provides SSR molecular markers for identifying resistance of apple on the glomerella leaf spot. The molecular markers are S0607039, S0607001, S0506206, S0506078, S0506001, S0405195, S0405127, S0304673 and S0304011 respectively. The invention further provides primers used for multiplying the SSR molecular markers for identifying the resistance of apple on the glomerella leaf spot. The genes, resistant to glomerella leaf spot, of the apple are subjected to molecular marking through the self-designed SSR markers, so that the position of chromosomes and the genetic distance can be determined, and a tightly linked genetic map is established. The molecular marker closest to the resistance gene can be used for accurately identifying the resistance of apple on the glomerella leaf spot, so that an effective tool is provided for apple production practice and resistance breeding, and a good basis is laid for next cloning and functional verification of the resistance gene.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
A method and system for automatic chromosome analysis based on deep learning
ActiveCN109344874BTake advantage ofImprove generalization abilityImage enhancementImage analysisChromosome localisationSpecific chromosome
The invention discloses a method and system for automatic analysis of chromosomes based on deep learning, which can adopt multi-level processing to process the independent and overlapping forms of chromosomes hierarchically, and perform cluster analysis on chromosome position coordinates, classification labels and classification confidence Output the karyotype map. Through the above method, the chromosome segmentation method based on deep learning can be adopted, which does not depend on specific chromosome morphological patterns, and has high generalization ability. Accuracy, multi-scale processing can be used, the image to be detected can be fully utilized, and the segmentation effect in the case of chromosome overlap and adhesion can be effectively improved.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Group of HLA-related SNP marks and detection primer and determination method thereof
ActiveCN107988352AHigh expressionIncrease or decrease expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCapillary electrophoresisNucleotide
The invention provides a group of HLA-related SNP marks and a detection primer and a determination method thereof, and aims at providing a primer and a method for transplanting risk evaluation. The technical scheme is that the SNP marks comprise a first SNP mark, a second SNP mark and a third SNP mark, wherein the first SNP mark is a basic group A or T in the 32623514 position of the human No.6 chromosome; the second SNP marker is a basic group G or T in the 32623555 position of the human No.6 chromosome; the third SNP mark is a basic group A or T in the 32623560 position of the human No.6 chromosome; a primer pair for detecting the group of SNP markers in the claim 1 have the nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO:1 to 2 or SEQ ID NO:1 and 5 or SEQ ID NO:3 and 5 or SEQ ID NO:4 and 5. Thedetermination method of the HLA-related SNP sites comprises the following steps of (1) extracting the genome DNA of a host cell; (2) performing PCR amplification on the template DNA; purifying the PCR product SAP / Exon I; (3) respectively performing forward and / or reverse sequencing amplification on the purified PCR product by a sequencing primer; purifying the sequencing product; performing ABI 37030xl capillary electrophoresis sequencing so as to determine the SNP site and genotype.
Owner:广州博富瑞医学检验有限公司
Method for characterization of modifications caused by the use of designer nucleases
Disclosed is a method for high-throughput detection of genome-wide modifications in a nucleic acid genome obtained from a cell or tissue caused by the activity of a designer nuclease comprising the following steps:a) Extraction of the genomic DNA from cells that were exposed to a designer nuclease under conditions which allow the designer nuclease to introduce a DNA double-strand break (DSB) in the genomic DNA of the cell,b) fragmentation of the nucleic acid to obtain random fragments,c) performing an end repair in order to obtain blunt ends,d) ligation with a linker comprising a sequence complementary to a so called “linker primer”,e) performing a first nucleic acid amplification reaction with a “linker primer” and a so called “ON-target primer”, whereby one primer is located upstream and one primer is located downstream of the on-target site, wherein at least one decoy primer is present in the reaction mixture,f) performing a second nucleic acid amplification reaction whereby so called “nested primers” are added to the reaction mixture, whereby one primer is complementary to the on-target locus and one primer complementary to the linker sequence,g) performing a further nucleic acid amplification reaction whereby at least one code containing primers are added to the reaction mixture,h) sequencing of the nested and barcoded amplification product, andi) aligning the sequenced products with suitable bioinformatic means to a reference sequence to identify a chromosomal location that contains a genomic modification based on at least one DNA double strand break.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG +1
HLA related SNP marker and detection primer pair and determination method thereof
ActiveCN107893113AHigh expressionIncrease or decrease expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCapillary electrophoresisNucleotide
The invention provides an HLA related SNP marker and a detection primer pair and a determination method thereof, and aims to provide a primer and method for evaluating transplantation risk. An SNP marker related with HLA is disclosed and is the base C or T on 32610275th site of human No.6 chromosome. A primer pair for detecting the SNP marker described by the claim one has nucleotide sequences represented by SEQ ID No1-2 or SEQ ID No3-4. A method of determining the SNP site comprises following steps: (1) extracting genome DNA of a host cell; (2) subjecting the template DNA to PCR amplification, and purifying the PCR product (SAP / Exon I); and (3) subjecting the purified PCR product to forward and / or backward sequencing amplification by using a sequencing primer, purifying the sequencing product, and carrying out ABI 3730x1 capillary electrophoresis sequencing to determine the SNP site and genotype thereof.
Owner:广州博富瑞医学检验有限公司
Method for identifying specific site interaction RNA based on CRISPR/cas9 and APEX2 system
PendingCN109957579AEfficient enrichmentEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAChromosome localisationMagnetic bead
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a method for identifying specific site interaction RNA. Based on a CRISPR / cas9 and peroxidase APEX2 system, the method comprises thesteps: plasmid transformation, wherein plasmids include plasmids expressing dcas9 proteins, sgRNA specific sequences or peroxidase APEX2 respectively; biotin labelling of proteins by APEX2; enrichment of biotin-labeled proteins, DNA or RNA complexes by streptomycin magnetic beads; extraction and purification of RNA; and reverse transcription and analysis of enriched RNA. The method is simple to operate, high in specificity, good in reproducibility and suitable for the study of interaction RNA at any given chromosome position.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Two dimensional linkage study methods and related inventions
InactiveUS20020090639A1Increase powerIncrease motivationMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsChromosome localisationAllele frequency
Versions of the invention are directed to methods (and related techniques) for a new type of association based linkage study technique using bi-allelic markers. The markers used in versions of the new linkage studies are chosen using a new two-dimensional concept of "closeness" in terms of marker distribution over a two-dimensional region having the orthogonal dimensions of chromosomal location and least common allele frequency. By using the two characteristics or two dimensions of marker chromosomal location and marker allele population frequency in this unique way, the power and systematic nature of genetic linkage studies using association based linkage tests is greatly increased. These unique two-dimensional linkage study techniques increase the power of association based linkage studies to localize trait causing genes or polymorphisms of modest effect such as human disease causing polymorphisms.
Owner:MCGINNIS RALPH EVAN +1
The use of snp markers in the preparation of kits for assisting in assessing the risk of transplant rejection
ActiveCN107988352BHigh expressionIncrease or decrease expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JNucleotide
The invention provides a group of HLA-related SNP marks and a detection primer and a determination method thereof, and aims at providing a primer and a method for transplanting risk evaluation. The technical scheme is that the SNP marks comprise a first SNP mark, a second SNP mark and a third SNP mark, wherein the first SNP mark is a basic group A or T in the 32623514 position of the human No.6 chromosome; the second SNP marker is a basic group G or T in the 32623555 position of the human No.6 chromosome; the third SNP mark is a basic group A or T in the 32623560 position of the human No.6 chromosome; a primer pair for detecting the group of SNP markers in the claim 1 have the nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO:1 to 2 or SEQ ID NO:1 and 5 or SEQ ID NO:3 and 5 or SEQ ID NO:4 and 5. Thedetermination method of the HLA-related SNP sites comprises the following steps of (1) extracting the genome DNA of a host cell; (2) performing PCR amplification on the template DNA; purifying the PCR product SAP / Exon I; (3) respectively performing forward and / or reverse sequencing amplification on the purified PCR product by a sequencing primer; purifying the sequencing product; performing ABI 37030xl capillary electrophoresis sequencing so as to determine the SNP site and genotype.
Owner:广州博富瑞医学检验有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com